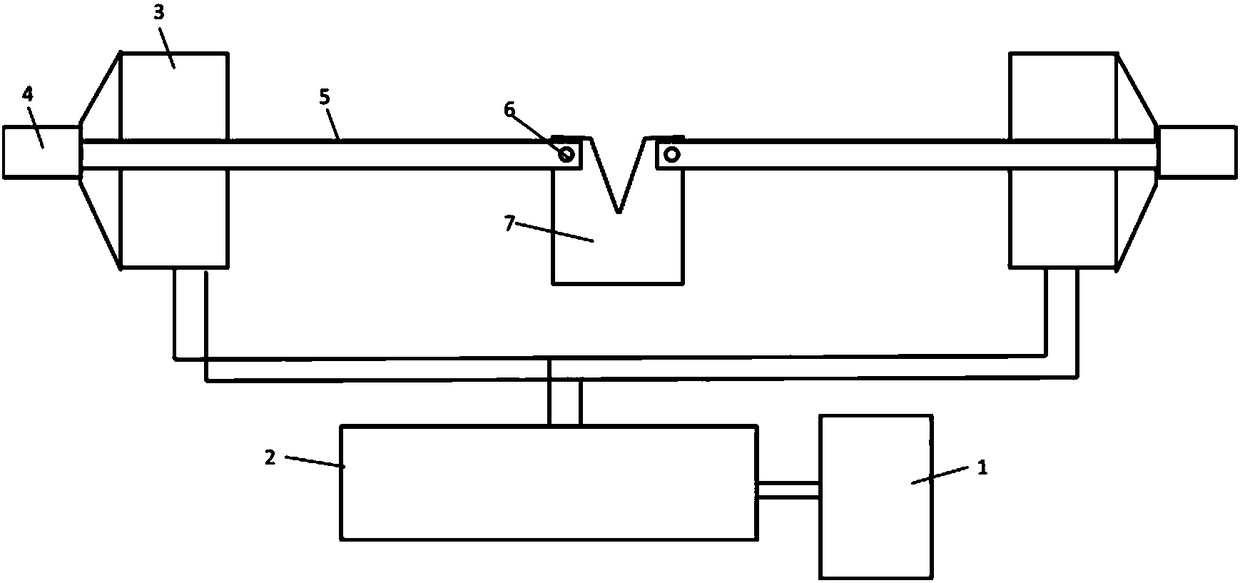
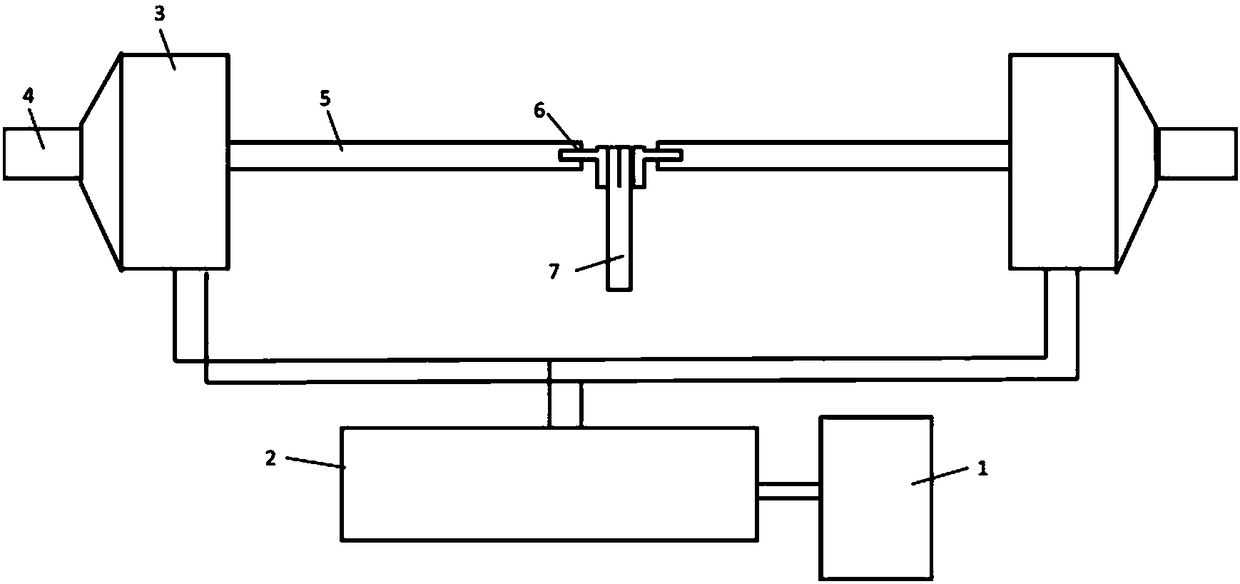
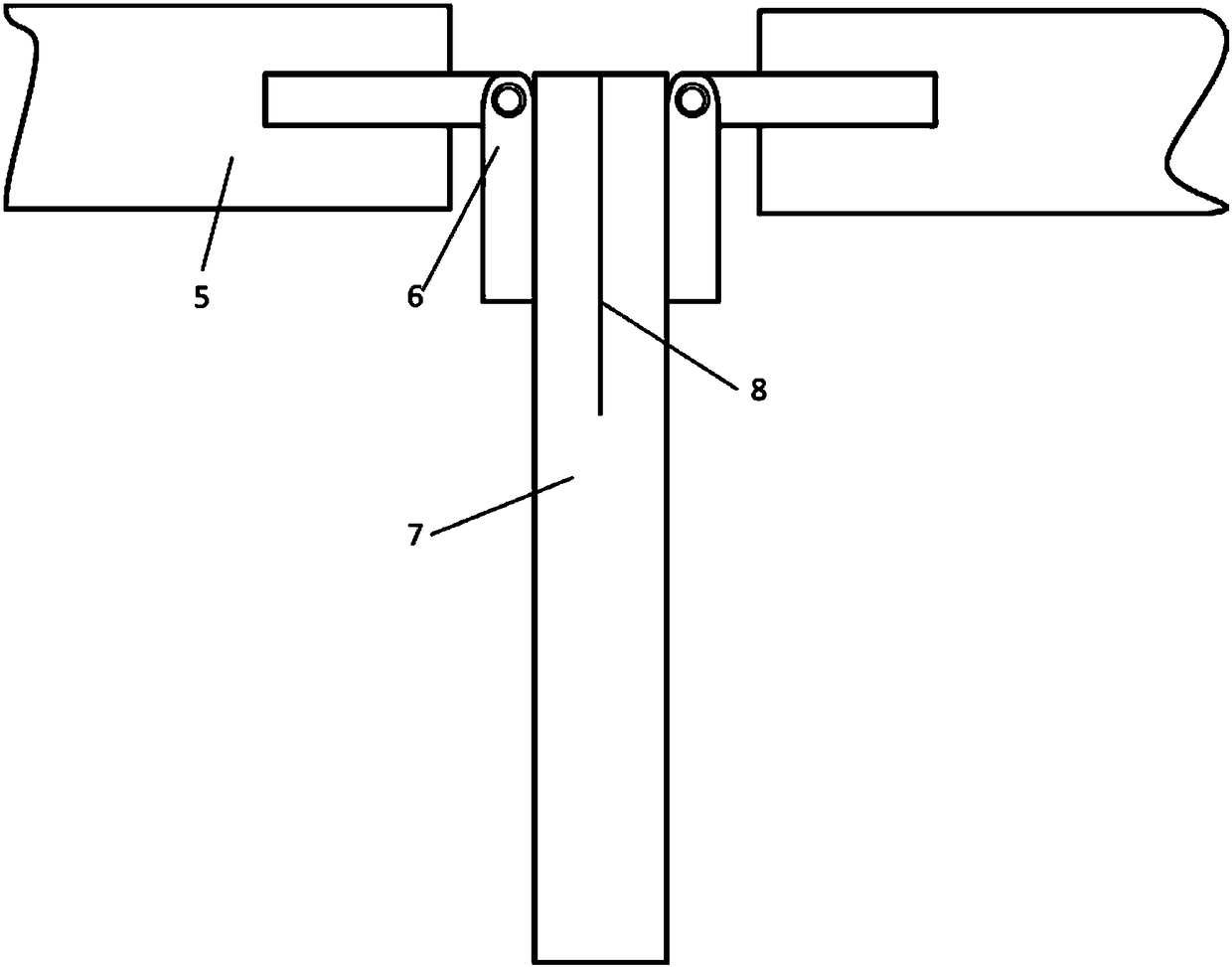
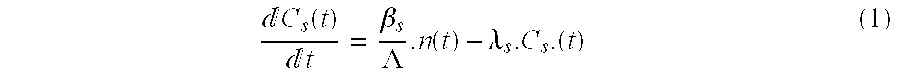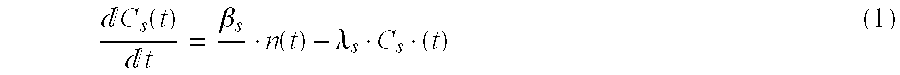Patents
Literature
88 results about "Spallation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
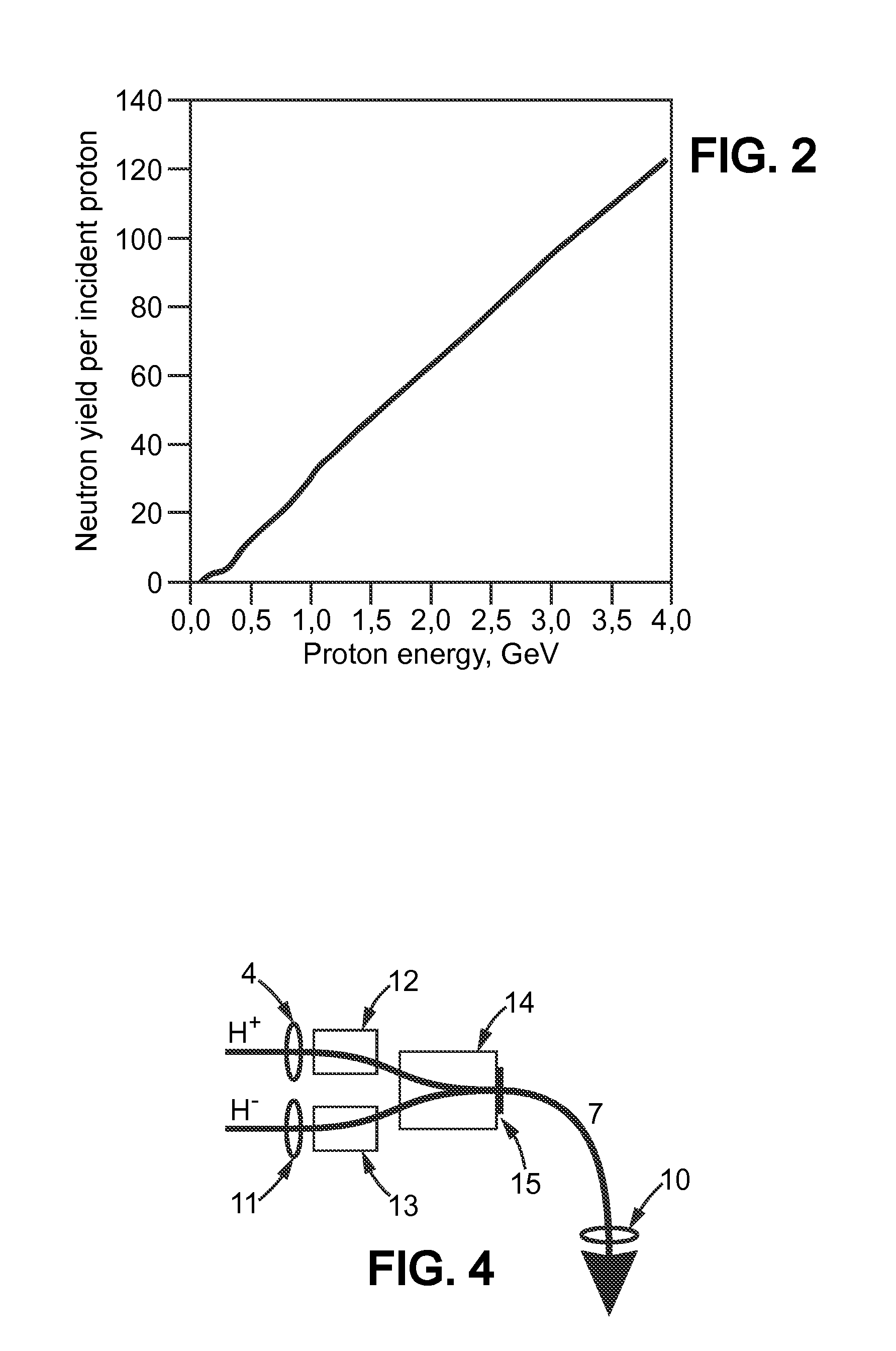
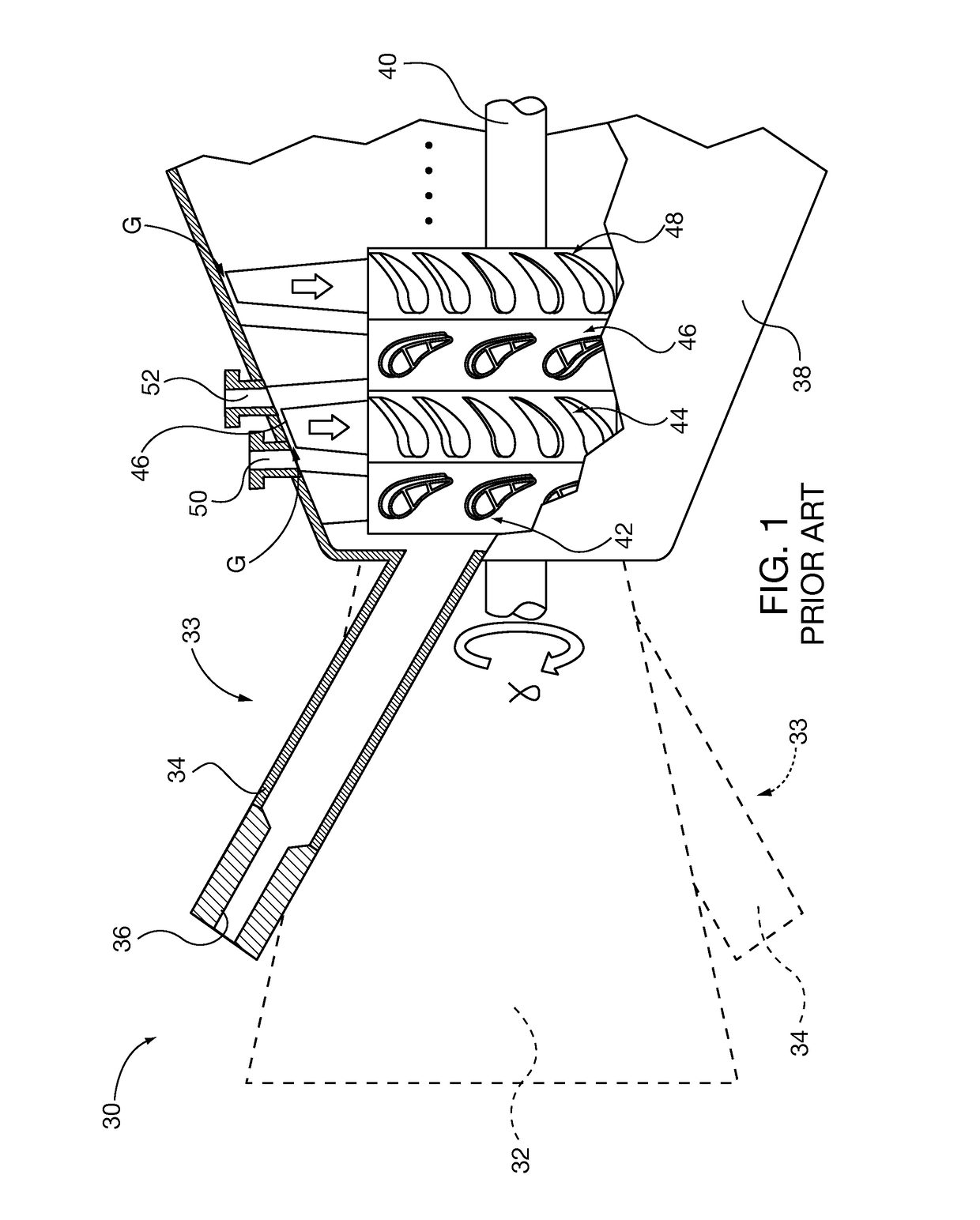
Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary physics, spallation describes meteoritic impacts on a planetary surface and the effects of stellar winds and cosmic rays on planetary atmospheres and surfaces. In the context of mining or geology, spallation can refer to pieces of rock breaking off a rock face due to the internal stresses in the rock; it commonly occurs on mine shaft walls. In the context of anthropology, spallation is a process used to make stone tools such as arrowheads by knapping. In nuclear physics, spallation is the process in which a heavy nucleus emits numerous nucleons as a result of being hit by a high-energy particle, thus greatly reducing its atomic weight.
