Patents
Literature
139 results about "Iron group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry and physics, the iron group refers to elements that are in some way related to iron; mostly in period (row) 4 of the periodic table. The term has different meanings in different contexts.
Coated cutting tool
InactiveUS20020187370A1Improve tool lifeIncrease resistanceTurning toolsCeramic layered productsIron groupSurface roughness
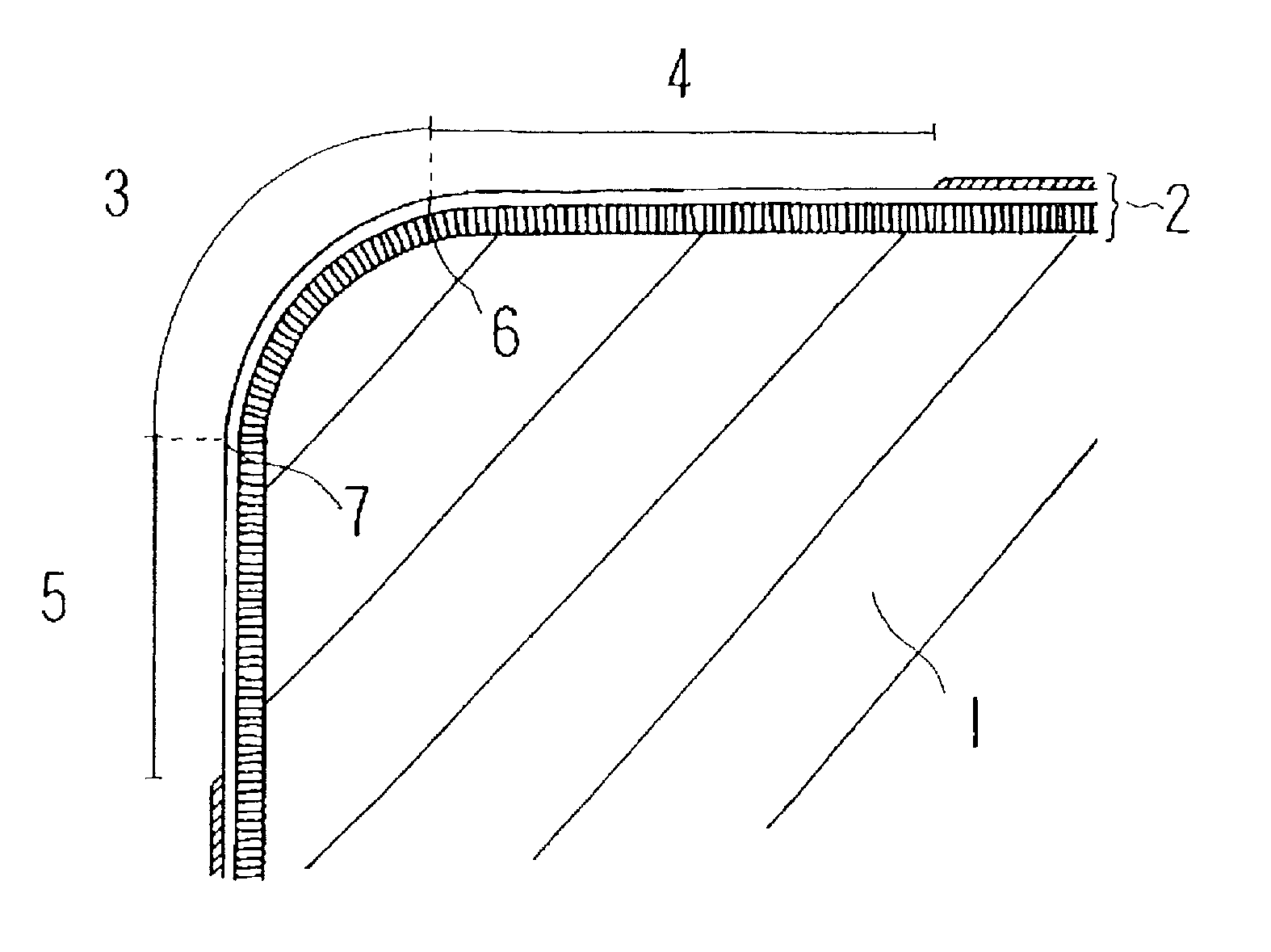
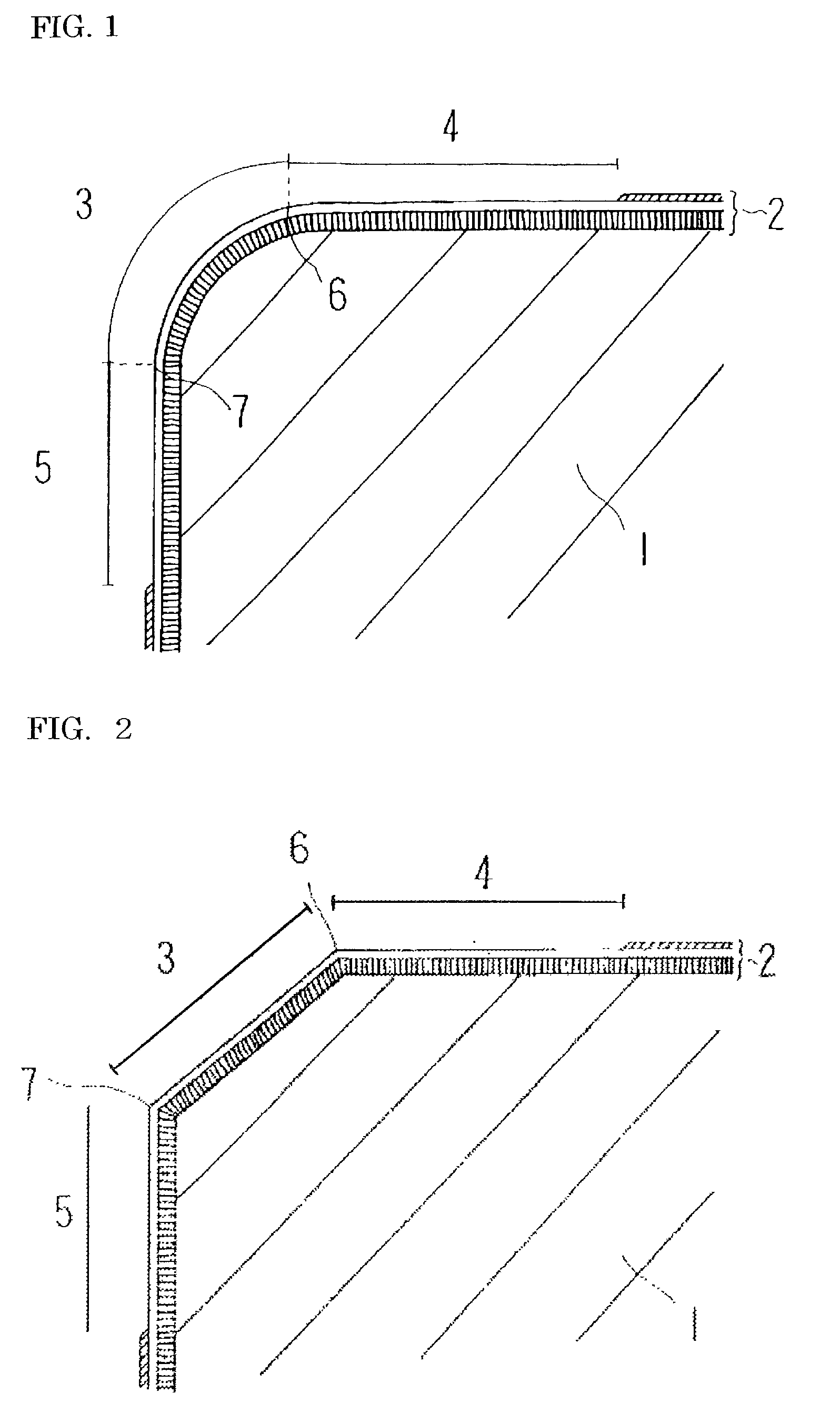
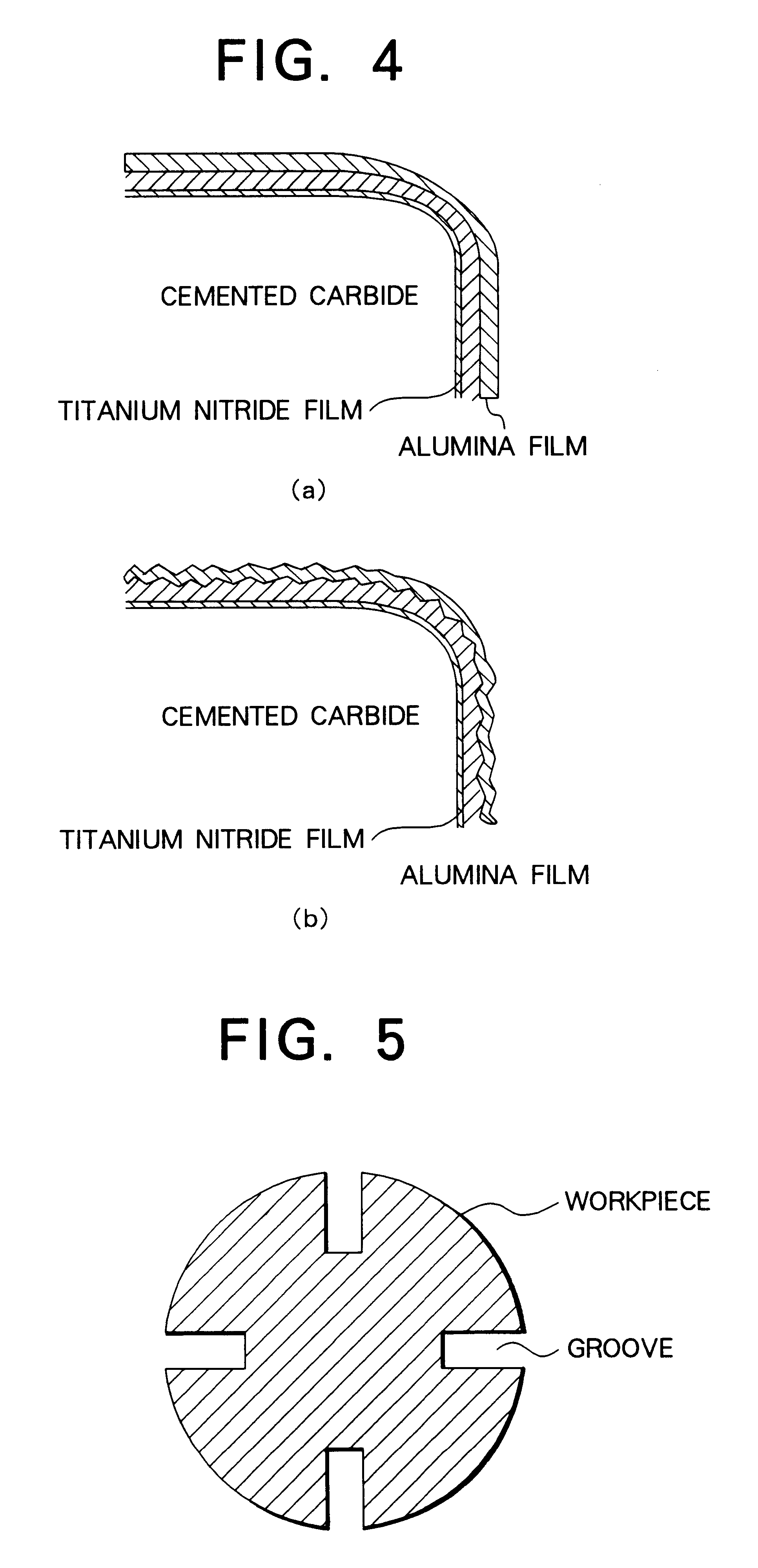
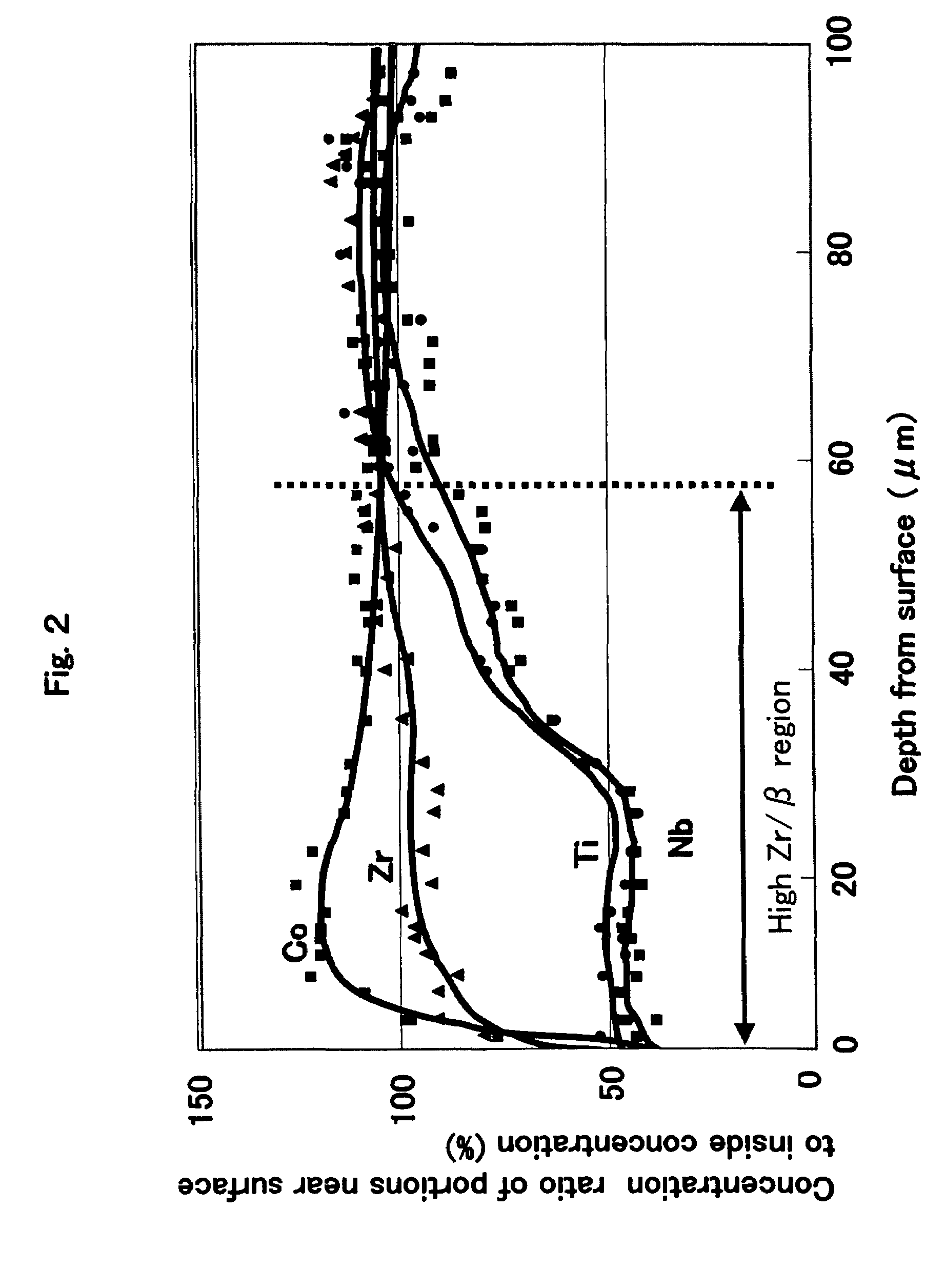
The present invention provides a coated cutting tool in which fracture resistance and wear resistance are simultaneously realized, tool life is improved, and surface roughness of machined workpiece is improved The coated cutting tool is provided with hard coating layer 2 on substrate 1. The substrate 1 is formed of a binder phase comprising one or more kinds of iron-group metals and a hard phase comprising one or more kinds of substances selected from the group consisting of carbides, nitrides, and oxides of the periodic table IVa-, Va-, and VIa-group elements, and solid solutions thereof. In the coating layer 2, blade-edge ridge 3, a range of at least 200 mum from the rake face side boundary 6 of the same ridge toward the rake face side, and a range of at least 50 mum from the flank side boundary 7 of the same ridge toward the flank side are formed to be smooth surfaces which substantially have surface roughness (Rmax) of 0.2 mum or less (reference length: 5 mum).
