Patents
Literature
55 results about "Depth of interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
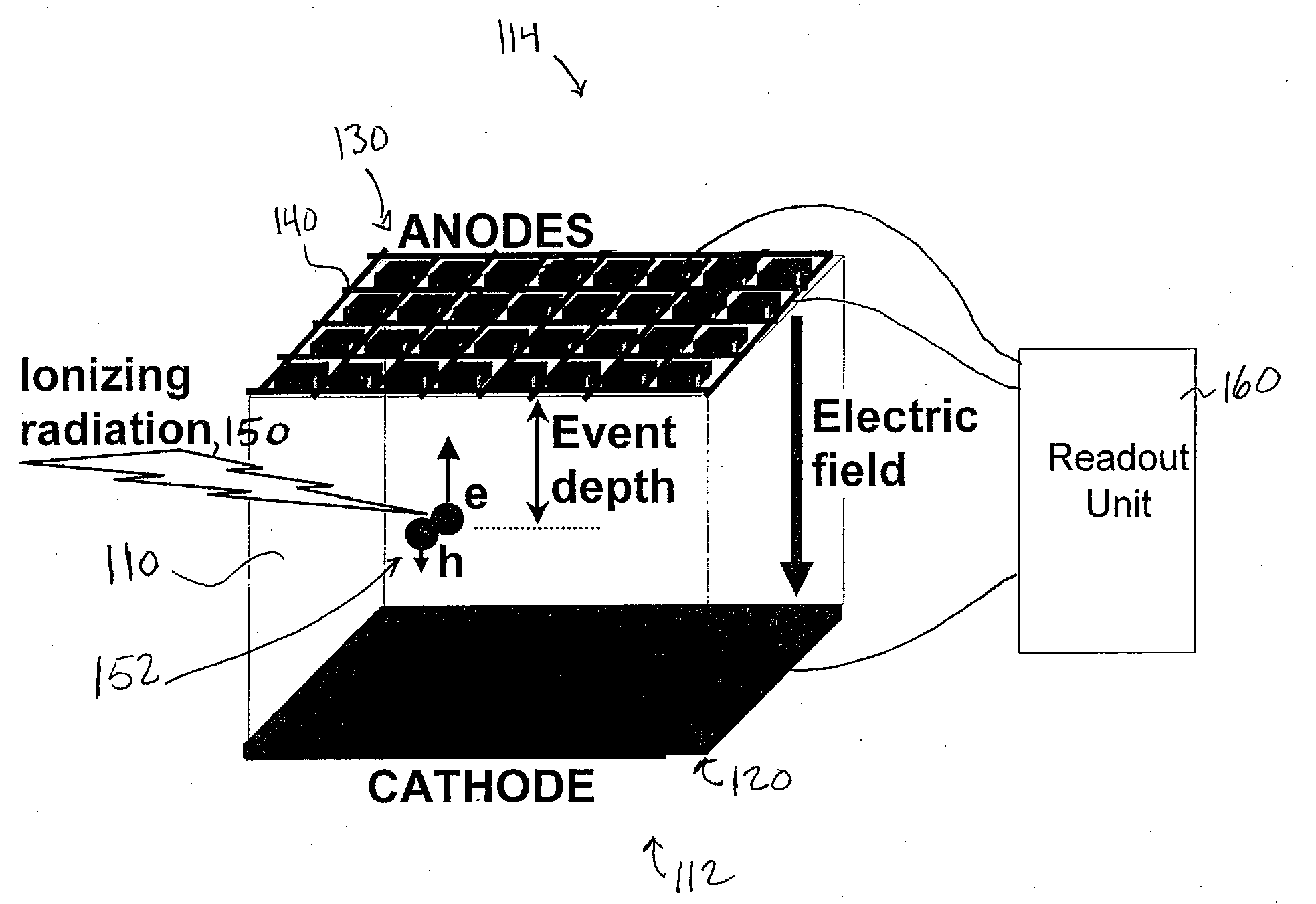
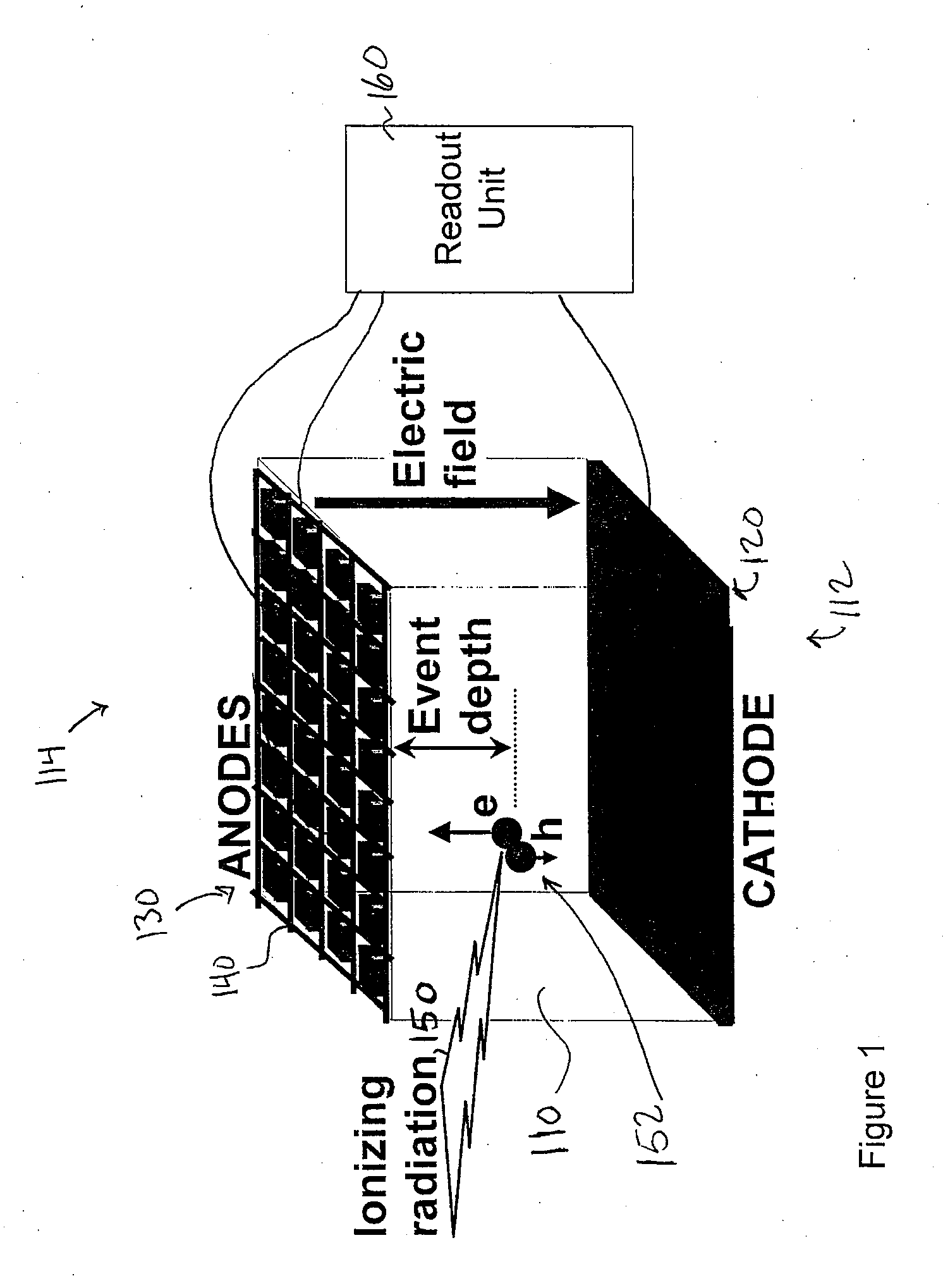
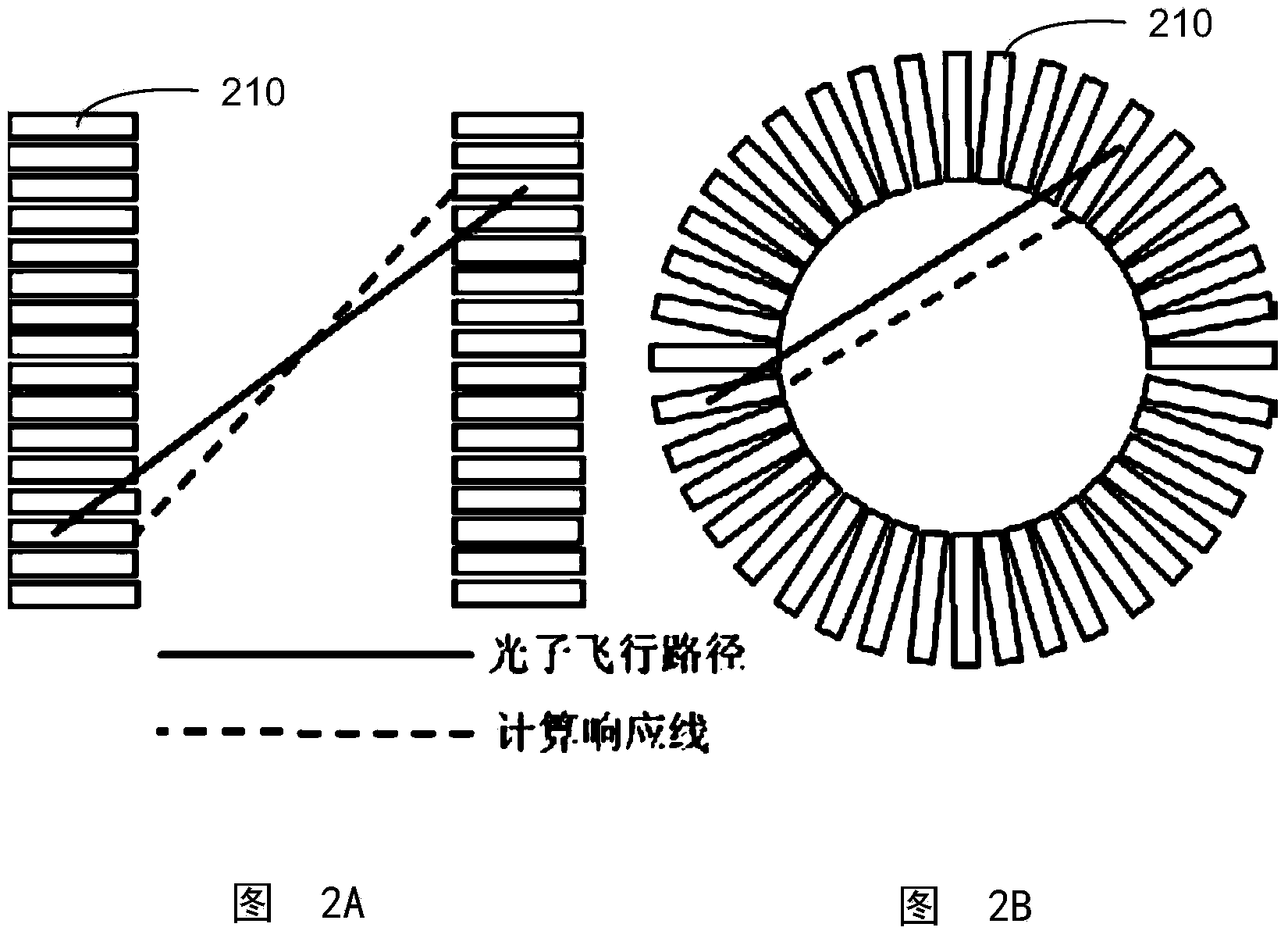
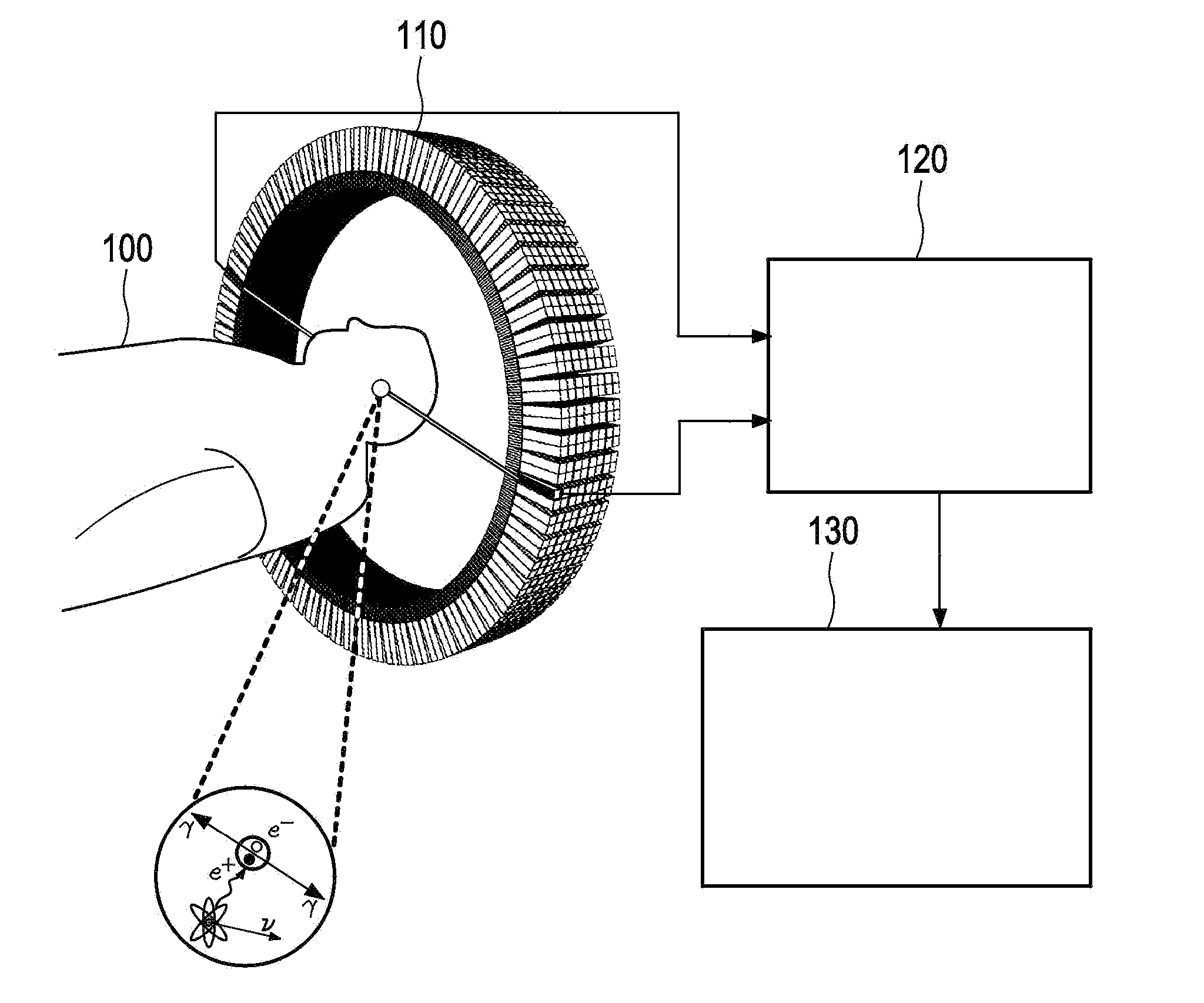
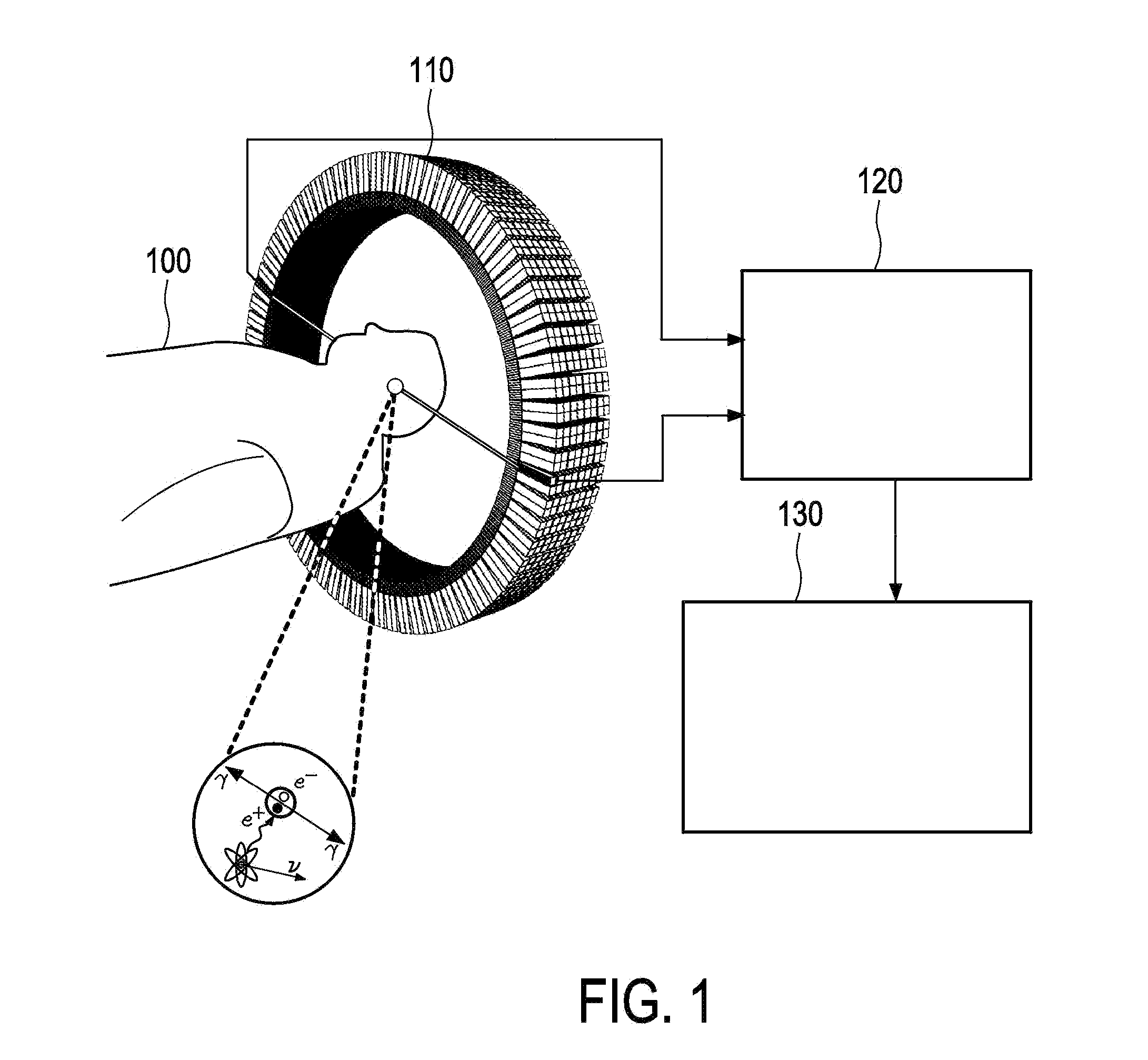
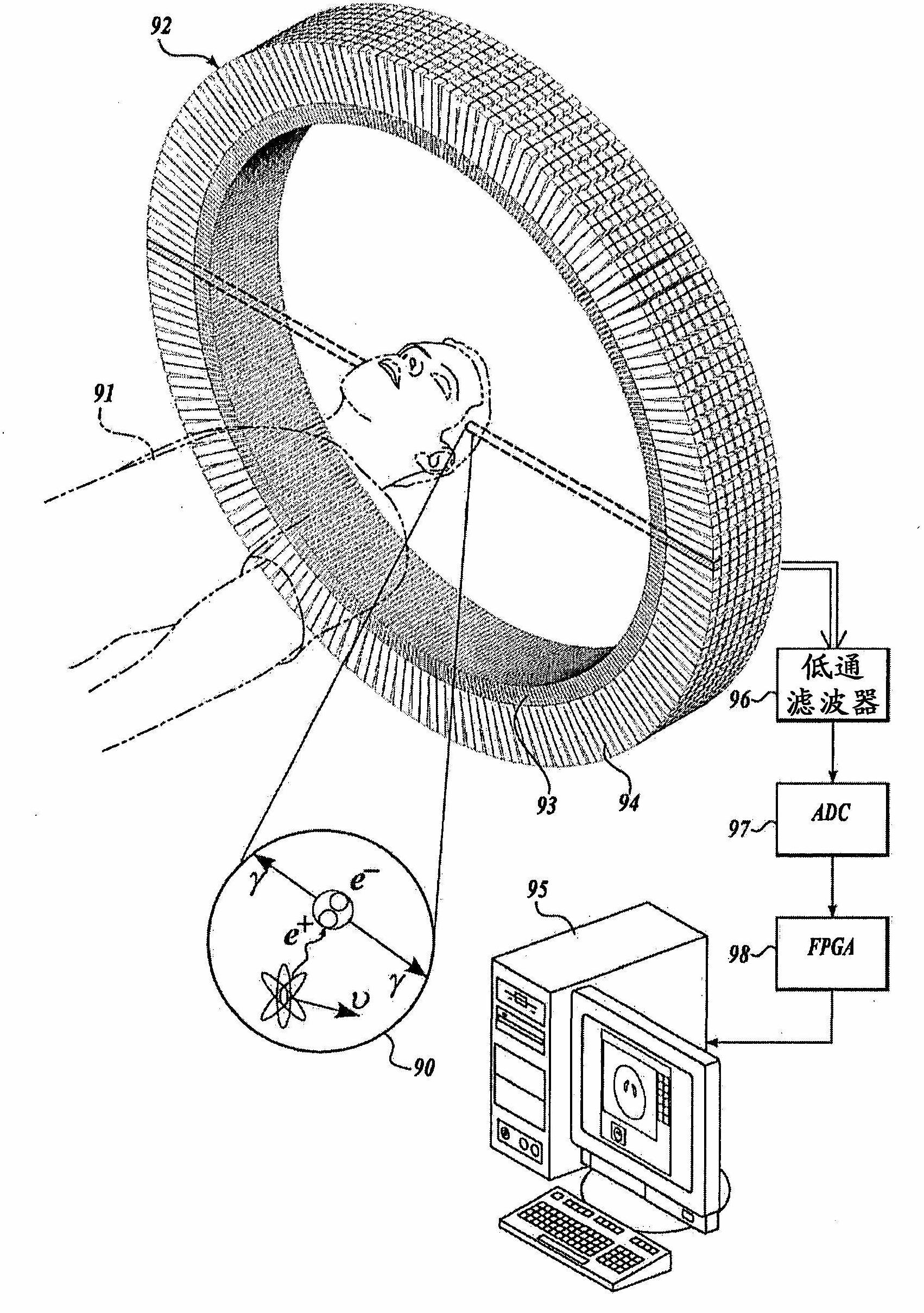
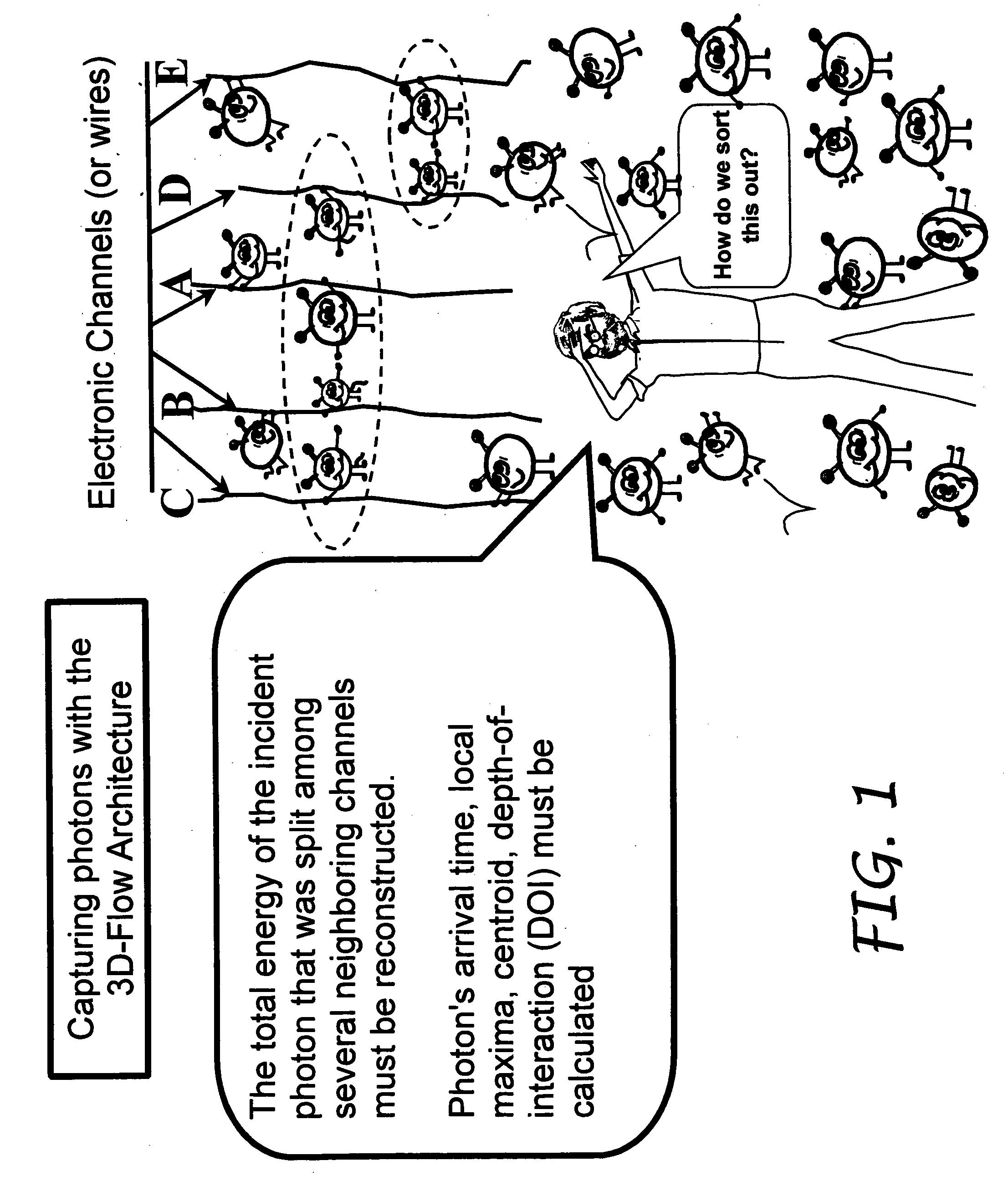
What is Depth Of Interaction (DOI) 1. Depth inside the scintillator crystal where a photon interacts and produces a light distribution.
