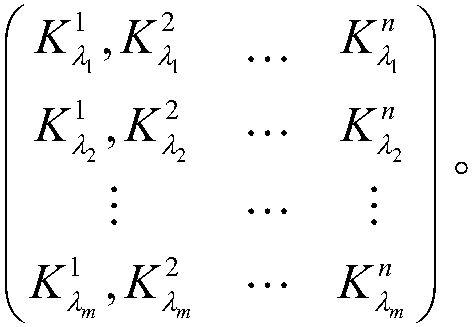
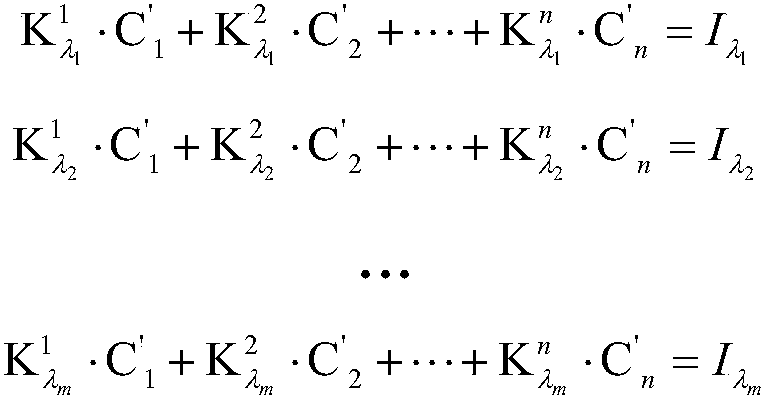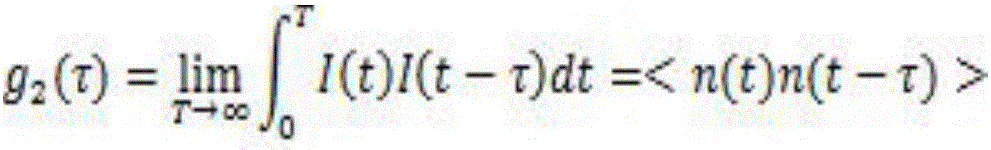Patents
Literature
53 results about "Light scattering measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
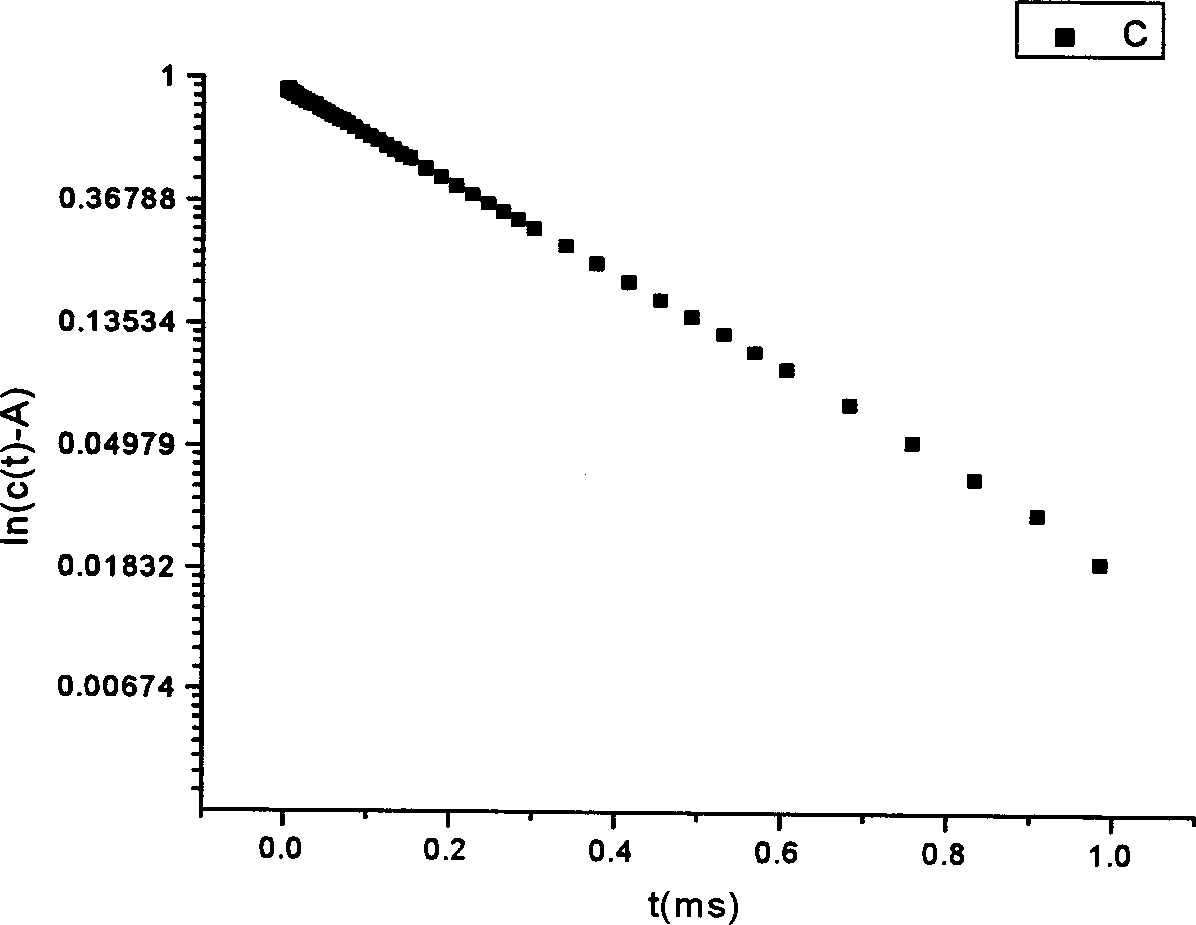
Particle size can be determined by measuring the random changes in the intensity of light scattered from a suspension or solution. This technique is commonly known as dynamic light scattering (DLS), but is also called photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS) and quasi-elastic light scattering (QELS).
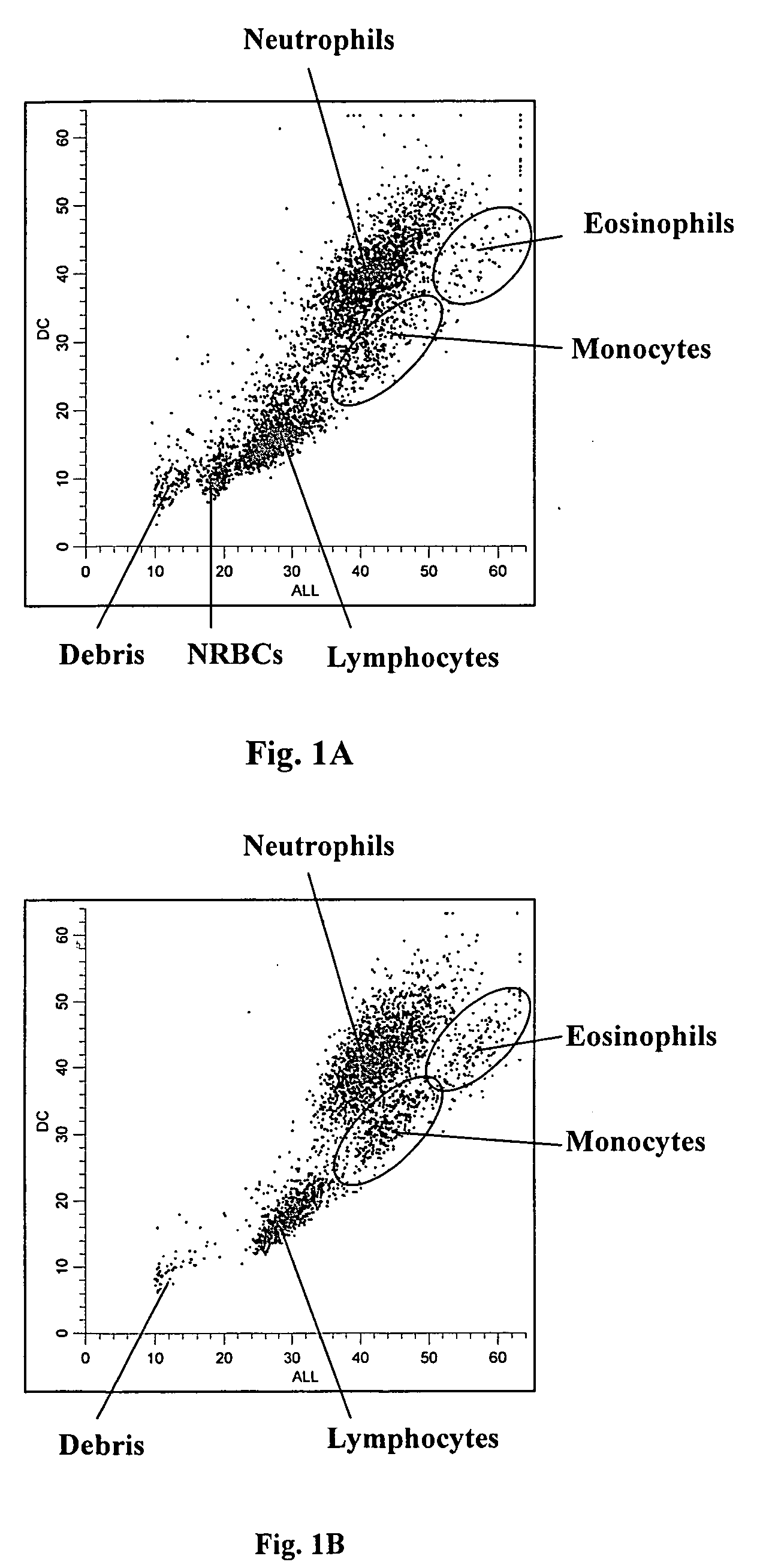
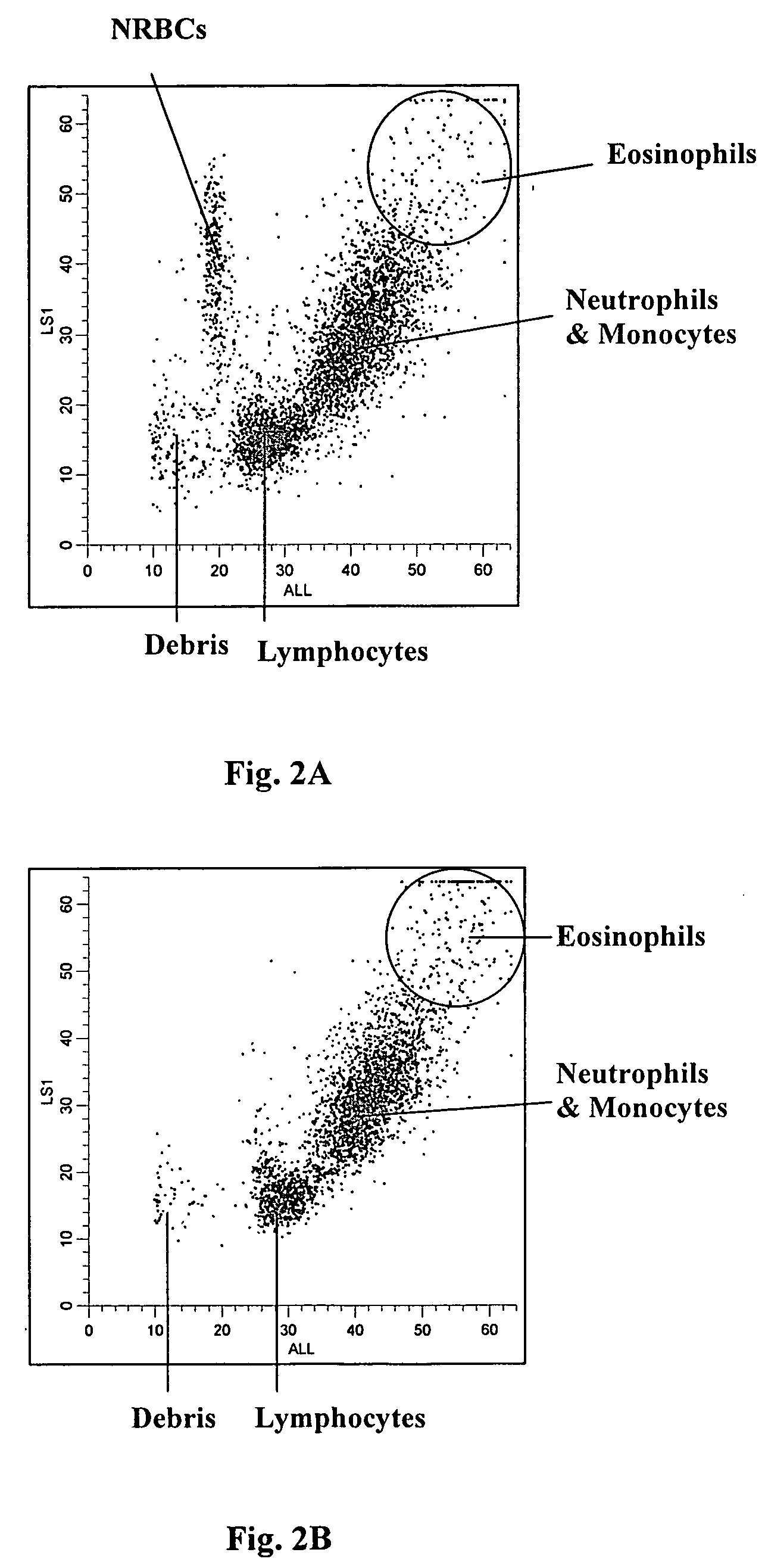
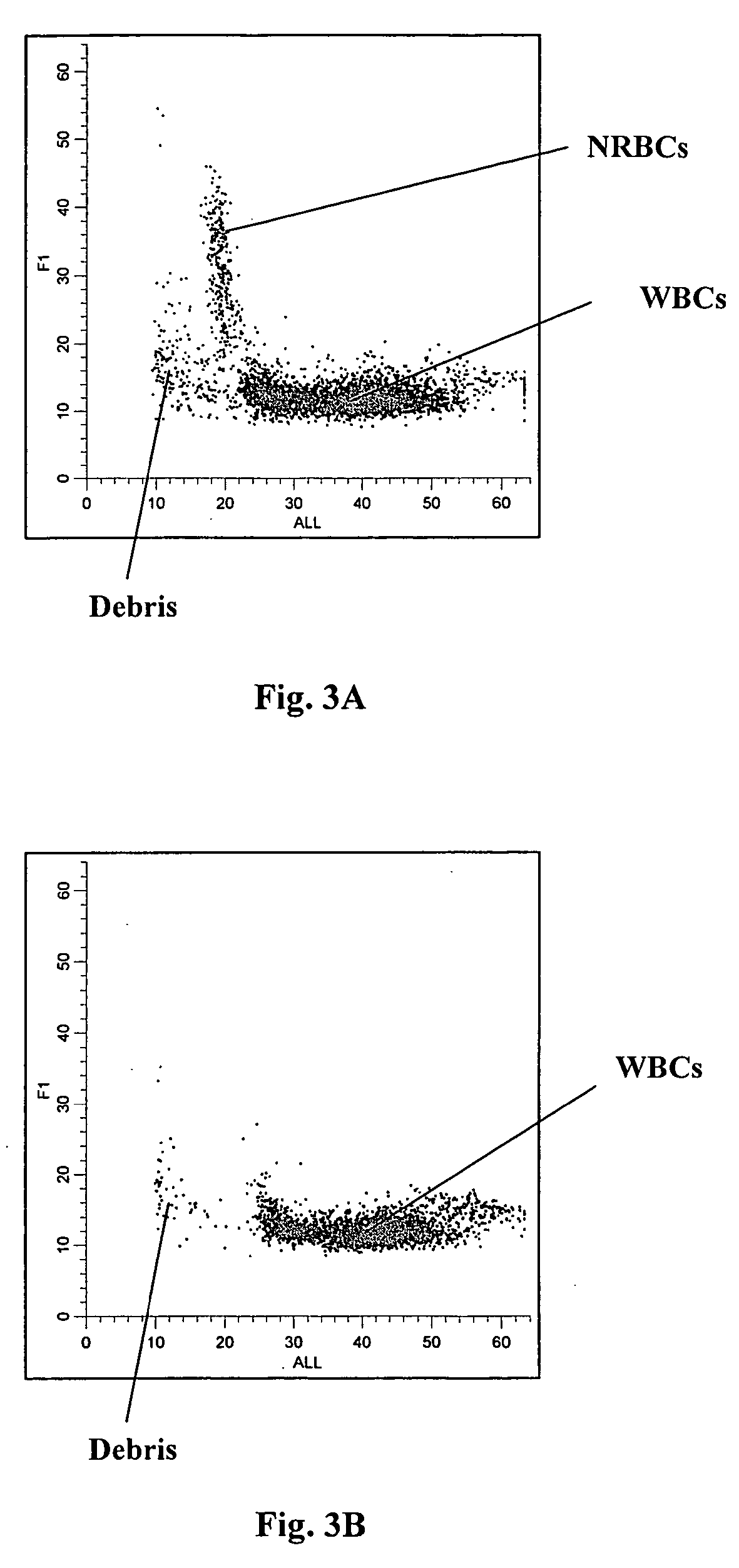
Method of measurement of nucleated red blood cells
Methods are provided for measurement of nucleated red blood cells in a blood sample. The methods include exposing a blood cell sample to a reagent system to lyse mature red blood cells, subsequently analyzing nucleated red blood cells in a flow cell by axial light loss, DC impedance, and medium angle light scatter measurements; by axial light loss, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; or by axial light loss, DC impedance, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; and then differentiating nucleated red blood cells from other cell types by using measured signals and / or functions thereof.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Counting Bacteria and Determining Their Susceptibility to Antibiotics
ActiveUS20090325210A1Analysis material containersMicrobiological testing/measurementSuspended particlesLight scatter measurement
A method for detecting and counting particles suspended in fluids, such as bacteria suspended in urine, utilizing dynamic features of the suspended particles and employing light scattering measurements. The disclosed method is suitable for determining the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. A cuvette for detecting bacteria in fluids, which is especially suited for the light scattering measurements, is provided.
