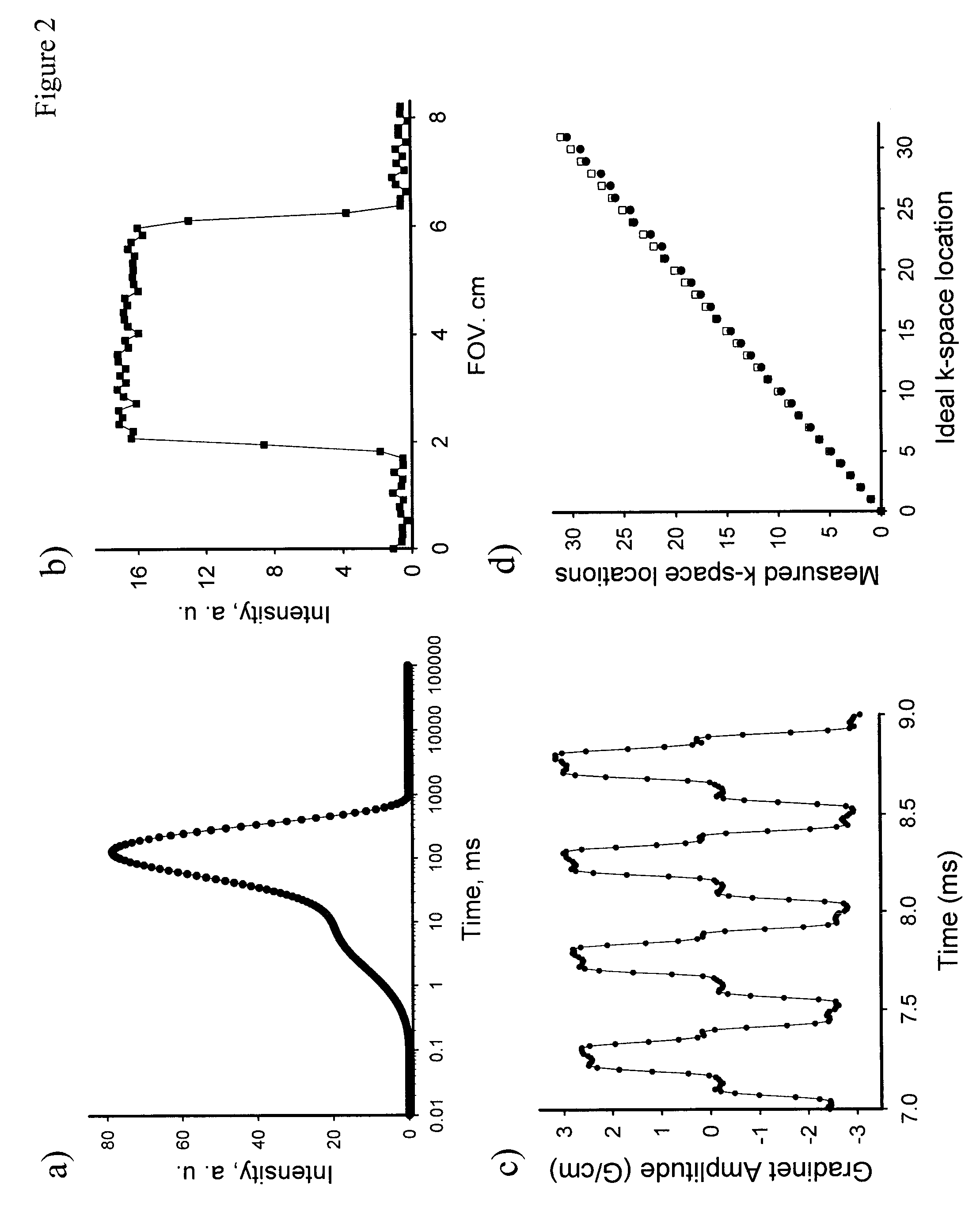
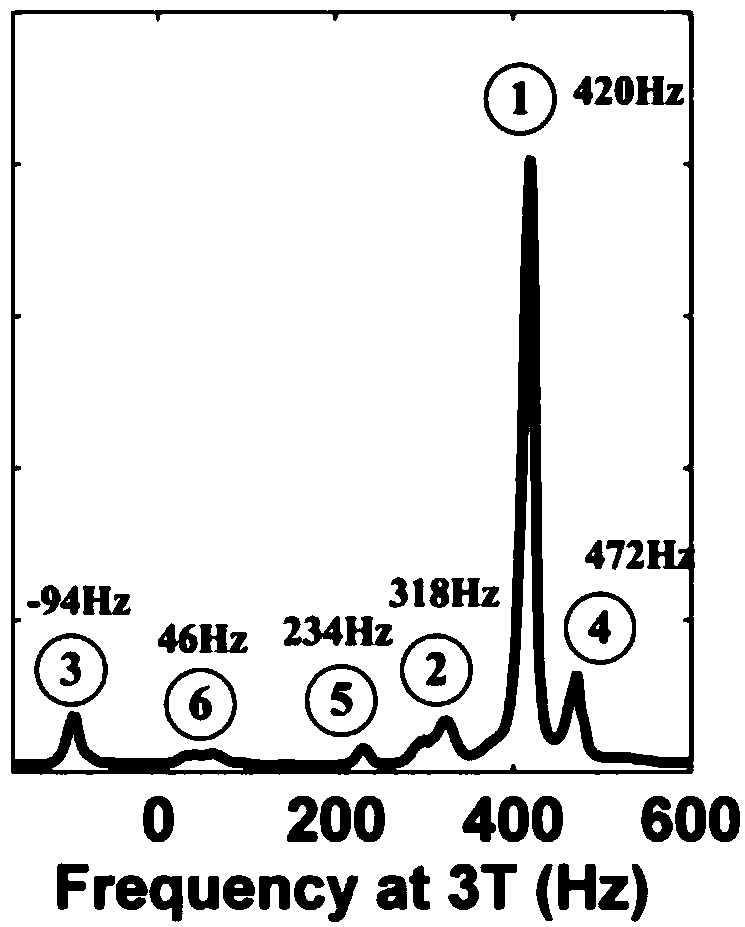
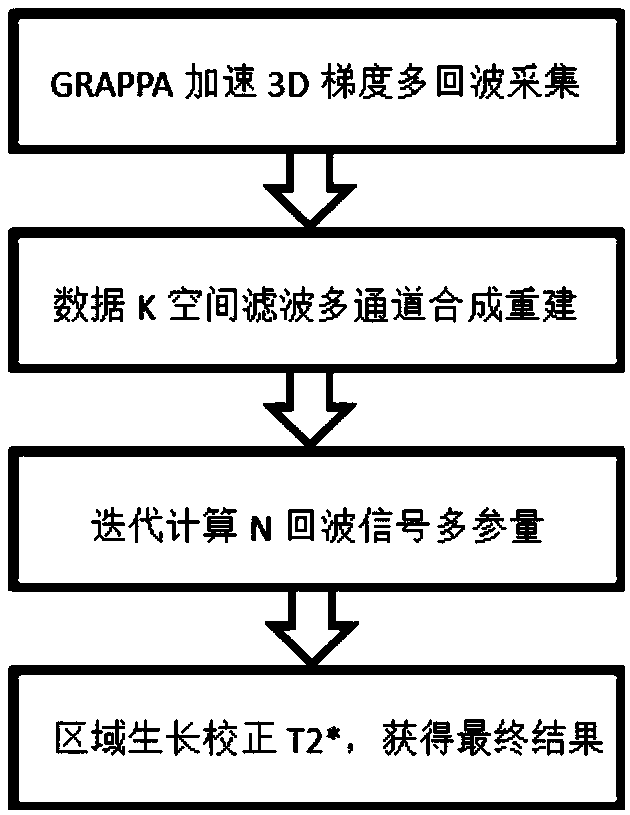
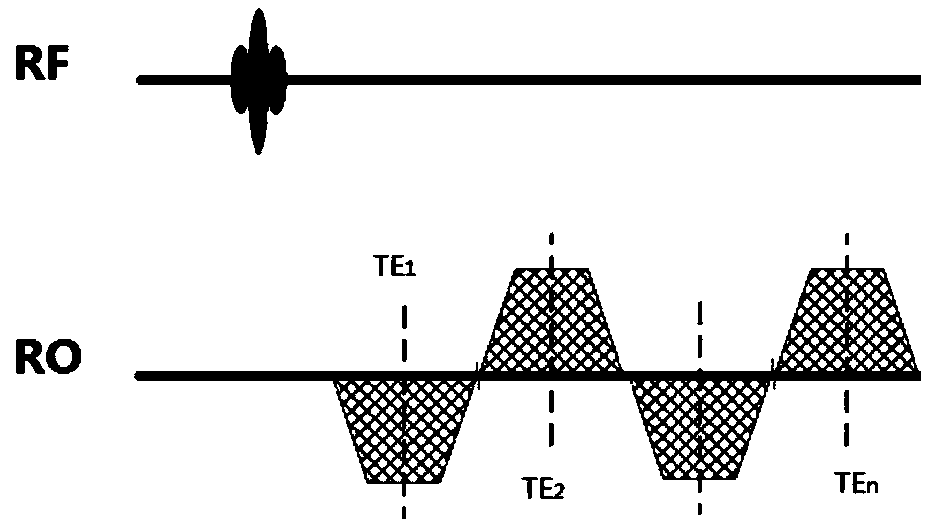
Patents
Literature
135 results about "Multi echo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
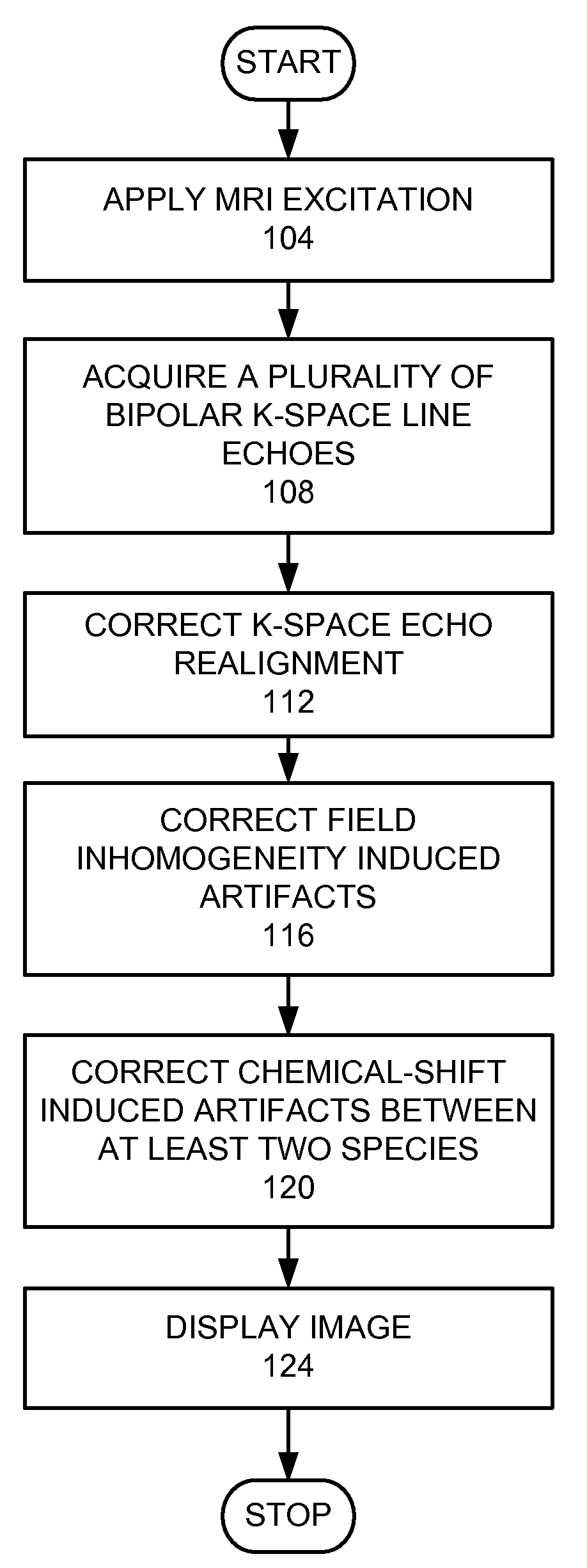
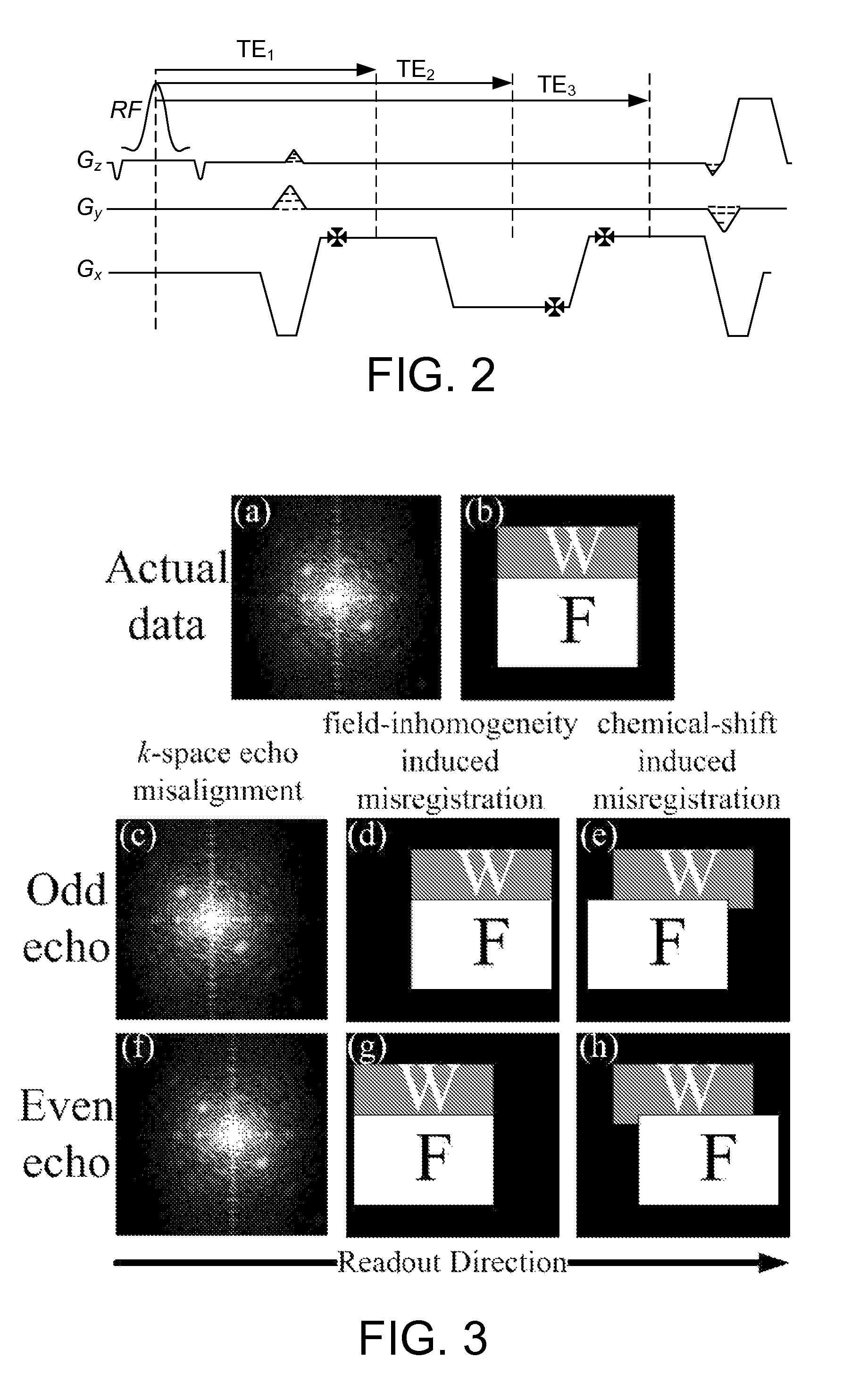
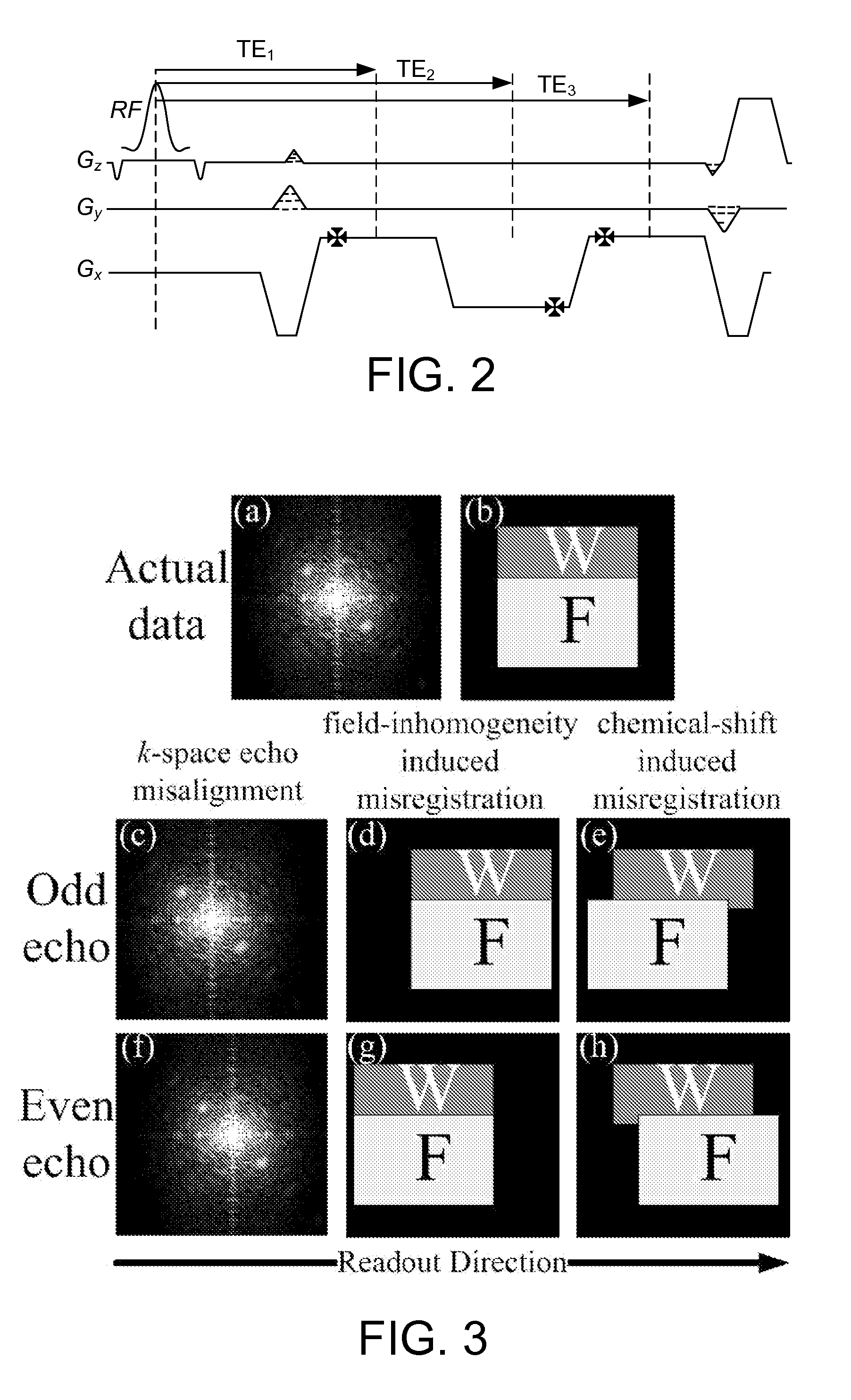
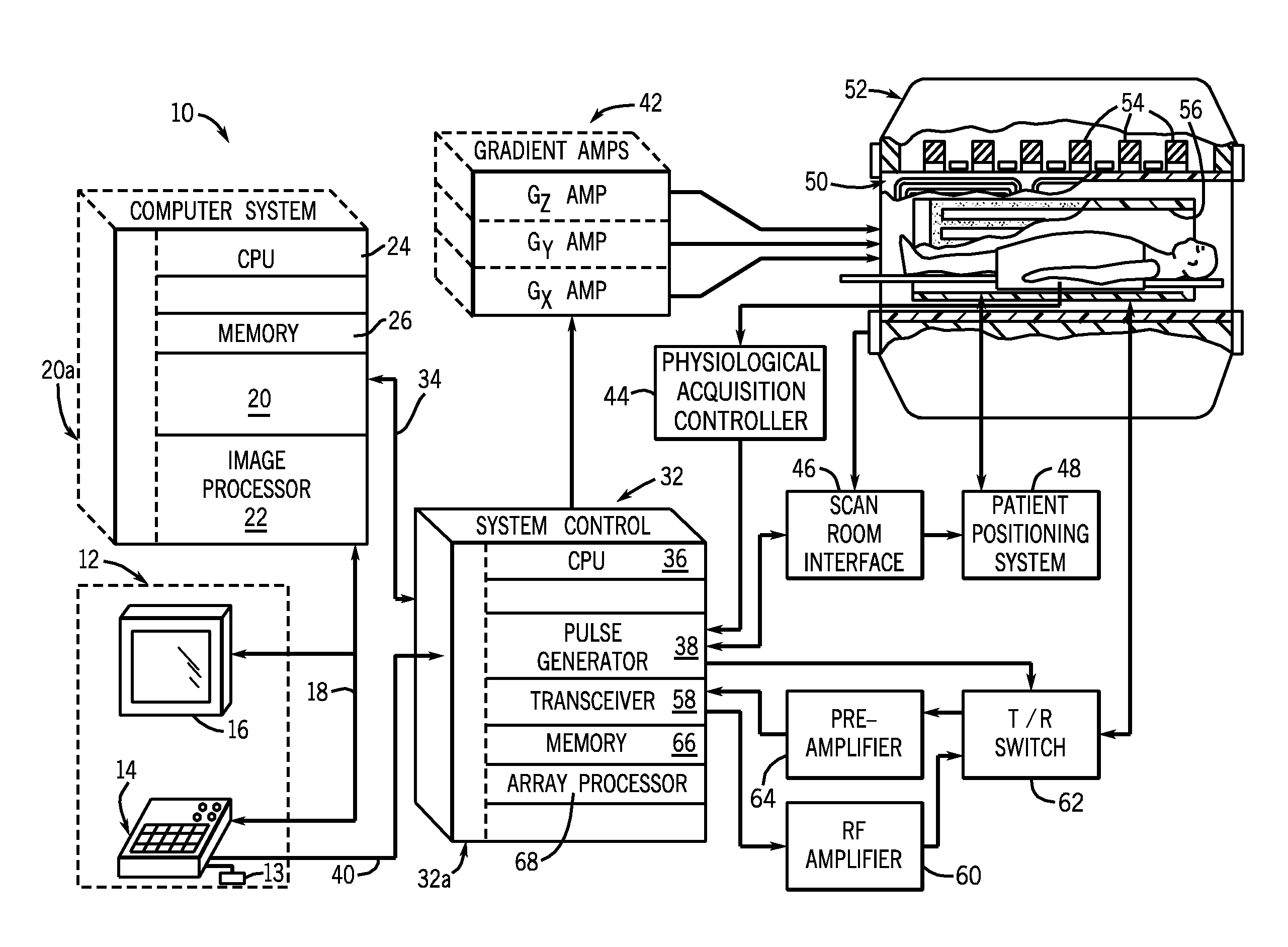
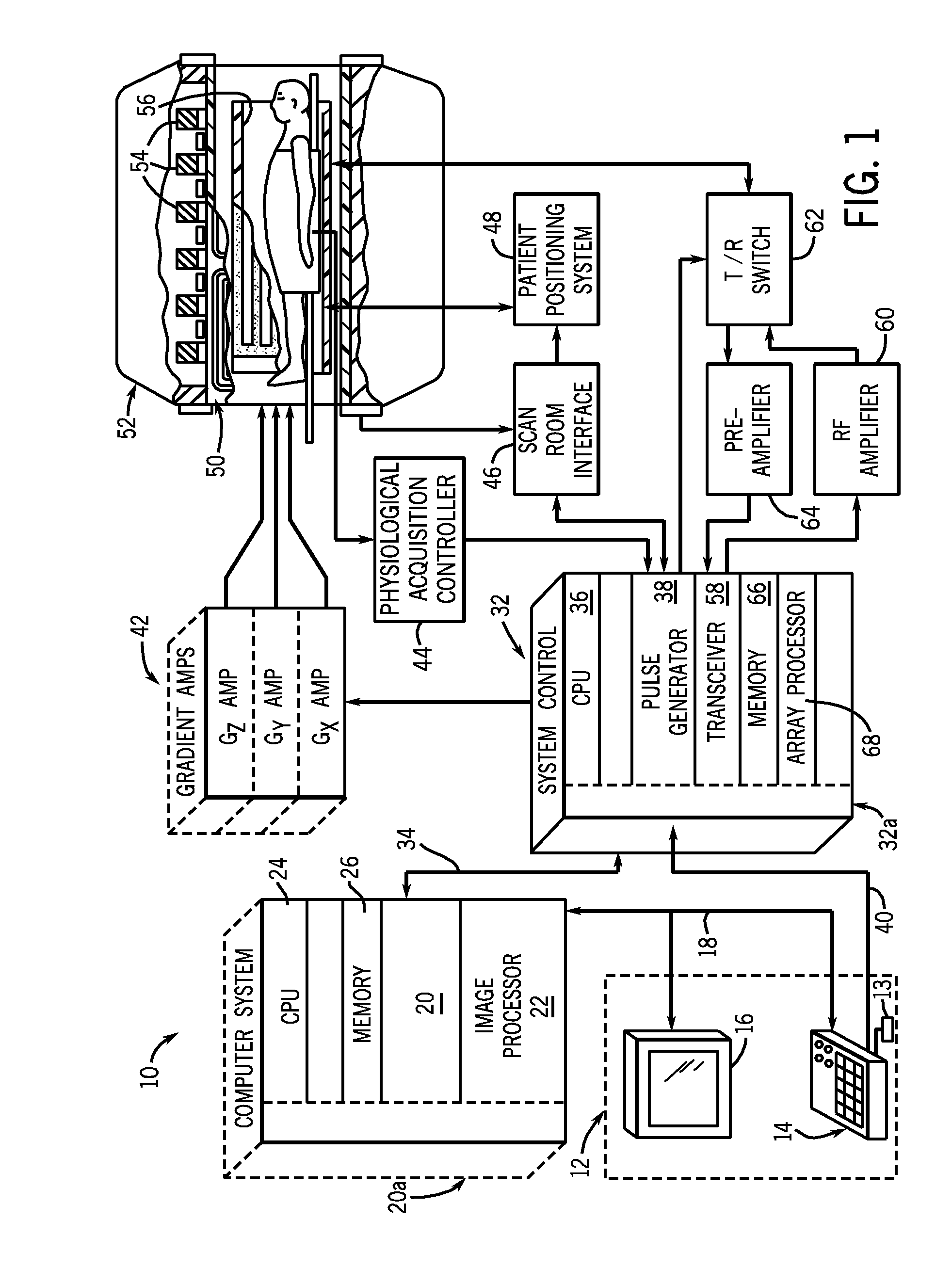
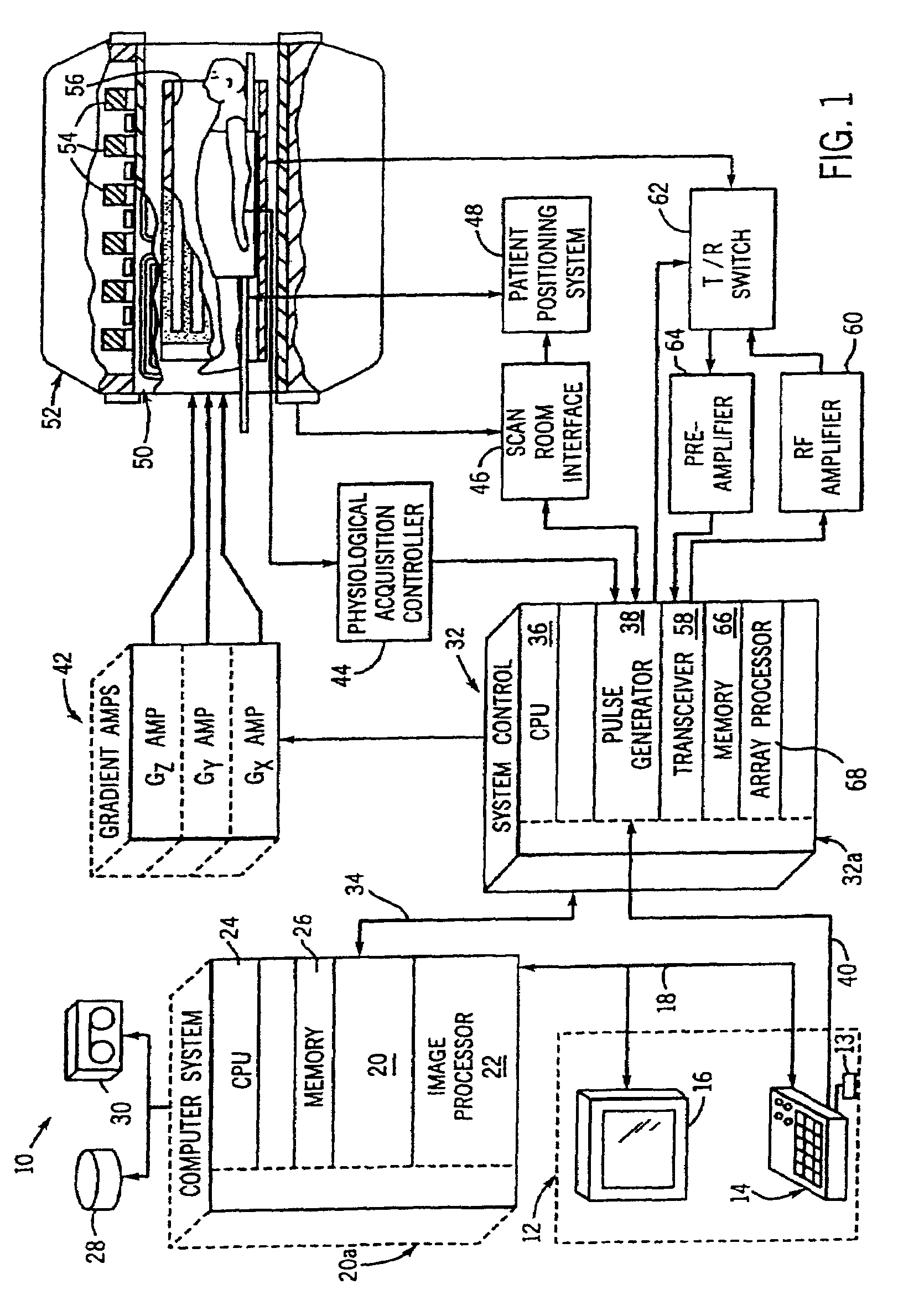
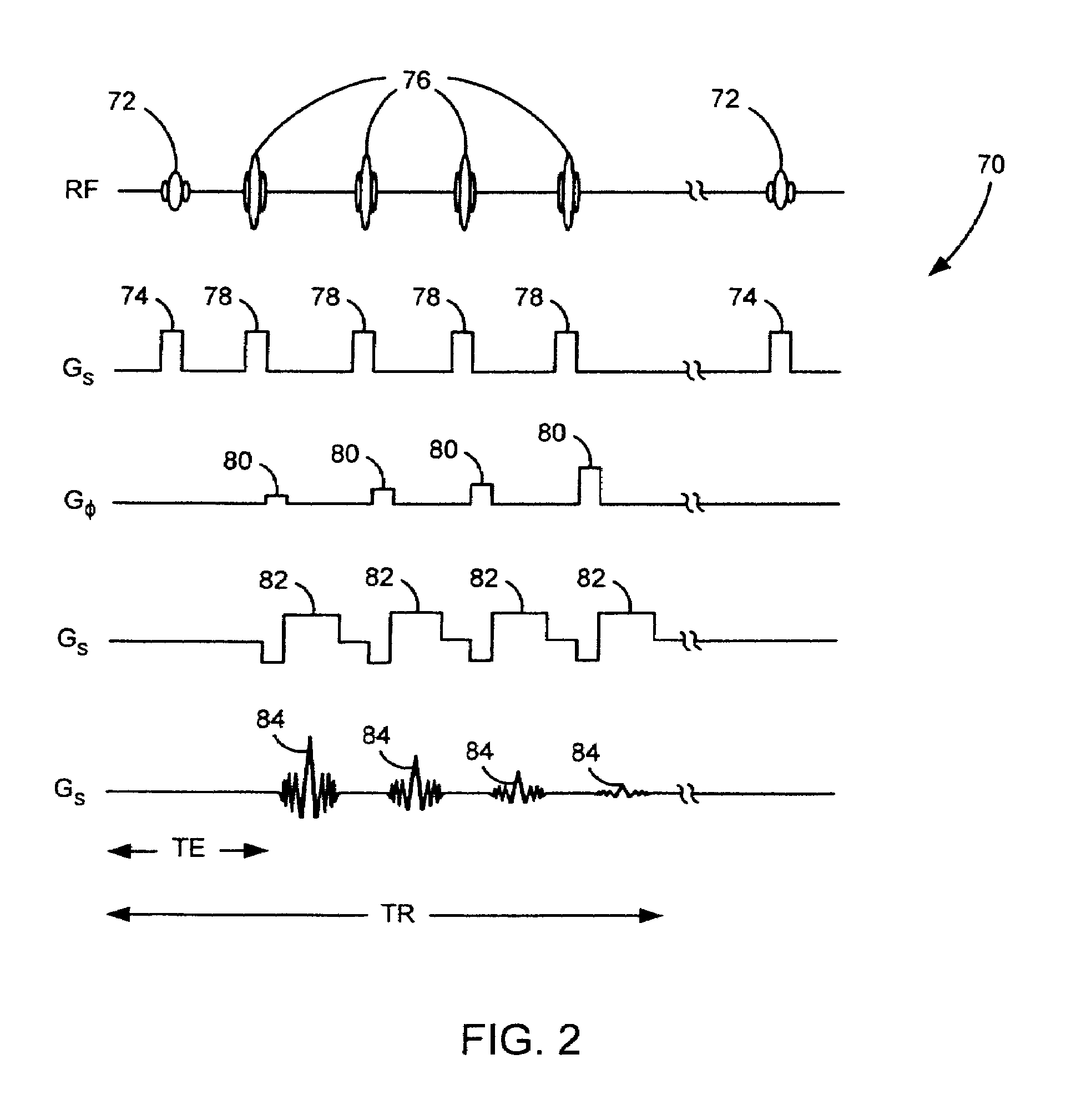
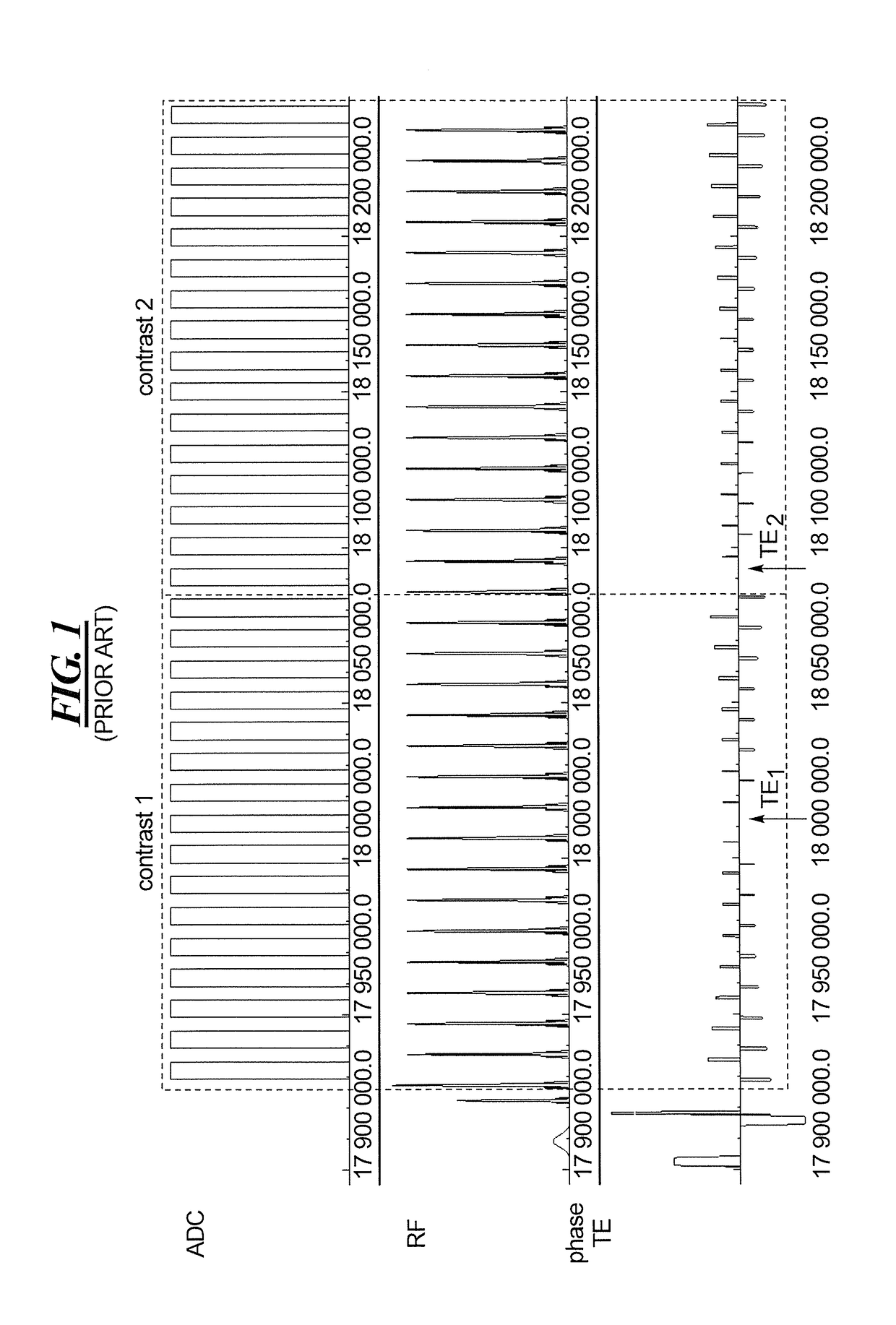
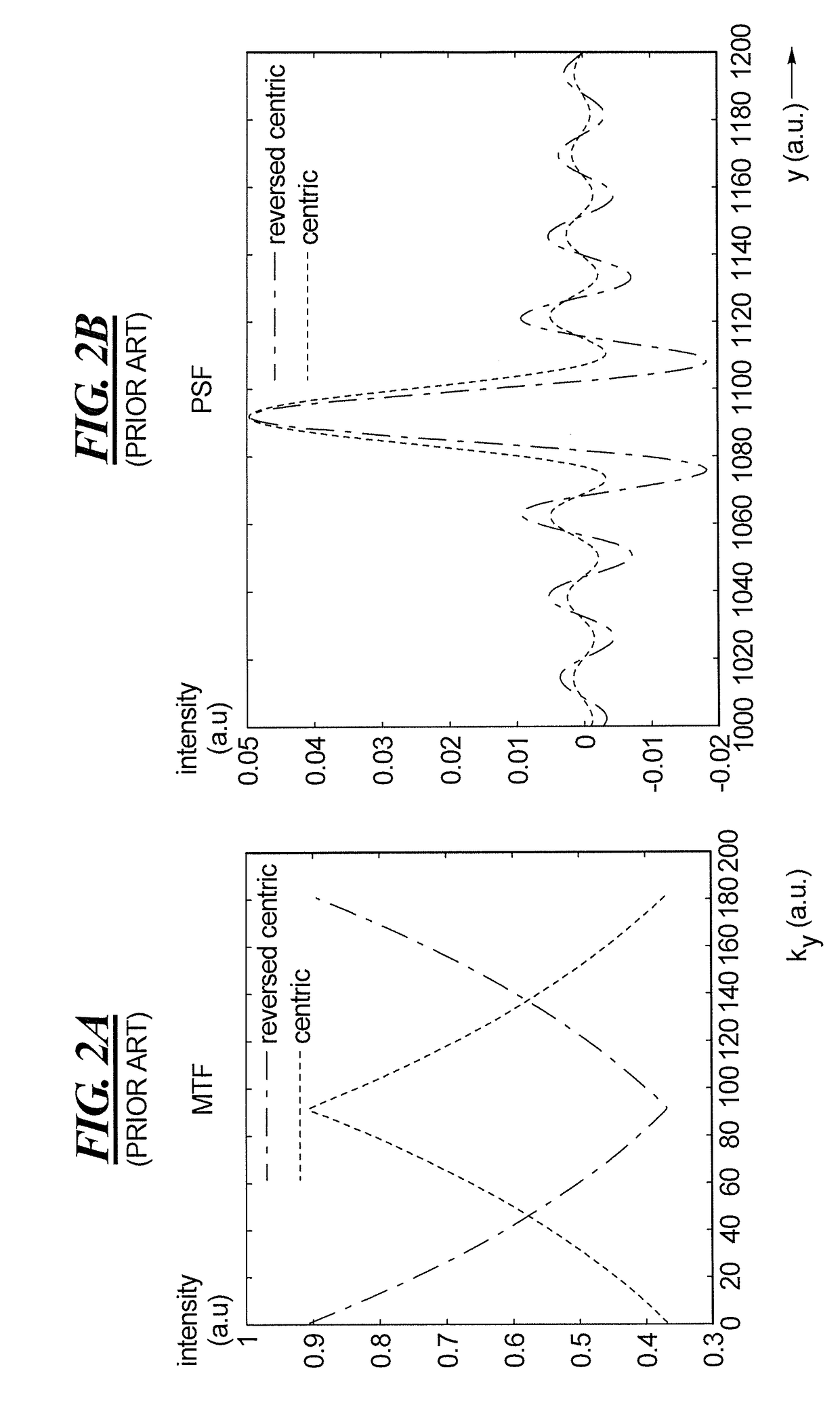
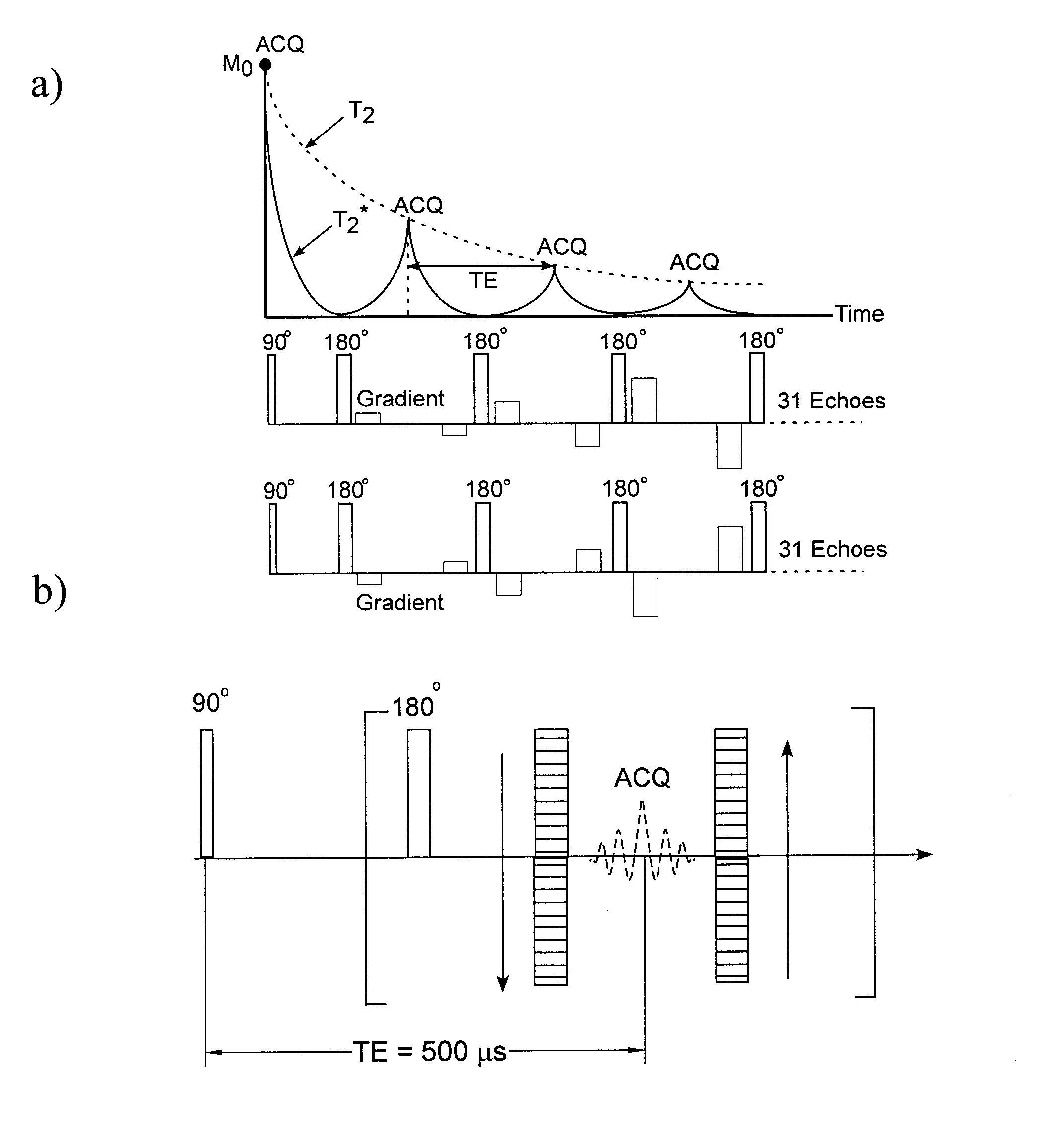
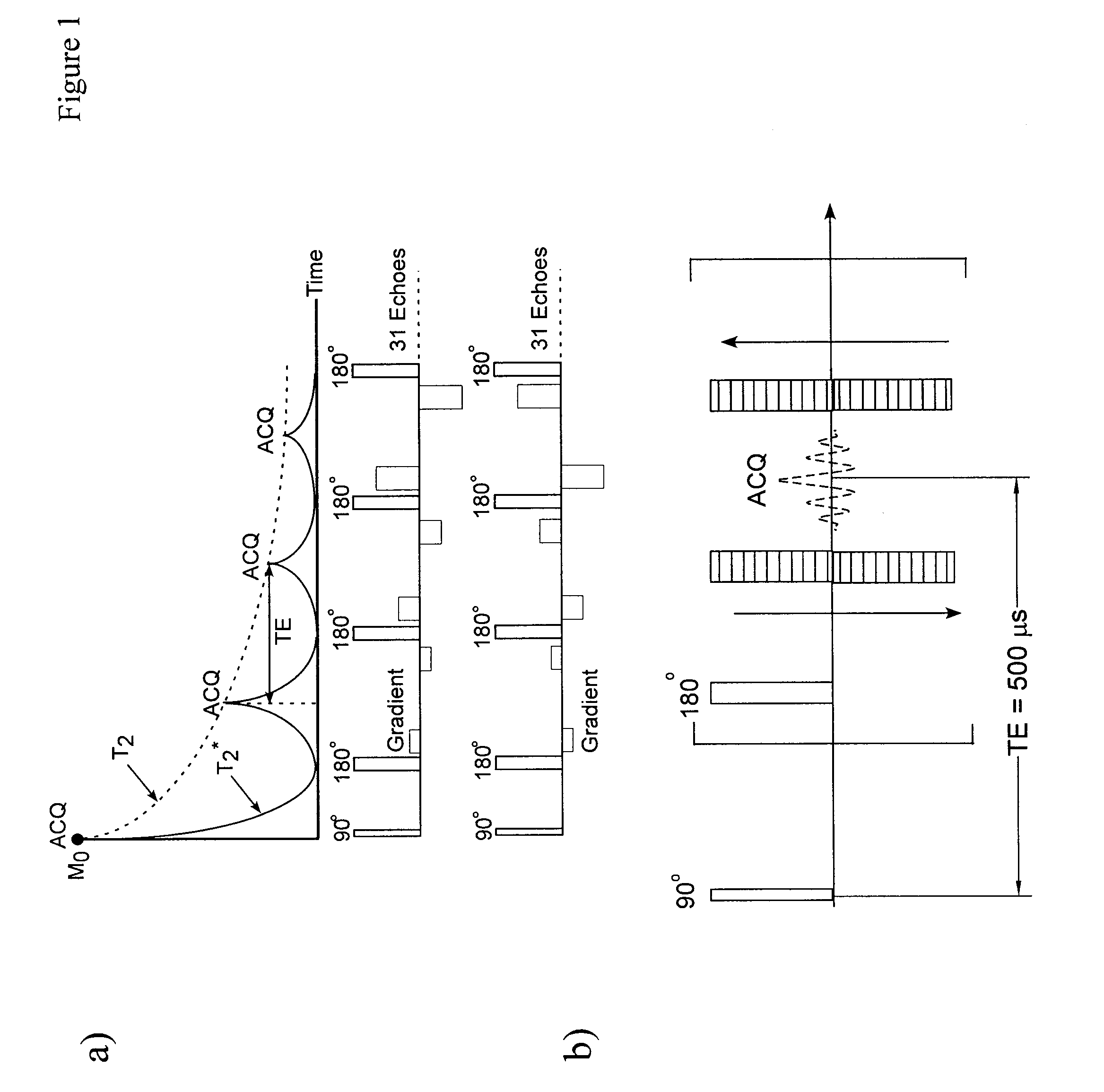
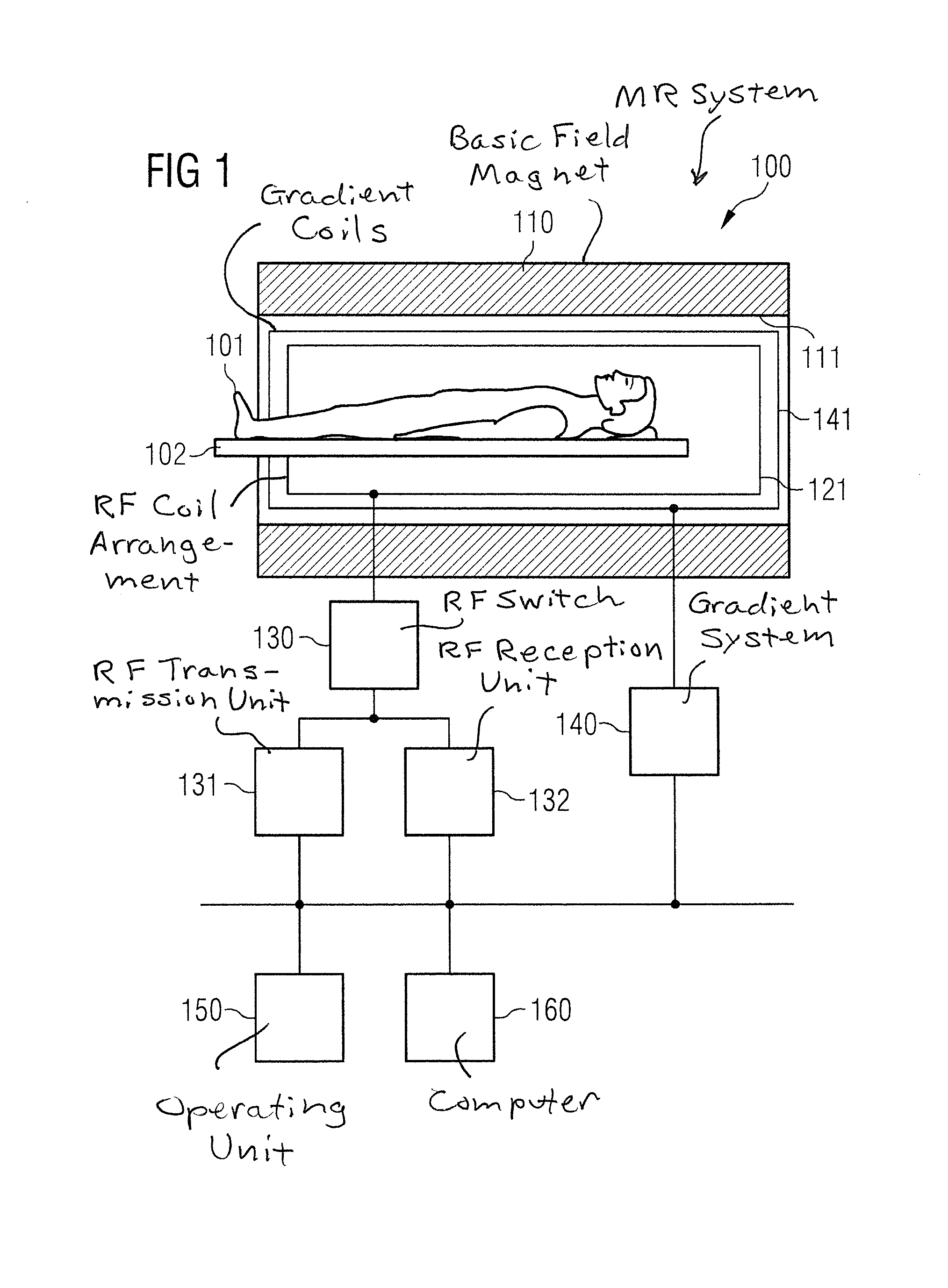
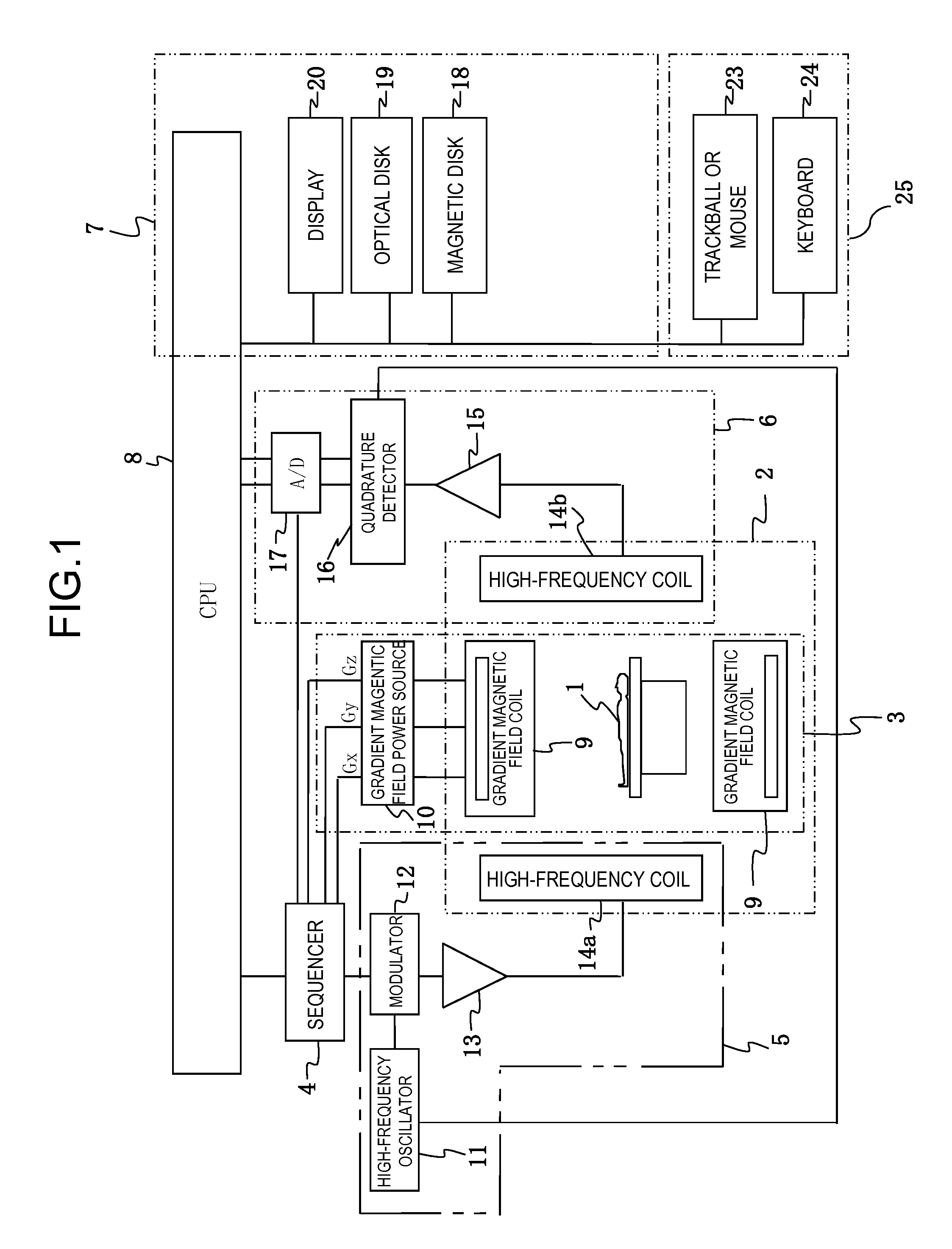
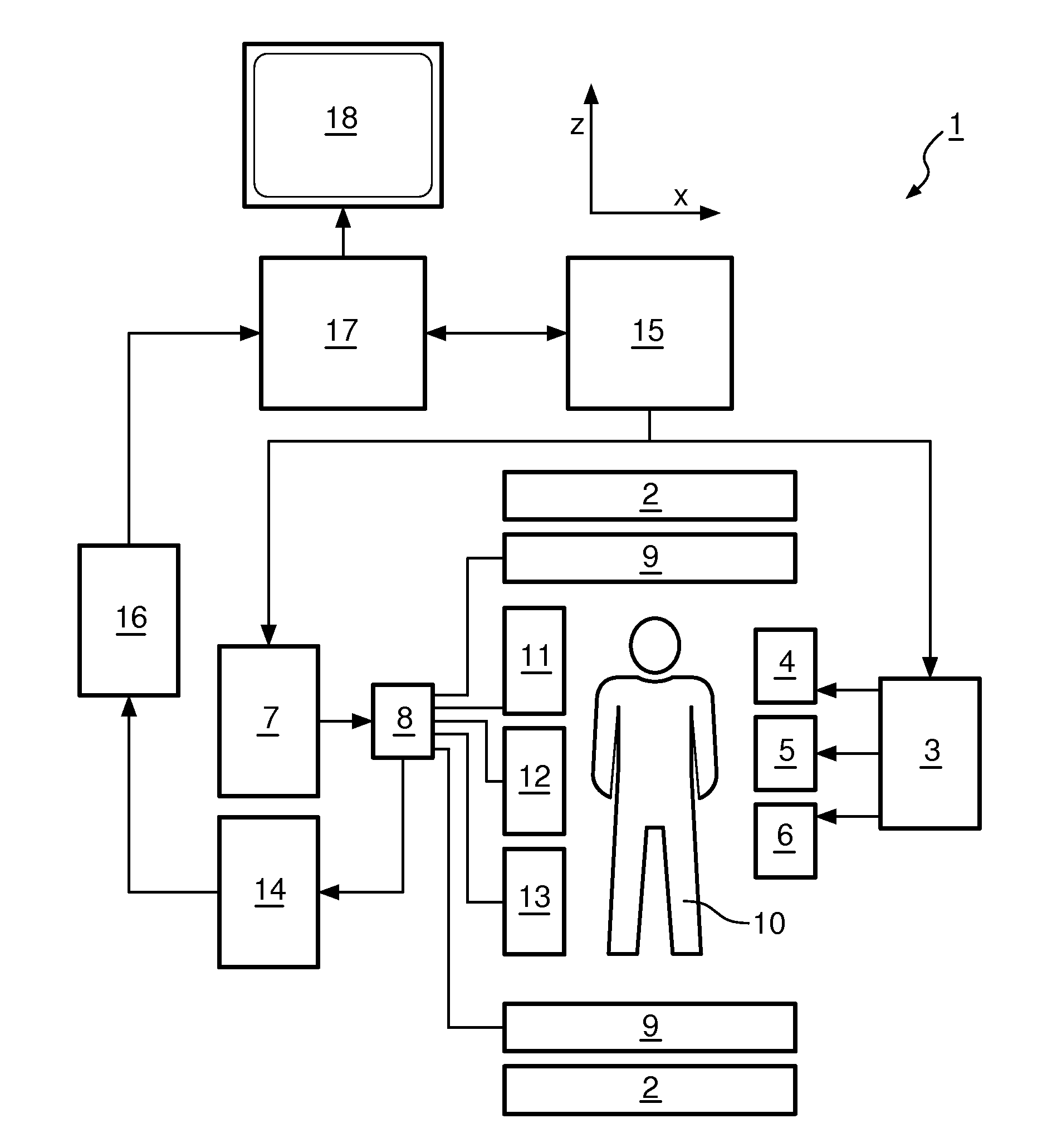
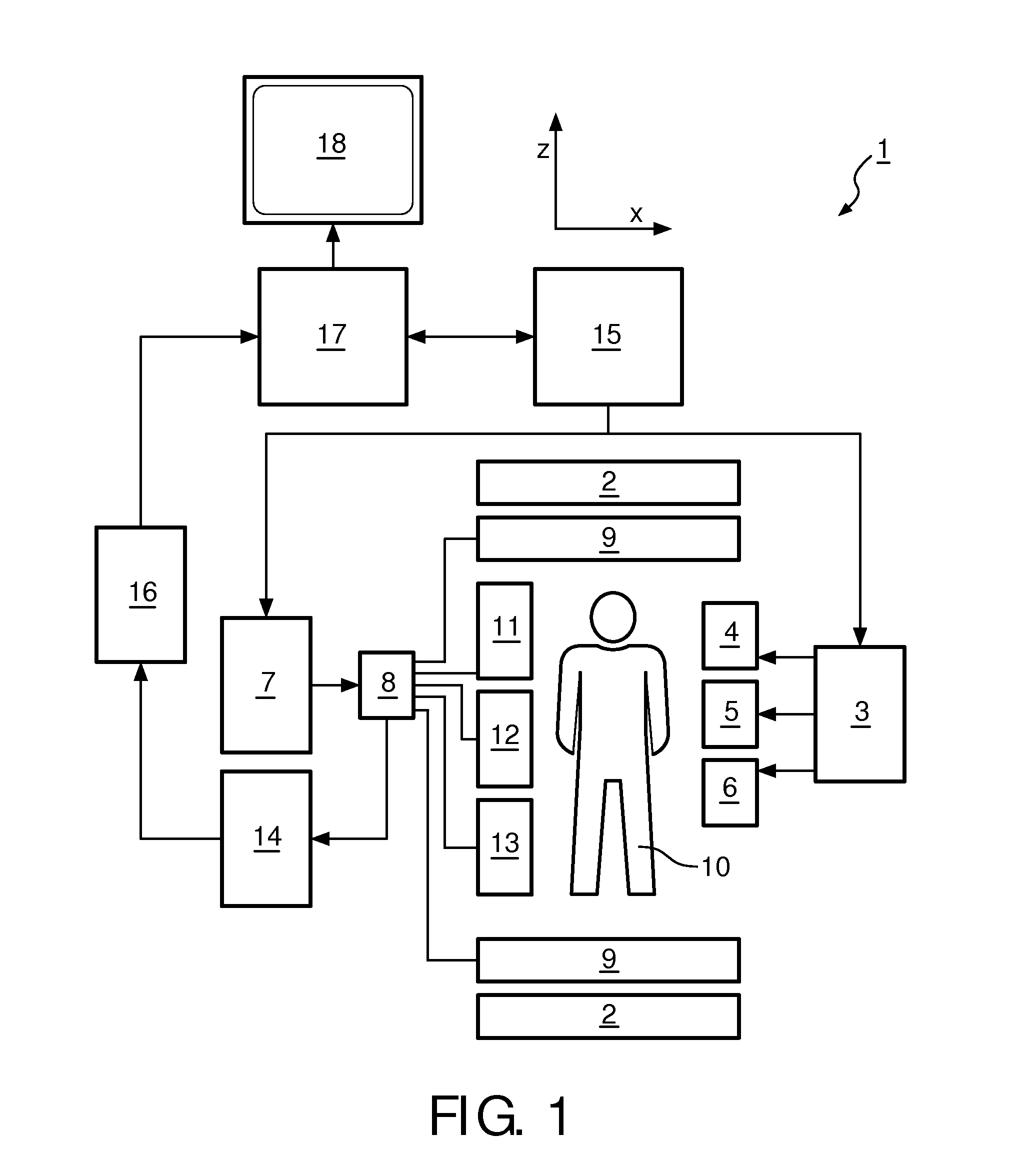
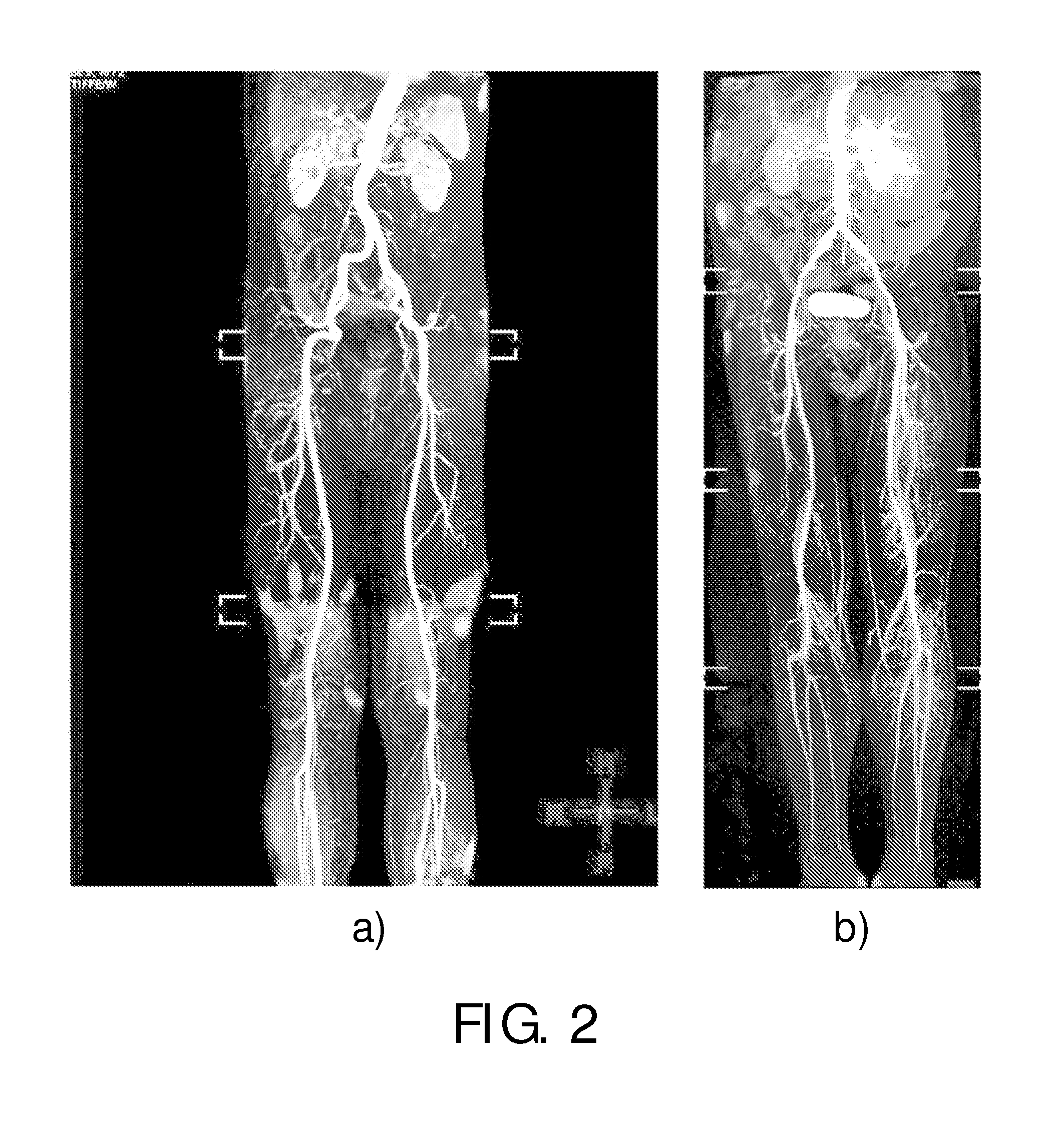
Magnetic resonance imaging with bipolar multi-echo sequences
ActiveUS7777486B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionProton magnetic resonanceResonance excitation
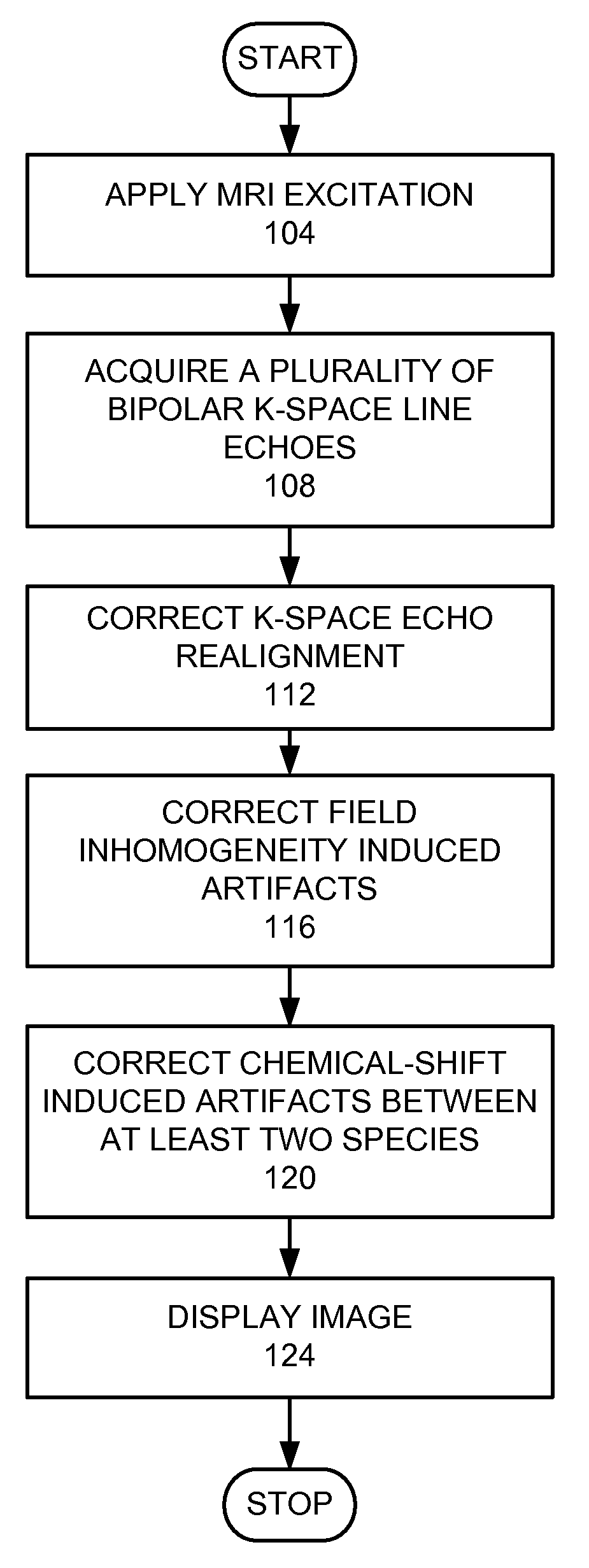
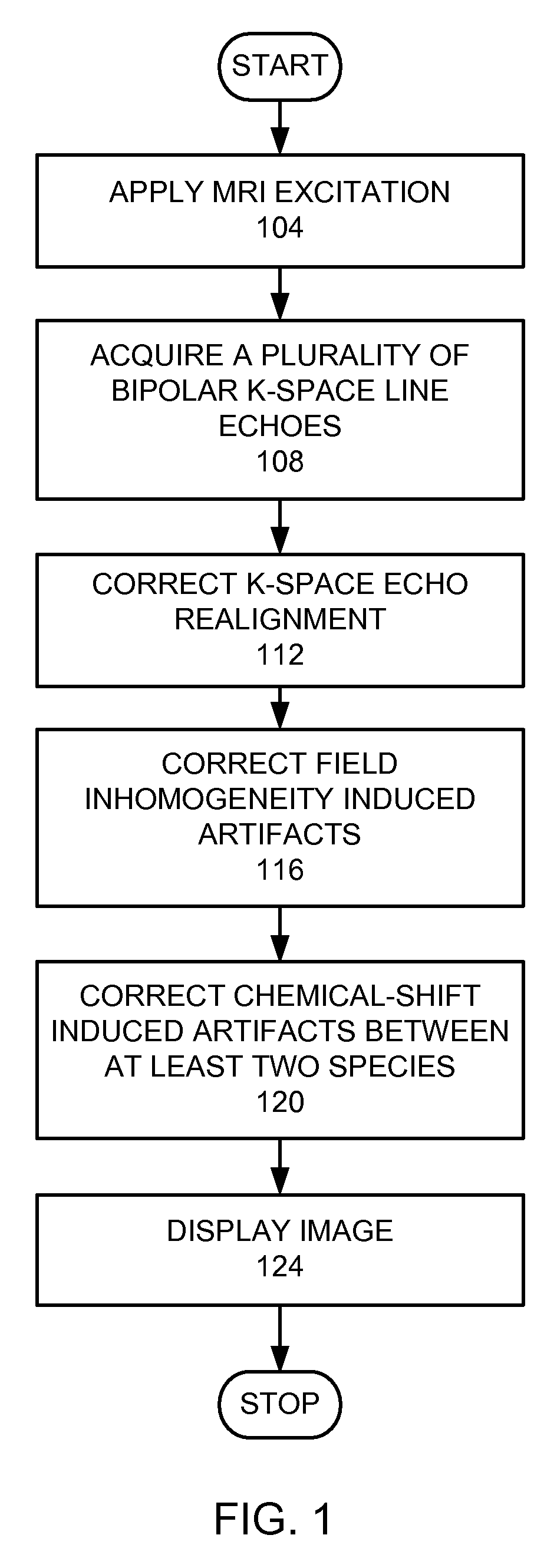
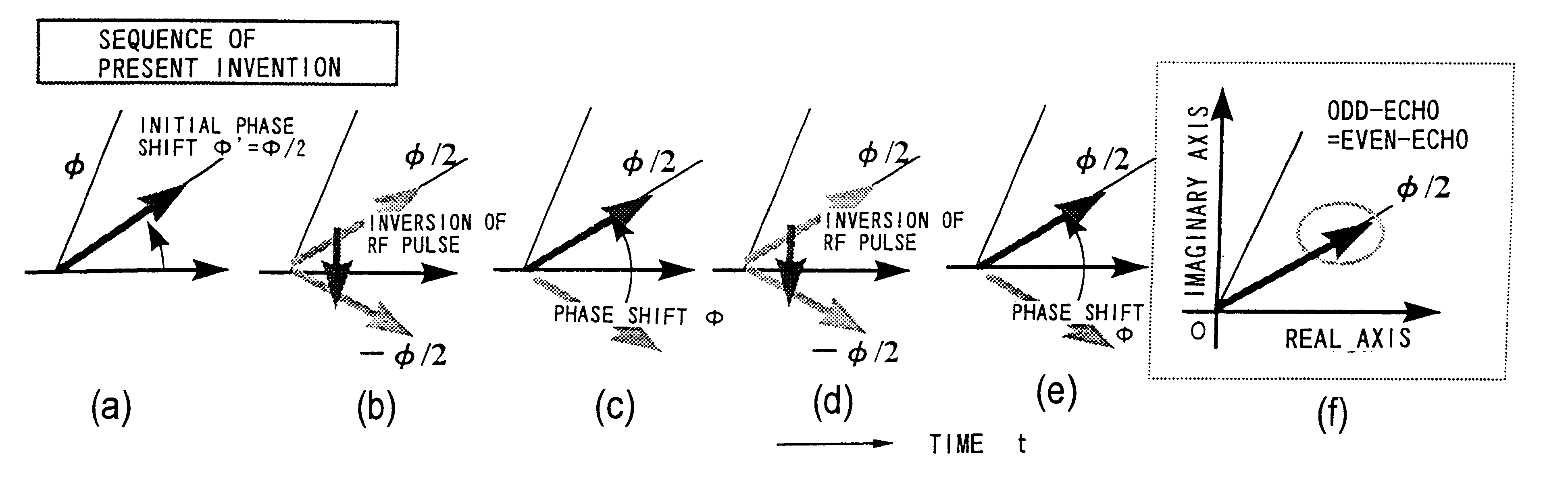
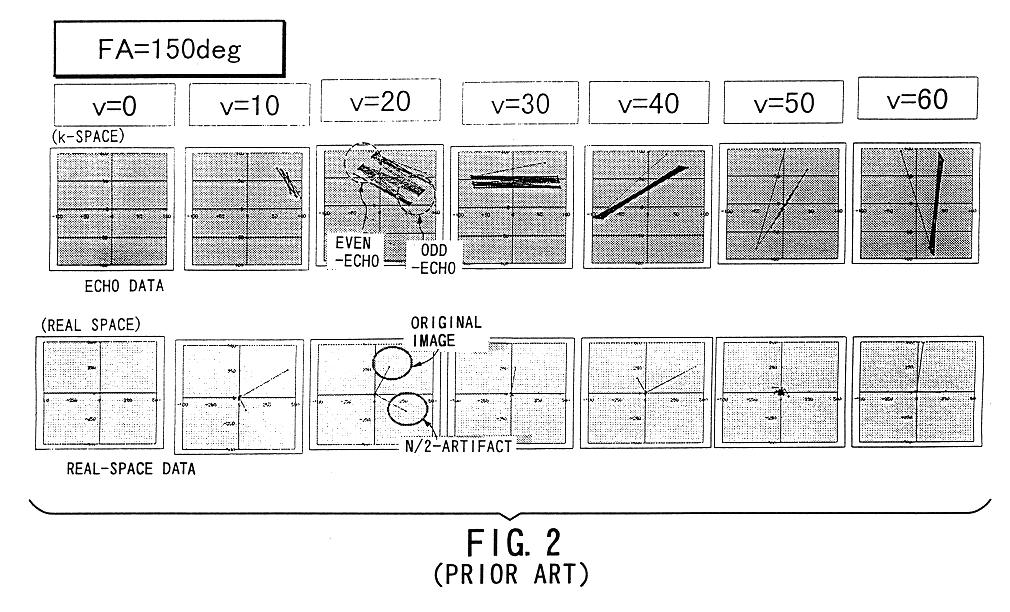
A method for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is provided. A magnetic resonance excitation is provided. A plurality of k-space echoes is acquired bi-directionally wherein at least one echo is an even echo acquired in a first direction and at least one echo is an odd echo acquired in a second direction opposite from the first direction. K-space echo realignment is corrected between the even and odd echoes. Field inhomogeneity induced artifacts are corrected. Chemical shift induced artifacts between at least two species are corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
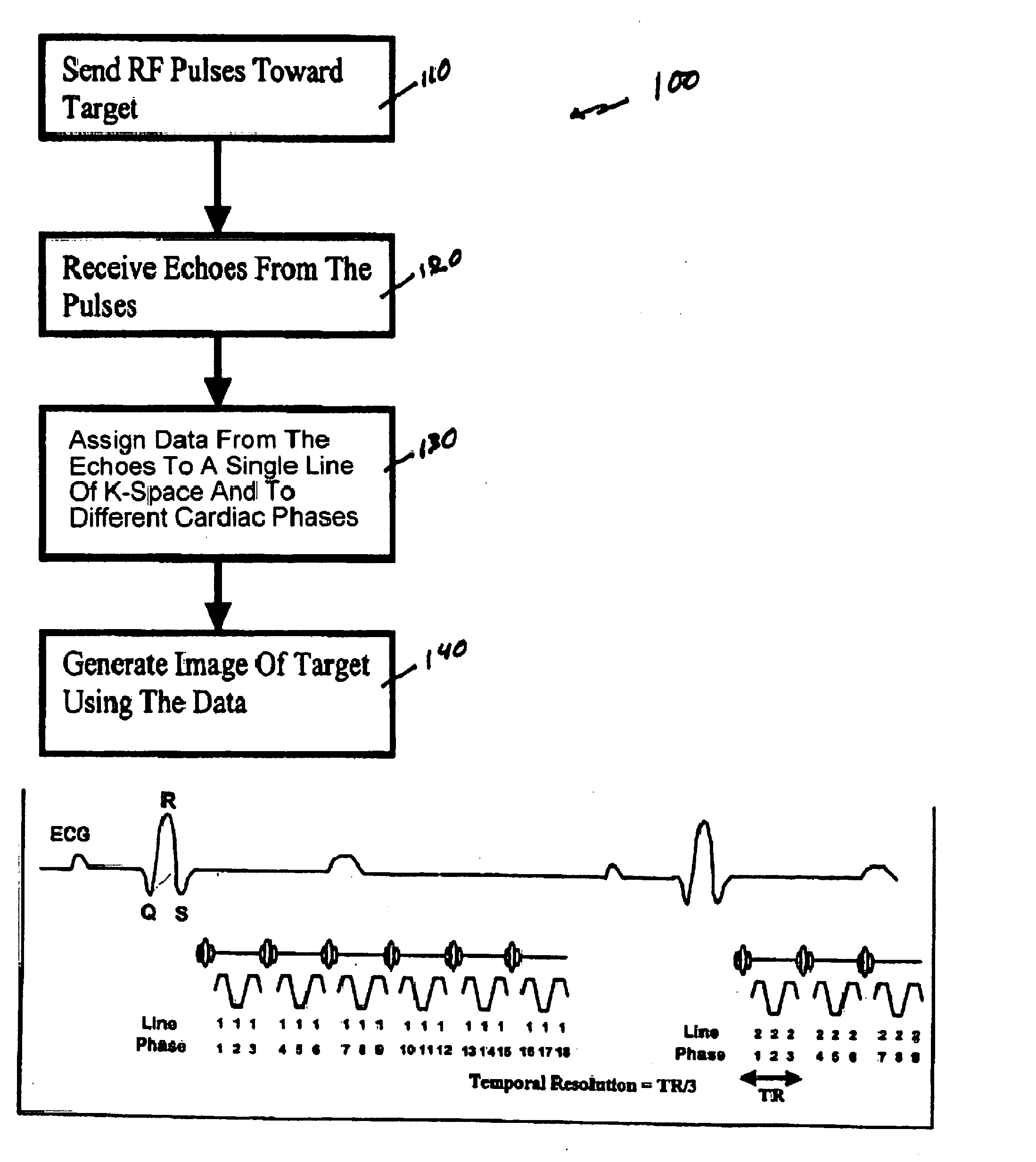
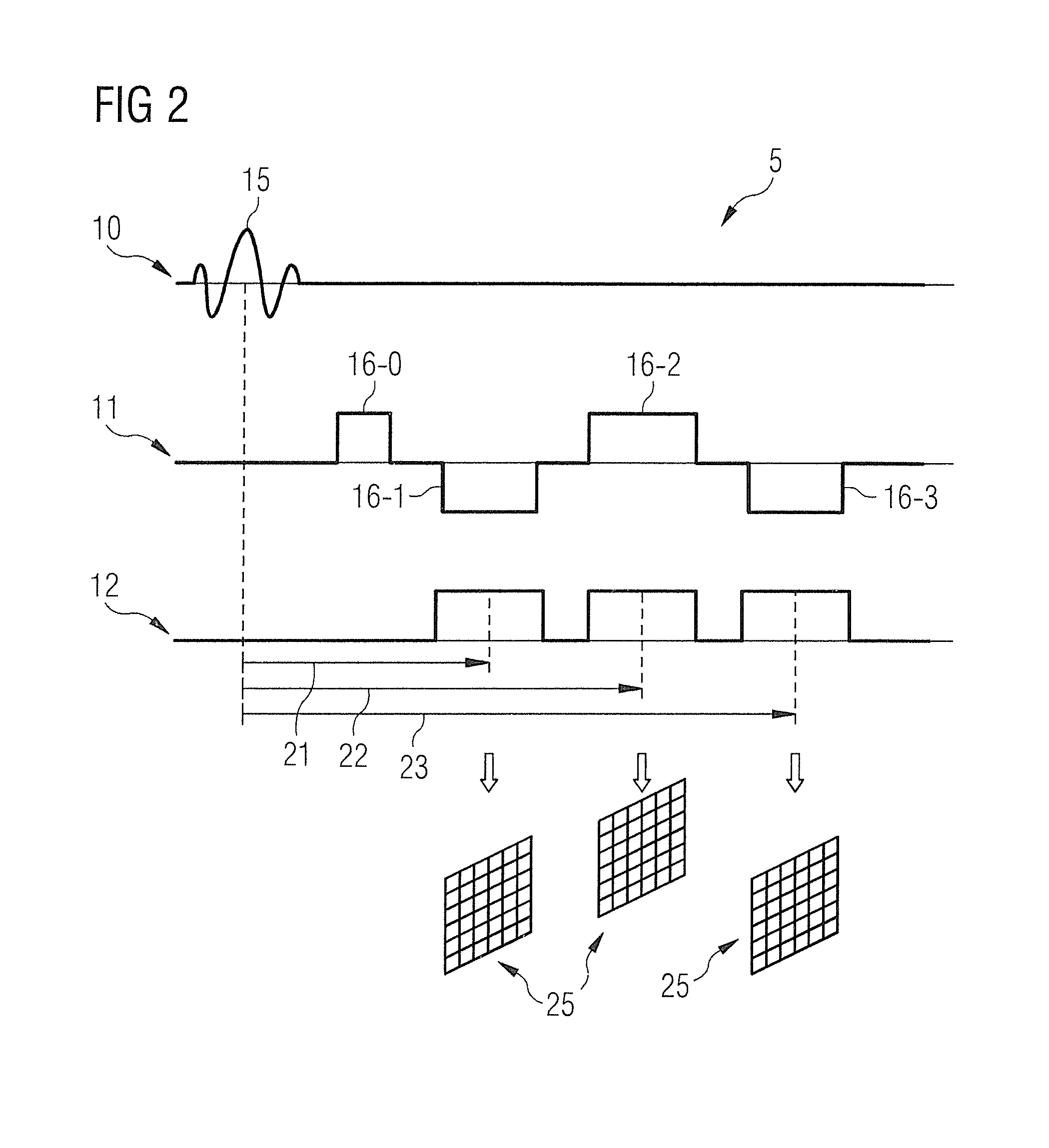