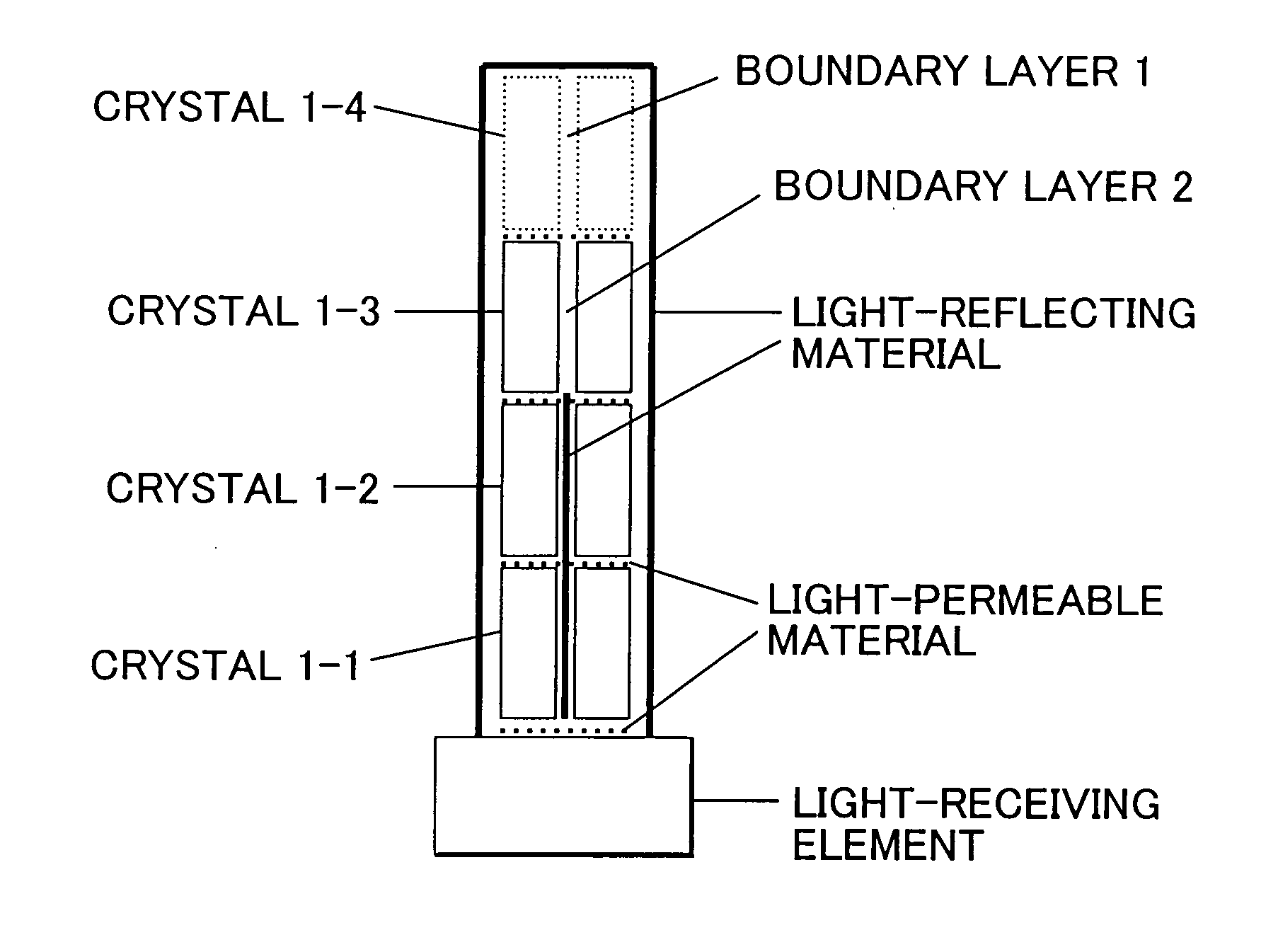
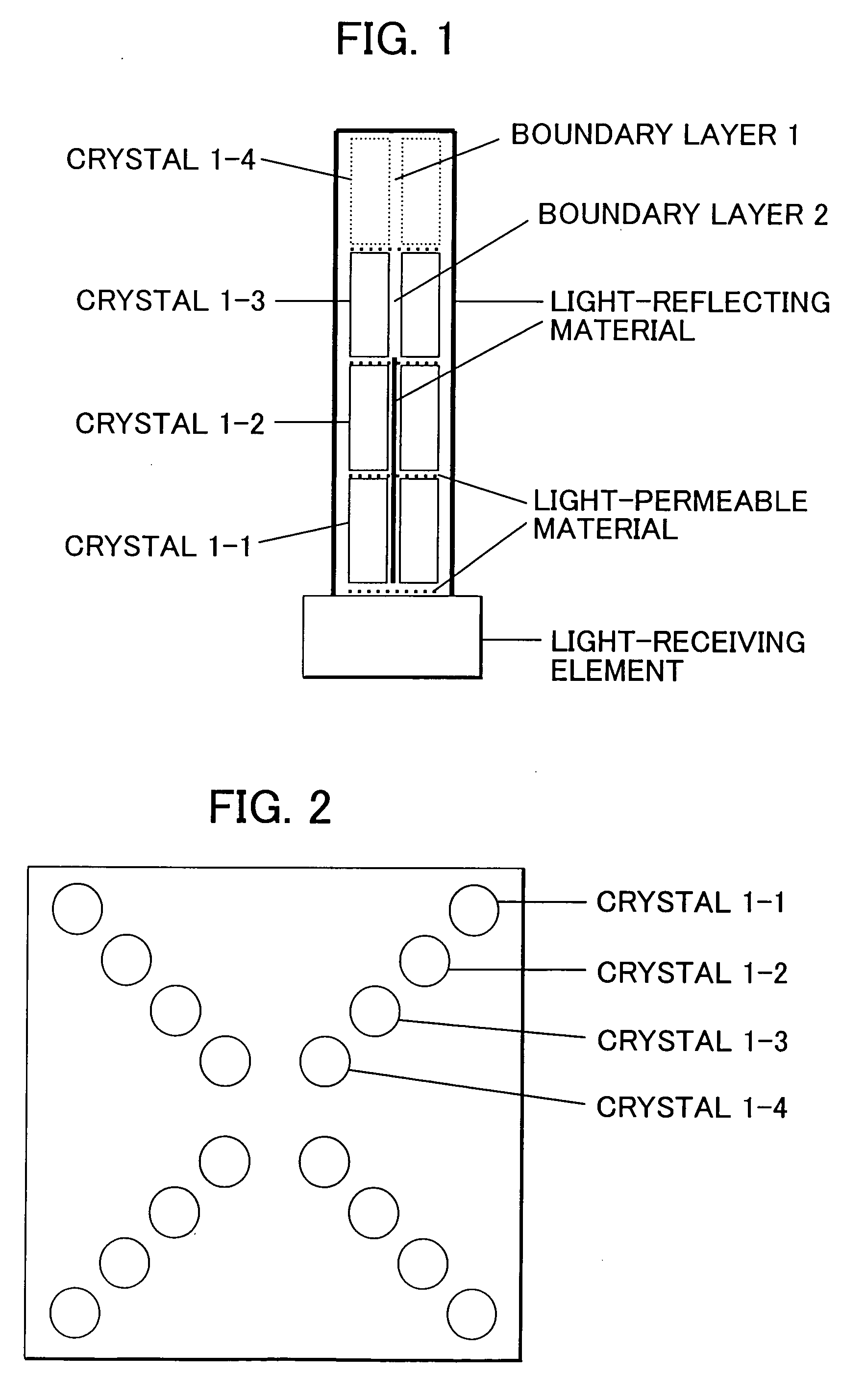
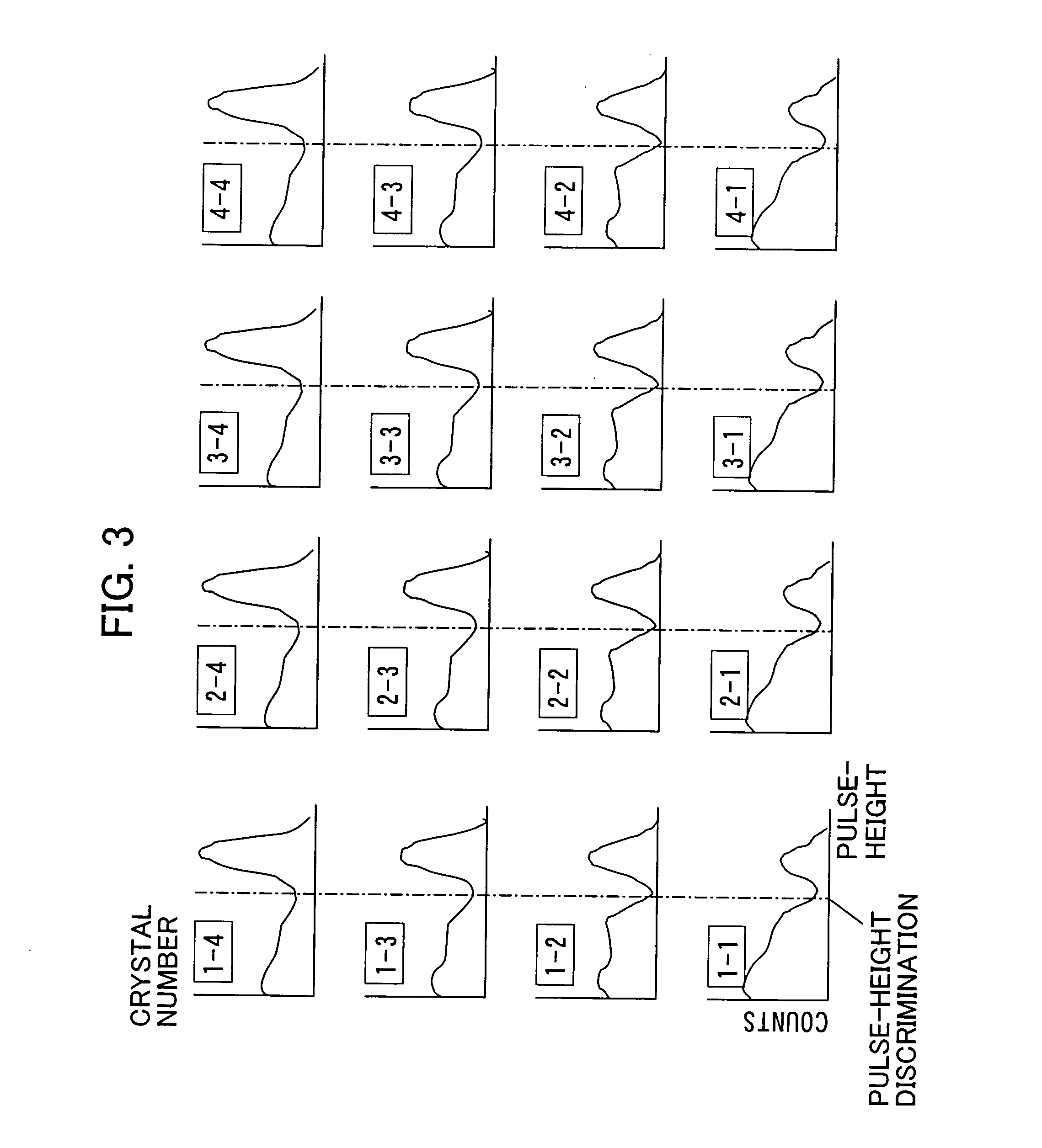
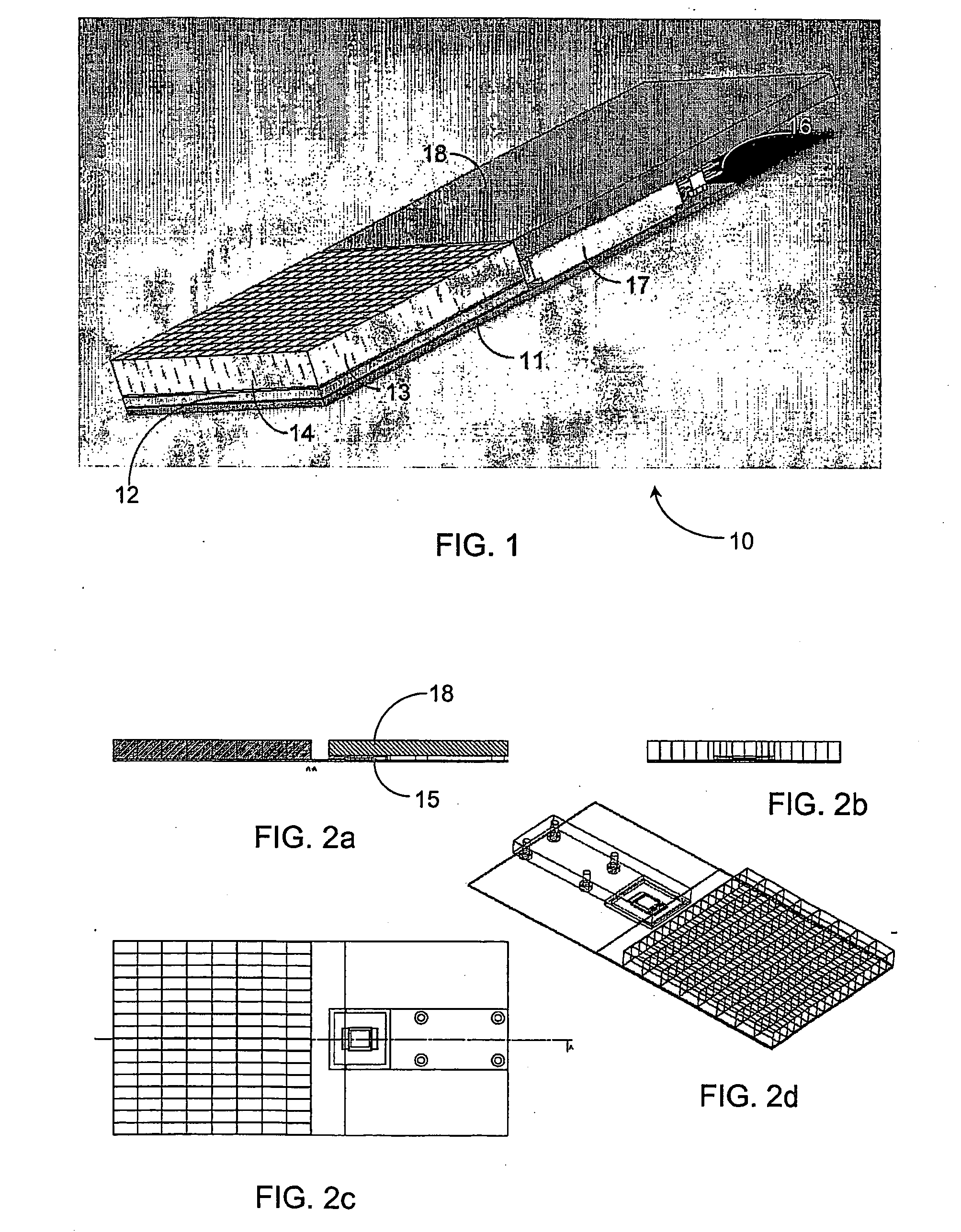
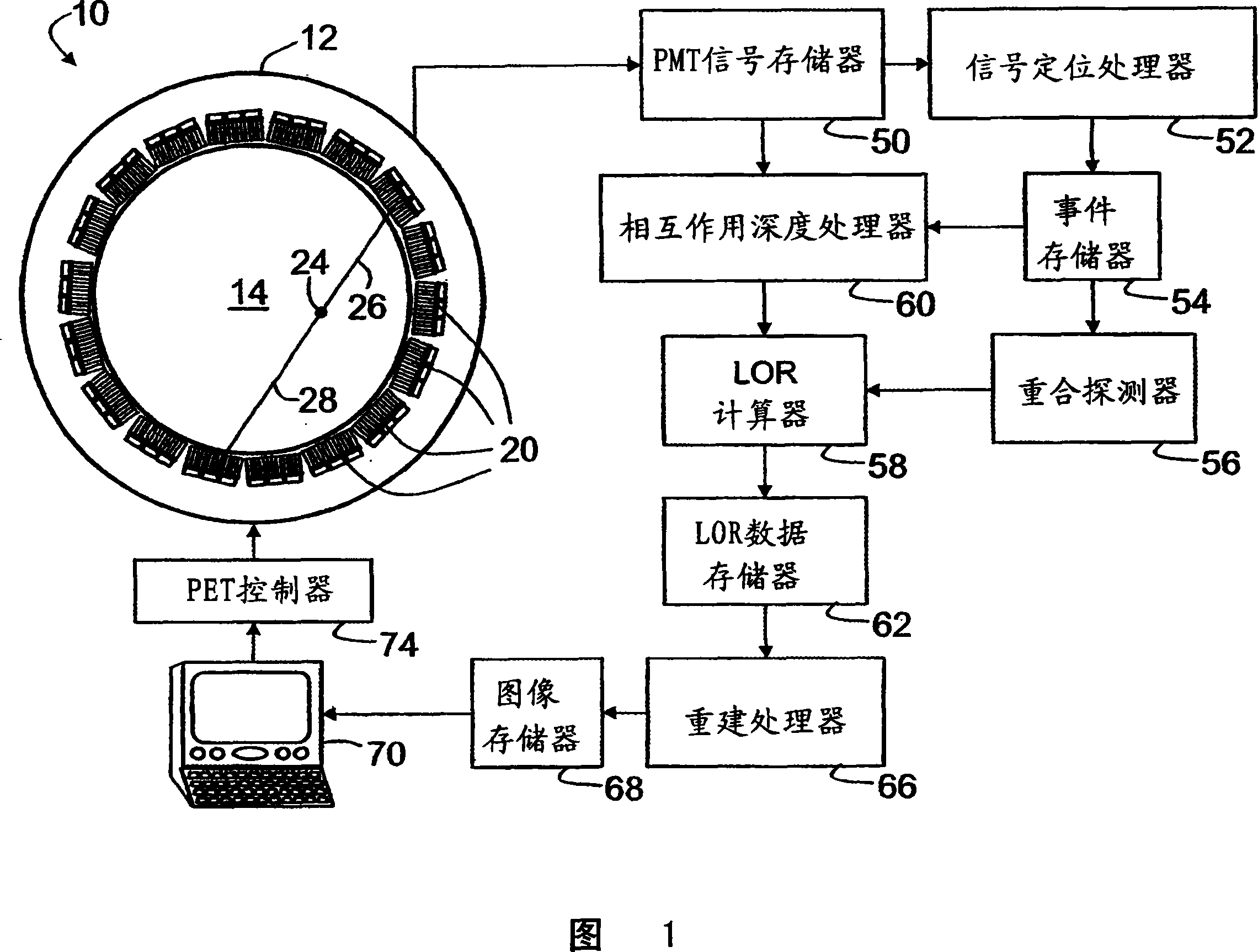
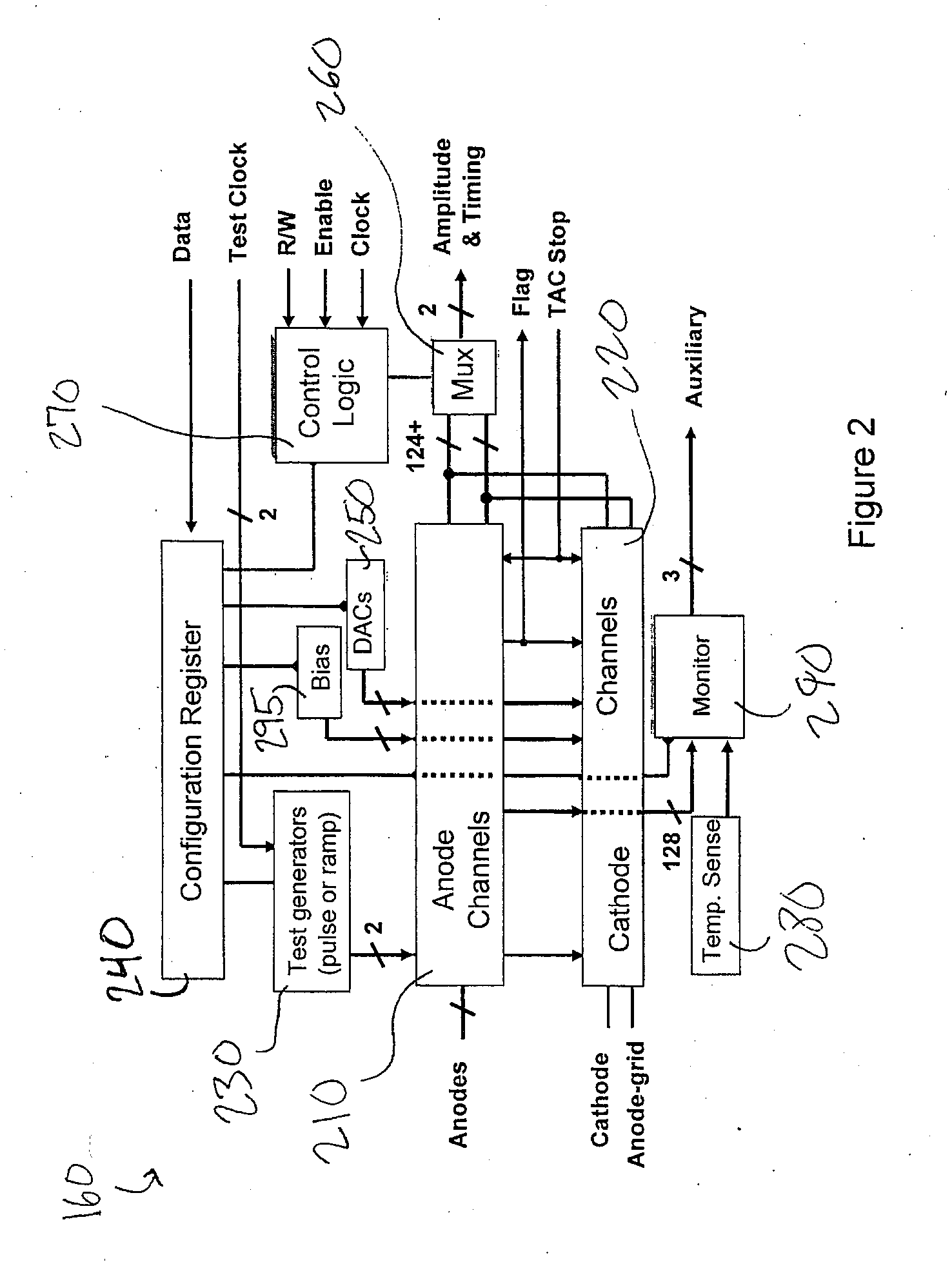
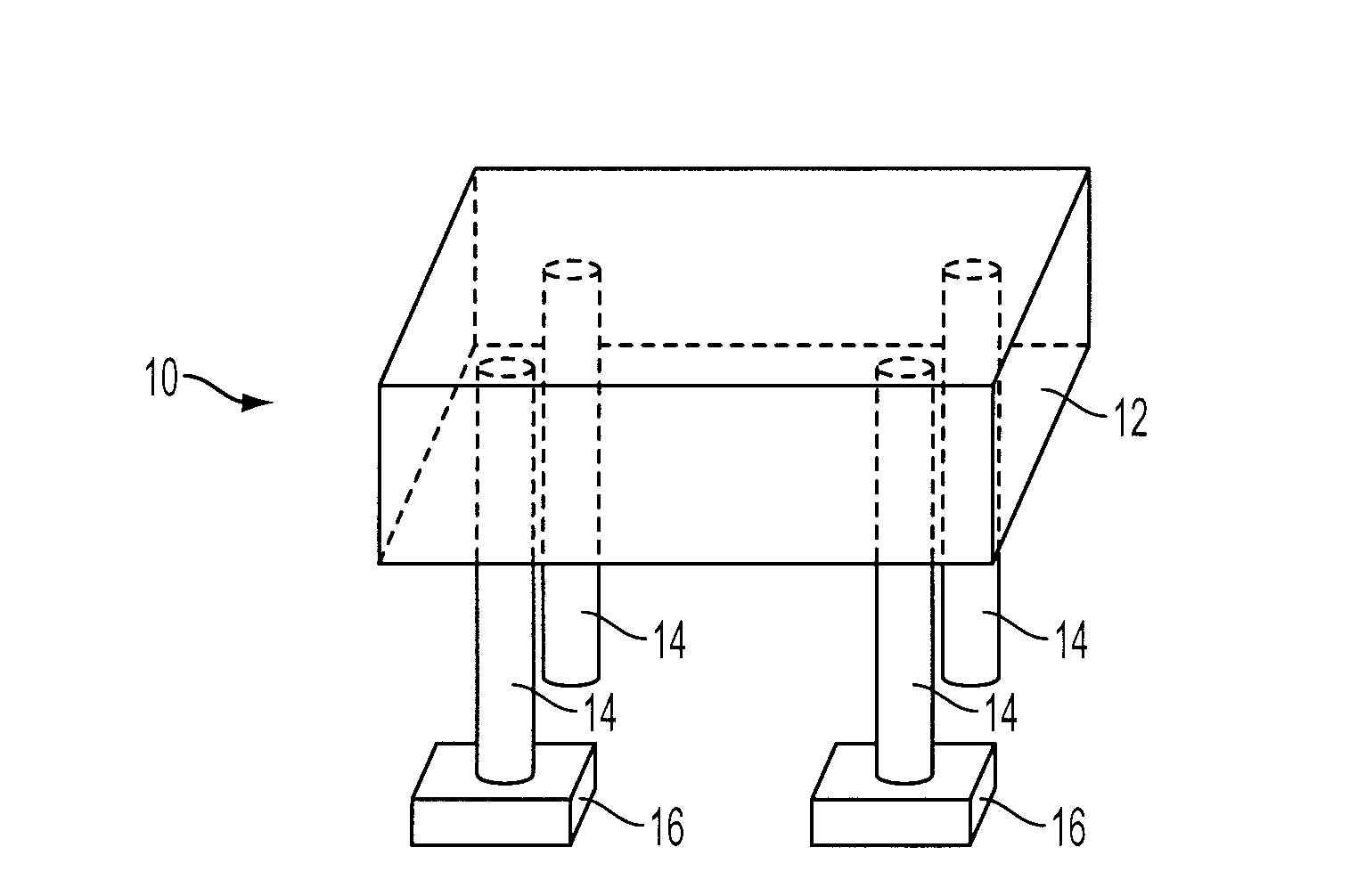
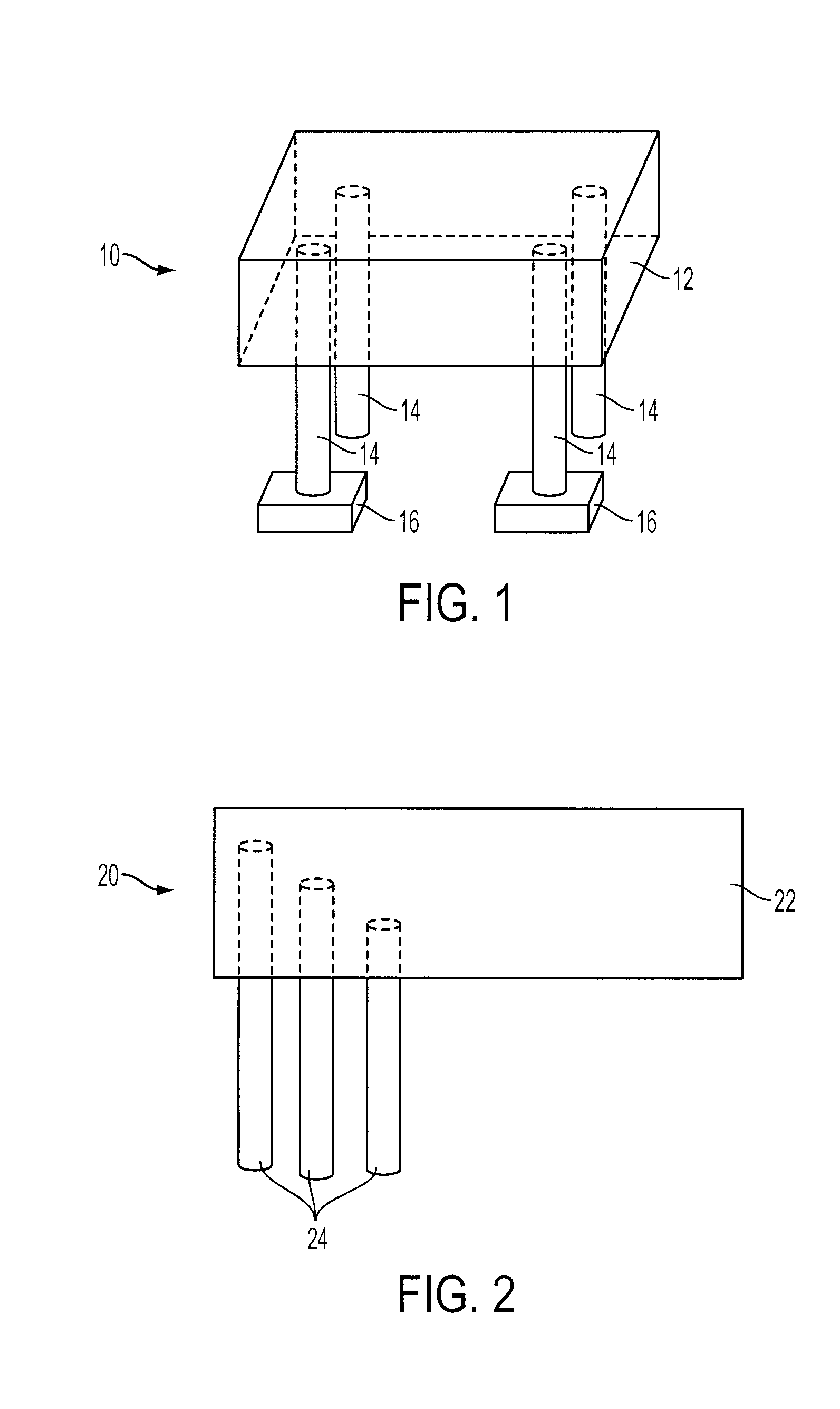
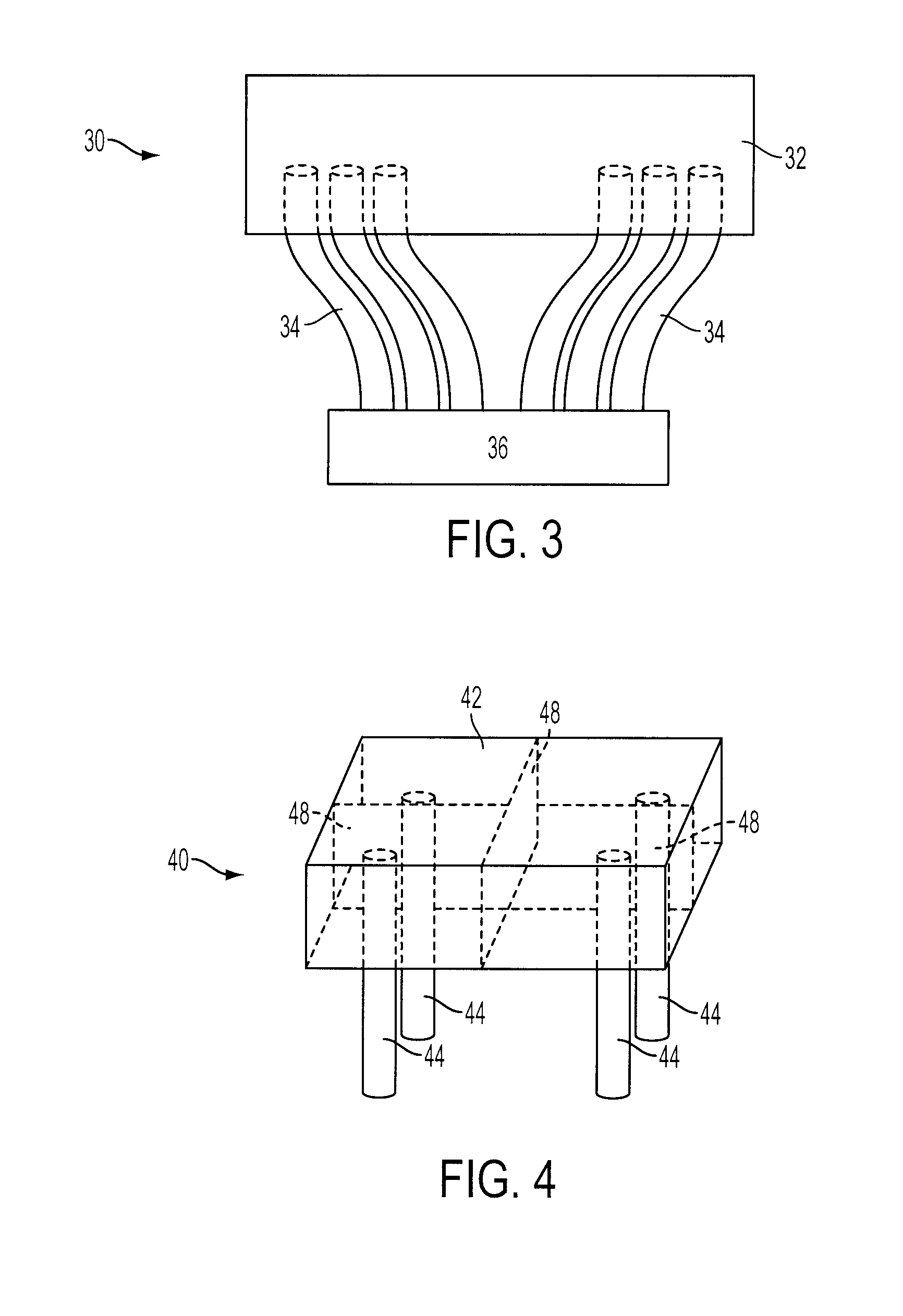
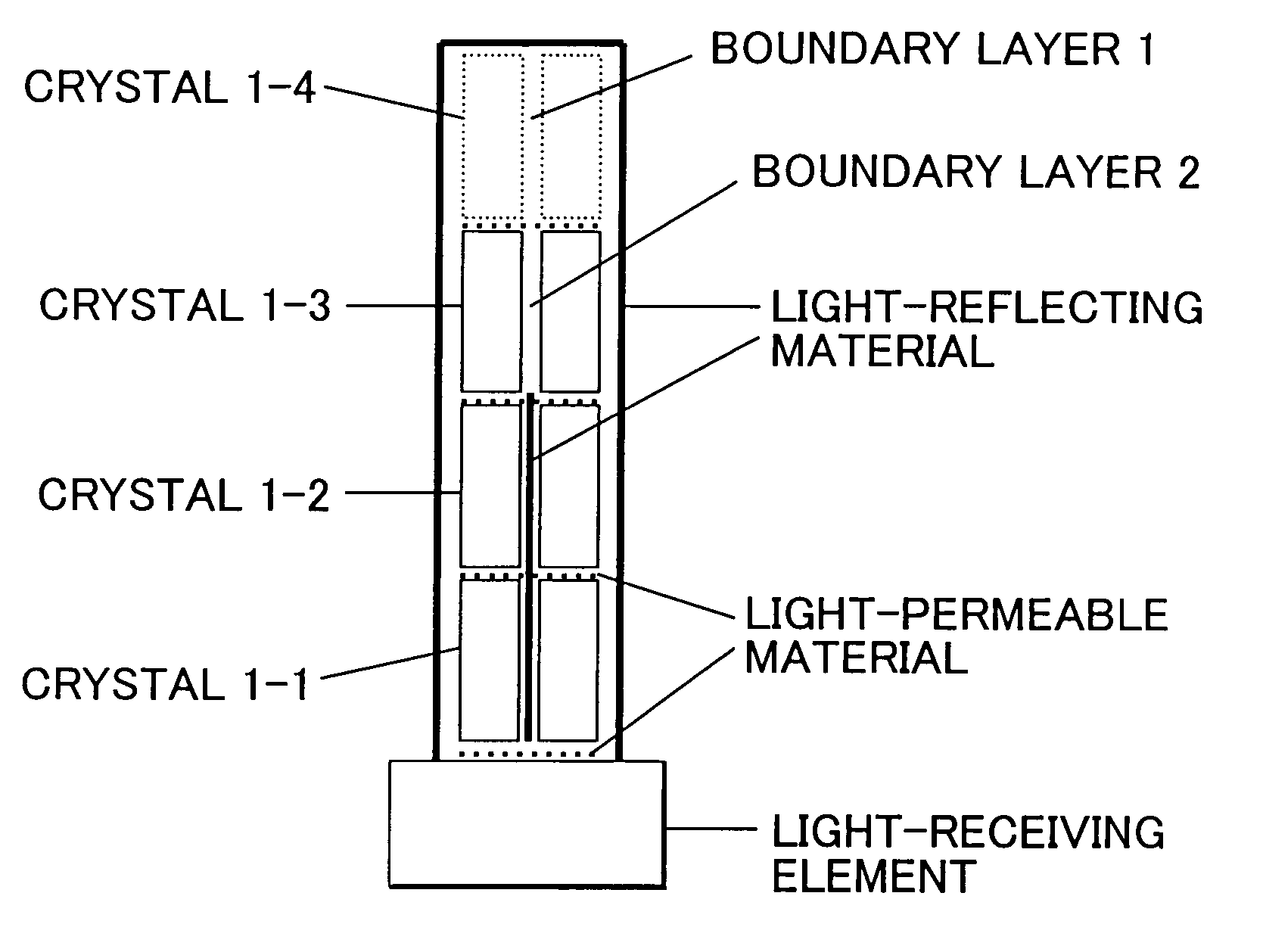
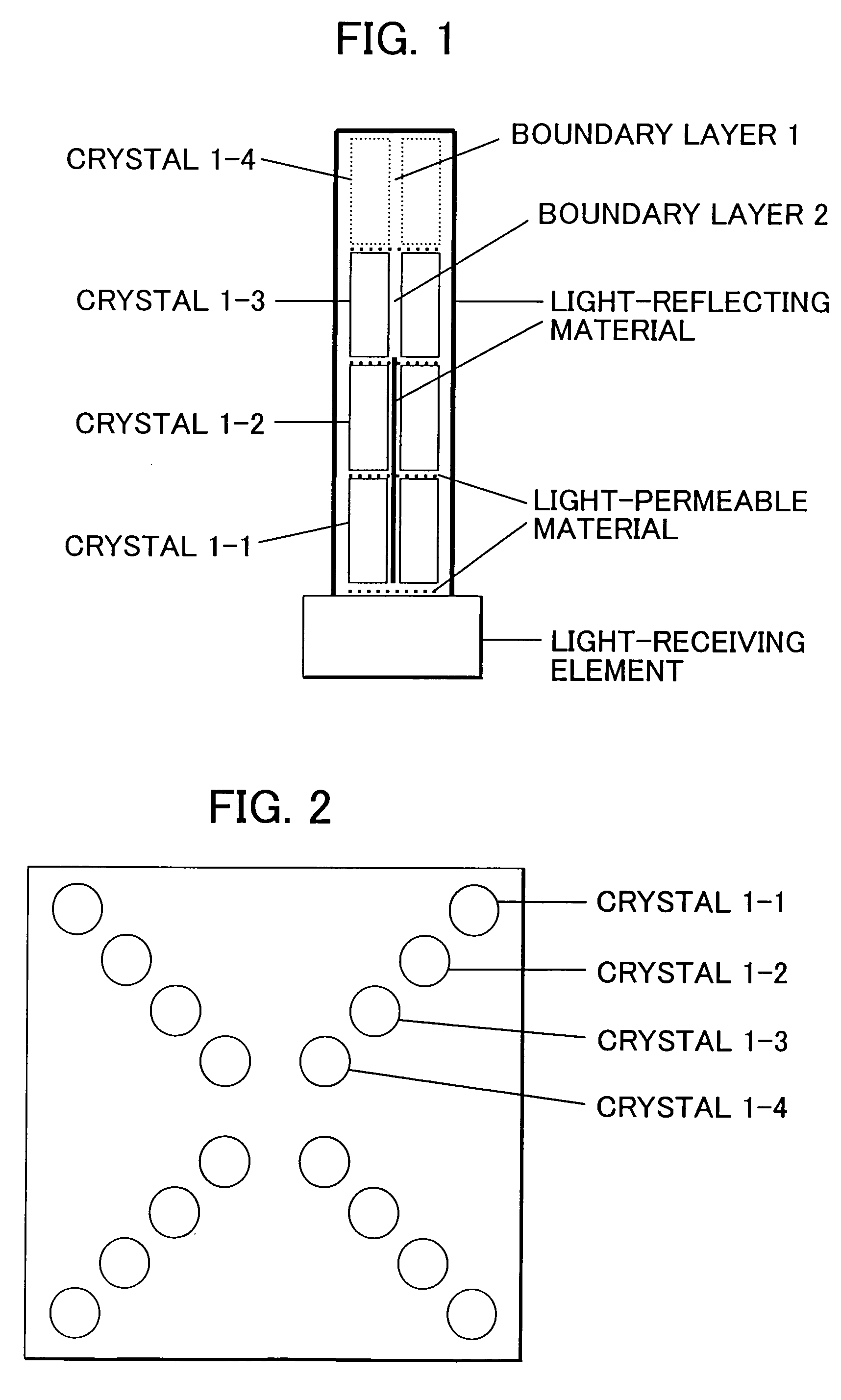
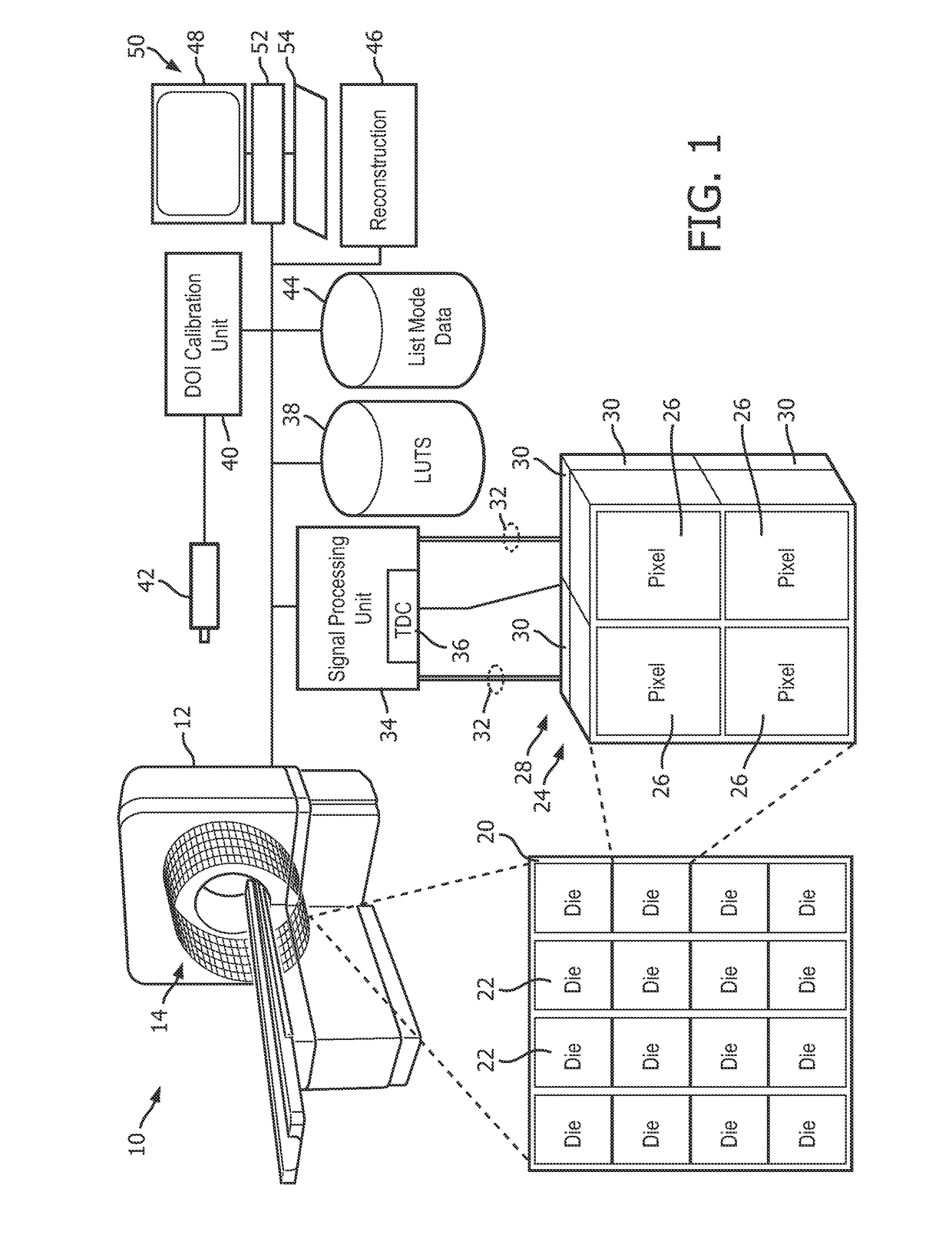
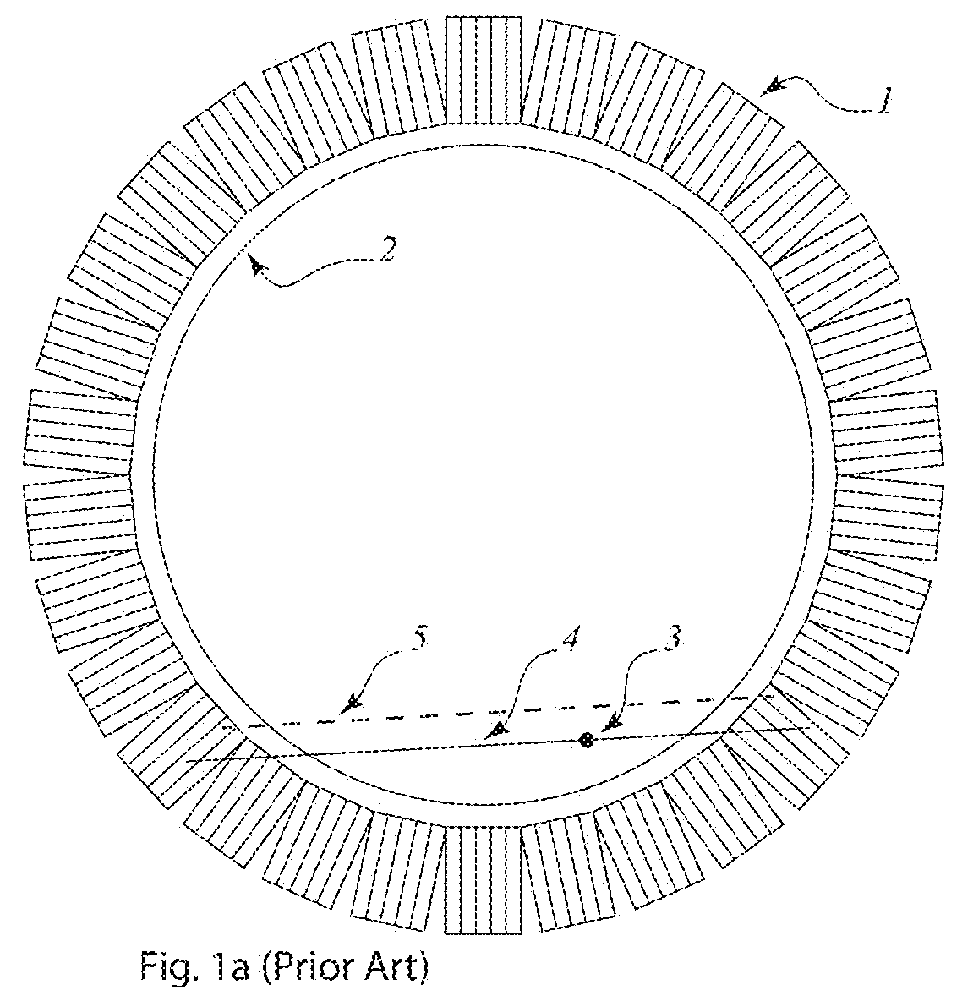
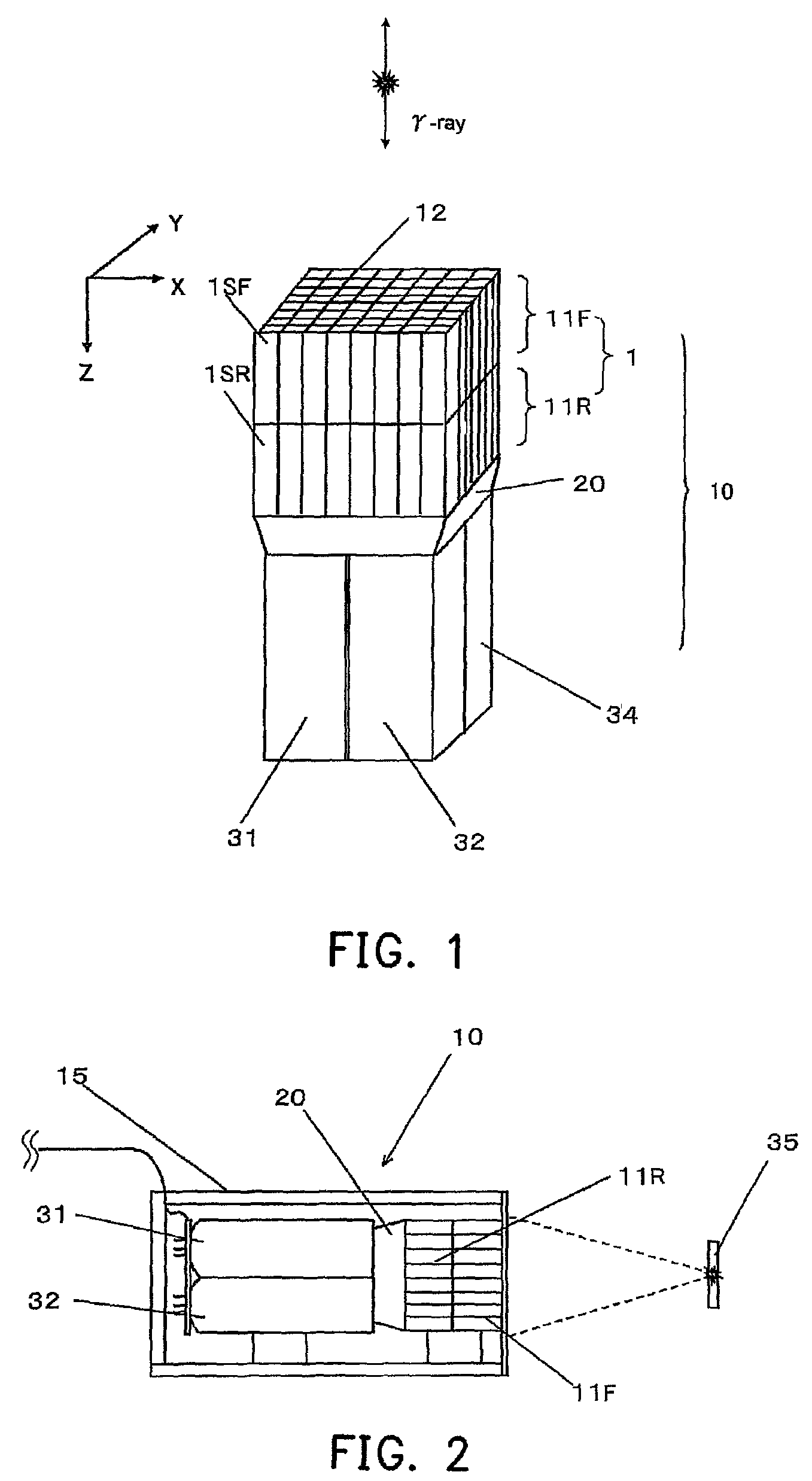
Depth of interaction detector with uniform pulse-height
ActiveUS20050087693A1Improve uniformityDifference in light collection efficiency between scintillator cells is reducedMaterial analysis by optical meansLuminescent compositionsDepth of interactionPulse height
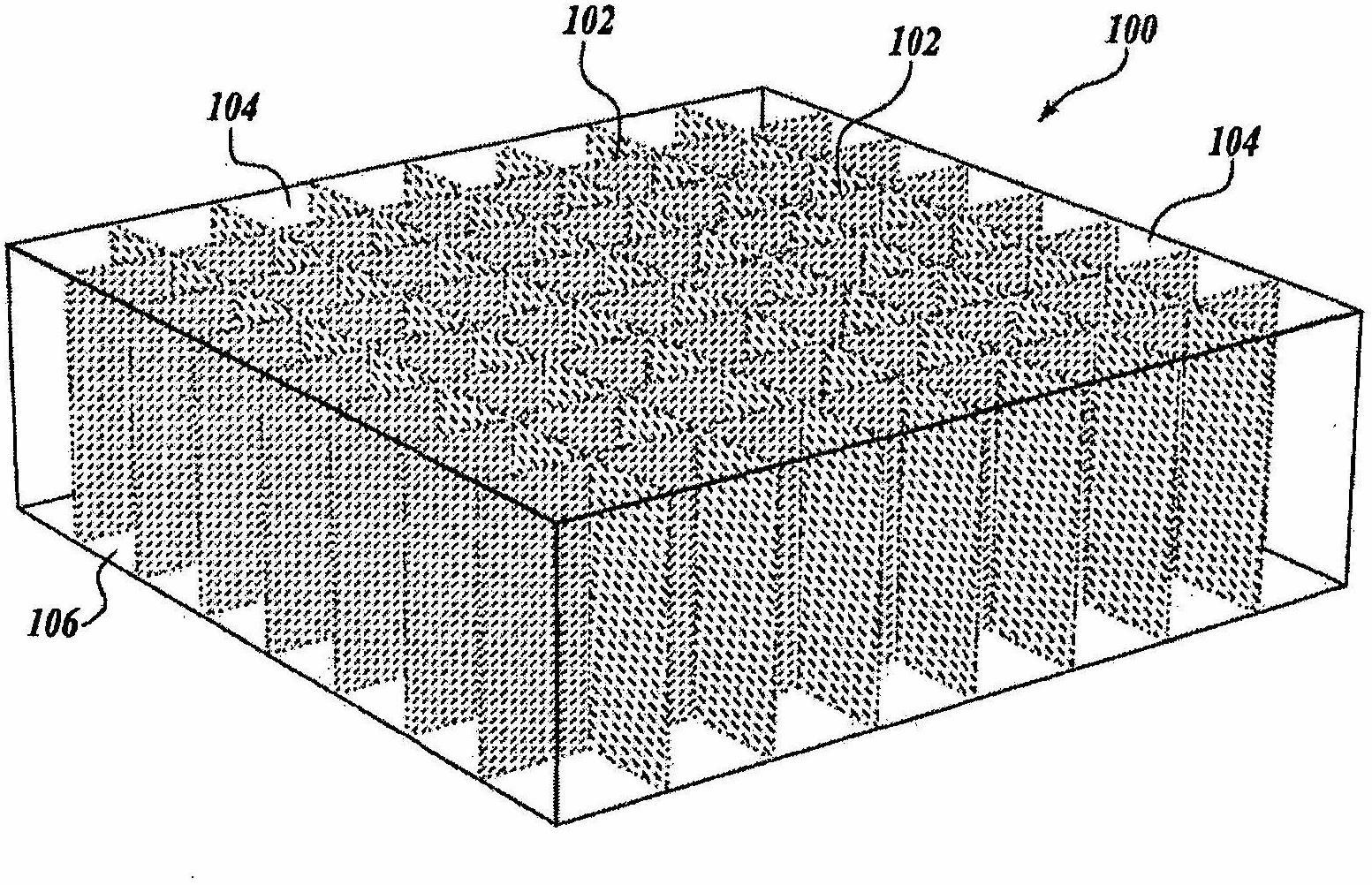
A depth of interaction detector with uniform pulse-height comprises a multi-layer scintillator obtained by coupling at least two scintillator cells on a plane and then stacking the planar coupled scintillator cells, in layers, up to at least two stages and a light-receiving element connected to the bottom face of each scintillator cell of this multi-layer scintillator, wherein the detector is provided with a means for discriminating the position of a scintillator cell, which receives radiant rays and emits light rays and a means for making, uniform, the quantity of the light emitted from each scintillator cell and received by the light-receiving element. The detector can provide precise detection information even when radiation is absorbed by and emitted from a scintillator layer positioned above the scintillator layer