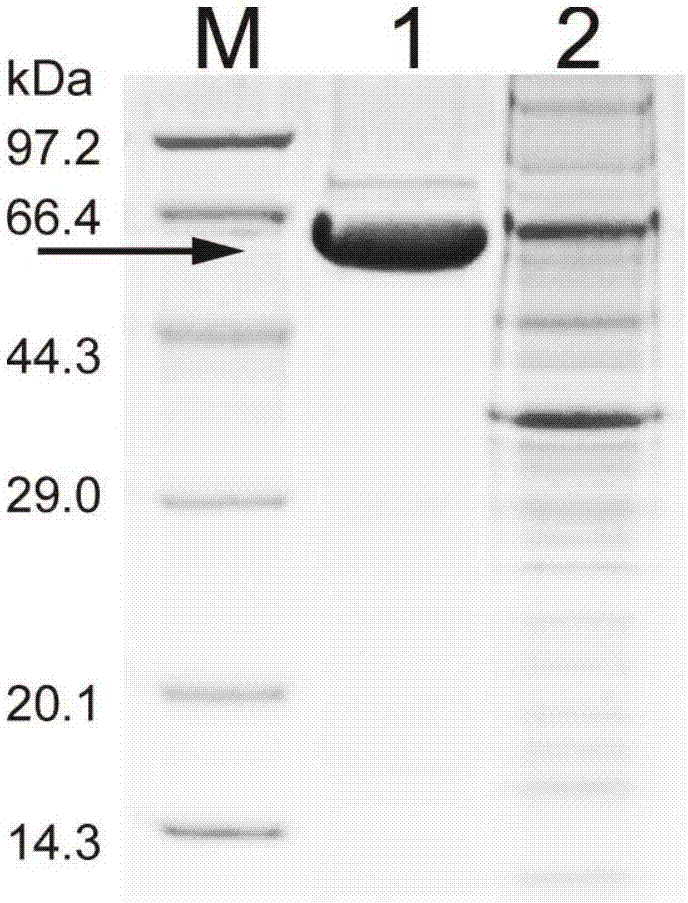
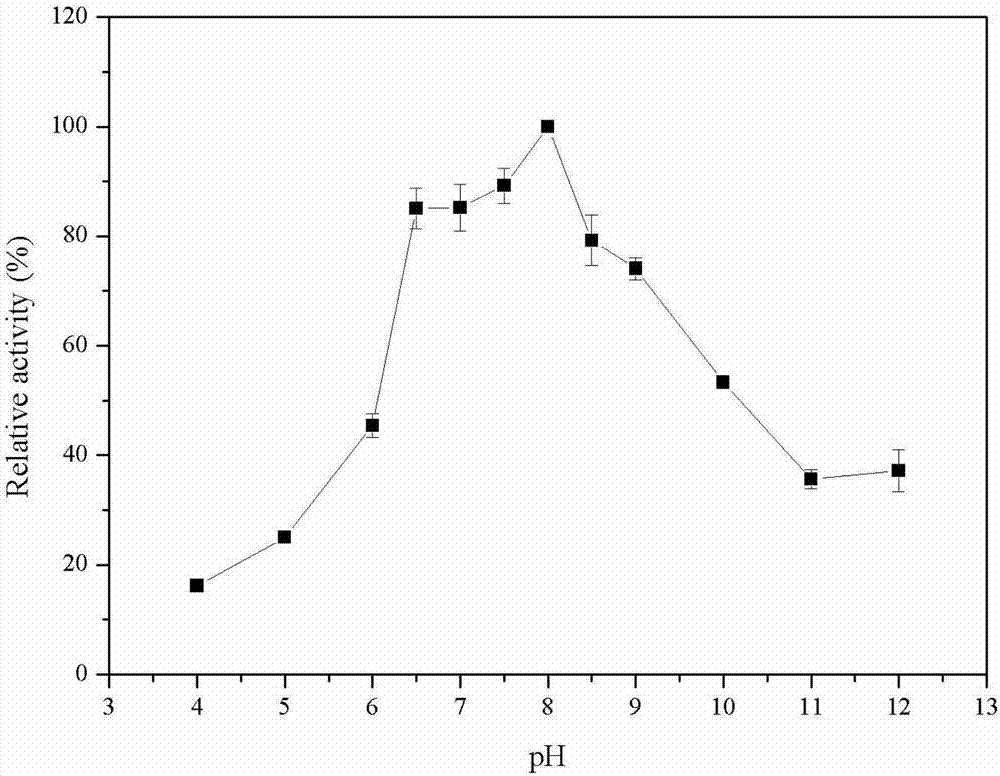
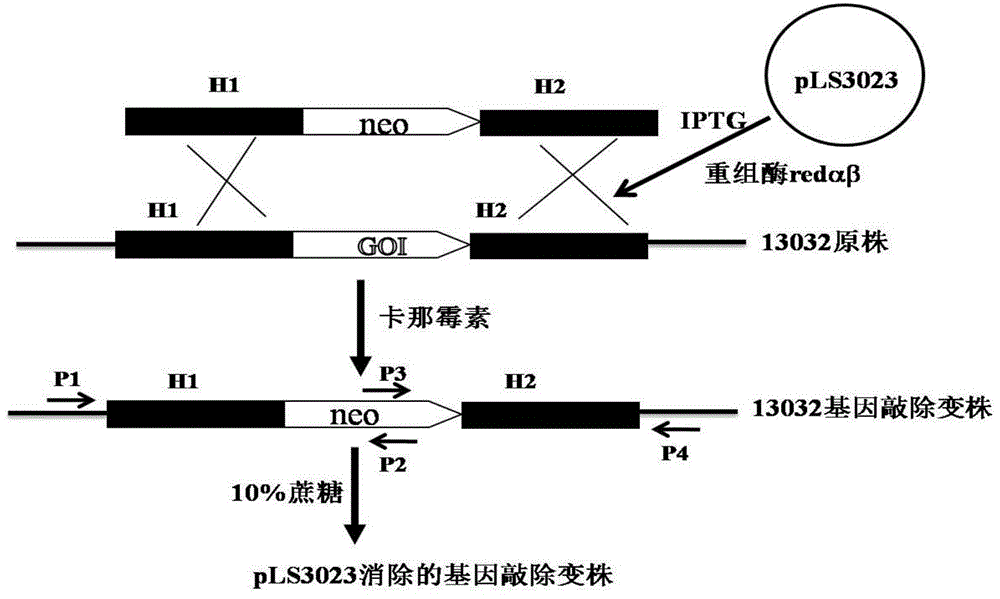
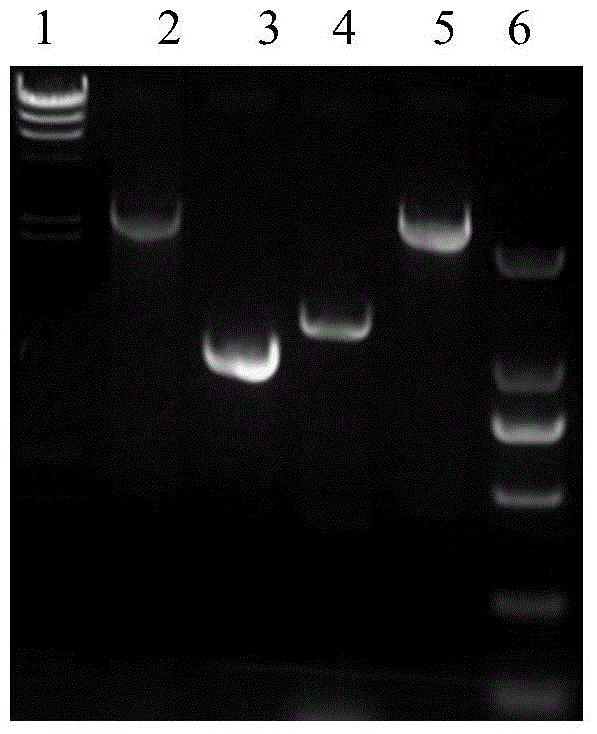
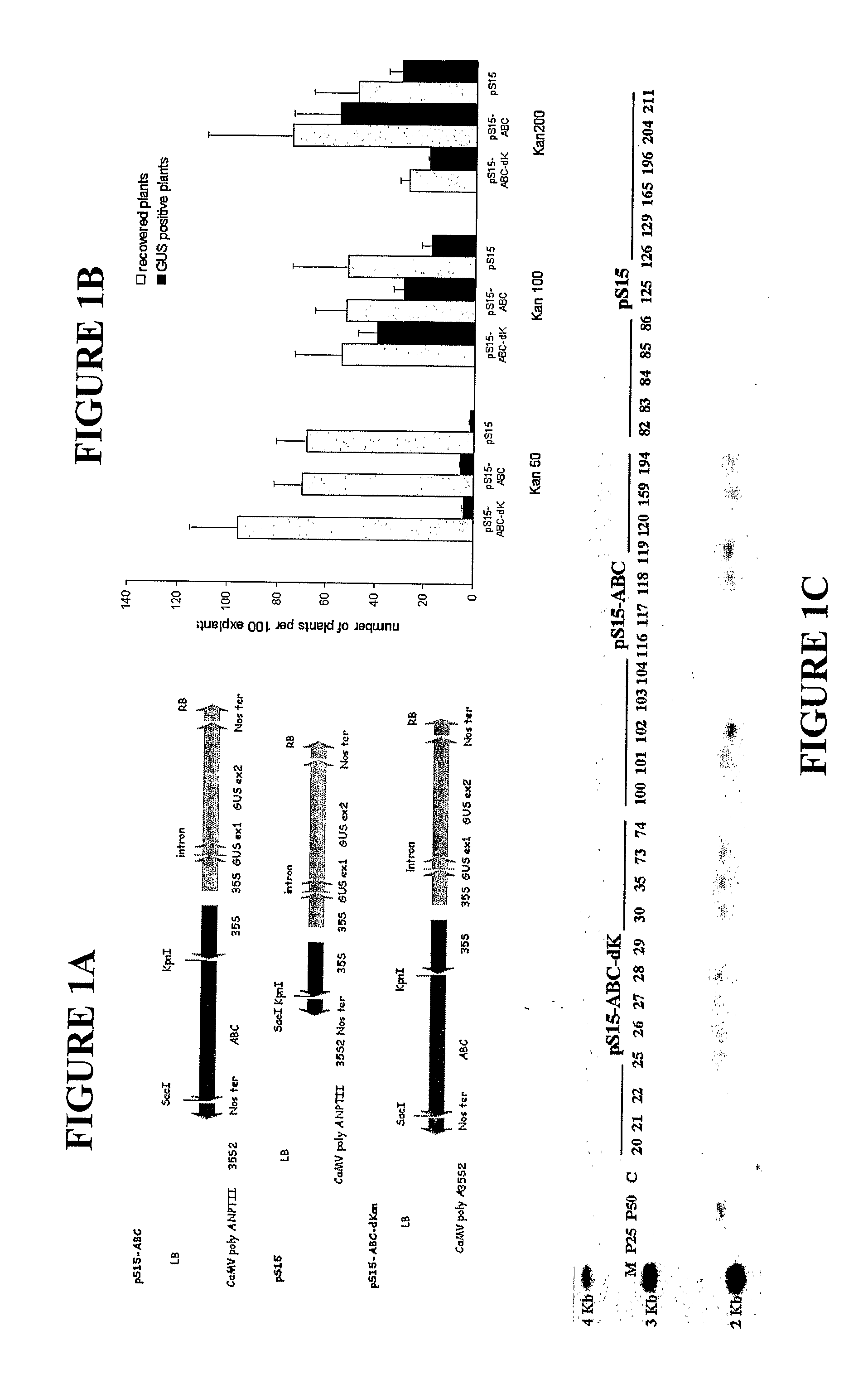
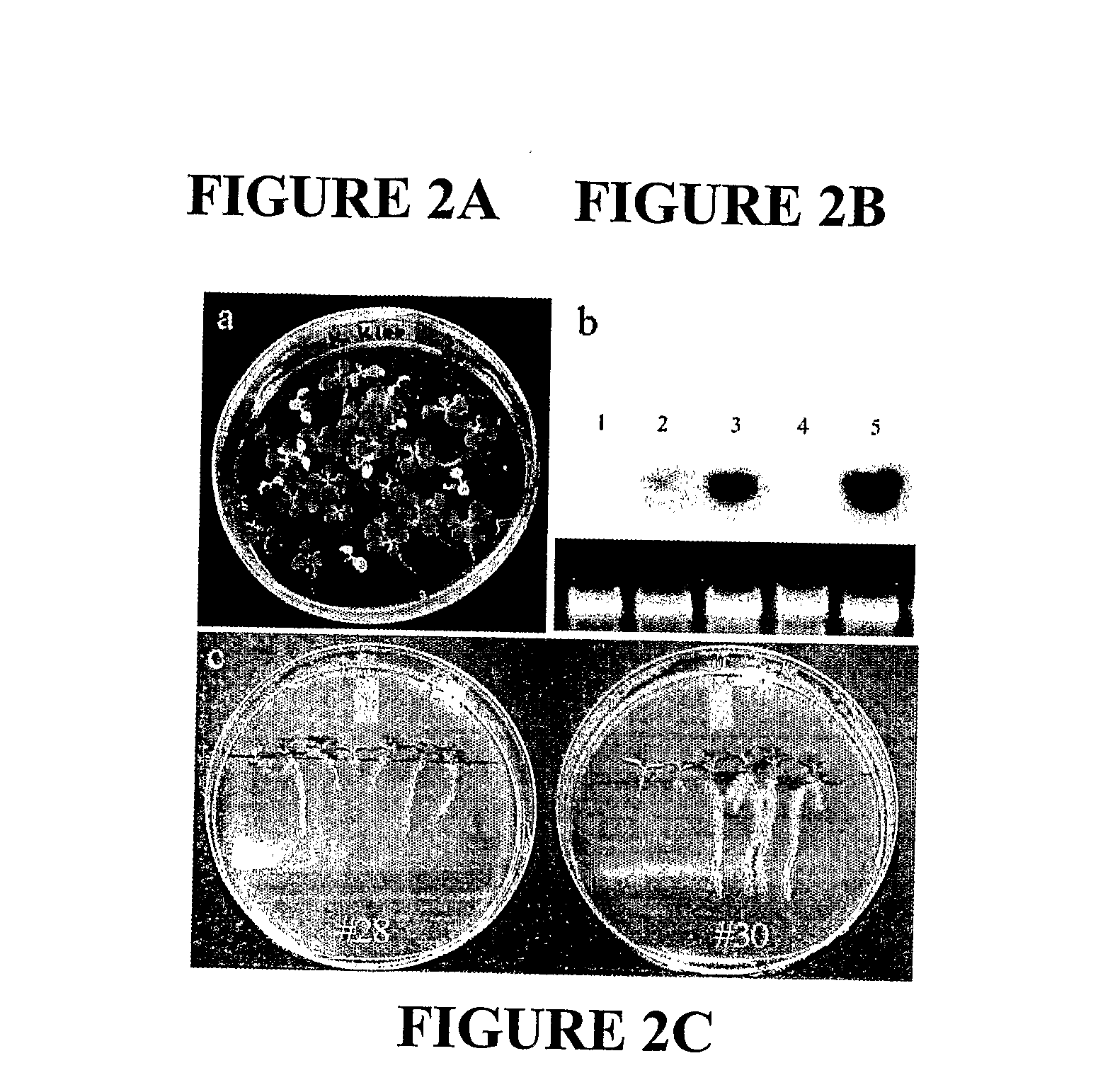
Patents
Literature
149 results about "Kanamycin Resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nonsusceptibility of bacteria to the antibiotic KANAMYCIN, which can bind to their 70S ribosomes and cause misreading of messenger RNA.
