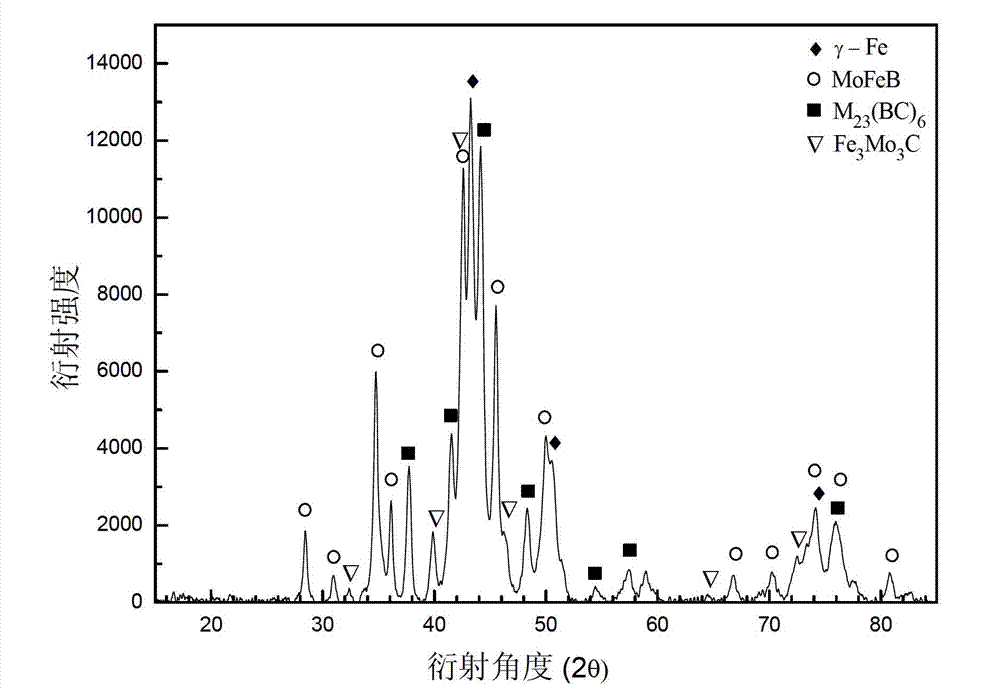
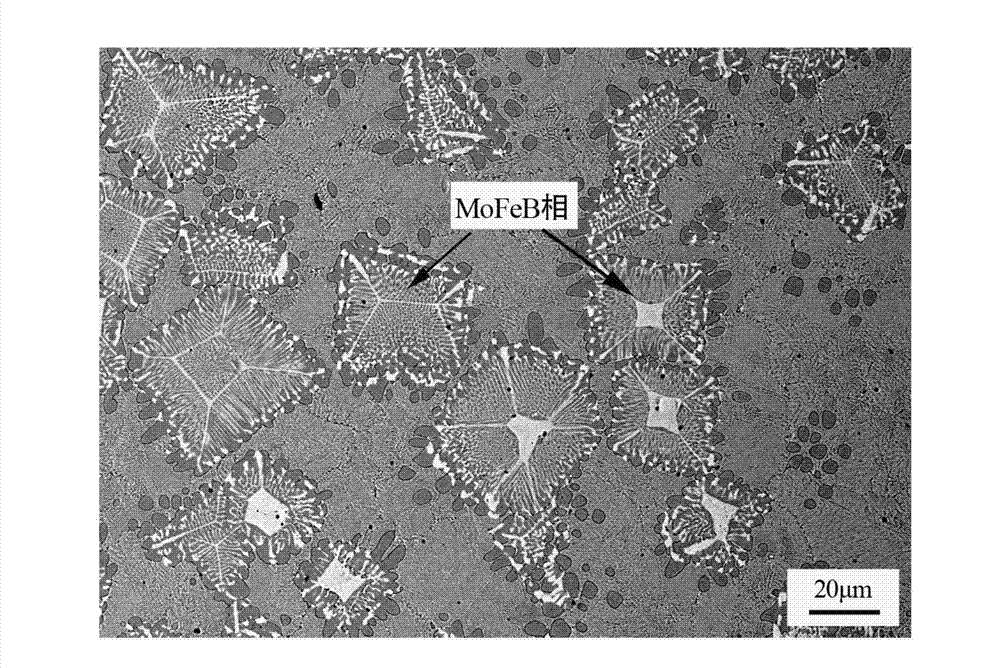
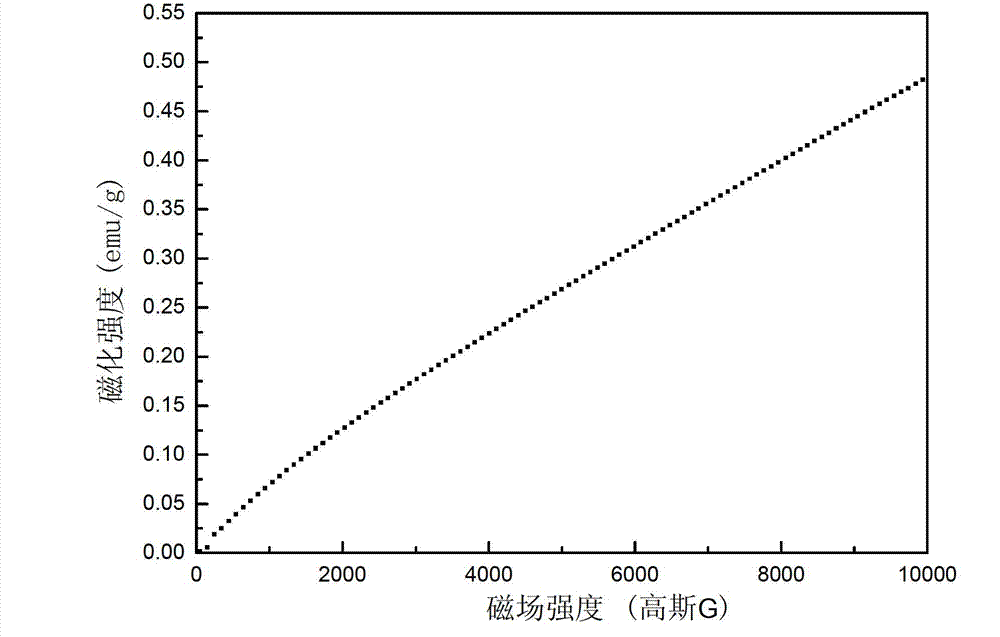
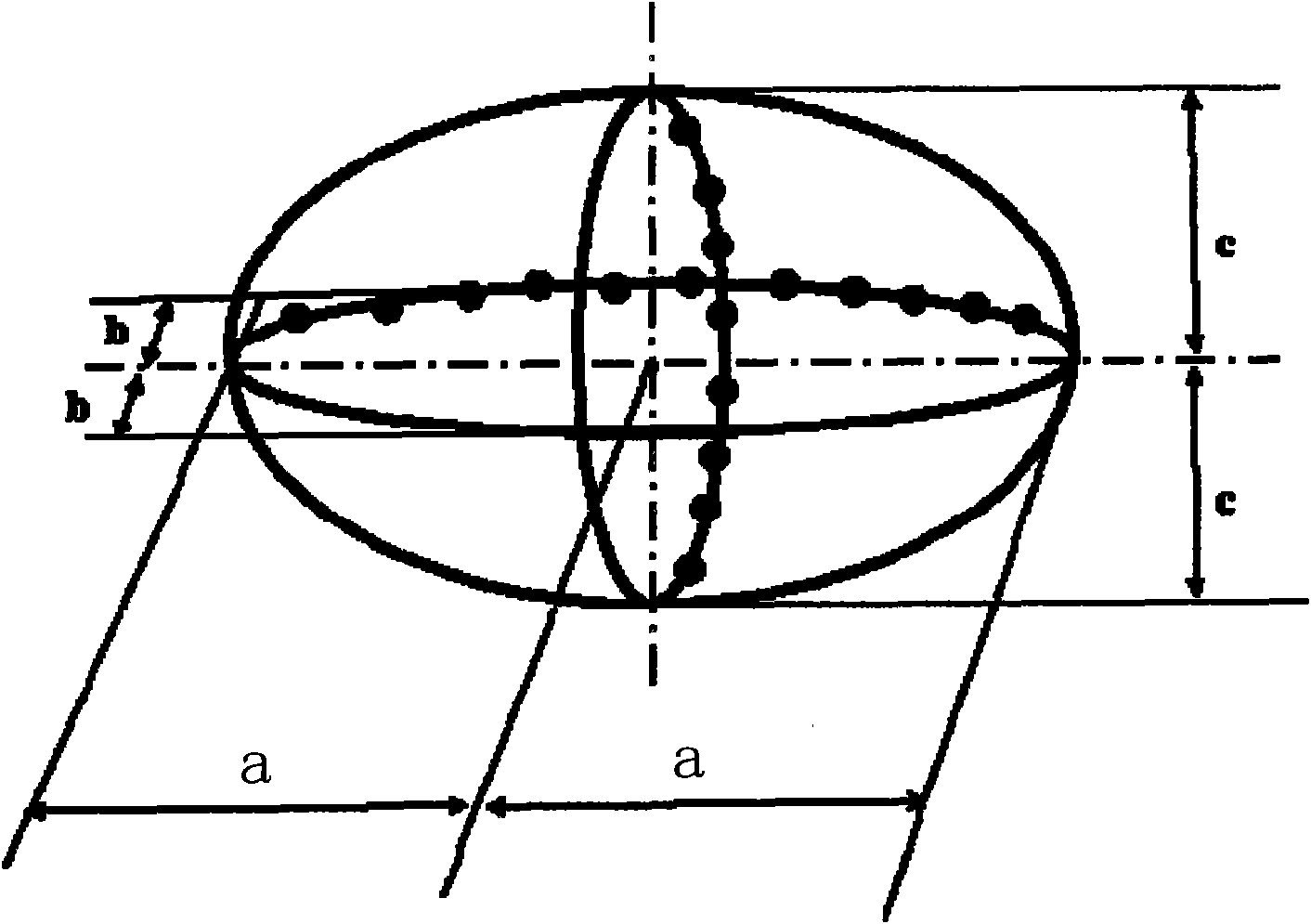Patents
Literature
1314 results about "Boron carbides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Boron carbides are boron–carbon compounds.