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveUS20060161060A1Faster and accurate perfusion mapImprove time resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac phaseRadio frequency
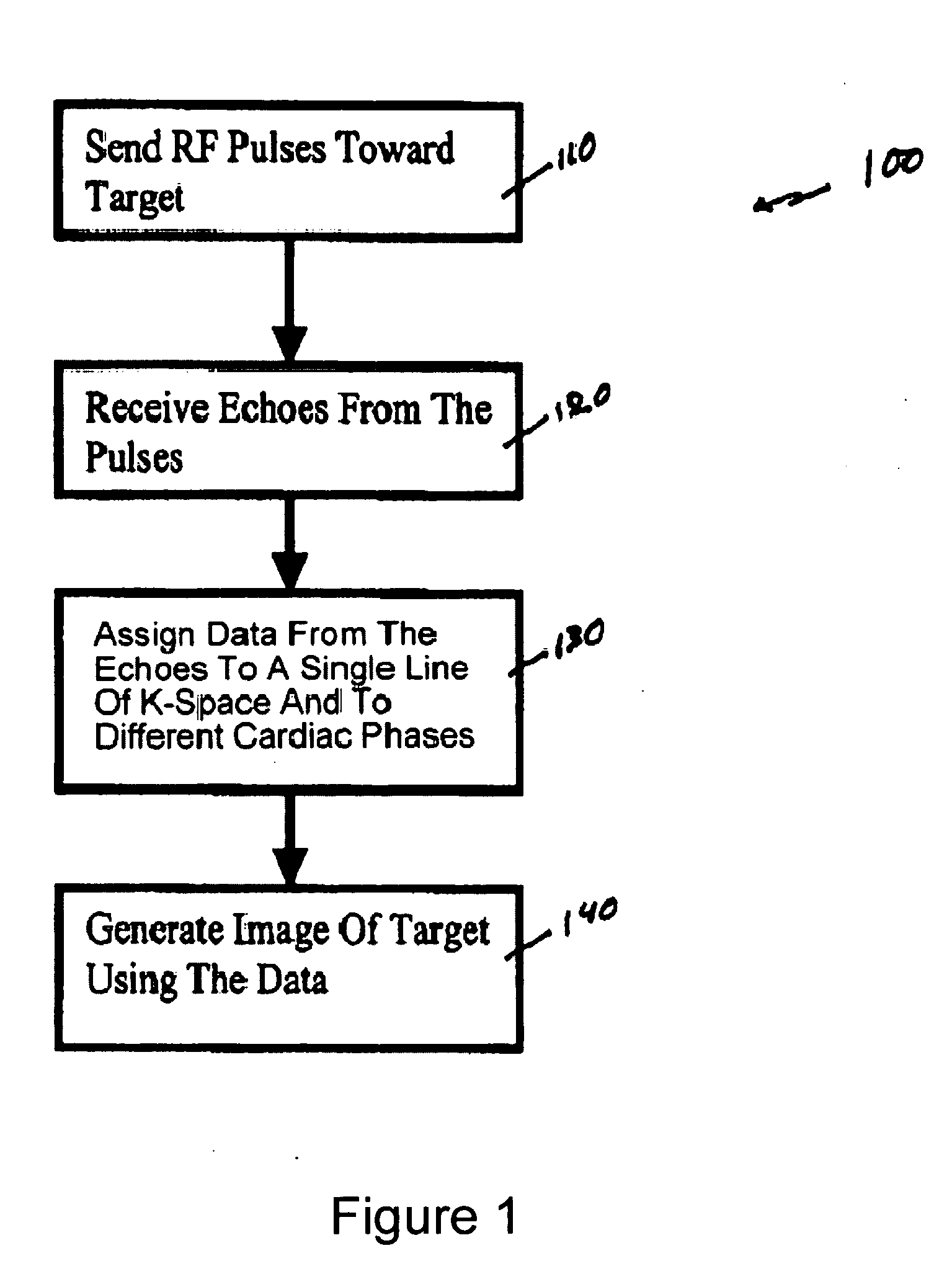
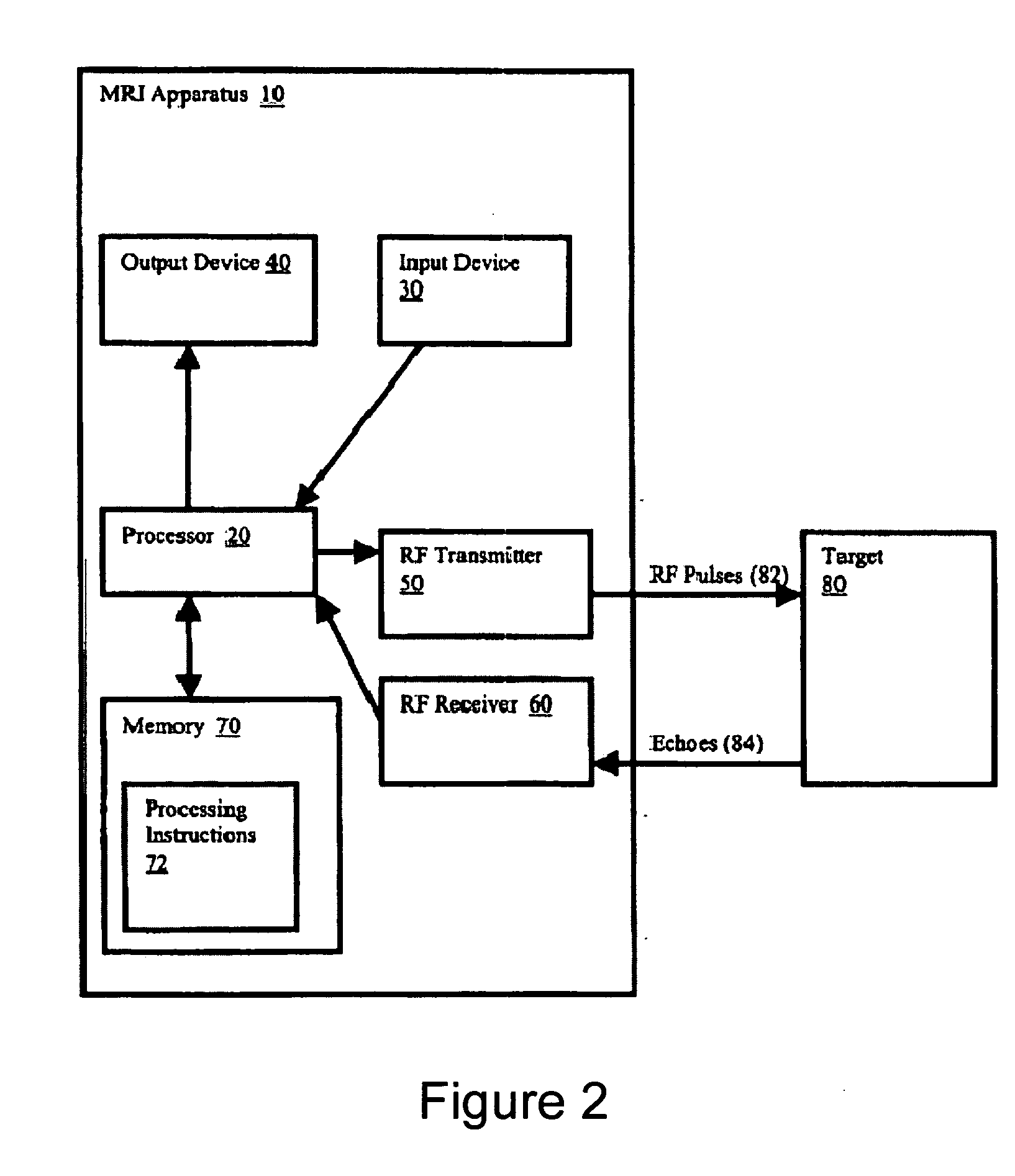
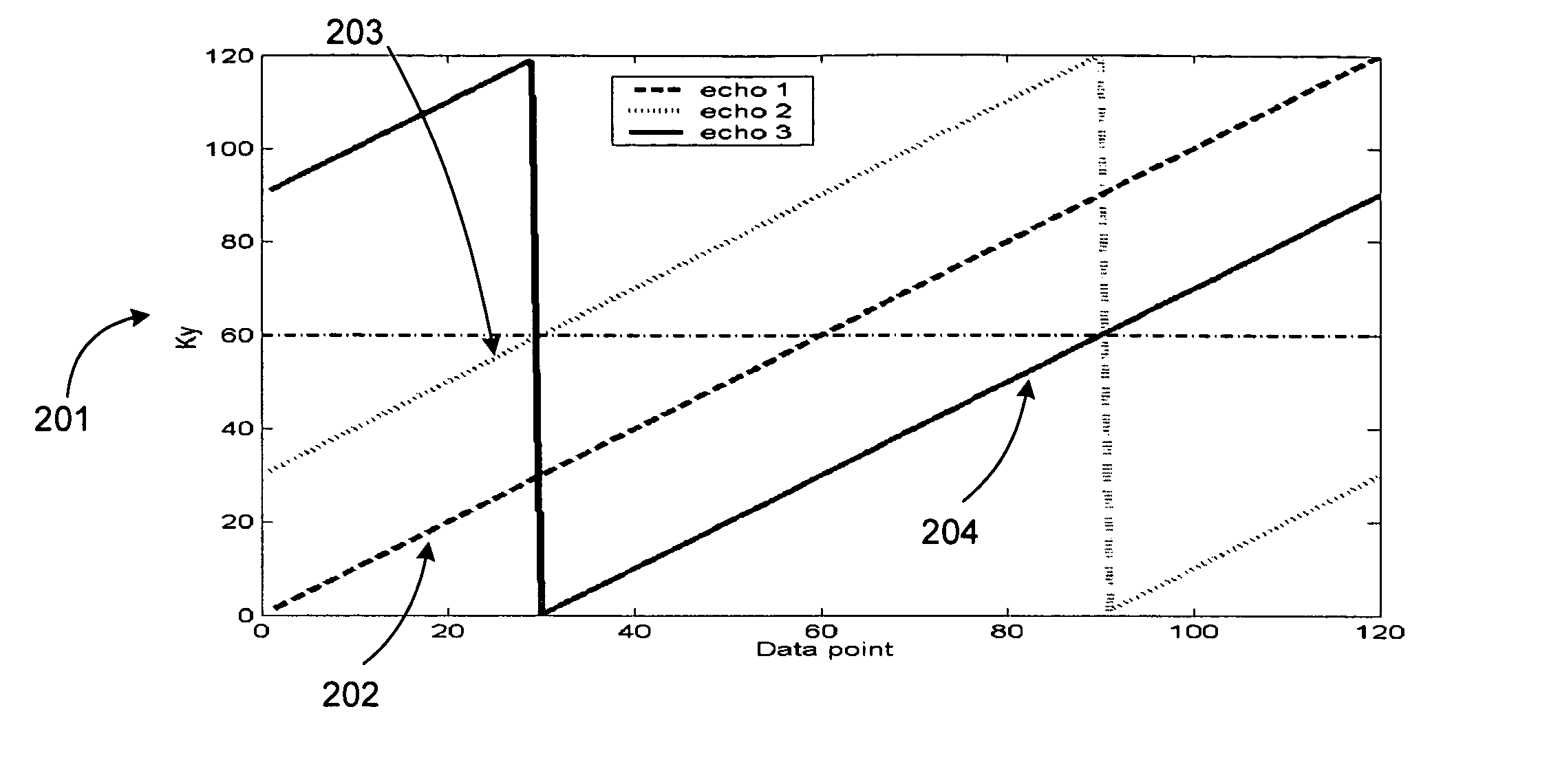
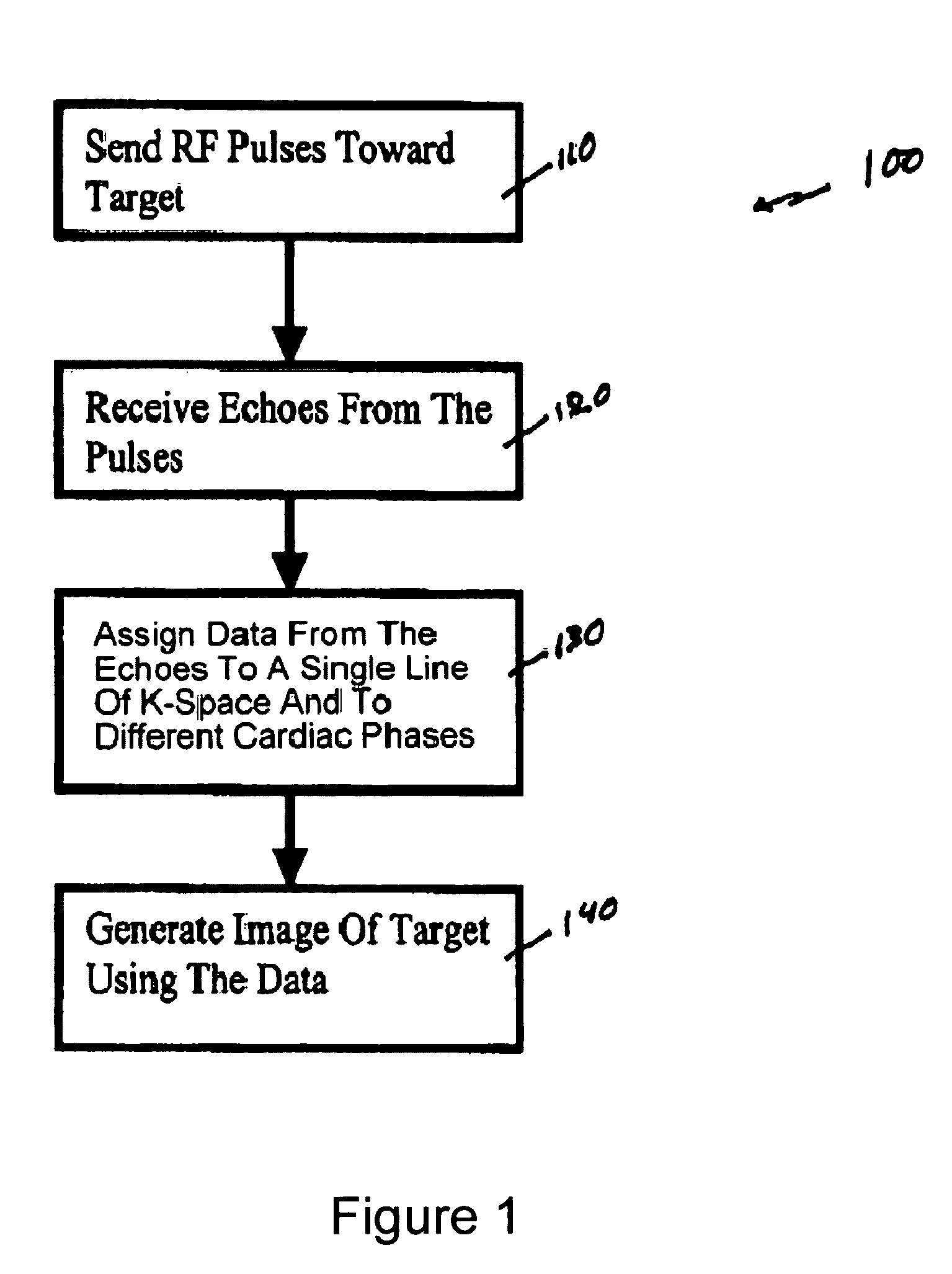
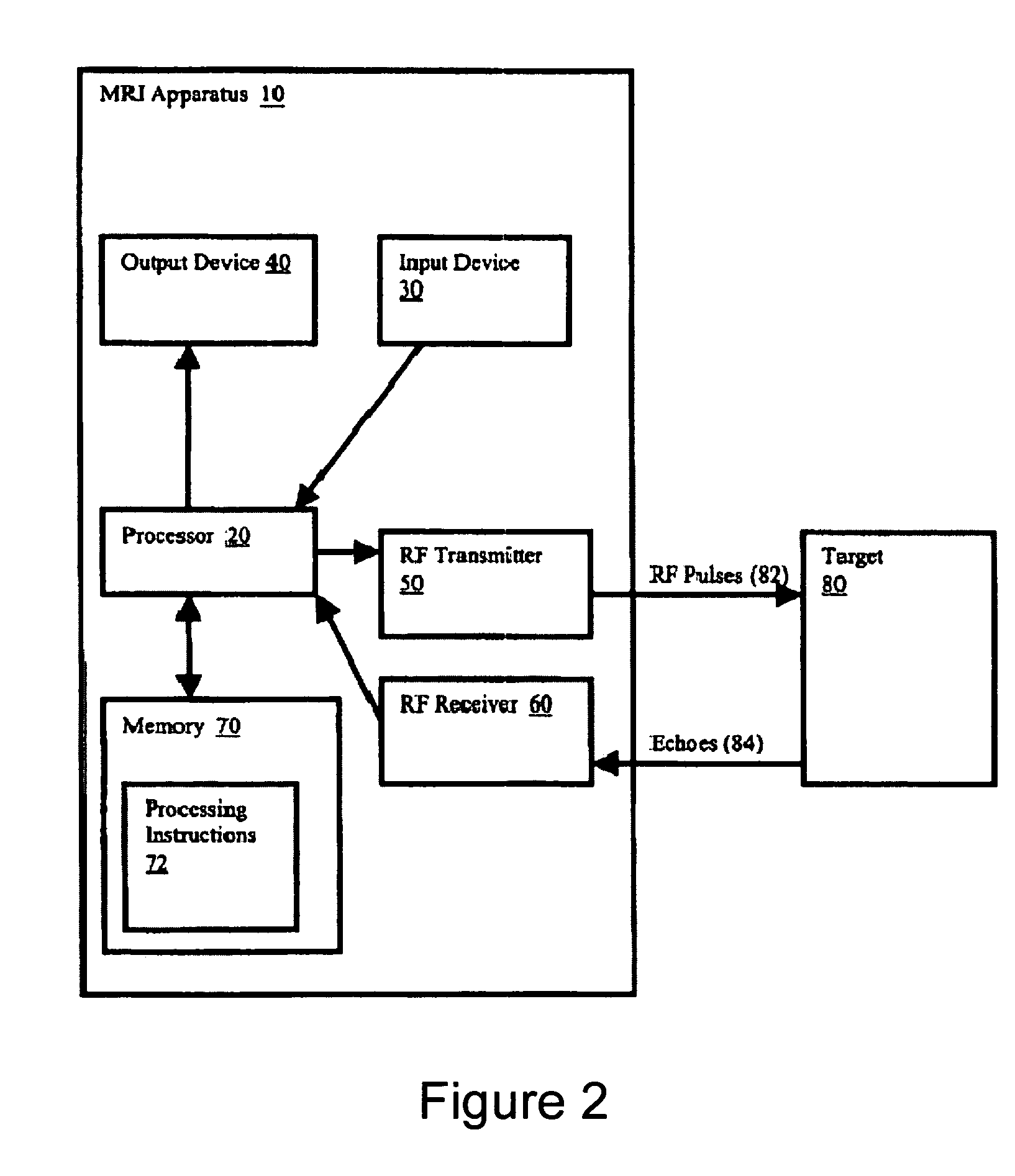
Method, systems and arrangements are provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target, such as a cardiac region of a patient. Radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by, e.g., an RF transmitter of an MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to the plurality of pulses may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, acceleration data and / or velocity data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes may be assigned to the same k-space line, and to different cardiac phases. In one further embodiment, parallel processing may be used to improve the resolution of the image acquired during a single breath-hold duration. In yet another embodiment, utilizing a segmented implementation, multiples lines of k-space are acquired for a given cardiac phase (or time stamp) per trigger signal. The present invention may be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest for the evaluation and study of flow dynamics with very high temporal resolution.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
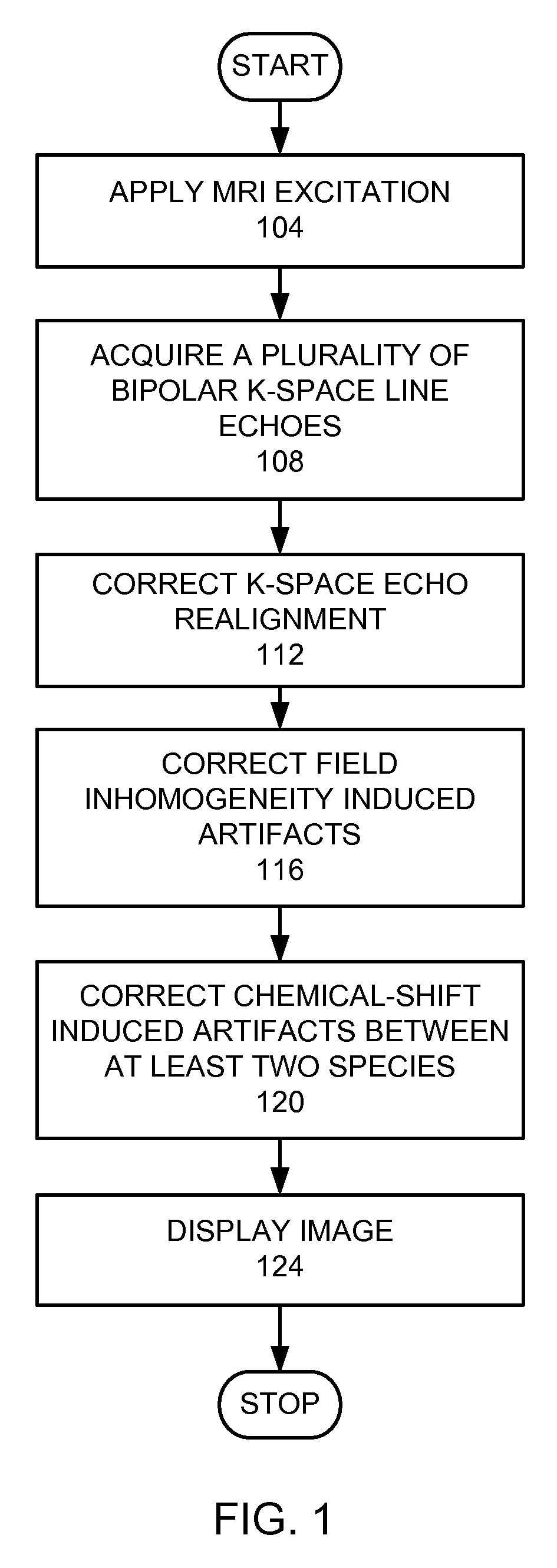
Magnetic resonance imaging with bipolar multi-echo sequences
ActiveUS20090072826A1Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonance excitationMulti echo