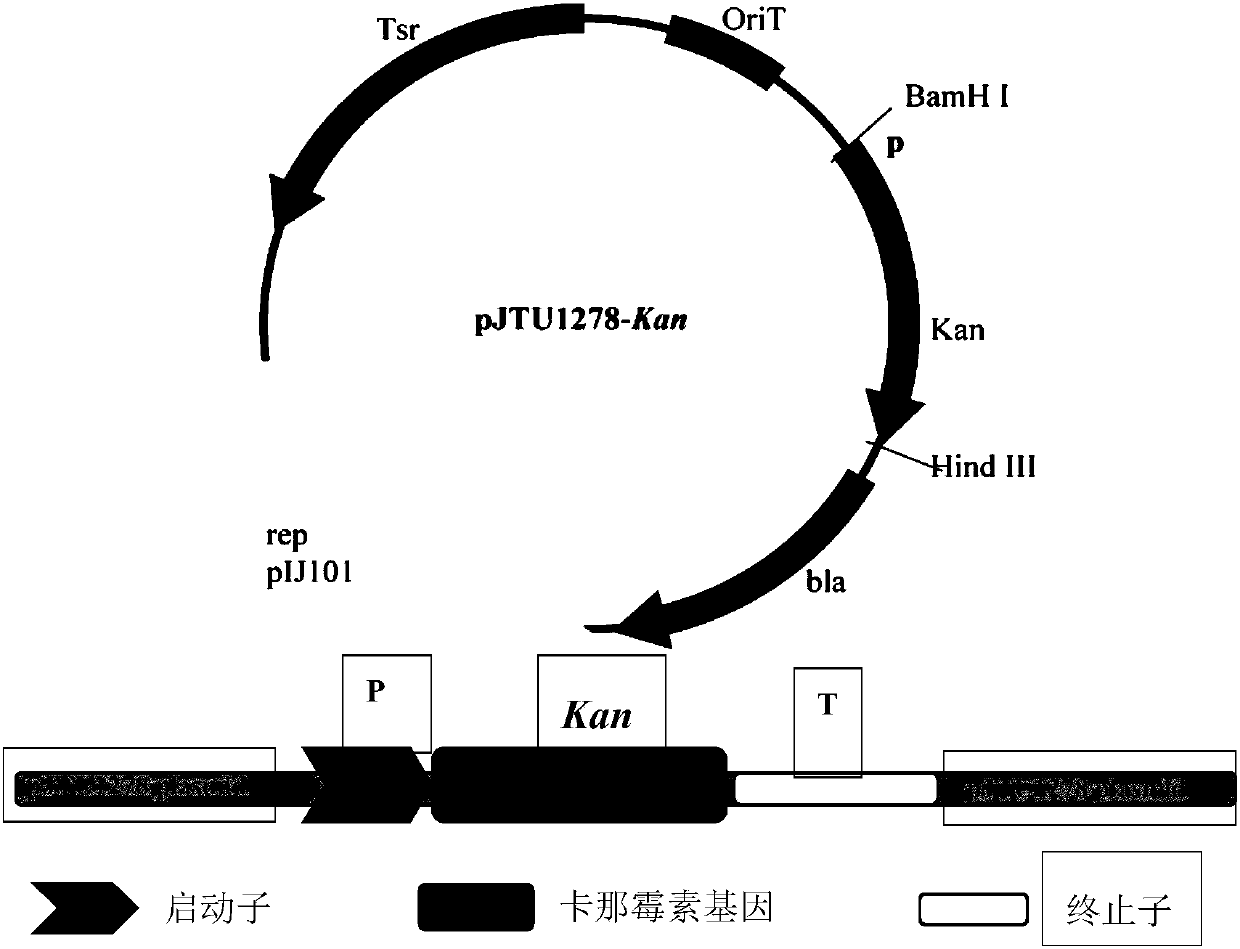
Recombinant vector for eliminating activity of kanamycin drug resistance gene and building method of recombinant vector
InactiveCN105463003AInhibitory activityHigh copy numberNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionNovel geneOrganism
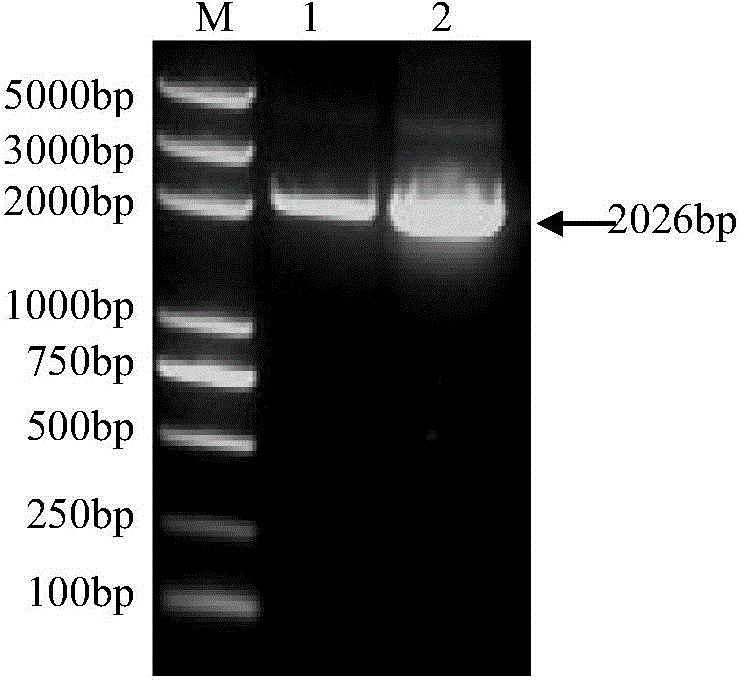
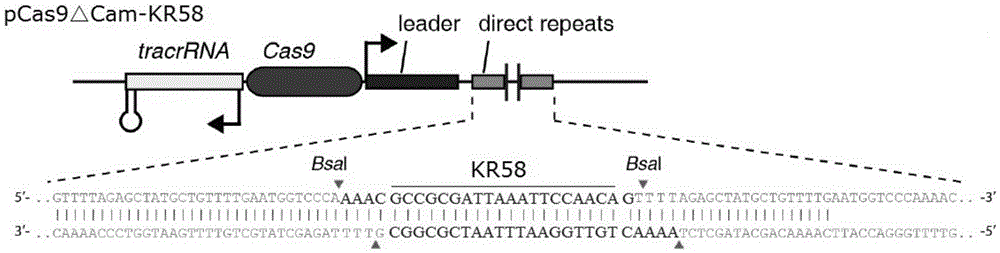
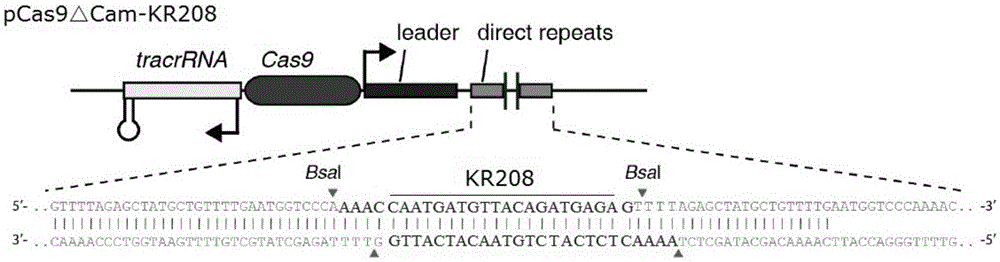
The invention provides a recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of a kanamycin drug resistance gene, and aims at eliminating drug resistance germs in organisms and solving the problem of kanamycin drug resistance of the germs. The recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of the kanamycin drug resistance gene is characterized by comprising a pCas9 vector subjected to chloramphenicol resistance elimination and a gRNA nucleotide sequence KR58 or KR208 aiming at a kanamycin resistance gene kan; the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR58 is GCCGCGAT TAAATTCCAACA, and the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR208 is CAATGATG TTACAGATGAGA. A building method of the recombinant vector mainly comprises the steps of carrying intergenic region nucleic acids by a novel gene editing tool CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system; removing a chloramphenicol resistance gene on the recombinant vector; transforming the gene into vaccine vector bacteria such as attenuated salmonella typhimurium; performing co-culture on the recombinant bacteria and the kanamycin drug resistance gene so that the recombinant vector in the recombinant bacterium cell enters the kanamycin drug resistance bacteria in an engaging mode. The activity of the kanamycin resistance gene kan is effectively inhibited, so that the original drug resistance bacterium cannot grow on a kanamycin culture medium.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Detection method of kanamycin residue based on nucleic acid aptamer
InactiveCN103335972ASimple methodHigh sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsAptamerNanoparticle
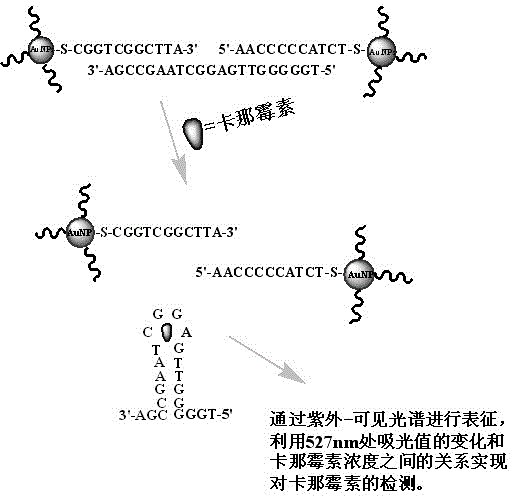
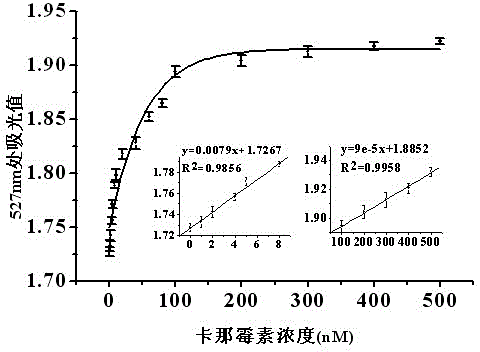
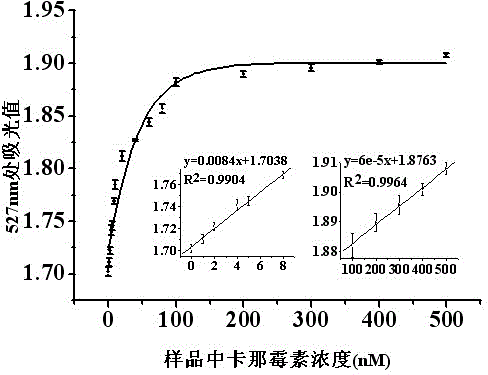
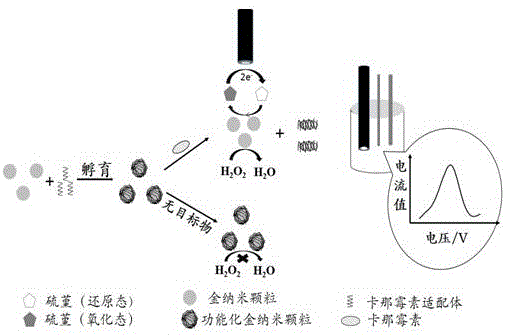
The invention discloses a detection method of a kanamycin residue based on a nucleic acid aptamer, and belongs to the technical field of analytic chemistry. The method comprises the steps that by using a sulfydryl covalent modification mode, ssDNA (single-stranded Deoxyribonucleic Acid) complementary with the two ends of a kanamycin aptamer is modified on the surfaces of AuNPs (Gold Nanoparticles) respectively; two kinds of functionalized AuNPs are obtained; the kanamycin aptamer is added and pairwise bound with ssDNA on the surfaces of the functionalized AuNPs; spatial distances among the AuNPs are closed; the AuNPs are mediated to be aggregated; after the AuNPs are mixed with kanamycin samples with different concentrations, specific binding between kanamycin and the aptamer allows an aggregation to be disaggregated, which is manifested by a change of an AuNPs characteristic absorption peak in an ultraviolet-visible spectrum; and the kanamycin residue is detected by using a relation between a change of the absorbency at a 527-nanometer part and the concentration of the kanamycin. The method is good in repeatability and stability, easy to operate and high in sensitivity, and can be used for directly determining the kanamycin residues in samples such as pretreated milk.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for specific integration of t7 rna polymerase gene in the chromosome of corynebacterial and the resultant corynebacteria-t7 promoter based shuttle vector system
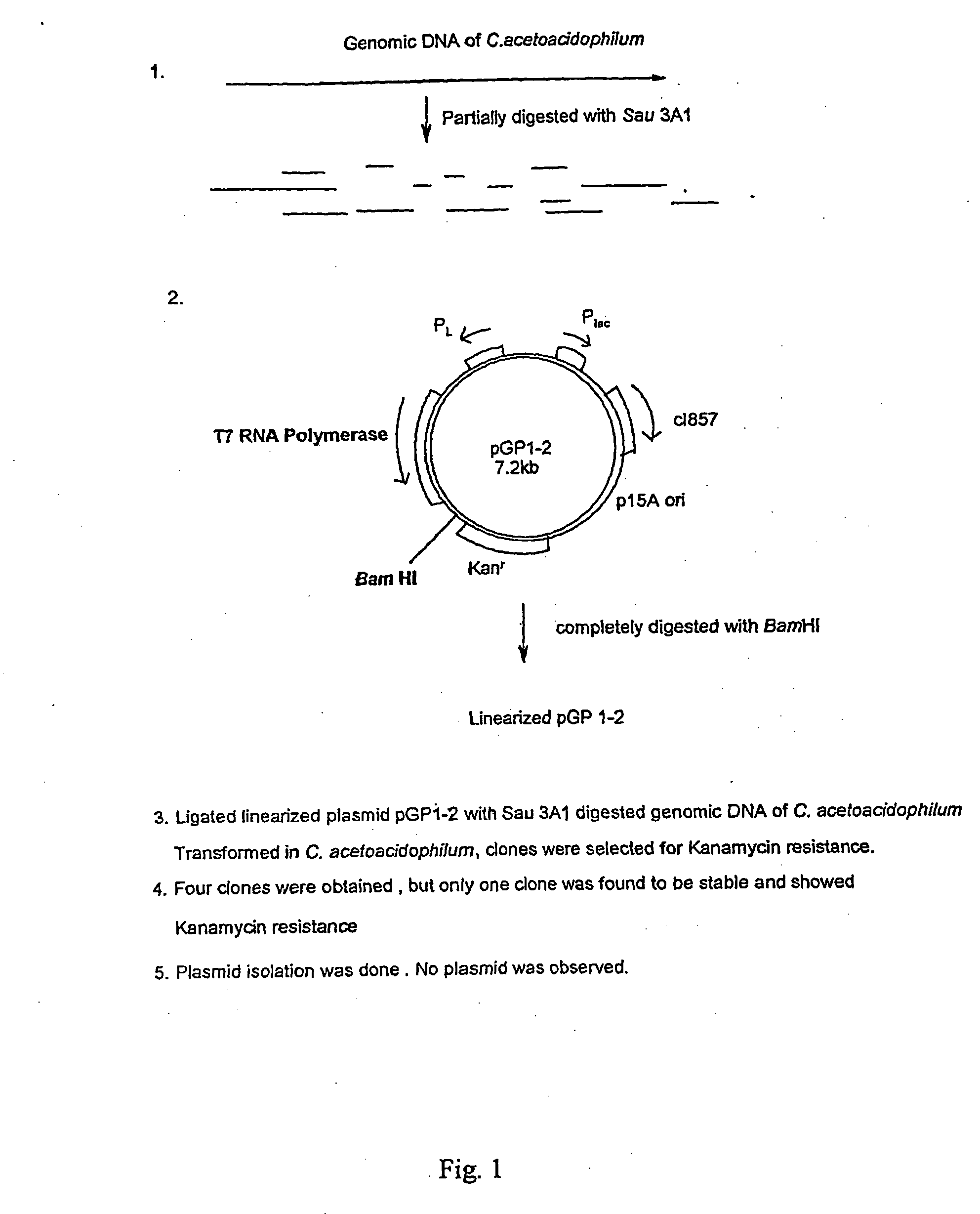
The present invention relates to method for obtaining optimum expressed proteins in a transformed gram positive bacteria by specific integration of T7 RNA polymerase gene into the chromosome of a gram positive bacteria exhibiting resistance to aminoglycosides, said method comprising:- digesting an E. coli plasmid with a restriction enzyme- digesting the genomic DNA of said gram positive bacteria- ligating the said digested plasmid to the digested genomic DNA of said gram positive bacteria- transforming the said gram positive bacteria protoplasts with the said ligation mixture of step 2 to yield transformed gram positive bacteria (transformants),- screening the said transformants for kanamycin resistance and aminoglycoside sensitivity to ensure that the targetting of the said plasmid vector into the chromosome of the said gram positive bacteria is successful- cloning of the desired gene in the said vector—culturing the transformant in a suitable culture medium- isolating the expressed proteins from the culture medium
Owner:INDIAN INST OF TECH
Electrochemical detection method for detecting kanamycin residues based on nucleic acid aptamer and nano analogue enzyme
ActiveCN105784799AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial electrochemical variablesPeroxidaseTyrosine
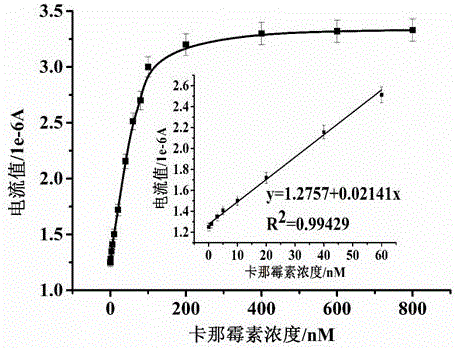
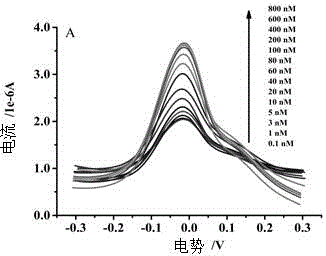
The invention provides an electrochemical detection method for detecting kanamycin residues based on a nucleic acid aptamer and a nano analogue enzyme and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. Gold nano-particles are synthesized by reducing chloroauric acid through tyrosine, and hydrogen peroxide and reduced-state thionine are catalyzed to react to generate oxidized-state thionine; and the thionine can be detected through a difference pulse voltammetry. The gold nano-particles are modified through utilizing a kanamycin specific aptamer; and the aptamer is adsorbed on the surfaces of the gold nano-particles so that the peroxidase activity is inhibited. When a target object kanamycin exists, the aptamer can be competitively replaced from the surfaces of the gold nano-particles to form a compound, so that the peroxidase activity is recovered. The detection of the kanamycin can be realized through detecting a relation between a reduction peak current value of the oxidized-state thionine and an antibiotic concentration by utilizing the difference pulse voltammetry. The method provided by the invention has good repeatability, good stability and high sensitivity, and can be used for effectively detecting kanamycin residues in food samples.
Owner:上海谱尼医学检验实验室有限公司
Genetic engineering antibiotic peptides as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a genetic-engineering antibacterial peptide, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: according to the characteristics of the amino acid sequence of Magainin and Cecropin P and LL-37 which are antibacterial peptide, a novel antibacterial peptide gene is designed; the sequence of the gene is synthesized and transformed to be expressed in pichia to form antibacterial-peptide gene transformation pichia engineering bacteria, and to be expressed in a fermentor to achieve the effects of high-density cultivation and efficient expression. Fermentation broth is separated and purified to be an antibacterial peptide product which can be applied to feed and food additives and be used as injection. The antibacterial peptide has the advantages of good antibacterial activity to most gram-negative bacteria and gram-positive bacteria, in particular better effects of inhibiting and killing ampicillin-resistant bacteria and kanamycin-resistant bacteria.