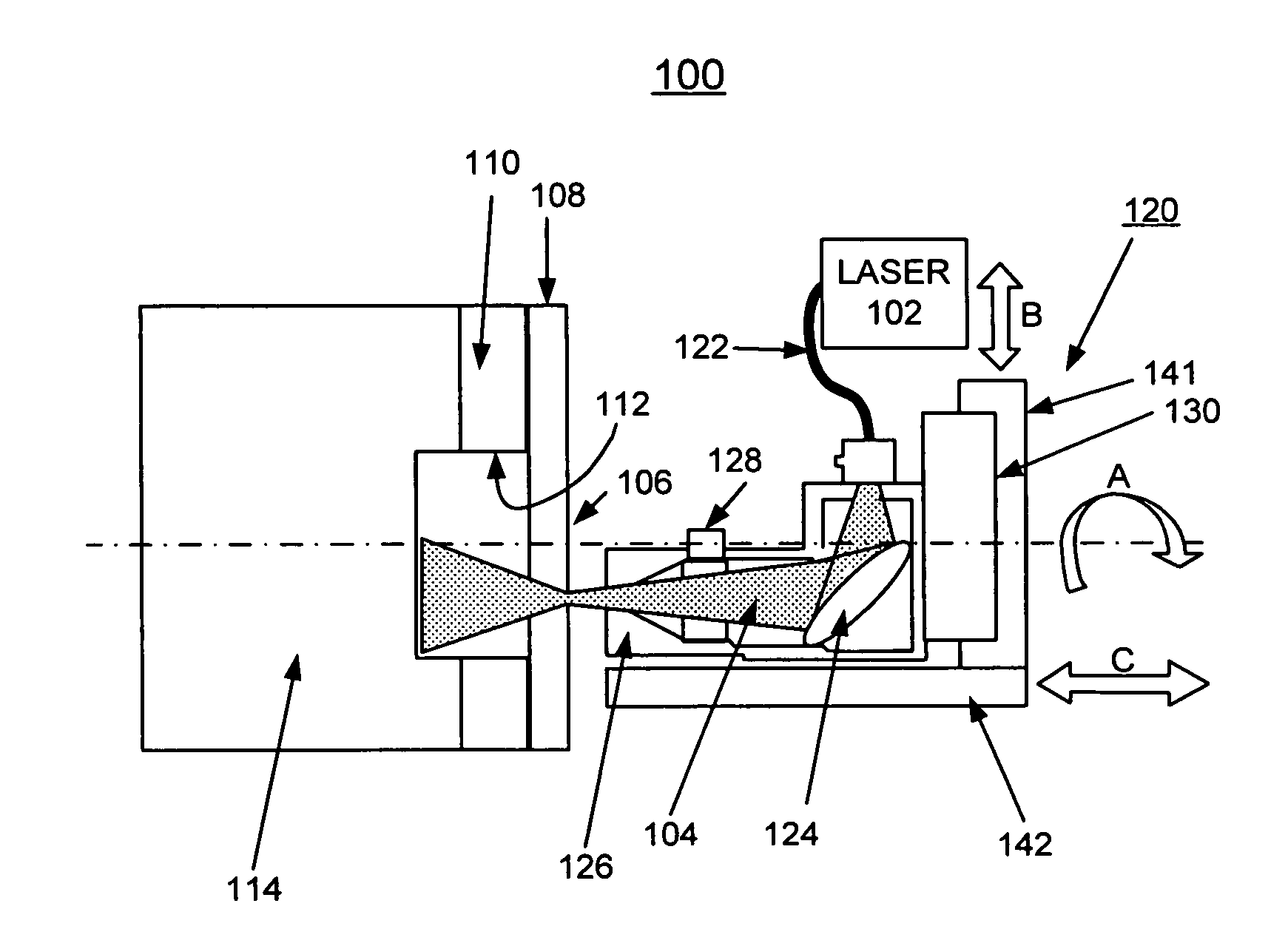
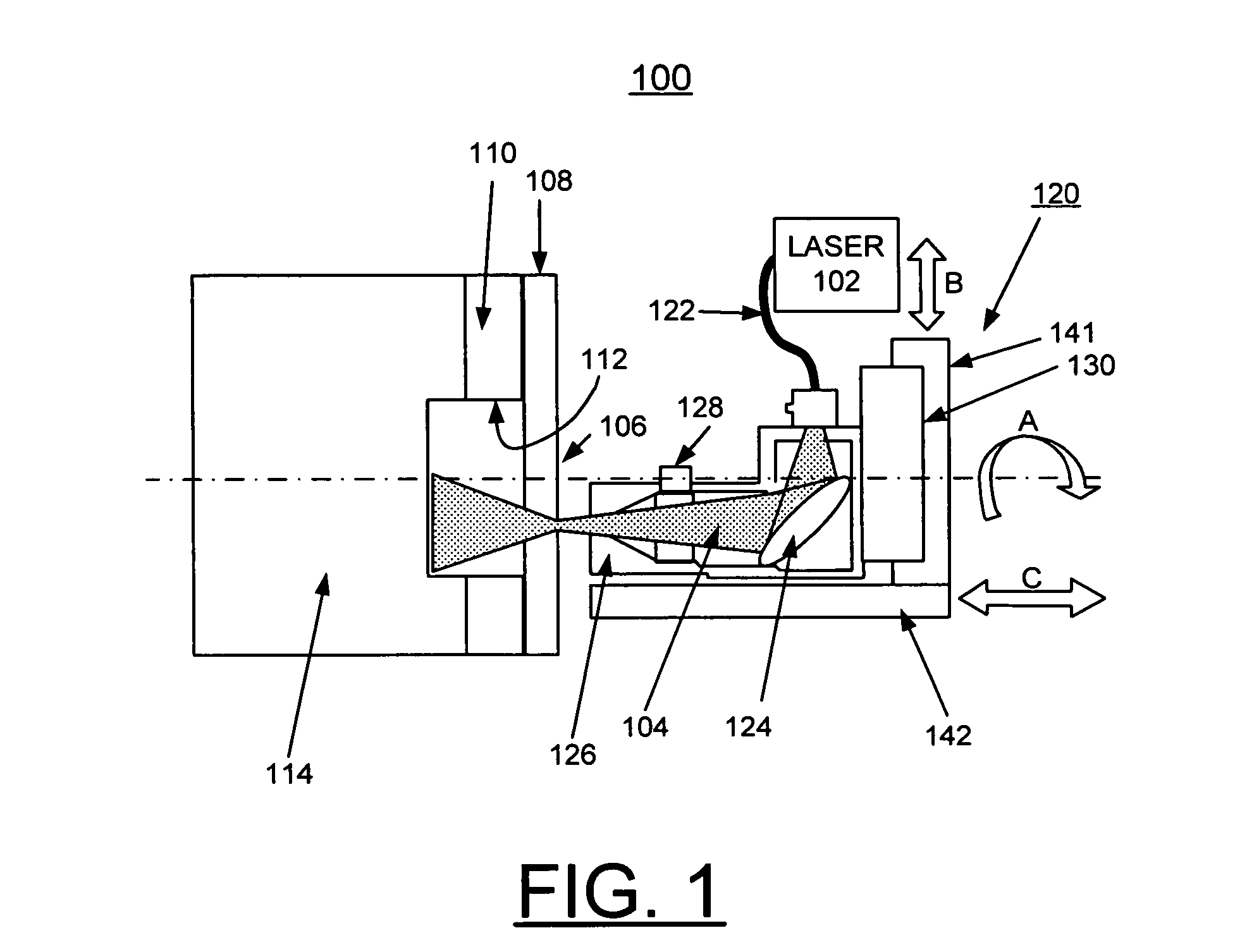
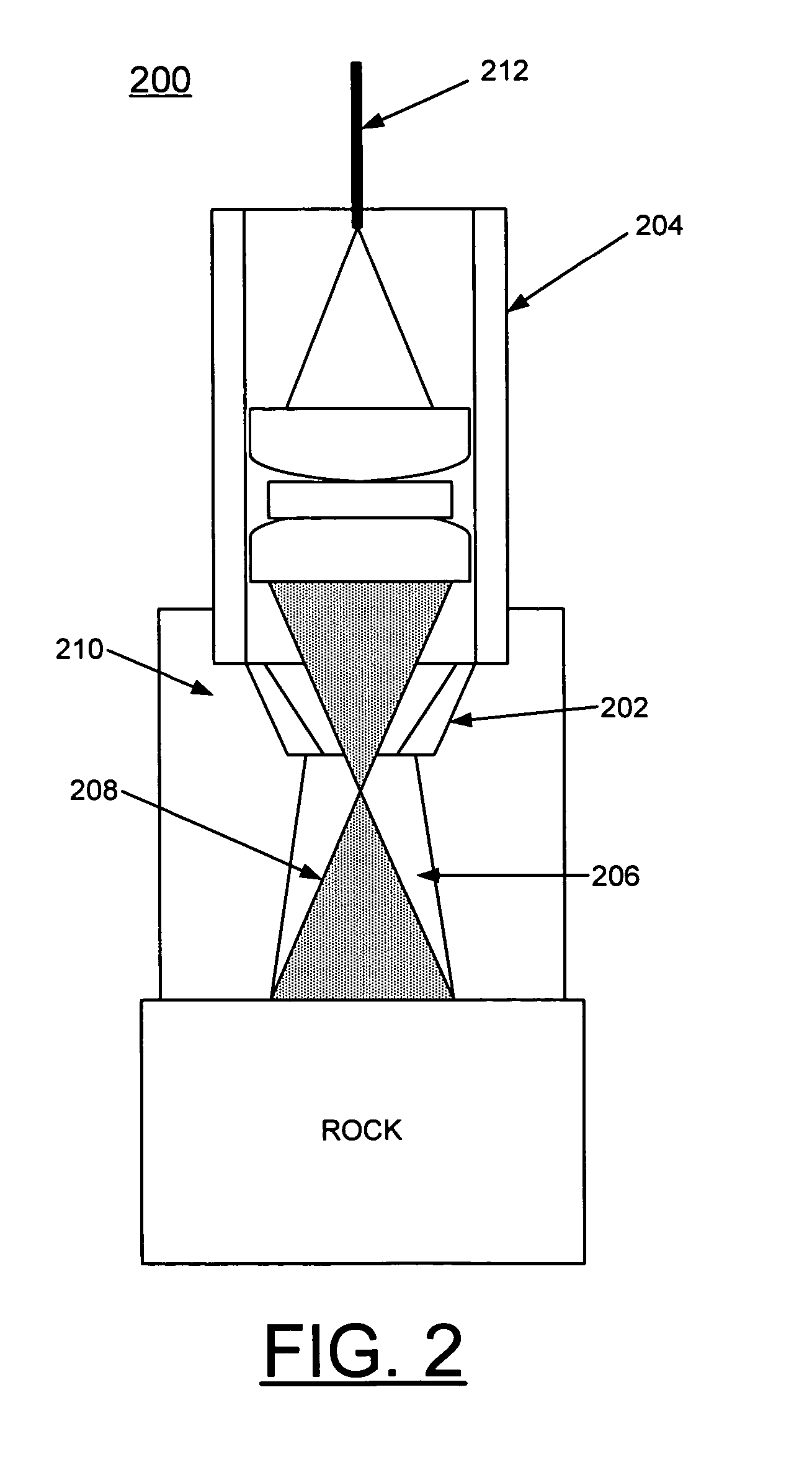
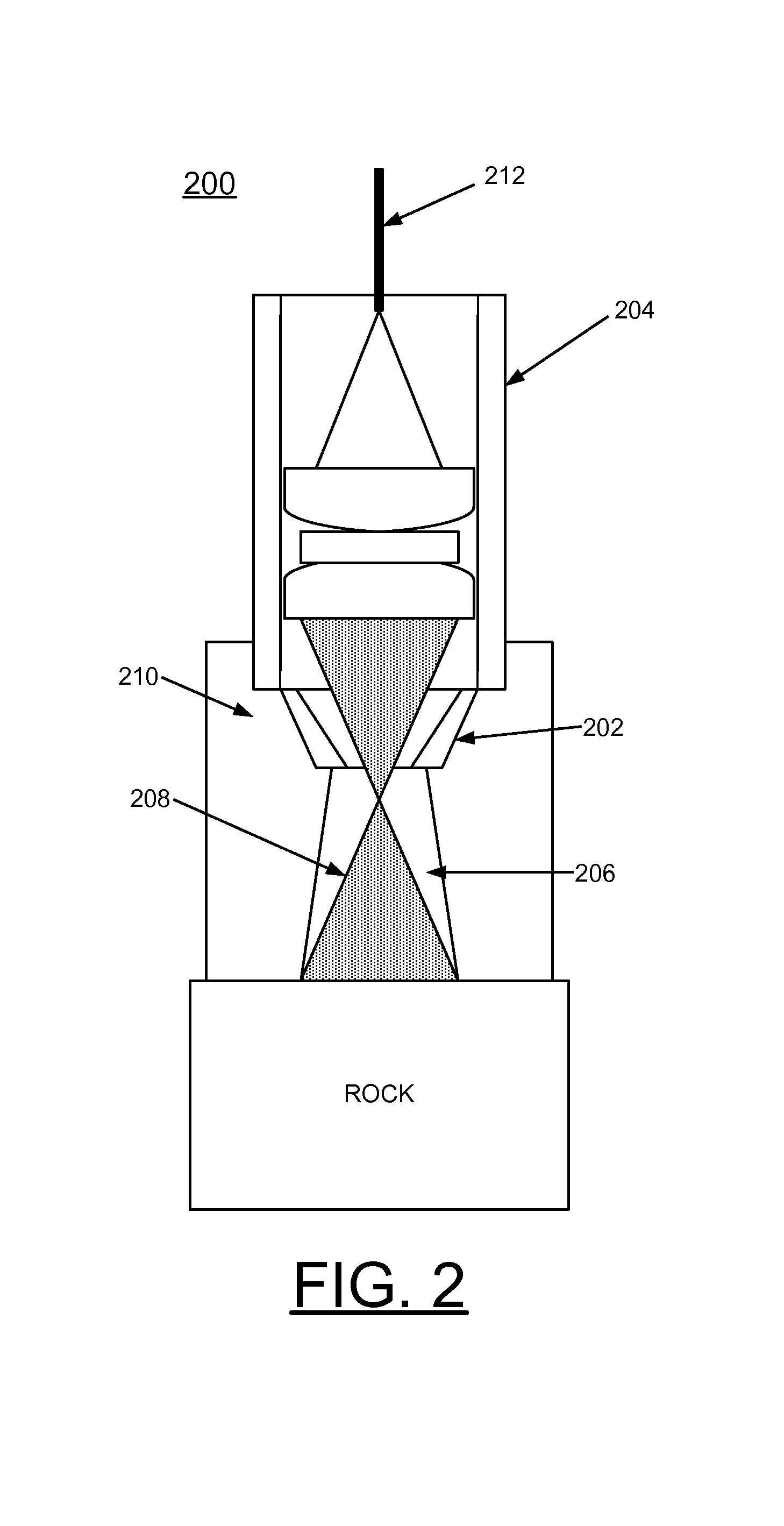
Methods of using a laser to perforate composite structures of steel casing, cement and rocks
ActiveUS20060231257A1Improve breathabilityReduce hole taperingDisloding machinesThermal drillingHigh power lasersSmall fragment
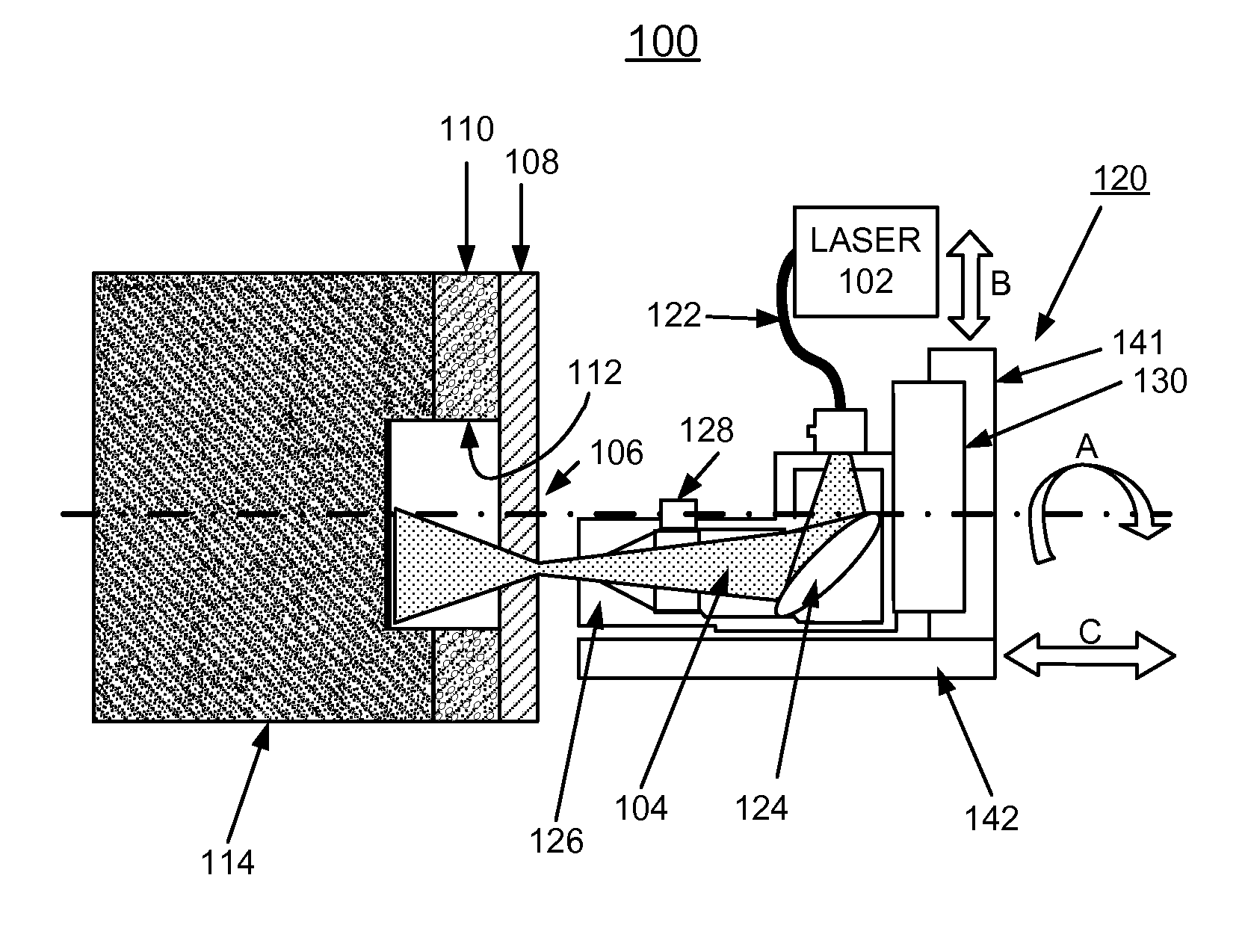
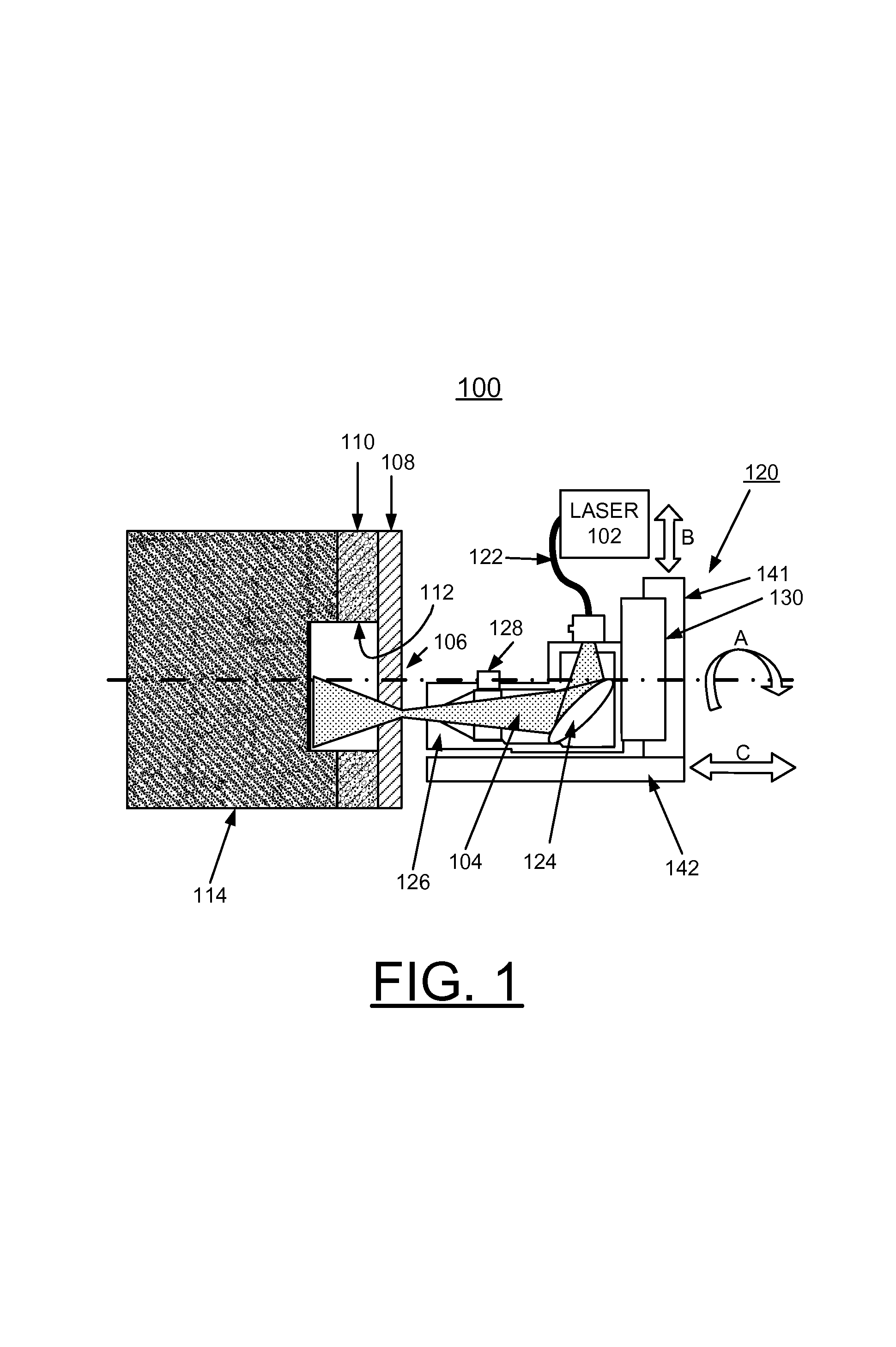
Apparatus and methods of using lasers are provided for the perforation of oil and gas well casings and rock formations. A rock removal process called laser spallation is provided that utilizes a combination of laser-induced thermal stress and laser induced superheated steam explosions just below the surface of the laser / rock interaction to spall or fracture the rock into small fragments that can then be easily removed from the rock formation. The use of high power laser beams of kilowatt level is provided to rapidly cut the steel casings and perforate into the formation. Techniques of the invention increase permeability and reduce hole tapering while perforating a deep hole in reservoir rock formations.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
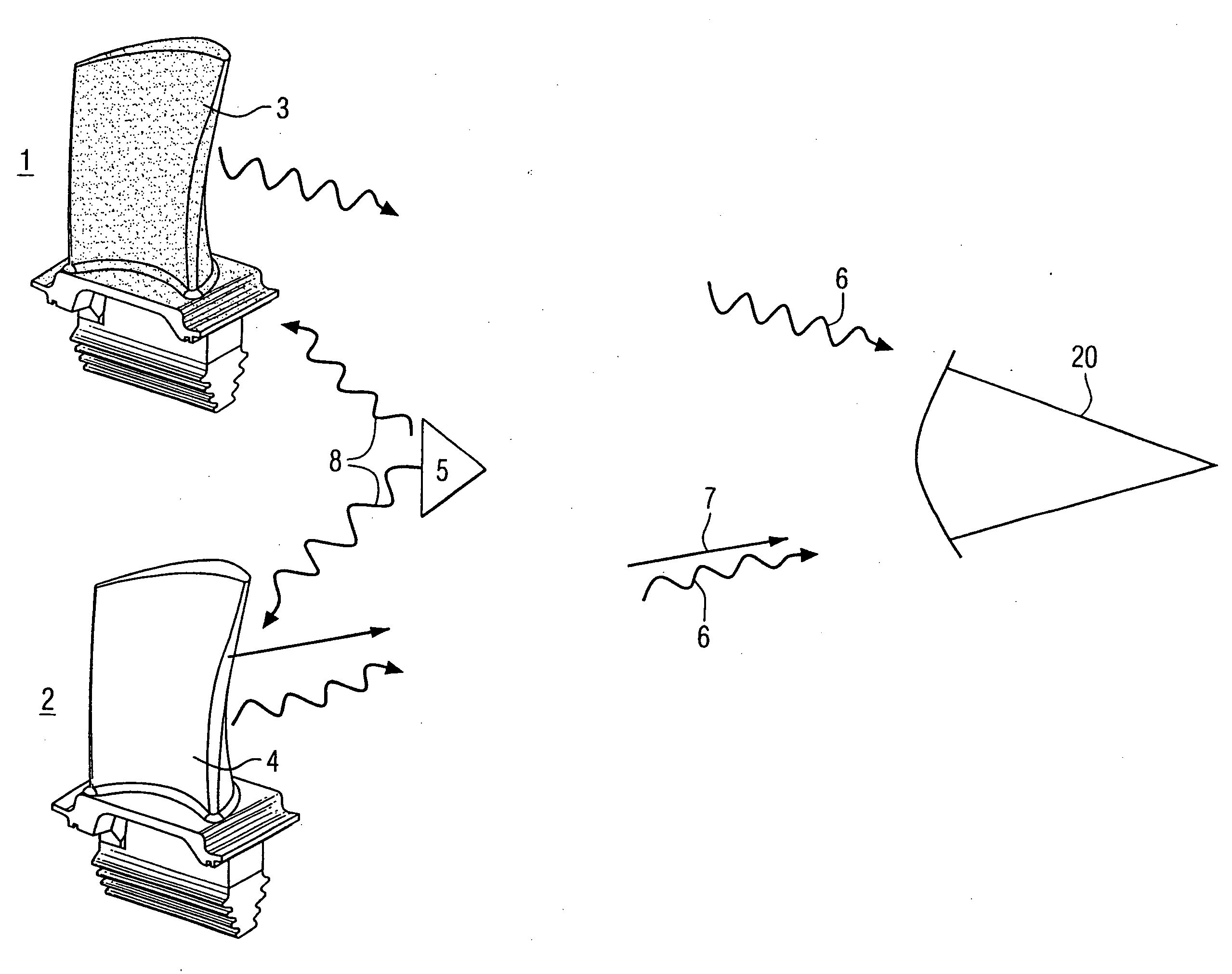
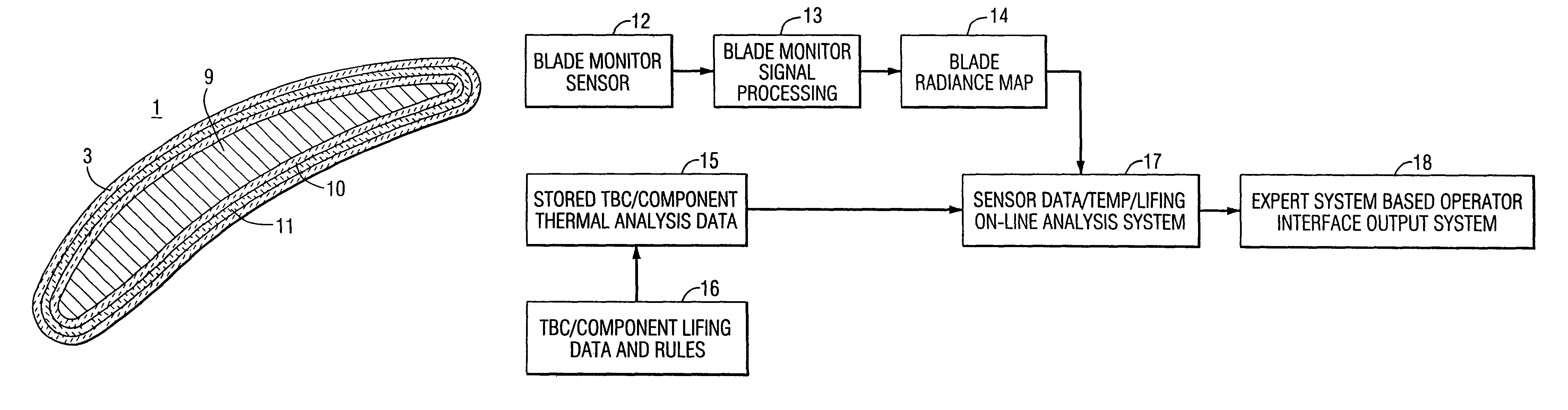
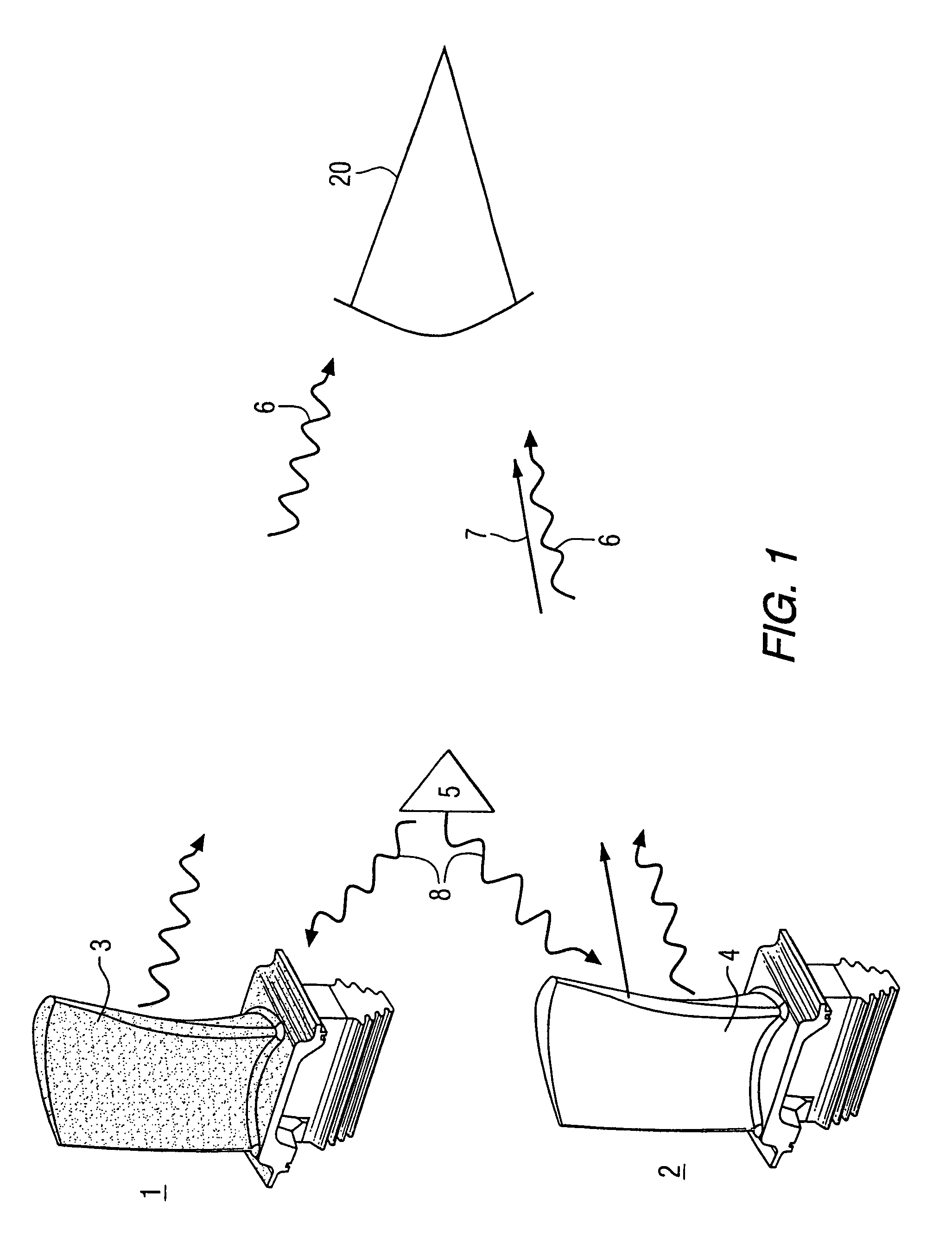
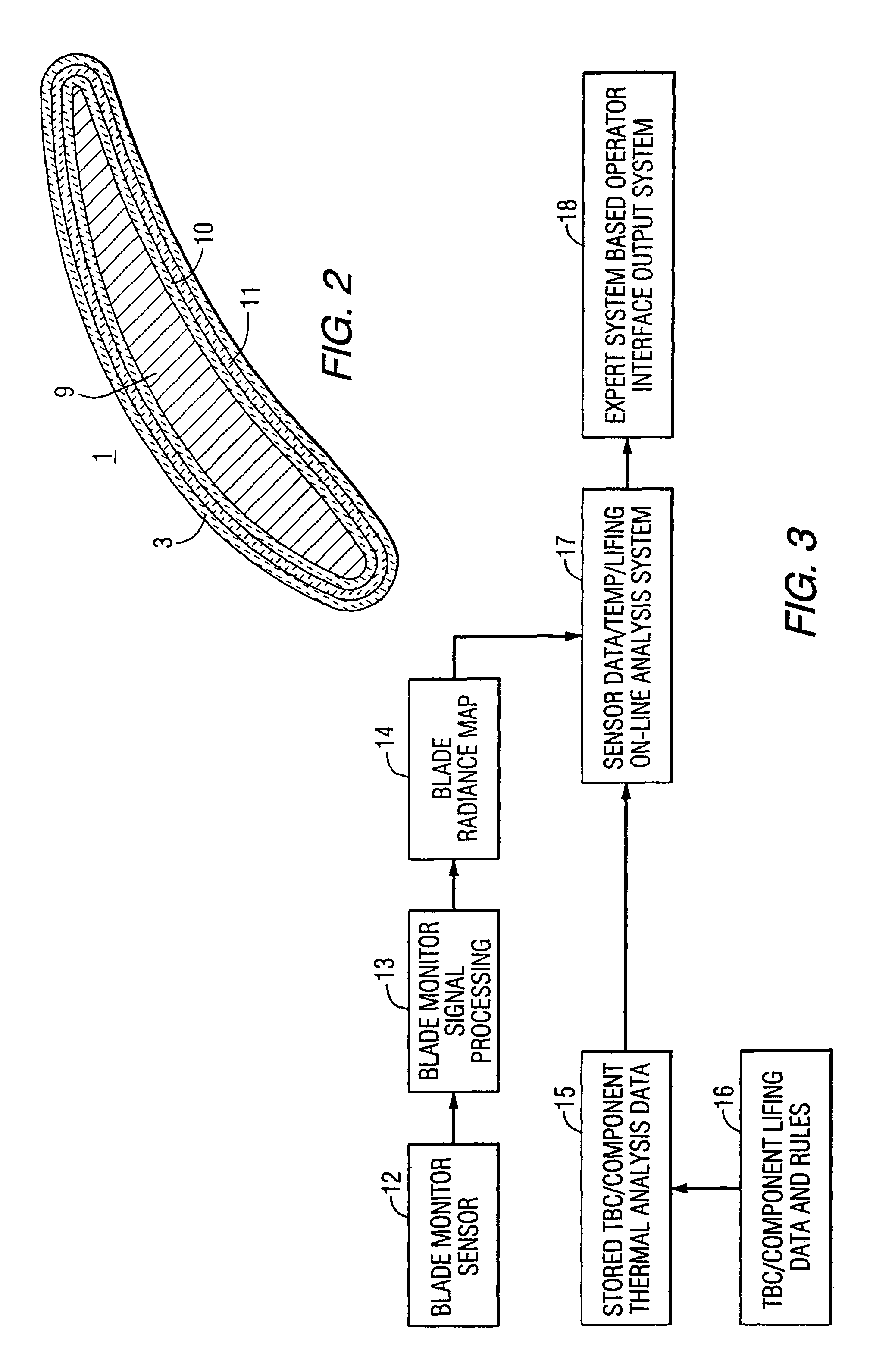
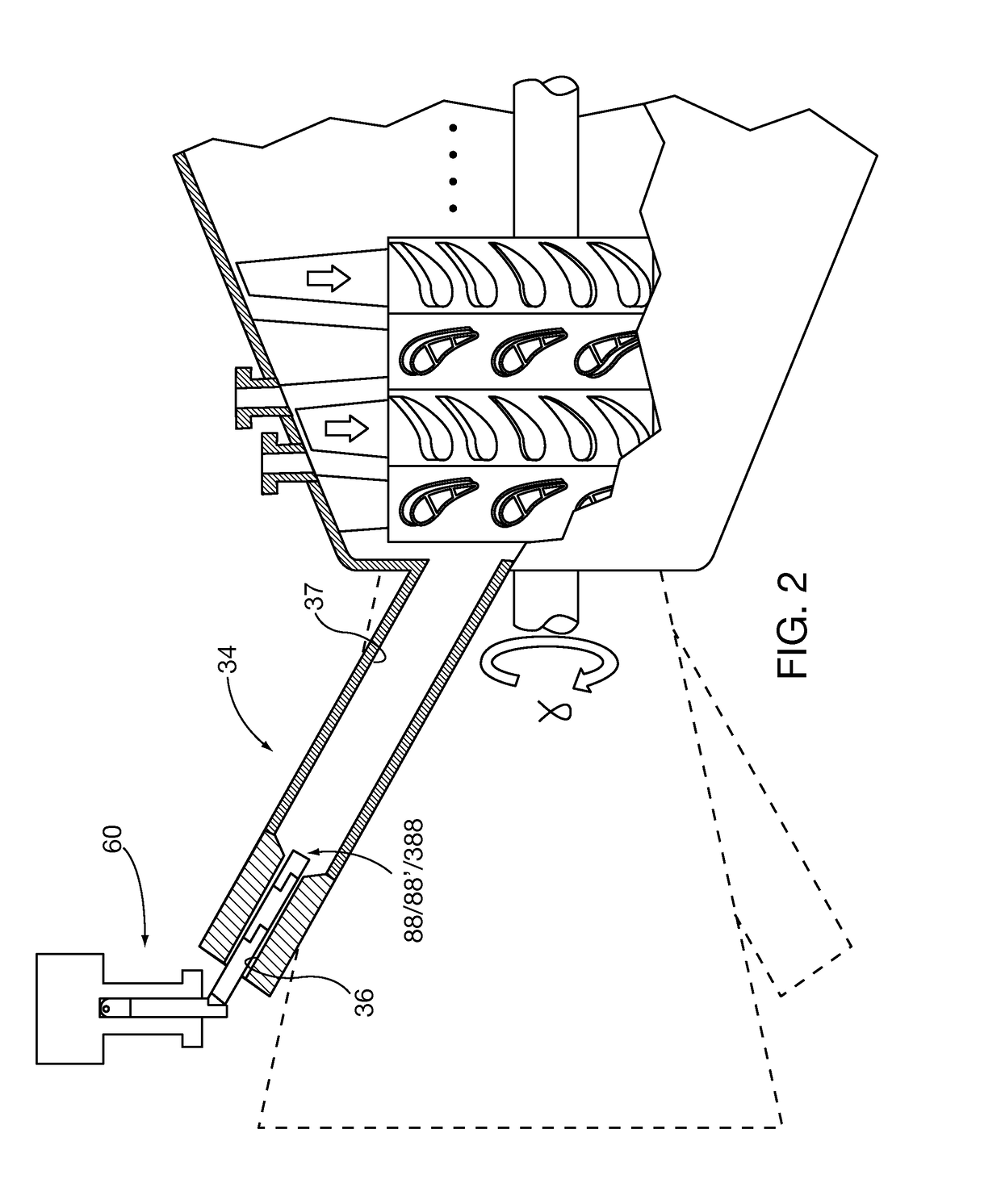
Method and apparatus for measuring on-line failure of turbine thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS20090312956A1Detect degradationAvoid severe repairThermometer detailsPlug gaugesTurbine bladeEngineering
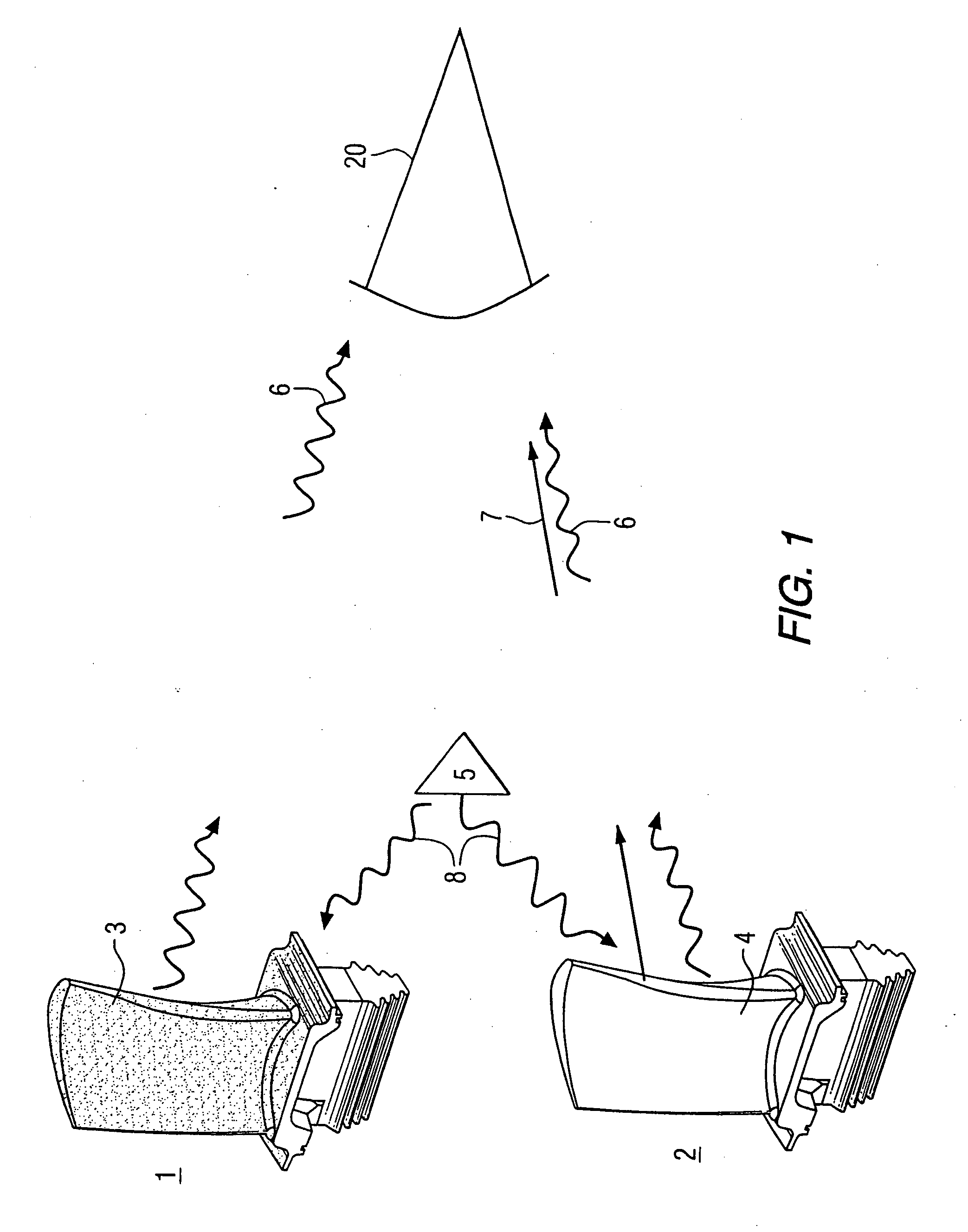
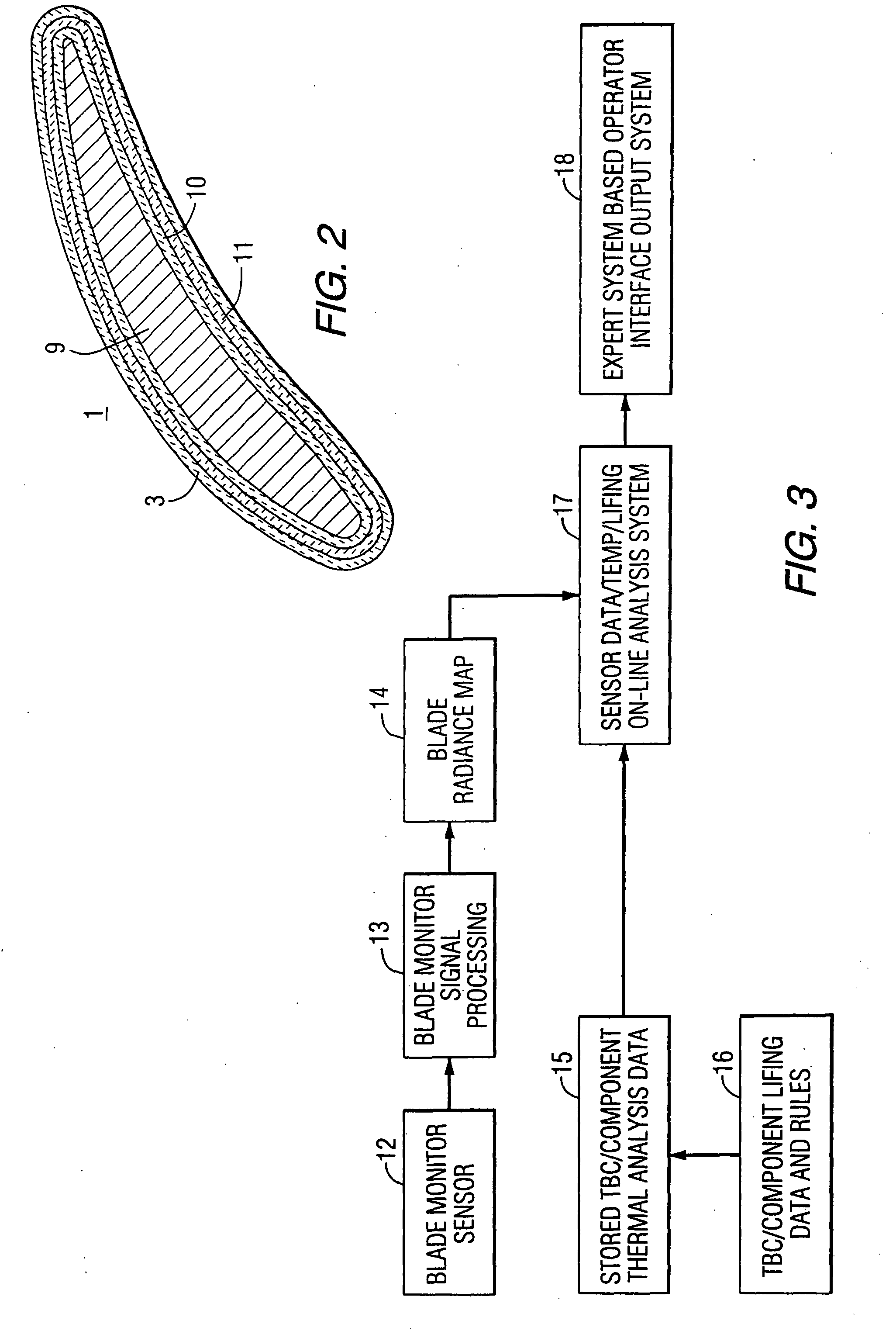