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Coated tool of cemented carbide
InactiveUS6187421B1Improve propertiesImprove tool lifePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCoated membraneCarbide coating
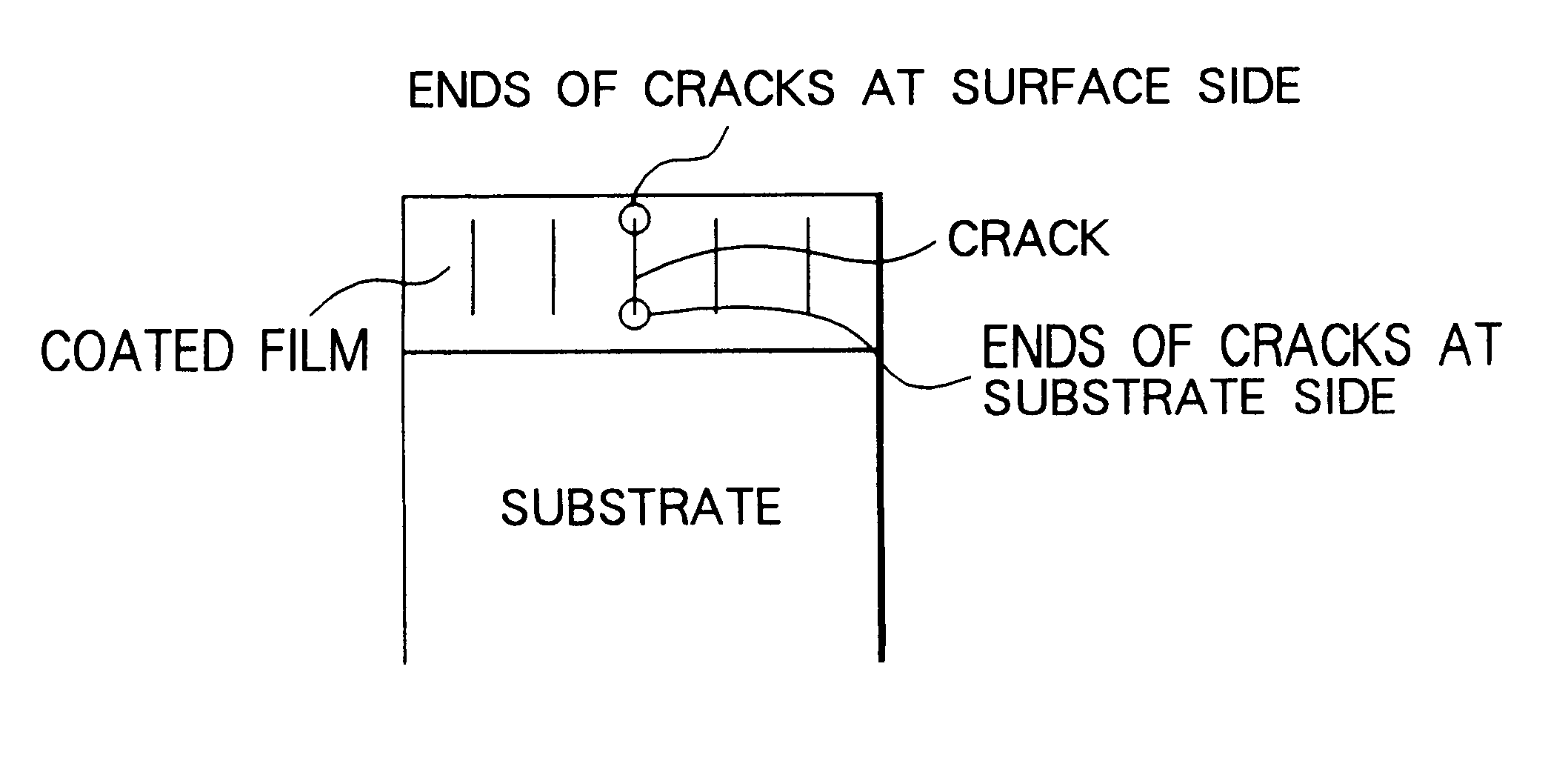
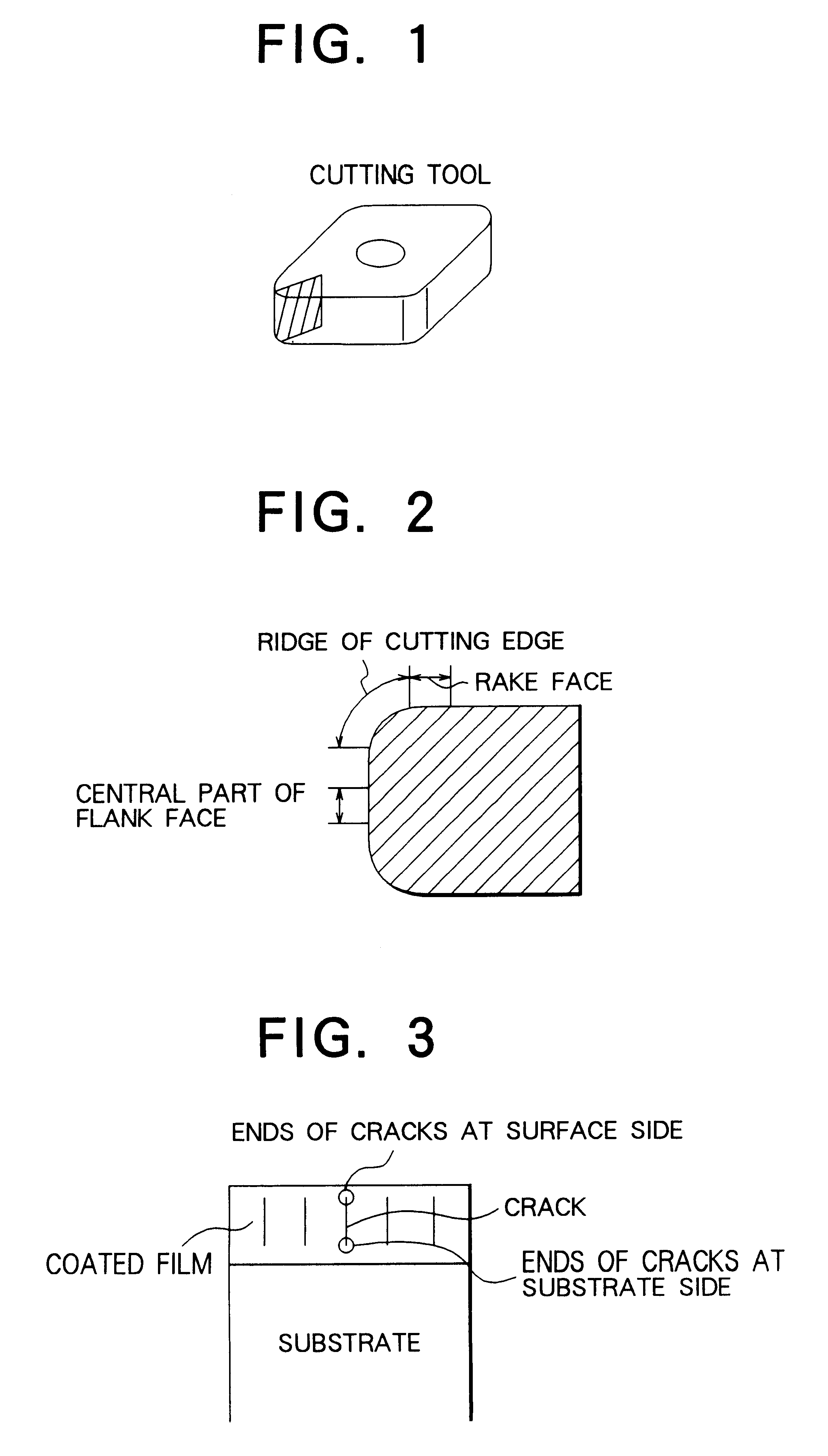
The principal object of the present invention is to provide a coated cemented carbide tool whose both properties of breakage resistance and wear resistance are improved and whose life is lengthened.The present invention has been made to achieve this object and is related with a coated cemented carbide cutting tool comprising a substrate consisting of a matrix of WC and a binder phase of an iron group metal and a plurality of coated layers provided on a surface of the substrate, in which (a) an innermost layer, adjacent to the substrate, of the coated layers consists essentially of titanium nitride having a thickness of 0.1 to 3 mum, (b) on a mirror-polished cross-sectional microstructure of the said tool, an average crack interval in the coated film on a ridge of a cutting edge and / or rake face is smaller than an average crack interval in the coated layer on a flank face, (c) at least 50% of the cracks in the coated film on the said ridge of the cutting edge and / or rake face have ends of the cracks in the said innermost titanium nitride layer, in a layer above the titanium nitride layer or in an interface between these layers and (d) an average crack length in the coated film on the said ridge of the cutting edge and / or rake face is shorter than an average film thickness on the flank face.According to the present invention, quantitatively specifying the crack intervals and positions of the ends of the cracks in the coated layer results in excellent breakage resistance as well as wear resistance.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method of manufacturing carbon nanotube
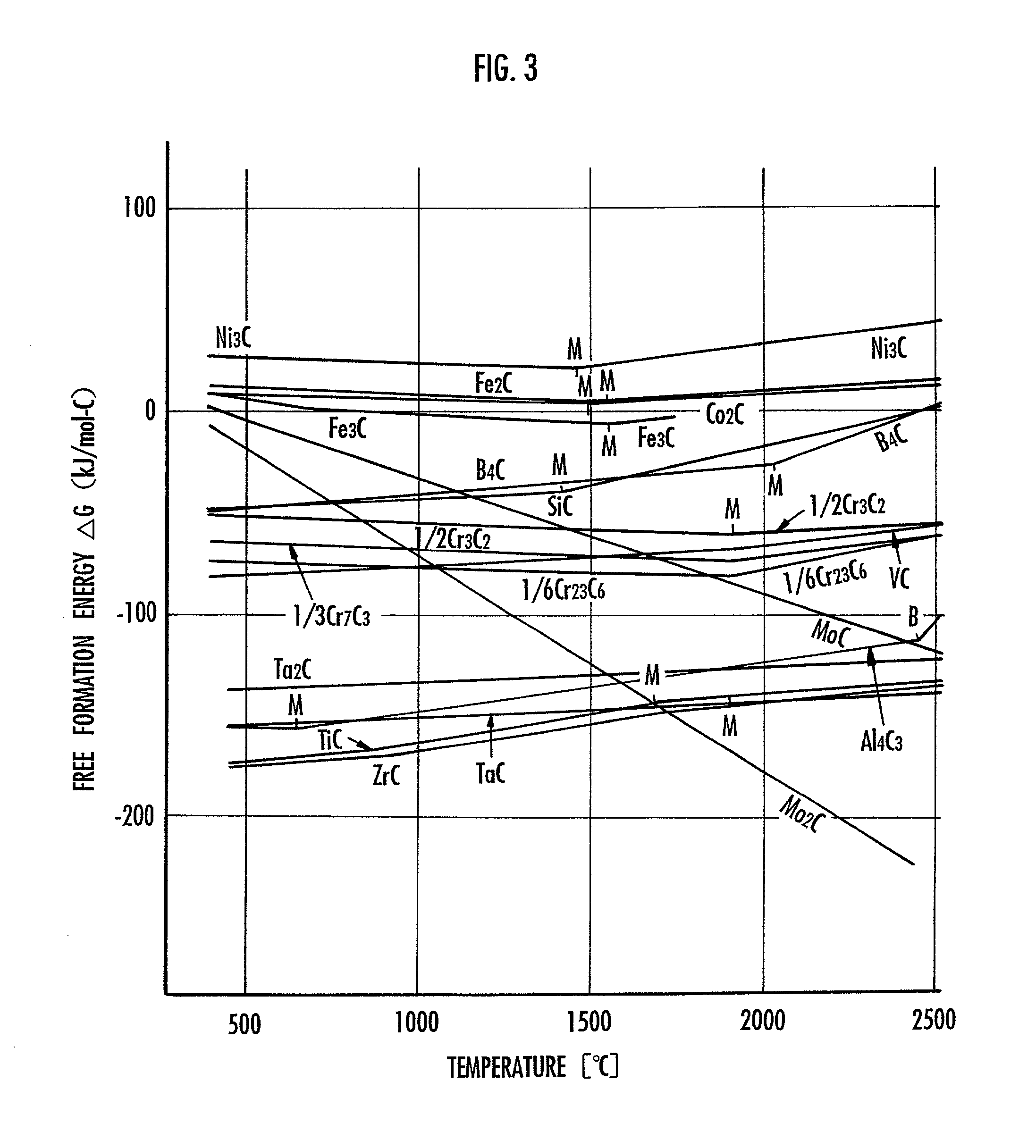
There is provided a method of manufacturing a carbon nanotube so as to be able to increase the yield of a web and to increase the amount of a carbon nanotube contained in the web. A high-energy heat source is caused to act on carbon in the presence of catalysts. The catalysts include a main catalyst made of at least one metal which is selected from the group consisting of an iron group element, a platinum group element, and a rare earth element, and an auxiliary catalyst made of a material which causes an exothermic reaction in a process of generating the web including the carbon nanotube. The auxiliary catalyst is made of a material for generating a carbide more stable in terms of thermal energy than a carbide generated by the main catalyst. The free formation energy of the carbide generated from the material is smaller than the free formation energy of the carbide generated by the main catalyst. The main catalyst is made of at least one metal which is selected from the group consisting of Fe, Co, Ni, Rh, Ru, Pd, Pt, Y, La, and Ce. The auxiliary catalyst is made of at least one material selected from the group consisting of Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W, B, Al, and Si. Typically the main catalyst is made of Ni-Y, and the auxiliary catalyst is made of Ti.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Process for the preparation of high activity carbon monoxide hydrogenation catalysts; the catalyst composition, use of the catalysts for conducting such reactions, and the products of such reactions
InactiveUS6313062B1High viscosity indexReduce pointsThermal non-catalytic crackingOrganic compound preparationIron groupHigh activity
A process for the preparation of a catalyst useful for conducting carbon monoxide hydrogenation reactions, particularly Fischer-Tropsch reactions; the catalyst compositions, use of the catalyst compositions for conducting such reactions, and the products of these reactions. The steps of the process for producing the catalyst comprise impregnating a powder, or particulate refractory inorganic oxide solids, preferably silica, with a) a soluble compound or salt of a catalytic metal of the Iron Group, preferably cobalt, and b) a soluble compound, or salt, of a Group VIII noble metal, preferably platinum, suitably by sequential contact of the solids with a solution of (a) and a solution of (b), by sequential contact of the solids with a solution of (b) and a solution of (a), or by contact with a solution which contains both (a) and (b). The metals impregnated solids, or particulate solids precursor material, after impregnation with the Group VIII noble metal, is washed with a hydrocarbyl ammonium hydroxide or ammonium hydroxide solution, the material shaped, dried and calcined, and the metals components thereof thereafter reduced to form the finished catalyst. The catalyst formed from the hydrocarbyl ammonium hydroxide or ammonium hydroxide-washed catalyst precursor, quite surprisingly, is more active and selective in conducting a carbon monoxide hydrogenation reaction to produce hydrocarbon waxes, with lower gas make, than a catalyst of corresponding composition similarly prepared except that the catalyst was prepared from a catalyst precursor which was not washed with a hydrocarbyl ammonium hydroxide or ammonium hydroxide solution.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Ammonia decomposition catalysts and their production processes, as well as ammonia treatment method
InactiveUS20110176988A1Efficient decompositionSimple and easy mannerGas treatmentNitrogen preparationDecompositionIron group
The ammonia decomposition catalyst of the present invention is a catalyst for decomposing ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen, including a catalytically active component containing at least one kind of transition metal selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel, preferably including: (I) a catalytically active component containing: at least one kind selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, tungsten, and vanadium; (II) a catalytically active component containing a nitride of at least one kind of transition metal selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel; or (III) a catalytically active component containing at least one kind of iron group metal selected from the group consisting of iron, cobalt, and nickel, and at least one metal oxide, thereby making it possible to effectively decompose ammonia into nitrogen and hydrogen at relatively low temperatures and at high space velocities to obtain high-pure hydrogen.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
High strength hard alloy and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS20070110607A1High hardnessImprove toughnessTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusBorideCrack resistance
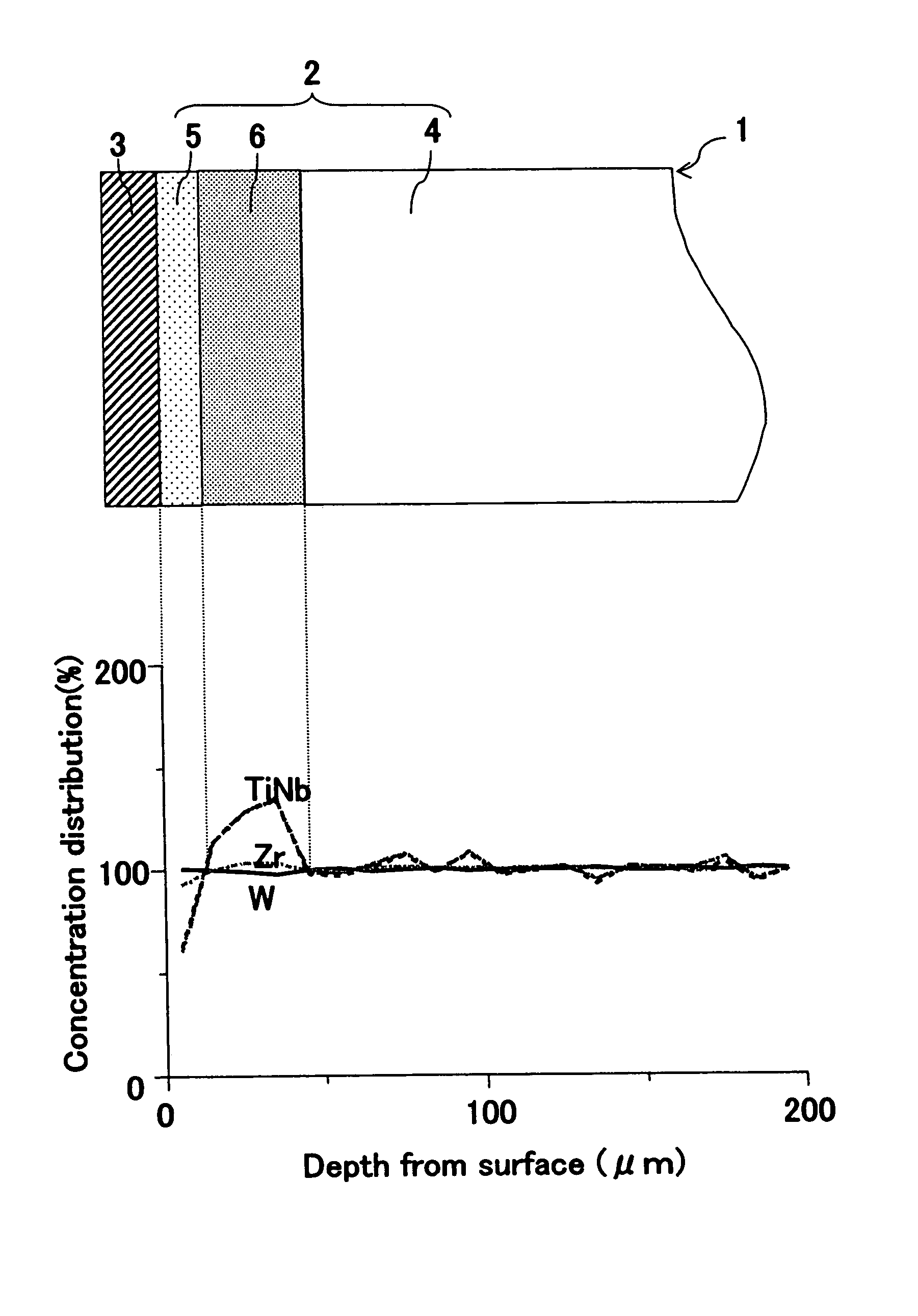
The present invention provides a WC—Co system (the WC—Co system in the present invention means that it comprises not only hard grains composed mainly of WC and iron group metal powder containing Co, but also at least one kind selected from carbide, nitride, carbonitride and boride of elements in Groups IVa, Va and VIa of the Periodic Table, excluding WC, as hard grains) cemented carbide having high strength and high toughness which is excellent in wear resistance, toughness, chipping resistance and thermal crack resistance. A WC—Co system compact containing an M12C to M3C type double carbide (M represents one or more kinds selected from the group consisting of Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo and W, and one or more kinds selected from the group consisting of Fe, Co and Ni) as a main component of the surface layer portion is subjected to a carburization treatment, and then subjected to liquid phase sintering so as to adjust the mean grain size of the surface layer WC depending on a liquid crystal sintering temperature as an indicator.