Owner:山东华辰制药有限公司
Escherichia coli t7 expression vector, vectors for the co-expression and co-purification of recombinant peptides in/with carrier proteins, use of expression vectors for obtaining complexes with multiple antigens and immonomodulators
InactiveUS20180135060A1Increase productionAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliAmpicillin
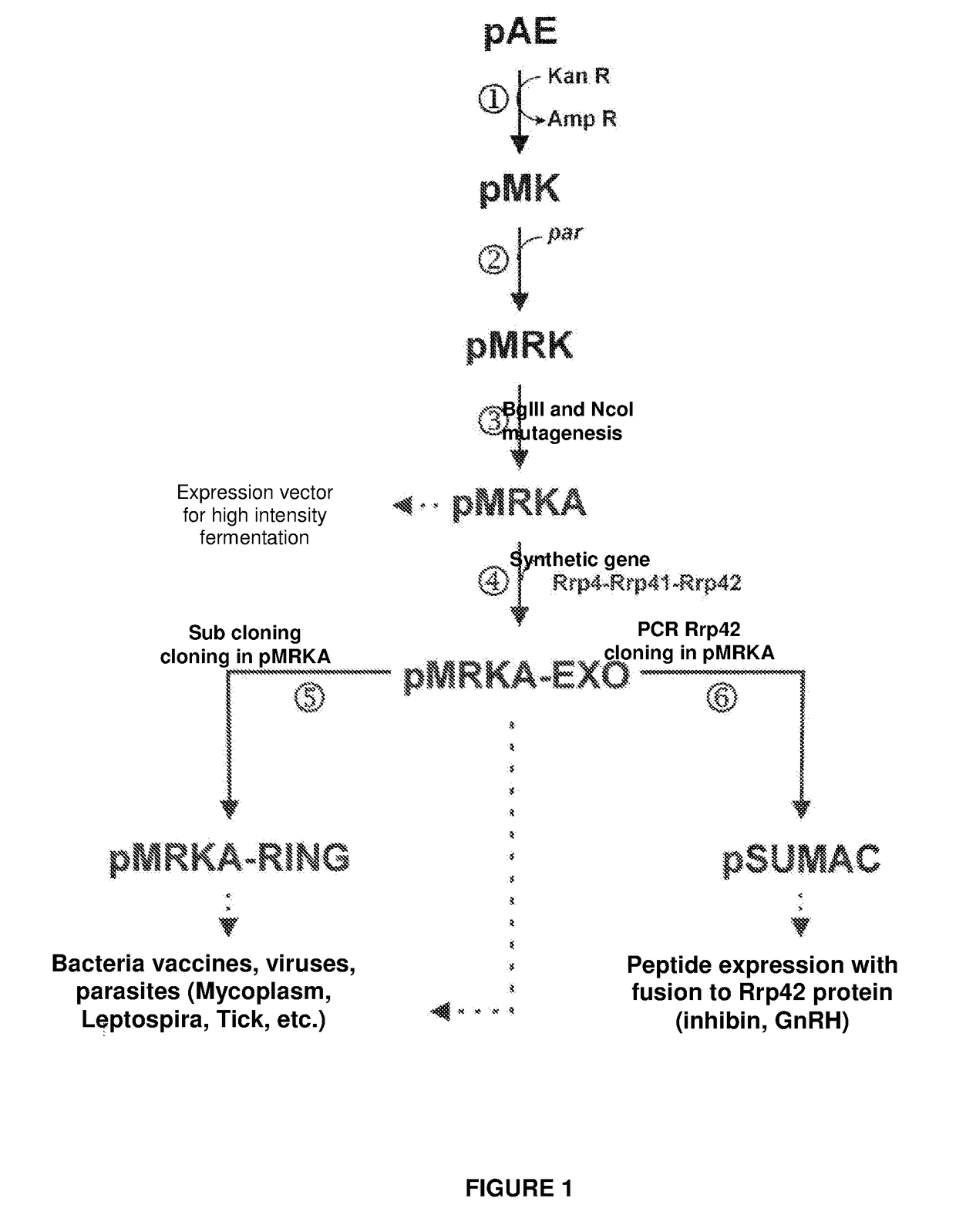
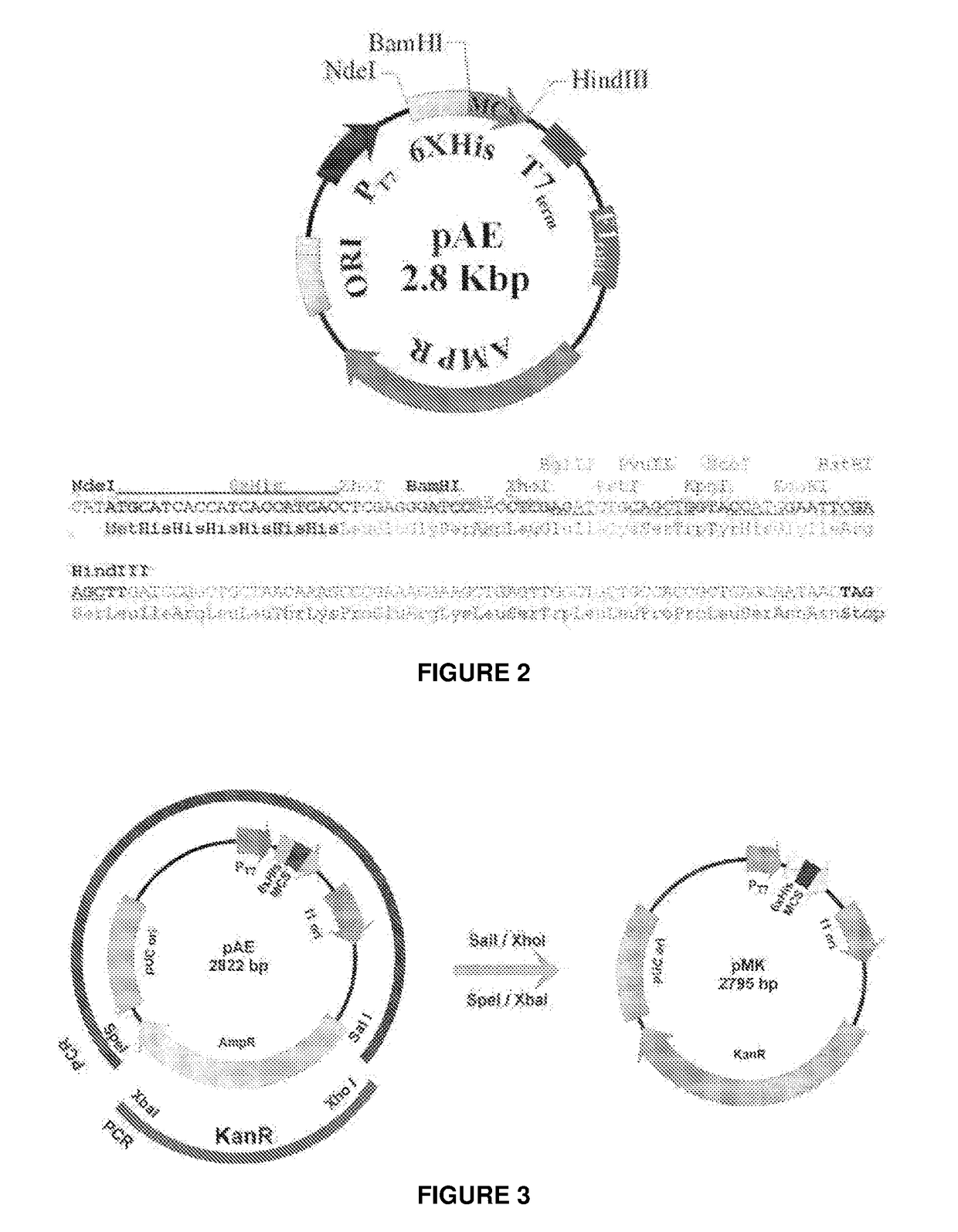
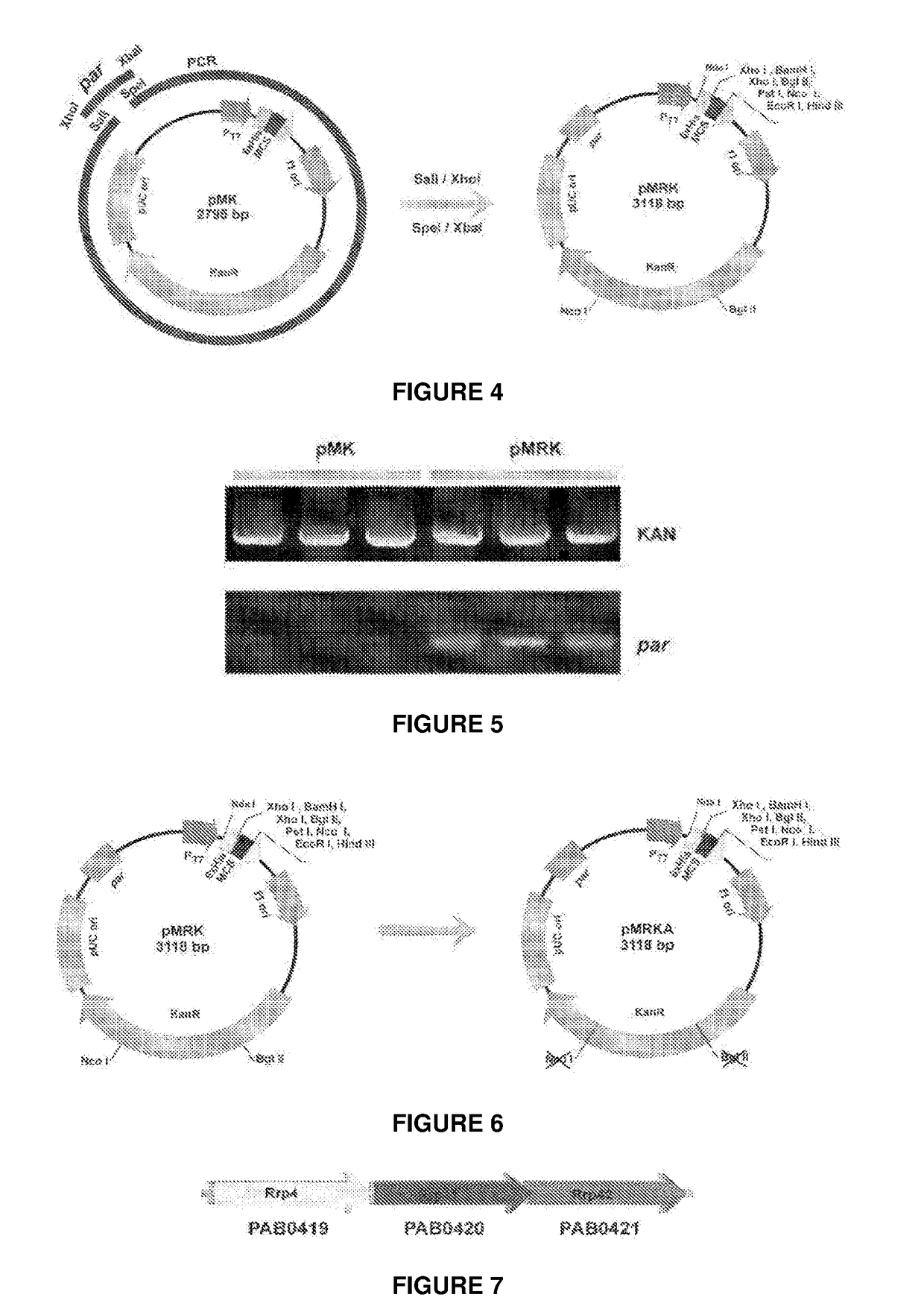
The present invention relates to a vector for the expression of recombinant proteins, antigens, pathogen-like particles and immunogenic complexes, said vector (pMRKA vector) being produced by modifying the plasmids containing the gene sequence of the T7 promoter of E. coli, this modification being mainly characterized by the substitution of the ampicillin-resistance gene by the kanamycin-resistance gene, and by the insertion of the par sequence (partition sequence which determines the efficient segregation of the plasmids in daughter cells during cell division). Also provided are expression vectors based on the pMRKA plasmid, which additionally comprise at least one of the gene sequences of the exosome of P. abyssi, which vectors are designated pMRKA-EXO, pMRKA-RING and pSUMAC. The invention also provides the vectors additionally comprising gene sequences with immunomodulatory or immunoregulatory activity, preferably the pMRKA-Z-Z-EXO and pMRKA-Z-Z-RING vectors. Other aspects of the invention include the method for producing said expression vectors and the use of the obtained vectors.
Owner:OURO FINO SAUDE ANIMAL
Recombined streptomyces nodosus capable of producing amphotericin B and application thereof
ActiveCN107893048AHigh purityQuality improvementBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
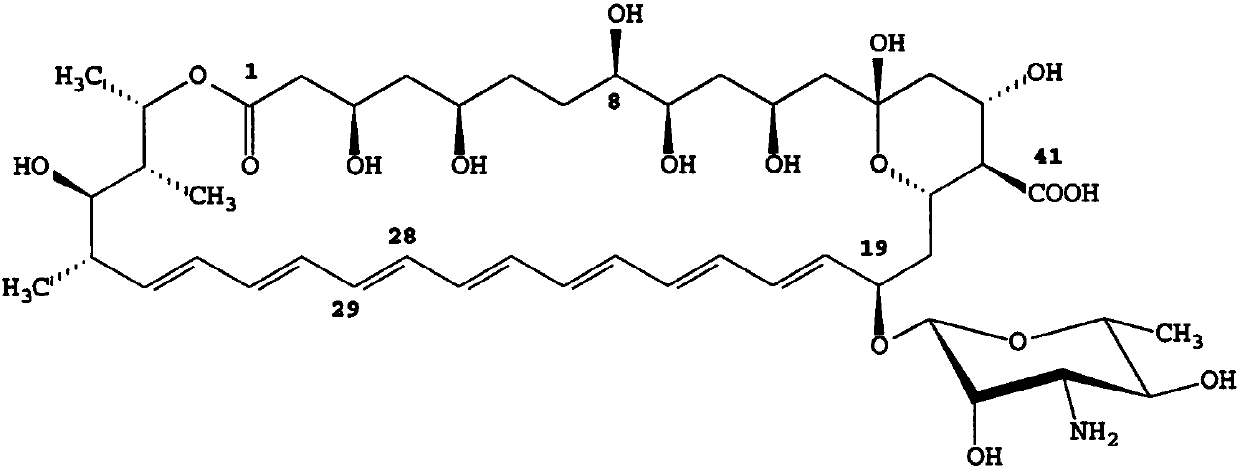
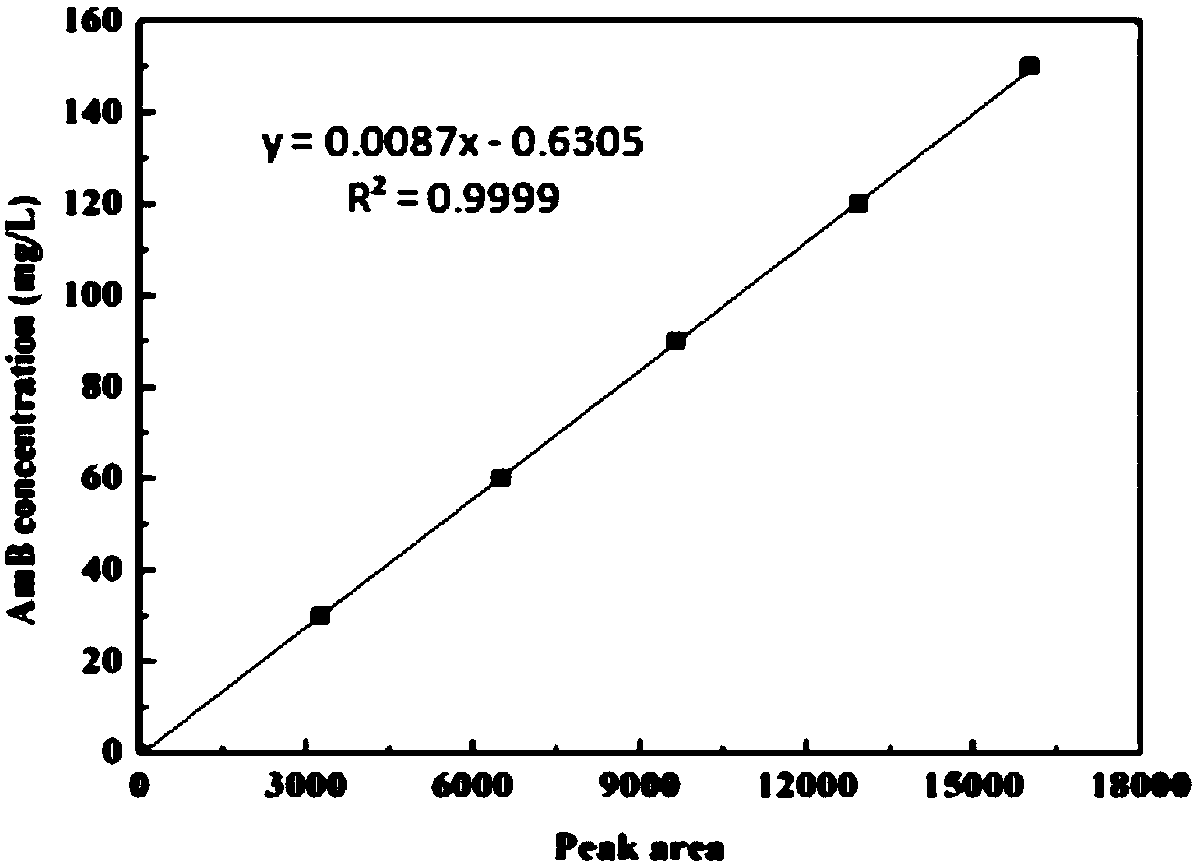
The invention discloses recombined streptomyces nodosus capable of producing amphotericin B and application thereof. The recombined streptomyces nodosus is obtained by introducing a kanamycin resistance gene sequence showed in SEQ ID NO.1 into streptomyces nodosus ZJB2016050; by introducing the kanamycin resistance gene, produced strains which have no resistance previously have kanamycin resistance, the purity and quality of the strains of seed culture mediums are improved, and strain contamination phenomena can be prevented from occurring during seed cultivation in a lab. By expressing a function gene, namely vitreoscilla hemoglobin (vhb), the yield of AmB is increased by 15%; by expressing a function gene, namely the S- adenosylmethionine synthetase gene (metk), the yield of AmB is increased by about 40%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Double knockout recombinant rhodococcus as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105420154AHigh expression activityQuality improvementBacteriaHydrolasesSaccharumLevansucrase
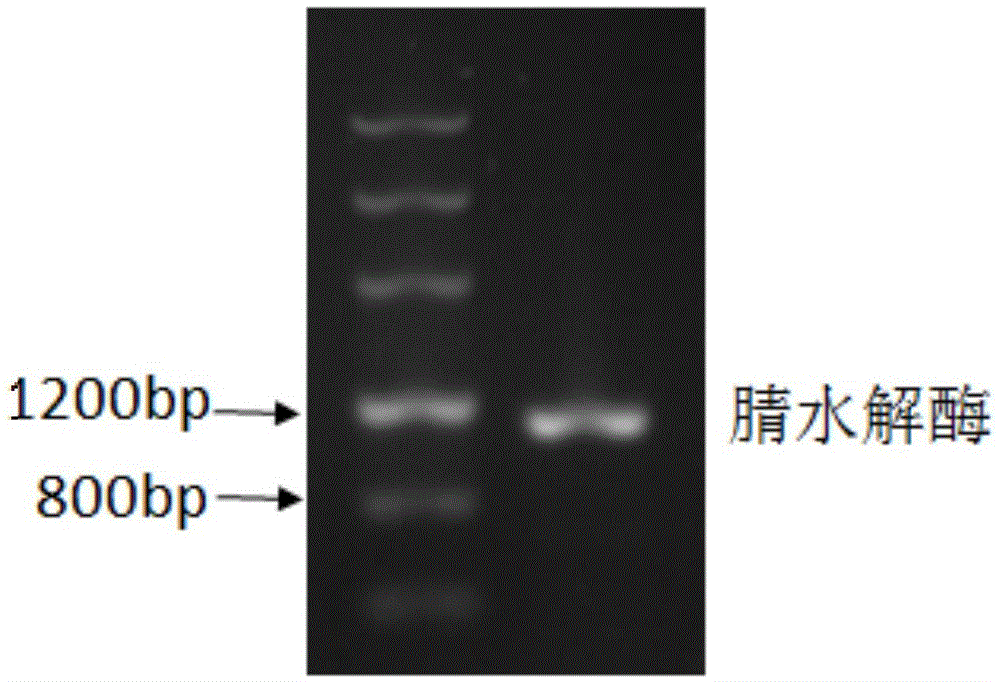
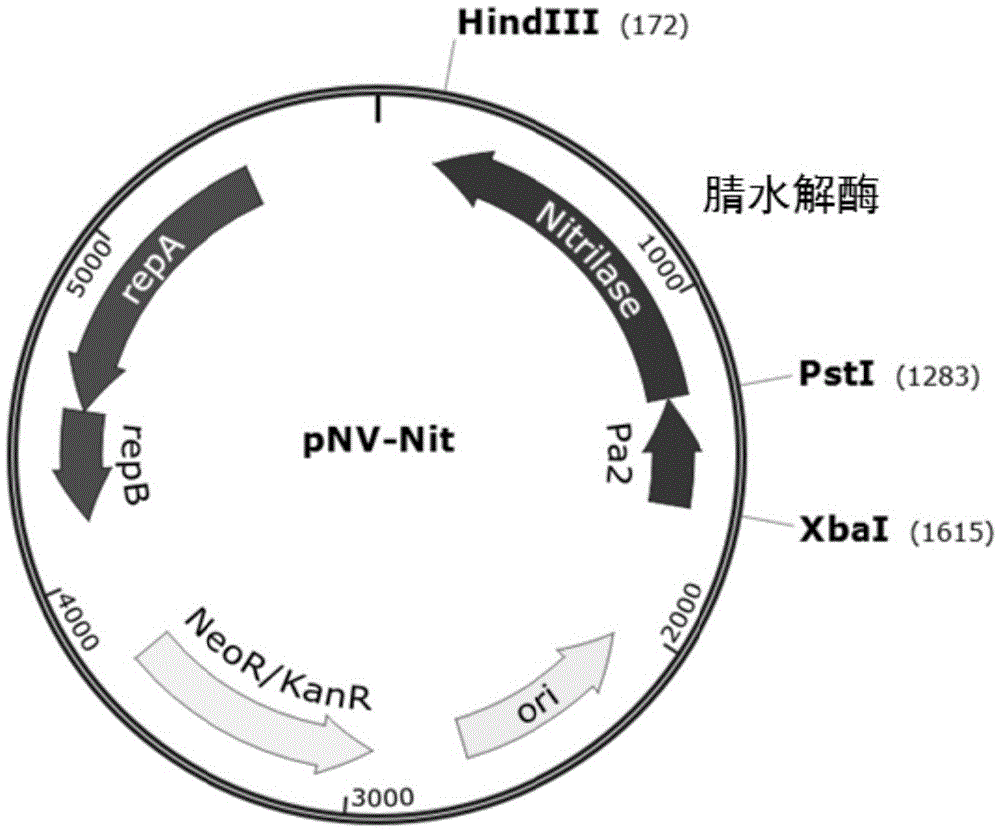
The invention discloses a construction method of double knockout recombinant rhodococcus. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) primers are designed according to nitrile hydratase gene sequence of the rhodococcus for respective amplification of an upstream sequence and a downstream sequence of a nitrile hydratase gene, and an upstream fragment and a downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are obtained; (2) the upstream fragment and the downstream fragment of the nitrile hydratase gene are inserted into a suicide plasmid, and a recombinant suicide plasmid is obtained, wherein the suicide plasmid carries