A method of remotely monitoring the radiant energy (6) emitted from a turbine component such as a turbine blade (1) having a low-reflective surface coating (3) which may be undergoing potential degradation is used to determine whether erosion, spallation, delamination, or the like, of the coating (3) is occurring.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Methods of using a laser to perforate composite structures of steel casing, cement and rocks
ActiveUS7487834B2Improve breathabilityReduce hole taperingDisloding machinesThermal drillingHigh power lasersSmall fragment
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
Method and apparatus for measuring on-line failure of turbine thermal barrier coatings
InactiveUS7690840B2Improve efficiencyAvoid maintenanceThermometer detailsPlug gaugesTurbine bladeEngineering
A method of remotely monitoring the radiant energy (6) emitted from a turbine component such as a turbine blade (1) having a low-reflective surface coating (3) which may be undergoing potential degradation is used to determine whether erosion, spallation, delamination, or the like, of the coating (3) is occurring.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
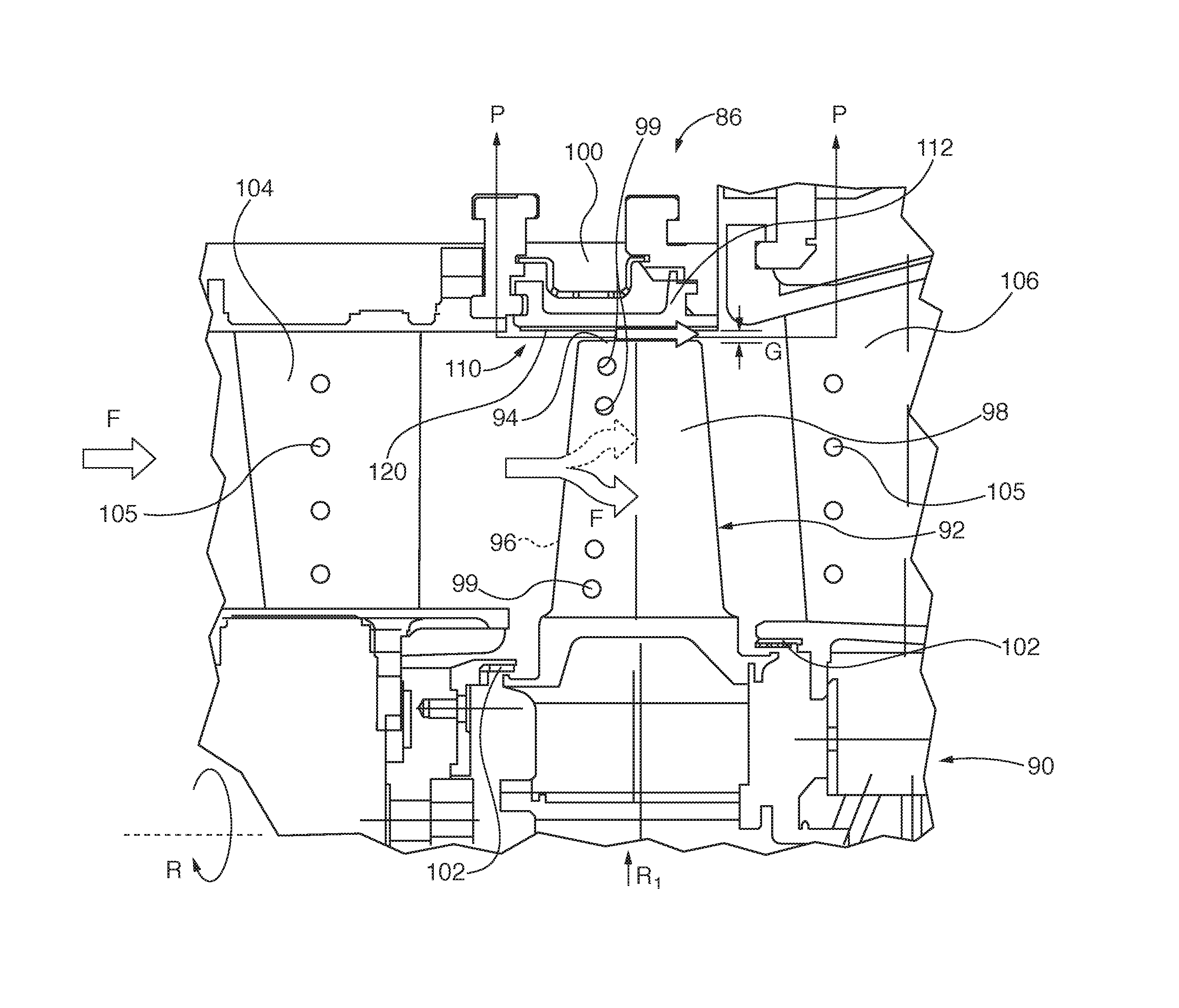
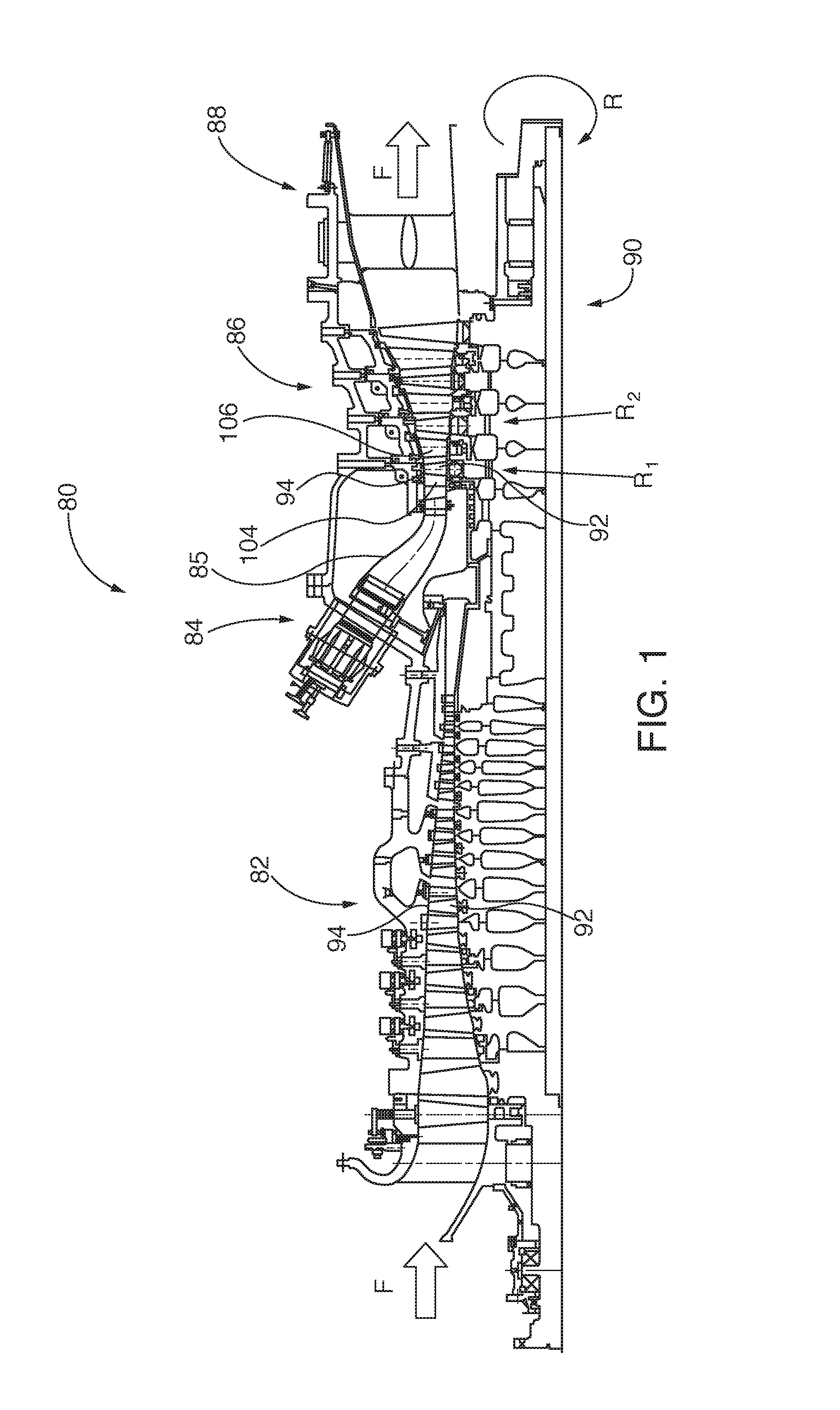
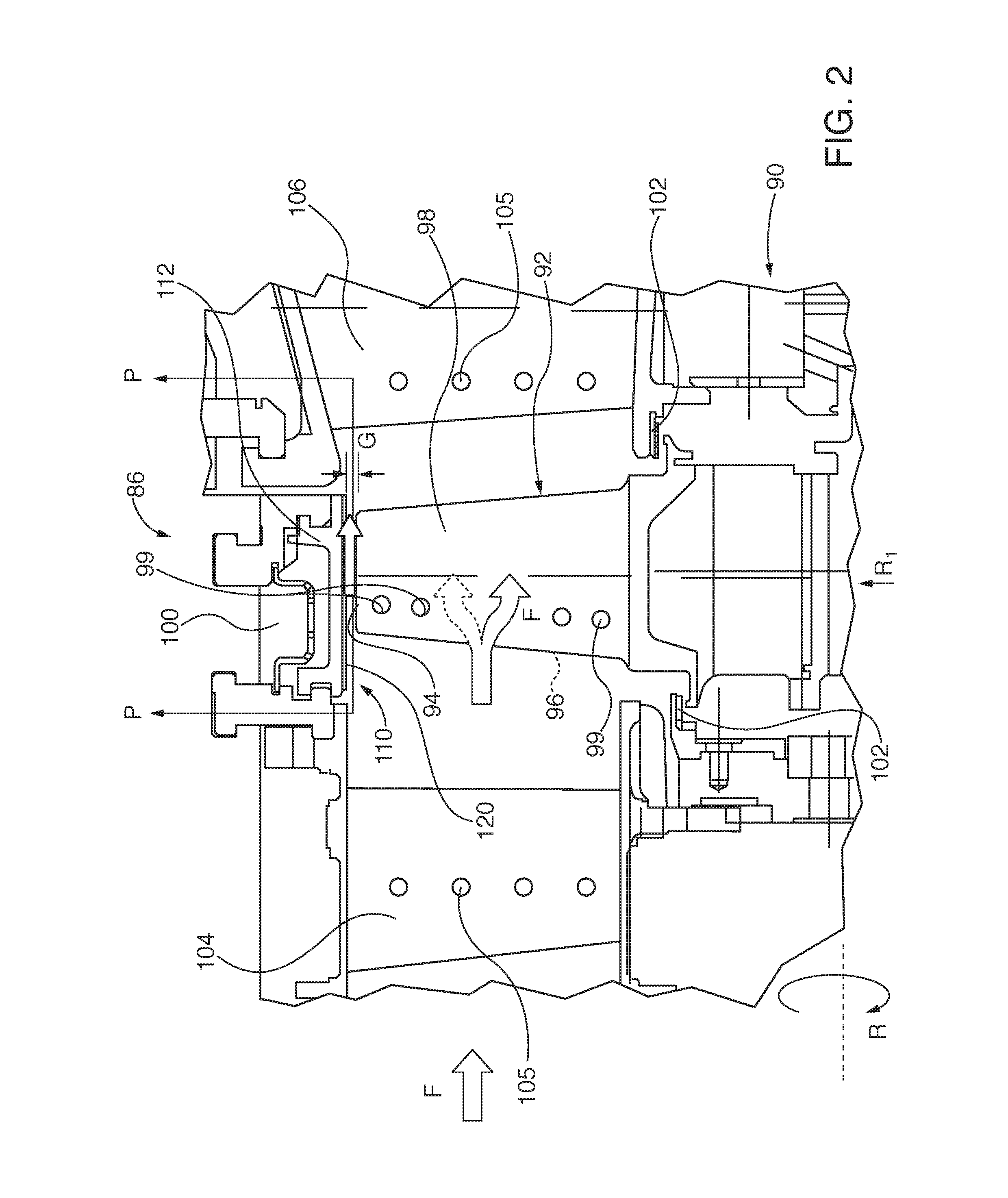
Method and system for surface profile inspection of off-line industrial gas turbines and other power generation machinery
ActiveUS20150300920A1Facilitates of dimensionalGathering informationGas-turbine engine testingMaterial analysis by optical meansIndustrial gasTime profile
Internal components of power generation machines, such as gas or steam turbines, are inspected with a laser profilometer inspection system that is inserted and positioned within the turbine, for example through an inspection port that is in communication with an open inter-row spacing volume between an opposing turbine vane