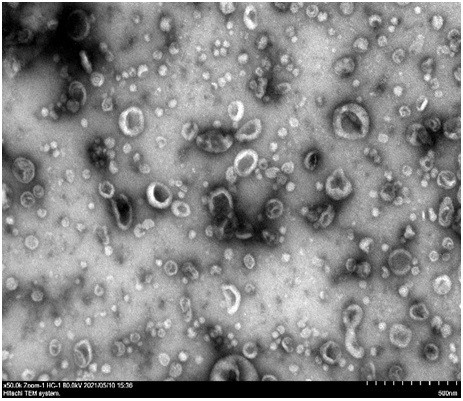
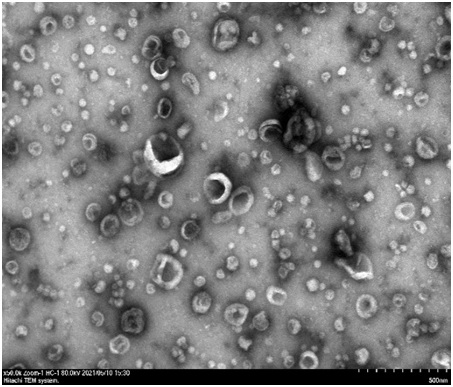
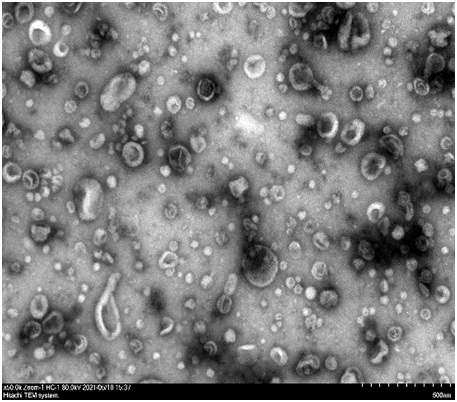
Exosome separation and purification method
A technology for separation and purification of exosomes, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of small processing volume, low cost, poor reproducibility of sample quality attributes, etc., and achieve the effect of high recovery rate and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] step one
[0065] 1.1 Acid precipitation
[0066] Take 1L of milk and use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH to 4.6. During the pH adjustment process, use a magnetic stirrer to stir at room temperature, and then let the acid settle for 60 minutes.
[0067] 1.2 Sample clarification
[0068] Place the sample after acid precipitation in a centrifuge cup, use a centrifuge to centrifuge at a centrifugal force of 3500g for 30min, and take the supernatant after centrifugation. Or use a bag filter with a cut-off pore size of 10 μm to filter with a filter speed of 50 ml / min, and take the filtered supernatant solution.
[0069] 1.3 Depth filtering
[0070] The centrifuged or filtered supernatant solution is further clarified and filtered using a depth filter with a cut-off pore size of 0.5-10 μm at a filtration rate of 10 ml / min to obtain a supernatant solution.
[0071] 1.4 Ultrafiltration concentrated liquid exchange
[0072] Ultrafiltration membrane bag: 100KD ultrafiltra...
Embodiment 2
[0112] step one
[0113] 1.1 Impurity removal
[0114] Take 1L of milk and put it in a beaker, add 0.5mol / L calcium chloride solution to the above solution to a final concentration of 0.001mol / L, then add rennet according to the final concentration of 5SU / ml, and use a magnetic stirrer at 30°C Stir well.
[0115] 1.2 Sample clarification
[0116] Place the sample after rennet-precipitated casein into a centrifuge cup, use a centrifuge to centrifuge at a centrifugal force of 4000g for 30min, and take the centrifuged supernatant. Or use a bag filter with a cut-off pore size of 10 μm to filter with a filter speed of 50 ml / min, and take the filtered supernatant solution.
[0117] 1.3 Depth filtering
[0118] The centrifuged or filtered supernatant solution is further clarified and filtered using a depth filter with a cut-off pore size of 0.5-10 μm at a filtration rate of 10 ml / min to obtain a supernatant solution.
[0119] 1.4 Ultrafiltration concentrated liquid exchange
[...
Embodiment 3
[0160] step one
[0161] 1.1 Acid precipitation
[0162] Take 10L of milk and use lactic acid to adjust the pH to 4.6. During the pH adjustment process, turn on the stirrer to stir at room temperature, and then let the acid settle for 60 minutes.
[0163] 1.2 Sample clarification
[0164] Place the sample after acid precipitation in a centrifuge cup, use a centrifuge to centrifuge at a centrifugal force of 4000g for 30min, and take the supernatant after centrifugation. Or use a Cobetter bag filter with a cut-off pore size of 10 μm for filtration at a filtration rate of 200ml / min, and take the supernatant solution after filtration.
[0165] 1.3 Depth filtering
[0166] The supernatant solution after centrifugation or filtration is further clarified and filtered with a depth filter with a cut-off pore size of 0.5-10 μm, and the filtration speed is 100 L / m 2 / h to obtain a supernatant solution.
[0167] 1.4 Ultrafiltration concentrated liquid exchange
[0168] Ultrafiltrati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com