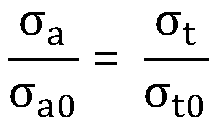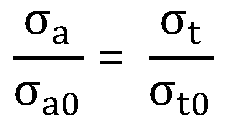Patents
Literature
78 results about "Foreign object damage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In aviation, foreign object debris (FOD) is any article or substance, alien to an aircraft or system, which could potentially cause damage. External FOD hazards include bird strikes, hail, ice, sandstorms, ash-clouds or objects left on the runway. Internal FOD hazards include items left in the cockpit that interfere with flight safety by getting tangled in control cables, jam moving parts or short-out electrical connections.
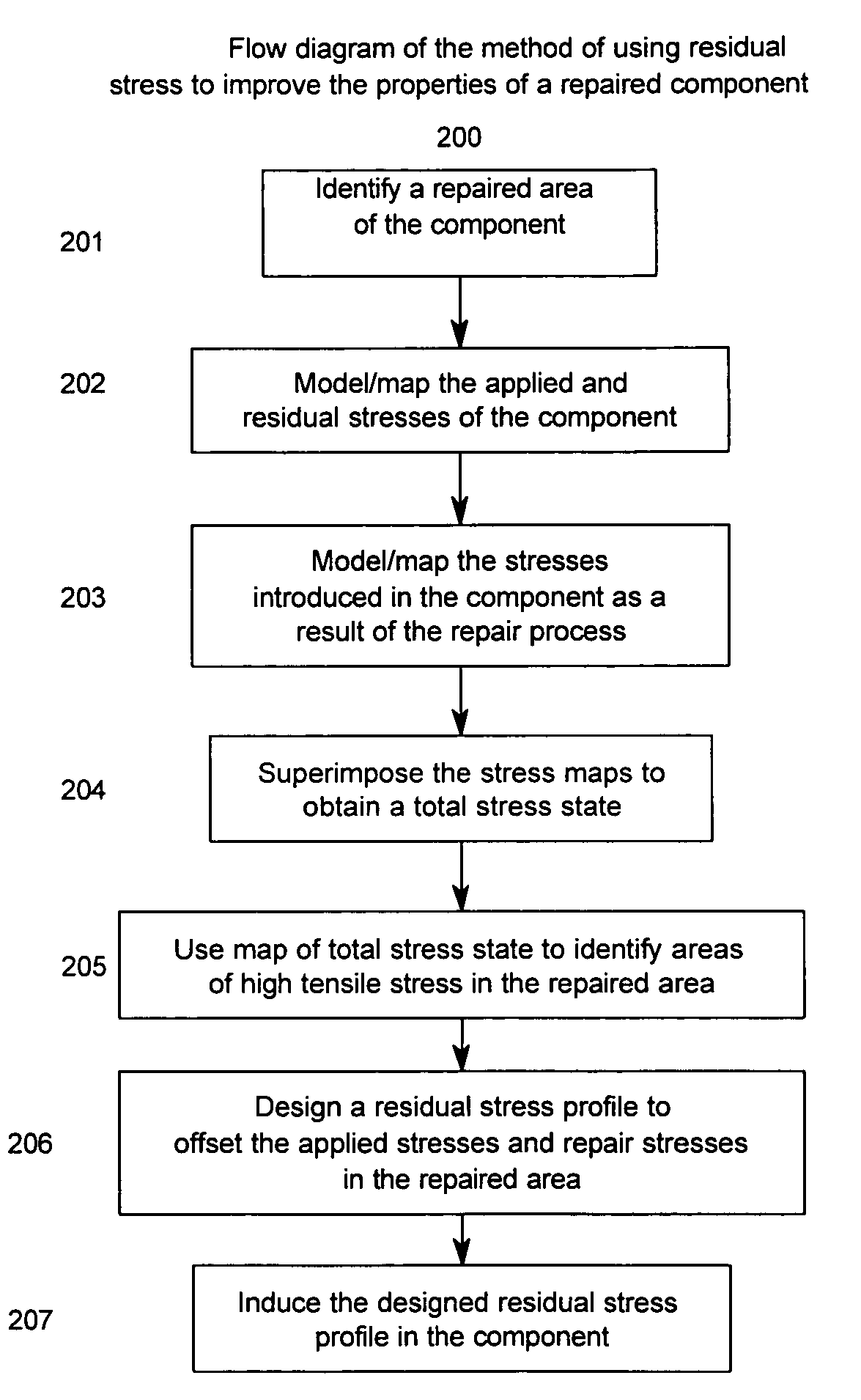
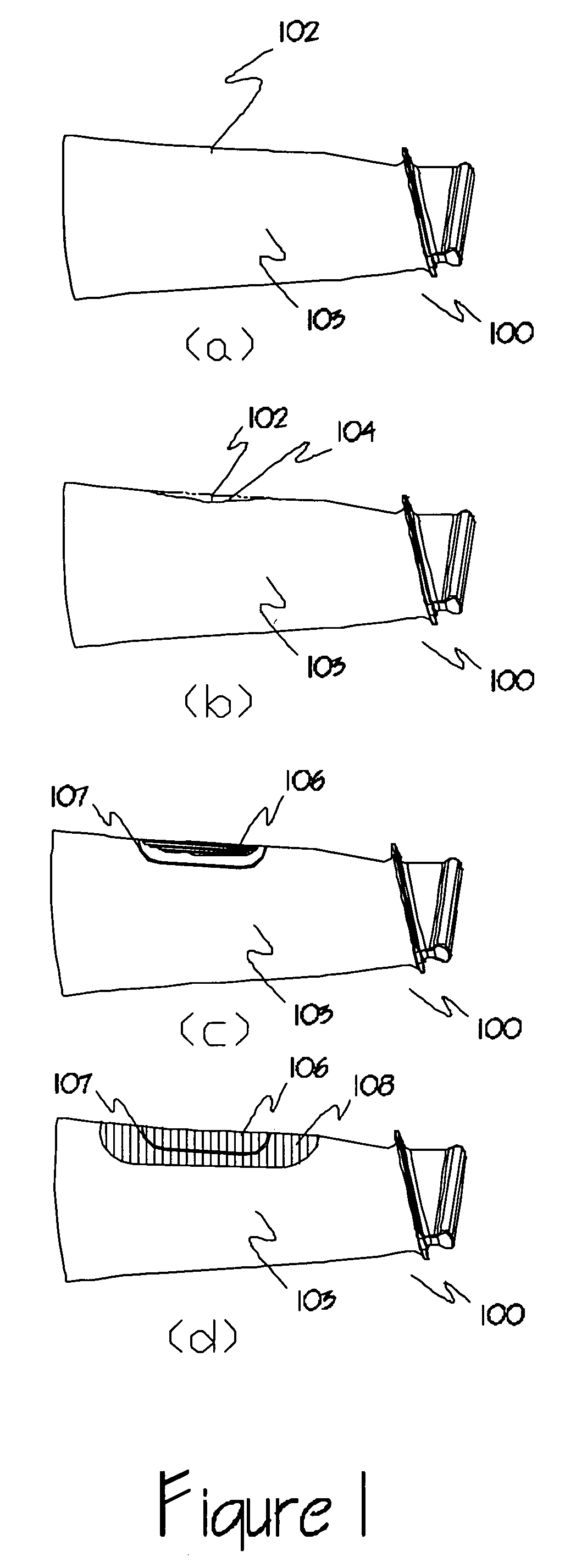
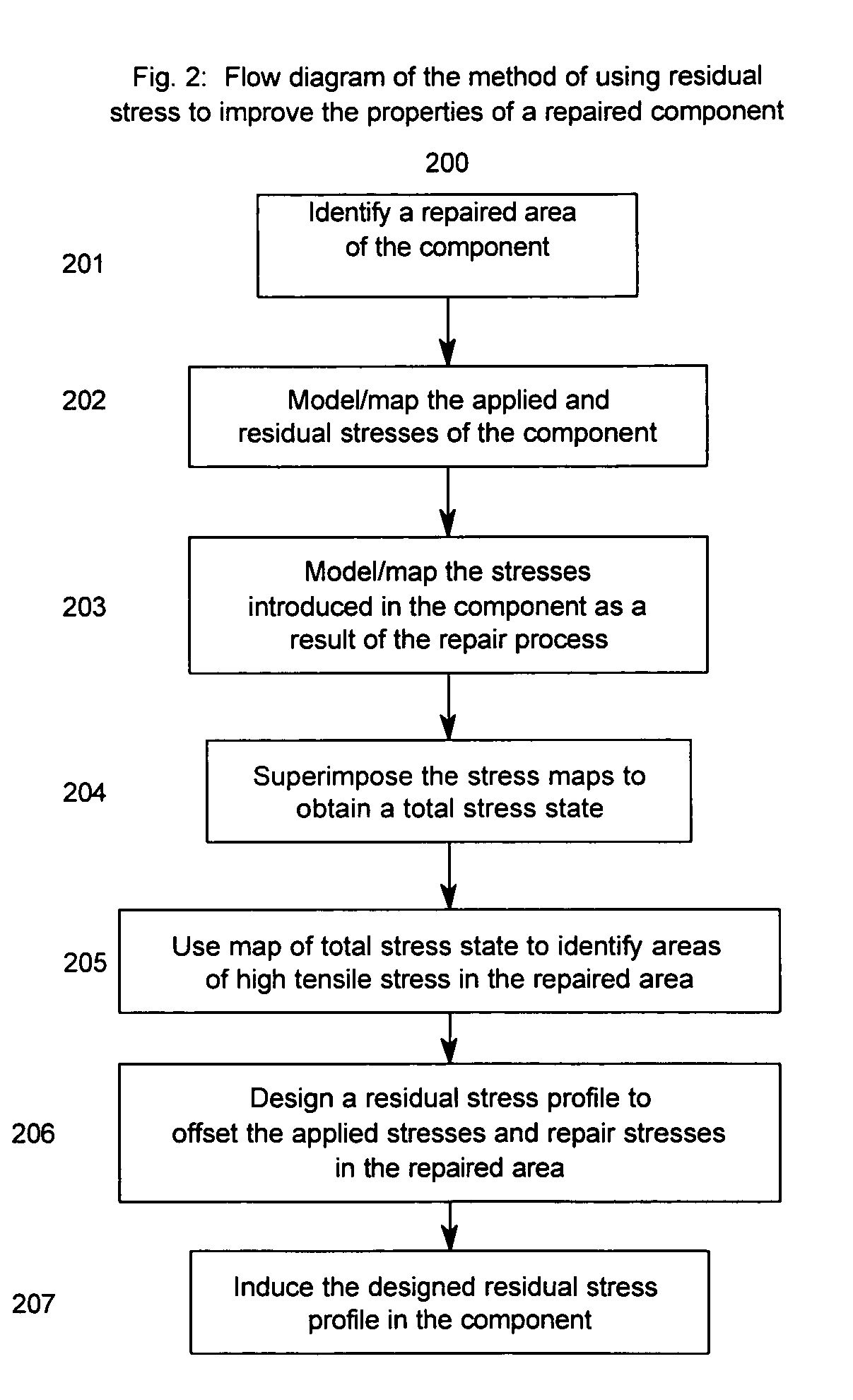
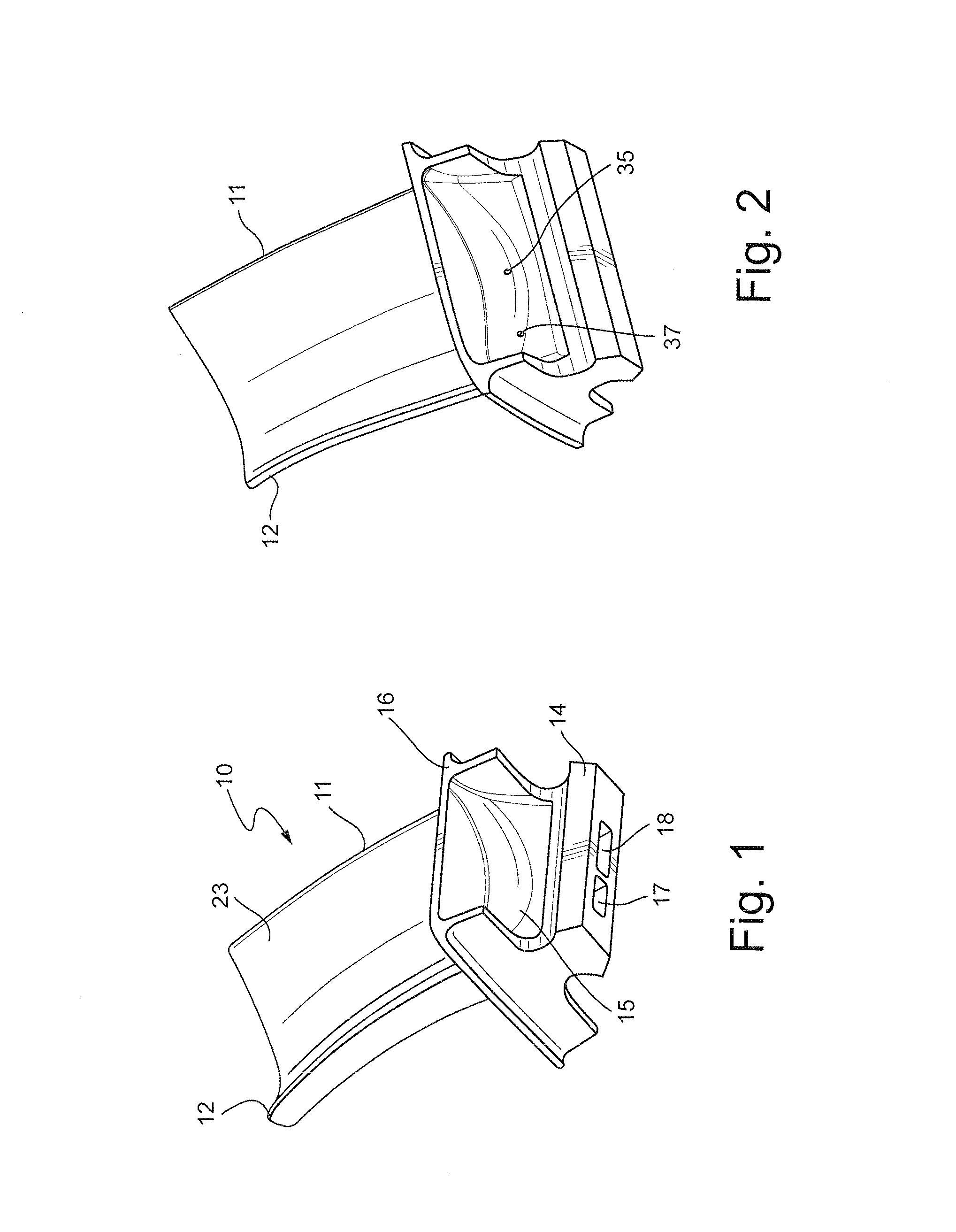
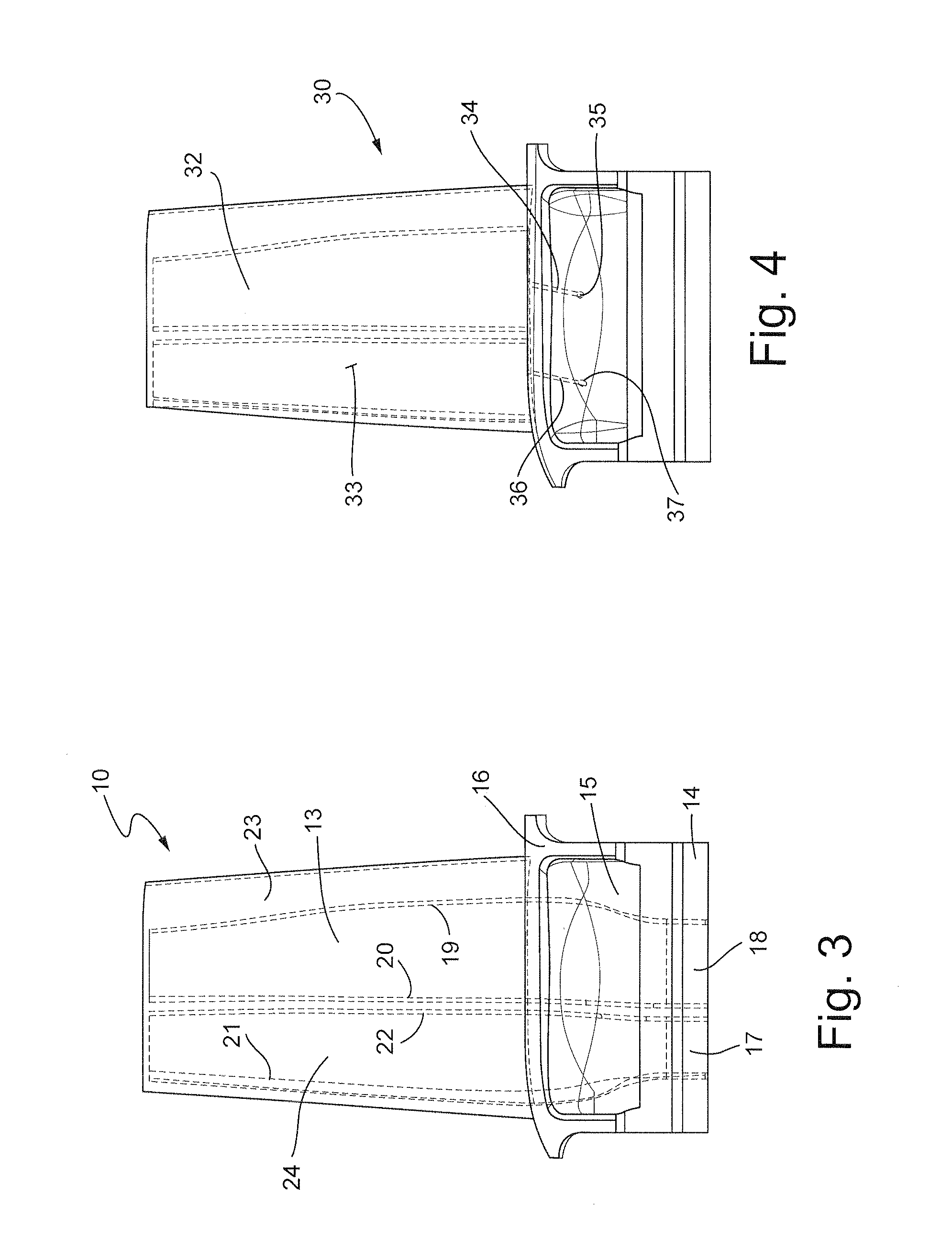
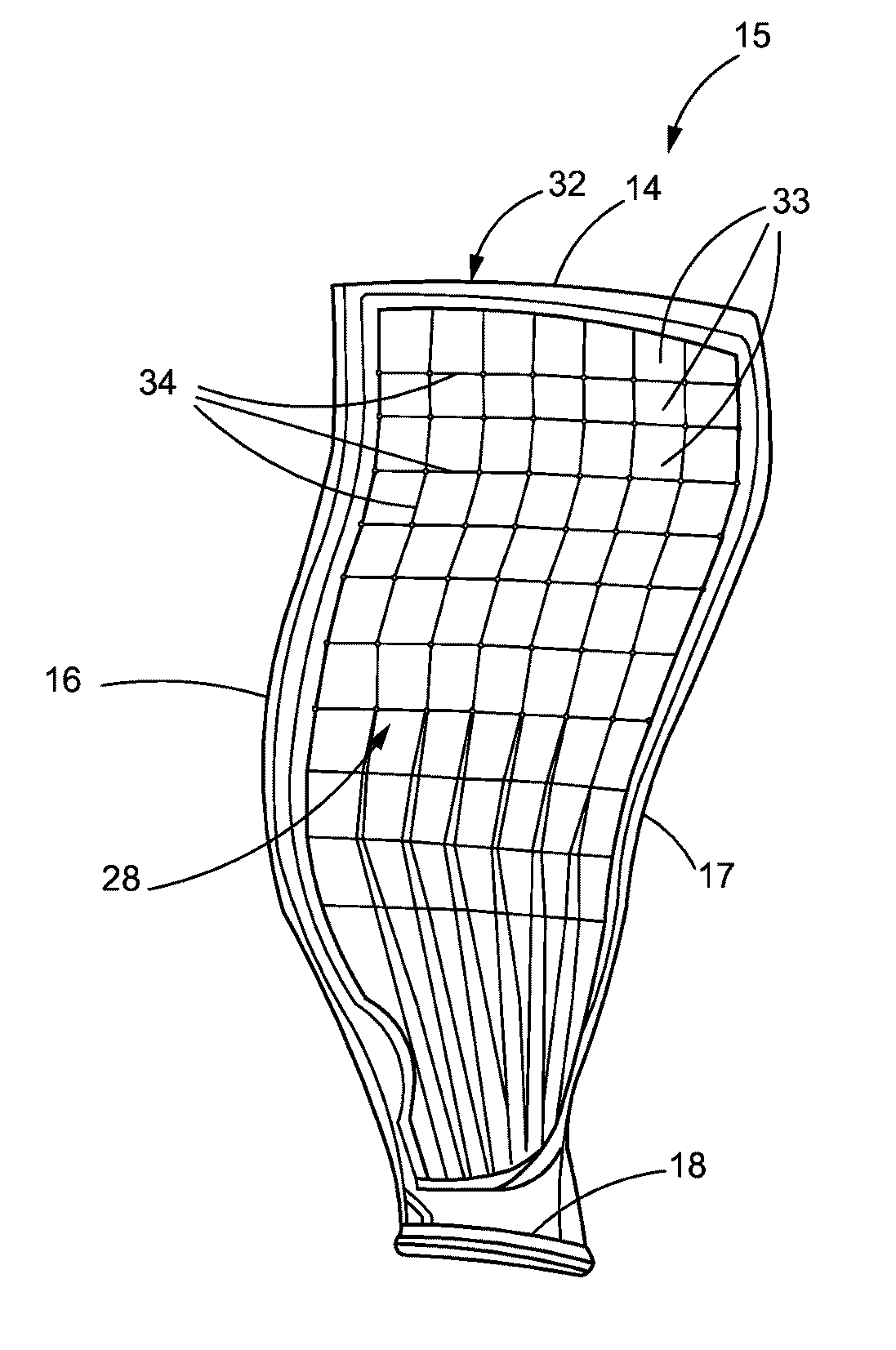
Method of improving the properties of a repaired component and a component improved thereby
InactiveUS20070157447A1Improved material and mechanical propertySimple materialBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesForeign matterForeign object damage
A repaired component with improved material and mechanical properties and a method of improving the properties of a repaired component are provided. The repaired component comprises a body, a repaired area integral with the body, and an area of compressive residual stress wherein the area of compressive residual stress comprises at least a portion of the repaired area. One method for improving the fatigue performance, foreign object damage tolerance, and resistance to stress related failure mechanisms of a repaired component includes inducing a designed residual compressive stress distribution with a controlled amount of cold work in the repaired area to offset high-applied tensile stresses and stresses introduced as a result of the repair procedure as well as to improve the properties of the material added to the component during the repair.
