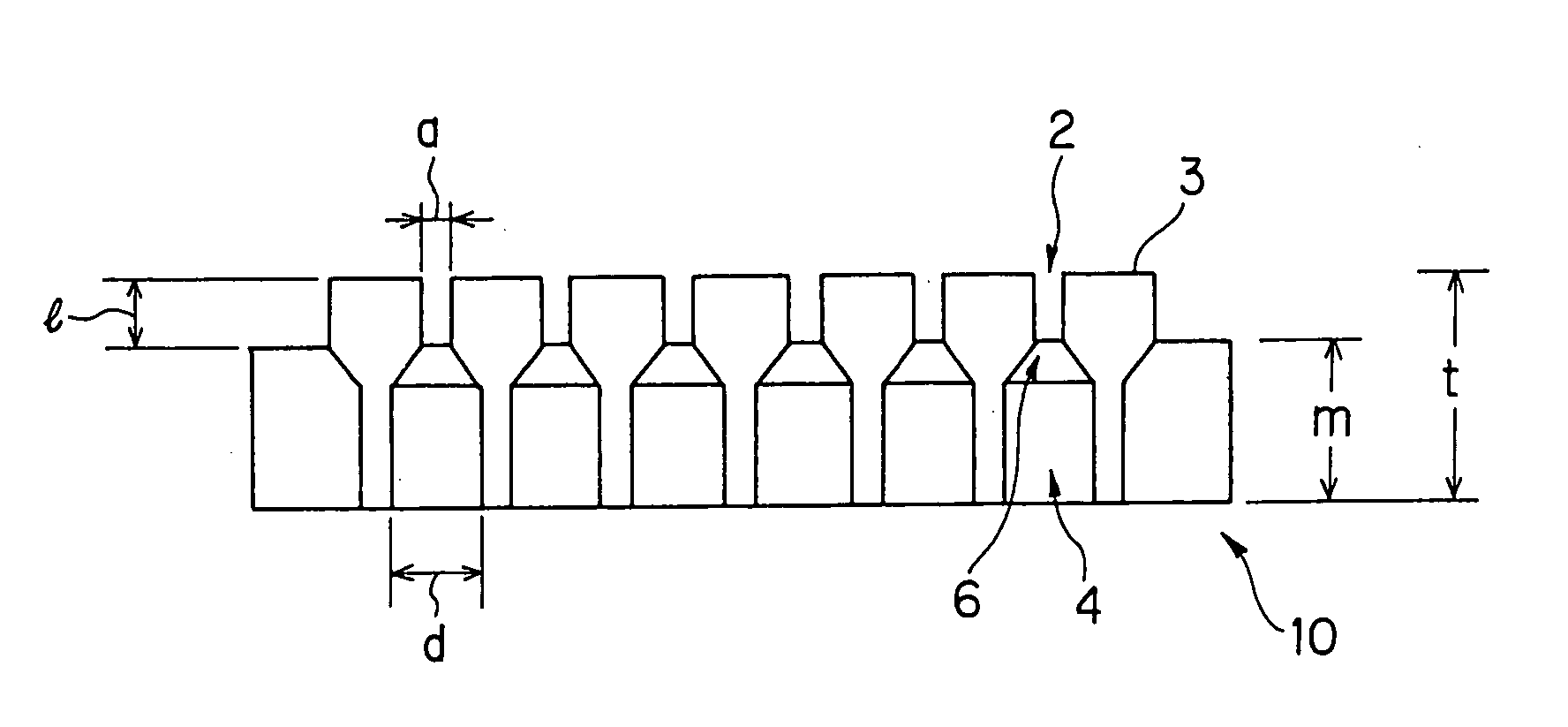
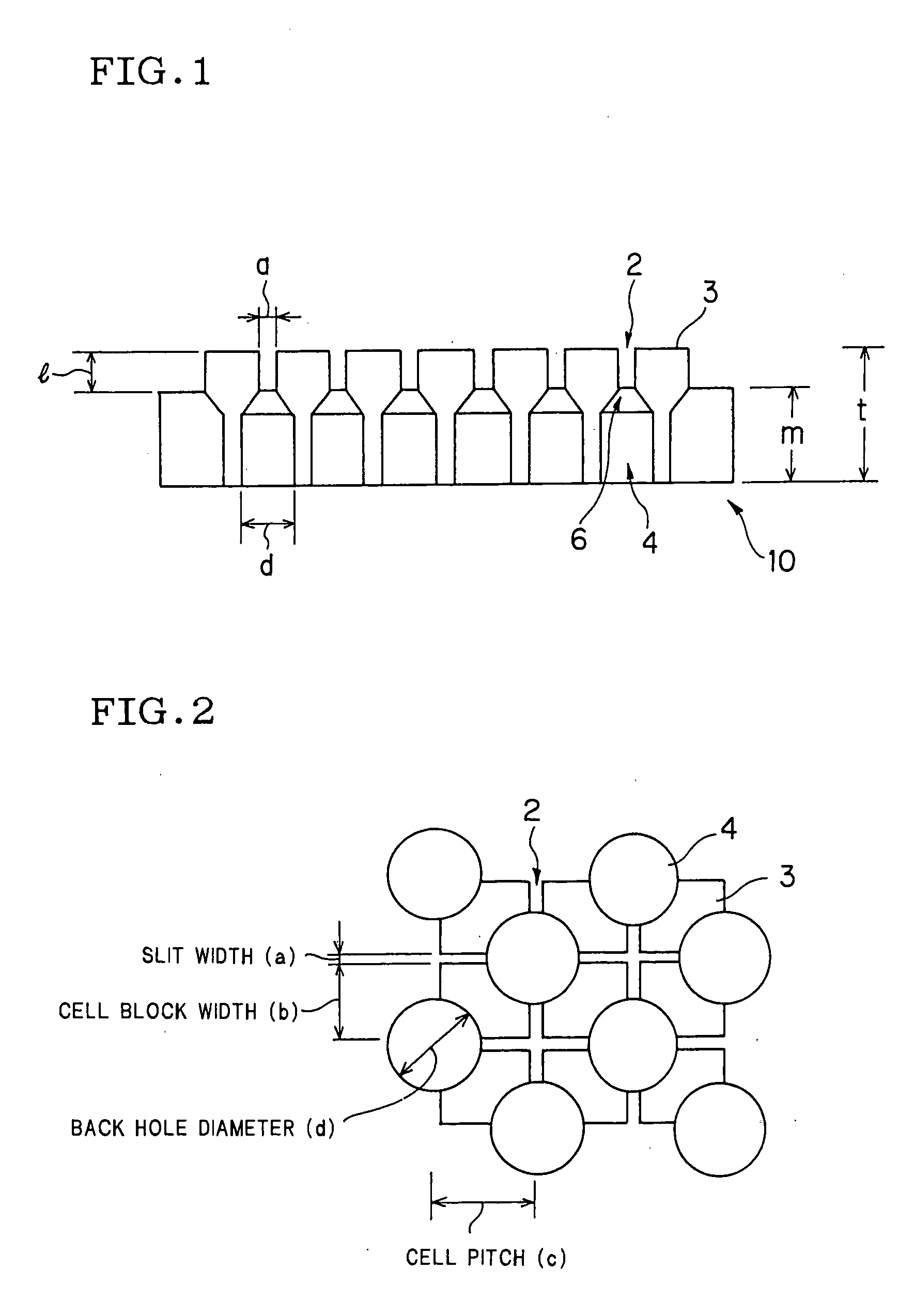
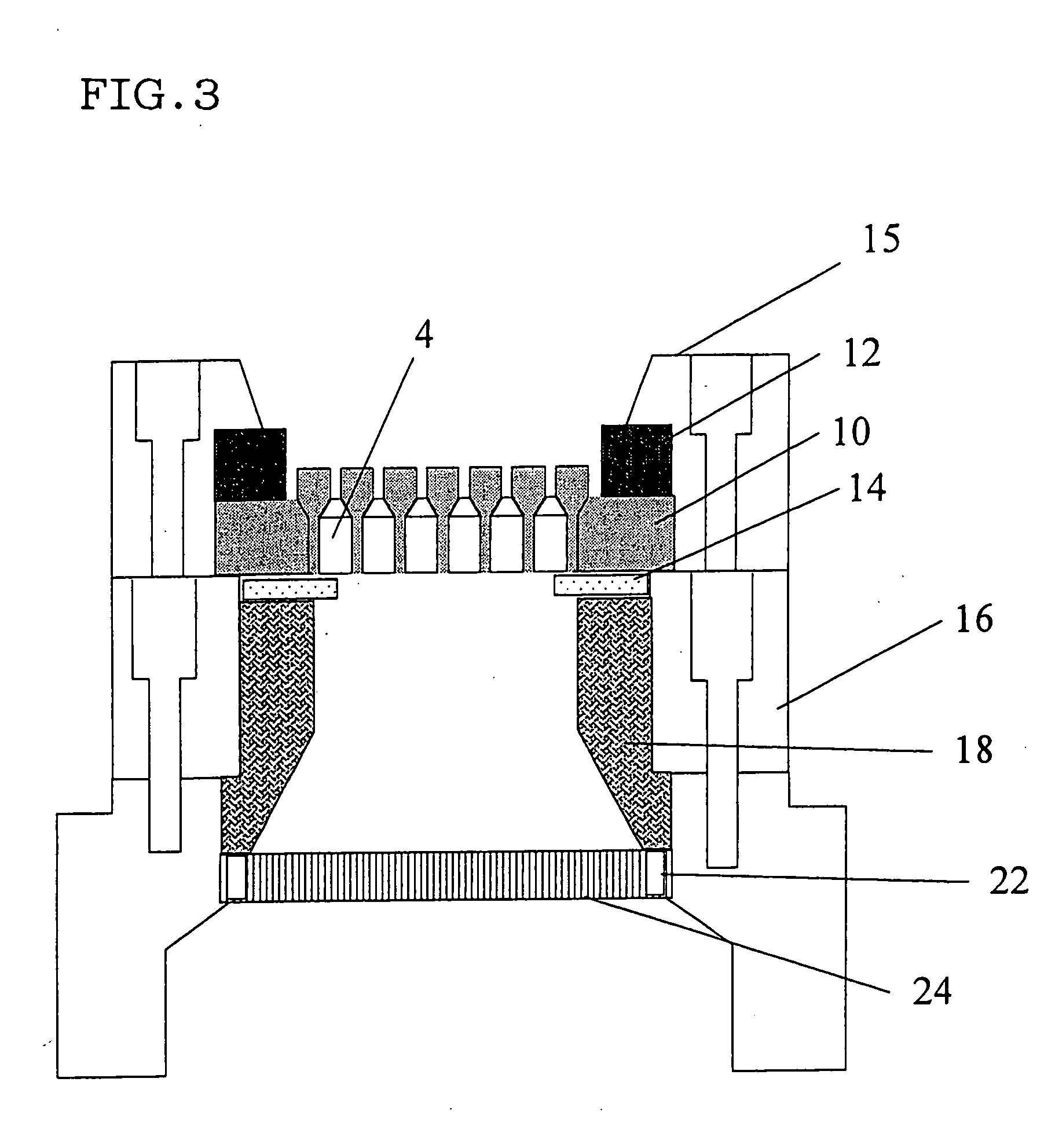
Honeycomb forming ferrule and jig for honeycomb forming ferrule using the ferrule
a technology of honeycomb and ferrule, which is applied in the direction of dough shaping, manufacturing tools, food shaping, etc., can solve the problems of large wear, unstable structure of extruded honeycomb, and large wear of the body, and achieve high toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Comparative Examples 1 and 2
[0038] Honeycomb structures were extruded, respectively using a cemented carbide die shown in Table 1 (embodiment 1; a connection area ratio of back holes and cell blocks was 50% (refer to FIG. 2) and the cell blocks had the height (1) of 3 mm) and surface-treated stainless steel dies (comparative examples 1 to 2) shown in Table 1. The results are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Dispersion ofType of dieWear resistanceconfiguration sBase materialSurface treatment(*1)(*2)Embodiment 1Cemented carbideAbsent1000.02(WC-Co)ComparativeStainless steelNon electrolytic 1 0.80example 1material (C-450)plating treatmentthickness: 50 μmComparativeCVD film thickness: 5 0.50example 215 μm