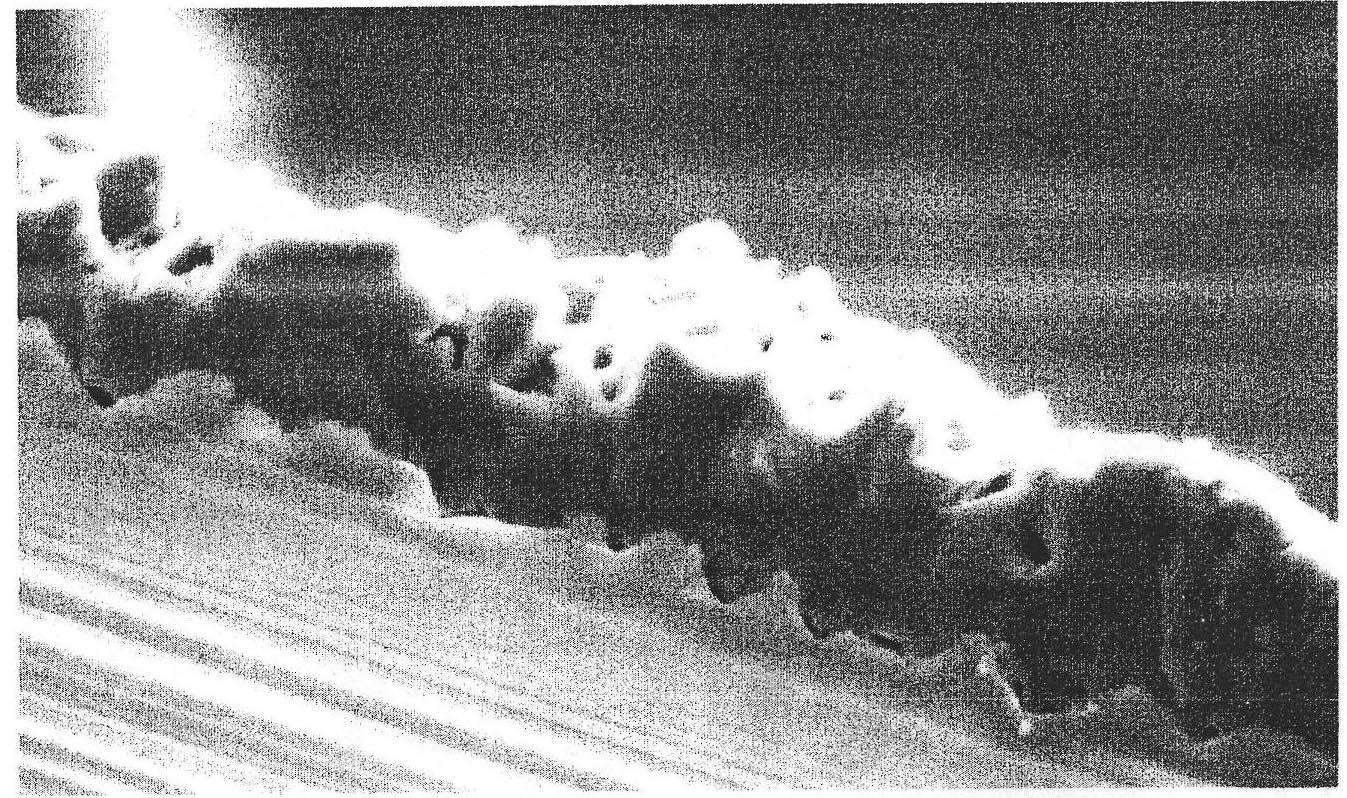
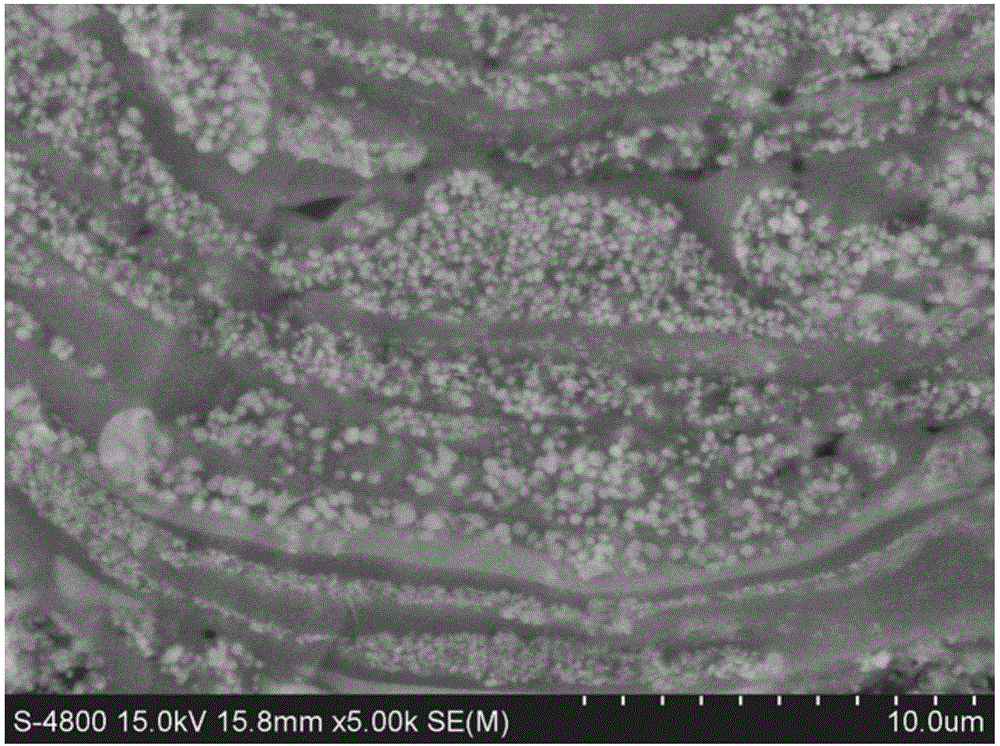
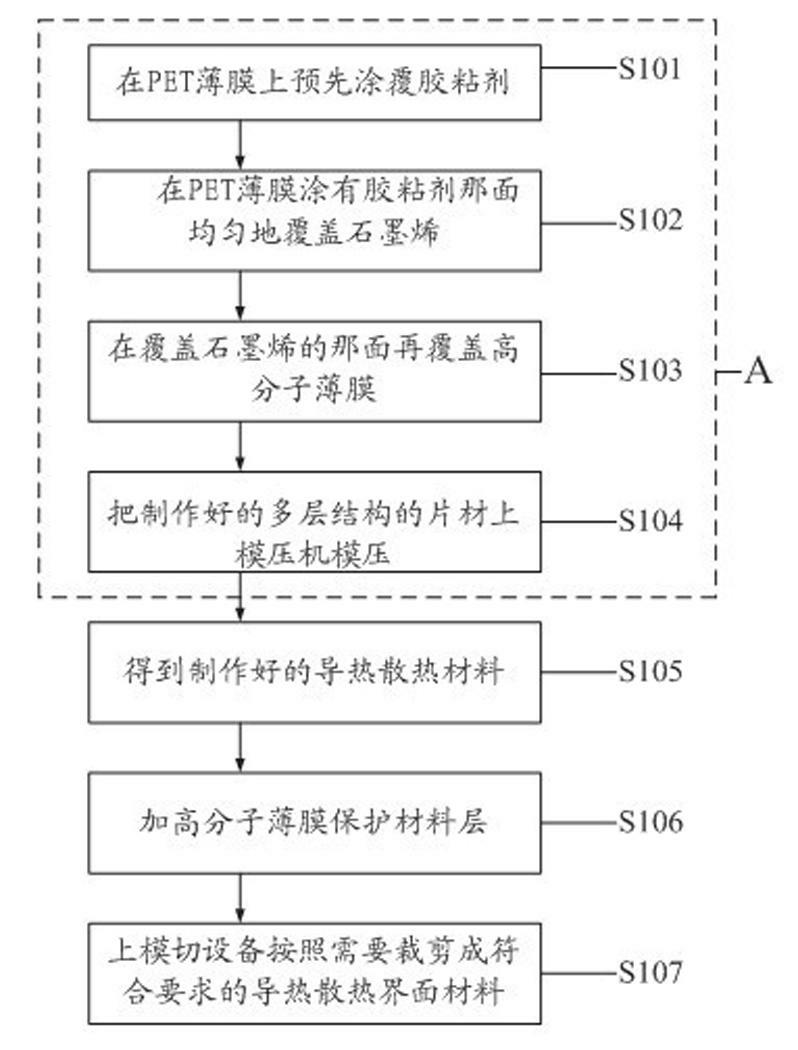
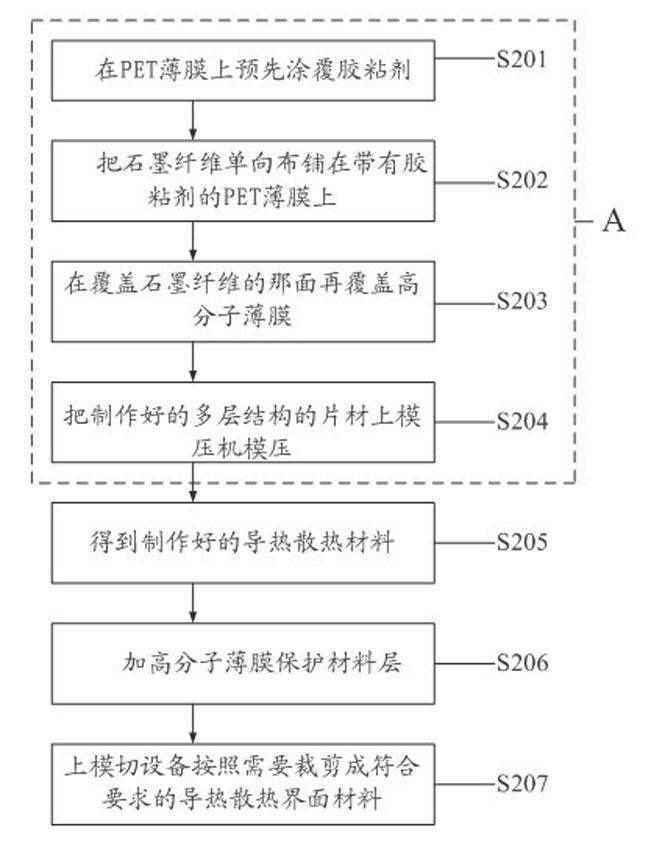
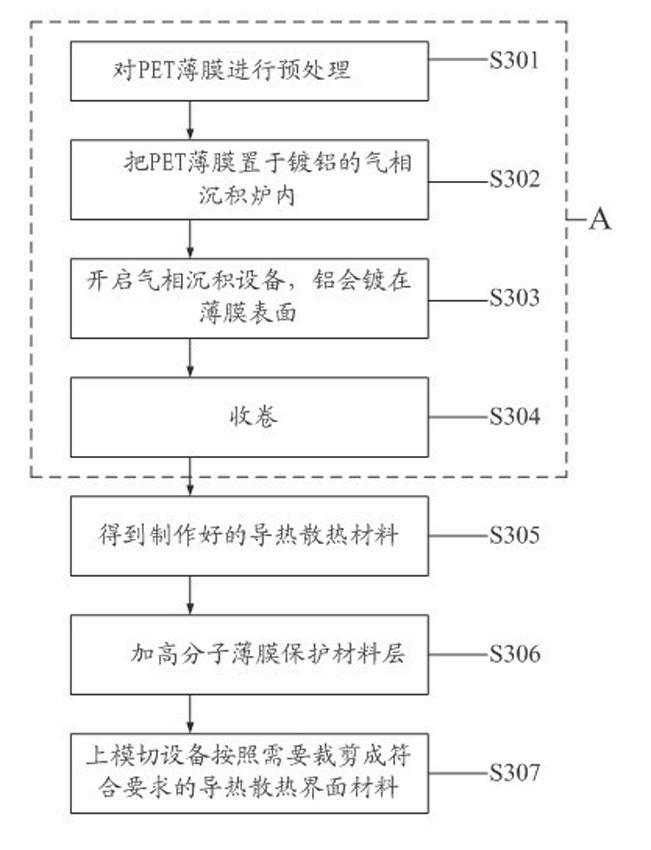
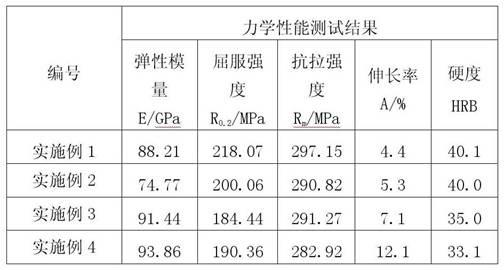
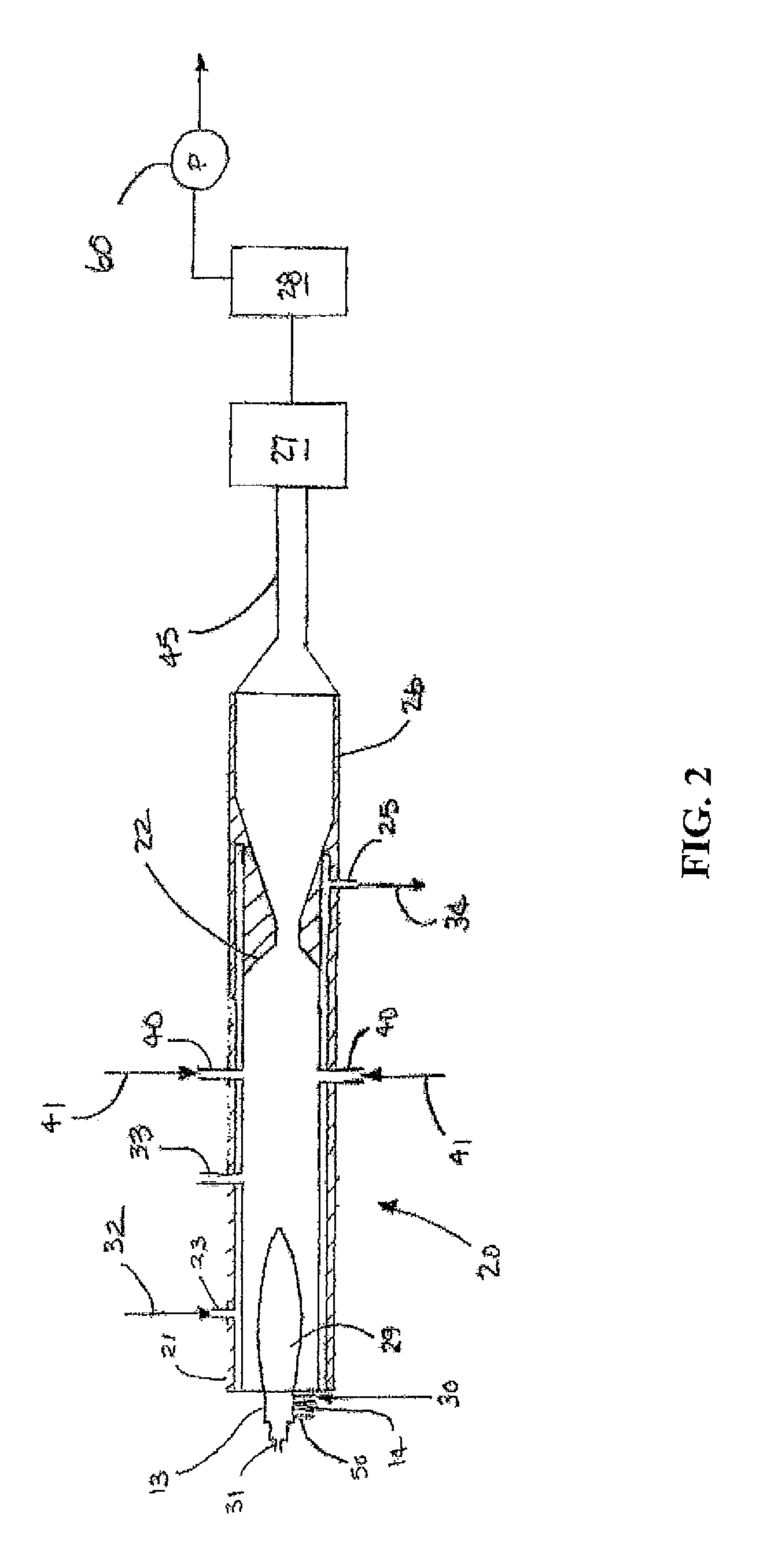
Heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102651961AReduce volumeThe overall thickness is thinLayered productsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsMetal fiberCalcium silicate
The invention provides a heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material is applied to the field of heat dissipation of electronic products. The heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material comprises a heat-conduction heat-dissipation layer and a surface protective material layer, wherein the heat-conduction heat-dissipation layer consists of one or more of graphite, nano graphite, crystalline flake graphite, graphene, pyrolytic carbon, pyrolytic graphite, graphite powder, carbon nano tubes, carbon fibers, graphite fibers, resin, ceramic fibers, quartz fibers, metal fibers, zirconia, boron nitride, silicon nitride, boron carbide, silicon carbide, magnesia powder, metasillicio acid fibers, calcium silicate aluminum fibers, aluminium oxide fibres, copper power, aluminium power, silver power, tungsten power and molybdenum power; and the surface protective material layer is a polymeric membrane. The heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material manufactured according to the materials and the method provided by the invention has the advantages of effectively improved heat-dissipation performance, small volume, light weight and small thickness, can be used for prolonging the service life of an electronic component, and simultaneously is easy to produce and process.