Owner:SANALLOY IND
Metal-ceramic bond diamond grinding wheel and production method thereof
ActiveCN103692371AGood self-sharpeningImprove gripAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesPowder mixtureCopper plating
The invention discloses a novel metal-ceramic bond diamond grinding wheel having the high strength and form-holding property in metal bond grinding wheels and the high self-sharpening property in ceramic bond grinding wheels, and a production method thereof. The metal-ceramic bond diamond grinding wheel is produced by: 1, preparing powder mixture out of 60-70% of copper-plated diamond powder, 15-20% of (W, Ti)C powder, 5-10% of tin powder, and 5-15% of iron group powders; mixing according to the above components and ratio to obtain the powder mixture; 2, forming, namely pressing the powder mixture into blanks by pressure forming; 3, sintering, namely subjecting the blanks to inert atmosphere low-pressure sintering, heating the blanks to 850-1050DEG C during sintering, and holding the temperature for 10-30 minutes. The copper-plated diamond powder is composed of particles with average particle size of 5-80 micrometers, and the particles are composed of diamond cores and copper coatings covering the diamond cores. Inert atmosphere during sintering is 5-10Mpa.
Owner:长沙市萨普新材料有限公司
METHOD FOR PRODUCING SINTERED NdFeB MAGNET
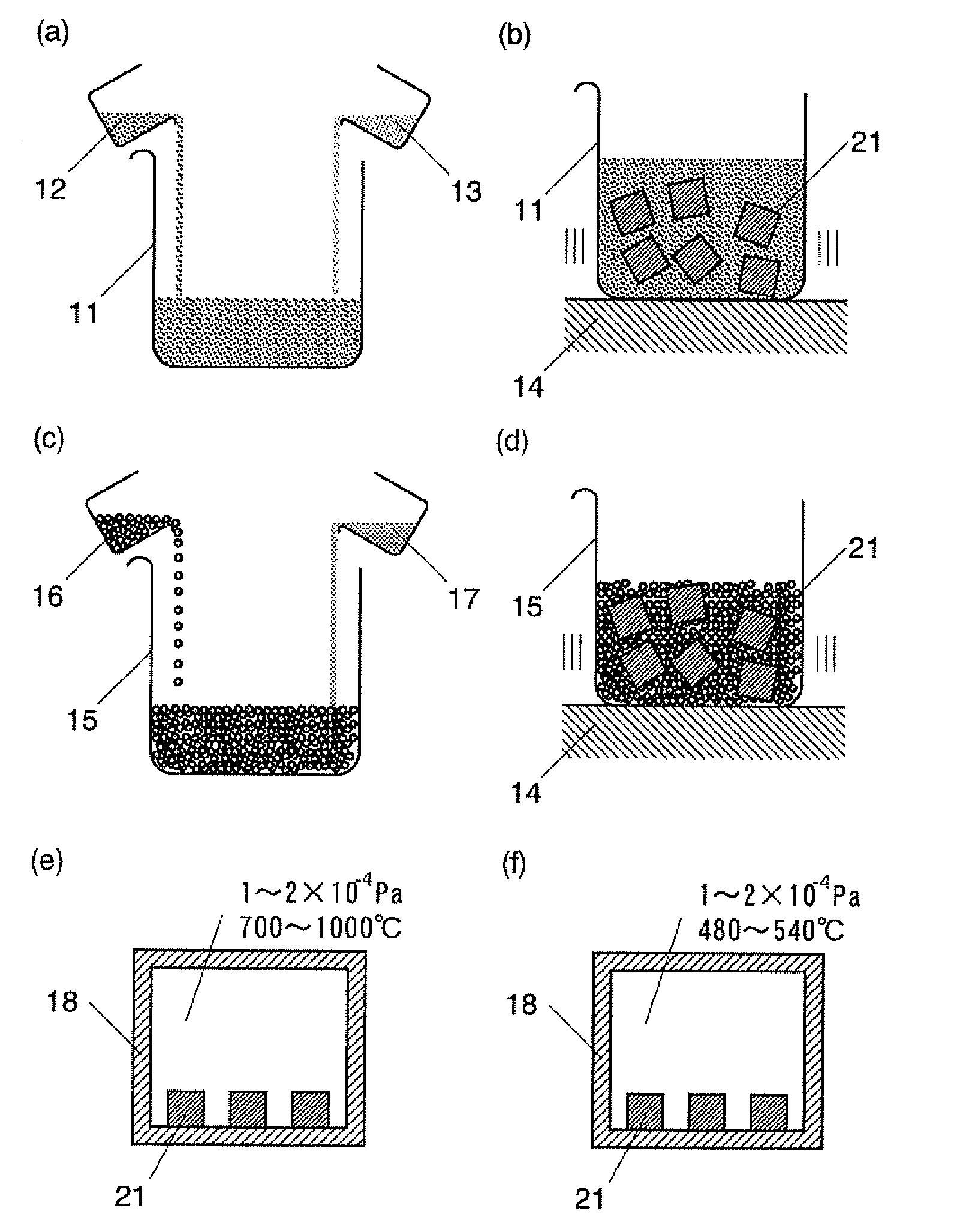
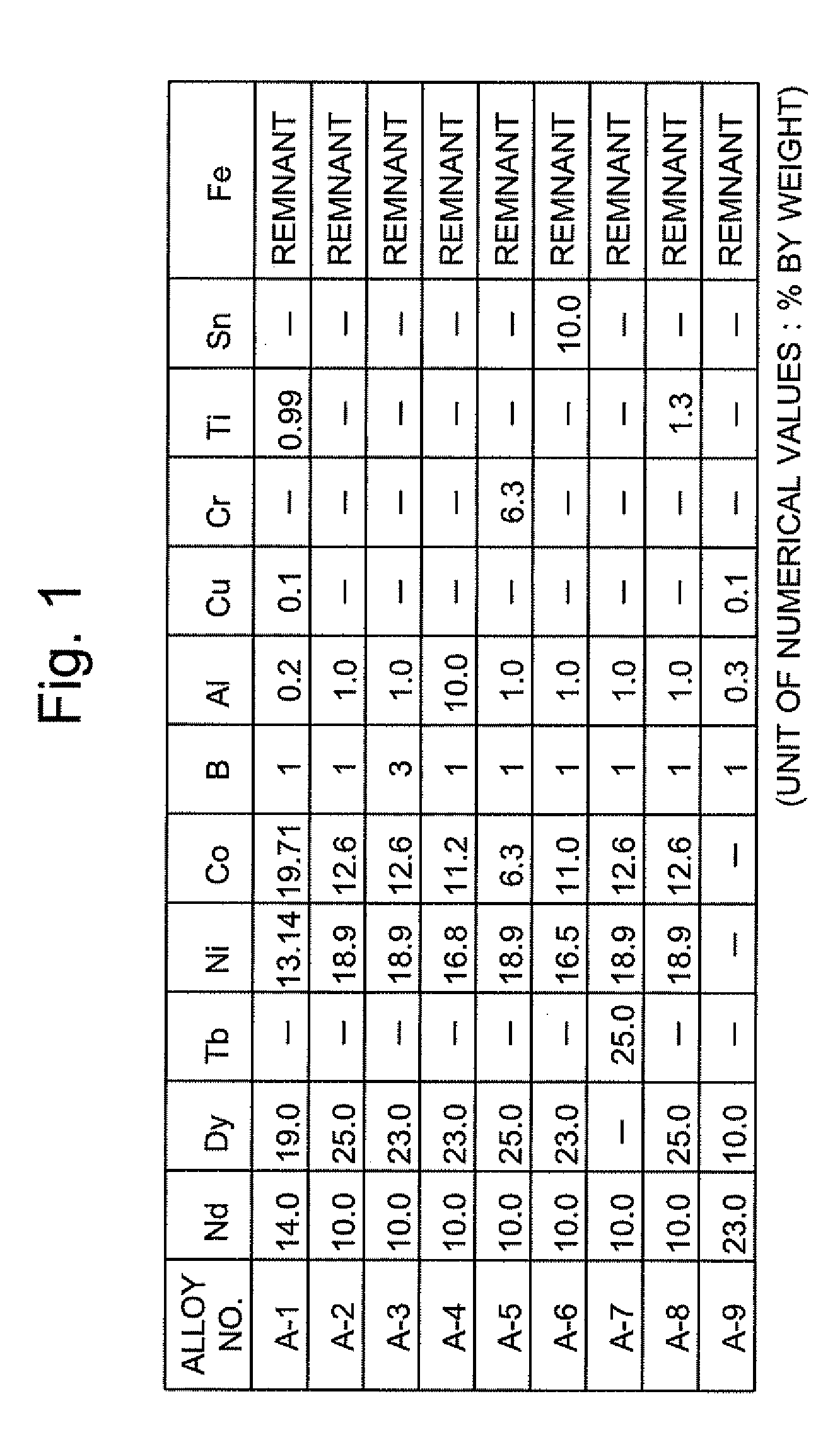
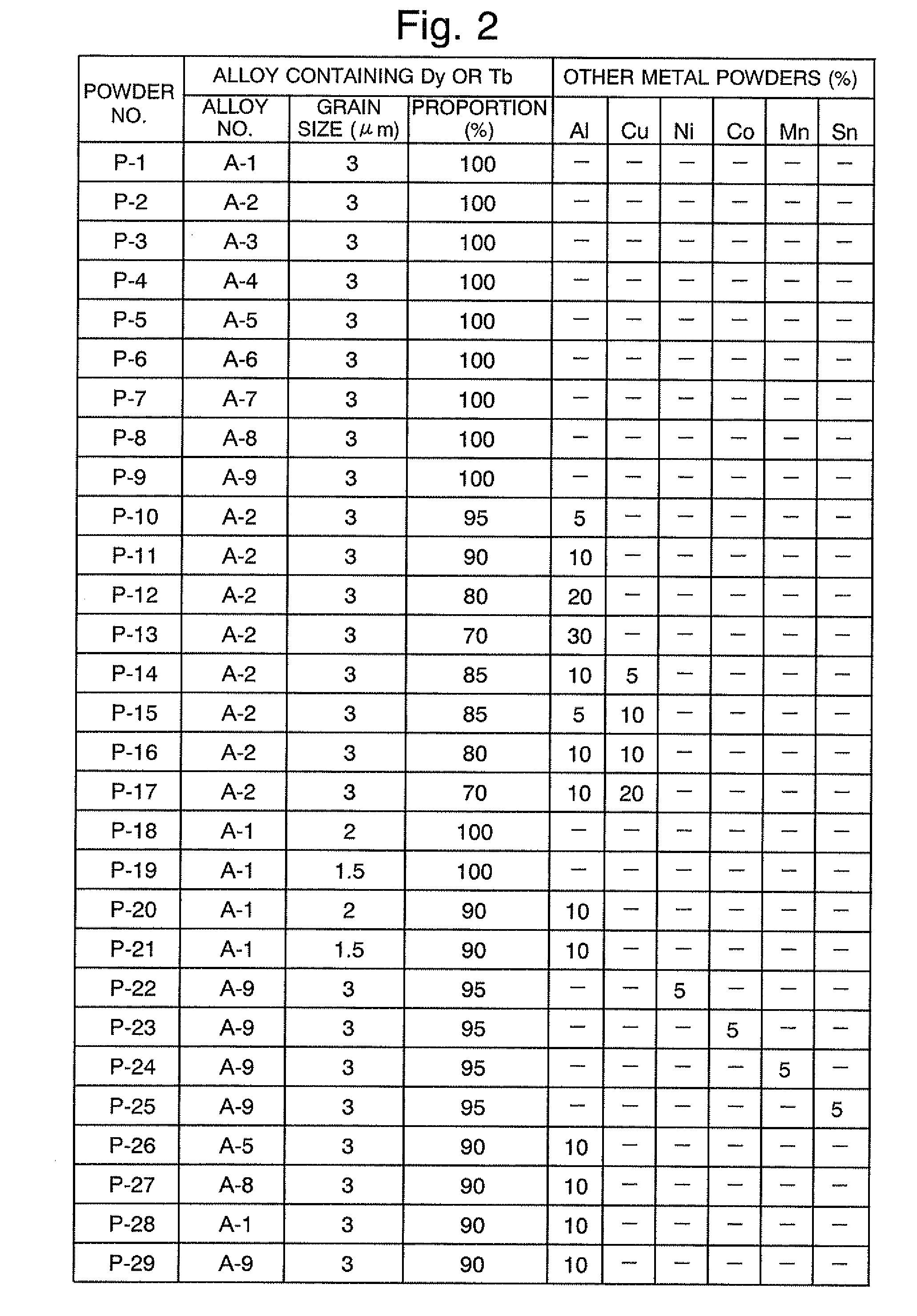
ActiveUS20090252865A1Increase in coercivityDeterioration of characteristicPretreated surfacesMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementIron group
The present invention provides a method for producing a sintered NdFeB magnet having high coercivity and capable of being brought into applications without lowering its residual magnetic flux density or maximum energy product and without reprocessing. The method for producing a sintered NdFeB magnet according to the present invention includes applying a substance containing dysprosium (Dy) and / or terbium (Tb) to the surface of the sintered NdFeB magnet forming a base body and then heating the magnet to diffuse Dy and / or Tb through the grain boundary and thereby increase the coercivity of the magnet. This method is characterized in that: (1) the substance containing Dy or Tb to be applied to the surface of the sintered NdFeB magnet is substantially a metal powder; (2) the metal powder is composed of a rare-earth element R and an iron-group transition element T, or composed of R, T and another element X, the element X capable of forming an alloy or intermetallic compound with R and / or T; and (3) the oxygen content of the sintered NdFeB magnet forming the base body is 5000 ppm or lower. The element T may contain nickel (Ni) or cobalt (Co) to produce an anticorrosion effect.