Owner:PREVEY PAUL S
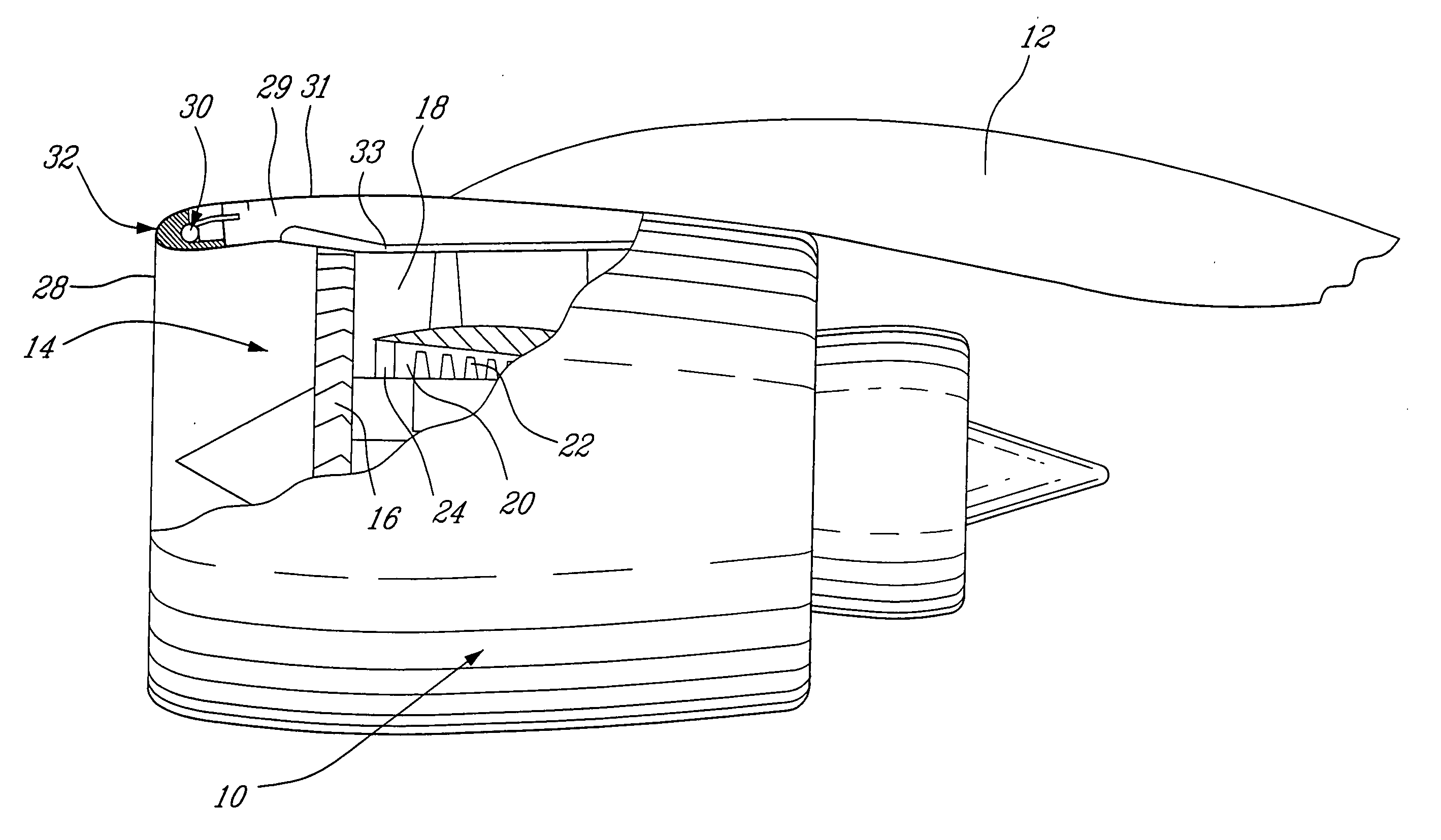
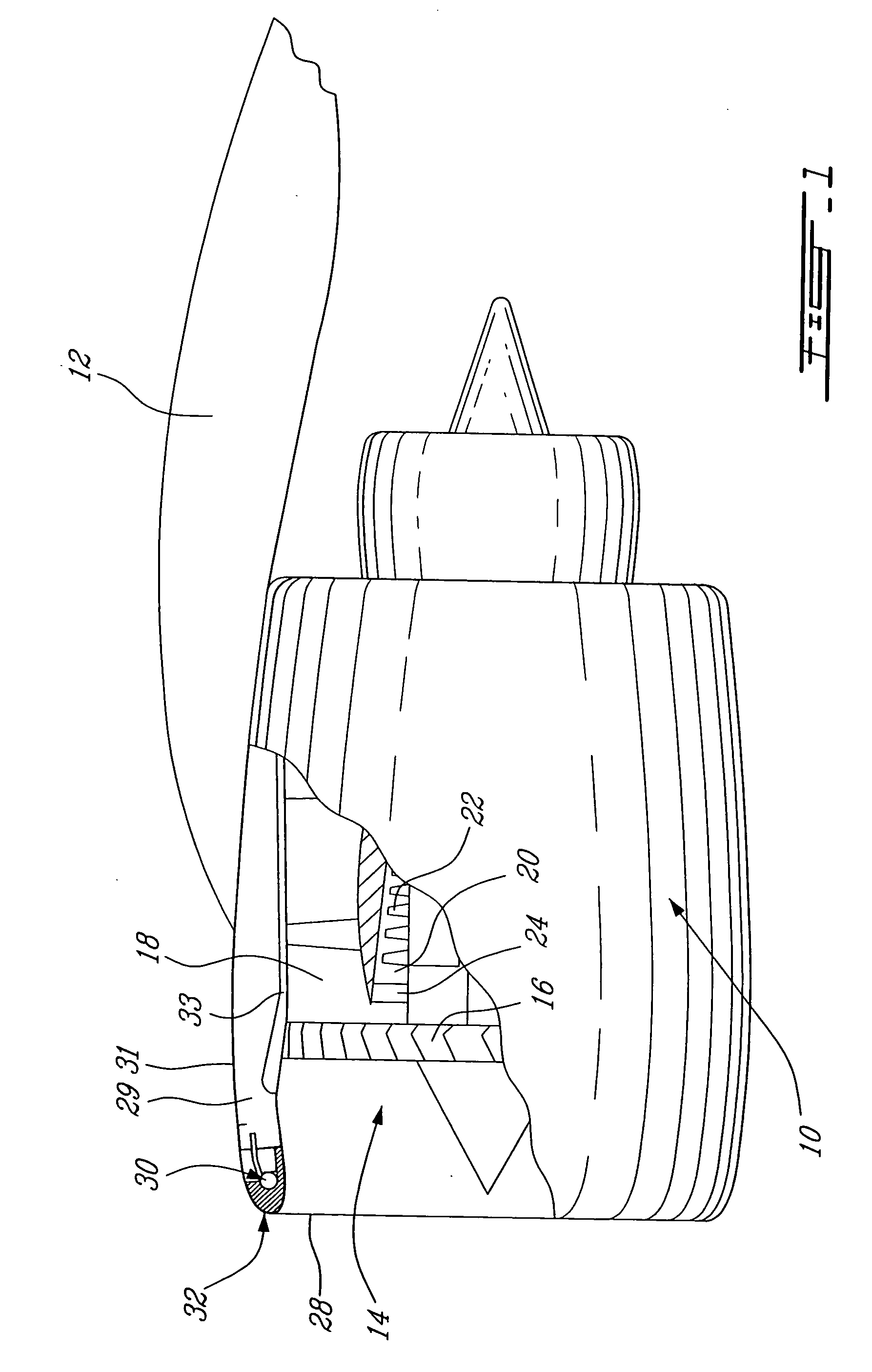
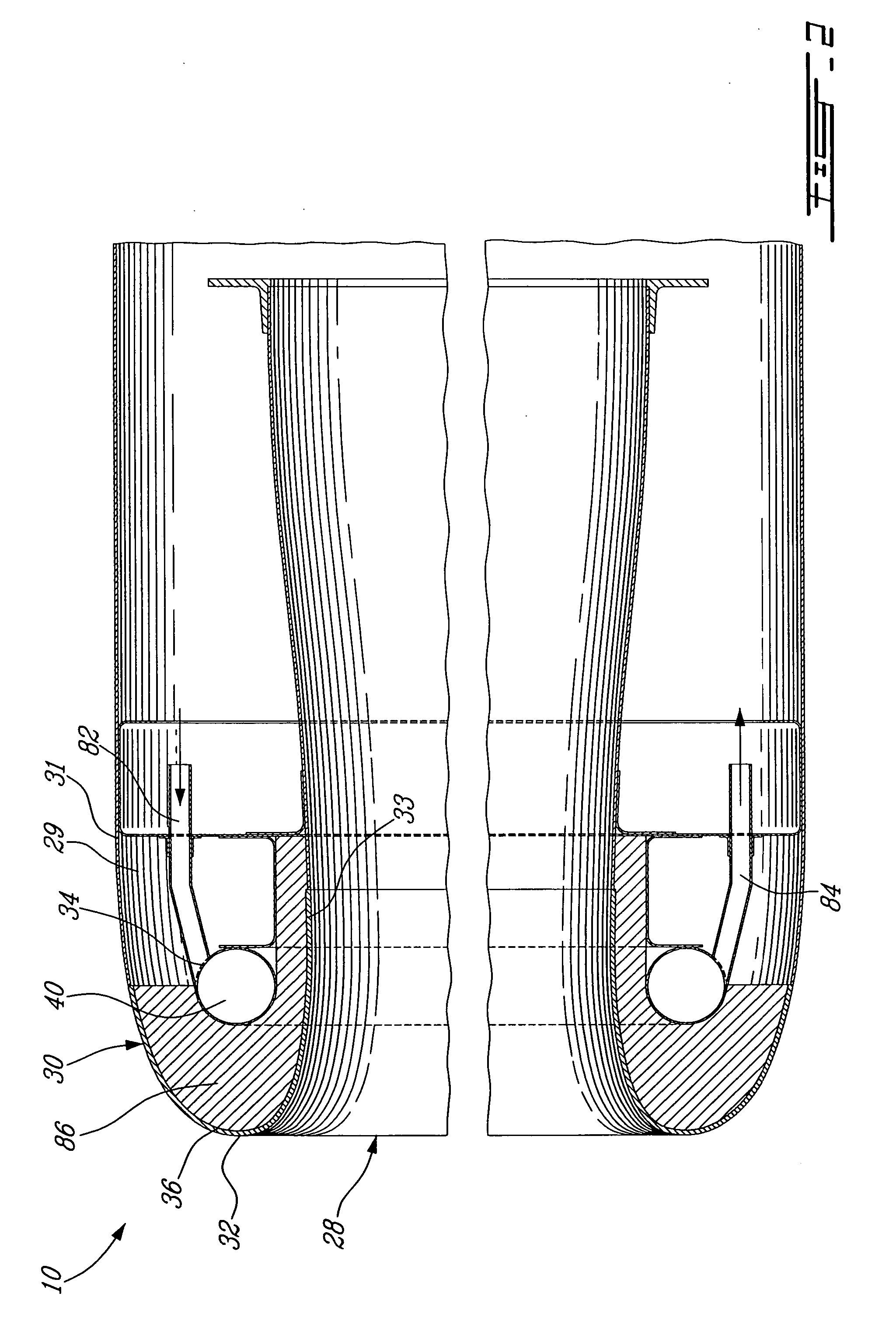
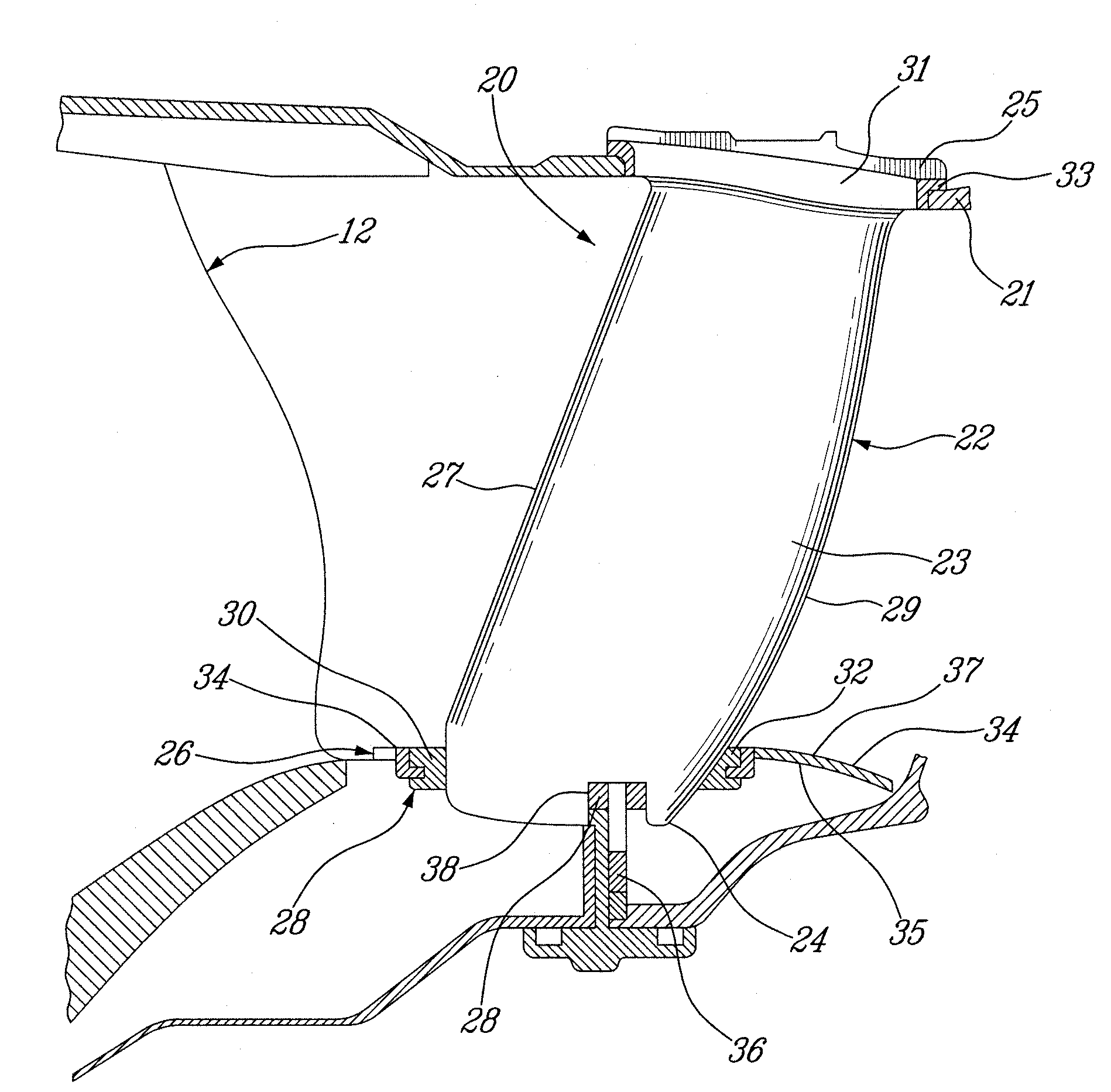
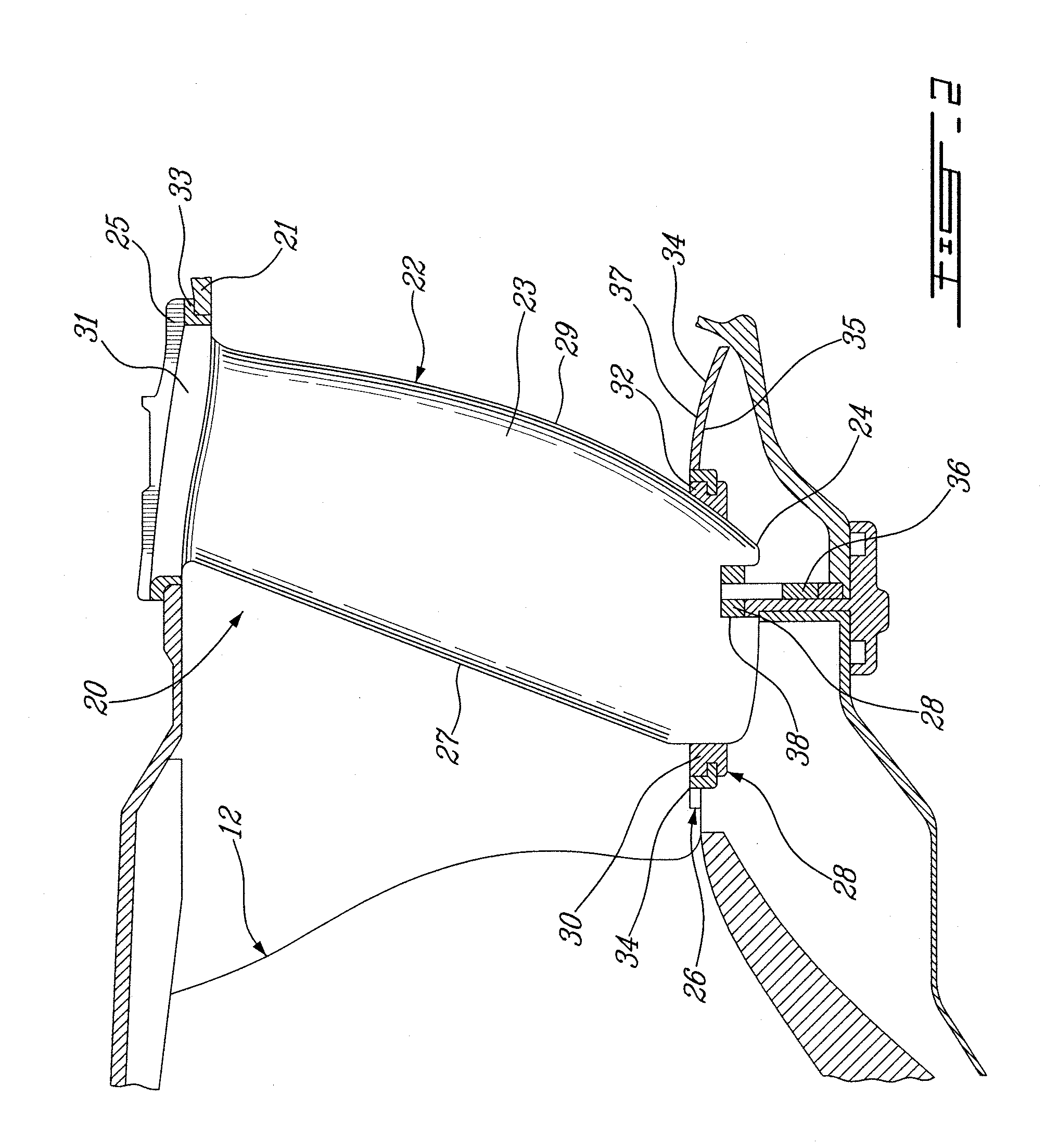
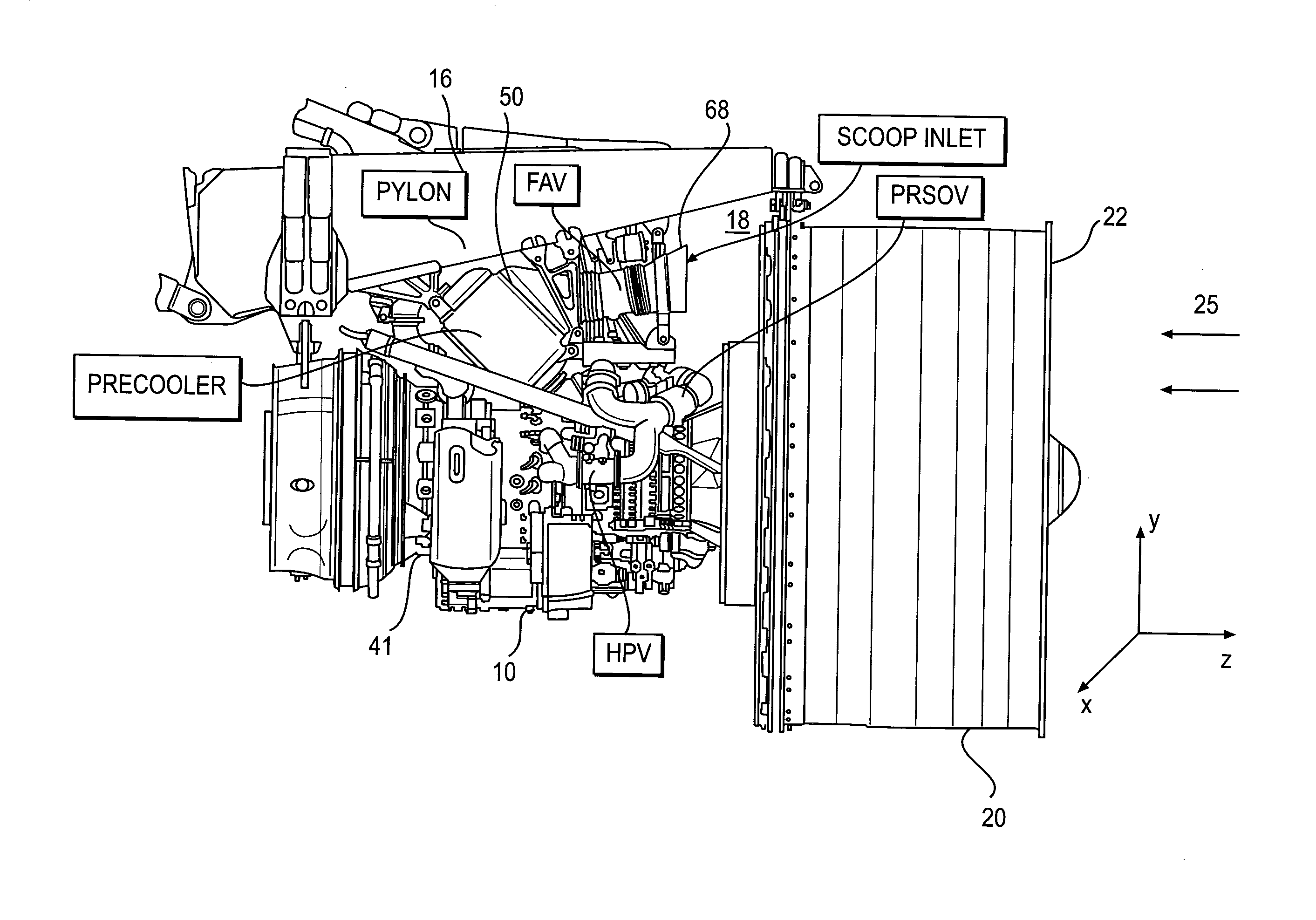
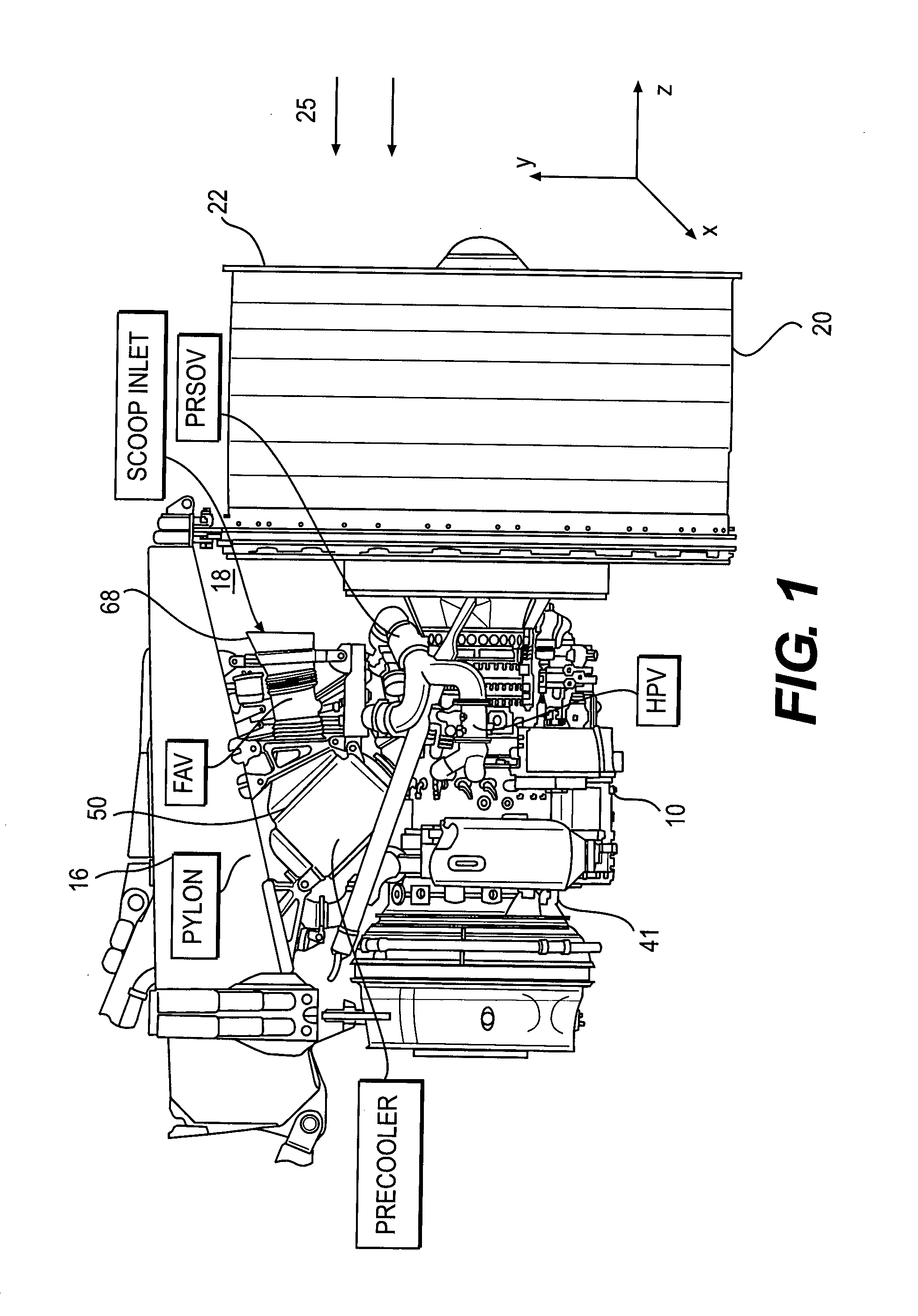
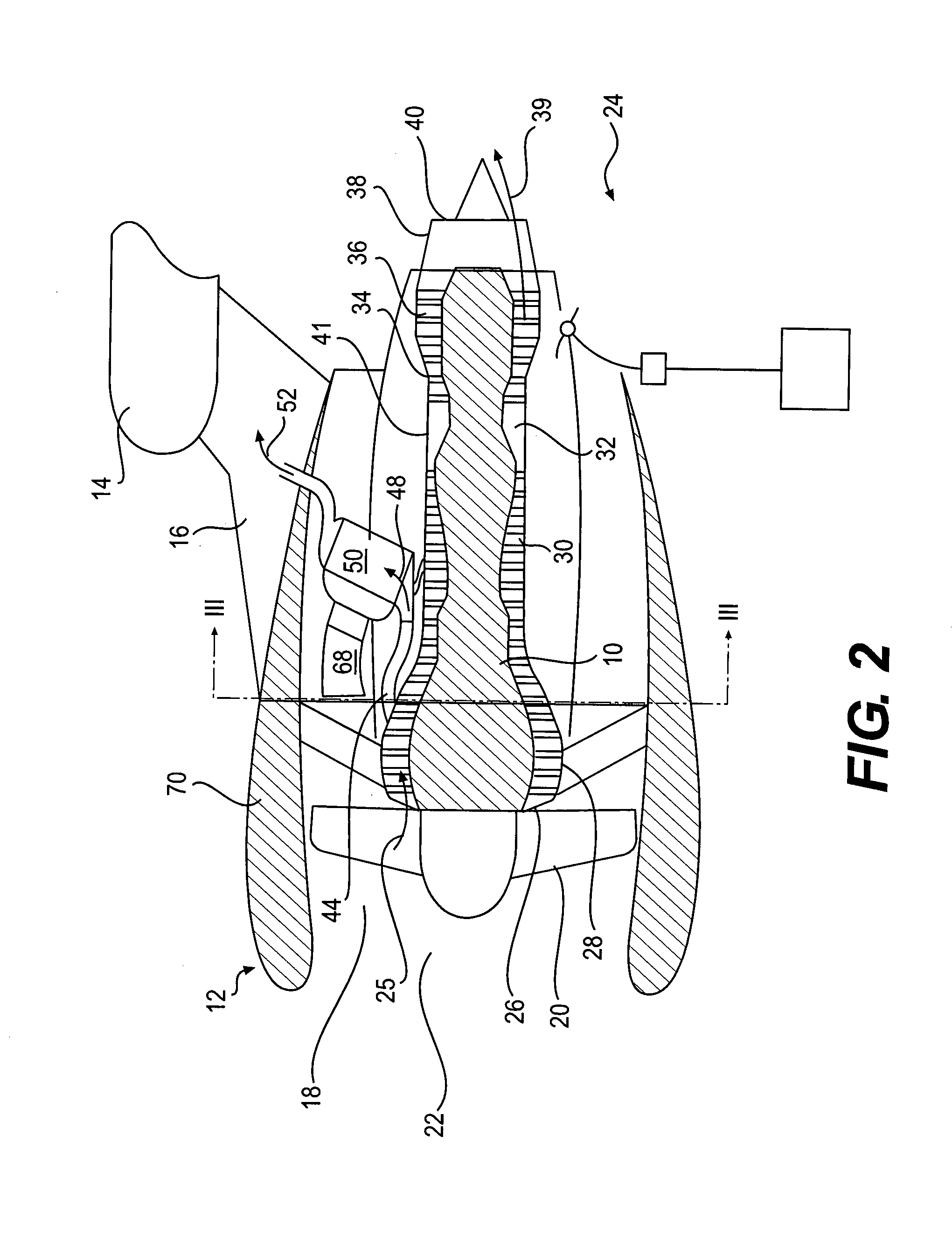
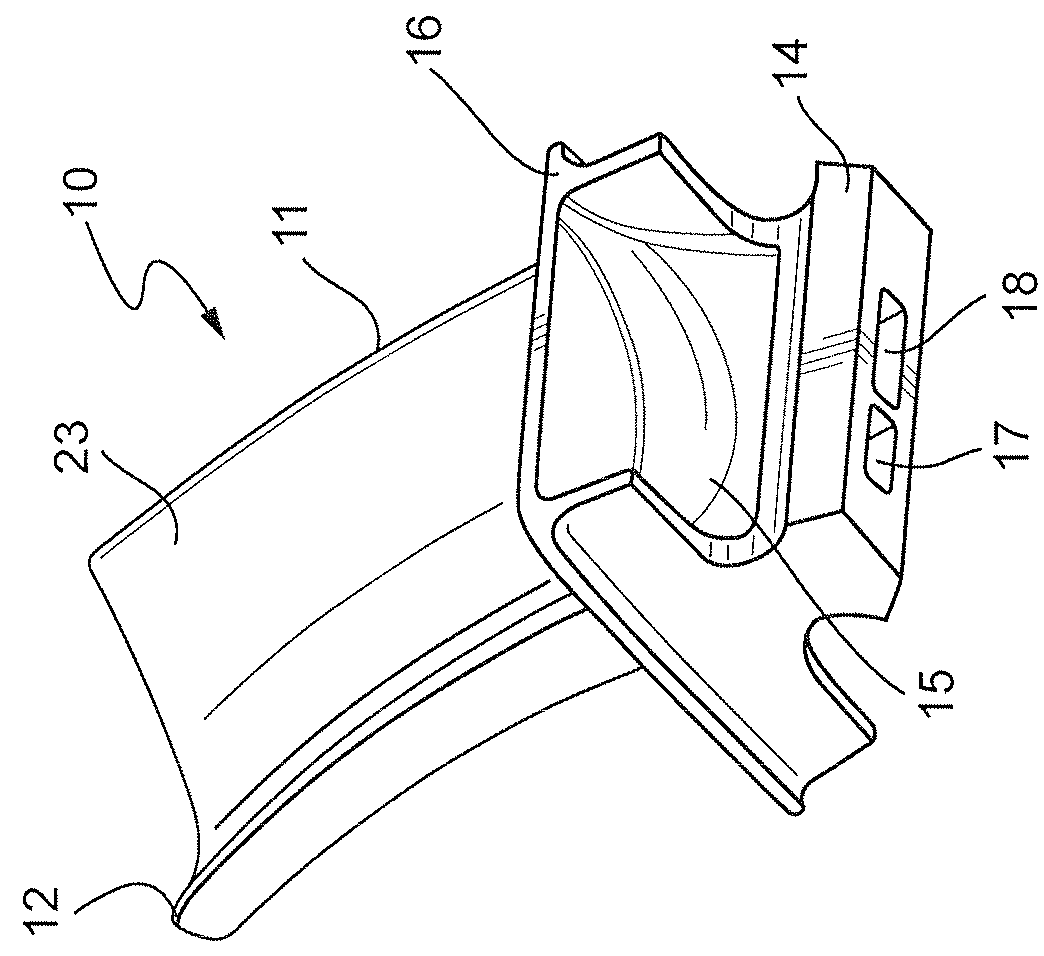
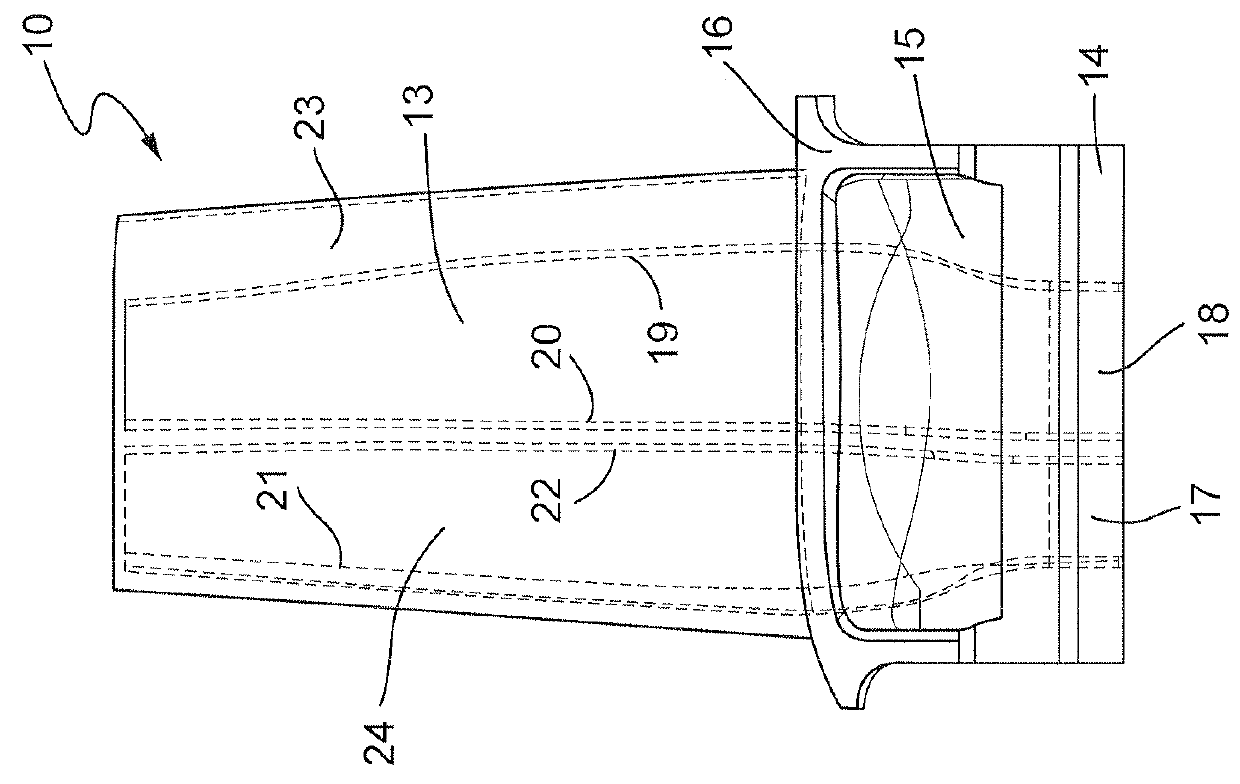
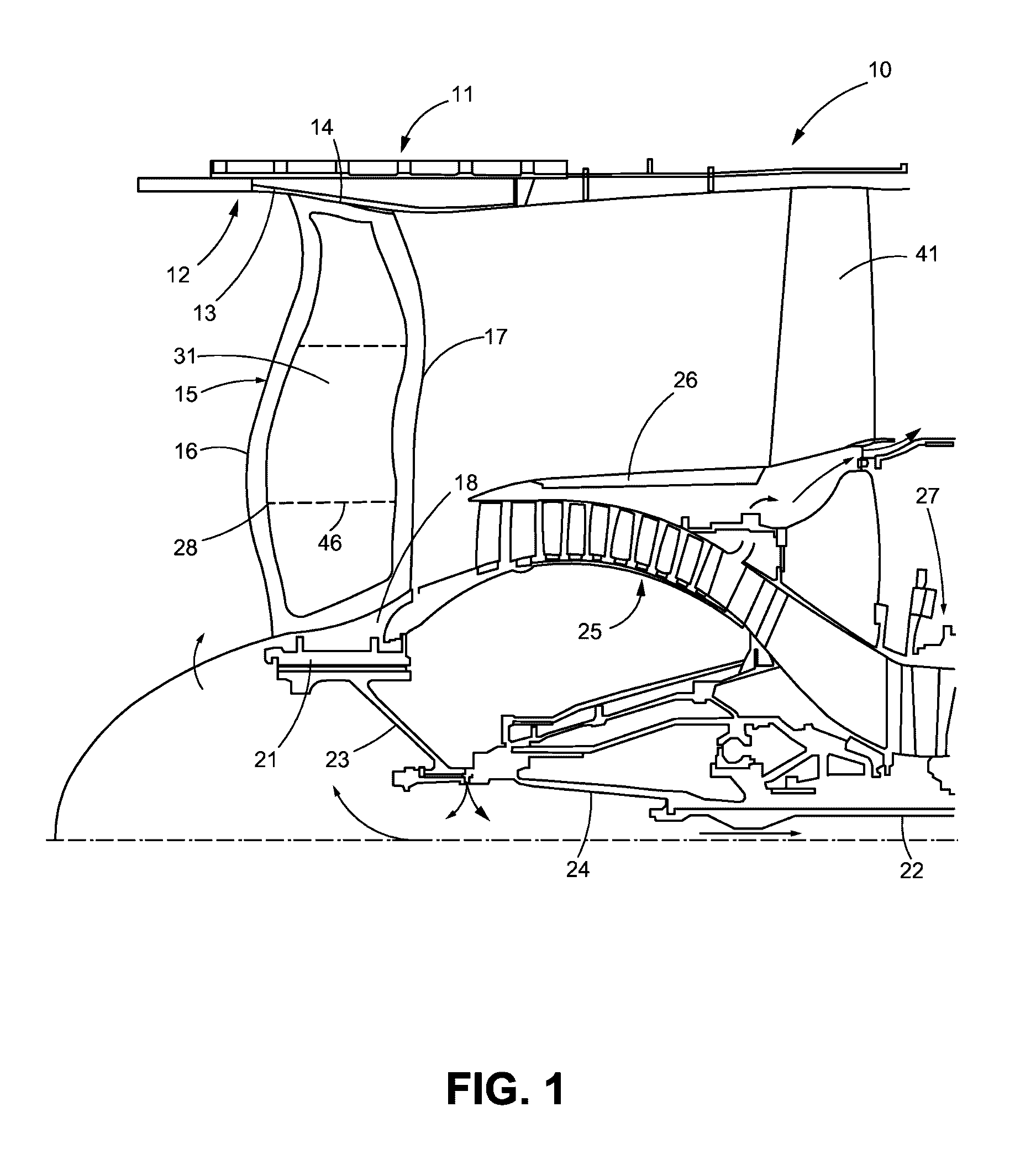
Foreign object damage tolerant nacelle anti-icing system
InactiveUS20060032983A1Prevent freezingSufficient thermal conductivityPower plant arrangements/mountingDe-icing equipmentsForeign matterLeading edge
A nacelle for housing a gas turbine engine is disclosed. The nacelle comprises an inlet lip defining a leading edge of the nacelle and a conduit located within the inlet lip, the conduit having a fluid circulating therein. The fluid provides a heat source. An energy attenuating member is located within the inlet lip between the leading edge and the conduit. The energy attenuating member provides protection to the conduit from foreign object damage and is thermally conductive such that heat transfer communication between the conduit and the leading edge is provided.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Method for Application of a Thermal Barrier Coating and Resultant Structure Thereof
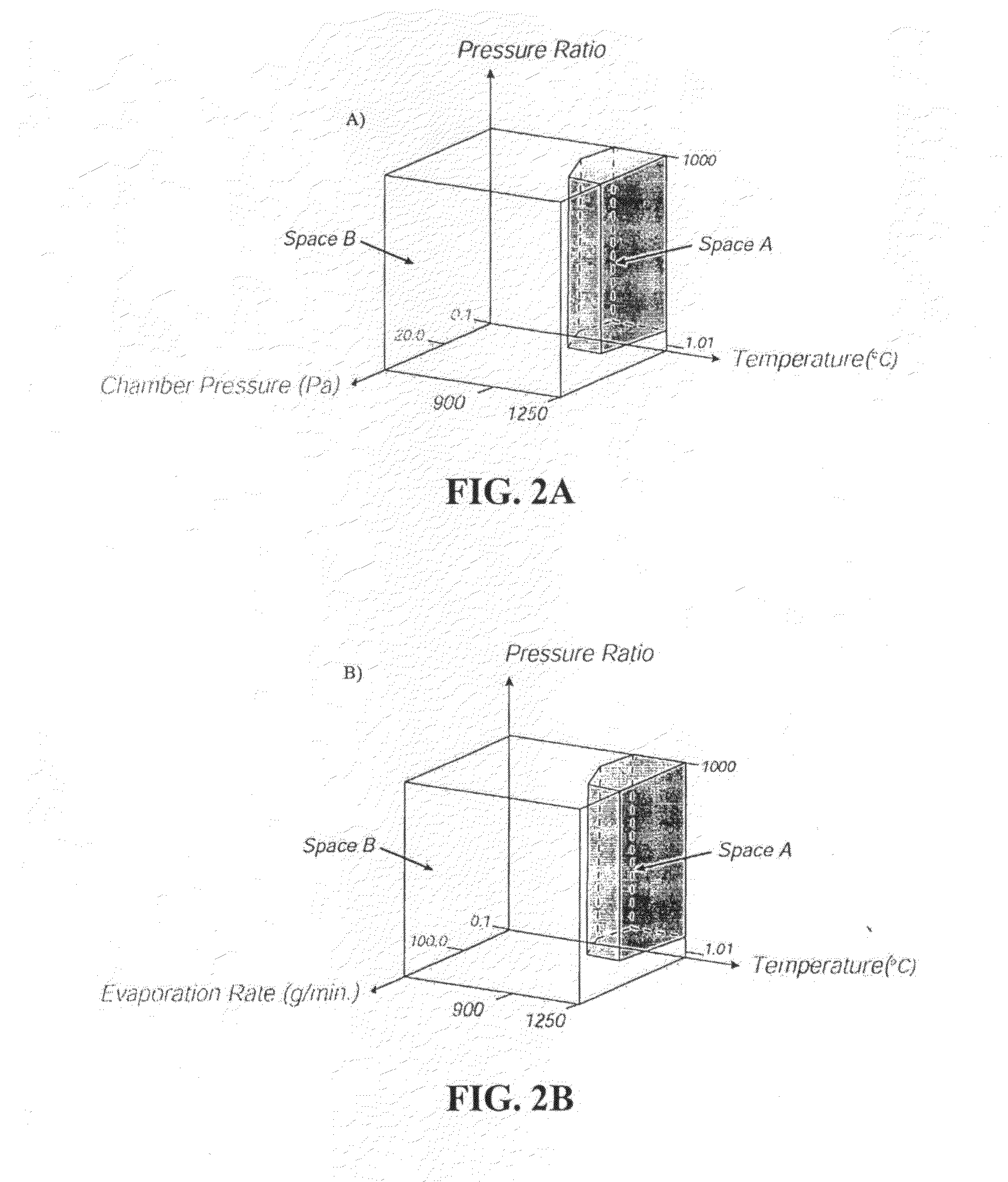
InactiveUS20080131611A1Low thermal conductivityHigh elastic complianceMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingIn planeForeign object damage
Provided herein are methods and apparatuses, and resulting structures, for depositing ceramic coatings with preferred coating density, morphology and adherence for applications such as thermal protection of internally cooled components. Such components are found in, but not limited thereto, the hot sections of gas turbine and