Owner:IP SPECIALISTS LTD
Nano scale particle size measuring method and device with scattered dynamic low-strength laser
InactiveCN1403797AWide measurement rangeKeep naturalScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisFiberRefractive index
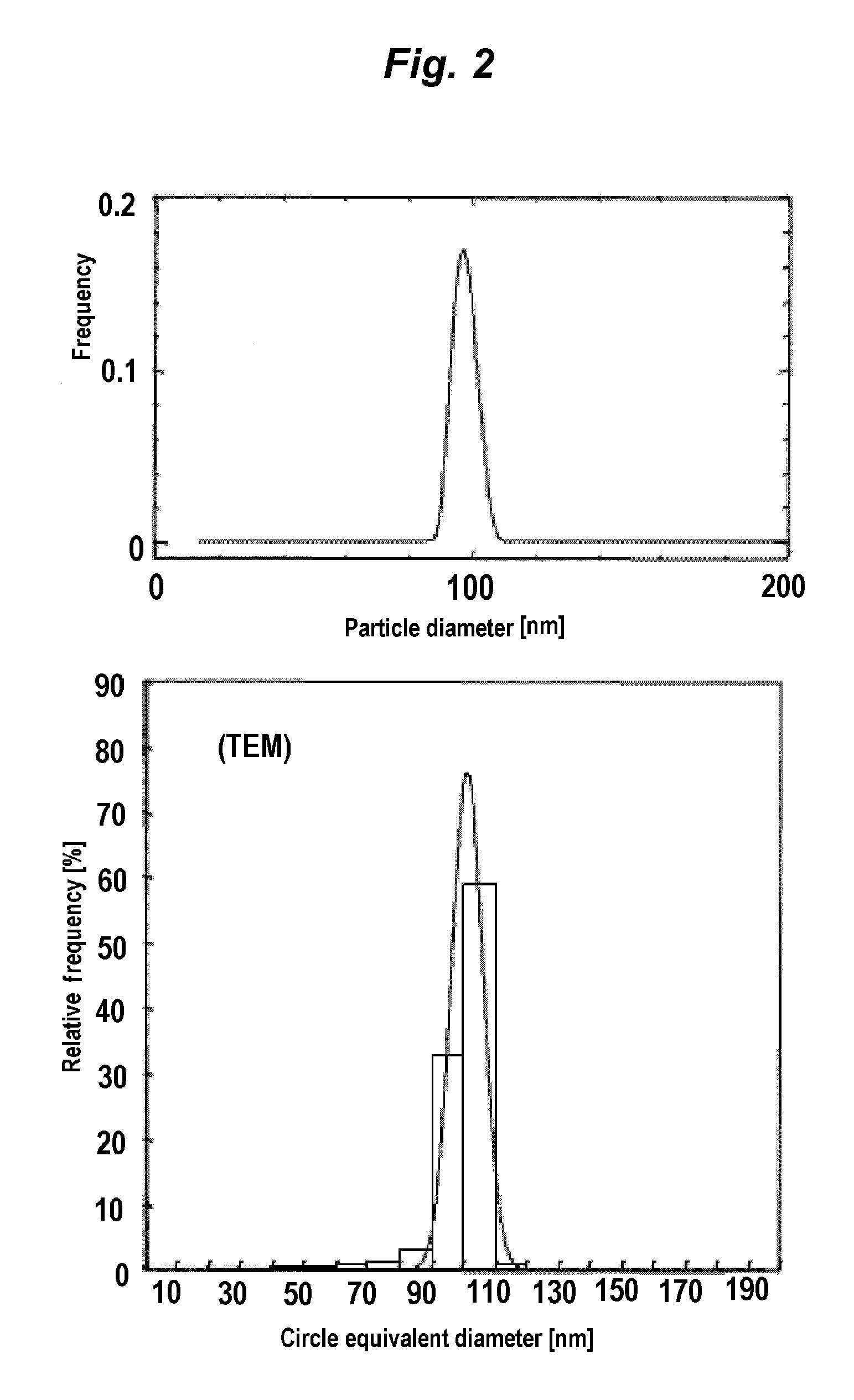
The present invention provides nano particle size measuring method and device with scattered dynamic low-strength laser. The method includes: radiating liquid sample with monochromic laser beam of proper length to produce scattered light signal; collecting and transmitting to light signal with single-modular fiber with gradient refractive index; recording with single-photon counter module the scattered photons and converting into output electric pulse signal; and processing the signal in an autocorrelator. The device includes: light source, polarizer, focusing lens, two-layered refractive index sample matching pool, fiber, single-photon counter module, autocorrelator and computer. The present invention can measure nano particle size fast and accurately.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Gas-barrier film and gas-barrier coating agent, and method for production thereof
InactiveUS7157147B2Excellent gas barrier performanceBroad usSynthetic resin layered productsPaper coatingHigh humidityHydrolysate
Provided are a gas-barrier film which is a laminate comprising a substrate layer comprising a thermoplastic resin film and a gas-barrier layer comprising a hydrolysate of a silicon alkoxide, a stratified silicate and a polyvinyl alcohol base resin, wherein a radius (Rg) of gyration of a scattering matter which is measured by light scattering in the gas-barrier layer described above is 2.4 μm or less, and the silicon alkoxide and / or the hydrolysate thereof are present between the layers of the stratified silicate present in the above gas-barrier layer. The above film shows an excellent gas-barrier property even under such a high humidity as exceeding 90% RH.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP +1
Localized dynamic light scattering system with doppler velocity measuring capability
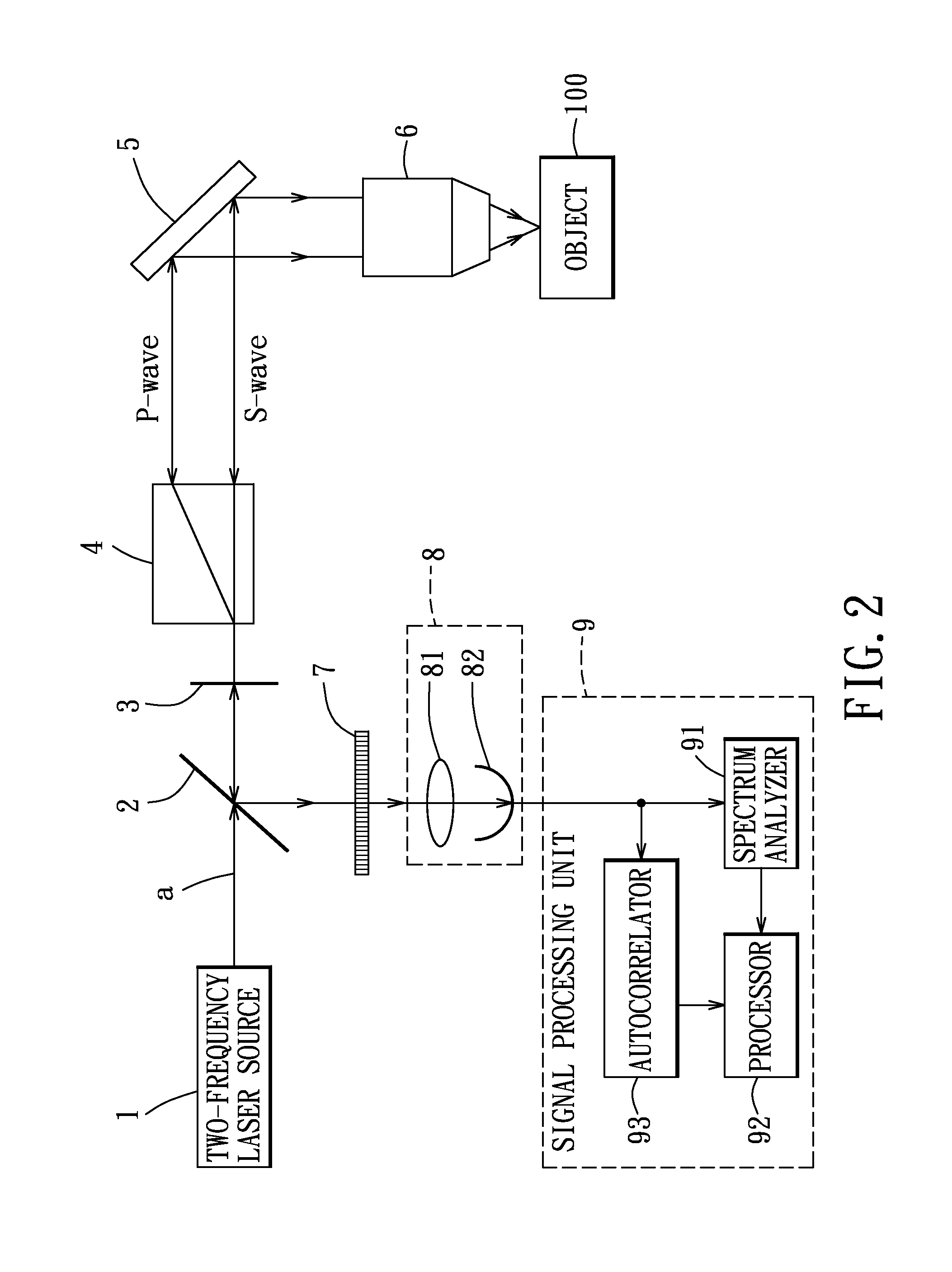
ActiveUS20140132943A1High sensitivityNanoparticle analysisScattering properties measurementsObject basedPolarizer
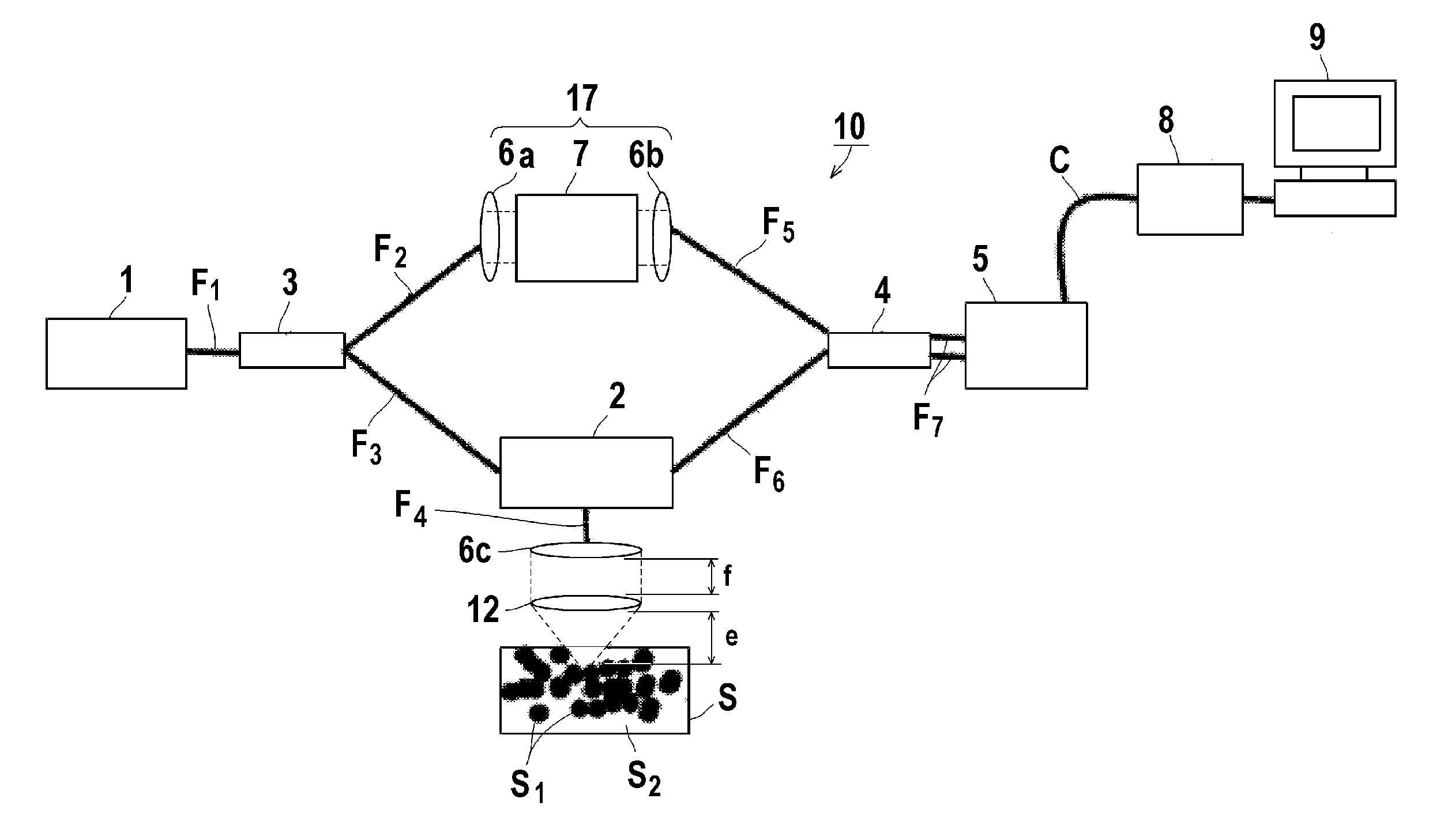
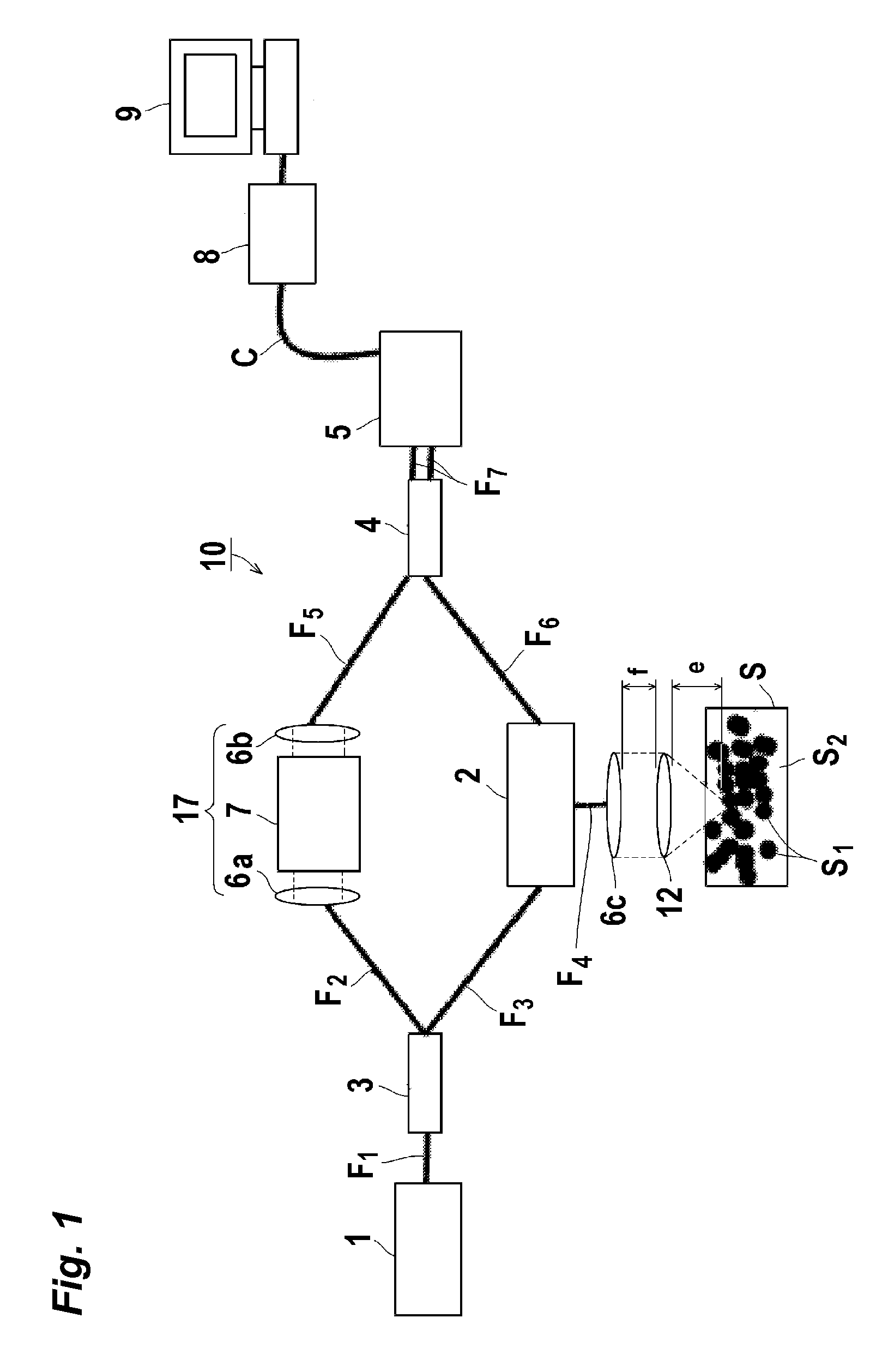
A localized dynamic light scattering measurement system includes a beam displacer for splitting an incident beam having two orthogonal linearly polarized beam components with slightly different frequencies into two orthogonal linearly polarized output beams focused onto an object to be measured. The beam displacer cooperates with an iris to collect and recombine scattering beams each reversely backscattered at 180 degrees from the object so as to form a signal beam, which is polarized by a polarizer to produce two polarization components, thereby generating a heterodyne interference signal associated with the polarization components. A signal processing unit obtains measurement data on the object based on power spectrum or autocorrelation data corresponding to the heterodyne interference signal.
Owner:CHOU LIDEK
Detecting and counting bacteria suspended in biological fluids
ActiveUS20100277734A1Lower Level RequirementsImprove noiseWithdrawing sample devicesScattering properties measurementsForward scatterCuvette
System and method for detecting and counting bacteria suspended in a biological fluid by means of light scattering measurements is provided. In accordance with the method of the invention the level of signal to noise of the measured intensities of light scattered by a sample of the biological fluid is significantly enhanced for forwardly scattered light within a range of scattering angles which are smaller compared to a predefined maximal scattering angle. The system of the invention includes a cuvette adapted to contain a sample of the biological fluid whose sidewalls and windows are suitably constructed and arranged to significantly reduce the level of reflected light obscuring the scattering patterns measured within the range of scattering angles considered.
Owner:BACTERIOSCAN LTD
Optical flow cell assembly incorporating a replaceable transparent flow cell
A new liquid flow cell assembly for light scattering measurements is disclosed which utilized a floating manifold system. The assembly operates with minimal stacked tolerances by aligning the cell to the windows within a manifold and independently aligning the cell to the read head directly. This configuration enables the ability to replace the flow cell or the flow cell / manifold assembly within a light scattering instrument without the need to realign the flow through elements with the light scattering illumination source while still maintaining reproducible, quality data. Some embodiments employ wide bore cells which enable the measurement of process analytic technology (PAT) including online monitoring of reactions.
Owner:WYATT TECH
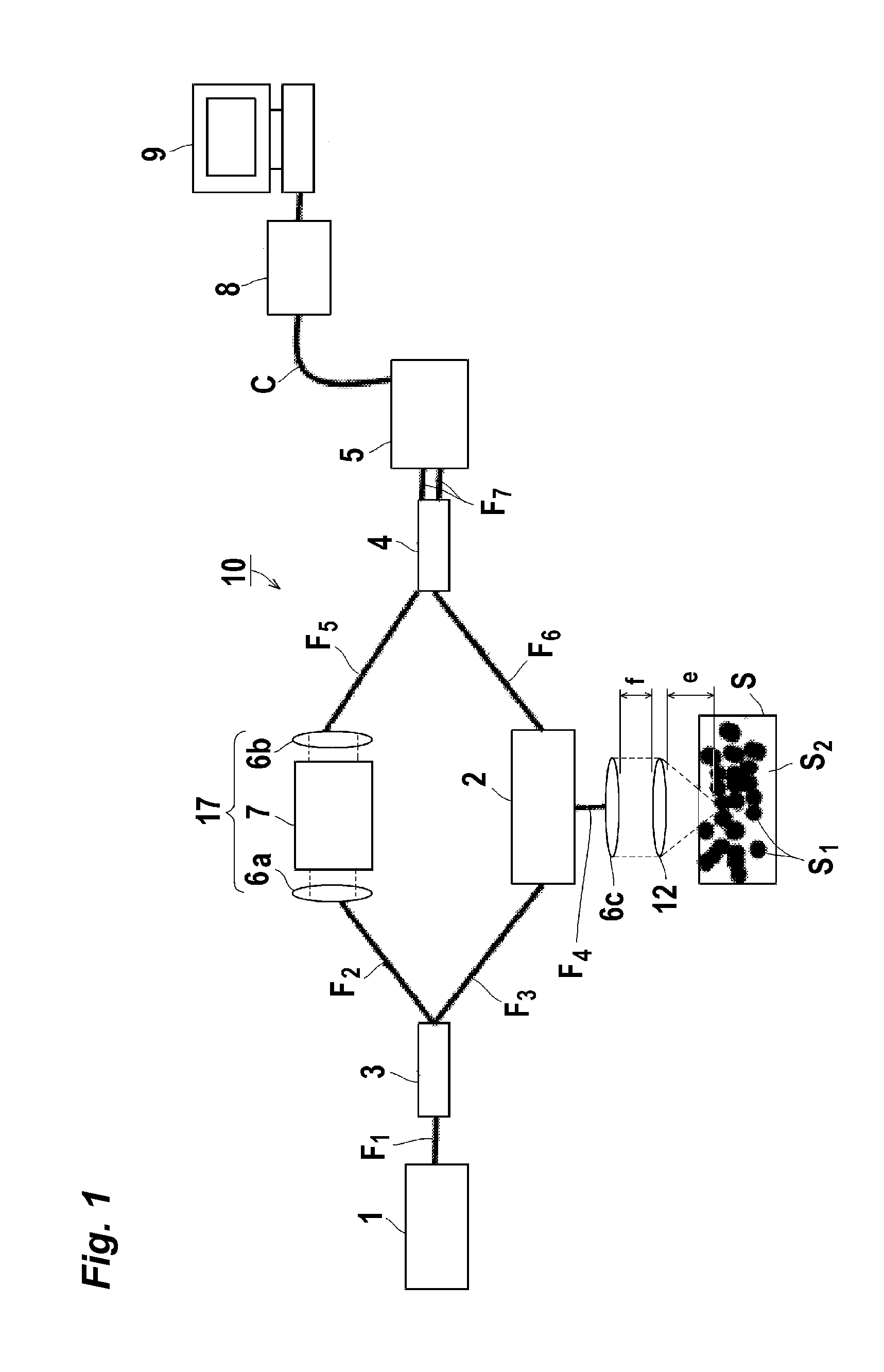
Dynamic light-scattering measuring apparatus using low-coherence light source and light-scattering measuring method of using the apparatus
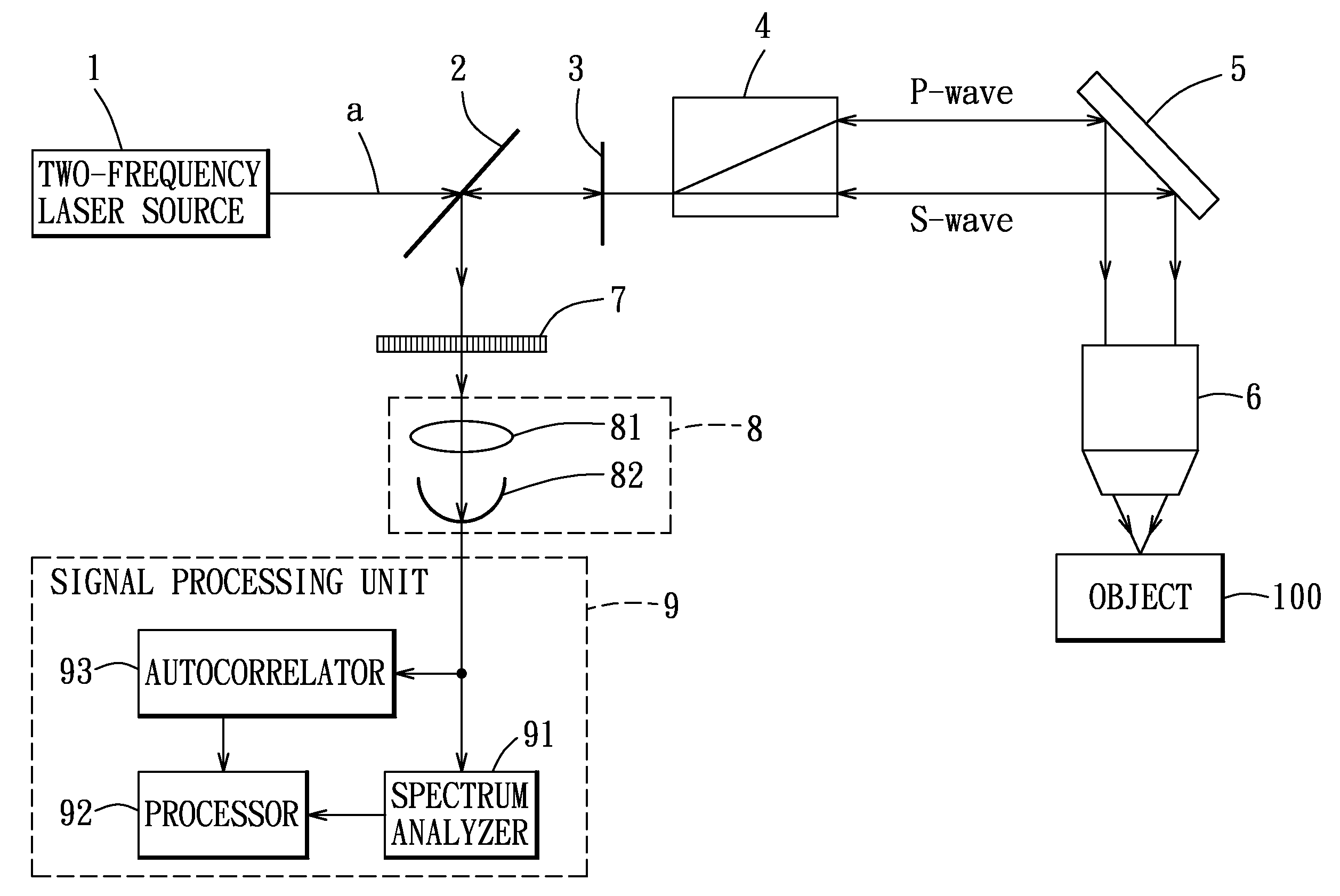
ActiveUS20110001969A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsDynamic light scatteringMach–Zehnder interferometer
There is provided a dynamic light-scattering measuring apparatus including: a Mach-Zehnder interferometer; and a low-coherence light source. Further, there is provided a method for measuring light-scattering intensity of particles in a medium, including the steps of: providing a Mach-Zehnder interferometer; and measuring light-scattering intensity from light emitted from a low-coherence light source, in accordance with a dynamic light-scattering intensity measuring process.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