Owner:DAIDO STEEL CO LTD
Process for the preparation of high activity hydrocarbon synthesis catalysts; and catalyst compositions
InactiveUS6090742AReduce the presence of impuritiesReduce dispersionHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesOrganic chemistry methodsHydrogenIron group
A process for the preparation of a catalyst which is highly active for the synthesis of hydrocarbons from mixtures of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. A silica or silica-containing support is treated with a solution containing both an Iron Group metal, or metals, and nitrous acid, nitric acid, or a nitro-containing organo, or nitro-containing hydrocarbyl compound, or compounds, sufficient to hydroxylate the surface thereof and increase the number of hydroxyl groups on the surface of the support such that the metal component will be highly dispersed, this increasing the activity of the catalyst in a hydrocarbon synthesis reaction as contrasted with that of a catalyst of similar composition, similarly prepared except that the support component of the catalyst was not contacted and simultaneously treated with both the Iron Group metal and the acid.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Honeycomb forming ferrule and jig for honeycomb forming ferrule using the ferrule
InactiveUS20050118296A1Improve toughnessImprove wear resistanceConfectioneryCeramic extrusion diesIron groupHoneycomb
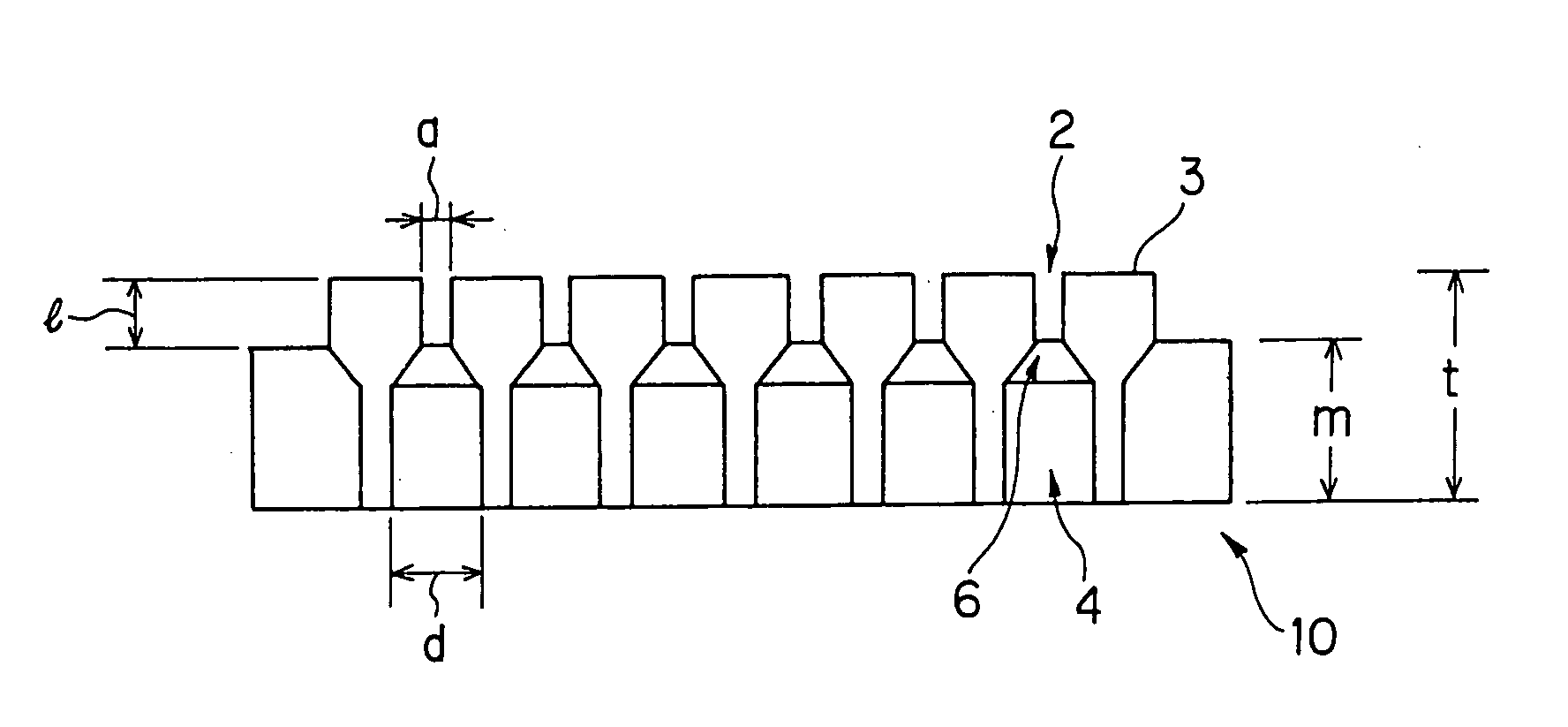
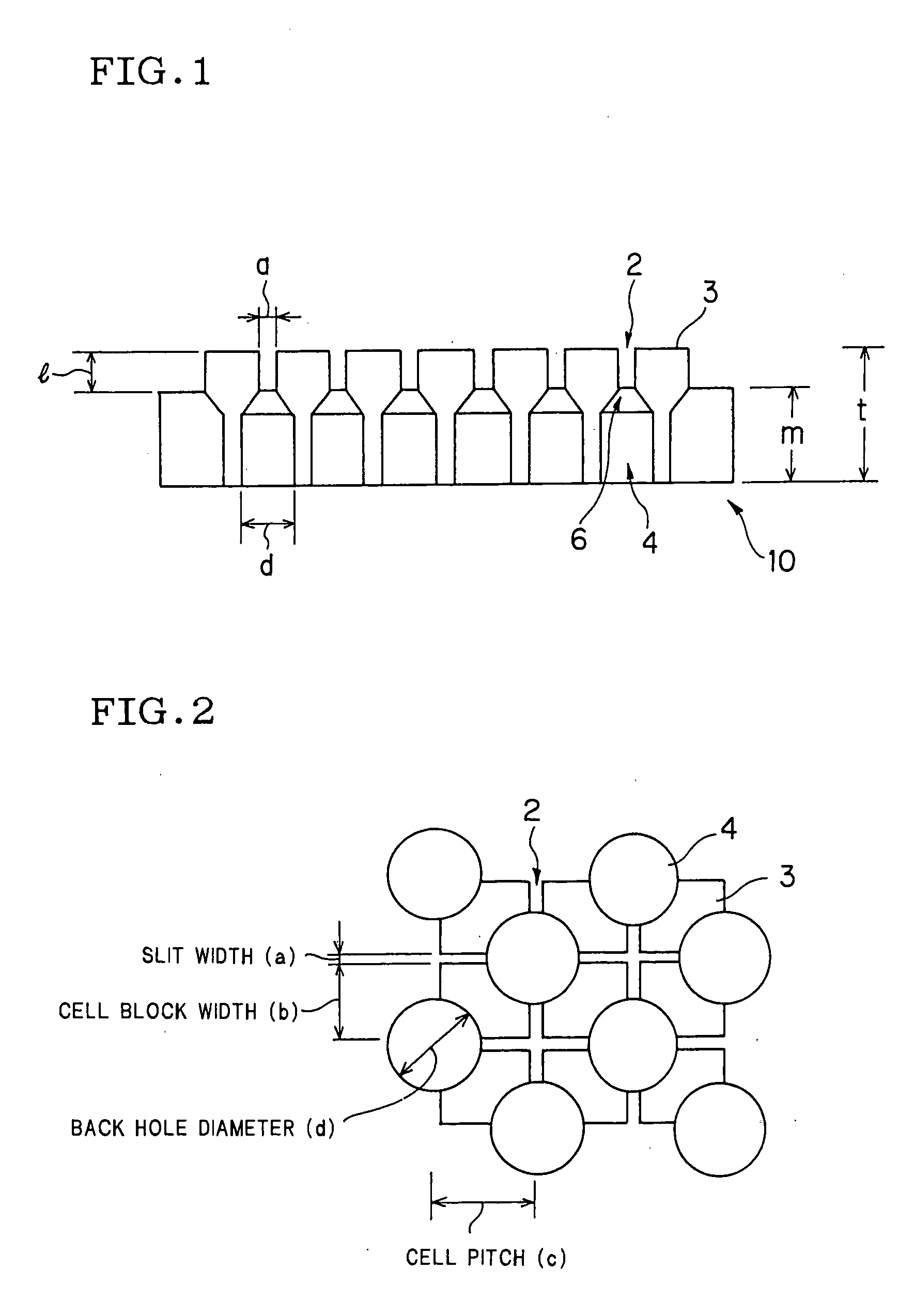
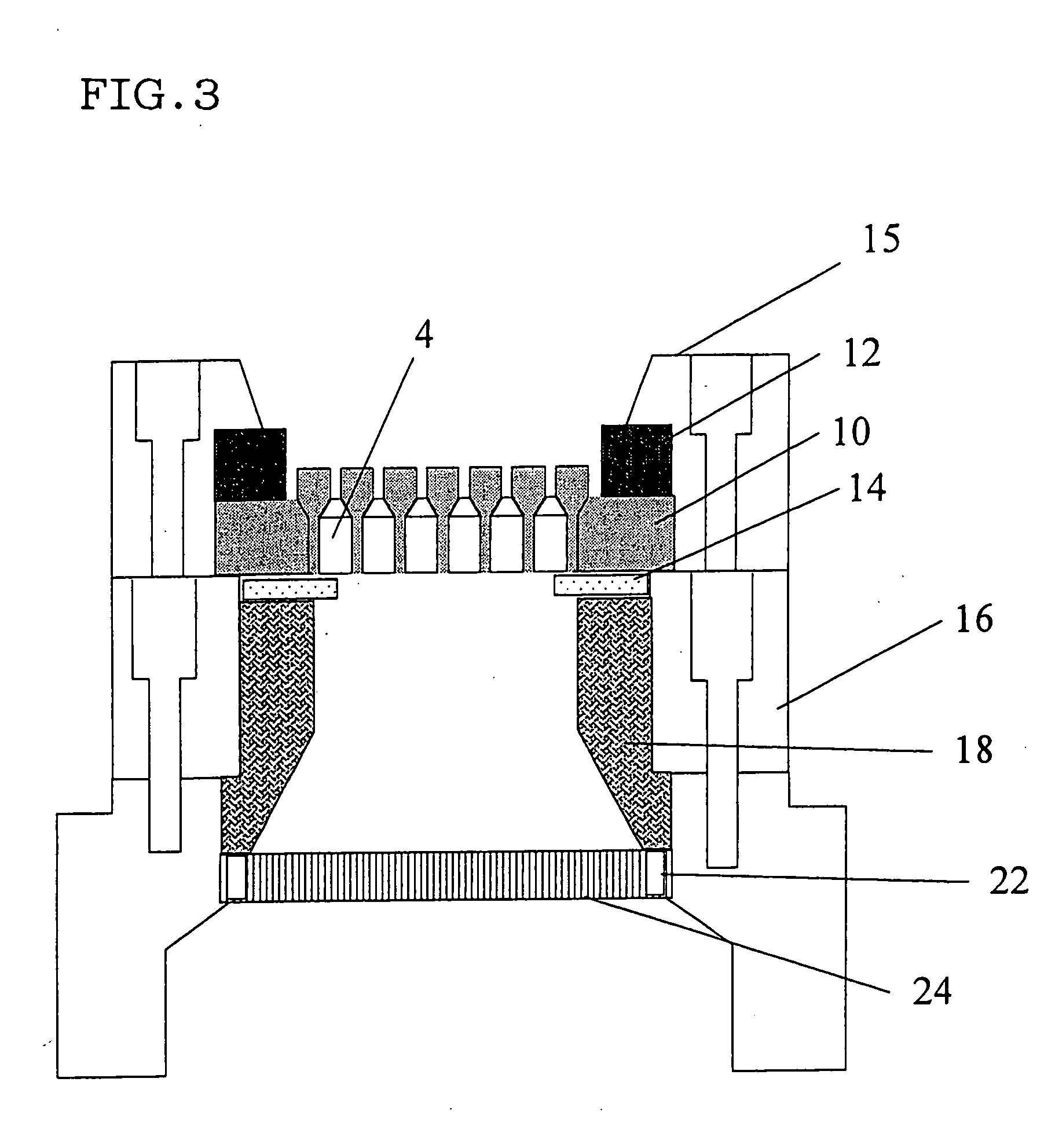
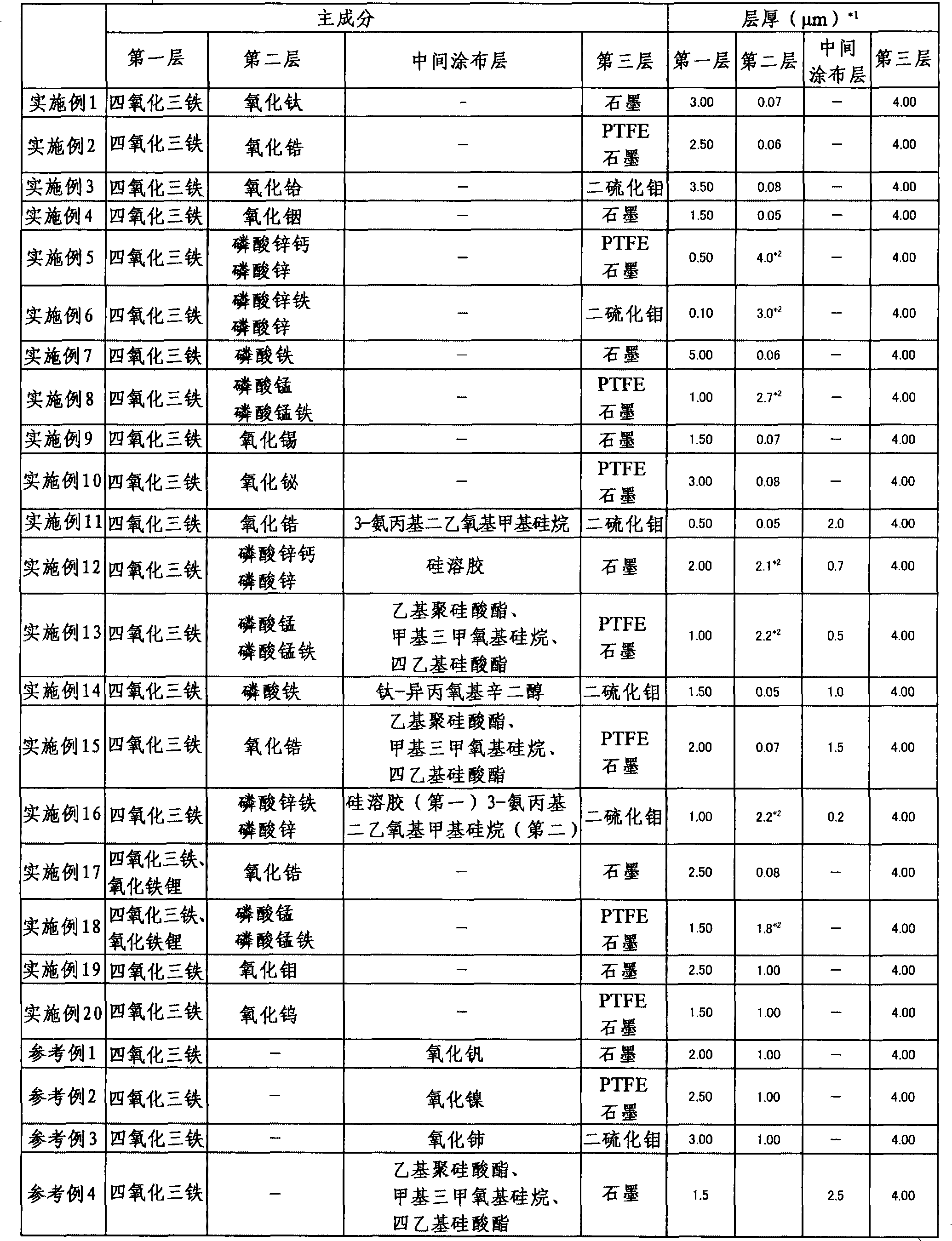
There is disclosed a die (10) for forming a honeycomb body having a structure provided with groovy slits (2) on a front face thereof, the slits being formed by cell blocks (3) and back holes (4) on a back surface thereof, each hole being communicatively connected with the slit. The die (10) is made of cemented carbide having wear resistance. The cemented carbide is formed by compacting, followed by sintering at high temperature, metal carbide powder of transition metal element series with an iron group metal binder having toughness. A connection area ratio of the back hole (4) and the cell block (3) is 35 to 65%. According to the die for forming a honeycomb body and the die jig for forming a honeycomb body using the same, wear resistance of the die or the die jig can be enhanced when the raw material containing the material having very high hardness such as SiC and the like is extruded as well as the defect in shape of an extruded body due to wear of the die can be overcome.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Iron group metal material after black surface treatment and manufacturing method thereof
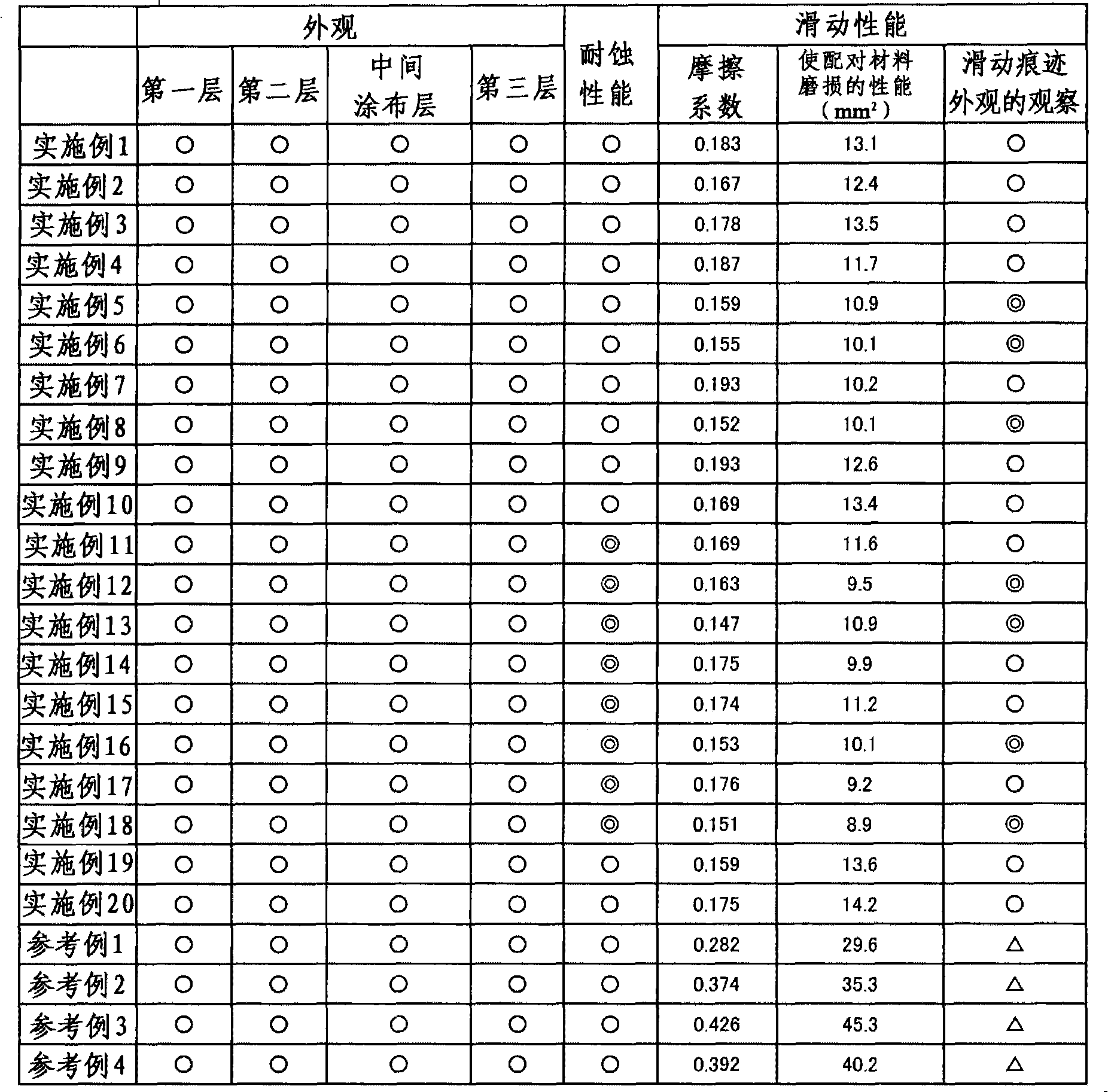
ActiveCN102011110AImprove corrosion resistanceEasy to slideMetallic material coating processesIndiumPhosphate
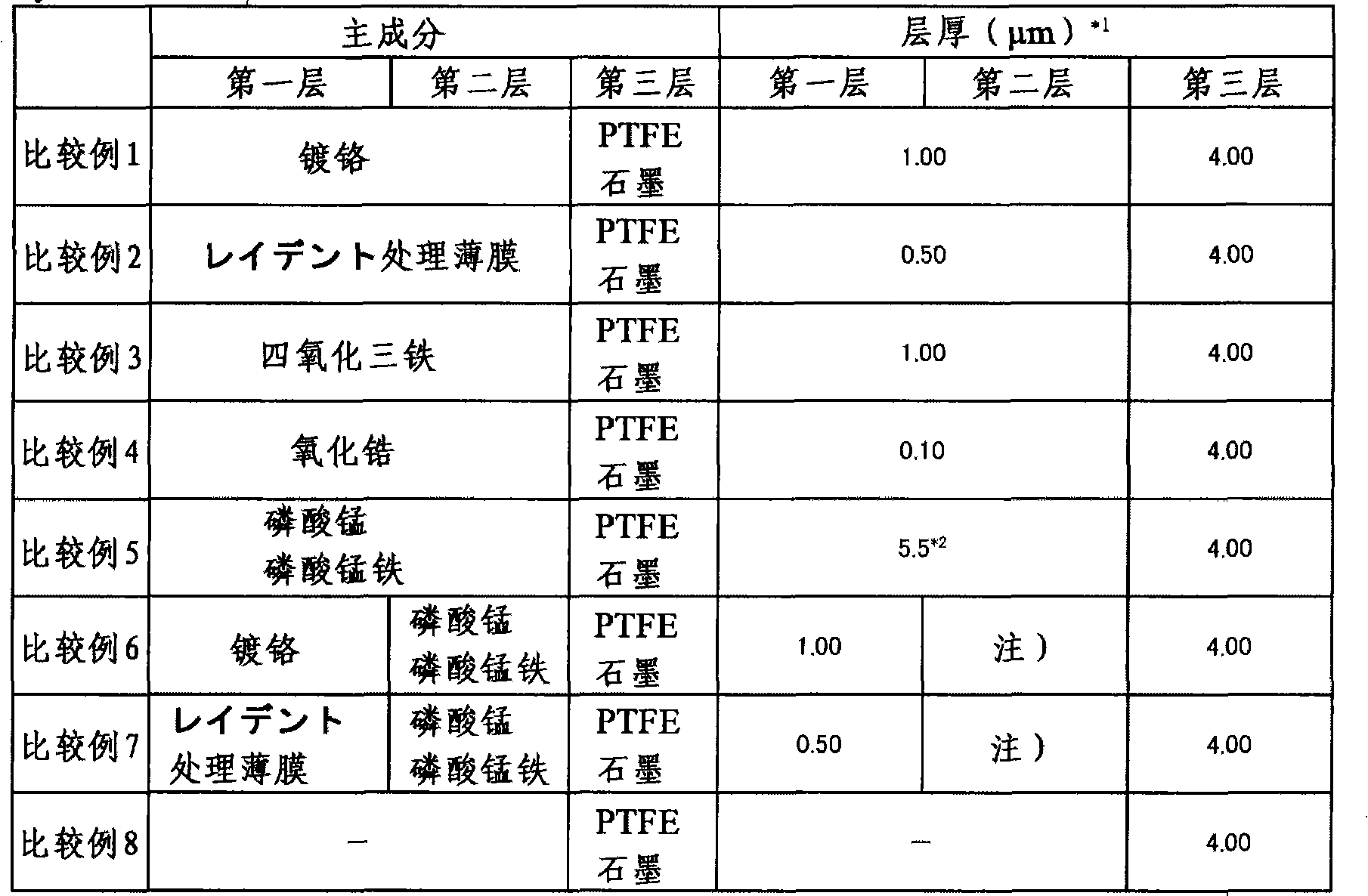
The present invention provides an iron group metal material after black surface treatment, which forms a black film that has excellent corrosion resistance and sliding performance and does not contain chromium. The surface of the iron group metal material is provided with the following components: a ferroferric oxide layer which is formed through chemical conversion treatment; a chemical conversion treatment layer which is formed on the ferroferric oxide layer and comprises at least one component selected from the following matters: phosphate of at least one element selected from zinc, tin, iron, manganese and calcium; oxide of at least one element selected from titanium, zirconium, hafnium, indium, tin, bismuth, vanadium, nickel, cerium, molybdenum and wolfram; fluoride of at least one element selected from titanium, zirconium, hafnium, indium, tin, bismuth, vanadium, nickel, cerium, molybdenum and wolfram; and a solid lubrication layer which is formed on the chemical conversion treatment layer.
Owner:NIHON PARKERIZING
Iron group fischer-tropsch synthesis catalyst and its preparation method