a kanamycin resistant gene and a levansucrase gene; (3) competent cells of recombinant rhodococcus of an amidase gene are knocked out through transformation of the recombinant suicide plasmid, and the double knockout recombinant rhodococcus is obtained: first screening is performed through kanamycin resistance, and a first recombinant colony is obtained and subjected to second screening through a sucrose plate. The invention further discloses recombinant rhodococcus with high nitrilase expression, a construction method of the recombinant rhodococcus and a method for preparing acrylamide.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
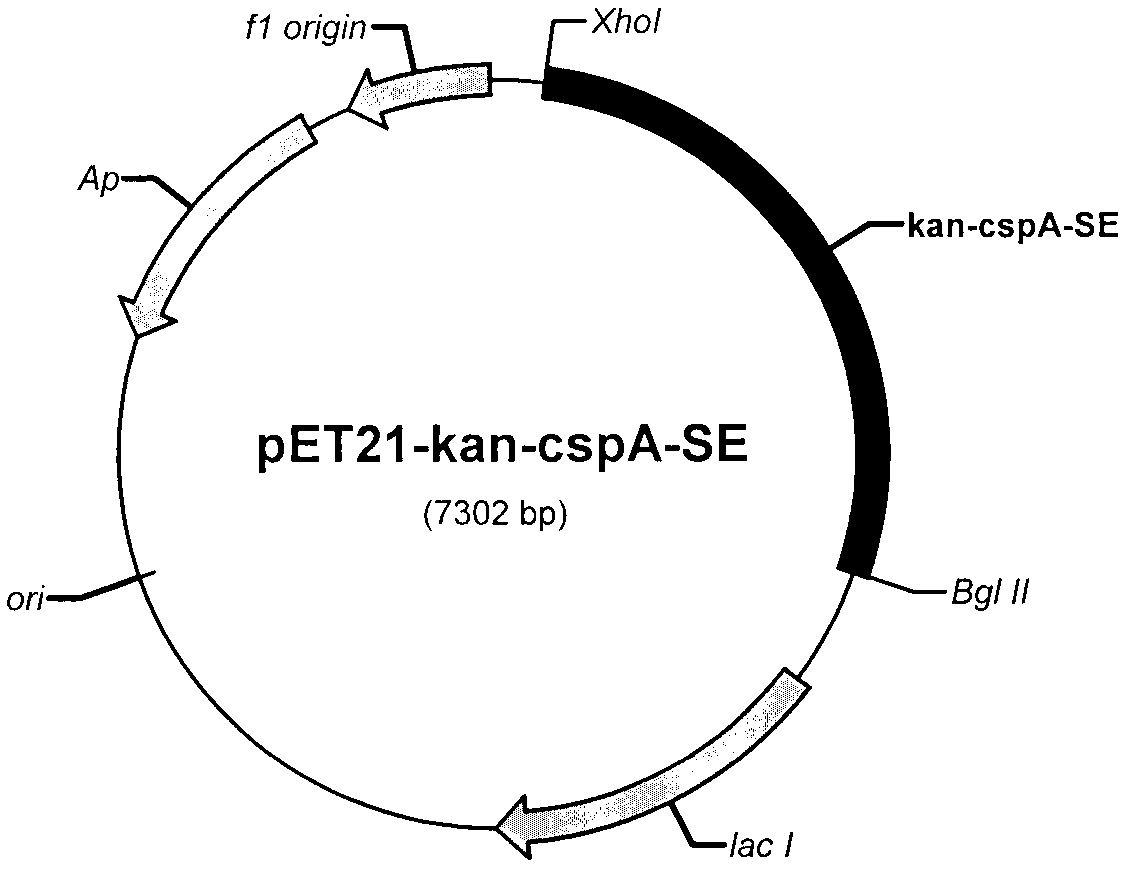
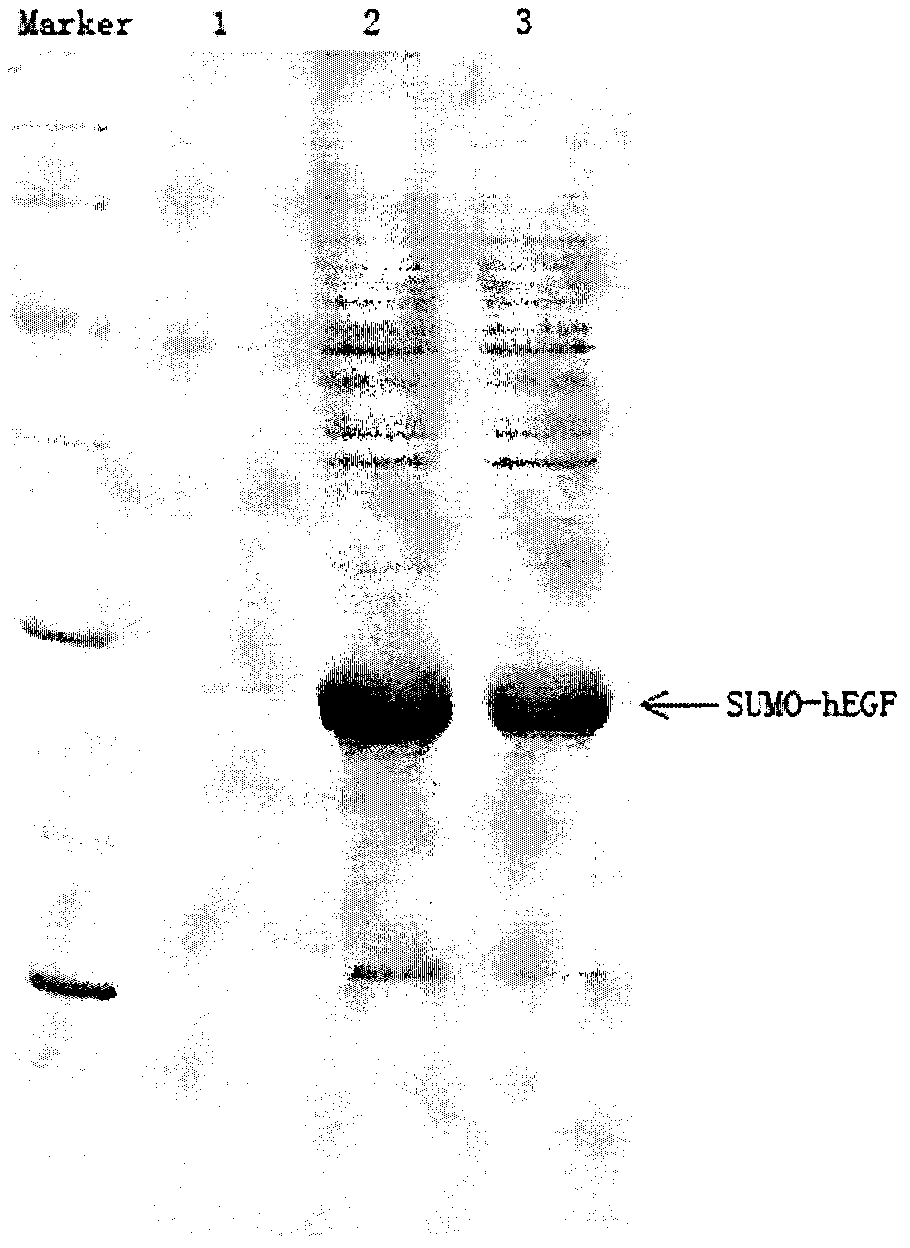
Construction and screening method for recombinant human epidermal growth factor engineering bacteria
InactiveCN102978231AGuaranteed homogeneityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisEscherichia coli
The present invention provides a construction and screening method for recombinant human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) engineering bacteria. The construction and screening method comprises the following main steps: 1, adopting a PCR technology to obtain kanamycin resistance gene, and adopting a chemical synthesis method to obtain an escherichia coli cspA gene function element; 2, respectively optimizing gene sequences encoding SUMO protein and hEGF, and then adopting chemical synthesis to obtain a large amount of expressed fusion protein gene sequences OPT-SUMO-hEGF; 3, linking the fragments obtained from the previous two steps into pET21 plasmid to obtain pET-Kan-cspA-SE plasmid; 4, adopting the pET-Kan-cspA-SE plasmid as a template to construct a transposition body; 5, transforming the transposition body into escherichia coli Origami 2 (DE3); and 6, screening a strain having high fusion protein SUMO-hEGF expression. According to the present invention, genome of the obtained strain is stable, a soluble rate of the expressed hEGF is high, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:天津强微特生物科技有限公司
Construction method of gene engineering strain without plasmid and antibiotic resistance screening marker
InactiveCN102604983AWon't cause floodingSuitable for industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
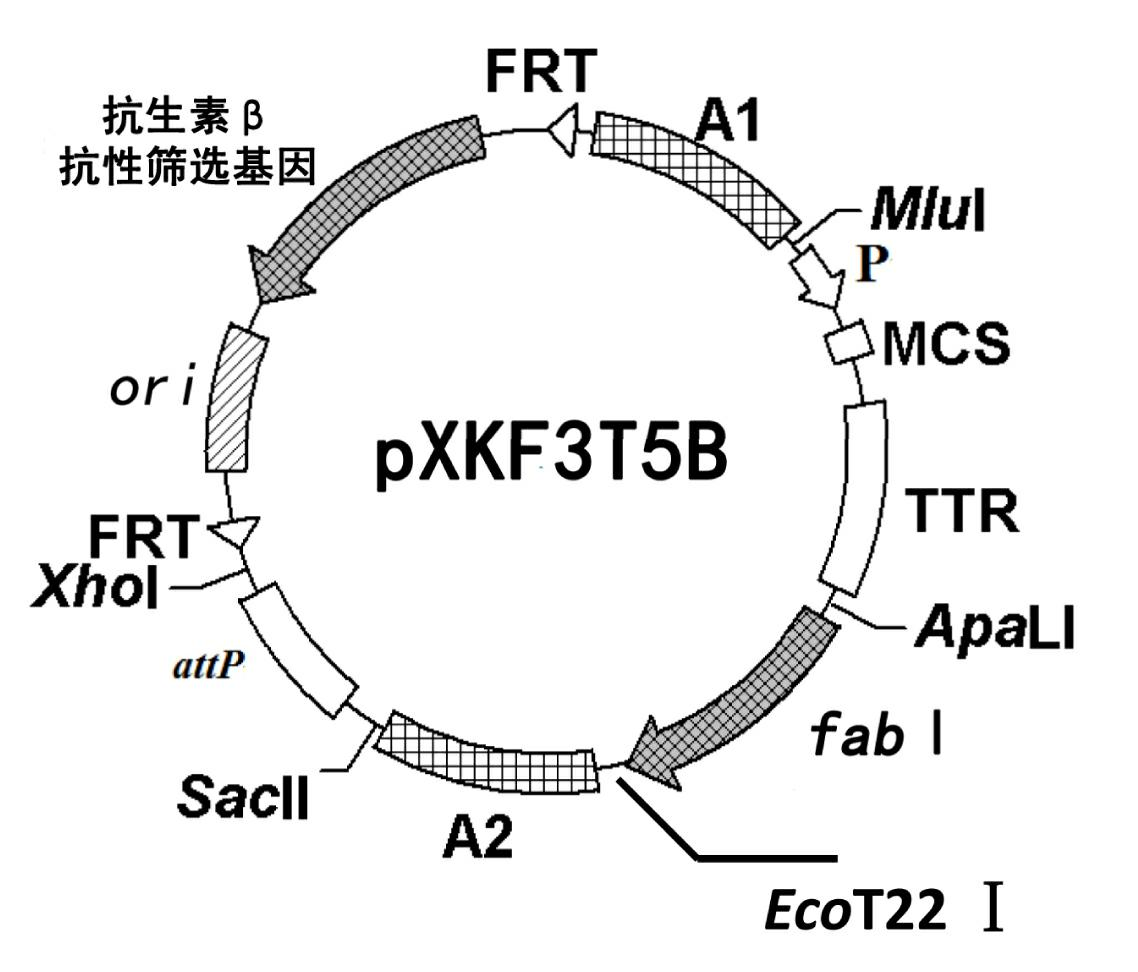
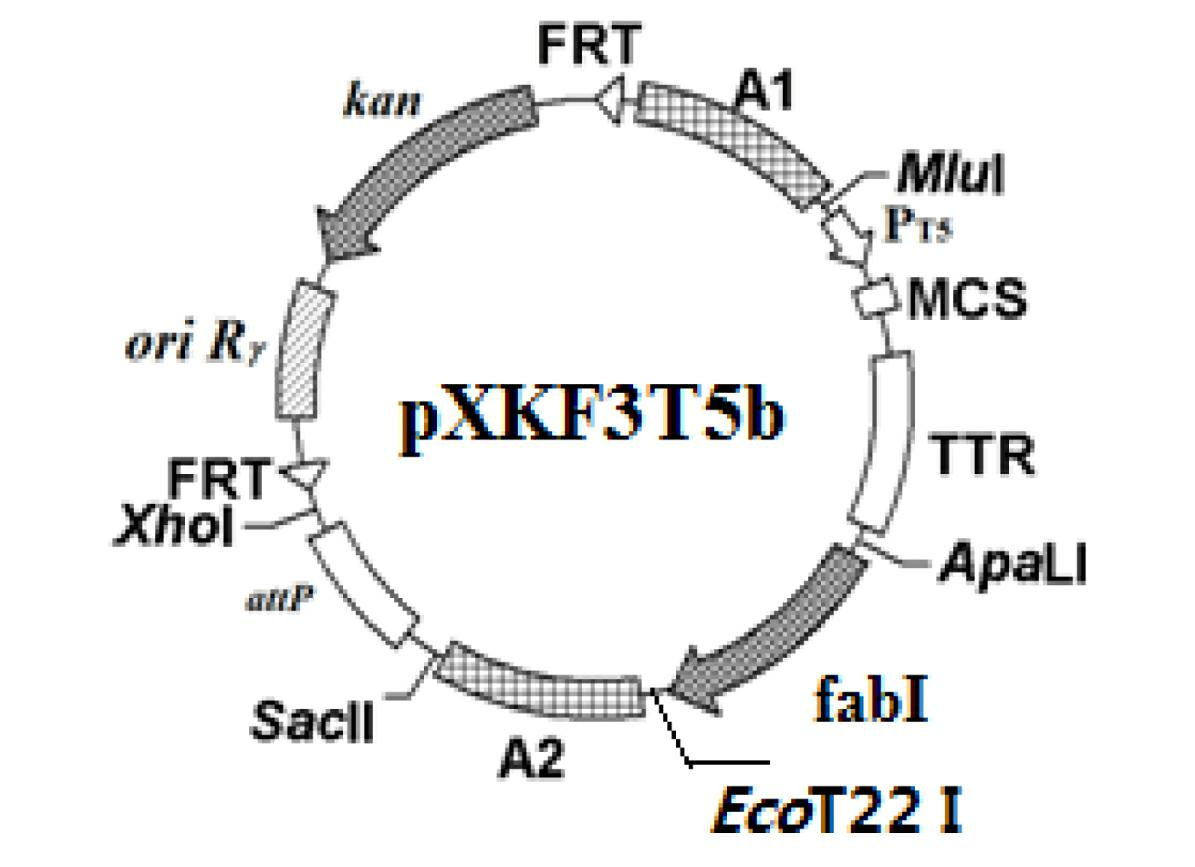
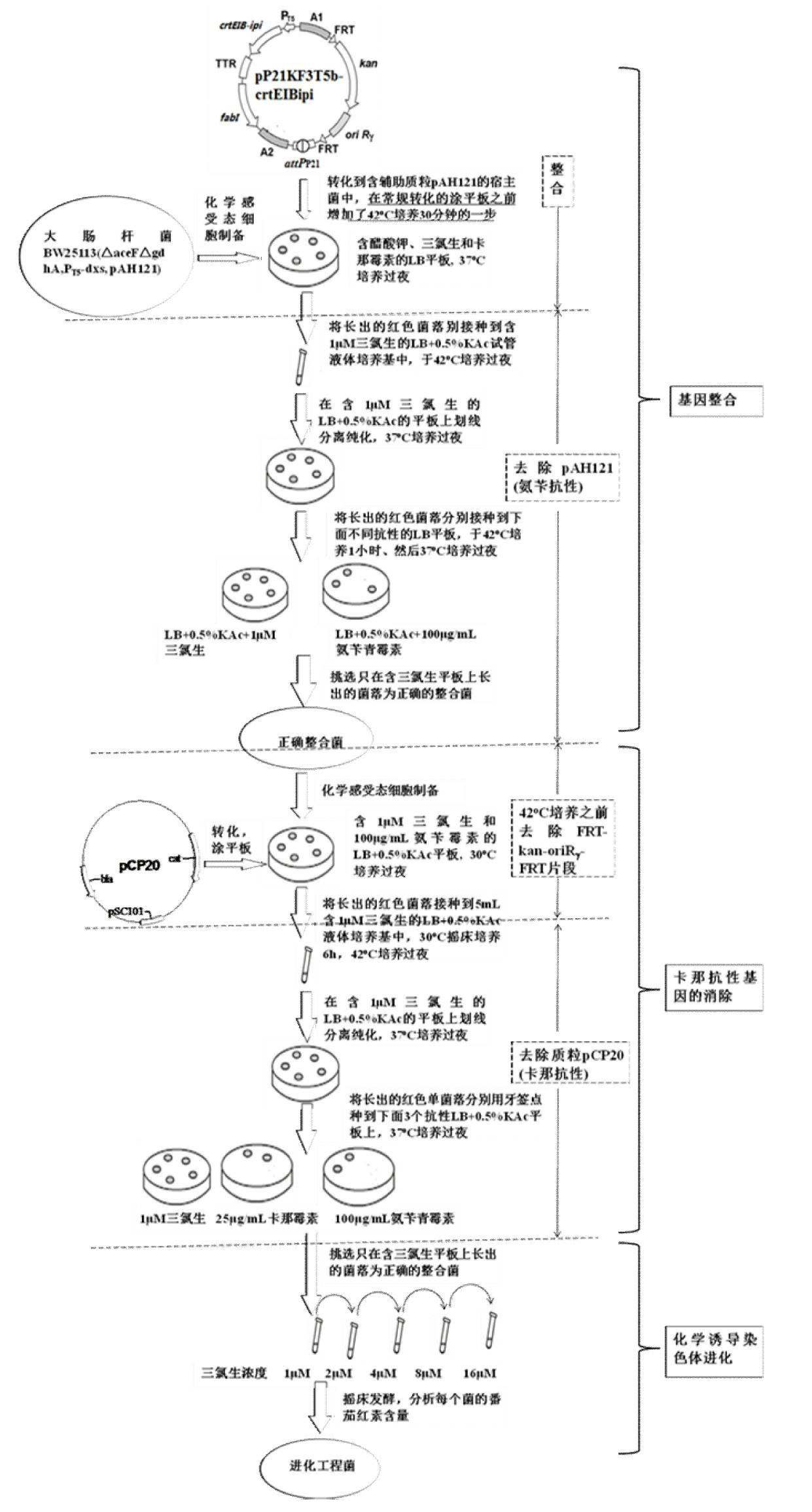
The invention discloses a construction method of a gene engineering strain without plasmid and antibiotic resistance screening marker. A pXKF3T5b plasmid is used as the carrier to transform a target gene into a host cell, and then an auxiliary plasmid for expressing the integrase is removed, a kanamycin resistance gene in the integrated carrier is removed, the chromosome is induced by the triclosan to evolve and the evolved strain is fermented and screened, so as to obtain the gene engineering strain without plasmid but with high gene copy number; moreover, a screen marker of the pXKF3T5b plasmid is the fabI gene (for coding enoyl-acetyl carrier protein reductase) in Escherichia coli and the fabI gene is the triclosan resistance gene, thus the obtained gene engineering strain does not have the antibiotic resistance screening marker, furthermore can not cause the spread of the antibiotics drug-resistant bacteria in the environment and can be suitable for the industrialized production. In addition, the target gene of the gene engineering strain is integrated into the chromosome, thus the gene engineering strain can not be lost during sub cultures, the genetic stability is high, and the production performance is stable.