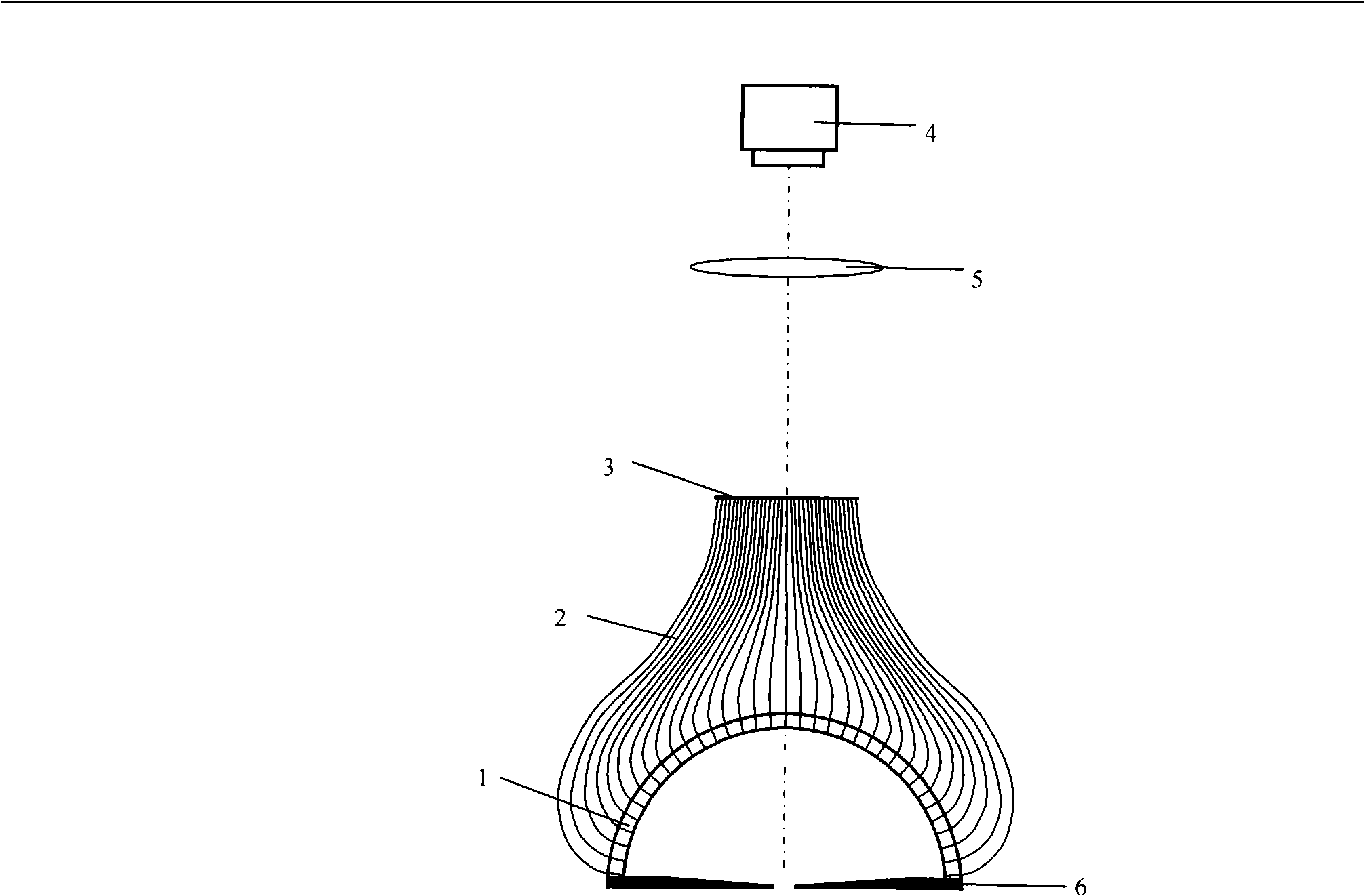
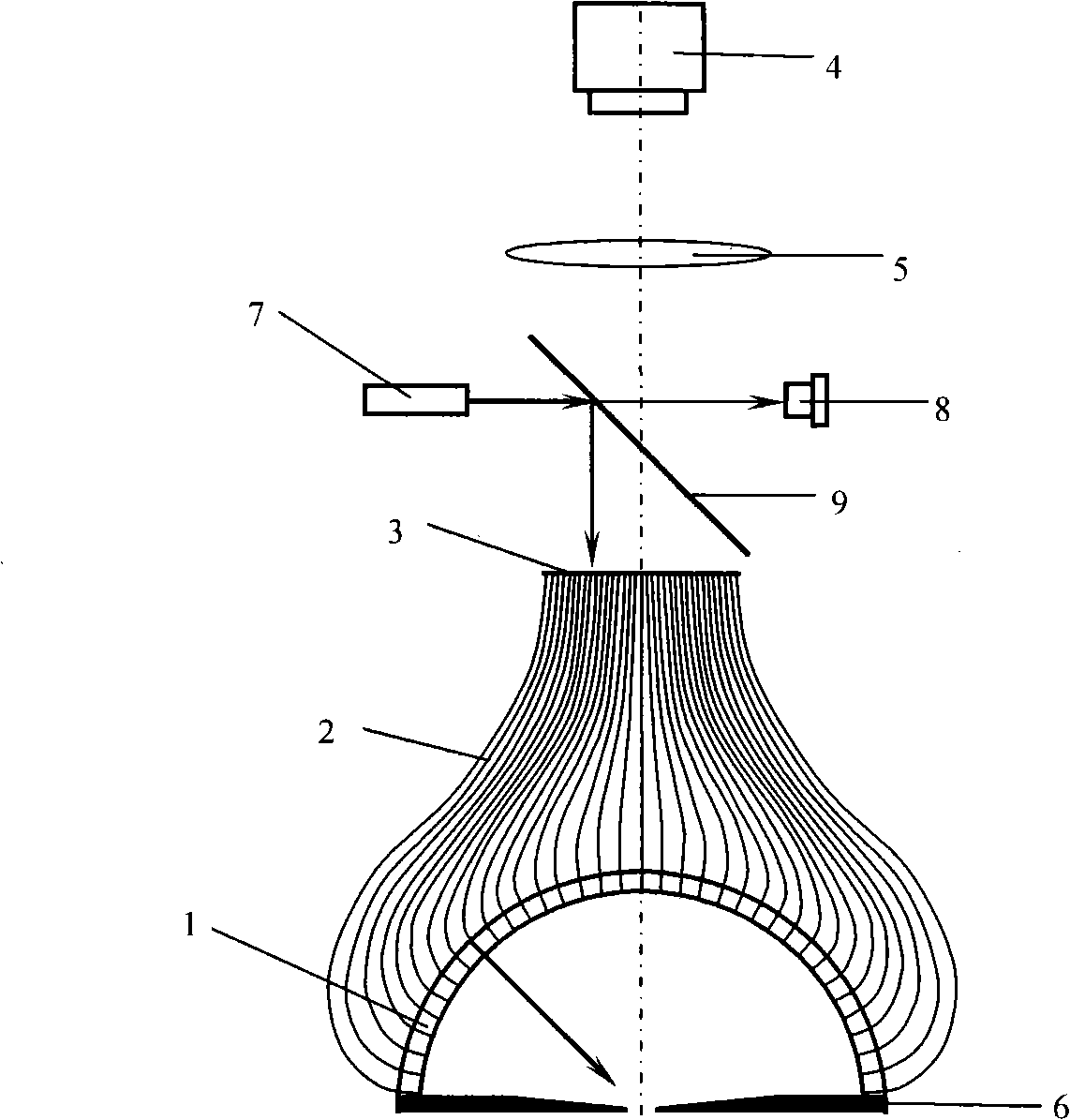
Device for measuring radiation and scattered light field three dimensional distribution
InactiveCN101285703AAvoid influenceAdjustable exposure timePhotometryCoupling light guidesFiberCircular disc
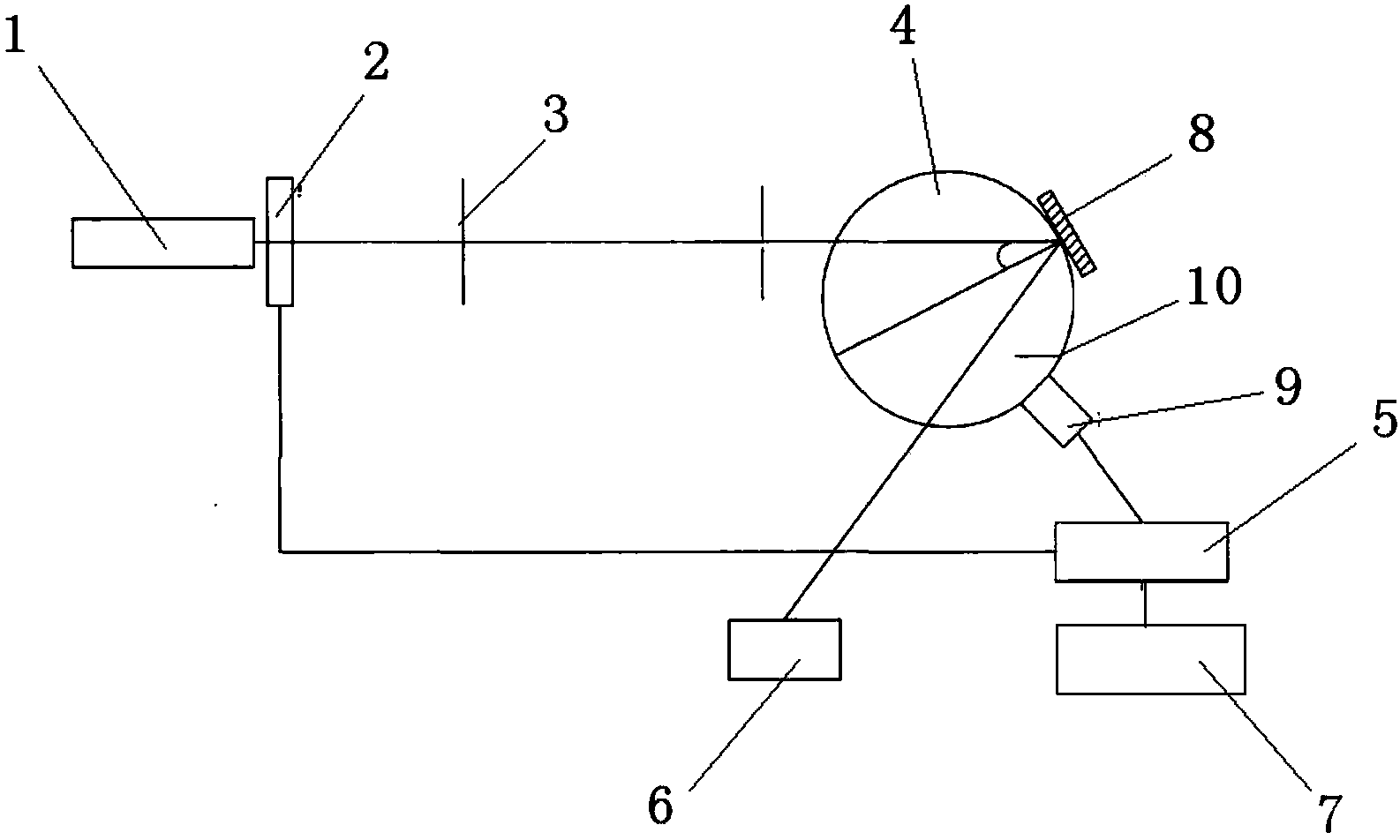
The invention relates to a device for measuring three-dimensional distribution of a radiated and scattered optical field. The device is characterized in that: an adjustable diaphragm 6 is positioned on the bottom of the device; a drilled semispherical shell 1 is positioned on the adjustable diaphragm 6; a drilled disc 3 is positioned on the drilled semispherical shell 1; the drilled disc 3 and the drilled semispherical shell 1 are connected by a plurality of fibers; a lens 5 is positioned on the disc 3; a CCD camera 4 is positioned on the lens 5; a beam splitter mirror 9 with 45 degree angle between a normal line and a main shaft of the device is fixed between the drilled disc 3 and the lens 5; a light source system 7 is positioned on one side of the beam splitter mirror 9 ; and a light source power monitor 8 coaxial with the light source system is positioned on the other side of the beam splitter mirror 9. The device has the advantages that: the fibers and the area array CCD camera can rapidly measure the spatial distribution of a light source radiation optical field or a scattering optical field of the object surface; in the process of the optical scattering measurement, the light source power monitor is utilized to carry out real-time monitoring to the output power of the light source, thereby avoiding the influence of the light source output stability on a measuring result.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Devices And Methods For Detection Of Microorganisms
InactiveUS20100136521A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsArduino microcontrollerLight scatter measurement
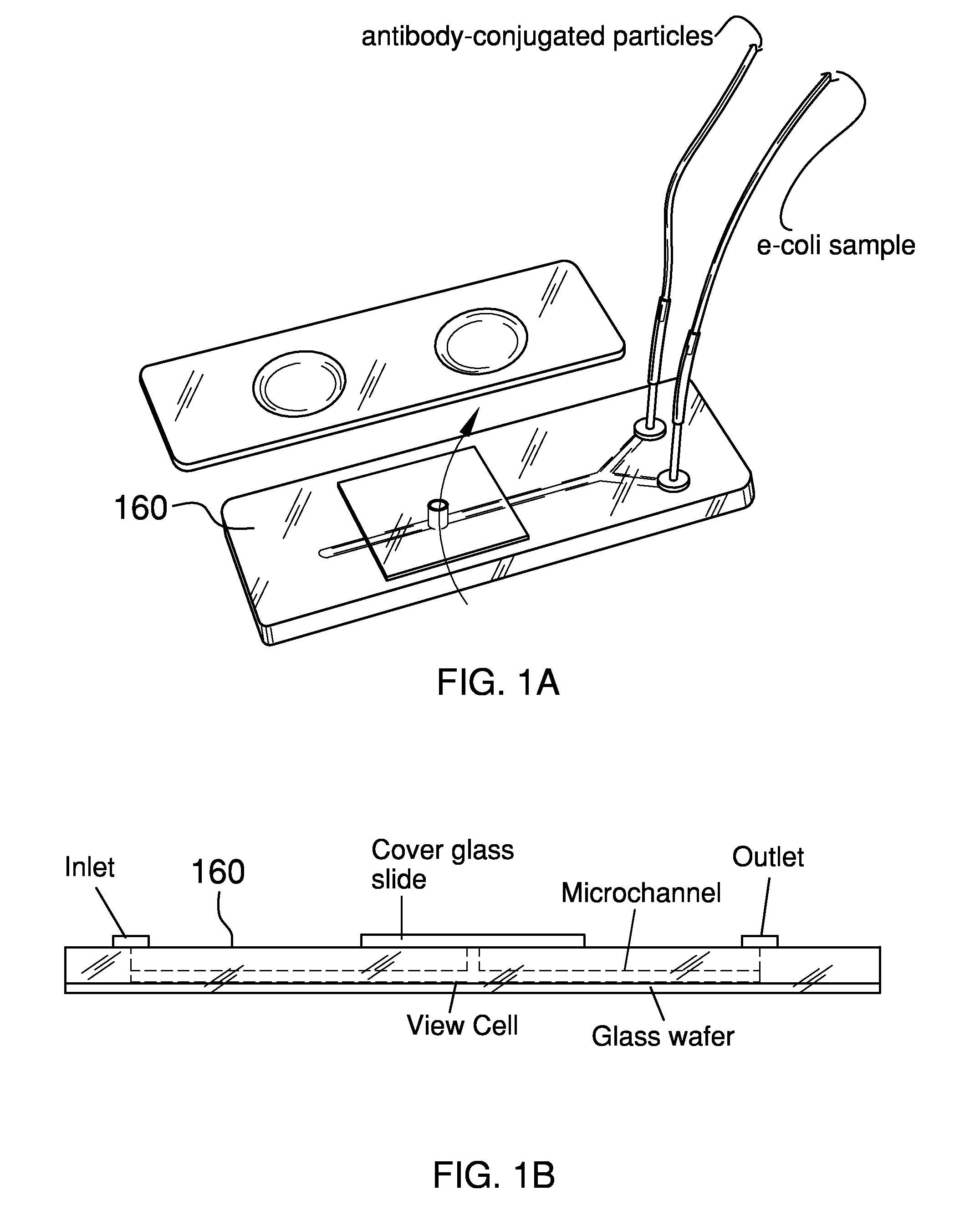
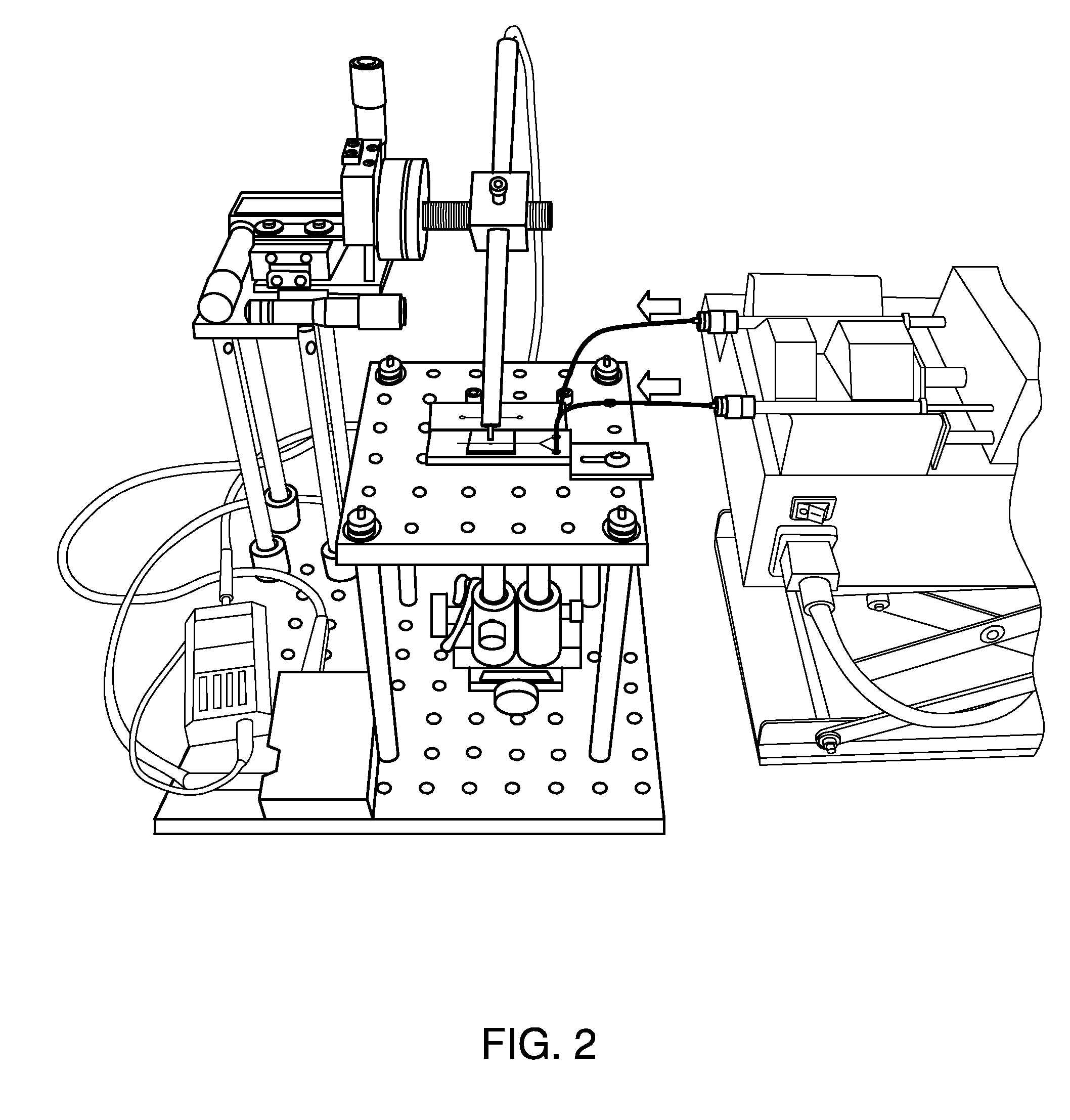
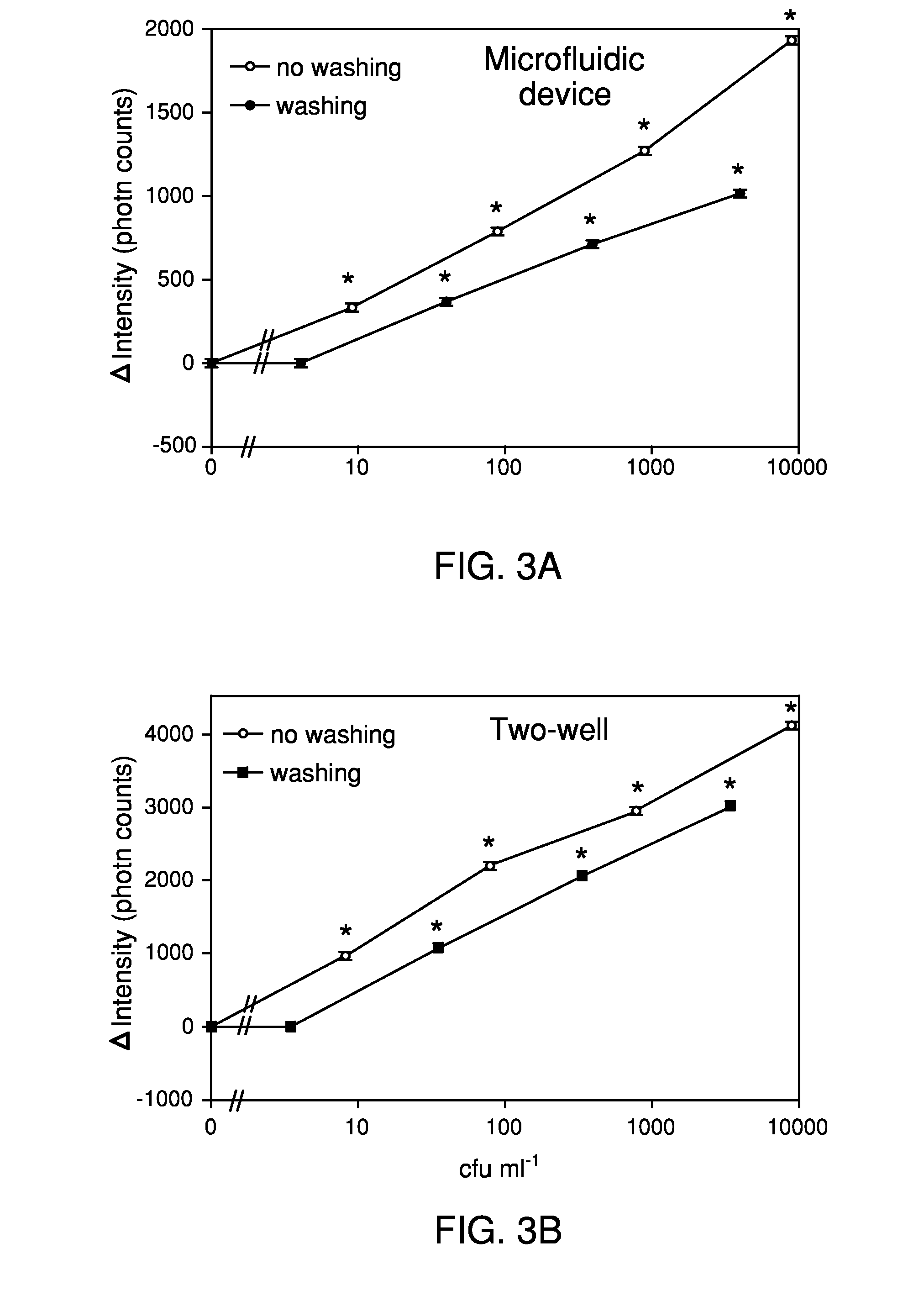
The present invention features methods and devices for microorganisms through detecting Mie light scattering from immunoagglutinated beads. The methods feature providing a first bead suspension with antibody specific for the microorganism conjugated to beads; mixing the first bead suspension with a sample to form a first mixture; irradiating the first mixture with first incident light; detecting forward light scattering at a first angle with respect to the first incident light, where the first angle being between about 30 to 60 degrees; determining l from the light scattering; providing a second bead suspension with no antibody and simultaneously measuring l0 in a similar manner; comparing l with l0. All light scattering measurements may be made in a two-well slide or a Y-channel microfluidic device. Samples, for example food samples (e.g., vegetable samples), may be prepared in a variety of ways. A vegetable sample may be chopped up and added to a buffer. In some embodiments, the sample is then filtered with a common cloth or tissue component. The present invention also features devices (or apparatuses) for detecting a microorganism in a sample. The apparatuses may be a large-scale device or a small-scale device. The large-scale device may consist of a portable spectrometer, light source, optical fibers, and adjustable positioning stages, in addition to, for example, a two-well slide or a microfluidic device. The small-scale device is made portable by using, for example, light-emitting diodes, avalanche photodiodes, an op-amp circuit, Arduino microcontroller board, an LCD display, and small batteries, in addition to, for example, a two-well slide or a microfluidic device. Therefore, the invention is adaptable for detecting microorganisms in vegetable sample preparations. Still further, the invention may be operated on a small-scale, for example, for use by workers in agriculture fields or food factories.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Small-size particle condensation growth counter
PendingCN108535168AMiniaturizationReduce wasteIndividual particle analysisParticulatesMeasuring instrument
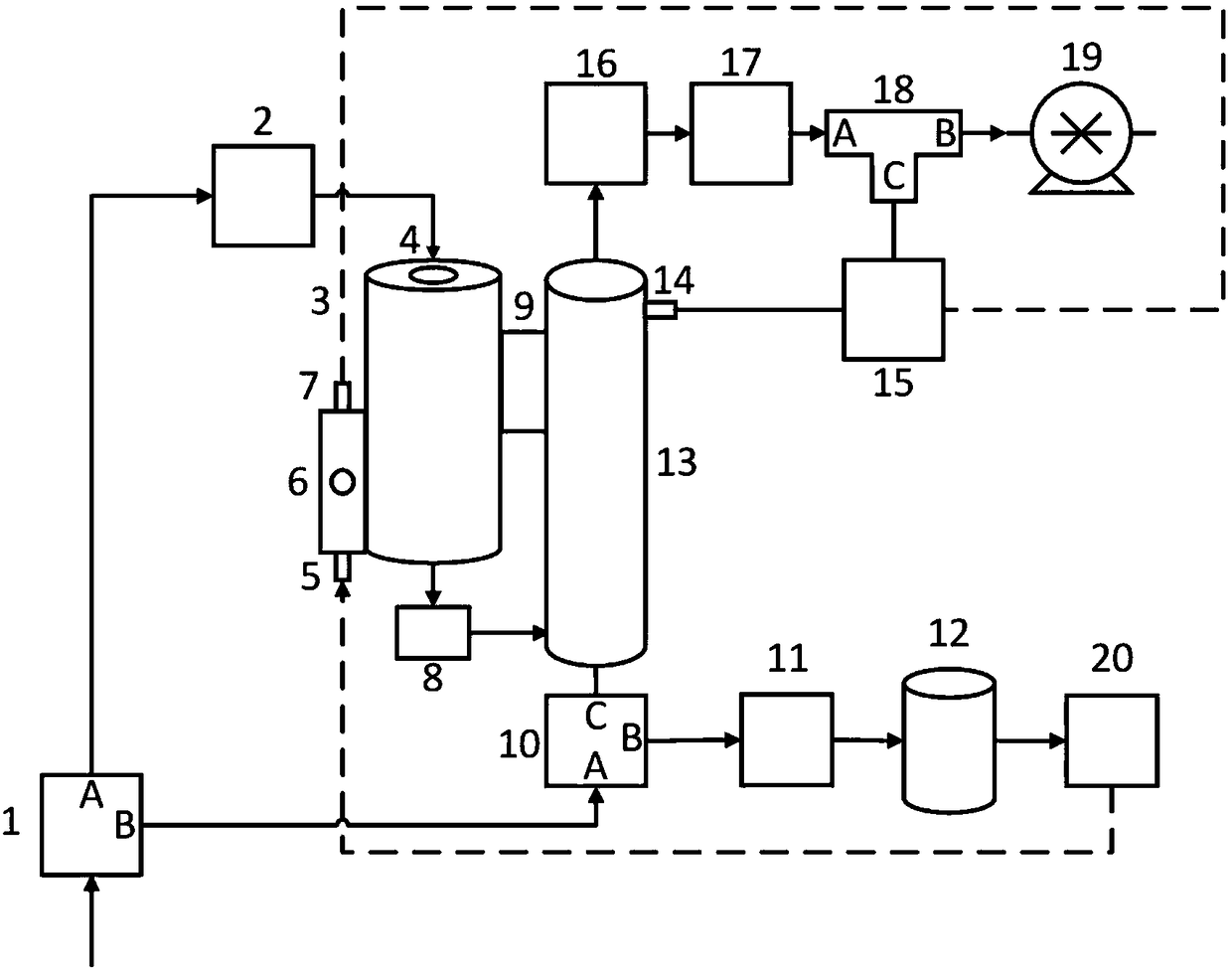
The invention discloses a small-size particle condensation growth counter. The small-size condensation particle counter comprises a flow splitting system, a filtering device, an evaporation chamber, aheat insulation device, a refrigeration sheet, an aerosol inlet and working solution recycling device, a working solution recycling pump, a working solution storage bottle, a condensation chamber, apressure measuring device, a light scattering measuring instrument, a flow limiting hole, a tee joint, a gas pump and a liquid inlet pump, wherein an inlet of the flow splitting system is connected with an object to be sampled; an outlet A of the flow splitting system is connected with the inlet of the filtering device through a hose; the outlet of the filtering device is connected with the evaporation chamber through a hose; a water absorption material is fixed in a middle cavity of the evaporation chamber. The counter disclosed by the invention adopts a back-to-back type design, and the arrangement manner of the evaporation chamber and the condensation chamber is changed into parallel arrangement from traditional axial arrangement, so that the space is effectively utilized and saved andthe miniaturization of a device is realized; the refrigeration sheet is arranged between the evaporation chamber and the condensation chamber and the heat generated by the refrigeration sheet in a refrigeration process is used for heating the evaporation chamber so that wastes of heat dissipation are reduced and a heat rejection fan is omitted.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Compact optical smoke detector system and apparatus