Owner:SHANGHAI QI JIE CARBON MATERIALS
Method for preparing B4C-Al composite material
ActiveCN102094132ALower requirementEasy to processAluminium alloyMechanical properties of carbon nanotubes
The invention relates to a method for preparing a B4C-Al composite material, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, uniformly mixing a certain proportion of raw material boron carbide powder with aluminum alloy powder in a high-energy ball milling way; 2, compressing the uniformly-mixed power for molding; 3, sintering compression-molded compact in the step 2 at certain temperatures; 4, extruding sintered compact sintered in the step 3 at certain temperatures; and 5, conducting multiple-time hot rolling for the extruding-molded material in the step 4 at certain temperatures to obtain B4C-Al composite boards. By adopting the preparation method in the invention, the ball milling efficiency is high, the preparation process almost has no material loss, and the prepared B4C-Al composite boards have the characteristics of uniform distribution of boron carbide and good mechanical property and can be applied to neutron absorption / shielding.
Owner:ANHUI YINGLIU JIUYUAN NUCLEAR ENERGY NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Process for preparing self-sealing silicon carbide ceramic based composite material
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a self-healing silicon carbide ceramic matrix composite. The method comprises the following steps: preparing fiber preform; filtrating a pyrolytic carbon interface layer by chemical gas phase; carrying out thermal treatment on the interface layer; infiltrating silicon carbide and boron carbide substrate by chemical gas phase alternately; and depositing three silicon carbide coatings by the chemical gas phase. The method has strong designability, simple process and good repeatability. The ceramic matrix composite manufactured by the method has good high temperature resistance and oxidation resistance, has excellent mechanical performance and thermal performance, and can meet the use requirement of a sealing strip / an adjustment sheet, an interior cone and other components of a high thrust-weight ratio aeroengine.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Lightweight dry refractory
A dry refractory composition having superior insulating value. The dry refractory composition also may have excellent resistance to molten metals and slags. The composition includes filler lightweight material, which may be selected from perlite, vermiculite, expanded shale, expanded fireclay, expanded alumina silica hollow spheres, bubble alumina, sintered porous alumina, alumina spinel insulating aggregate, calcium alumina insulating aggregate, expanded mulllite, cordierite, and anorthite, and matrix material, which may be selected from calcined alumina, fused alumina, sintered magnesia, fused magnesia, silica fume, fused silica, silicon carbide, boron carbide, titanium diboride, zirconium boride, boron nitride, aluminum nitride, silicon nitride, Sialon, titanium oxide, barium sulfate, zircon, a sillimanite group mineral, pyrophyllite, fireclay, carbon, and calcium fluoride. The composition also may include dense refractory aggregate, which may be selected from calcined fireclay, calcined Chamotte, a sillimanite group mineral, calcined bauxite, pyrophyllite, silica, zircon, baddeleyite, cordierite, silicon carbide, sintered alumina, fused alumina, fused silica, sintered mullite, fused mullite, fused zirconia, sintered zirconia mullite, fused zirconia mullite, sintered magnesia, fused magnesia, sintered spinel, and fused spinel refractory grog, a heat activated bonding agent, and a dust suppressant.
Owner:ALLIED MINERAL PROD
Diamond/cubic boron nitride saw blade for cutting metal and fabricating method therefor
ActiveCN1669708ANo harmHuman and Environmental HazardsMetal sawing toolsSawing tools dressing arrangementsBoron carbideBoron nitride
This invention relates to a saw bit belonging to mechanical working field, which comprises metal base being alloy steel or carbon steel, with Phi8-Phi10mm radiating holes equispaced on its surface; Carcass including alumina, zircite, quartz, tungsten carbide, zirconium diboride, molybdenum disilicide; common abradant including brown fused alumina, carbofrax, green silicon carbide, cubic carbofrax, boron carbide; superhard abradant including diamond and cubic boron nitride. The produce process includes mixing carcass flour, working layered material batching-mixing process, welding layered material batching-mixing process, koldflo, thermal pressing-sintering formation, arc milling, welding, dressing and making edge. The invention has improved working efficiency, lowered product cost, and is suitable for cutting metal tube, plate such as this materials.
Owner:SF DIAMOND CO LTD
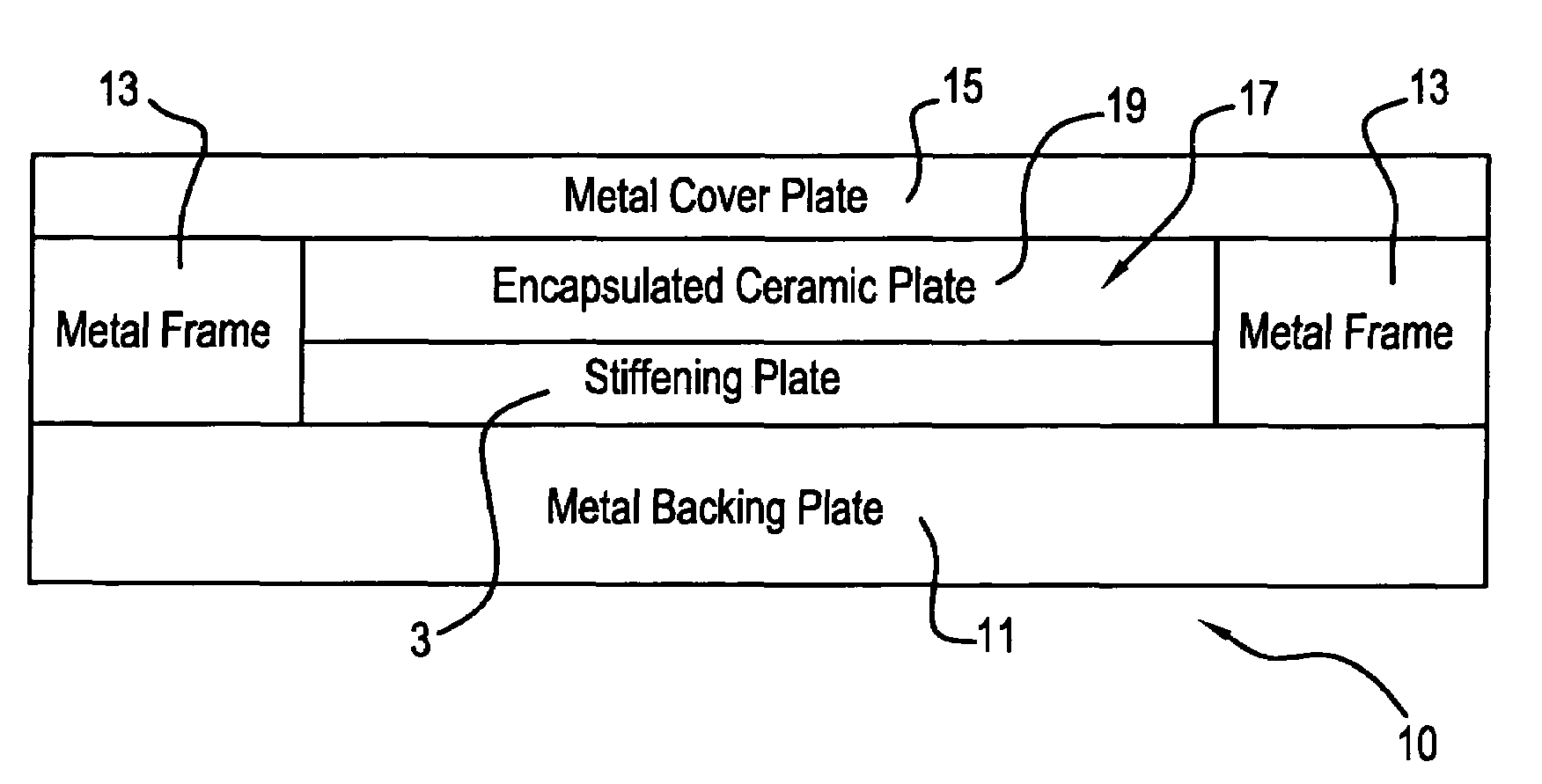
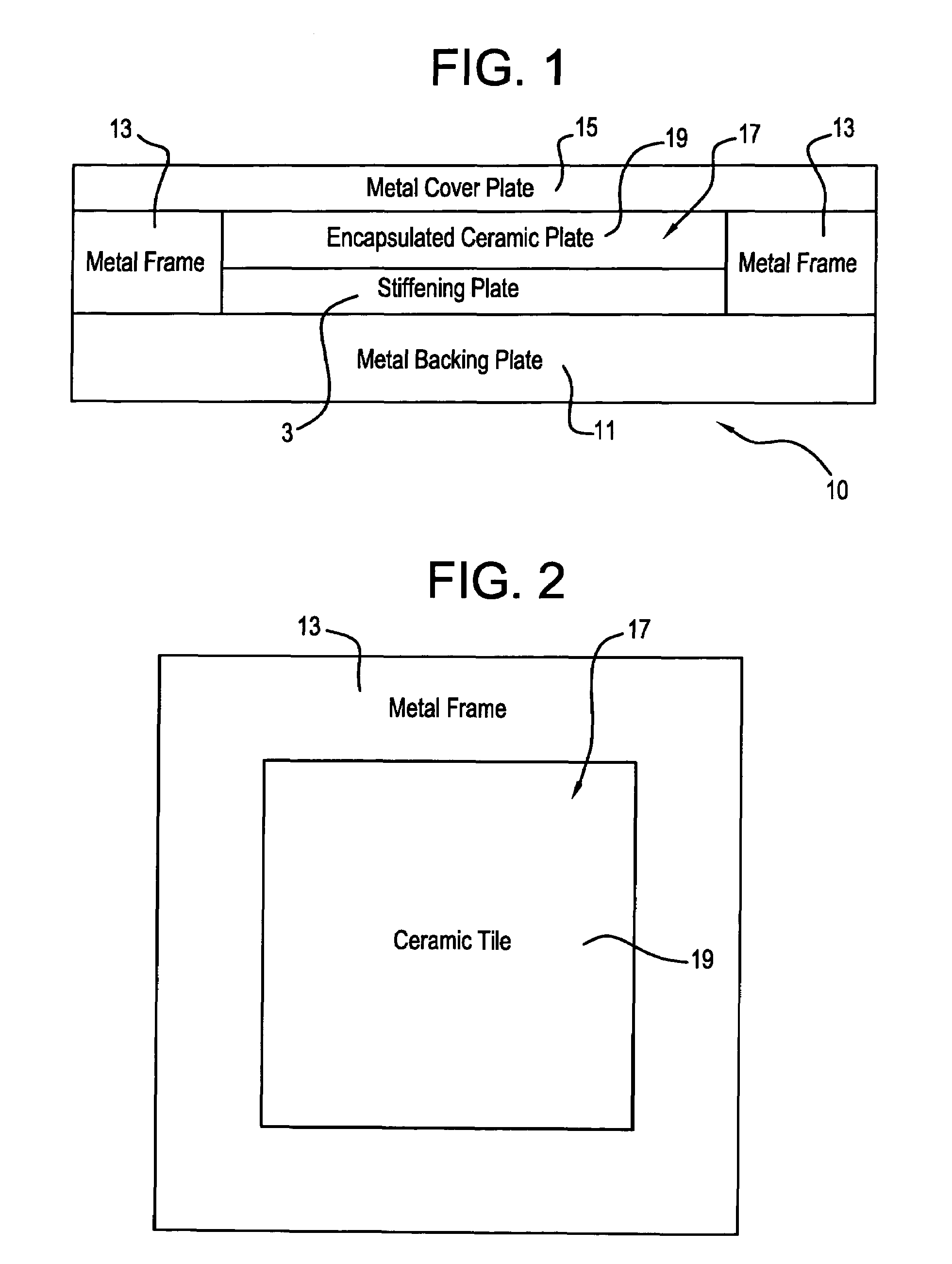
Ceramic armor and method of making by encapsulation including use of a stiffening plate
InactiveUS7069836B1Improve simplicityDoor/window protective devicesArmoured vehiclesCeramic compositeBoron carbide
A ceramic armor is disclosed in several embodiments. In a first embodiment, a metal base plate has a metal frame assembled on it having a central opening into which the ceramic material and stiffening plate are placed. A cover plate is placed over the frame to enclose the ceramic material on all sides. In a second embodiment, the frame has an open central area that has two crossing walls that define four sub-chambers. Four sets of ceramic material and stiffening plate are placed in the respective sub-chambers and a covering plate is placed over them. In a further embodiment, the frame has a plurality of cavities mechanically formed in it. A stiffening plate and a ceramic tile or plate are placed in each cavity and a cover plate is placed over the frame. The metal used to encapsulate the ceramic material may, if desired, comprise a Titanium alloy such as Ti-6Al-4V, and the ceramic material may comprise Silicon Carbide, Boron Carbide, Tungsten Carbide, Titanium Diboride, Aluminum Oxide or Aluminum Nitride. The stiffening plate is preferably made of a Ti—TiB cermet composite but may also be comprised of an armor ceramic such as WC, TiB2, Al2O3 or B4C. A hot pressing procedure is carried out on the armor to cause the metal to plastically deform about the encapsulated ceramic material.