and turbine blade row. Component surface profile scans are performed to determine relative profile heights along a two-dimensional scan line generated by the profilometer. Three-dimensional profile information is obtained by translating the scan line across the surface. Real time profile information is gathered without physical contact, which is helpful for extracting off-line engineering information about component surface conditions, including surface spallation, perforation, and gaps between components. The system is capable of determining blade tip gap between a turbine blade tip and its opposing abradable surface in the turbine casing.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
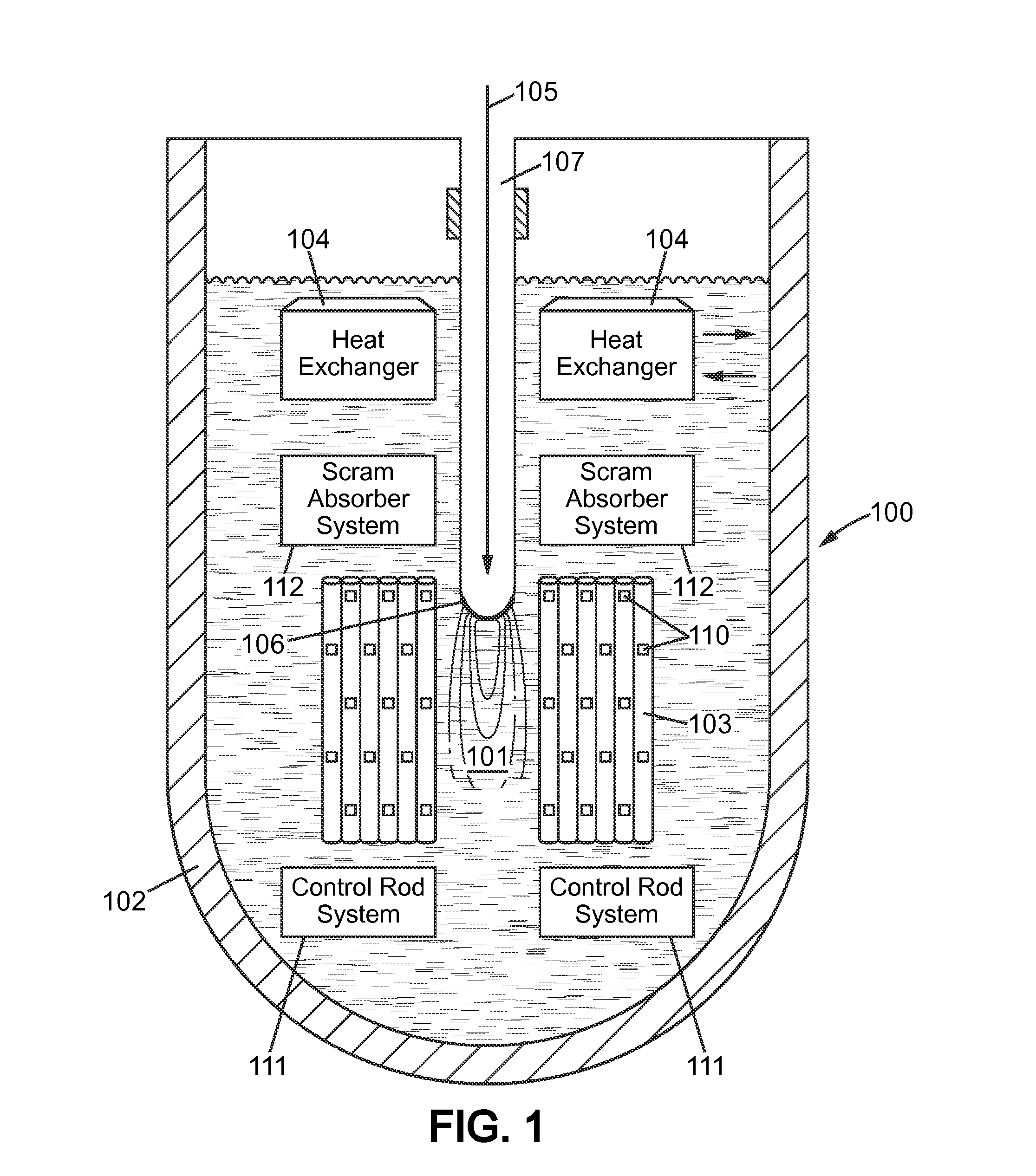
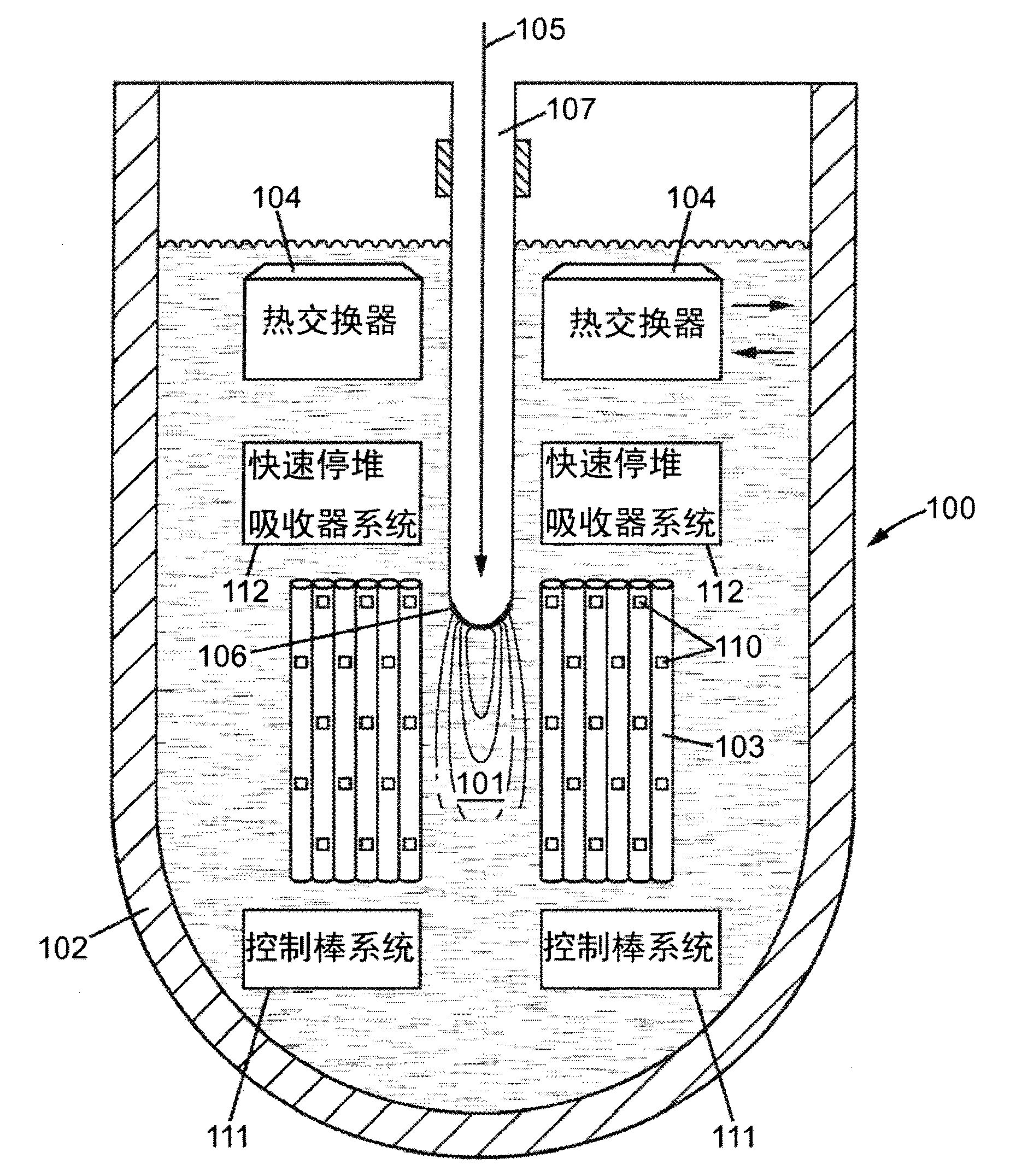
Accelerator-Driven Nuclear System with Control of Effective Neutron Multiplication Coefficent
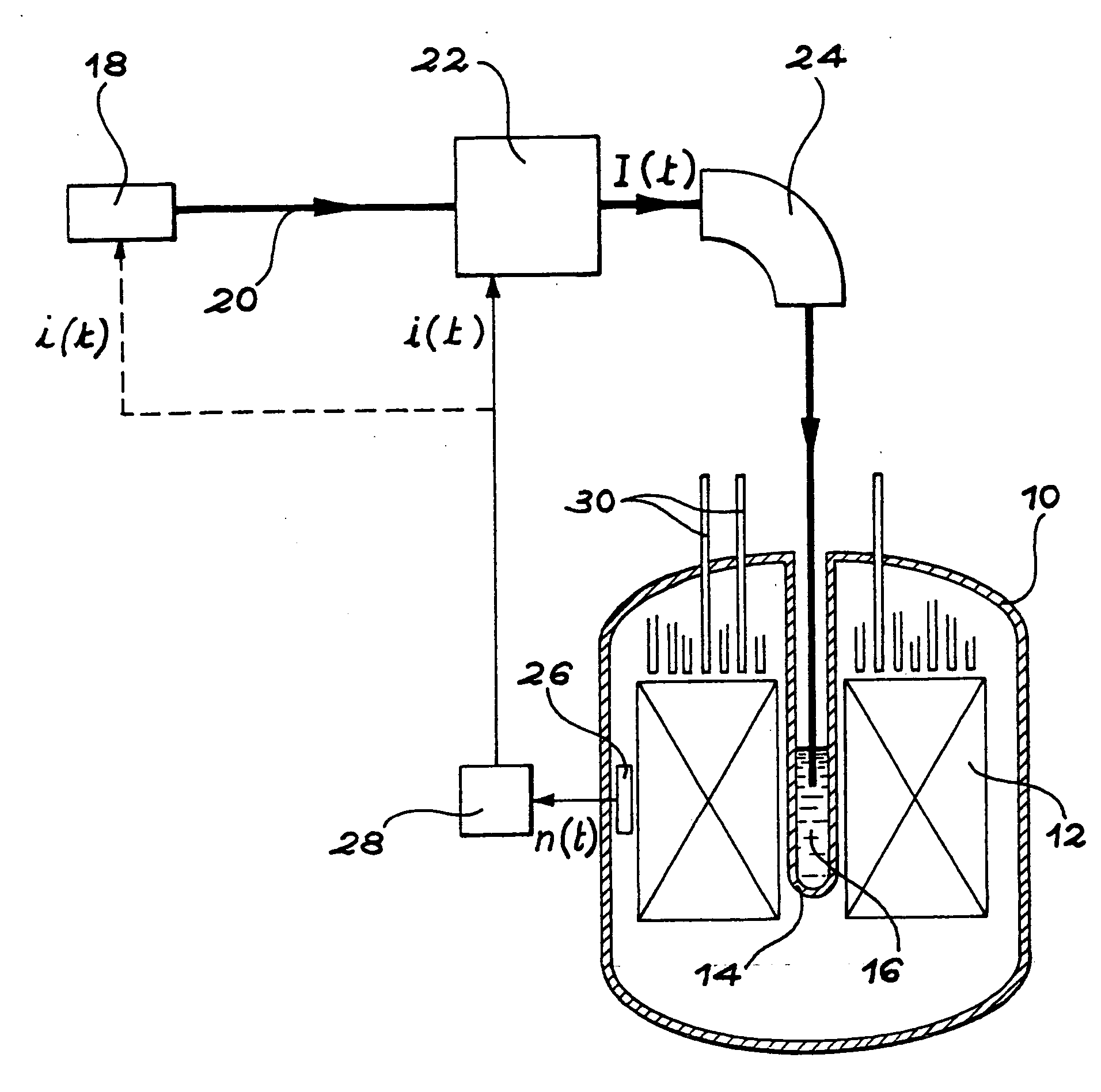
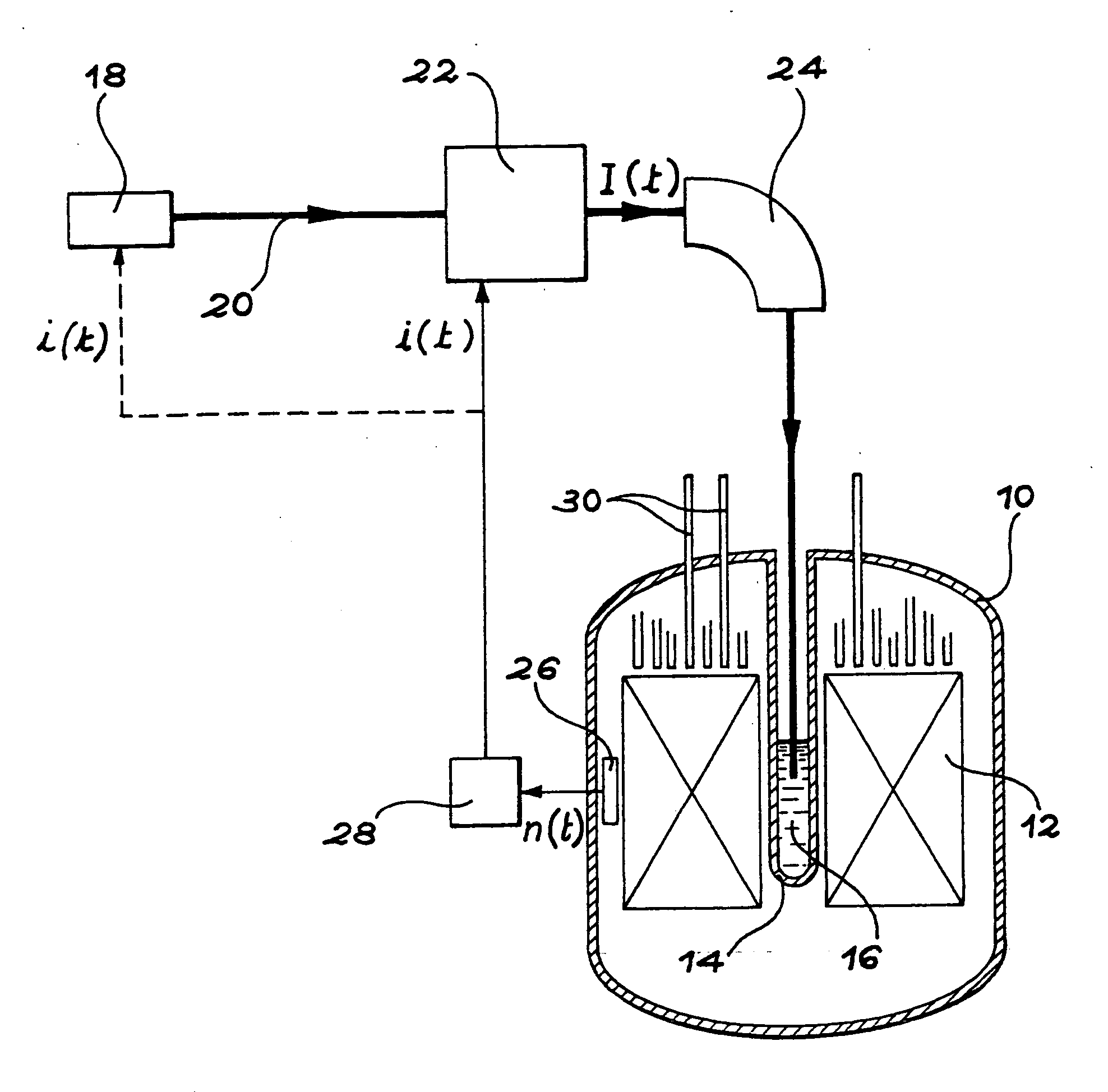
An accelerator-driven subcritical breeding reactor is operated with a neutron multiplication coefficient as large as possible in order to require a small input power from the accelerator, reducing its dimension and hence its cost and complexity. The beam-generated spallation neutron yield then becomes comparable to the fraction of delayed neutrons from the fissioned elements. This can be exploited to ensure an accurate on-line determination of the reactivity. Resulting changes can be adjusted with the help of neutron absorbing control rods and / or variations of the proton current. In addition, the temperature variations during operation can be continuously monitored and adjusted in order to avoid that the subcritical systems approaches too closely the (delayed) criticality condition and that the neutron multiplication coefficient remains within acceptable limits.