ActiveUS20190187037A1Solution value is not highRapid responseFire alarmsParticle suspension analysisSmoke detectorsEngineering
Device for optically detecting smoke and implementing thereof. Apparatus and methods for detecting the presence of smoke in a small, long-lasting smoke detector are disclosed. Specifically, the present disclosure shows how to build a very compact housing around the smoke detector while keeping the reflections from the housing structure to a very low value while satisfying all the other peripheral needs of fast response to smoke and preventing ambient light. This allows very small measurements of light scattering of the smoke particles to be reliable in a device resistant to the negative effects of dust.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
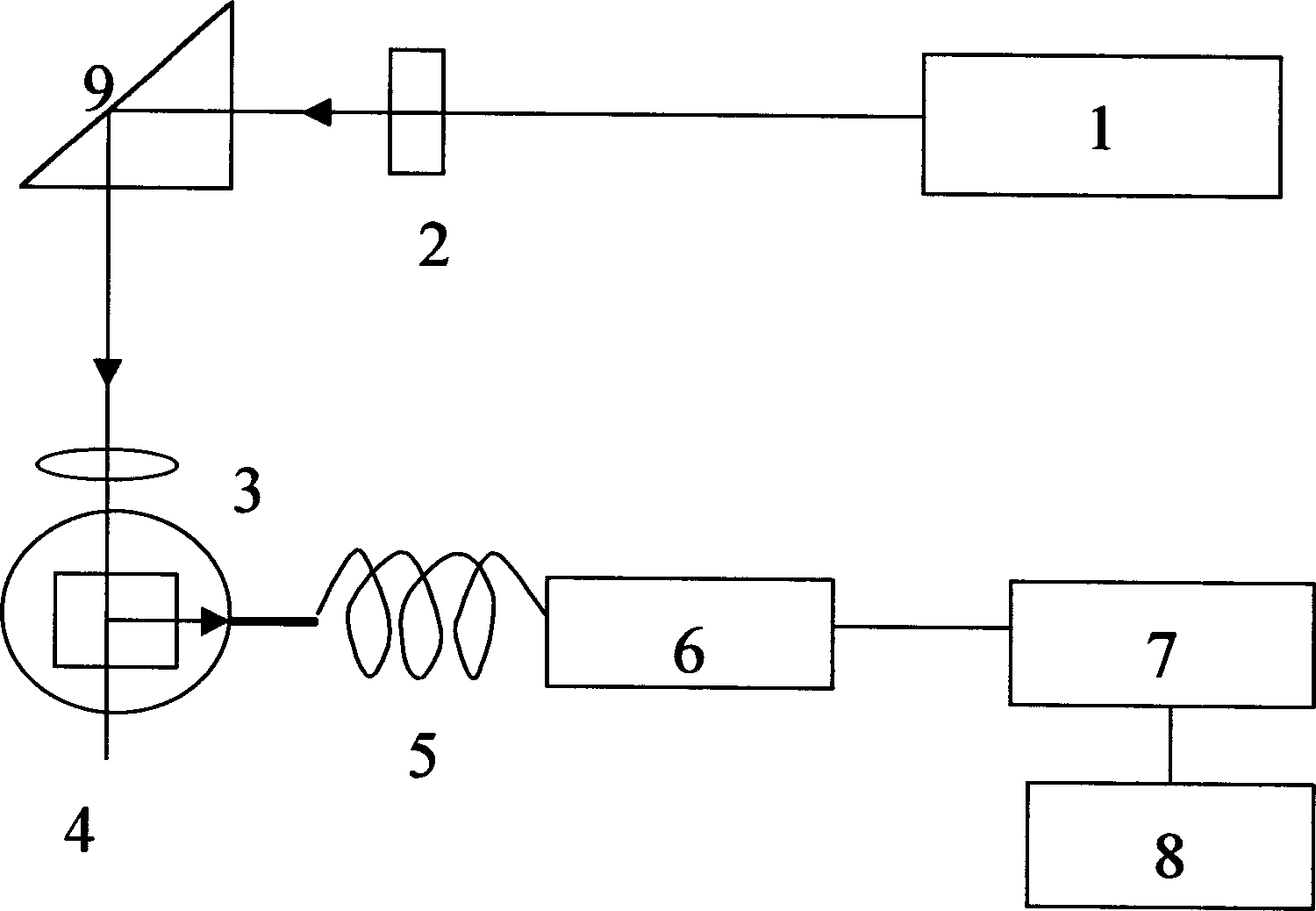
Polarized light scattering measurement system and method based on magneto-optic modulation
InactiveCN103163051ANo distractionNo damagePolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementDivergence angle
The invention relates to a polarized light scattering measurement system and method based on magneto-optic modulation. Coherent light sent out by a laser is changed to linear polarized light through a polarizer, and the linear polarized light is focused into a sample matching tank through a focusing lens. Scattered light coming out from the sample matching tank passes through an expanded beam collimating lens to reduce a divergence angle of the scattered light and collimate the diameter of an outgoing beam, and then the scattered light passes through a Faraday coil, a polarization analyzer and an expanded beam lens in sequence to obtain linear polarized light with periodic changes which can be received by a photomultiplier tube after passing through an aperture diaphragm capable of limiting a photosensitive area, signals are sent into a phase-locked amplifier by the photomultiplier tube to filter and remove external noise and white noise inside equipment, and then sent into a sampling integrator and a computer for sampling integration and digital average to obtain the particle size distribution. Compared with the prior art, the polarized light scattering measurement system and method based on the magneto-optic modulation can be used for low-intensity laser measurement without interference or damage to a sample, can be used for quickly and accurately measuring the nanoparticle size, suppressing the noise to the maximum extent and improving the measurement accuracy to enable the system to be suitable to be used in various environments.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method and device for measuring particulate matters by using dual wavelength polarized light scattering
InactiveCN108844865AReduce in quantityLarge amount of informationParticle size analysisParticulatesLevel line
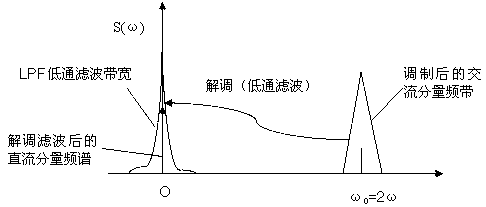
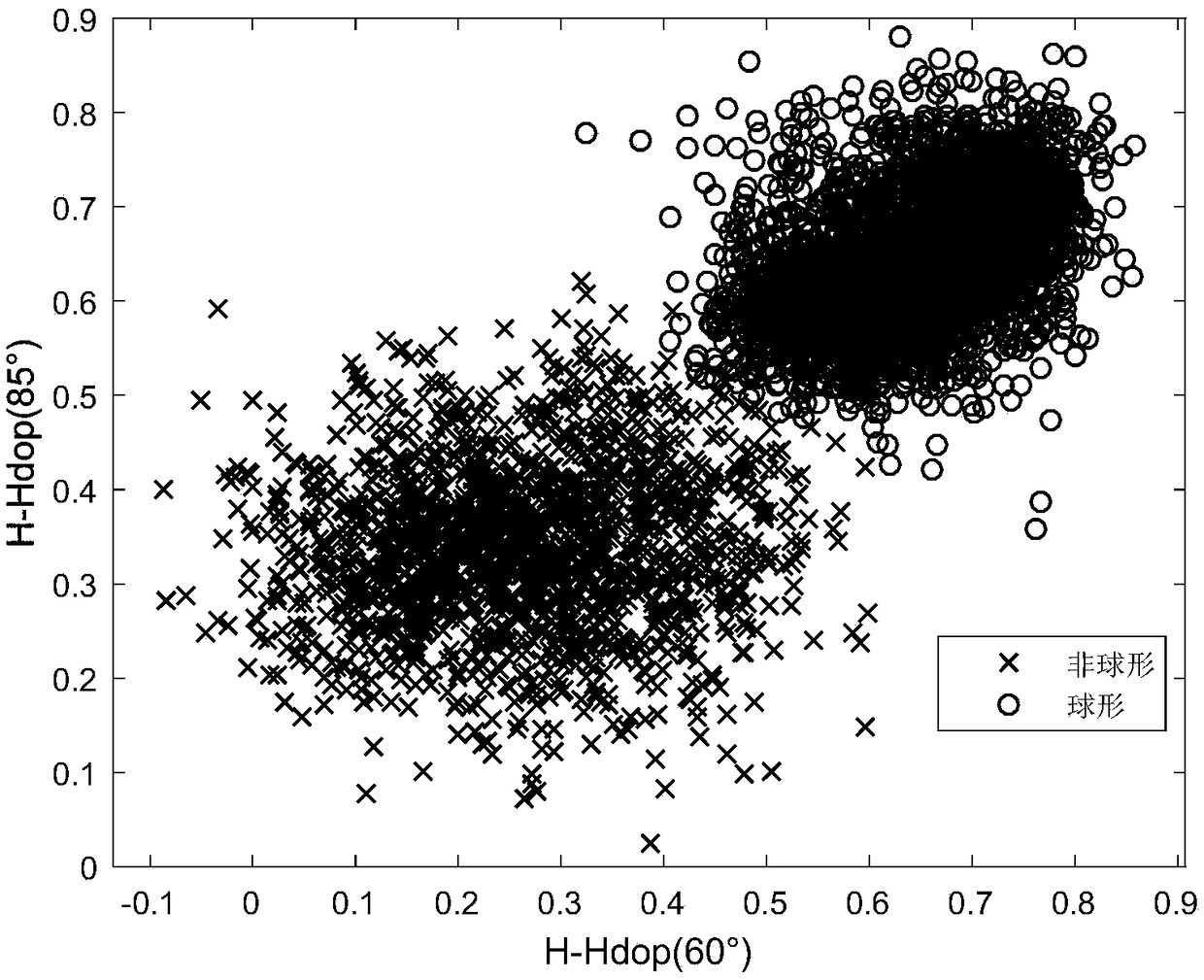
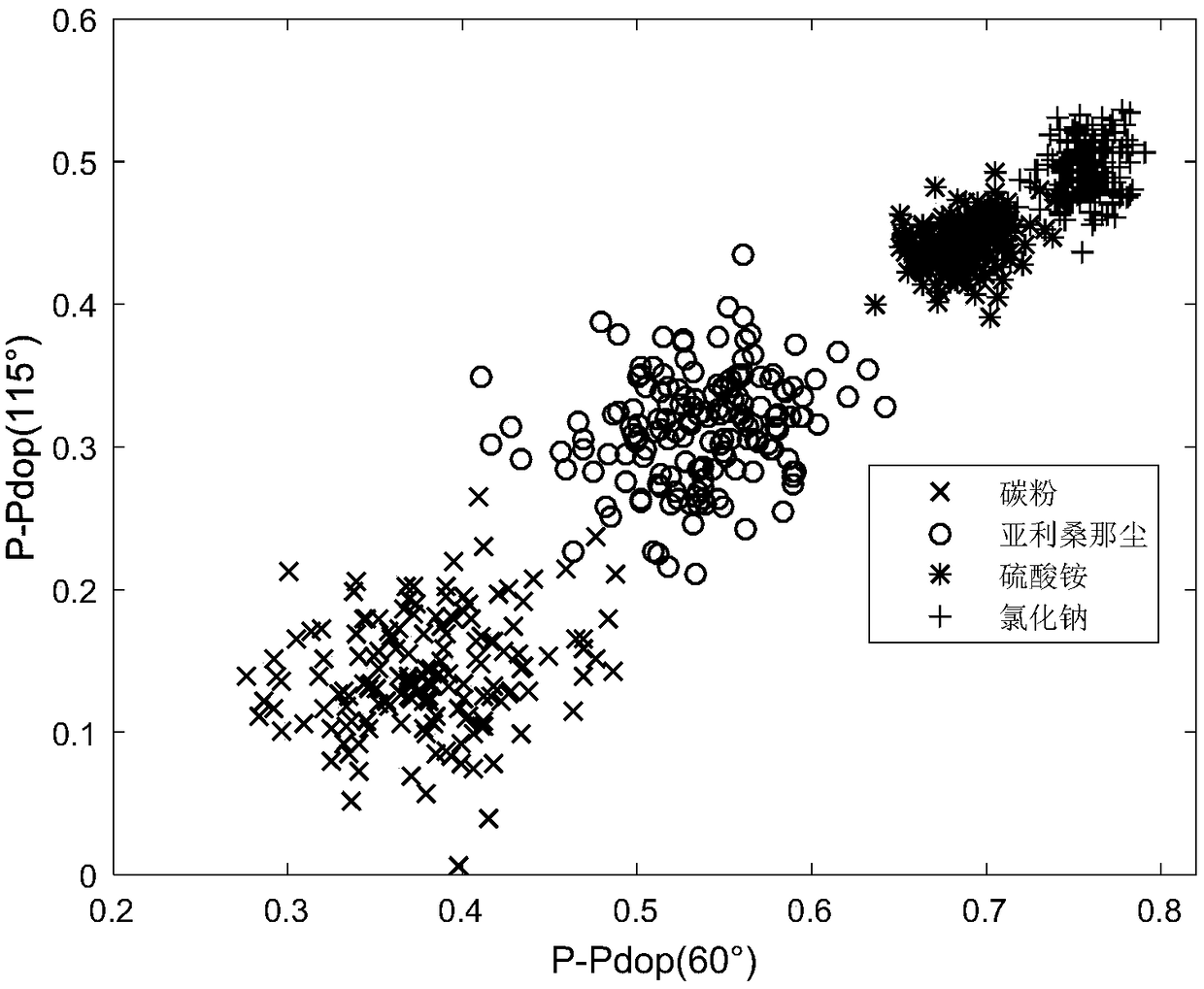
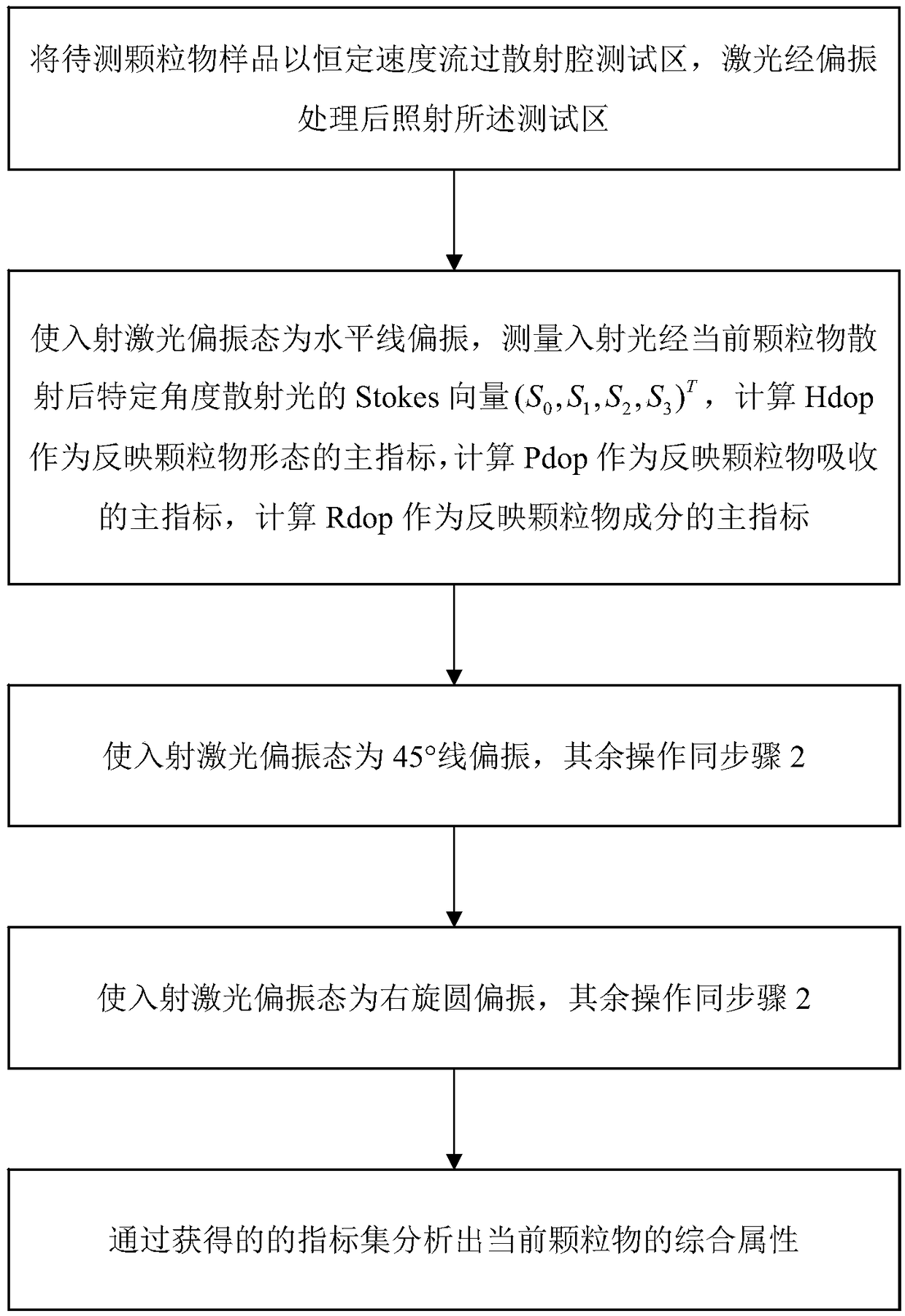
The invention discloses a method and device for measuring particulate matters by using dual wavelength polarized light scattering. The method includes the following steps: 1) letting a to-be-measuredparticulate matter sample flow through a scattering cavity test area with a constant speed, and irradiating the test area after a laser is processed through polarization; 2) making an incident laser polarization state horizontally polarized, measuring the Stokes vector (S0, S1, S2, S3)<T> of scattered light at a specific angle after incident light is scattered by current particulate matters, calculating Hdop as a main index reflecting particulate matter morphology, calculating Pdop as a main index reflecting particulate matter absorption, and calculating Rdop as a main index reflecting particulate matter components; 3) making the incident laser polarization state being 45 DEG linear polarization, the rest operation being the same with the step 2); 4) making the incident laser polarizationstate being right-hand circular polarization, the rest operation being the same with the step 2); and 5) analyzing the integration attribute of the current particulate matters through an obtained index set. The method can realize on-line rapid comprehensive analysis on the integration attribute of particulate matters. In addition, the device can maximumly reduce the number of detectors.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Surface light scattering measuring device
InactiveCN104297211AEfficient measurementAccurate measurementScattering properties measurementsMeasurement deviceVoltmeter
The invention discloses a surface light scattering measuring device comprises a laser, a chopper, an attenuator, an integrating sphere, a phase locking amplifier, a receiver and a digital voltmeter, wherein the light emitted by the laser passes the chopper, then passes the attenuator, enters the integrating sphere and illuminates the surface of a sample; the light is reflected by the sample and received by the receiver; a detector and a pre-amplifier are arranged on the integrating sphere; the chopper is connected with the phase locking amplifier; the phase locking amplifier is connected with the detector and the pre-amplifier; the phase locking amplifier is further connected with the digital voltmeter. According to the surface light scattering measuring device, as the laser light source is adopted, the surface light scattering measuring device is especially useful and the procession is high; the laser light source is particularly suitable for providing high-quality monochromatic source, the surface light scattering can be measured quickly and effectively; surface light scattering measuring device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the measurement result is accurate, the operation is simple and the applicability is high.