Owner:BAE SYST ADVANCED CERAMICS
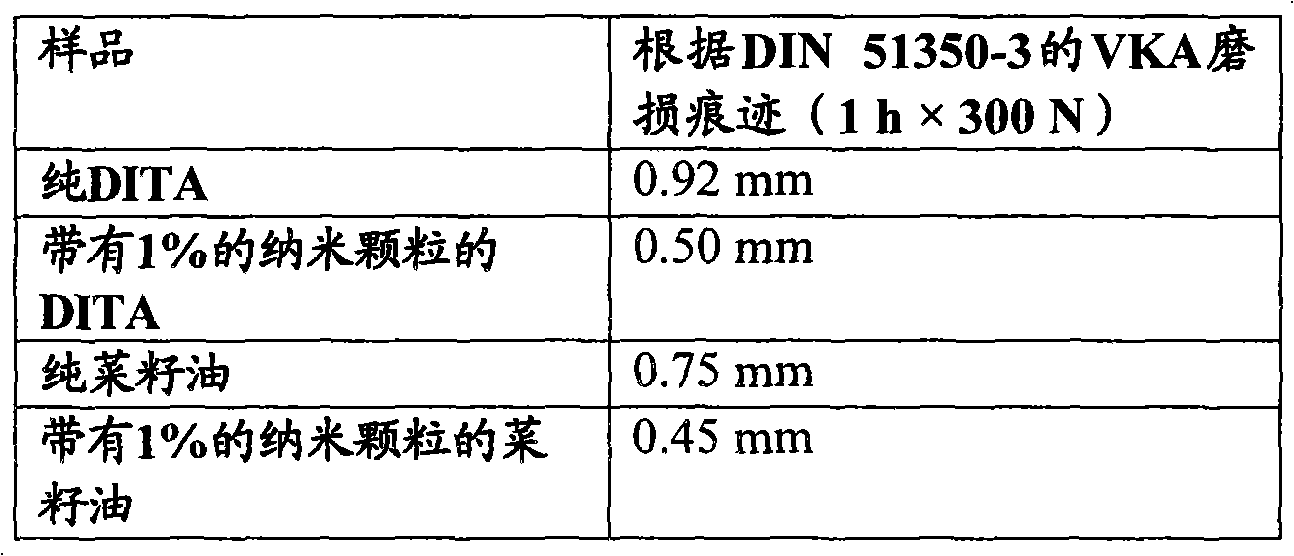
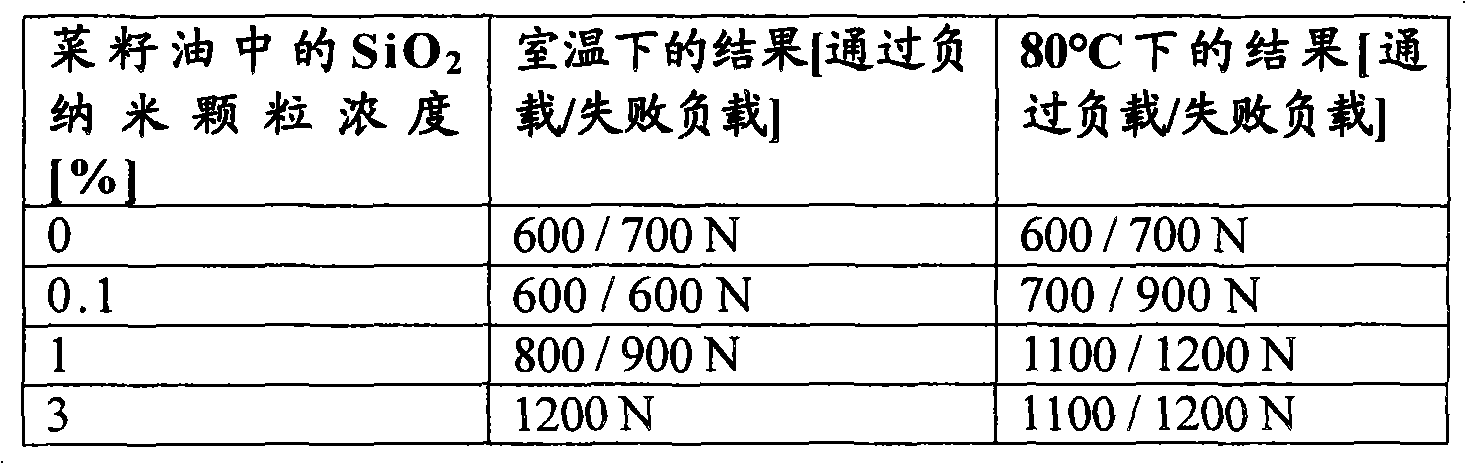
Additive for lubricant for improving the tribologic properties, a method for its production and application
The present invention relates to novel lubricant additives for improving the tribological properties, novel lubricants containing these additives, processes for the preparation thereof and the use thereof. Lubricant comprises ceramic nanoparticles as additives comprising aluminum oxide, aluminum nitride, silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, zirconium oxide, yttrium oxide, tungsten oxide, tantalum pentoxide, vanadium pentoxide, niobium pentoxide, cerium dioxide, boron carbide, aluminum titanate, boron nitride, molybdenum disilicide, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, titanium carbide, titanium nitride, zirconium diboride and / or clay minerals, and thermally stable carbonates and / or sulfates. The nanoparticles represent an ellipsoid with three semi-axes a, b and c, which are not equal to each other, or equal to each other. The ratio of a and b is 1-100, a and c is 1-1000, and b and c is 1:100.
Owner:แลนด์เซสส์ ดอยช์แลนด์ จีเอ็มบีเอช
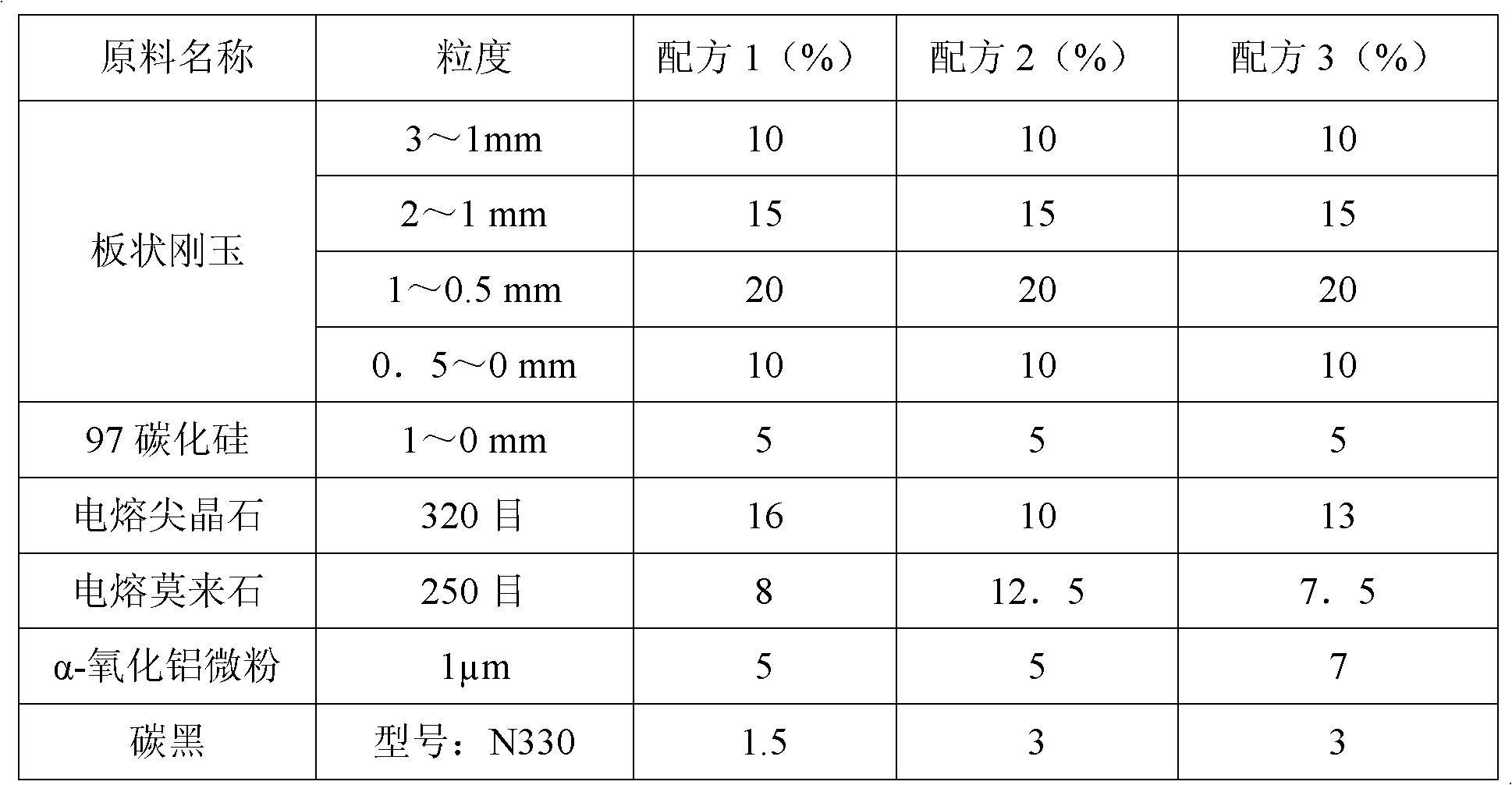
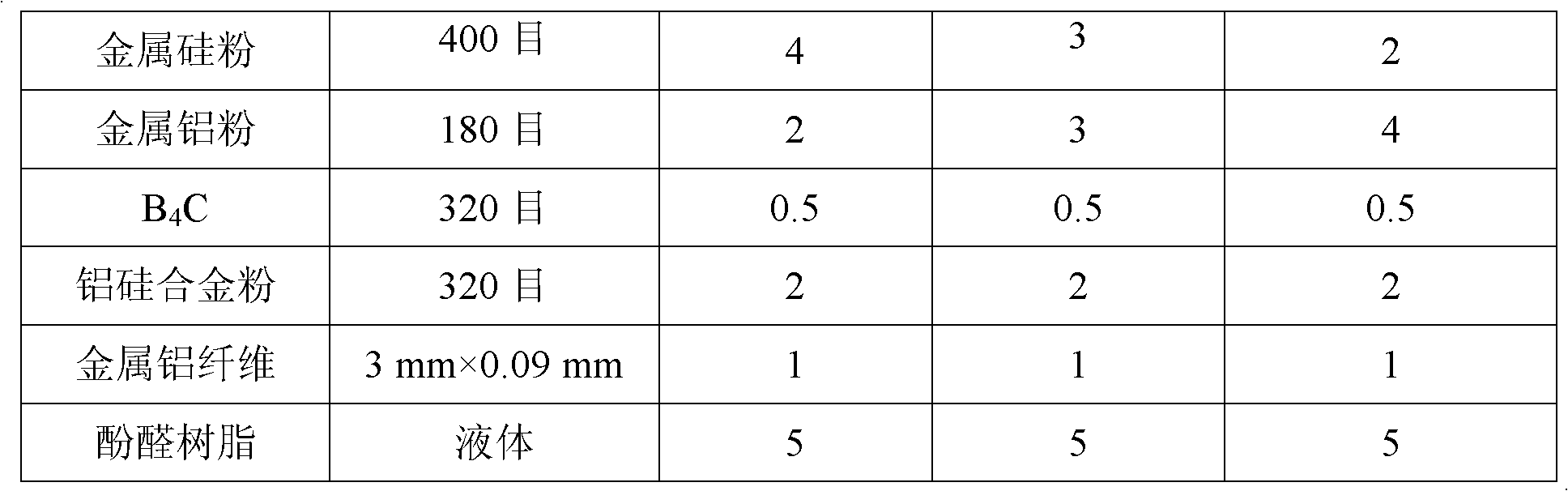
Metal ceramic combination sintering free low carbon sliding plate brick and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a metal ceramic combination sintering free low carbon sliding plate brick and a preparation method thereof. The sliding plate brick comprises the following components according to weight percentage: 50%-60% of sintered plate shape alundum, 10%-25% of electric melting akerite, 5%-15% of electric melting mullite, 1%-3% of soot carbon, 3%-8% of Alpha- aluminum oxide micropowder, 5%-10% of silicon carbide, 2%-5% of metallic silicon powder,1%-5% of metallic aluminium powder, 0.5%-1% of boron carbide, 1%-3% of aluminum-silicon alloy powder, and 0.5%-2% of metallic aluminium fiber. In the invention, the product has low carbon, high thermal state strength, thermal shock resistance and good oxidation resistance, hole reaming is uniform, galling is less and the crack is verysmall; the process of the invention is characterized in that drying is carried out at a low temperature, the production cycle is shortened from 30 days originally to 7 days, the natural gas consumption is reduced to 2.5% of original technology, and the sintering free low carbon sliding plate brick is indeed belongs to the environmental protective and energy-saving and environmental material resistance product.