A method for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is provided. A magnetic resonance excitation is provided. A plurality of k-space echoes is acquired bi-directionally wherein at least one echo is an even echo acquired in a first direction and at least one echo is an odd echo acquired in a second direction opposite from the first direction. K-space echo realignment is corrected between the even and odd echoes. Field inhomogeneity induced artifacts are corrected. Chemical shift induced artifacts between at least two species are corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
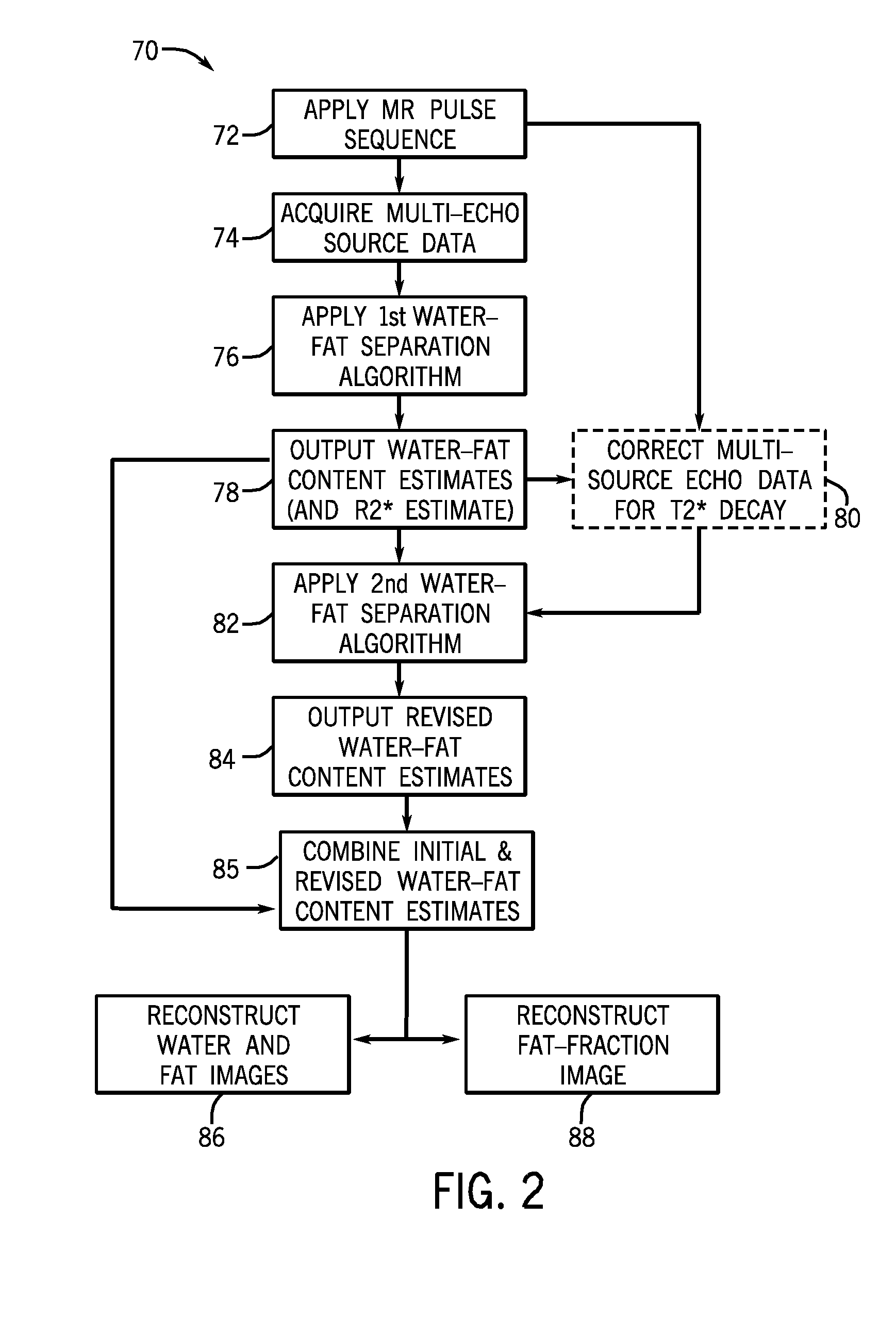
System and method for quantitative species signal separation using mr imaging
InactiveUS20110140696A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPulse sequenceComputer program
A system and method for quantitative species signal separation in MR imaging is disclosed. An MR imaging apparatus includes an MRI system and a computer programmed to cause the MRI system to apply a pulse sequence and acquire multi-echo source data for the pulse sequence that includes a phase component and a magnitude component. The computer is further programmed to determine a first estimate of a first species content and a first estimate of a second species content based on the multi-echo source data, and determine a second estimate of the first species content and a second estimate of the second species content based on the multi-echo source data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Object-oriented airborne laser radar point cloud filtering method
InactiveCN105488770AHigh precisionEffective WaysImage enhancementImage analysisRadarLidar point cloud
The invention discloses an object-oriented airborne laser radar point cloud filtering method. The method comprises the following steps: loading airborne laser radar point cloud data; identifying and removing a gross error point in airborne laser radar point cloud; performing smooth surface growth based airborne laser radar point cloud segmentation to obtain an object; analyzing a multi-echo ratio feature of the object to identify a potential earth object, and removing the earth object and a laser radar point contained