Owner:SUZHOU PTC OPTICAL INSTR
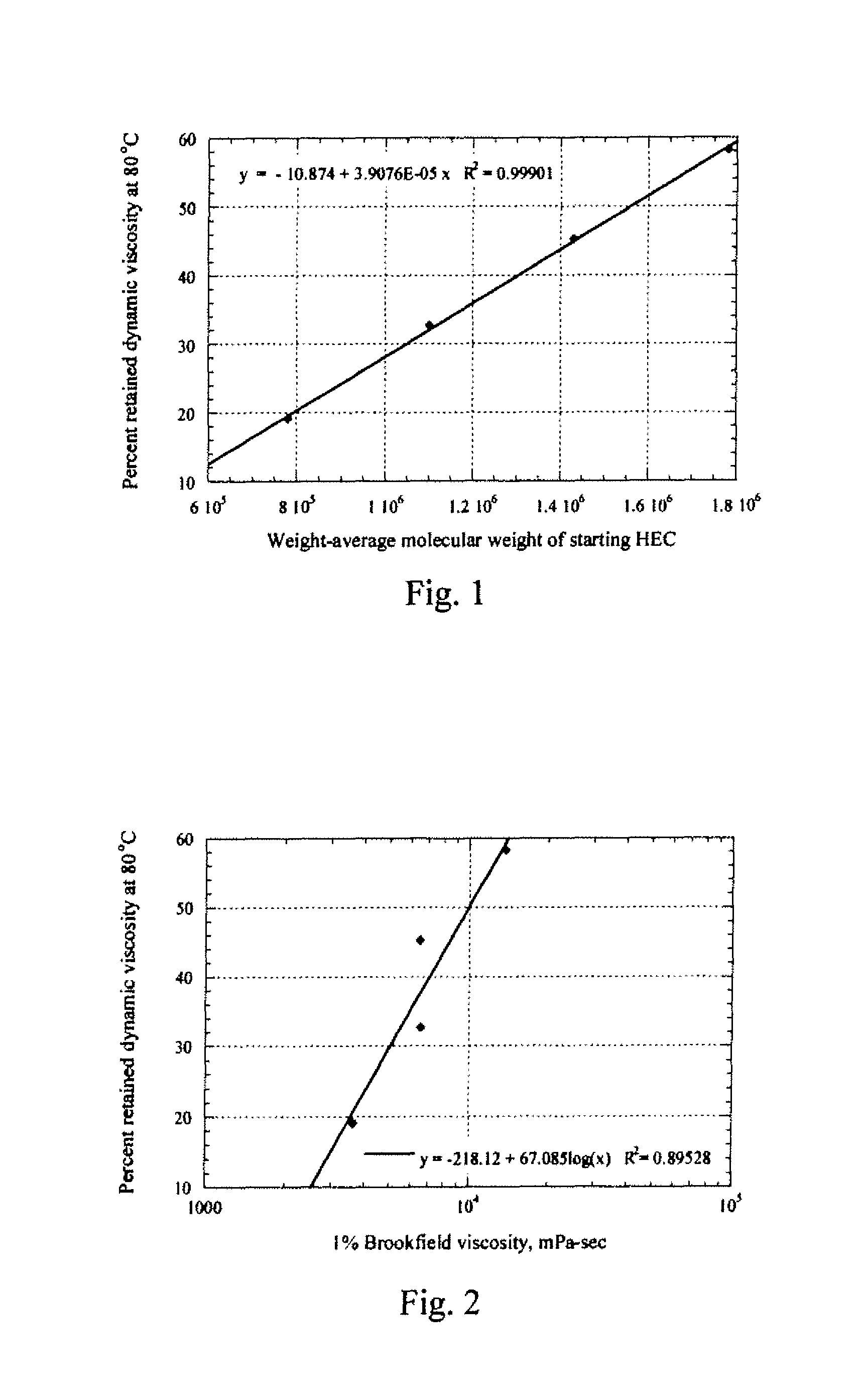
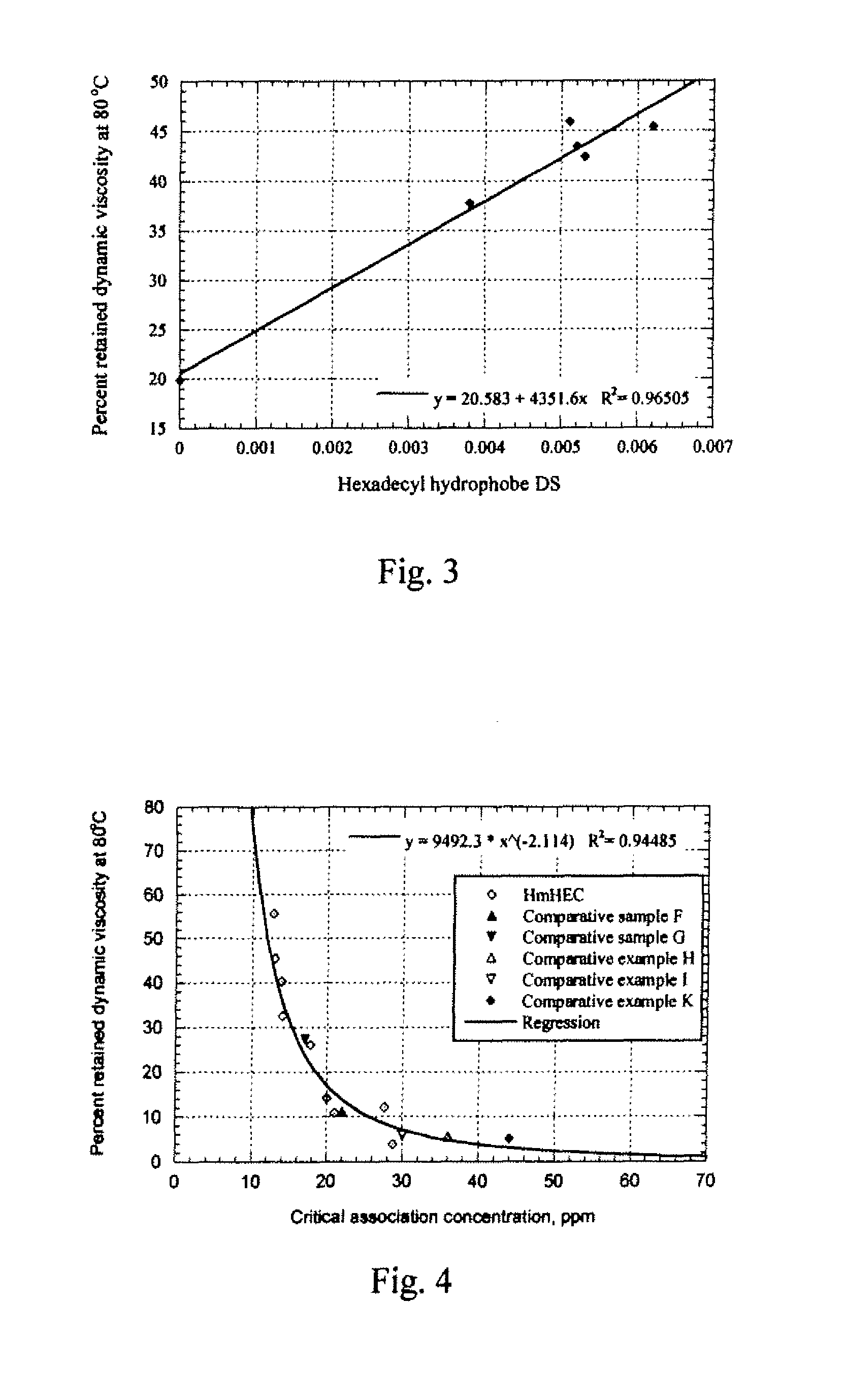
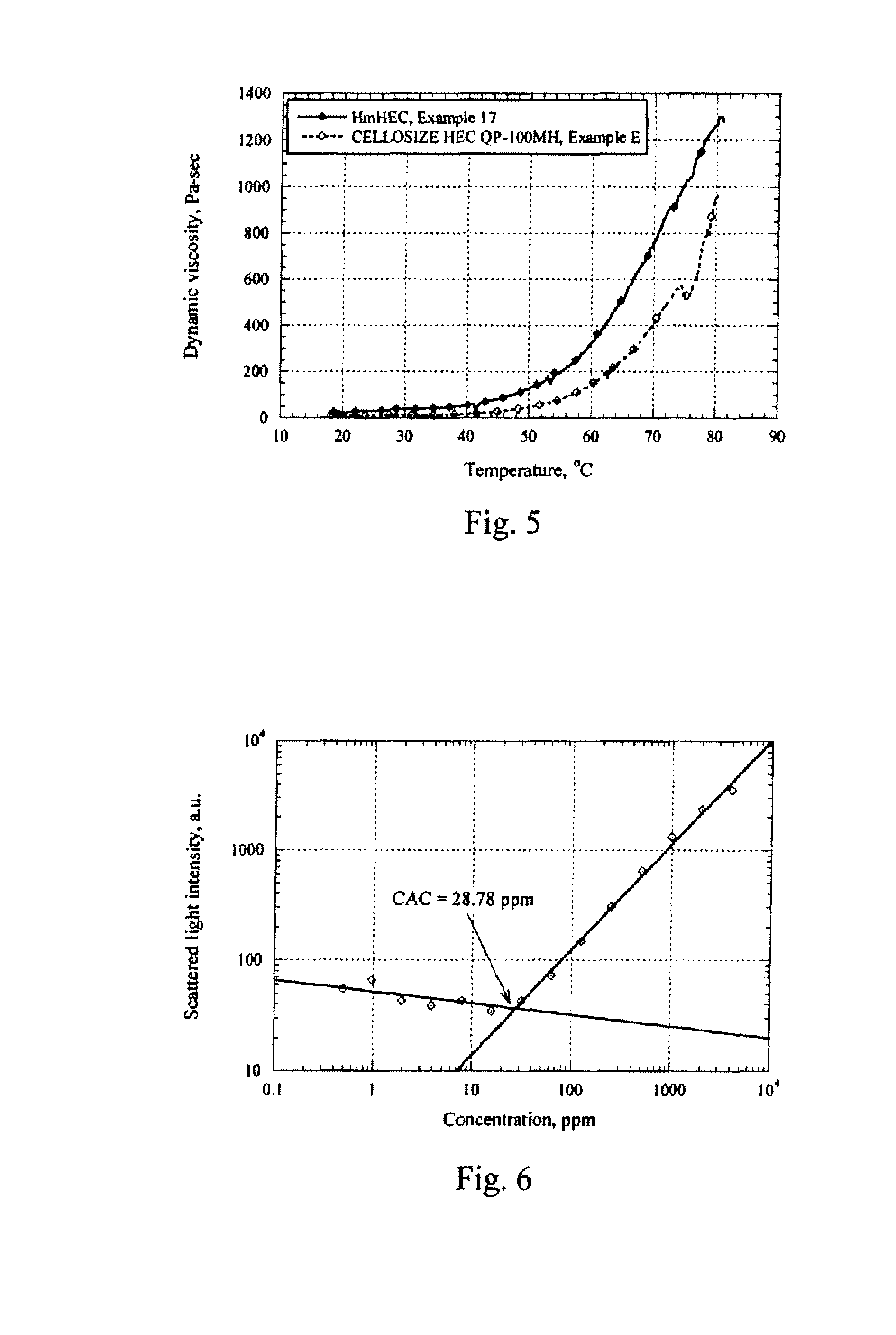
Nonionic hydrophobically substituted cellulose ethers
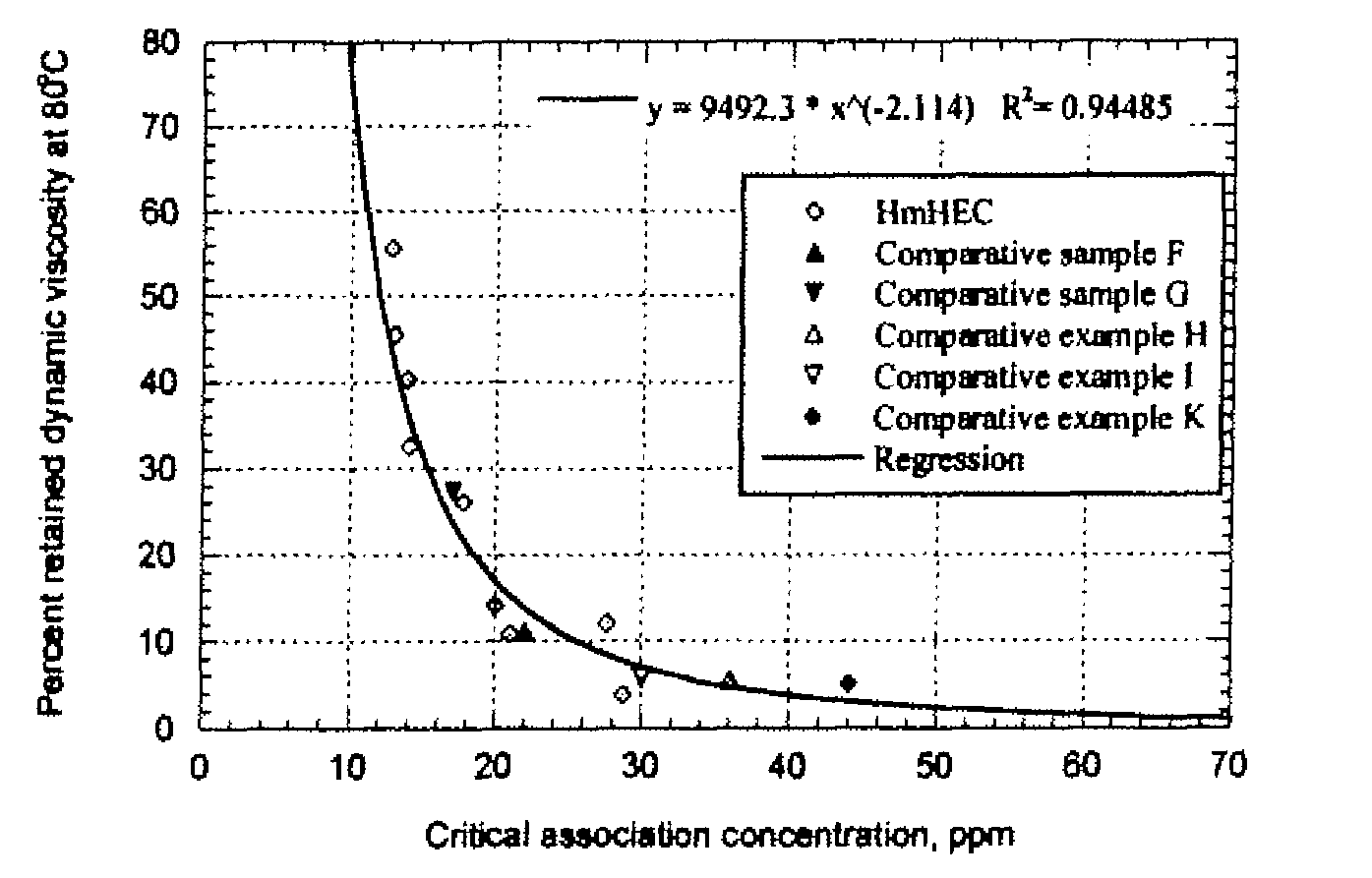
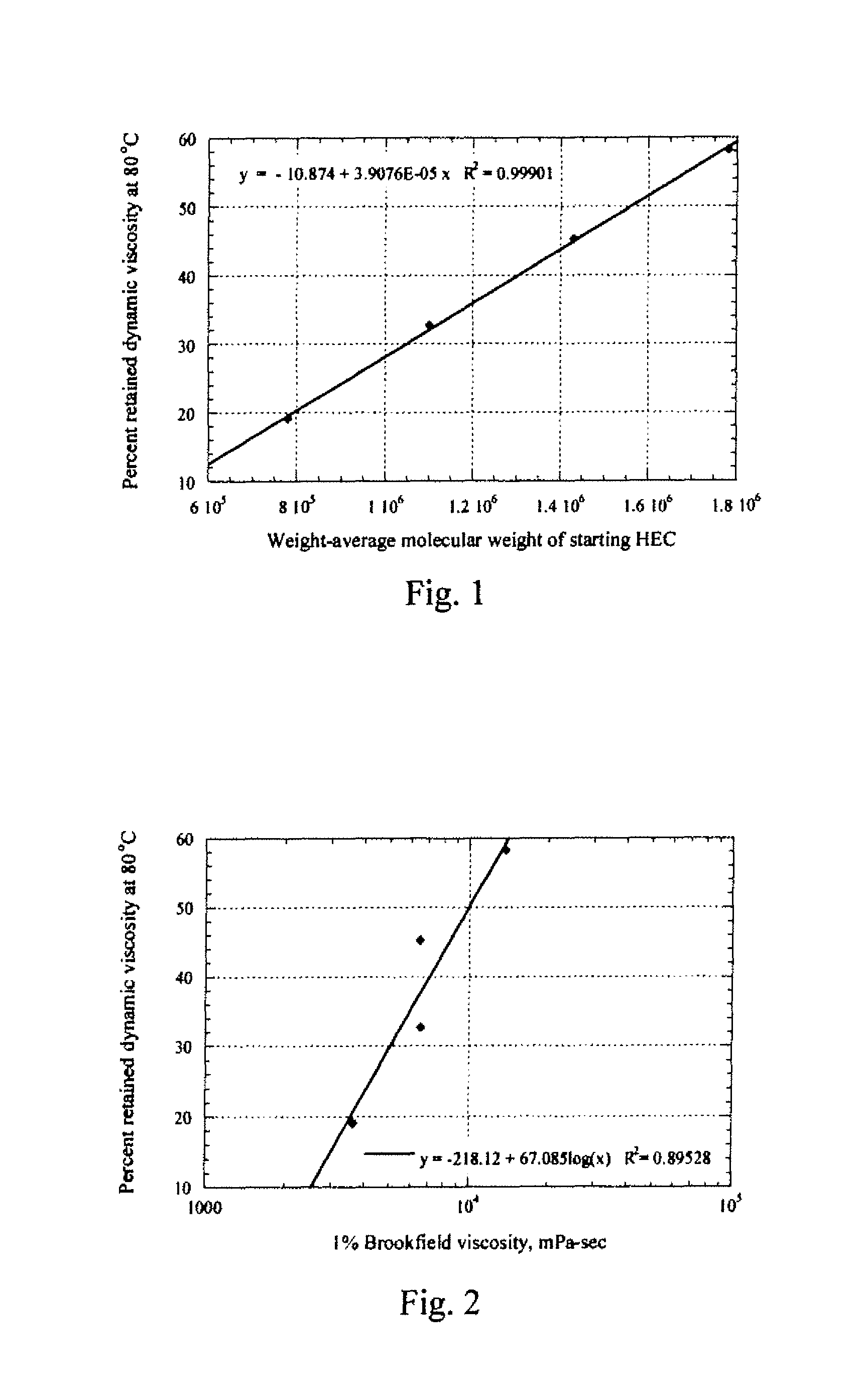
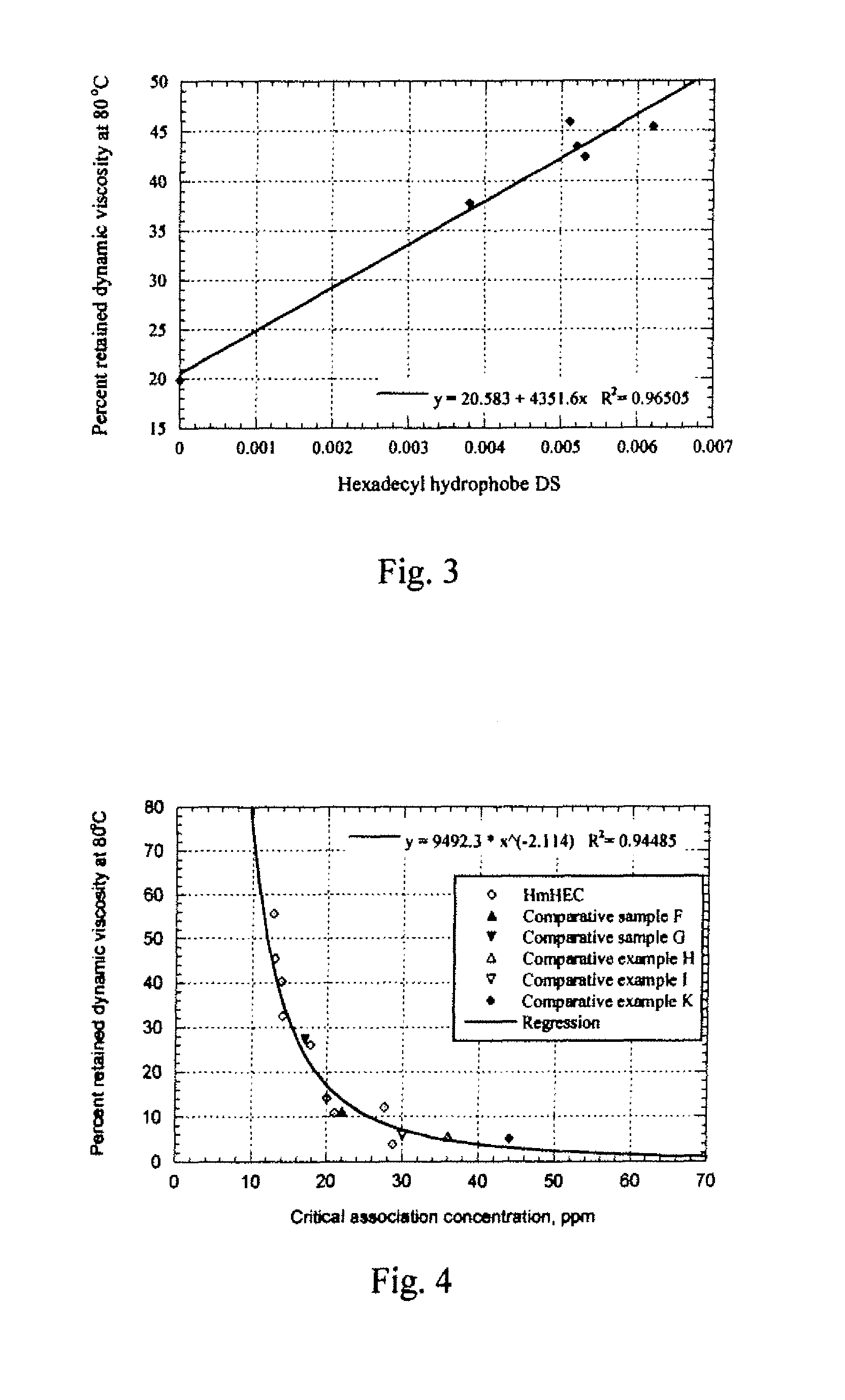
Novel nonionic cellulose ethers exhibit a reduced degree of thermal thinning and are efficient thickeners at elevated temperatures. The nonionic cellulose ether has hydroxyethyl groups and is further substituted with one or more hydrophobic substituents. The cellulose ether further has at least one of the properties a), b) or c): a) a retained dynamic viscosity, % η80 / 25, of at least 30 percent, wherein % η80 / 25=[dynamic solution viscosity at 80° C. / dynamic solution viscosity at 25° C.] 100, the dynamic solution viscosity at 25° C. and 80° C. being measured as 1% aqueous solution; b) a storage modulus of at least 15 Pascals at 25° C. and a retained storage modulus, % G′80 / 25, of at least 12 percent, wherein % G′80 / 25=[storage modulus at 80° C. / storage modulus at 25° C.] 100, the storage modulus at 25° C. and 80° C. being measured as a 1% aqueous solution; c) a critical association concentration of less than 15 ppm as measured by light-scattering.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
Nonionic hydrophobically substituted cellulose ethers
ActiveUS20130118743A1Reduced degree of thermal thinningFluid removalDrilling compositionCelluloseEther
Novel nonionic cellulose ethers exhibit a reduced degree of thermal thinning and are efficient thickeners at elevated temperatures. The nonionic cellulose ether has hydroxyethyl groups and is further substituted with one or more hydrophobic substituents. The cellulose ether further has at least one of the properties a), b) or c): a) a retained dynamic viscosity, %η80 / 25, of at least 30 percent, wherein % η180 / 25=[dynamic solution viscosity at 80° C. / dynamic solution viscosity at 25° C.┐ 100, the dynamic solution viscosity at 25° C. and 80° C. being measured as 1% aqueous solution; b) a storage modulus of at least 15 Pascals at 25° C. and a retained storage modulus, % G′80 / 25, of at least 12 percent, wherein %G′80 / 25=[storage modulus at 80° C. / storage modulus at 25° C.] 100, the storage modulus at 25° C. and 80° C. being measured as a 1% aqueous solution; c) a critical association concentration of less than 15 ppm as measured by light-scattering.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
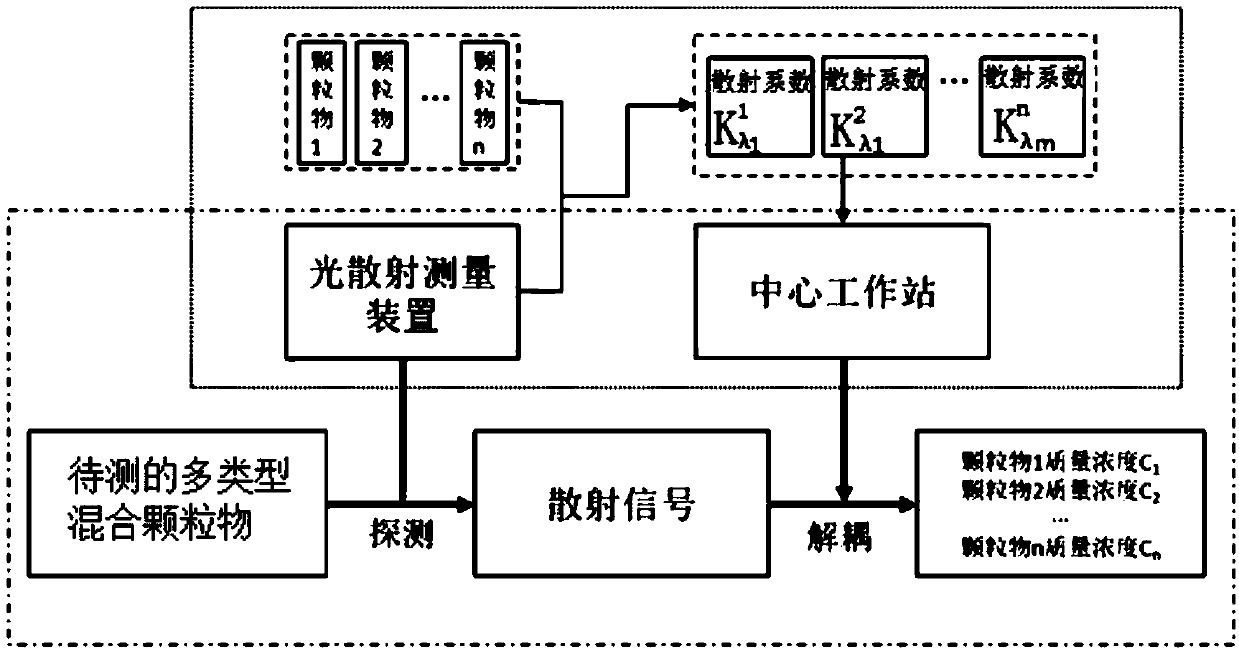
Online measurement method for multi-type mixed particle mass concentration
ActiveCN108645817AImplement classification measurementOvercoming Effects of Mass Concentration MeasurementsScattering properties measurementsParticulatesCorrelation coefficient
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental monitoring, and discloses an online measurement method for multi-type mixed particle mass concentration, the method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a database of particle wavelength scattering correlation coefficients; 2) placing a multi-type mixed particle into a light scattering measuring device, and using the light scattering measuring device to measure to obtain scattered light intensities generated by the multi-type mixed particle at m wavelengths; and 3) transmitting scattered light intensity signals measured bythe light scattering measuring device to a central workstation, and using the central workstation to obtain the mass concentration of each particle in the multi-type mixed particle according to the scattered light intensities obtained in the step 2) and the database of the particle wavelength scattering correlation coefficients obtained in the step 1). The method is based on the difference of light scattering caused by particle types, realizes the classification measurement of the particle types, overcomes the influence of the particle types on the mass concentration measurement of the particles, and improves the measurement precision of the mass concentration of the particles.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Smoke detector chamber boundary surfaces
ActiveUS20190187038A1Solution value is not highRapid responseFire alarmsParticle suspension analysisSmoke detectorsLight scattering measurement
Device for optically detecting smoke and implementing thereof. Apparatus and methods for detecting the presence of smoke in a small, long-lasting smoke detector are disclosed. Specifically, the present disclosure shows how to build a very compact housing around the smoke detector while keeping the reflections from the housing structure to a very low value while satisfying all the other peripheral needs of fast response to smoke and preventing ambient light. This allows very small measurements of light scattering of the smoke particles to be reliable in a device resistant to the negative effects of dust. In particular, geometrical optical elements, e.g., cap and optical defection elements, are disclosed.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Apparatus and method for measuring depth-of-interaction using light dispersion and positron emission tomography using the same
ActiveUS8476600B2Improve spatial resolutionResolve discontinuityMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusLight dispersionDepth of interaction
The present invention provides an apparatus for measuring a Depth-Of-Interaction (DOI), comprising a crystal layer 10 of a mono layer in which a plurality of crystals for absorbing gamma rays are consecutively arranged, scintillation light detectors disposed at one end of the crystals and configured to detect scintillation light emitted from the crystal layer 10 by the gamma rays, change means included in the crystals and configured to linearly change transmittance in a length direction of the crystals, and a control unit 30 configured to calculate the DOI in the crystal layer 10 on a basis of the first output signal and the second output signal. The scintillation light detector outputs the first output signal in one direction and the second output signal in a direction at a right angle to the one direction.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Dynamic light-scattering measuring apparatus using low-coherence light source and light-scattering measuring method of using the apparatus
ActiveUS8467067B2Raman/scattering spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansDynamic light scatteringMach–Zehnder interferometer
There is provided a dynamic light-scattering measuring apparatus including: a Mach-Zehnder interferometer; and a low-coherence light source. Further, there is provided a method for measuring light-scattering intensity of particles in a medium, including the steps of: providing a Mach-Zehnder interferometer; and measuring light-scattering intensity from light emitted from a low-coherence light source, in accordance with a dynamic light-scattering intensity measuring process.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Localized dynamic light scattering system with doppler velocity measuring capability
A localized dynamic light scattering measurement system includes a beam displacer for splitting an incident beam having two orthogonal linearly polarized beam components with slightly different frequencies into two orthogonal linearly polarized output beams focused onto an object to be measured. The beam displacer cooperates with an iris to collect and recombine scattering beams each reversely backscattered at 180 degrees from the object so as to form a signal beam, which is polarized by a polarizer to produce two polarization components, thereby generating a heterodyne interference signal associated with the polarization components. A signal processing unit obtains measurement data on the object based on power spectrum or autocorrelation data corresponding to the heterodyne interference signal.