(*1) Wear resistance: when wear resistance of the comparative example was set to 1.
(*2) Dispersion of configuration: a standard deviation of 100 diagonal line cross points was calculated.
[0039] From the results of Table 1, wear resistance of the cemented carbide die (embodiment 1) is at le...
examples 2 to 4
Comparative Examples 3 and 4
[0040] Honeycomb bodies were extruded, respectively using cemented carbide dies (embodiments 2 to 4 and comparative example 3 to 4, in which cell blocks had a height (1) of 3 mm) in which a connection area ratio of cell blocks and back holes was set as shown in Table 2. The results are shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2Connection arearatio of cellblock - kneadedPresence / absenceExtrusion ofclay introductionof broken cellDispersion ofhoneycombhole (%)blockconfiguration (s) *2structureEmbodiment 235Absent0.30◯Embodiment 350Absent0.02◯Embodiment 465Absent0.20◯Comparative30Present0.50Δexample 3Comparative70Present—Xexample 4
*2 Dispersion of configuration: a standard deviation of 100 diagonal line cross points was calculated.
[0041] From the results of Table 2, the honeycomb structures could be excellently extruded without breakage of the cell blocks in the dies in extrusion and with a less amount of change of configuration by setting the connection area ratio of the ...
examples 5 to 7
Comparative Examples 5 and 6
[0044] Honeycomb bodies were extruded, respectively using cemented carbide dies (embodiments 5 to 7 and comparative examples 5 to 6) made such that a connection area ratio of cell blocks and back holes was set to 50% (refer to Table 2) and that the cell blocks had a height (1) as shown in Table 3, respectively. The results are shown in Table 3.
TABLE 3OutsideHeightPresence / appearance ofof cellabsenceproductExtrusion ofblockof broken(presence / absencehoneycomb(mm)cell blockof crack)structureEmbodiment 52AbsentAbsent◯Embodiment 63AbsentAbsent◯Embodiment 75AbsentAbsent◯Comparative1AbsentPresentXexample 5Comparative7PresentAbsentXexample 6
[0045] From the results of Table 3, extruded honeycomb structures and products molded after the honeycomb structures were extrude had an excellent outside appearance in the embodiments 5 to 7 because the cell blocks of the dies were not broken in extrusion by setting a height of the cell blocks to 2 to 5 mm.
[0046] Note tha...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com