in the earth object; extracting a feature point of the object, and performing subsequent operation by utilizing the feature point instead of an original laser radar point contained in the object; performing feature point based object type judgment, and updating the type of the original laser radar point contained in the object. According to the method, a complete object-oriented airborne laser radar point cloud filtering technical process is formed, so that the airborne laser radar point cloud filtering precision is effectively improved; and the method has wide applicability for various geomorphic types such as a mountainous area, an urban area and the like.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
Synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN107271937AIncrease optionalityReduce dependenceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsReconstruction methodT2 weighted
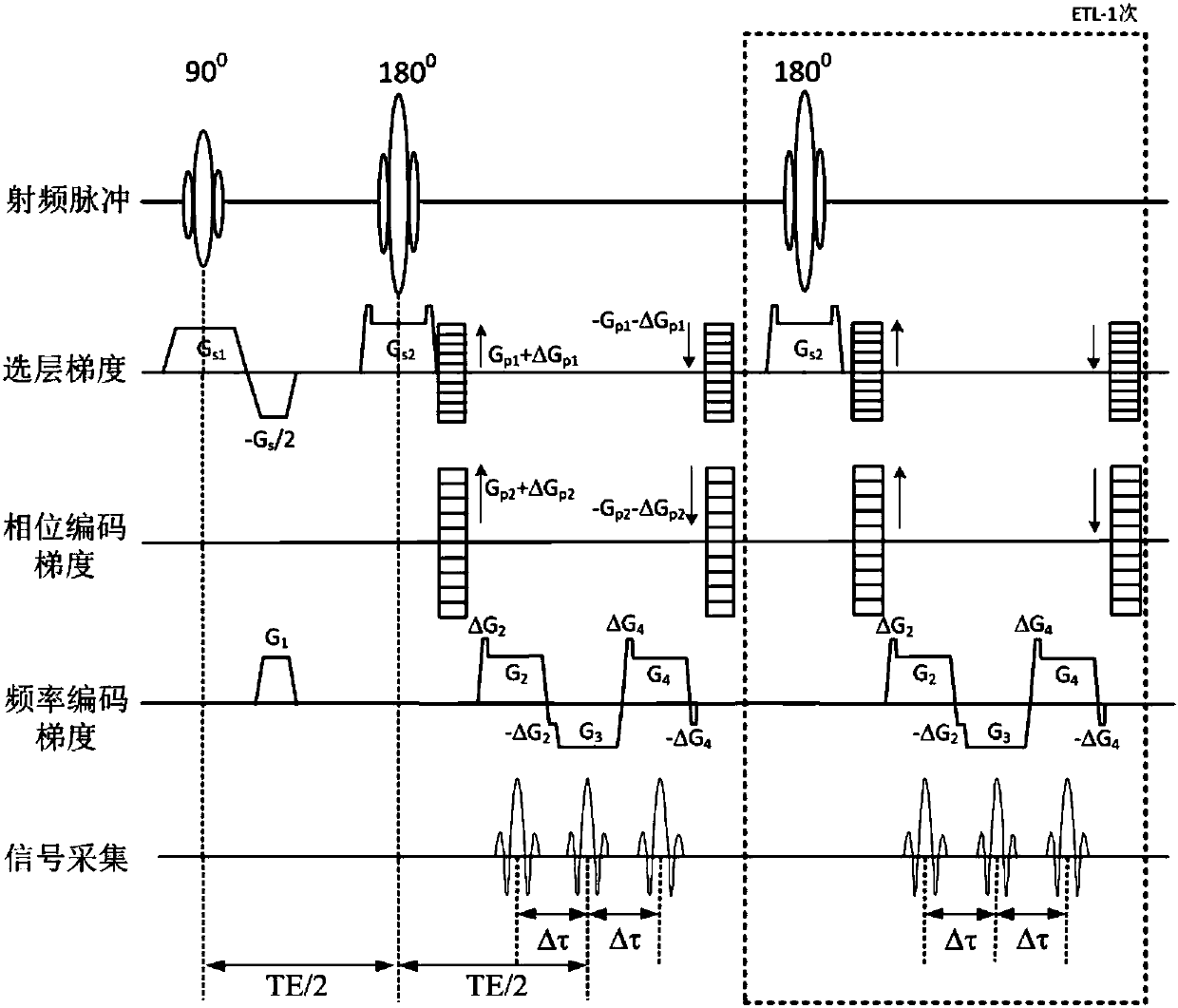
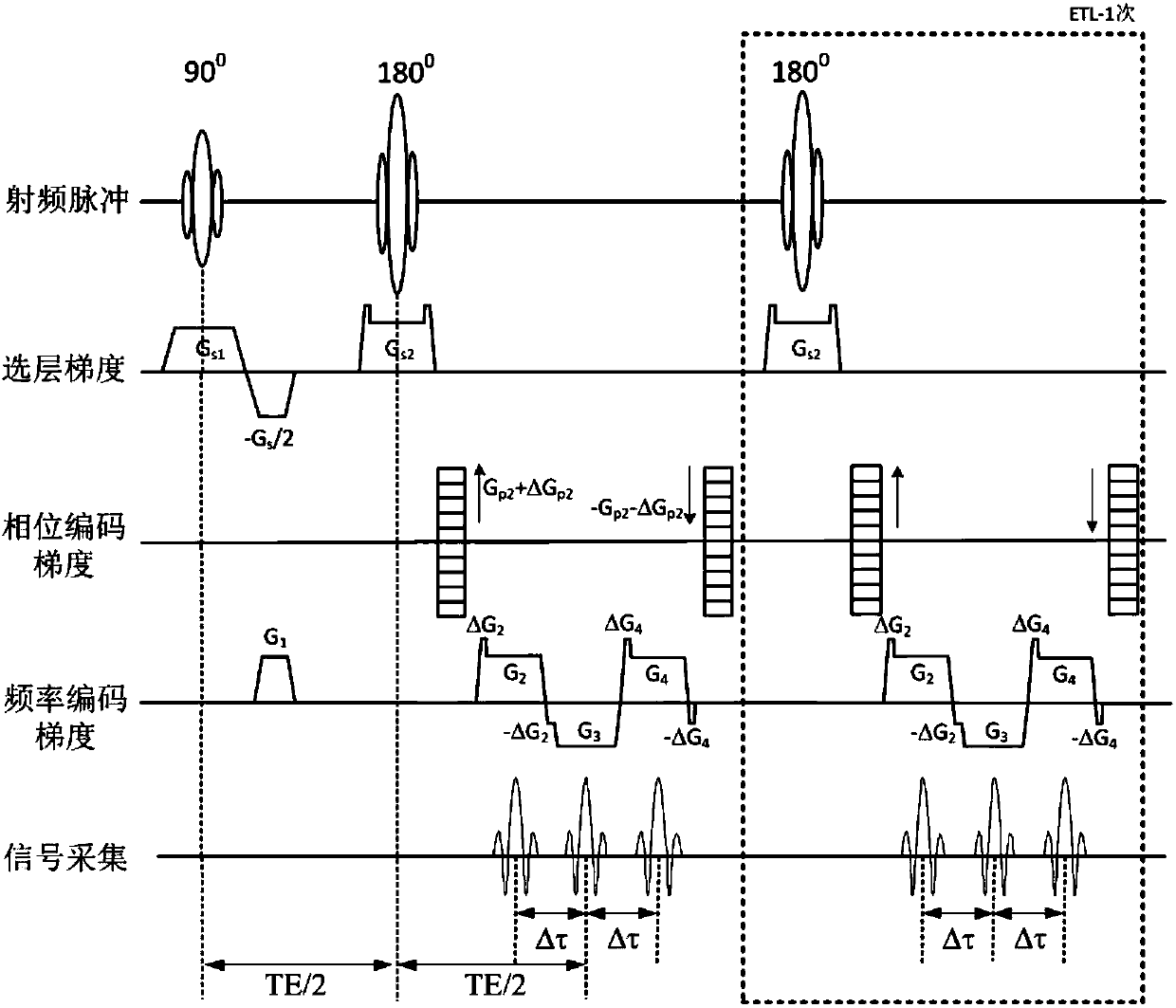
The invention discloses a synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging. A three-dimensional / two-dimensional fast multi-echo water-fat separation sequence and a signal debugging method, a pre-scanning method, a scanning method, a data preprocessing method and an image reconstruction method thereof can obtain a water-fat separation image and T2 weighted (T1 weighted or PD weighted) image by one-time scanning. The three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted synchronous scanning and calibration method can maximize the number of images obtained in a single scan, including, an in-phase image, a reverse-phase image, a fat image, a fat-pressed image water, a conventional T2 weighted (or T1 weighted / PD weighted ) image, and a T2weighted images, significantly shortens clinical scanning time and increases the selectivity of clinical scanning schemes, and has less reliance on the hardware performance of an MRI system.