optically coupled to the light-receiving element, permits the production of a depth of interaction detector having a three-dimensional depth of interaction-detecting function and can provide the same total output signal, which is independent of the position or a specific scintillator cell practically emitting light if the radiation energy is identical.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK +1
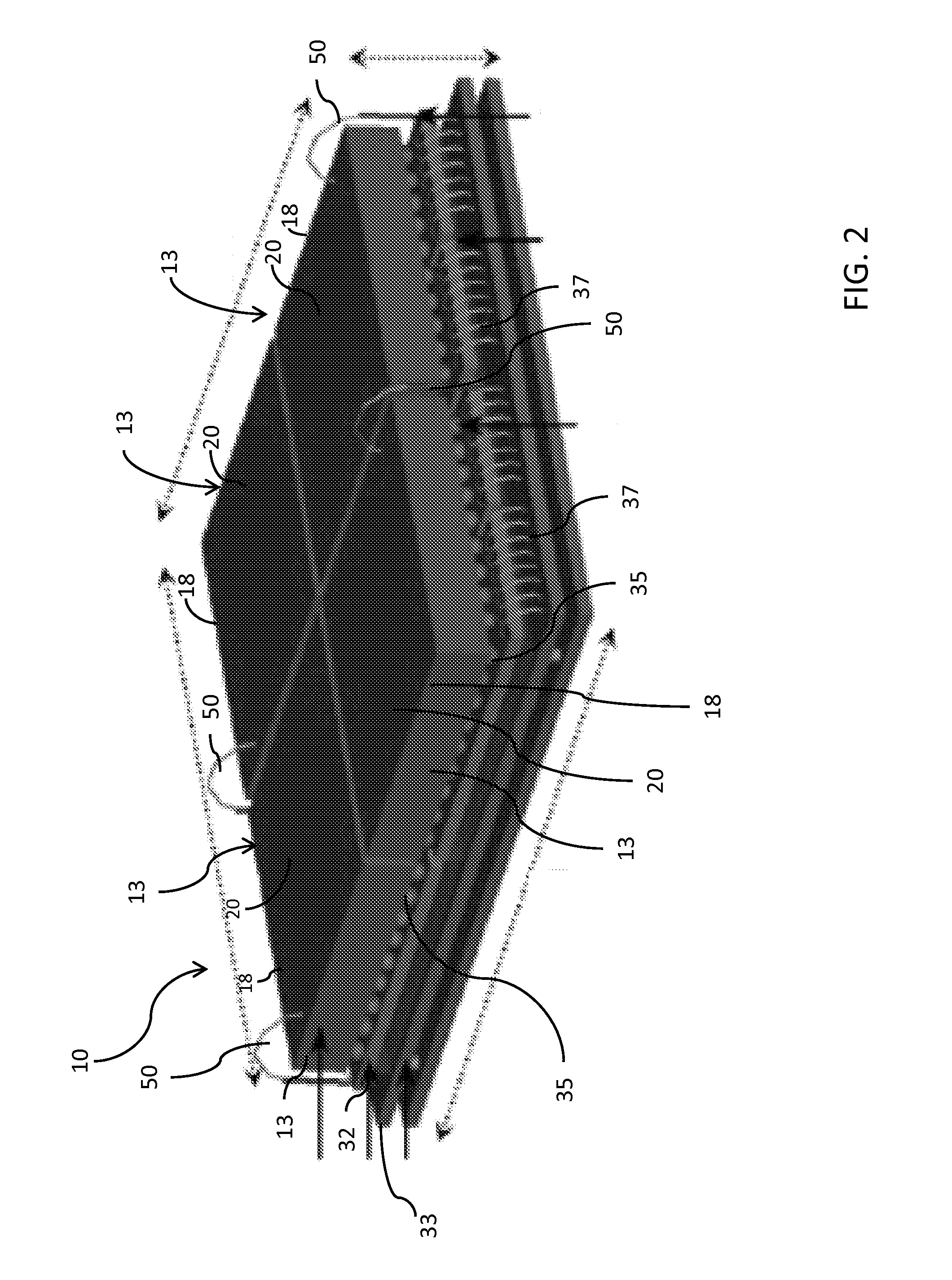
Modular radiation detector with scintillators and semiconductor photodiodes and integrated readout and method for assembly thereof
InactiveUS20070096031A1Avoid lightReduce designMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyHigh rateDepth of interaction
A modular radiation detector (10) with scintillators (13) and semi-conductor photodiodes (12) and integrated readout (15) can be used in positron emission tomography (PET) for functional imaging of humans and animals. Spatial resolution is improved by measuring the depth-of-interaction and modules using photodiodes and integrated readout circuits according to the invention instead of photo-multipliers give rise to lighter and less bulky tomographic instruments. The invention uses very large scale integrated (VLSI) electronic readout circuits for measuring signals from photo-diodes. The electronic readout circuits (15) are located on the module and allow data to be measured and processed at very high rates on the module level rather than on the system level. The use of photodiodes promises greater stability during operation and improved reliability over photo-multipliers. The invention can be used in magnetic fields and therefore allows PET and MRI / NMR imaging techniques to be combined.