diesel engines and in turbo machinery. These coatings require a low thermal conductivity in the through thickness of the coating, high in-plane elastic compliance, high erosion and foreign object damage resistance and resistance to hot corrosion. The methods and apparatuses discussed herein provide, among other things, how to manipulate the process conditions in EB-DVD systems to deposit high quality, highly efficient TBS top coats as well as how to deposit high quality TBC top coats onto positions that are in the line-of-sight, as well as non-line of sight, of the vapor source.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
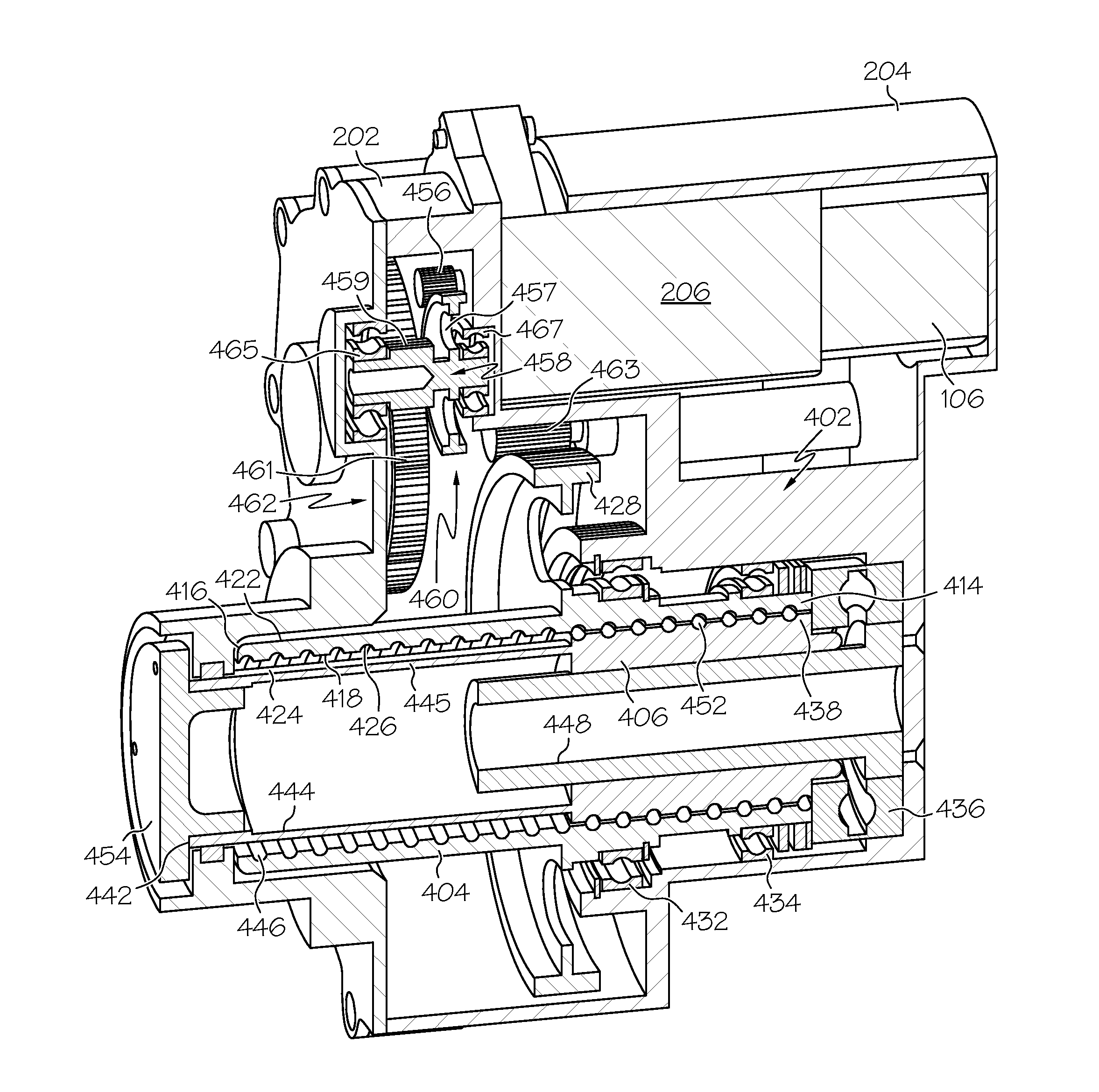
Brake actuator assembly with line replaceable motor features
ActiveUS20110132704A1Aircraft brake actuating mechanismsBrake actuating mechanismsForeign object damageControl theory
An aircraft brake system electromechanical actuator is provided. The actuator is configured with features that allow the electric motor to be a line replaceable unit. One such feature is a foreign-object-damage shield that inhibits dust, debris, and / or other particulate contaminants from entering the electromechanical actuator during electric motor removal and replacement.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
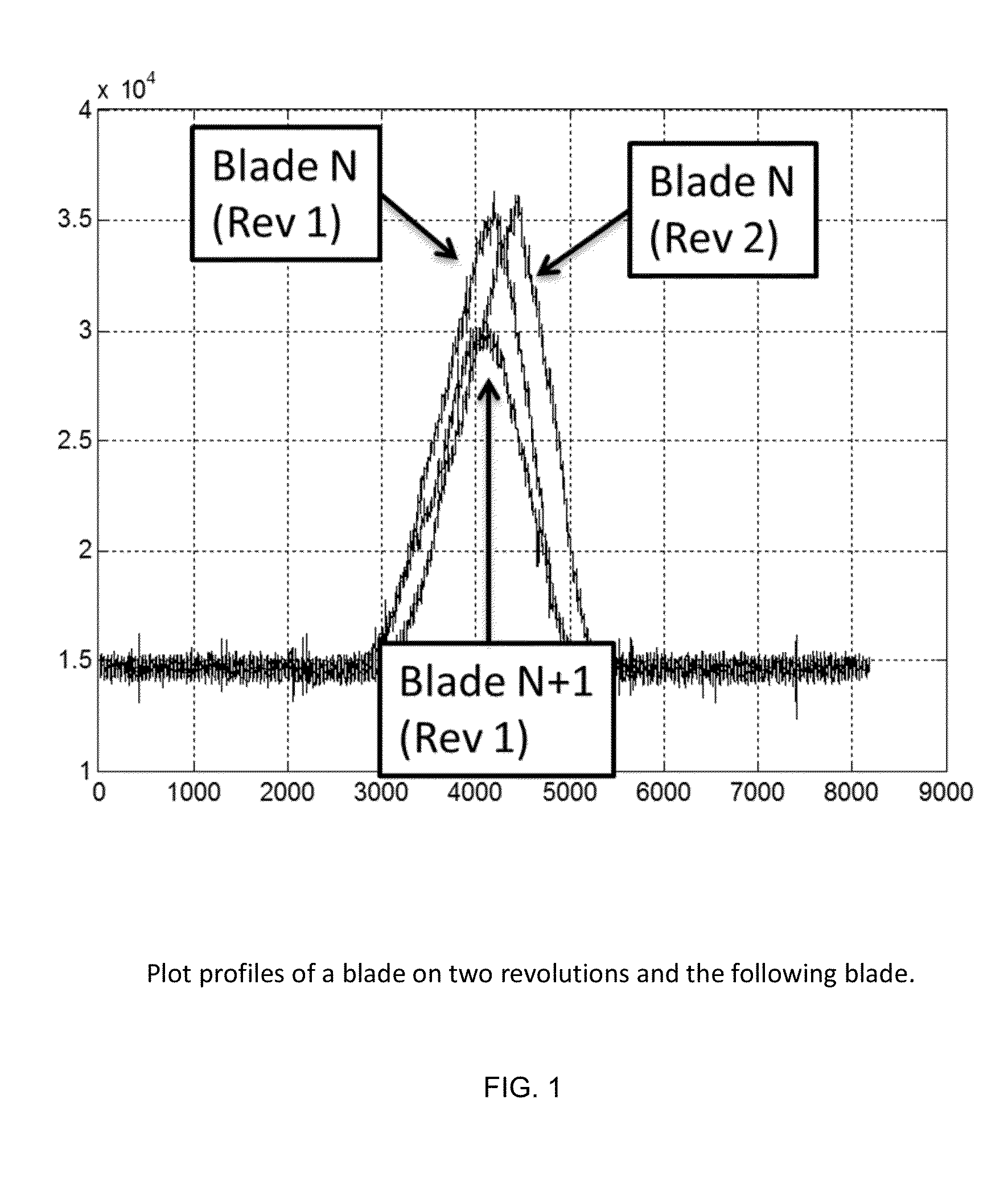
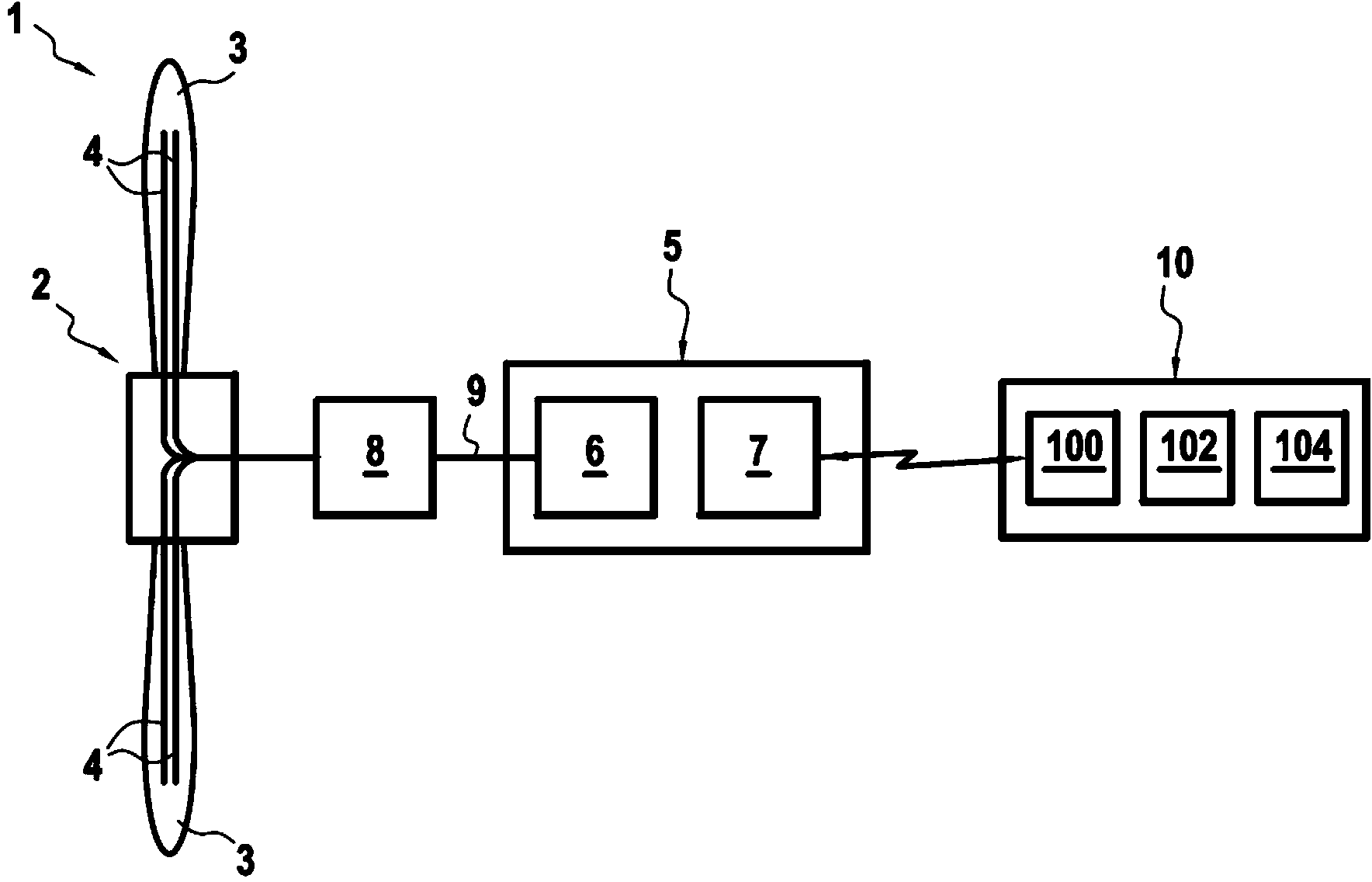
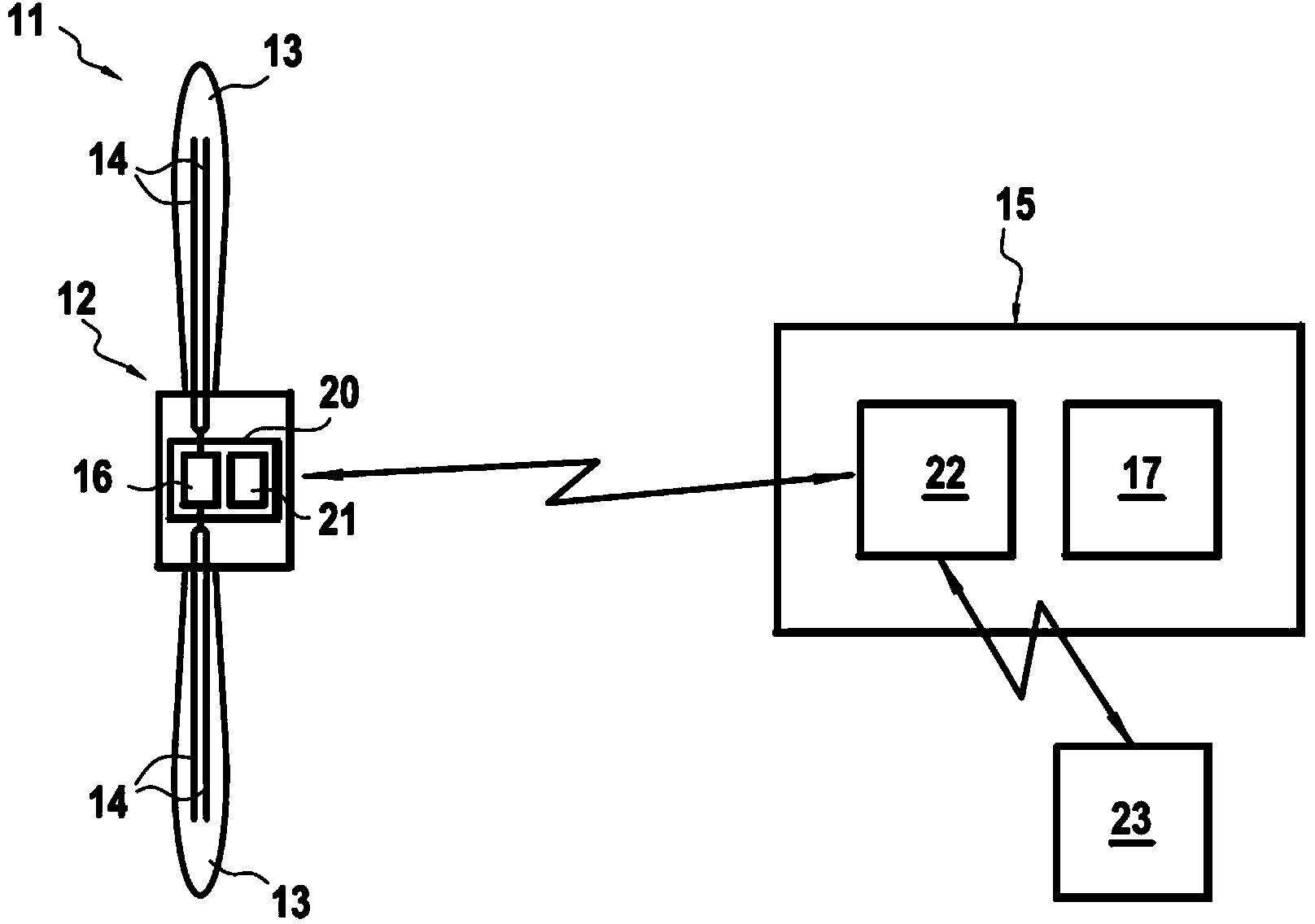
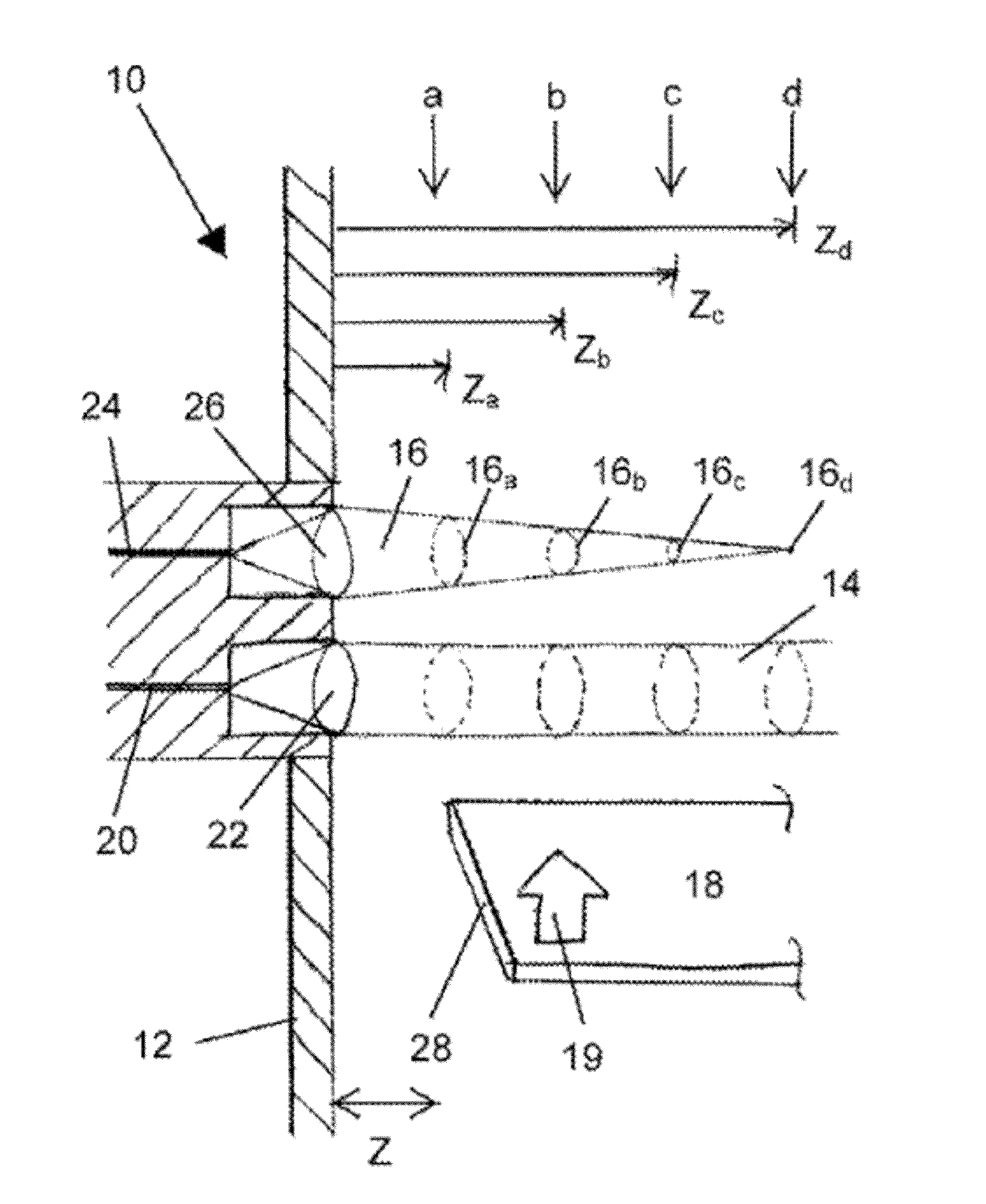
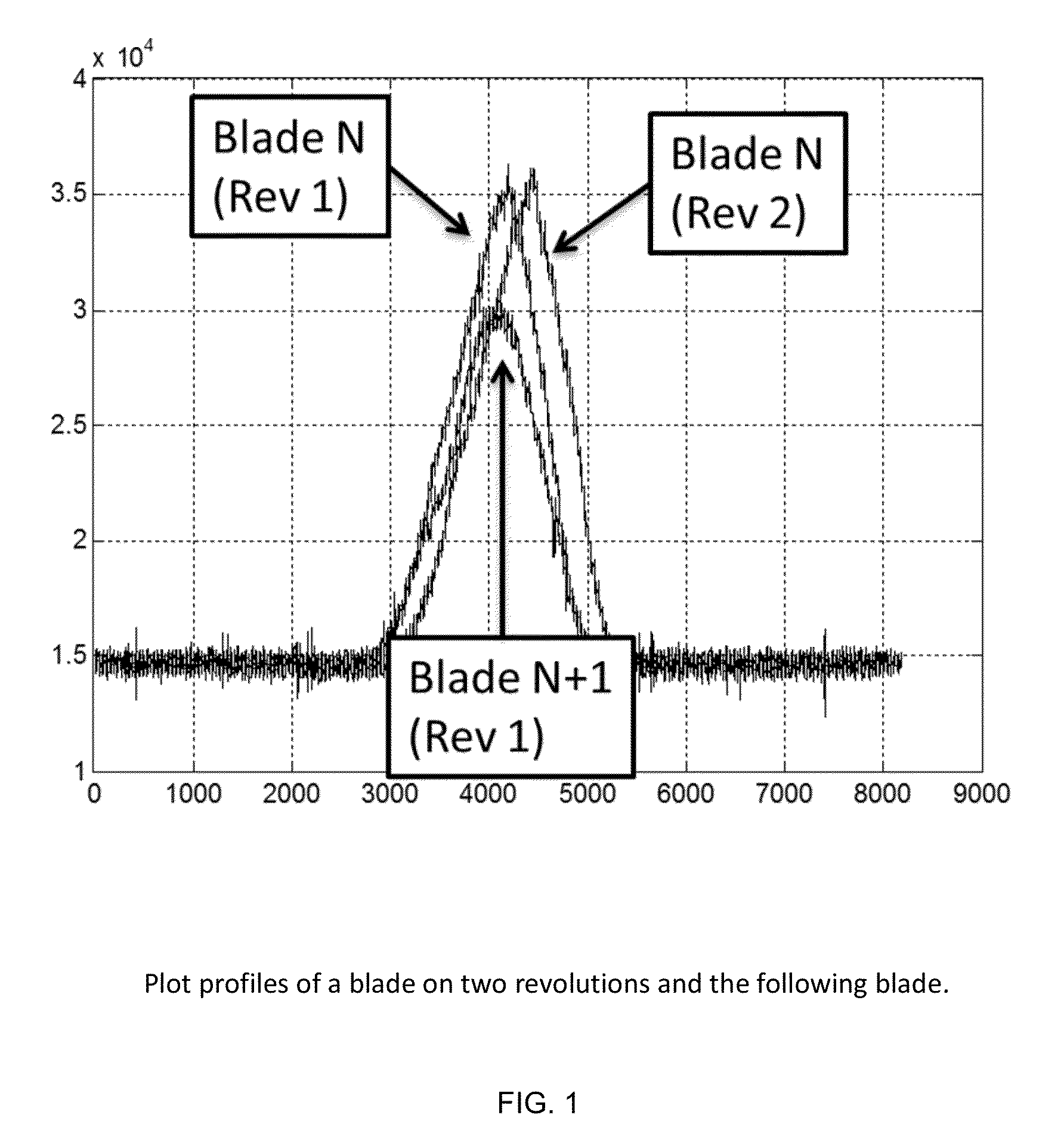
Method for Detecting Foreign Object Damage in Turbomachinery
ActiveUS20130006541A1Low costRemoval costPlug gaugesEngine fuctionsForeign object damageOperational costs