Owner:南京拓谱医疗科技有限公司
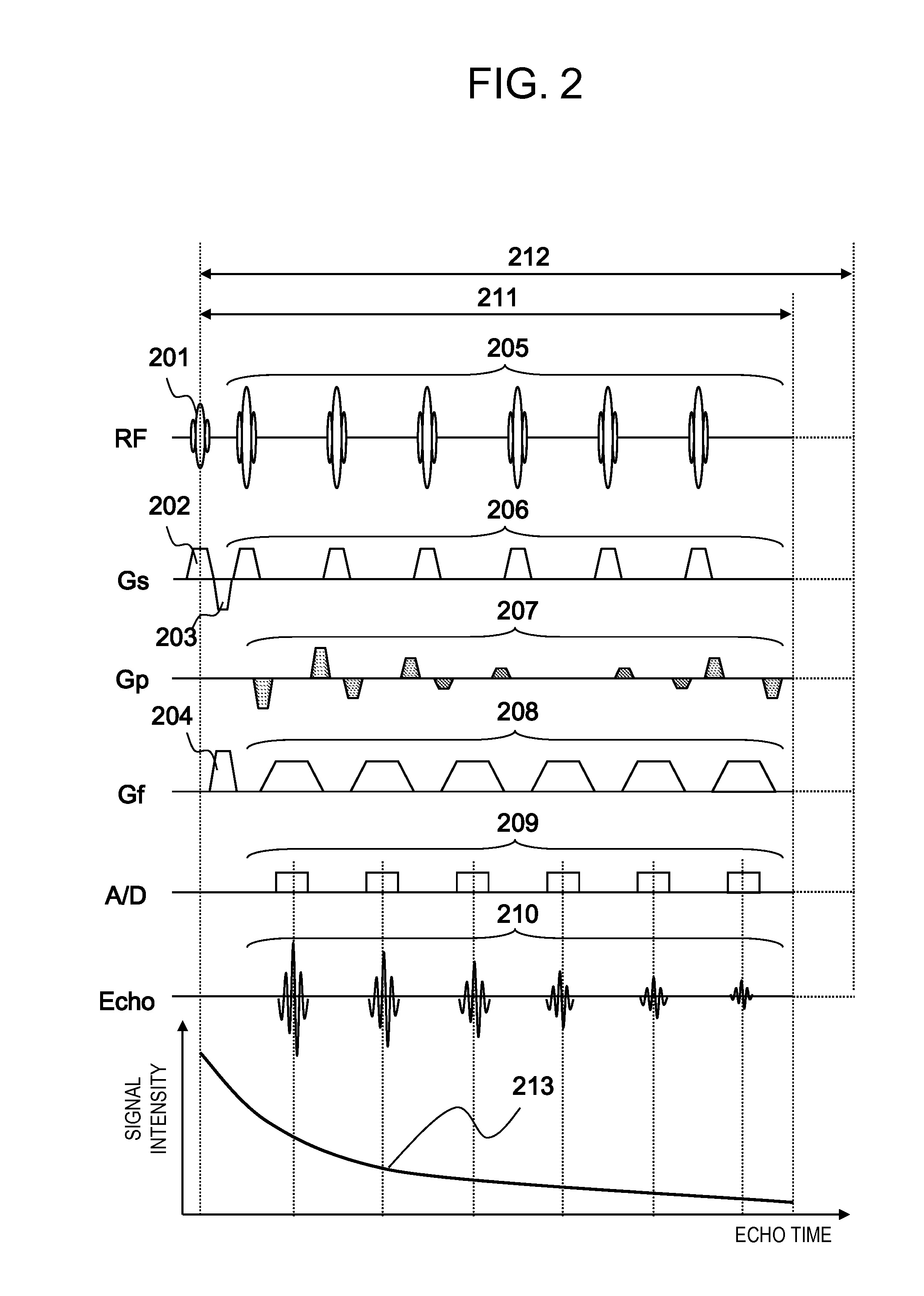
Method and apparatus of multi-echo MR data acquisition with non-discrete flip angle train
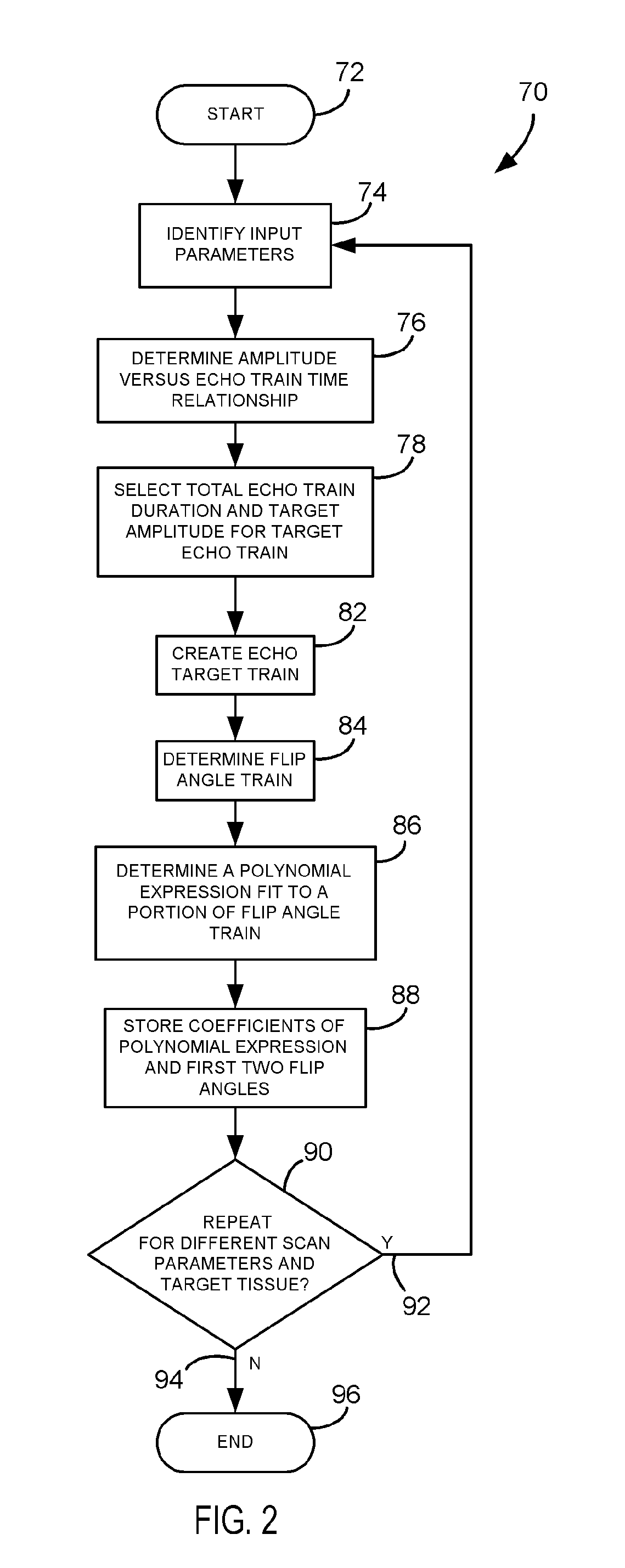
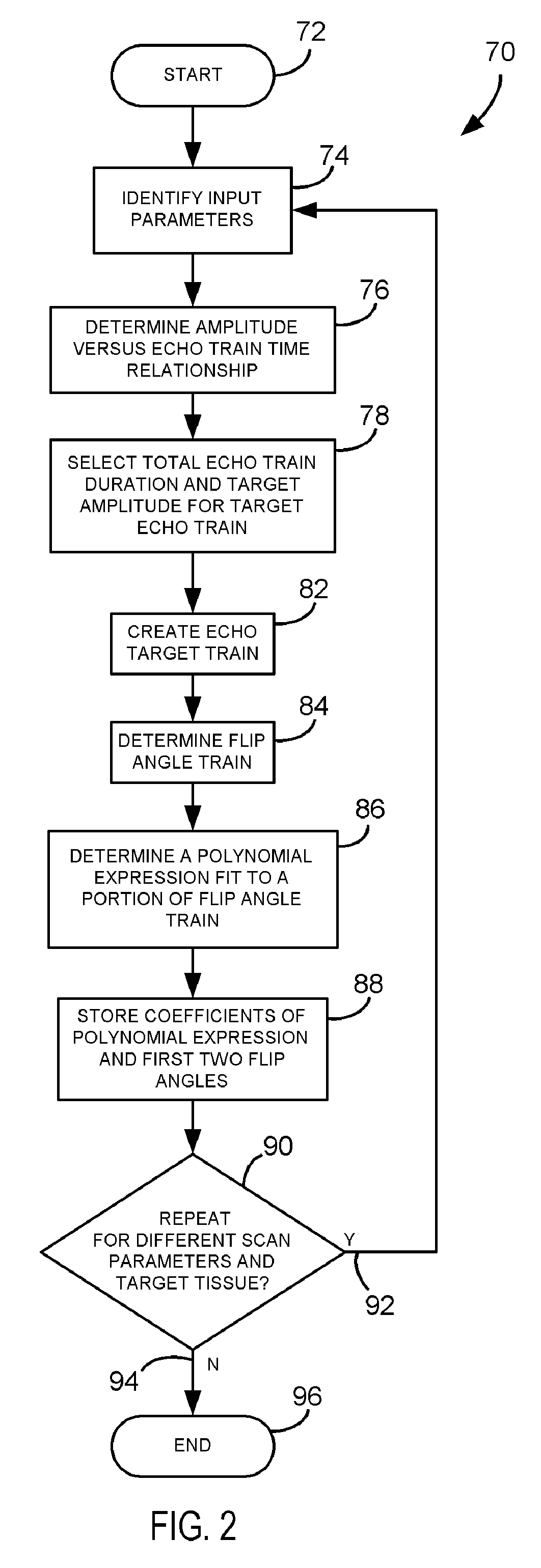
ActiveUS7227356B1Reduced ringing artifactsOvercomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImaging qualityData acquisition
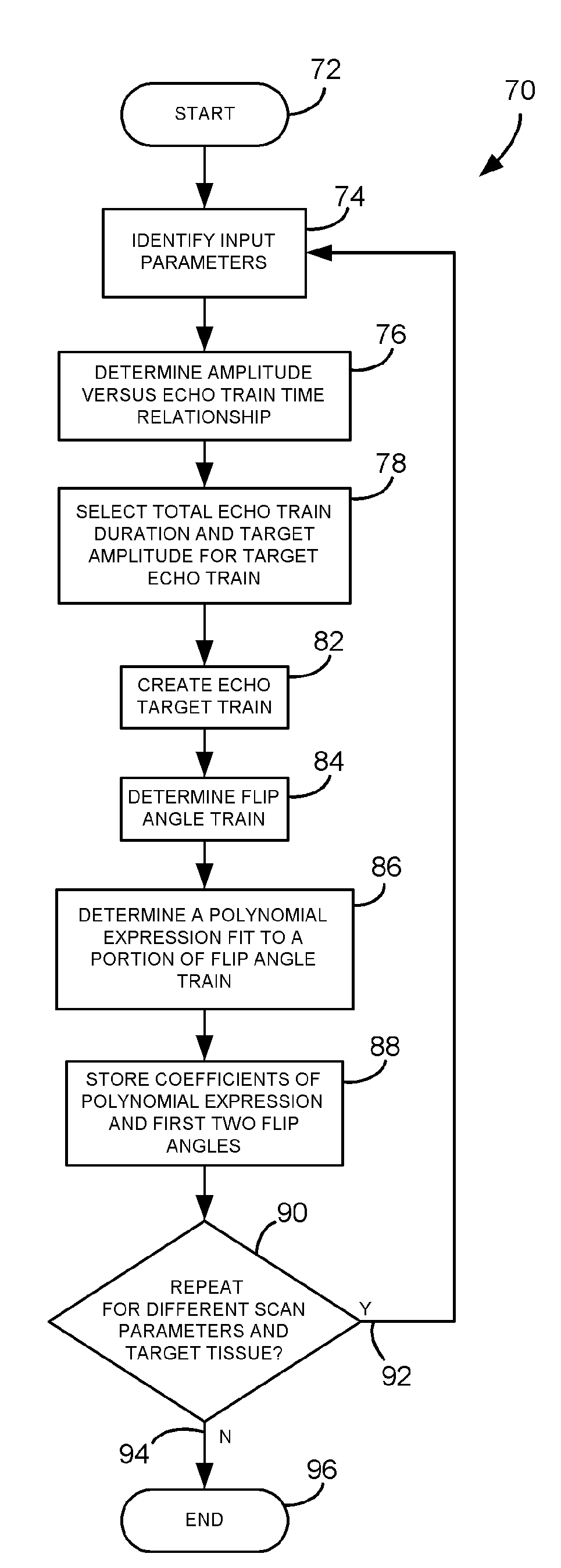
An imaging technique is disclosed to reduce ringing artifacts from amplitude decay in MR multi-echo acquisition. A flip angle train is determined to match scan parameters for an MR scan to acquire MR data from a given tissue. Reducing the effects of amplitude decay in the echo signal reduces ringing artifacts and thereby improves image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-echo sequence based MR imaging for fluid in motion
InactiveUS6380739B1Wide velocity rangeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPulse sequenceContrast medium
An FSE-system multi-echo MRI pulse sequence is used to steadily depict objects such as blood flows without a contrast medium. The pulse sequence has a gradient pulse set such that, among the plurality of echoes, an amount M' of a j-th (j=1, 1, 2, . . . ) gradient moment accumulated up to an n-th (n=1, 2, 3, . . . ) echo is approximately half an amount M (considered to be approximately constant when k>=n ) of the j-th gradient moment from a k-th (k=n, n+1, n+2, . . . ) echo to a "k+1"-th echo. This pulse sequence is performed and generated multi-echoes are acquired. An MR image is produced using echoes generated after the n-th echo among the acquired multi-echoes. For example, the n-th echo is an echo for n>=2 and a readout gradient to be applied during an interval down to the "n-1"-th echo is altered in time or amplitude, with a given gradient moment.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Parallel MRI with bo distortion correction and multi-echo dixon water-fat separation using regularised sense reconstruction
ActiveUS20160124064A1Accurate representationReduce in quantityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionGeometric distortionComputer program
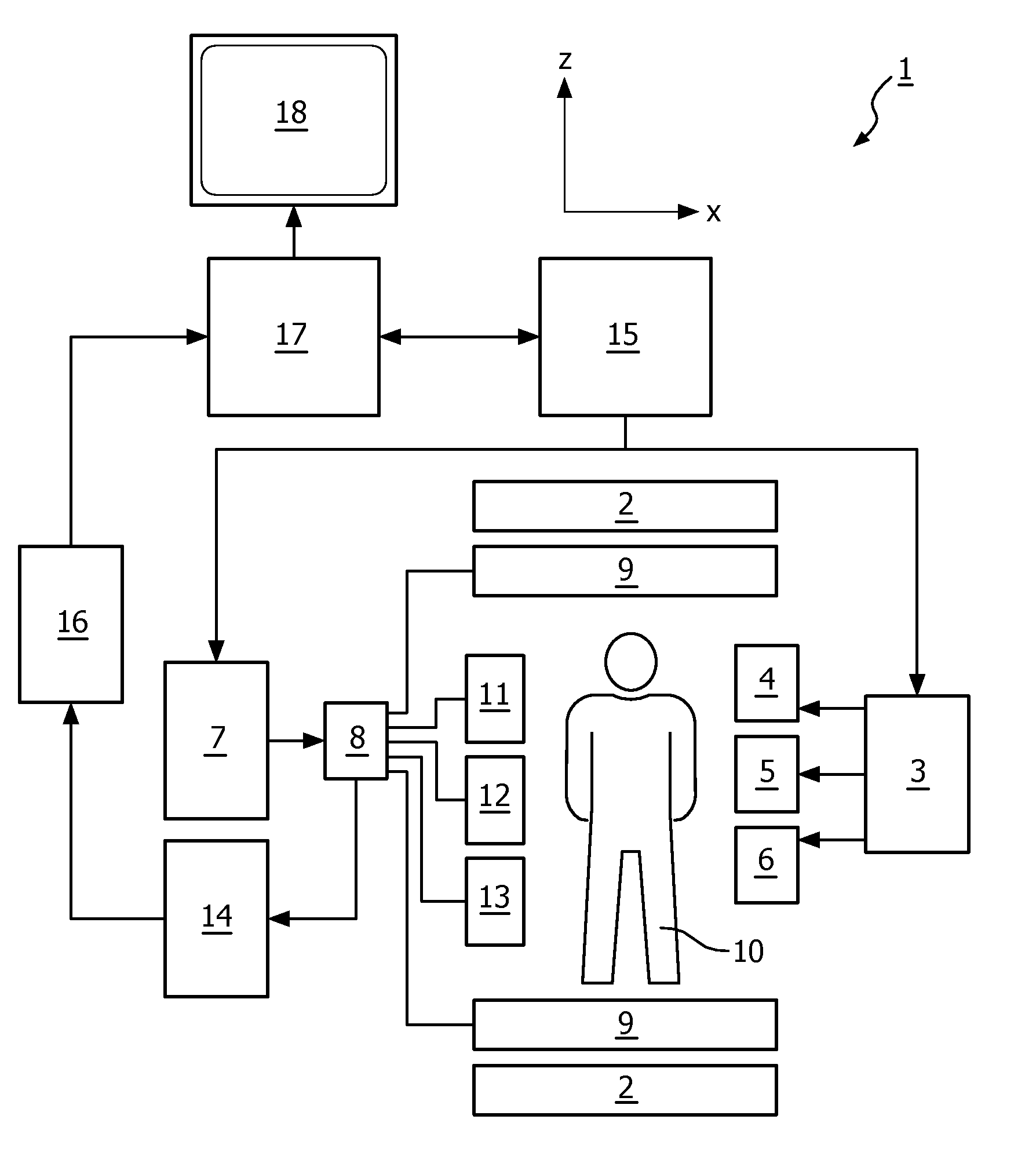
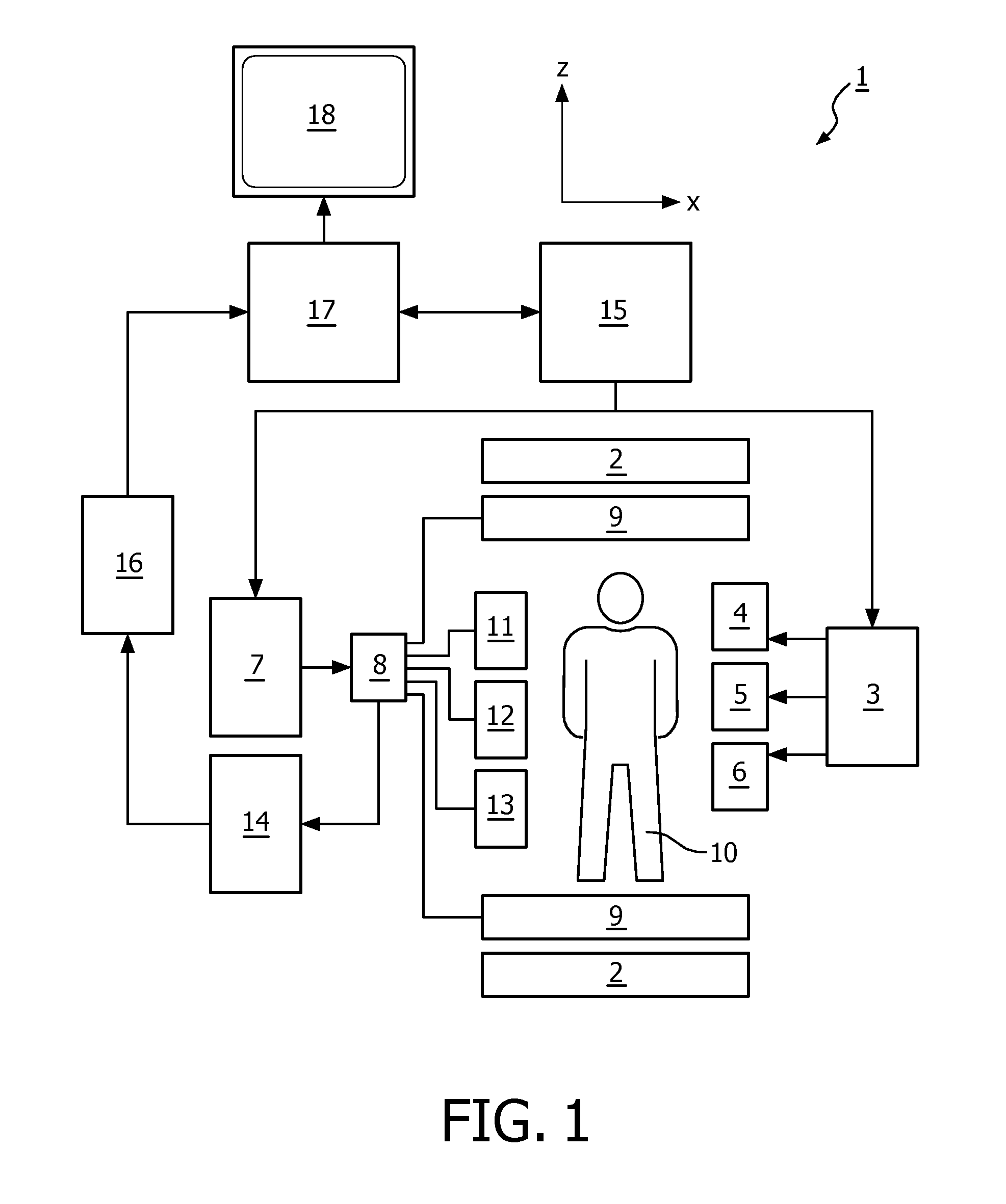
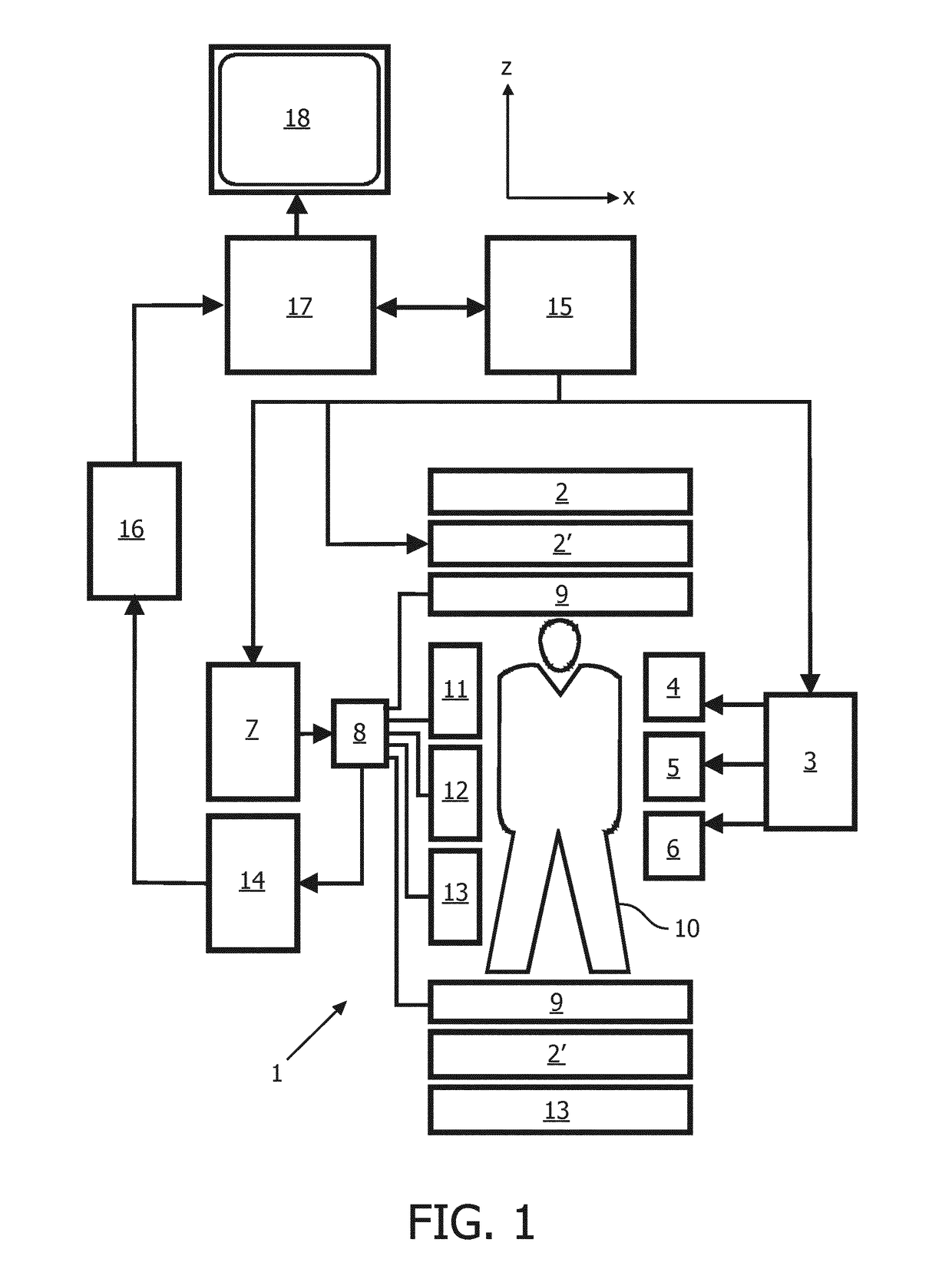
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of an object positioned in an examination volume of a MR device (1). The method comprises the steps of: acquiring reference MR signal data from the object (10); deriving a Bo map from the reference MR signal data; adapting sensitivity maps according to the B0 map, which sensitivity maps indicate spatial sensitivity profiles of one or more RF receiving coils (11, 12, 13), to correct for geometric distortions of the sensitivity maps; acquiring imaging MR signal data from the object (10) via the one or more receiving coils (11, 12, 13) with sub-sampling of k-space; and reconstructing a MR image from the imaging MR signal data, wherein sub-sampling artefacts are eliminated using the adapted sensitivity maps. In a preferred embodiment, the reference MR signal data are acquired using a multi-point Dixon technique, wherein a water map and a fat map are derived from the reference MR signal data. A water image and a fat image are reconstructed from the imaging MR signal data using separate water and fat sensitivity maps. The water and fat images are preferably reconstructed using regularised SENSE, wherein a water regularisation map and a fat regularisation map are derived from the multi-point Dixon reference MR signal data. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) for carrying out the method, and to a computer program to be run on a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and device for acquiring laser imaging echo waveform and level characteristics
ActiveCN101839981AImaging RealizationEasy to adjustElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudPulse broadening
The invention relates to a method and a device for acquiring laser imaging echo waveform and level characteristics, a laser imaging device is adopted for transmitting laser pulse to a target, and a multi-echo time delay measurement unit and a maximum undistorted waveform collection unit of the device are utilized for respectively extracting multi-echo time delay data and full waveform data of the same transmitted pulse. The full waveform data is utilized for extracting the echo pulse broadening characteristic, the power characteristic, the waveform distribution characteristic and the like as target characteristics and saving in an echo pulse database. The multi-echo time delay data is utilized for generating a target multi-level point cloud image, and the echo power characteristic is further utilized for generating a target gray image. The method and the device fully utilize time delay, peak power and waveform information contained in echo pulse, and can not only obtain the target conventional point cloud image, but also realize the target multi-level imaging and the target gray imaging, generate the waveform characteristic database and achieve the purpose of acquiring the laser imaging echo waveform and level characteristics.