Owner:GAMMA MEDICA - IDEAS NORWAY
Nuclear medical imaging method and device
ActiveCN102755172AEnhance the imageComputerised tomographsTomographyLines of responseDepth of interaction
The invention provides a nuclear medical imaging method and device for obtaining optimal images. The nuclear medical imaging method comprises a first determining step of determining a line of response set by the positions of a pair detector crystals, a defining step of defining an array of radiation points corresponding to the line of response, a second determining step of determining a solid angle with the bottom surface being surfaces of the pair of detector crystals defining the line of response for each point in the array of the radiation points corresponding to the line of response, a generating step of averaging the solid angle for generating an average solid angle, a third determining step of determining a position factor related to depth-of-interaction, and a calculation step of multiplying the reciprocal of the average solid angle by the position factor for calculating a geometric corrective factor for the line of response.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
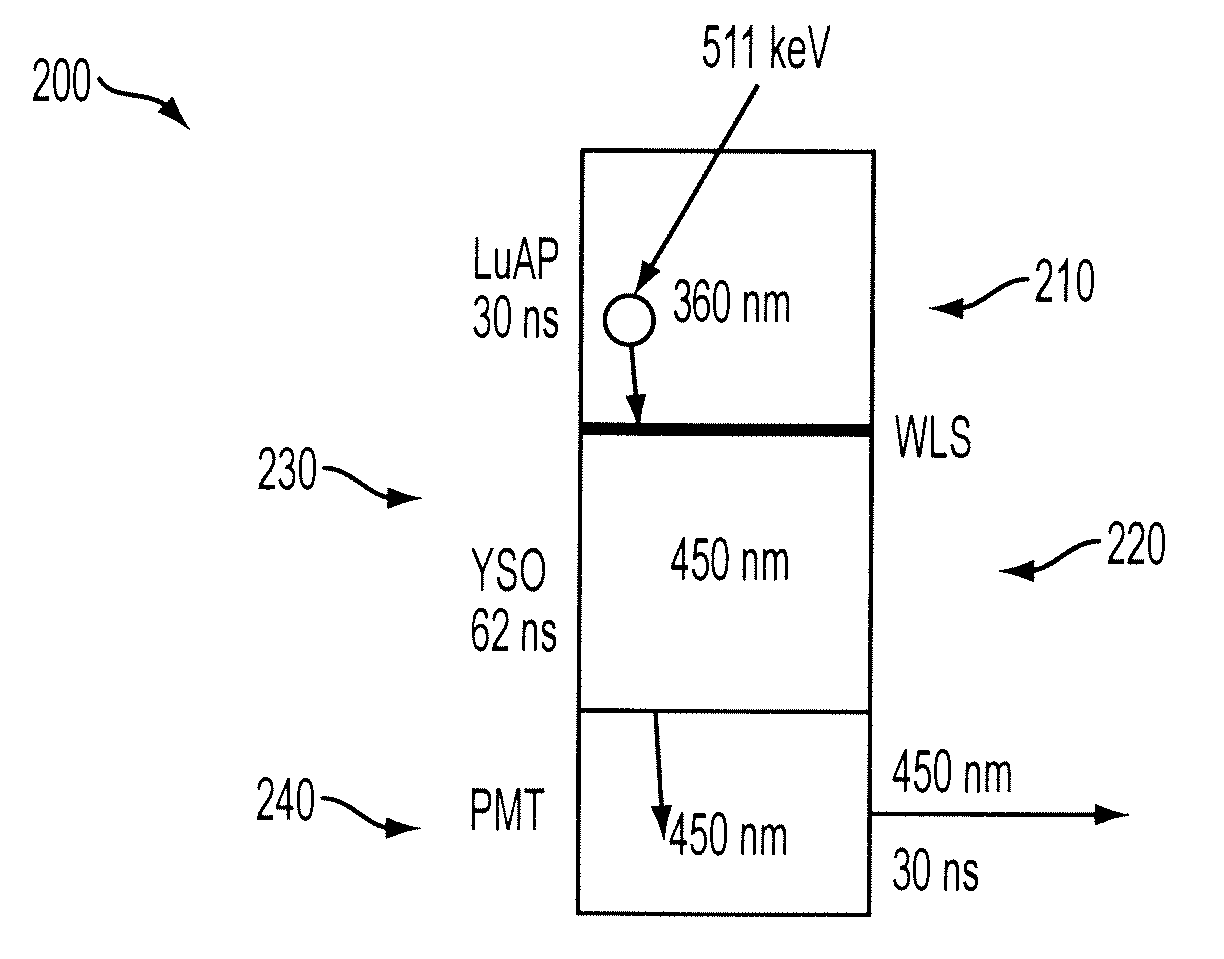
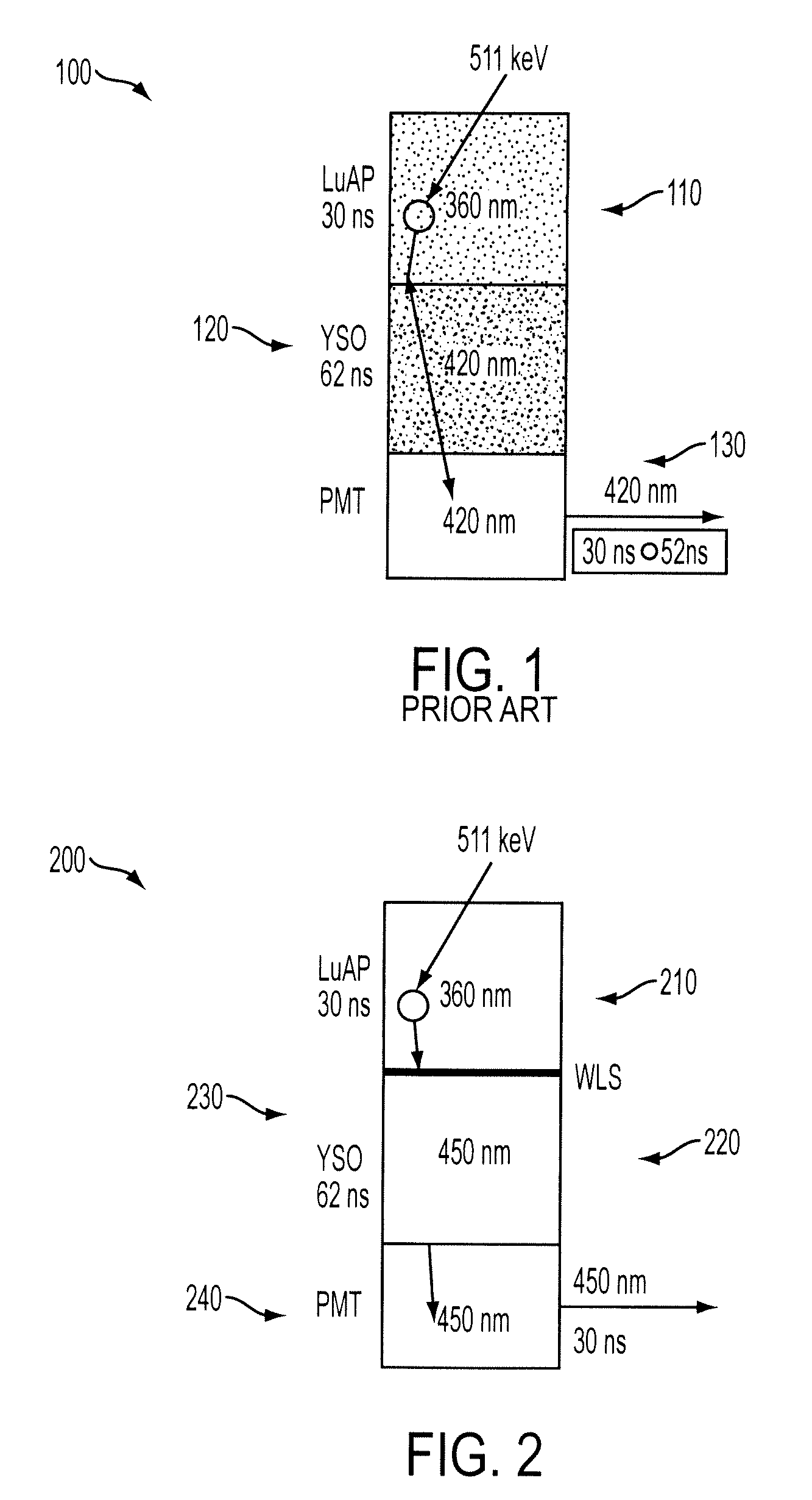
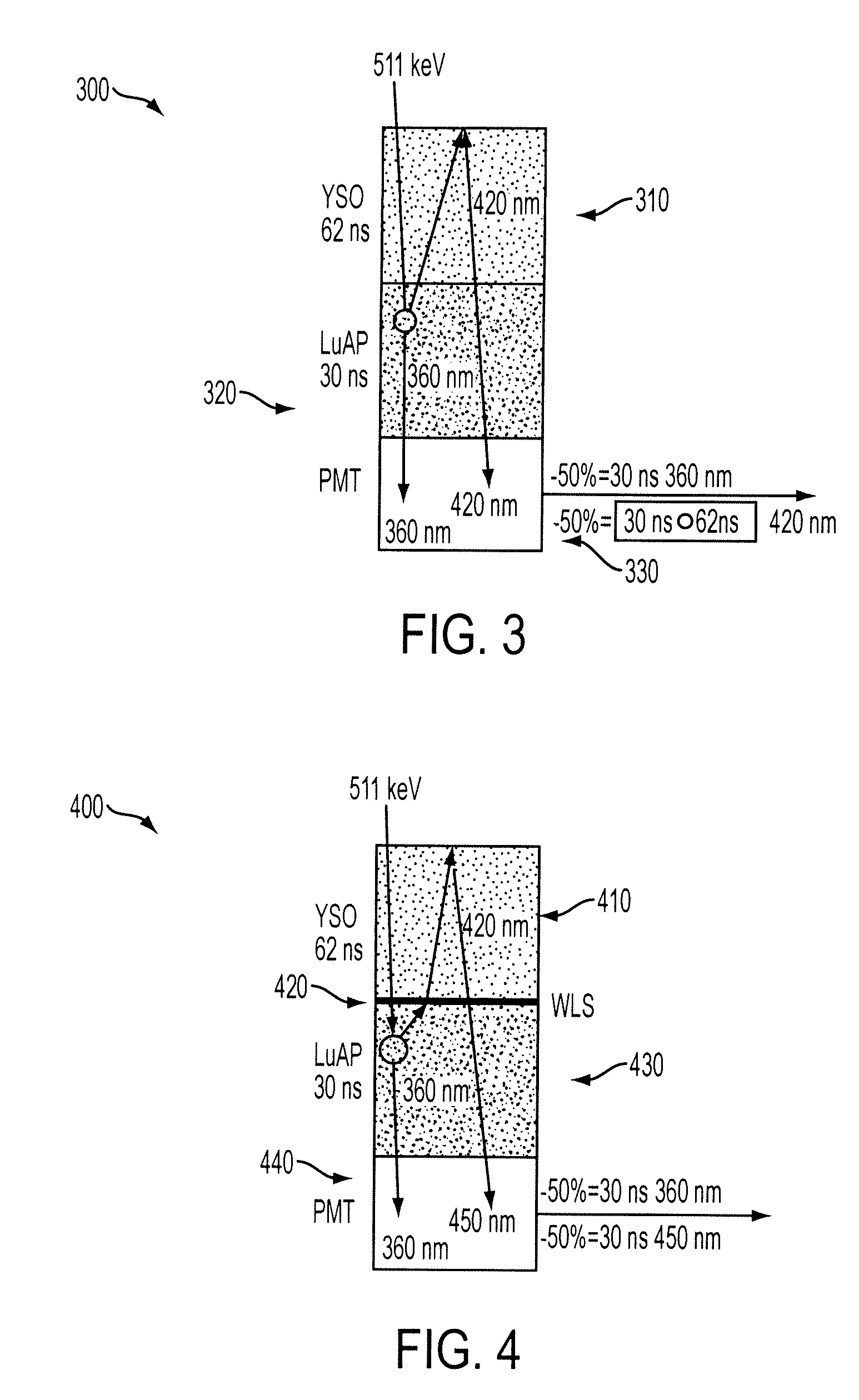
Implementation of wavelength shifters in phoswich detectors
ActiveUS20090121141A1Solve needsPhotometryFluorescence/phosphorescenceGamma photonDepth of interaction
A phoswich device for determining depth of interaction (DOI) includes a wavelength shifting layer between first and second scintillators of different scintillation materials and having different decay time characteristics. The wavelength shifting layer allows a true phoswich device to be constructed where the emission wavelength of one scintillator is in the peak excitation band of the other scintillator, by shifting the scintillation light outside of this excitation band to prevent scintillation light of one scintillator from exciting a response in the other scintillator, thus enabling unique identification of the location of a gamma photon scintillation event. The phoswich device is particularly applicable to positron emission tomography (PET) applications.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
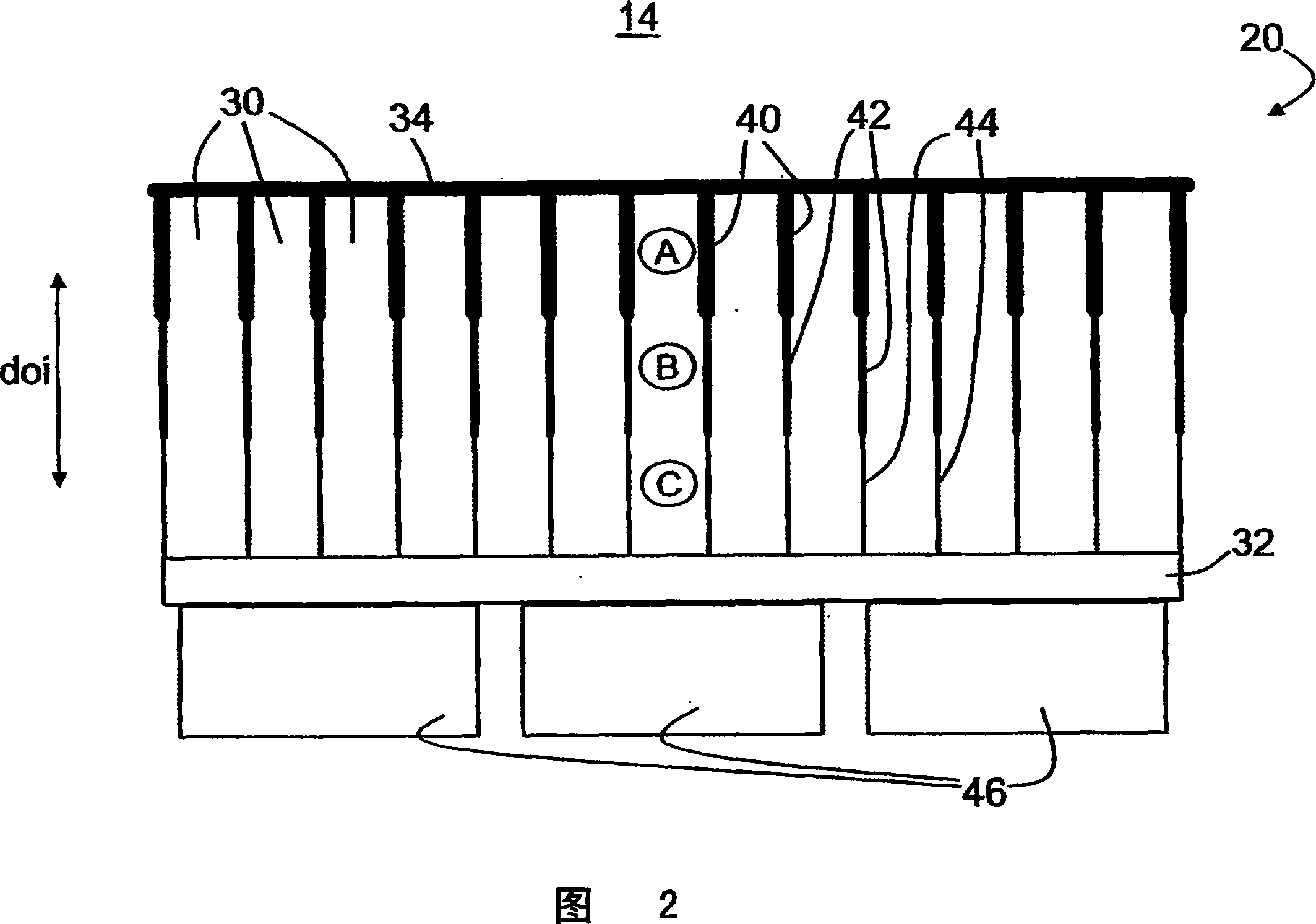
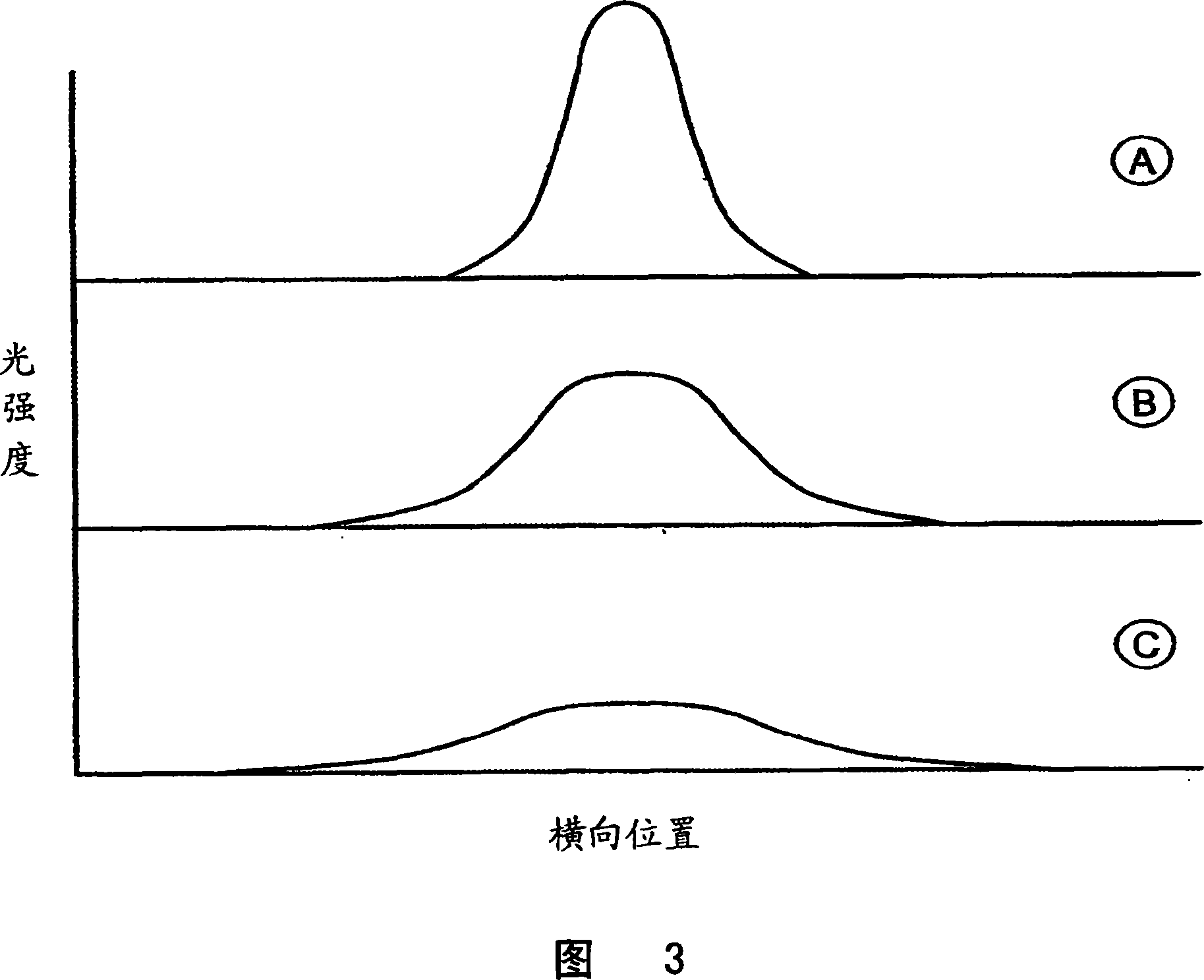
Pixelated detectors with depth of interaction sensitivity
InactiveCN101073019AHigh resolutionTomographyX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentDepth of interactionLight detector
A radiation detector (20, 20') includes scintillator pixels (30) that each have a radiation-receiving end, a light-output end, and reflective sides extending therebetween. The reflective sides have a reflection characteristic (40, 40', 42, 44) varying between the radiation-receiving end and the light-output end such that a lateral spread of light emanating from the light-output ends of the scintillator pixels responsive to a scintillation event generated in one of the scintillator pixels depends upon a depth of the scintillation event in the scintillator pixel. A plurality of light detectors (46) optically communicate with the light-output ends of the scintillator pixels to receive light produced by scintillation events.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
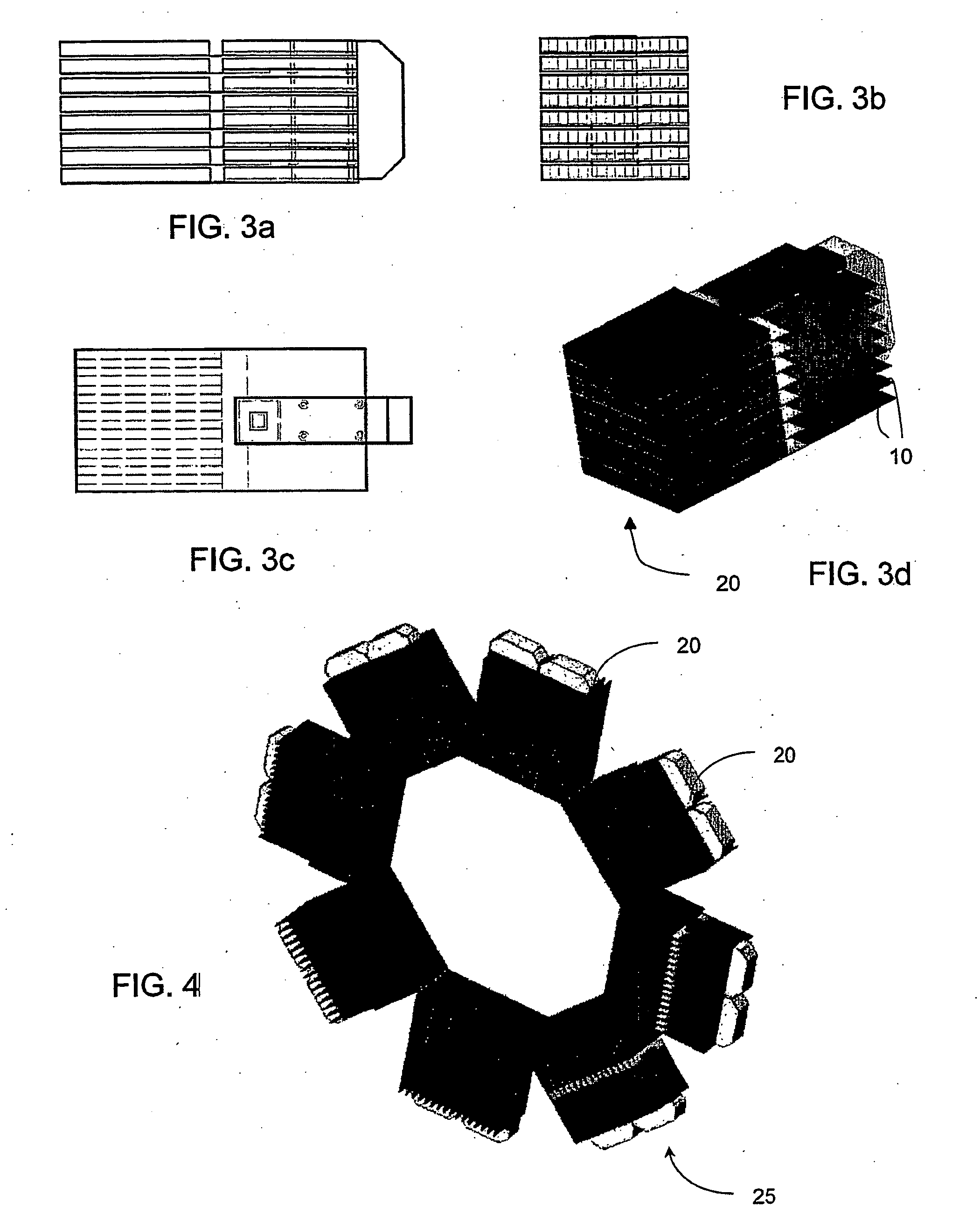
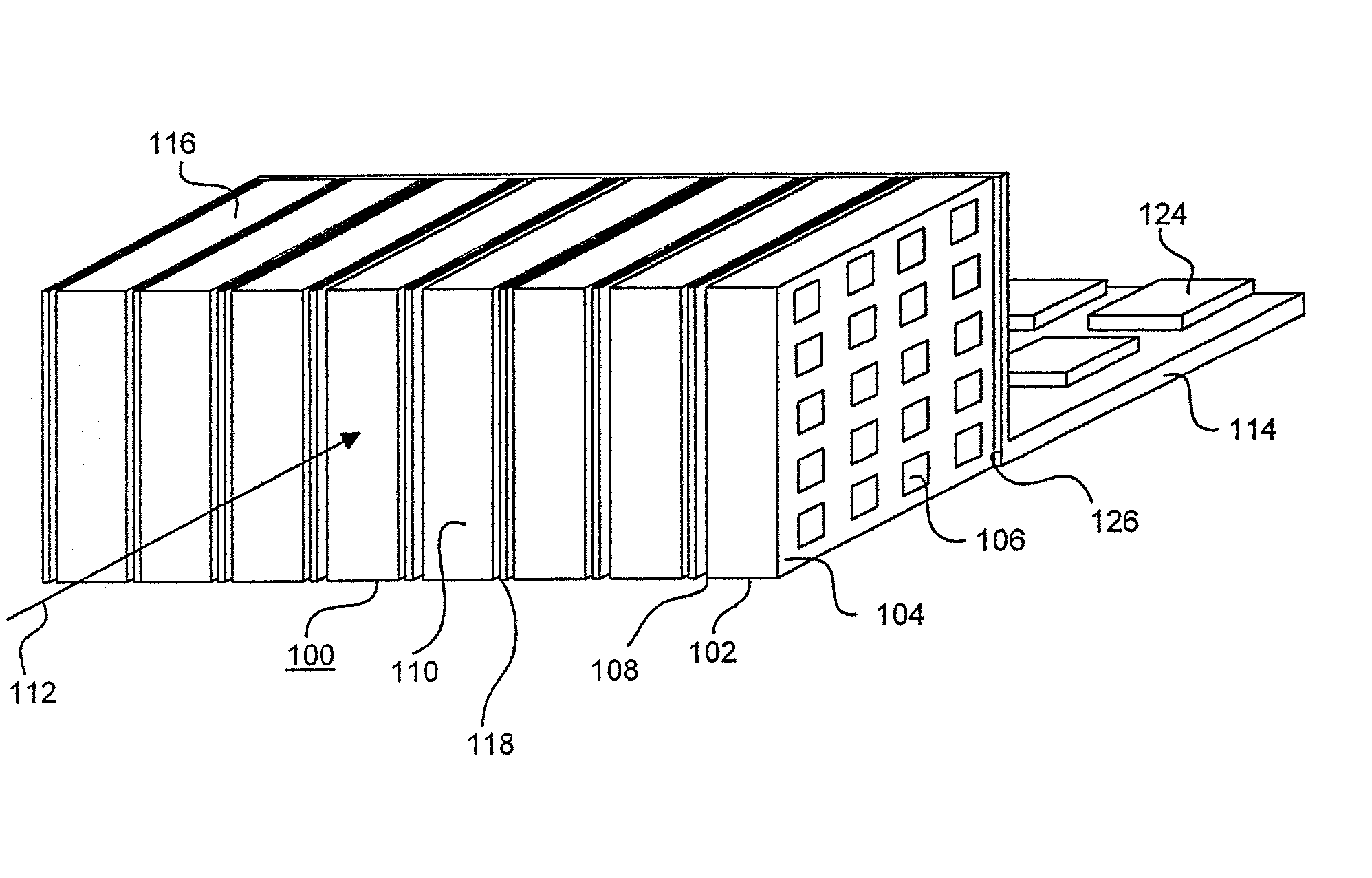
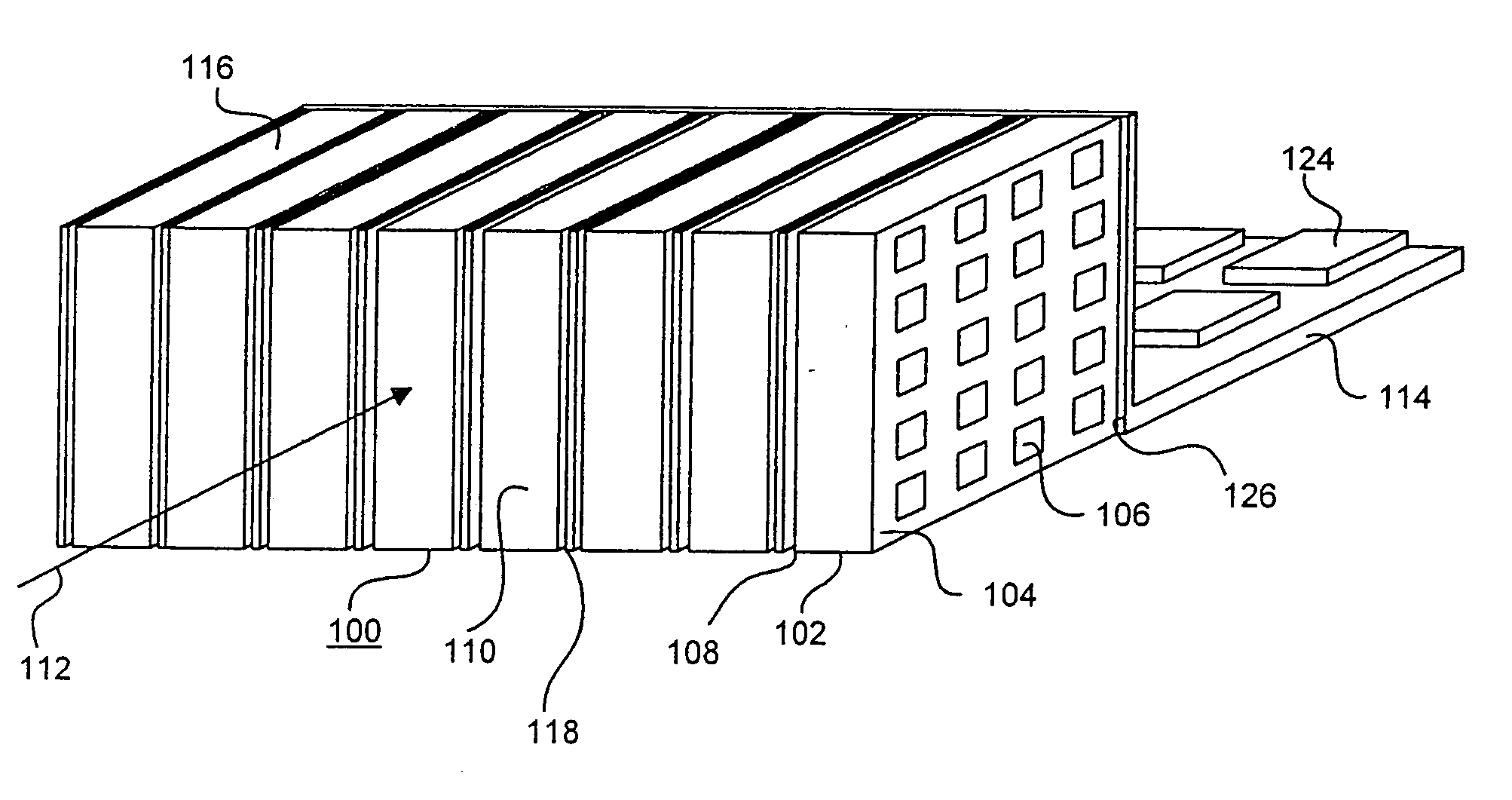
Three dimensional radiation detector
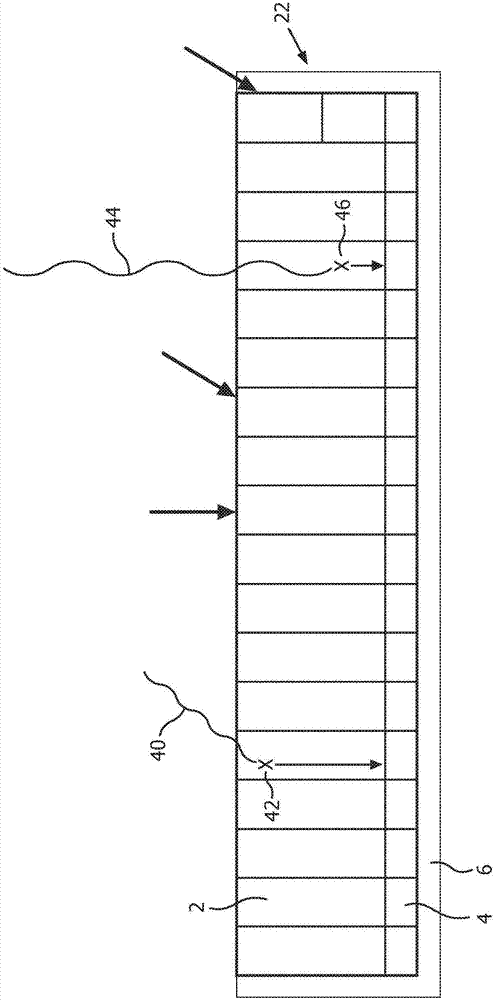
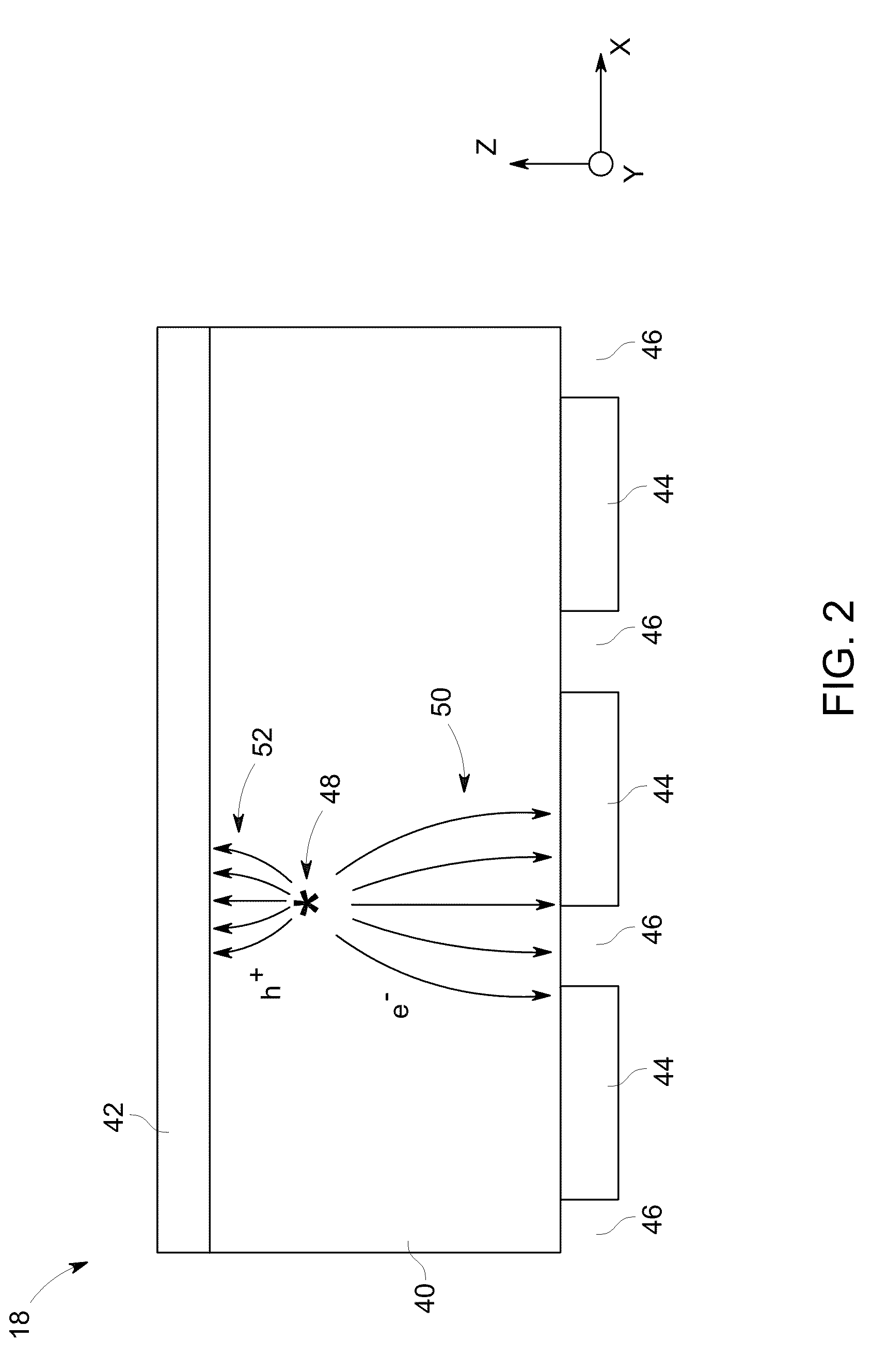
InactiveUS7166848B2Easy to useImprove capacity utilizationSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansInteraction pointHigh energy
A pixelated detector assembly comprising a stack of thin detector crystals, each detector crystal having a pair of planar surfaces bound by edges substantially thinner than the dimensions of the surfaces. The stack is disposed such that the radiation to be detected is incident on one set of edges of the stack of detector crystals. The dimension of the planar surfaces in the general direction of incidence of the radiation incidence is sufficient to ensure that substantially all of the high energy photons to be detected are absorbed within the depth of the detector assembly. Each of the detector crystals has a two-dimensional pixelated anode array formed on one of its planar surfaces. A cathode is formed on its opposite planar surface, preferably covering substantially all of the surface. The position of interaction of a photon in the plane perpendicular to the direction of the incident radiation, is determined by which of the detector crystals in the stack detects the absorption, and by which of the rows of pixelated anodes in that crystal detects the absorption. The depth of interaction of a photon is determined by the location of the particular anode pixel in the above-mentioned row of pixelated anodes where the photon absorption is detected. The detector assembly is thus able to detect the point of interaction of a photon in all three dimensions.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
Method and Apparatus for the Measurement of Signals from Radiation Sensors
ActiveUS20100051818A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDepth of interactionRadiation sensor
The preferred embodiments of the present invention include a device for measuring an ionizing event in a radiation sensor. The device can include a charge amplifier and a timing shaper. The charge amplifier receives a cathode signal and is configured to output an amplified cathode signal. The timing shaper is operatively connected to the charge amplifier to receive the amplified cathode signal. The timing shaper is configured to generate a first pulse in response to a beginning of the ionizing event and a second pulse in response to an end of the ionizing event. The first and second pulses are associated with a depth of interaction of the ionizing event and are generated in response to a slope of the amplified cathode signal changing.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS +1
Three dimensional radiation detector
InactiveUS20070040126A1Easy to useImprove capacity utilizationSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyInteraction point
A pixelated detector assembly comprising a stack of thin detector crystals, each detector crystal having a pair of planar surfaces bound by edges substantially thinner than the dimensions of the surfaces. The stack is disposed such that the radiation to be detected is incident on one set of edges of the stack of detector crystals. The dimension of the planar surfaces in the general direction of incidence of the radiation incidence is sufficient to ensure that substantially all of the high energy photons to be detected are absorbed within the depth of the detector assembly. Each of the detector crystals has a two-dimensional pixelated anode array formed on one of its planar surfaces. A cathode is formed on its opposite planar surface, preferably covering substantially all of the surface. The position of interaction of a photon in the plane perpendicular to the direction of the incident radiation, is determined by which of the detector crystals in the stack detects the absorption, and by which of the rows of pixelated anodes in that crystal detects the absorption. The depth of interaction of a photon is determined by the location of the particular anode pixel in the above-mentioned row of pixelated anodes where the photon absorption is detected. The detector assembly is thus able to detect the point of interaction of a photon in all three dimensions.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
