Patents
Literature
307results about "Plant parameters regulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
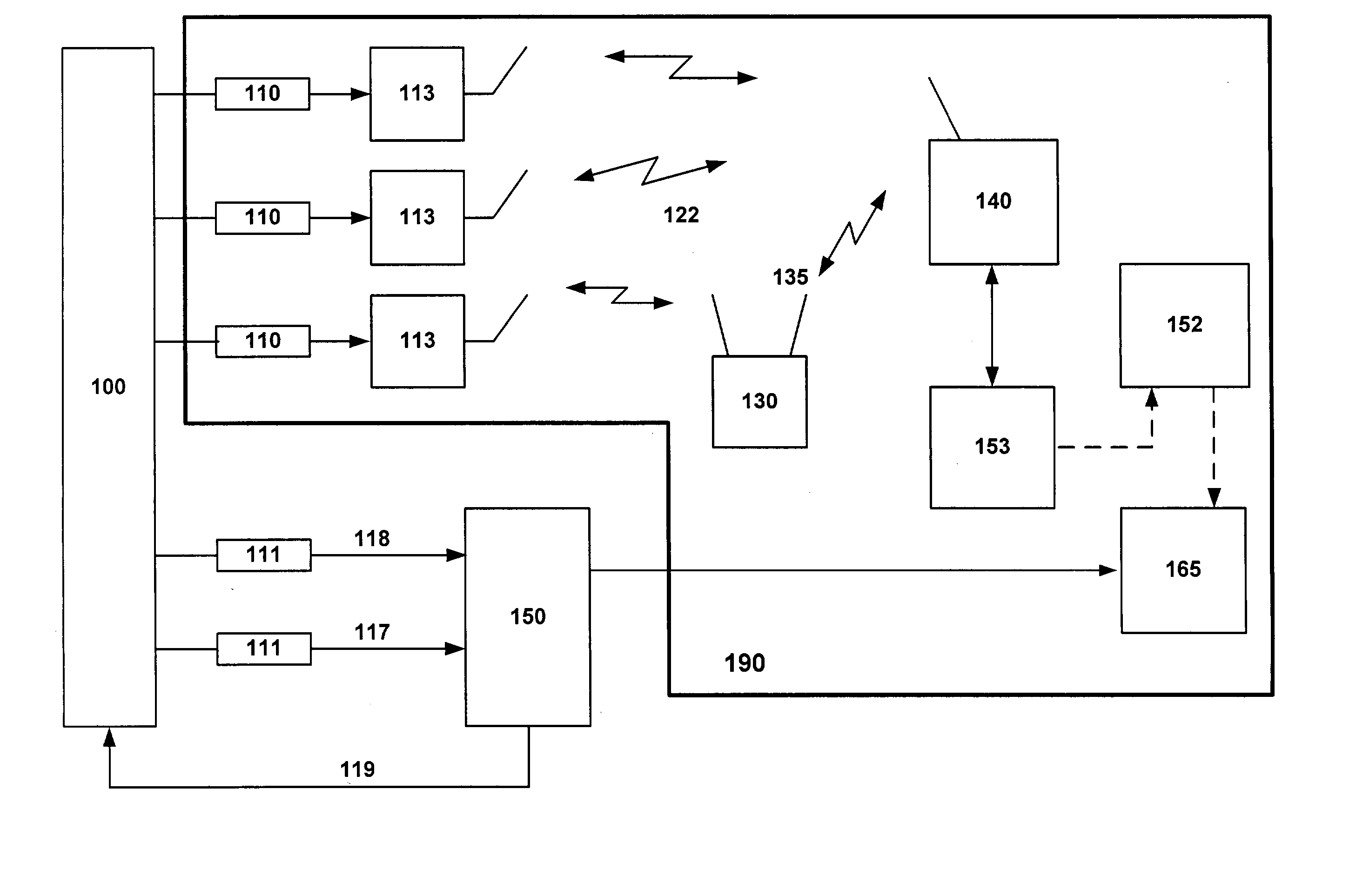
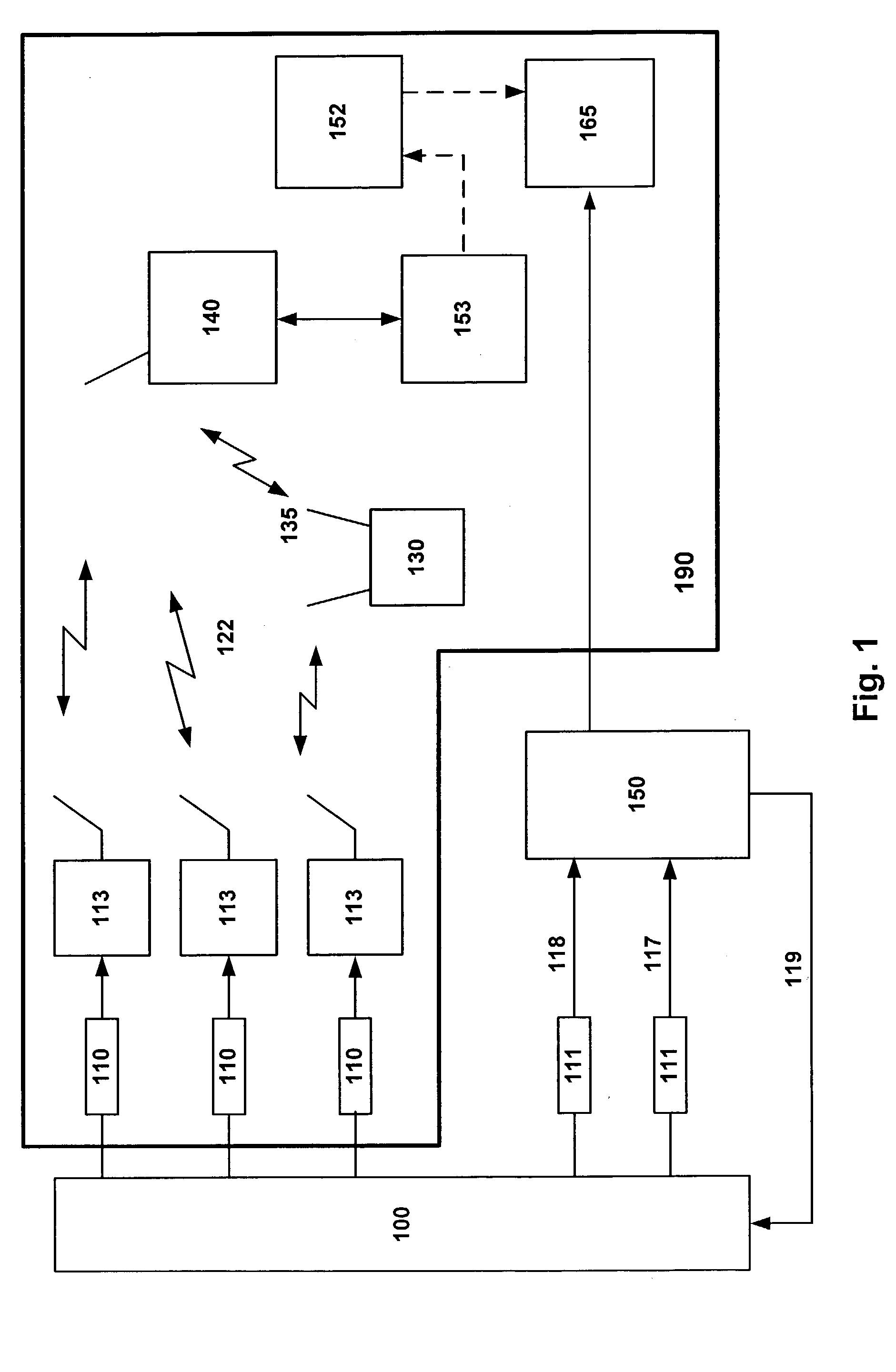
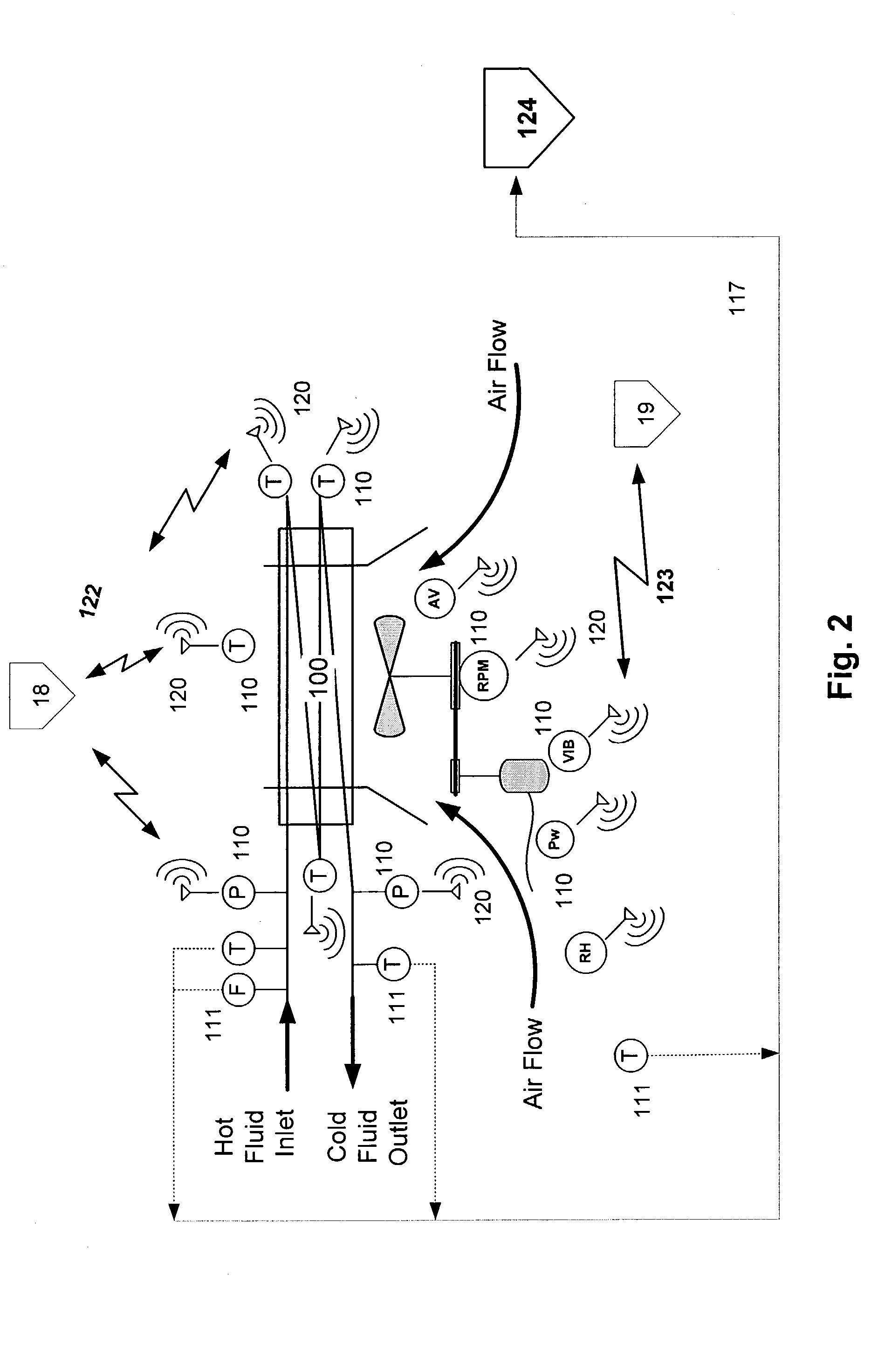
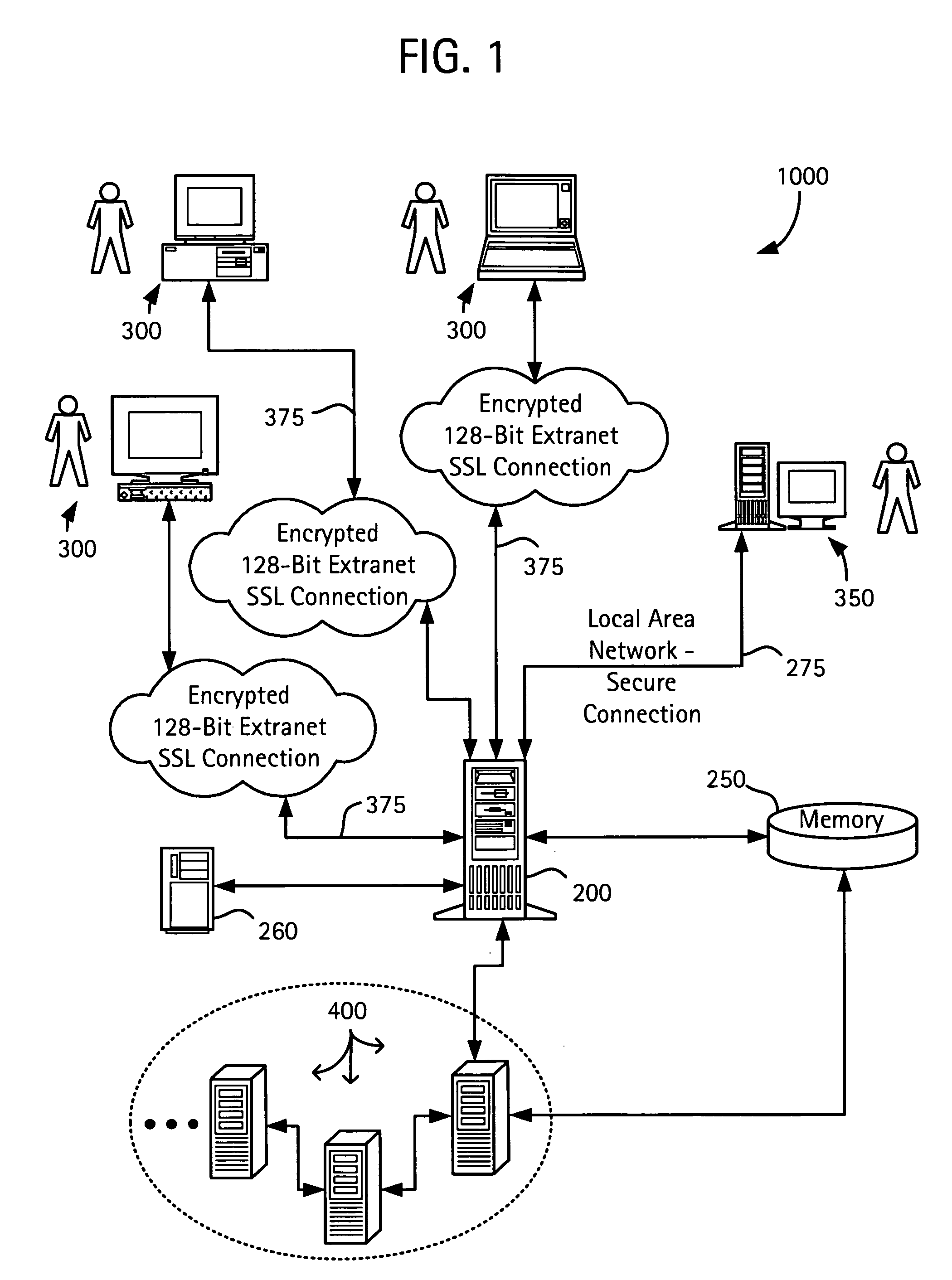
Temporary wireless sensor network system
InactiveUS20030204371A1Plant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationData streamNetworked system
The invention is an integrated temporary wireless network system for controlling, collecting, processing, and responding to data generated by a plurality of sensors configured for measuring data associated with operation of, and the environment related to, commercial, industrial and manufacturing operations, processes and equipment located within a fixed geographic area; a plurality of Wireless-Nodes, one coupled to each sensor, configured and adapted for wirelessly transmitting the data, via a Repeater if necessary, to a Base-Station, configured for receiving the data and connected to a primary computer; a CPU coupled with the primary computer and; a memory operatively connected to the CPU, the memory containing a program adapted to be executed by the CPU and the CPU and memory cooperatively adapted to perform data flow control from the plurality of Wireless-Nodes, data storage, and diagnostic analysis of the transmitted sensor data.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
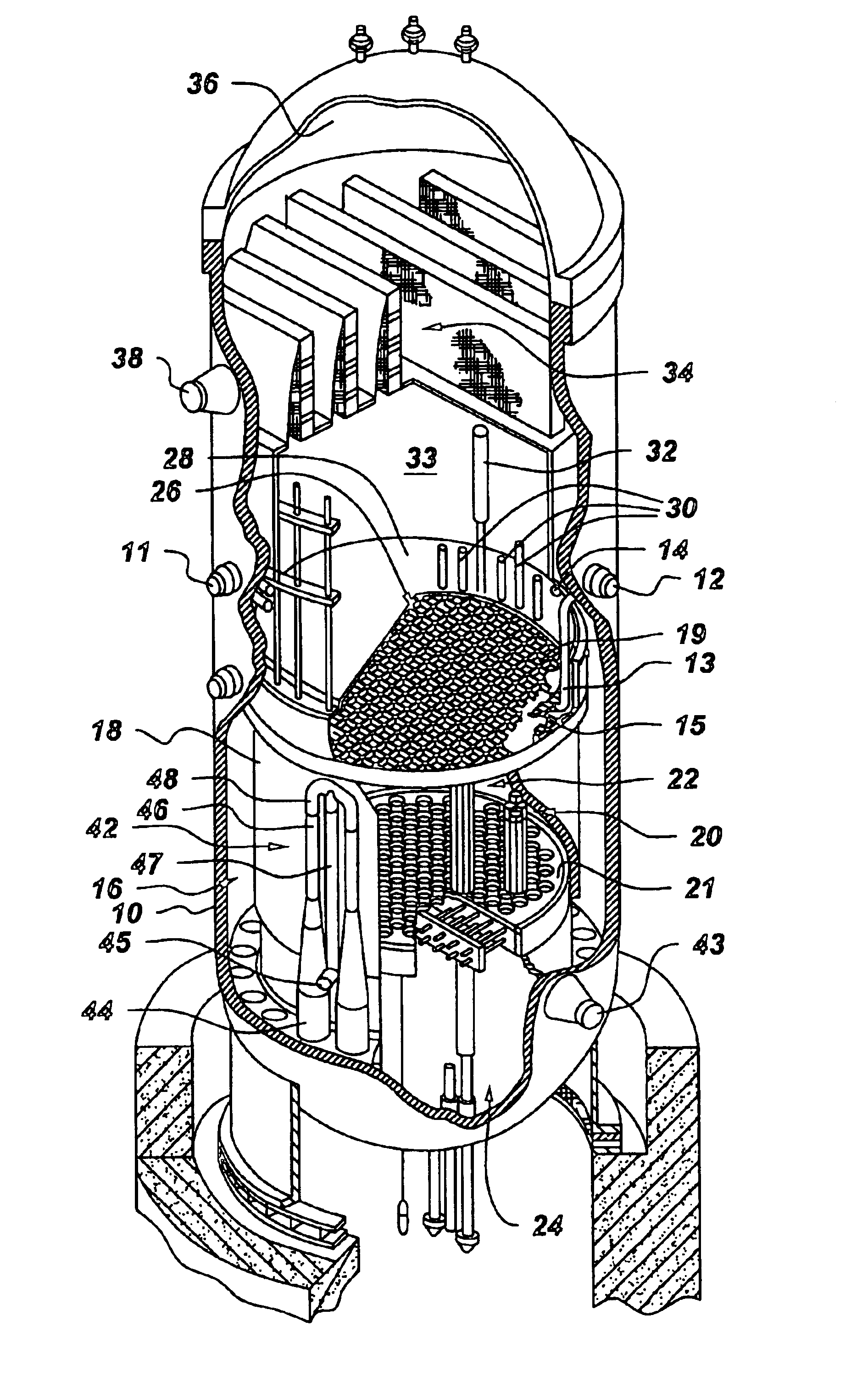
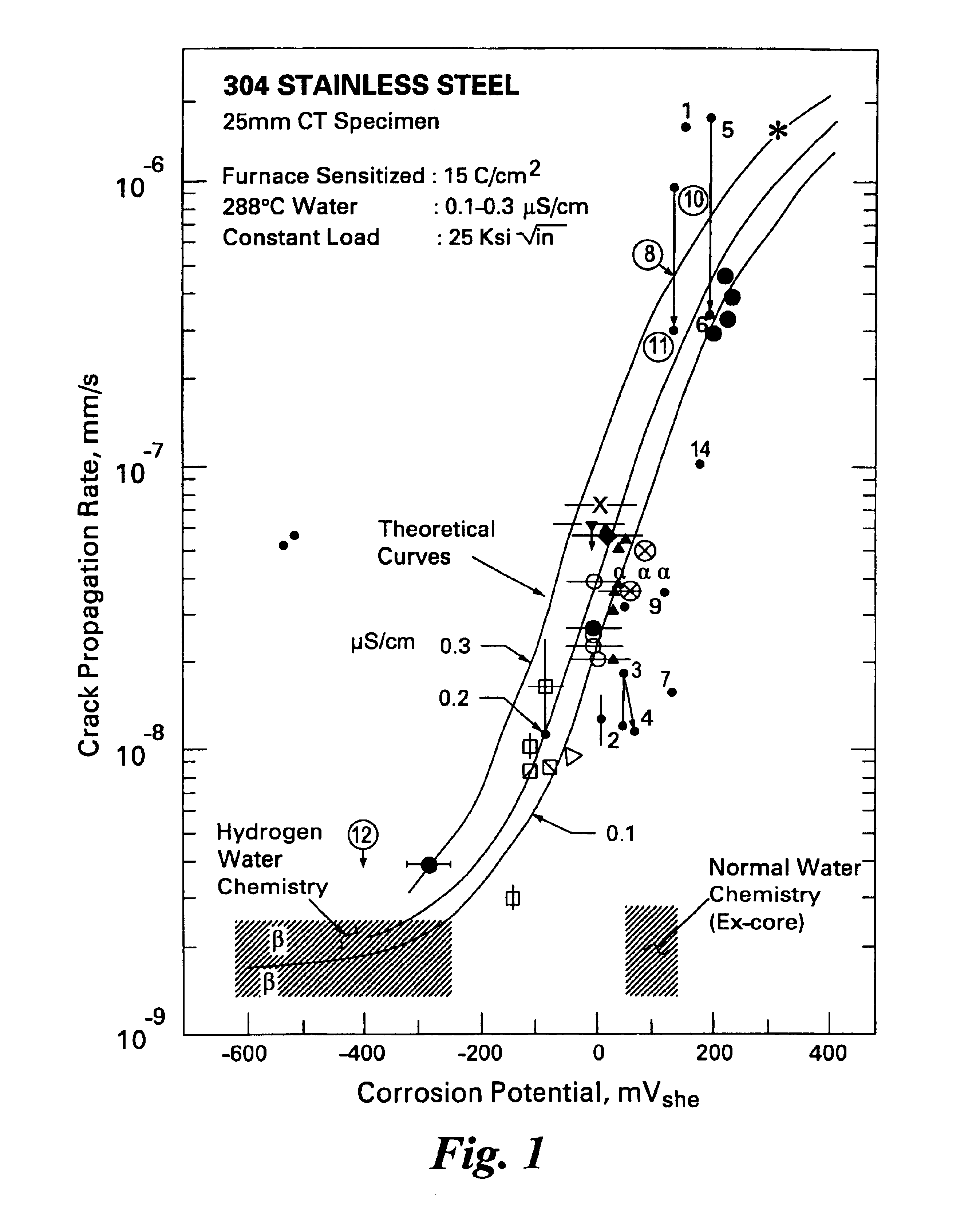
Process to mitigate stress corrosion cracking of structural materials in high temperature water
InactiveUS6724854B1Reduce crackingReducing the electrochemical corrosion potentialPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNanoparticleStress corrosion cracking
A method for mitigating stress corrosion cracking in high temperature water includes introducing catalytic nanoparticles and dielectric nanoparticles to the high temperature water in an amount effective to reduce a electrochemical corrosion potential of the high temperature water.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
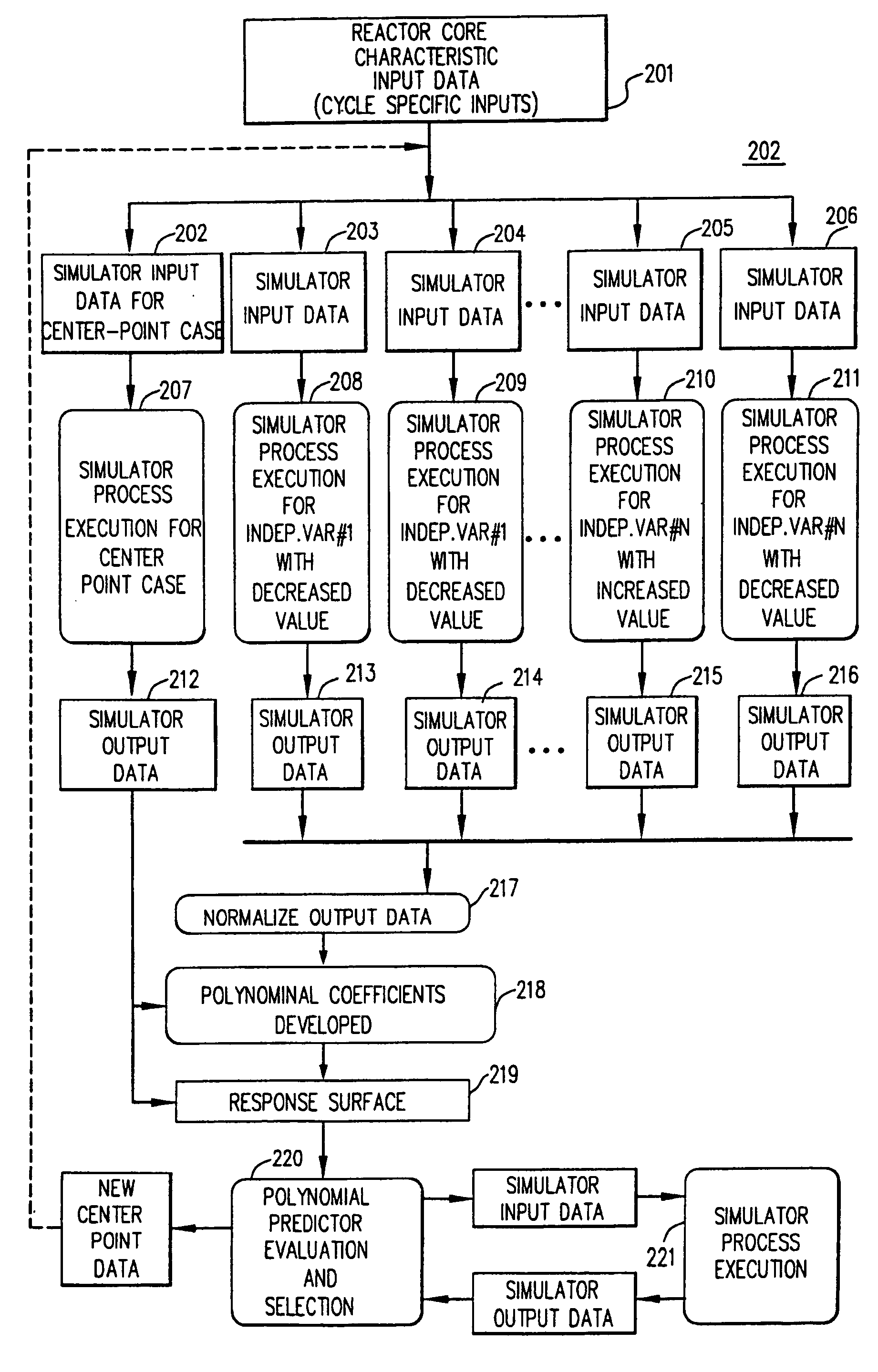
Method for predicted reactor simulation
ActiveUS20050089831A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsPlant parameters regulationEngineeringDefining relationship
In the method for reactor simulation, a user modifies one or more design inputs used in creating a response surface. The response surface defines relationships between the design inputs and operational outputs of at least one or more aspects of a core design. A reactor simulation is then generated based on the response surface for the core design and the modified design input.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
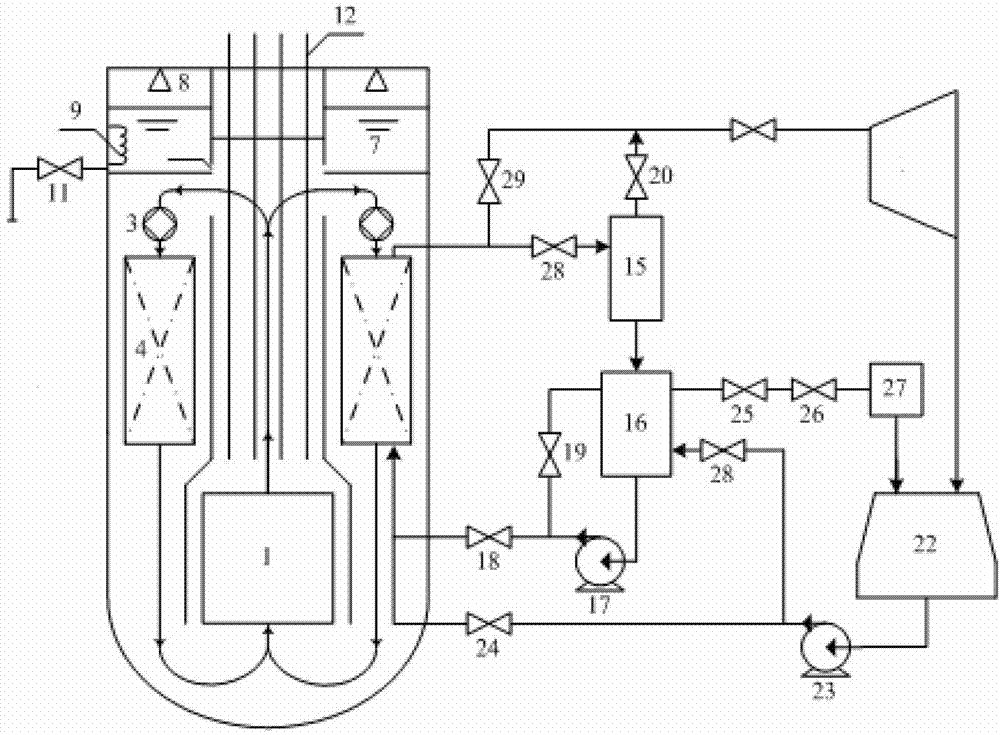
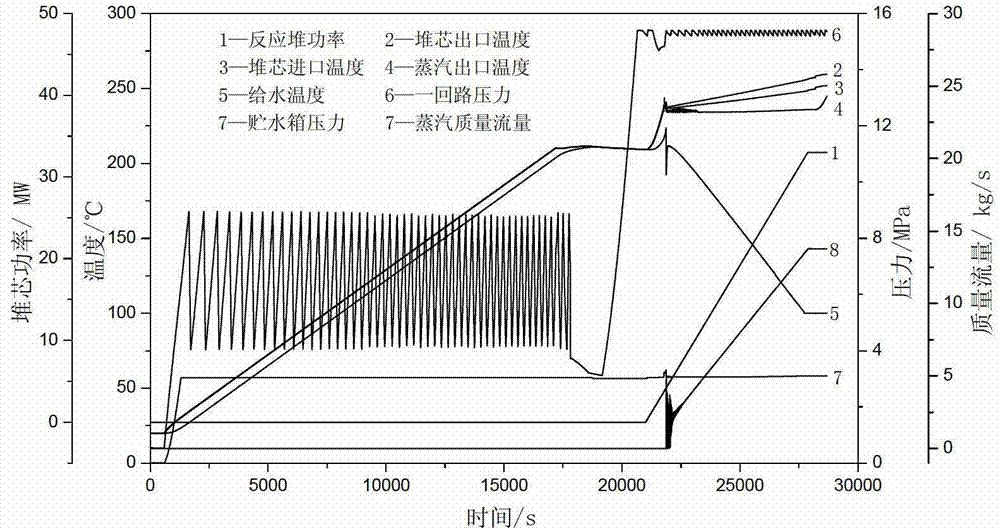
Start-stop auxiliary device used in integral reactor and cold starting method of integral reactor
ActiveCN103117101AShorten the timeSafe and stable operationPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationStart timeWater storage tank