Owner:ELECTRONICS ENG COLLEGE PLA
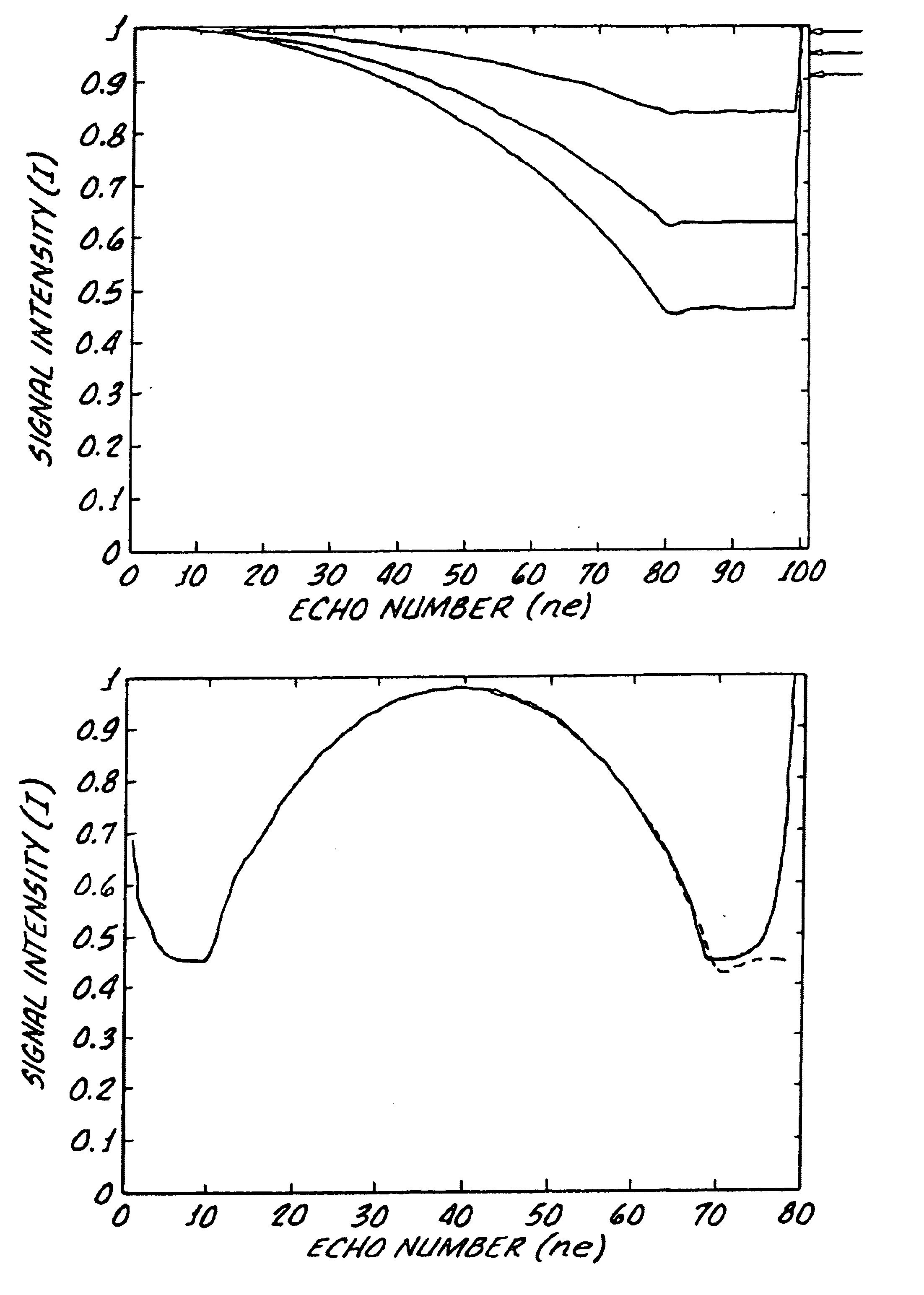
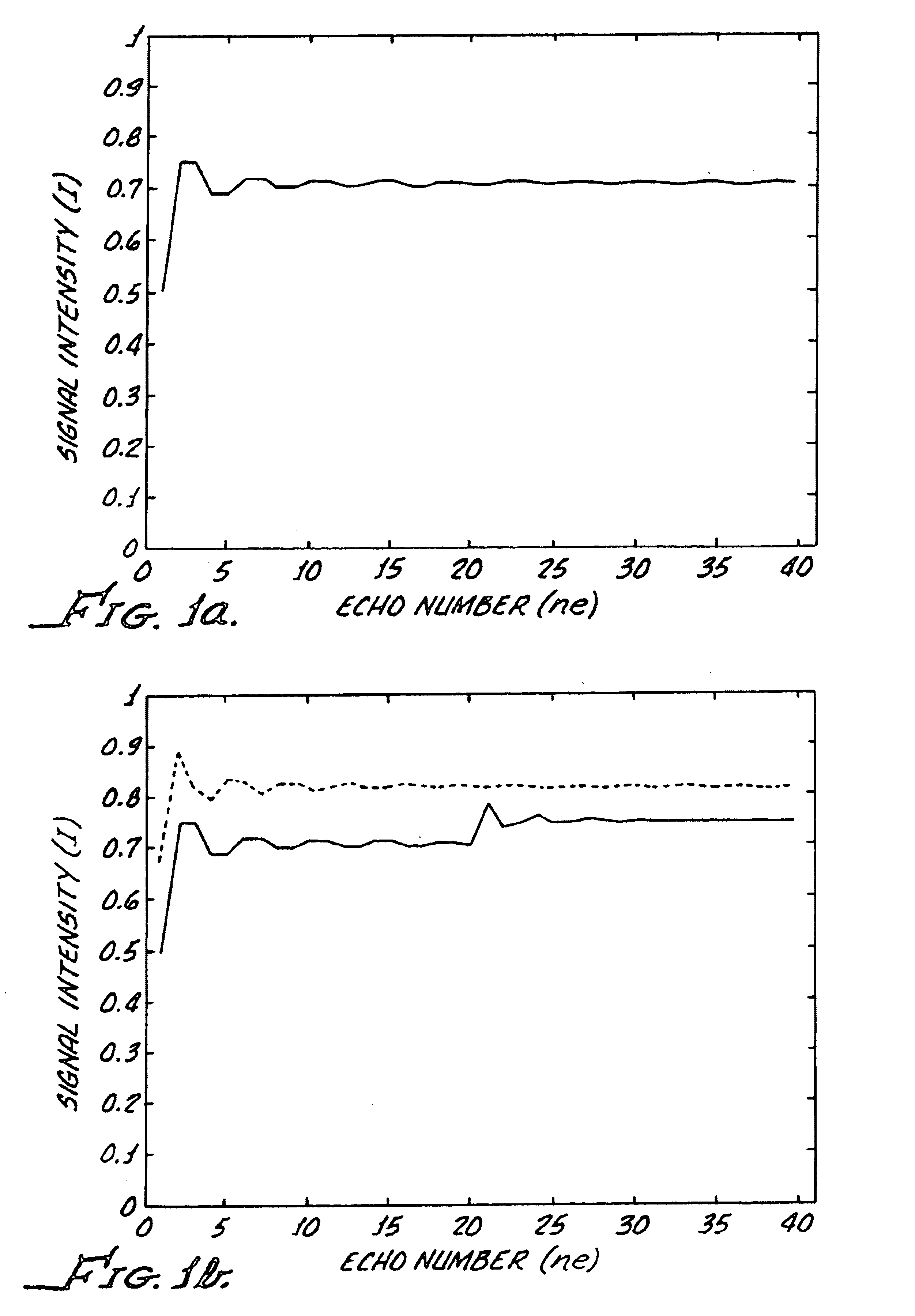
Method and apparatus to correct amplitude modulation in multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7075299B1Reduce ghostingImprove image qualityElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsStimulated echoImaging quality
An imaging technique is disclosed for multi-echo, magnetic resonance imaging that addresses amplitude modulations, such as those caused by T2 decay and stimulated echo refocusing, in acquired MR data. Acquired MR data is corrected by non-phase encoded data such that amplitude modulations in the echo signal are addressed. Reducing the effects of amplitude modulations in the echo signal reduces ghosting and thereby improves image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for measuring the magnetic resonance (NMR) by means of spin echoes
InactiveUS6850063B2Reduce trainingReducing RF energyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationSpectroscopy
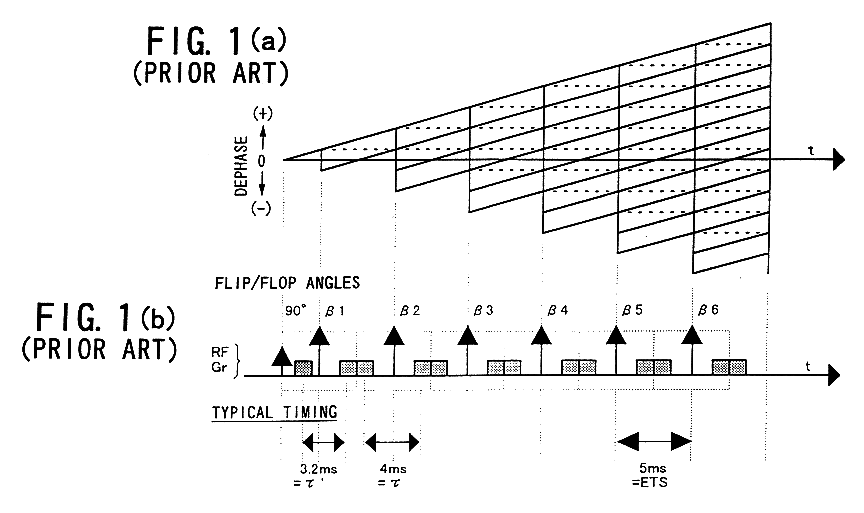
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy or tomography method wherein a sequence of temporally mutually offset radio frequency (RF) pulses is applied onto a spin ensemble like a CPMG multi echo experiment, and wherein the magnetization produced after an initial excitation pulse is transferred to or close to the static pseudo steady state of the initially applied refocussing flip angle α1 is characterized in that magnetization is transferred through gradual change of the refocussing flip angle in subsequent refocussing intervals to or close to the static pseudo steady state of the respectively used refocussing pulse with refocussing flip angle αn such that the echo amplitude of the nth echo generated in this fashion approaches the maximum possible value corresponding to the respective refocussing pulse with refocussing flip angle αn. The RF energy required for excitation of the nuclear spins can thereby be considerably reduced without having to accept signal intensity losses.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method
ActiveCN107153169AHigh precisionSuppresses Motion ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRadio frequencyImage sequence
The invention discloses a steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method. The steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method comprises the following steps of on the basis of a steady-state procession imaging sequence for conventional scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging system, repeatedly exciting the imaging area by a radio frequency pulse at the interval of 10ms magnitude or smaller short cycle TR; setting a pulse flip angle into +alpha / 2 in a first sequence repetition cycle, and eliminating the sampling period; alternatively setting the pulse flip angle into +alpha and -alpha in the subsequent sequence repetition cycle; using the layer selection gradient, phase encoding gradient and frequency encoding gradient to perform three-dimensional encoding, wherein the sum of integral areas of gradients in each bearing is zero, and the proton magnetizing vector procession is approximate to the steady state; enabling the magnetizing vectors to form three or two gradient echoes under the action of three or two positive and negative alternating frequency encoding gradients in each TR period, wherein the integral area of gradients in the frequency encoding direction is zero; performing direct phase encoding on the three or two echoes according to echo peak interval and water and grease chemical displacement difference value.
Owner:谱影医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
Coronary magnetic resonance angiography with signal separation for water and fat
ActiveUS20120301000A1High repetition rateReliable separation of imageMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setComputer science
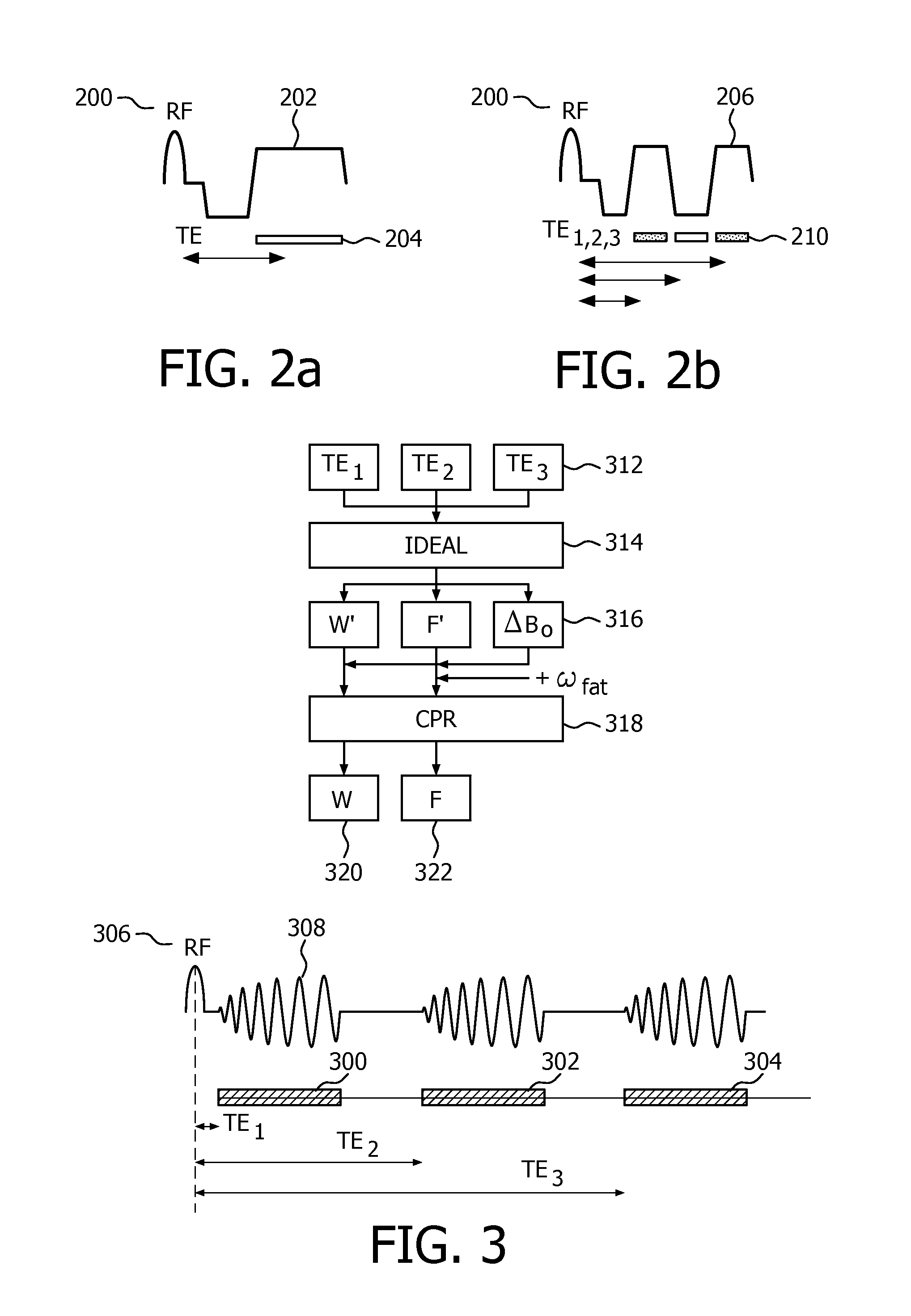
The invention relates to a method of performing coronary magnetic resonance angiography with signal separation for water and fat, the method comprising: acquiring coronary magnetic resonance angiography datasets using multi-echo Dixon acquisition, processing (314; 316; 318) the datasets for reconstruction of a first (320) and second (322) image data set, the first and second image data set comprising separate water and fat image data, wherein the processing of the datasets comprises a Dixon reconstruction technique.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
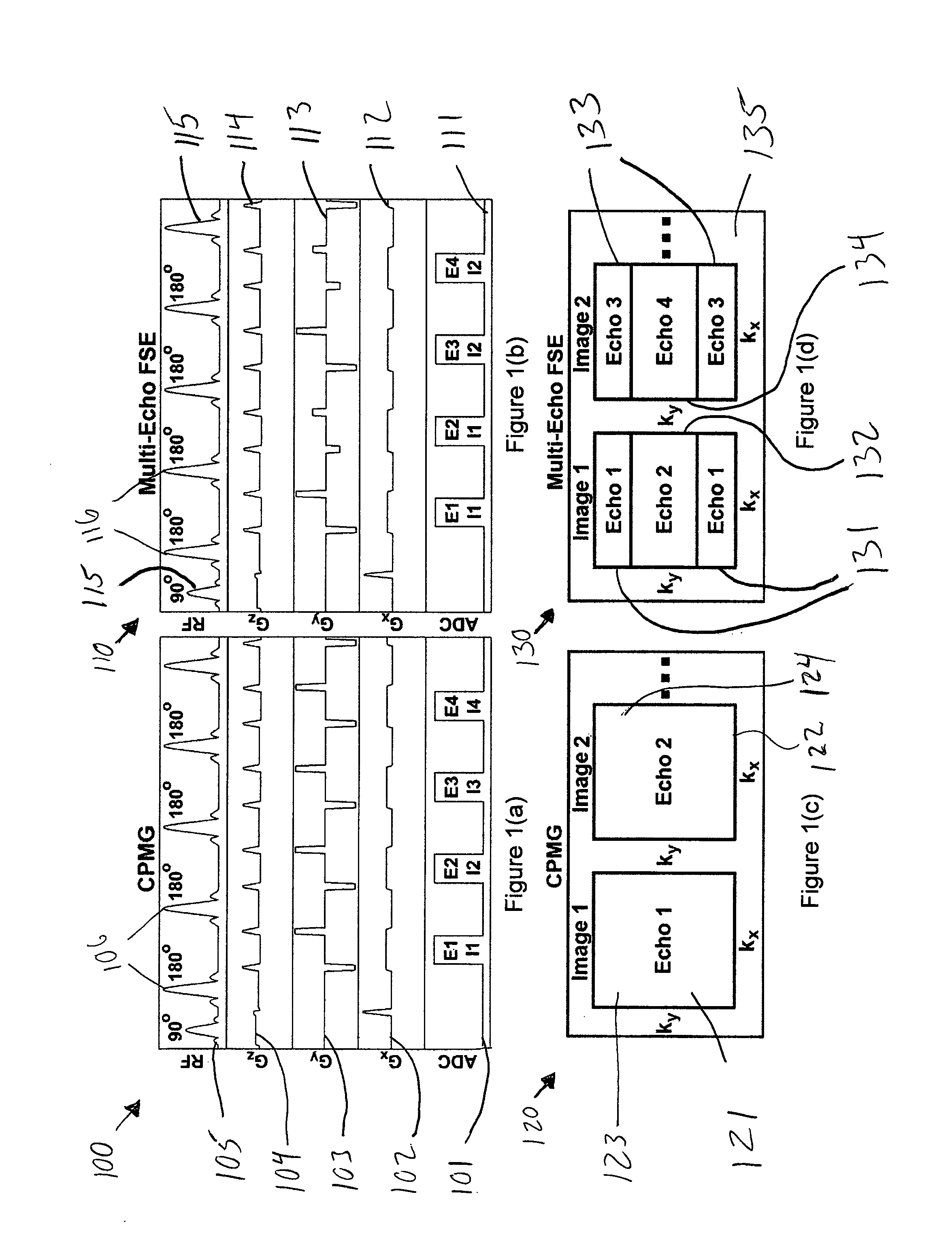
Simultaneous multi-slice multi-echo turbo spin echo (TSE) imaging
In a method and apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance (MR) raw data, an MR data acquisition scanner is operated to execute a turbo spin echo (TSE) or a turbo gradient spin echo (TGSE) sequence wherein nuclear spins are excited in multiple slices of the examination object simultaneously by radiating at least one radio-frequency (RF) pulse from an RF radiator of the MR data acquisition scanner, thereby causing the excited nuclear spins in said multiple slices to produce an echo train. A multi-band refocusing pulse is radiated that refocuses nuclear spins in at least one of said multiple slices that follows a first of the multiple slices, and readout gradients are activated to acquire MR signals, with respectively different contrasts, at respectively different readout times of the echo train. The read out MR signals are entered into an electronic memory organized as k-space.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Spin echo SPI methods for quantitative analysis of fluids in porous media
ActiveUS9018950B2Rapid determinationSimple methodElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpatially resolvedCapillary pressure
A method of measuring a parameter in a sample by imaging at least a portion of the sample using a spin-echo single-point imaging (SE-SPI) pulse sequence. This method involves applying a pure phase encoding to the SE-SPI pulse sequence, acquiring a multiplicity of echoes, and determining the spatially resolved T2 distribution. In another embodiment, individual echoes are separately phase encoded in a multi-echo acquisition and the SE-SPI pulse sequence is a hybrid SE-SPI sequence. In another embodiment, an external force can be used to build up a distribution of saturations in the sample, and a T2 distribution can be measured for the sample, which is then used to determine a parameter of the sample. A spatially resolved T2 distribution can also be measured and a resulting spatially resolved T2 distribution used to determine the T2 distribution as a function of capillary pressure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Gradient-echo multi-echo water and fat separation method and magnetic resonance imaging system using method
ActiveCN108720834AFast scanningQuick correctionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImage domainPhase coding
The invention discloses a gradient-echo multi-echo water and fat separation method. The method includes the following steps of 1, using a three-dimensional gradient-echo N echo sequence for conductingimaging scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging region, collecting N pieces of echo data, and using a GRAPPA technology for accelerating data collection during collection, wherein N is greater thanor equal to 4; 2, using the GRAPPA technology for fitting and restoring to-be-collected phase encoding data of the N pieces of echo data within respective K spaces, and then conducting preliminary data processing to obtain complete image domain data of N echoes; 3, substituting the image domain data of the N echoes into a water and fat separation algorithm of a multi-peak water-fat model, introducing T2* variables, conducting iterative calculation, obtaining a T2* distribution map of an imaged object, and meanwhile obtaining water and fat images through calculation. According to the method, the T2* distribution can be accurately estimated, the signal attenuation between the echoes is effectively corrected, and phase changes caused by inhomogeneity of a magnetic field are reduced, so that results of the quantitative analysis images are more accurate and stable. A magnetic resonance imaging system using the method is also provided.