Owner:刘紫琦
Method and application for creating purple fruit tomato mutant using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system
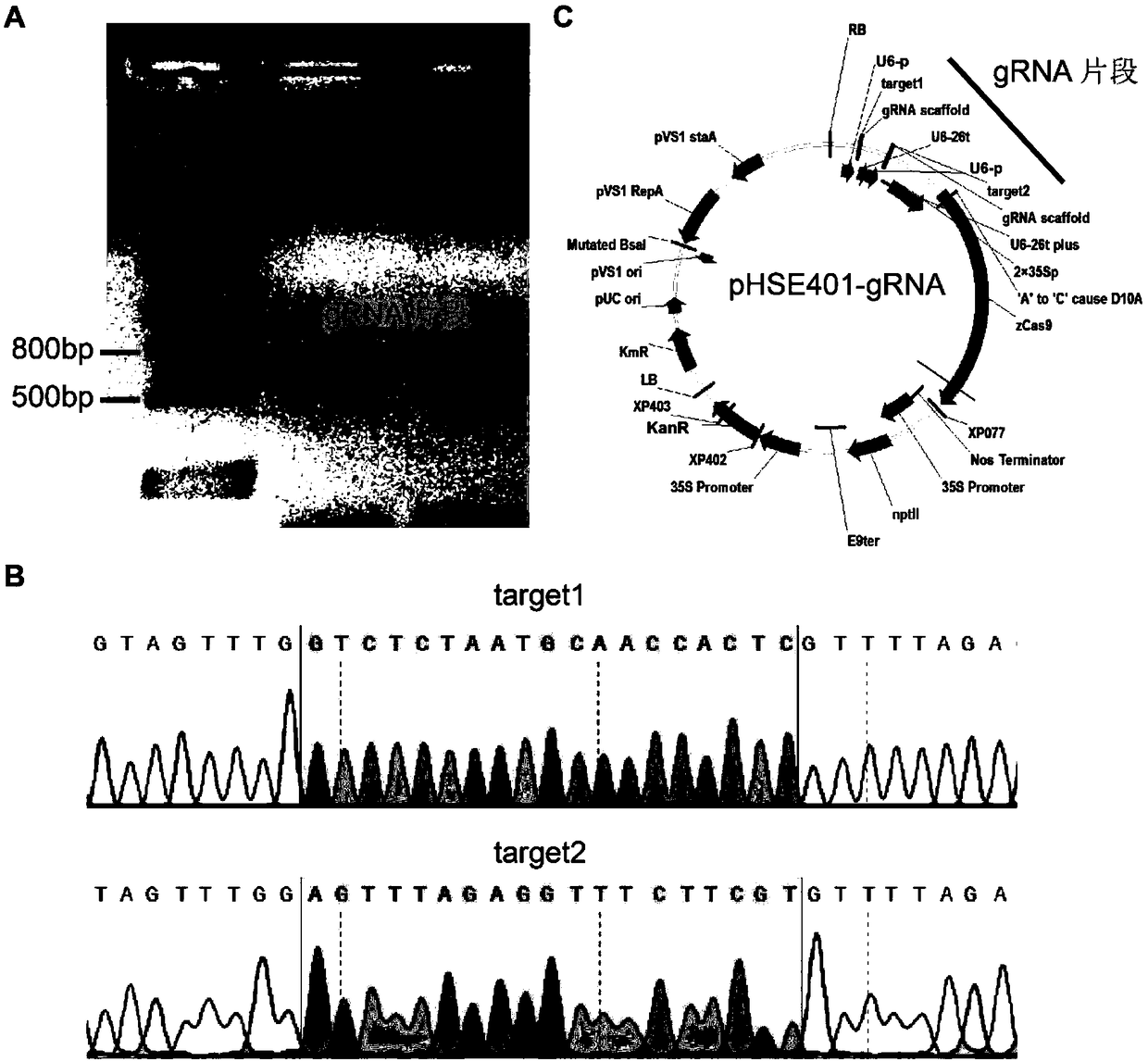
ActiveCN109097387AIncrease contentPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
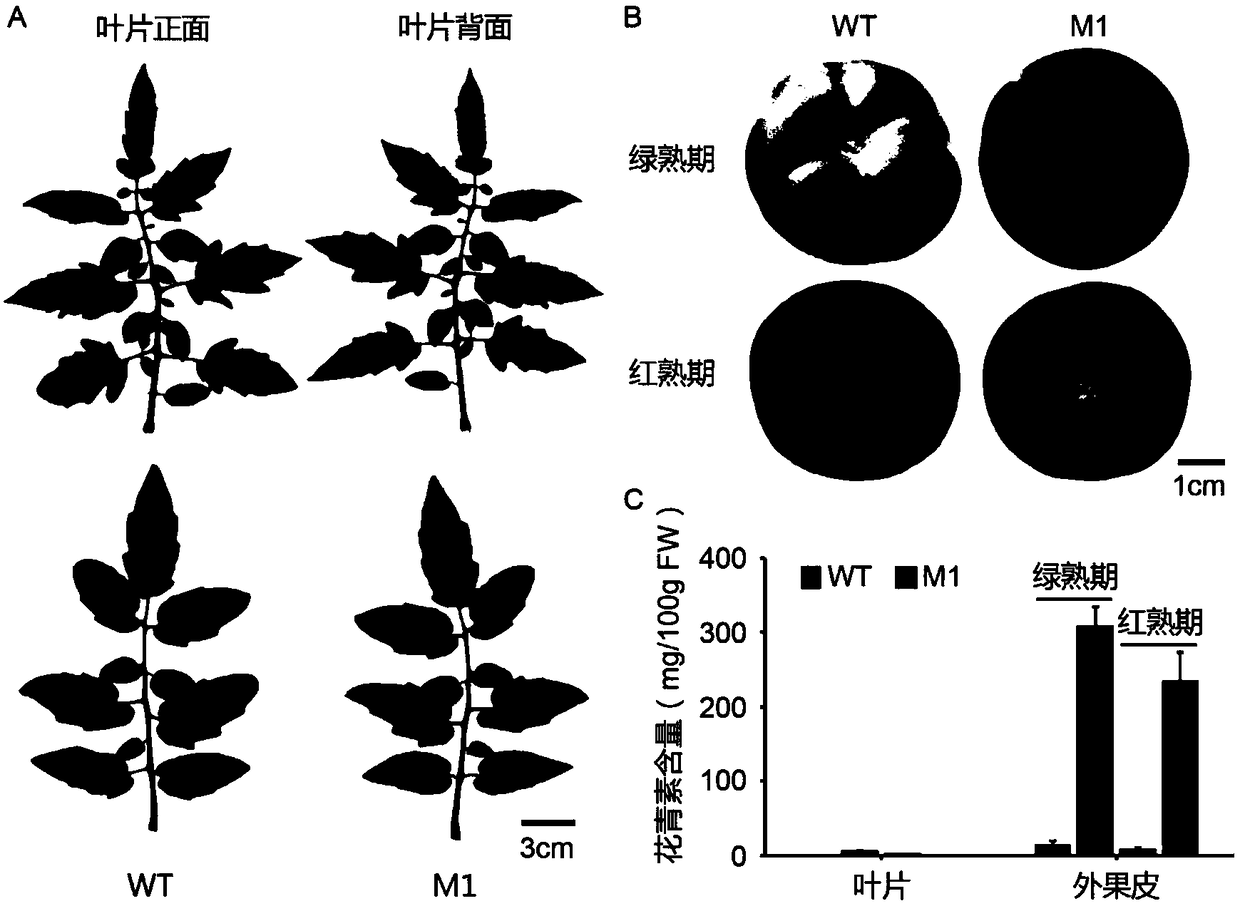
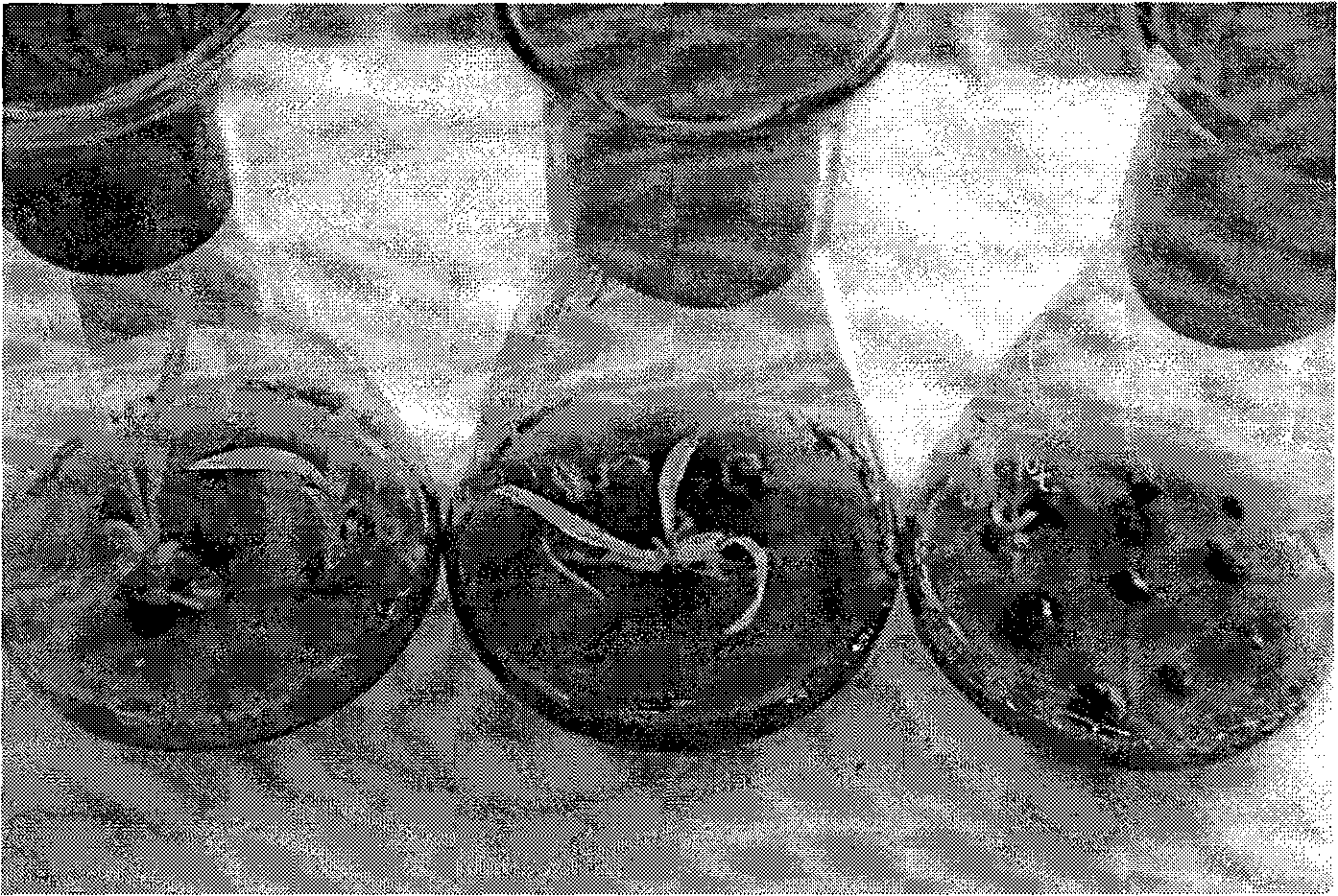
The invention discloses a method and application for creating a purple fruit tomato mutant using a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system, and relates to the field of tomato biotechnology and transgenic technology. The method includes constructing a CRISPR / Cas9-gRNA (pHSE401-gRNA) expression vector by designing a mutant target site of SlMYBATV, introducing a cultivated tomato LA1996 containing an Aft site by an agrobacterium-mediated method and conducting kanamycin resistance marker screening to obtain a positive transgenic plant. A strain with homozygous mutation determined by gene sequencing and phenotypic observation and containing no foreign aid gene insertion is a tomato mutant that completely loses the SlMYBATV function and has purple fruit. According to the method and application, the content of anthocyanins in tomato peels can be significantly improved. The method and application have good application prospects in high quality molecular breeding of tomatoes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Efficient gene knockout method of pseudomonas putida KT2440
The invention relates to a method for performing gene knockout on pseudomonas putida KT2440 by a recombinant engineering measure. The method comprises the following specific steps of: amplifying through an overlapped-extension polymerase chain reaction so as to obtain a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragment of which both sides are provided with target genes to be knocked, the upstream and downstream are provided with homologous genes of about 500 base pairs and the middle is provided with a kanamycin resistance gene; electrically transforming the DNA fragment into a pseudomonas putida KT2440 electro-transformation competent cell which is expressed by toluic acid induction recombinase with the final concentration of 2mM; and replacing the target genes by the kanamycin resistance gene through homologous recombination between homologous fragments of a recombinase mediate so as to directly obtain a mutant strain from which target genes are knocked. The method is simple and convenient and can become a genetic operating measure of an environmental microorganism, namely pseudomonas putida KT2440 which has important application value in the aspects of organic compound biodegradation and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Construction of arginase production engineering bacteria and application of arginase production engineering bacteria in production of L-ornithine
InactiveCN103923936AIncrease vitalityMeet the needs of industrial scale productionBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention describes a construction method of arginase production engineering bacteria and application of the arginase production engineering bacteria in production of L-ornithine by transformation of L-arginine, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the method, by means of molecular biology, thermophilic bacteria Bacillus caldovelox (DSM411) is cloned to obtain arginase gene, a constructed expression plasmid is transfected into E.coli BL21 (DE3), and expression vector high-copy recombine ant arginase-containing engineering bacteria pET28a-ARG is obtained by kanamycin resistance plate screening. The enzyme can still show high activity after induced expression in E.coli. The bacteria obtained by fermentation can be directly used for transformation without breaking, in the condition of 60 DEG C, the engineering bacteria has higher permeability, and is more conducive to the substrate uptake and product release, the reaction speed is greatly improved, the transformation period is only 2-4h, the ornithine yield can reach 120.1g / L, and the transformation rate is 98.9%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
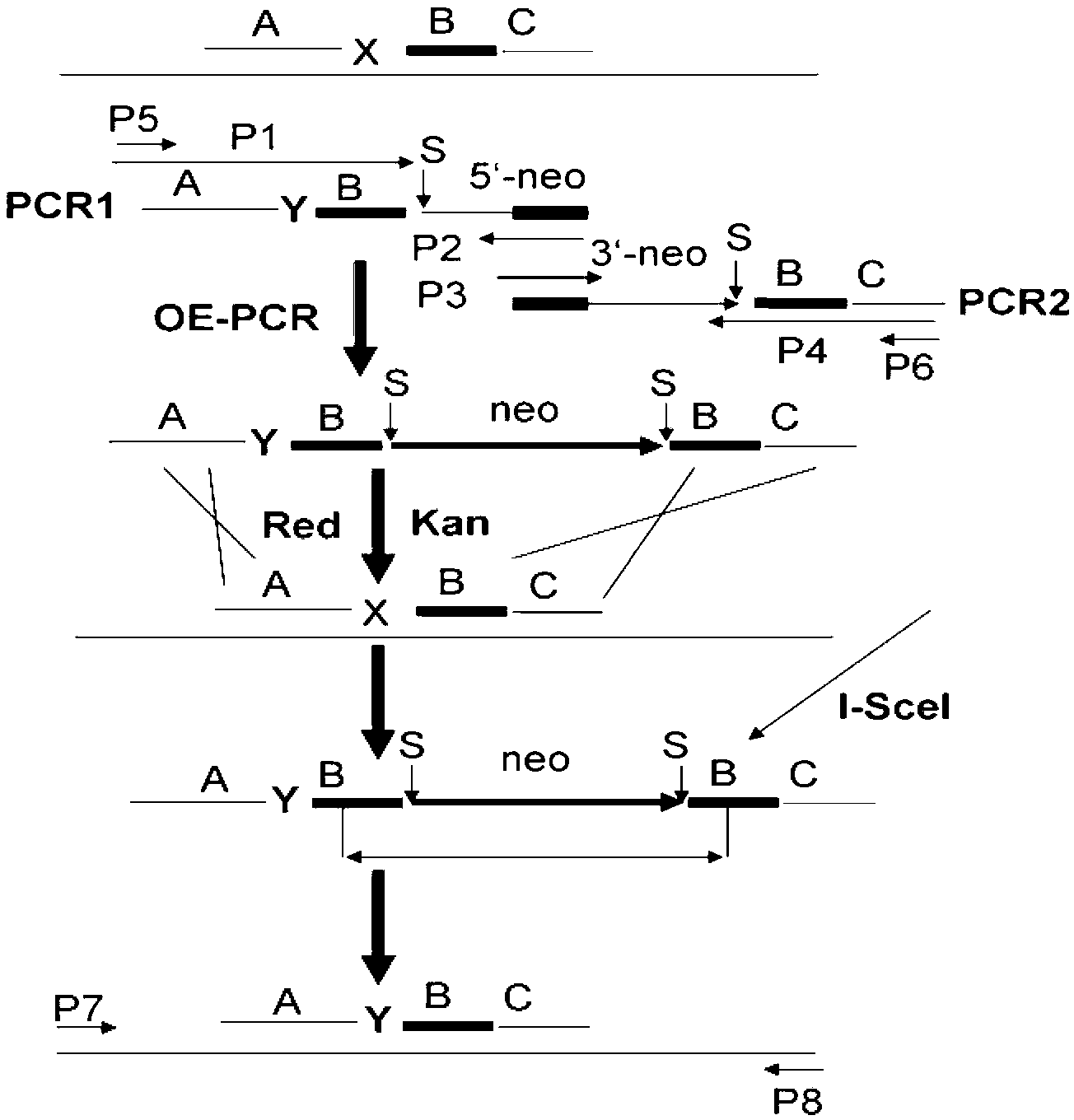
Method for recombination-mediated escherichia coli genome point mutation
InactiveCN102703424AThe method is simple and fastEfficient methodVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliNuclease
The invention relates to a method for recombination-mediated escherichia coli genome point mutation, which is realized as follows: a modified fragment is obtained through overlapping-extending polymerase chain reaction, wherein two 50bp homologous arms are located at two ends of the modified fragment and are consistent with two sides of a target site in sequence, and further, the middle part of the homologous arm comprises a mutation site, a 30bp homologous fragment consistent with downstream sequences of the target site, and a kanamycin resistance gene with two homing nuclease I-SceI enzyme cutting sites on two sides; and then, the fragments between the two 50bp homologous arms are integrated to a colon bacillus genome, the mutation site replaces the target site on the genome, and a kanamycin resistance mutant strain is obtained. Subsequently, heat-inactivated chlorotetracycline induces the expression of the I-SceI enzyme, and catalyze the 30bp homologous fragment to undertake homologous recombination with the 30bp homologous fragment downstream the target site, as a result, the 30bp homologous fragments, the two I-SceI enzyme cutting sites and the kanamycin resistance gene are eliminated, and a colon bacillus mutant strain with point mutation can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Escherichia coli strain secreting human granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)
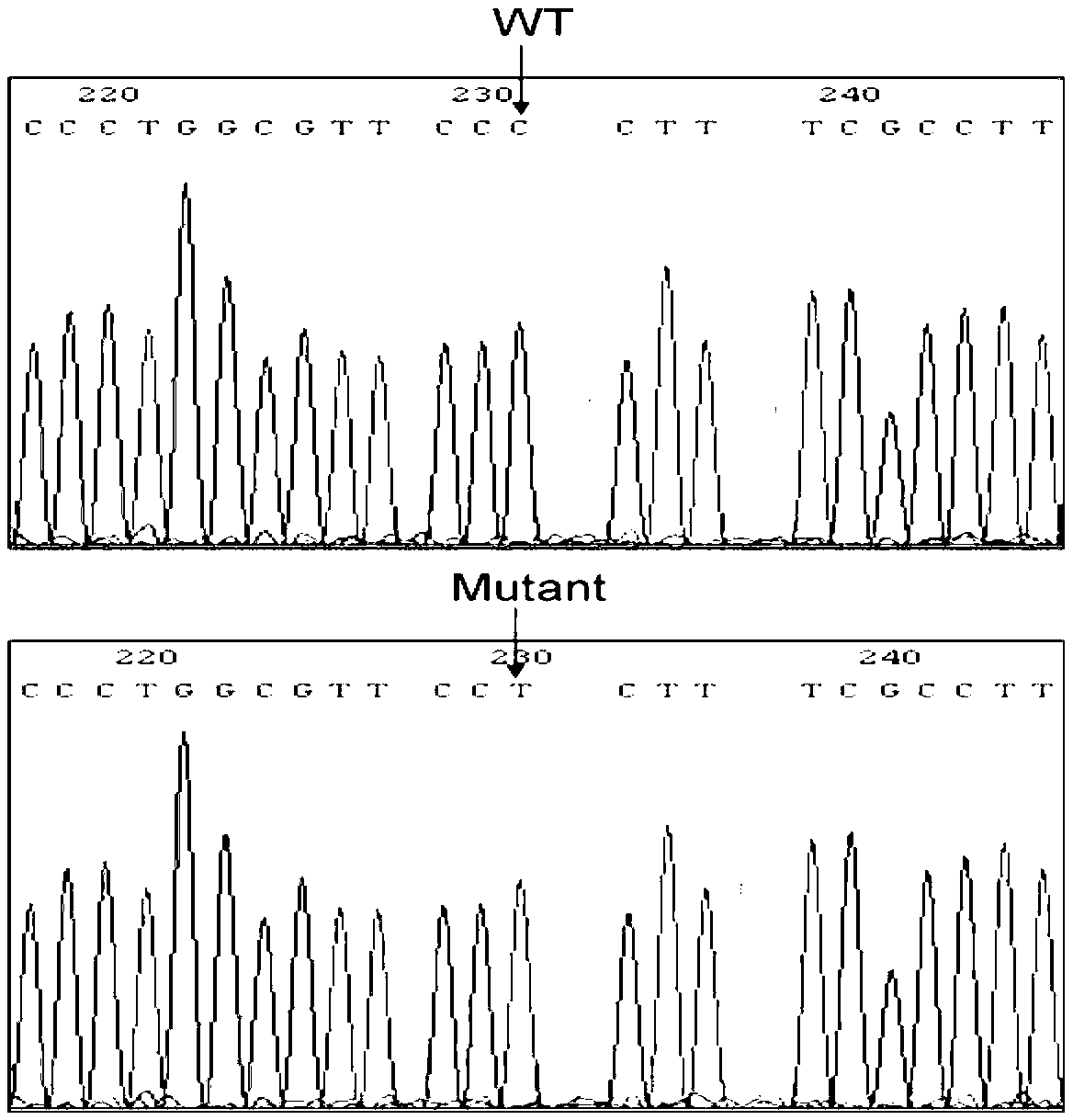
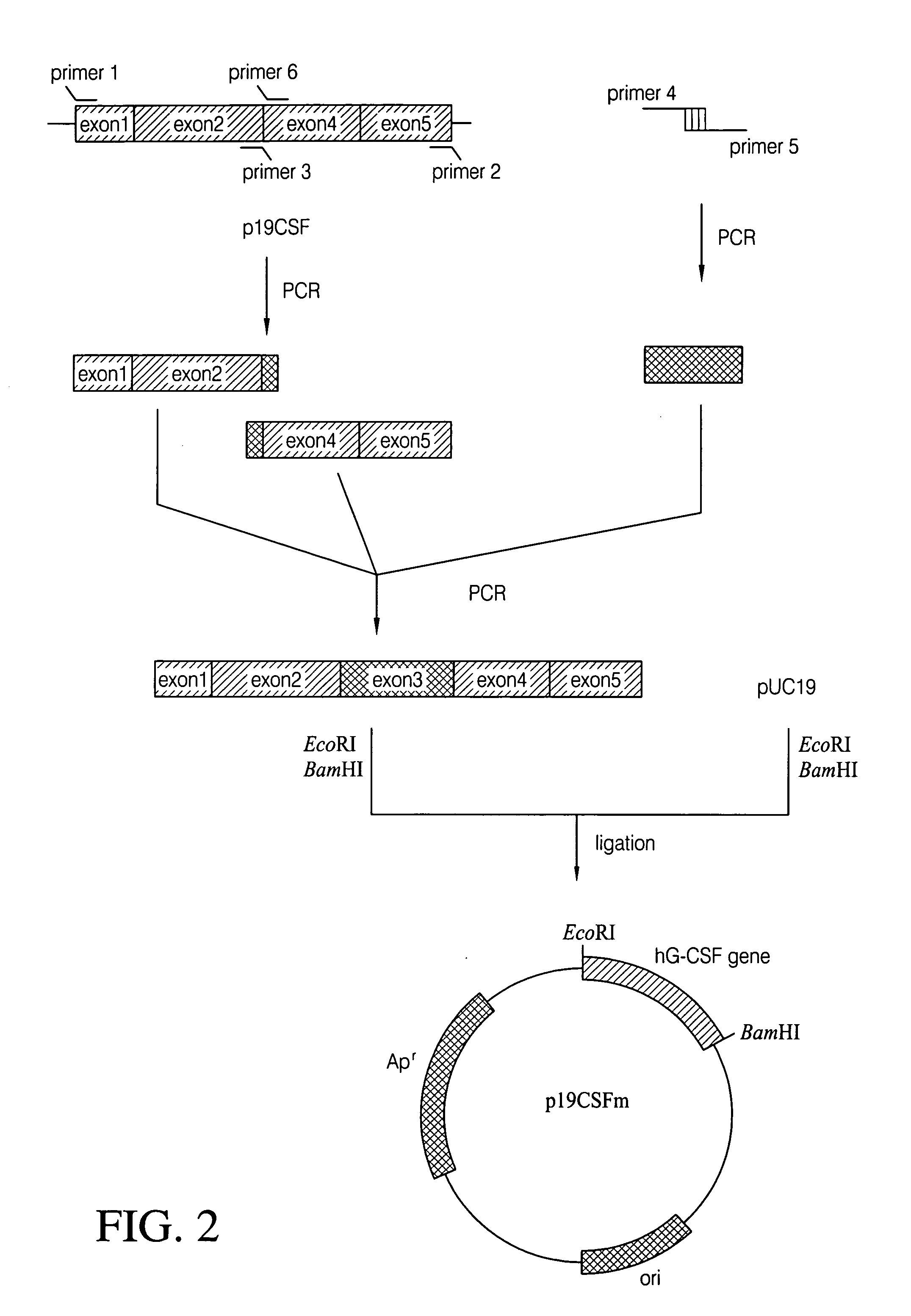
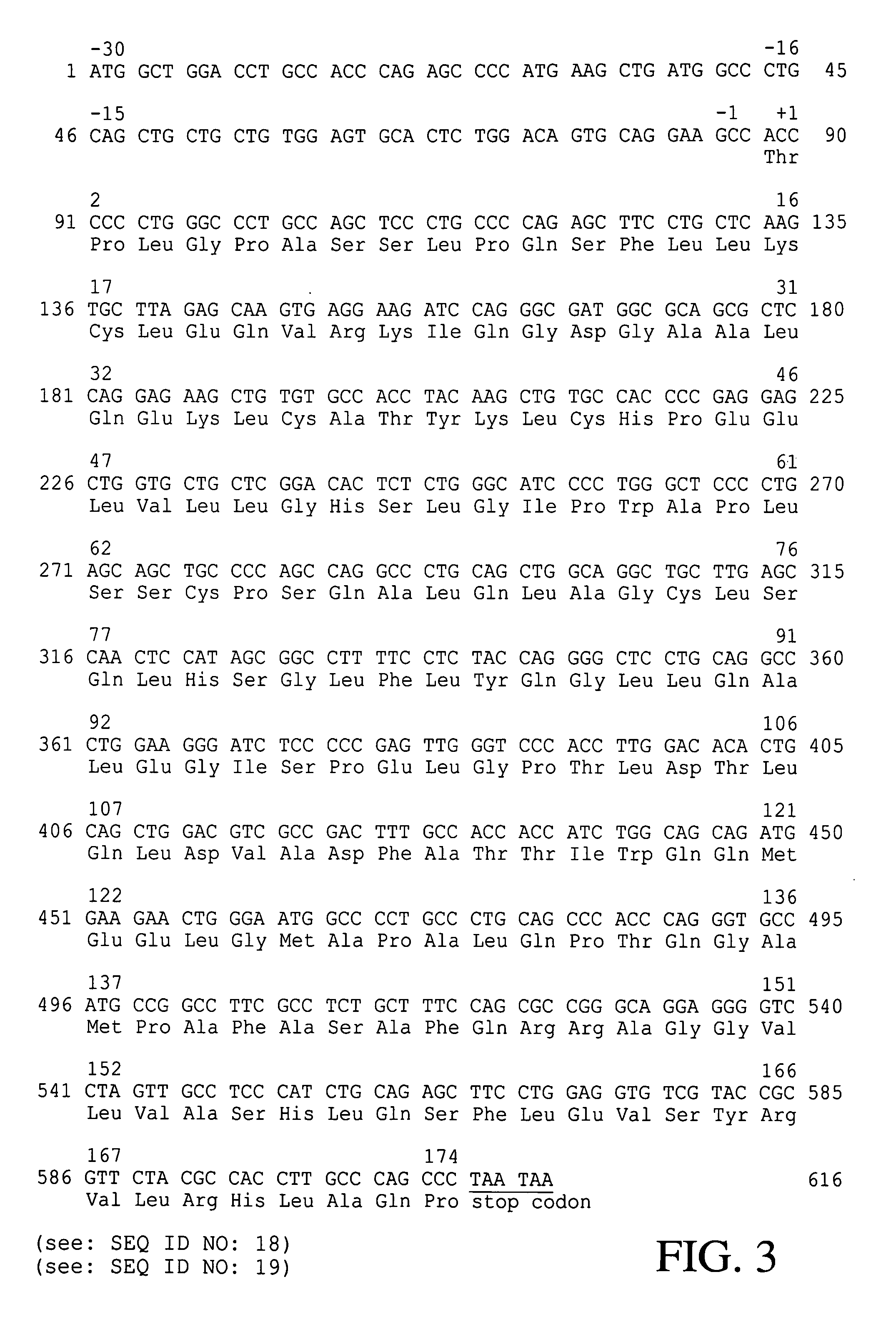
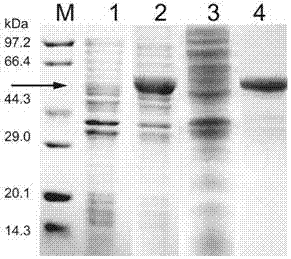