The invention provides a start-stop auxiliary device used in an integral reactor and a cold starting method of the integral reactor. An inlet of a starting separator is connected with an outlet conduit of a once-through steam generator, an outlet of the starting separator is connected with a main steam pipe through a steam valve, and a drain outlet is connected with a water storage tank. An outlet at the bottom of the water storage tank is connected with a circulating water pump, and one conduit at the outlet of the water storage tank is connected with a condenser through an outlet stop valve of the water storage tank, a water storage tank water level control valve and a thermoreduction and dropping device. The circulating water pump is connected with a water supply conduit at the inlet of the once-through steam generator through a circulating water-carrying control valve. A water feed pump is connected with the condenser, the water feed pump is further connected with the inlet conduit of the once-through steam generator through a main water feed valve and with the water storage tank through a cold water valve. The start-stop auxiliary device is capable of increasing the temperature and pressure of refrigerant in a first circuit when the reactor starts, starting pressure and starting flow of a second circuit are established effectively, phenomenon of unstable flow is avoided, working media and heat energy are recycled effectively, and starting time is shortened.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
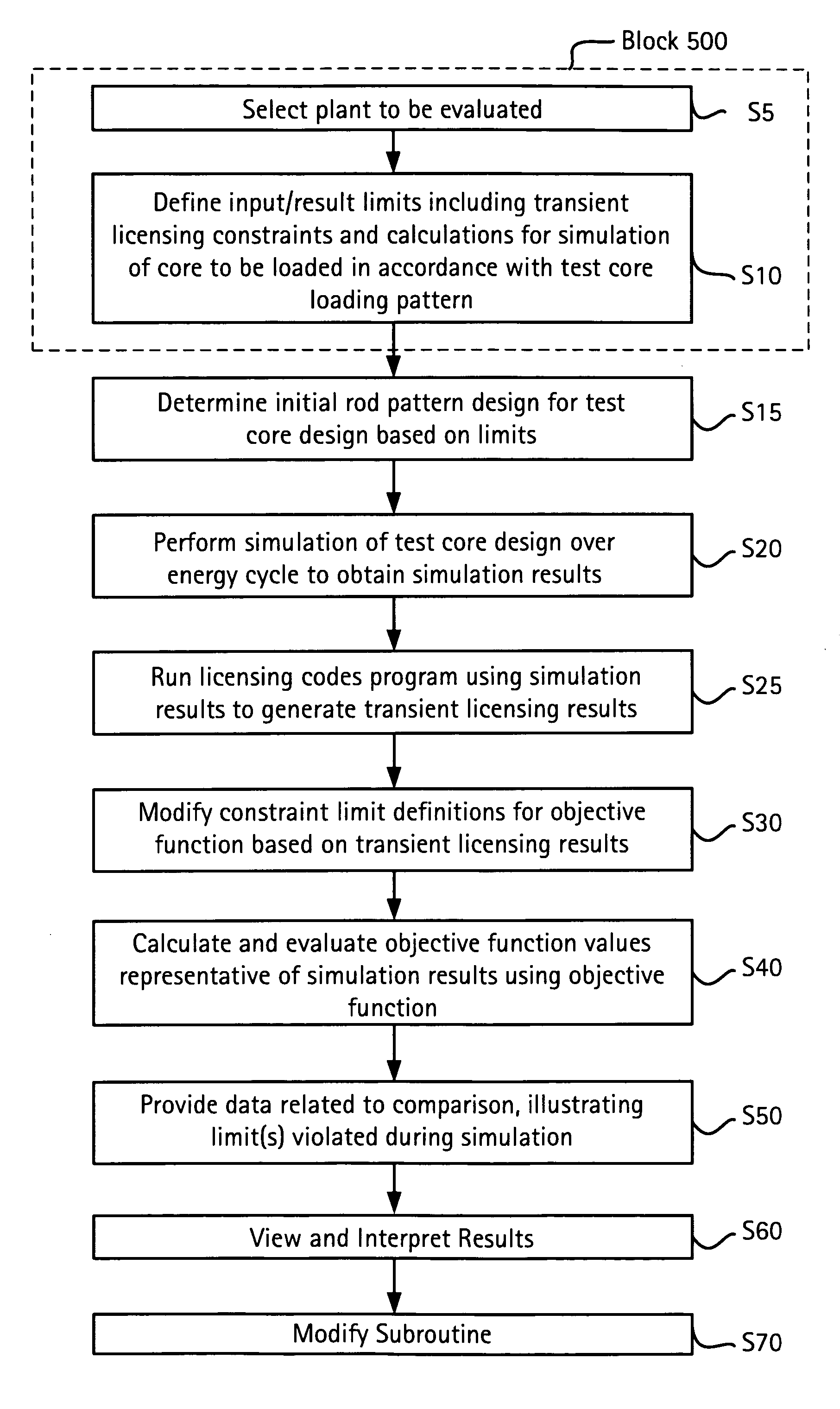
Computer-implemented method and system for designing a nuclear reactor core which satisfies licensing criteria
ActiveUS20070213959A1Power plant safety arrangementPlant parameters regulationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
In a computer-implemented method of designing a nuclear reactor of a given reactor plant, an initial, test reactor core design is generated for the given plant based on a plurality of limits input by a user. The limits include a plurality of transient licensing constraints to be satisfied for operating the given plant. The method includes selecting, from a set of automated tools, one or more automated tools to evaluate the test core design, and operating one of more of selected automated tools to output data for display to the user. The displayed data is related to a core design that satisfies the limits inclusive of the transient licensing constraints.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
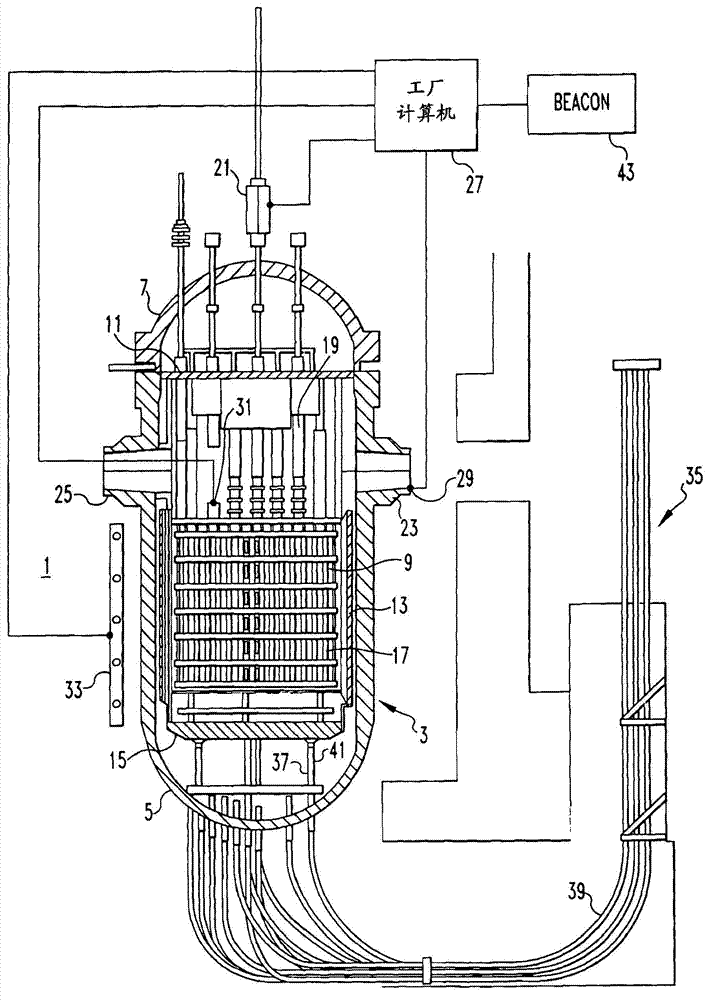
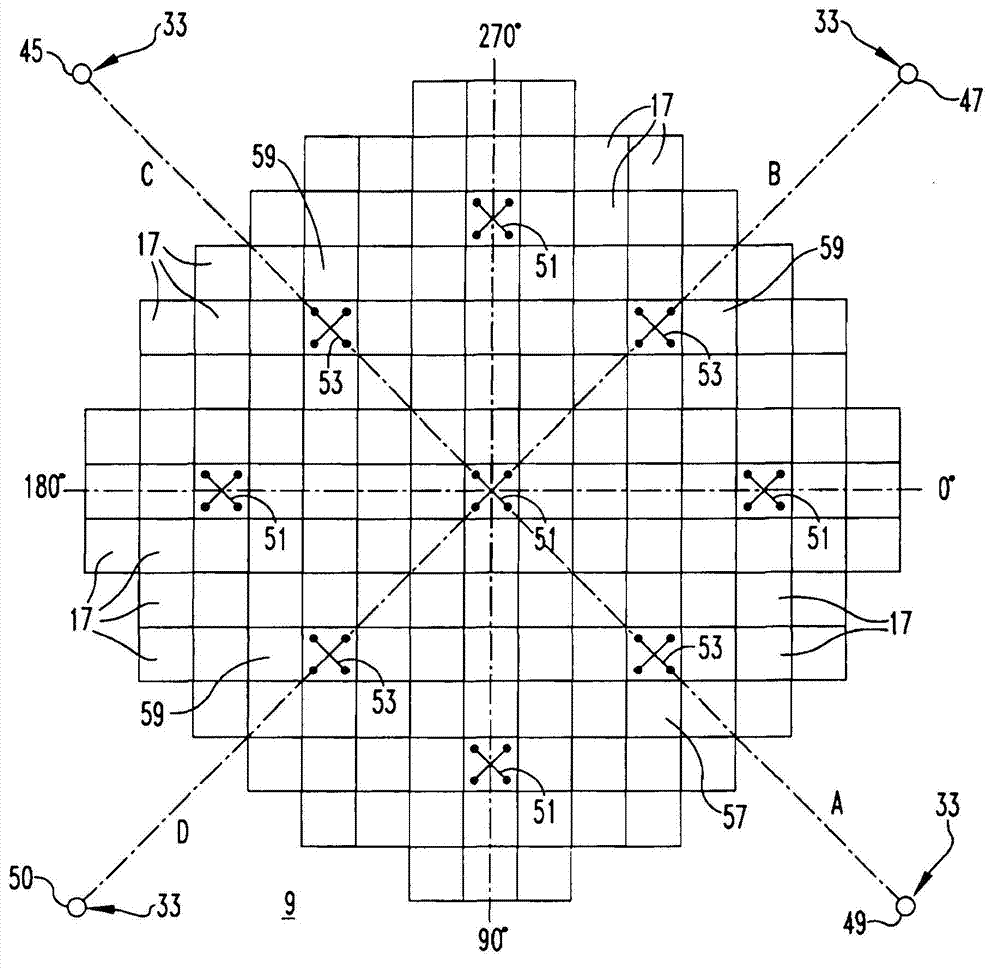
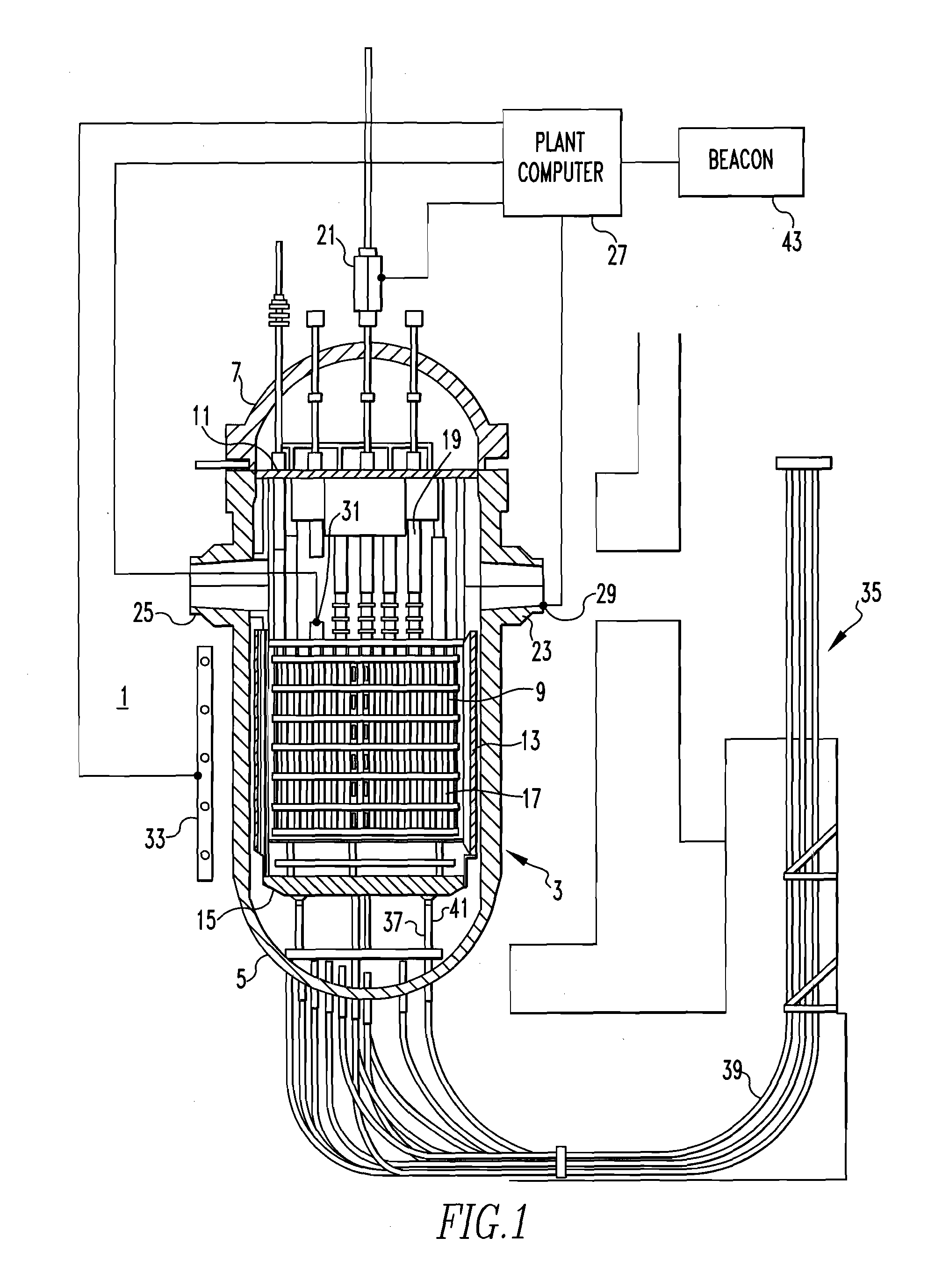
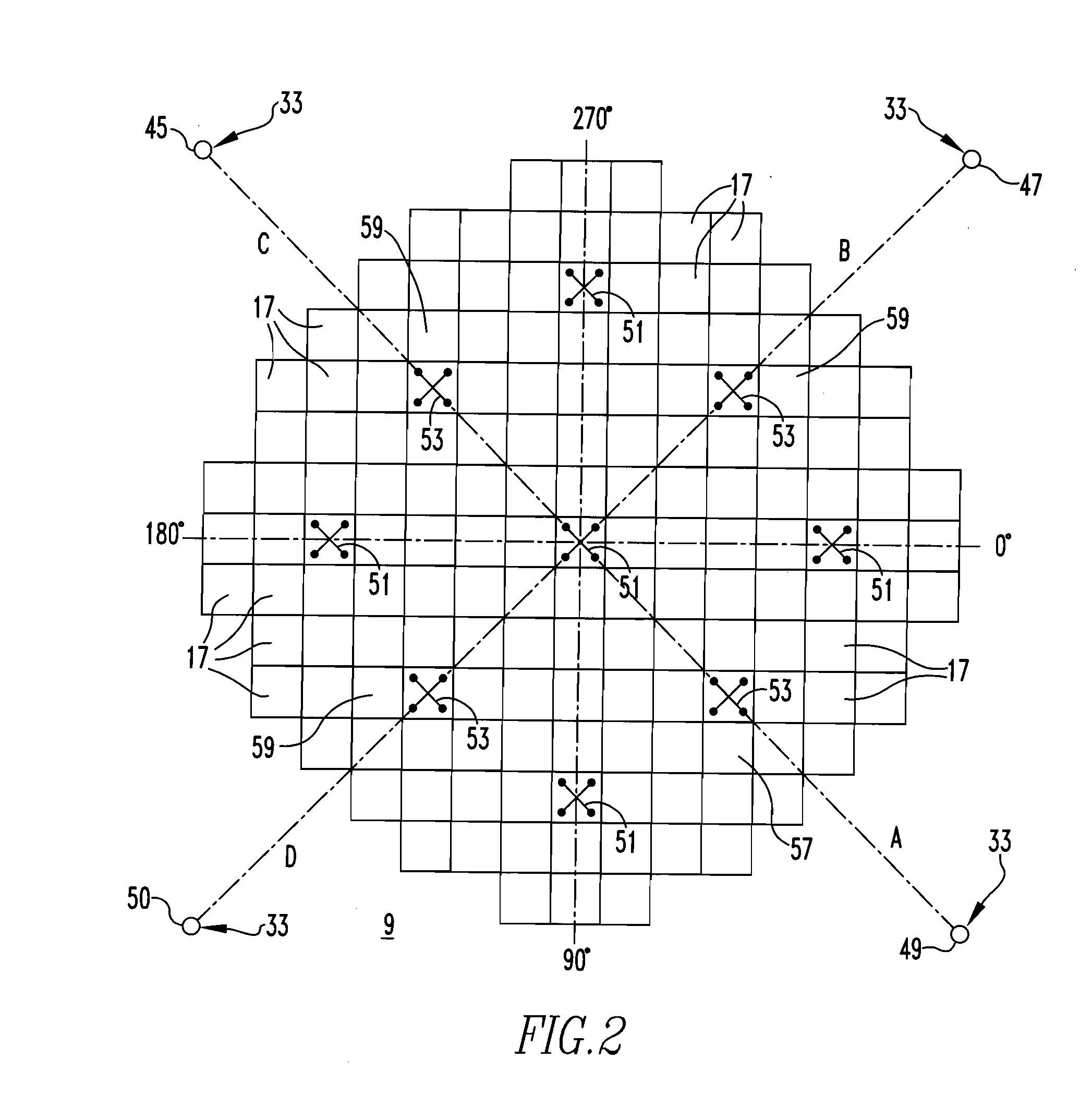
Method of calibrating excore detectors in a nuclear reactor
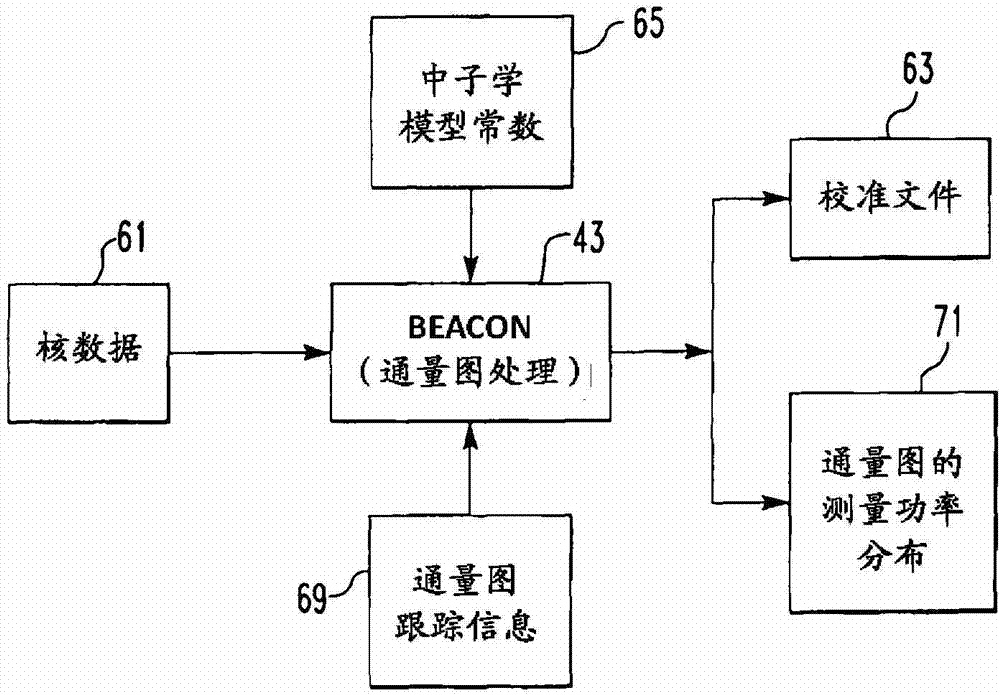
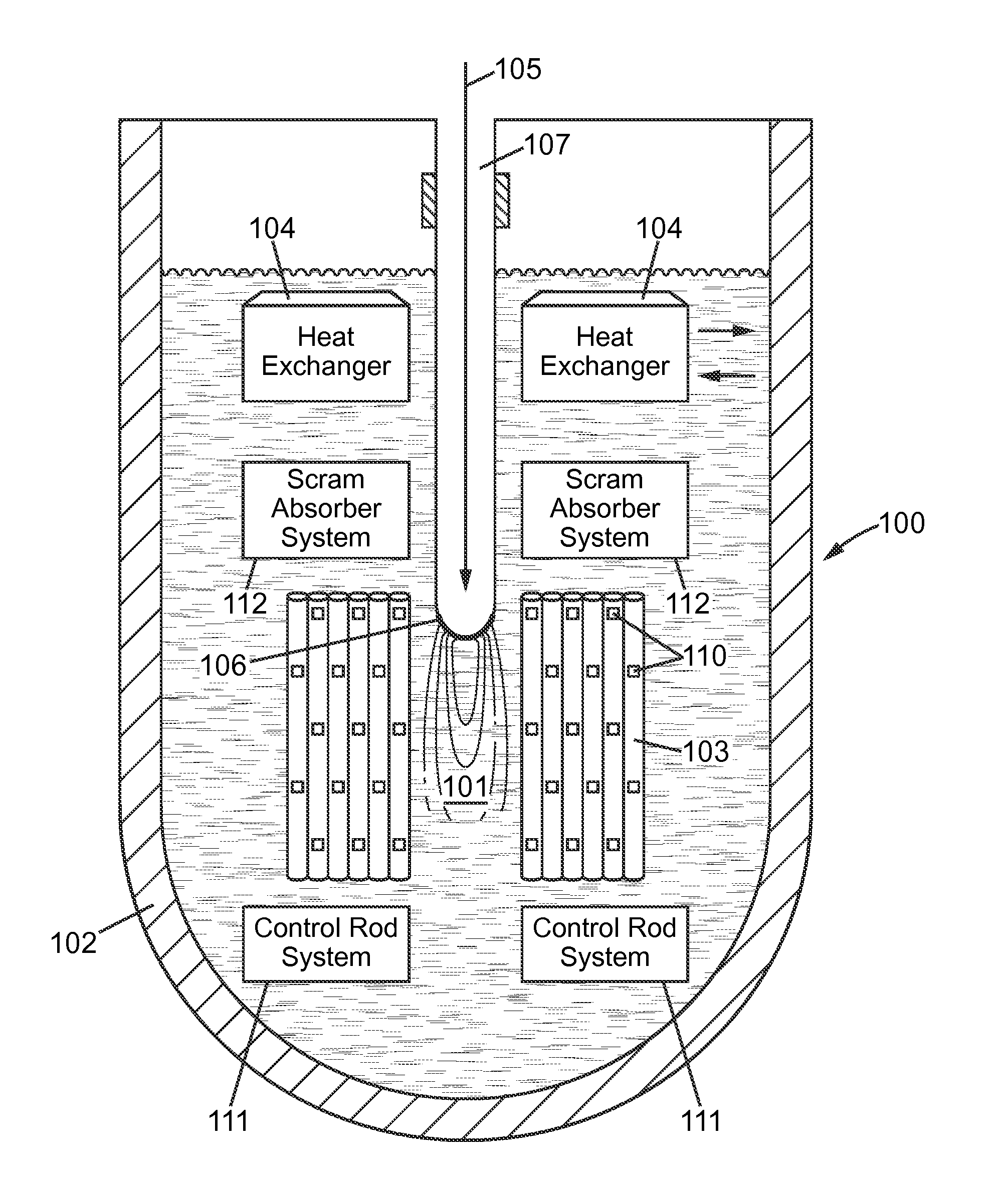
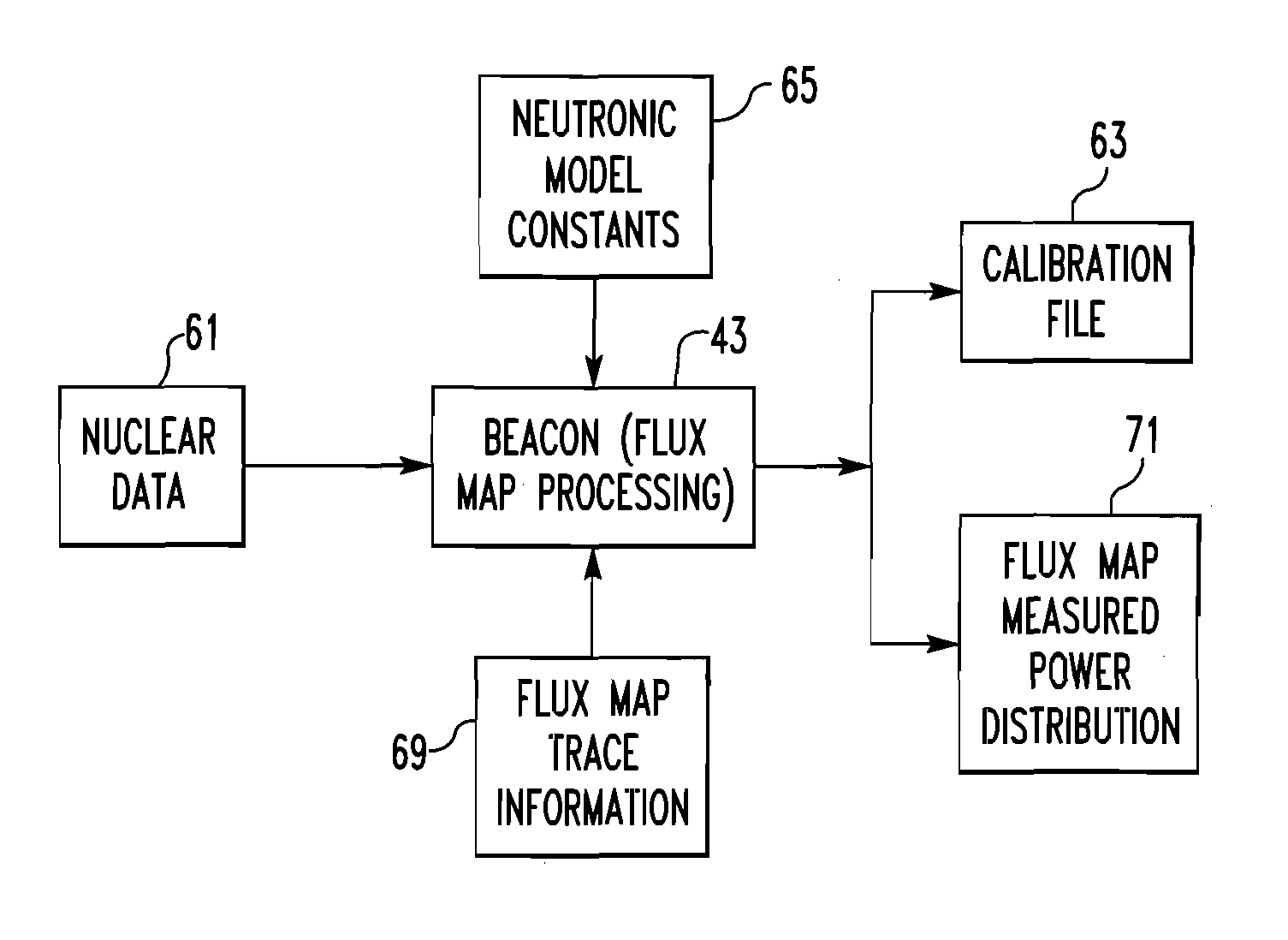
A method of calibrating excore detectors for a pressurized water reactor (PWR) (1) includes: measuring peripheral core flux signals using excore detectors (33) disposed at a plurality of locations spaced about the periphery of the core (9), and using the measured power distribution from either a core monitoring system (43) or in-core flux measurement (69). Calibration of the excore detectors (33) is broken into two parts: (1) the relation between the excore detector signal and weighted peripheral assembly axial offset, and (2) the relation between weighted peripheral assembly axial offset and core average axial offset. Relation (2) can be determined by a representative neutronics model. Accuracy of the neutronics solution is improved by applying (83) nodal calibration factors, which represent the ratio of the measured three-dimensional power distribution (75) to the nodal predicted three- dimensional power distribution and correct the neutronic results to match what would be measured if predictive scenarios were actually performed in the actual reactor core (9).