Owner:SUZHOU LONWIN MEDICAL SYST
Non-cartesian under-sampled multi-echo MRI
ActiveUS20110175610A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData setPulse sequence
Example apparatuses and methods control a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus to perform a non-Cartesian, under-sampled, multi-echo MRI process. One example process includes controlling the MRI apparatus to excite an object to be imaged using a multi-echo Gradient Recalled Echo (GRE) pulse sequence. The example process also includes controlling the MRI apparatus to acquire a data set from the object to be imaged as a function of performing a non-Cartesian, under-sampling acquisition. The data set includes data acquired at two or more echo times (TE) per repetition (TR) and an element in the data set is sampled two or more times as a function of a non-Cartesian trajectory that crosses itself at least once. The process also includes controlling the MRI apparatus to reconstruct an image of the object to be imaged from the data set. The image may map brain activity.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance data acquisition using a multipoint dixon technique
ActiveUS20150061672A1Short measurement durationPrecise determination of spectral componentsMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceData acquisition
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) apparatus to acquire MR data from a subject, a predetermined spectral model of a multipoint Dixon technique is used that includes at least two spectral components with respective associated relaxation rates, a first phase due to field inhomogeneities; and a second phase due to eddy current effects. MR data are acquired using a bipolar multi-echo MR measurement sequence for multiple image points wherein, for each image point, the multi-echo MR measurement sequence alternately uses positive and negative readout gradient fields for the readout of MR signals of the MR data at at least three echo times. The at least two spectral components are determined based on the MR data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
System and method for image processing with highly undersampled imaging data
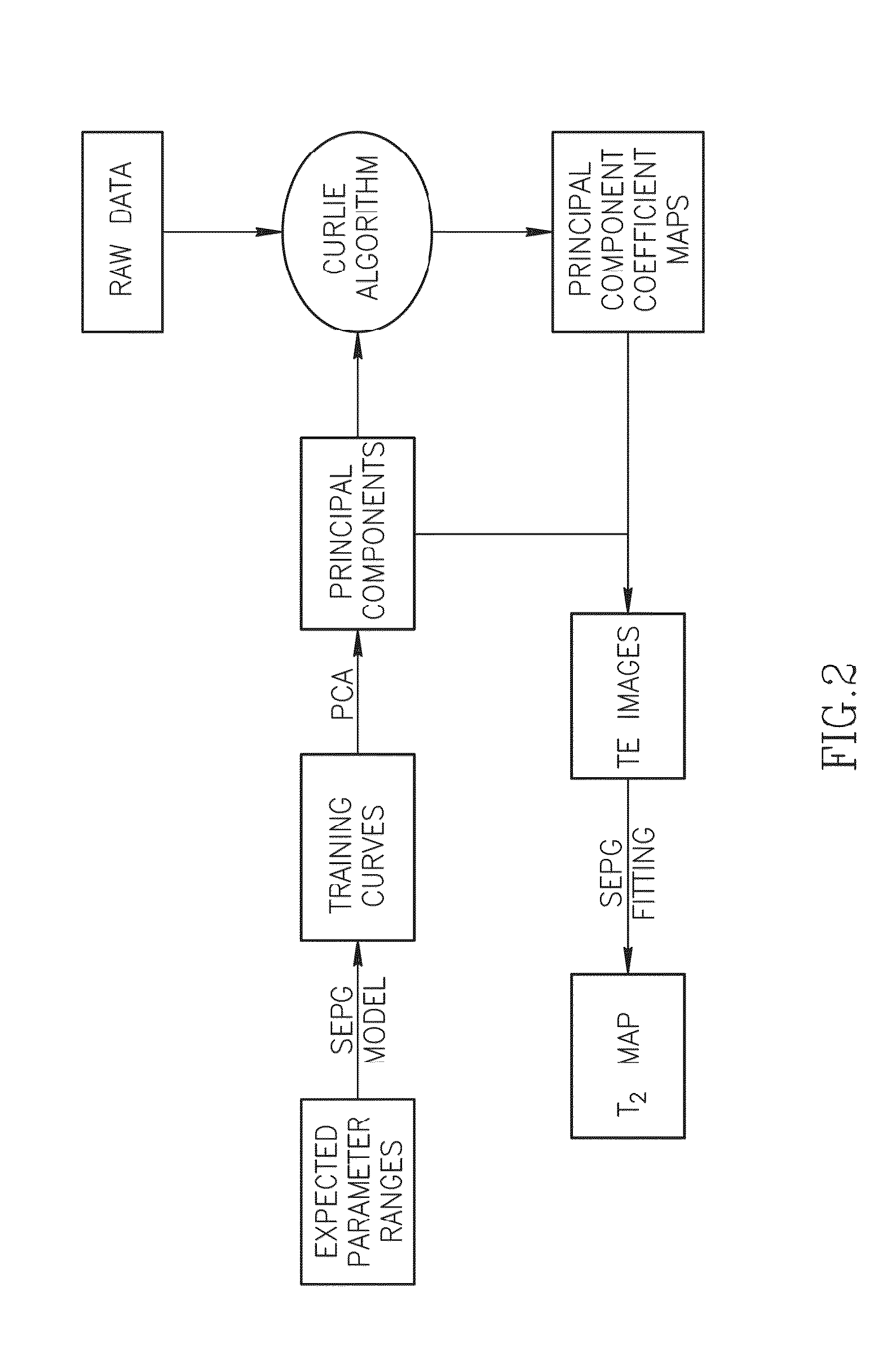
ActiveUS20150006114A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsVoxelImaging processing
A system and method for processing highly undersampled multi-echo spin-echo data by linearizing the slice-resolved extended phase graph model generates highly accurate T2 maps with indirect echo compensation. Principal components are used to linearize the signal model to estimate the T2 decay curves which can be fitted to the slice-resolved model for T2 estimation. In another example of image processing for highly undersampled data, a joint bi-exponential fitting process can compensate for image variations within a voxel and thus provide partial voxel compensation to produce more accurate T2 maps.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Method and apparatus of multi-echo mr data acquisition with non-discrete flip angle train
ActiveUS20070161890A1Reduce artifactsReduced ringing artifactsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringImaging qualityData acquisition
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
InactiveUS8060180B2Improve time resolutionHigh resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceCardiac phase
Exemplary method, systems and arrangements can be provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target. For example, radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by a RF transmitter of a MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to each pulse may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space of a distinct image, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, velocity data and / or acceleration data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes can be assigned to the same k-space line and to different cardiac phases. The exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure can be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and multi-contrast acquiring method
ActiveUS20100296717A1Improve image contrastIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonanceMulti contrast
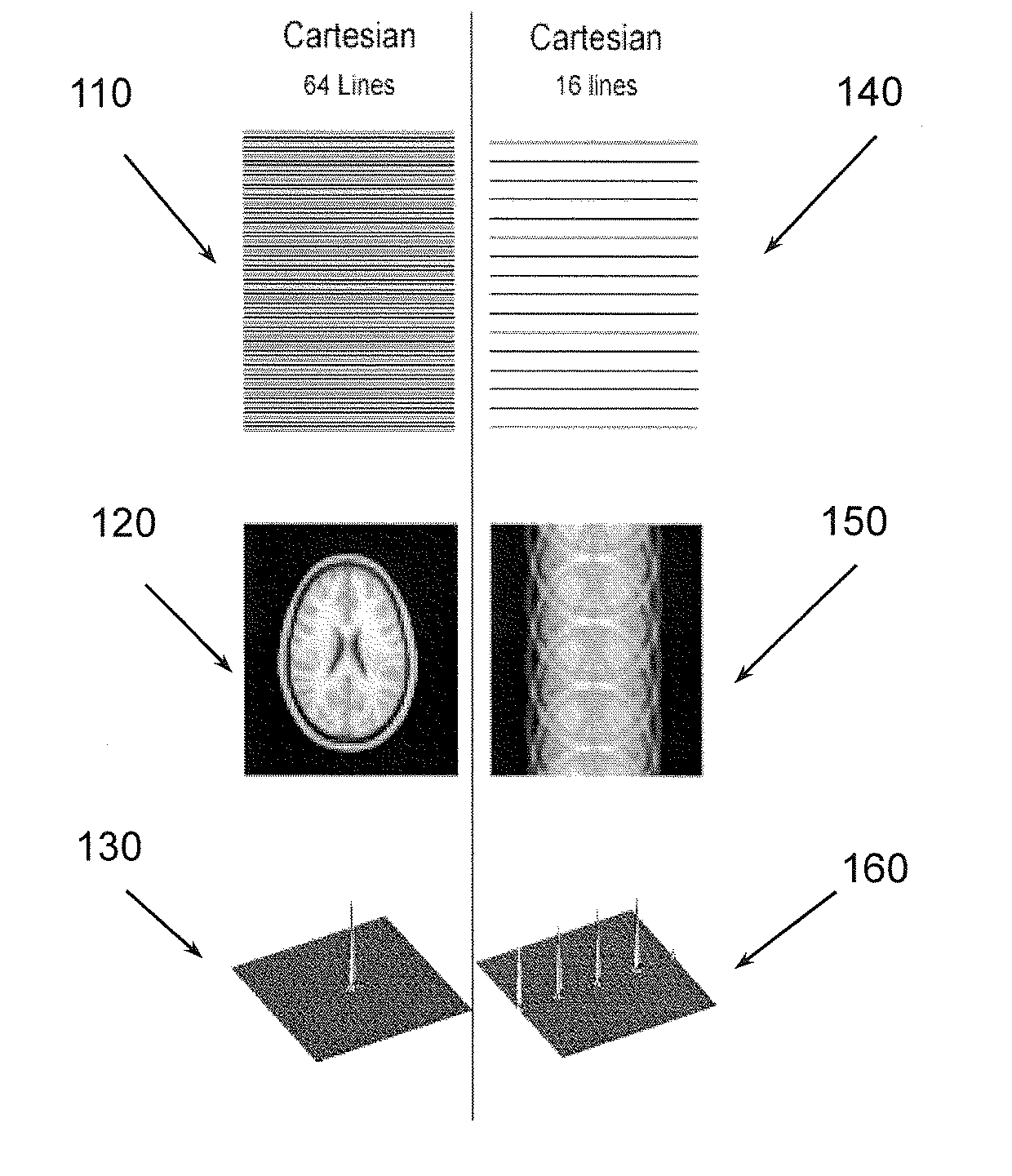
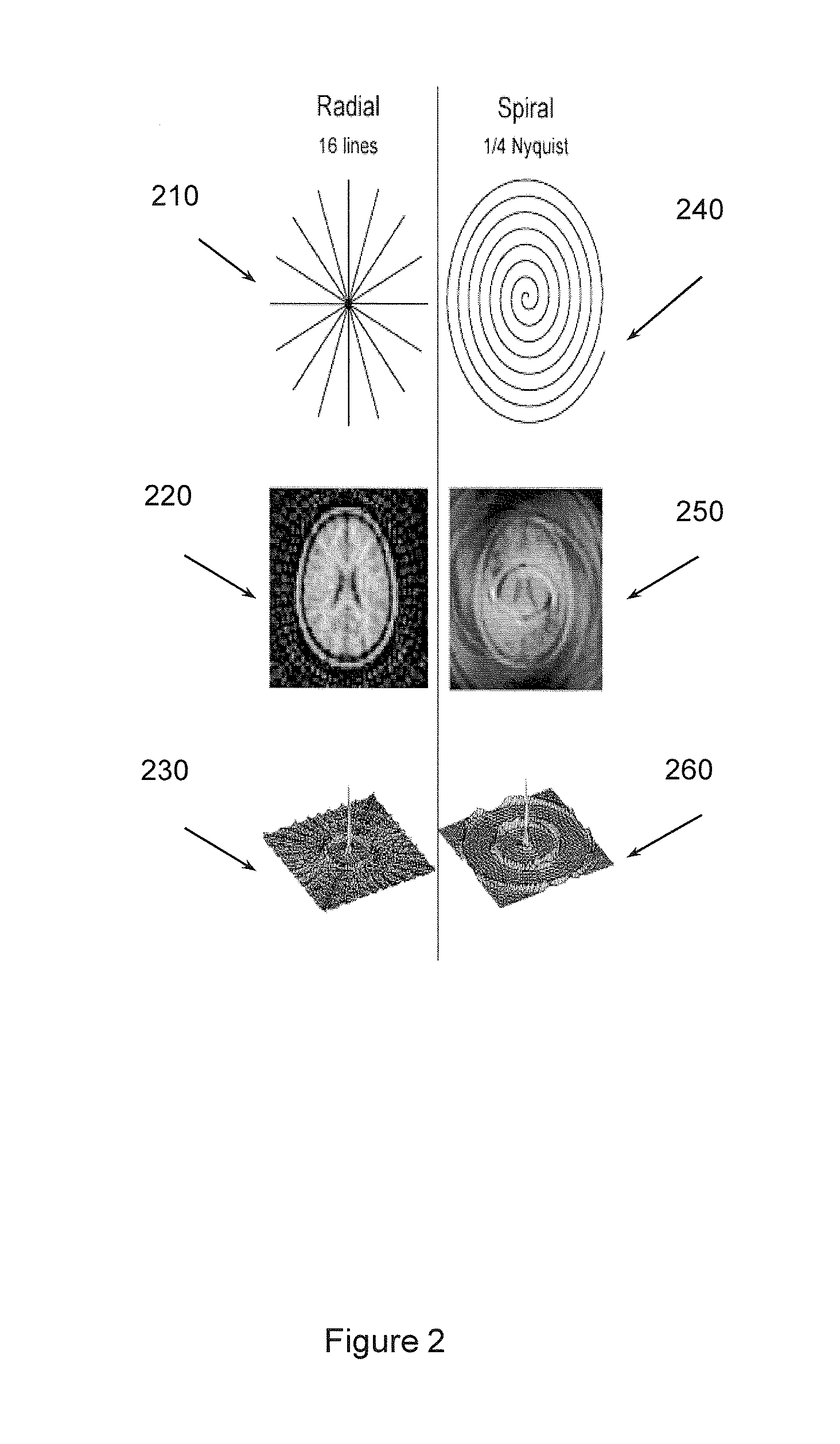
The contrast of an image captured by imaging using a multi-echo sequence by radial sampling is improved.Images are simultaneously captured by using a multi-echo sequence by radial sampling, and echo signal groups of one or more blocks measured by executing the imaging using the multi-echo sequence are divided into a plurality of partial echo signal groups.Using the partial echo signal groups, images with different contrasts are reconstructed.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Method for obtaining magnetic resonance image data using a multi-echo mr sequence with improved signal-to-noise ratio of the phase information
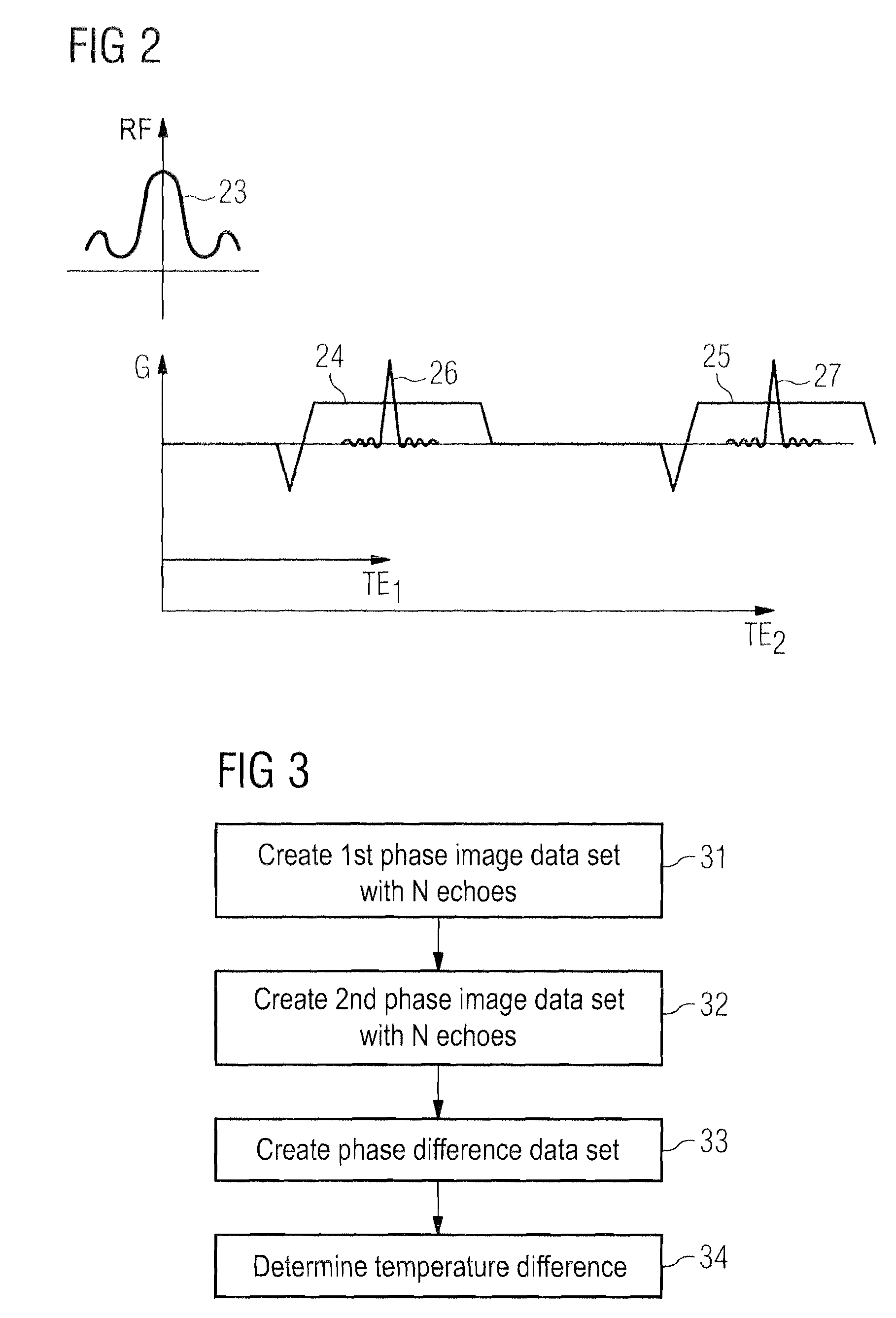
ActiveUS20110092801A1High precisionReduce errorsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) system to create an MR magnitude image data set and a phase image data set of an examination subject, first echo signals in a first raw MR data set are detected after a first echo time TE1 and at least second echo signals in at least one second raw MR data set are detected after a second echo time TE2 that is longer than TE1, a magnitude image data set is generated on the basis of the first raw MR data set and the at least one second raw MR data set with averaging of the first and the at least one second raw MR data set, and the phase image data set is generated based on the phase information contained in the at least two raw MR data sets, with averaging of the respective phase information contained in the at least two raw MR data sets.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
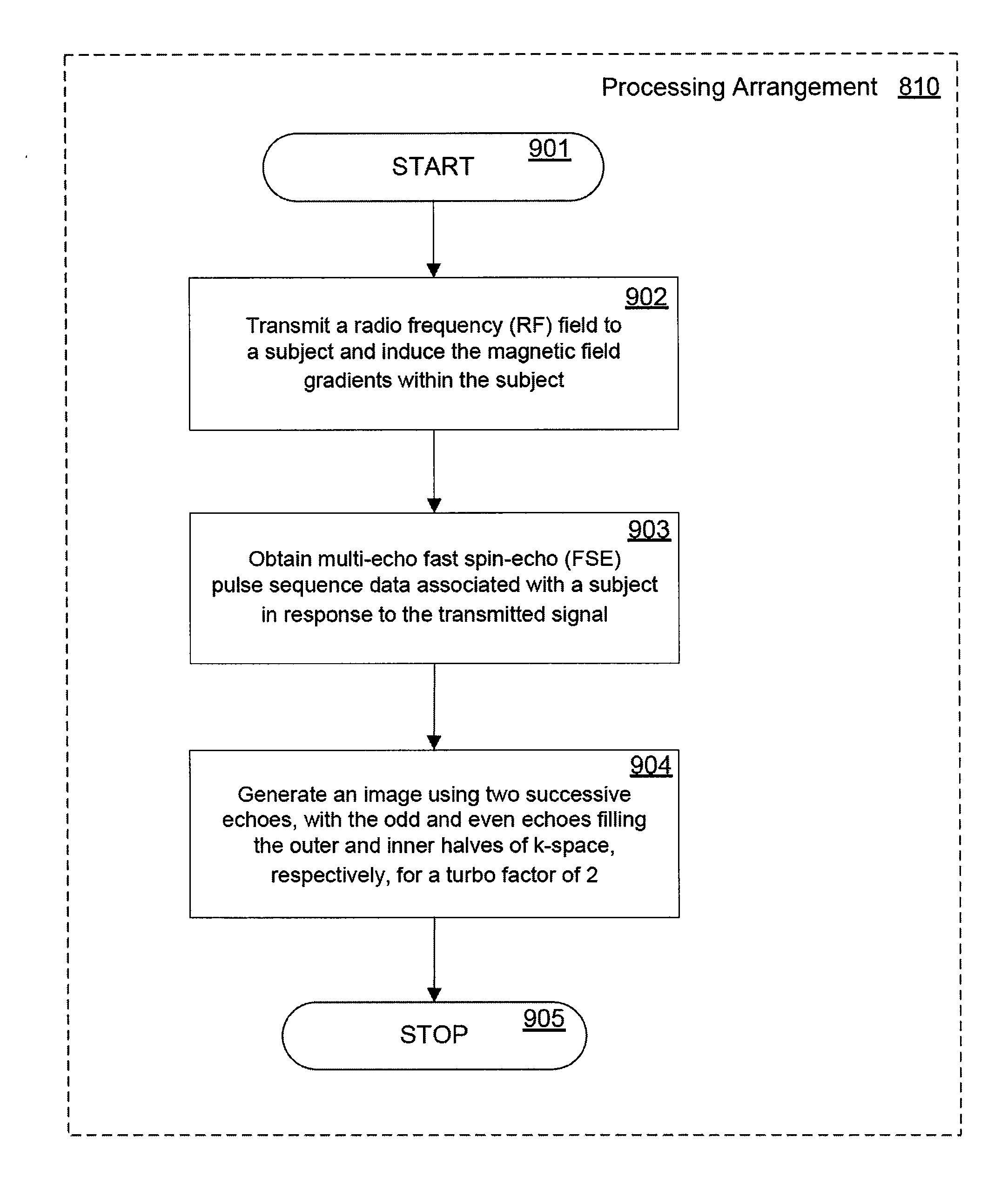
System, method and computer-accessible medium for providing breath-hold multi-echo fast spin-echo pulse sequence for accurate r2 measurement
ActiveUS20100301860A1Accurate measurementMean usedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionAnatomical structuresFast spin echo