Owner:无锡市南方耐材有限公司
Light-weight Al2O3-SiC-C refractory casting material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a light-weight Al2O3-SiC-C refractory casting material and a preparation method thereof. The light-weight Al2O3-SiC-C refractory casting material comprises the following raw materials: 40-55 wt% of porous corundum particle, 8-12 wt% of corundum particle, 6-12 wt% of SiC particle, 6-10 wt% of SiC fine powder, 5-8 wt% of corundum fine powder, 8-12 wt% of active aluminum oxide micropowder, 3-5 wt% of calcium aluminate cement, 2-4 wt% of silicon oxide micropowder, 2-4 wt% of ball asphalt, 1.5-2.0 wt% of silicon powder, 0.1-0.3 wt% of aluminum powder and 0.1-0.3 wt% of boron carbide powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the raw materials with 8-15 wt% of water, 0.2-0.6 wt% of water reducing agent and 0.02-0.04 wt% of organic explosion-proof fiber, stirring, casting, molding, and naturally drying at 110 DEG C for 12-48 hours to obtain the light-weight Al2O3-SiC-C refractory casting material. According to the invention, the process is simple; and the prepared product has the characteristics of high strength, excellent thermal shock stability, low heat conductivity and high medium erosion resistance, and also has the advantage that the apparent porosity and pore size can be controlled.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High corrosion resistant integral stopper for continuous casting
The invention relates to the technical field of carbonaceous refractory materials, especially to a high corrosion resistant integral stopper for continuous casting. The stopper contains a stopper head and a stopper body, wherein the stopper body comprises the following components of: by weight, 15-25 parts of graphite, 20-70 parts of magnesium aluminate spinel, 0-30 parts of magnesia, 0-10 parts of alumina, 1-9 parts of an additive, and phenolic resin which accounts for 8-12% of the total weight of the above ingredients, wherein the additive contains one or more ingredients selected from metal silicon powder, metal aluminium powder and boron carbide. By the optimization of the material of the stopper body, porosity of the stopper body can be reduced, slag penetration resistance can be enhanced, erosion of alkaline slag to the stopper body of the integral stopper can be decreased, and service life of the stopper can be raised.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING +1
Ceramic material suitable for repair of a space vehicle component in a microgravity and vacuum environment, method of making same, and method of repairing a space vehicle component
A precursor of a ceramic adhesive suitable for use in a vacuum, thermal, and microgravity environment. The precursor of the ceramic adhesive includes a silicon-based, preceramic polymer and at least one ceramic powder selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, aluminum nitride, boron carbide, boron oxide, boron nitride, hafnium boride, hafnium carbide, hafnium oxide, lithium aluminate, molybdenum silicide, niobium carbide, niobium nitride, silicon boride, silicon carbide, silicon oxide, silicon nitride, tin oxide, tantalum boride, tantalum carbide, tantalum oxide, tantalum nitride, titanium boride, titanium carbide, titanium oxide, titanium nitride, yttrium oxide, zirconium, diboride, zirconium carbide, zirconium oxide, and zirconium silicate. Methods of forming the ceramic adhesive and of repairing a substrate in a vacuum and microgravity environment are also disclosed, as is a substrate repaired with the ceramic adhesive.
Owner:COI CERAMICS
Abrasion-resistant composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an abrasion-resistant composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material disclosed by the invention consists of the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of plastic resin, 5-30 parts of filler, 0.1-2 parts of coupling agent and 0.1-2 parts of processing aid. The composite material disclosed by the invention has excellent abrasion-resistant property, so that the application field of B4C (boron carbide) is expanded; the composite material with excellent abrasion-resistant property can be prepared by compounding the abrasion-resistant composite material with polytetrafluoroethylene powder; the abrasion-resistant property thereof is better than the effect of independent utilization of B4C or polytetrafluoroethylene; the application field is board; and the composite material is applied to the fields of automobiles, electron and electric, aerospace, weaponry and the like.
Owner:HEFEI GENIUS NEW MATERIALS
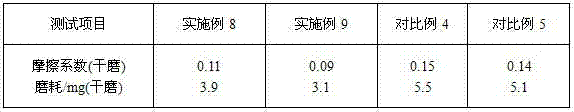
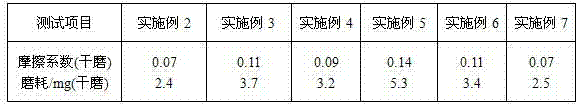
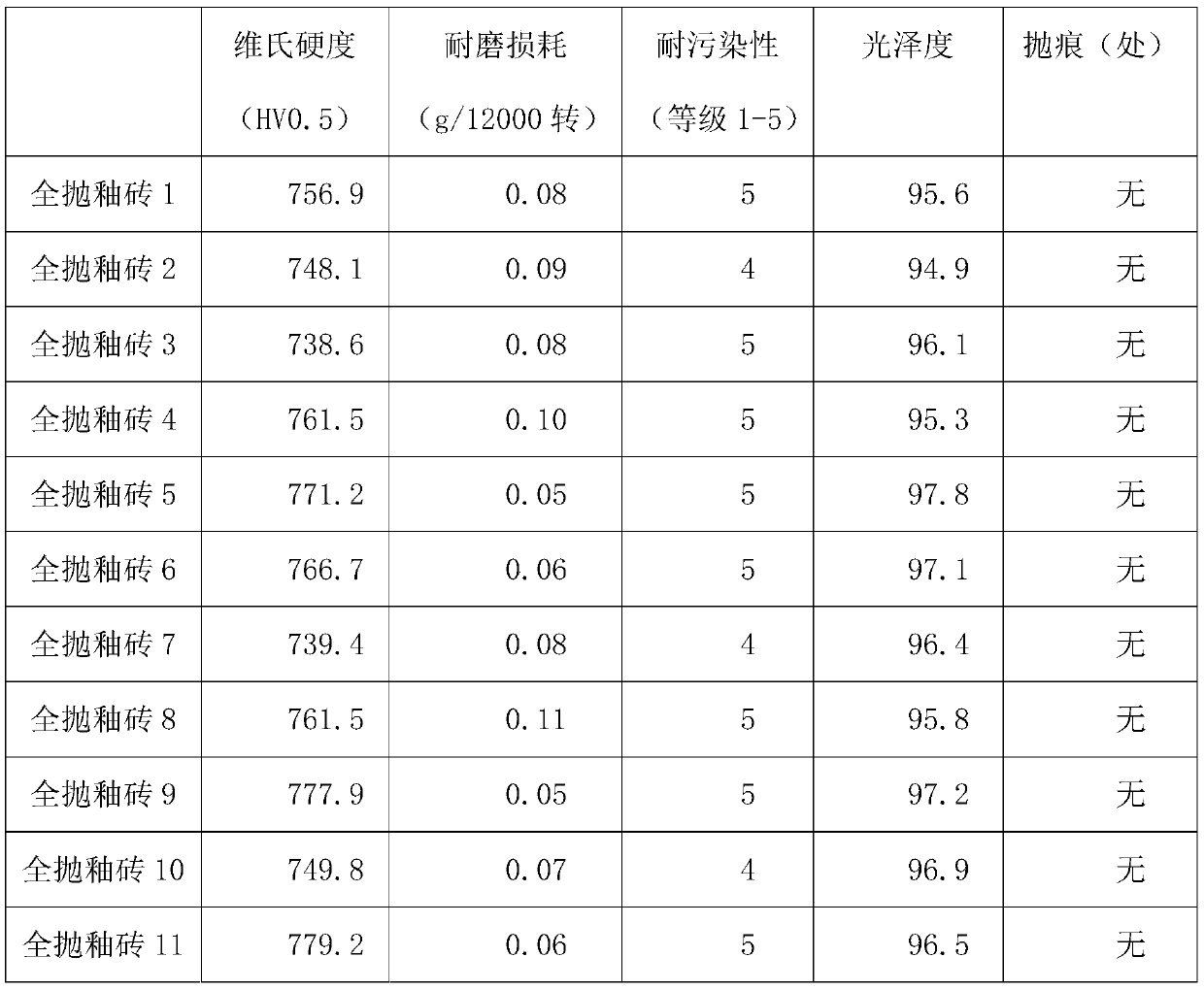
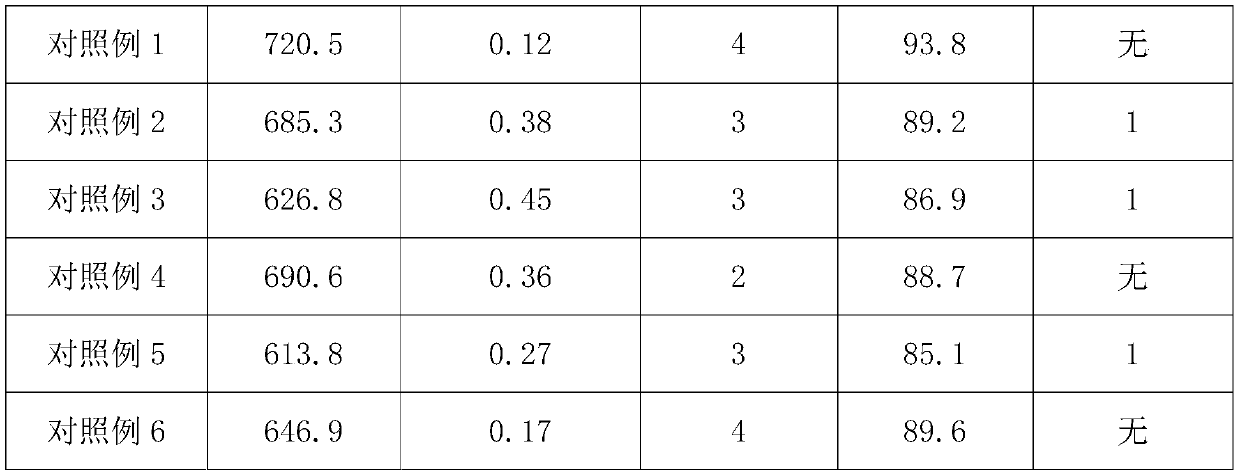
Wearing-resistant high-hardness ceramic glaze and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wearing-resistant high-hardness ceramic glaze and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of ceramic glazes. The wearing-resistant high-hardness ceramic glaze comprises the following raw materials: albite, potassium feldspar, kaolin, quartz sand, zinc white, high-aluminum clay, calcite, talc, lithium porcelain, cordierite, zirconium sand, mullite powder, wollastonite, boron carbide, niobium pentoxide, zinc oxide and frit. Both the Vickers hardness and the wearing resistance of a full polish glaze brick made of the glaze disclosed by the invention can be improved, and market requirements on full polish glaze bricks with high hardness and wearing resistance can be met; when a glaze surface is sintered, a great number of bubbles are not generated, and the product is good in antifouling performance and high in glossiness after polishing; expansion coefficients of the full polish brick and a glaze layer are approximate to those of a porcelain blank, the glaze layer is subjected to small inner stress, polishing omission or partial exposure phenomena can be avoided in polishing, and thus product quality can be ensured.