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Method of stress corrosion cracking mitigation for nuclear power plant structural materials
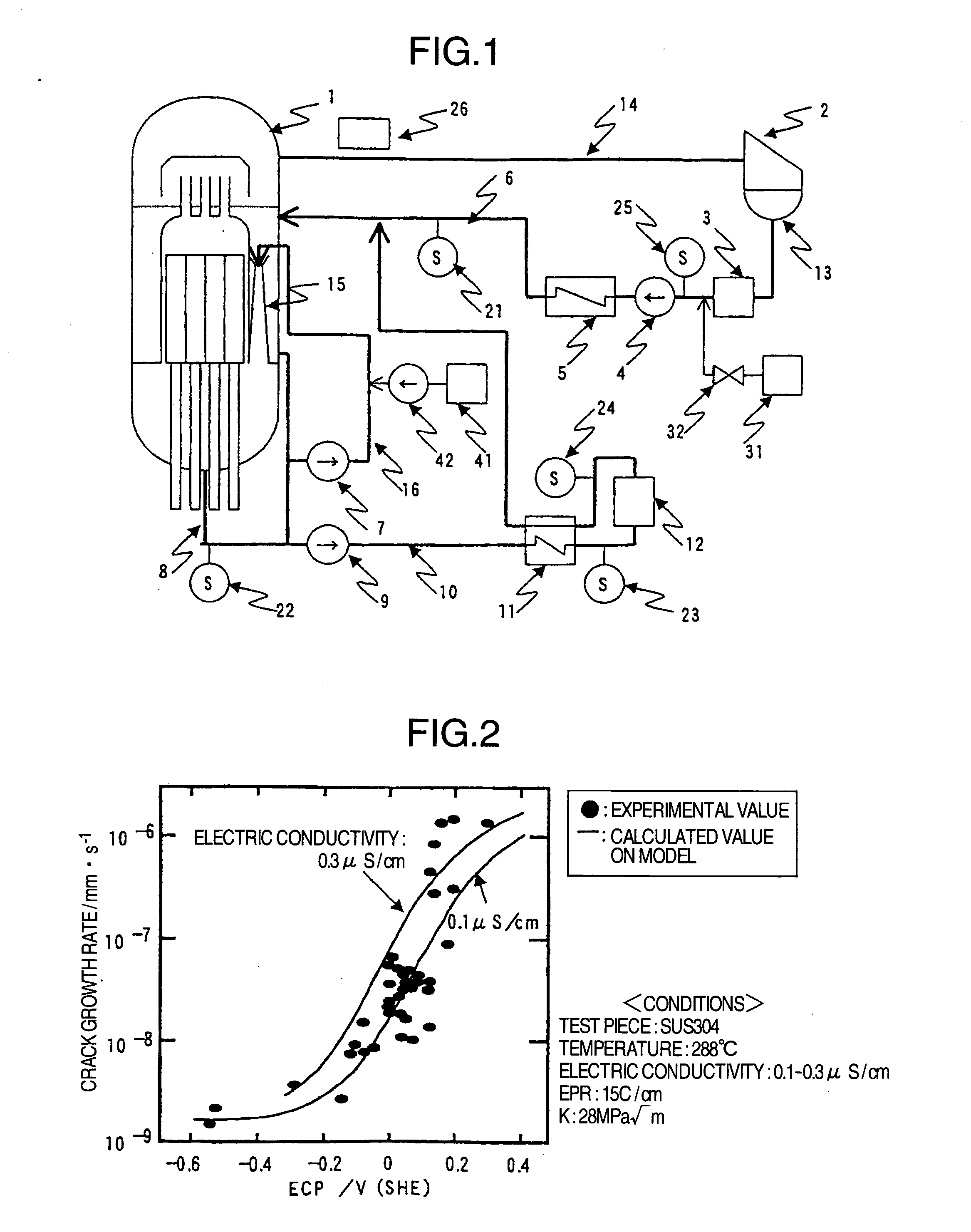
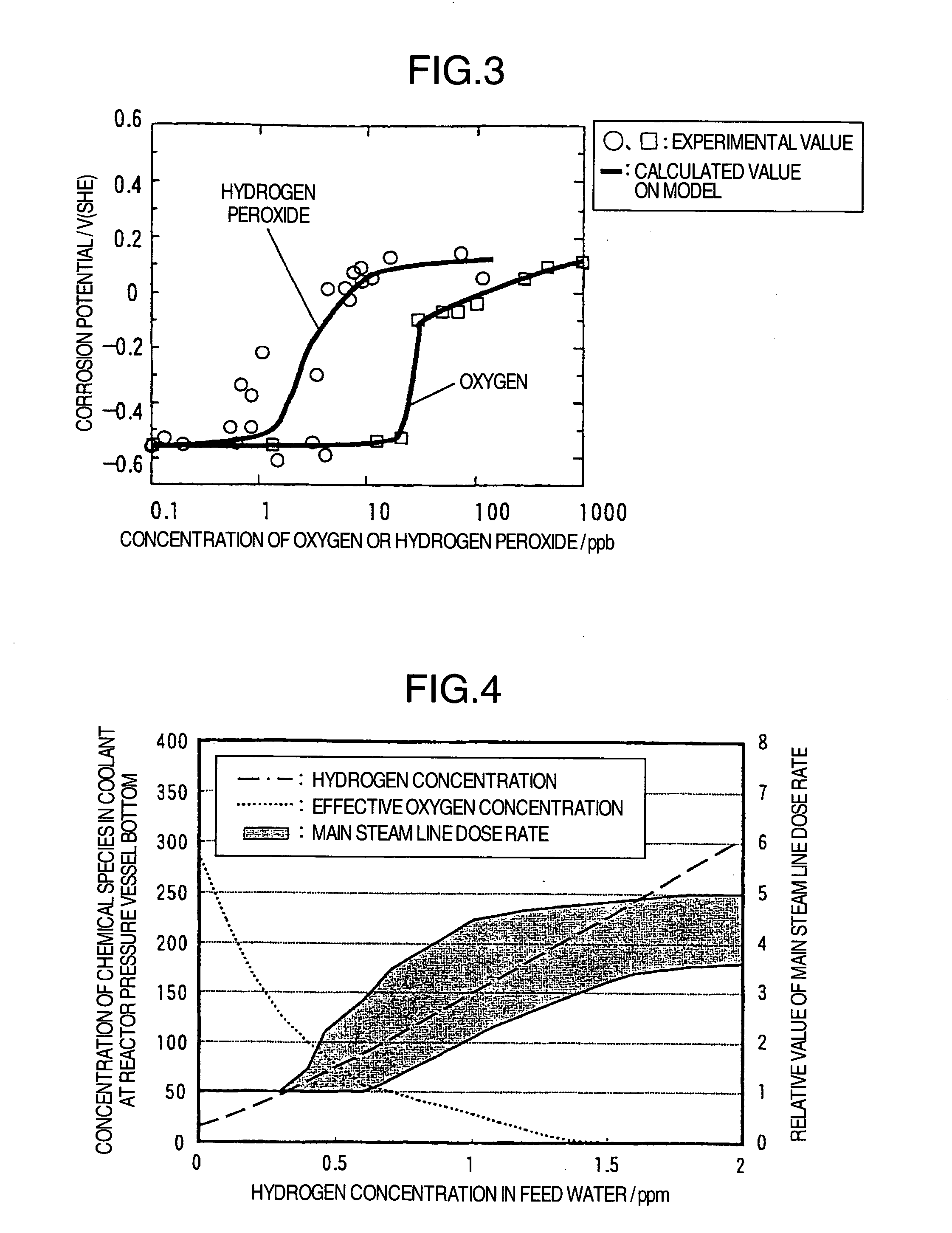
InactiveUS20050018805A1Reduce stress corrosion crackingReduce stressPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationDose rateHydrazine compound
The object of this invention is to provide a method for mitigating a stress corrosion cracking of reactor structural material which makes it possible to suppress the rise in the main steam line dose rate without secondary effects such as a rise in the concentration of radioactive cobalt-60, etc. in the reactor water. Hydrogen and a reductive nitrogen compound containing nitrogen having a negative oxidation number (for example, hydrazine) are injected into the core water of boiling water nuclear power plant. By injecting the reductive nitrogen compound containing nitrogen having a negative oxidation number into the core water, the stress corrosion cracking of structural material of reactor can be mitigated without side reactions such as a rise in the concentration of cobalt-60, etc.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Accelerator-Driven Nuclear System with Control of Effective Neutron Multiplication Coefficent
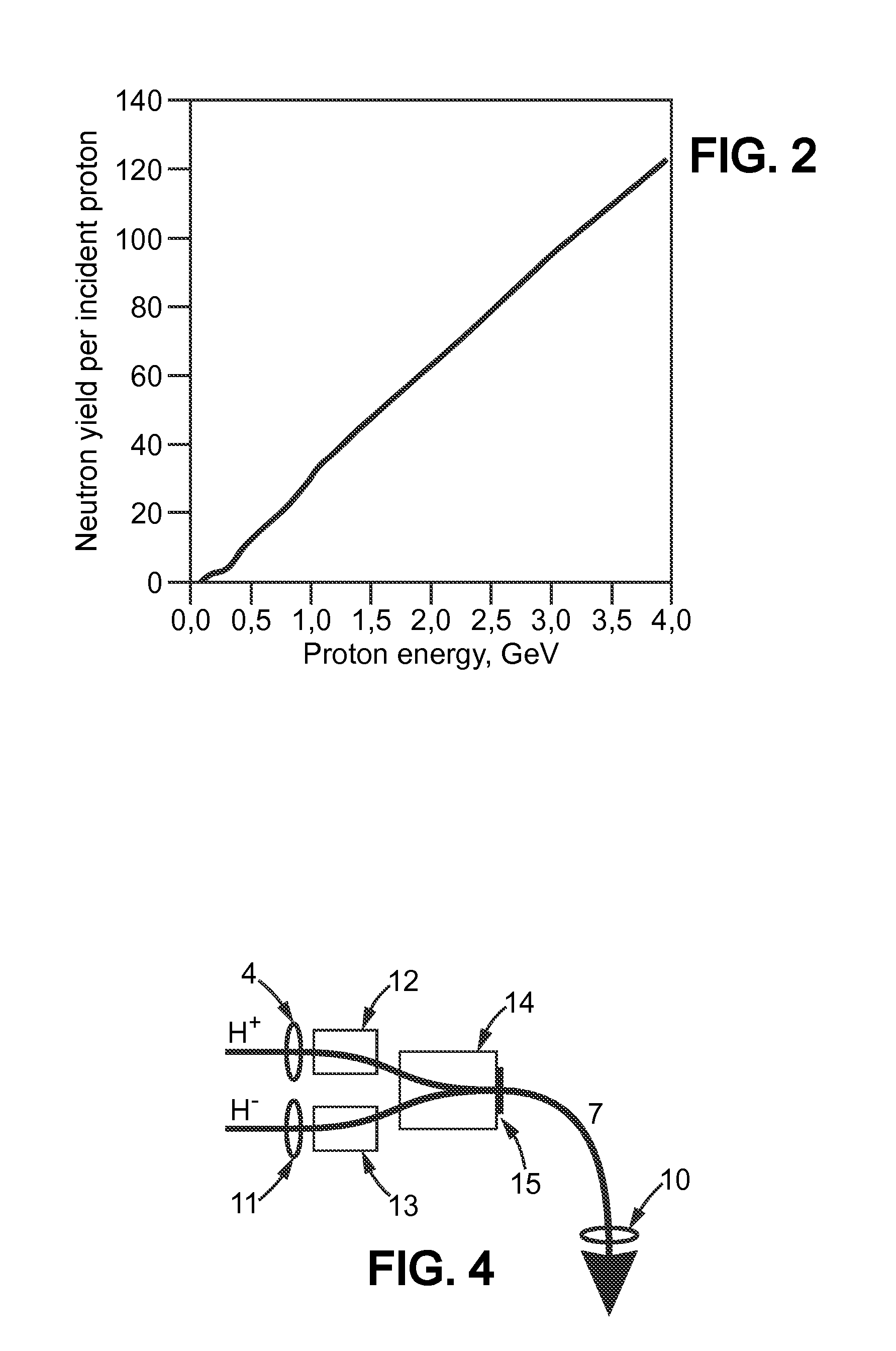
An accelerator-driven subcritical breeding reactor is operated with a neutron multiplication coefficient as large as possible in order to require a small input power from the accelerator, reducing its dimension and hence its cost and complexity. The beam-generated spallation neutron yield then becomes comparable to the fraction of delayed neutrons from the fissioned elements. This can be exploited to ensure an accurate on-line determination of the reactivity. Resulting changes can be adjusted with the help of neutron absorbing control rods and / or variations of the proton current. In addition, the temperature variations during operation can be continuously monitored and adjusted in order to avoid that the subcritical systems approaches too closely the (delayed) criticality condition and that the neutron multiplication coefficient remains within acceptable limits.
Owner:JACOBS U K
Method of calibrating excore detectors in a nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20110268239A1Improve accuracyImprove excore detector calibrationPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNODAL
A method of calibrating excore detectors for a pressurized water reactor (PWR) includes: measuring peripheral core flux signals using excore detectors disposed at a plurality of locations spaced about the periphery of the core, and using the measured power distribution from either a core monitoring system or in-core flux measurement. Calibration of the excore detectors is broken into two parts: (1) the relation between the excore detector signal and weighted peripheral assembly axial offset, and (2) the relation between weighted peripheral assembly axial offset and core average axial offset. Relation (2) can be determined by a representative neutronics model. Accuracy of the neutronics solution is improved by applying nodal calibration factors, which represent the ratio of the measured three-dimensional power distribution to the nodal predicted three-dimensional power distribution and correct the neutronic results to match what would be measured if predictive scenarios were actually performed in the actual reactor core.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
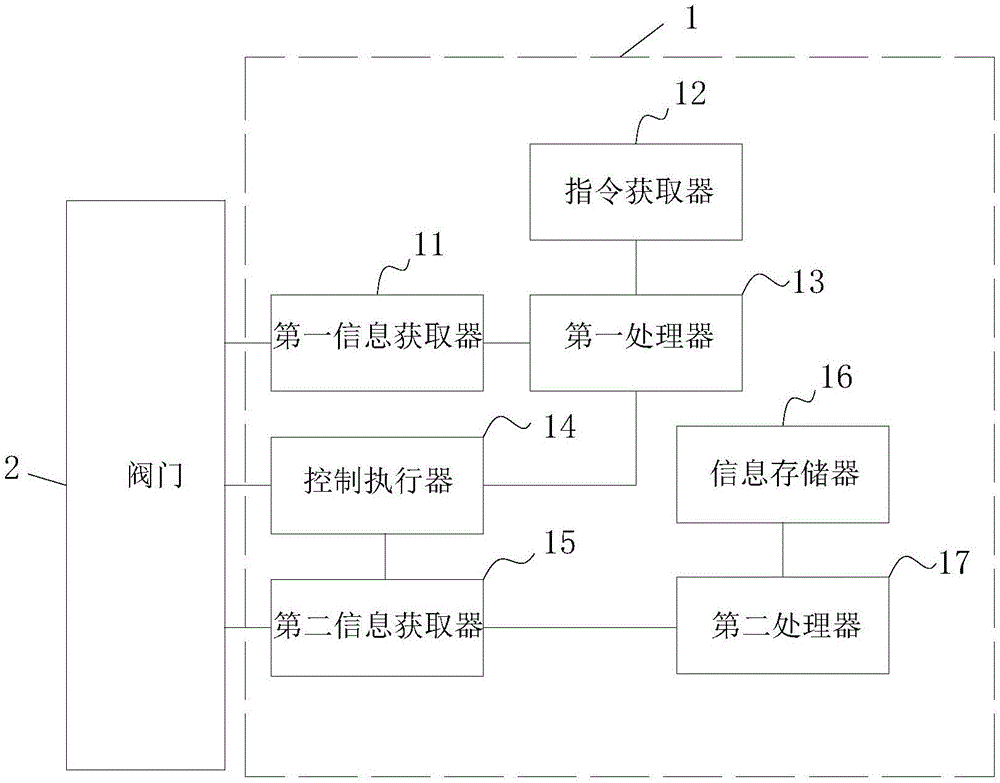
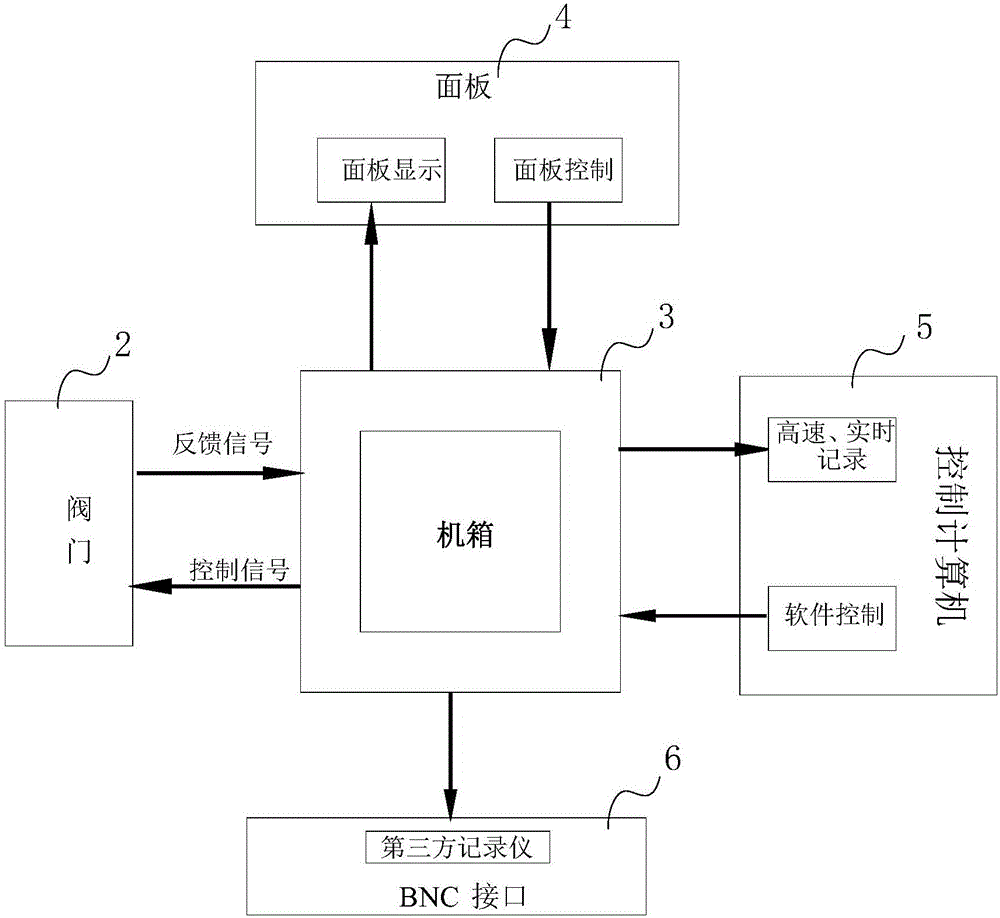
Nuclear power plant steam turbine valve fault diagnosis method, auxiliary diagnosis method thereof, and test device
ActiveCN106340334AImprove accuracyImprove diagnostic efficiencyPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationDiagnosis methodsState switching
The invention discloses a nuclear power plant steam turbine valve fault diagnosis method, an auxiliary diagnosis method thereof, and a test device. Through a user instruction corresponding to preset parameter information, the control of state switching action of a valve is carried out, and when the valve acts, the parameter information of switching action of the valve is recorded. Then whether the recorded parameter information and the preset parameter information are matched or not is judged, fault information is generated if not, thus the online fault diagnosis of the steam turbine valve of a nuclear power plant is realized, through comparing the various parameter information generated in the action of the valve and the preset parameter information, the accuracy of judging a problem in a diagnose or test is improved, the applicability is strong, the fault information of most valves in action can be diagnosed, and the efficiency of diagnosis is improved.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
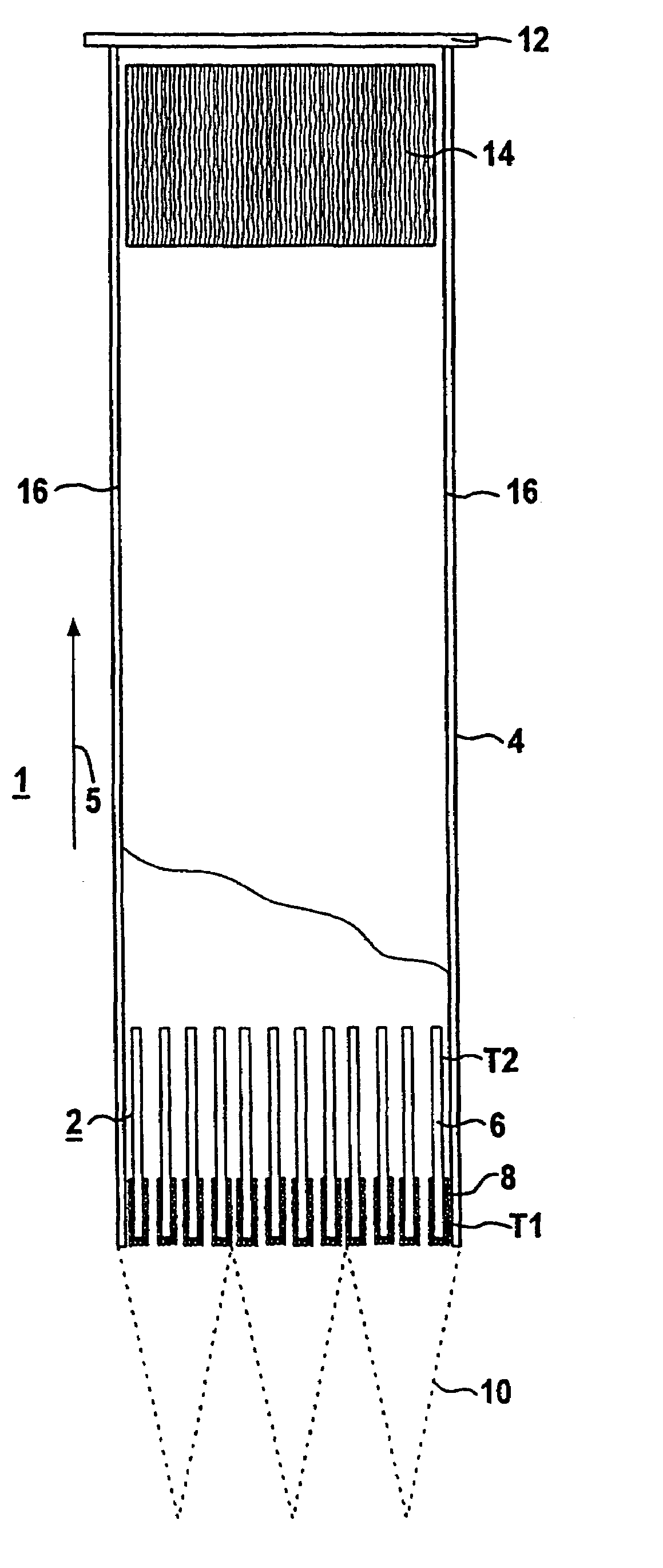
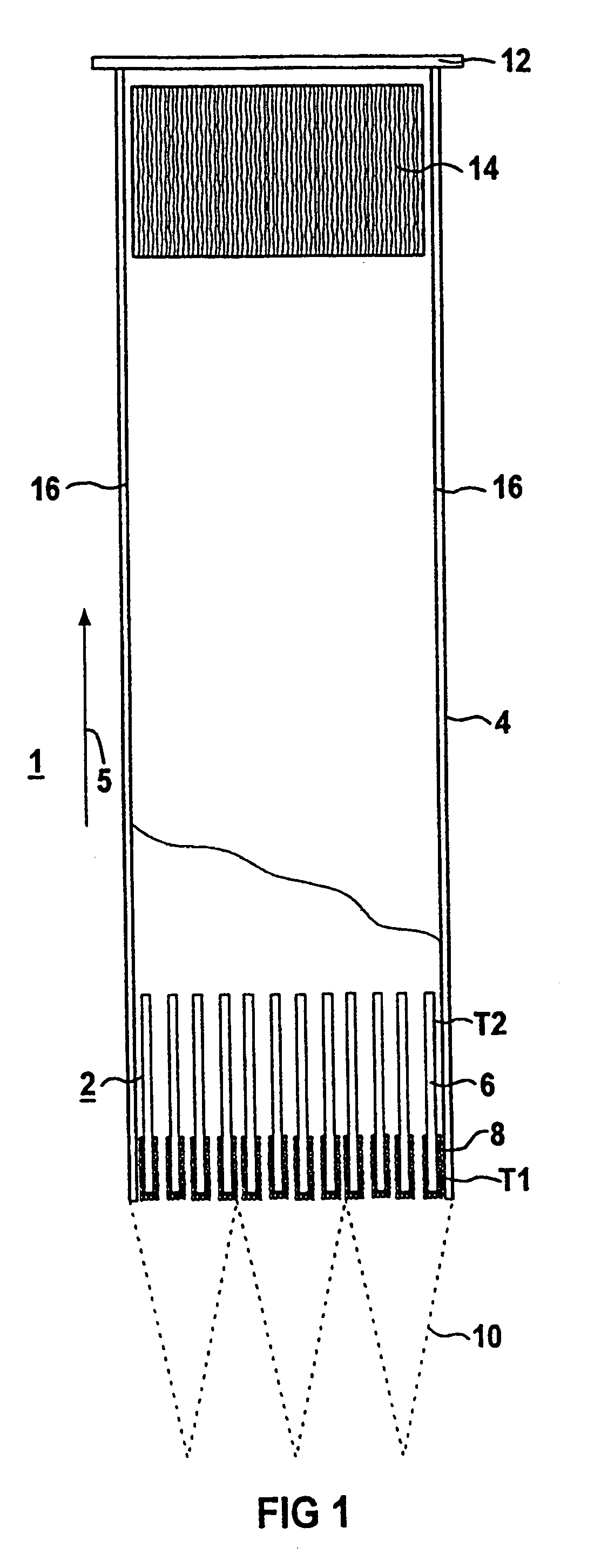
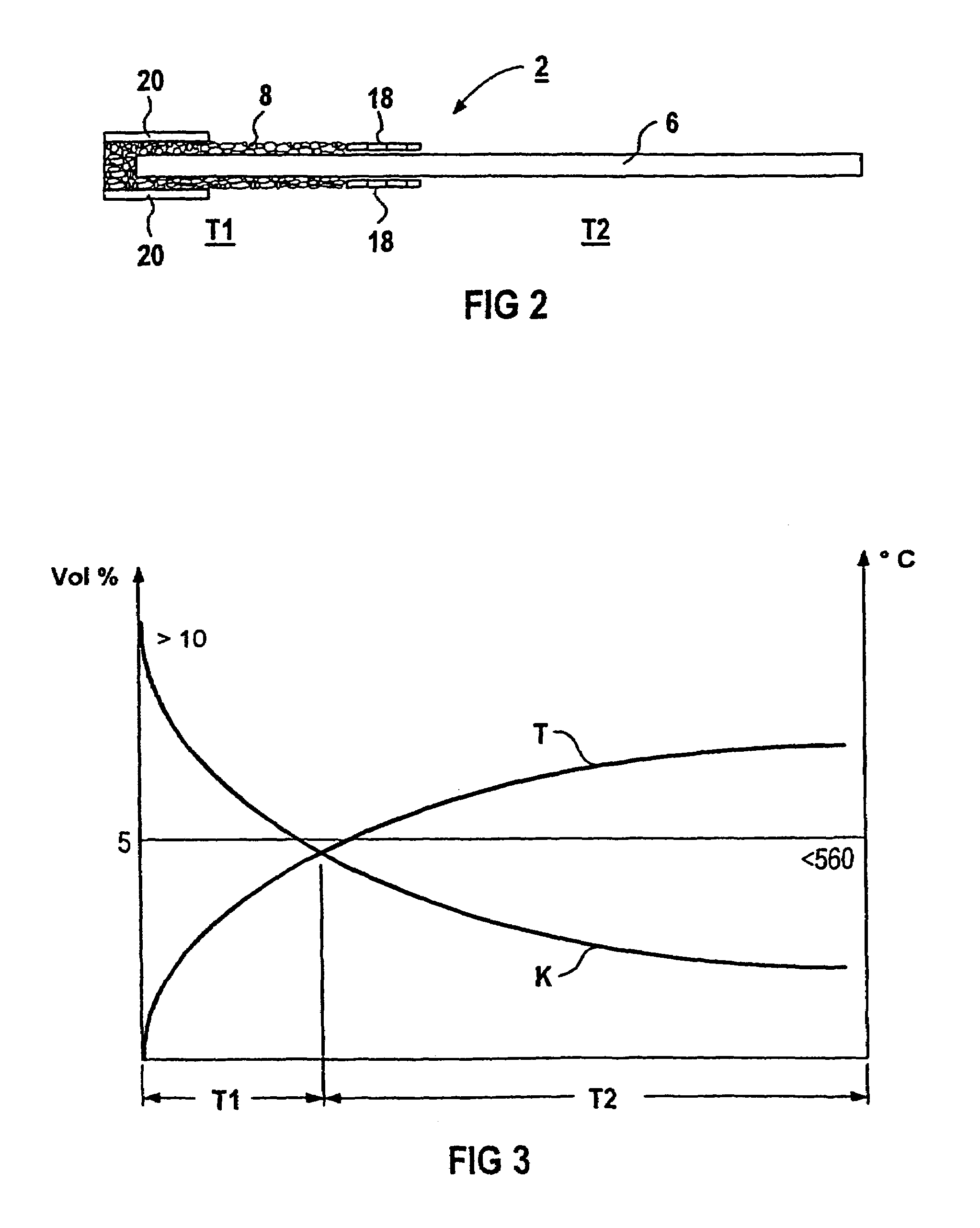
Recombination device and method for catalytically recombining hydrogen and/or carbon monoxide with oxygen in a gaseous mixture
InactiveUS6942846B1Secure and particularly active catalytic recombinationAvoid ignitionCombination devicesPhysical/chemical process catalystsDiffusionHydrogen
A recombination device (1, 1′) for catalytically recombining hydrogen and / or carbon monoxide with oxygen in a gaseous mixture comprises at least one catalyst system (2) in which a housing (4) is mounted through which the gaseous mixture can flow in free convection in the operational phase. According to the invention, said catalyst system (2) is provided with a plurality of sub-areas (T1, T2) in the direction of flow. A first sub-area (T1) comprises in the incoming direction a catalyst body (6) with a surrounding throttle layer (8) for inhibiting the diffusion of the incoming and / or discharged reaction gases. A second sub-area (T2) that adjoins the first sub-area (T1) comprises at least one catalyst body (6) that is directly accessible by the reaction gases.