ActiveCN102380390AEasy to prepareSuitable for mass productionLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWater-gas shift reactionIron group
The invention relates to an iron group fischer-tropsch synthesis catalyst and its preparation method. The iron group fischer-tropsch synthesis catalyst comprises the components of Fe, Cu, K, Li and SiO2 with weight proportion of 100:0.1-15:0.1-10:0.05-10:2-50. On the premise of good fischer-tropsch synthesis activity and methane selectivity, the iron group fischer-tropsch synthesis catalyst is capable of reducing water gas shift reaction activity in a system and enhancing the effective utilization rate of CO reaction gas.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +2
Binder for the Fabrication of Diamond Tools
Owner:NATIONAL RESEARCH TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY +3
Tungsten carbide particle enhanced steel/iron-base composite wearable plate and preparation technique thereof
The patent is about a kind of steel / iron group complex wear resistant board enhanced by tungsten carbide grain and the preparation technology of it. It is made by the compound of tungsten carbide hard grain and tenacious steel / iron group. The volume percent of tungsten carbide grain is -2.5-+2mm: 30-40%; -2-+1mm: 30-40%; -1- +0.3mm: 25-30%, the steel / iron groups will infiltrate into the interspace of the tungsten carbide hard grains, after they has been melt, the thickness of the composite layer is 4-5mm. This patent has also published the preparation technology of it, adhesion agent is not need according to this patent, the complex board gained not only owns high rigidity and great flexibility module as cream grain, but also owns the high tenacity of metal, and it greatly improves the shock abrasion resistance ability of the wear resistance board.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Cemented Carbides
InactiveUS20080276544A1Avoid grain growthHigh hardnessPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesIron groupAlloy
The present invention provides a cemented carbide with superior strength and toughness by refining the WC in the alloy uniformly and by restricting the growth of coarse WC efficiently. In this cemented carbide, WC with a mean particle diameter of no more than 0.3 microns serves as a hard phase and at least one type of iron group metal element at 5.5-15 percent by mass serves as a binder phase. In addition to this hard phase and binder phase, this cemented carbide contains 0.005-0.06 percent by mass of Ti, Cr at a weight ratio relative to the binder phase of at least 0.04 and no more than 0.2, with the remaining portion being formed from inevitable impurities. In particular, this cemented carbide does not contain Ta.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Diamond single crystal surface metallization treatment method
ActiveCN106835054AImprove the efficiency of graphitization transformationPromote the graphitization processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEtchingIron group
The invention discloses a diamond single crystal surface metallization treatment method. The method comprises steps as follows: the surface of a diamond single crystal is bombarded and sputtered with Fe, Co or Ni as a source electrode target material with a double-glow plasma diffusion metallizing technique; the single crystal is soaked in an acid solution, so that remaining metal and graphite are removed; a metal diffusion coating is prepared on the surface of the diamond single crystal with strong carbide metal as a target material with a double-glow plasma diffusion metallizing technique. Uniformly distributed micro pits are formed in the surface of the single crystal under the bombardment and sputtering functions of the double-glow plasma and the graphitized catalytic function of Fe, Co, Ni and other iron group metals, surface roughening and activation are realized, strong carbide metallic elements react with a part of carbon atoms on the surface of the diamond so that chemical bond combination is realized, and the bonding strength of the surface metallization coating and the single-crystal diamond is improved. Bombardment etching and metallization treatment are realized with one device, the process is simple, the cost is low, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:山西国脉金晶碳基半导体材料产业研究院有限公司