Owner:CHOU LIDEK
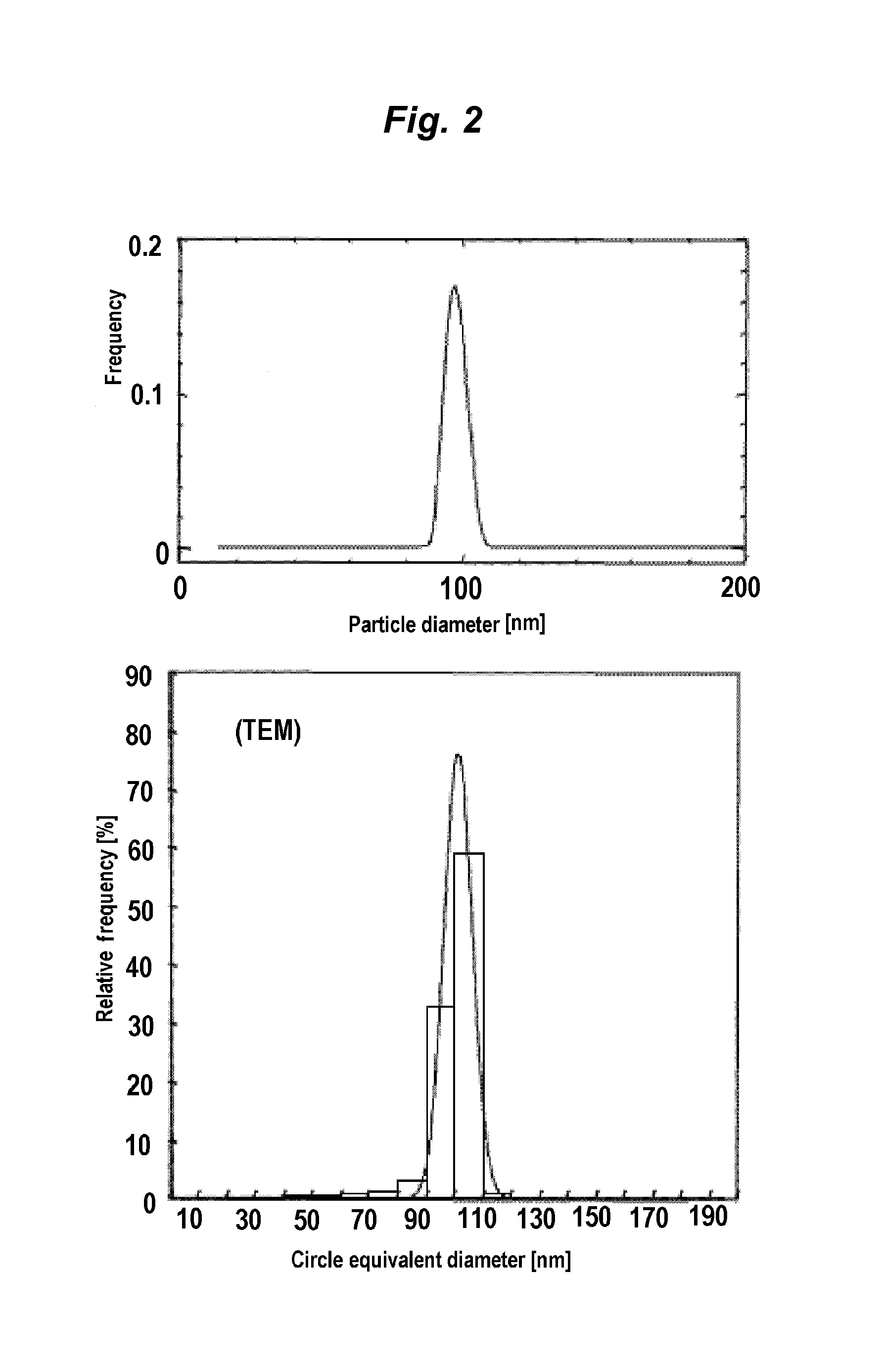
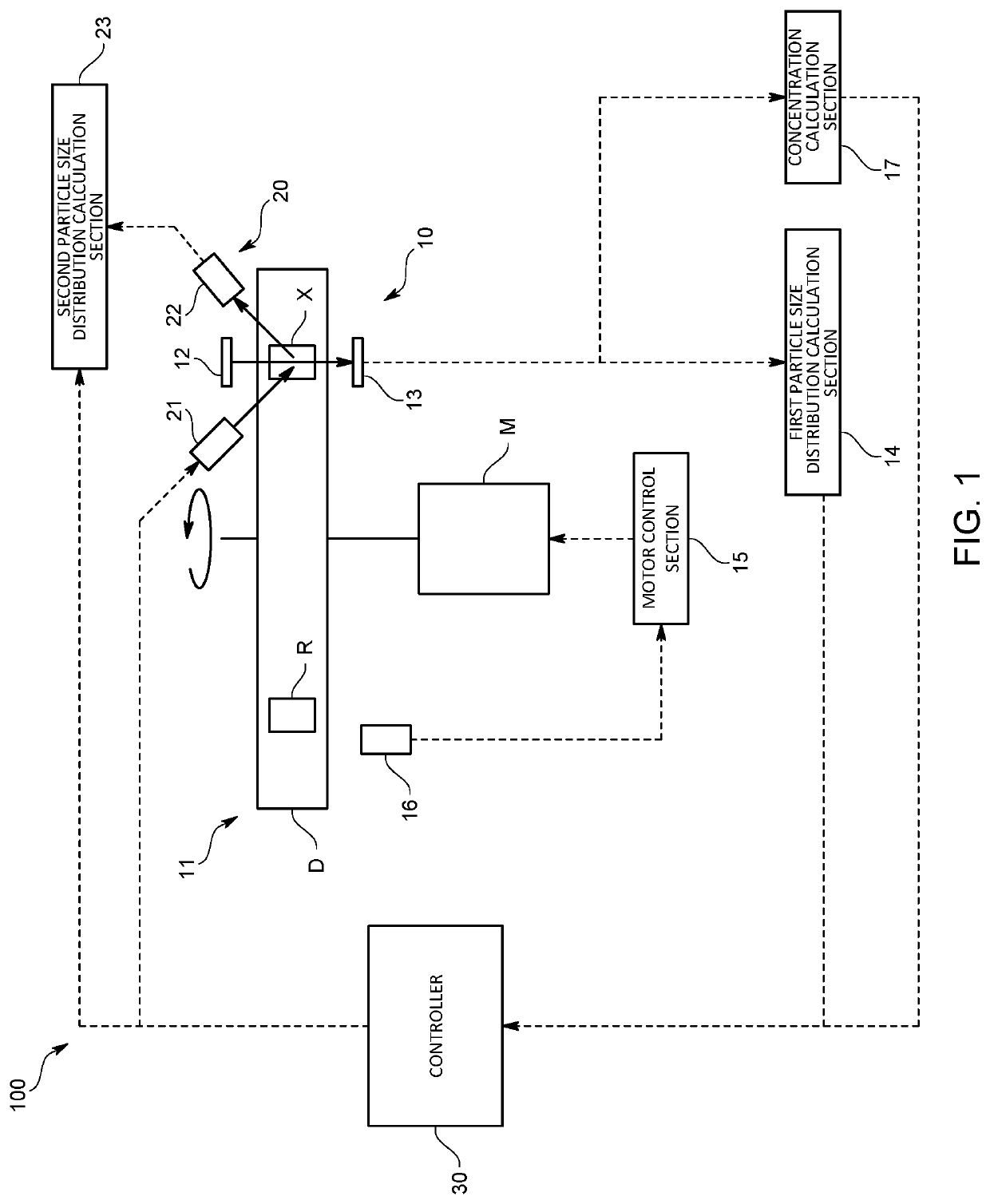
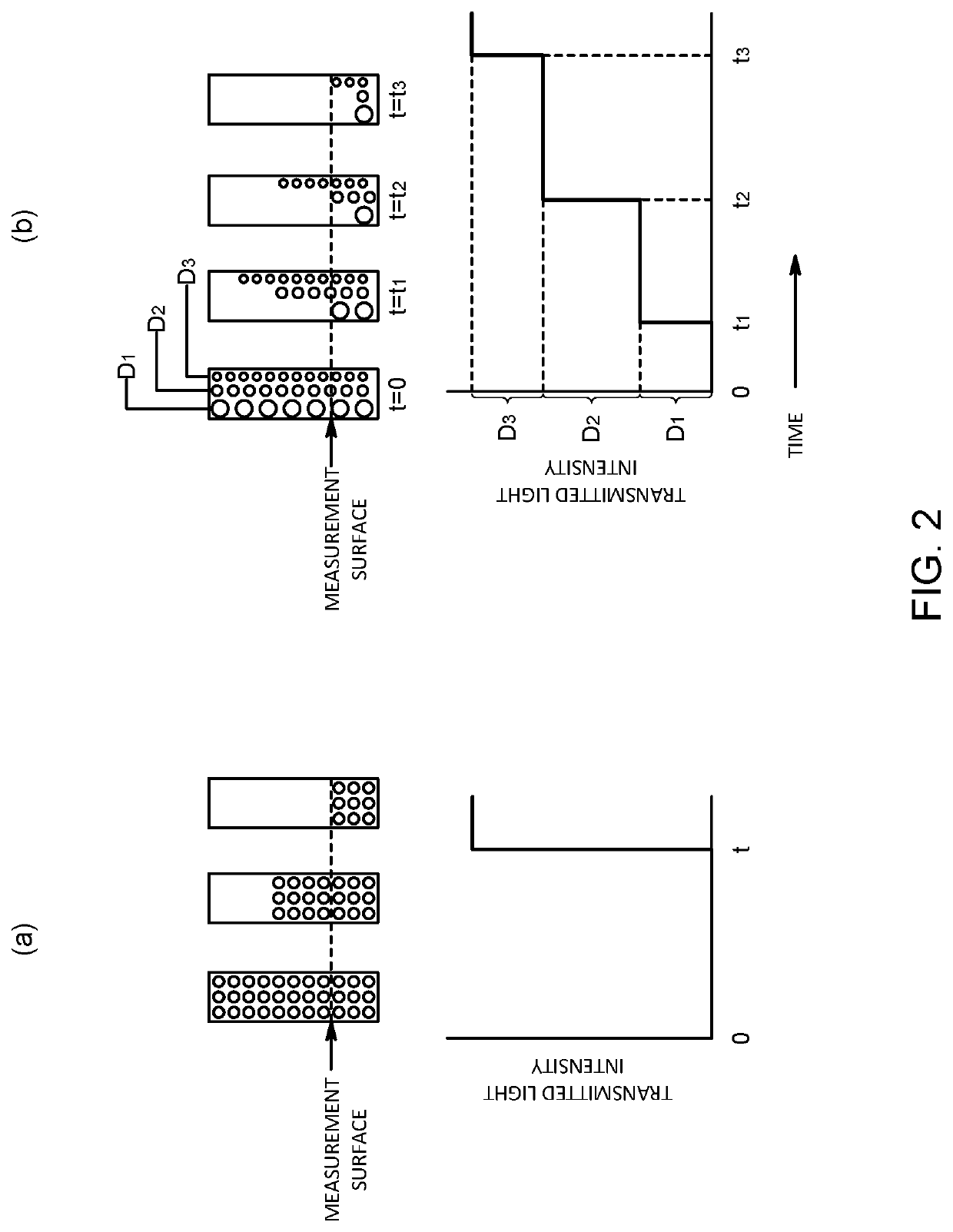
Apparatus and method for measuring particle size distribution, and program for particle size distribution measuring apparatus
ActiveUS11047786B2High precision measurementParticle size analysisParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
The particle size distribution measuring apparatus includes a centrifugal sedimentation measuring mechanism and a dynamic light scattering measuring mechanism. The centrifugal sedimentation measuring mechanism causes particles to settle out by rotating a measurement cell accommodating particles dispersed in a dispersion medium and detects transmitted light by irradiating light to the measurement cell to measure a first particle size distribution on a basis of a change of transmitted light intensity of the transmitted light. The dynamic light scattering measuring mechanism detects scattered light occurred upon irradiation of light to particles so as to measure a second particle size distribution based on a change of scattered light intensity of the scattered light occurred due to Brownian motion of particles. After the centrifugal sedimentation measuring mechanism detects the transmitted light, the dynamic light scattering measuring mechanism measures the second particle size distribution by irradiating light onto the measurement cell.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
Resin Composition, Molded Article and Film Including Vinylidene Fluoride-Based Resin
ActiveUS20180208758A1Suppresses light scatteringHigh crystallinityMaterial heat developmentLight scatter measurementFluoride
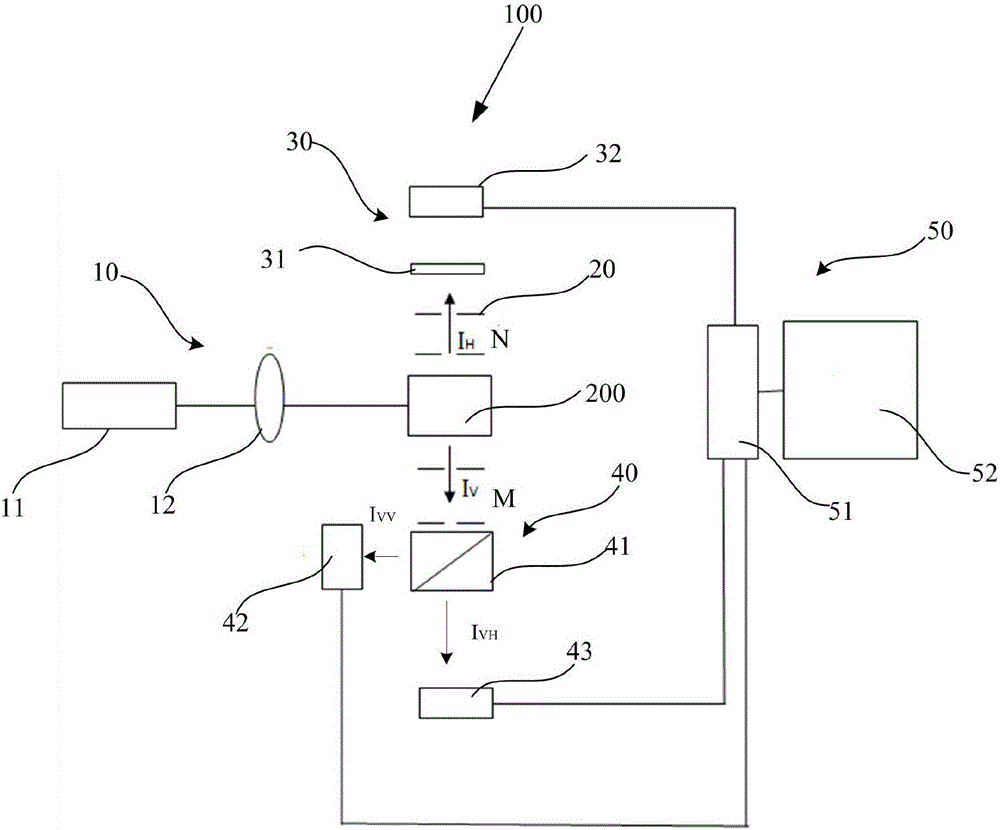
The present invention provides a resin composition including a vinylidene fluoride-based resin (A), having a crystal melting enthalpy of 10 to 45 J / g as measured with a differential scanning calorimeter, and having (2) IHv of 60 or less as obtained by (1) a light scattering measurement.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Systems for Measuring Properties of a Physiological Fluid Suspension
ActiveUS20090225316A1Volume/mass flow measurementScattering properties measurementsPhysiological fluidEngineering
A method of evaluating a property of a physiological fluid suspension comprises measuring a value of the property of a liquid portion of the physiological fluid suspension via light scattering, and comparing the measured value with a reference value to evaluate the property of the liquid portion of the physiological fluid suspension.
Owner:AGGREDYNE
Nanotube geometric dimension measuring device and method based on photon counting
InactiveCN106595491AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to measure the length of nanotubesQuick measurementUsing optical meansBeam splitterInformation analysis
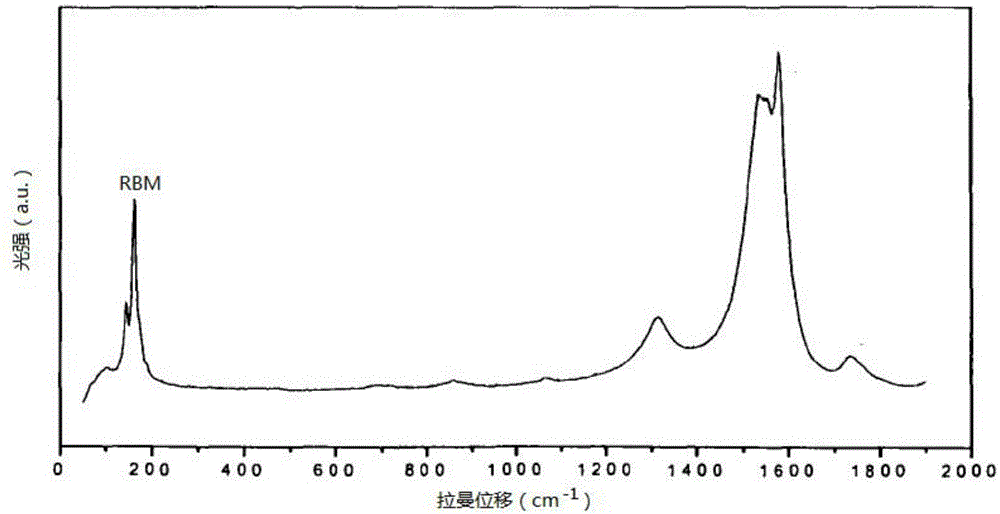