Owner:AREVA GMBH
Debugging method, device and system of nuclear power station steam turbine control system
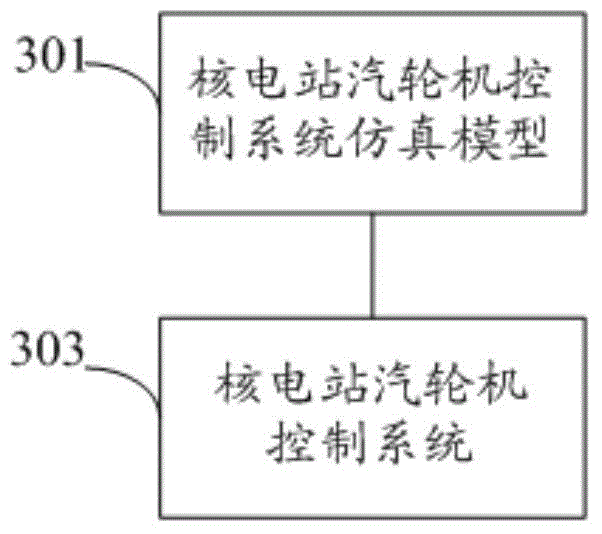
ActiveCN103559924AReduce riskEfficient test design functionPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear plantControl system
The invention discloses a debugging method of a nuclear power station steam turbine control system. The method comprises the steps that a nuclear power station steam turbine control system simulation model is established, the simulation model at least comprises a simulation debugging device; the nuclear power station steam turbine control system is connected with the simulation model, the nuclear power station steam turbine control system at least comprises one of a steam turbine adjusting subsystem, a steam turbine protecting subsystem, a steam turbine monitoring subsystem (GME) and a steam turbine shaft seal subsystem, each subsystem is subjected to simulation debugging through the simulation debugging device, and according to the simulation debugging results, the functions of the subsystems are verified. According to the debugging method of the nuclear power station steam turbine control system, the simulation model is used for being connected with the steam turbine control system, system function verifying is carried out in advance, nuclear power plant debugging scheme optimizing is achieved, the debugging period is shortened, and the risk of steam turbine unexpected halt and the risk of reactor unexpected tripping after a nuclear power unit is started are lowered. In addition, the invention further discloses a debugging device and system of the nuclear power station steam turbine control system.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Diversified driving method, diversified driving device and diversified driving system for nuclear power station
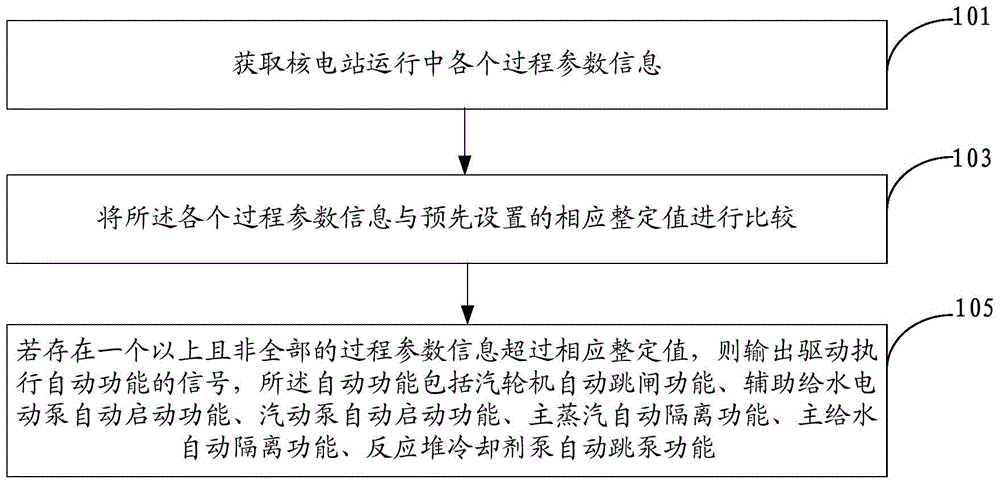
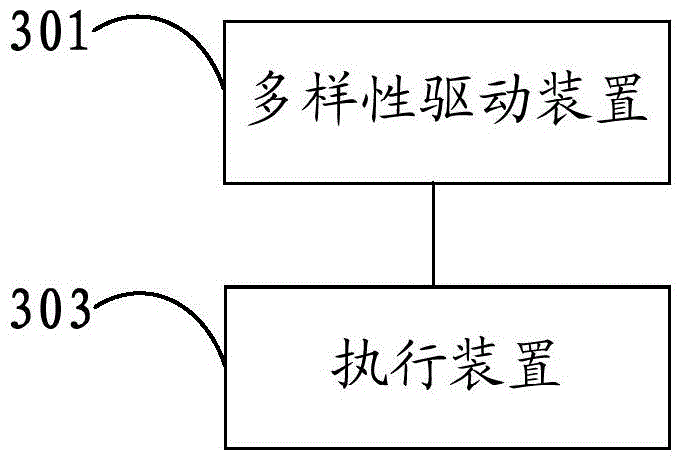
InactiveCN104485142AAchieve protectionReduce common cause failure problemsPower plant safety arrangementPlant parameters regulationNuclear powerCoolant pump
The invention discloses a diversified driving method for a nuclear power station. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring parameter information of each process in operation of the nuclear power station; comparing the parameter information of each process with a preset corresponding set value; outputting a signal for driving the execution of automatic functions if more than one but not all of the process parameter information exceeds the corresponding set value, wherein the automatic functions include an automatic tripping function of a steam turbine, an automatic start function of an auxiliary water supply electric pump, an automatic start function of a steam driven pump, a main steam automatic isolation function, a main water supply automatic isolation function and an automatic pump shutdown function of a reactor coolant pump. Besides, the invention also discloses a diversified driving device and a diversified driving system for the nuclear power station.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
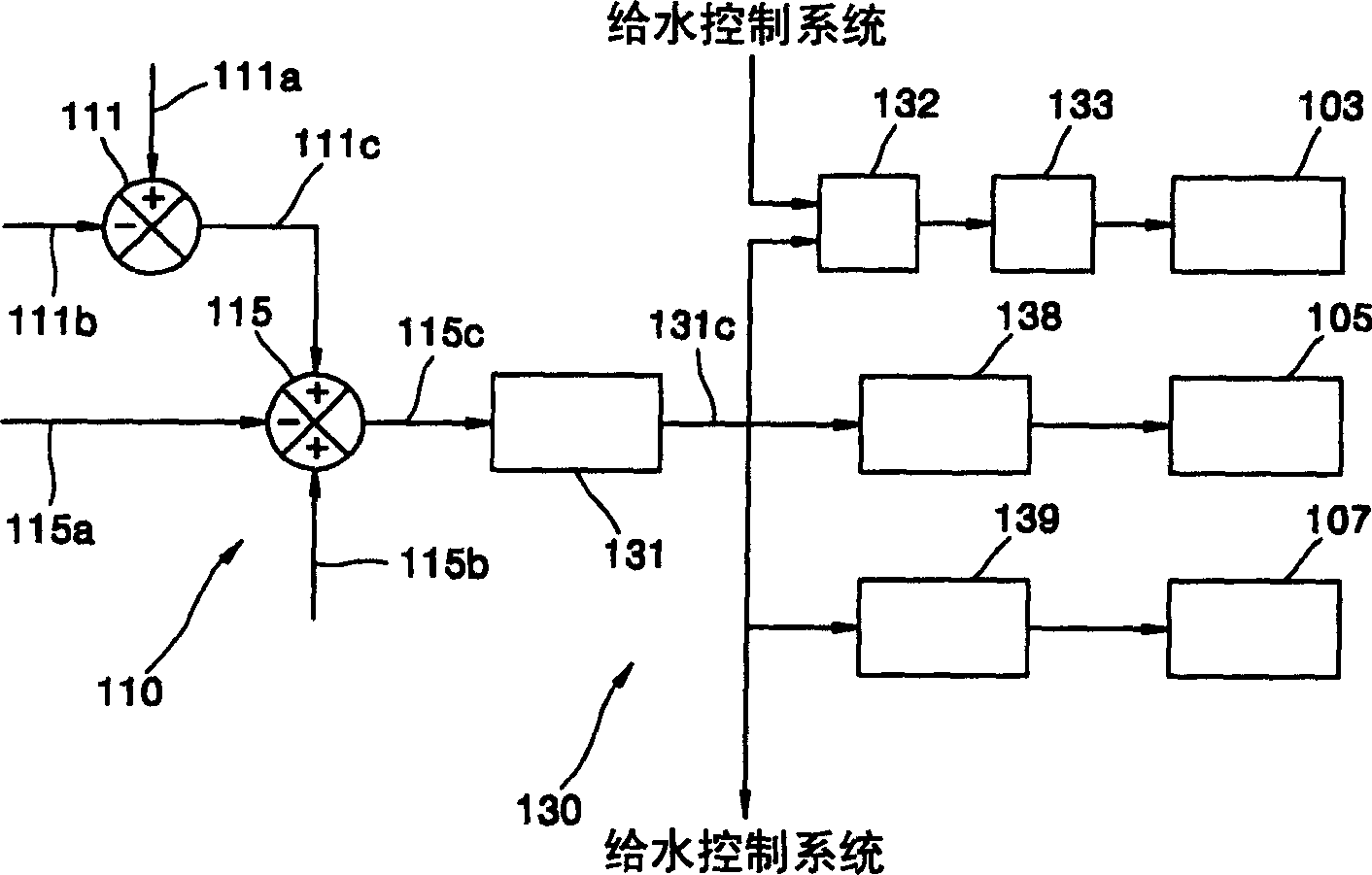
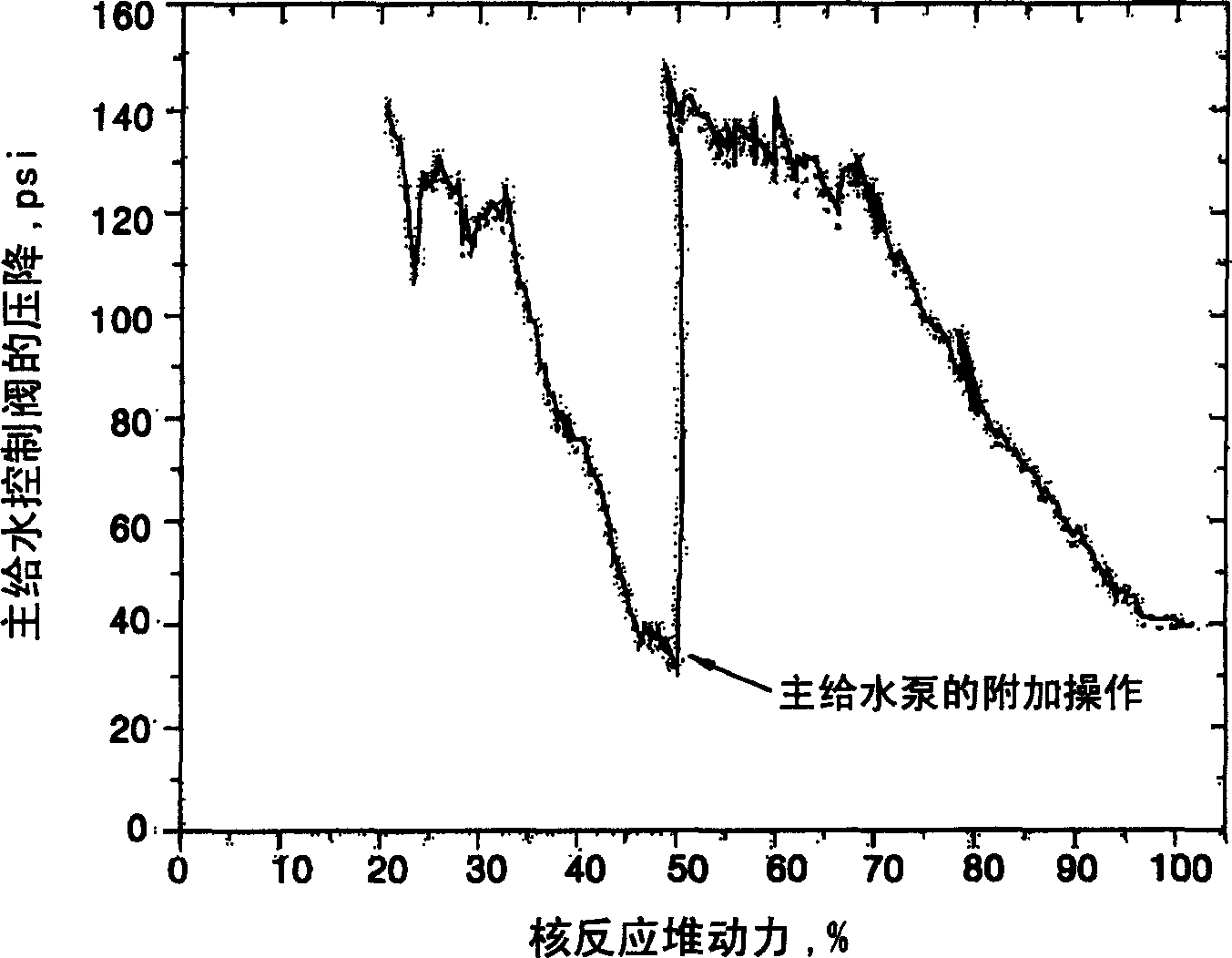
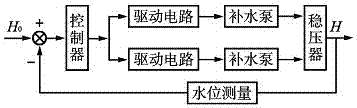
Water supply control system and control method considering pressure drop of water supply control valve in nuclear power station
ActiveCN1577636ASimplify the process of setting valuesFix stability issuesPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationDifferential pressureControl signal
Owner:KEPCO ENG & CONSTR CO INC
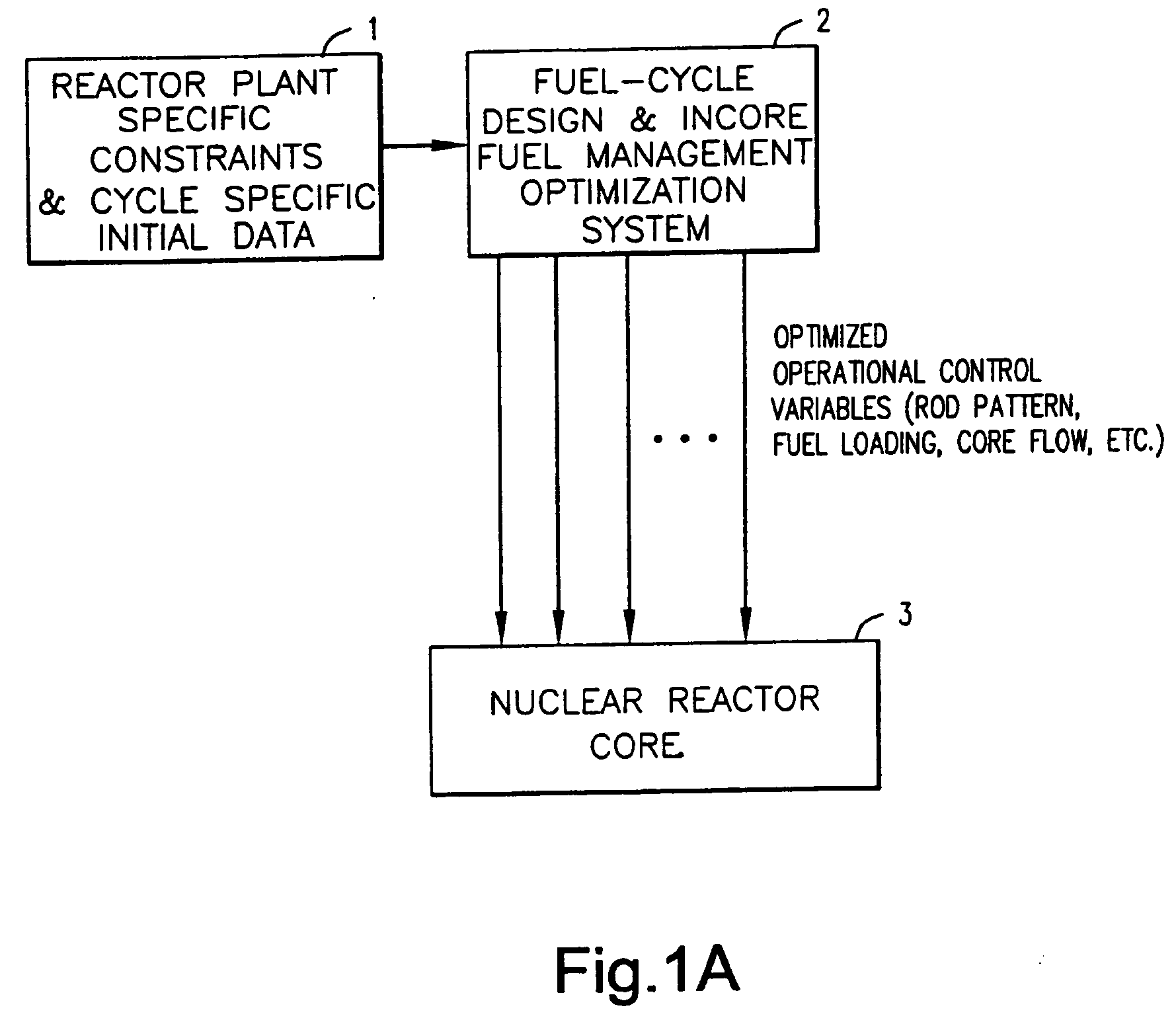
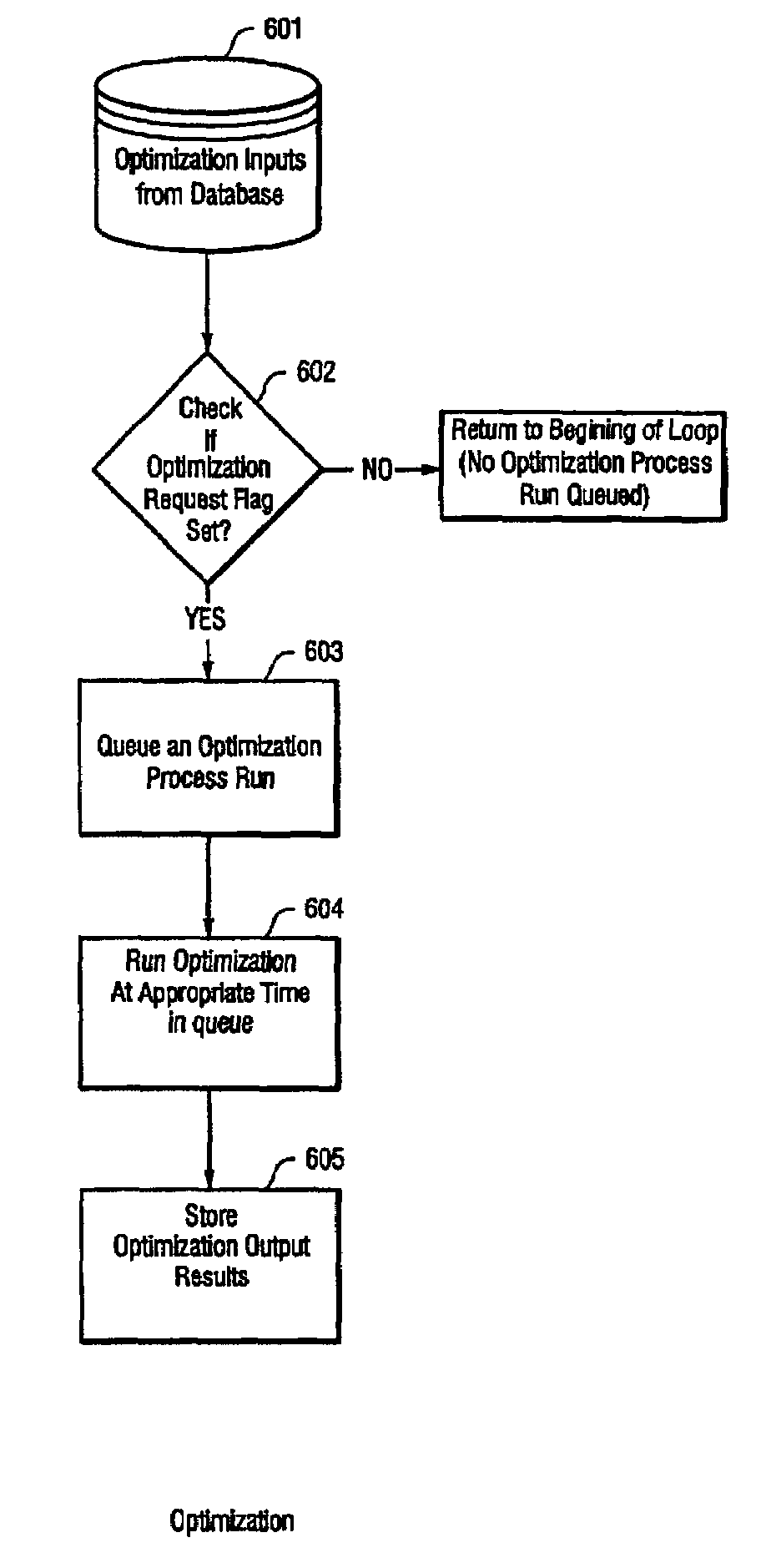
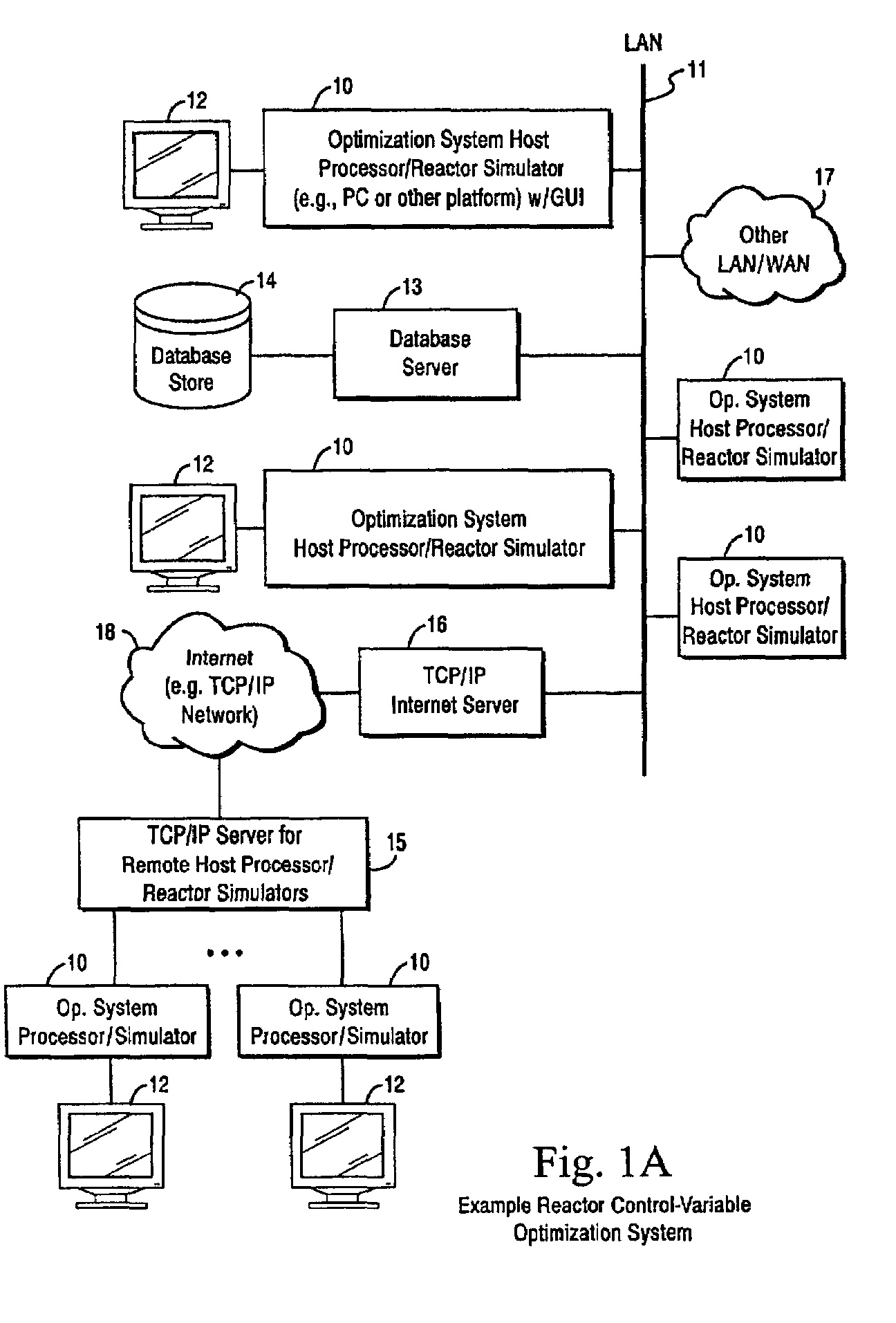
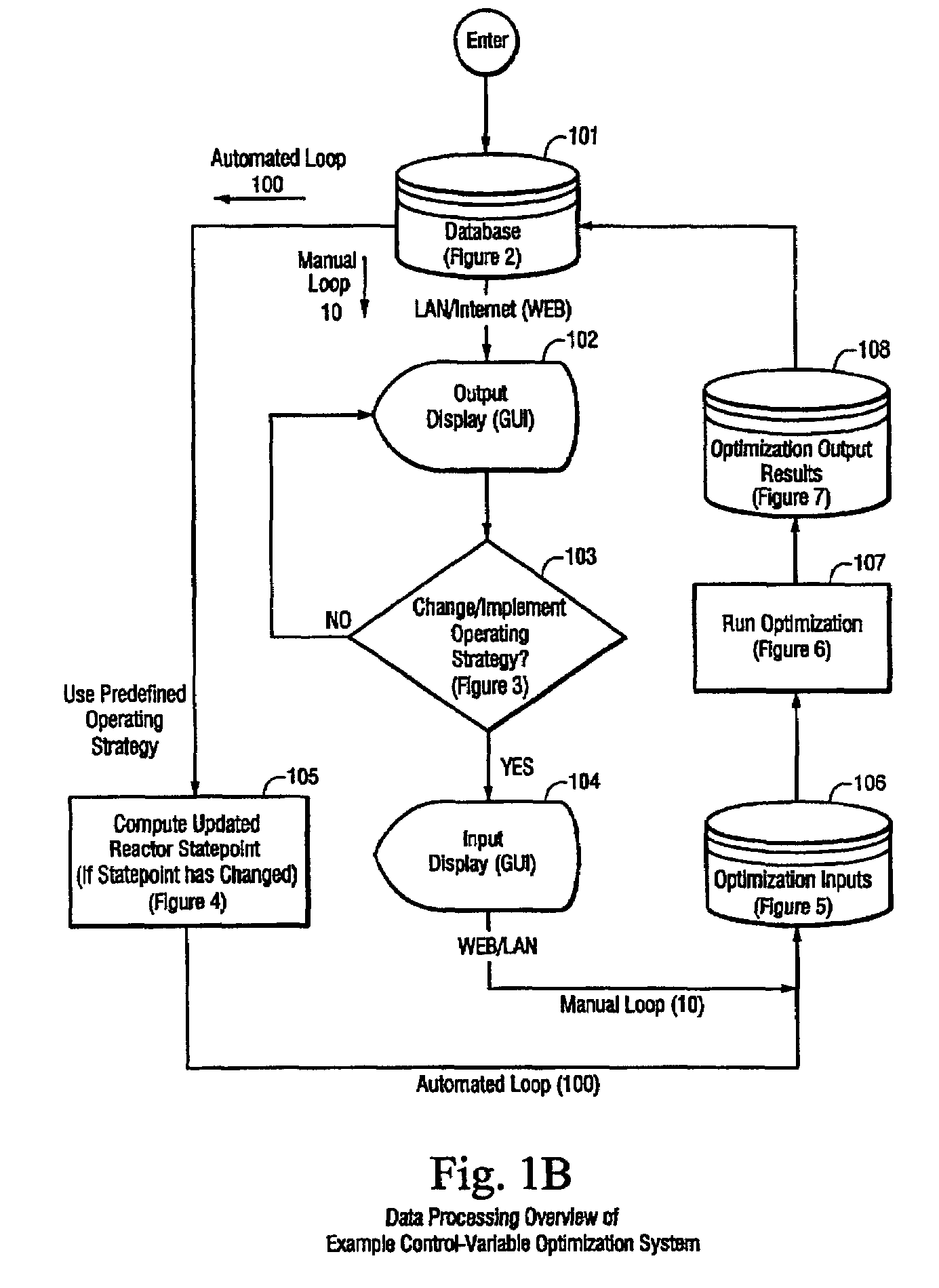
System and method for continuous optimization of control-variables during operation of a nuclear reactor
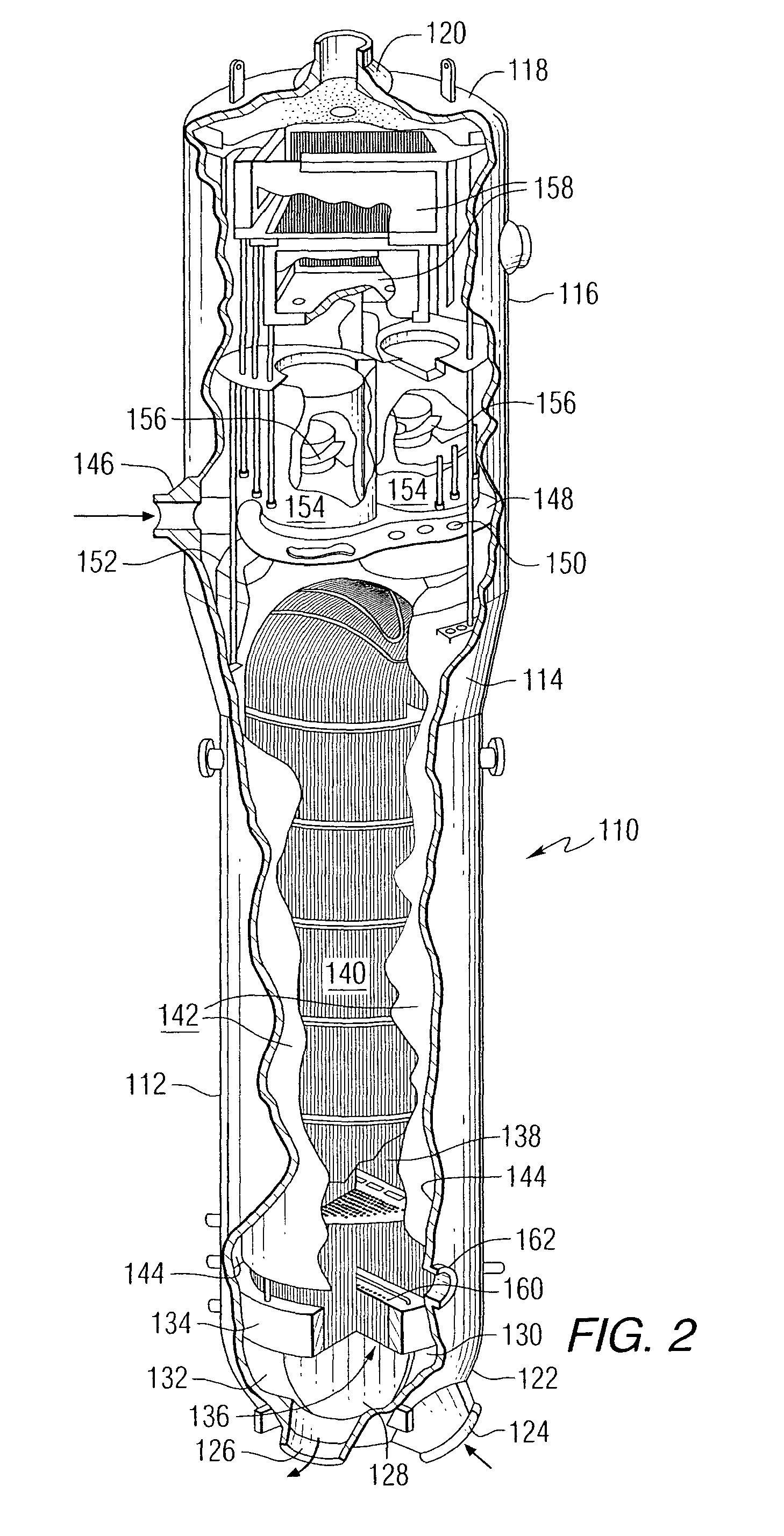
InactiveUS7555092B2Flexible and economical and safe manner of operationFlexible and economical and safe mannerPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
A system and method is provided for a continual updating of the optimization of multiple operational control-variables during the operation of a nuclear reactor over a plurality of fuel cycles. A networked computer system includes one or more hosts programmed to execute an optimization process to identify and make changes in quantitative values of operational control-variables that result in improved efficiency and operational flexibility. Optimization and updating of operational control-variables may proceed selectively under manual control for inputting specific optimization constraints and reactor state-point information or may proceed autonomously through a repetitive performing of the optimization process based upon a predetermined user-defined strategy stored on the network. Communications between users and networked processors is facilitated by use of a TCP / IP server connected to the Internet so that portions of the optimization process may be conducted contemporaneously at remote locations and / or the results made accessible to users via conventional browser enabled computers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