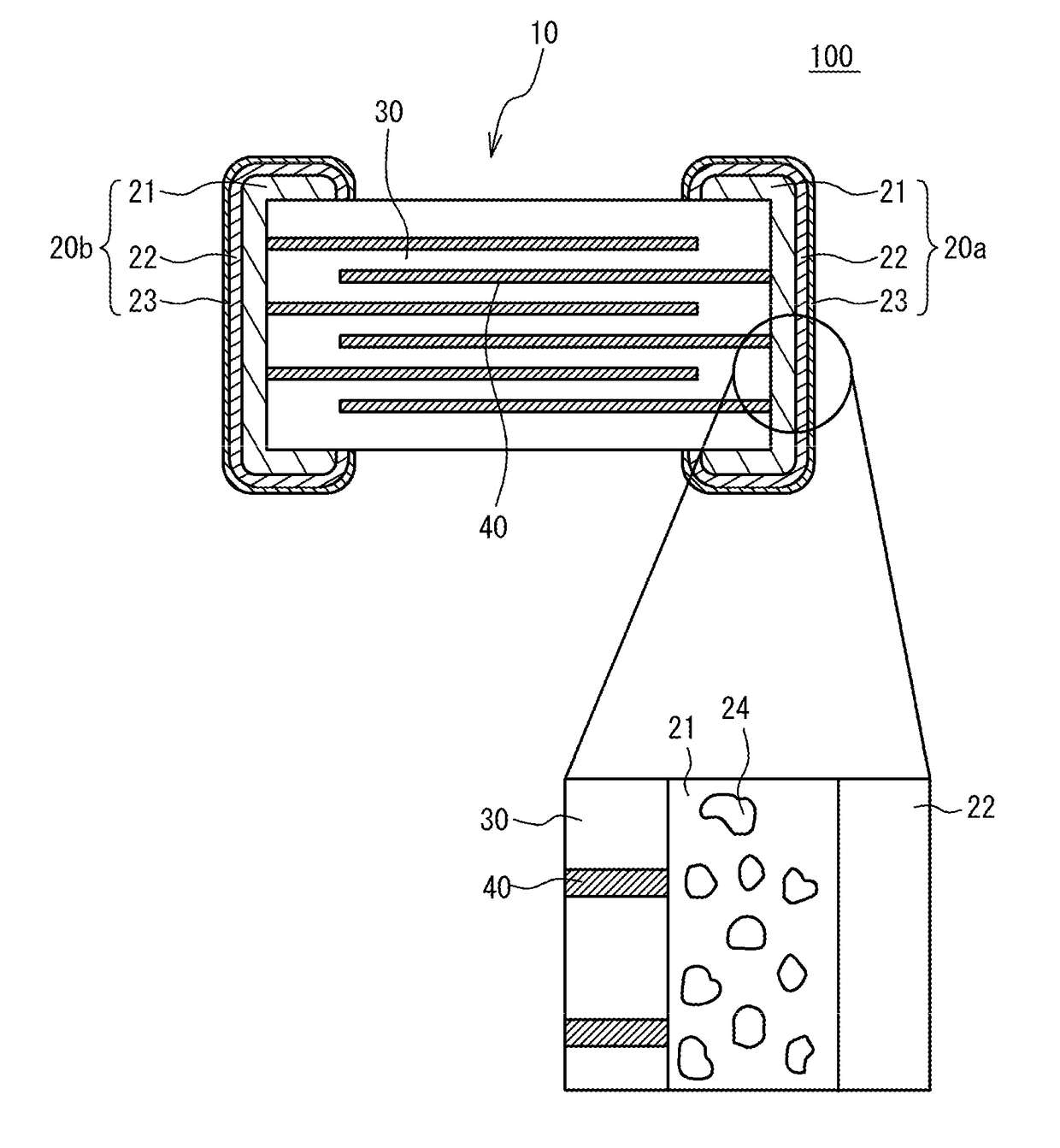
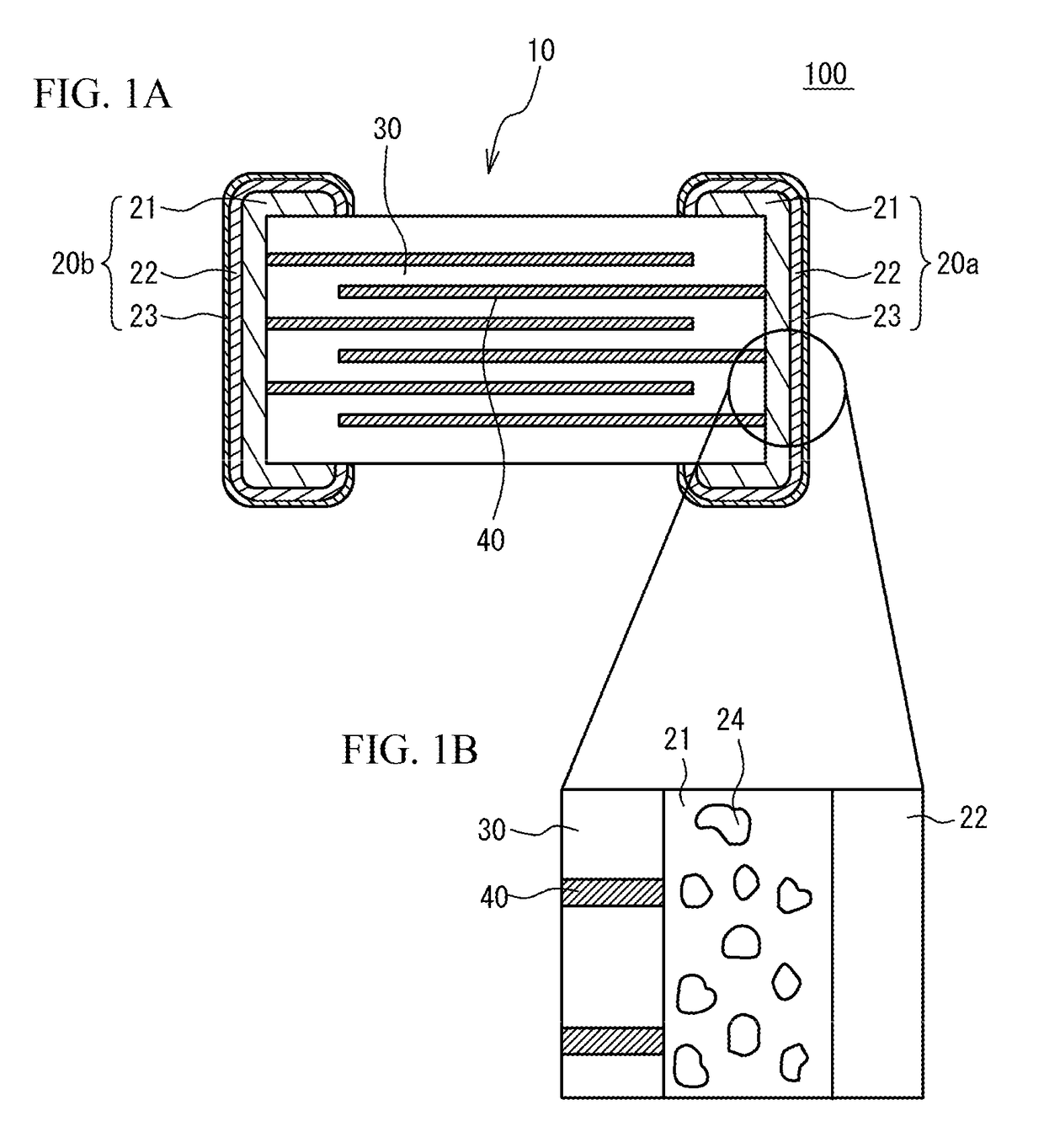
Multilayer ceramic capacitor and manufacturing method of multilayer ceramic capacitor
ActiveUS20170345570A1Fixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricIron groupCeramic capacitor
A multilayer ceramic capacitor includes: a ceramic multilayer structure having ceramic dielectric layers and internal electrode layers alternately stacked, the internal electrode layers being mainly composed of a transition metal other than an iron group, end edges of the internal electrode layers being alternately exposed to a first end face and a second end face; and a pair of external electrodes provided on the first end face and the second end face, wherein the external electrode includes a base conductive layer that includes glass of less than 7 weight % and is mainly composed of a transition metal other than an iron group or a noble metal, and a first plated film that covers the base conductive layer, has a thickness that is half of a thickness of the base conductive layer or more and is mainly composed of a transition metal other than an iron group.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Electroplating solution composition for organic polymer-zinc alloy composite plating and plated metal material using such composition
Disclosed is an electroplating solution composition which enables to obtain a plating with excellent corrosion resistance which exhibits excellent adhesion with a coating film without being subjected to a surface treatment. Such an electroplating solution composition for an organic polymer-zinc alloy composite plating is characterized by containing (A) 1-600 g / l of Zn ions, (B) 1-600 g / l of iron group element ions, (C) 0.1-200 g / l of a tungstic acid compound as W ions and (D) 0.5-500 g / l of a water-soluble or water-dispersible organic polymer compound having a number-average molecular weight of 1,000-1,000,000.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Method for producing WC-Fe composite powder of ultra fine grain by tungsten alloy scrap
A method of producing a superfine composite powder with tungsen carbon-element belong to iron group. It comprises: pulverizing the waste material containing tungsen, oxidizing and baking, grinding, wet grinding and mixing, reducing, adding carbon and carbonizing, then obtaining the superfine composite powder with tungsen carbon-element belong to iron group. It is characterized in, before reducing, adding carbon black powder, adjusting tungen and / or element of iron group, forming superfine WxCy compounds, adding some vanadium and chromium to prevent crystals from expanding.
Owner:ZIGONG CEMENTED CARBIDE CORP +1
Magnetic material having high magnetic heating performance and preparation thereof
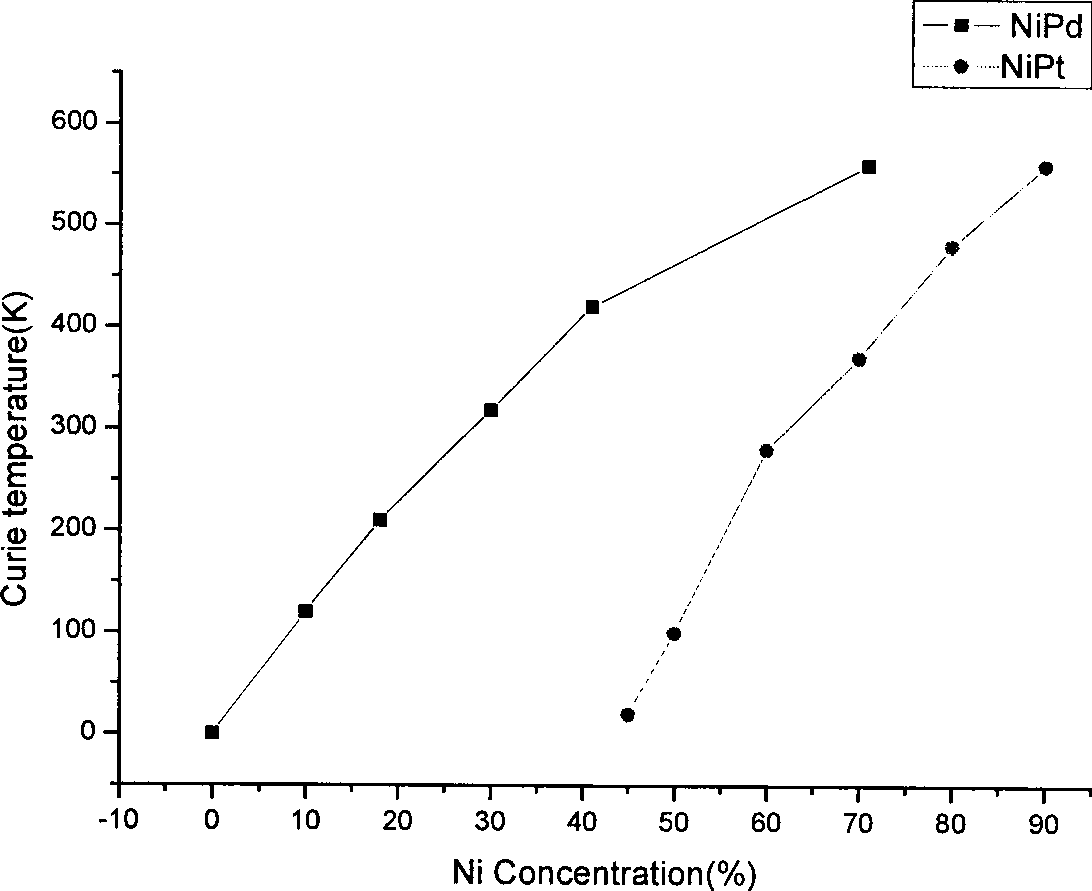
InactiveCN101477867ALow Curie temperatureImprove magnetocaloric performanceInorganic material magnetismTherapeutic coolingHysteresisPolyol
The invention relates to a novel magnetic material and a preparation method thereof. The novel magnetic material is a magnetic material which consists of iron group metals and platinum group metals. The preparation method uses a polyol as a reaction solvent and a reducing agent; various metal ions forming the magnetic material are simultaneously reduced from a solution; and the magnetic material is manufactured. The magnetic material is provided with high hysteresis heating property; at the same time, through changing the composition of the magnetic material, Curie temperature of the magnetic material can be adjusted to be close to the physiological temperature of a human body; and the magnetic material has the advantages of little metal dissolving amount and biological safety, and can be applied to cure a tumor through a magnetic-thermo method.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Cemented carbide and cutting tool