The present invention relates to systems and methods for real-time health monitoring of engines to monitor turbomachinery blades during engine operation and report anomalous behavior and shape of the blades if it occurs, such as damage by FOD. The system comprises sensor(s) for obtaining a blade reflection profile from a blade passing by the sensor(s) during a revolution of the rotor in combination with a processor for performing timing calculations and / or fingerprint comparisons with reference data to identify a change in blade fingerprint relative to the reference data, which may indicate blade damage. Such systems can reduce operational costs, enhance safety and improve operational readiness by facilitating condition-based maintenance of engine rotors as opposed to schedule-based solutions. The invention can prevent the needless loss of life and assets caused by undetected minor levels of blade damage that may lead to unexpected catastrophic failure of an engine.
Owner:PRIME PHOTONICS LC
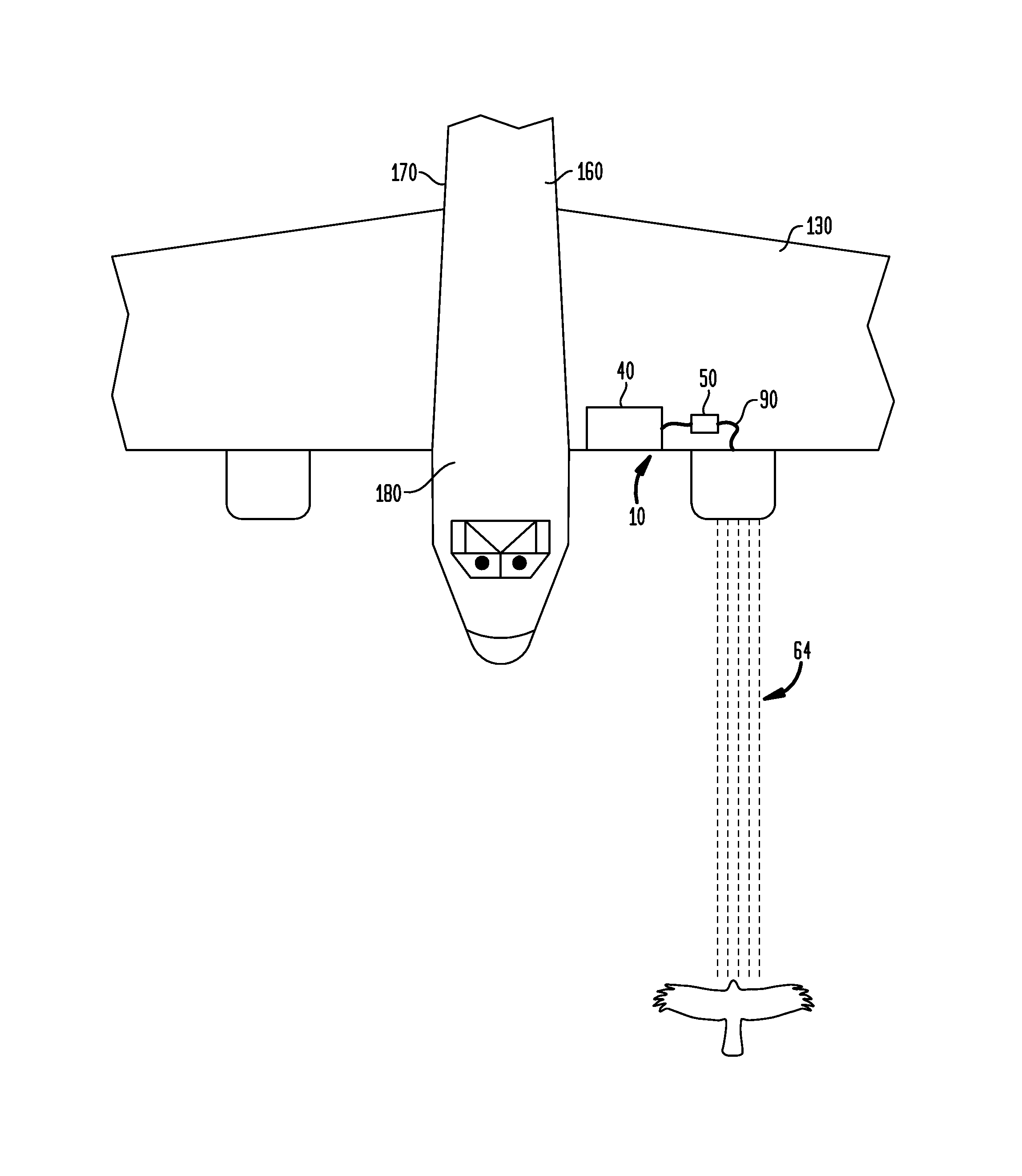
Foreign object damage protection device and system for aircraft
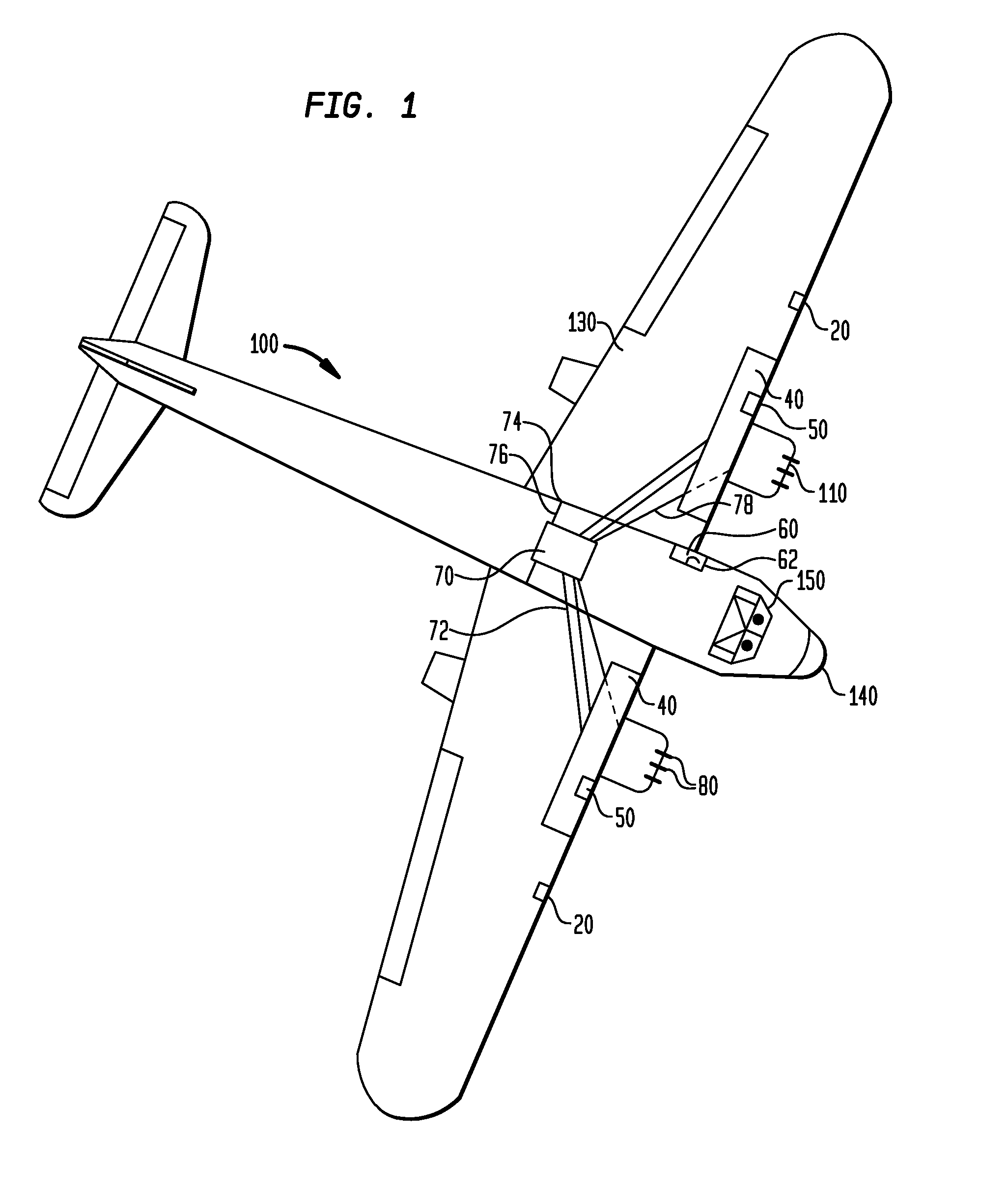
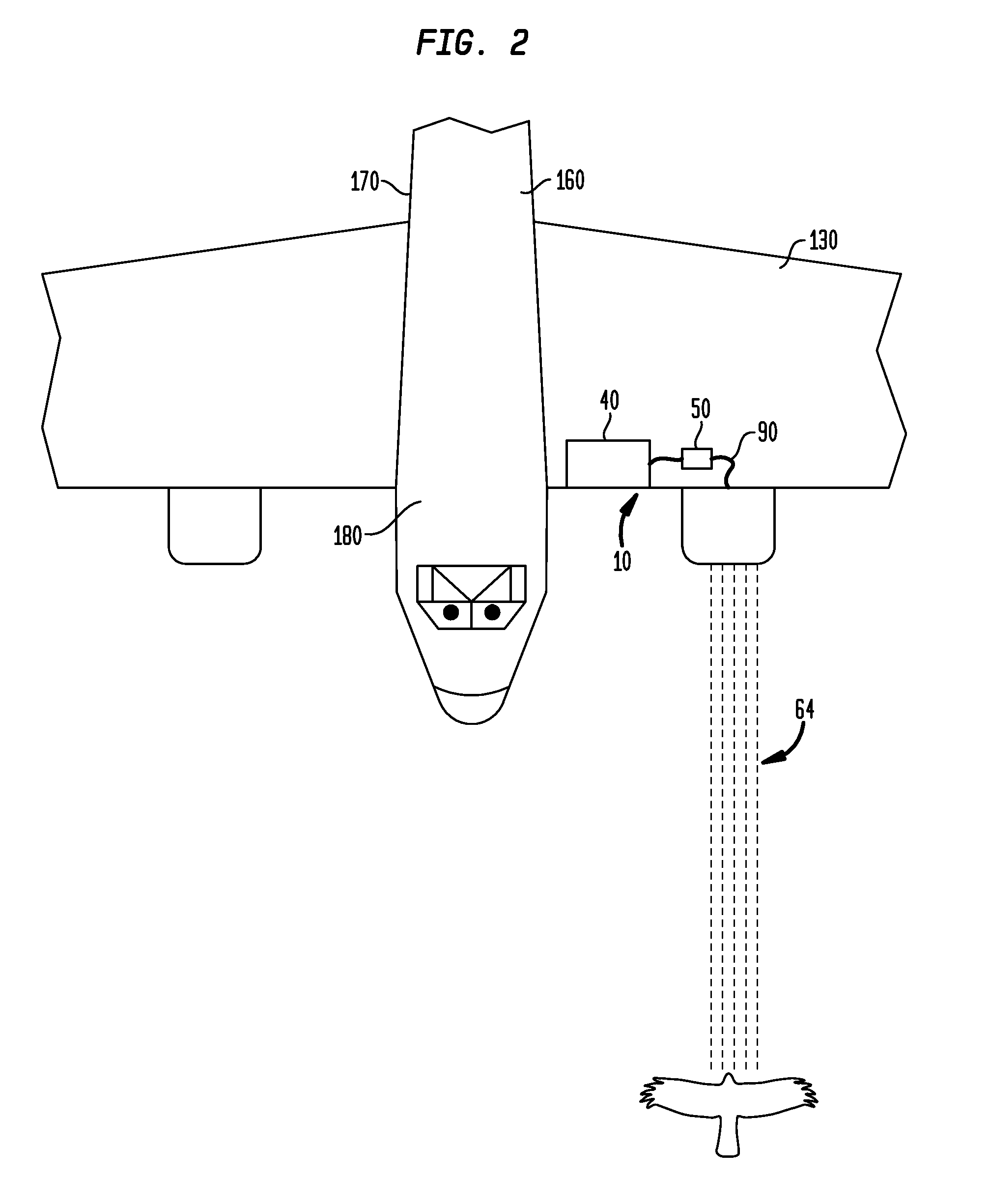
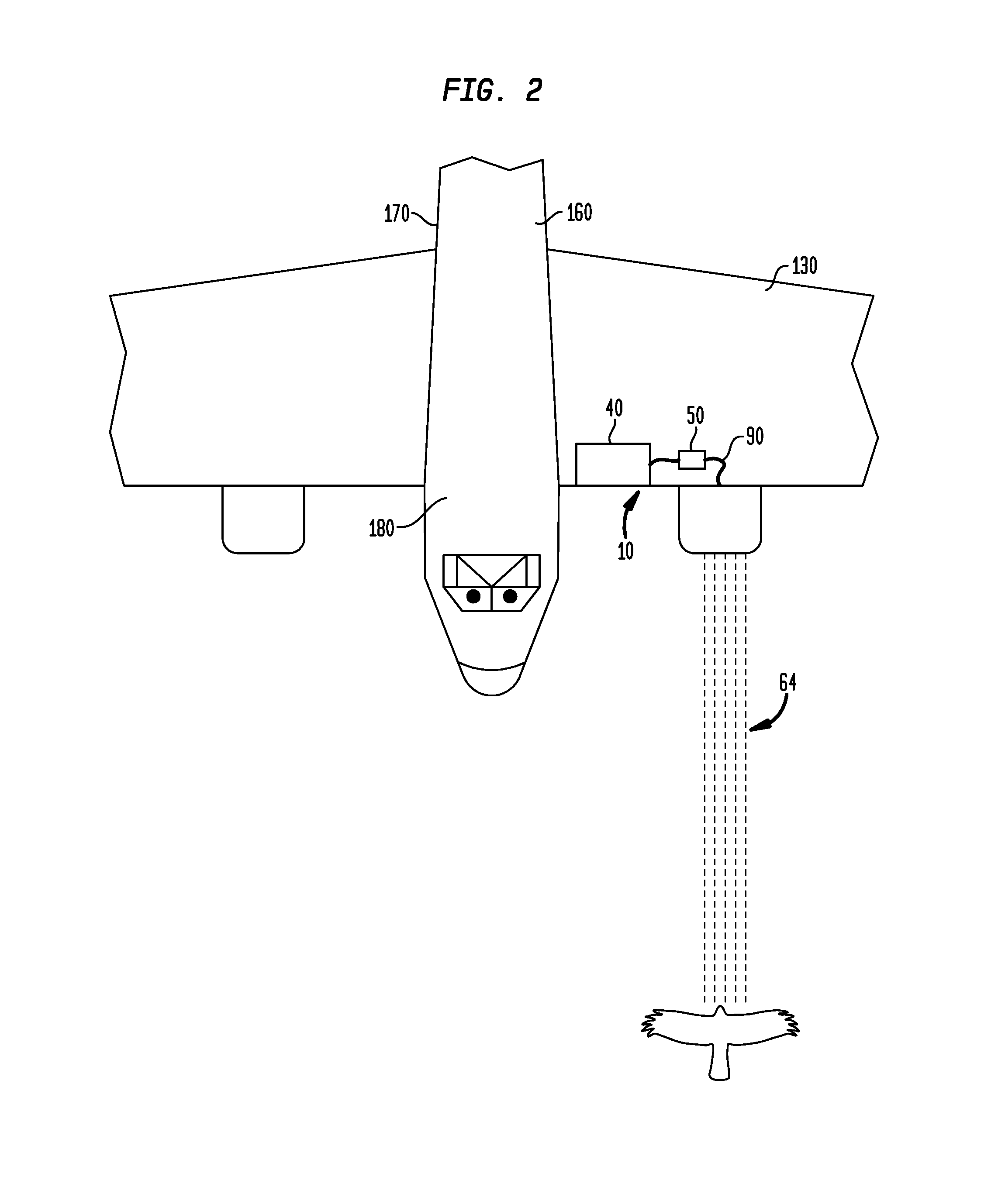
A foreign object damage protection system comprises a sensor for detecting a foreign object, a fluid in a reservoir, a means for dispensing the fluid, the means for dispensing the fluid in communication with the reservoir, and a control unit, whereby when the sensor detects a foreign object, the control unit causes fluid to be dispensed from the reservoir through the means for dispensing and towards the foreign object. The sensor is attachable to one or more locations on an aircraft, such as a wing, nose, windshield, fuselage or tail. The sensor can be a radar sensor, weather radar sensor, weather radar sensor modified to detect objects at short ranges, infra-red sensor, forward-looking infrared sensor, a light detection and ranging sensor, motion sensor, thermal sensor, or video sensor. The system provides a way to protect an aircraft from striking foreign objects, such as birds, in the path of the aircraft.