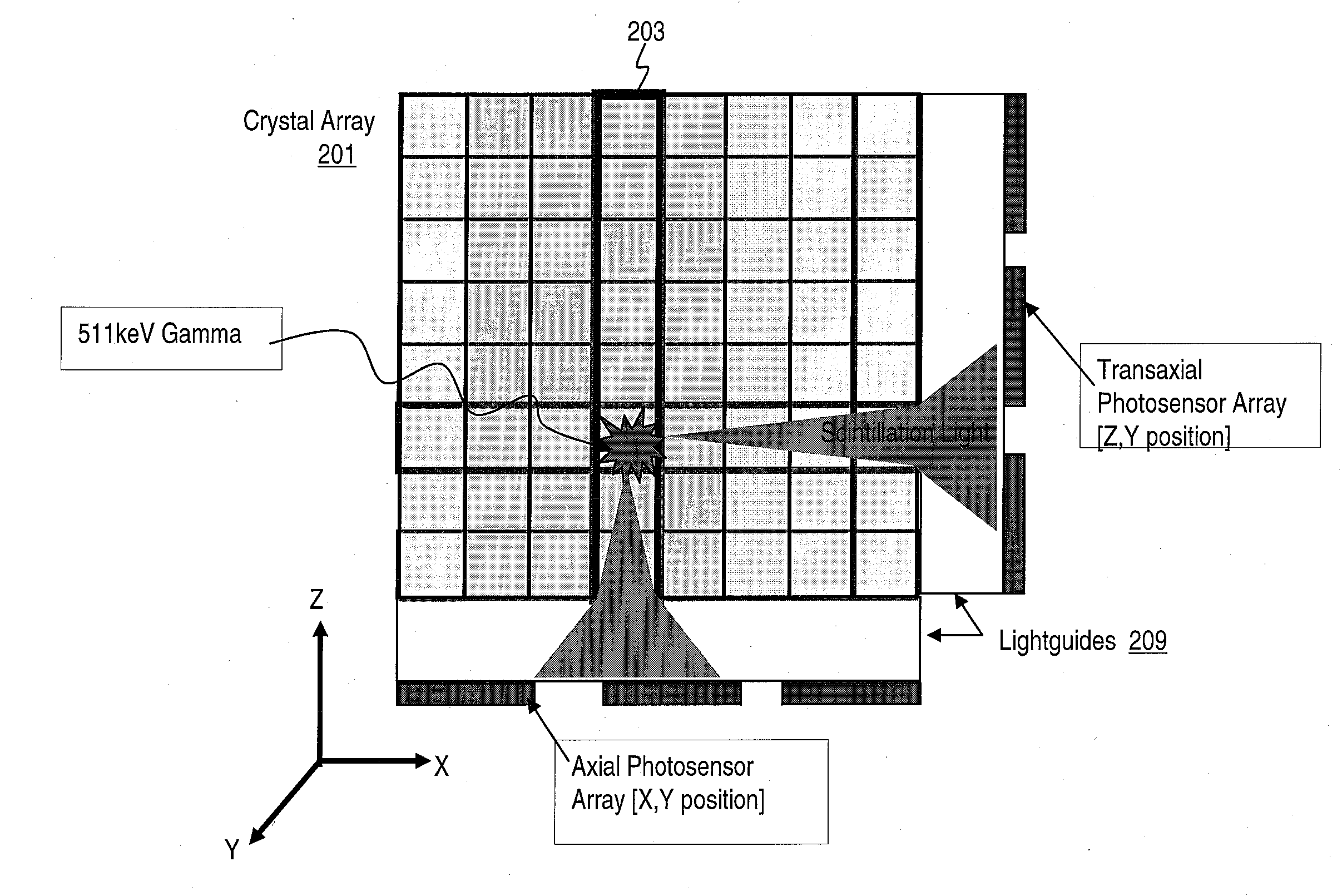
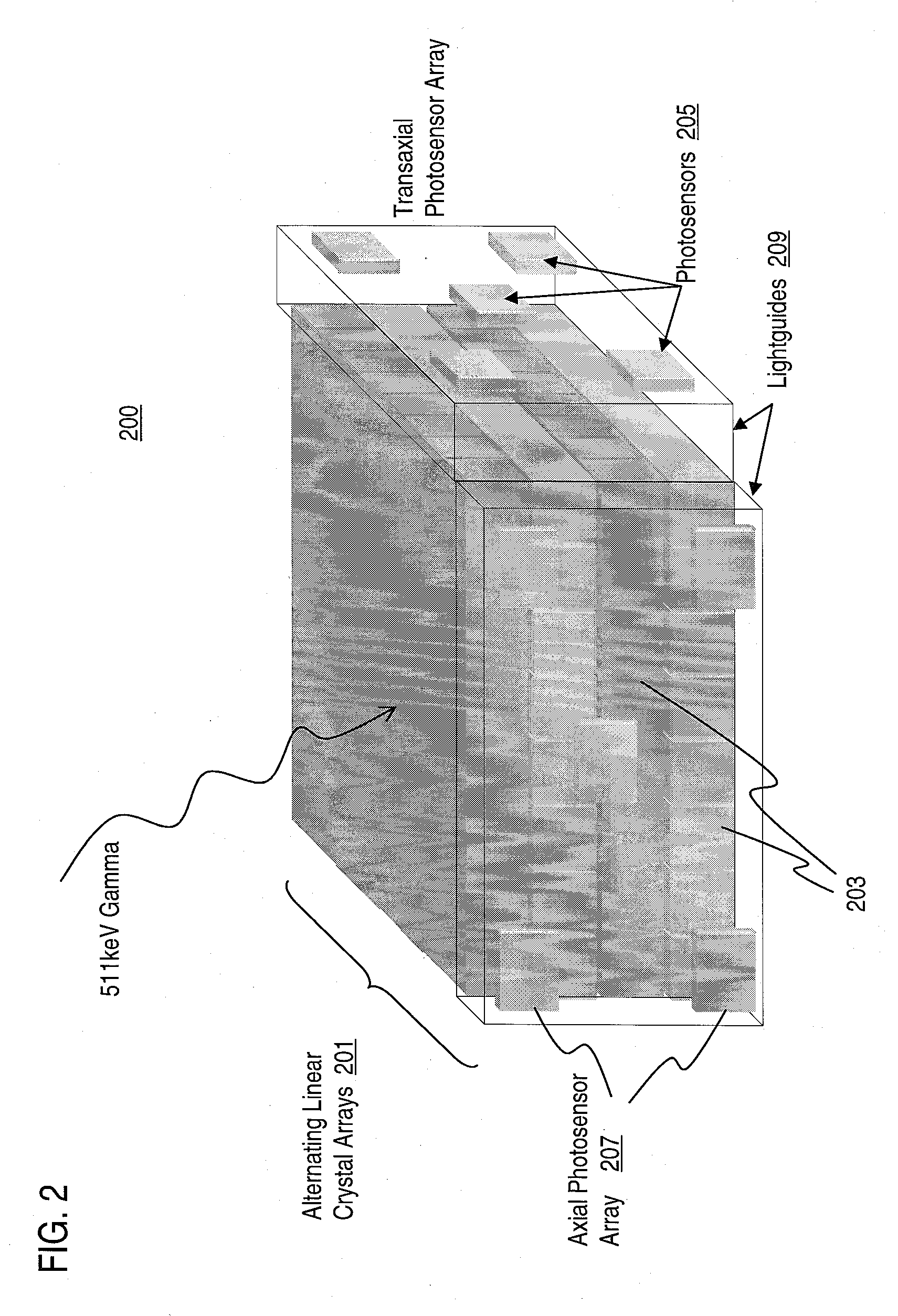
Method and Apparatus for Providing Depth-of-Interaction Detection Using Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
ActiveUS20090008562A1Minimizes edge effectHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyDepth of interactionOpto electronic
A detector is provided for nuclear medicine imaging. Scintillator pixels form an axial array and a transaxial array. A first photosensor is positioned along the axial array; and a second photosensor is positioned along the transaxial array, wherein the first photosensor and the second photosensor provide dual event localization for nuclear medicine imaging.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Grid mould, detector including same and emission imaging equipment
ActiveCN104237924AImprove spatial resolutionHigh sensitivityRadiation intensity measurementImage resolutionScintillation crystals
The invention provides a grid mould, a detector including the grid mould and emission imaging equipment. The grid mould comprises a plurality of transverse walls, a plurality of longitudinal walls and light reflecting layers. The transverse walls and the longitudinal walls extend transversely and longitudinally respectively to form a plurality of grid troughs which are arranged in a m*n matrix mode and used for containing scintillation crystal of the detector, m and n are positive integers, and light-transmitting windows with light capable of penetrating side walls are formed in the side walls of the grid troughs. The light reflecting layers are arranged on the areas, except for the light-transmitting windows, of the side walls. The grid mould obtains the information of the depth of interaction (DOI) of the scintillation crystal, and the space resolution ratio and the system detection sensitivity of the emission imaging equipment can be improved.
Owner:ZHONGPAI S&T SHENZHEN CO LTD
MODELLING OF ToF-DOI DETECTOR ARRAYS
ActiveUS20140231655A1Losing timing resolutionLosing resolution energyMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyDepth of interactionCompanion animal
The invention is directed to several crystal arrangements for time-of-flight (ToF) positron emission tomography (PET) with depth of interaction (DOI) encoding for high spatial, energy and timing resolution. Additionally, several implementations of the ToF-DOI PET detector arrays are proposed with related measurements which all show that no timing degradation is visible in the used setup for first photon trigger for digital silicon photo multipliers (dSiPMs).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
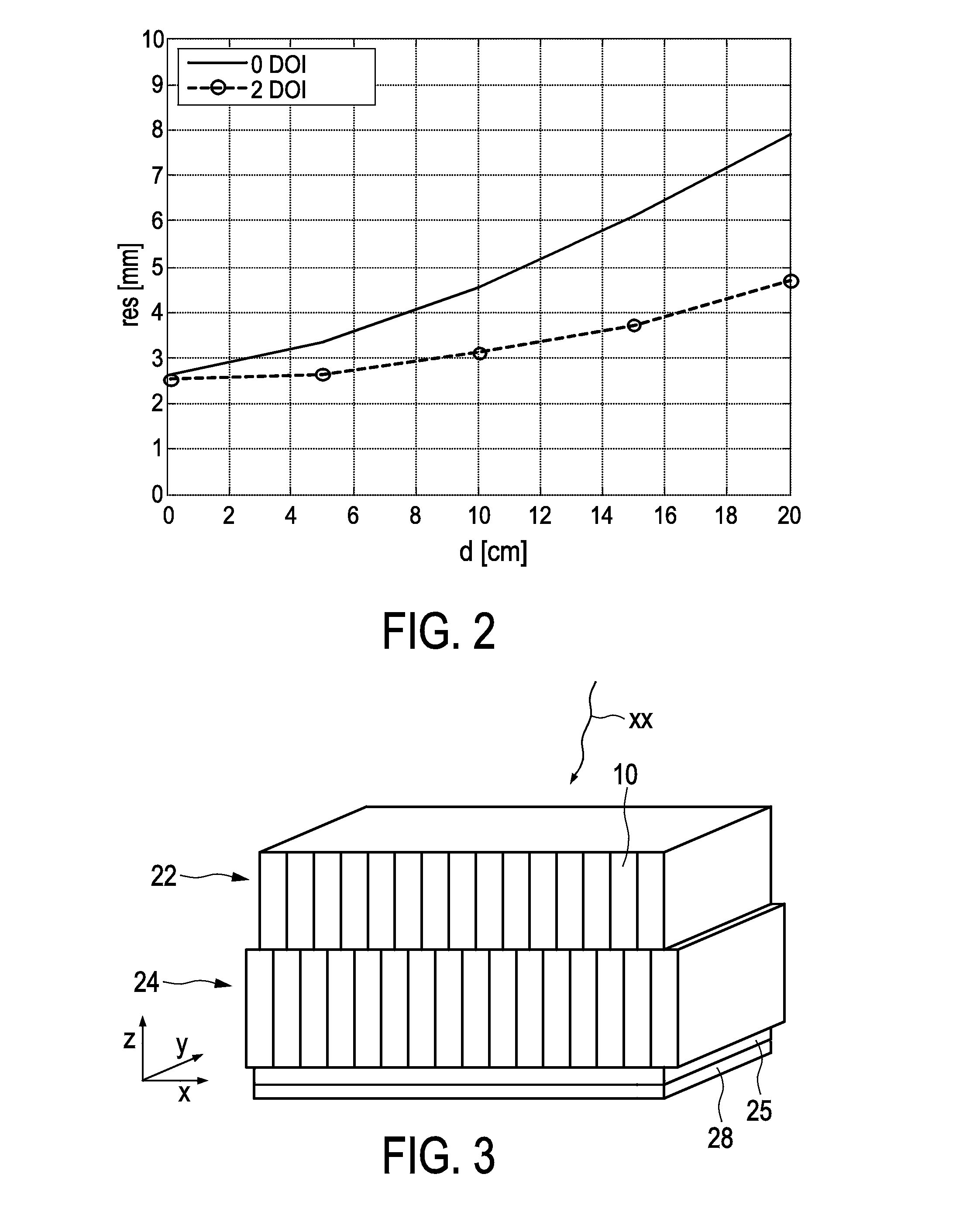
Depth-of-Interaction in an Imaging Device
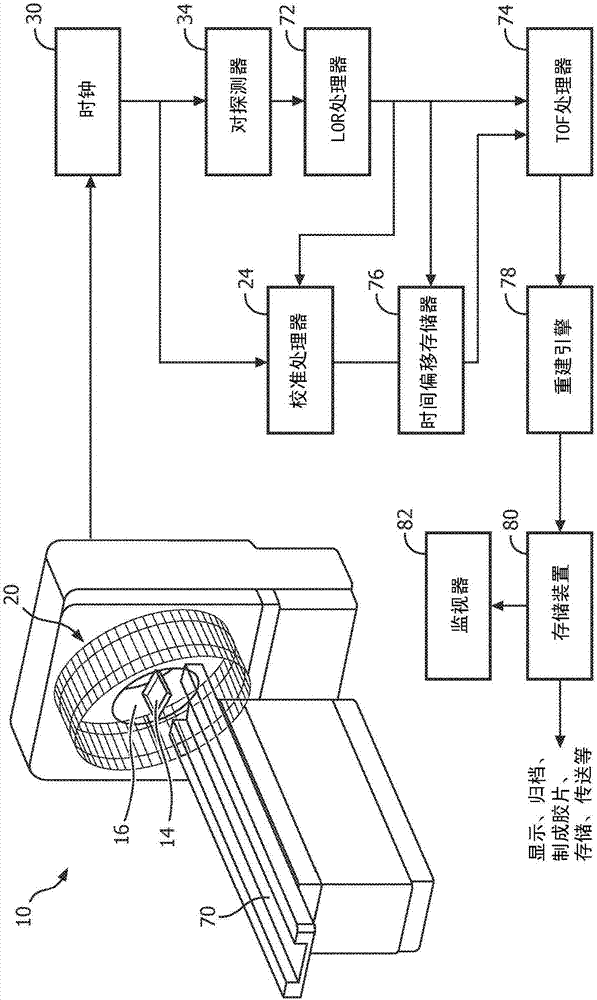
ActiveUS20130020487A1Material analysis by optical meansTomographyLines of responseDepth of interaction
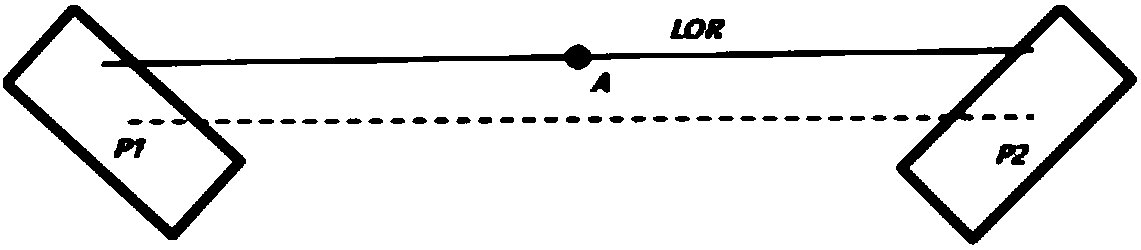
A method (70) of operation of a PET scanner (10) that determines the depth of interaction of the annihilation photons within the scintillator (32) in localizing a temporal photon pair along a line of response (LOR).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Optical-interface patterning for radiation detector crystals
A radiation detector is disclosed that includes a scintillation crystal and a plurality of photodetectors positioned to detect low-energy scintillation photons generated within the scintillation crystal. The scintillation crystals are processed using subsurface laser engraving to generate point-like defects within the crystal to alter the path of the scintillation photons. In one embodiment, the defects define a plurality of boundaries within a monolithic crystal to delineate individual detector elements. In another embodiment, the defects define a depth-of-interaction boundary that varies longitudinally to vary the amount of light shared by neighboring portions of the crystal. In another embodiment the defects are evenly distributed to reduce the lateral spread of light from a scintillation event. Two or more of these different aspects may be combined in a single scintillation crystal. Additionally, or alternatively, similar SSLE defects may be produced in other light-guiding elements of the radiation detector.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Method and apparatus for the measurement of signals from radiation sensors
ActiveUS8269180B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDepth of interactionRadiation sensor
The preferred embodiments of the present invention include a device for measuring an ionizing event in a radiation sensor. The device can include a charge amplifier and a timing shaper. The charge amplifier receives a cathode signal and is configured to output an amplified cathode signal. The timing shaper is operatively connected to the charge amplifier to receive the amplified cathode signal. The timing shaper is configured to generate a first pulse in response to a beginning of the ionizing event and a second pulse in response to an end of the ionizing event. The first and second pulses are associated with a depth of interaction of the ionizing event and are generated in response to a slope of the amplified cathode signal changing.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS +1
Pet detector timing calibration
ActiveCN107110988AQuick calibrationShorten the counting processComputerised tomographsTomographyAngle independentLines of response
A diagnostic imaging system comprises a plurality of radiation detectors (20) configured to detect radiation events emanating from an imaging region. The system comprises a calibration phantom (14) configured to be disposed in the imaging region spanning substantially an entire field of view and to generate radiation event pairs that define lines-of-response, wherein the calibration phantom is thin such that each LOR intersects the calibration phantom along its length, the thickness of the phantom being smaller than the length of the LORs. A calibration processor (24) receives input of the radiation detectors and calculates an incidence angle independent crystal delay tau i for each detector. The calibration processor (24) constructs a first look-up table for the timing correction of each LOR and a second look-up table for the angle depth of interaction correction for each crystal by combining tau i and eta i.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and apparatus for determining depth of interactions in a detector for three-dimensional complete body screening
InactiveUS20050035297A1Efficient and cost-effectiveImaging is clear and accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyParallaxCost effectiveness
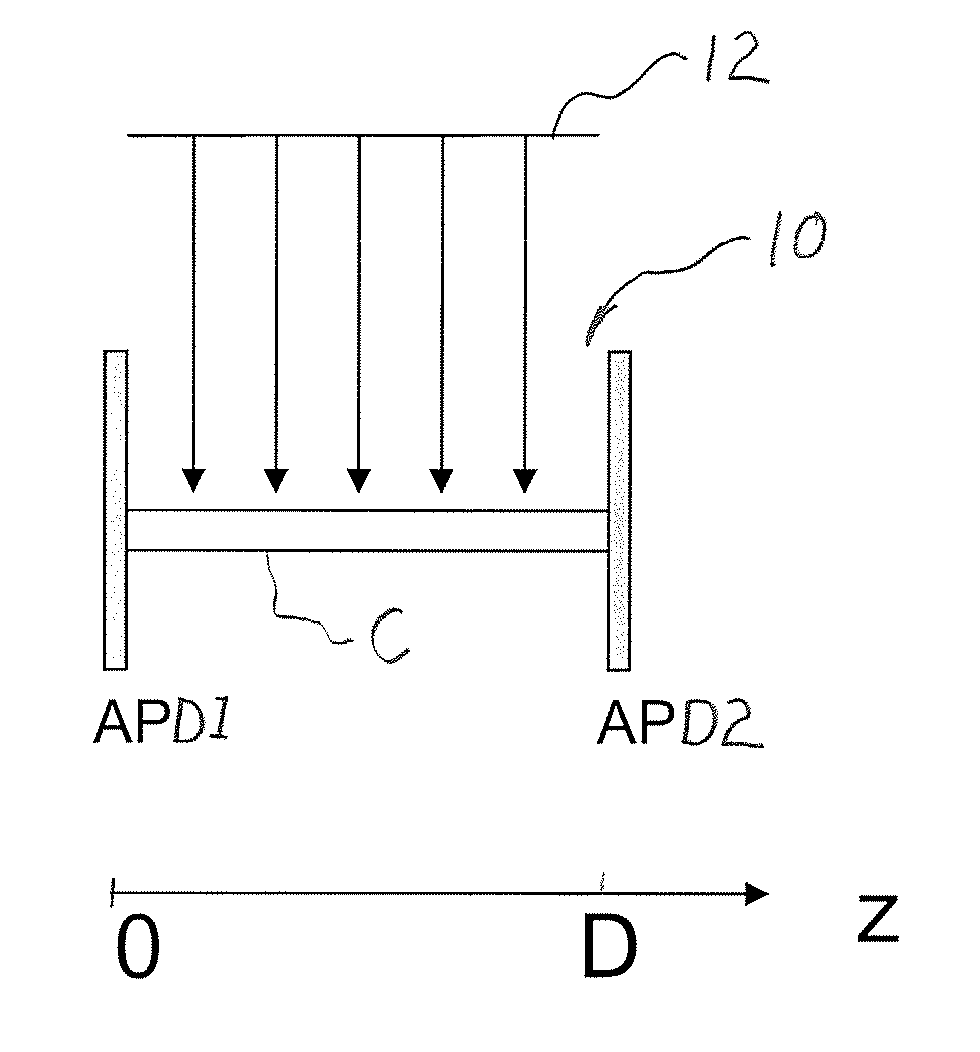
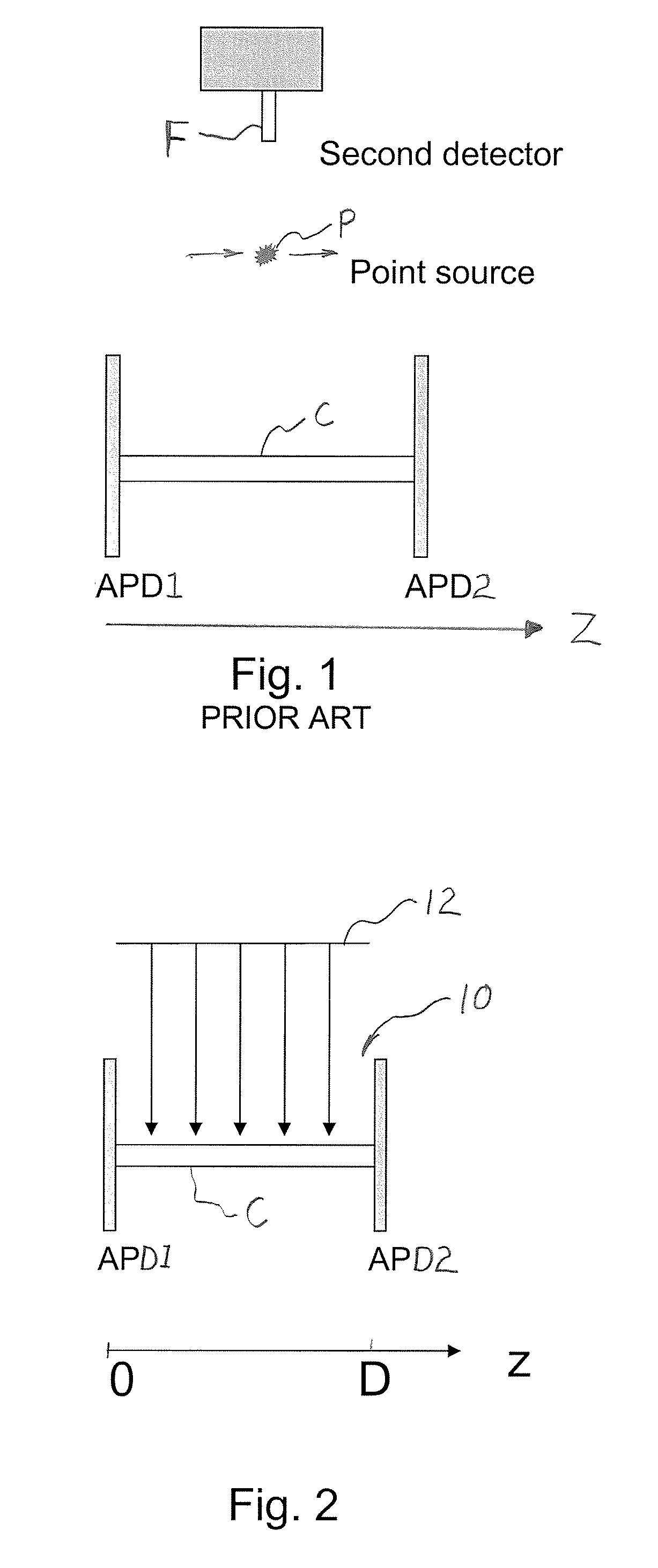
The present invention is directed to a system and method for efficiently and cost effectively determining an accurate depth of interaction for a crystal that may be used for correcting parallax error and repositioning LORs for more clear and accurate imaging. The present invention is directed to a detector assembly having a thin sensor (e.g., APD) deployed in front of the detector (the side where the radioactive source is located and the photon is arriving to hit the detector) and a second sensor (APD or photomultiplier) on the opposite side of the detector. The light captured by the two interior and exterior sensors which is proportional to the energy of the incident photon and to the distance where the photon was absorbed by the detector with respect to the location of the two sensors, is converted into an electrical signal and interpolated for finding the distance from the two sensors which is proportional to the location where the photon hit the detector.