InactiveUS7018726B2High hardnessImprove toughnessRecord information storageBonded abrasive wheelsIron groupHardness
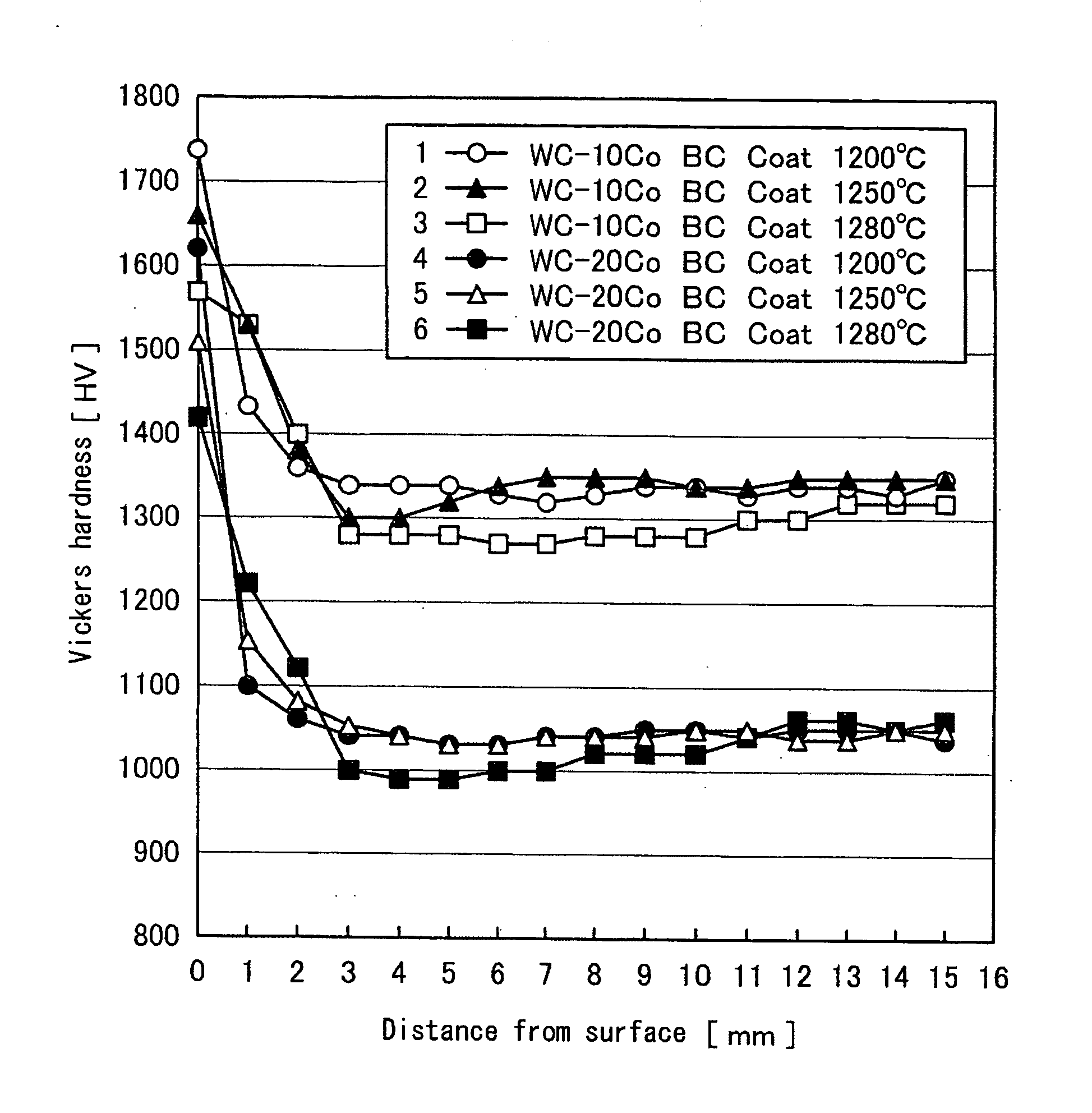
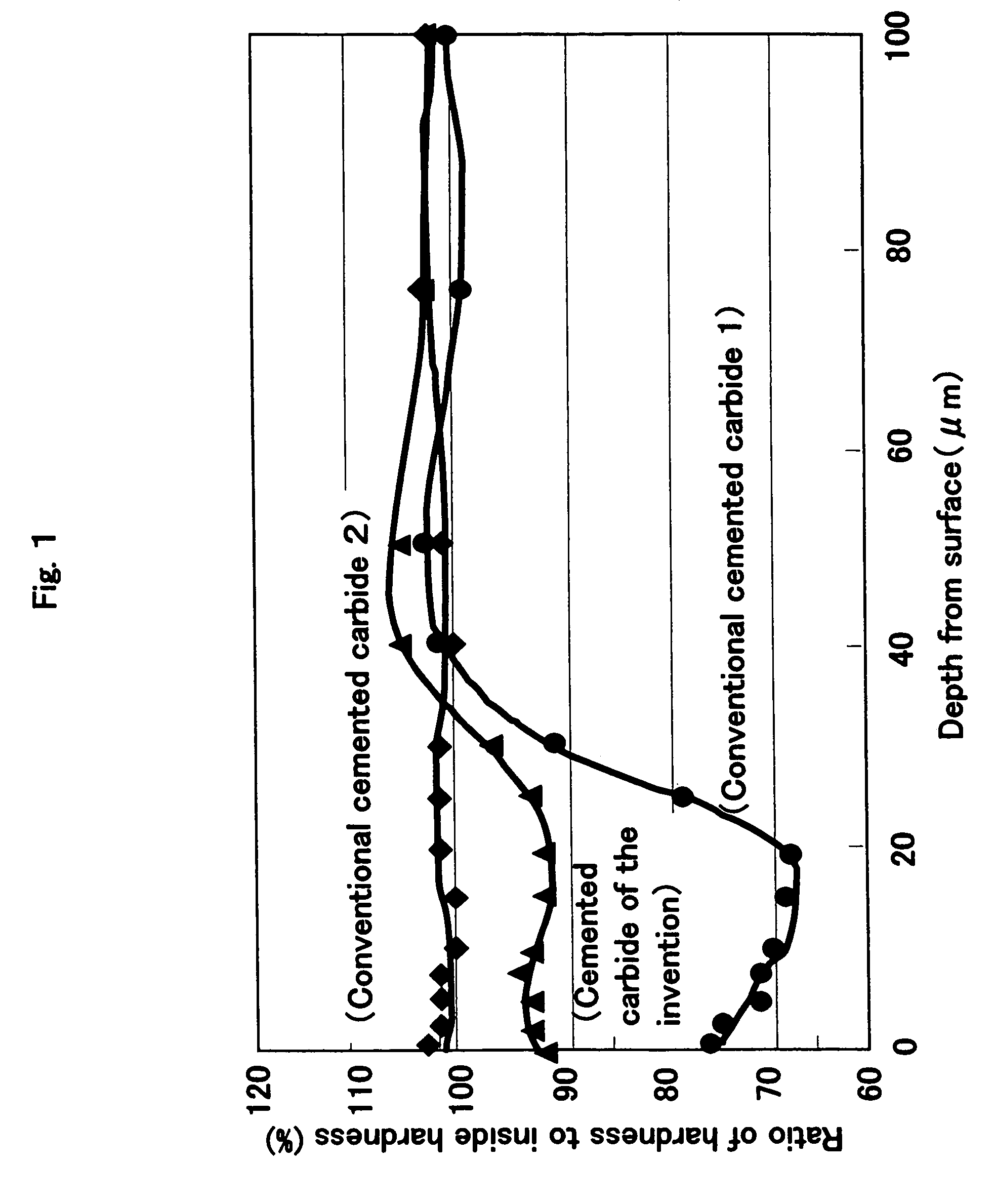
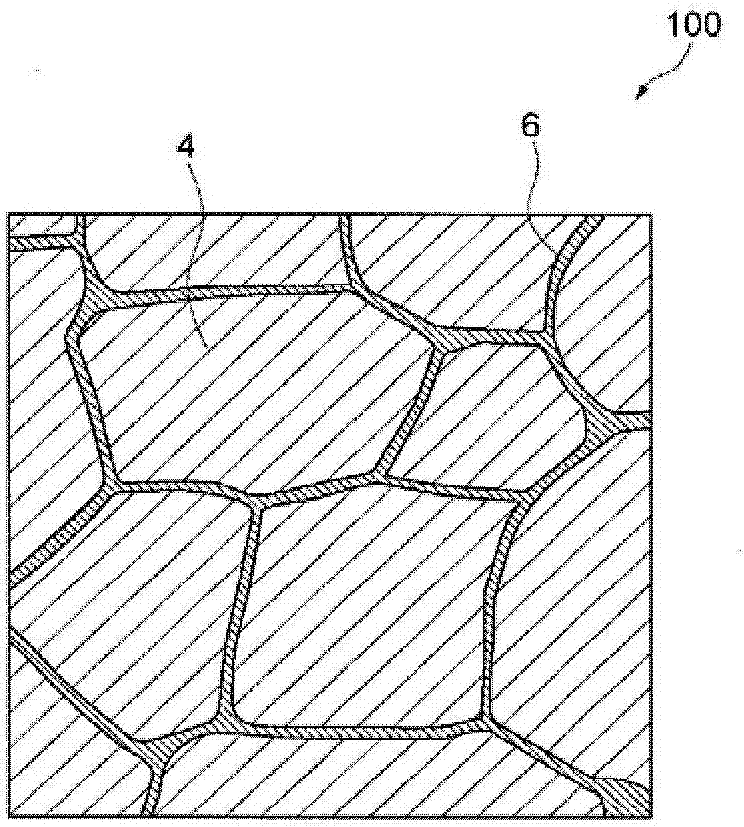
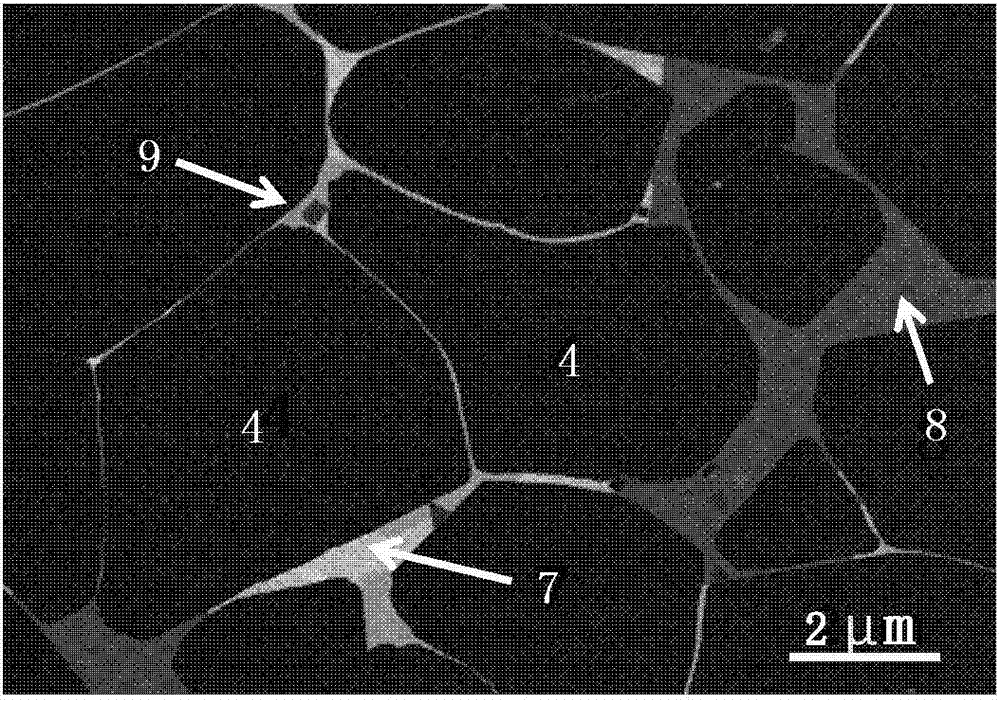
There is provided a cemented carbide comprising a hard phase component which comprises a tungsten carbide (WC) and at least one selected from carbides, nitrides and carbonitrides of metals of the groups 4a, 5a and 6a in the periodic table; and a binder phase component comprising at least one of iron-group metals, wherein the surface region of the cemented carbide has 90–98% of the minimum hardness as compared with internal hardness, thereby having high hardness and toughness which is suitable to using as a cutting tool.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
R-t-b based permanent magnet
ActiveCN107130183AReduce usageImprove coercive forceFurnace typesMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementIron group
An R-T-B based permanent magnet includes main phase grains composed of R2T14B type compound. R is a rare earth element. T is iron group element(s) essentially including Fe or Fe and Co. B is boron. The magnet contains at least C, Ga, and M selected from Zr, Ti, and Nb in addition to R, T, and B. B is contained at 0.71 mass % to 0.88 mass %. C is contained at 0.15 mass % to 0.34 mass %. Ga is contained at 0.40 mass % to 1.40 mass %. M is contained at 0.25 mass % to 2.50 mass %. A formula (1) of 0.14 <= [C] / ([B]+[C]) <= 0.30 and a formula (2) of 5.0 <= [B]+[C] / [M] <= 5.6 are satisfied, where [B], [C], and [M] are respectively a content of B, C, and M by atom %.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Cutting member
InactiveUS6872234B2Easy to useImprove wear resistancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesIron groupCarbide
The cutting member comprises WC, two or more solid solutions of WC and compounds selected from carbides, nitrides and carbonitrides of metals of the groups 4a, 5a and 6a in the Periodic Table, and at least one metal of the iron group; and at least one of the two or more solid solutions being a solid solution having a high Nb or Zr content, whereby the wear resistance and plastic deformation resistance are improved in case of cutting hardly machinable materials such as stainless steel, thereby making it possible to prolong the service life of the cutting member.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Method of coating cutting inserts
InactiveUS6033735AImprove wettabilityPretreated surfacesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPresent methodIron group
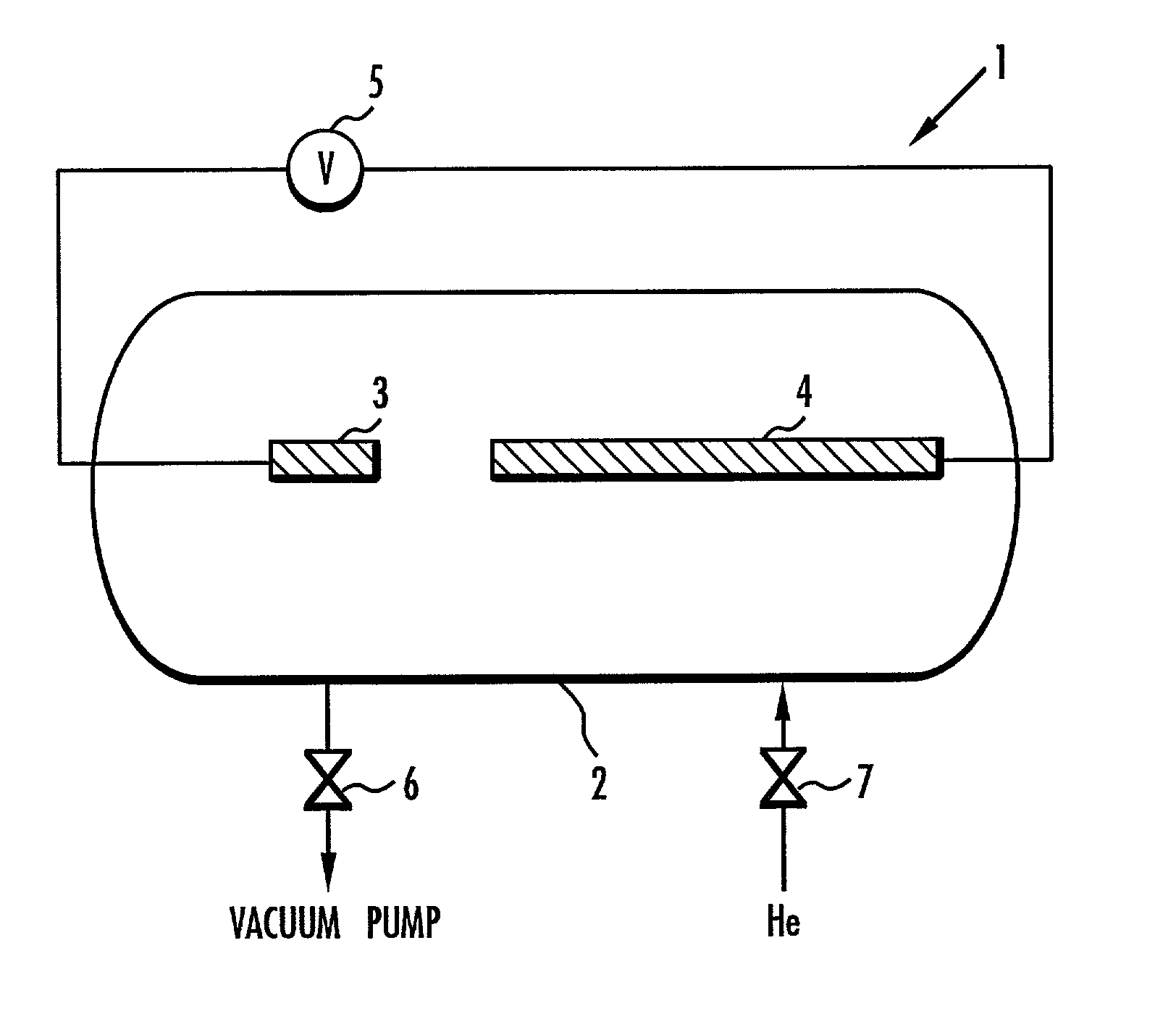
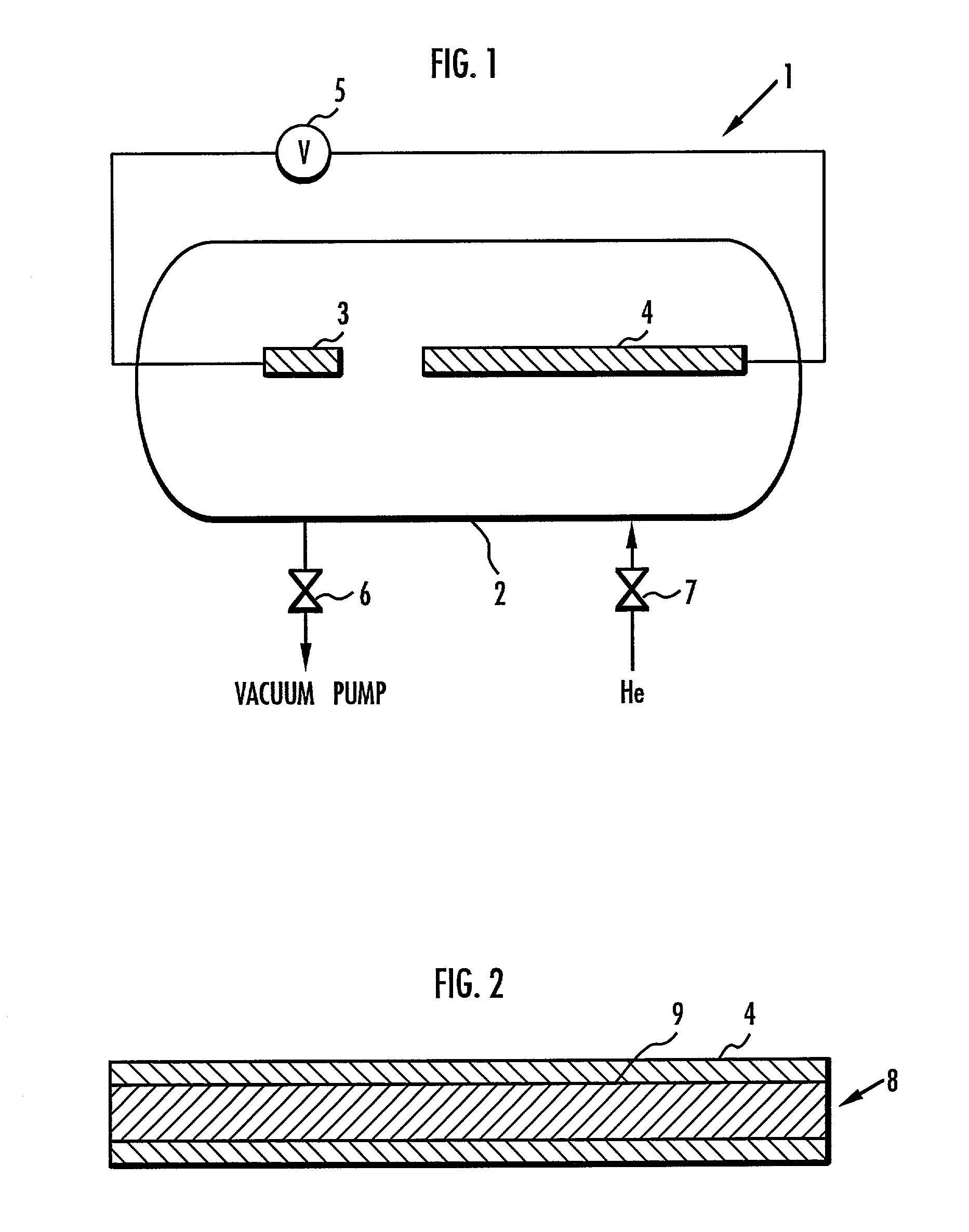
PCT No. PCT / SE95 / 01586 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 18, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 18, 1997 PCT Filed Dec. 27, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 21051 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 11, 1996There is disclosed a method of coating cemented carbide inserts at least partly with a layer of at least one iron group metal. When inserts coated with such a layer are brazed to a tool holder, a joint with improved strength is obtained. According to the present method, one or more metal salts of at least one iron group metal containing organic groups are dissolved and complex bound in at least one polar solvent with at least one complex former comprising functional groups in the form of OH or NR3 (R=H or alkyl). A soluble carbon source is added to the solution which is subsequently at least partly applied to the cemented carbide inserts by dipping, spraying or painting. The inserts are dried and heat treated in an inert and / or reducing atmosphere. As a result, cemented carbide inserts are obtained at least partly coated with a layer of an iron group metal.