Owner:MARGALIT ZAMIR
A method for evaluating the FOD resistance of an aero-engine blade
ActiveCN109815521AHigh cycle fatigue strengthAssessing the ability to resist FODSpecial data processing applicationsForeign object damageForeign object
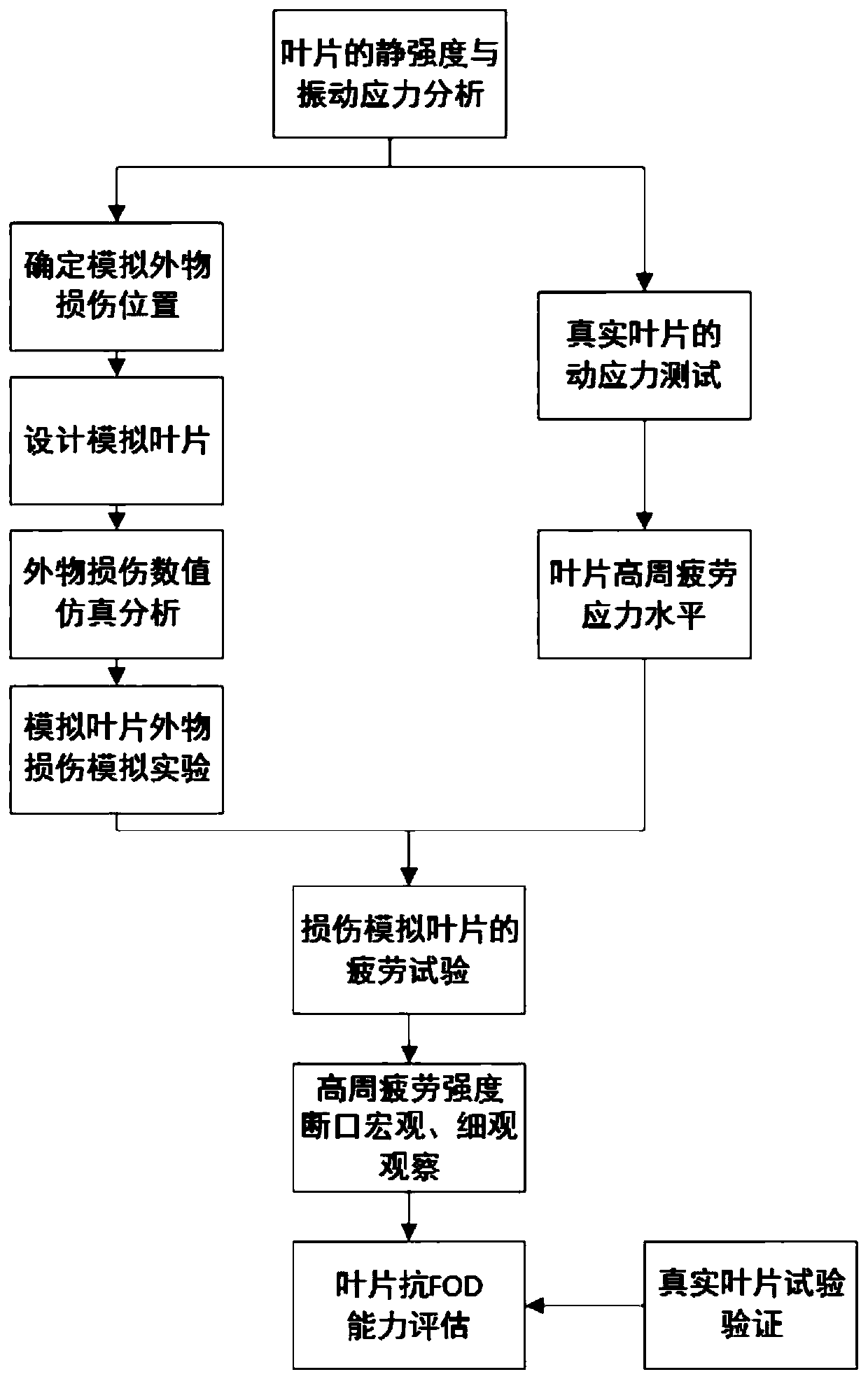
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the FOD resistance of an aero-engine blade. The method comprises steps of carrying out impact dynamics simulation of foreign object damage on a simulated blade numerical model; obtaining the relation between the macroscopic characteristics of the notch and the foreign object type, the impact speed and the impact angle, determining foreign object damage test conditions on the basis of the relation, carrying out an external simulated object damage test on the simulated blade by using an air cannon, and observing the macroscopic characteristics ofthe impact notch; Taking the static stress and the dynamic stress under the working load at the dangerous position of the front edge of the blade as the initial static load and the dynamic load of thehigh-cycle fatigue test, carrying out the high-cycle fatigue test on the damaged simulated blade, obtaining the high-cycle fatigue strength of the blade through a stepping method, and evaluating theFOD resistance of the blade according to the result of the high-cycle fatigue test; And carrying out foreign object damage simulation and high-cycle fatigue test on a small number of real blades to obtain the high-cycle fatigue strength of the real blades so as to verify the conformity of the simulated blades and the real blade test result.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
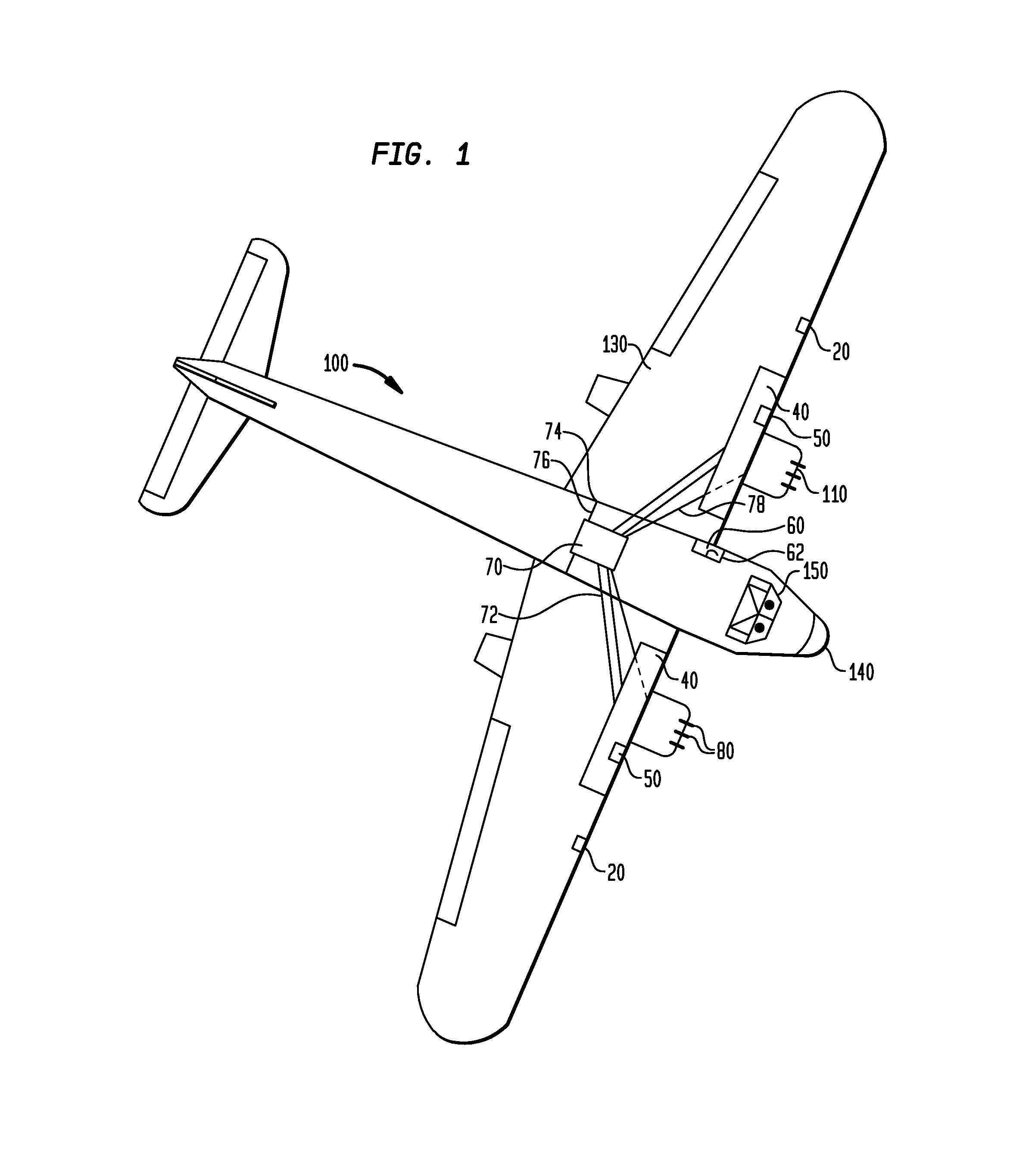
Apparatuses and methods for preventing foreign object damage to aircraft engines
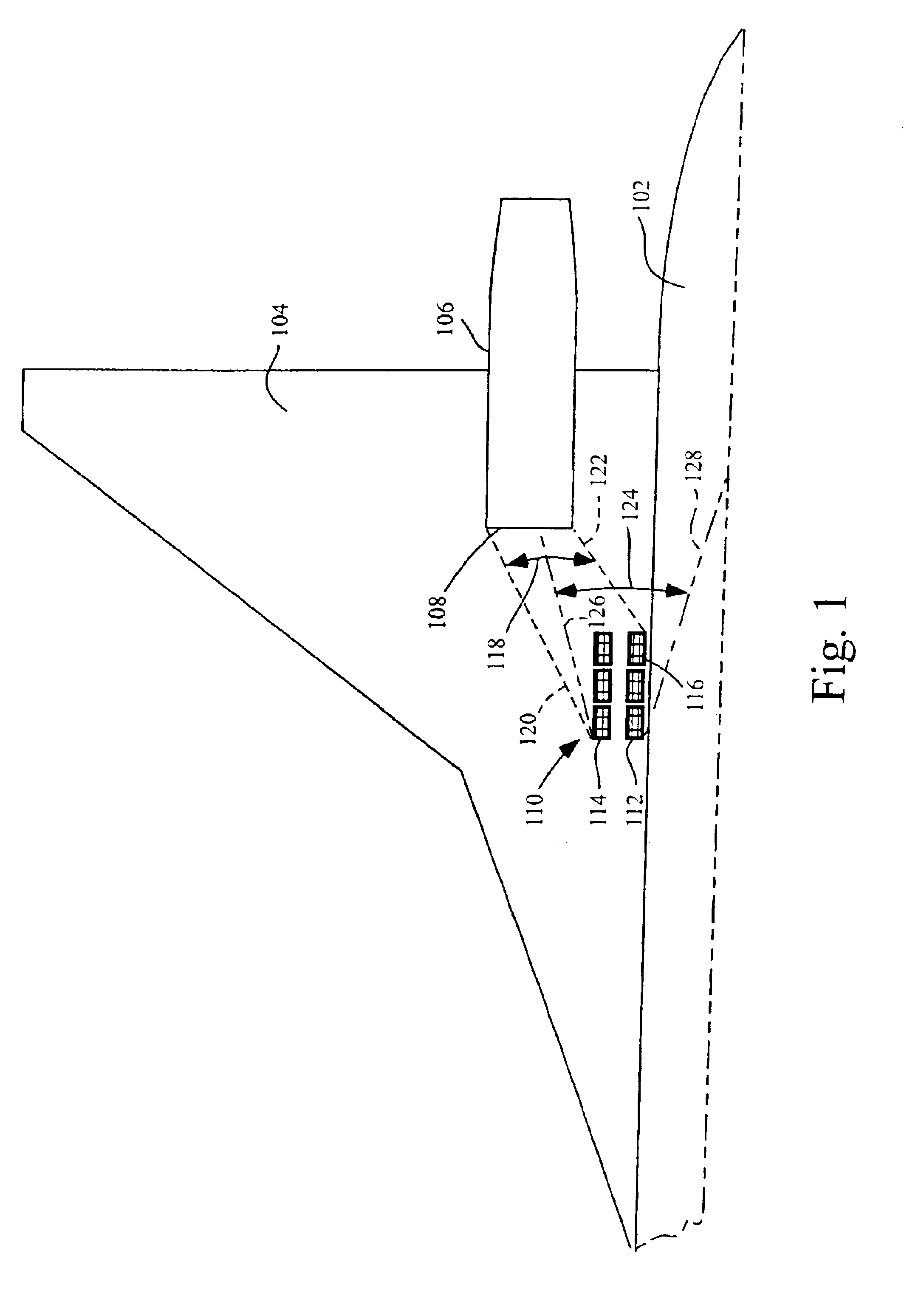
InactiveUS6845943B2Lower surfaceMilitary adjustmentFuselage bulkheadsForeign matterForeign object damage
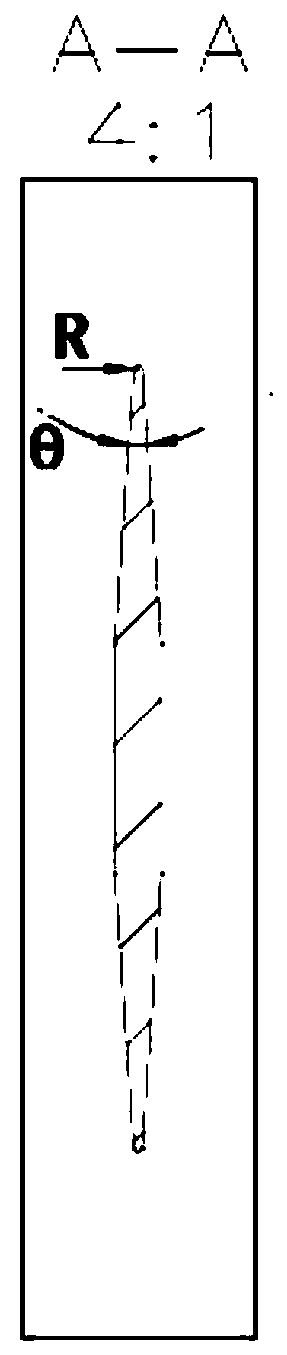
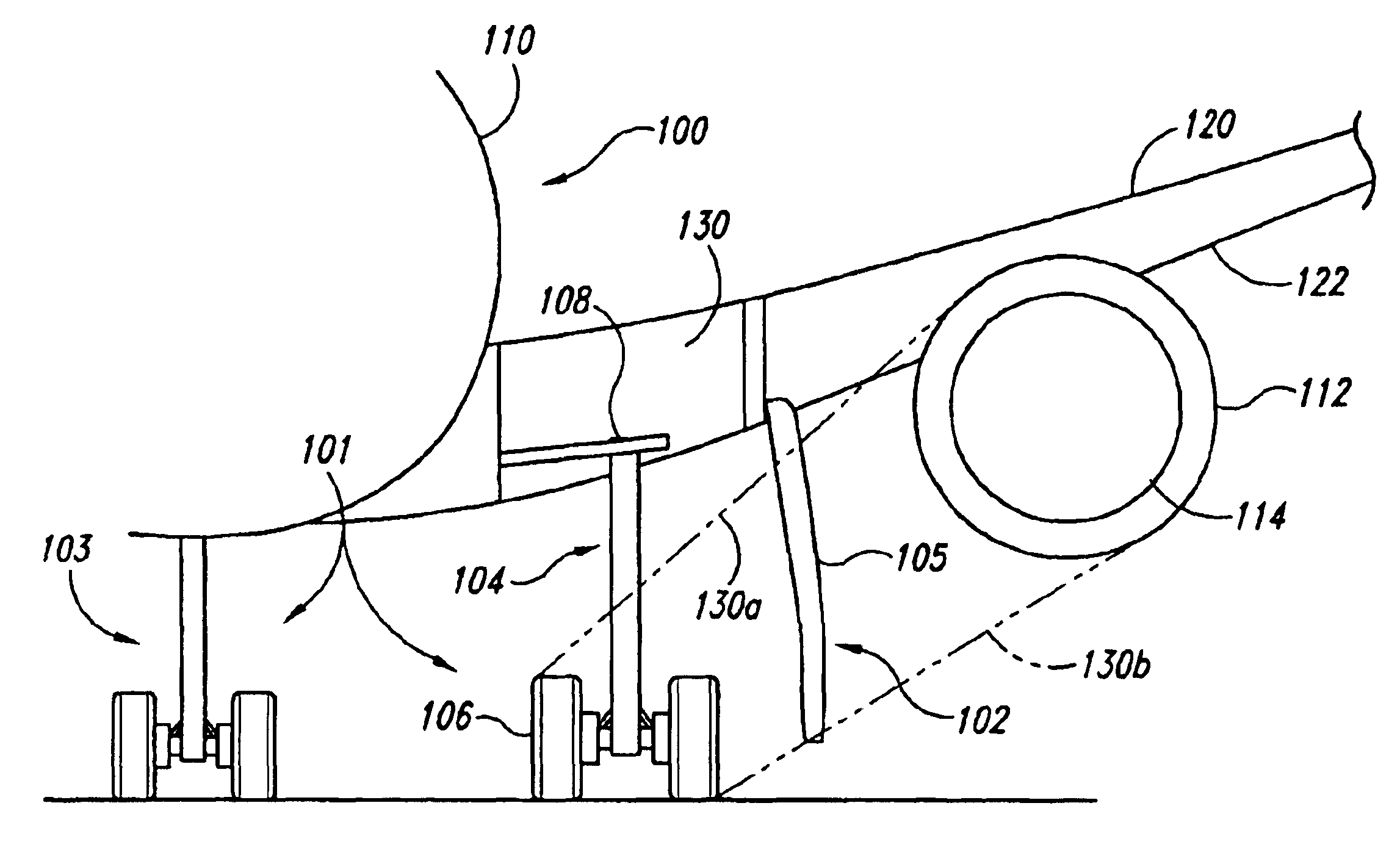
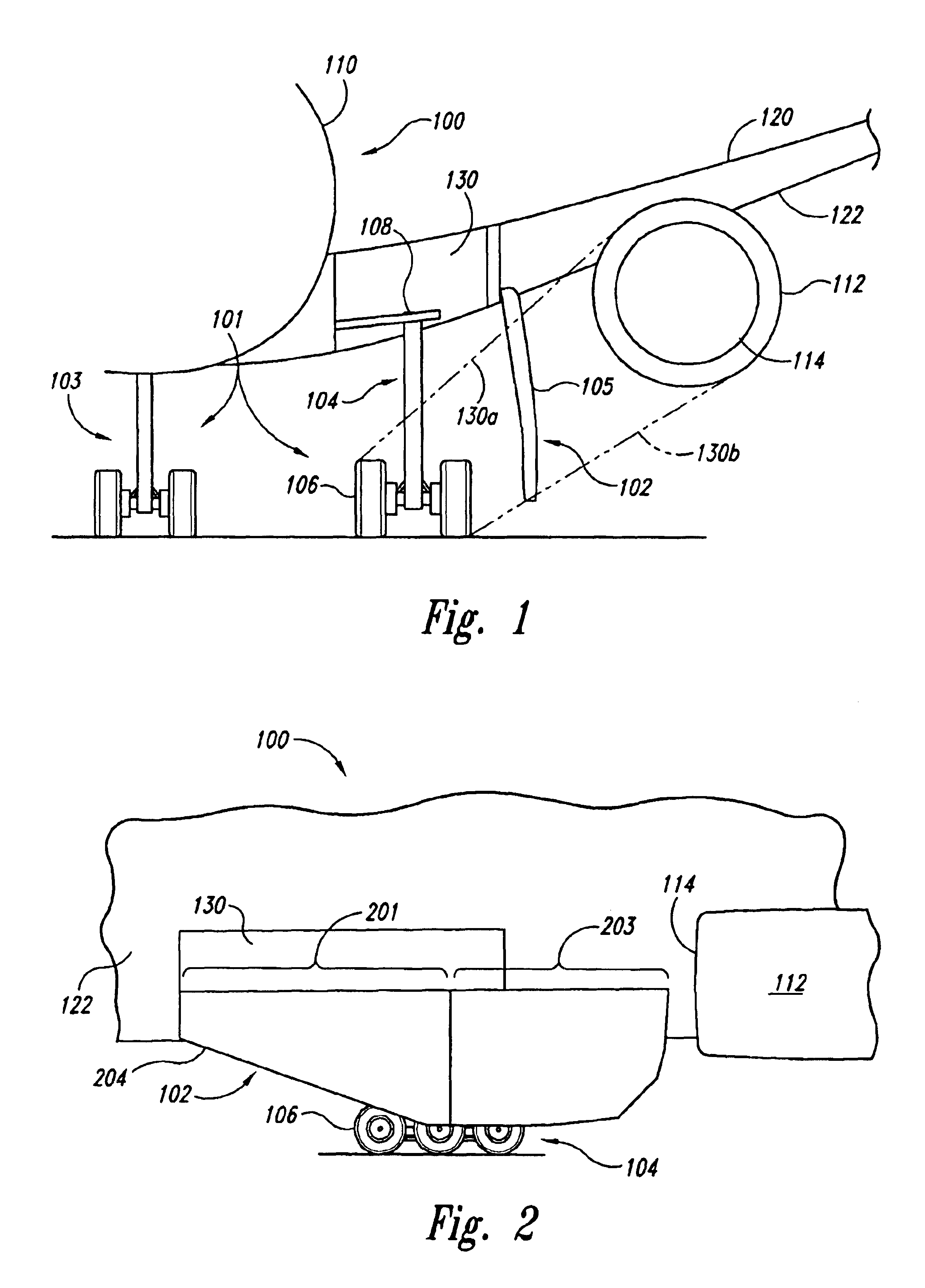
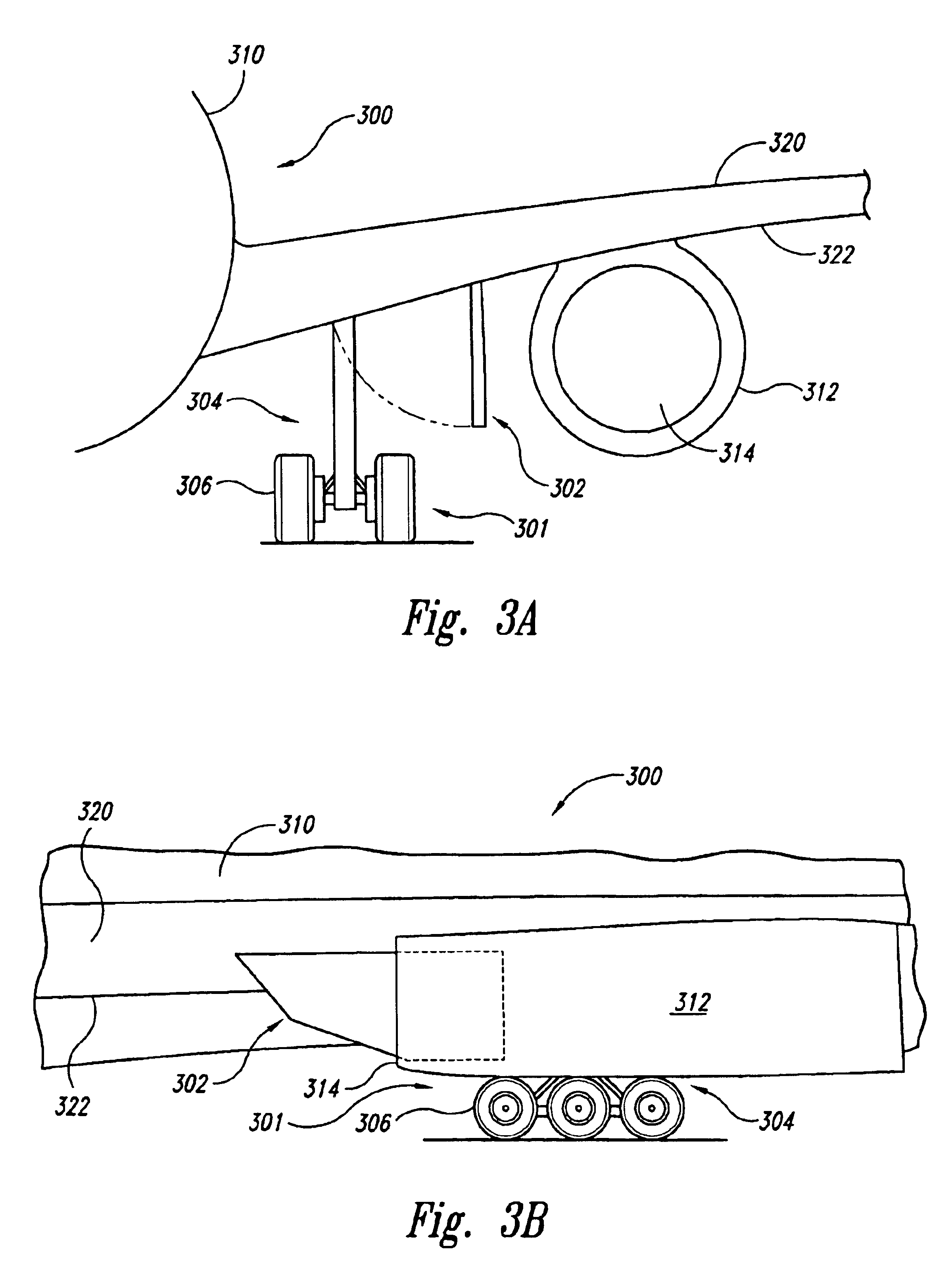
Apparatuses and methods for preventing foreign object damage (FOD) to aircraft engines are disclosed. In one embodiment, a deployable blocker is coupled to a wing portion and / or a fuselage portion of the aircraft and is configured to prevent debris from travelling on a direct trajectory from a landing gear wheel to an engine air inlet. In other embodiments, the blocker can prevent debris from bouncing off the wing lower surface into the engine inlet, or sticking to the wing lower surface and falling into the engine inlet. The deployable blocker can cover at least a portion of the landing gear when the landing gear is retracted and the blocker assembly stowed. In another embodiment, the blocker can be mounted to the landing gear.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Foreign object damage resistant vane assembly
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Method of mitigating the effects of damage in an article
InactiveUS20080127476A1Reduce impactLow costMetal working apparatusStress concentrationForeign object damage
A method of mitigating the effects of damage to a metallic, ceramic, or intermetallic article through the introduction of compressive residual stresses taking into account the effects of the stress concentration factor associated with a damage notch under compression. A layer of compressive residual stress is introduced into the surface of the article to a depth greater than the depth to which damage, such as corrosion pitting or foreign object damage, extends into the surface of the part. The induced compressive residual stresses improve the fatigue and stress corrosion cracking performance of the article while the stress concentrating properties associated with a damage notch under compression prevents cracks from initiating from within the notch under applied loads.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
Safety improvements for airport runways and taxiways
InactiveUS20060088380A1Improve securityRisk minimizationIn situ pavingsTemporary pavingsForeign matterForeign object damage
Safety improvements of airport runways and taxiways are achieved by providing a flexible, water-impermeable surfacing material on a compacted soil base directly adjacent to an edge of airstrip shoulders. A synthetic grass surface is provided on the area beyond the surfacing material so that foreign objects such as loose particles of the airstrip shoulder materials will be driven by jet blasts and run-off across the relatively smooth texture of the surfacing material and will be trapped by the synthetic grass, thereby minimizing foreign object damage to aircraft engines, particularly to those overhanging engines which extend well beyond the existing runway and taxiway shoulders.