Owner:黄奕雯
Aluminum electrolysis carbon anode oxidation coating and coating method thereof
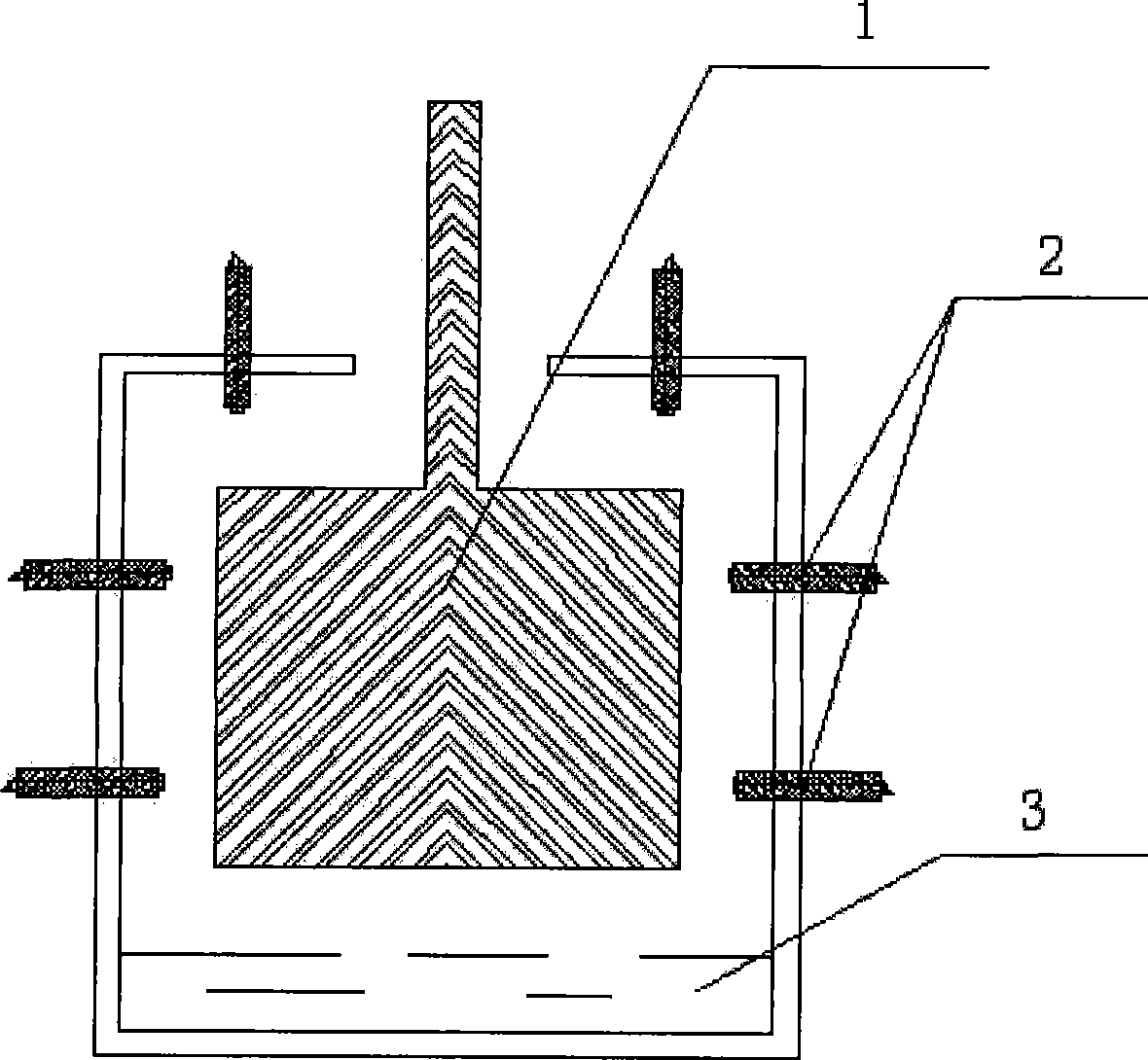
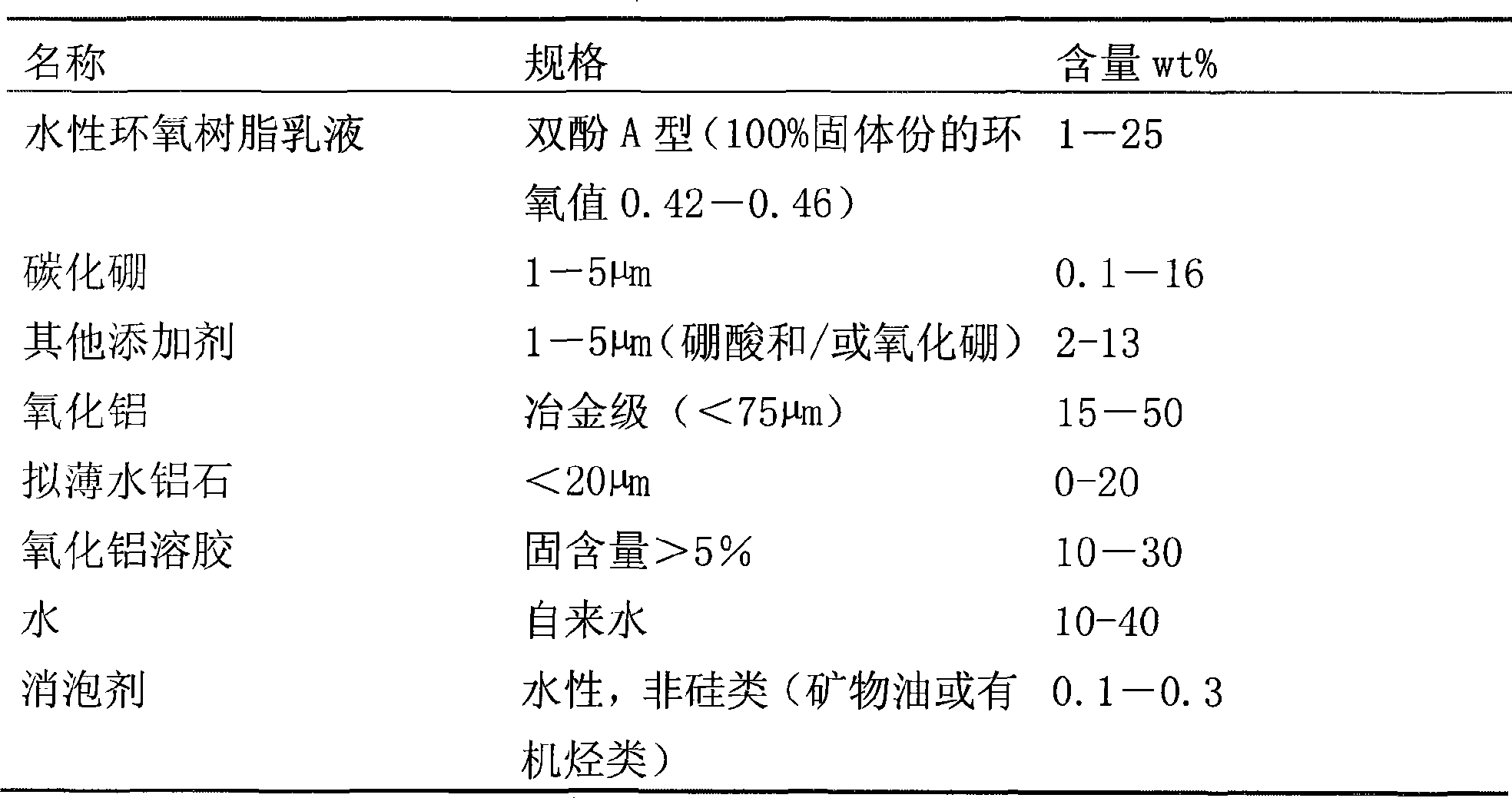
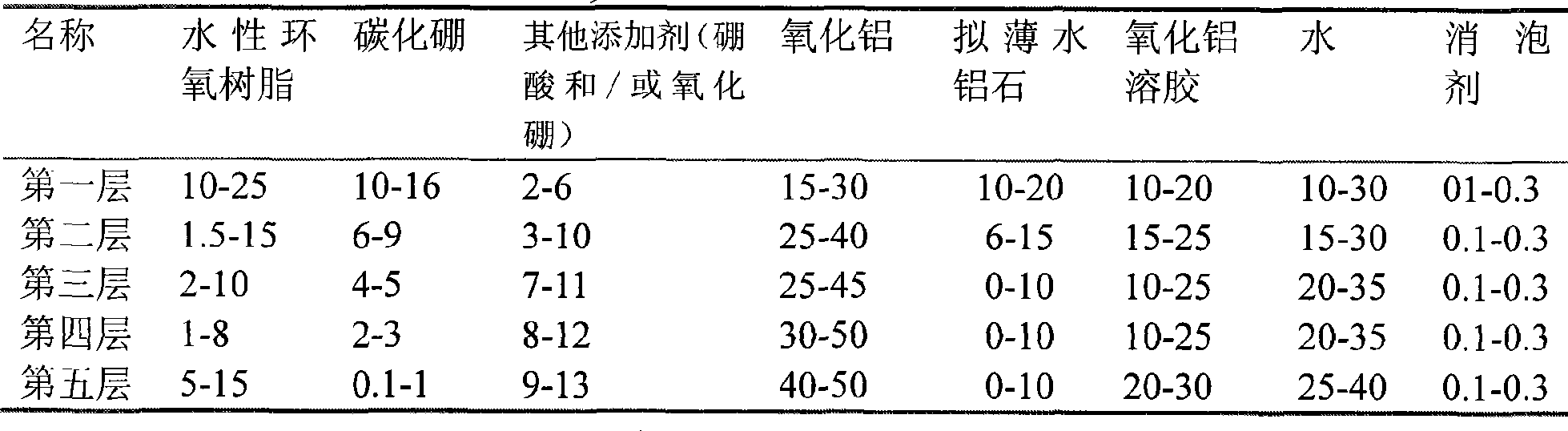
The invention relates to an oxidation resistant coating for aluminum electrolytic carbon anode and a coating method thereof. The method is characterized in that the surface of the aluminum electrolytic carbon anode is provided with an anti-oxidation coating formed by dried and mixed coat which is sprayed on the surface of the electrode, wherein the mixed coat comprises the following compositions in weight percentage: 1 to 25 percent of bisphenol A-type waterborne epoxy resin, 0.1 to 16 percent of boron carbide, 2 to 13 percent of boric acid and / or boric oxide, 15 to 50 percent of alumina, 0 to 20 percent of pseudo-boehmite, 10 to 30 percent of alumina sol, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of foam suppressor, and the balance being water. The coating and the method adopt an alumina-based gradient boron carbide oxidation resistant coating with a multilayer structure, and effectively blocks the contact of air and CO2 with carbon anode carbon, thereby avoiding or reducing excessive consumption of the carbon anode carbon. The method can realize carbon conservation by aluminum electrolytic prebaked anode by 10 to 20 kilogram / ton-Al.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND +1
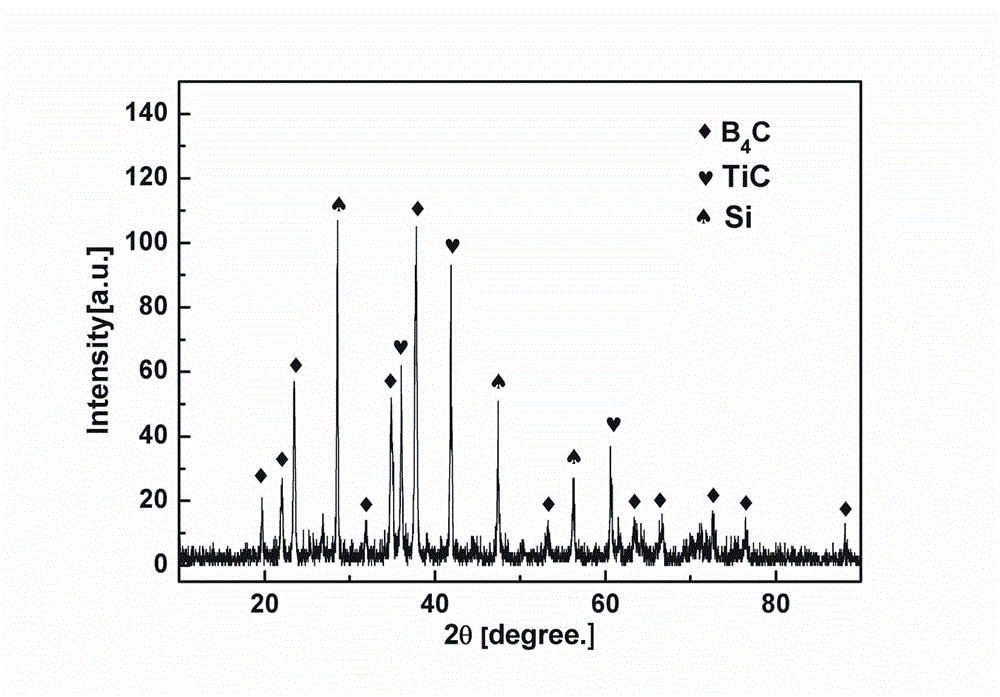
High-hardness ceramic composite material of boron carbide-titanium boride-silicon carbide and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-hardness ceramic composite material of boron carbide-titanium boride-silicon carbide and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a ceramic material. The composite ceramic is prepared from boron carbide, silicon carbide and silicon powder in a hot-pressing sintering manner via reaction. The composite ceramic contains 50-90wt% of boron carbide, 27-5.4wt% of titanium boride and 23-4.6wt% of silicon carbide. The defects of overhigh sintering temperature, and difficulty of improvement of the toughness and the hardness at the same time of the existing boron carbide ceramic are solved; carbon generated by reaction of the boron carbide and the titanium boride is removed by monatomic silicon; and the carbon for reducing the hardness of the base material is converted into hard material silicon carbide which is evenly dispersed, so as to play roles in enhancing the toughness and improving the material hardness. The high-toughness boron carbide composite ceramic can be prepared at low temperature on the premise of not reducing the hardness of a base body.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
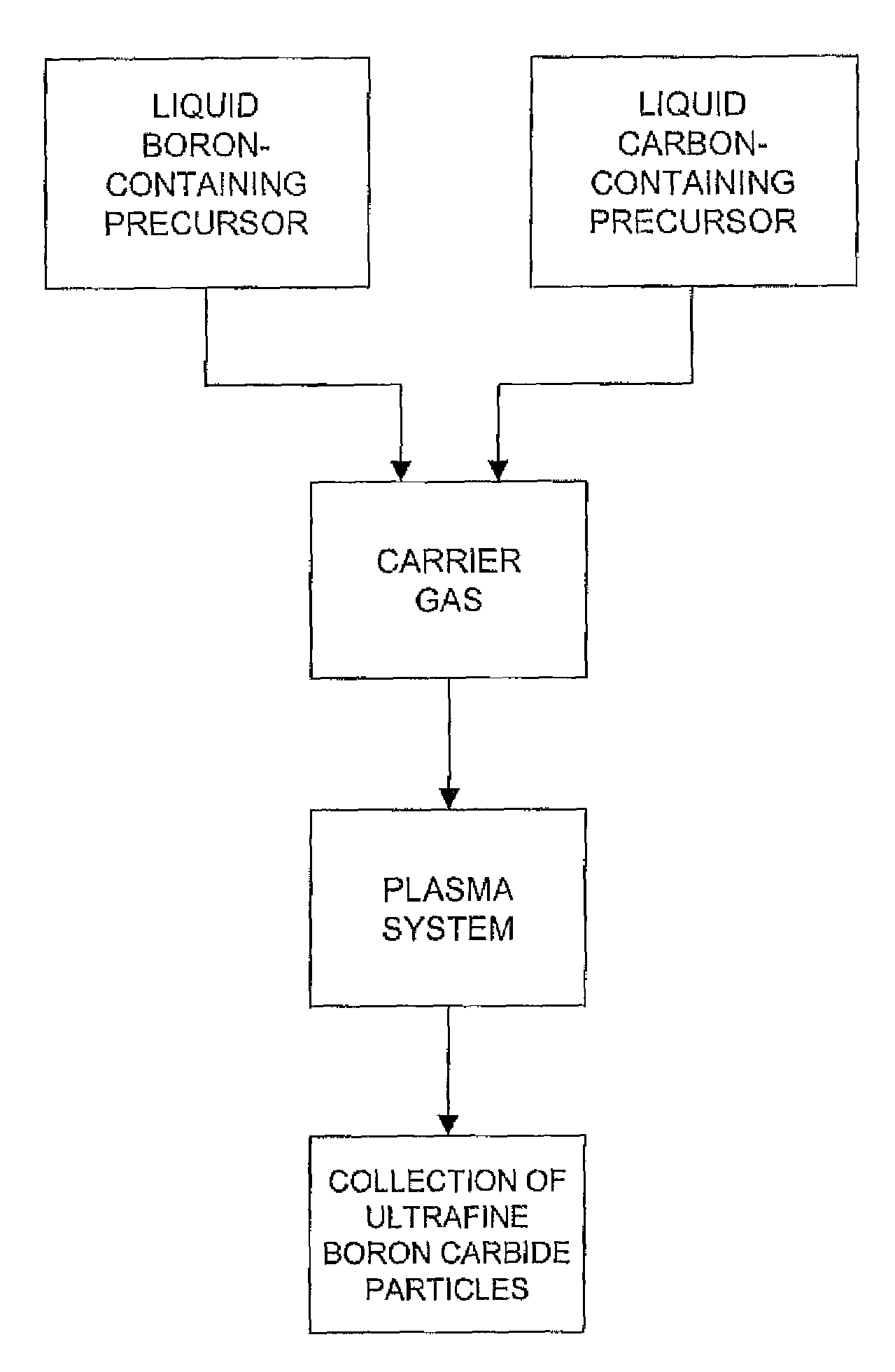
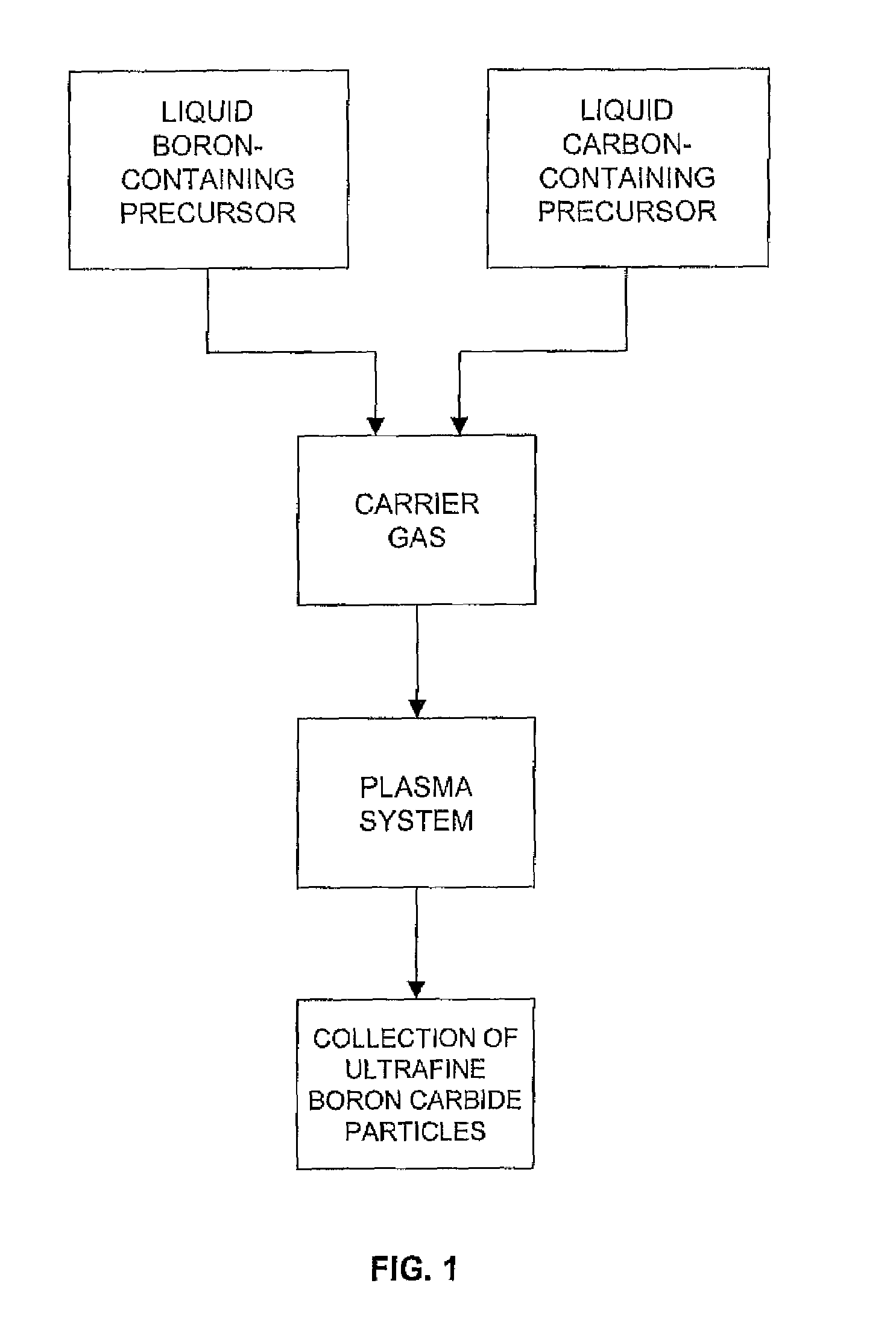
Production of ultrafine boron carbide particles utilizing liquid feed materials
The production of ultrafine boron carbide powders from liquid boron-containing precursors and / or liquid carbon-containing precursors is disclosed. The liquid precursors are fed together or separately to a plasma system where the precursor materials react to form boron carbide in the form of ultrafine particles.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Process for manufacturing centrifugally-cast easy-cutting high-speed steel roll