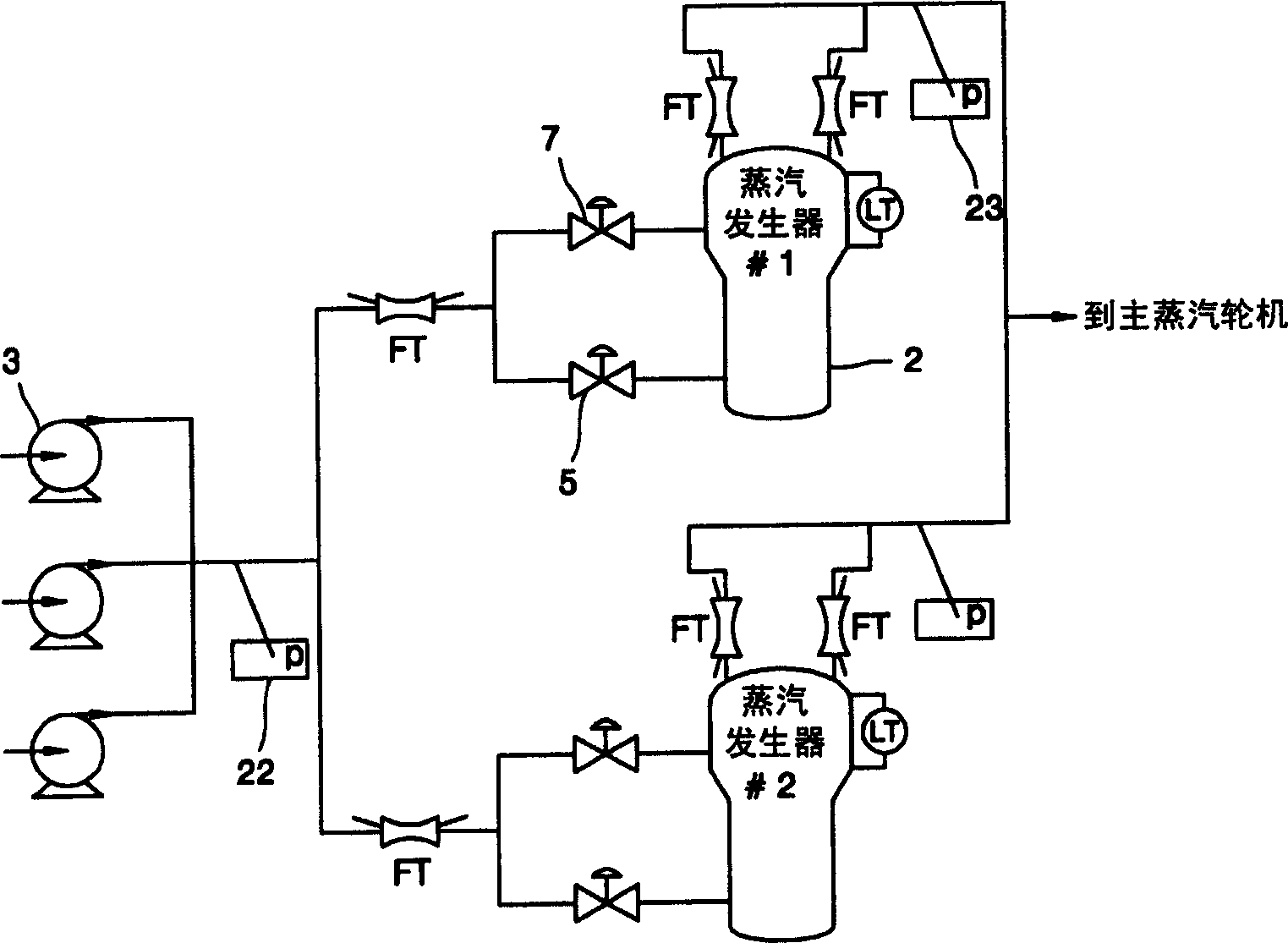
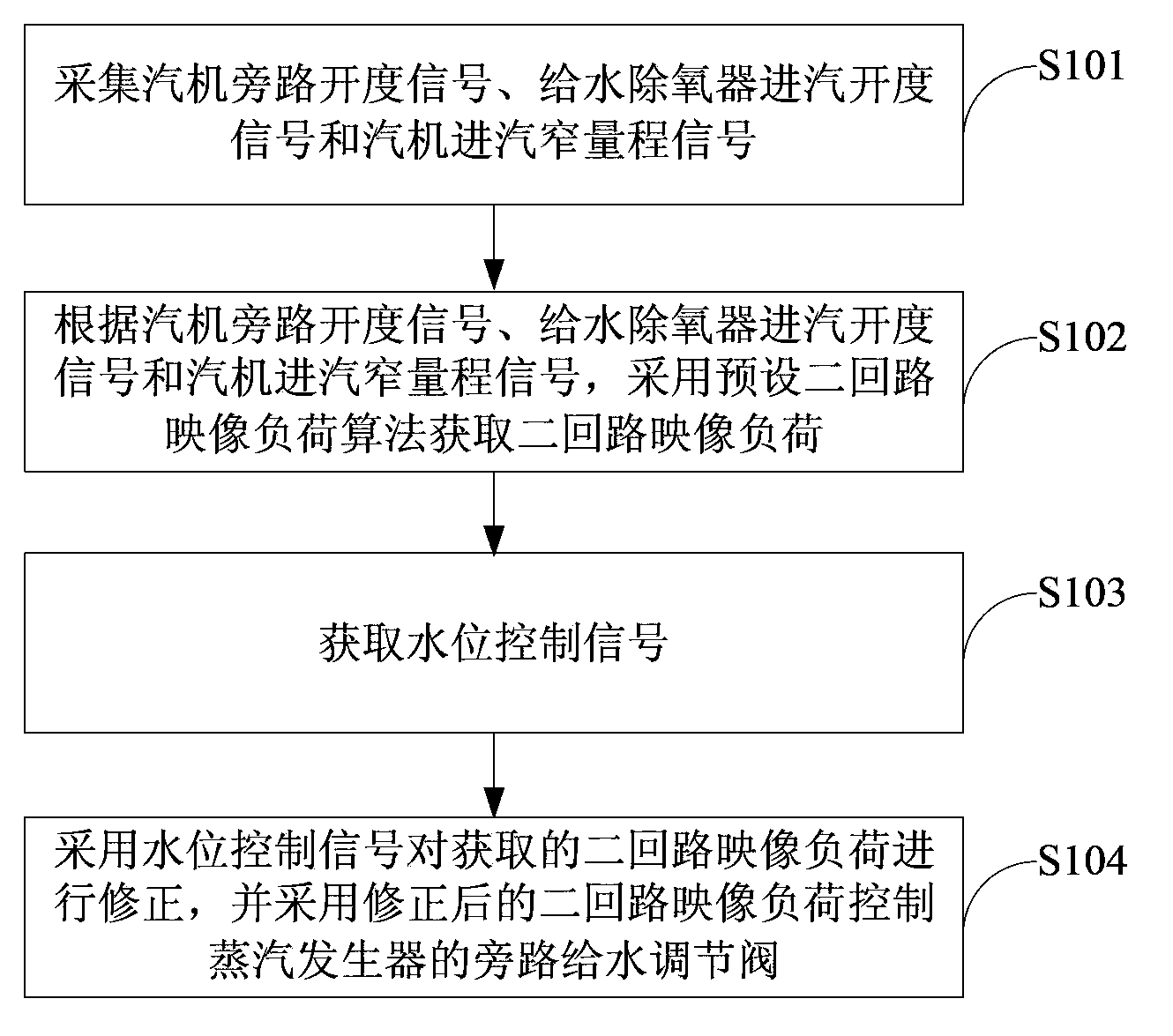
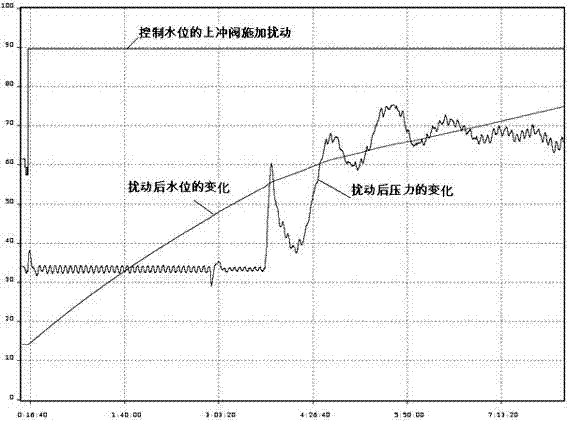
Pressurized water reactor nuclear power station steam generator water level control method and system
ActiveCN103811090AAvoid the problem of runaway water levelsPrevent jumpingPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNarrow rangeNuclear engineering
The invention is applicable to the professional technical field of mega-kilowatt-class pressurized water reactor nuclear power stations and provides a pressurized water reactor nuclear power station steam generator water level control method and system. The method includes a steam engine bypass drain valve openness signal, a water feeding deaerator steam inlet valve openness signal and a steam engine steam inlet narrow range signal; adopting a preset secondary loop image load algorithm to acquire secondary loop image load according to the steam engine bypass drain valve openness signal, the water feeding deaerator steam inlet valve openness signal and the steam engine steam inlet narrow range signal; acquiring a water level control signal; adopting the water level control signal to modify the acquired secondary loop image load and adopting the modified secondary loop image load to control a bypass water feeding adjusting valve of the steam generator. By means of the method and system, the steam generator water level out-of-control problem is solved, and heap jumping caused by the fact that the steam generator water level is out of control is avoided.
Owner:CHINA GENERAL NUCLEAR POWER CORP +1
Method for regulation of operational parameters of the core of a pressurised water nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20080069288A1Great range of operating powerIncrease powerPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorCircumflex
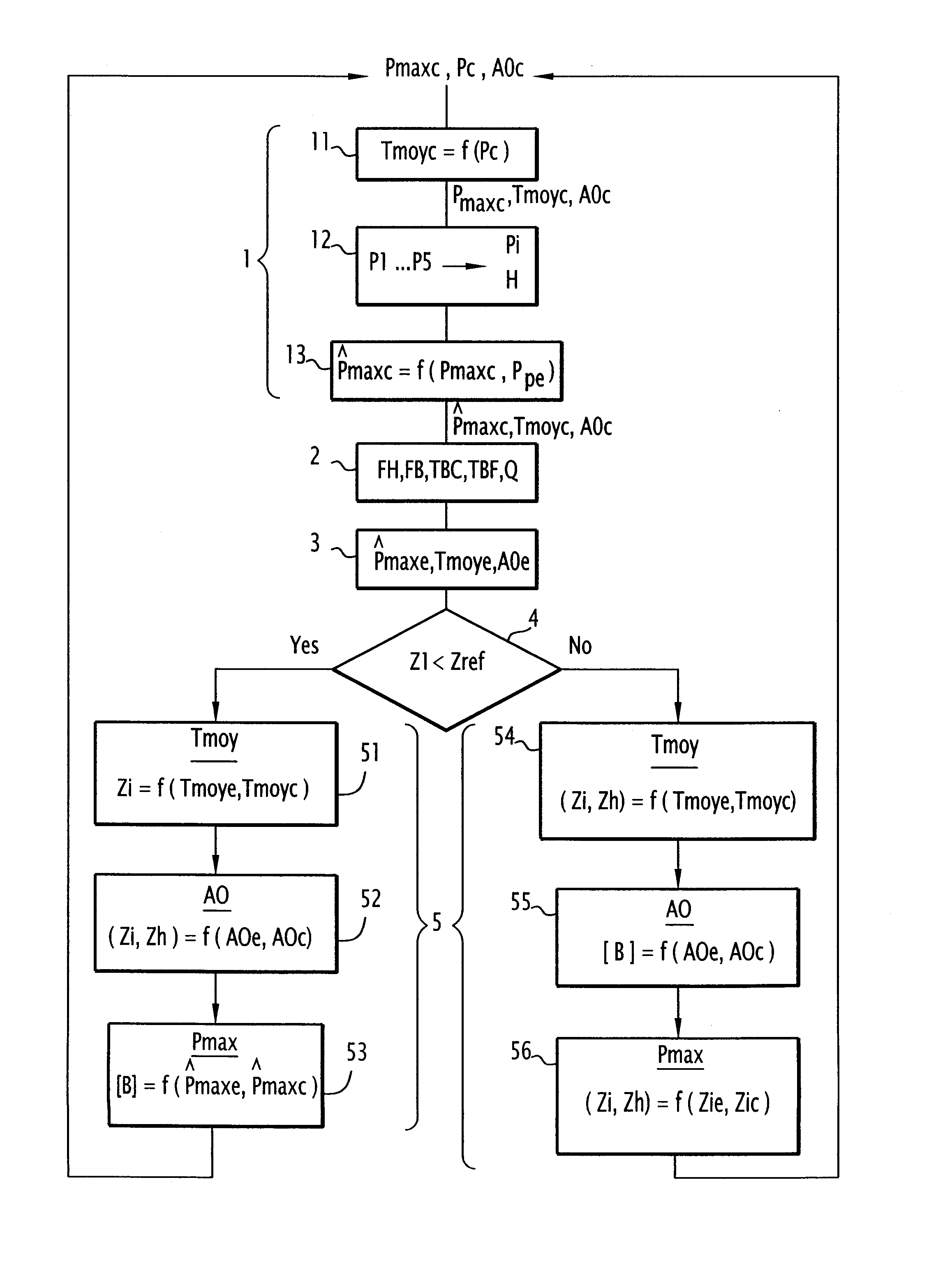
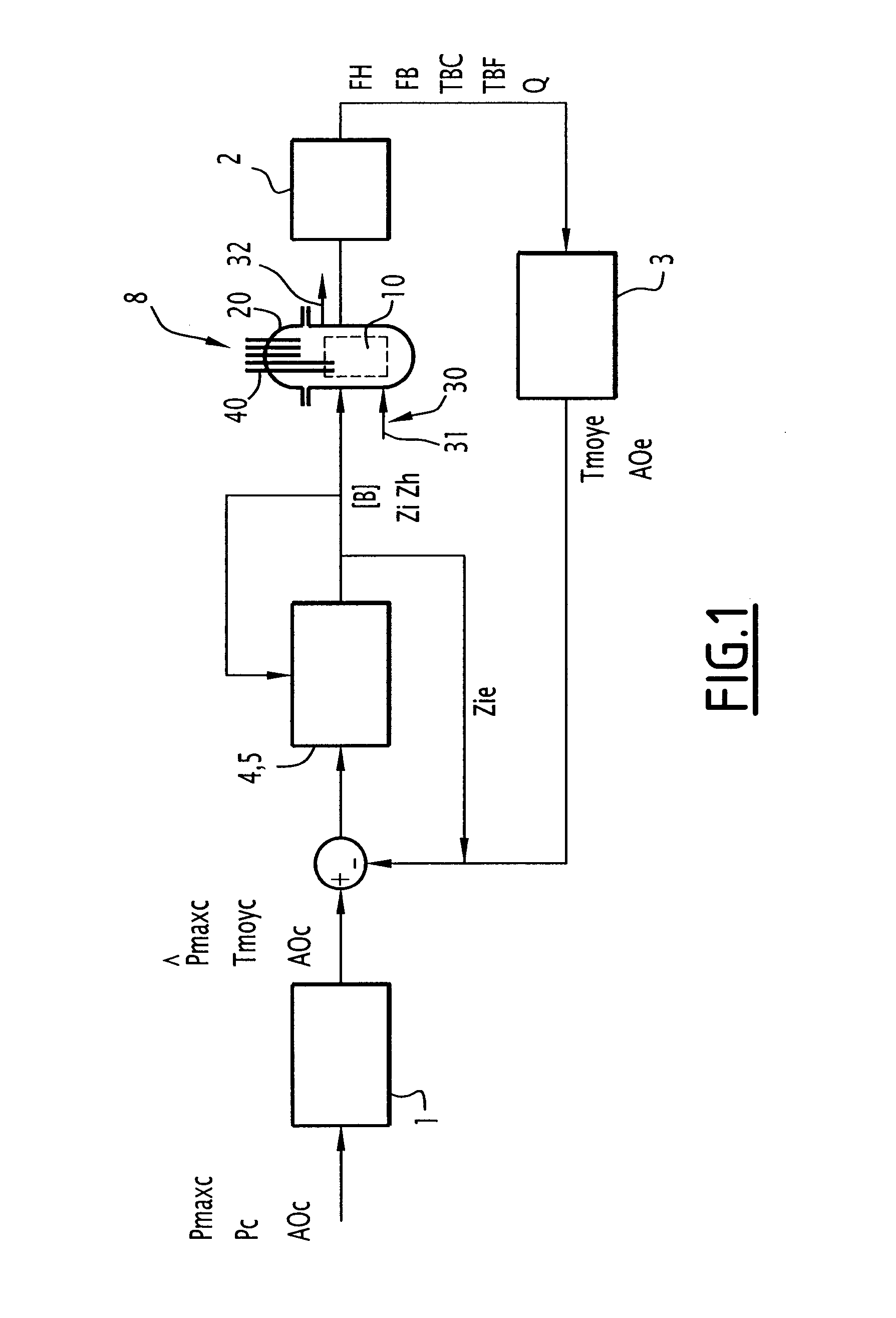
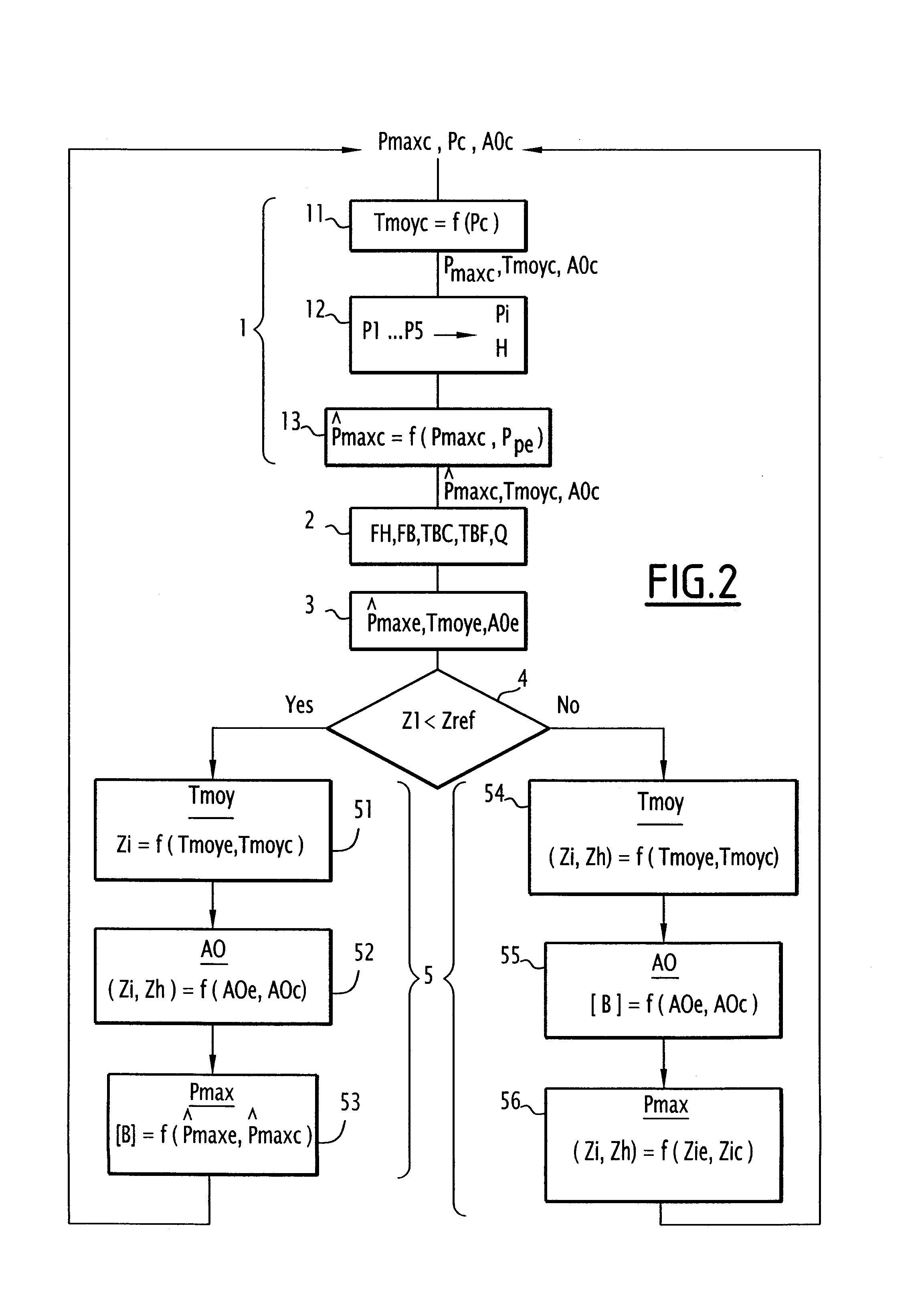
The invention relates to a method for regulation of operational parameters of the core of a pressurised water nuclear reactor comprising: a step of acquisition of values (FH, FB, TBC, TBF, Q) which are representative of the conditions of operating of the core of the reactor; a step of evaluation of the actual values (Tmoye, AOe, {circumflex over (P)} maxe) of the operational parameters at least according to the values acquired (FH, FB, TBC, TBF, Q); a step of selection of a control law for the concentration of a neutron-absorbent component ([B]) and for the positions of insertion (Z1 to Z5) of the groups (P1 to P5) of rods selected from at least the first and second control laws which are different from one another; and a step of regulation of the operational parameters by means of the control law selected, according to set points (Tmoyc, AOc, {circumflex over (P)} maxc) relative to the said parameters and to the actual values (Tmoye, AOe, {circumflex over (P)} maxe) evaluated.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
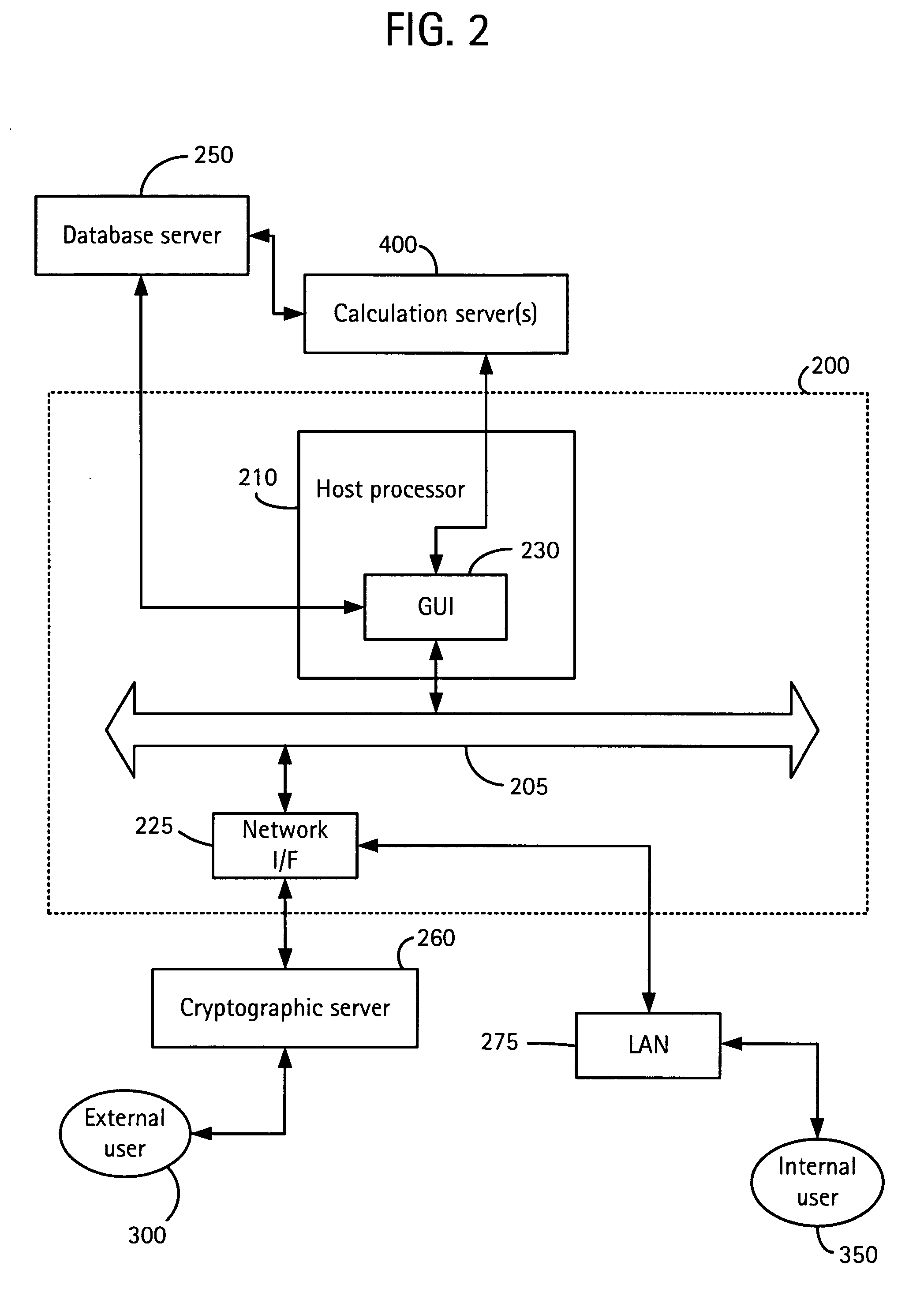
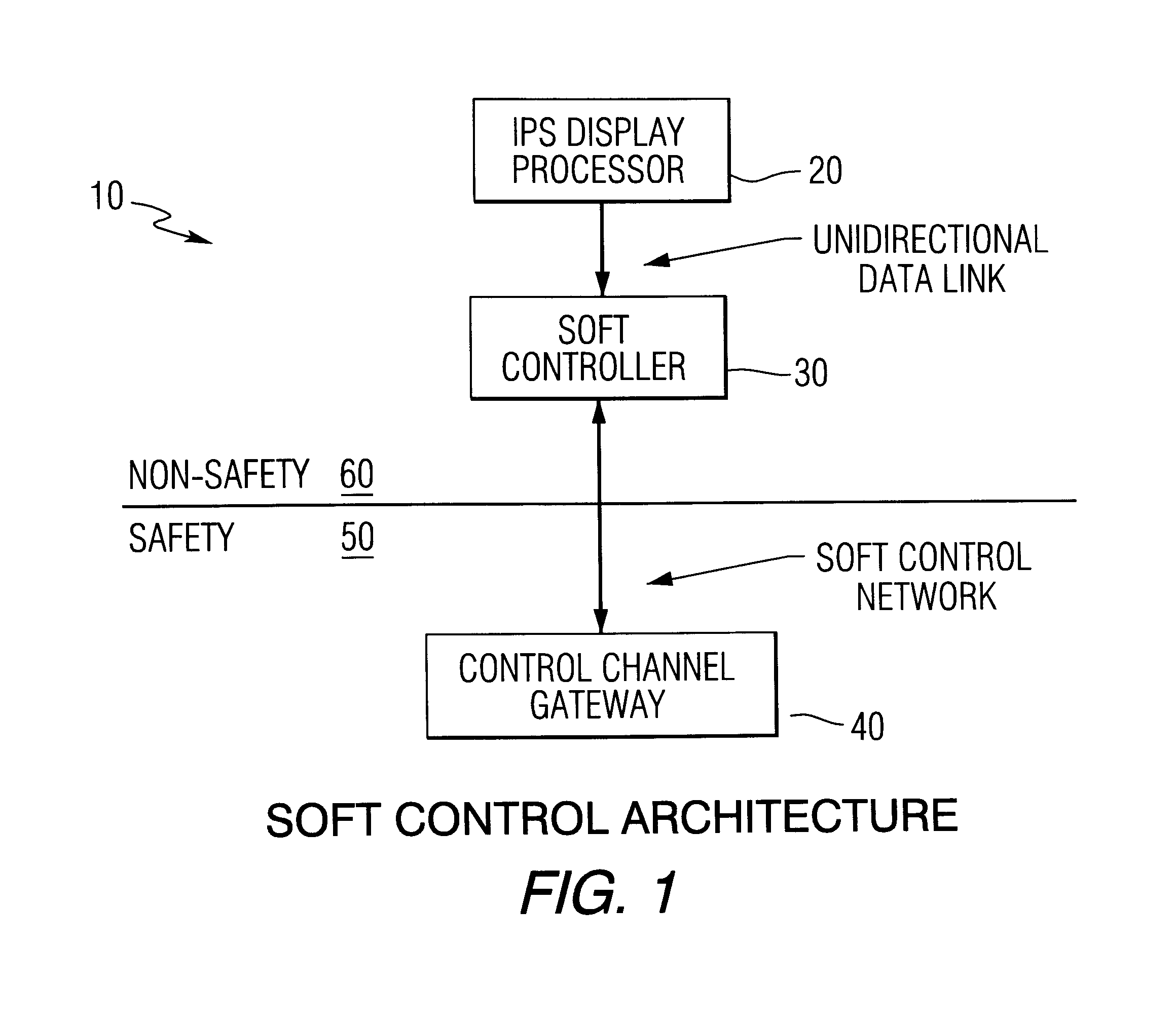
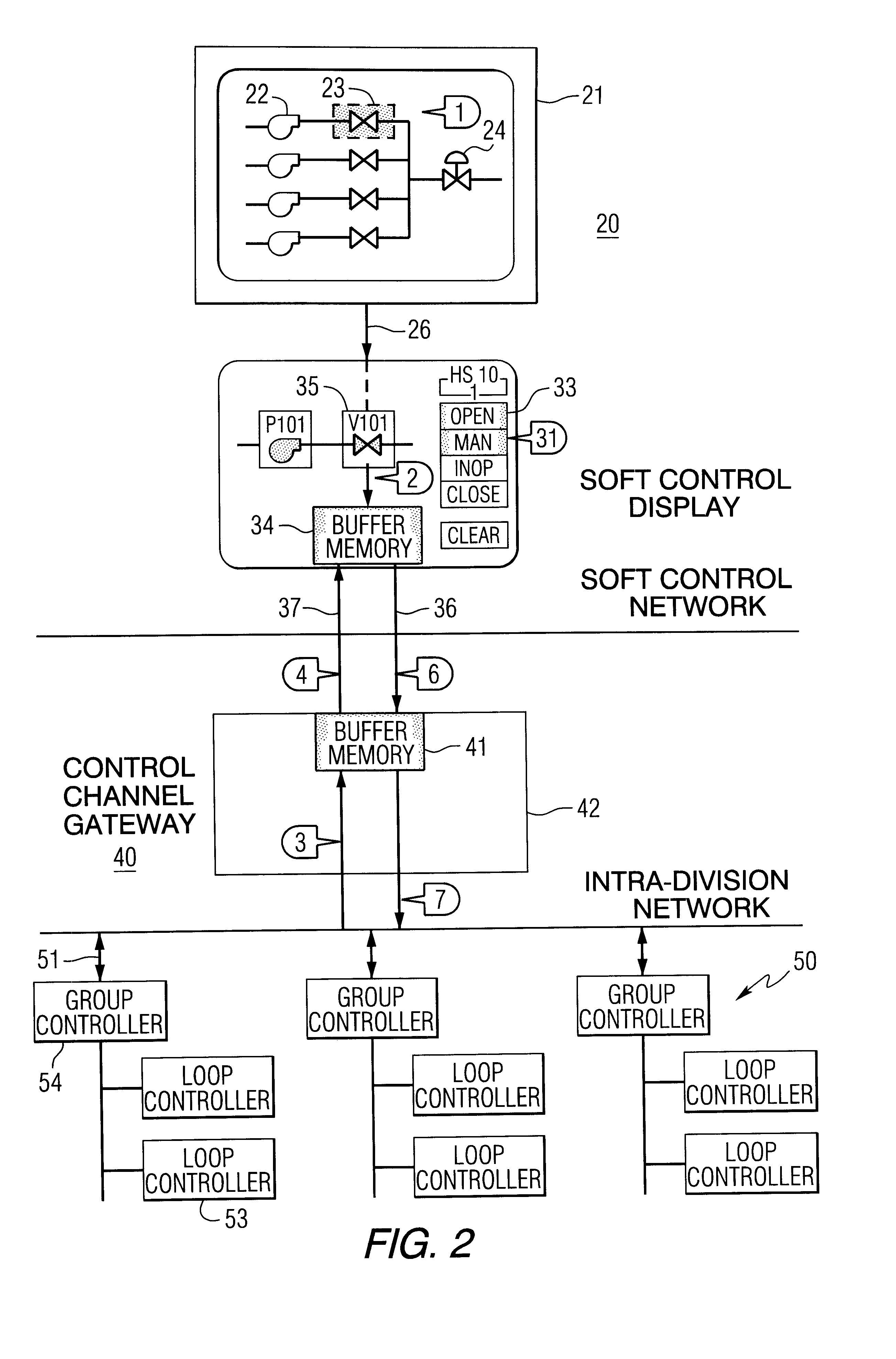
Method and apparatus to eliminate confirmation switches and channel demultiplexer from soft control man-machine interface (MMI)
InactiveUS6516041B1Eliminate needMaintain compliancePlant parameters regulationMan-machine nuclear interfaceImaging processingHuman–machine interface
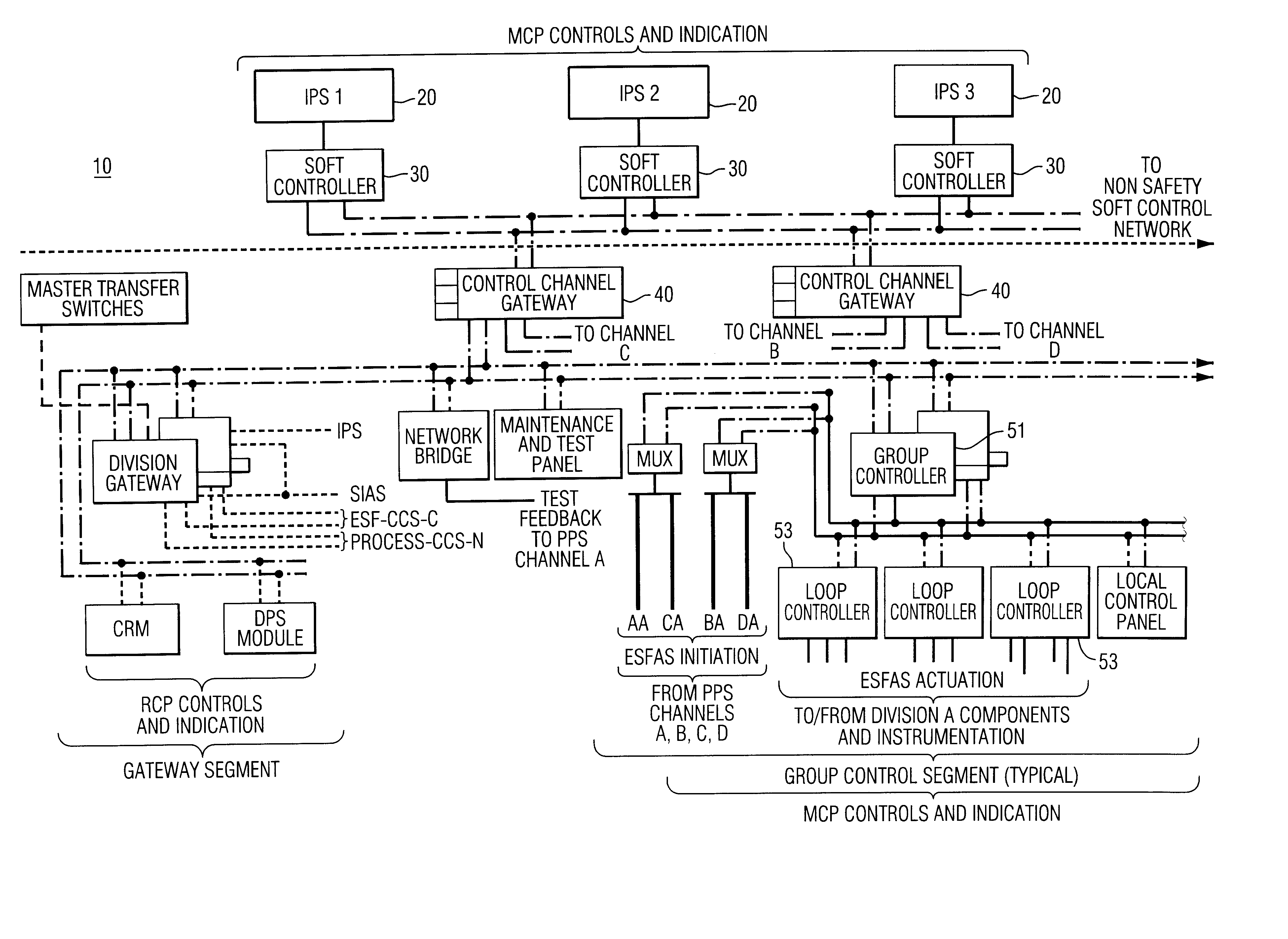
A method and apparatus for controlling components in a component control system in a nuclear power plant includes an image processing system and display processor (IPS-DP) for issuing an encrypted command for a selected component in a component command system (CCS) in the nuclear power plant; a soft controller for receiving the encrypted command and matching the command with the selected component in the CCS for issuing a control command to the selected component; and control channel gateway for receiving the encrypted command from the IPS-DP and soft controller, deciphering the encrypted command, and, if authenticated, issuing a control command for said selected component in the CCS. Security and isolation, while complying with applicable codes and regulations, are assured.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
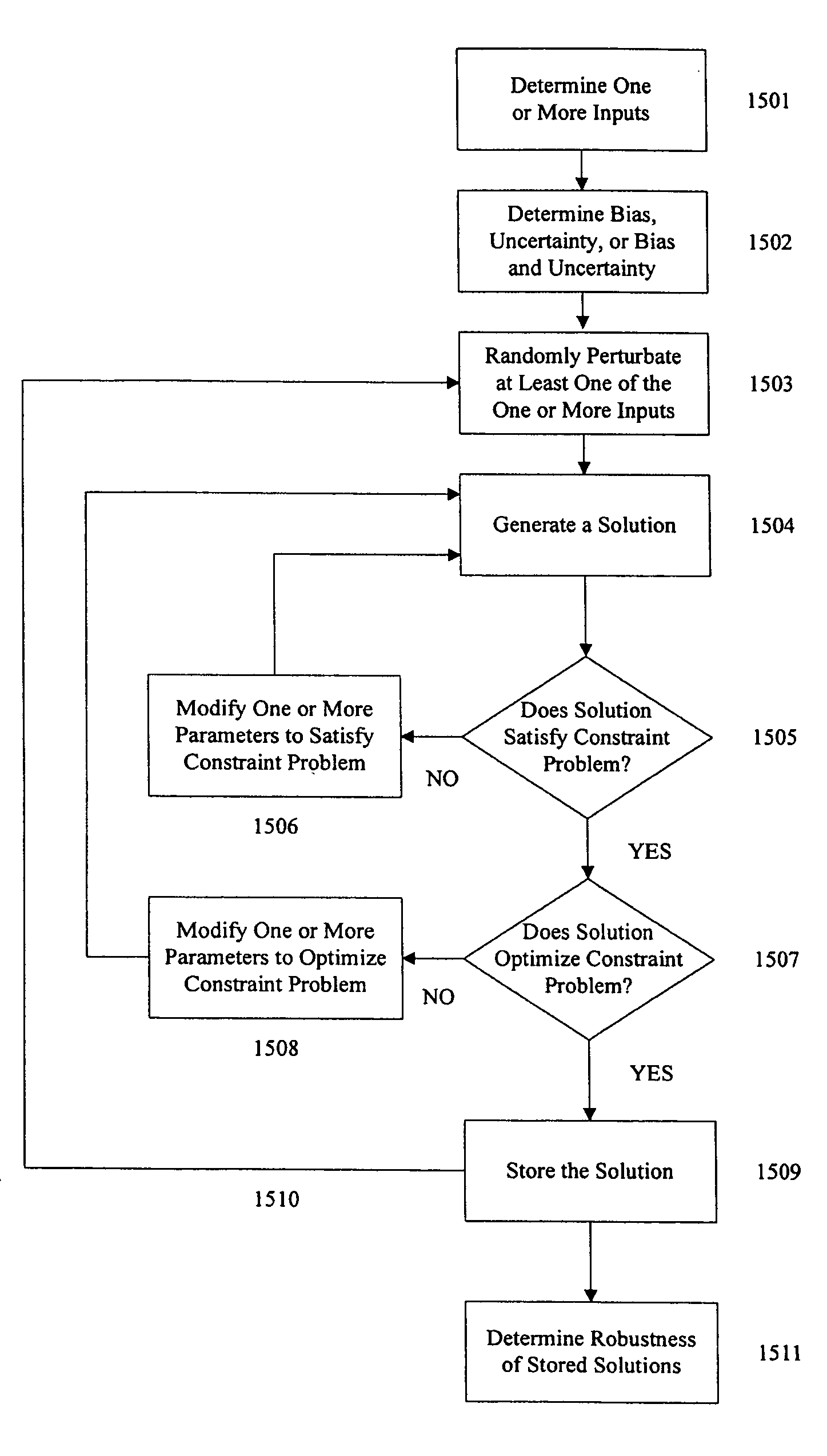
Methods for evaluating robustness of solutions to constraint problems
InactiveUS20080154838A1Reduce sensitivityPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationAlgorithm
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
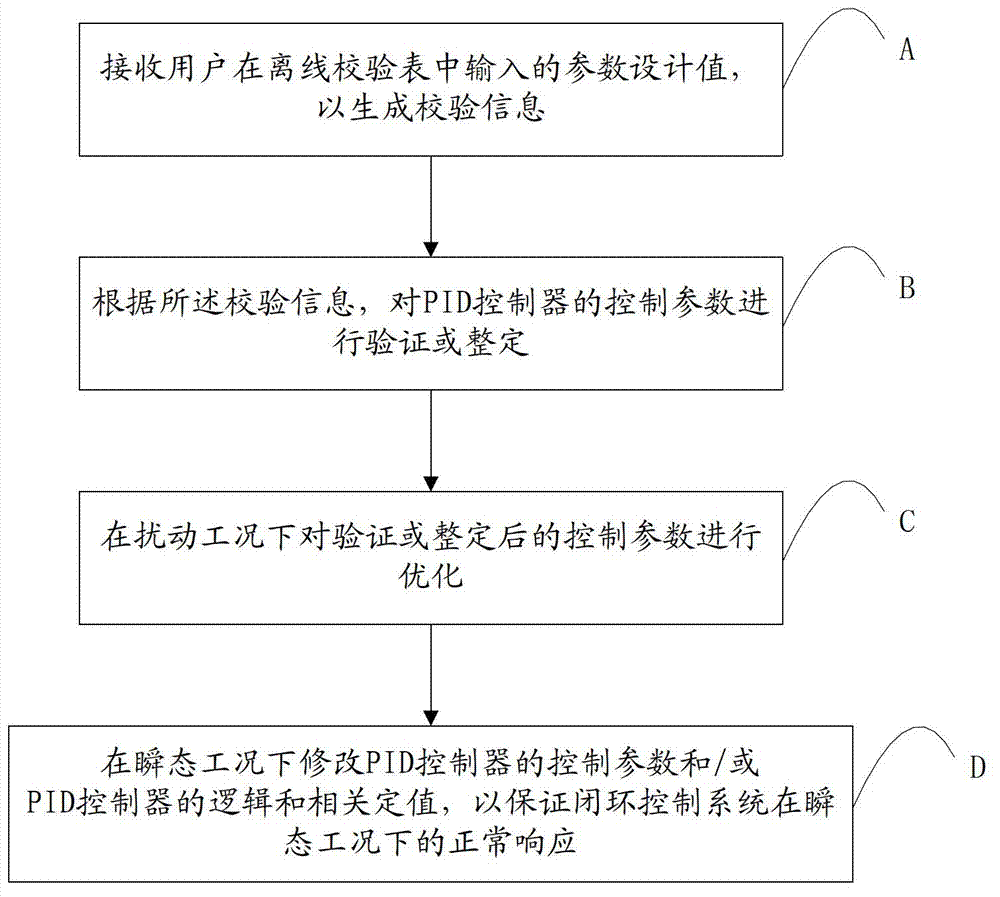
Debugging method and system for closed-loop control system of nuclear power plant
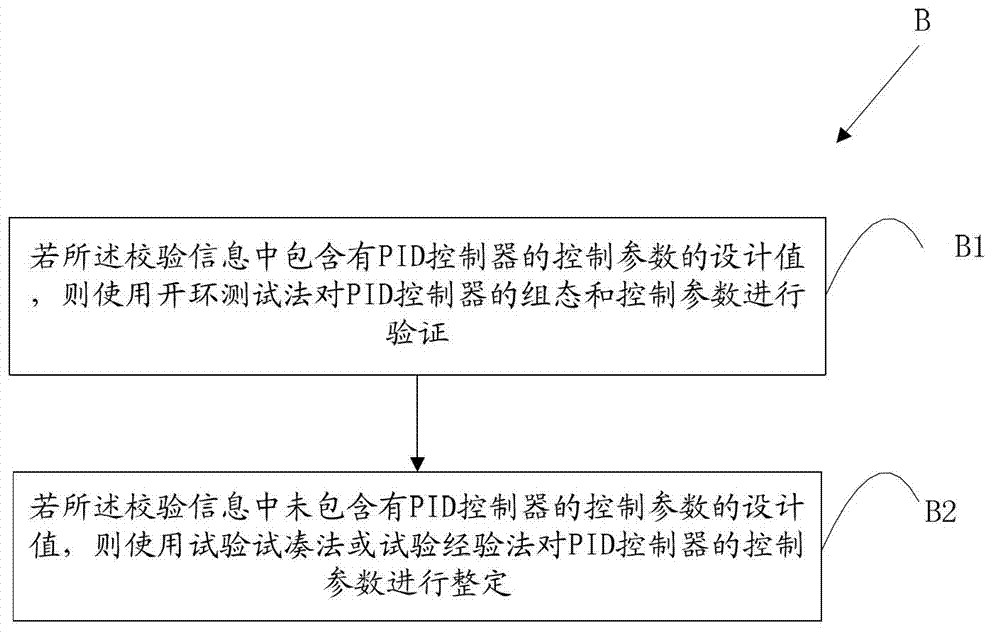
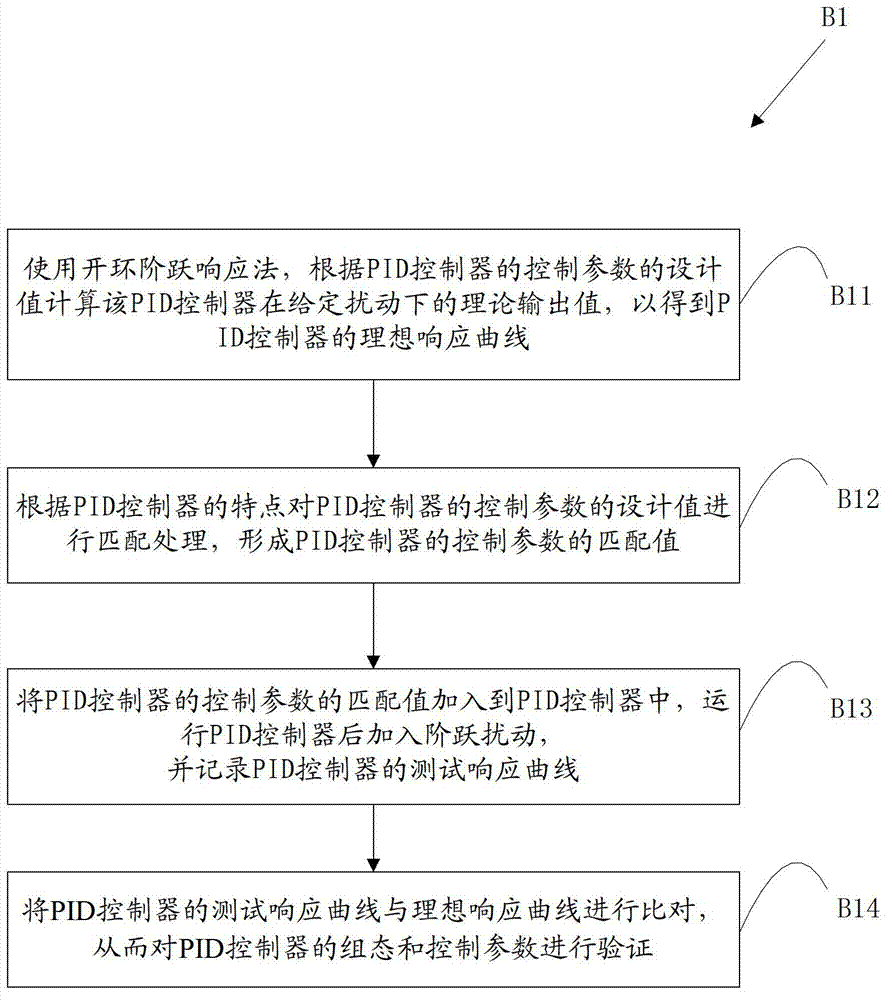
ActiveCN102789824AReduced commissioning riskShorten the debugging cyclePlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationLoop controlProportion integration differentiation
The invention discloses a debugging method and system for a closed-loop control system of a nuclear power plant. The debugging method comprises the following steps: A, a parameter design value input in an off-line checking table by a user is received to generate a checking message; B, a control parameter of a PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) controller is verified and adjusted according to the checking message; C, the verified and adjusted control parameter is optimized under a disturbance operating condition; D, the control parameter of the PID controller and / or the logic and related constant value of the PID controller are / is modified under an instantaneous condition so as to ensure the normal response of the closed-loop control system under the instantaneous condition. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the debugging risk of the closed-loop control system is reduced, the debugging cycle of the closed-loop control system is shortened, the operation quality of a unit is improved, and good economic benefits are obtained.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Nuclear power plant, water level control method and system for steam generator
InactiveCN101483078AObtain intuitivelyFull accessLevel controlPlant parameters regulationNuclear plantNuclear engineering
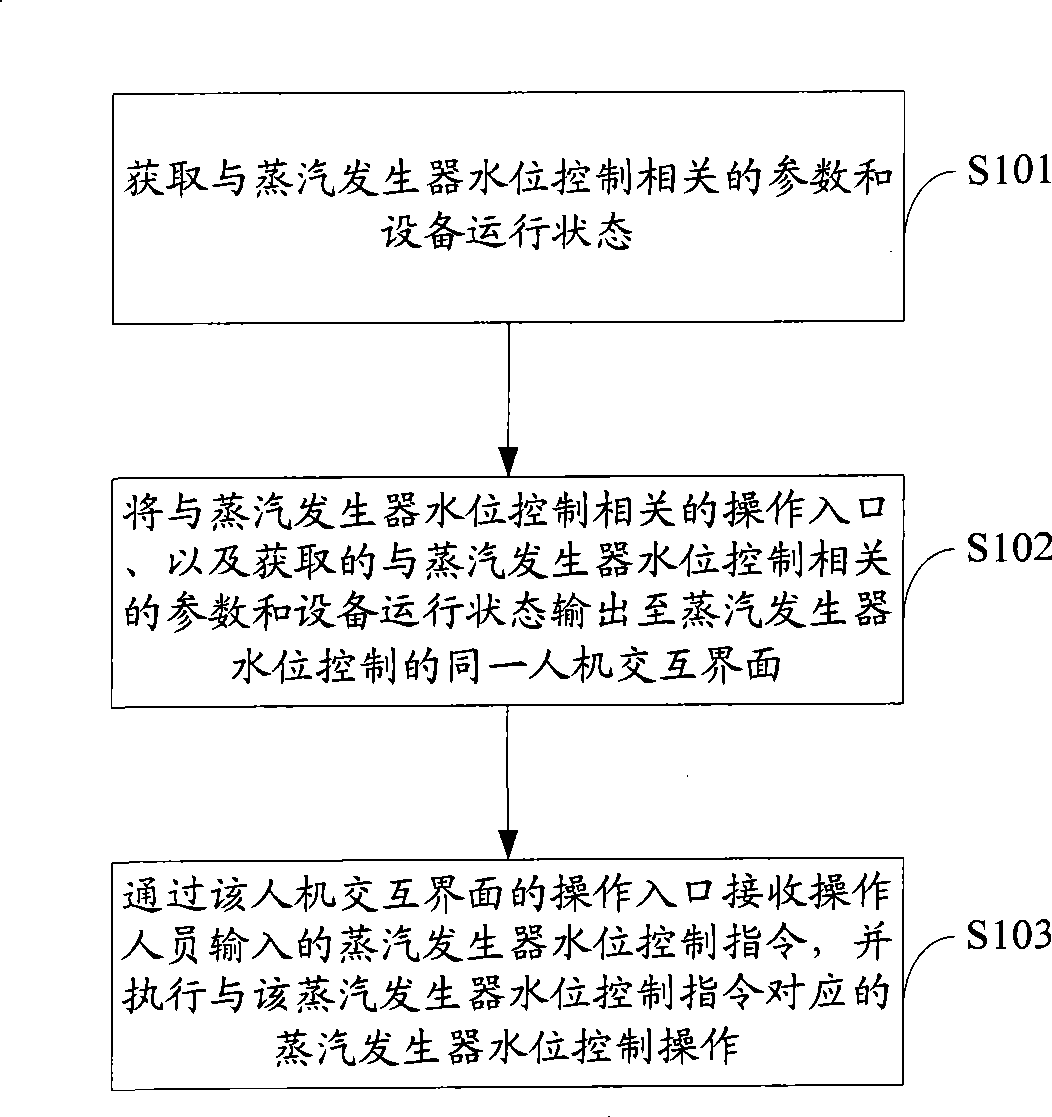
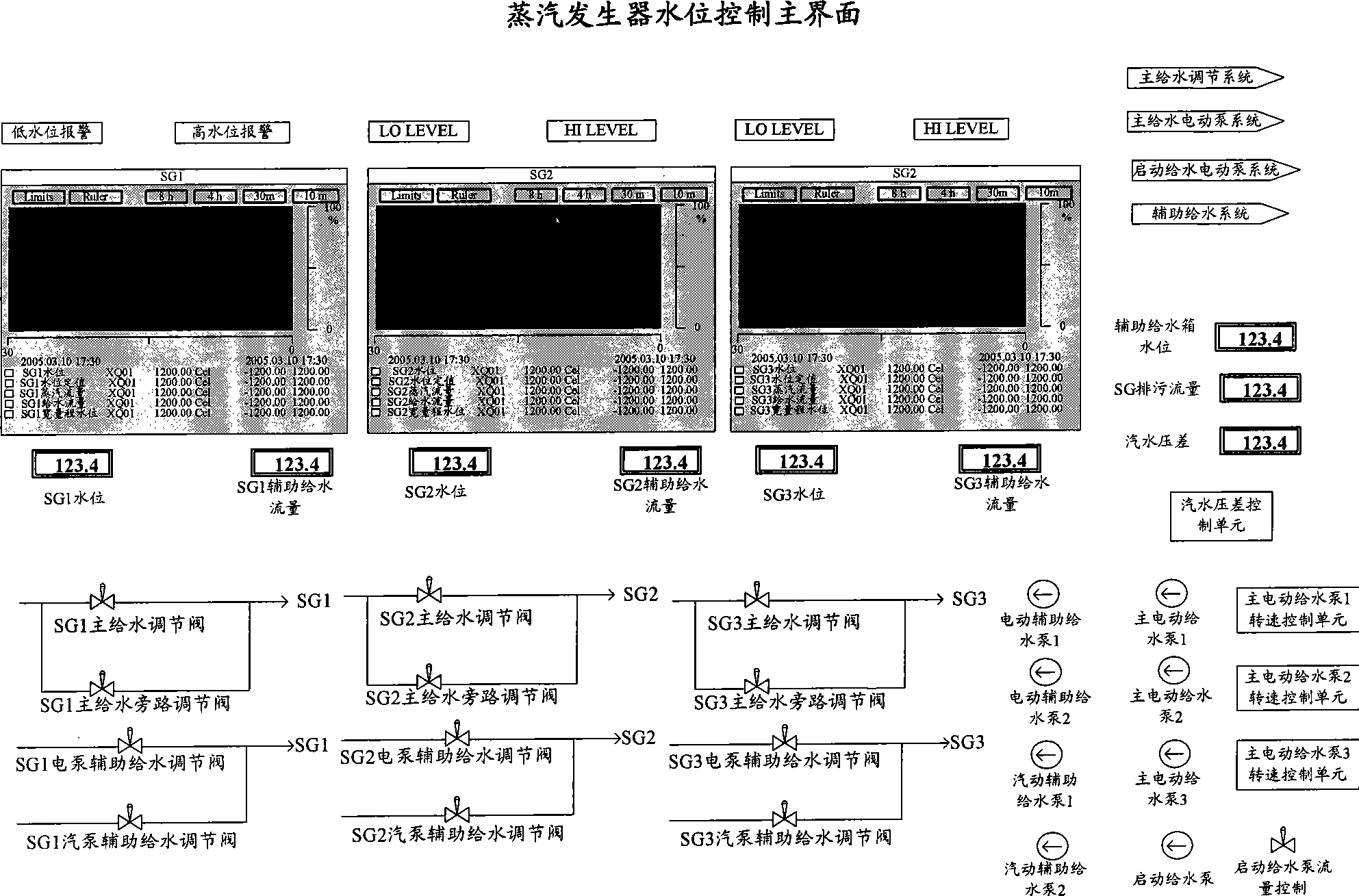
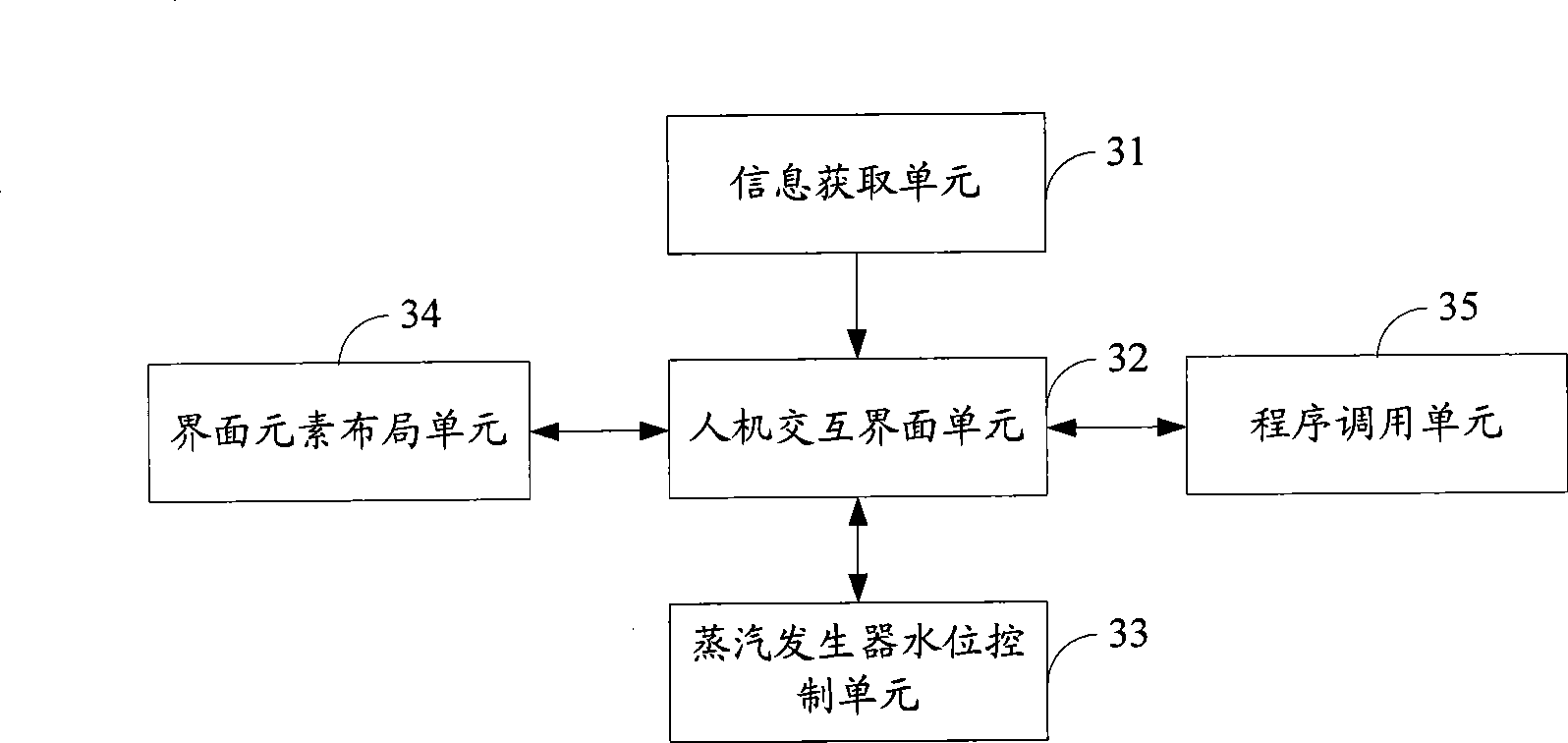
The invention is applied to the field of nuclear power control, which provides a nuclear power plant and steam generator water level control method and system thereof. The method includes the following steps: acquiring the parameter and equipment running status related to the steam generator water level control; outputting the operation entrance related to the steam generator water level control and the acquired parameter and equipment running status related to the steam generator water level control to a steam generator water level control main interface; receiving the input steam generator water level control instruction from the operations entrance of the steam generator water level control main interface, and executing the steam generator water level control operations corresponding to the steam generator water level control instruction. The inventive embodiment outputs the information related to the steam generator water level control to a same man-machine interactive interface, so that operators can intuitively, comprehensively and fast acquire parameters and judge the reason that the exceptional steam generator water level occurs, and rapid intervention can be realized by the man-machine interactive interface.
Owner:CHINA GENERAL NUCLEAR POWER CORP +1
Method for finishing out-of-pile detector scales through single in-pile flux measurement
ActiveCN107492399AAvoid Nuclear Safety RisksIncrease power generationPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorNuclear power
The invention discloses a method for finishing out-of-pile detector scales through single in-pile flux measurement. The method is combined with site actual measurement and software numerical simulation calculation, pile core numerical simulation software is utilized to generate different axial power distribution shapes which are obtained by actually performing operation on a reaction pile in a traditional method, meanwhile primary in-pile flux measurement results of a nuclear power plant are utilized to obtain flexibility of all out-of-pile detectors, furthermore the detector flexibility is applied to correcting out-of-pile detector current obtained by software calculation, and finally a traditional data treating method is utilized to generate out-of-pile detector scale coefficients. According to the method disclosed by the invention, artificial disturbance is prevented from being introduced into the nuclear reaction pile, a nuclear accident risk is reduced, meanwhile considerable economical benefit is brought to the nuclear power plant, and finally the method can be applied to all active-service nuclear power units in China.
Owner:上海核星核电科技有限公司 +1
Method for calibrating steam generator water level measurement
ActiveUS7120218B2Plant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationPower stationDifferential pressure
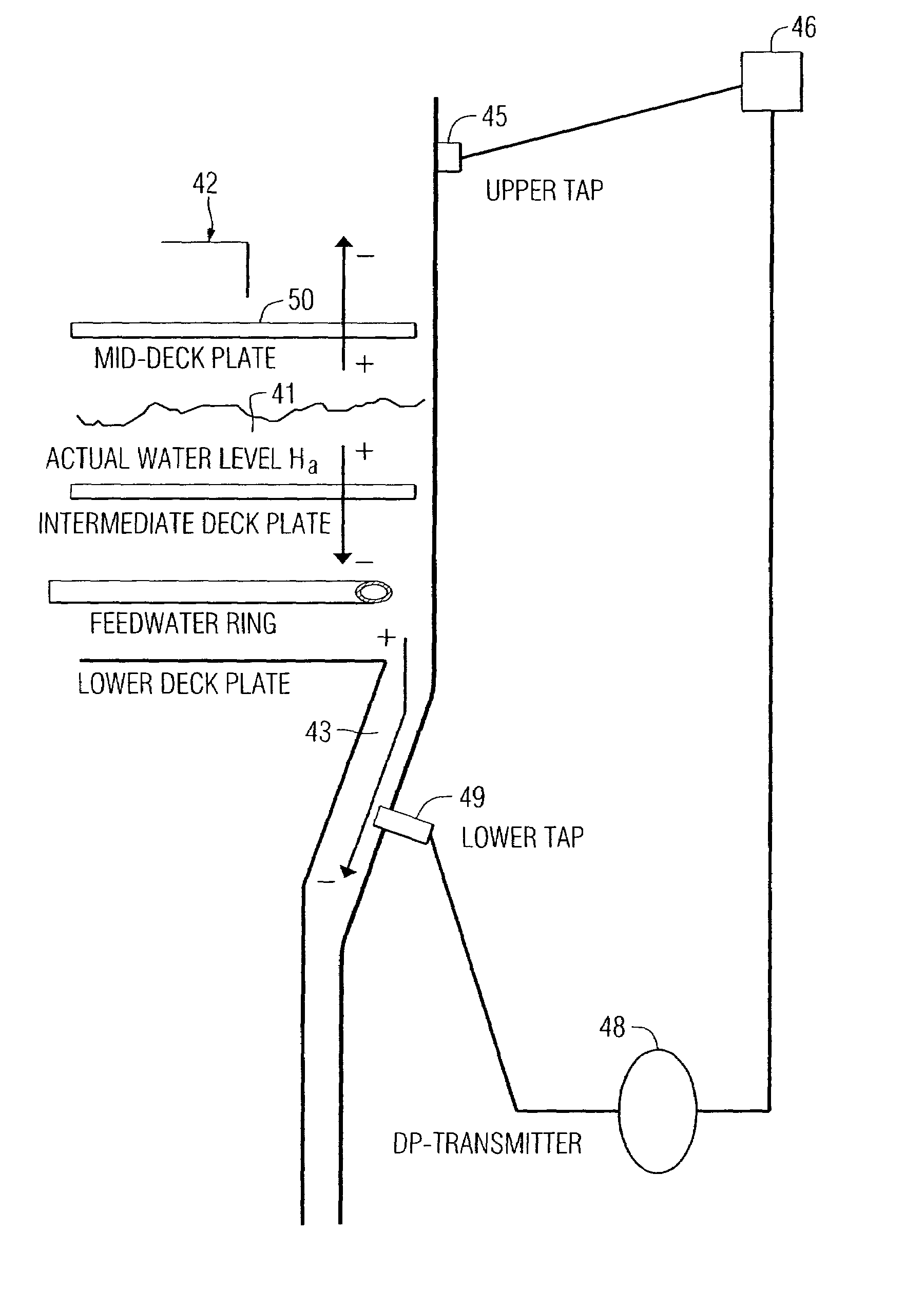
