Method for recombination-mediated escherichia coli genome point mutation
A technology of Escherichia coli and genome, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of long homologous fragments, difficulty in popularization and application, and time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of high efficiency and good economic prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
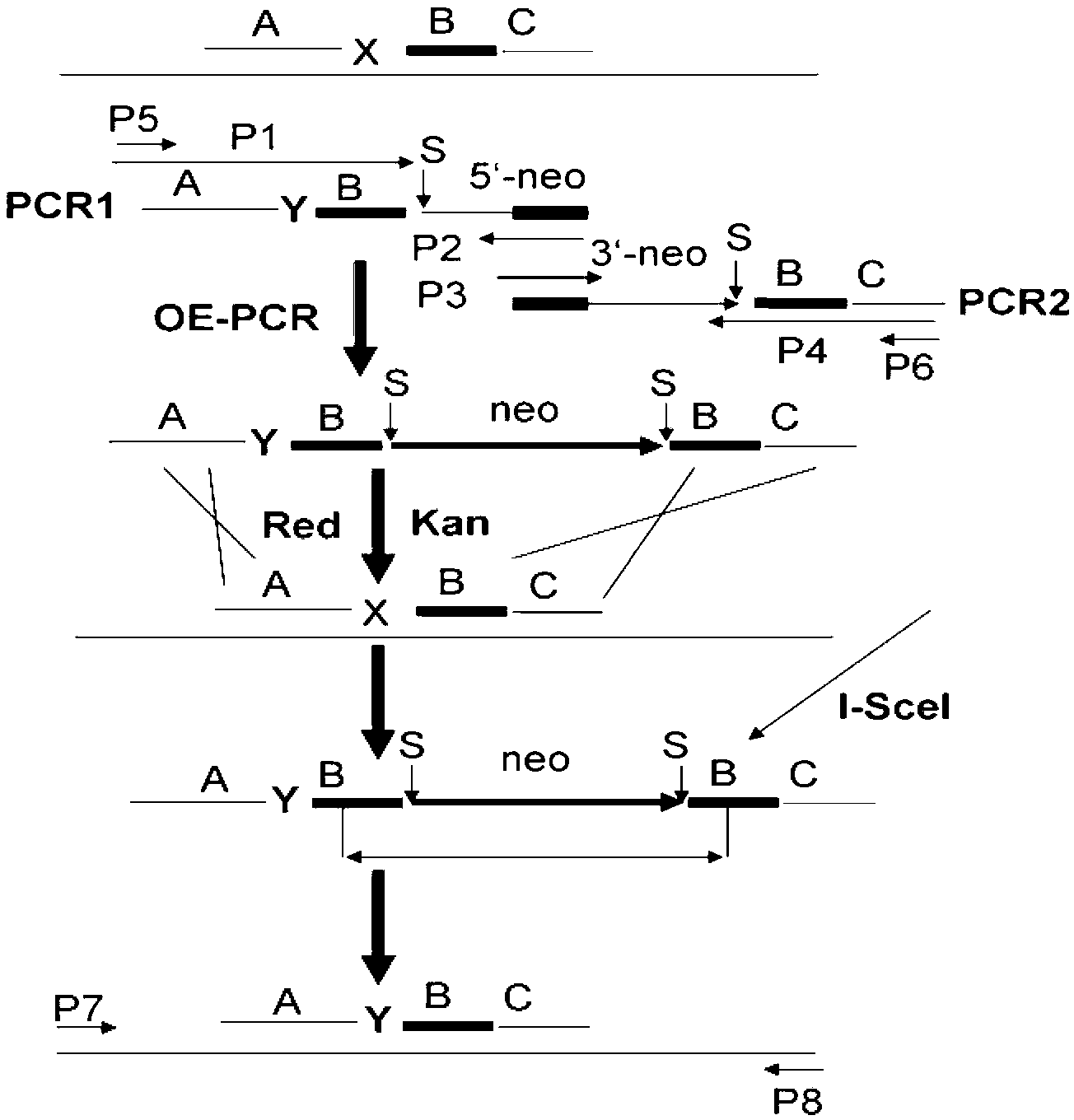
[0042] Example 1. Construction of the vector
[0043] 1. Construction of recombinant enzyme and I-SceI expression vector
[0044] Design primers IPM1: 5'-GGGATGCATTTAAGACCACTTTCACATTTAAG-3', (SEQ ID NO.1); IPM2: 5'-GGGATGCATTTATTTCAGGAAAGTTTCGGAG-3', (SEQ ID NO.2). Using pST98-AS as a template, IPM1 and IPM2 were amplified to obtain a 1.4kb tetR-ptetA-I-SceI fragment. The 1.4kb fragment was digested with NsiI and cloned into the NsiI site of pBAD322 to obtain a recombinant clone pLS133.