ActiveCN103805902AEasy to processReduce processing difficultyTemperature controlManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing a centrifugally-cast easy-cutting high-speed steel roll, belonging to the technical field of manufacturing metallurgical rolls. The technical scheme is as follows: the process comprises the process steps of determining chemical components of a material of a roll body; determining parameters of a mold; performing multi-component composite breeding graphitization on high-speed molten steel of a working layer; spheroidizing a spheroidal graphite cast iron material of a core part; controlling the pouring temperature; controlling the rotating speed of a centrifuge to be 300-800 revolutions per minute; controlling cooling parameters; and controlling an annealing process, a quenching process and a tempering process of heat treatment. The process disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the processability of the produced easy-cutting high-speed steel is improved, so that the processing difficulty and processing cycle of the high-speed roll can be reduced, the labor hour and cutting tools are saved, and significant economic benefits are achieved; when a boron carbide cutting tool is used for processing the easy-cutting high-speed steel roll and under the condition that the linear velocity of a processed part is 20m, the cutting depth is improved from 2mm to 3-5mm; and the feed speed is improved from 0.2mm / r to 0.4-0.5mm / r.
Owner:朝阳联强轧辊有限公司
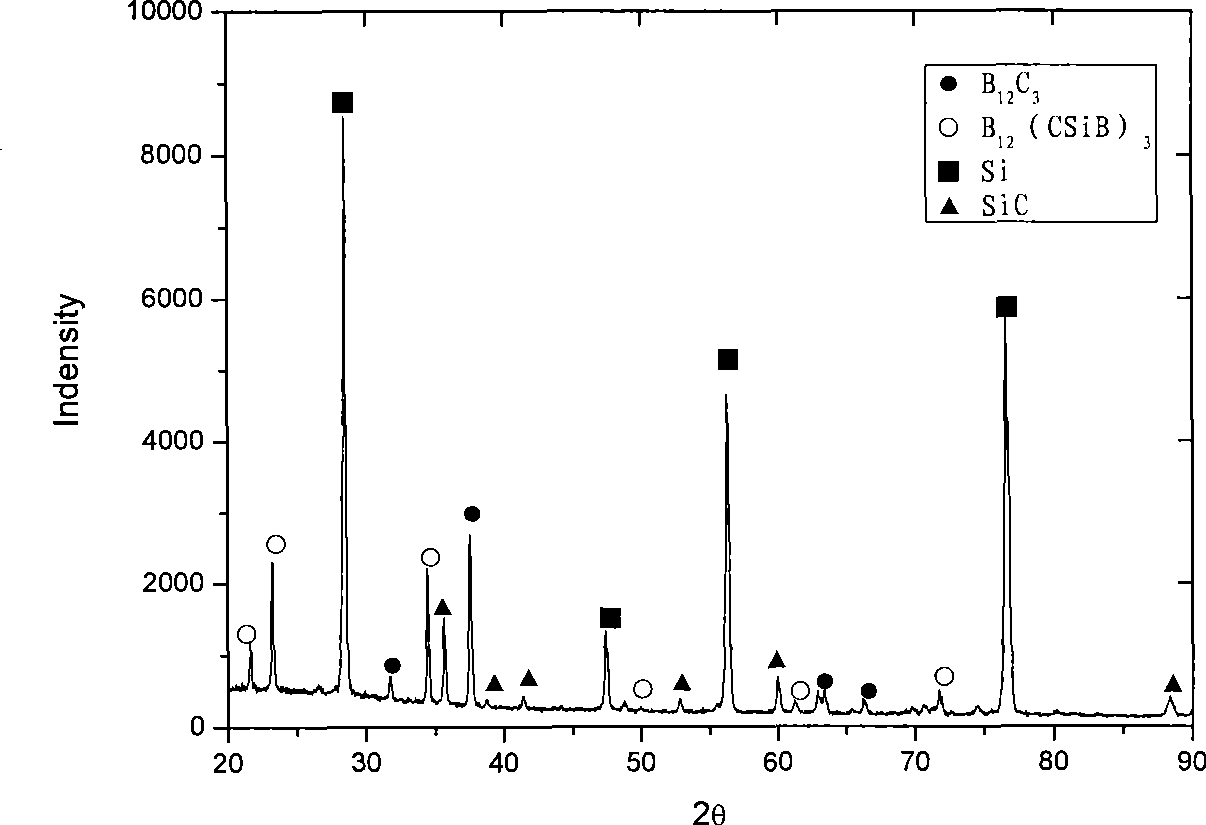
Boron carbide base composite ceramic and preparation method thereof
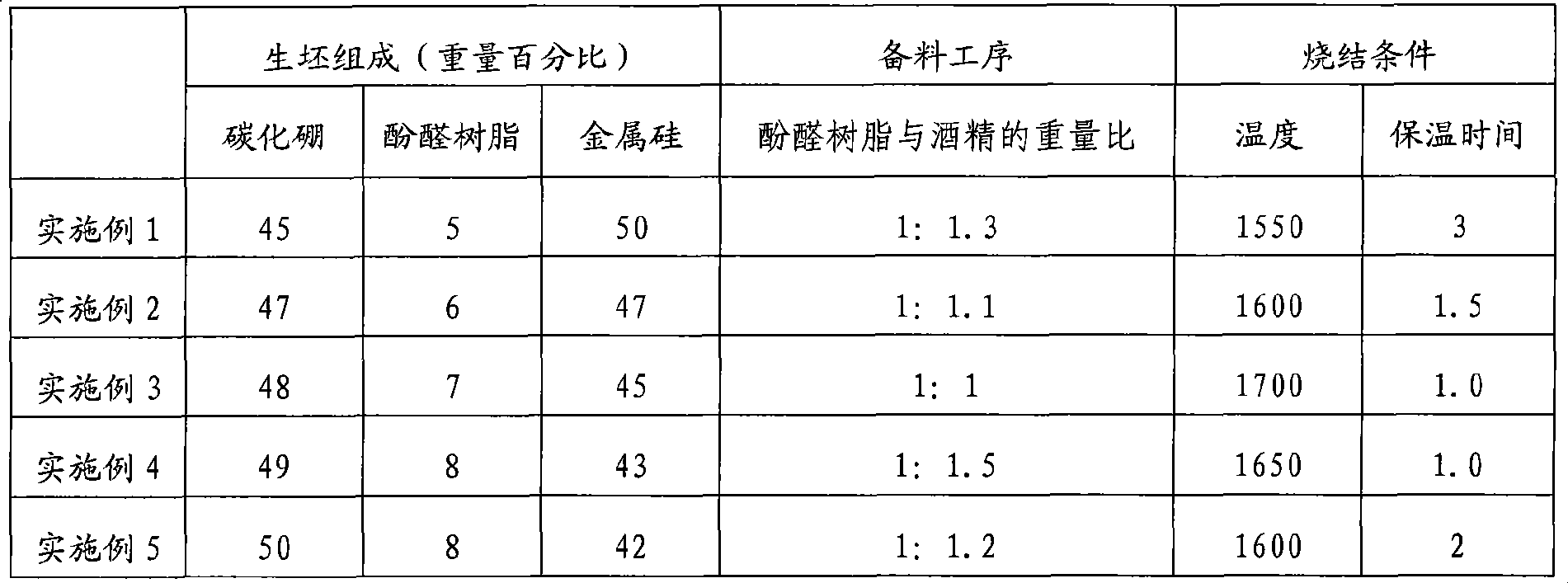
The invention discloses a boron carbide based composite ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The boron carbide based composite ceramic comprises the following compositions by weight percentage: 45 to 50 percent of boron carbide powder, 5 to 8 percent of phenolic resin, and 42 to 50 percent of metallic silicon. After the compositions are weighed, the phenolic resin is dissolved by alcohol first, and the boron carbide powder is added for mechanical ball milling to be mixed evenly; a granulator is used for granulation, and a green body with a shape of the needed product is obtained through compression molding; the compressed green body is placed into a baking oven for drying solidification; the weighed metallic silicon is added into a graphite crucible, the solidified green body is placed on the metallic silicon and is placed into a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace for sintering along with the crucible, the sintering temperature is between 1,550 and 1,700 DEG C, and the green body is cooled with the furnace after the thermal insulation for 1 to 3 hours to obtain the boron carbide based composite ceramic. The phenolic resin plays a role in an adhesive and a carbon source during the preparation of the composite ceramic, and can also play a role in providing the green body with excessive air holes during the sintering, so that the infiltrability of silicon is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Chemical-mechanical polishing composition and method for using the same
InactiveUS20050211950A1Other chemical processesDecorative surface effectsTitanium nitrideNuclear chemistry
The invention provides a chemical-mechanical polishing composition comprising: (a) an abrasive comprising α-alumina, (b) about 0.05 to about 50 mmol / kg of ions of at least one metal selected from the group consisting of calcium, strontium, barium, and mixtures thereof, based on the total weight of the polishing composition, and (c) a liquid carrier comprising water. The invention also provides a chemical-mechanical polishing composition comprising: (a) an abrasive selected from the group consisting of α-alumina, γ-alumina, δ-alumina, θ-alumina, diamond, boron carbide, silicon carbide, tungsten carbide, titanium nitride, and mixtures thereof, (b) about 0.05 to about 3.5 mmol / kg of ions of at least one metal selected from the group consisting of calcium, strontium, barium, magnesium, zinc, and mixtures thereof, based on the total weight of the polishing composition, and (c) a liquid carrier comprising water. The invention further provides methods of polishing a substrate using each of the above-described chemical-mechanical polishing compositions.