Owner:CROSETTO DARIO B
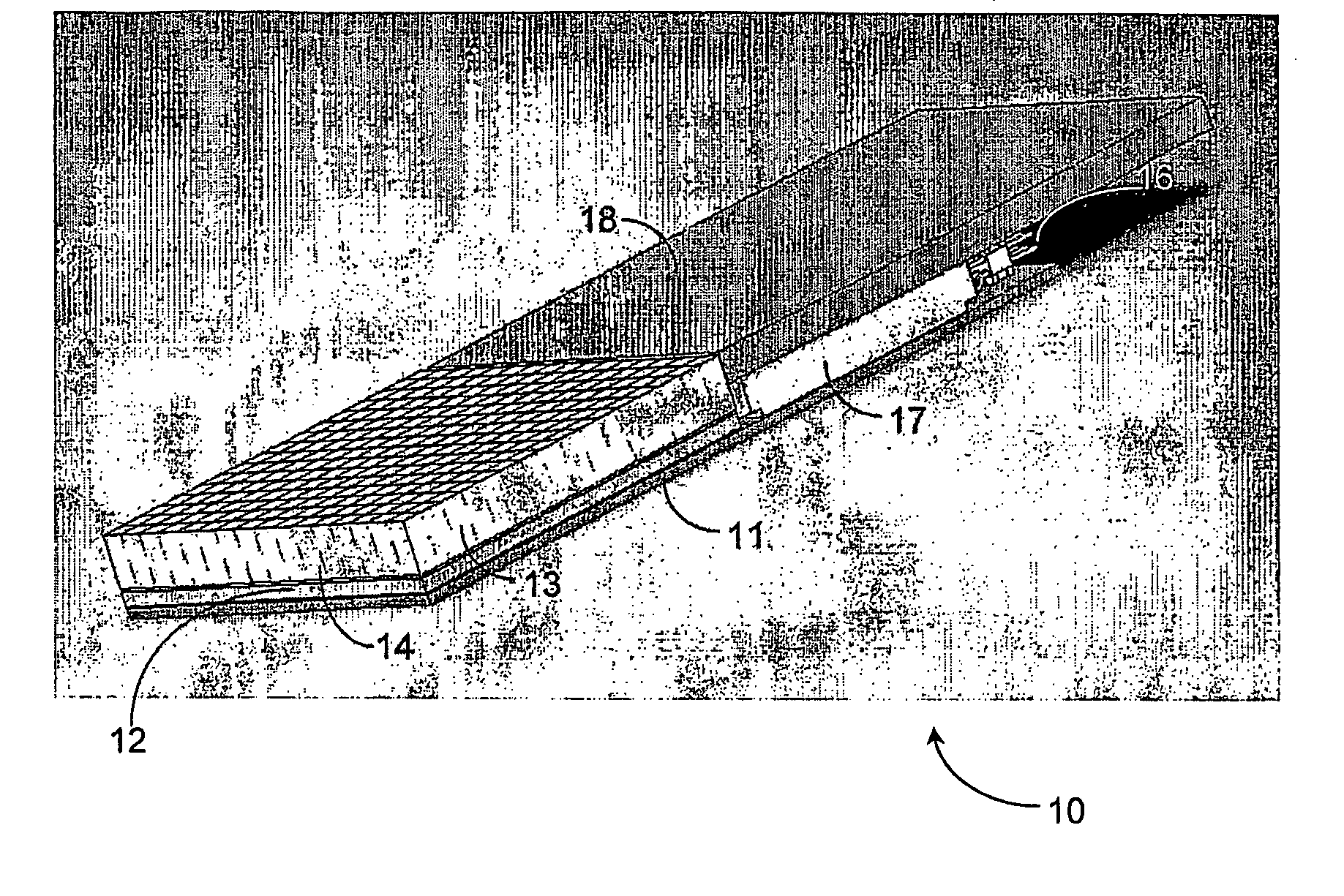
Monolithic Scintillators With Optical Fiber Read-Out
InactiveUS20090026375A1High resolutionEasy to manufactureMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementImage resolutionScintillation crystals
A scintillation detector according to an embodiment of the invention features a monolithic scintillation crystal and a plurality of optical fibers coupled to the scintillation crystal. The optical fibers are arranged to convey scintillation light to an optical sensor that is located exterior to the scintillation crystal. Because the optical fibers are extremely small in diameter, a multiplicity of them can be coupled to the scintillation crystal to provide the extremely high resolution of a pixelated scintillation crystal while the comparative manufacturing simplicity of a monolithic scintillation crystal is maintained. In preferred embodiments, the optical fibers are further arranged so that depth of interaction information can be obtained.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
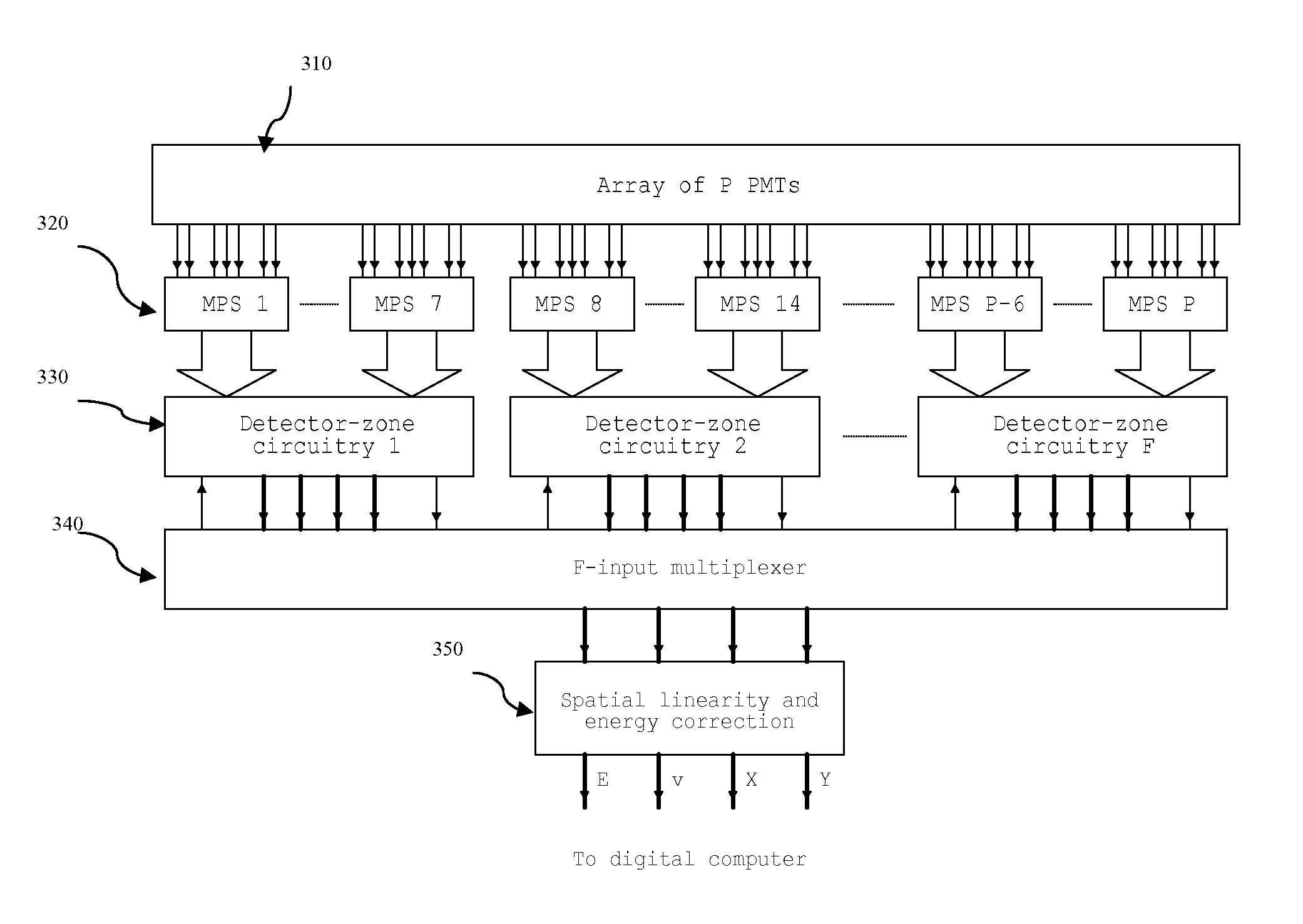
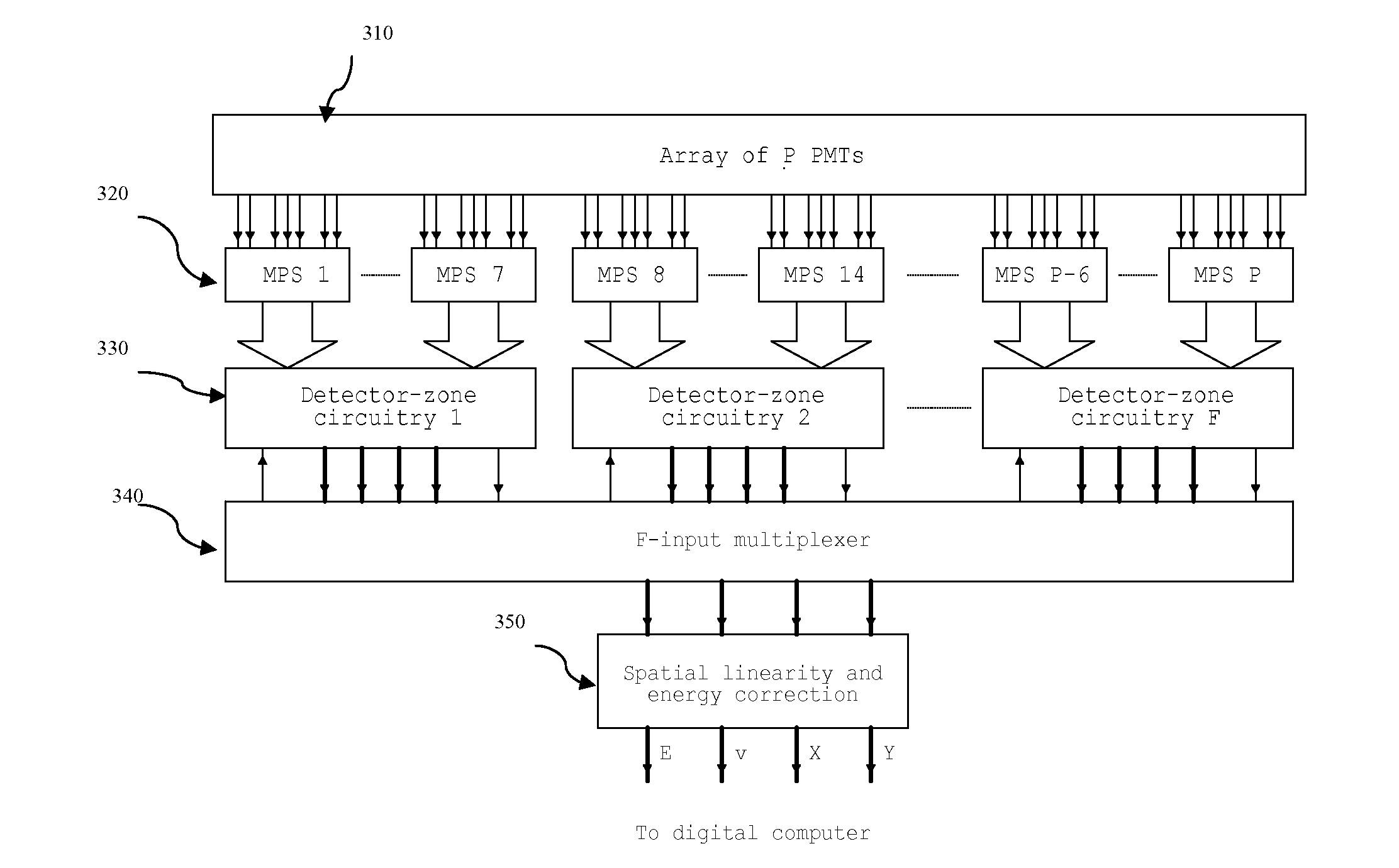
Method and system for nuclear imaging using multi-zone detector architecture
InactiveUS8809790B2Raise the ratioImprove resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementFiberPhotodetector
A method and system for nuclear imaging normally involves detection of energy by producing bursts of photons in response to interactions involving incident gamma radiation. The detector sensitivity is increased by as much as two orders of magnitude, so that some excess sensitivity can be exchanged to achieve unprecedented spatial resolution and contrast-to-noise (C / N) ratio comparable to those in CT and MRI. Misplaced pileup events due to scattered radiation are rejected for each of the central groups to reduce image blurring, thereby further improving image quality. The reduction in detector thickness minimizes depth-of-interaction (DOI) blurring as well as blurring due to Compton-scattered radiation. The spatial sampling of the detector can be further increased using fiber optic coupling to reduce effective photodetector size. Fiber-optic coupling also enables to increase the packing fraction of PMTs to 100% by effectively removing the glass walls.
Owner:WOLDEMICHAEL TILAHUN WOLDESELASSIE
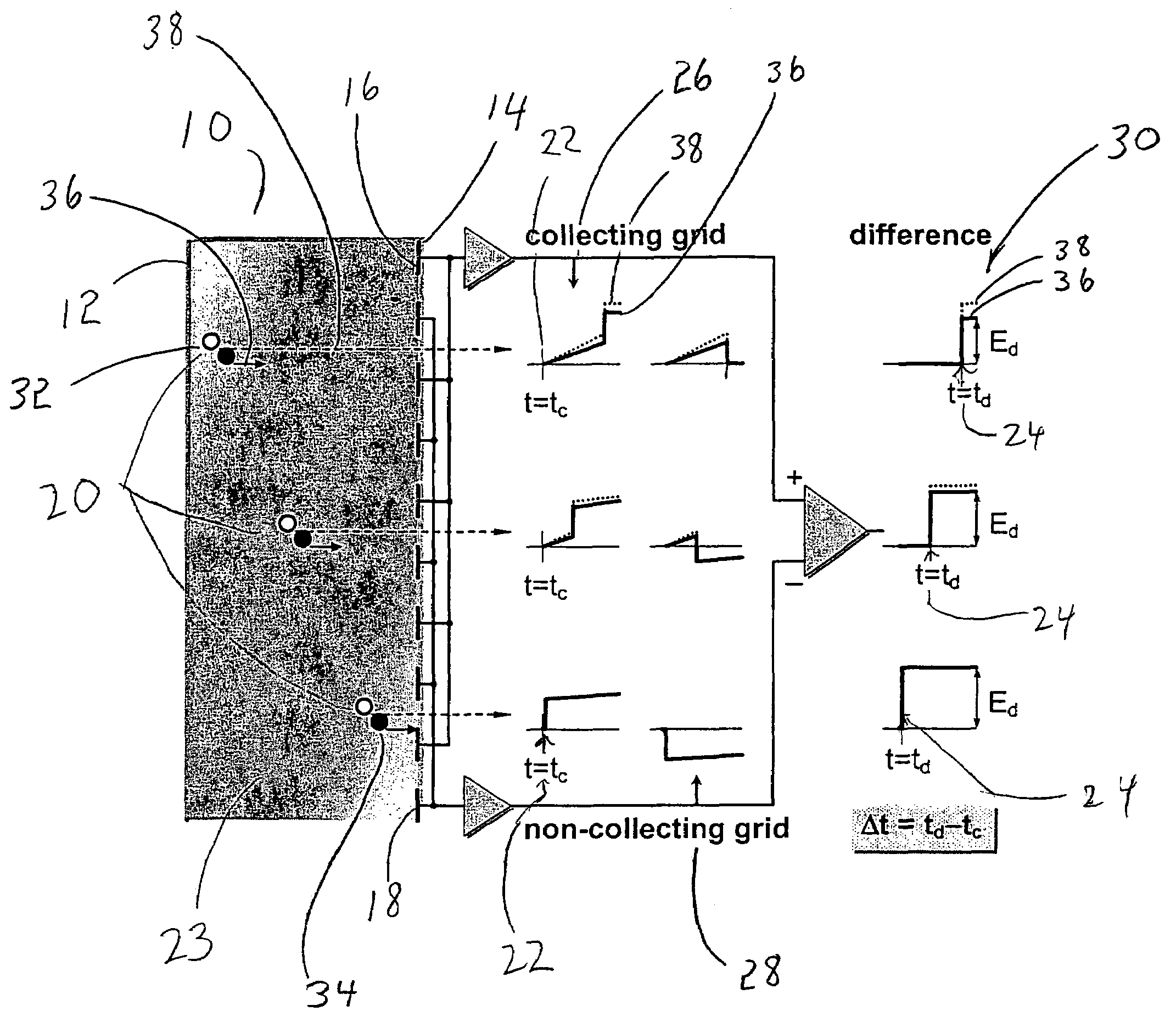
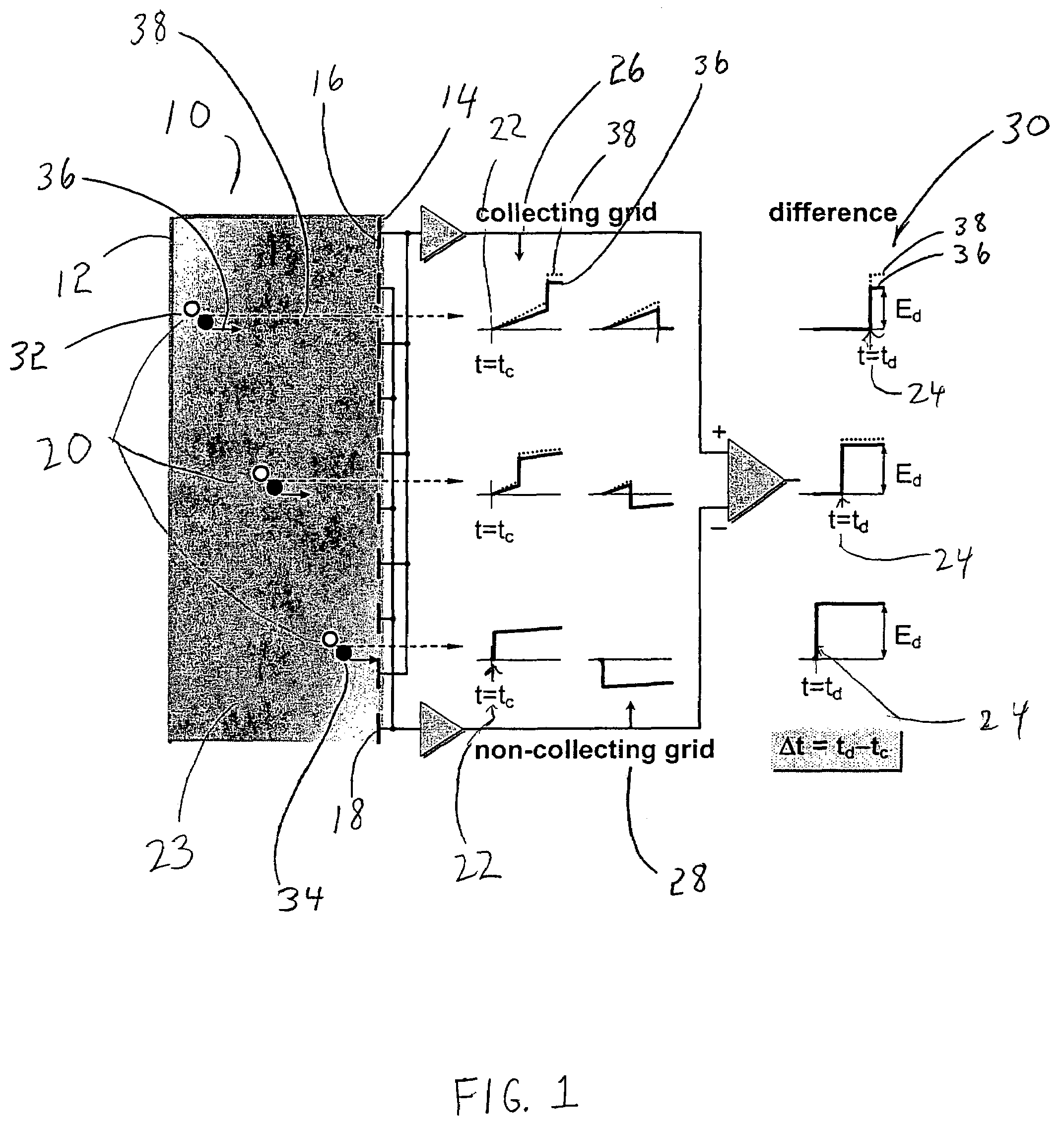
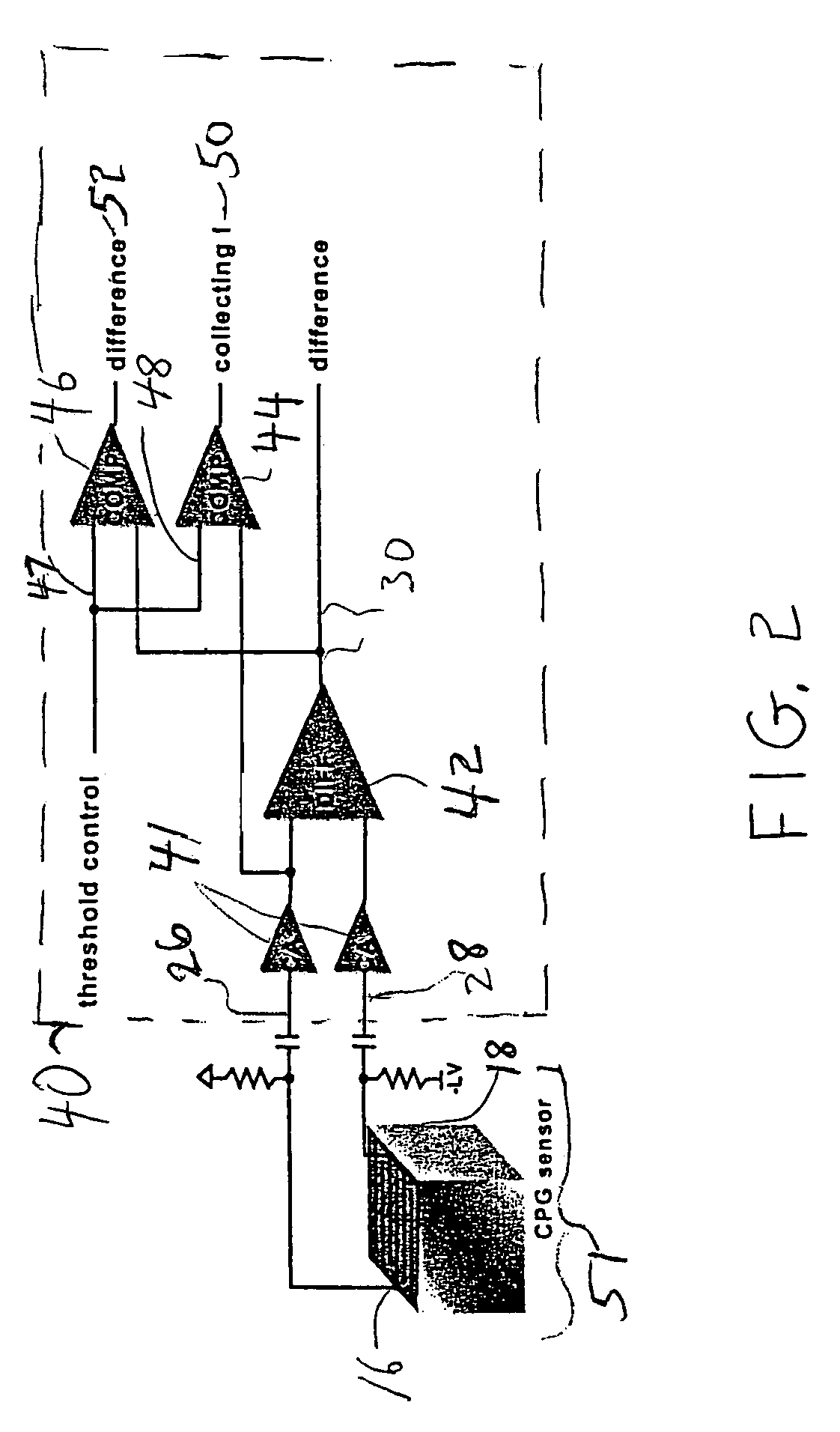
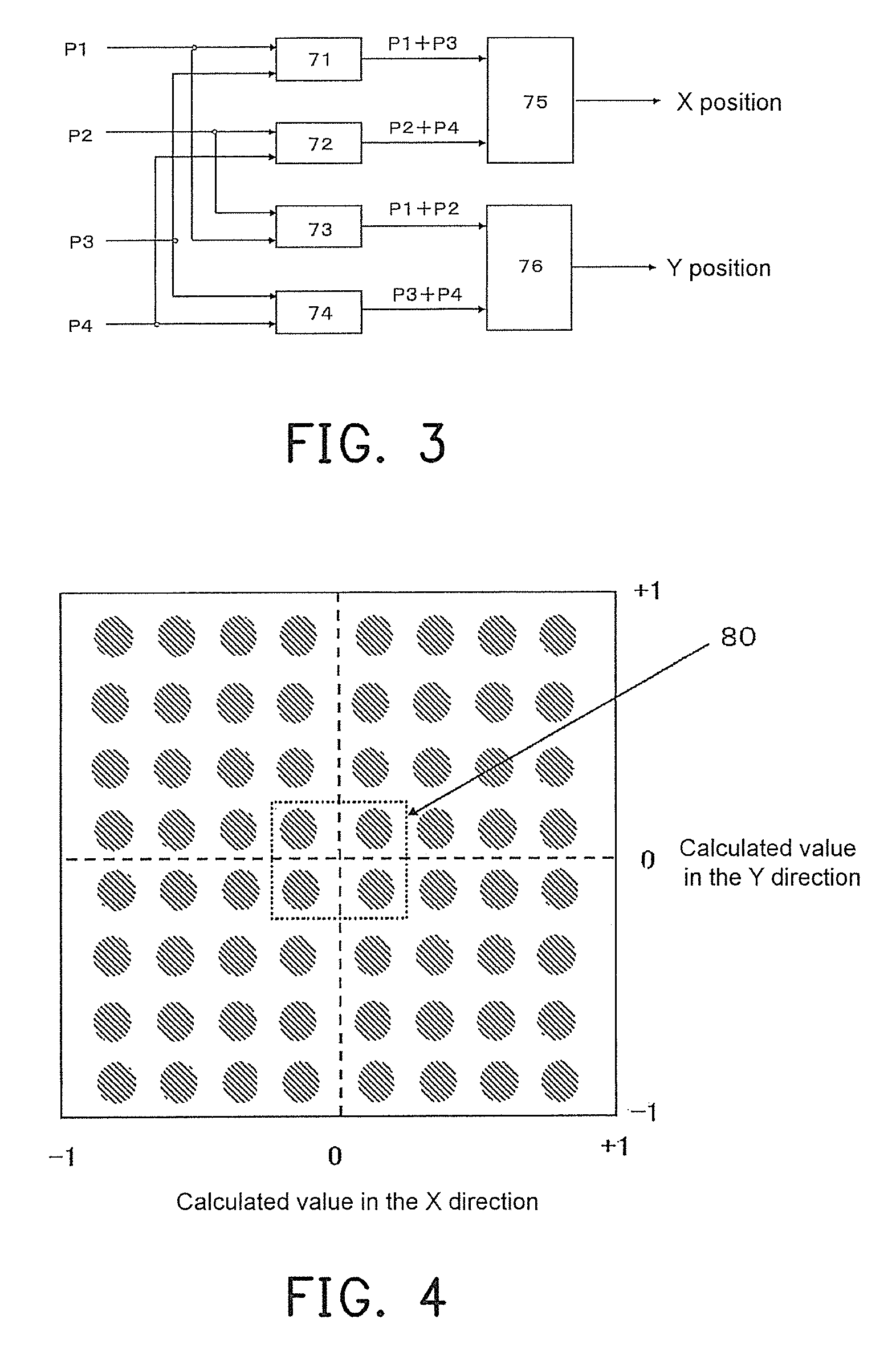
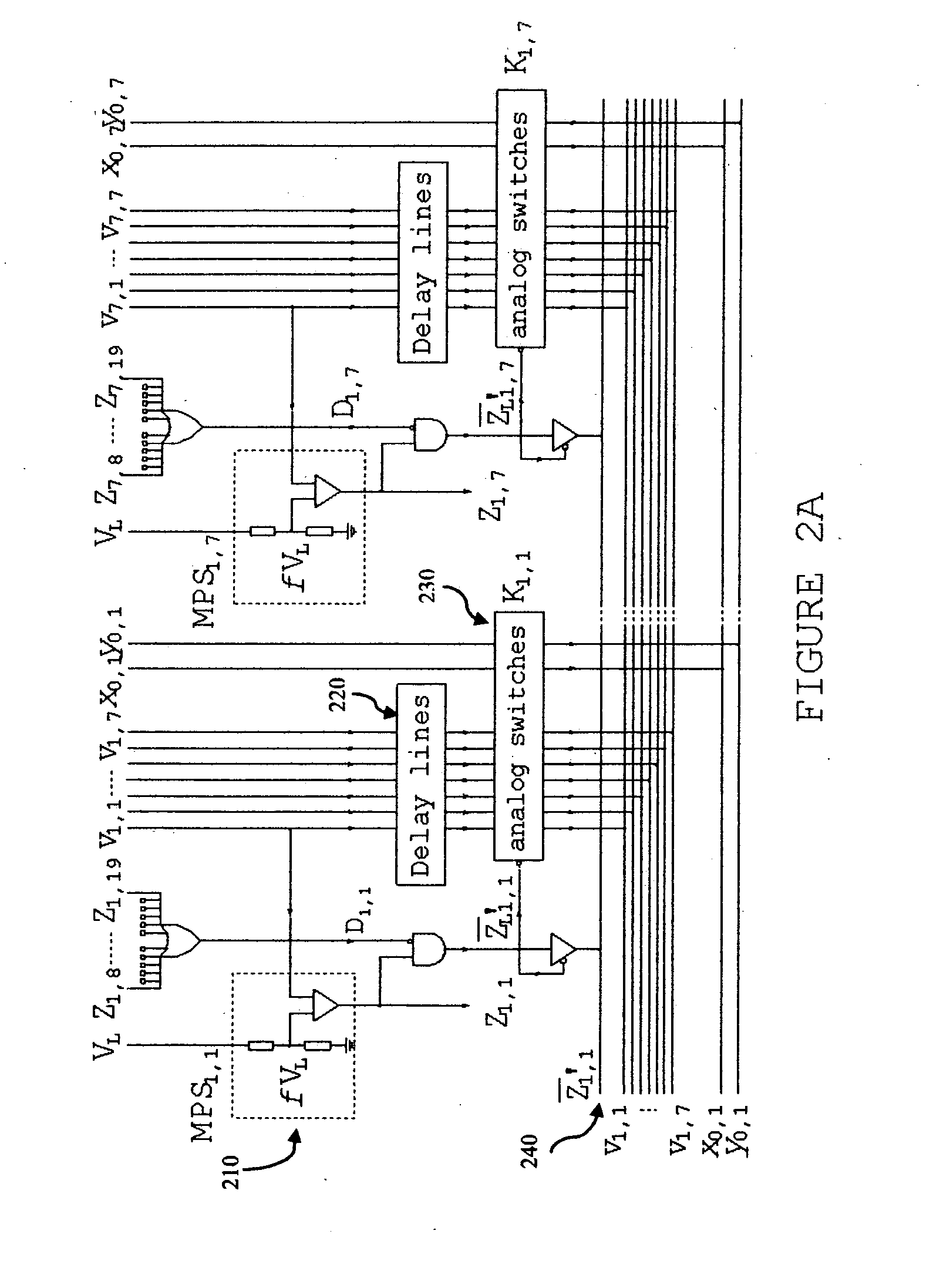
Device and method for the measurement of depth of interaction using co-planar electrodes
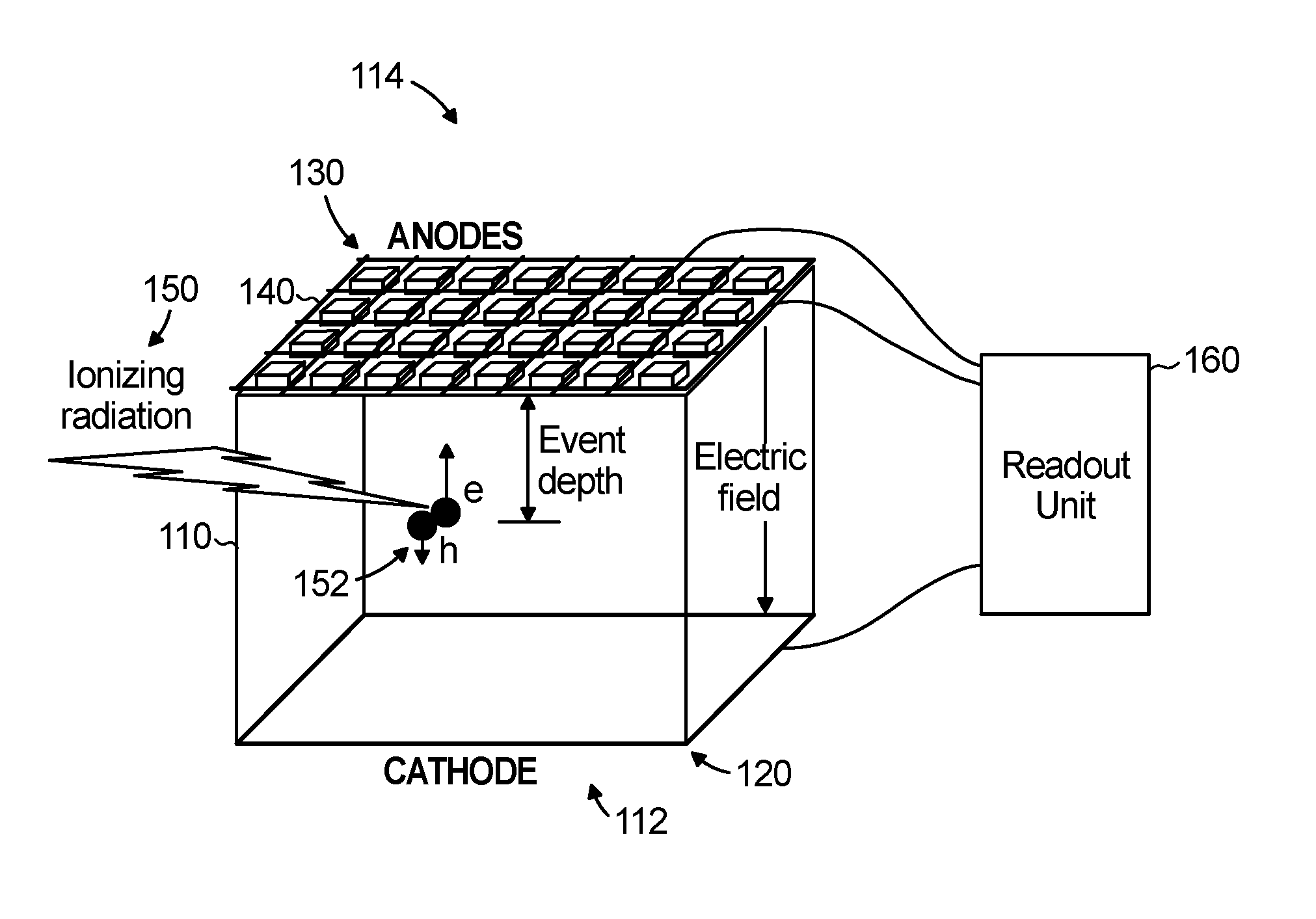
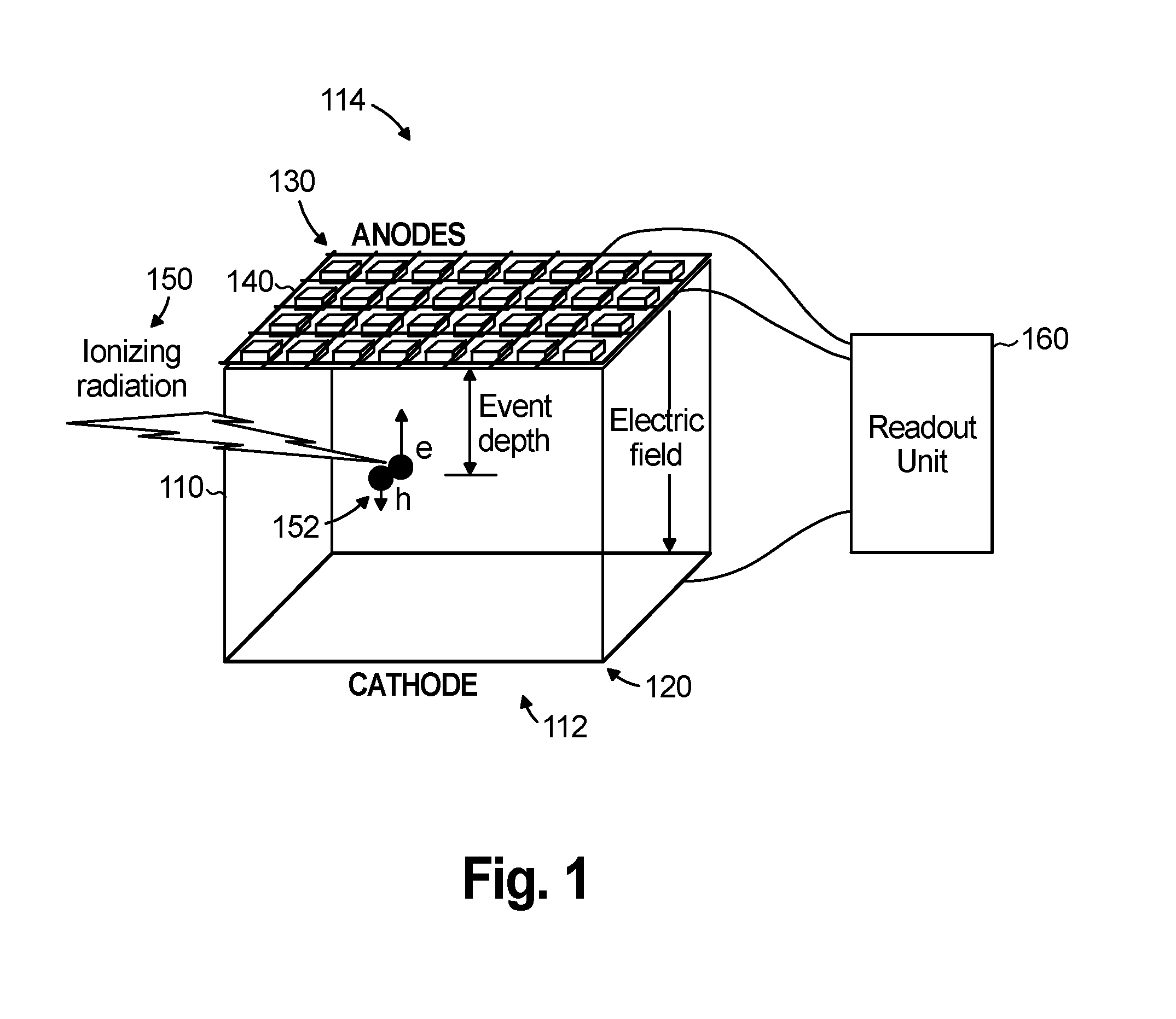
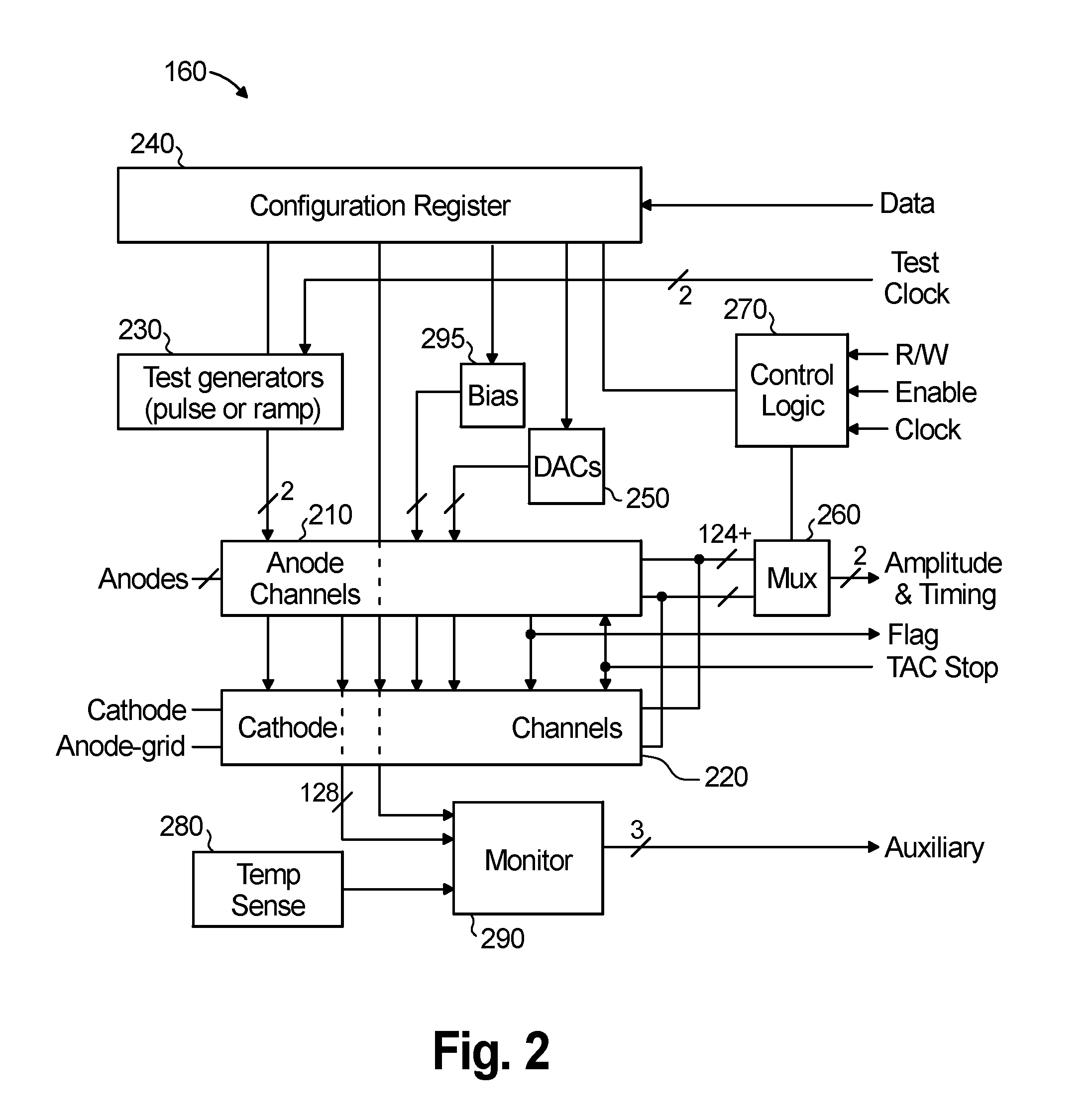
ActiveUS7271395B2Improve detection resolutionHigh resolutionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDepth of interactionGamma ray
A device and method for measuring a depth of interaction of an ionizing event and improving resolution of a co-planar grid sensor (CPG) are provided. A time-of-occurrence is measured using a comparator to time the leading edge of the event pulse from the non-collecting or collecting grid. A difference signal between the grid signals obtained with a differential amplifier includes a pulse with a leading edge occurring at the time-of-detection, measured with another comparator. A timing difference between comparator outputs corresponds to the depth of interaction, calculated using a processor, which in turn weights the difference grid signal to improve spectral resolution of a CPG sensor. The device, which includes channels for grid inputs, may be integrated into an Application Specific Integrated Circuit. The combination of the device and sensor is included. An improved high-resolution CPG is provided, e.g., a gamma-ray Cadmium Zinc Telluride CPG sensor operating at room temperature.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