Owner:FIELDTURF TARKETT
Low foreign object damage (FOD) weighted nose decoy flare
ActiveUS8191478B2Easy to optimizeEasy to igniteAmmunition projectilesFirework flares/torchesForeign matterNose
Owner:KILGORE FLARES
Apparatus for protecting aircraft components against foreign object damage
ActiveUS20160017804A1Turbine/propulsion engine coolingGas turbine plantsForeign matterForeign object damage
A device for protecting aircraft equipment against contact by a foreign object including an interference arrangement disposed in an air inlet upstream from the aircraft equipment where the interference arrangement is configured to physically obstruct passage of the foreign object within the air inlet.
Owner:AIRBUS CANADA LLP
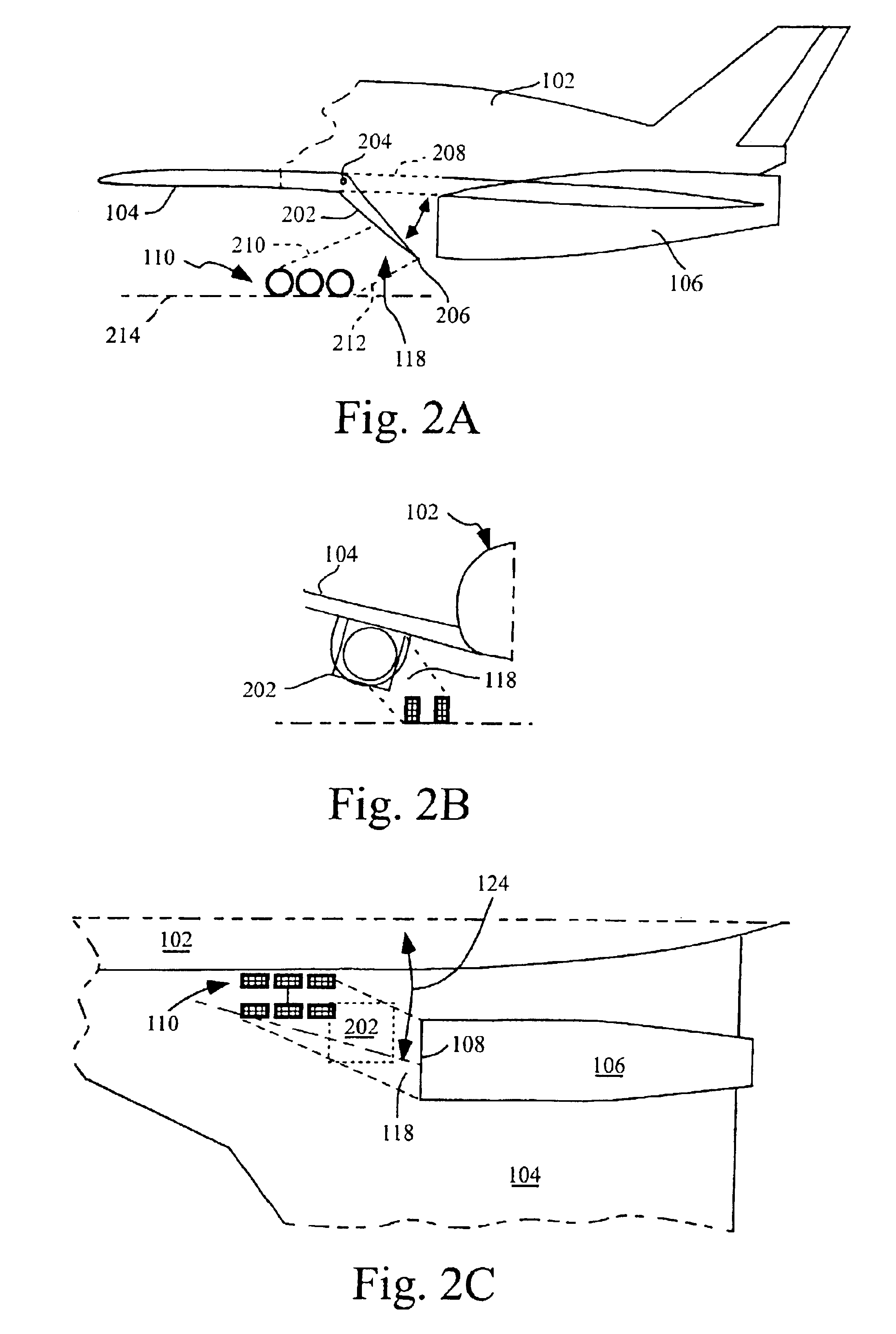
Apparatus and method for preventing foreign object damage to an aircraft
InactiveUS6883751B2Avoid damagePower plant air intake arrangementsForeign object damageFlight vehicle
An aircraft designed to prevent foreign object damage to the aircraft. The aircraft includes an engine coupled aft of the aircraft's landing gear, and a deflecting member is coupled to the aircraft between the landing gear and an inlet of the engine so that when the deflecting member is extended, it intersects with a portion of lines of sight between the landing gear and an inlet of the engine.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Turbine component thermal barrier coating with crack isolating engineered groove features
InactiveUS20160362989A1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyAvoid accumulationMolten spray coatingEngine manufactureForeign object damageEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Crossfire tube assembly for gas turbines
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
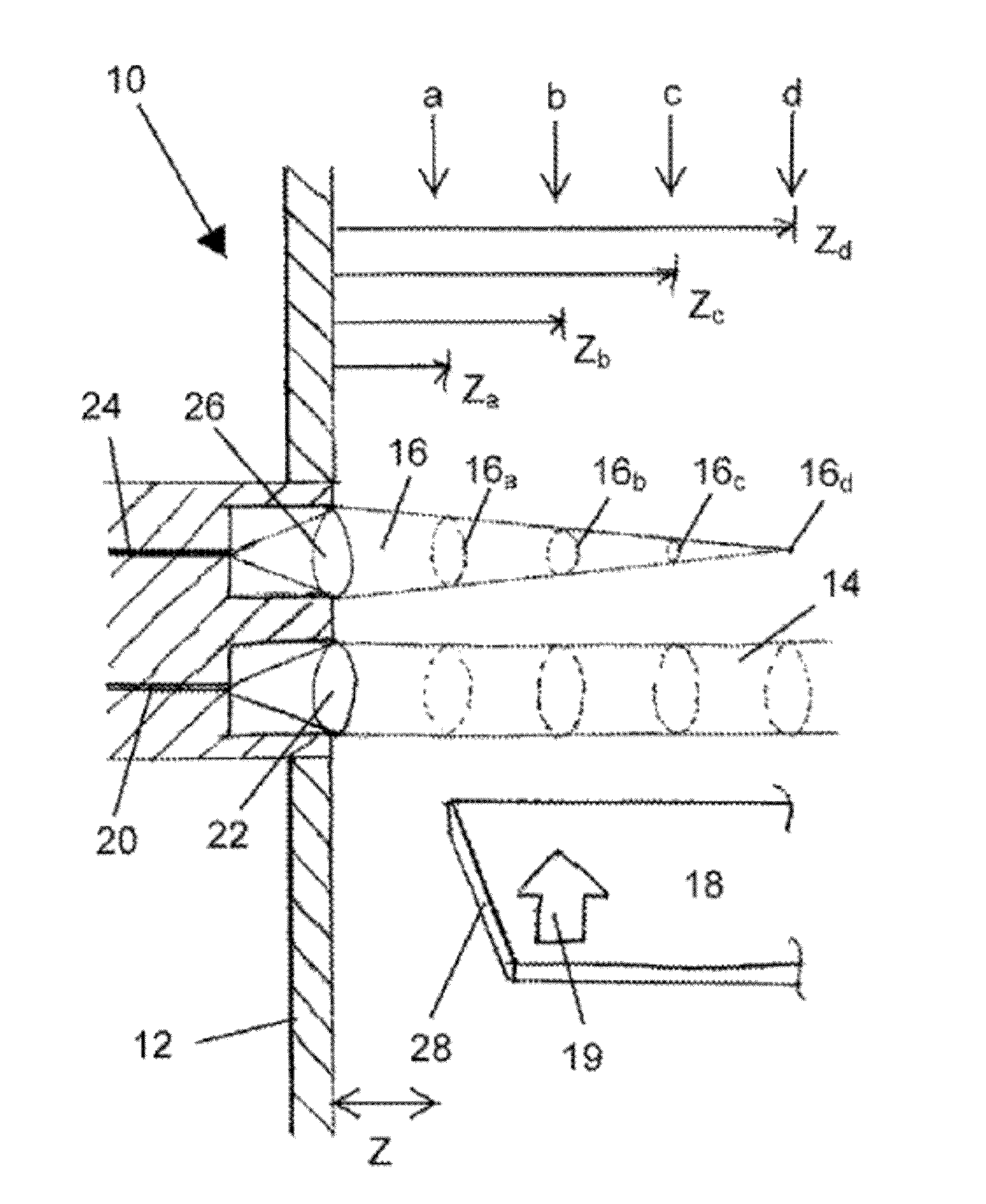
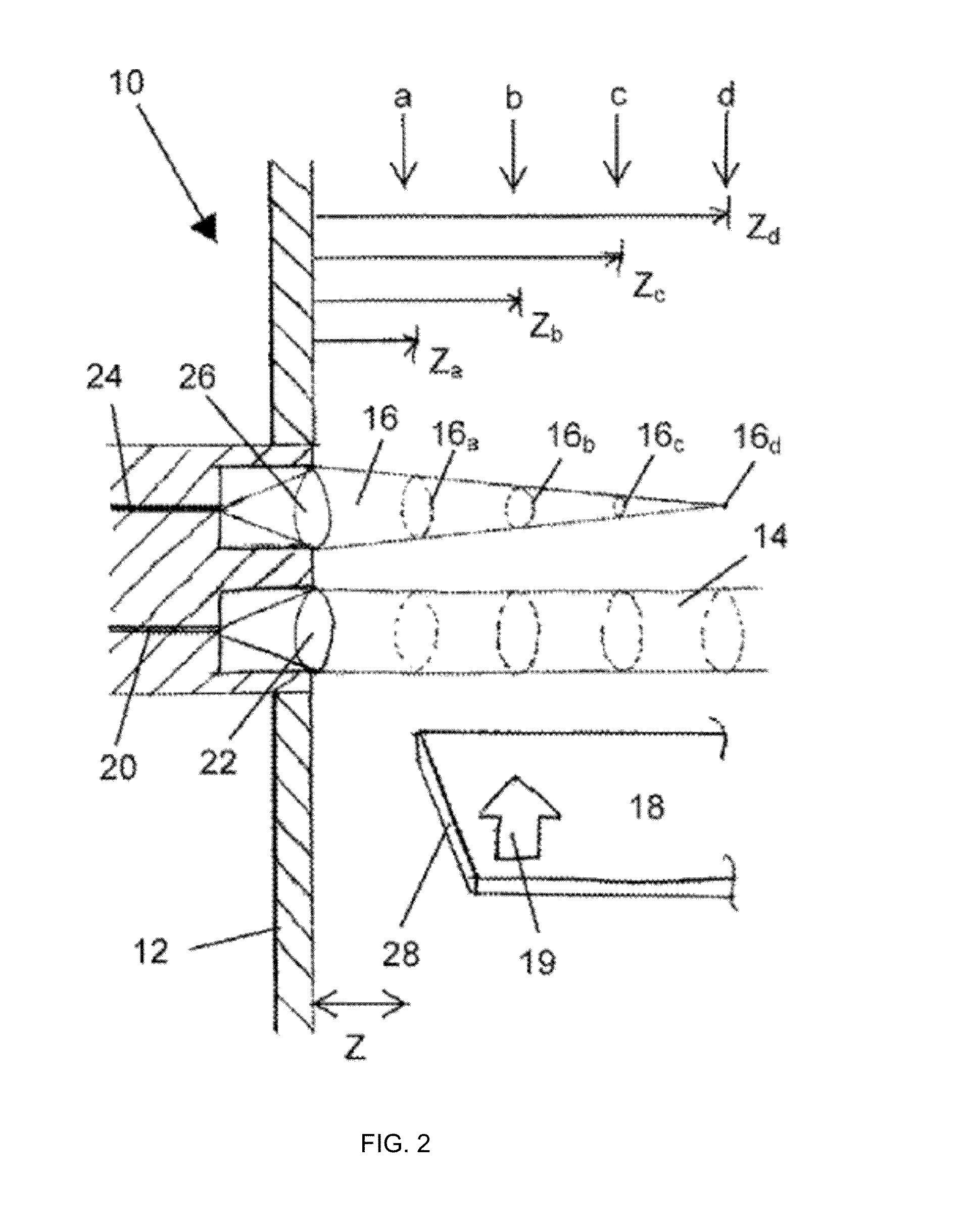
Detection and tracking of damage or impact of a foreign object on an aircraft engine fan
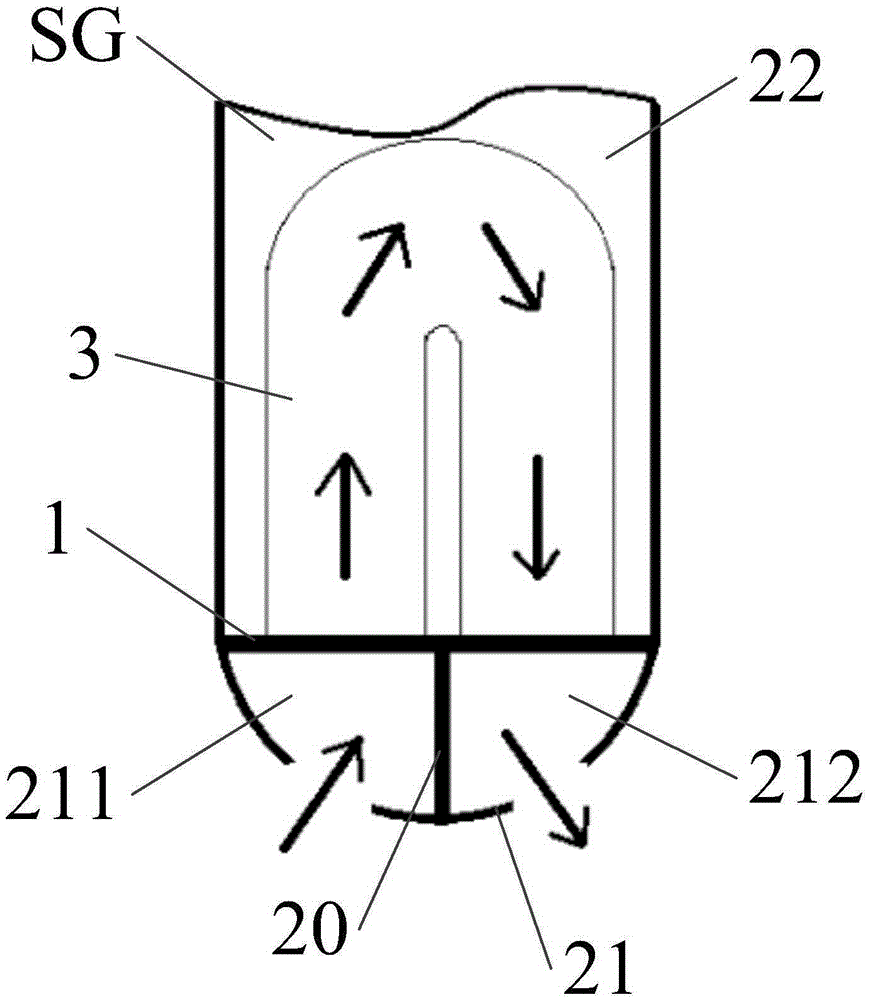
The invention relates to a system for detecting a deformation on a fan (1) for an aircraft engine comprising a rotor (2) equipped with a plurality of blades (3) made of a composite material including woven fibres. This system is noteworthy in that at least one of the fibres of each of the blades (3) is an optical fibre (4) comprising at least one portion defining a Bragg grating, the system furthermore comprising an emitter / receiver (6) linked to the optical fibre (4) and able to send an optical signal down this optical fibre (4) and to receive in response an optical signal from the optical fibre (4) and a detection module (7, 17) linked to the emitter / receiver for detecting a deformation on the fan (1, 11) when the optical signal received exhibits a correlation with a predetermined signature of a damped shock on a blade at a determined rotation speed. This deformation may arise from an impact of a foreign object on a blade of the fan or be consequent upon the development of an internal defect.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION (S N E C M A)
Method for detecting foreign object damage in turbomachinery
ActiveUS9046000B2Removal costEliminates of numberPlug gaugesEngine fuctionsForeign matterForeign object damage
The present invention relates to systems and methods for real-time health monitoring of engines to monitor turbomachinery blades during engine operation and report anomalous behavior and shape of the blades if it occurs, such as damage by FOD. The system includes sensor(s) for obtaining a blade reflection profile from a blade passing by the sensor(s) during a revolution of the rotor in combination with a processor for performing timing calculations and / or fingerprint comparisons with reference data to identify a change in blade fingerprint relative to the reference data, which may indicate blade damage. Such systems can reduce operational costs, enhance safety and improve operational readiness by facilitating condition-based maintenance of engine rotors as opposed to schedule-based solutions. The invention can prevent the needless loss of life and assets caused by undetected minor levels of blade damage that may lead to unexpected catastrophic failure of an engine.