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
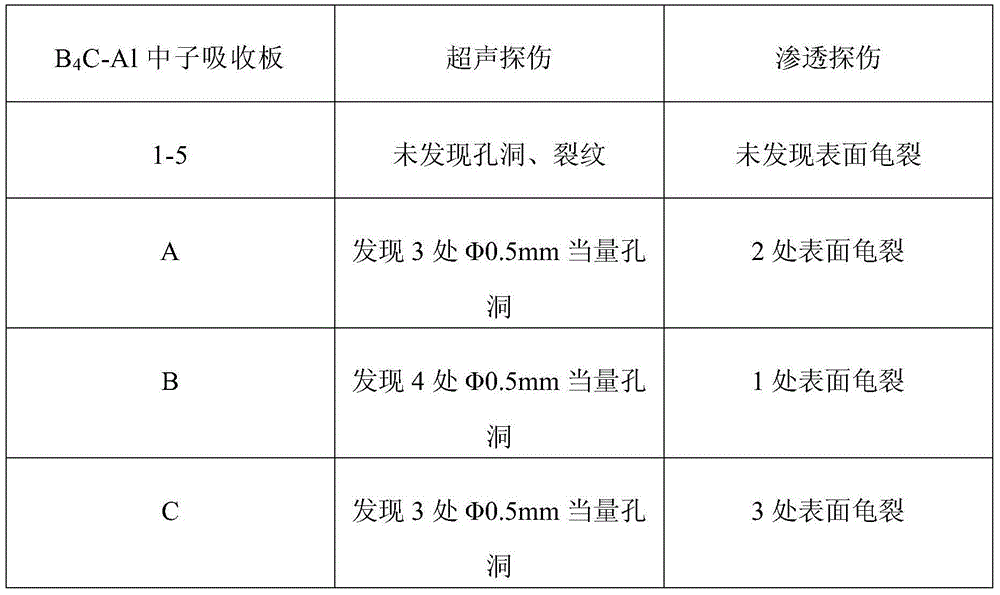
Large-dimension B4C-Al neutron absorption plate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104372191ANo need for sintering processOvercoming the problem of further increase in defectsShieldingNuclear reactorNuclear power
A disclosed preparation method for a large-dimension B4C-Al neutron absorption plate comprises: 1) crushing boron carbide powder, aluminium powder and silicon powder and mixing uniformly, so as to obtain a mixed powder with the particle size of 3.5-63 mu m; 2) putting the mixed powder into a can, vacuumizing at 200-350 DEG C, sealing, and then performing heat isostatic pressing processing on the sealed can under the conditions that the pressure is 80-150 MPa, the temperature is 400-600 DEG C and the time is 20 min; 3) removing the can at the outer side of the blank material, performing multiple times of rolling at 450-600 DEG C, controlling the deformation amount of each time rolling to be 10-20%, so as to obtain a plate with the needed thickness; and 4) processing the plate. The invention also discloses the dimension of the B4C-Al neutron absorption plate obtained by using the above method. The prepared B4C-Al neutron absorption plate is applicable to nuclear industry fields such as nuclear reactors, nuclear power stations and the like.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Foamed neutron absorber material
The invention discloses a foamed neutron absorber material. The foaming neutron absorber material is prepared from the mixture of 10-60% of neutron absorber and 40-90% of matrix material through foaming, wherein the neutron absorber is one or more than one of boron carbide, ferrite, rare earth compound, lithium hydride and paraffin wax, and the matrix material is cement, or macromolecular polymer or their mixture. 'Foaming' process is innovatively applied, massive synthesized neutron absorber are dispersed on walls of the pores formed by foaming. The matrix cellular caves greatly expand capacity for capturing neutron rays, neutron rays in the interior of foamed body are diffused by virtue of electromagnetic vortex pore wall, and the scattered neutron waves are gradually attenuated and absorbed.
Owner:李勇
Alloy powder material for Fe-based nonmagnetic cladding layer and cladding layer preparing method
InactiveCN103042317AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceMolten spray coatingPlasma welding apparatusChromium carbideFerrosilicon
The invention discloses an alloy powder material for a Fe-based nonmagnetic cladding layer and a cladding layer preparing method, and belongs to the field of surface coating. The alloy powder comprises reduction ferrous powder, electrolytic manganese powder, high carbon ferro-chrome, ferro-molybdenum, ferrosilicon, ferro-boron, chromium carbide and boron carbide, and comprises following elementary compositions: 5-20wt% of Cr, 15-30wt% of Mo, 1-4wt% of C, 0.5-3wt% of B, 0.1-1.5wt% of Si, 0-15wt% of Mn, and the balance Fe. The Fe-based multi-element alloy cladding layer is prepared by plasma arc overlaying technology. The prepared cladding layer is nonmagnetic, high in hardness, and less prone to cracking and generating other cladding defects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Coated cbn
InactiveUS20100213247A1Reduced strengthHigh retention ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesSecondary layerBoride
The invention relates to a coated boron or nitrogen containing superhard abrasive material selected from cBN, boron suboxide and boron carbide comprising: cBN, boron suboxide and / or boron carbide superhard abrasive material substrate; a primary layer of a carbide / nitride / boride forming metal, such metal preferably being Ti and preferably being substantially in the form of the carbide, nitride or boride; a secondary layer of a high melting point metal selected from W, Mo, Cr, Ni, Ta, Au, Pt, Pd and alloys thereof; and an overcoat of Ag, Ni, Cu, Au, Pd, Pt, Rh, Os, Ir, Re, combinations and alloys thereof such as bronze (Cu / Sn), silver / bronze and silver / tin, the metal of the secondary layer being different to the metal of the overcoat. The invention further relates to methods for the manufacture of such material, use of such materials in tools and tools including such material.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102529239AFull functionHigh shielding efficiencySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationResin matrixBoron fiber
The invention discloses a laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material and a preparation method thereof; the laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material is in a three-layer composite structure, wherein a bottom layer is a polyethylene fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix, a middle layer is a boron fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix, and an upper layer is a polyethylene fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix which is grafted with acrylic lead. The epoxy resin matrixes comprise materials basically in the following weight portions: 100 portions of bisphenol A epoxy resin, 8 portions to 15 portions of imidazole curing agent and 3 portions to 7 portions of silane coupling agent. In addition, boron carbide (B4C) which occupies 5 weight percent to 20 weight percent of the total weight of the epoxy resin is added into the epoxy resin matrix on the bottom layer; and lead oxide which occupies 10 weight percent to 30 weight percent of the total weight of the epoxy resin is added into the epoxy resin matrix on the upper layer. The laminated neutron radiation shielding composite material is specially manufactured to overcome the defects of a traditional neutron radiation shielding composite material that slowing and absorption functions are not separated so that the functions of an absorbing body cannot be displayed well.
Owner:南京核安核能科技有限公司
High purity ultra fine zirconium biboride powder and its preparation method
The present invention relates to a high-purity ultrafine zirconium diboride powder material and its preparation method. It is characterized by that the described powder material contains zirconium oxychloride, boron carbide powder and active carbon powder, their mole ratio is ZrOcl2:B4C:C=1:0.4-0.8:1.4-1.8. Its preparation method includes the following steps: firstly, mixing boron carbide powder, active carbon powder and water according to mixing ratio, regulating pH value to obtain mixed suspension; dissolving zirconium oxychloride in deionized water to obtain the zirconium oxychloride solution; mixing the above-mentioned suspension and zirconium oxychloride solution, adding ammonia water, making the zirconium oxychloride be fully hydrolyzed and precipitated; making suspension undergo the processes of solid-liquor separation, waster-washing, removing NH4+ and Cl-, drying and sieving; then placing the powder material into a vacuum furnace to make reaction synthesis, its synthesis temperature is 1500-1600 deg.C, heat-insulating for 0.5-4 h; grinding powder and sieving so as to obtain the invented powder material.
Owner:칭다오정왕철강수통제주식유한회사
Raw material composition for graphite-silicon carbide crucible and manufacturing process thereof
The invention discloses a raw material composition for a graphite-silicon carbide crucible. The raw material composition comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 40% to 50% of flake graphite, 20% to 50% of silicon carbide, 4% to 10% of elemental silicon powder, 1% to 5% of boron carbide powder, and 5% to 15% of clay. The manufacturing process of the graphite-silicon carbide crucible comprises the following steps: mixing raw materials evenly, and manufacturing qualified mud materials; loading the qualified mud materials into moulds, putting the moulds into an isostatic press cylinder, and pressing and shaping; demoulding, drying blanks, and coating anti-oxidation glaze when the blanks are hot; then burning the blanks in a naked manner so that the glaze is melted into glass glaze; inspecting, and when burned blanks are qualified, obtaining finished products. The process disclosed by the invention is simple; the prepared crucible is uniform in texture, large in density, low in air hole rates, high in heat conduction, and strong in corrosion resistance; in addition, the clay is used as bonding agents, so that the situation that phenolic resin or tar, as the bonding agents, is decomposed to release harmful smoke in the course of sintering to pollute environment is avoided.
Owner:QINGDAO BAIDUN CRUCIBLE CO LTD
Multielement-reinforced heat-resistant magnesium alloy and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a multielement-reinforced heat-resistant magnesium alloy and a manufacturing method thereof. The multielement-reinforced heat-resistant magnesium alloy is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1000 parts of magnesium, 65-85 parts of aluminum, 5-8 parts of zinc, 10-30 parts of yttrium, 1.5-5 parts of manganese, 5-15 parts of neodymium, 3-4 parts of cerium, 1-4 parts of calcium, 0.4-1 part of strontium, 0.1-0.5 part of silicon, 3-6 parts of silver and 10-40 parts of boron carbide. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out acid washing, drying and preoxidation on the boron carbide, preheating the materials, smelting the magnesium and aluminum while introducing protective gas, adding an aluminum-manganese alloy and a pure zinc ingot to carry out alloying, adding an aluminum-silver alloy, a magnesium-silicon alloy, a magnesium-yttrium alloy, a magnesium-cerium alloy, a magnesium-neodymium alloy, a magnesium-calcium alloy and a magnesium-strontium alloy, smelting, adding the boron carbide particles for reinforcement, carrying out gas refinement on the melt by using argon, carrying out extrusion casting, and finally, carrying out solid solution aging treatment to obtain the heat-resistant magnesium alloy finished product. The magnesium alloy has excellent comprehensive properties under high-temperature conditions.
Owner:YANGZHOU FENG MING METAL PROD
Boron carbide composite materials
The invention relates to a boron carbide composite material comprising diamond particles and boron carbide, the composite material having a porosity of less than 2 percent by volume. The invention further relates to a method for manufacturing such materials, the method including coating a plurality of diamond particles with boron carbide, combining the plurality of diamond particles to form a green body and subjecting the green body to a temperature in the range from about 1,200 degrees centigrade to about 2,000 degrees centigrade and pressure or vacuum not exceeding about 2,000 Mpa.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX PRODION
Preparation method of composite hard alloy used as cutter material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite hard alloy used as a cutter material. The composite hard alloy material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 35-40 parts of nano titanium carbide, 5-15 parts of nano titanium nitride, 7-9 parts of tungsten carbide, 5-8 parts of niobium carbide, 3-7 parts of silicon carbide, 3-5 parts of cobalt powder, 1-3 parts of yttrium oxide, 1-3 parts of boron carbide and 1-5 parts of copper powder. The method comprises the following steps: preparing materials, preparing carbon-depleted alloy powder, preparing a presintering matrix, carrying out carbonization and carrying out firing step by step. The composite hard alloy prepared by the preparation method has high strength, good toughness and good wear resistance and thermal shock resistance.
Owner:CHENGDU BANGPU CUTTING TOOLS CO LTD
Preparation method for zirconium boride-based coating
The invention relates to a preparation method for a zirconium boride-based coating and relates to plating of a material by a boride. The method of in-situ synthesizing the zirconium boride-based coating comprises the steps of: preparing zirconium oxide / boron carbide / aluminum compound powder for thermal spraying; pre-treating a base material; and spraying the prepared zirconium oxide / boron carbide / aluminum compound powder for thermal spraying to the surface of the pre-treated base material by adopting a thermal spraying method so as to form the zirconium boride-based coating. The method provided by the invention overcomes the defects that in the prior art, the prepared zirconium boride-based coating is high in porosity, poor in uniformity, rough in tissue, low in toughness, small in thickness, poor in bonding force with a matrix, easy to crack and poor in thermal shock resistance; and the defects in the prior art that the preparation process is complicated, the process cost is high, the depositing efficiency is low, the cost of raw materials is high, the energy consumption is great, the efficiency is low, and the preparation method is not suitable for being applied to industrial production on a large scale.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com