Owner:JACOBS U K
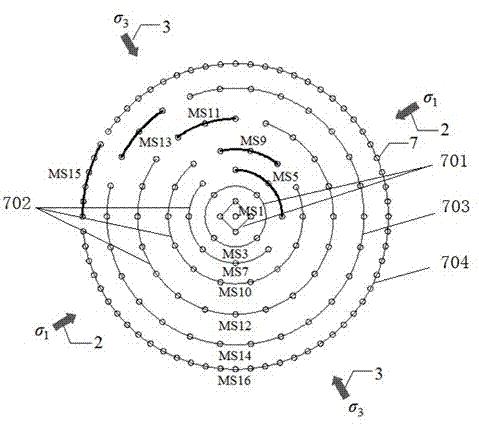
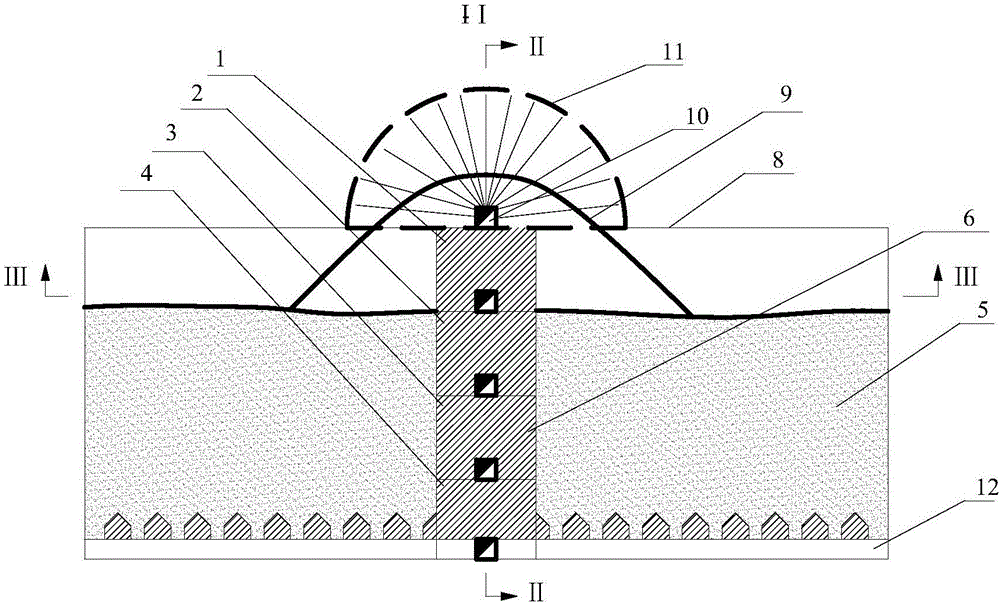
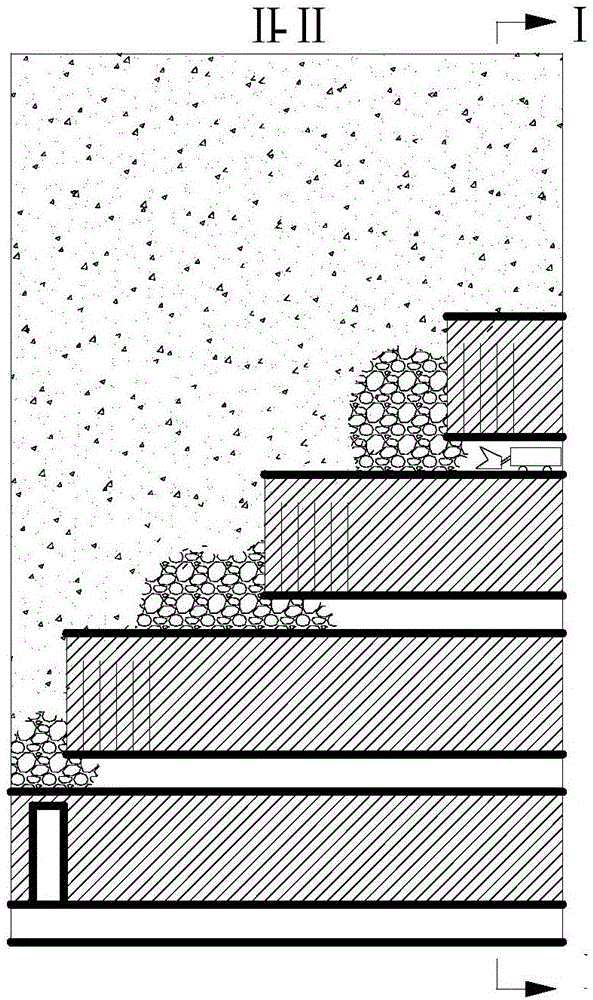
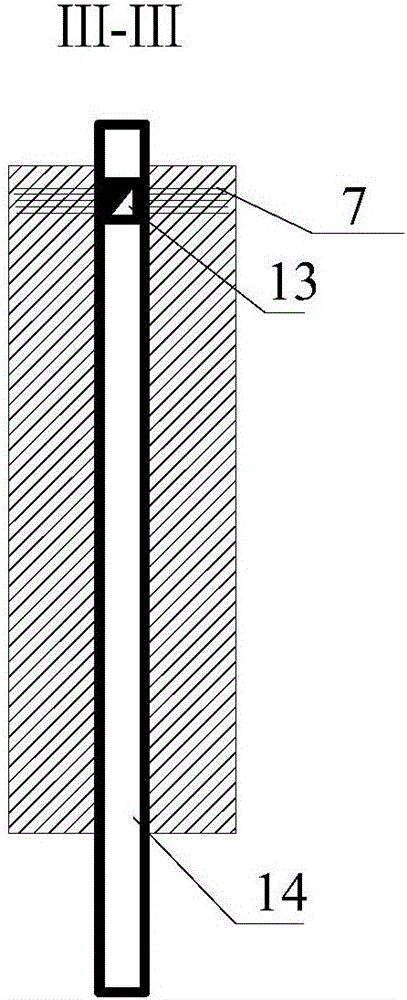
Quick surrounding rock stress measuring method applicable to buried circular tunnels
The invention discloses a quick surrounding rock stress measuring method applicable to buried circular tunnels. The method includes: setting each circle of spallation blastholes, buffering blastholes and smooth blasting blastholes to be detonated in two sections, determining main stress on a tunnel face to determine axial stress of the tunnel according to the maximum main stress on the tunnel face. The quick surrounding rock stress measuring method applicable to the buried circular tunnels has the advantages that conventional blasting operations and vibration monitoring are utilized, no extra equipment is needed, operation is convenient, and real-time and dynamic estimation of the surrounding rock stress close to the tunnel face during blasting construction can be realized. The quick surrounding rock stress measuring method applicable to the buried circular tunnels is mainly applicable to quick measuring of the surrounding rock stress of the deep buried underground constructions in the field of hydropower, communication, mines and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Foam concrete preform release agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102191120ABroaden applicationFast film formationLubricant compositionFoam concretePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a foam concrete preform release agent and a preparation method thereof. The foam concrete preform release agent comprises the following components by weight percent: 50-60% of waste oil, 1.5-1.8% of stearic acid, 1.0-1.5% of alkylphenol polyoxyethylene ether (OP-10 emulsifier), 0.02-0.05% of flake caustic soda, 12-15% of talc, 0.01-0.03% of phosphoric acid and 40-45% of water (60-80 DEG C). When the release agent prepared by adopting the formula is used for mould release, the foam concrete preform has no oil stain on the surface, no spallation and no edge defect and is good for second construction; and the preform has low dimensional deviation, the film-forming speed is high, the production cycle is short and the work efficiency is increased. In addition, the prepared release agent can be used to prevent the wooden mould from warping and deforming.
Owner:ZUNYI JIANTAI LIGHT ENERGY SAVING MATERIAL
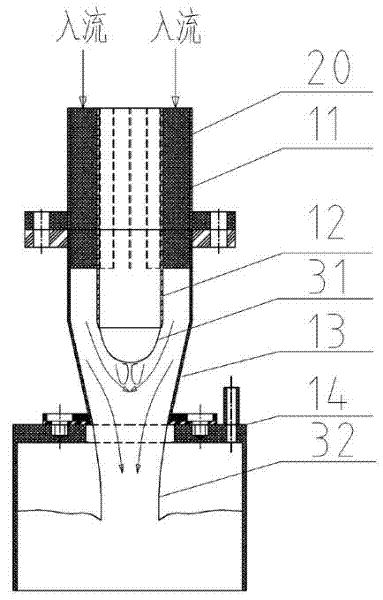
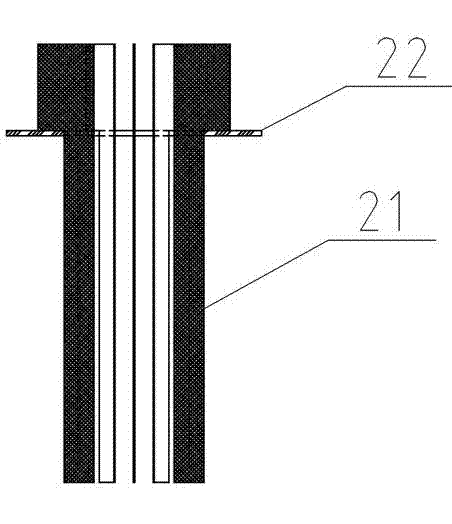
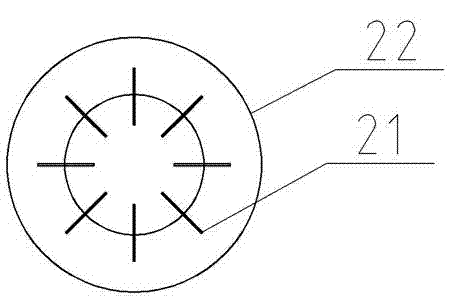
Free interface forming device and windowless spallation target system
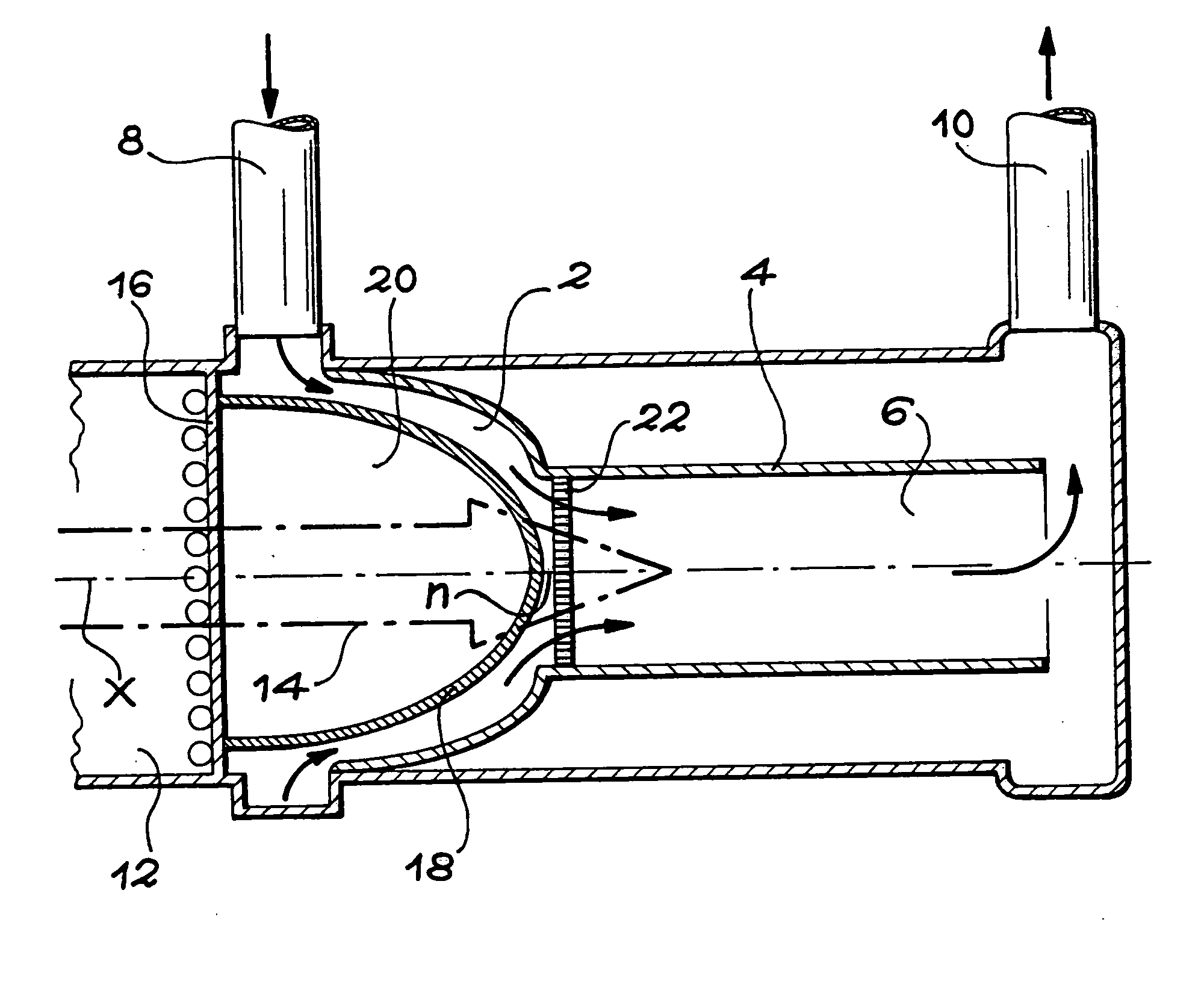
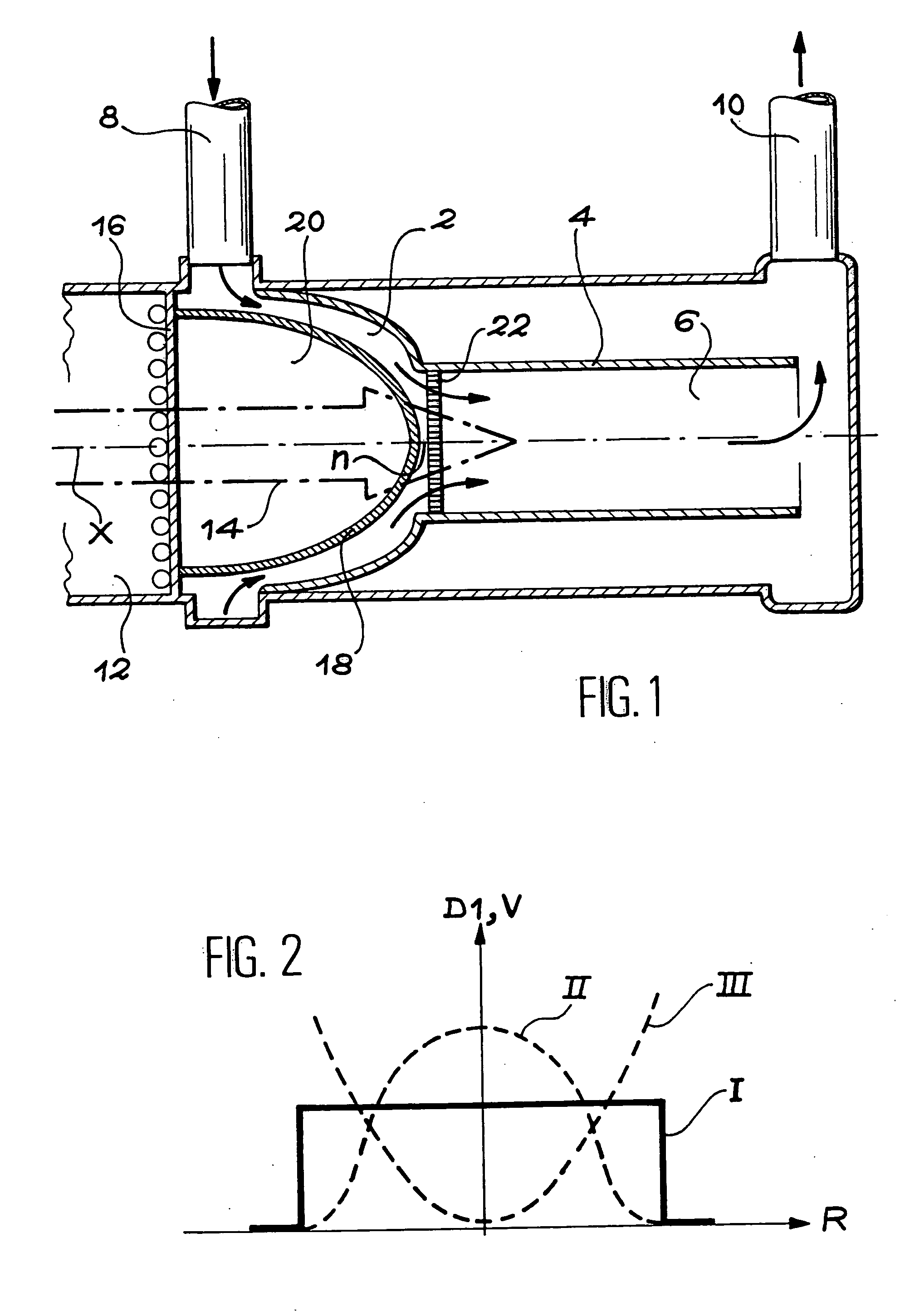
InactiveCN102647848ASimple componentsWide range of industrial applicationsDirect voltage acceleratorsNuclear targetsFree fallingFree interface
The invention relates to a free interface forming device which is used for a windowless spallation target of a subcritical system driven by an accelerator. The free interface forming device comprises an annular inlet flow-equalizing section, a taper-shaped gathering section and a lower pressure-control cavity, wherein the annular inlet flow-equalizing section, the taper-shaped gathering section and the lower pressure-control cavity are formed into a communicated fluid channel; the annular inlet flow-equalizing section is used for supplying a stable inlet flowing condition to the taper-shaped gathering section; the taper-shaped gathering section is arranged between the annular inlet flow-equalizing section and the lower pressure-control cavity and is used for forming a free interface by gathering the fluid entering the annular inlet flow-equalizing section at a preset conical angle; and the fluid is discharged into the lower pressure-control cavity in a free falling form at an outlet of the taper-shaped gathering section. The invention provides the free interface forming device for the windowless spallation target, which can be used for forming more stable and complete free interface; the size of a cycling area on a fluid side of the free interface is reasonably and effectively reduced by a flowing field of the free interface formed by the device; and the heat removing capacity of the flowing field is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for determining safe drilling fluid density of coal bed based on structural element analysis model
InactiveCN102230373ASurveySpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesCoal briquetteInstability
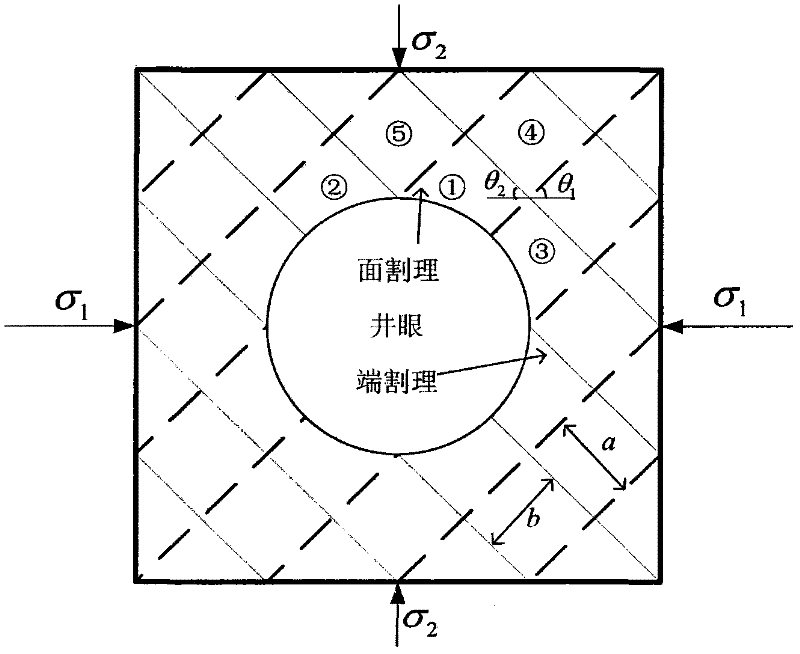
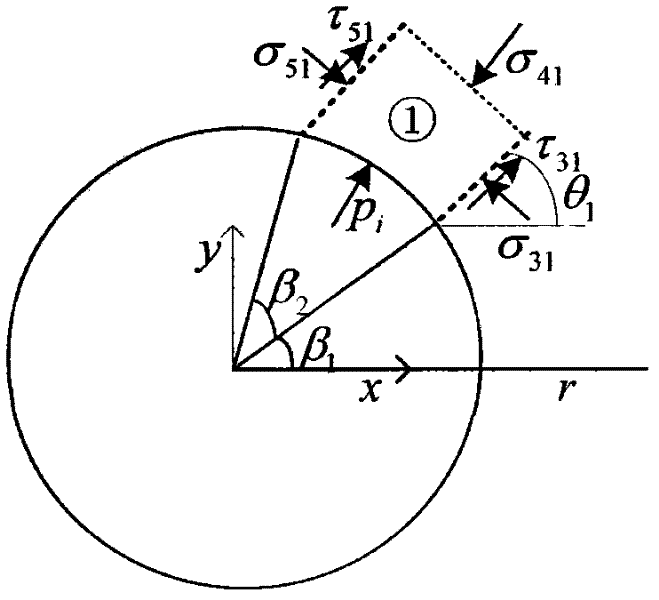
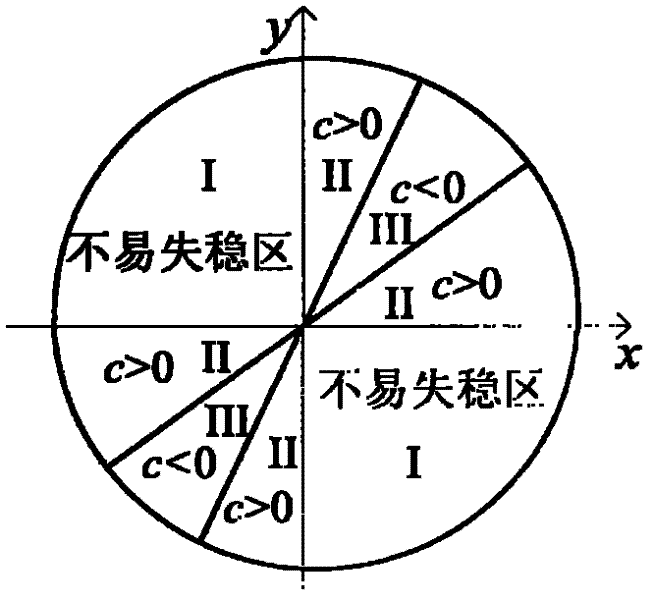
The invention discloses a method for determining the safe drilling fluid density of a coal bed based on a structural element analysis model. The method has the advantages of coal bed cleat and fracture development, big rock brittleness, low strength and obvious anisotropy and discontinuity. The borehole wall instability characteristics of the method are different from those of the common sandstone stratum. The phenomenon that the traditional borehole wall stability model based on the mechanics of continuous media is difficult to be successful for solving coal bed instability problems can be eliminated. In the method, the coal bed is composed of discrete blocks. A coal briquette which has the biggest possibility of generating spallation between surface cleats is analyzed to carry out force analysis. A structural element model of collapse pressure is built by the stressed balance condition among pressure stress, shearing strength and shaft pressure. A coefficient c is introduced to judge the stable relationship of borehole pressure and borehole wall so as to judge the range of the safe drilling fluid density.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Pre-control roof open stoping spallation subsequent filling mining method
InactiveCN101725348AReduce the amount of mining and cuttingImprove efficiencyUnderground miningSurface miningEngineeringSpallation
'pre-control roof open stoping spallation subsequent filling mining method' is characterized in that advantages of backfill mining method and spallation mining method are adopted, respective disadvantages are made up, a bran new mining technology is formed, and the method has the advantages of low ratio of mined tonnage to development, high efficiency, good safety and strong practicability and is especially applicable to the mine industry.