Owner:PRIME PHOTONICS LC
Crossfire tube assembly for gas turbines
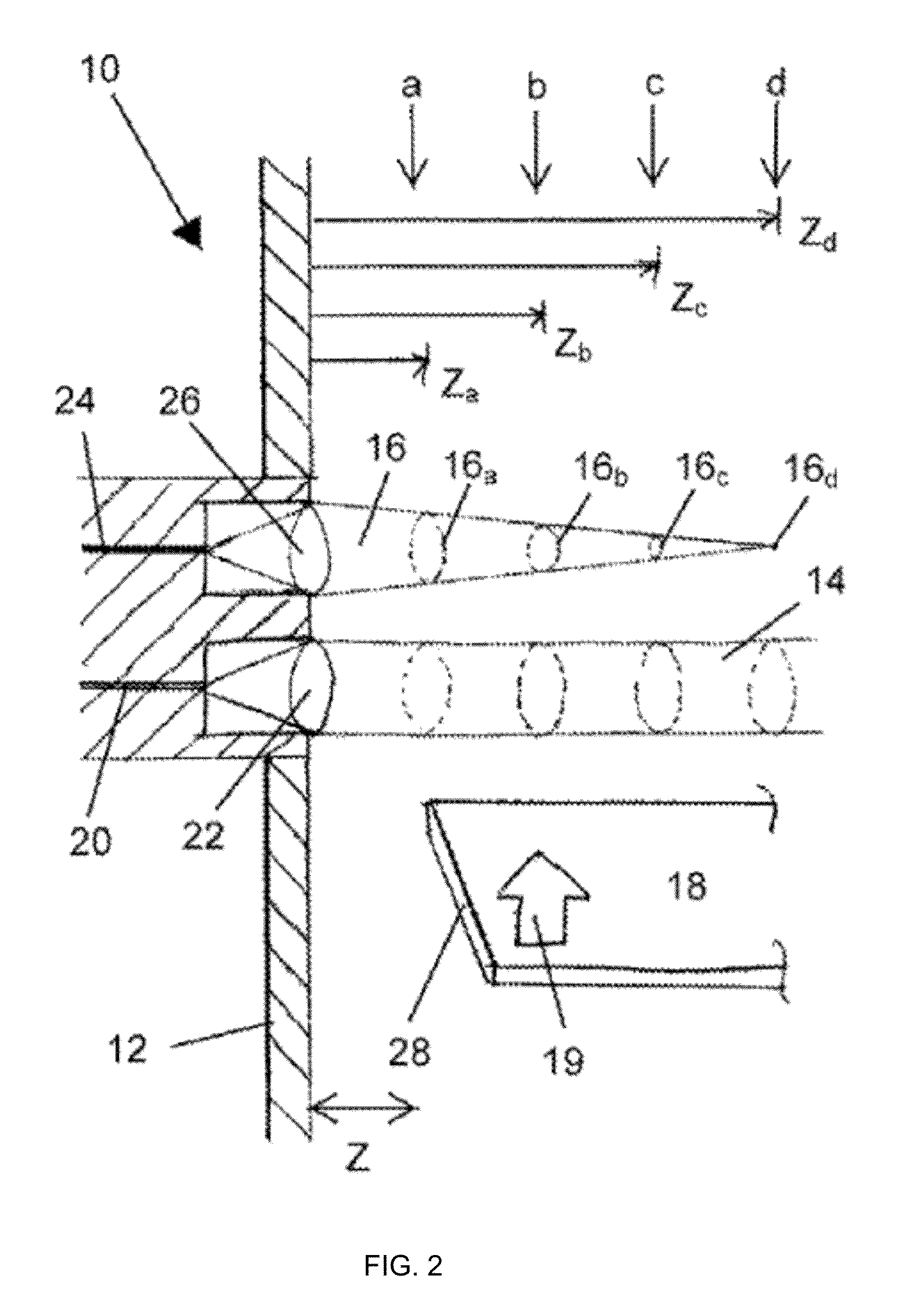
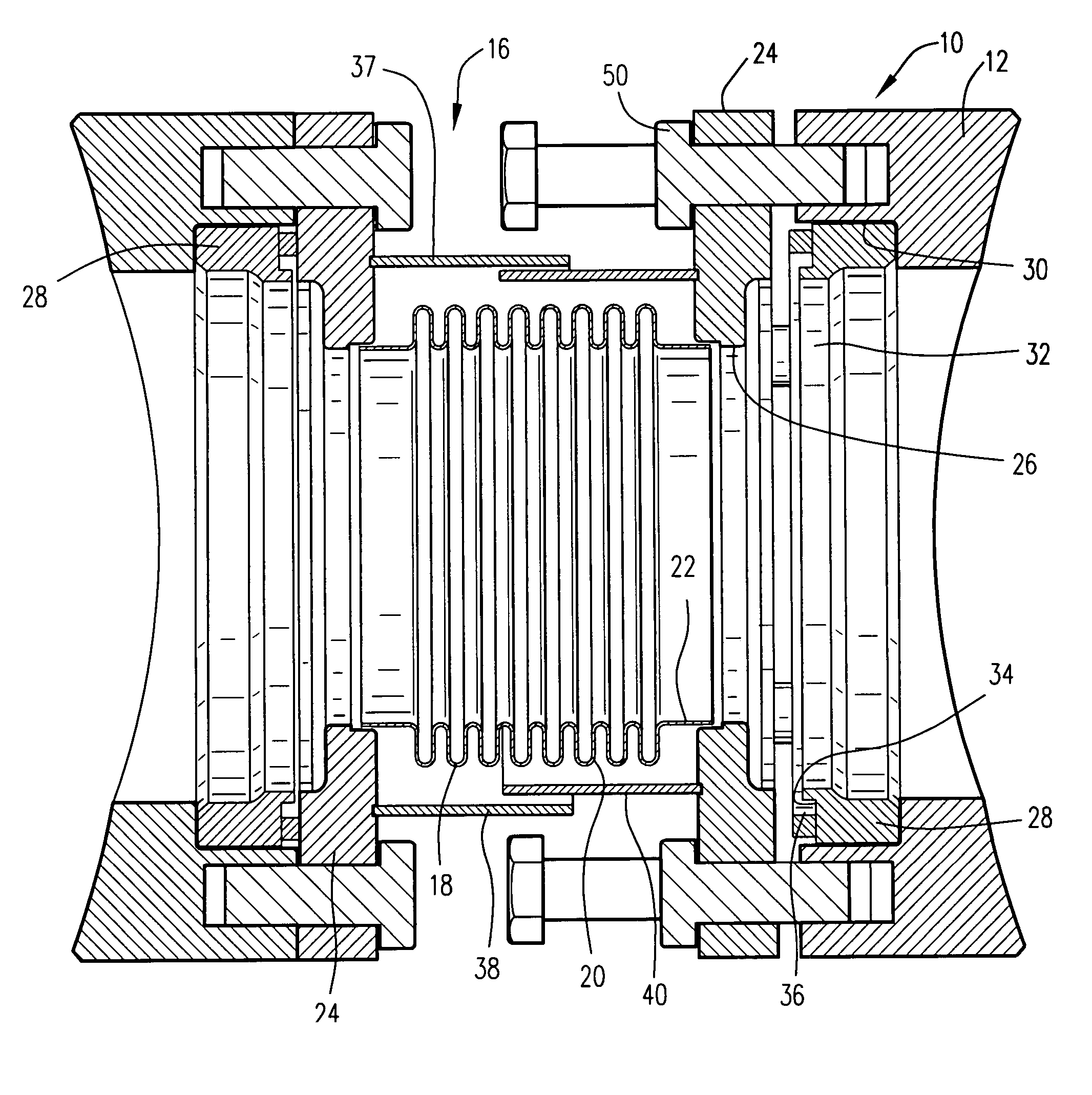
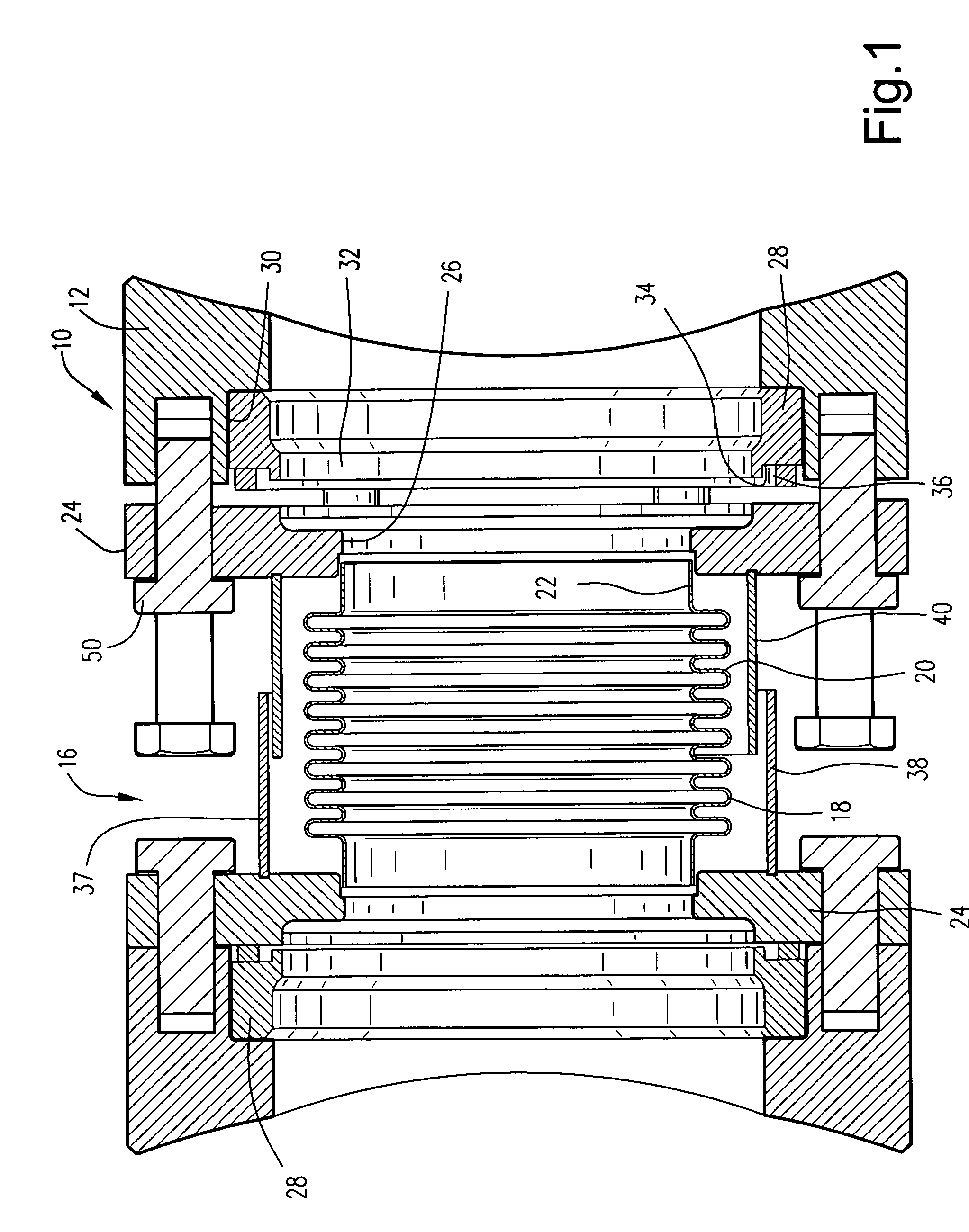
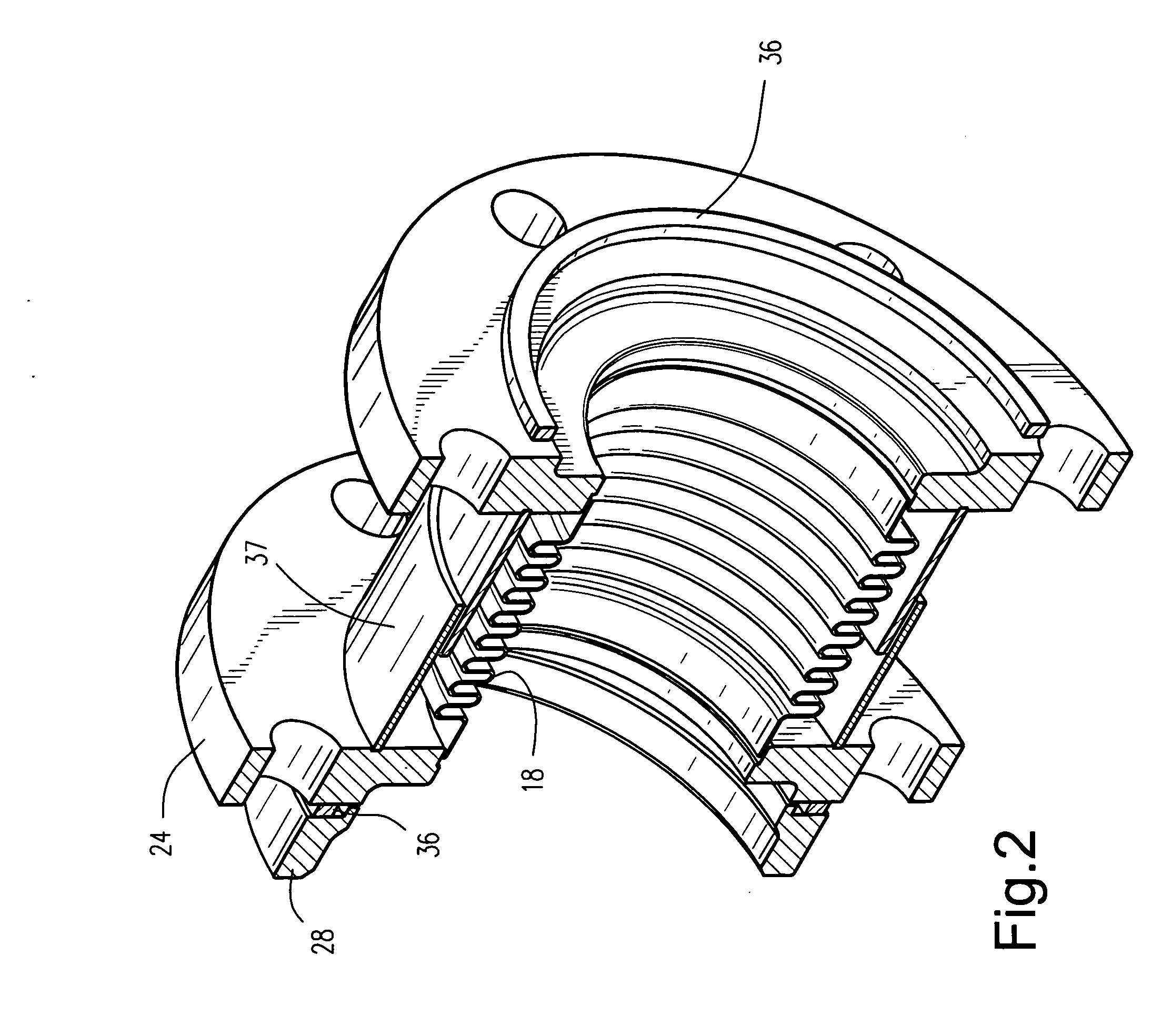
A crossfire tube for attachment between casing bosses of combustors includes a bellows assembly having a bellows with opposite cylindrical ends welded to annular flanges. The annular flanges include a bolt circle for securing the flanges to the combustor bosses. The flanges bear against a gasket for sealing against inserts welded to the casing bosses for retrofit in the sealing assembly to combustors or to seats where the inserts and bosses are formed integrally during original equipment manufacture. A telescoping cylindrical sleeve surrounds the bellows to protect from falling foreign object damage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
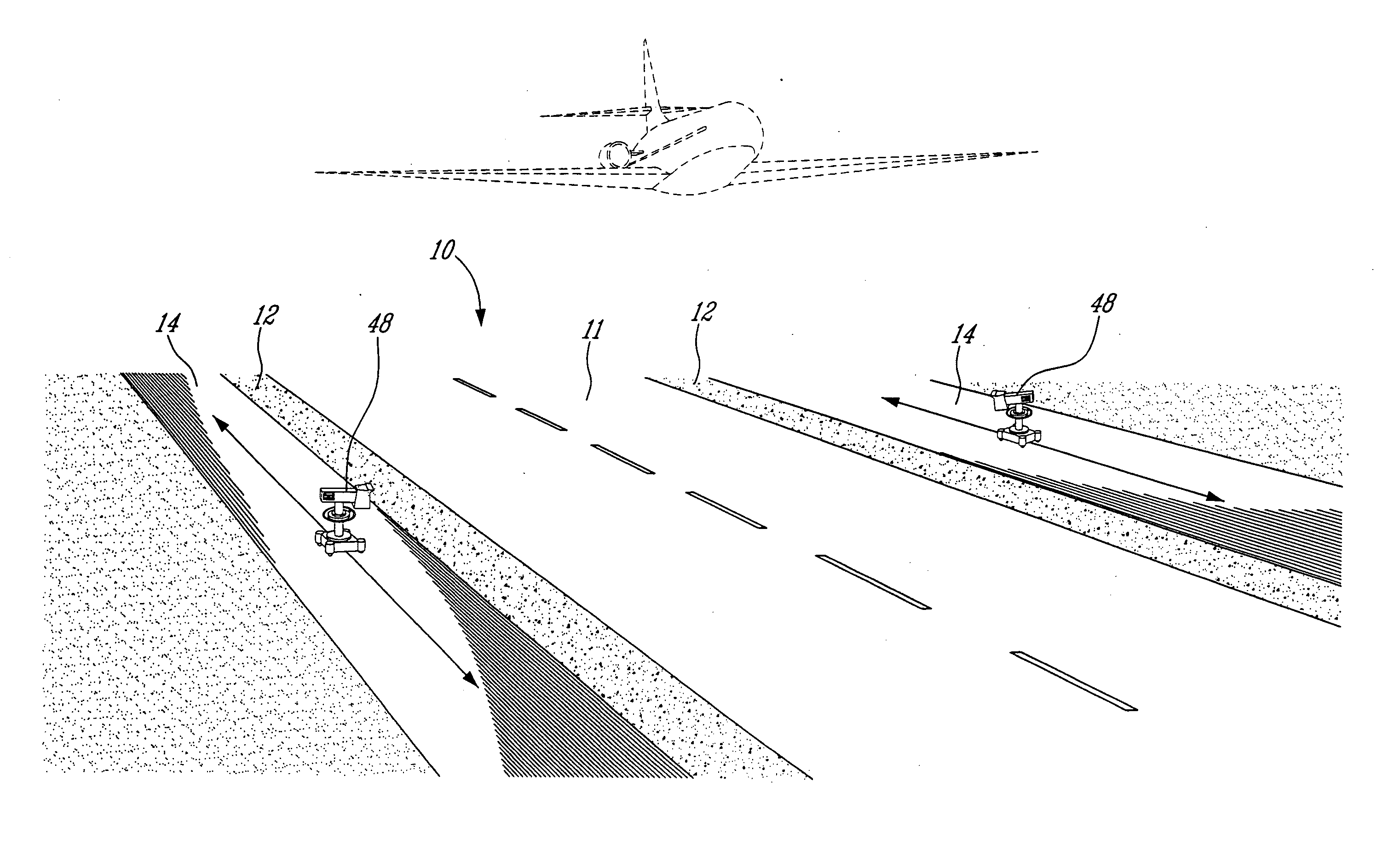
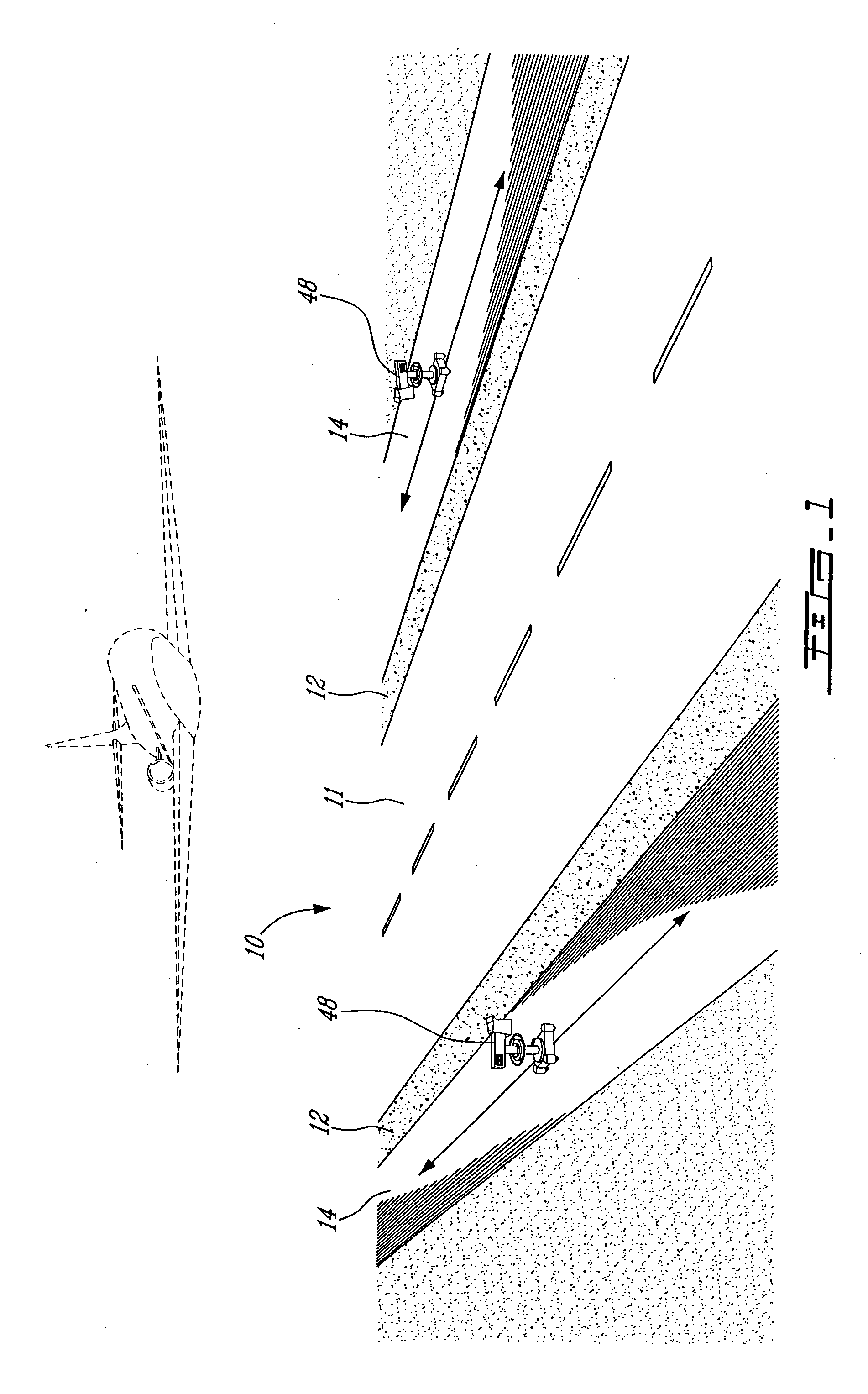
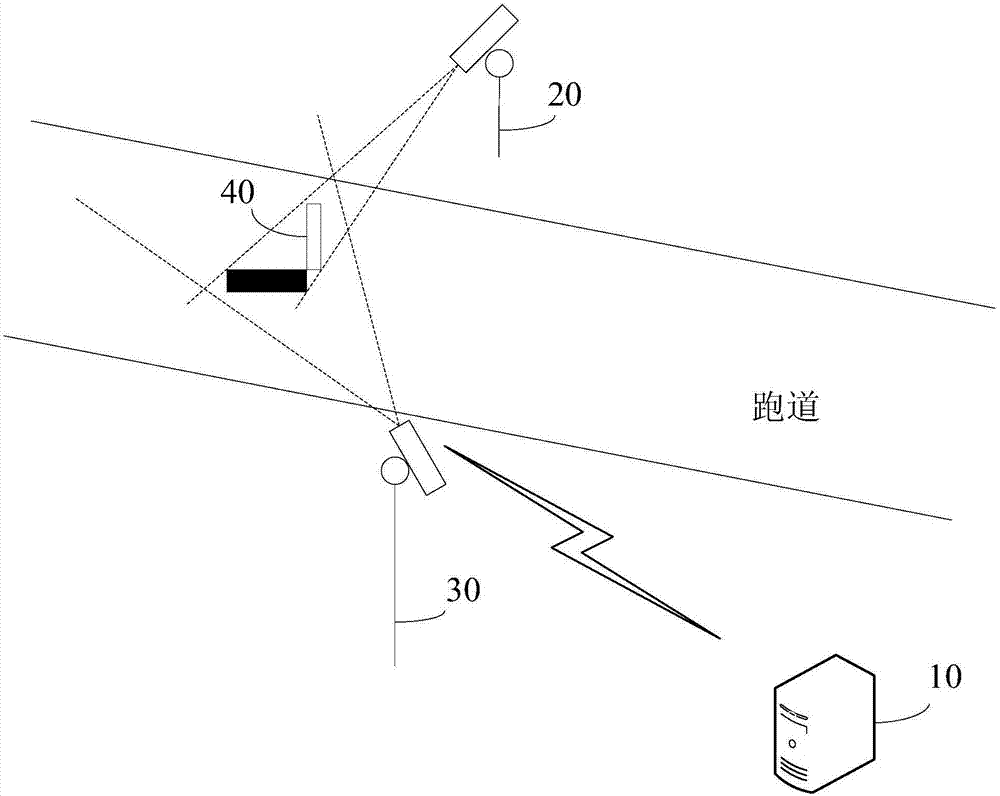
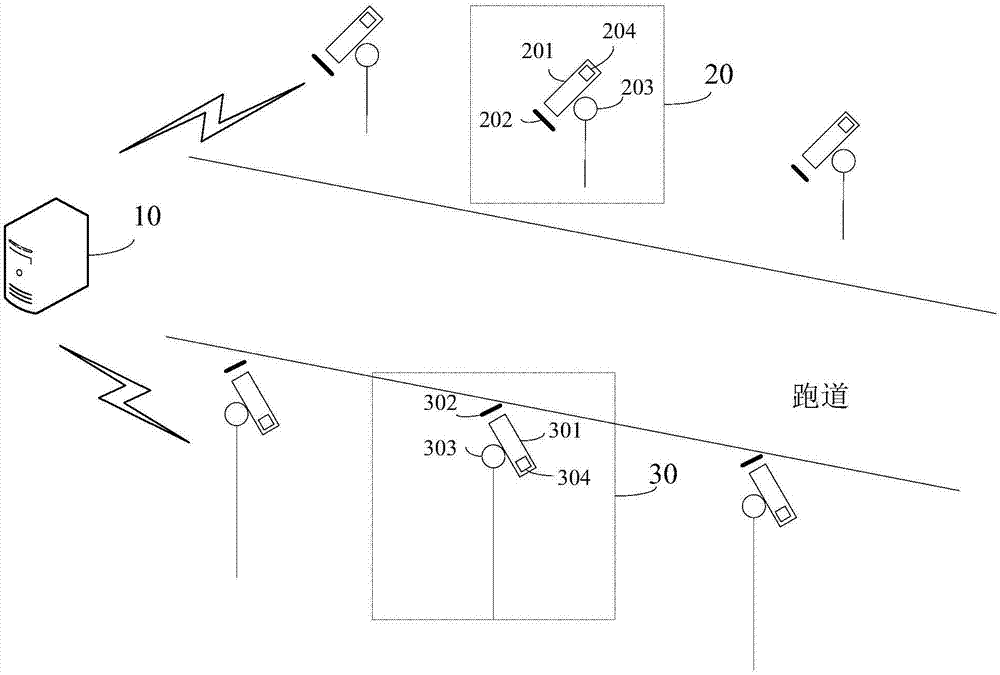
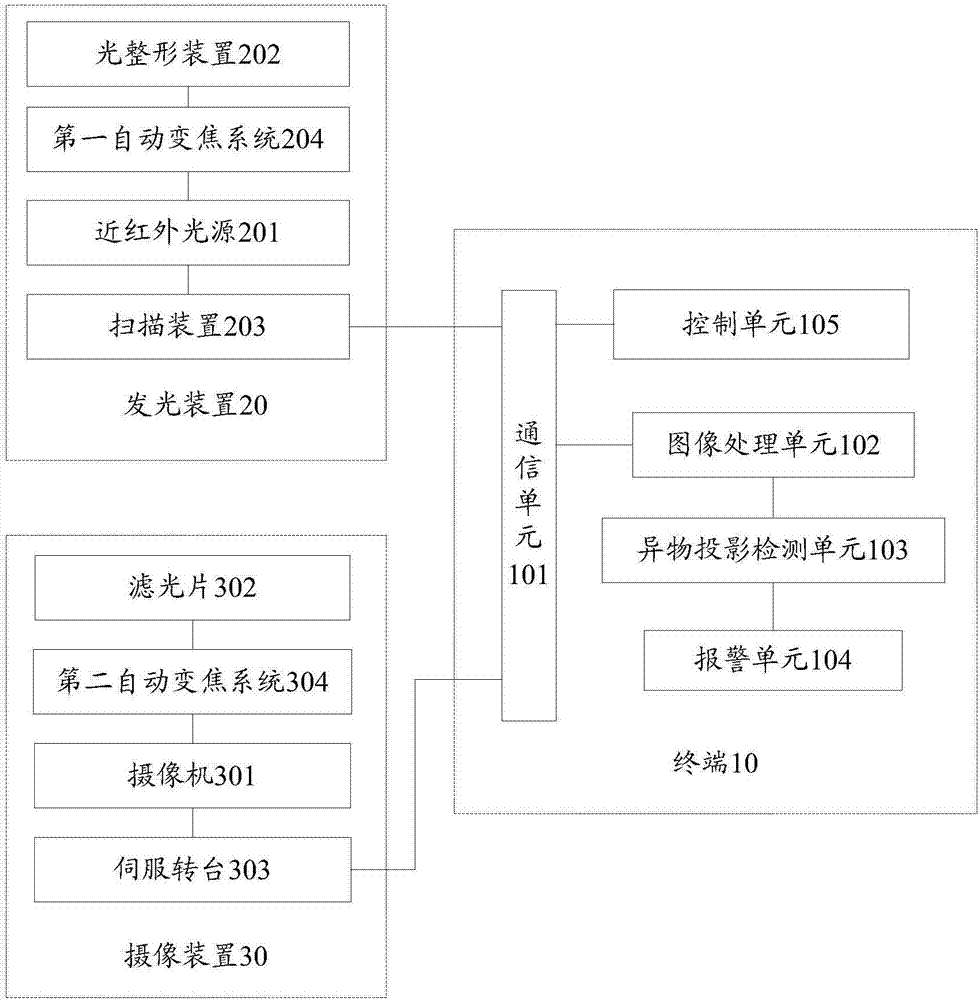
Airport runway foreign object damage detection system
PendingCN107300722ARealize identificationEasy to identifyOptical detectionForeign object damageLight spot
The invention relates to an airport runway foreign object damage detection system which comprises a terminal and at least one light emitting device and at least one camera device connected to the terminal. Each light emitting device is arranged at one side of a runway and is used for emitting near infrared light to illuminate the runway to generate light spots, and a projection of a foreign object is generated when the foreign object exists on the runway covered by the light spots. Each camera device is arranged at the other side of the runway and is used for shooting the light spots on the runway to obtain an image of the light spots. The terminal is used for processing the image, obtaining position information of the foreign object when the projection of the foreign object in the image is detected, and carrying out alarming. The invention provides the airport runway foreign object damage detection system, the identification of a micro foreign object is facilitated, the sensitivity of monitoring is improved, the automatic identification of FOD is realized, problems of low accuracy and low efficiency of artificial identification of FOD are avoided, and the projection of the foreign object can be quickly and accurately captured even under a strong sunlight background or in a condition of low visibility and water or oil on the runway.