A method is provided for determining and controlling feed water level in a steam generator of a nuclear power plant, whereby the water level sensor is calibrated in terms of the pressure drop across structural components in the feed water path. The water level differential pressure sensor is calibrated so that maximum water level is indicated as the level corresponding to the upper tap level plus the pressure drop across the foregoing structural components at maximum power plant power.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Control modes for PWR (Pressurized Water Reactor) core of nuclear power plant
ActiveCN105139908AReduce the burden onSimple designPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationTemperature controlNuclear power
The invention discloses control modes for a PWR core of a nuclear power plant. Two control rod groups, i.e., a T rod group and a D rod group, which are controlled independently are arranged. In the load tracking mode, a reactor is controlled in the manner that the average temperature of a coolant is controlled by the independent T rod group, reactive change of the core is controlled, the axial power distribution shape is controlled by the independent D rod group, soluble boron is adjusted periodically, and the control rod groups are recovered to an operation range. In other modes except the load tracking mode, the reactor is controlled in the manner that the average temperature of a coolant is controlled by the independent D rod group, the D rod group is also used to adjust the axial power shape and slight reactive change of the core. The control modes of the invention have the advantages that the control rod is used to reactive control of the core in the load tracking mode, so that burden of operators is greatly reduced; and generated wasted boron solution is reduced, the operation cost as well as the wasted solution processing cost is reduced, and the environment is protected.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
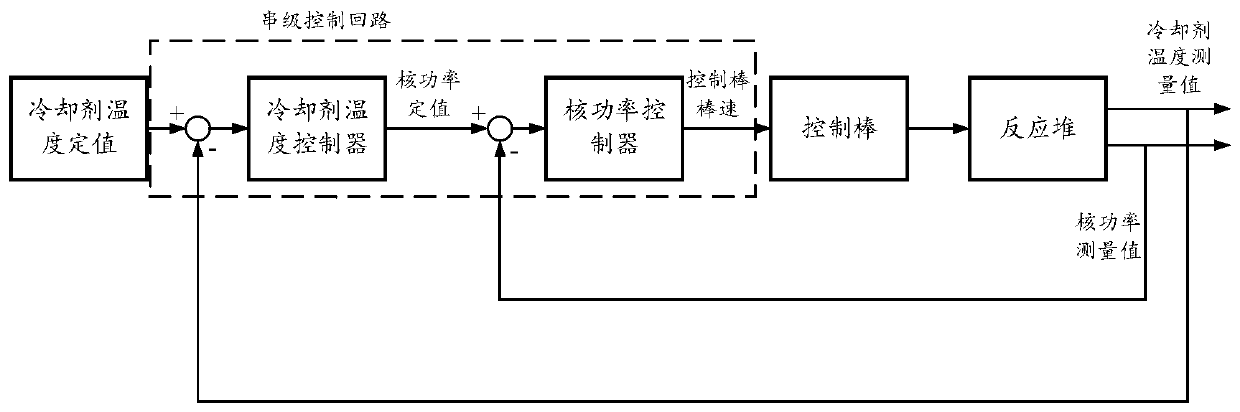
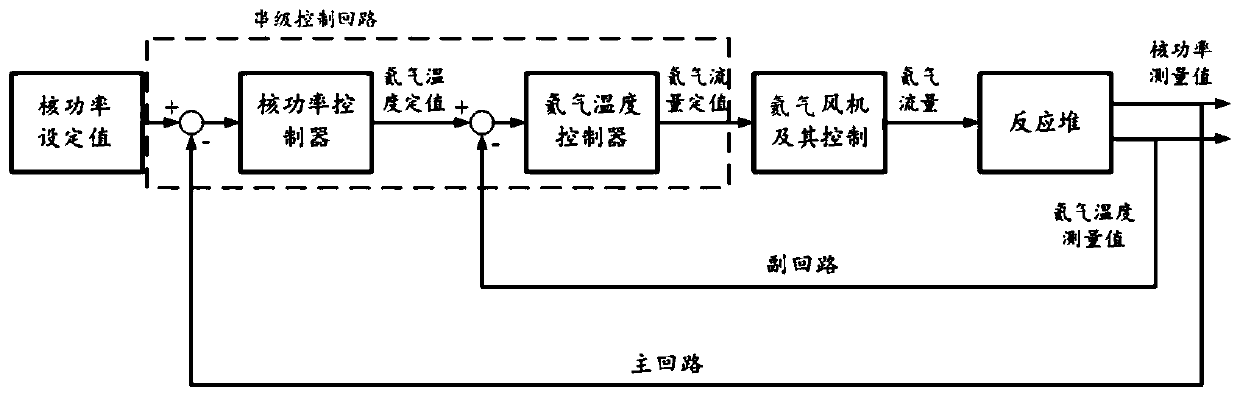
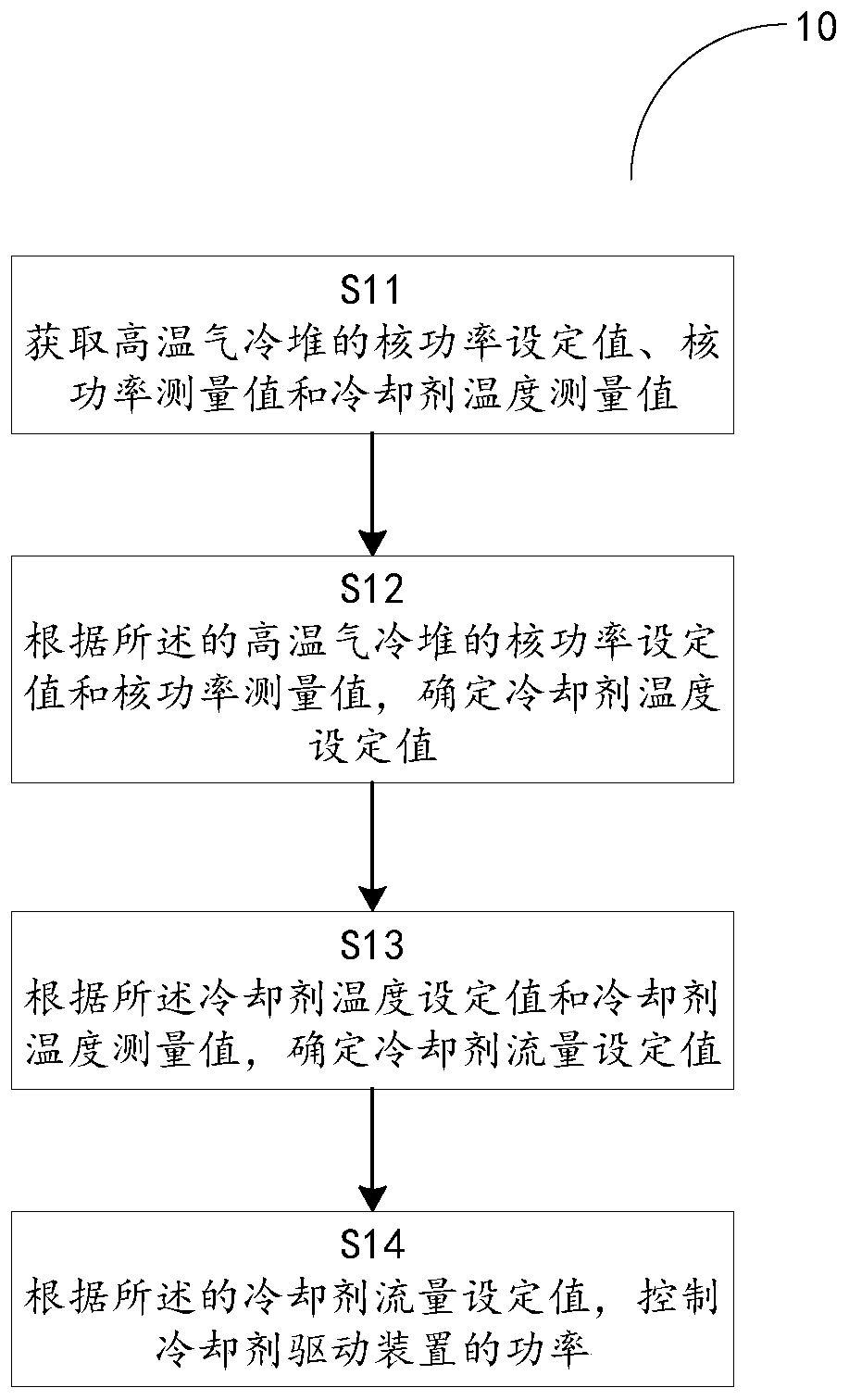
High temperature gas cooled reactor power control method, control system and high temperature gas cooled reactor nuclear power station
ActiveCN110289114APlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationControl powerNuclear engineering
The invention provides a power control method of a high temperature gas cooled reactor, comprising the following steps: acquiring a nuclear power set value of the high temperature gas cooled reactor, a nuclear power measured value and a coolant temperature measured value; determining a coolant temperature set value according to the nuclear power set value and the nuclear power measured value of the high temperature gas cooled reactor; determining a coolant flow set value according to the coolant temperature set value and the coolant temperature measured value; and controlling power of a coolant drive unit according to the coolant flow set value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Combined method for controlling water level and pressure of voltage stabilizer for nuclear power plant of pressurized water reactor
InactiveCN102543232AIncreased level of controlConvenient researchPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationPressurized water reactorNuclear power
The invention relates to a combined method for controlling a water level and pressure of a voltage stabilizer for a nuclear power plant of a pressurized water reactor. The water level and the pressure are completely decoupled through an intensive study according to coupling conditions of the water level and the pressure of the voltage stabilizer. On this basis, the water level and the pressure of the voltage stabilizer are integrally controlled in a combined manner, so as to achieve better control effects. The method disclosed by the invention has a higher practical application value of the water level and the pressure of the voltage stabilizer with power of 900 MW. With the adoption of the method, the advanced intelligent control can be prompted to researches and applications of a nuclear power unit, so that a control level of the unit is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
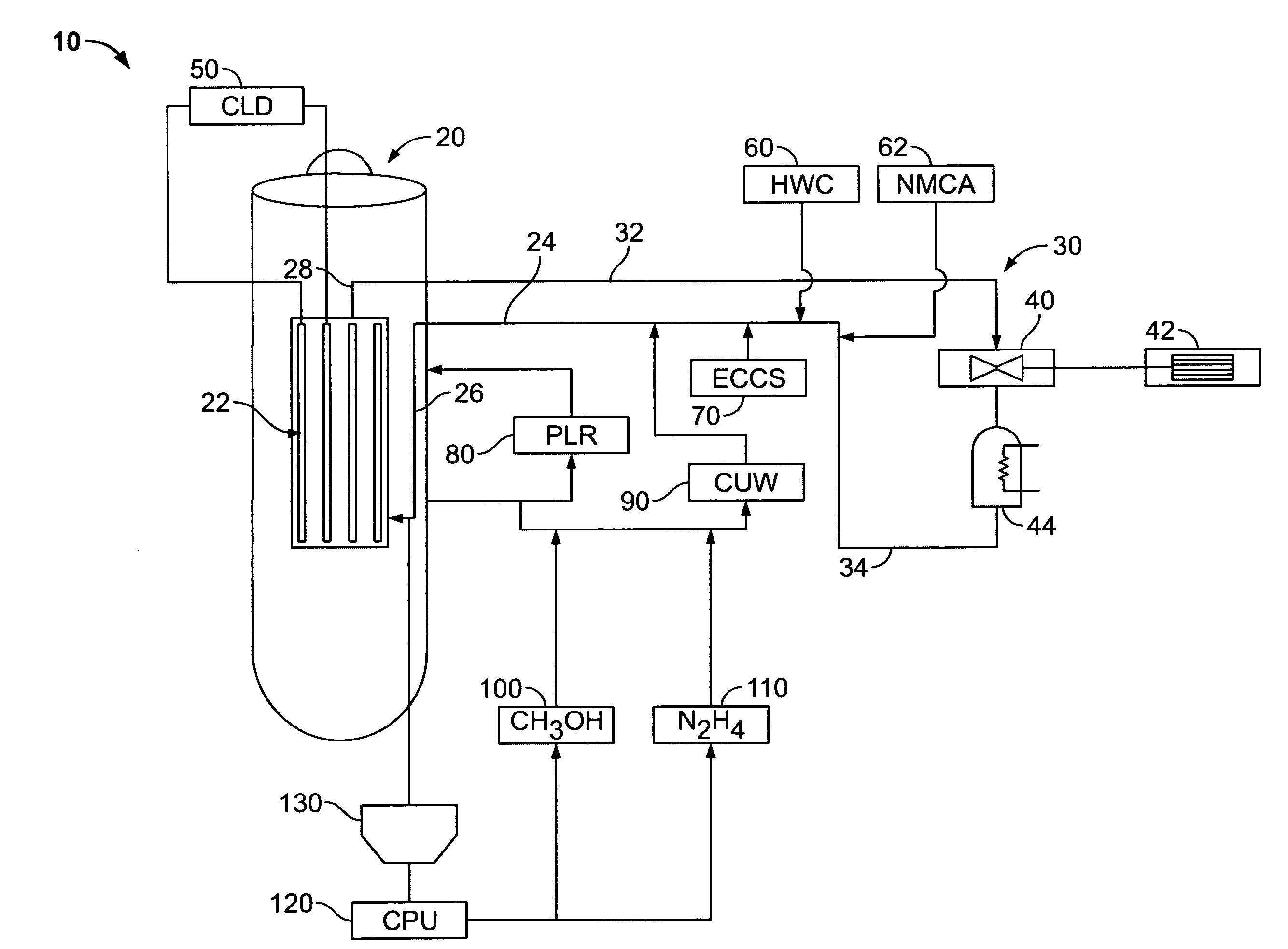
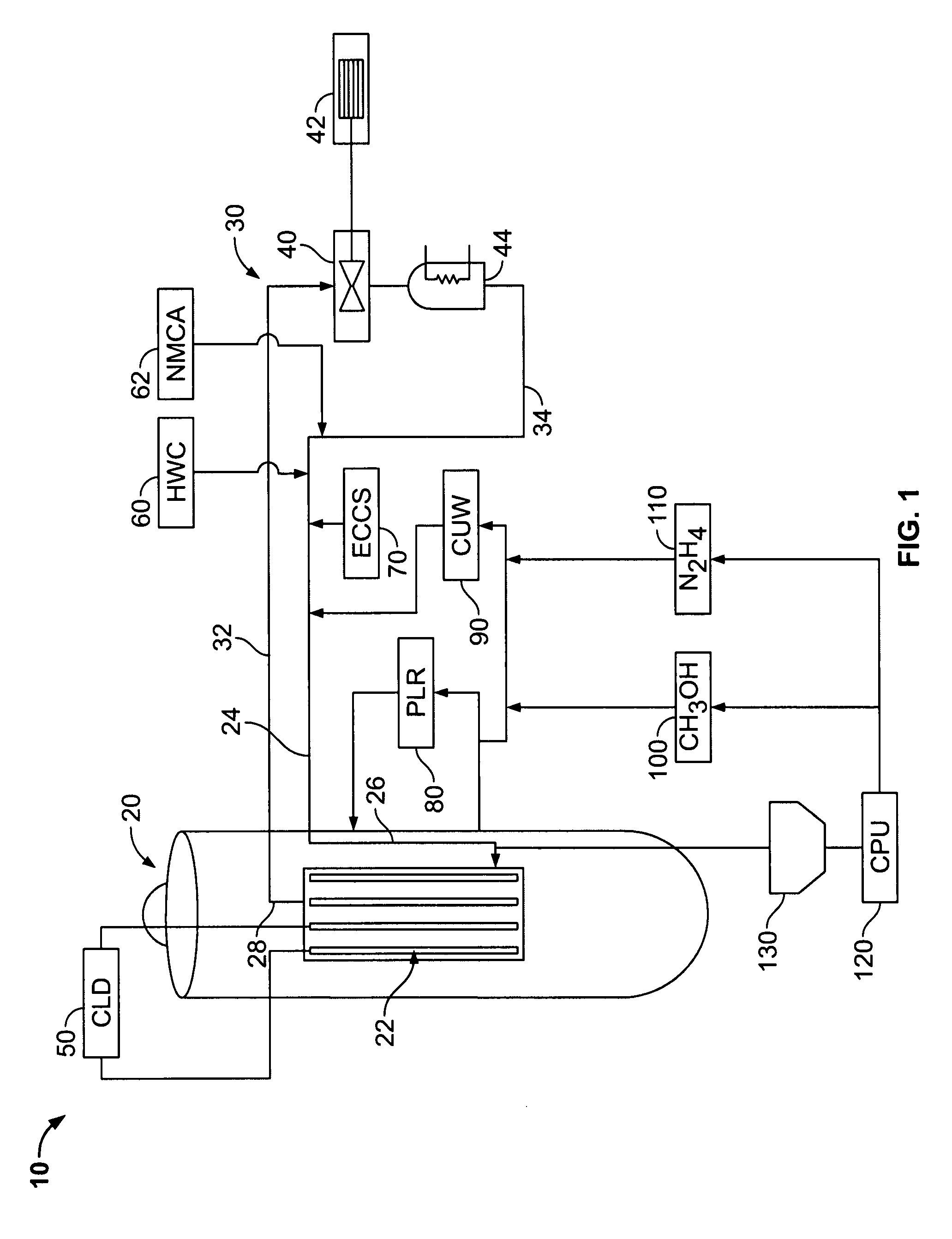
Boiling water reactor nuclear power plant with alcohol injection
ActiveUS20090086878A1Adequate oxidation reductionReduce the amount requiredWater treatment parameter controlPlant parameters regulationAlcoholHydrogen
A nuclear power plant is provided including a BWR, a reactor cooling system cooling the BWR, an HWC hydrogen injection system connected to the reactor cooling system and an alcohol injection system connected to the reactor cooling system. Methods for providing methanol and hydrogen are also provided.