Owner:招金矿业股份有限公司大尹格庄金矿
Method and system for surface profile inspection of off-line industrial gas turbines and other power generation machinery
ActiveUS9709463B2Facilitates of dimensionalGathering informationGas-turbine engine testingMaterial analysis by optical meansTime profileEngineering
Internal components of power generation machines, such as gas or steam turbines, are inspected with a laser profilometer inspection system that is inserted and positioned within the turbine, for example through an inspection port that is in communication with an open inter-row spacing volume between an opposing turbine vane and turbine blade row. Component surface profile scans are performed to determine relative profile heights along a two-dimensional scan line generated by the profilometer. Three-dimensional profile information is obtained by translating the scan line across the surface. Real time profile information is gathered without physical contact, which is helpful for extracting off-line engineering information about component surface conditions, including surface spallation, perforation, and gaps between components. The system is capable of determining blade tip gap between a turbine blade tip and its opposing abradable surface in the turbine casing.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Turbine component thermal barrier coating with crack isolating engineered groove features
InactiveUS20160362989A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyAvoid accumulationMolten spray coatingEngine manufactureForeign object damageEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS AG
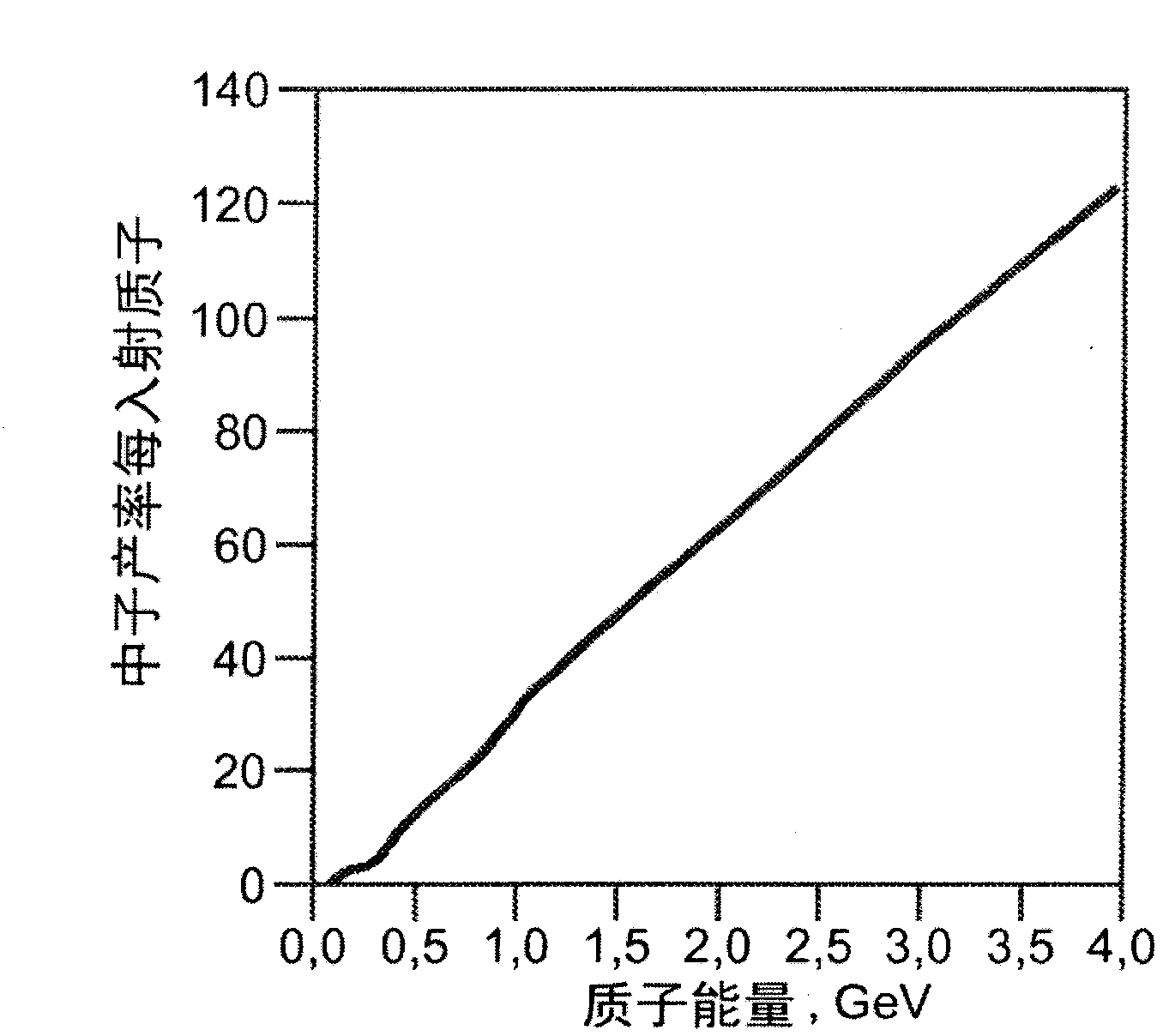
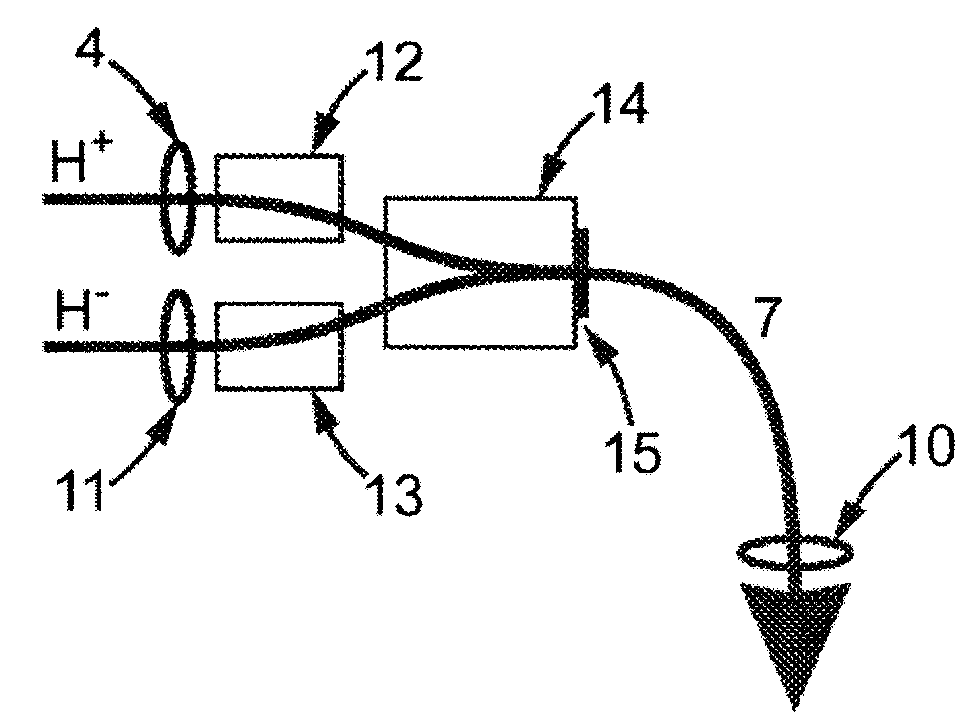
Spallation device for producing neutrons
InactiveUS20050220248A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationParticle beamAtomic physics
A spallation device for production of neutrons includes a solid spallation target that produces neutrons by interaction with a hollow particle beam propagating within a first chamber, a second chamber containing the spallation target, and a leak tight partition separating the first and second chambers.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Incineration process for transuranic chemical elements and nuclear reactor implementing this process
InactiveUS20060215799A1Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorChemical element
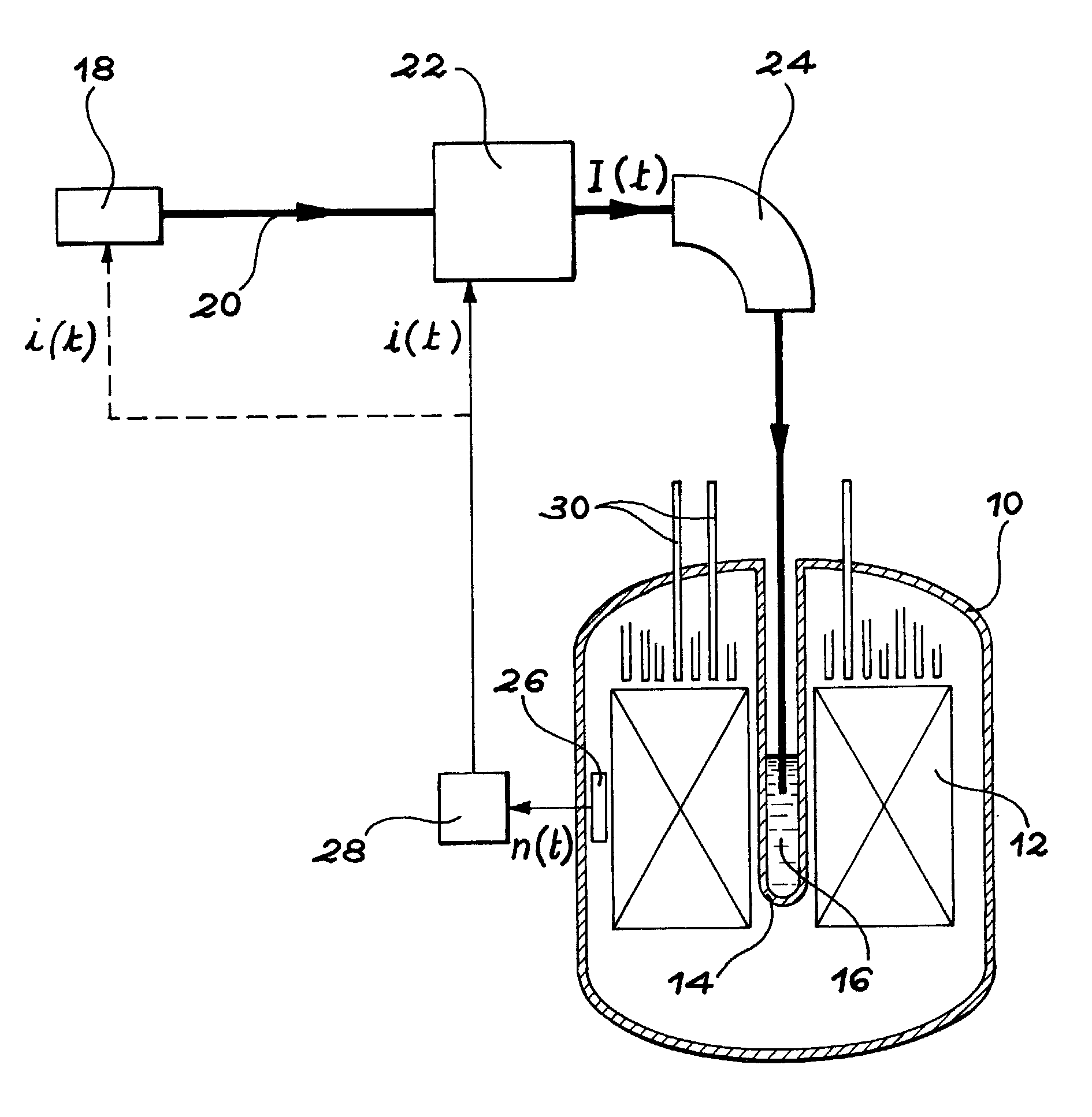
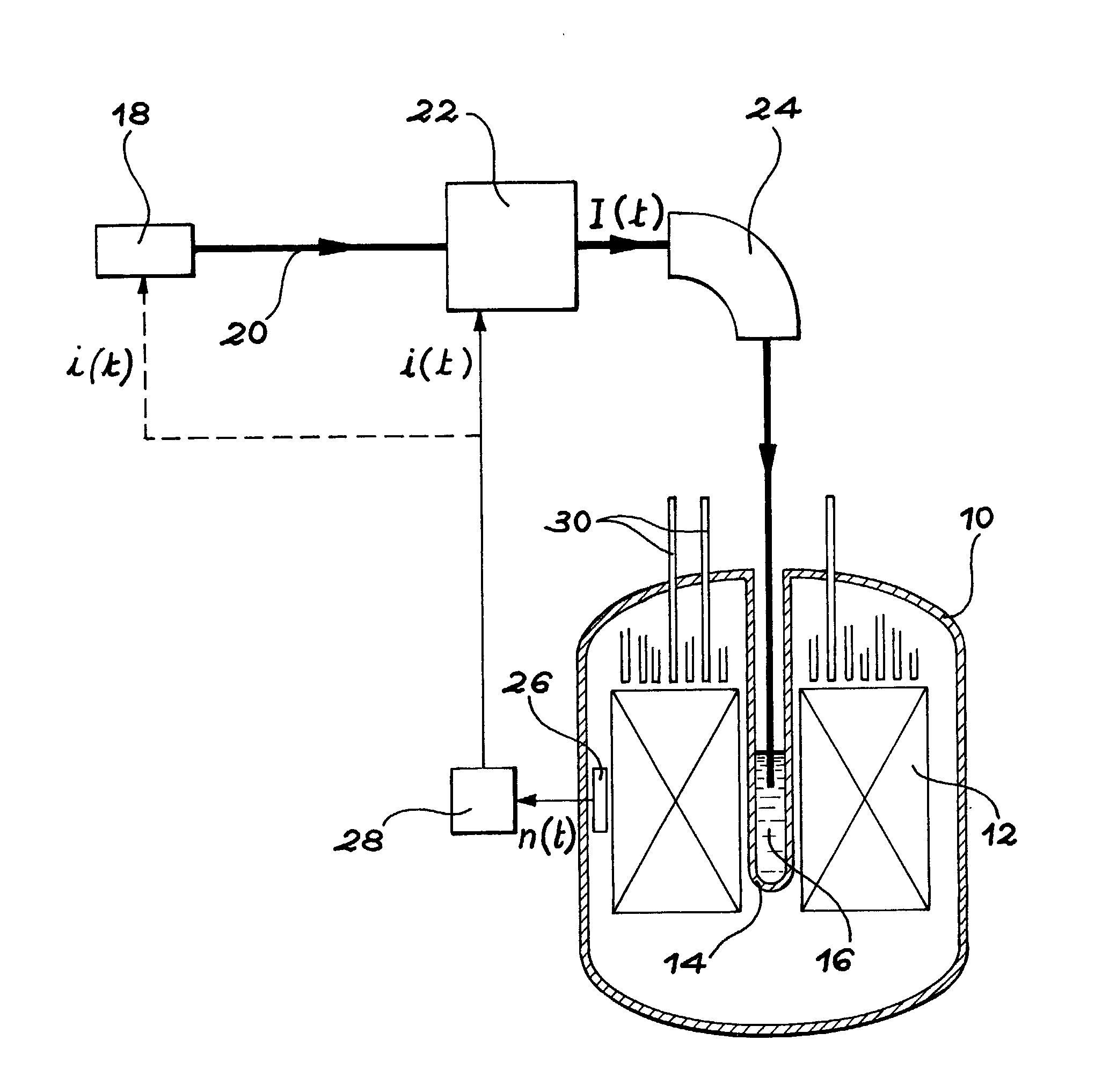
A process incinerate transuranic chemical elements and nuclear reactor implement this process. In order to incinerate transuranic chemical elements, such as long-lived nuclear waste and plutonium, a nuclear reactor is used in which the core operates at a low level of sub-criticality. This level is chosen substantially equal to the difference βs between a desired fraction βt of delayed neutrons in the core and the real fraction β. An external source of spallation neutrons includes a proton accelerator in which one adjusts the power, in real time, on the neutron flux measured in the core. A supplementary fraction of delayed neutrons equal to the difference βs is thus injected into the reactor core. The reactor then behaves and controls itself like a classical critical reactor.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Bundled monocapillary optics
InactiveUS6415086B1Coupling light guidesBundled fibre light guideElectron probe microanalysisEtching
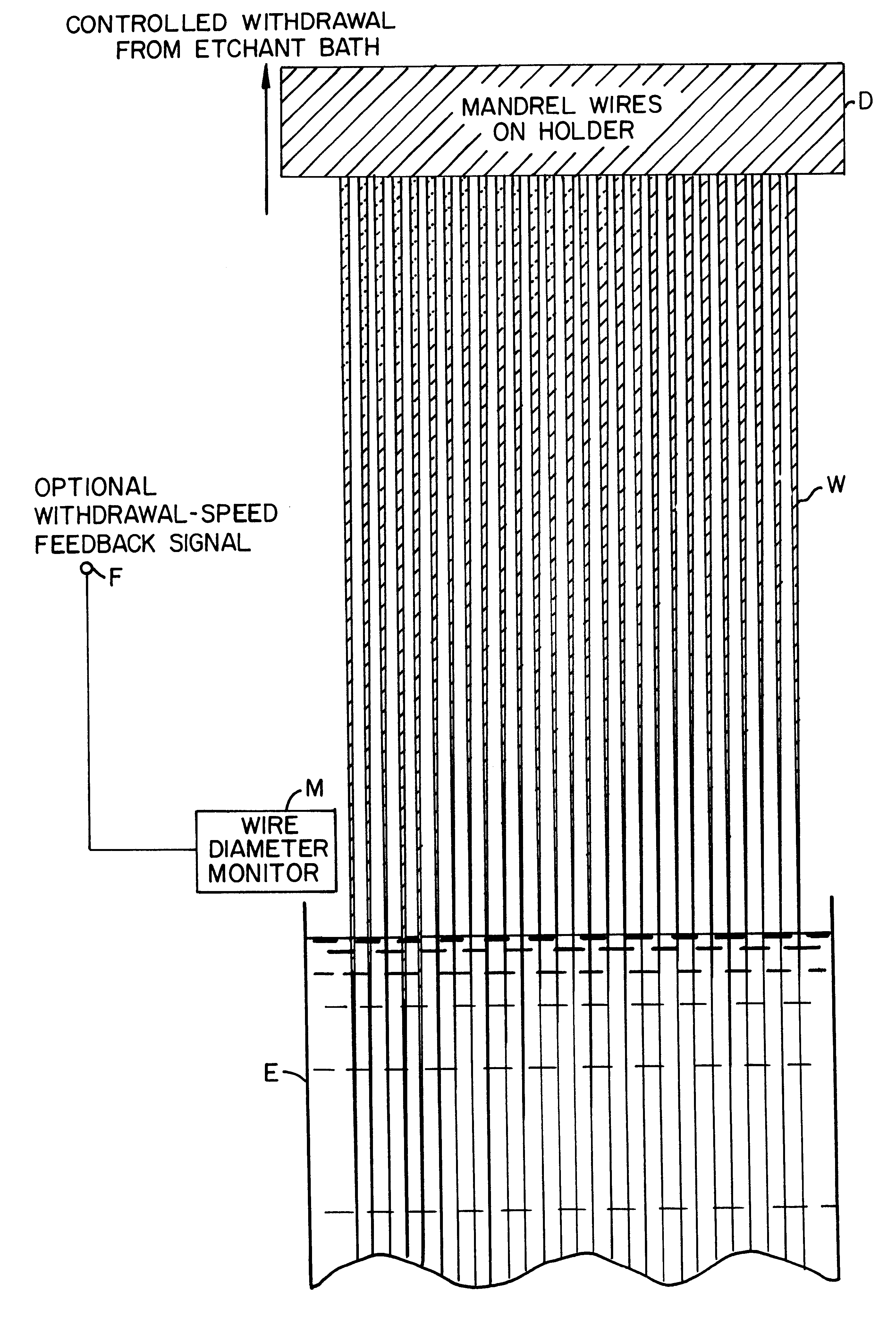
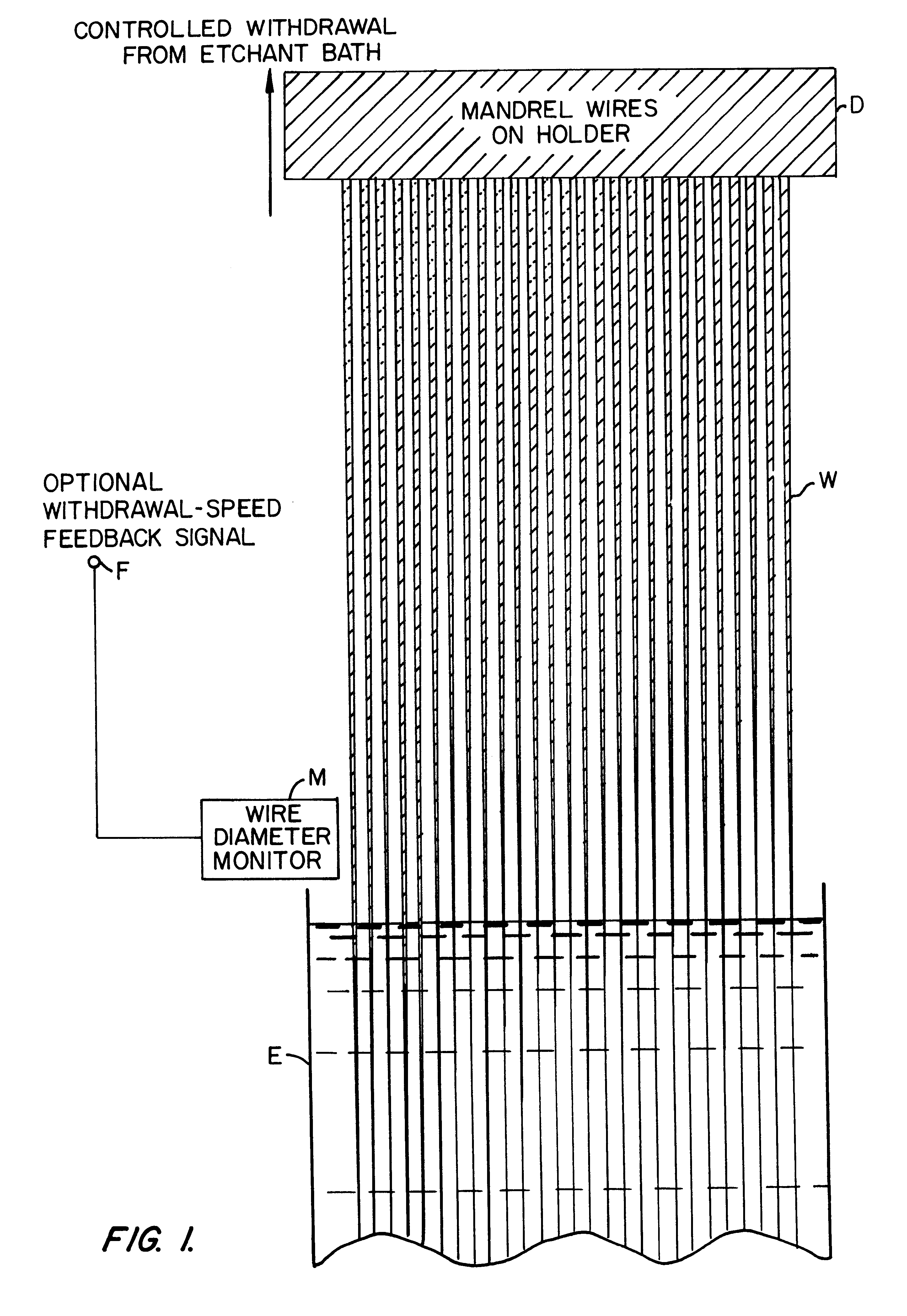
A plurality of glass or metal wires are precisely etched to form the desired shape of the individual channels of the final polycapillary optic. This shape is created by carefully controlling the withdrawal speed of a group of wires from an etchant bath. The etched wires undergo a subsequent operation to create an extremely smooth surface. This surface is coated with a layer of material which is selected to maximize the reflectivity of the radiation being used. This reflective surface may be a single layer of material, or a multilayer coating for optimizing the reflectivity in a narrower wavelength interval. The collection of individual wires is assembled into a close-packed multi-wire bundle, and the wires are bonded together in a manner which preserves the close-pack configuration, irrespective of the local wire diameter. The initial wires are then removed by either a chemical etching procedure or mechanical force. In the case of chemical etching, the bundle is generally segmented by cutting a series of etching slots. Prior to removing the wire, the capillary array is typically bonded to a support substrate. The result of the process is a bundle of precisely oriented radiation-reflecting hollow channels. The capillary optic is used for efficiently collecting and redirecting the radiation from a source of radiation which could be the anode of an x-ray tube, a plasma source, the fluorescent radiation from an electron microprobe, a synchrotron radiation source, a reactor or spallation source of neutrons, or some other source.