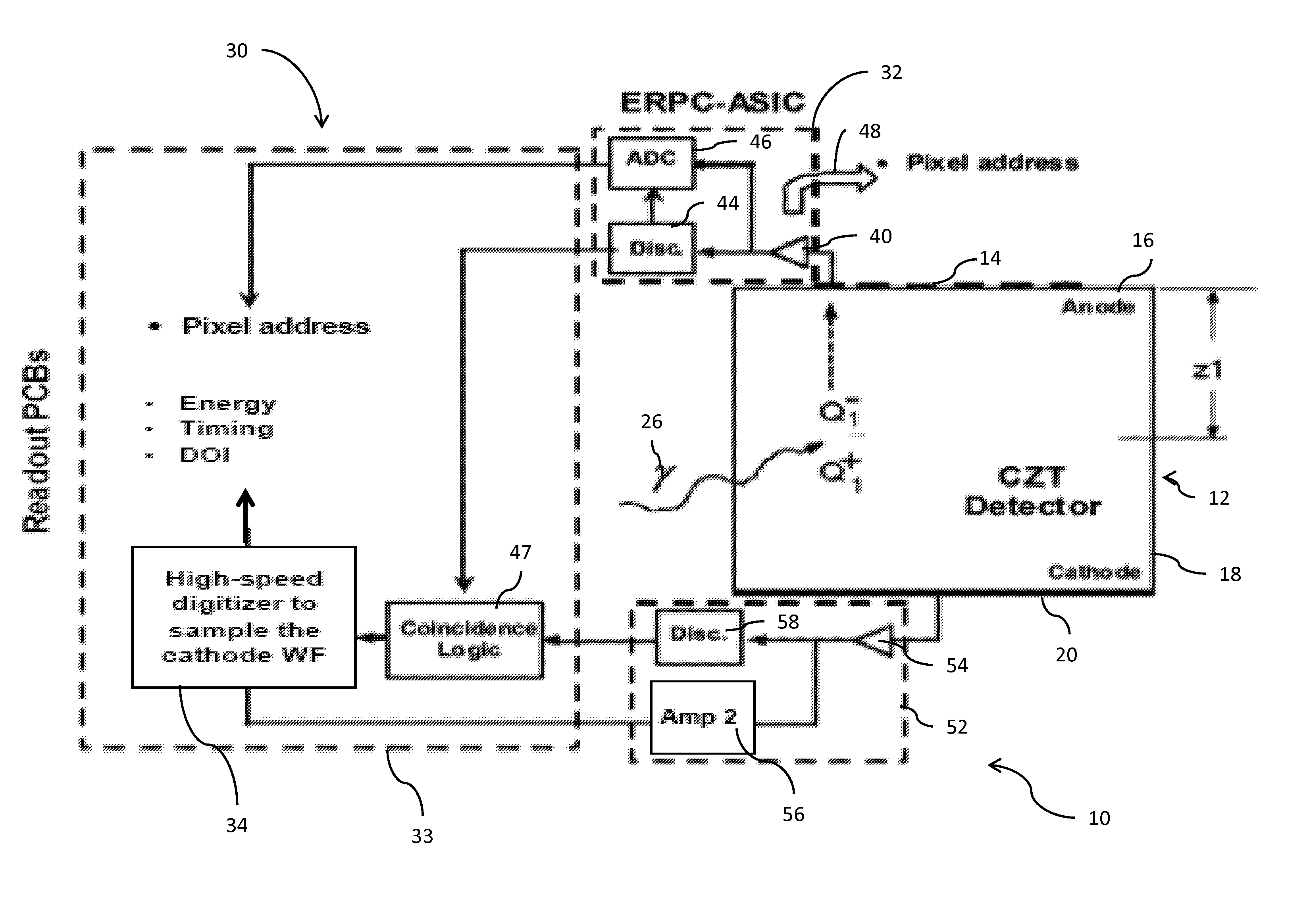
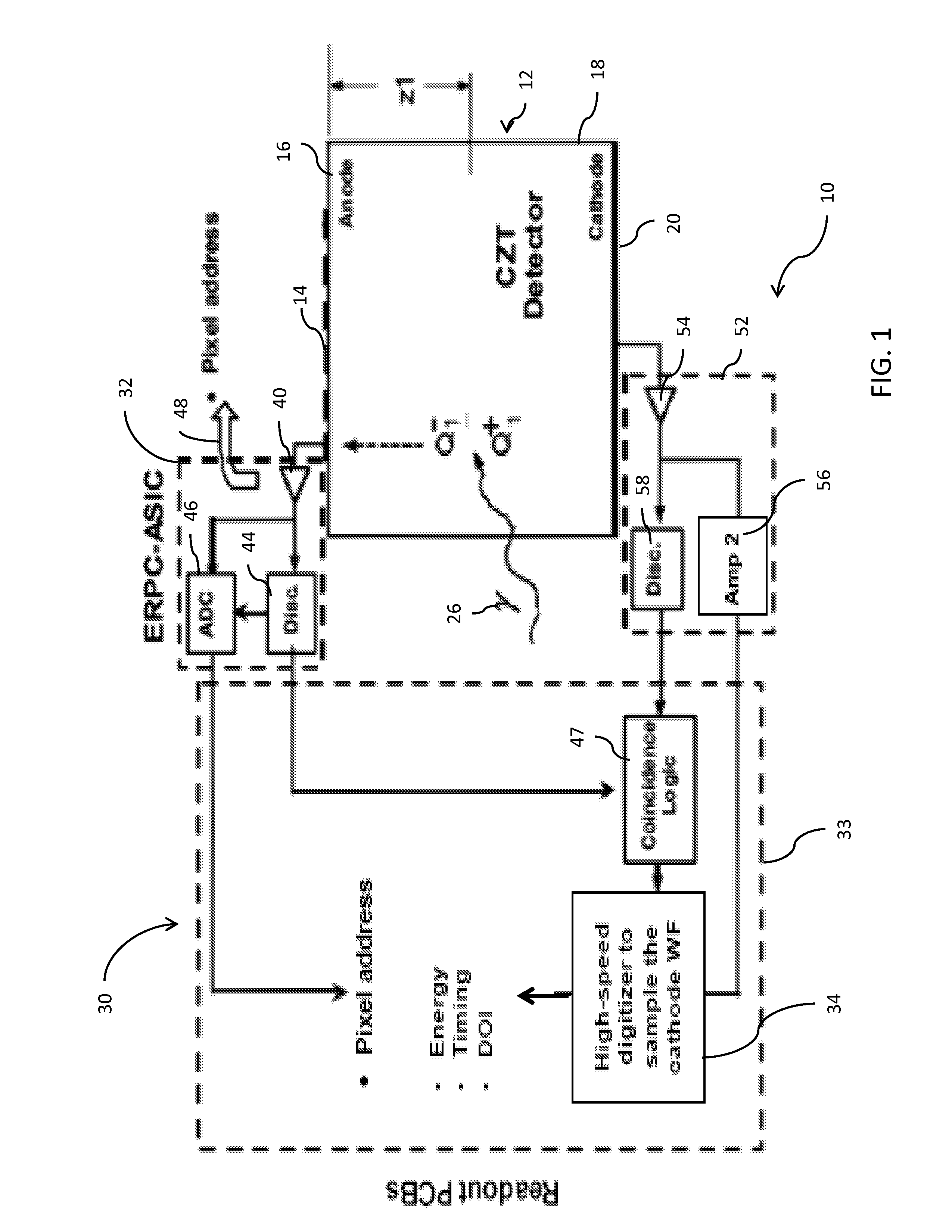
Detector apparatus having a hybrid pixel-waveform readout system
ActiveUS8866097B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSolid state detectorDepth of interaction
A gamma ray detector apparatus comprises a solid state detector that includes a plurality of anode pixels and at least one cathode. The solid state detector is configured for receiving gamma rays during an interaction and inducing a signal in an anode pixel and in a cathode. An anode pixel readout circuit is coupled to the plurality of anode pixels and is configured to read out and process the induced signal in the anode pixel and provide triggering and addressing information. A waveform sampling circuit is coupled to the at least one cathode and configured to read out and process the induced signal in the cathode and determine energy of the interaction, timing of the interaction, and depth of interaction.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method To Determine The Depth-Of-Interaction Function For PET Detectors
InactiveUS20070090298A1Avoid the needThe calibration result is accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyDepth of interactionScintillation crystals
A three-dimensional PET detector of a type having a scintillation crystal and first and second photosensitive detectors arranged one at each opposite end face of the crystal for detecting scintillation interactions within the crystal is calibrated to determine a depth-of-interaction (DOI) function thereof by irradiating the crystal to cause a predetermined distribution of interactions along a depth axis of the crystal, and applying probability theory to signal data collected by the two photosensitive detectors. The method provides a DOI function that indicates DOI position as a function of a signal ratio R obtained from the signal data.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and apparatus for determining depth of interactions in a detector for three-dimensional complete body screening
InactiveUS20050230626A1Efficient and cost-effectiveDepth accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyParallaxCost effectiveness
The present invention is directed to a system and method for efficiently and cost effectively determining an accurate depth of interaction for a crystal that may be used for correcting parallax error and repositioning LORs for more clear and accurate imaging. The present invention is directed to a detector assembly having a thin sensor (e.g., APD) deployed in front of the detector (the side where the radioactive source is located and the photon is arriving to hit the detector) and a second sensor (APD or photomultiplier) on the opposite side of the detector. The light captured by the two interior and exterior sensors which is proportional to the energy of the incident photon and to the distance where the photon was absorbed by the detector with respect to the location of the two sensors, is converted into an electrical signal and interpolated for finding the distance from the two sensors which is proportional to the location where the photon hit the detector.