Owner:AREVA GMBH +1
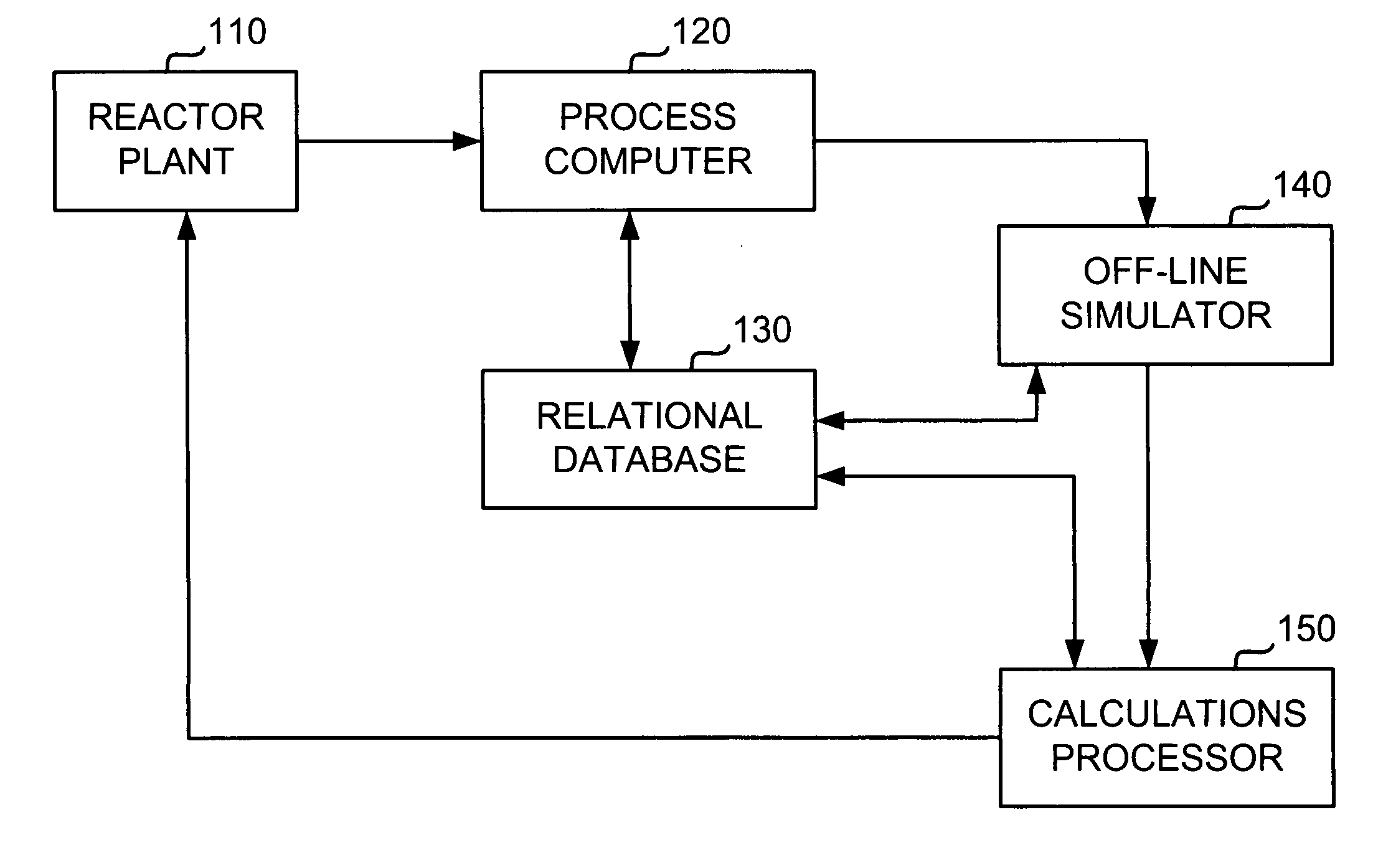
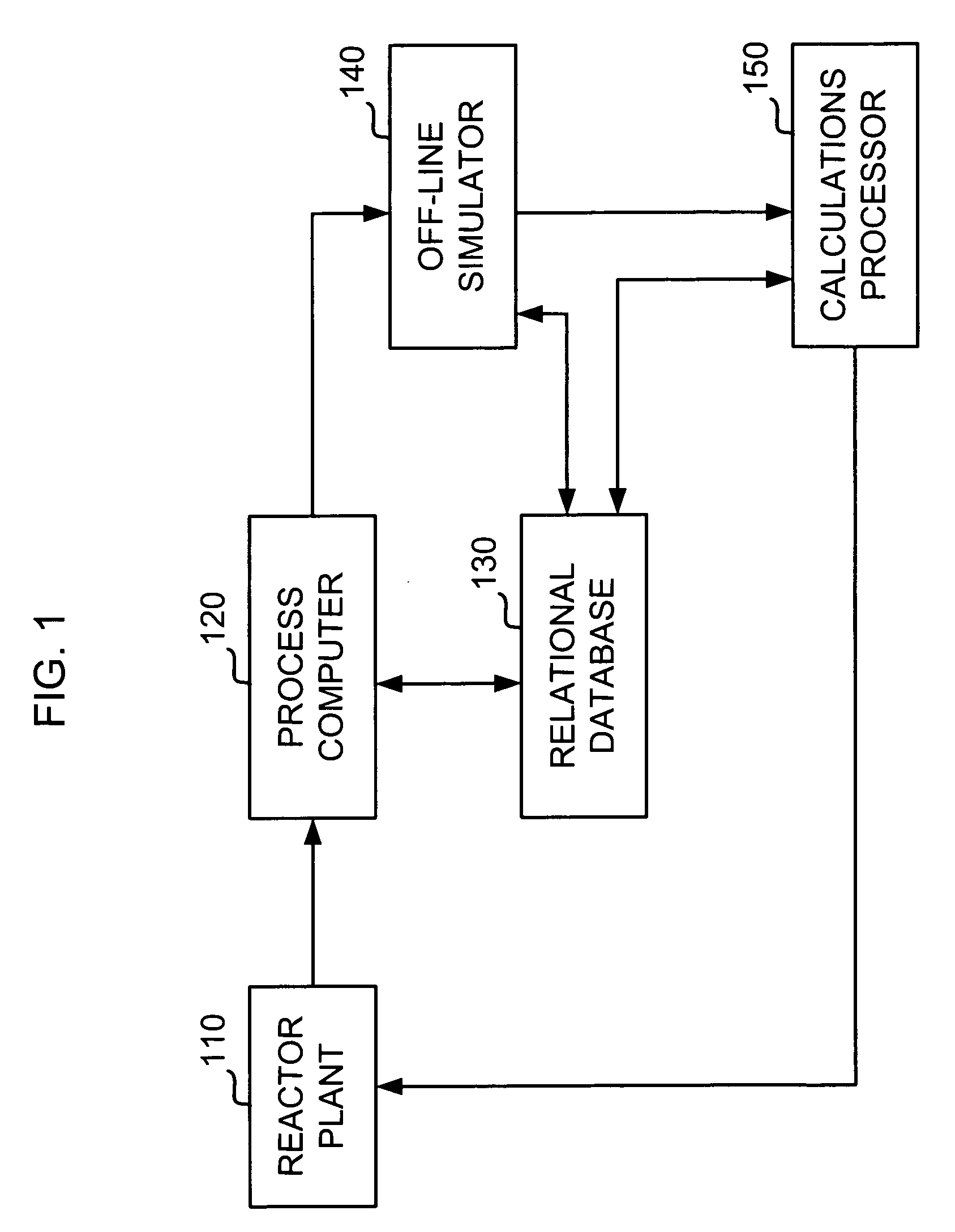
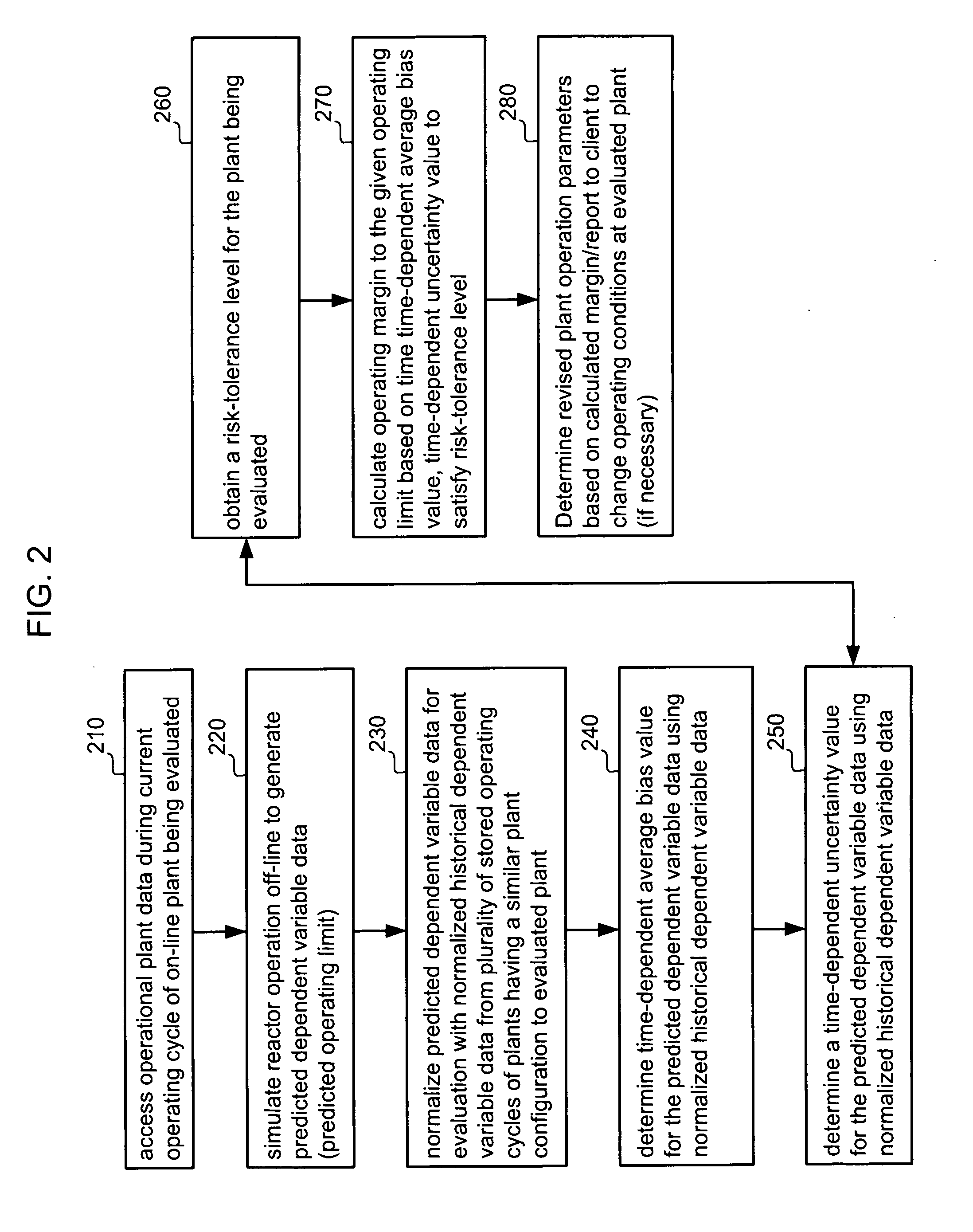
Method of determining margins to operating limits for nuclear reactor operation
ActiveUS20070153958A1Power plant safety arrangementPlant parameters regulationNuclear reactorOperating limit
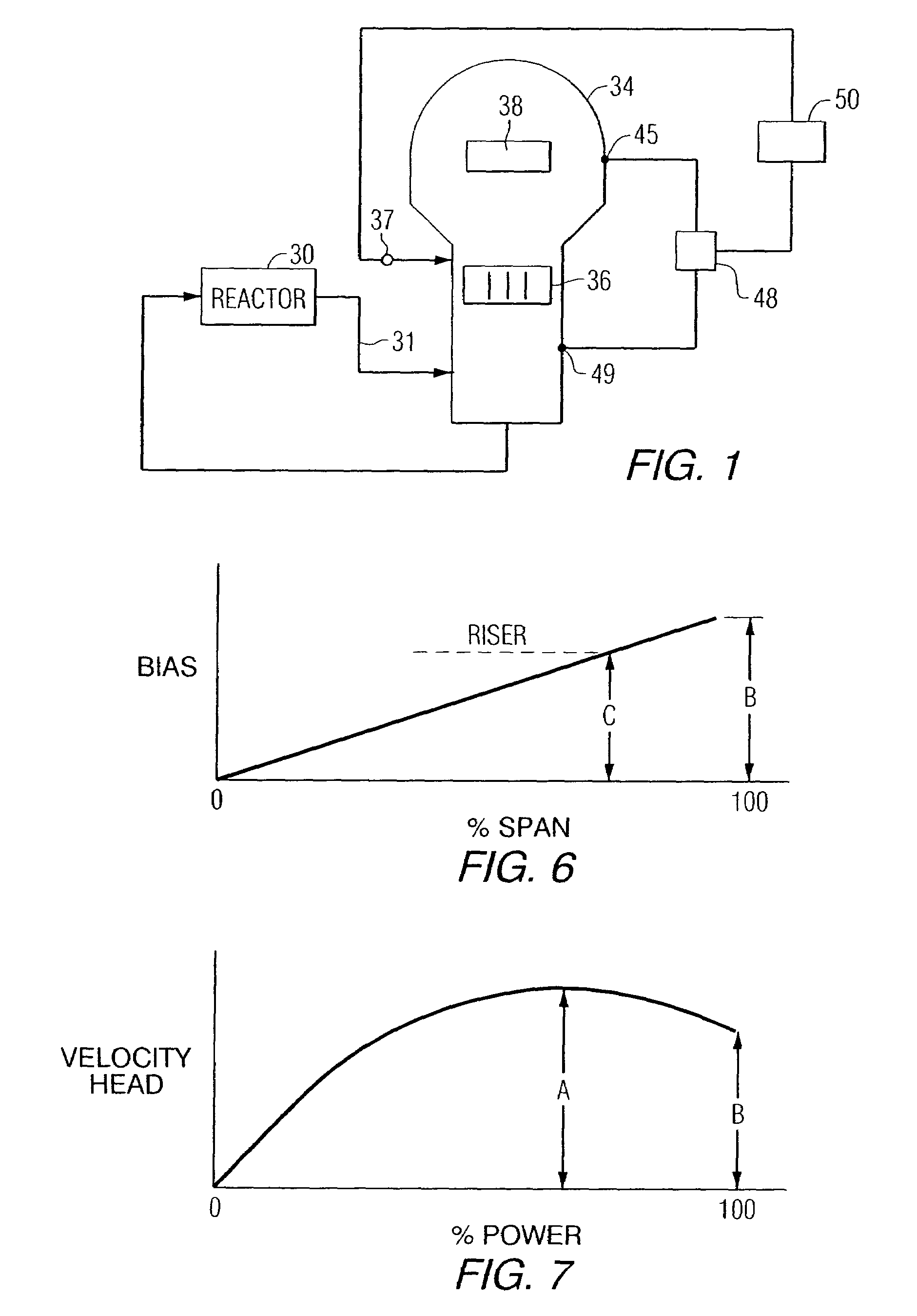
In a method of determining an operating margin to a given operating limit in a nuclear reactor, operational plant data from an on-line nuclear reactor plant is accessed, and reactor operation is simulated off-line using the operational plant data to generate predicted dependent variable data representative of the given operating limit. The predicted dependent variable data is normalized for evaluation with normalized historical dependent variable data from stored operating cycles of plants having a similar plant configuration to the on-line plant. A time-dependent average bias and a time-dependent uncertainty value for the predicted dependent variable data are determined using the normalized historical dependent variable data, and a risk-tolerance level for the on-line plant is obtained. An operating margin to the given operating limit is determined based on the determined time time-dependent average bias value and time-dependent uncertainty value so as to satisfy the risk-tolerance level of the evaluated plant.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
System and method for verifying functions of starting and stopping reactor of high-temperature gas cooled reactor
ActiveCN106981322AEnsure reliabilityEnsure safetyPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationProcess engineeringEngineering
The invention discloses a system and a method for verifying functions of a starting and stopping reactor of a high-temperature gas cooled reactor. A secondary side inlet of a steam generator is communicated with an outlet of a secondary circuit main water supply system; an outlet of an auxiliary boiler is divided into two paths, wherein one path is communicated with an inlet of a steam superheater; the other path, an outlet of the steam superheater and an outlet of the steam generator are subjected to pipe combining through a pipeline and then divided into two paths, wherein one path is communicated with an inlet of a steam separator; the other path is communicated with an inlet of a main steam by-pass; a steam side outlet of the steam separator is communicated with an inlet of the main steam by-pass; a water draining side outlet of the steam separator is communicated with an inlet of a condenser; and an outlet of the main steam by-pass is communicated with the condenser. The system and the method can be used for verifying the functions of the starting and stopping reactor before a unit is started and operated, thereby guaranteeing the reliability and the safety in the process of starting and stopping a high-temperature gas cooled reactor unit.
Owner:XIAN THERMAL POWER RES INST CO LTD
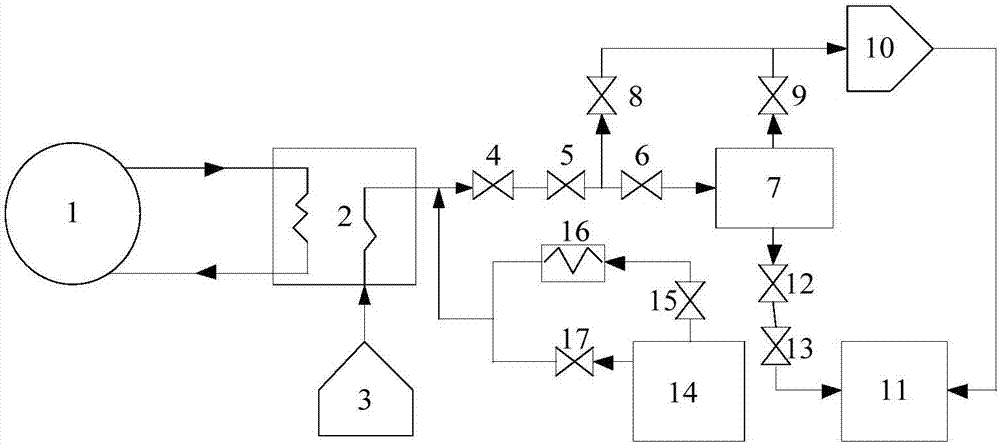
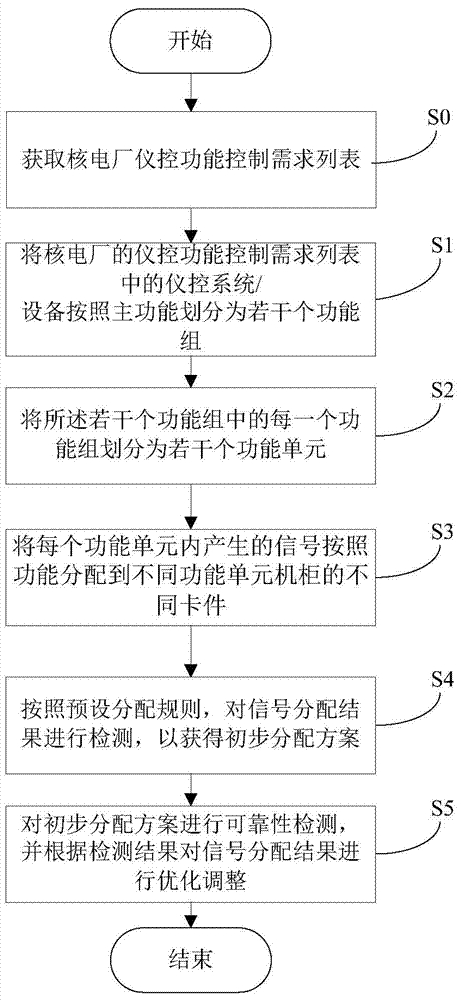
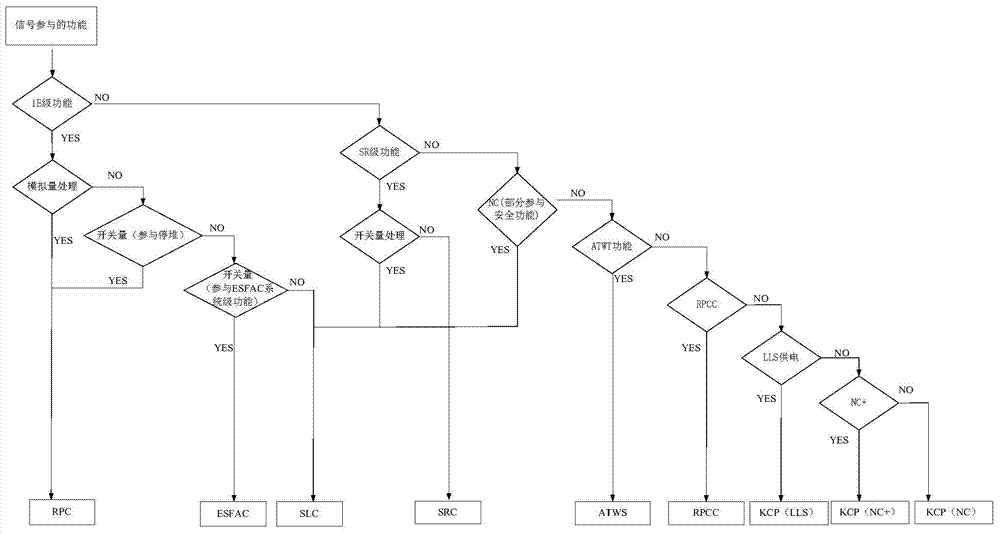
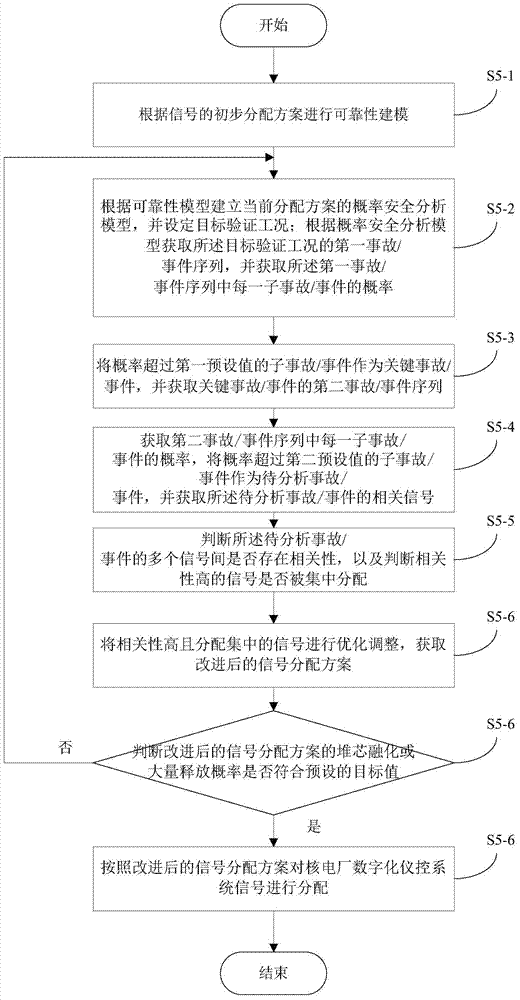
Signal distribution method and signal distribution system of digital instrument control system (DCS) of nuclear power plant
ActiveCN104240781AReduce security risksMinimize potential risksPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear powerDistribution method
The invention discloses a signal distribution method and a signal distribution system of a digital instrument control system (DCS) of a nuclear power plant. The signal distribution method includes: acquiring an instrument control function control demand list of the nuclear power plant; dividing the instrument system / equipment into a plurality of function groups in the instrument control function control demand list of the nuclear power plant according the main functions; distributing each function group of the function groups into a plurality of function units; distributing signals generated form the function units into different cards of different function unit cabinets; according preset distribution rules, detecting signal distribution results to acquire initial distribution modes; subjecting the initial distribution modes to reliability detection and subjecting the signal distribution results to optimization and adjustment according to detection results. By the signal distribution method and system, correlation influence among the function signals can be lowered, and security risk of the nuclear power plant due to potential failure / fault of the digital instrument control system of the nuclear power plant is lowered.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com