The present invention provides a recombinant plasmid vector comprising a kanamycin resistance gene, a promoter, an endoxylanase signal sequence, a nucleotide sequence coding for an oligopeptide consisting of 13 amino acids including 6 consecutive histidine residues, and a human granulocyte colony stimulating factor(hG-CSF) gene; an E. coli transformed with the said vector; and, a process for producing complete hG-CSF protein with high purity from the protein pool secreted by the said microorganism. In accordance with the invention, the hG-CSF protein can be prepared with high purity through rather simple process facilitating secretion of large amount of hG-CSF fusion protein into the periplasm, which does not require complicated processes such as solubilization and subsequent refolding required for isolation of the hG-CSF protein produced in cytoplasm as insoluble inclusion bodies by conventional techniques, thus, the hG-CSF protein can be widely used as an active ingredient in the development of supplementary agents for anticancer therapy.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli for producing phospholipase D and an application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. A phospholipase D gene is obtained through clone in Streptomyces ambofaciens by means of molecular biology measures, constructed expression plasmid is guided into E. coli BL21(DE3), and phosphatase-containing engineering bacteria formed by highly copying and recombining an expression carrier are obtained through kanamycin resistant plate screening. The recombinant phospholipase D is used for converting phosphatidylcholine and serine to generate phosphatidylserine, and efficient production of vitamin C-2-phosphate is achieved. By carrying out reaction for 2 h at the temperature of 40 DEG C with the pH value of 4.5, the yield of phosphatidylserine can reach 15.8 g / L, the conversion rate is 63.9%, and the space time yield is 7.9 g / L / h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for assortative breeding cotton variety by molecular-marking, auxiliary modifying and backcross aggregate
InactiveCN1405327AImprove qualityMeet the requirements of high-quality cottonMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationFiberAgricultural science
The invention is a molecular-marking aided-decorating backcross-polymerization selecting-cotton method. Use Si-mian 3 in the Changjiang River valley as recurrent parent, and Shanxi 94-24 and 7235 series as anti-insect and good-quality aim-character supplying parent (non-recurrent parent), and respectively make them carry through hybridization and further backcross or self-cross for 2-3 generations, each of which adopts field observing method to comprehensively select agricultural character of recurrent parent, and adopts kanamycin fastness filtration, combination of anti-insect and detecting Bt gene's PCR detection and QTL molecule-marking aided-selection to respectively obtain destination middle material, and then make the material intercross, F1 generation self-cross aided with molecule-marking aided-selection to obtain new multiple-destination self-cross aided with molecular-marking
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032
InactiveCN104561077AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSaccharumThiogalactosides
The invention relates to a recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. The gene knockout method comprises the following specific implementation steps: obtaining a DNA fragment which is provided with 500-bp homologous sequences on two sides aiming at genes to be knocked out and a kanamycin resistance gene in the middle through a polymerase chain reaction amplification; carrying out electrotransformation on the DNA fragment into a corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 cell in which recombinase is induced to express by isopropyl-Beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside, and enabling the kanamycin resistance gene to replace the target gene through the resistance selection of kanamycin to obtain gene knockout strains; finally, cultivating mutant strains in a solid medium containing cane sugar to eliminate plasmids containing recombinase genes. The gene knockout method adopts simple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and electrotransformation supplemented by the resistance selection of kanamycin, is free of operating steps, such as gene cloning in molecular biology and other certain operating steps, and simple and rapid, and has important application in the aspects of researching gene functions and producing amino acid.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
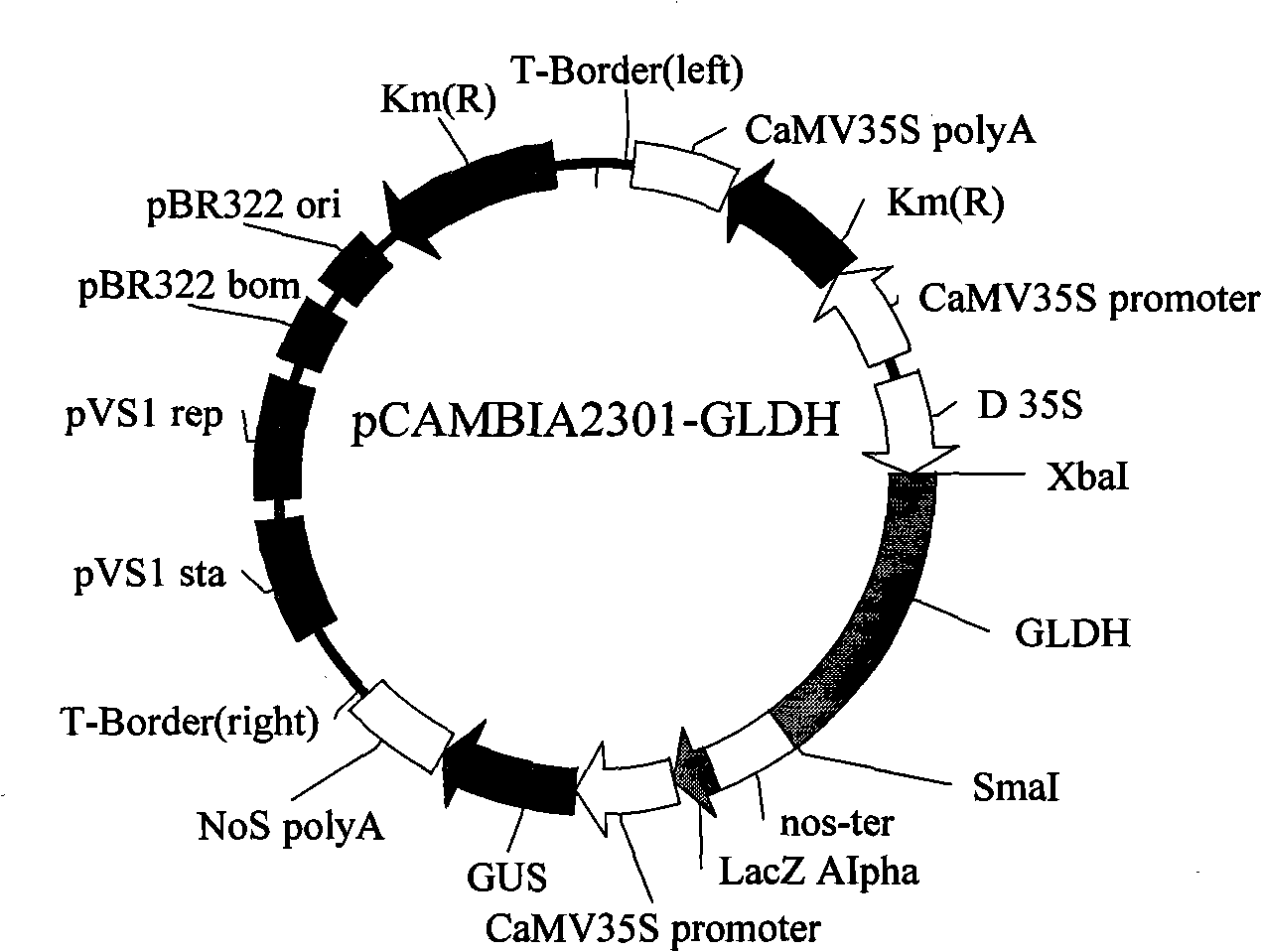
Applications of GLDH gene of brassica campestris ssp. Chinensis makino for enhancing Vc content of Brassica norinosa
ActiveCN101307318AIncrease Vc contentReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
The invention relates to an application of non-heading Chinese cabbage GLDH gene in increasing Vc content in Wuta-tsai, belonging to the molecular biology and biotechnological field. A GLDH gene integrated coding region sequence is obtained by means of a RT-PCR technology so as to further construct the plant excessive expression carrier of the sequence and to introduce agrobacterium LBA4404. Technical proposals such as a culture medium-containing formula and an operation flow are optimized, and a Wuta-tsai transgenic genetic transformation system is established. An agrobacterium mediating method is adopted to convert the plant excessive expression carrier into Wuta-tsai. A transgenic plant is obtained through a kanamycin resistant sieve, and a PCR technology is adopted to complete the identification of target gene integrated Wuta-tsai genome. The application verifies that the gene plays an important role in Vc synthesis pathway, and successfully obtains the transgenic plant of excessive expressed GLDH; compared with a non-transgenic plant, the maximum GLDH gene expression of the transgenic plant is 28.5 times of that of the non-transgenic plant, and maximum plant Vc content is 1.8 times of that of the non-transgenic plant. Therefore, the application provides both theoretical foundation and practical experience for improving vegetable quality through genetic engineering in the future.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
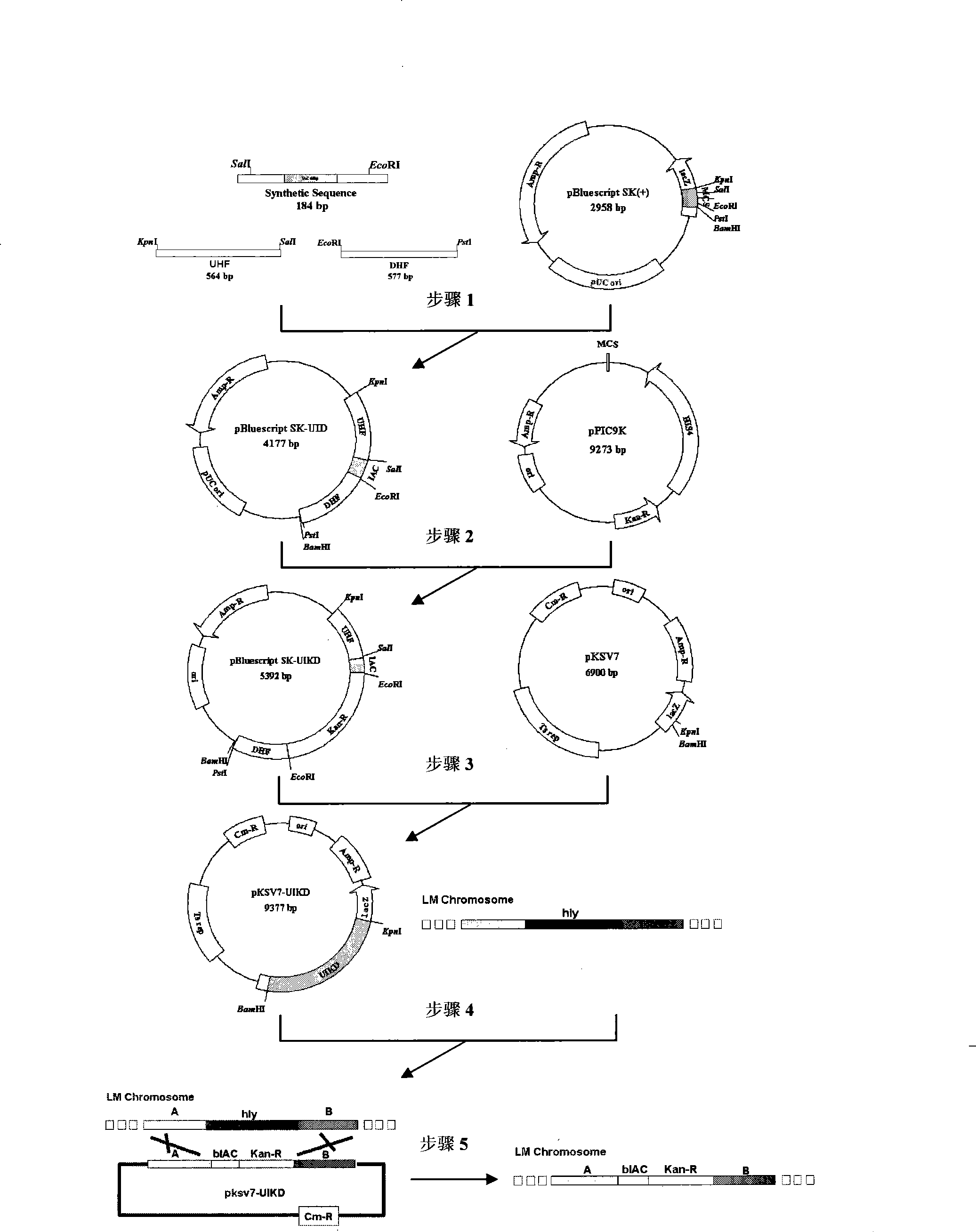
Method for preparing live bacteria internal standard based on gene substitution technique