The invention provides a nanotube geometric dimension measuring device and method based on photon counting, and is characterized in that the measuring device includes a light beam focusing unit that includes a light source and a lens, a Raman scattering unit that includes an optical filtering component and a first photoelectric conversion element, a depolarization dynamic scattering unit that includes a beam splitter prism, a second photoelectric conversion element and a third photoelectric conversion element, and an information analysis and processing unit that includes a photon counting card used for counting electric pulse signals to obtain a count value and a computer connected with the photon counting card and processes and analyzes the count value to obtain the diameter and length of a nanotube. The nanotube geometric dimension measuring device and method based on photon counting combines a depolarization dynamic scattering method with a Raman spectrum method, can not only make up for the defect that the depolarization dynamic light scattering measuring range is insufficient, but can also overcome the defect that the Raman spectrum method cannot measure the length of a nanotube, and is fast in measurement, low in cost and high in accuracy.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Preparation of solid capsules comprising flavours
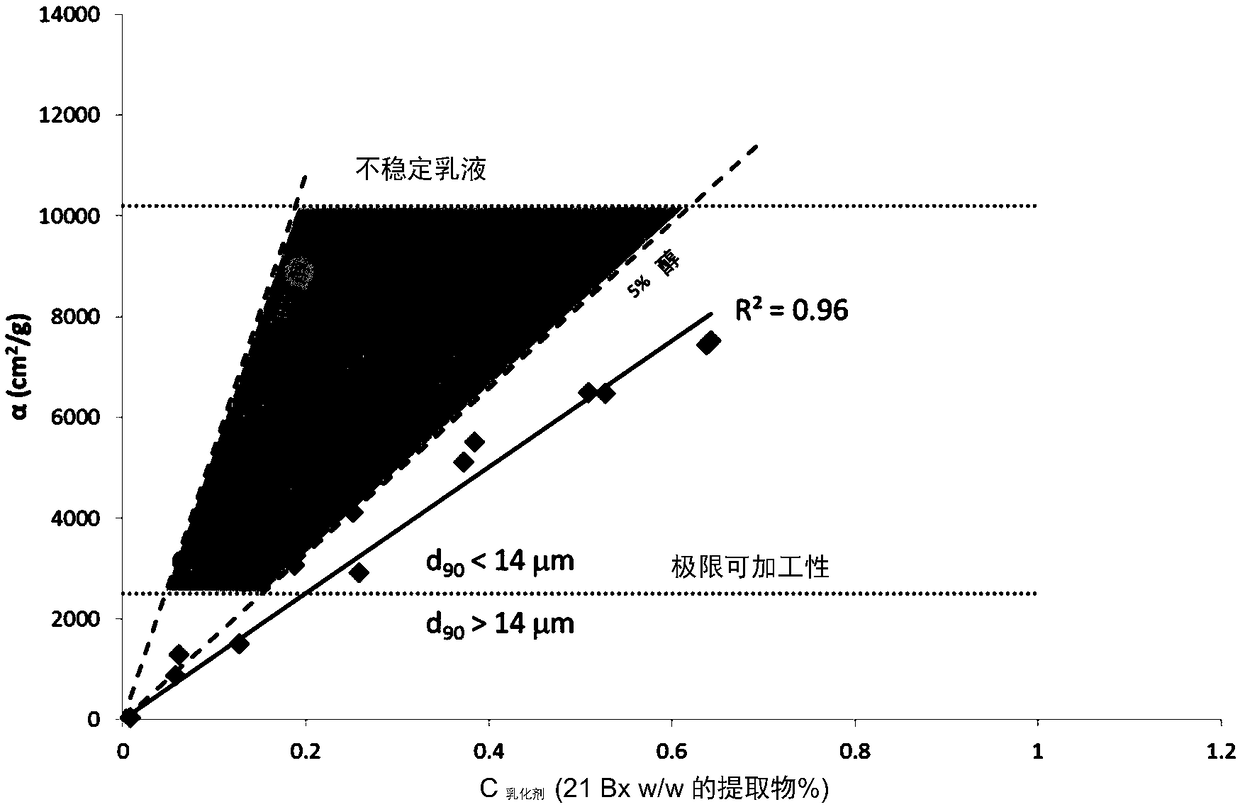
Provided herein is a process for preparing a solid particle comprising: preparing an emulsion comprising: from 0.01 to 0.24%, by weight, of the final weight of the solid particle, of a saponin; from 5to 55%, by weight, of the total weight of the emulsion, a water soluble biopolymer having a molecular weight below 100 KDa; from 5 to 60%, by weight, of the final weight of the solid particle, a flavor or fragrance comprising from about 50% to about 95% of limonene; from about 5% to about 50%, by weight, of the final weight of the solid particle an alcohol; and from about 15% up to about 80 % ofwater; the percentages being defined by weight; 1. spray-drying the emulsion obtained in step 1) so as to obtain solid capsules; 2. the solid capsule in which the droplet size measured by Diffusion Light Scattering is characterized by a characteristic diameter D90 (90% of the population) equal or below 14 micrometers; 3. and in which the alcohol is aliphatic saturated or unsaturated (from C6 to C12) pure or in mixture with logP ranging from 1.8 to 4.8 as calculated by the Suzuki method; or cyclic (i.e. phenol, vanillin...); in the flavor or fragrance that will be used as a co-surfactant in conjunction with the natural extract comprising saponins when the concentration of the solid extract of saponin is equal or lower than 0.06%w / w to guaranty a droplet size below the limit according to 3)even under reduced quantity of surfactant. e) An [alpha] value as calculated by the model that is between 2,500 and 10,250 cm2 / g.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
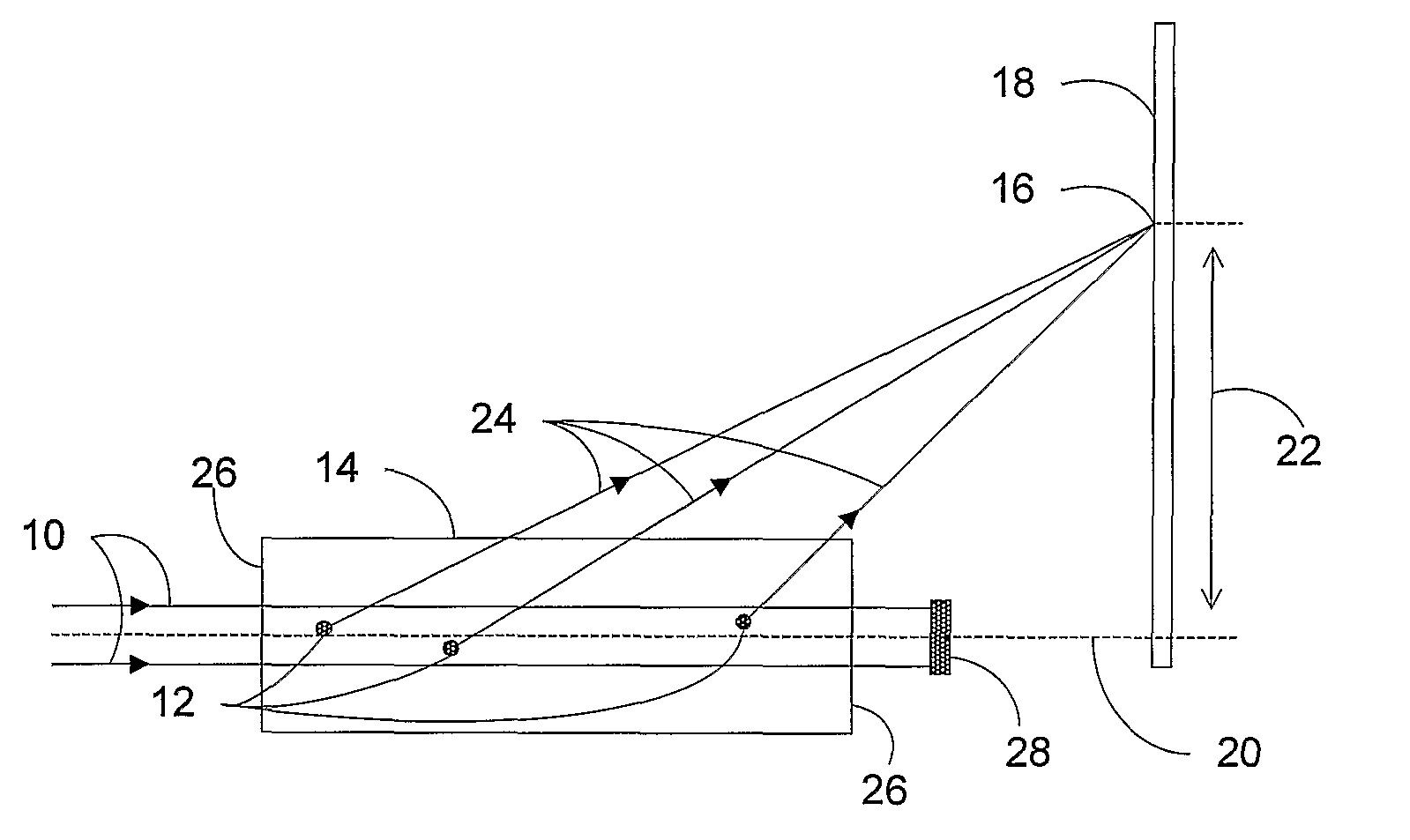
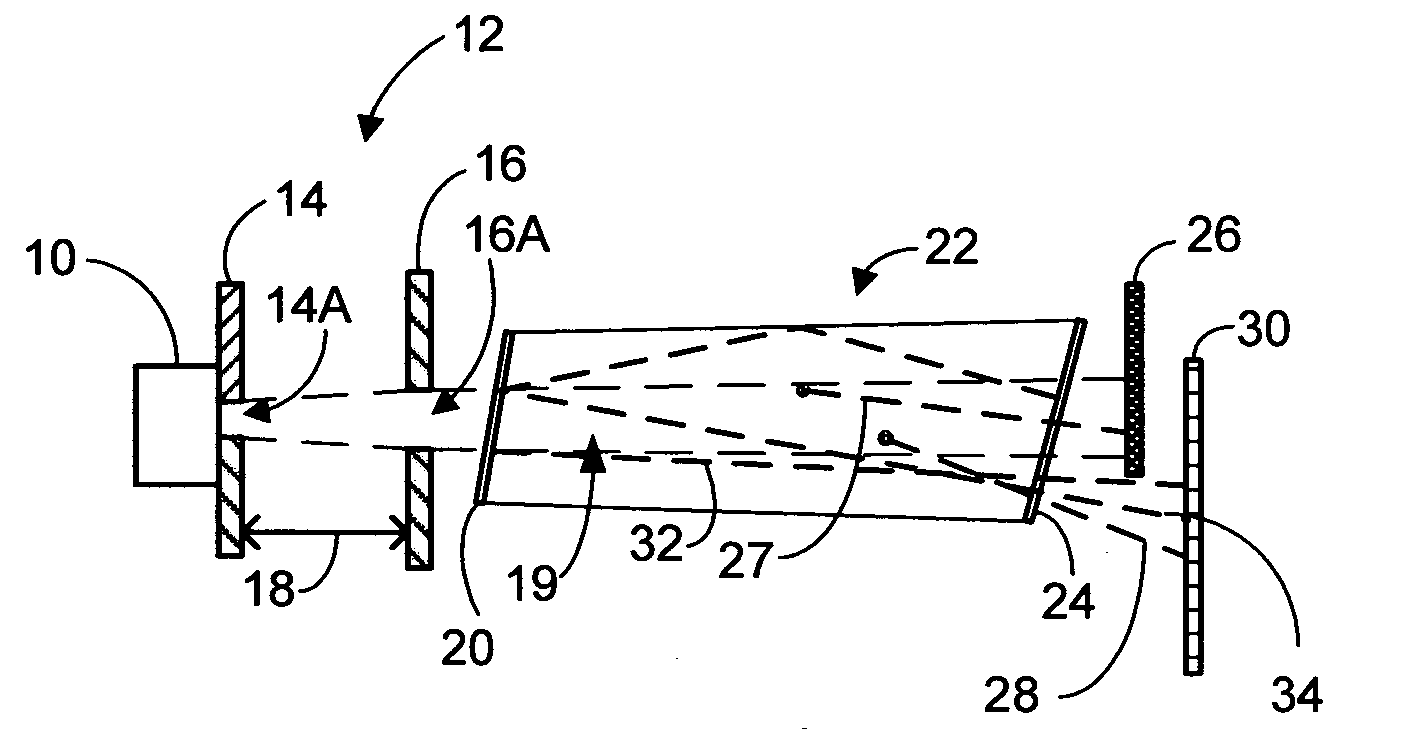
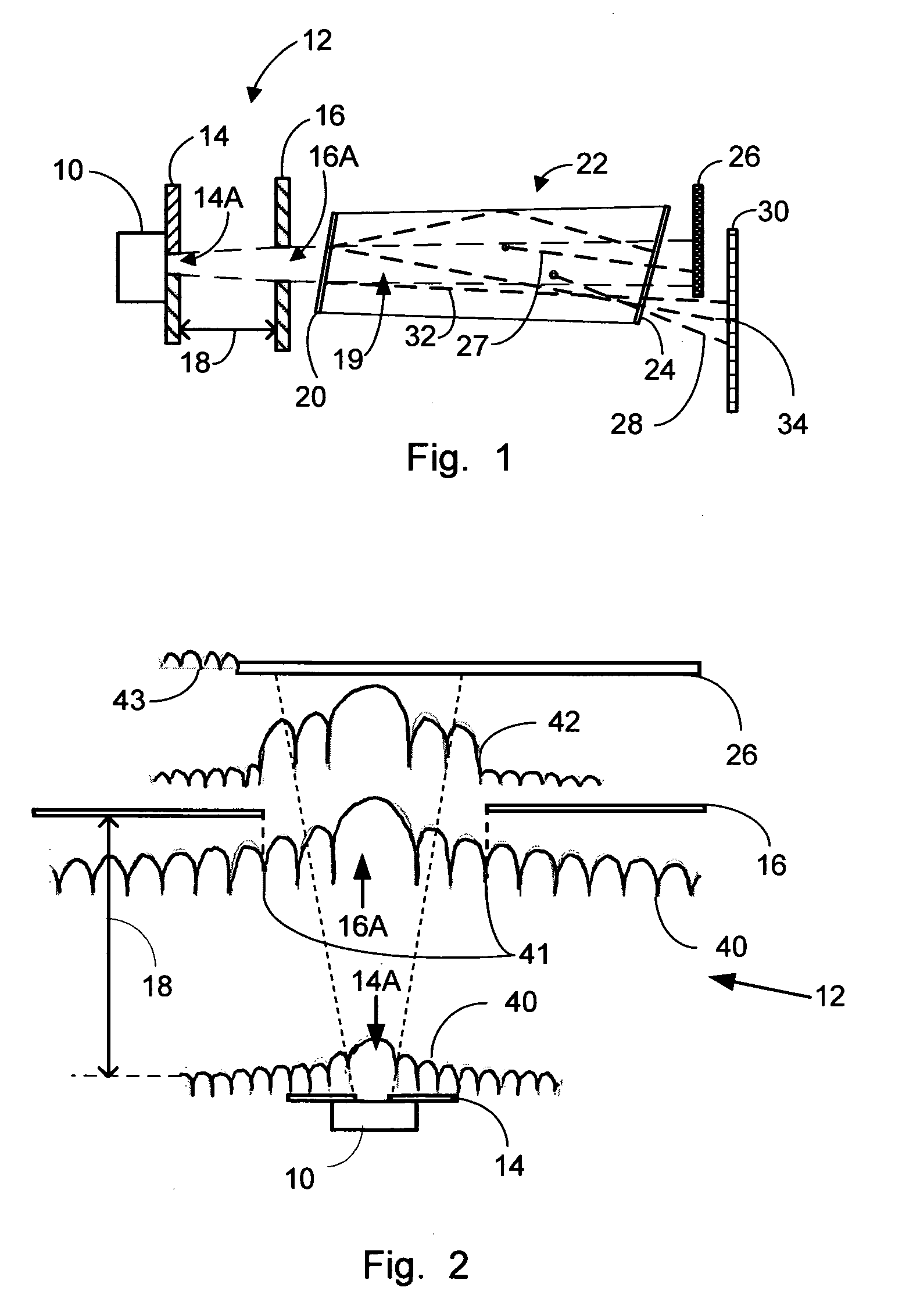
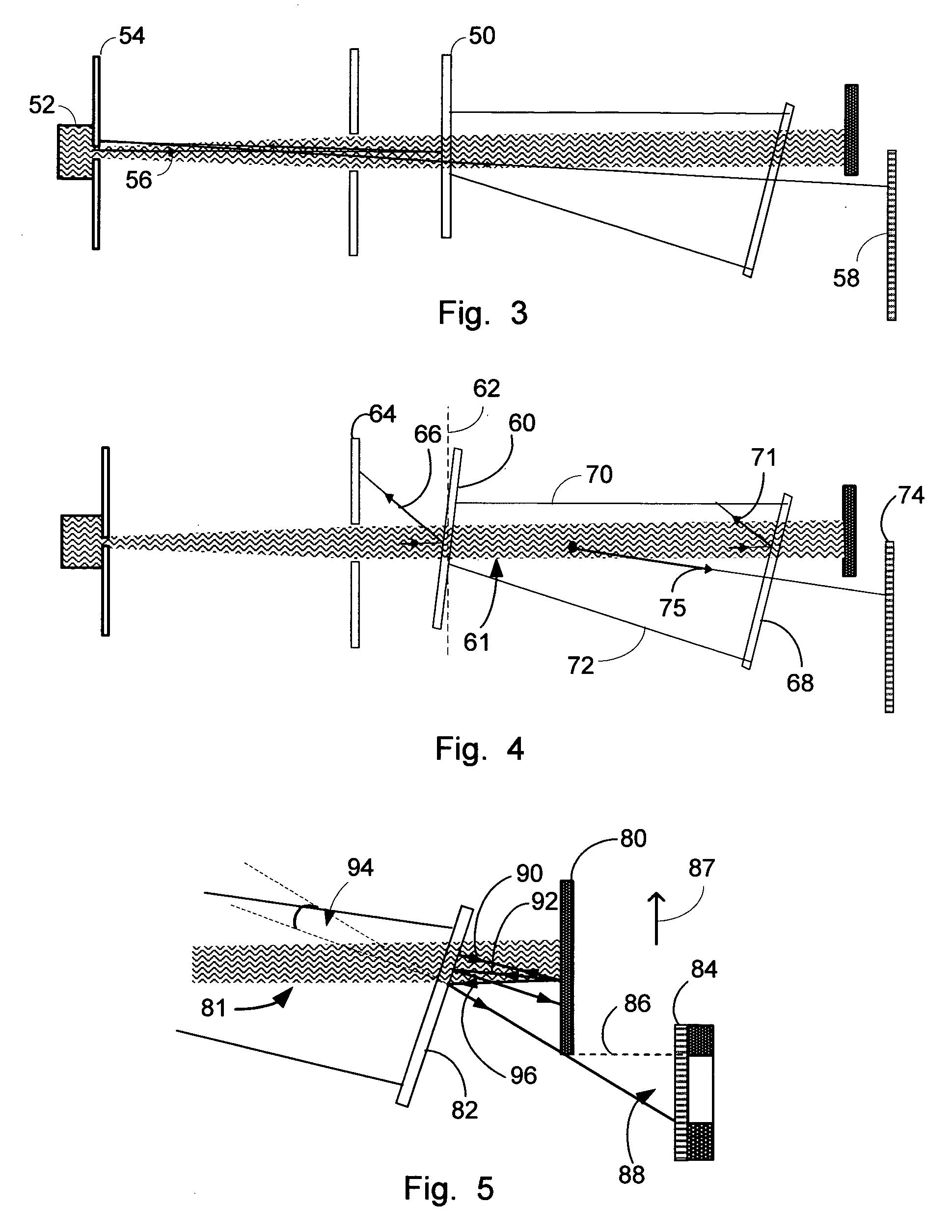
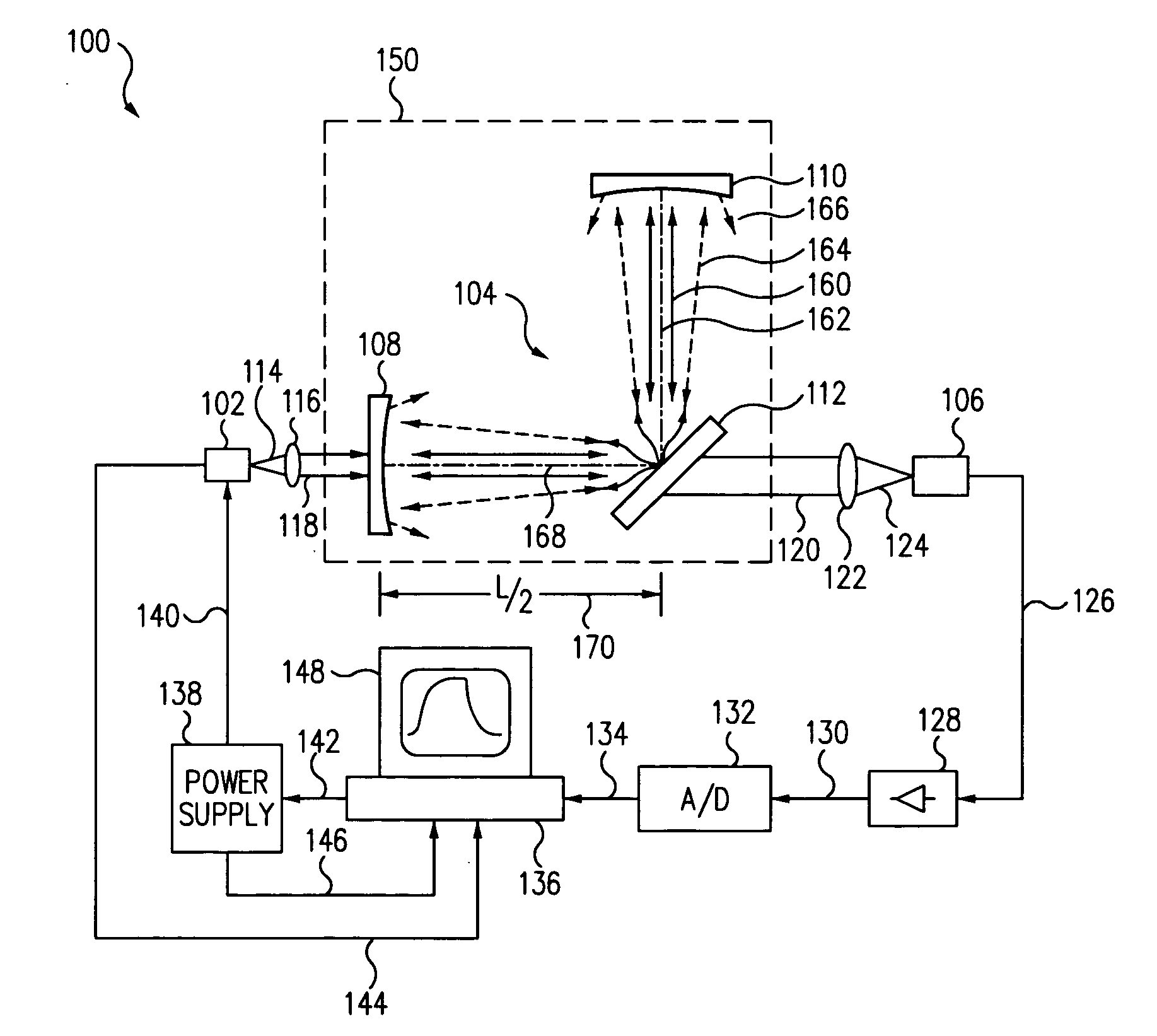
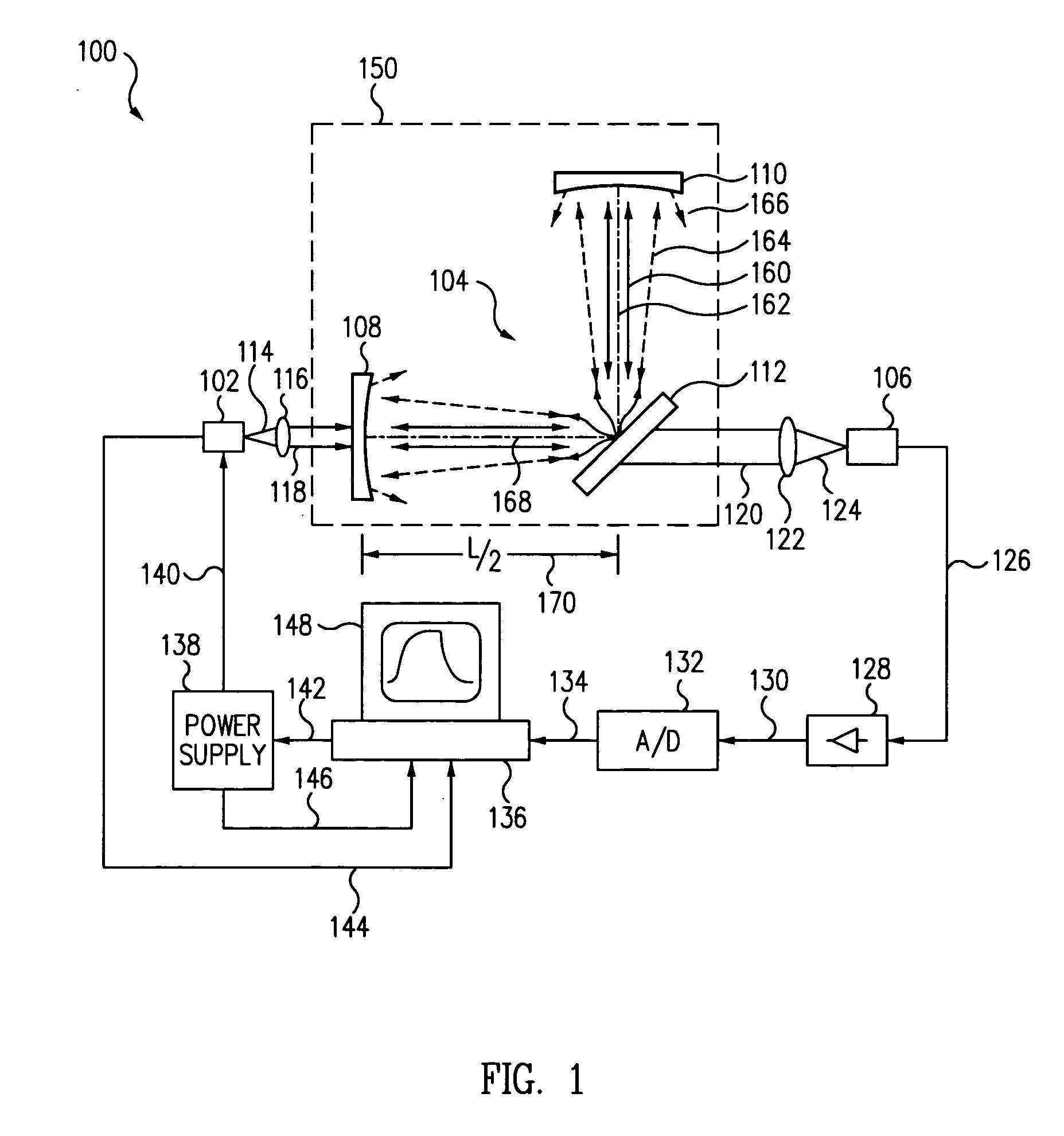
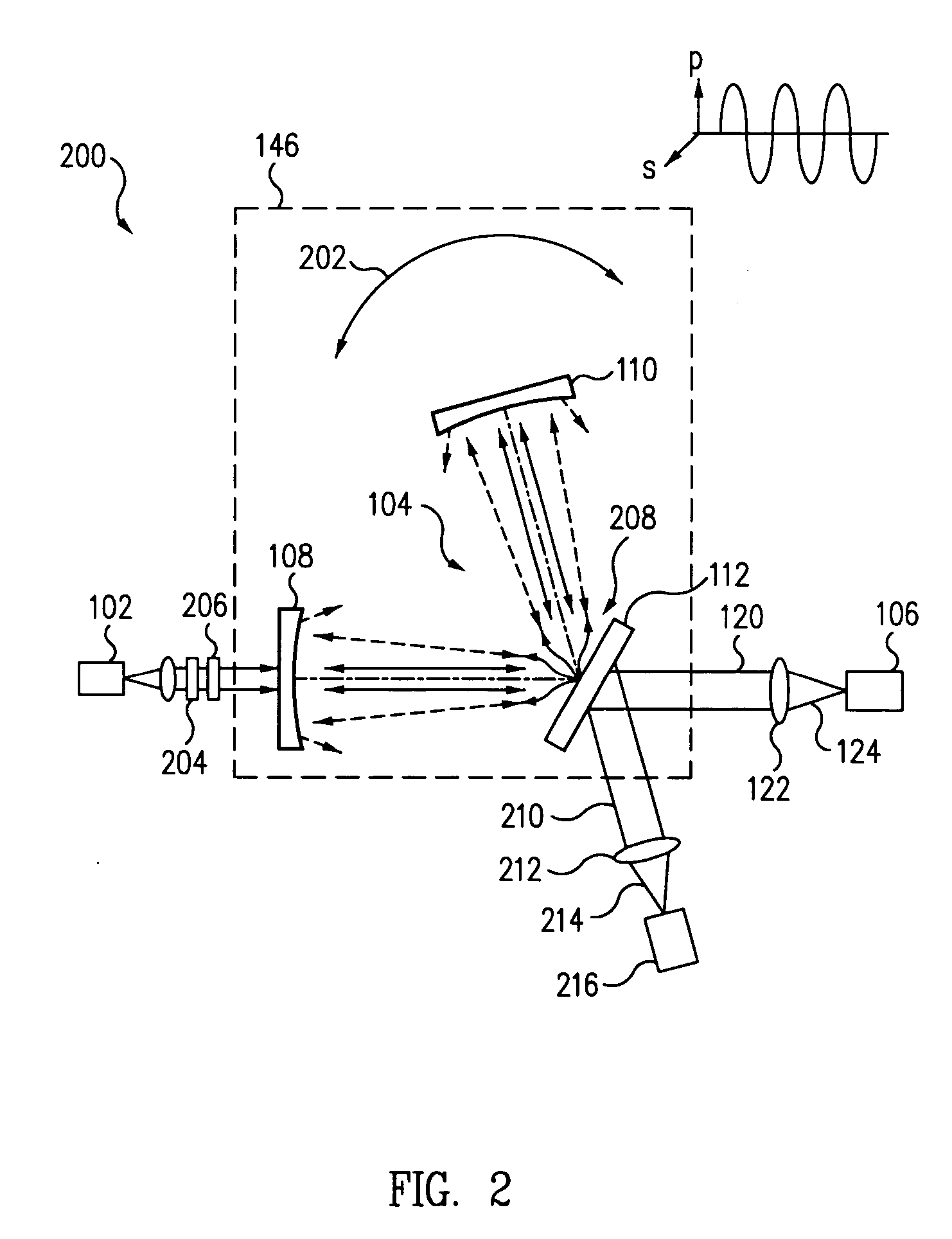
Light scatter measurement apparatus and method