Owner:SANDVIK AB
Compound sintered compact cutting tool and compound sintered compact cutting tool with coated surface
ActiveCN107107204AAvoid deformationInhibition of contractionWorkpiecesTurning toolsCoated surfaceIron group
The present invention is a compound sintered compact cutting tool (1) obtained from a compound sintered compact of a TiCN-based cermet layer (2) and a WC-based hard metal layer (3), wherein: the TiCN-based cermet layer contains, in mass%, 4-25% iron group metal components, less than 15% W, 2-15% Mo, 2-10% Nb and 0.2-2% Cr and the Co content ratio with respect to the total content of the iron group metal components Co and Ni is a mass ratio of 0.5-0.8; the WC-based hard metal layer contains, in mass%, 4-17% iron group metal components and at least 75% W and has WC as the main hard phase component; the angle formed by the cutting face (4) and the flank (5) is 90 degrees; the cutting face including the cutting edge is configured from the WC-based hard metal layer; the thickness of the WC-based hard metal layer is 0.05-0.3 times the thickness of the compound sintered compact; and the change in height from the upper end to the lower end of the flank in a cross-section that passes through the center of the cutting face of the cutting tool is such that the maximum height difference (10) is not more than 0.01 with respect to the thickness of the compound sintered compact.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Electroplating solution composition for organic polymer-zinc alloy composite plating and plated metal material using such composition
InactiveUS20070170067A1Improve adhesionImprove corrosion resistanceElectrolytic coatingsWater dispersibleIron group
An object of the invention is to provide an electroplating solution composition capable of obtaining a plated film excellent in adhesiveness to a coated film and excellent in corrosion resistance without surface treatment. The present invention relates to an organic polymer composite zinc alloy electroplating solution composition containing: (A) 1 to 600 g / l of Zn ion, (B) 1 to 600 g / l of an iron-group-element ion, and (C) 0.1 to 200 g / l, in terms of W ion, of tungstic acid-based compound, and (D) 0.5 to 500 g / l of water-soluble or water-dispersible organic polymer compound having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 1,000,000.
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Electrode for electric discharge machining
ActiveCN103003016AExcellent electron emission characteristicsReduce consumption rateElectrical-based machining electrodesElectric dischargeIron group
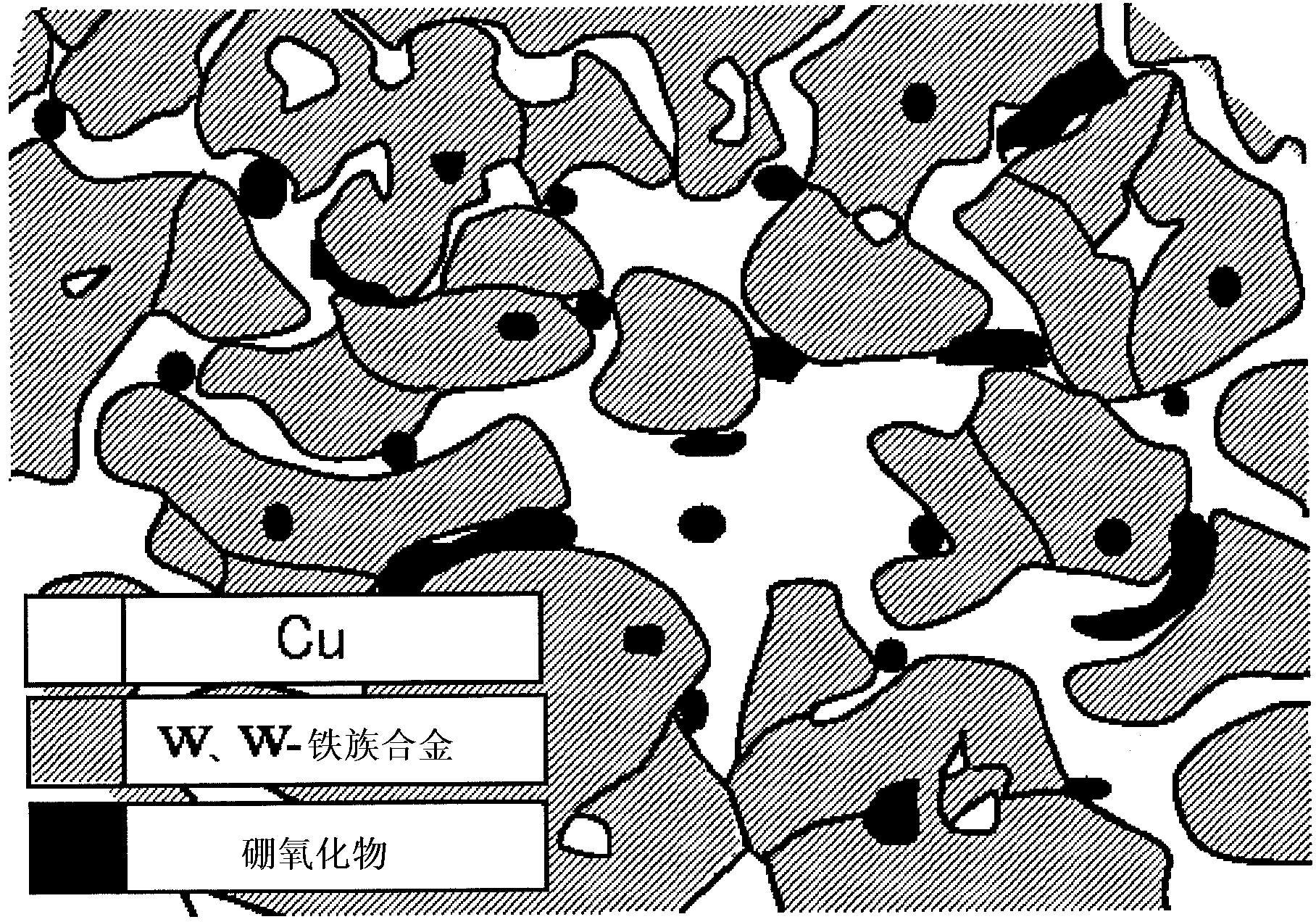
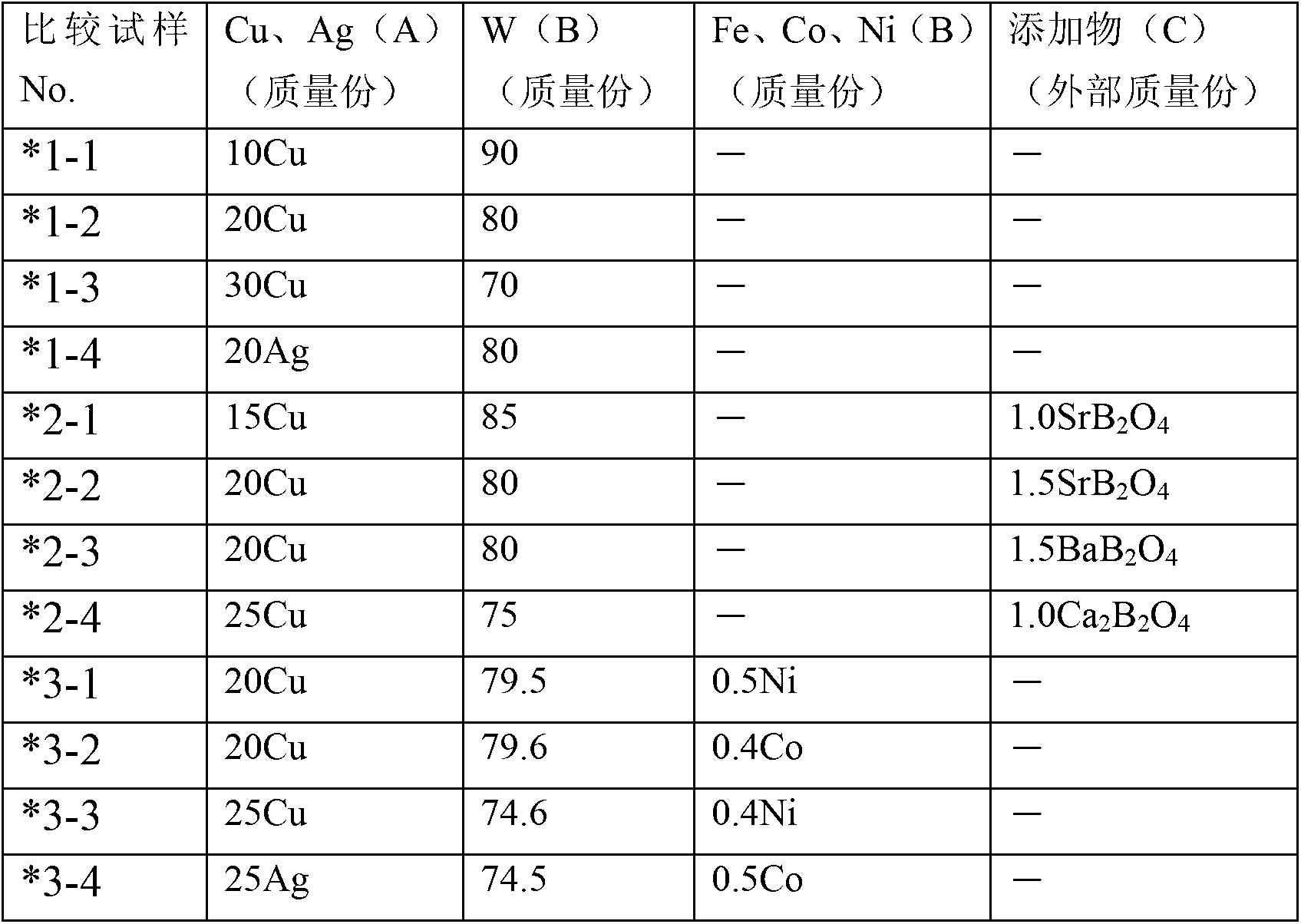
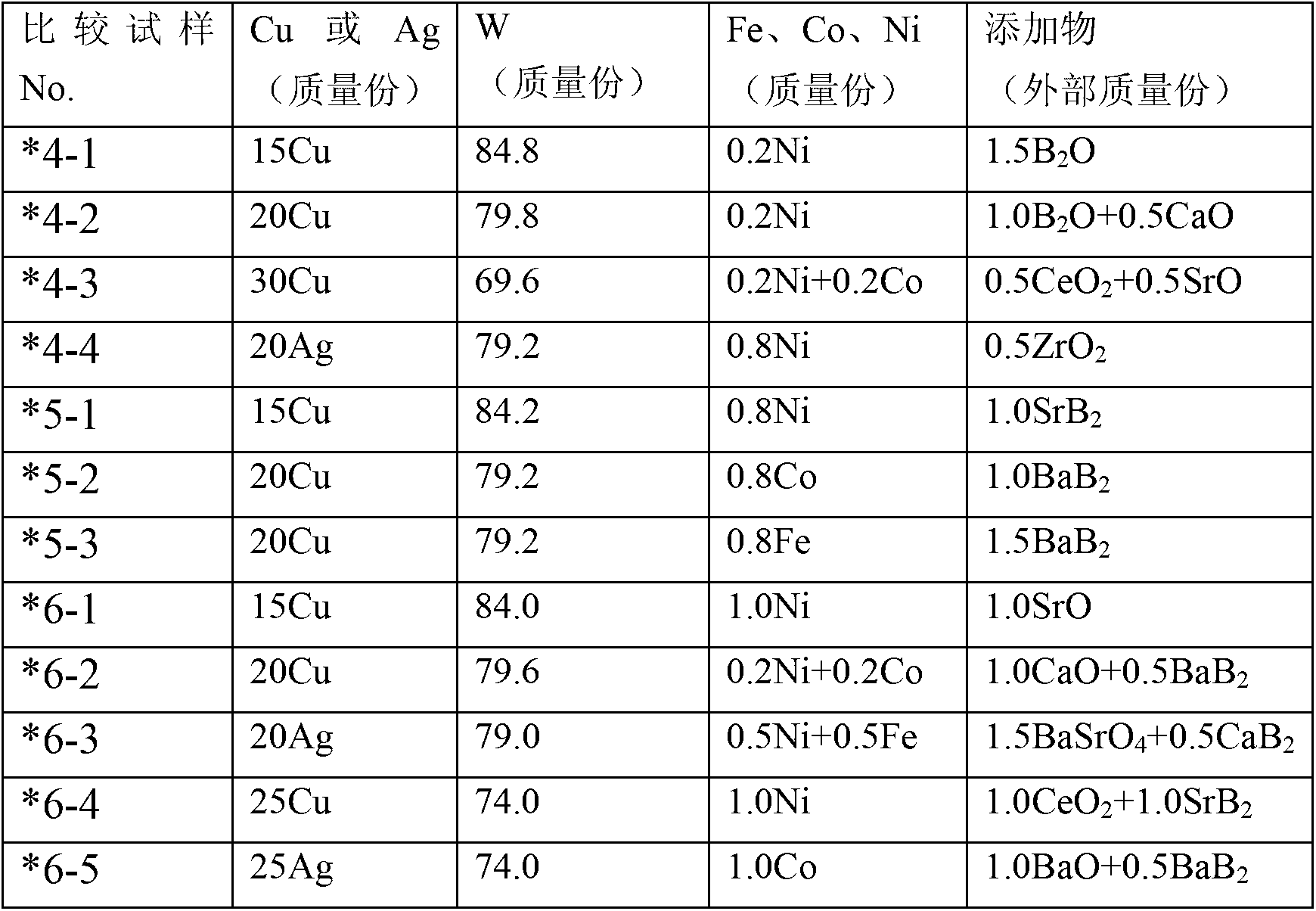
In electric discharge machining in which a Cu(Ag)-W(Mo) based electrode is employed, the present invention improves the machining speed, electrode wear rate, and surface roughness of an object to be machined. For this purpose, suitable amounts of an iron-group metal and a boric oxide of an element selected from the group (M3) comprising Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Sc, Y, and lanthanide are added to a Cu(Ag)-W(Mo) based material. For the boric oxide, a boric oxide represented by M32B2O5 or M3B2O4 is preferably used.
Owner:NIPPON TUNGSTEN CORP
R-t-b based permanent magnet
ActiveUS20170250015A1Improve coercive forceIncrease in coercivityFurnace typesMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementIron group
An R-T-B based permanent magnet includes main phase grains composed of R2T14B type compound. R is a rare earth element. T is iron group element(s) essentially including Fe or Fe and Co. B is boron. The magnet contains at least C, Ga, and M selected from Zr, Ti, and Nb in addition to R, T, and B. B is contained at 0.71 mass % to 0.88 mass %. C is contained at 0.15 mass % to 0.34 mass %. Ga is contained at 0.40 mass % to 1.40 mass %. M is contained at 0.25 mass % to 2.50 mass %. A formula (1) of 0.14≦[C] / ([B]+[C])≦0.30 and a formula (2) of 5.0≦[B]+[C]−[M]≦5.6 are satisfied, where [B], [C], and [M] are respectively a content of B, C, and M by atom %.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Wear part with hard facing
ActiveUS20120177828A1Sufficiently robust to handleDegree of flexibilityPretreated surfacesSuperimposed coating processWear resistantIron group
The invention relates to a wear part or tool comprising a body containing an iron-group metal or alloy, a wear-resistant layer metallurgically bonded to a surface of the body through an intermediate layer, characterised in that the wear-resistant layer comprises at least 13 vol. % of grains of metal carbide selected from the group consisting of WC, TiC, VC, ZrC, NbC, Mo2C, HfC and TaC and grains of (Cr,Me)xCy and a metal based phase comprising of a solid solution of 0.5 to 20% Cr, 0.2 to 15% Si, and 0.2 to 20% carbon, where Me is Fe, Co and / or Ni; and the intermediate layer has a thickness of 0.05 to 1 mm and comprises Si in amount of 0.1 to 0.7 of that in the wear-resistant layer, chromium in amount of 0.1 to 0.6 of that in the wear-resistant layer and the metal of the metal carbide in amount of 0.2 to 0.6 of that in the wear-resistant layer and to a method of producing such a wear part.
Owner:KONYASHIN IGOR YURI +2
Composite wear-resistant member and method for manufacture thereof
Owner:TIX HLDG COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com