ActiveCN101397587AImprove accuracyRealize full monitoringBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for preparing internal standard of viable bacteria based on the gene substitution technology, which pertains to the field of biotechnology and comprises the steps: (1) the selection of homologous recombination sequences, amplification internal standard sequences and kanamycin-resistant gene sequences of double-exchange DNA and the design of corresponding enzyme-cutting sites are carried out between the upstream and the downstream and target genes in the gene substitution process; (2) homologous recombination plasmids pKSV7-UIKD containing the upstream and downstream homologous sequences, the internal standard sequences and the kanamycin-resistant gene are prepared; (3) the screening of electroporation-competent listeria monocytogenes of the homologous recombination plasmids and recipient cell transformant having donator properties after the corresponding electroporation is carried out; (4) the screening of viable listeria monocytogene internal standard which carries out gene substitution is carried out; and (5) the prepared amplification internal standard is verified by adding the viable bacteria internal standard in the samples to be detected and the like. The method avoids the occurrence of false negative phenomenon caused by the inhibiting ingredients, thus greatly improving the accuracy of microbial fluorescence quantitative PCR detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Shuttle plasmid and derivative plasmid thereof
The invention discloses a shuttle plasmid and a derivative plasmid thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the shuttle plasmid which is provided by the invention is a sequence 1 in a sequence table and a 4872-5664th deoxyribonucleotide from 5'end of the sequence 1 in the sequence table is a kanamycin resistance gene and a promoter thereof. The invention also discloses the derivative plasmid thereof, which is obtained through inverting the kanamycin resistance gene of the 4872-5664th deoxyribonucleotide from the 5'end of the sequence 1 in the sequence table and the promoter of the kanamycin resistance gene and through inserting transcription terminators of a reporter gene and a corynebacterium glutamate LeuB gene in multiple cloning sites, the direction of the reporter gene is opposite to the direction of the kanamycin resistance gene and the promoter of the kanamycin resistance gene, and the transcription terminators of the corynebacterium glutamate LeuB gene are located between the reporter gene and the kanamycin resistance gene. The two plasmids have high stability and can obtain wide application on stic engineering.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for Brucella shell vaccine strain
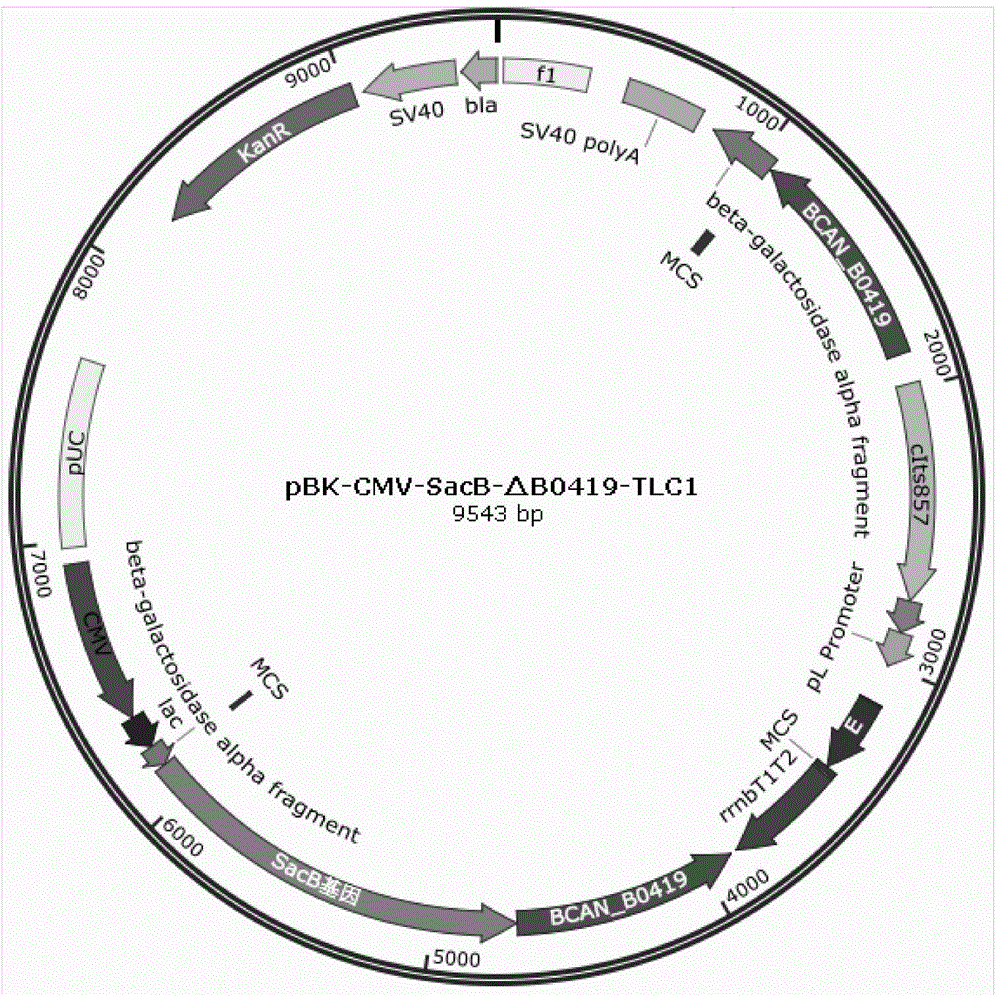
InactiveCN103952428AGood genetic stabilityImprove securityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTemperature controlLysis
A preparation method for Brucella shell vaccine strain is disclosed, relates to the field of molecular biology and microbiology, and helps to solve the problem that conventional bacteria shell preparation method is high in cost and not suitable for large-scale production. The method comprises: respectively cloning PCR products of homogenous arms at the upstream and at the downstream of a specific gene of Brucella strain genome to a pMD18-T Simple vector to construct recombinant plasmids, performing double digestion on the recombinant plasmids, successively connecting with plasmid pBK-CMV-SacB subjected to digestion processing for constructing a suicide plasmid, performing PCR amplification on a temperature-control lysis part of a temperature-control expression plasmid pBV220-E, performing digestion processing on the amplification product, inserting into the suicide plasmid; and transforming the temperature-control lysis type suicide plasmid into competent Brucella, and performing positive and negative screening by utilizing kanamycins resistance and fructose sucrase gene, so as to obtain the Brucella shell vaccine strain. The Brucella shell vaccine strain has good heredity stability, security, effectiveness and immunogenicity.
Owner:MILITARY VETERINARY RES INST PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Mutant strains of Brucella melitensis and immunogenic compositions
InactiveUS20050249755A1Easy to useStop the spreadAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntibiotic resistanceMedicine
Live attenuated vaccines against brucellosis are described. New mutant strains of Brucella melitensis have been developed, which are attenuated via deletion of the hfq and / or purEK sites. The purEK deletion site does not include insertion of a kanamycin resistance determinant marker or any other introduced antibiotic resistance marker. The hfq deletion site preferably does not include insertion of a kanamycin resistance determinant marker or any other introduced antibiotic resistance marker.
Owner:NIKOLICH MIKELJON +3
Mammalian expression vector pUHAB
The present invention relates to the construction and utilization of a new mammalian expression vector that contains a unique multiple cloning site (MCS), designated pUHAB. The pUHAB vector comprises a high copy replication origin (ColE1), a drug resistance gene (TK-Hygromycin), and a human cytomegalovirus promoter operably associated with a unique intron (hCMV / intron). Further, pUHAB comprises a selectable marker conferring resistance to kanamycin in bacterial cells, and a phage f1(+) region. pUHAB can be used to transiently or stably express cloned genes when transfected into mammalian cells. The invention also encompasses kits and host cells and cell lines comprising pUHAB, and methods of producing a recombinant protein using pUHAB.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Method for simultaneously detecting 17 genes
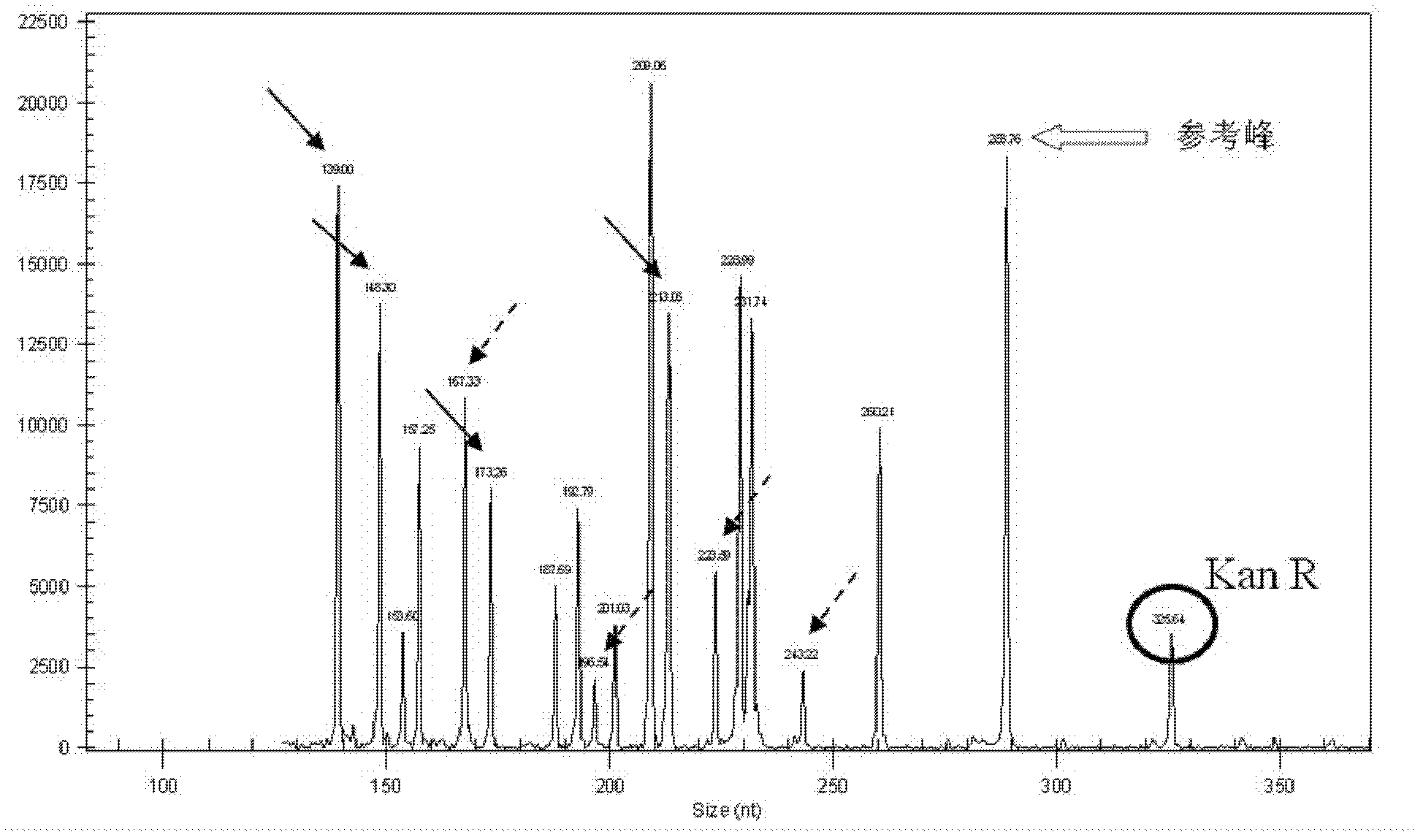
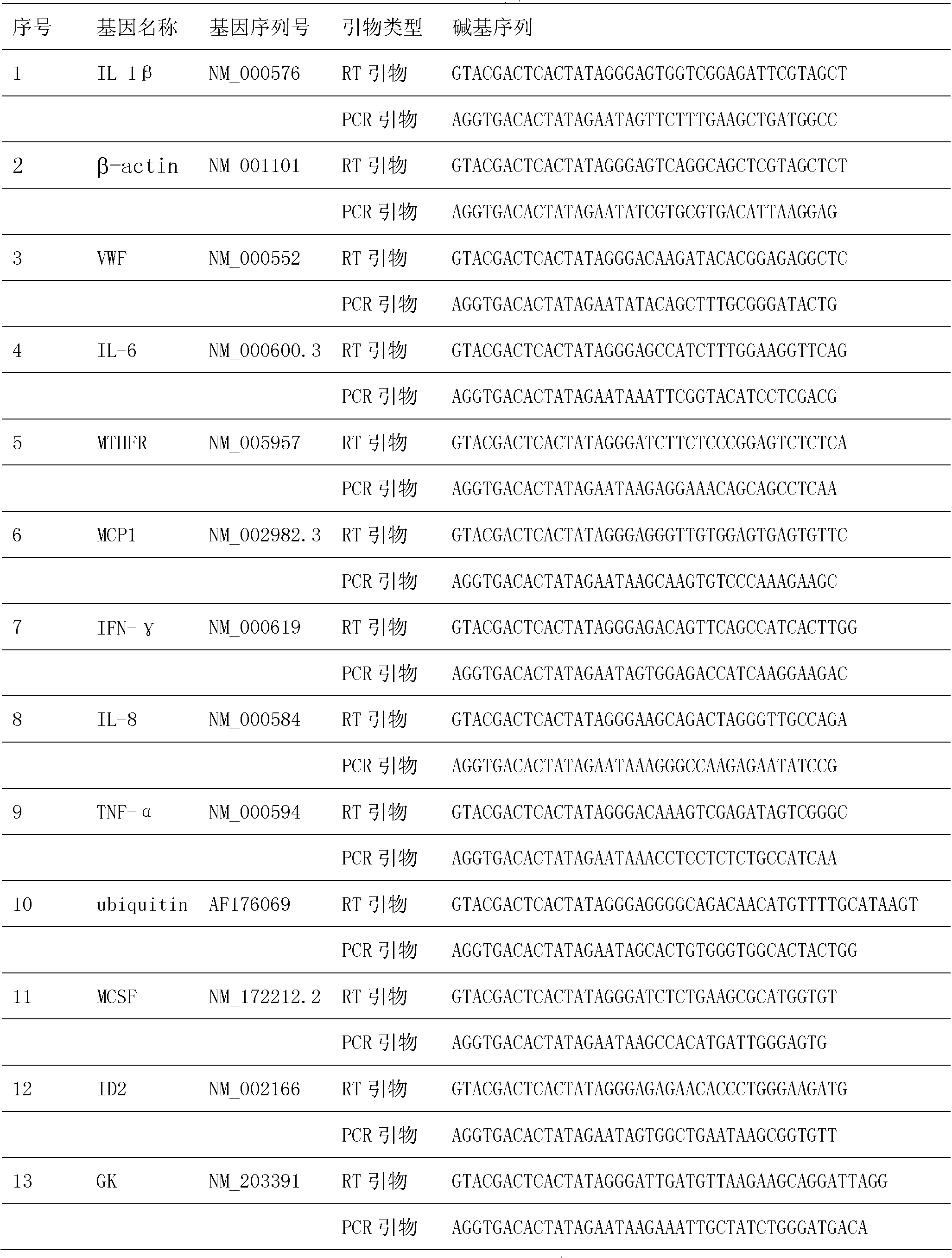
InactiveCN102251036ASmall sample sizeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSmall sampleWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously detecting 17 genes. Sequences of mRNA of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta, NM-000576, etc.) and sapiens glycerol kinase (NM-203391) are referred to on PUBMED; a reverse transcription primer and a PCR primer are designed; reverse transcription, PCR amplification and capillary electrophoresis are performed; and quantitative analysis is performed by a Gexp analysis system. The detection method not only comprises a quality control gene of a kanamycin resistance gene (Kan, R) for monitoring the reaction system, but also designs two amplified products for L-selectin which are used to detect the stability of the reaction system. The invention has the advantages of small sample size required, high sensitivity and accuracy. The method analyzes the properties and components of an atherosclerotic plaque by detecting the expression situation of peripheral blood related genes, and establishes a technical platform for batch screening of differential genes between cardiovascular diseases and controls.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Pig breed brucella bax inhibitor-1 (BI-1) gene deletion strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110699312APromote growthHigh degree of polymerizationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBrucellaTGE VACCINE