Owner:HIRSCH GREGORY
Rescue method after ball spallation in big tree transplanting
The invention relates to a rescue method after ball spallation in big tree transplanting. The method adopts the treatment steps as follows: (1) pouring gaps of a soil ball by adopting mud mixed with a rooting agent after transplanting so as to form a whole; (2) swathing boughs of a tree trunk and below and trunk parts by adopting a plastic film until the bottom of the trunk; and (3) conducting transfusion treatment to the trunk. Leaves and / or branches with leaves of the tree can be further pruned towards special trees before transplanting, and anti-transpirant spraying and / or overshadowing tothe whole tree can be conducted after being transplanted. With the method, a root system can be better contacted with soil and water, new roots of the root system can be quickened, water and nutrientcan be timely supplemented, cells of the tree and enzyme activity can be stimulated, water transpirating of the tree can be slow down, the absorption strength of the tree body can be reduced, nutrition consumption can be decreased, the up and down balance of the tree can be increasingly achieved again, and the survival rate of the whole canopy transplanted tree can be improved.
Owner:北京正和恒基国际城市规划设计有限公司
Method for incinerating transuranian chemical elements and nuclear reactor using same
InactiveUS20030179843A1Lower levelSimple processConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreChemical element
Incineration process for transuranic chemical elements and nuclear reactor implementing this process. In order to incinerate transuranic chemical elements, such as long-lived nuclear waste and plutonium, a nuclear reactor is used in which the core (12) operates at a low level of sub-criticality. This level is chosen substantially equal to the difference betas between a desired fraction betat of delayed neutrons in the core and the real fraction beta. An external source of spallation neutrons includes a proton accelerator in which one adjusts the power, in real time, on the neutron flux measured in the core (12). A supplementary fraction of delayed neutrons equal to the difference betas is thus injected into the reactor core. The reactor then behaves and controls itself like a classical critical reactor.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Studding recovery method for reconstructing covering layer through dead zone wastefill and top surrounding rock spallation collaboratively
ActiveCN106522955AFlexible mining processIncrease flexibilityUnderground miningSurface miningRecovery methodGeomorphology
Provided is a studding recovery method for reconstructing a covering layer through dead zone wastefill and top surrounding rock spallation collaboratively. The method comprises the specific steps that after waste rock is exploited out from a chamber and a top column through an open-stope method, a goaf is filled with the waste rock to reach a certain height, surrounding rock at the top of a studding is collapsed off once, and the studding covering layer is reconstructed collaboratively; the studding is divided into a plurality of layers, and a drilling drift is tunneled in the center of the bottom of the layers; an end non-through cutting groove is formed in the tail end of the drilling drift through a cutting courtyard slot broaching method; the cutting groove serves as the ore breaking free face, and the studding is subjected to sequential top-to-bottom interlamination advance and in-layers retreating type recovery; and broken ore is shoveled to a winze through a scooptram and is conveyed to the surface of the earth by an ore pocket through an electric locomotive. The invention first provides the method for collaboratively reconstructing the studding covering layer, the safety of studding recovery is improved, and the ore recovery rate is increased effectively.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
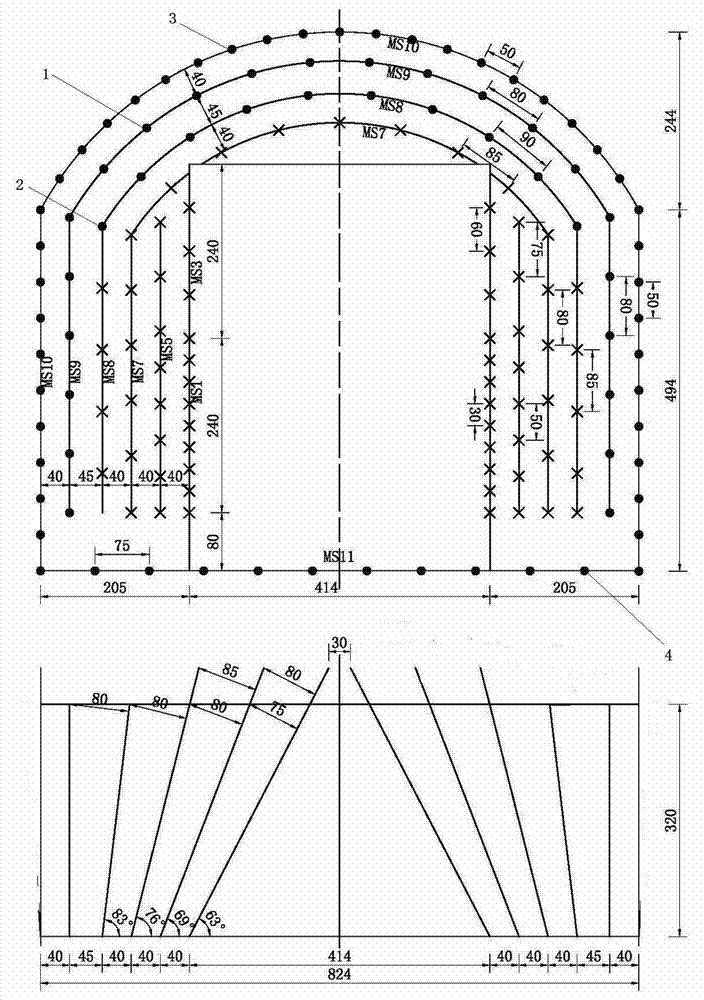
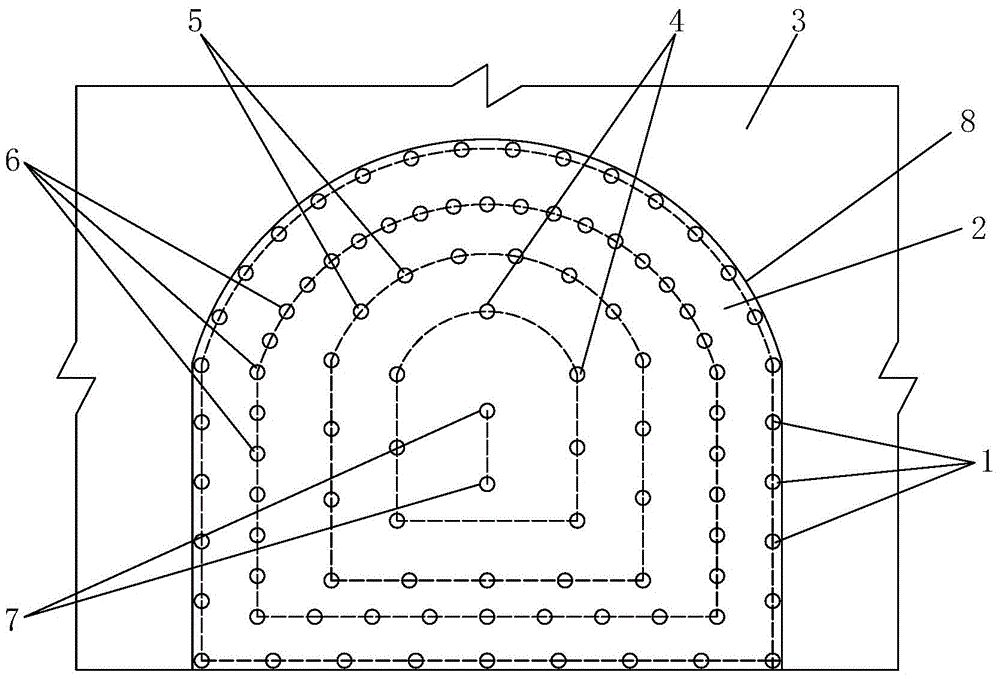
Smooth blasting method based on phi 32 mm cartridges
The invention provides a smooth blasting method based on phi 32 mm cartridges. The method includes the steps that punching, powder charging and the initiation process are conducted on a working face, and a smooth blasting layer is composed of a peripheral smooth blasting hole array located on the outer side and more close to the boundary of the top, and an outer ring spallation hole array located in the peripheral smooth blasting hole array. The density coefficient m of peripheral smooth blasting holes ranges from 1.25 to 1.43. Charged powder in the peripheral smooth blasting holes in the peripheral smooth blasting hole array comprises bottom charged powder located at the bottoms and multiple bags of middle charged powder located at different depths in the holes. The powder charging amount of the middle charged powder is smaller than that of the bottom charged powder. The intervals between the bottom charged powder and the middle charged powder and between the bags of the middle charged powder are the same, and the initiation time of the peripheral smooth blasting hole array is later than that of the outer ring spallation hole array. Smooth blasting powder string processing procedures and processing materials are reduced; smooth blasting powder string processing cost, and cost of materials such as bamboo chips and adhesive tape are saved, and over-excavation is effectively controlled, so that a large amount of concrete backfill caused by over-excavation is reduced, and construction cost is reduced.
Owner:SINOHYDRO BUREAU 5
Experiment method taking dynamic tensile stress amplitude value as variable and impact experiment device
InactiveCN105784512AIndividual change controlEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationStrength propertiesClassical mechanicsDynamic stretching
The invention provides an experiment method taking a dynamic tensile stress amplitude value as a variable and an impact experiment device and relates to the field of impact dynamics. The experiment method taking the dynamic tensile stress amplitude value as the variable comprises the following steps: S1. preparing a plurality of sample targets; S2. preparing a plurality of flying plate groups, wherein each flying plate group comprises a first flying plate layer and a second flying plate layer which is collided with the corresponding sample target; the first flying plate layers are fitted with the second flying plate layers and the resistance of each first flying plate layer is smaller than that of each second flying plate layer; S3. forming an impact experiment group by corresponding each flying plate group to one sample target; and S4. carrying out a collision experiment on each impact experiment group. In an experiment, experiment data of spallation caused by the single variable, which is controlled by the change of the dynamic tensile stress amplitude value, is only acquired, and the difficulty of theoretical analysis of a tensile stress amplitude value effect can be remarkably reduced. The invention further provides the impact experiment device.
Owner:INST OF FLUID PHYSICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Solid spallation target for ADS (Accelerator Driven Sub-critical System)
ActiveCN103313503AFlexible designExtend your lifeDirect voltage acceleratorsNuclear targetsProtonEngineering
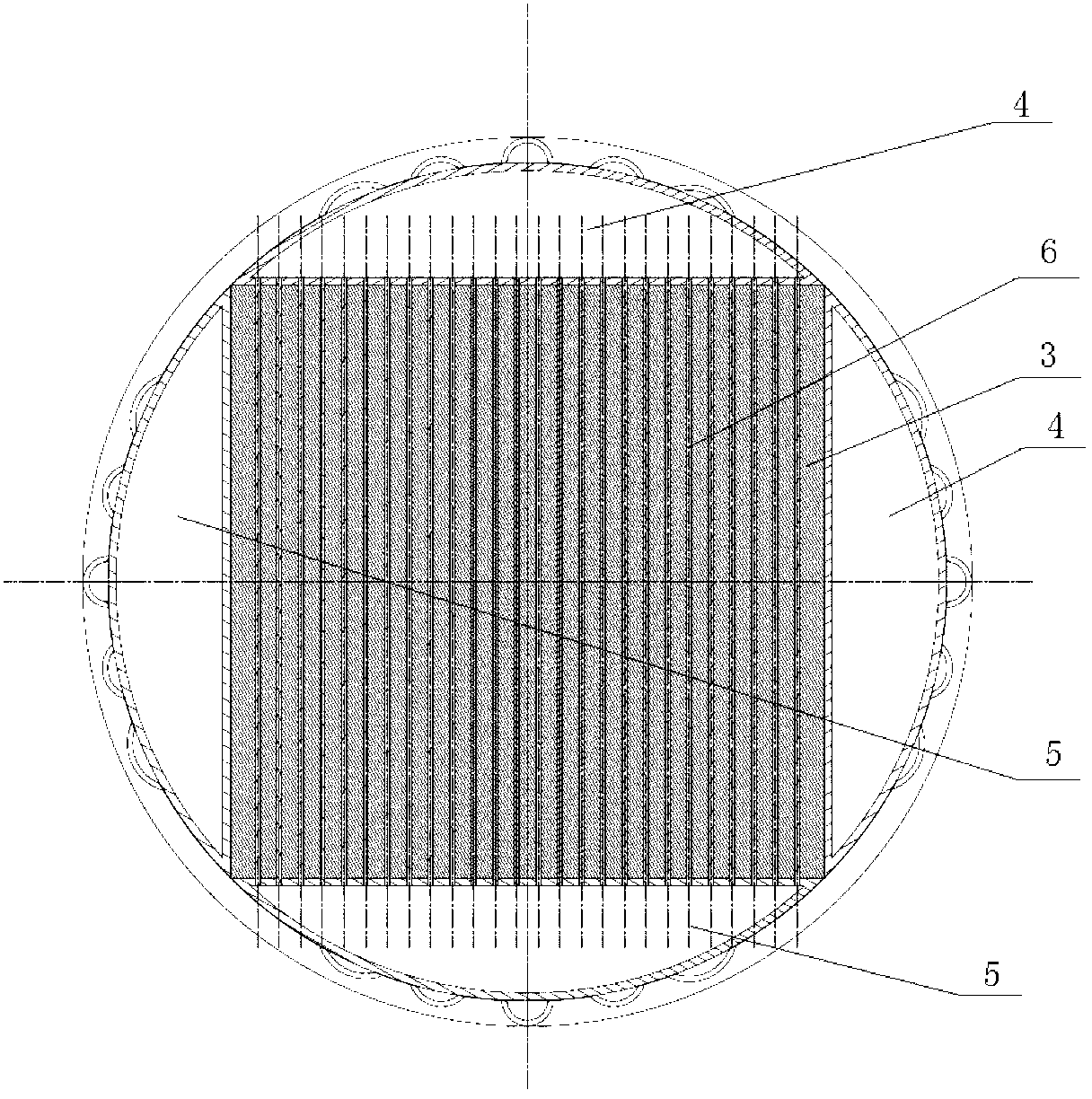
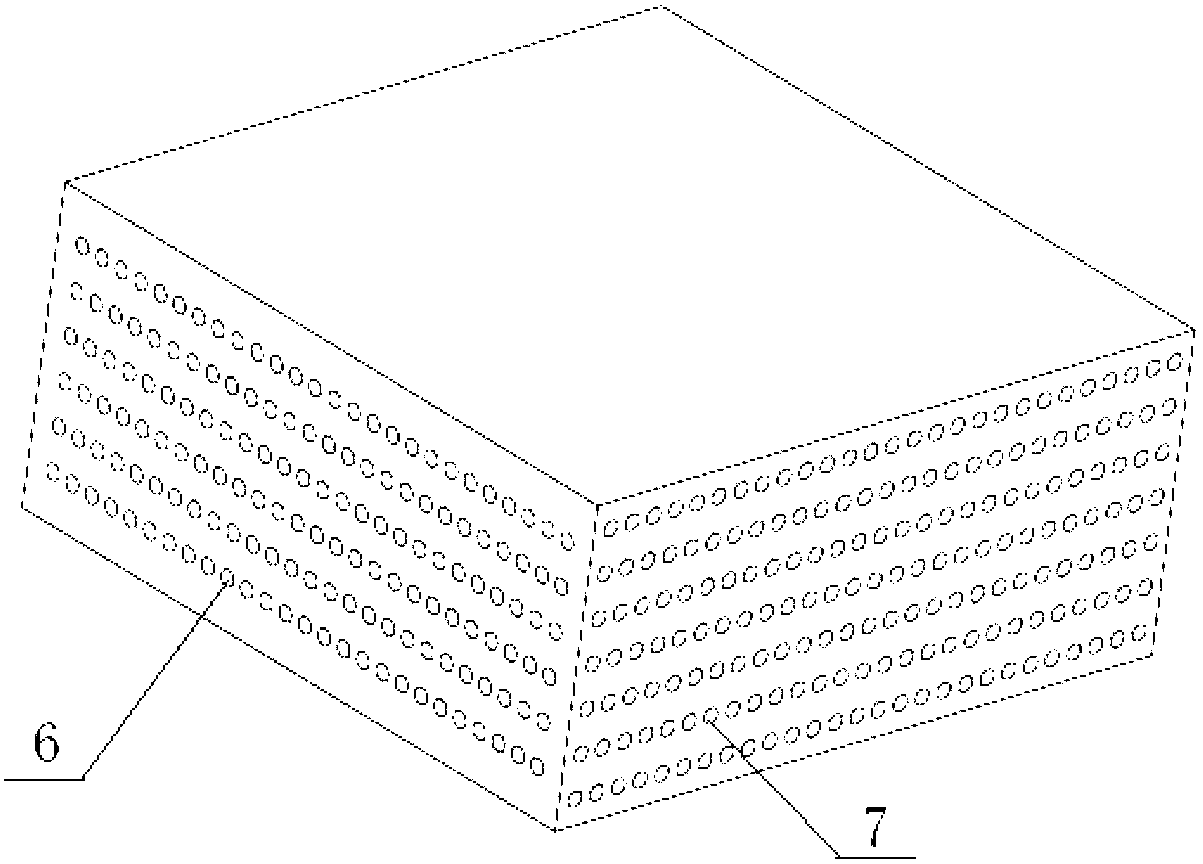
The invention relates to a solid spallation target structure for ADS (Accelerator Driven Sub-critical System), which belongs to the technical field of nuclear energy. A solid spallation target for the ADS is mainly characterized in that a target body is arranged at the end head of an inner cavity of a proton beam passage, the target body is provided with multiple rows of cooling through holes, one ends of the multiple rows of the cooling through holes are provided with a helium inlet connecting box, the helium inlet connecting box is connected with a helium inlet connecting box connecting pipe, the other ends of the multiple rows of the cooling through holes are provided with a cooled helium outlet connecting box, and a helium outlet connecting box is connected with a helium outlet connecting box connecting pipe. The solid spallation target disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the solid spallation target structure can be easily processed and manufactured, the welding can be easier as the same material is adopted, and the requirements of the ADS system on other functions of the spallation target can be met by the solid spallation target structure.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Spallation-resistant multilayer thermal spray metal coatings
A wear- and corrosion-resistance coating over a metal substrate having a first-layer carbide material, a second metal coating layer over the first metal coating layer, and a surface metal coating layer over the second metal coating layer; and thermal spray method for applying the coating.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
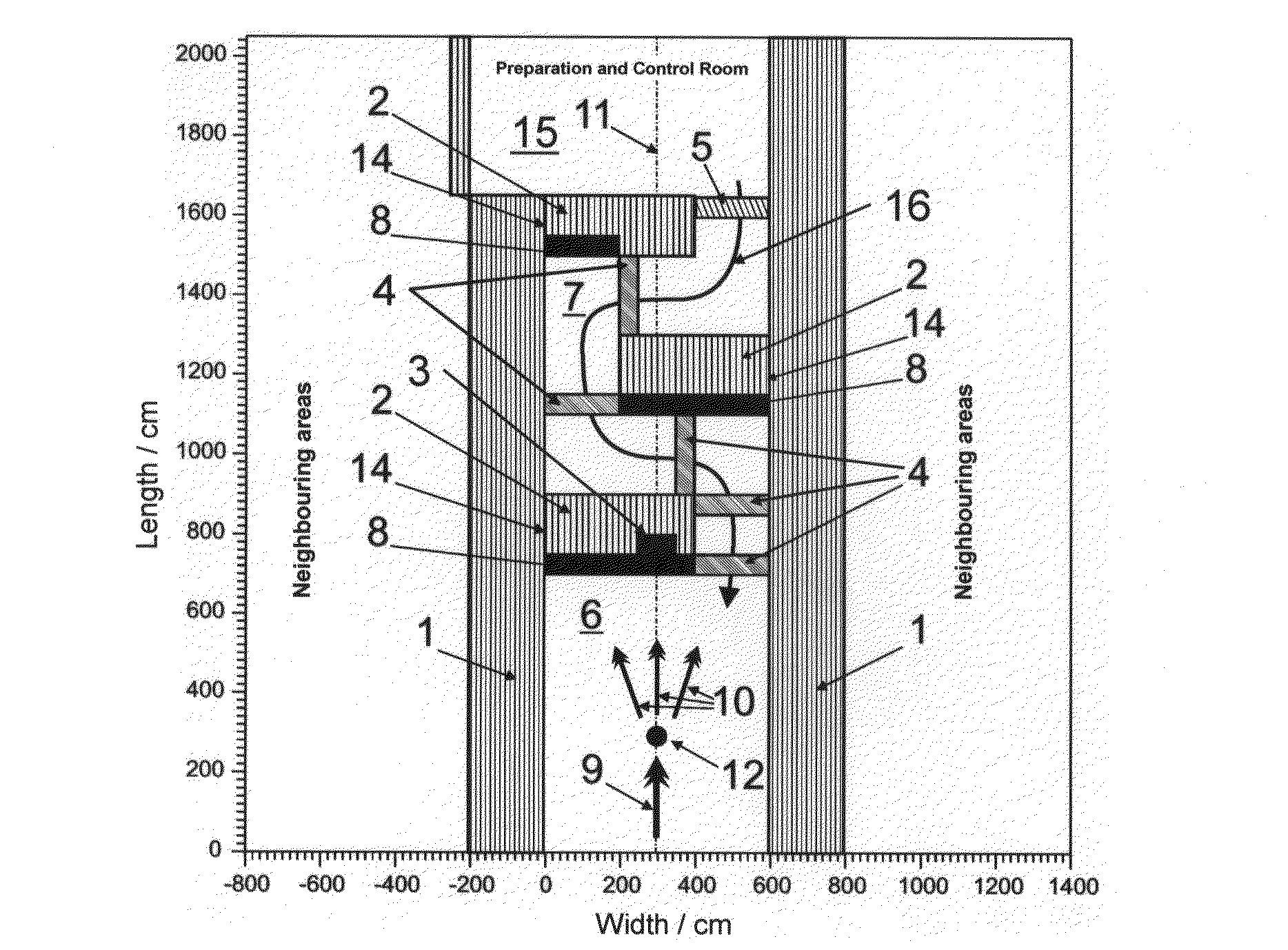
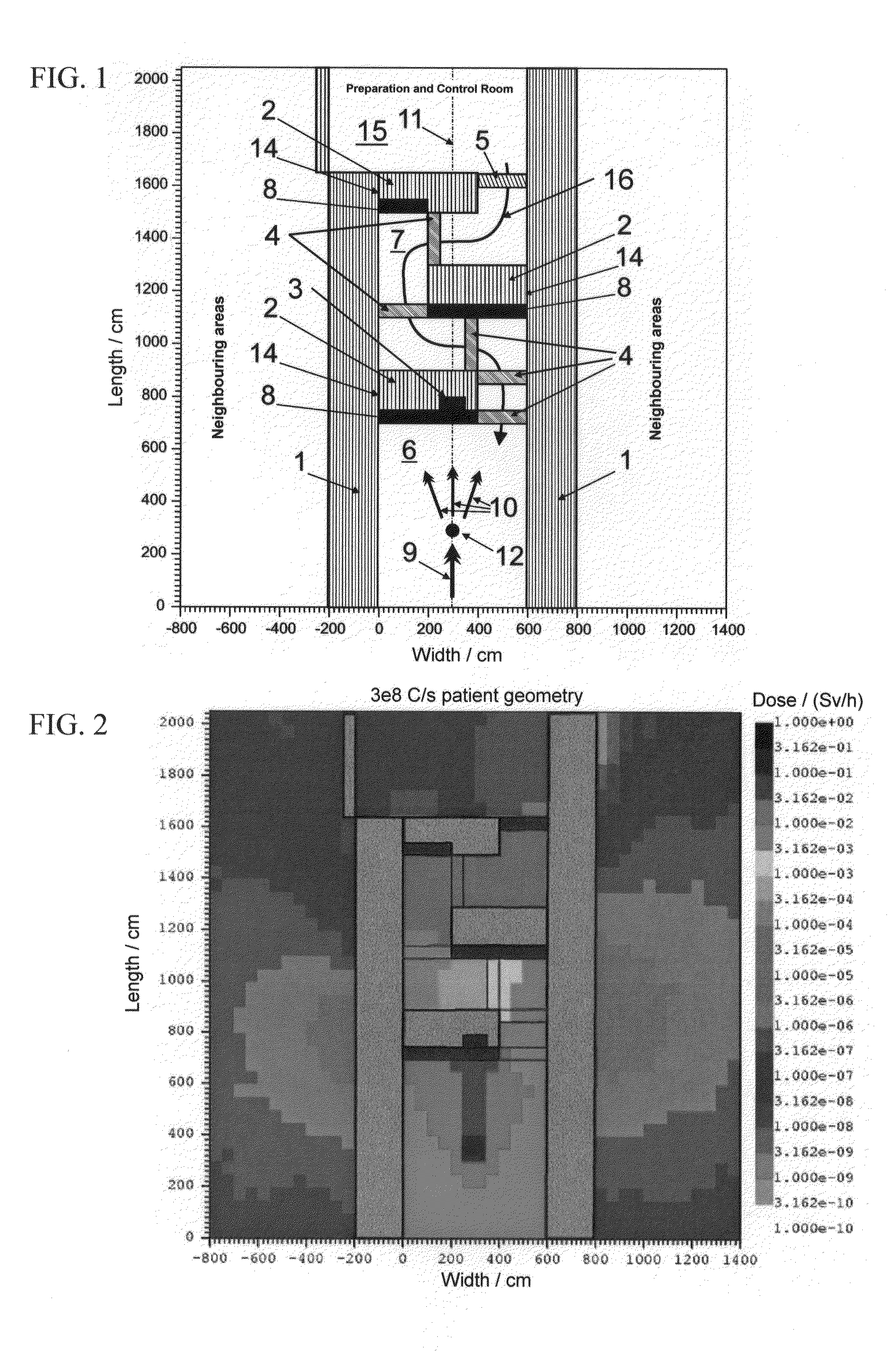
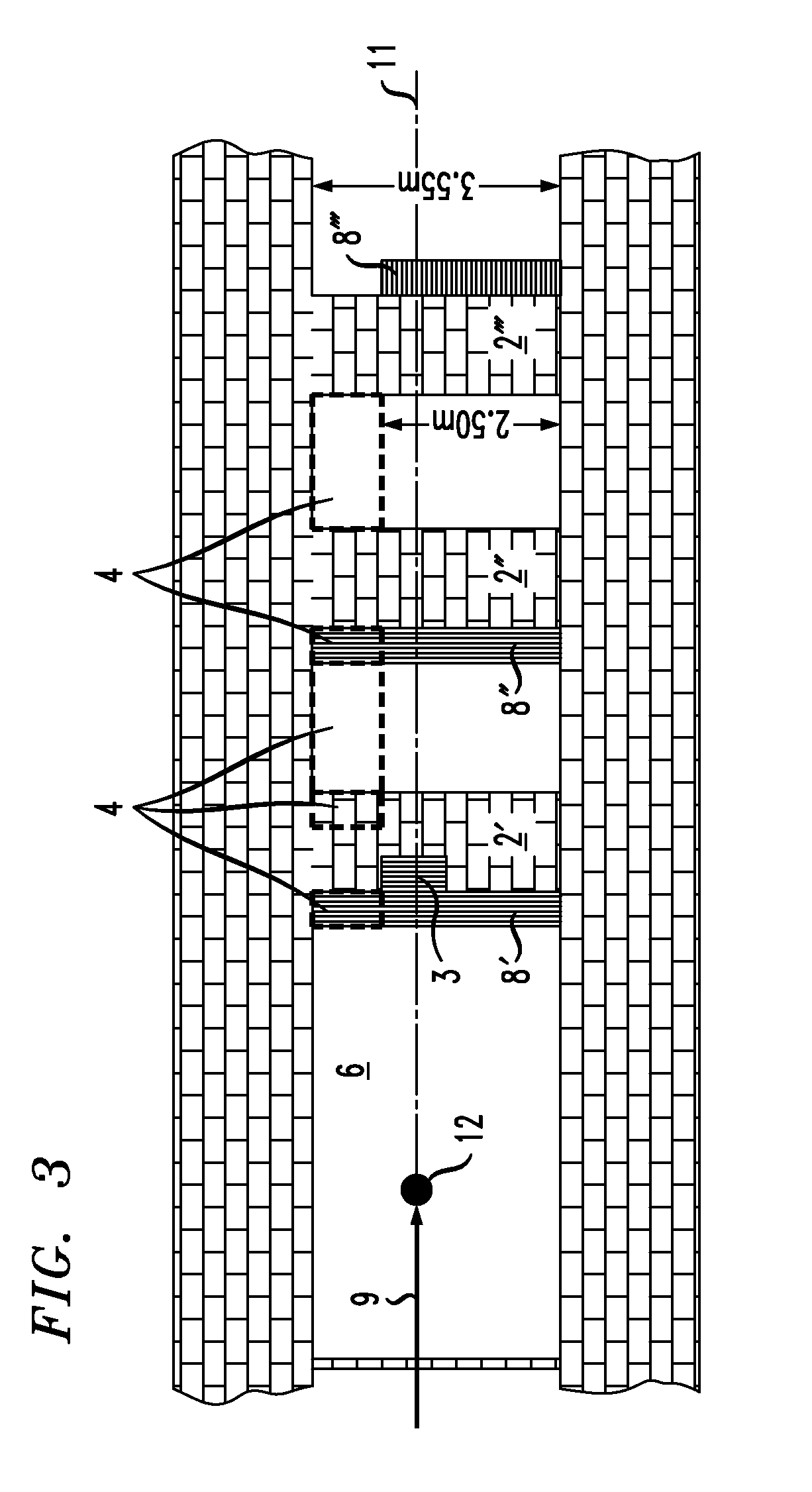
