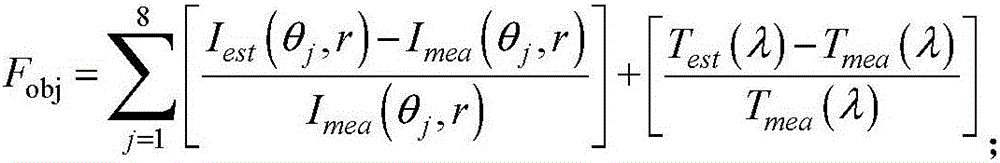Method for synchronous measurement of optical constant and particle size distribution of spherical particles based on multi-angle light scattering-transmission process
A technology of multi-angle light scattering and optical constants, which is applied in the directions of transmittance measurement, scattering characteristic measurement, particle and sedimentation analysis, etc. It can solve the problems of large error in measurement value and weak measurement signal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
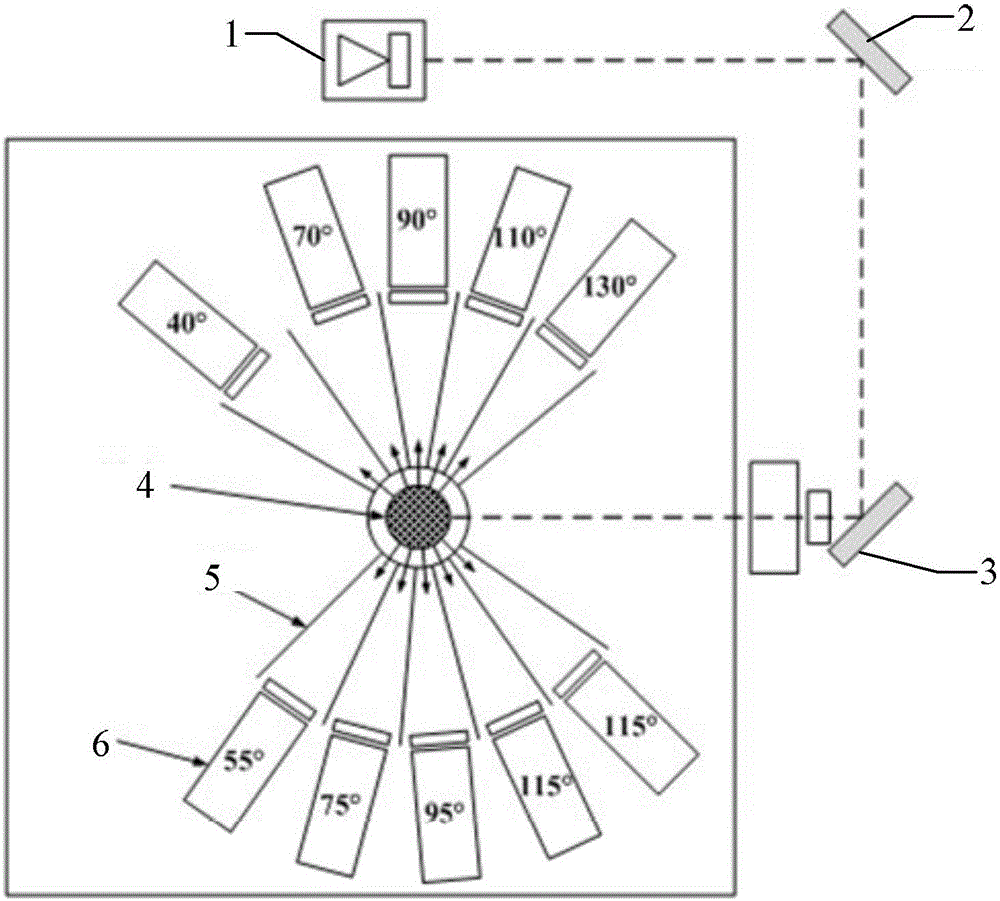
[0021] Specific embodiments 1. The method for simultaneously measuring the optical constant and particle size distribution of spherical particles based on the light scattering-transmission method described in this embodiment, the specific operation steps of the method are:
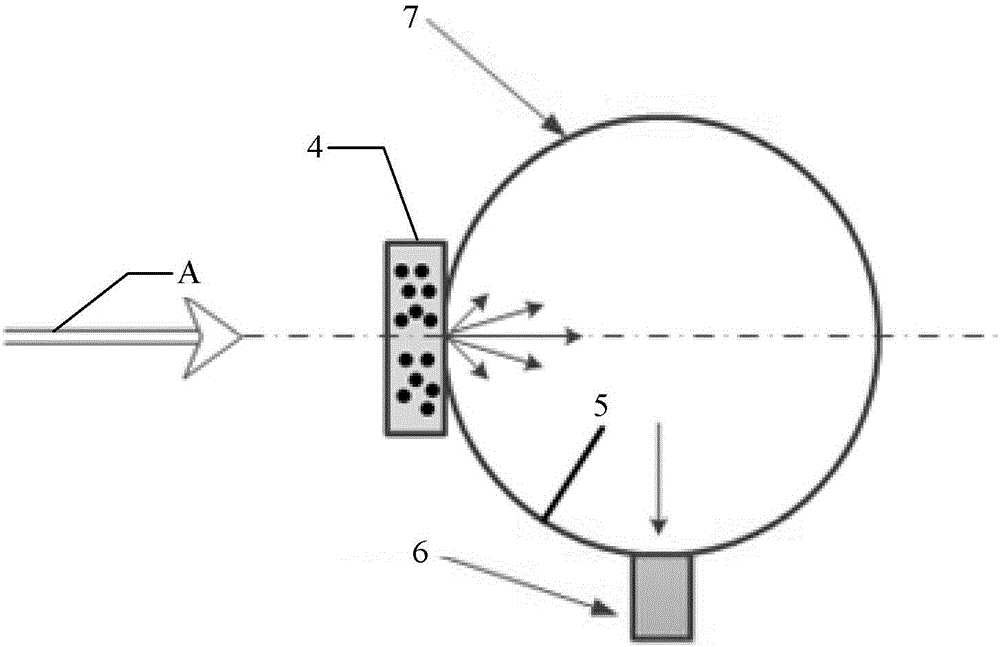
[0022] Step 1: Put the particles to be tested at the same concentration into a semi-cylindrical first sample container with a radius r and a second sample container with a thickness L, so that the sample particles to be tested in the two sample containers are in a suspended state ;
[0023] Step 2: Using the wavelength λ, the continuous steady-state laser light vertically irradiates the arc-shaped surface of the first sample container with a radius of r along the diameter direction of the first sample container, and is incident on the to-be-measured surface in the first sample container. The sample particle system, the scattered light is transmitted and output along the arc-shaped surface of the first samp...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific embodiment two, this embodiment will further explain embodiment one, the inverse problem in step 3 and step 6 is realized by the improved quantum particle swarm algorithm, and the improved quantum particle swarm algorithm includes the following steps:
[0035] Step A. Input system control parameters, namely: particle population size N s , the search space of the problem R=[low i , high i ], the maximum number of iteration steps N t , the dimension N of the problem and the maximum tolerance ε allowed by the objective function o the value of; i=1,2,...,N;
[0036] Step B. Using the chaos theory model in the search space R, for each particle position X i Initialize and evaluate the position of each particle and calculate the corresponding objective function F obj (X i ); Then, take the position of the current particle as the optimal position of the individual particle history P i ;Finally, find the particle with the smallest objective function value of the ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0046] Specific implementation mode three. This implementation mode further explains the implementation mode one. The specific method for obtaining the radiation intensity field in the calculation domain in step four is:
[0047] The scattered light intensity and spectral hemispherical transmittance were calculated using the following Mie theoretical equation:
[0048] I ( Θ , r ) = N ∫ 0 χ m a x I ( Θ , r , χ ) f ( χ ) d χ
[0049] I ( Θ , r , χ ) = I 0 λ 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com