Exemplary embodiments of system, method and computer-accessible medium can be provided in accordance with the present disclosure can be provided for generating a plurality of images associated with at least one anatomical structure using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. For example, using such exemplary embodiments, it is possible to obtain at least one multi-echo fast spin-echo (FSE) pulse sequence based on the MRI data, which can include, e.g., hardware specifications of the MRI system. Further, it is possible to generate each of the images based on a particular arrangement of multiple echoes produced by the multi-echo FSE pulse sequence(s).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Radar level instrument signal processing method based on curve fitting
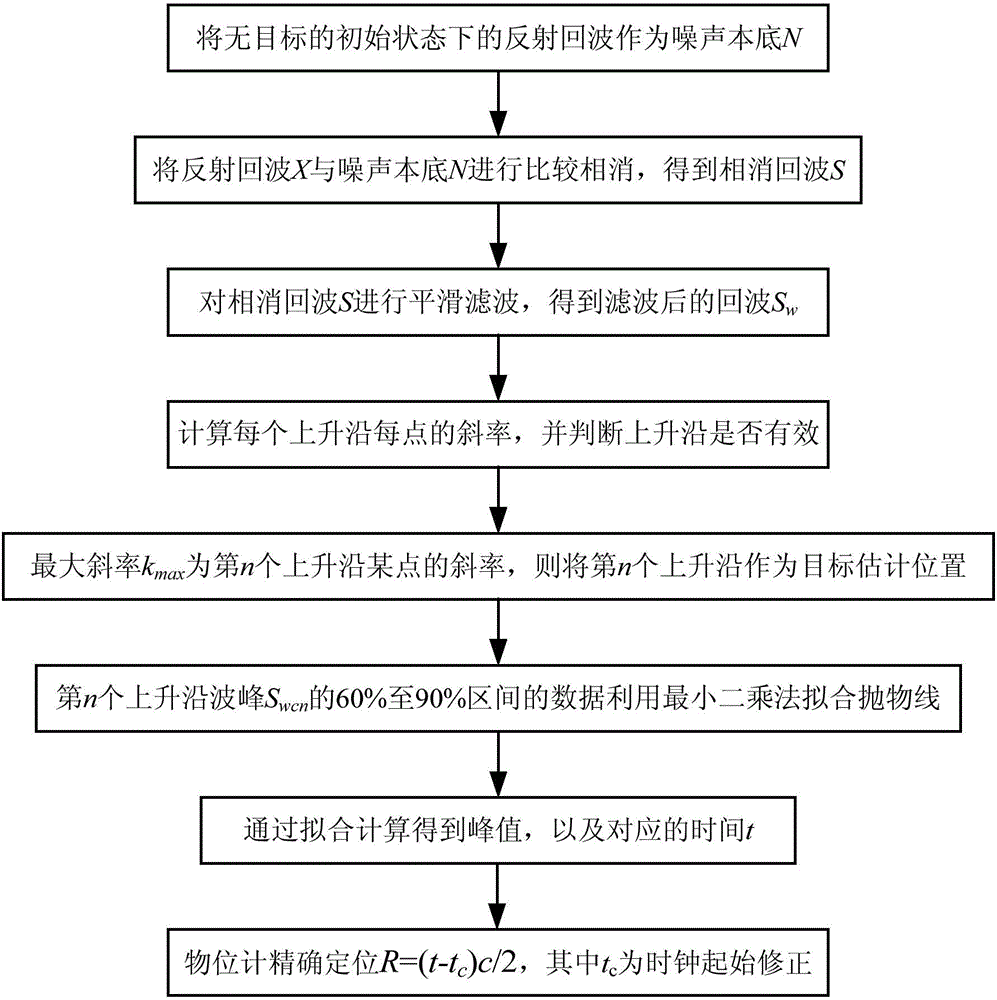
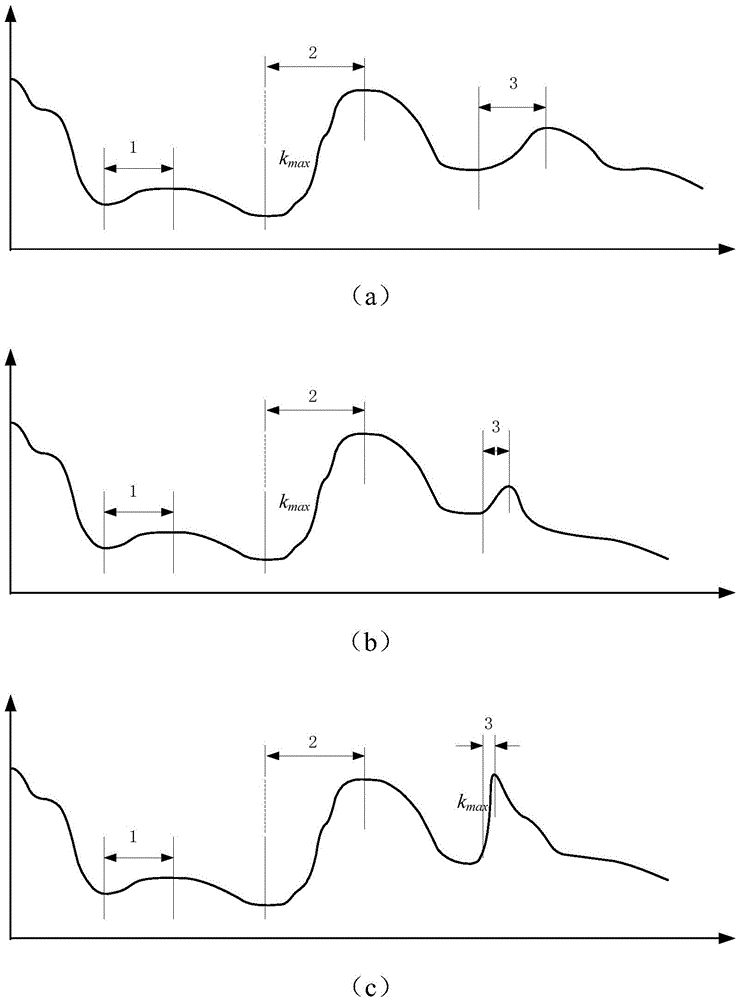
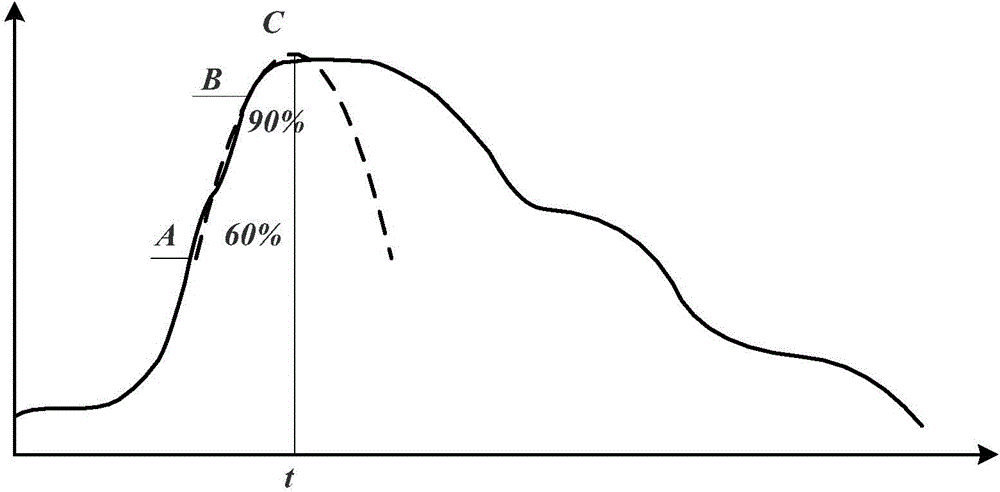
The invention relates to a radar level instrument signal processing method based on curve fitting. The method includes the steps of calculating the slope of each point of an echo rising edge, judging whether the duration time of the rising edge meets the minimum keeping time or not, determining a certain rising edge as a target estimation position through the maximum slope, fitting a parabola through the least square method according to data of a 60% to 90% section of a crest of the rising edge at the target estimation position, calculating the peak value and corresponding time, and finally accurately positioning a level instrument. By means of the method, the purpose of positioning the multi-diameter multi-echo crest is effectively achieved, the influences of the measurement environment and a target object itself on an echo rear edge are eliminated, and the positioning accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
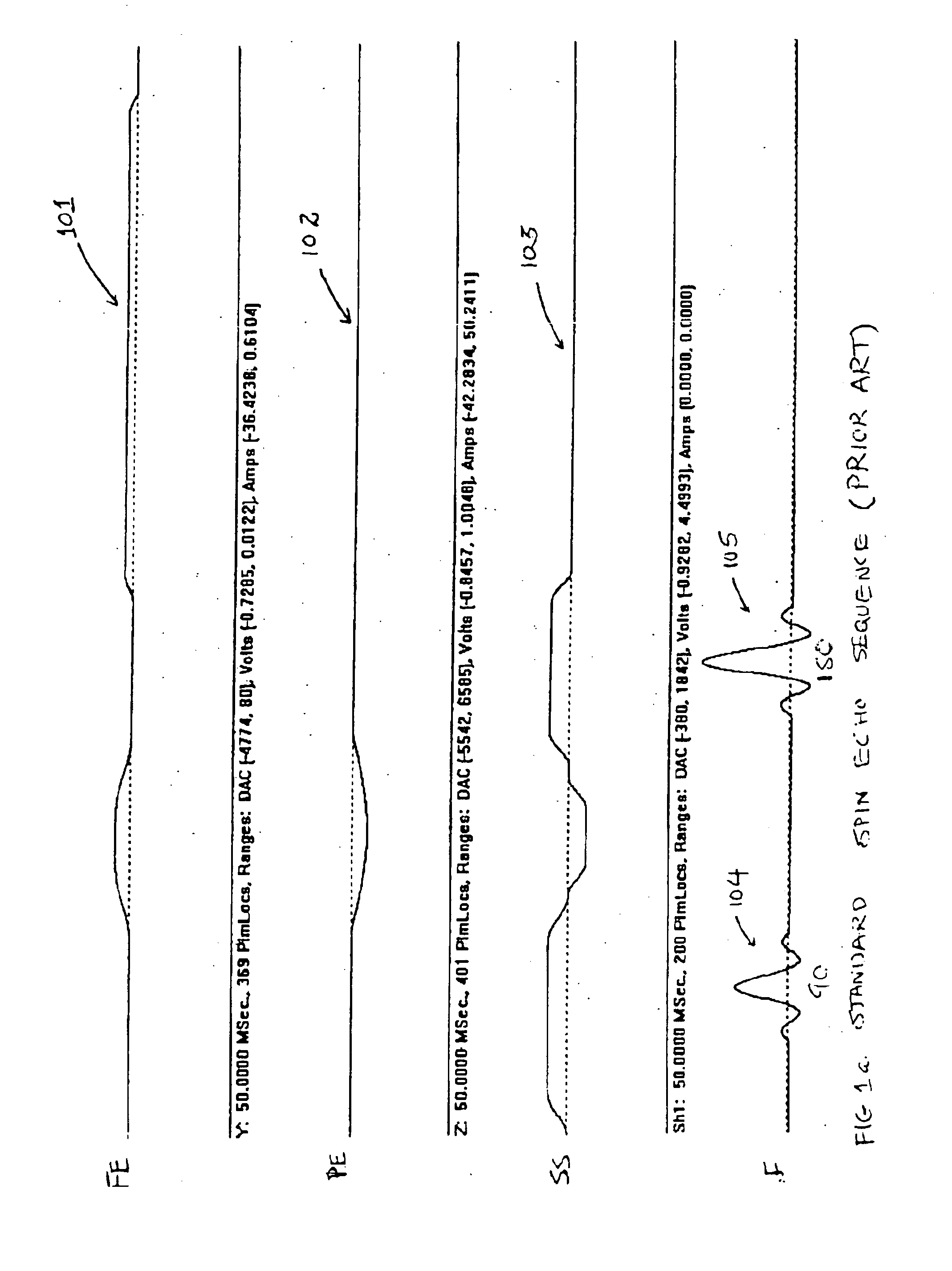
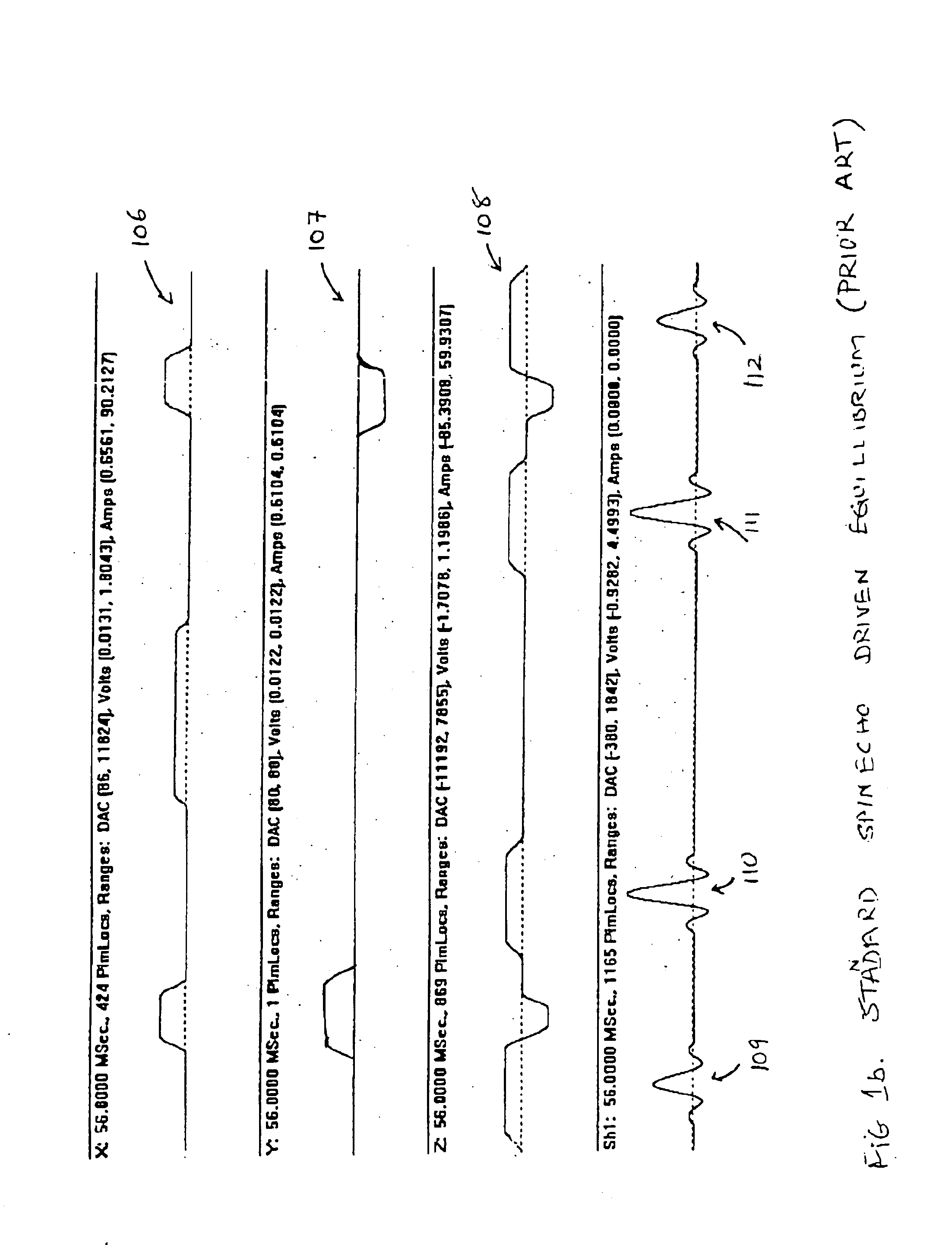
Driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo scanning
InactiveUS6847209B2Time periodShorten the time periodMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoSpins
An NMR imaging process utilizes both driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo techniques to acquire image data. The fast-spin echo technique is a multi-echo imaging sequence, where a 90-degree RF pulse applied at the center of any echo turns the magnetization back in the direction of the static magnetic field. Within a short waiting time after that pulse, the spins are ready to be excited again. The sequence follows a first 90-degree RF pulse by a series of n 180-degree RF pulses, followed by n echoes. A second 90-degree RF pulse applied to the nth echo returns the magnetization. A multiple single-slice mode is utilized to acquire individual slice images one at a time. A continuous single-slice mode is utilized to acquire individual slice images automatically in sequence over the region of interest. In either mode, adjacent slices can be made to overlap to a degree ranging from 0% to 100%.
Owner:FONAR
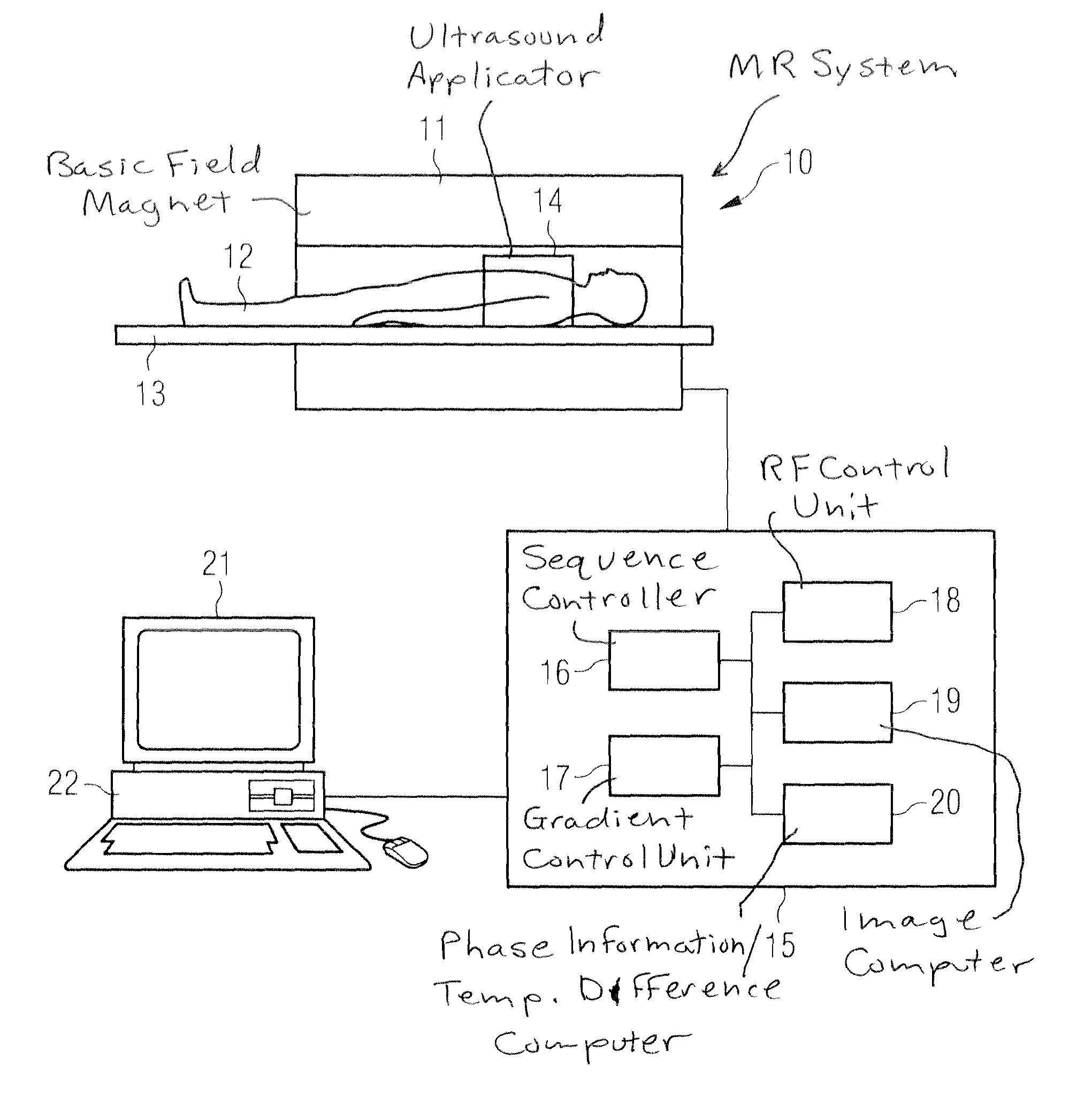
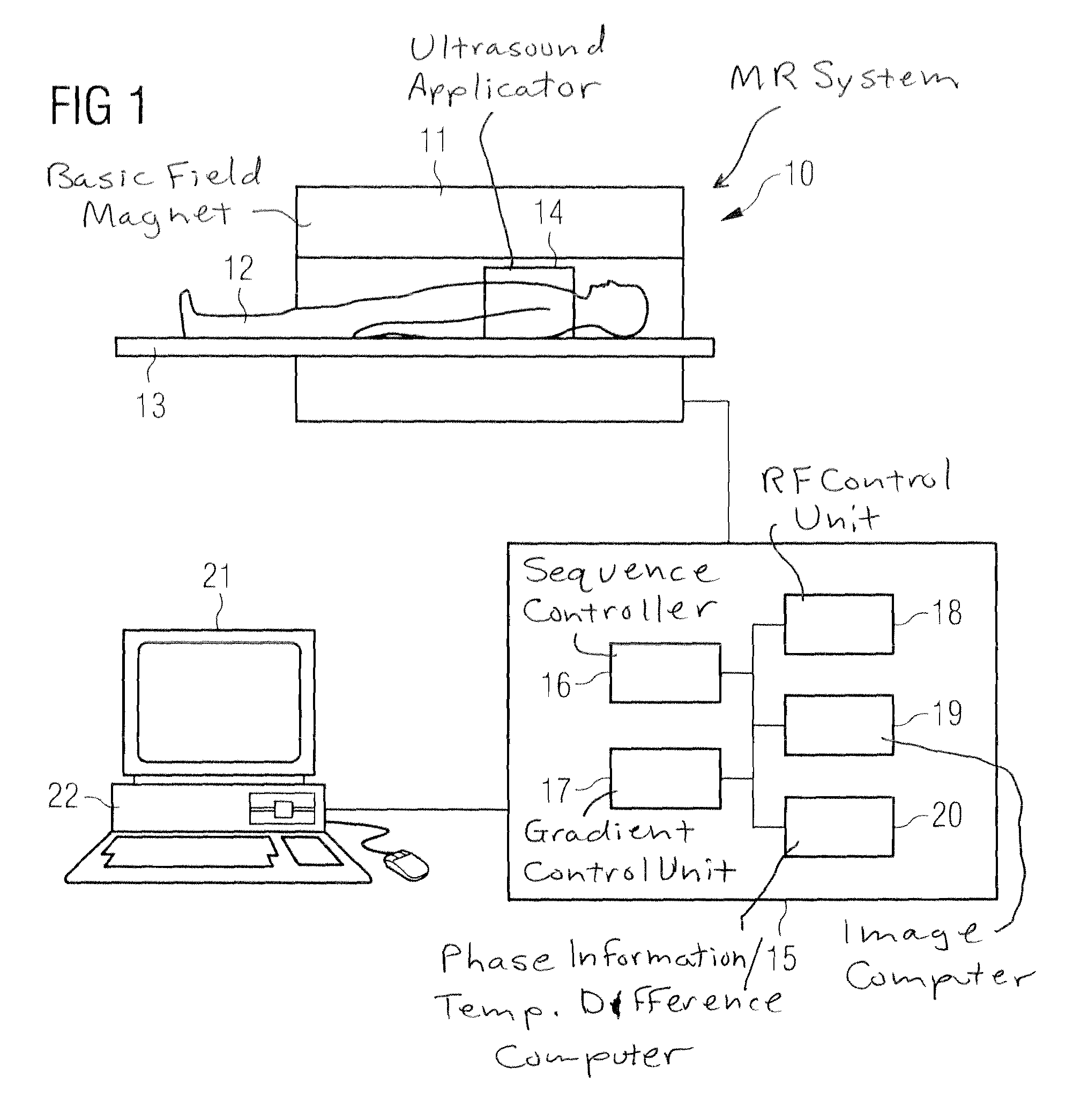
Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography with chemical shift encoding for fat suppression
ActiveUS20140043022A1Rapid and reliable mannerEfficiently signaledDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFat suppressionData set
The invention relates to a method of performing contrast enhanced first pass magnetic resonance angiography, the method comprising: acquiring (302) magnetic resonance datasets of a region of interest using a single- or multi-echo data acquisition technique, wherein the echo times of the one or multiple echoes are flexible, wherein at the time of the data acquisition the region of interest comprises fat, water and a contrast agent, processing (304) the datasets using a generalized Dixon water-fat separation technique to eliminate the signal originating from the fat from the background for reconstruction of an image data set.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
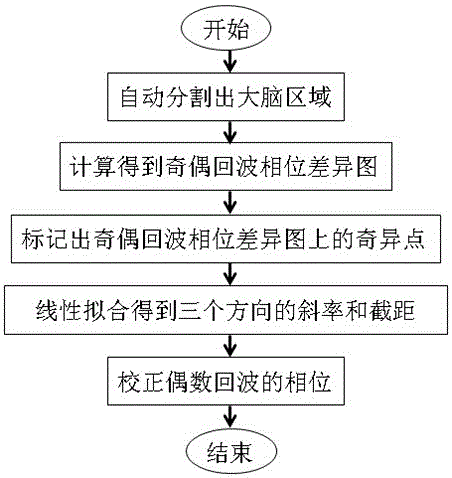
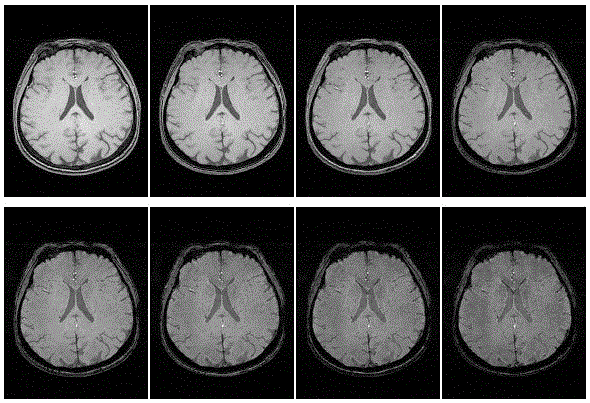
Method eliminating magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) gradient echo sequence odd-even phase difference
ActiveCN106646301AEliminates even and odd phase differencesThe result is accurateMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic susceptibilityPhase difference
The invention discloses a method eliminating magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) gradient echo sequence odd-even phase differences; the method comprises the following steps: 1, automatically segmenting a brain area on a modular figure obtained by MRI; 2, calculating phase images of the first 3 echo obtained by MRI so as to obtain an odd-even echo phase difference chart; 3, tagging singular points on the odd-even echo phase difference chart; 4, linear fitting the phase difference chart in three space directions so as to obtain slopes and intercepts of the three directions; 5, correcting the phase of even ocho. The method can eliminate the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) multi-echo gradient echo sequence odd-even phase differences, and can automatically select the phase difference fitting area. Compared with a manual selection area method, the method is time saving and labor saving, more objective, and can provide an accurate result for a MRI quantify magnetic susceptibility chart.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Mr imaging using multi-echo k-space acquisition
ActiveUS20170199258A1Improved MR imaging techniqueFast MR imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImaging techniqueCondensed matter physics
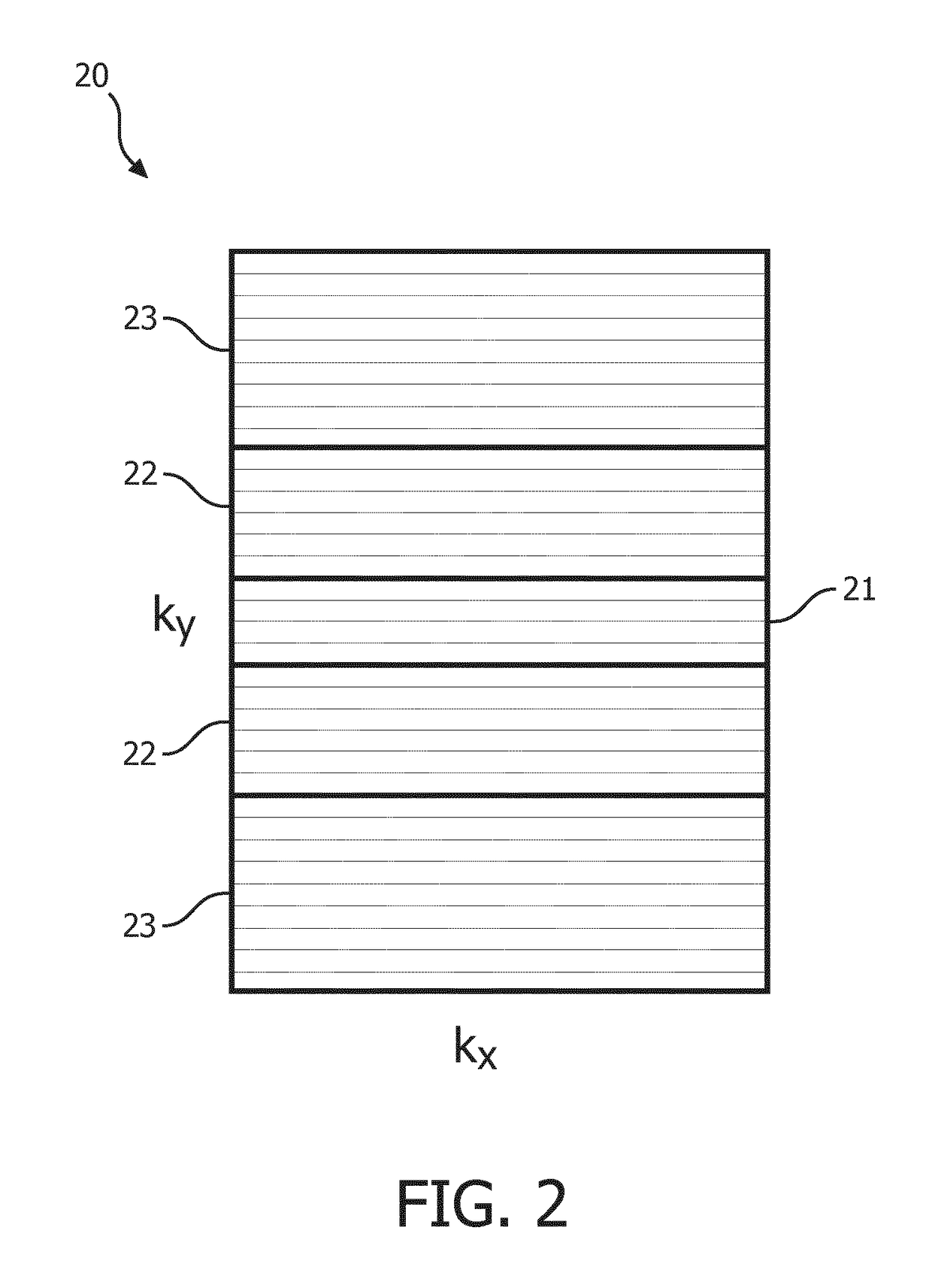
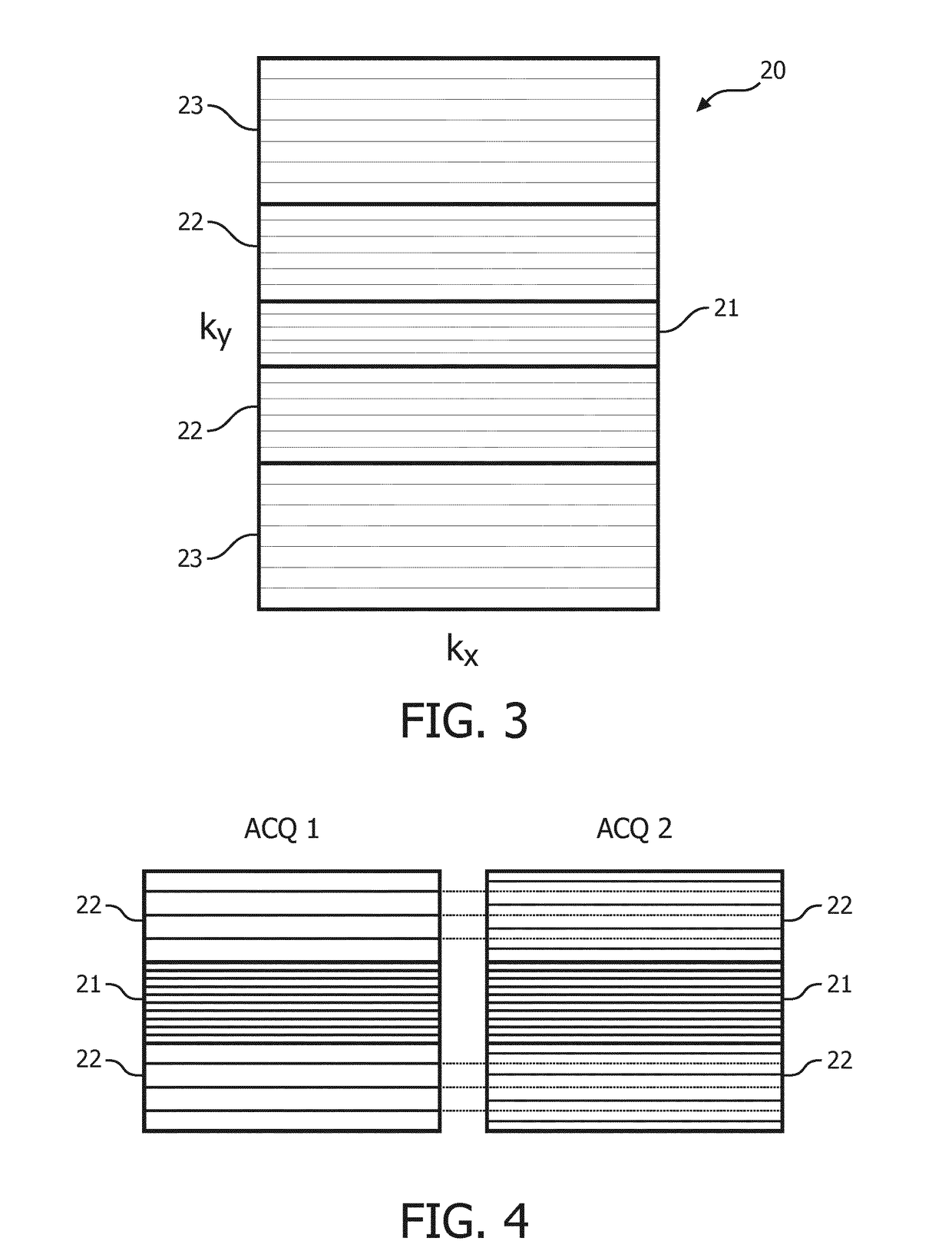
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least an object (10) placed in an examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to enable fast MR imaging using a multi-echo imaging technique which is robust with respect to motion. The method of the invention comprises the steps of:—generating echo signals by subjecting the object (10) to an imaging sequence,—acquiring the echo signals, each echo signal being attributed to a k-space line, wherein a number of k-space lines, which are adjacently arranged in a part of k-space, are repeatedly sampled, with said number of k-space lines being sampled in a different sequential order per repetition, and—reconstructing a MR image from the acquired echo signals. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device for carrying out this method as well as to a computer program to be run on a MR device.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com