Screened chamber for ion therapy
InactiveUS8139705B2Constant efficiencyConstant interaction probabilitiesConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationHigh energyLight beam
In a shielded chamber for neutron therapy including a therapy room which has a central beam axis along which a high-energy therapy beam is introduced into the Chamber through one end wall thereof and which includes at the opposite end a labyrinth entrance with at least two shielding wall sections displaced longitudinally along the central beam axis and extending into the room from opposite side walls, the wall sections include structures for causing spallation to thereby generate from the high energy neutrons in the high energy neutron beam a plurality of low energy neutrons which are then moderated by the wall sections.
Owner:GSI HELMHOLTZZENT FUR SCHWERIONENFORSCHUNG
Tunnel blasting method
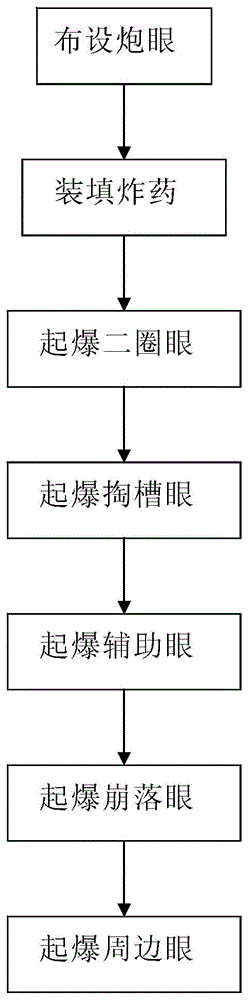
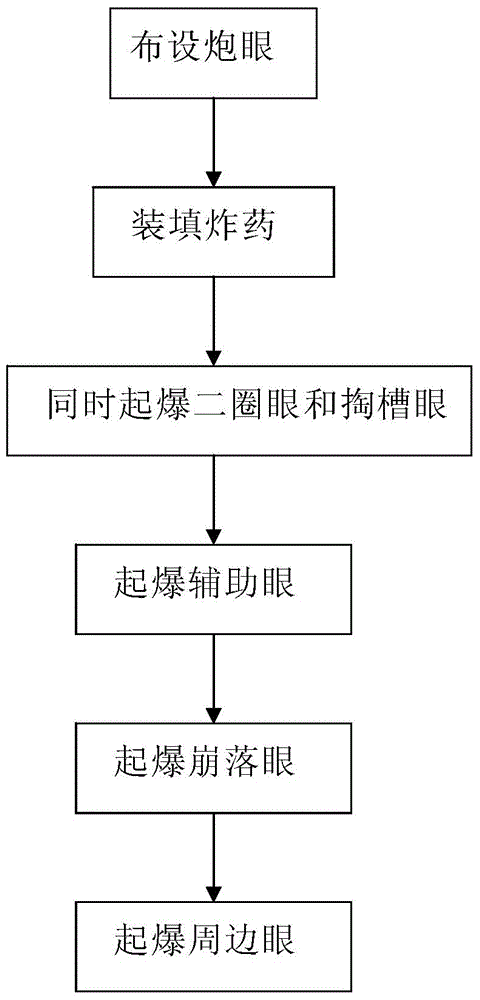
InactiveCN104792237ANovel and reasonable designImprove blasting effectBlastingDetonationStructural engineering
The invention discloses a tunnel blasting method. The method comprises the steps of arranging a circle of periphery holes at the positions, close to a tunnel excavation outline, on a tunnel blasting working surface, arranging a circle of secondary-circle holes at the positions, on the inner sides of the periphery holes, on the tunnel blasting working surface, arranging spallation holes at the positions, on the inner sides of the secondary-circle holes, on the tunnel blasting working surface, and arranging breaking-in holes at the positions, on the inner sides of the spallation holes, on the tunnel blasting working surface; filling explosives, wherein the periphery holes, the breaking-in holes, the spallation holes and the secondary-circle holes are filled with explosives; detonation, wherein the secondary-circle holes, the breaking-in holes, the spallation holes and the periphery holes are detonated in sequence, or the secondary-circle holes and the breaking-in holes are detonated firstly at the same time and then the spallation holes and the periphery holes are detonated in sequence. By the adoption of the method, tunnel surrounding rock can be effectively protected, the influence of blasting disturbance on the surrounding rock is reduced, crack formation on the tunnel surrounding rock is reduced, and the completeness of the tunnel surrounding rock can be well maintained.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Inspection and strength measurement of solder and structural joints using laser generated stress waves
InactiveUS20080212067A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesForce measurement by measuring optical property variationSolder ballUltimate tensile strength
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for direct measurement of the tensile strength of joints with use of laser spallation. A laser pulse is directed at a surface in communication with a solder joint, generating a stress wave to separate the solder ball from its underlying structure. The solder joint may be measured either prior to joining of a PCB board or CSP package, or after they have been joined. The joints for testing may be prepared by polishing either the PC board or the CSP package to expose the desired solder joint for testing. The tensile strength of the embedded joints may also be measured in-situ.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Combined strengthening treatment method for plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition on surfaces of spallation target balls
ActiveCN108977759AImprove wear resistanceHigh hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingBinding forceMaterials science
The invention relates to the technical field of powder metallurgy, and more specifically, discloses a combined strengthening treatment method for metal plasma immersion ion implantation and depositionon the surfaces of spallation target balls. The strengthening treatment method comprises the steps of carrying out pre-treatment of the spallation target balls, carrying out TiSiN, TiAlN, TiAlSiN, TiAlSiN / h-BN ion implantation and deposition, and the like. The method has the advantages that the problems that the wear rate of the spallation target tungsten-iron-nickel target balls in a non-intermetallic compound form prepared through a powder metallurgy technology is high, the residual stress between a thin film and a matrix is large, the film-matrix binding force is poor, and the bearing capacity of a single film layer is poor can be solved, the surface of the thin film is effectively prevented from being peeled off, and a functionally gradient composite material which is high in film-matrix binding force, high in hardness, low in friction coefficient and high in wear resistance can be prepared.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Type I crack specimen dynamic symmetrical tensile device for and experimental method thereof
ActiveCN108333047AUniform discharge currentGuaranteed waveform synchronizationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCapacitanceExperimental methods
The invention relates to an experimental method for testing fracture mechanical properties in the field of material, and discloses a type I crack specimen dynamic symmetrical tensile device and an experimental method thereof. The specimen dynamic symmetrical tensile device includes a power supply, a capacitor charger, loading guns and a waveguide-rod rod system. The capacitor charger adopts a power supply part of a conventional electromagnetic riveting device; two loading guns with the same parameters are connected in parallel and then access the capacitor charger. The invention also relates to the experimental method based on the specimen dynamic symmetrical tensile device. Because the parameters of the two loading guns are the same and access the capacitor charger in parallel, the discharge current can be synchronously and evenly distributed into the two loading guns, same compression stress waves are produced in the two loading guns, are reflected into tensile waves in two convex platforms respectively and then enter tensile rods, and the specimen is loaded; therefore, the specimen can be symmetrically loaded, and a specimen crack is guaranteed to be extended into a type I spallation crack.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Accelerator-driven nuclear system with control of effective neutron multiplication coefficent
An accelerator-driven subcritical breeding reactor is operated with a neutron multiplication coefficient as large as possible in order to require a small input power from the accelerator, reducing its dimension and hence its cost and complexity. The beam-generated spallation neutron yield then becomes comparable to the fraction of delayed neutrons from the fissioned elements. This can be exploited to ensure an accurate on-line determination of the reactivity. Resulting changes can be adjusted with the help of neutron absorbing control rods and / or variations of the proton current. In addition, the temperature variations during operation can be continuously monitored and adjusted in order to avoid that the subcritical systems approaches too closely the (delayed) criticality condition and that the neutron multiplication coefficient remains within acceptable limits.
Owner:JACOBS E&C
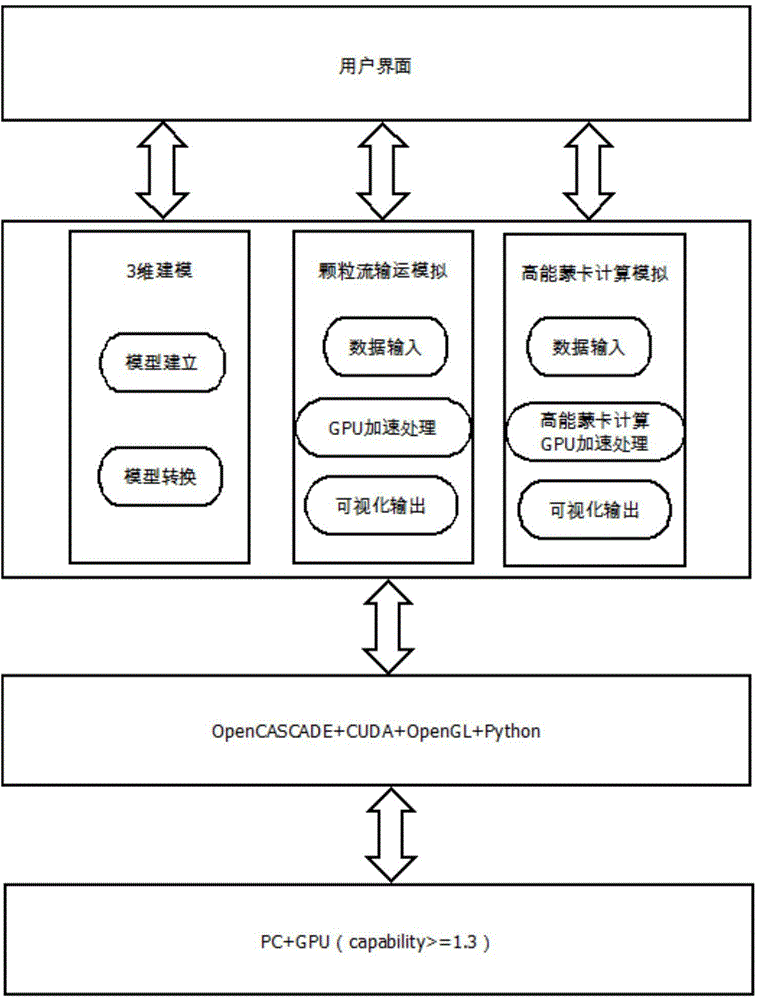
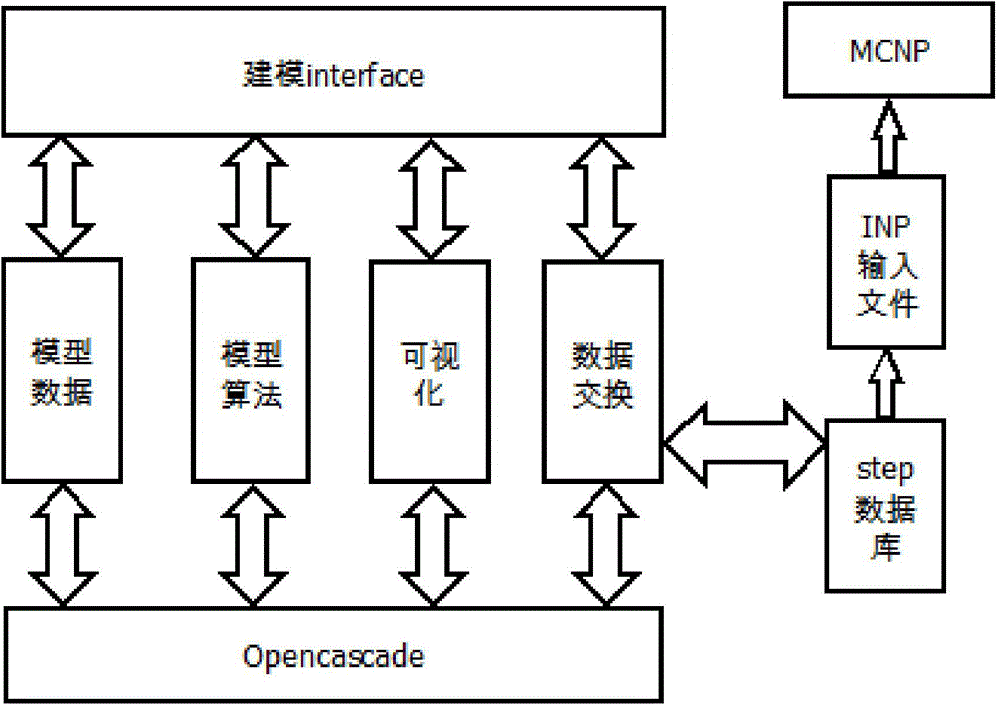
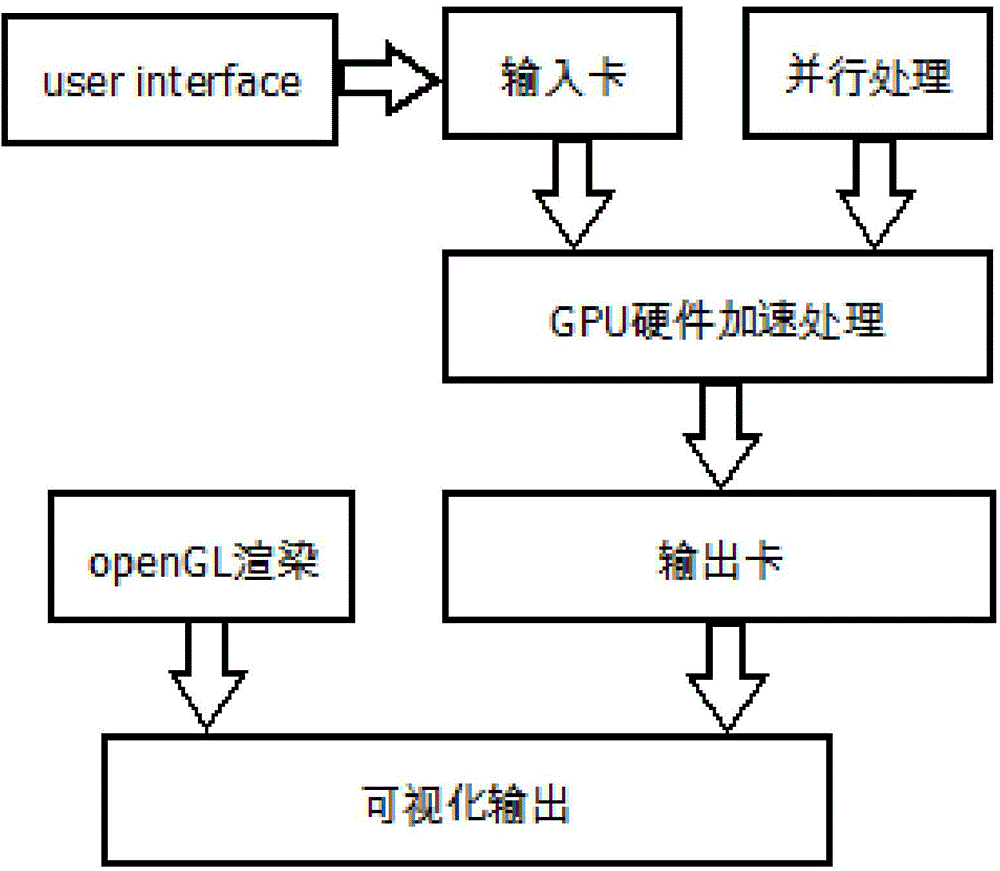
Spallation target visual auxiliary system and method based on GPU hardware acceleration
InactiveCN104978462AReduce error rateAchieve scaleSpecial data processing applicationsHigh energyNuclear reaction
The invention discloses a spallation target visual auxiliary system and a spallation target visual auxiliary method based on GPU hardware acceleration. The spallation target visual auxiliary system is characterized in that: firstly, a geometrical modeling module establishes a module by virtue of a visual method, so that direct conversion of a common CAD module to an MCNP module is completed; secondly, a grain flow simulative transportation module, based on a molecular dynamics algorithm, realizes blending GPU hardware acceleration to visually stimulate movement, in various containers, of grains, and to output associated physical quantity; thirdly, a high-energy Monte Carlo computing module develops a simulation program of intermediate-high-energy atomic nucleus spallation reaction in a GPU edition, so that nuclear reaction processes of particles such as neutrons, protons and the like in an ADS (accelerator driven sub-critical system) spallation target and atoms in a target material can be efficiently stimulated. The modeling module has the advantages of visually generating a three-dimensional model and quickly converting the three-dimensional model into an input file which can be identified by MCNP. The grain flow module and the high-energy Monte Carlo computing module adopt the concurrent thought, so that the computing can be accelerated by GPU. Very critical effect on the design and the stimulation process of the spallation target is achieved.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com