The invention discloses a pig breed brucella bax inhibitor-1 (BI-1) gene deletion strain and a construction method and application thereof. The strain is obtained by replacing a pig breed brucella BI-1 gene with a kanamycin resistance gene, and the method includes the main steps that a pig breed brucella S2 vaccine strain genome is taken as a template, PCR amplification is conducted to obtain an upstream homologous arm and a downstream homologous arm of the BI-1 gene, the upstream homologous arm and the downstream homologous arm of the BI-1 gene and a kanamycin resistance gene fragment also obtained through PCR amplification are together cloned into a pUC18 plasmid, and a homologous recombination deletion plasmid pUC18-BI1-KanR is obtained. The plasmid is used for electrotransformation ofa pig breed brucella competent cell, and through PCR identification, an obtained positive transformant is the pig breed brucella BI-1 gene deletion strain. Compared with a wild strain, the deletion strain shows the characteristics of decreasing the growth rate, reducing colonies, increasing cell membrane permeability, enhancing cell polymerization and the like, and it is indicated that the deletion strain has the potential of serving as a brucella attenuated live vaccine.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for agrobacterium mediated gene conversion of grass sorghum
InactiveCN101319226ASolve the problem of not being able to obtain resistant callusPromote differentiationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationTransformation efficiencyAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a method for transforming Sudan grass through an agrobacterium mediating gene, which belongs to the biotechnology field. When the agrobacterium mediating method is used to transforming exogenous gene of Sudan grass, a faint yellow granular callus which is obtained from the in-vitro culture and induction of a Sudan grass young ear is taken as acceptor material; after the infection and co-culturing of the agrobacterium , the acceptor material undergoes 10 to 20mg / L kanamycin resistance screening to obtain a resistance callus in a subculture medium of carbenicillin with attached antibiotics of 500mg / L; the resistance callus is translated into a differentiation culture medium of the carbenicillin with the attached antibiotics of 500mg / L to obtain a regenerated plantlet; the plantlet is cultured to have sound seedling and root and survives after transplantation; and a transgenic plant is obtained after the plant passes a PCR test. The Sudan grass genetic transformation method established by the invention has a transformation rate of more than 3 percent, thereby laying the foundation for carrying out the transgenic breeding of the multi-purpose Sudan grass through the agrobacterium mediating method.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Colibacillus expression carrier and its application
ActiveCN1912127AHigh yieldLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGlutaryl-7-aminocephalosporanic acidMutant
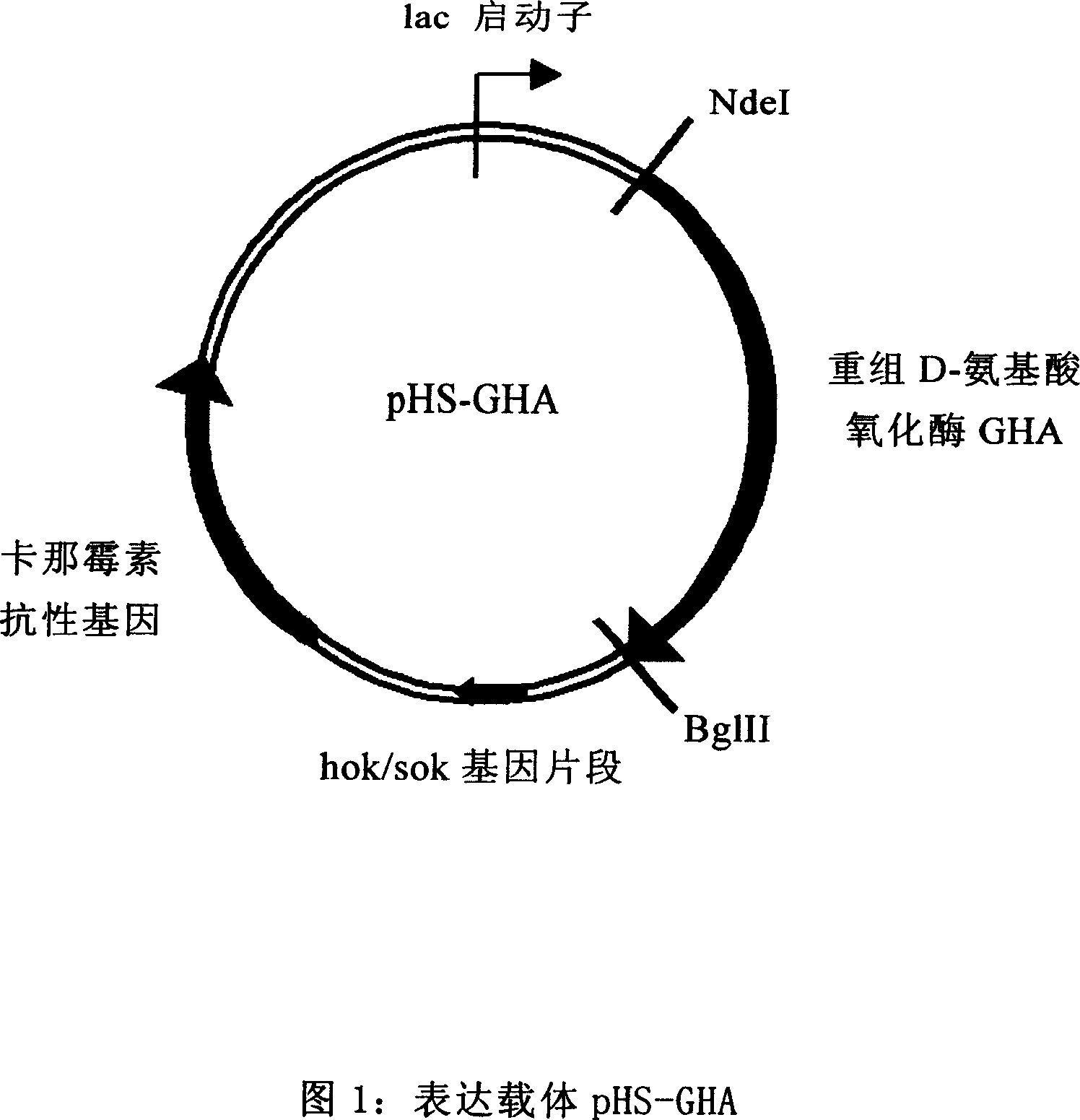
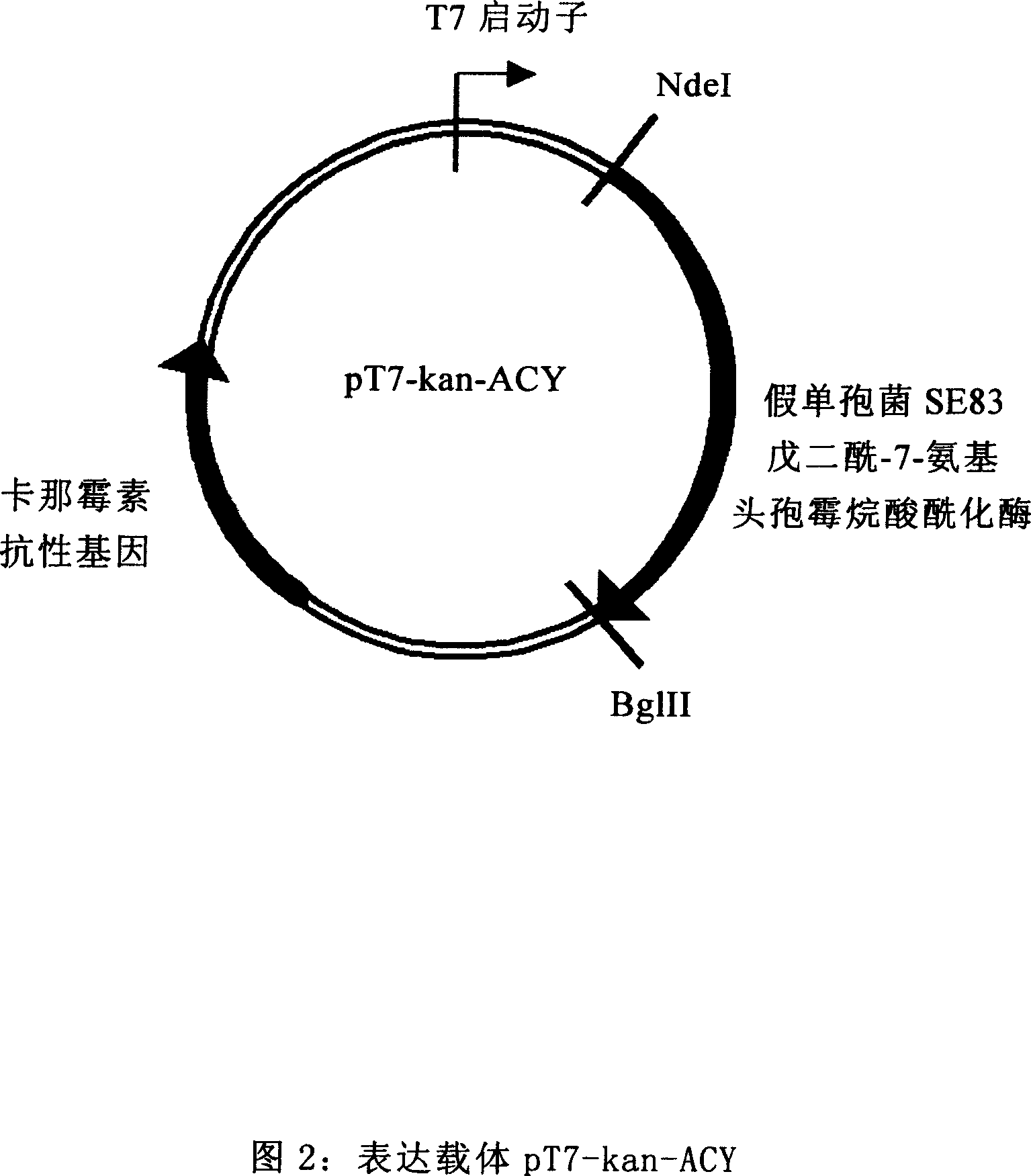
The invention provides Escherichia coli expression vector and its using method. The expression vector is formed by vector pRSET-A whose ampicillin resistant gene is replaced by kanamycin resistant gene. And it can be used to express the enzyme needed in making 7-aminocephalosporanic acid but no beta-lactamase reduced its yield. The invention also provides two concrete expression vectors that pHS-GHA and pT7-kan-ACY whose gene products are respectively D-amino acid oxidase mutant GHA and Pseudomonas sp.SE83 glutaryl-7-aminocephalosporanic acid acidylating enzyme.
Owner:常熟盈赛生物科技有限公司 +1
Antibiotic Resistance Conferrred by a Plant Abc Transporter Gene when Expressed in Transgenic Plants
InactiveUS20080250527A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesAntibiotic resistanceArabidopsis thaliana
The use of selectable marker genes, such as the kanamycin resistance encoding neomycin phosphotransferase (nptII), has been invaluable in transgenic plant production. The subject invention provides a new selectable marker gene, an Arabidopsis thaliana ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter, Atwbc19 and methods of using the gene for the identification of transgenic plants. Since ABC transporters are endogenous to plants, there should be less controversy using Atwbc19, as a selectable marker in transgenic plants with regards to concerns of horizontal gene transfer.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
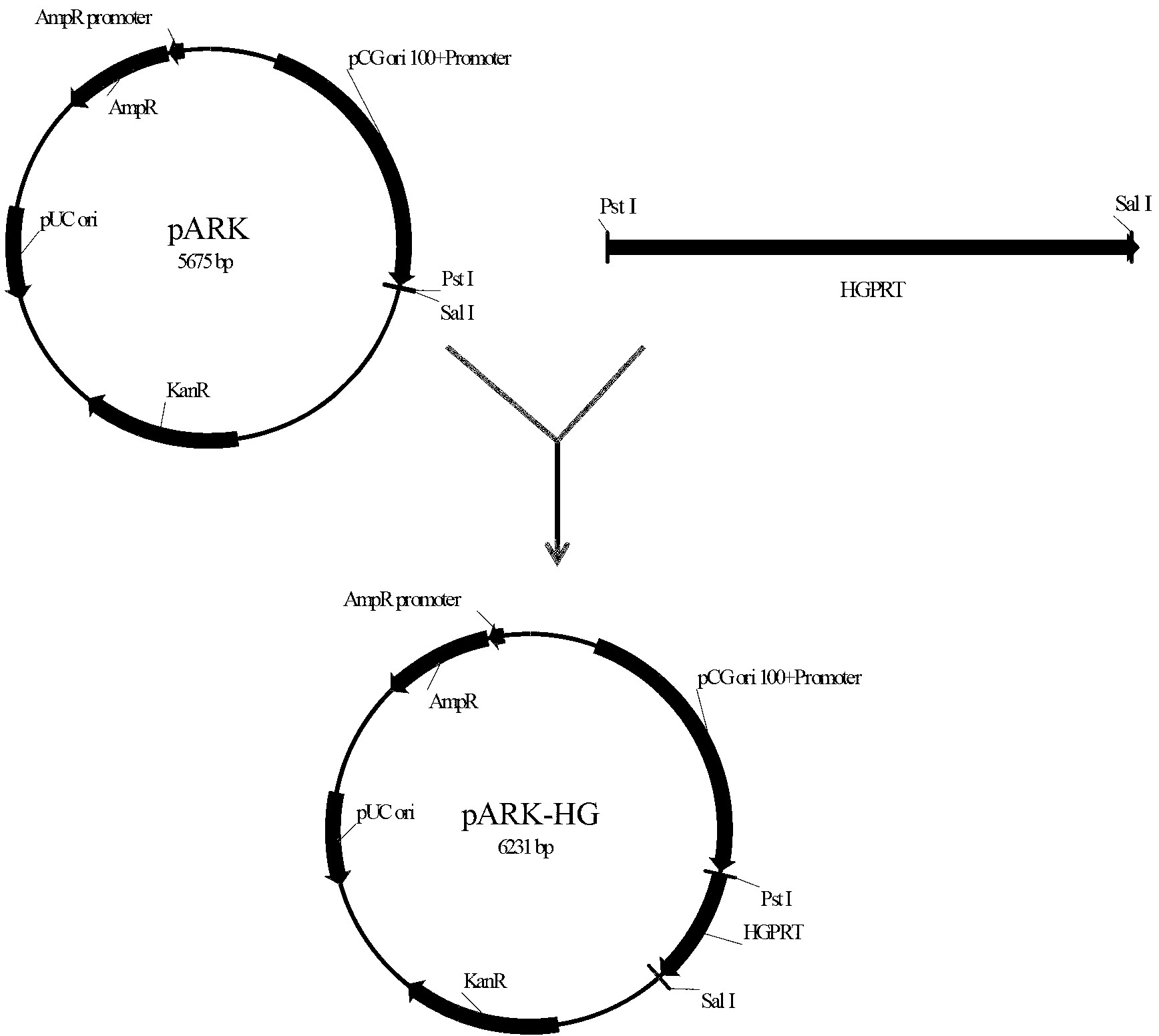
Arthrobacterium for overexpression of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene, and building method and application thereof
ActiveCN103320373AImprove synthesis abilityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses arthrobacterium for overexpression of a hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene, and a building method and an application thereof, and clones key enzyme hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene (hgprt) of a purine salvage pathway, and rebuilds recombinant expression plasmids by using escherichia coli-arthrobacter shuttle plasmids. The recombinant plasmids are led to the arthrobacterium through an electrotransformation method; a converter is screened by kanamycin resistance, and then genetically engineered bacterium is validated by plasmid PCR (polymerase chain reaction). Thus, the recombinant arthrobacterium AR-HG is built. The yield of the recombinant arthrobacterium AR-HG disclosed by the invention is improved by 16.6% in comparison with that of an original strain; the synthesis ability of unit thallus cAMP (cyclic adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate) is improved by 27.0%; and the arthrobacterium can be directly used for industrial production of the cAMP. Thus, the yield is improved; and the cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com