Owner:CROSETTO DARIO B
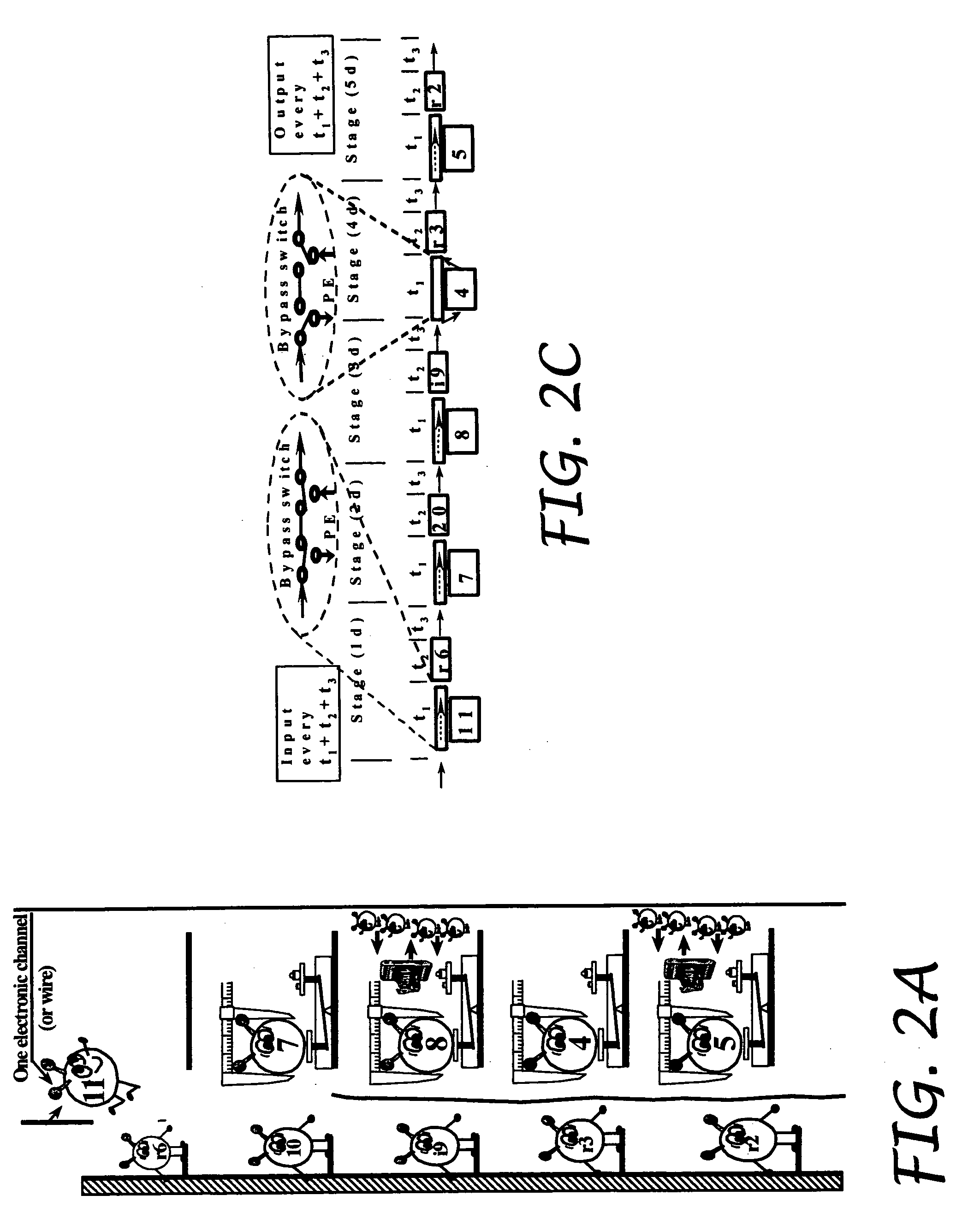
Depth of interaction detector with uniform pulse-height
ActiveUS7091490B2Improve uniformityDifference in light collection efficiency between scintillator cells is reducedMaterial analysis by optical meansLuminescent compositionsDepth of interactionPulse height
A depth of interaction detector with uniform pulse-height comprises a multi-layer scintillator obtained by coupling at least two scintillator cells on a plane and then stacking the planar coupled scintillator cells, in layers, up to at least two stages and a light-receiving element connected to the bottom face of each scintillator cell of this multi-layer scintillator, wherein the detector is provided with a means for discriminating the position of a scintillator cell, which receives radiant rays and emits light rays and a means for making, uniform, the quantity of the light emitted from each scintillator cell and received by the light-receiving element. The detector can provide precise detection information even when radiation is absorbed by and emitted from a scintillator layer positioned above the scintillator layer optically coupled to the light-receiving element, permits the production of a depth of interaction detector having a three-dimensional depth of interaction-detecting function and can provide the same total output signal, which is independent of the position or a specific scintillator cell practically emitting light if the radiation energy is identical.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK +1
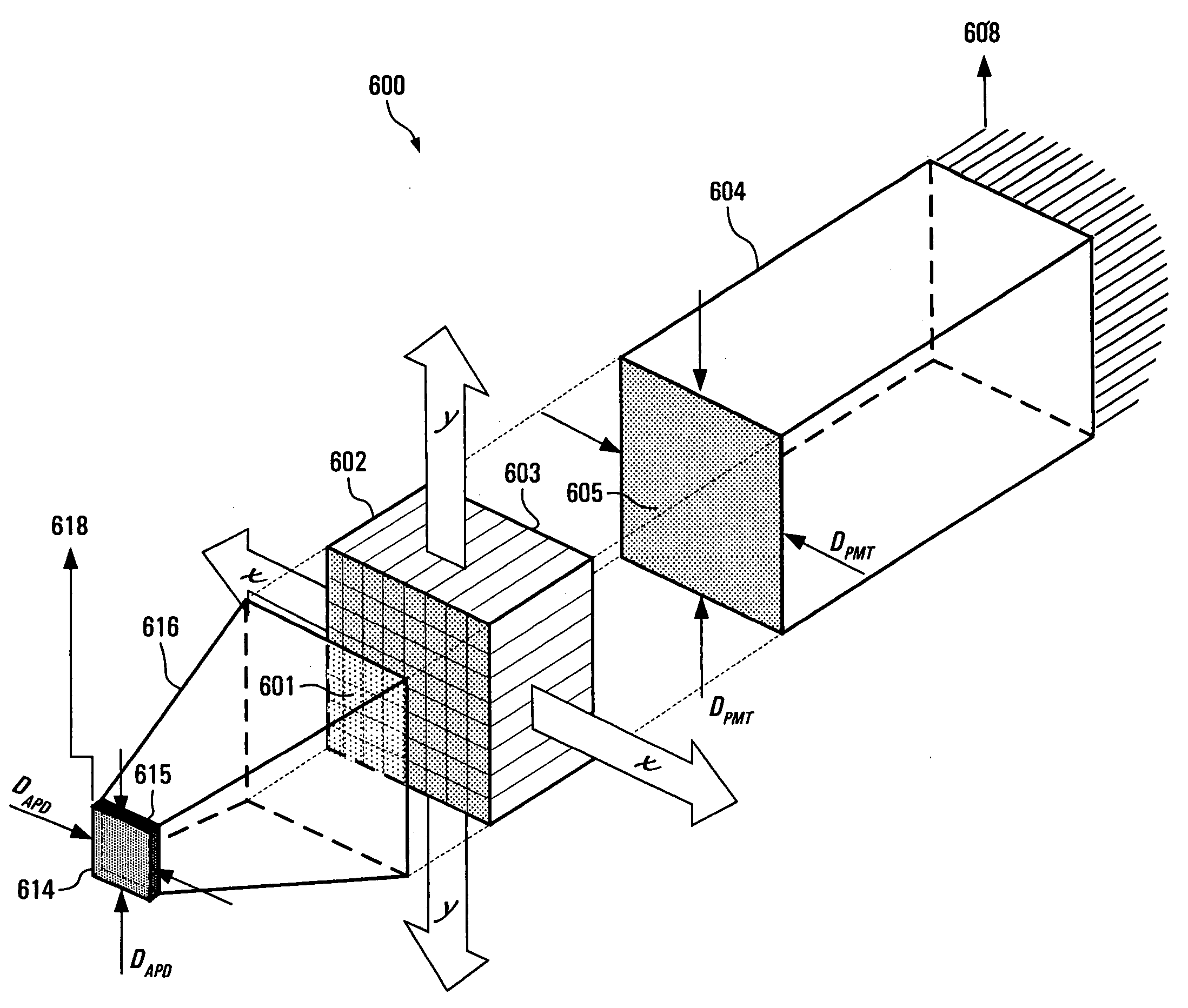
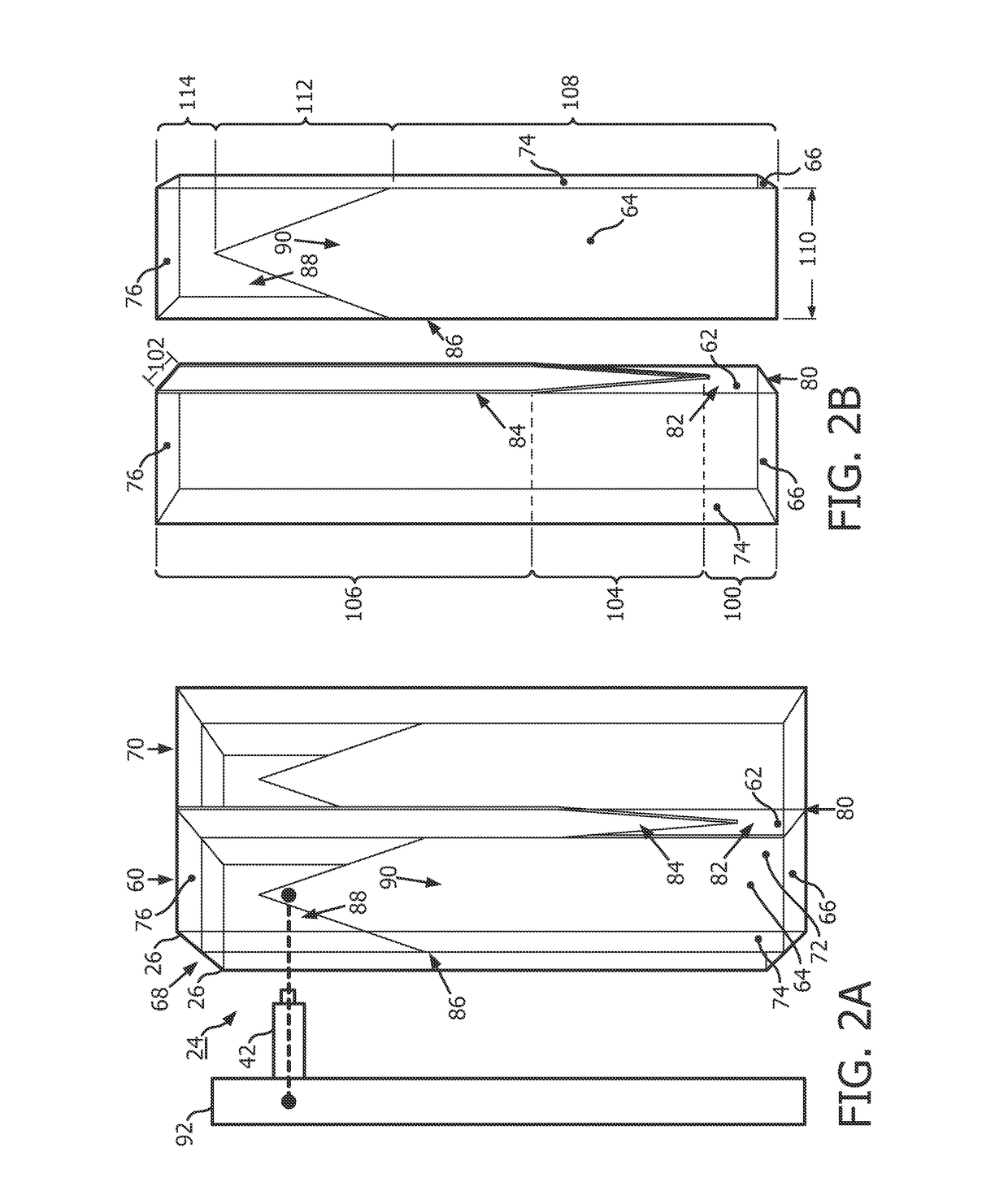
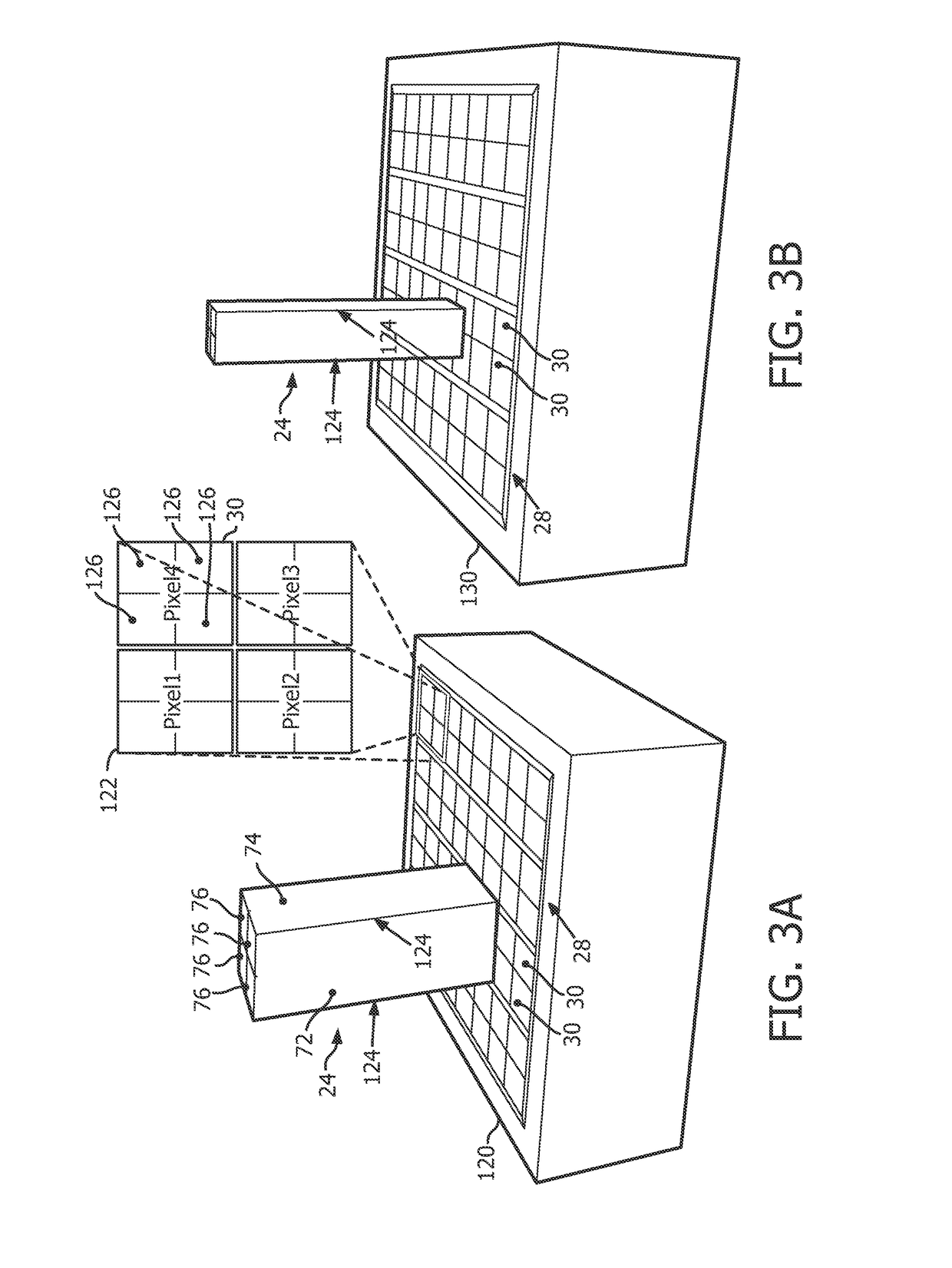
Pet detector scintillator arrangement with light sharing and depth of interaction estimation
ActiveUS20170234990A1Accurate detection timeFine time resolutionRadiation intensity measurementSensor arrayGamma photon
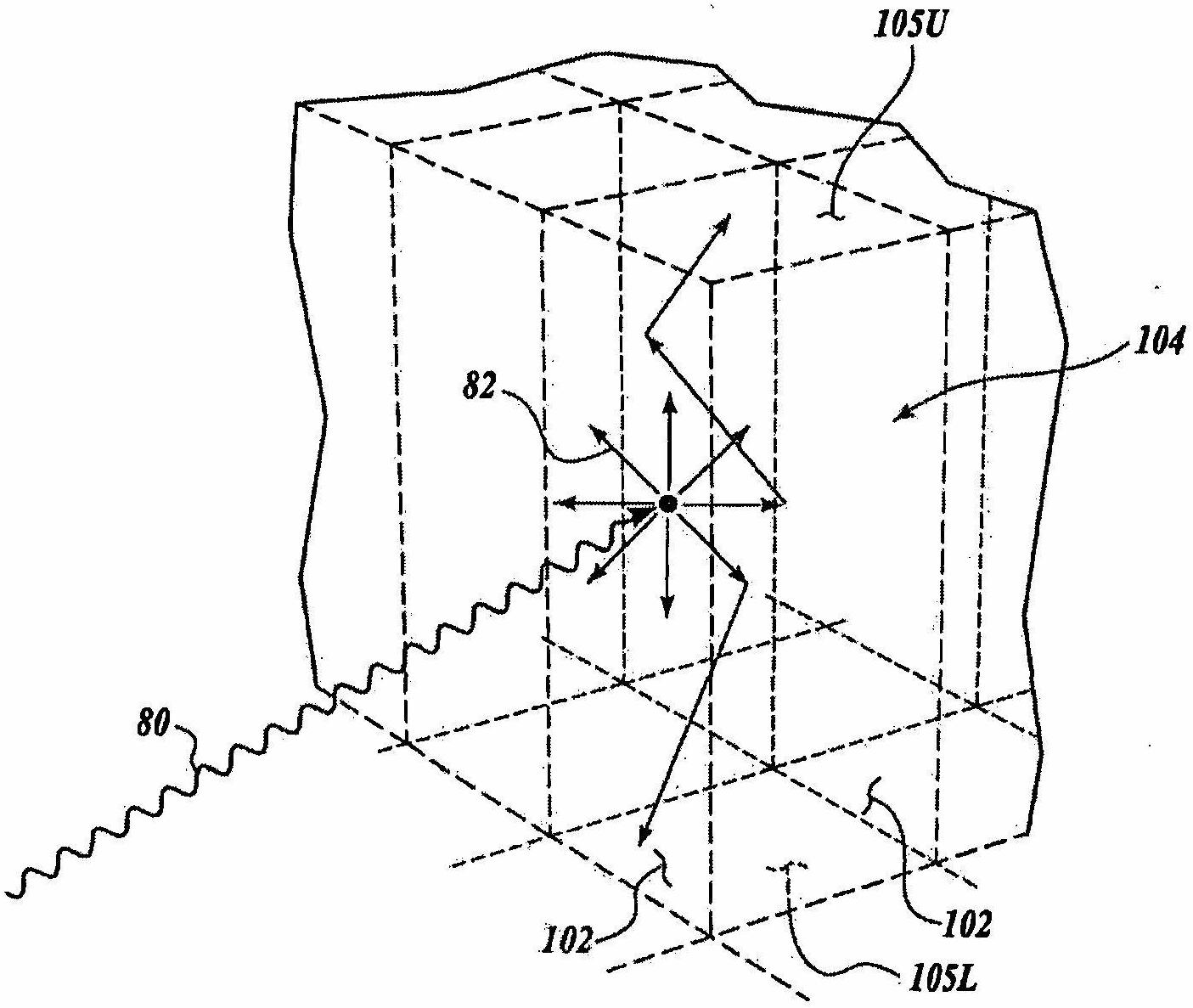
A photon detector includes a sensor array of optical sensors disposed in a plane and four substantially identical scintillation crystal bars. Each optical sensor is configured to sense luminescence. Each of the four scintillator crystal bars being a rectangular prism with four side surfaces and first and second end surfaces, each scintillation bar has two side surfaces which each face a side surface of another scintillation bar, and each scintillation crystal bar generating a light scintillation in response to interacting with a received gamma photon. A first layer (80) is disposed in a first plane disposed between and adjacent facing side surfaces of the four substantially identical scintillation crystal bars with a light sharing portion (82) adjacent the first end surface and a reflective portion (84) adjacent the second end surface. A second layer (68) is disposed in a second plane orthogonal to the first plane and disposed between and adjacent facing side surfaces of the four substantially identical scintillation crystal bars with a light sharing portion (88) adjacent the second end surface and a reflective portion (90) adjacent the first end surface.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV +1
Depth-of-interaction scintillation detectors
ActiveUS20140299777A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementGamma photonDepth of interaction
The invention disclosed herein relates to a scintillation detector for registering the position of gamma photon interactions, an comprises an array of two or more elongated first and second scintillation crystal elements connected together along their respective long sides, and an array of discrete photosensitive areas disposed on a common substrate of a solid-state semiconductor photo-detector. The array of first and second scintillation crystal elements have proximal output windows optically coupled to the array of discrete photosensitive areas in a one-to-one relationship. The invention may be characterized in that the first and second scintillation crystal elements include a rooftop portion at their distal ends, wherein the rooftop portion optically couples one of the first and second scintillation crystal elements to the other and is configured to reflect and transmit light resulting from a gamma photon interaction from one of the first and second scintillation crystal elements to the other.
Owner:ZECOTEK IMAGING SYST PTE
Nuclear medical diagnostic device
InactiveUS7791030B2Allocation is accurateHigh-quality tomogramMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementUltrasound attenuationDepth of interaction
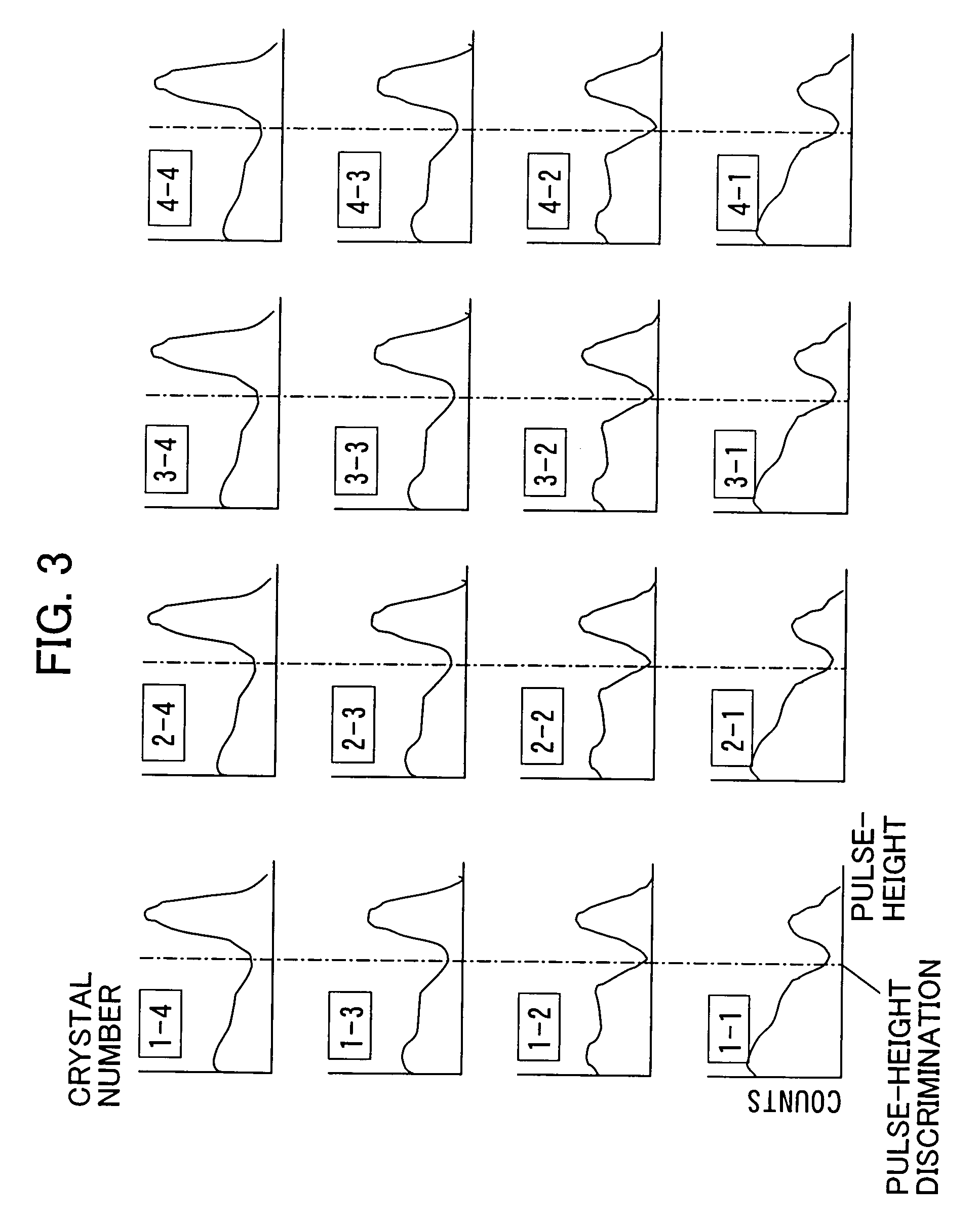
Parameters T1, T2, and K required by a scintillator array identification mechanism in a two-stage scintillator γ-ray detector (depth of interaction (DOI)) are accurately and easily determined. The parameters required by the scintillator array identification mechanism are determined with reference to a first signal count ratio, which is obtained by irradiating a γ-ray on each scintillator array with luminescence pulses in an incident depth direction of the γ-ray having different attenuation time during an inspection stage of the γ-ray detector single unit. Furthermore, a second signal count ratio is obtained by irradiating the γ-ray on a front surface of the γ-ray detector single unit, and then a third signal count ratio is obtained by irradiating the γ-ray on the front surface after the γ-ray detector single unit is installed in a PET device.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method and system for nuclear imaging using multi-zone detector architecture
InactiveUS20130320218A1Raise the ratioImprove resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentFiberPhotodetector
A method and system for nuclear imaging normally involves detection of energy by producing bursts of photons in response to interactions involving incident gamma radiation. The detector sensitivity is increased by as much as two orders of magnitude, so that some excess sensitivity can be exchanged to achieve unprecedented spatial resolution and contrast-to-noise (C / N) ratio comparable to those in CT and MRI. Misplaced pileup events due to scattered radiation are rejected for each of the central groups to reduce image blurring, thereby further improving image quality. The reduction in detector thickness minimizes depth-of-interaction (DOI) blurring as well as blurring due to Compton-scattered radiation. The spatial sampling of the detector can be further increased using fiber optic coupling to reduce effective photodetector size. Fiber-optic coupling also enables to increase the packing fraction of PMTs to 100% by effectively removing the glass walls.
Owner:WOLDEMICHAEL TILAHUN WOLDESELASSIE
Charge loss correction
ActiveUS8466420B2Restore performanceImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyDepth of interactionCharge loss
The present disclosure relates to the correction of charge loss in a radiation detector. In one embodiment, correction factors for charge loss may be determined based on depth of interaction and lateral position within a radiation detector of a charge creating event. The correction factors may be applied to subsequently measured signals to correct for the occurrence of charge loss in the measured signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Autonomous gamma, X-ray, and particle detector
ActiveUS9835737B1Rapidly and reliably screenSmall amountComputerised tomographsTomographyX-rayDepth of interaction
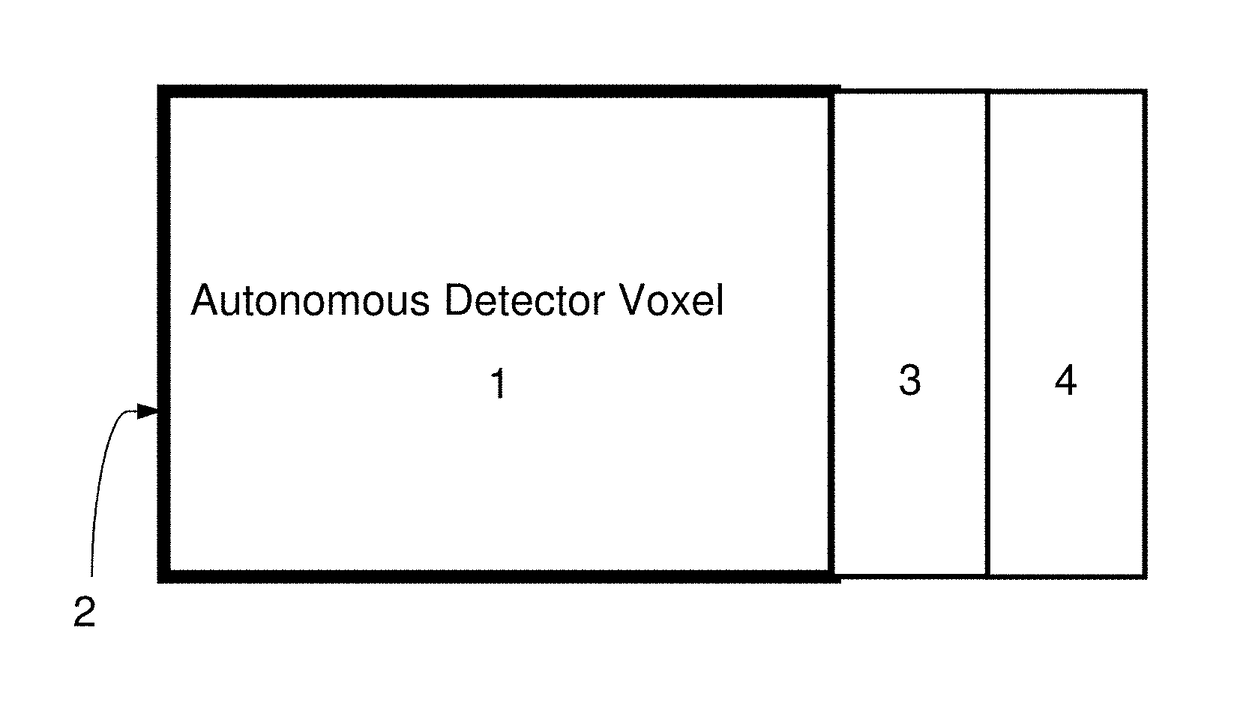
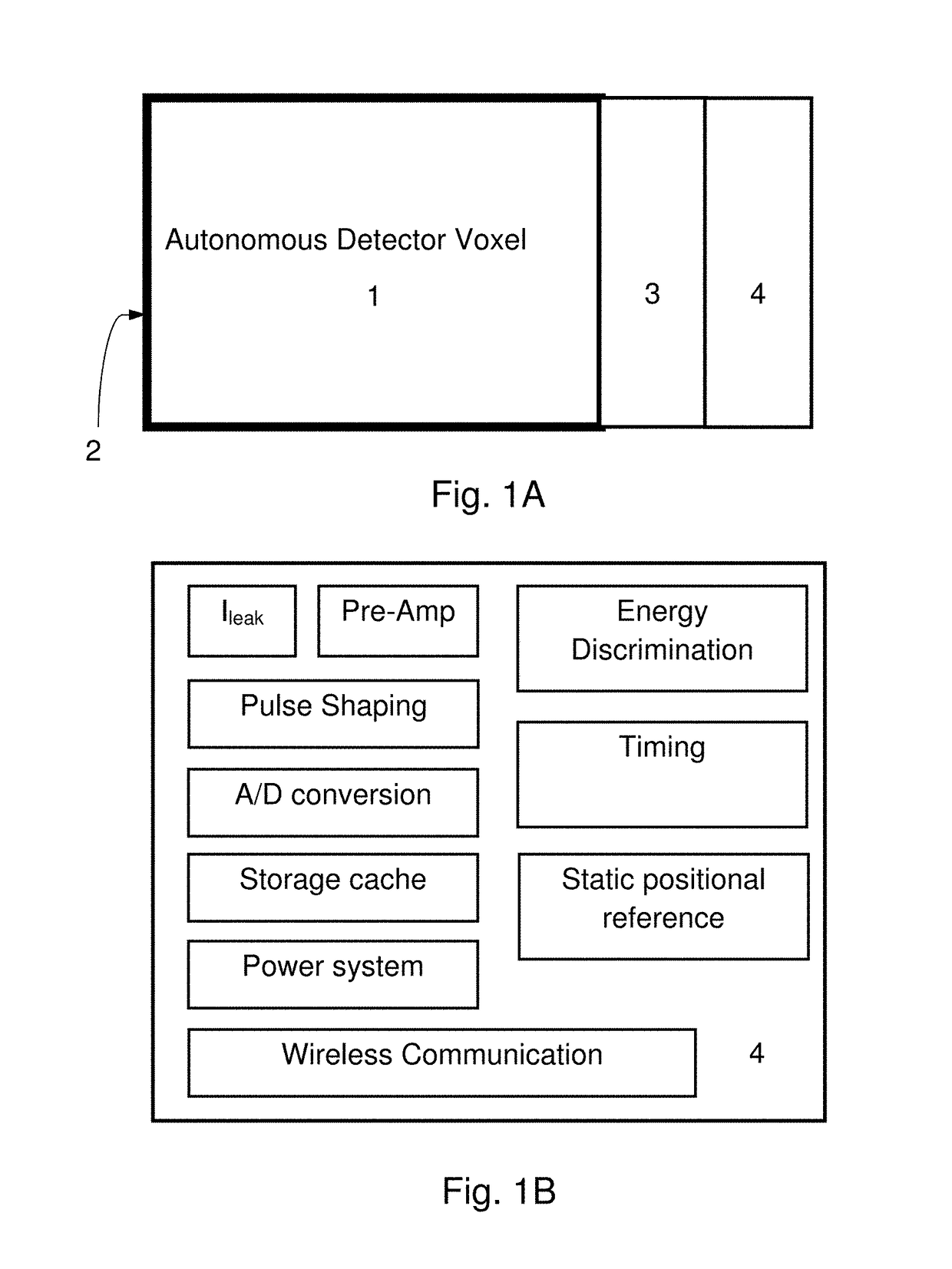
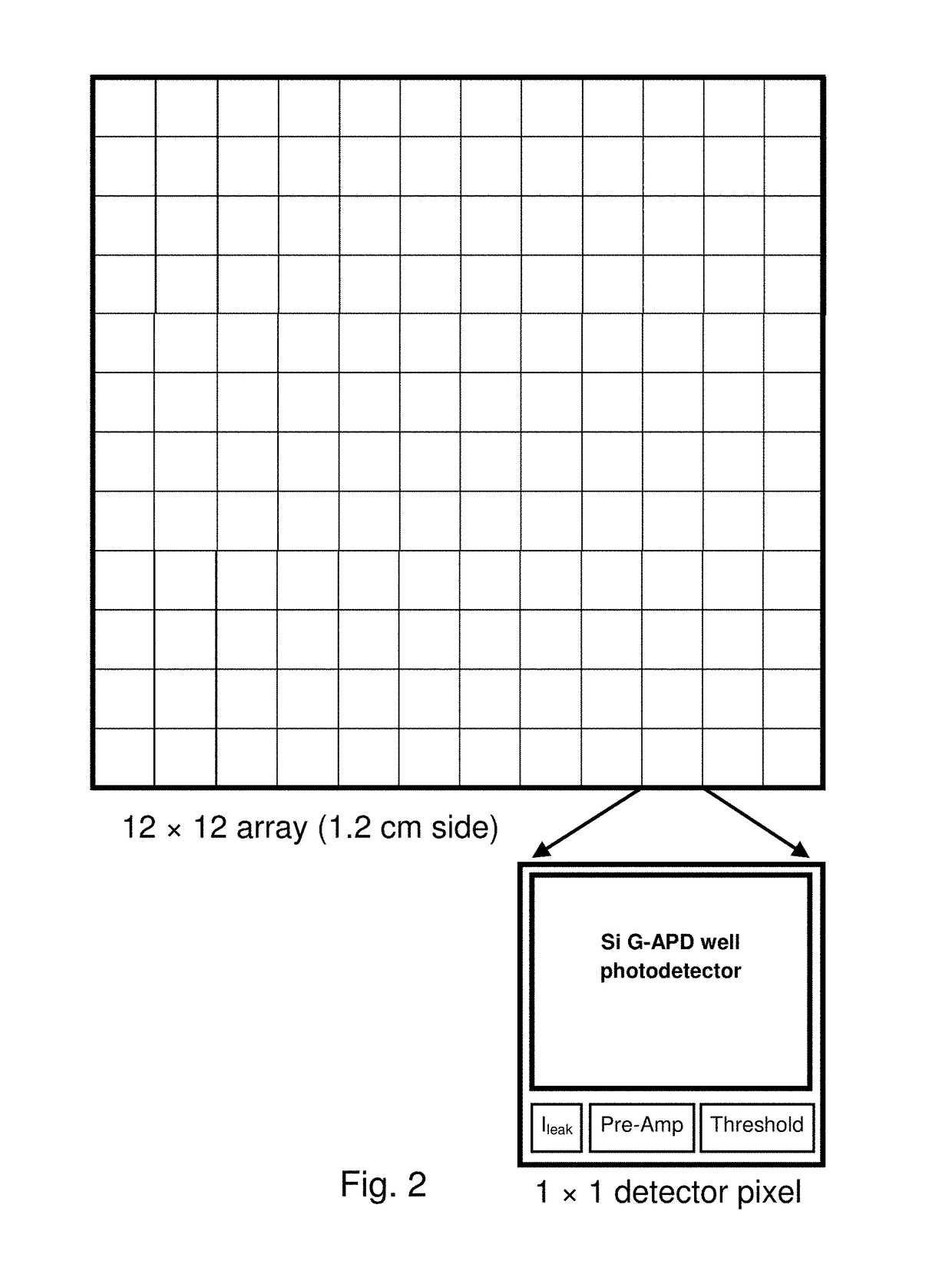
A system and method for imaging gamma- and x-ray, and charged particles sources employing a three dimensional array of scintillation elements arranged surrounding an emission source. According to a preferred embodiment, each element of the array comprises a scintillator element, a solid-state photon detector, and processing electronics to output an electronic signal. The elements may be efficiently packed in both the X-Y plane and stacked in the Z-axis, to provide depth of interaction information. The elements of the array are preferably hierarchically arranged with control electronics provided together for subarray modules (e.g., an n×m×1 module), and synchronization electronics provided at a larger scale. The modules preferably communicate with a control system through a shared addressable packet switched digital communication network with a control and imaging system, and receive control information from that system through the network.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA +3
Method of improving PET (positron emission tomography) image reconstruction quality by constructing virtual DOI (depth of interaction) and corresponding system matrix
InactiveCN108428253AHigh-resolutionUnrestricted geometric distributionReconstruction from projectionLines of responseSystem matrix
The invention discloses a method of improving PET (positron emission tomography) image reconstruction quality by constructing a virtual DOI (depth of interaction) and a corresponding system matrix. The method comprises the following steps: 1) virtual DOIs are divided: a scintillation crystal in a PET detector ring is divided into a plurality of regions which correspond to different DOIs; 2) the detection probability of a virtual DOI is calculated: the virtually-divided DOI regions are paired, and the probability of each pair being detected at a different signal source position is calculated; 3) a virtual LOR (Line of response) event in the virtual DOI is divided: one LOR event in one original pair of crystals is divided to multiple sub events in the virtual DOI; 4) a conventional system matrix is optimized: multiple factors that affect the image reconstruction quality are considered; 5) image reconstruction is carried out: a statistical iterative algorithm is used to reconstruct an image; and 6) a GPU platform is used for distributed operation, and the data processing time can be greatly reduced. Through the method disclosed in the invention, the resolution of PET-class equipment after image reconstruction can be greatly improved, the location of a tumor can be positioned accurately, and important clinical value and significance are achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com