In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, an apparatus for measuring light scatter loss from a test piece includes a light source, an optical cavity including the test piece and at least one mirror located along a path, and a light detector. The cavity receives an input beam from the light source, circulates a beam within the cavity as a circulating beam, and produces an output beam. Irregularities on the surface of the test piece result in a progressive diffusion of the circulating beam about the path. The light detector provides an output signal based on the intensity of the output beam. The output signal has an initial slope that determines a first saturation value. The output signal has a second saturation value. The difference between the first saturation value and the second saturation value provides a scatter loss measurement.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
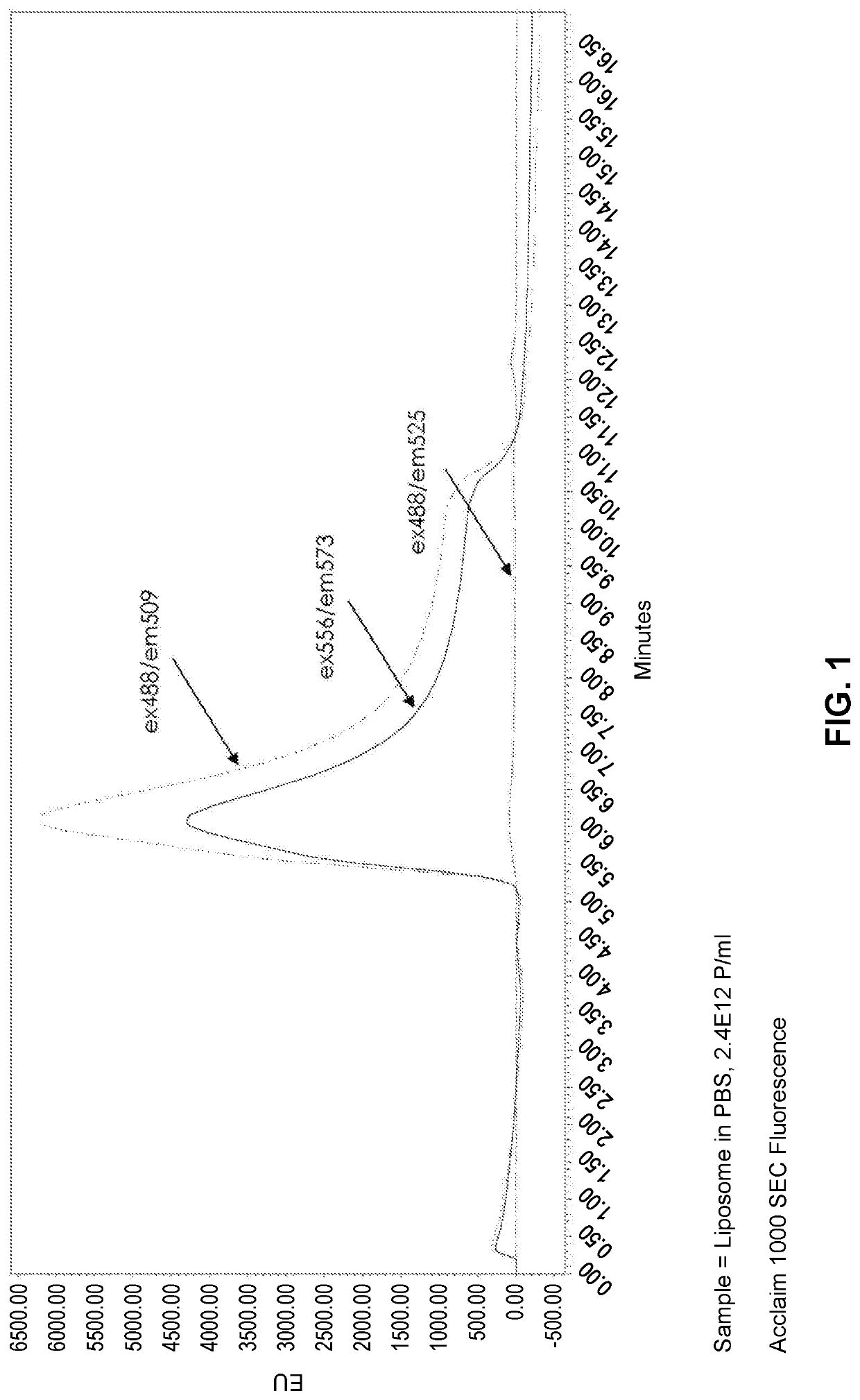
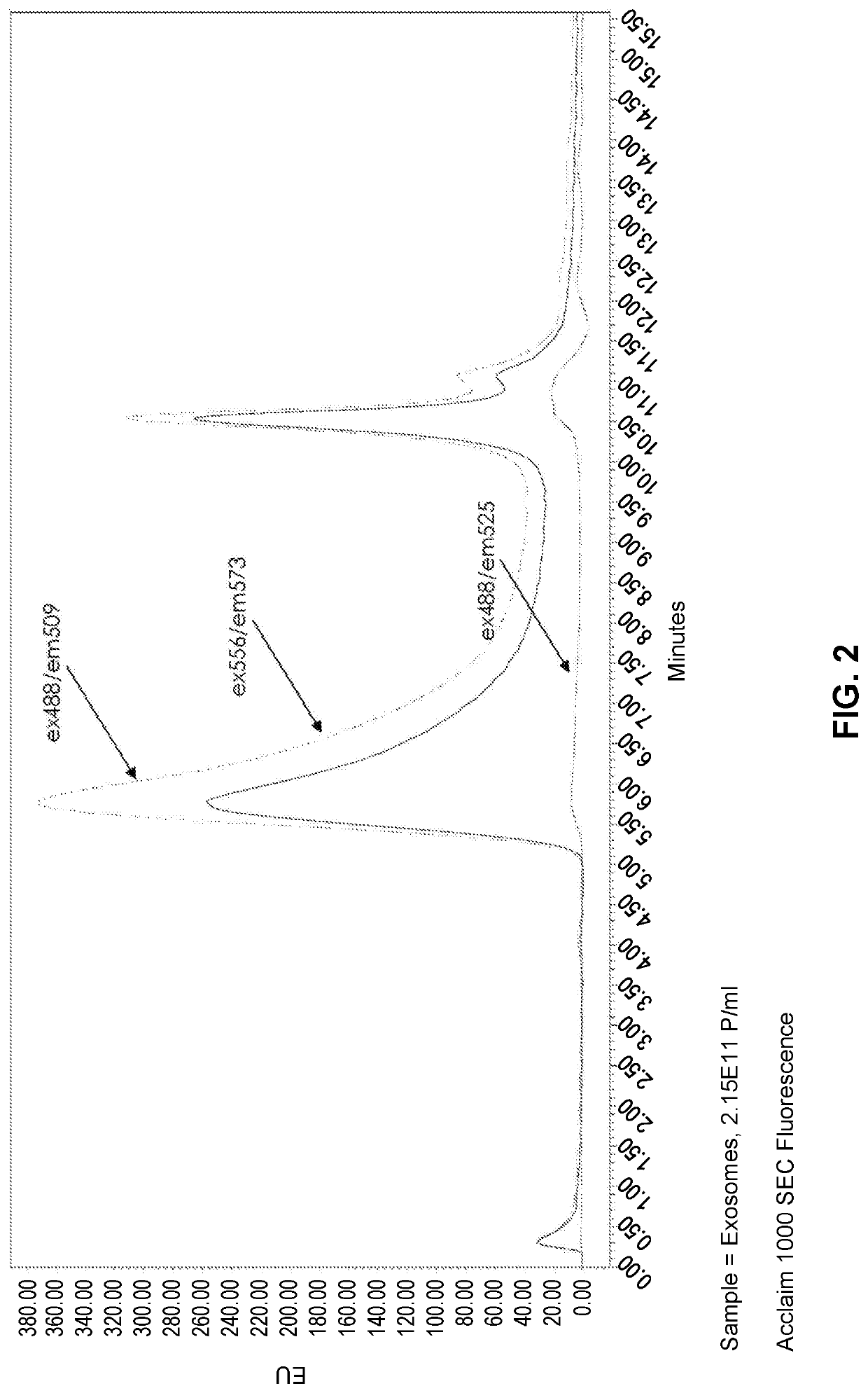
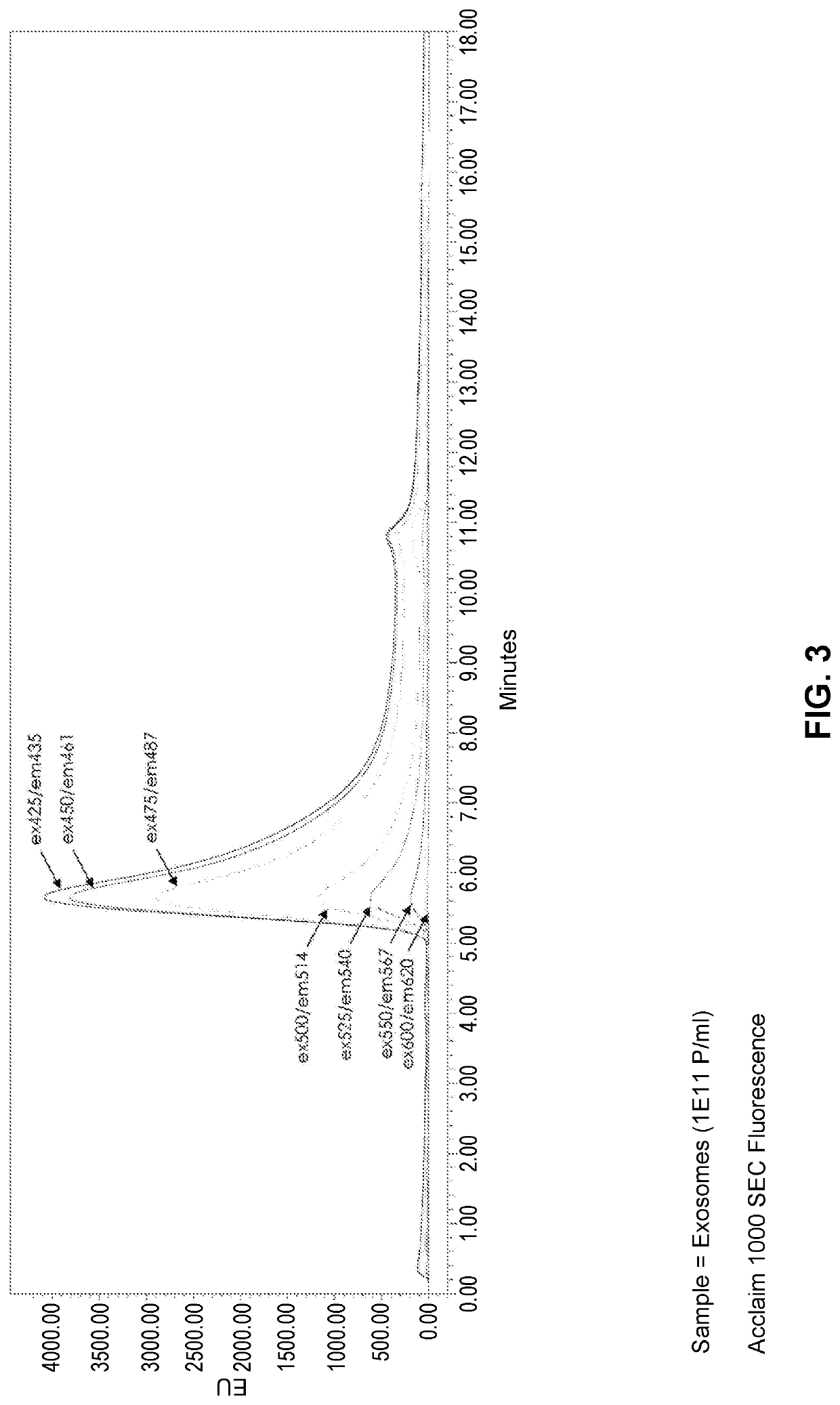
Methods of measuring extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles in complex matrices by light scattering
PendingUS20210262931A1Nanoparticle analysisScattering properties measurementsExtracellular vesicleNanoparticle
Described herein are novel rapid and reliable methods of detection of extracellular vesicles and quantifying extracellular vesicle concentrations and absolute number from various sources, including raw cell harvest. The methods described herein comprise detection of light scattering of extracellular vesicles in biological samples. Extracellular vesicles analyzed by the methods of this application have a stereotypical elution profile distinct from known contaminants. The methods described herein are a significant improvement over the state of the art and fulfills an unmet need in the field of extracellular vesicle manufacturing and quality control.
Owner:LONZA SALES AG
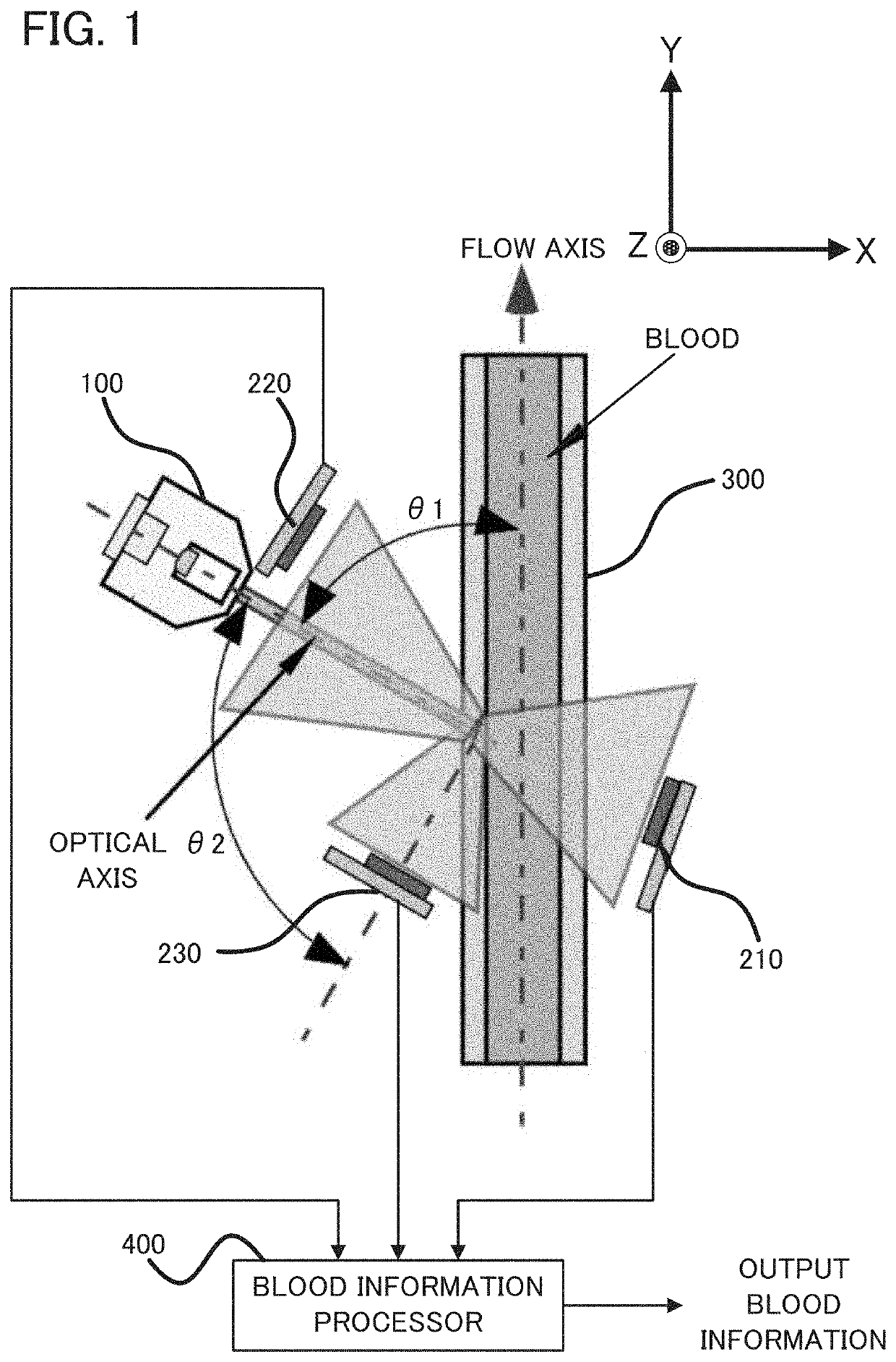
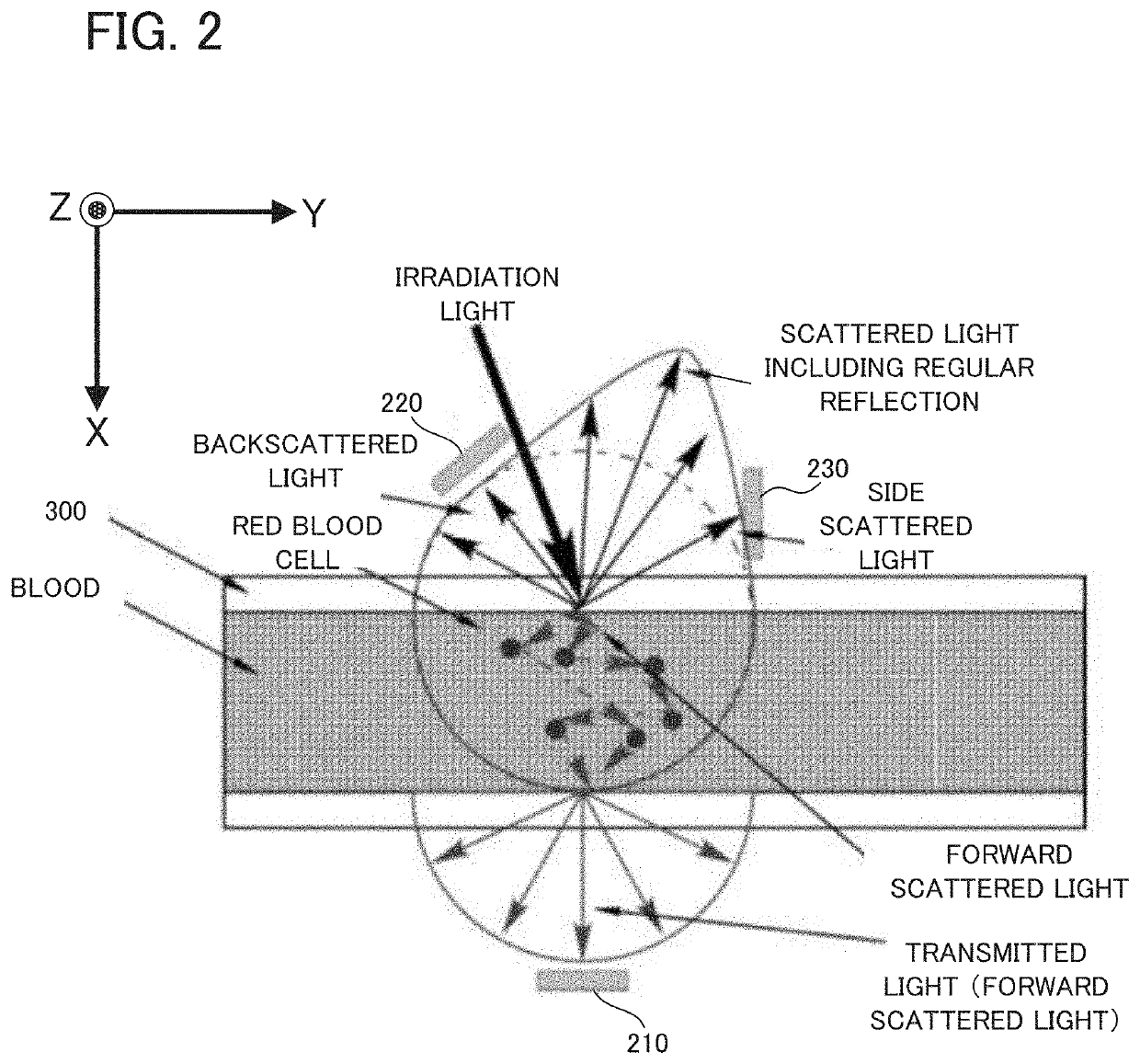
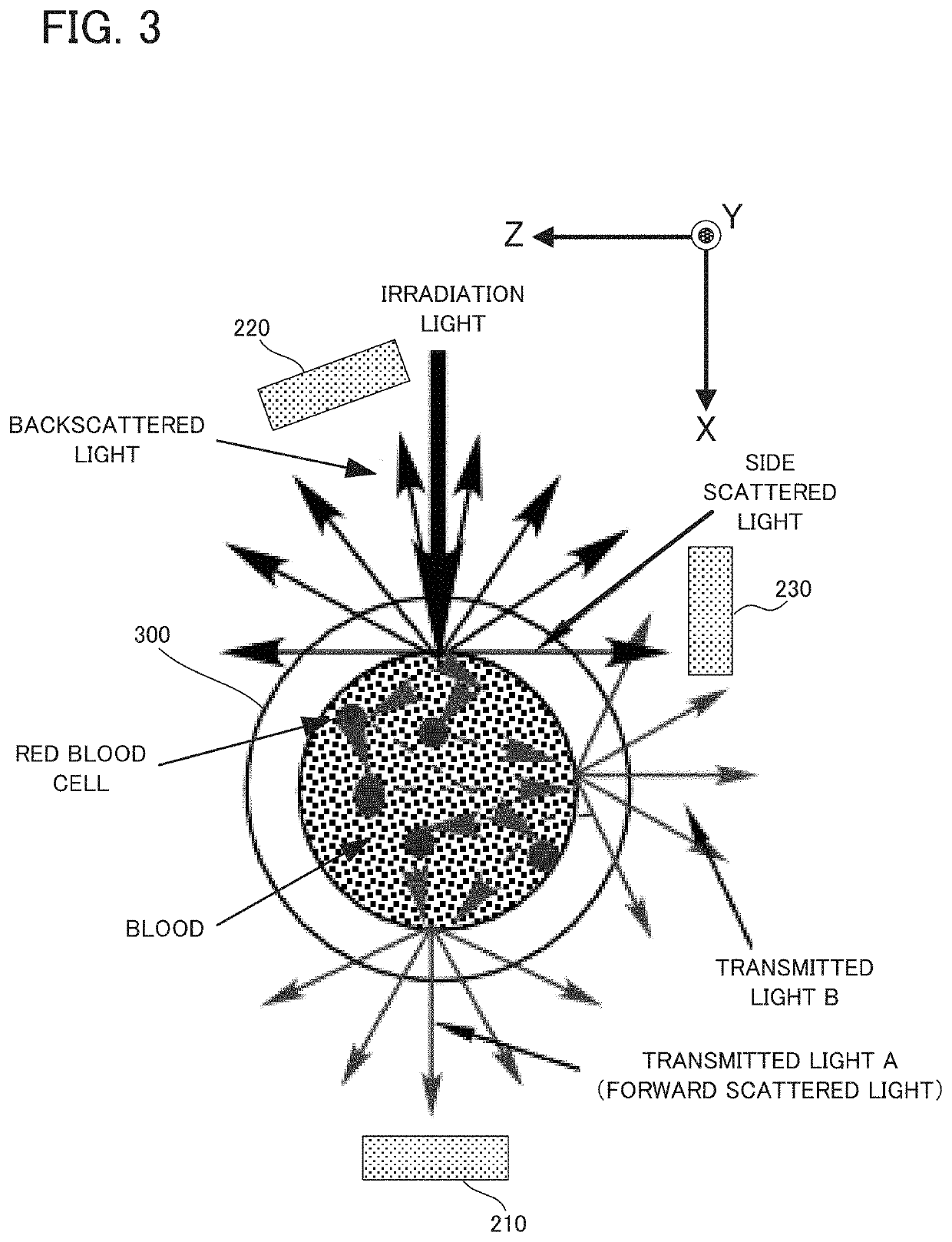
Apparatus and method for measuring fluid information from light scattering
ActiveUS11209359B2Reduce measurementScattering properties measurementsBiological testingForward scatterPhoto irradiation
A measuring apparatus is provided with: an irradiator configured to irradiate fluid with light; a first light receiver configured to receive a forward scatter component of scattered light scattered by the fluid; a second light receiver configured to receive a backscatter component of the scattered light; a third light receiver configured to receive a side scatter component of the scattered light; and an outputting device configured to output fluid information about the fluid, which is obtained on the basis of light receiving signals of the first light receiver, the second light receiver, and the third light receiver. According to this measuring apparatus, it is possible to output accurate fluid information because of the use of the forward scatter component, the backscatter component, and the side scatter component of the scattered light.
Owner:AIR WATER BIODESIGN INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com