[0045] Design primers IPM3: 5'-GGGCCATGGATTAATACTGAAACTG-3', (SEQ ID NO.3); IPM4: 5'-GGGCTCGAGCTATCGCCATTGCTCCCCAAATAC-3', (SEQ ID NO.4). Using HindIII-digested lambda phage DNA (purchased from Dalian Bao Biological Co., Ltd.) as a template, IPM3 and IPM4 were amplified to obtain a 1.9kb red gene fragment, which was digested with NcoI and XhoI and cloned into the NcoI and SaII positions of pLS133 Click to obtain the target clone pLS134. XhoI and SaII are homologous enzymes, which can be l...
Embodiment 2
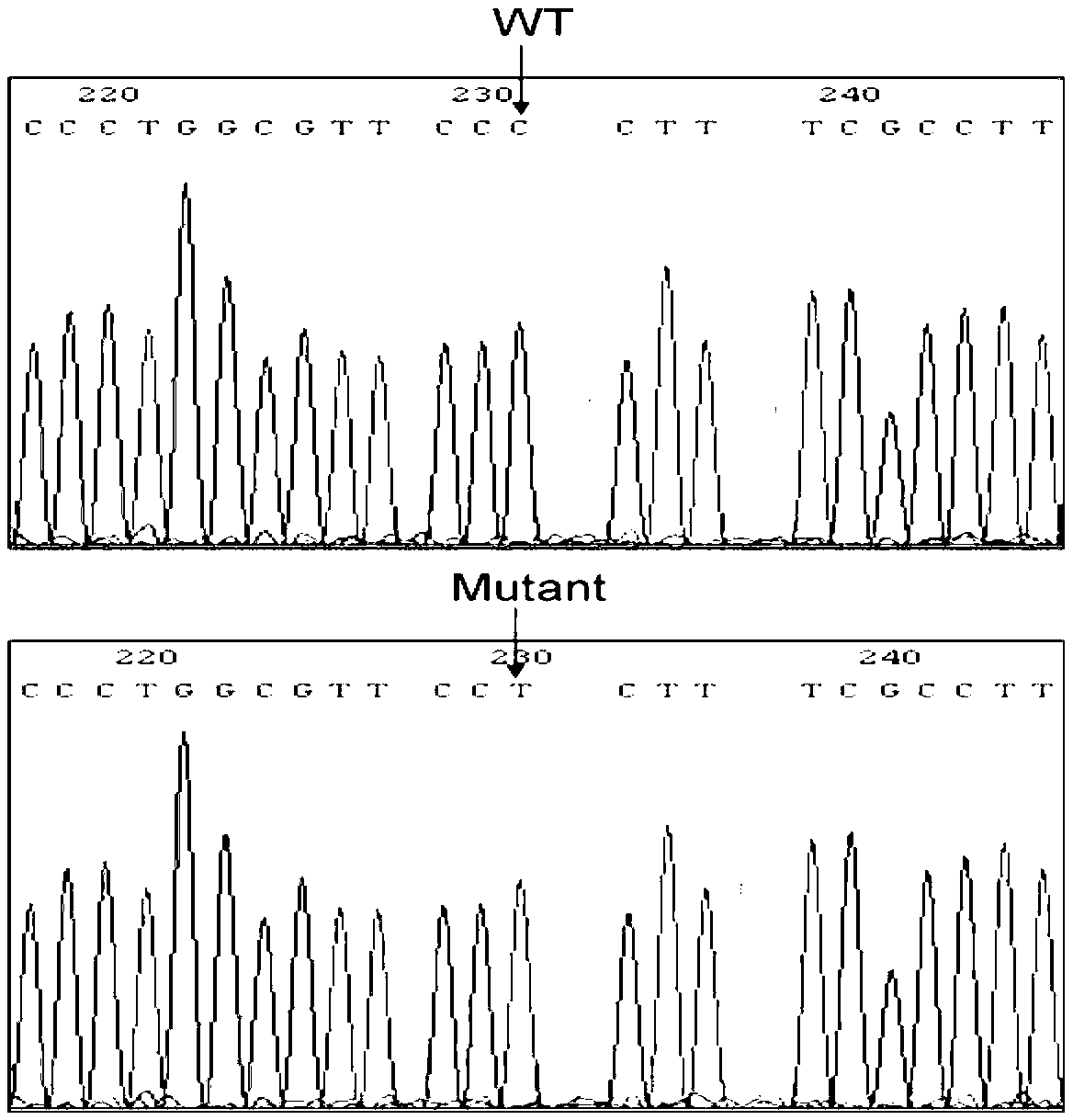
[0049] Example 2 The 70th base C in the open reading frame of the lacZ gene is mutated to T
[0050]1. Preparation and transformation of Escherichia coli competent cells expressing the Red recombinase gene
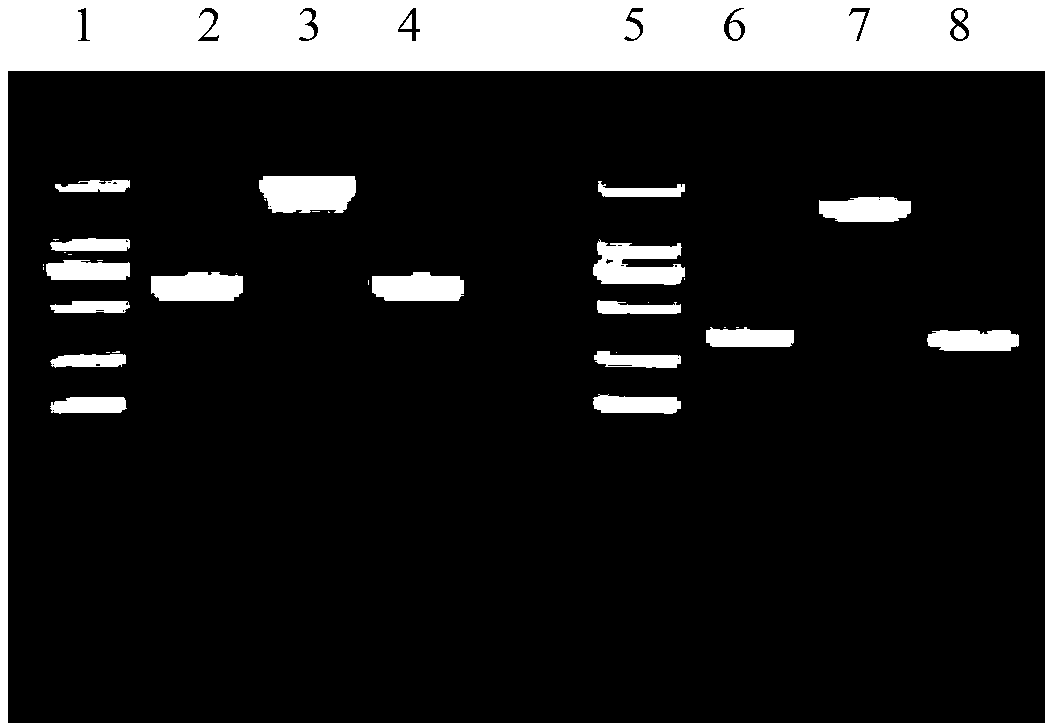
[0051] pLS134 was transformed into MG1655 and selected for resistance to ampicillin containing 50 μg / ml. Inoculate the single colony of the obtained bacterial strain into 3ml LB liquid medium, shake overnight at 37°C, transfer to 50ml LB with 1 / 50 volume, and shake and cultivate until the cell OD 600 At about 0.2, add L-arabinose at a final concentration of 0.15% to induce recombinase, and continue culturing until OD 600 About 0.4, pour the bacterial solution into a pre-cooled centrifuge tube, ice bath for 10 minutes, centrifuge at 5000rpm for 5 minutes at 4°C, and discard the supernatant. The precipitate was washed twice with ice-cold 10% glycerol, and finally suspended in 200 μl ice-cold 10% glycerol, 50 μl per tube.
[0052] Add the DNA dissolved in double distilled ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3 The 574-576th base GAA of the open reading frame of the nanA gene is mutated into AAC
[0062] In this embodiment, the target site is the 574th-576th base GAA of the open reading frame of the nanA gene, and the mutation site is AAC, that is, GAA is mutated into AAC.
[0063] Design primer R1171: 5'- AACAAATAGGGGTTCCGCGC -3', (SEQ ID NO.15), in this primer, the 50bp homology arm upstream of the target site is indicated by lowercase letters, the mutation site is indicated by bold letters, and the 30bp homology fragment downstream of the target site is indicated by The italic letters indicate that the amplification primers are underlined; R1172: 5'-GTACTGCCGATACCACCATCAGC TTCCTATTCCGAAG -3', (SEQ ID NO.16), in this primer, the reverse complementary sequence of 20 bp downstream of the 30 bp homologous fragment downstream of the target site is indicated by regular letters, and the reverse complement of the 30 bp homologous fragment downstream of the targ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com