Owner:孙天宇
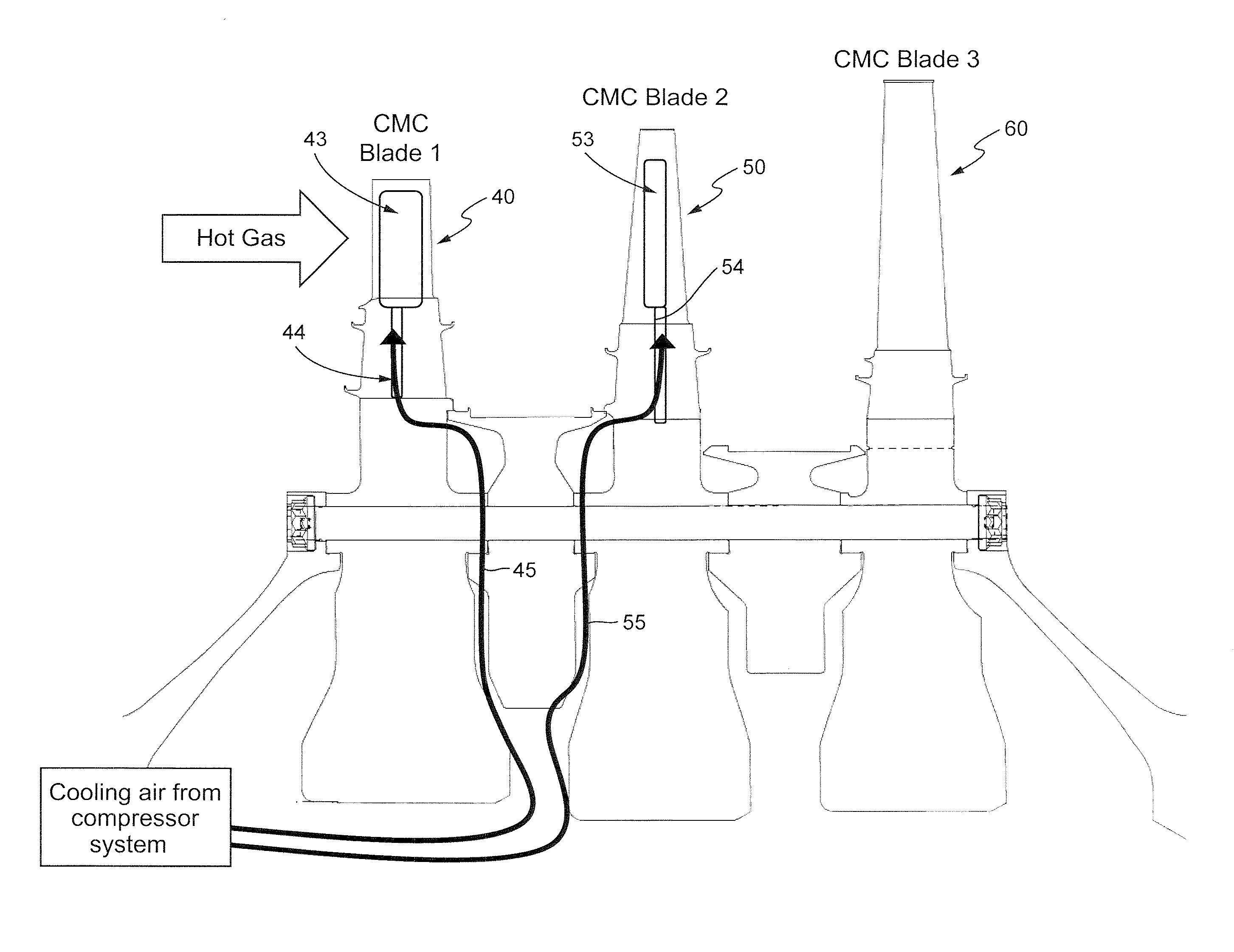
CMC blade with pressurized internal cavity for erosion control
ActiveUS9249669B2Increased longevityImproves Structural IntegrityPropellersPump componentsForeign object damageLeading edge
A ceramic matrix composite blade for use in a gas turbine engine having an airfoil with leading and trailing edges and pressure and suction side surfaces, a blade shank secured to the lower end of each airfoil, one or more interior fluid cavities within the airfoil having inlet flow passages at the lower end which are in fluid communication with the blade shank, one or more passageways in the blade shank corresponding to each one of the interior fluid cavities and a fluid pump (or compressor) that provides pressurized fluid (nominally cool, dry air) to each one of the interior fluid cavities in each airfoil. The fluid (e.g., air) is sufficient in pressure and volume to maintain a minimum fluid flow to each of the interior fluid cavities in the event of a breach due to foreign object damage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Foreign object damage protection device and system for aircraft
A foreign object damage protection system comprises a sensor for detecting a foreign object, a fluid in a reservoir, a means for dispensing the fluid, the means for dispensing the fluid in communication with the reservoir, and a control unit, whereby when the sensor detects a foreign object, the control unit causes fluid to be dispensed from the reservoir through the means for dispensing and towards the foreign object. The sensor is attachable to one or more locations on an aircraft, such as a wing, nose, windshield, fuselage or tail. The sensor can be a radar sensor, weather radar sensor, weather radar sensor modified to detect objects at short ranges, infra-red sensor, forward-looking infrared sensor, a light detection and ranging sensor, motion sensor, thermal sensor, or video sensor. The system provides a way to protect an aircraft from striking foreign objects, such as birds, in the path of the aircraft.
Owner:MARGALIT ZAMIR
Method and system for damage repair of tube plate and caulk weld of steam generator of nuclear power station
ActiveCN105234573AMeet sizeMeet the hardened layerHeat exchange apparatusMetal working apparatusForeign object damageNuclear power
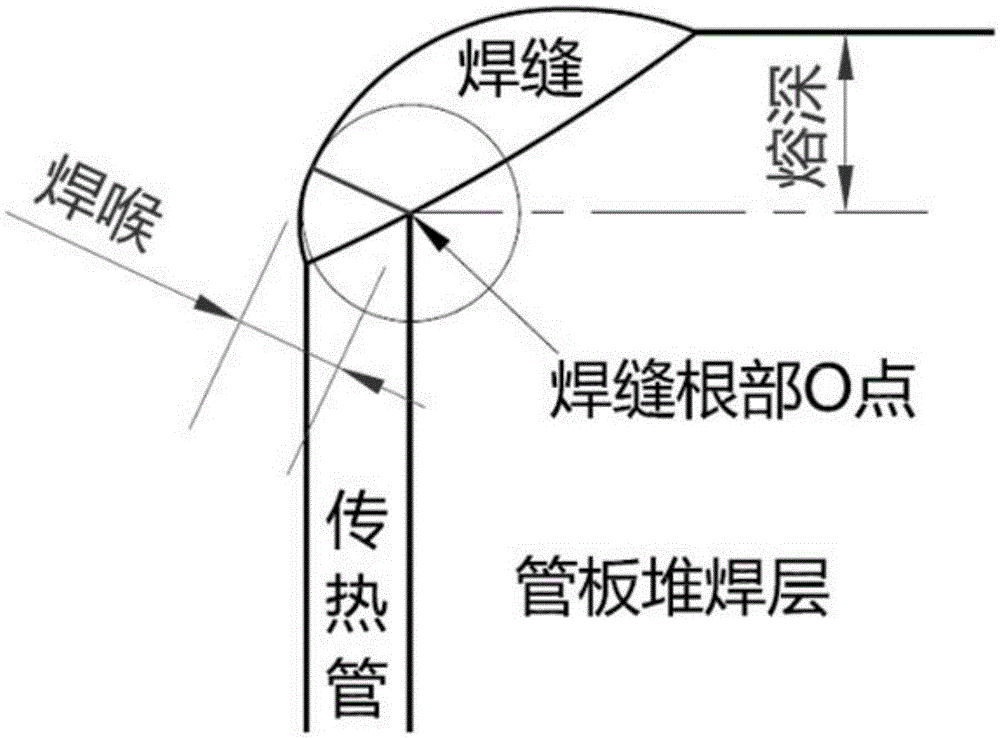
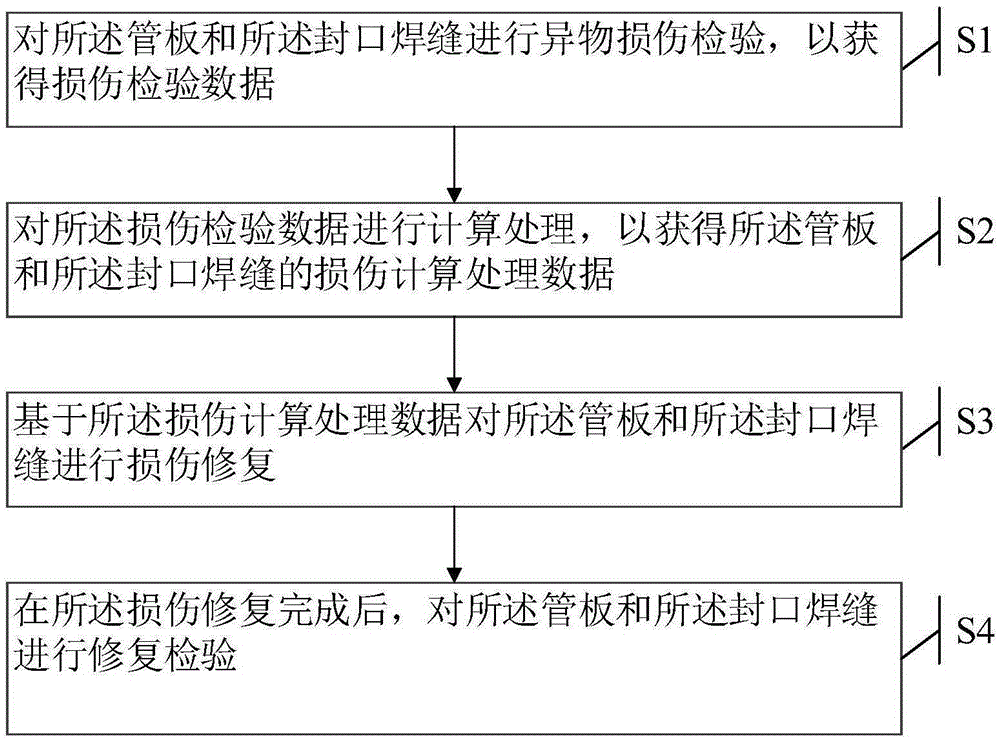
The invention discloses a method and a system for damage repair of a tube plate and a caulk weld of a steam generator of a nuclear power station, and solves the technical problem that a conventional SG site repair technology cannot completely eliminate the influence of foreign object damage on SG. The method comprises the following steps: S1, conducting foreign object damage inspection on the tube plate and the caulk weld to obtain damage inspection data; S2, calculating the damage inspection data to obtain damage calculation data of the tube plate and the caulk weld; S3, conducting damage repair on the tube plate and the caulk weld based on the damage calculation data; and S4, after damage repair is finished, conducting repair inspection on the tube plate and the caulk weld to ensure that the repaired tube plate and the repaired caulk weld meet the equipment code requirement. Through the adoption of the method and the system, that the size of the repaired caulk weld meets the requirement is ensured, and a hardened layer and a stress corrosion risk can be eliminated.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
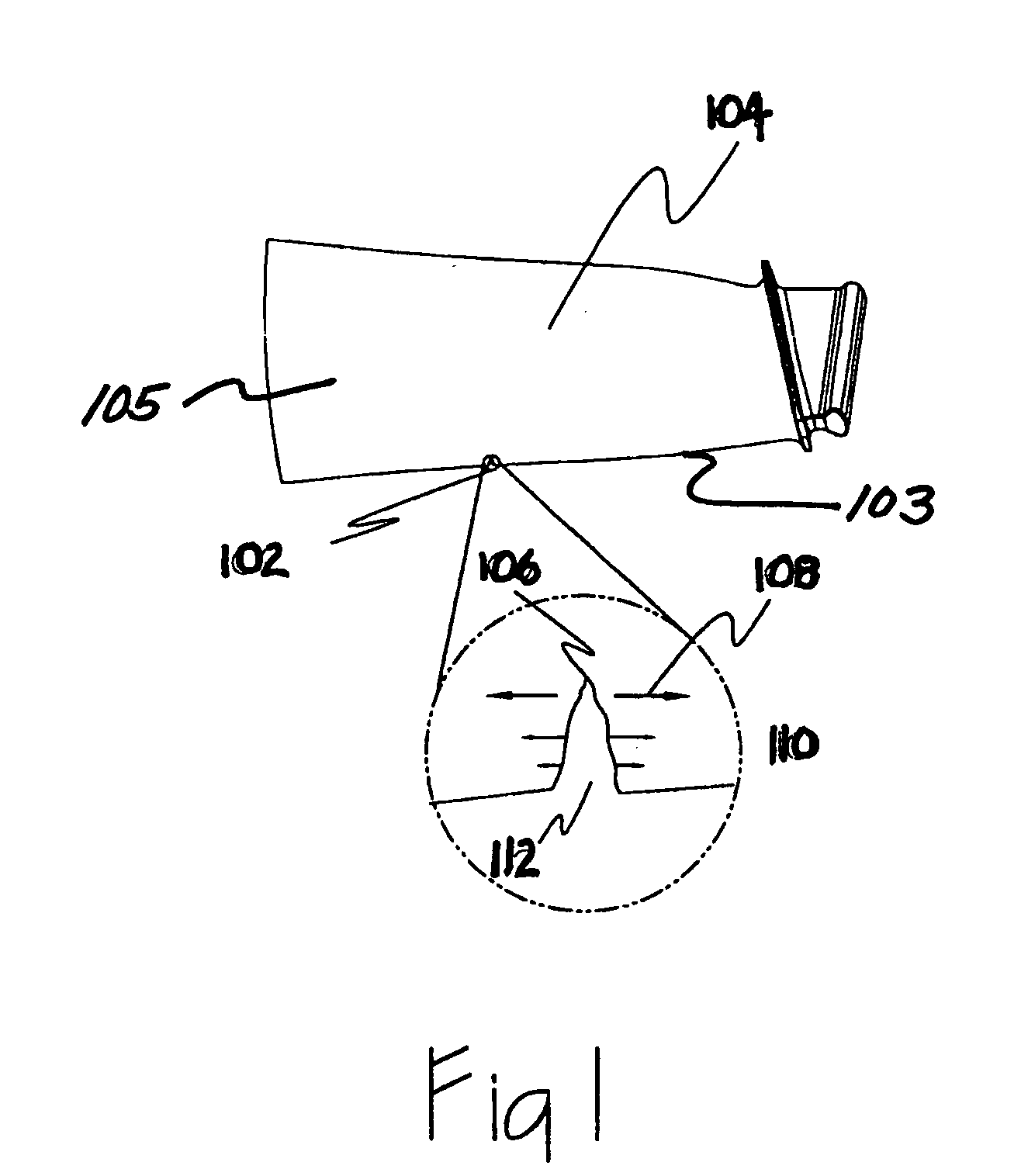
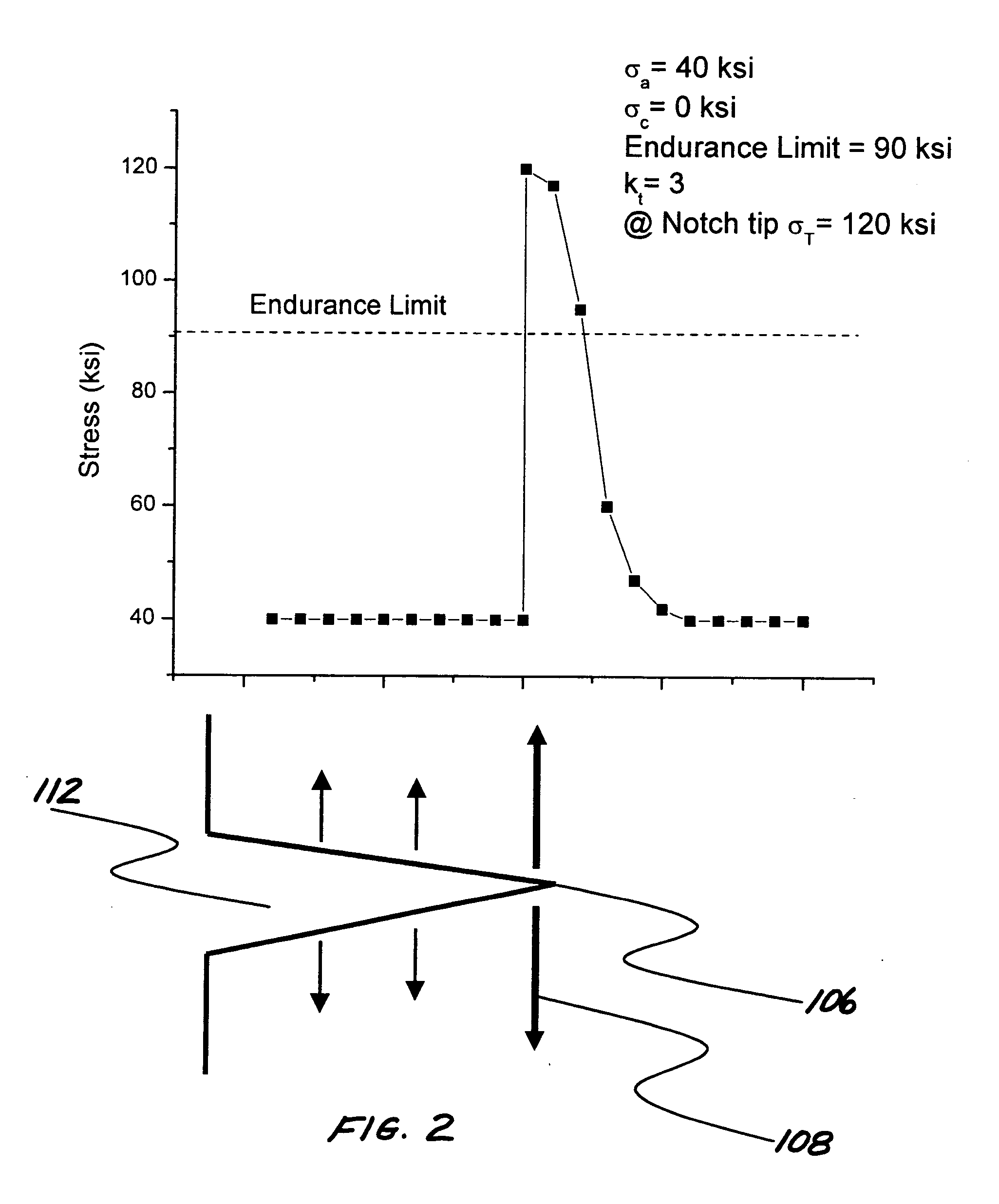
Foreign object damage notch calibration method with stress concentration coefficient not smaller than 3
ActiveCN110987389AGuaranteed accuracyMachine part testingGas-turbine engine testingForeign object damageElement analysis
The invention provides a foreign object damage gap calibration method capable of ensuring that a stress concentration coefficient is not less than 3. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, prefabricating an FOD notch in a blade, carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction on FOD damage through a three-dimensional optical scanning system to establish an FOD damage model; performingfinite element analysis on the blade model with an FOD, which is reversely obtained by three-dimensional reconstruction, calculating to obtain a stress concentration coefficient of the blade model, and recording a stress concentration coefficient value corresponding to the typical damage size; and building a neural network model by using a programming language, taking the damage size as the inputof the neural network, taking the stress concentration coefficient as the output of the neural network, and training the neural network model through loop iteration; and calibrating the damage size corresponding to the type of blade Kt = 3 through the trained network. When the anti-FOD capacity of the blade is assessed, an FOD notch can be prefabricated in the front edge of the blade through an air cannon method or a notch machining method according to the calibrated damage size.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
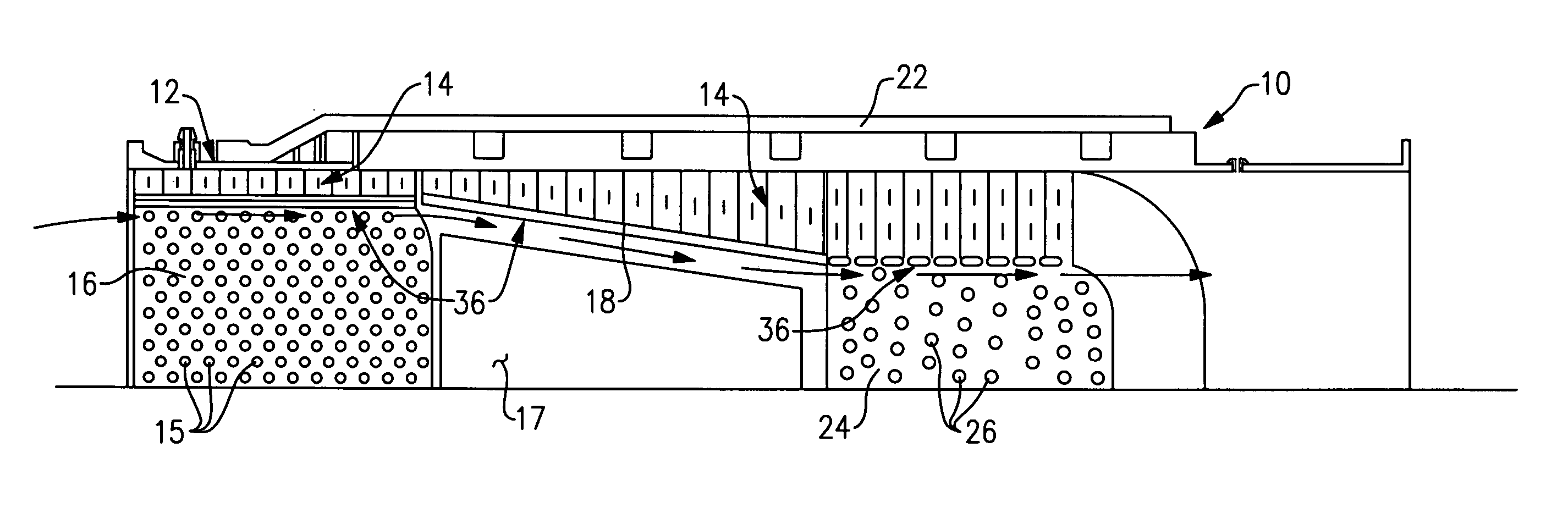
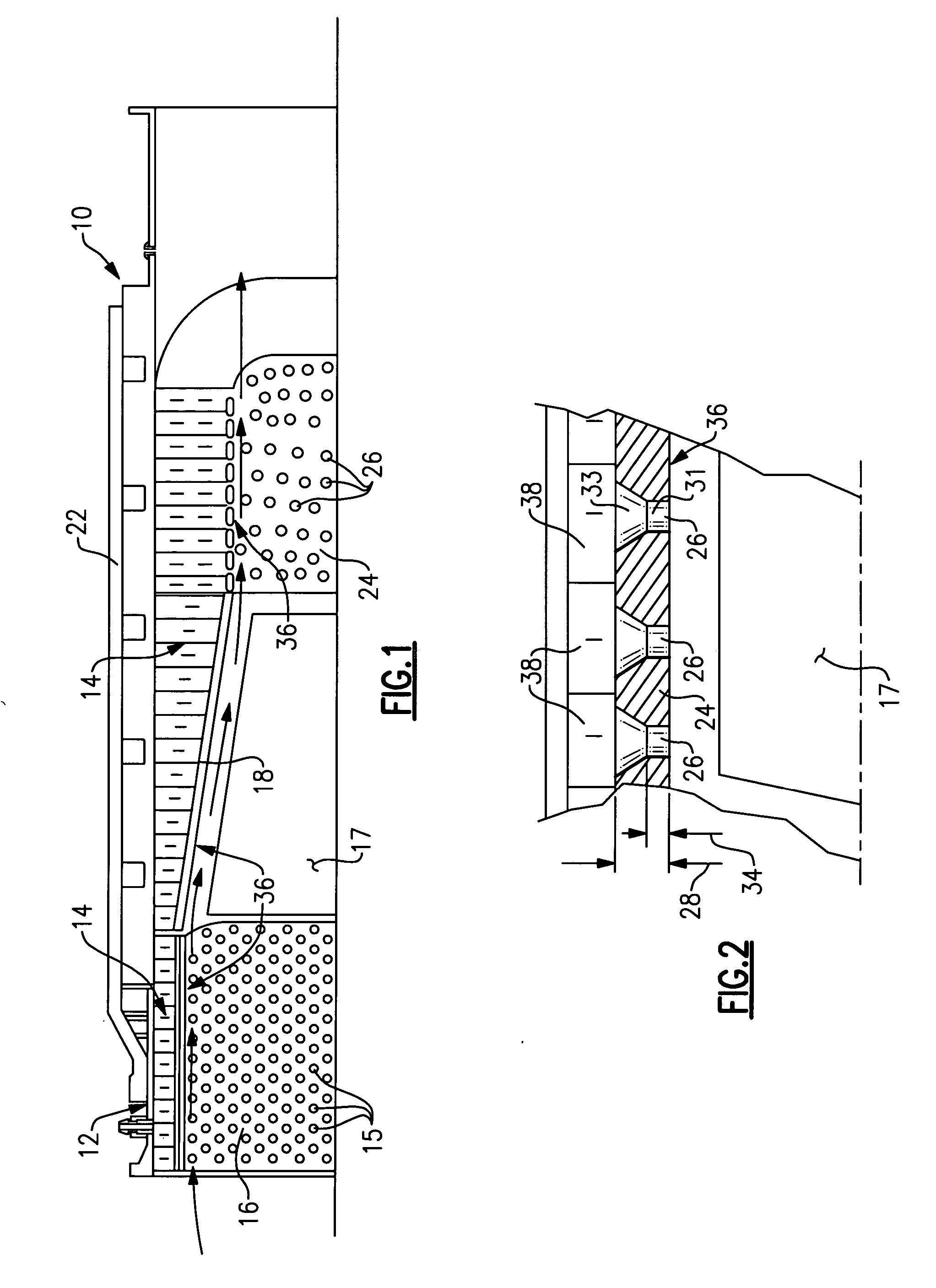
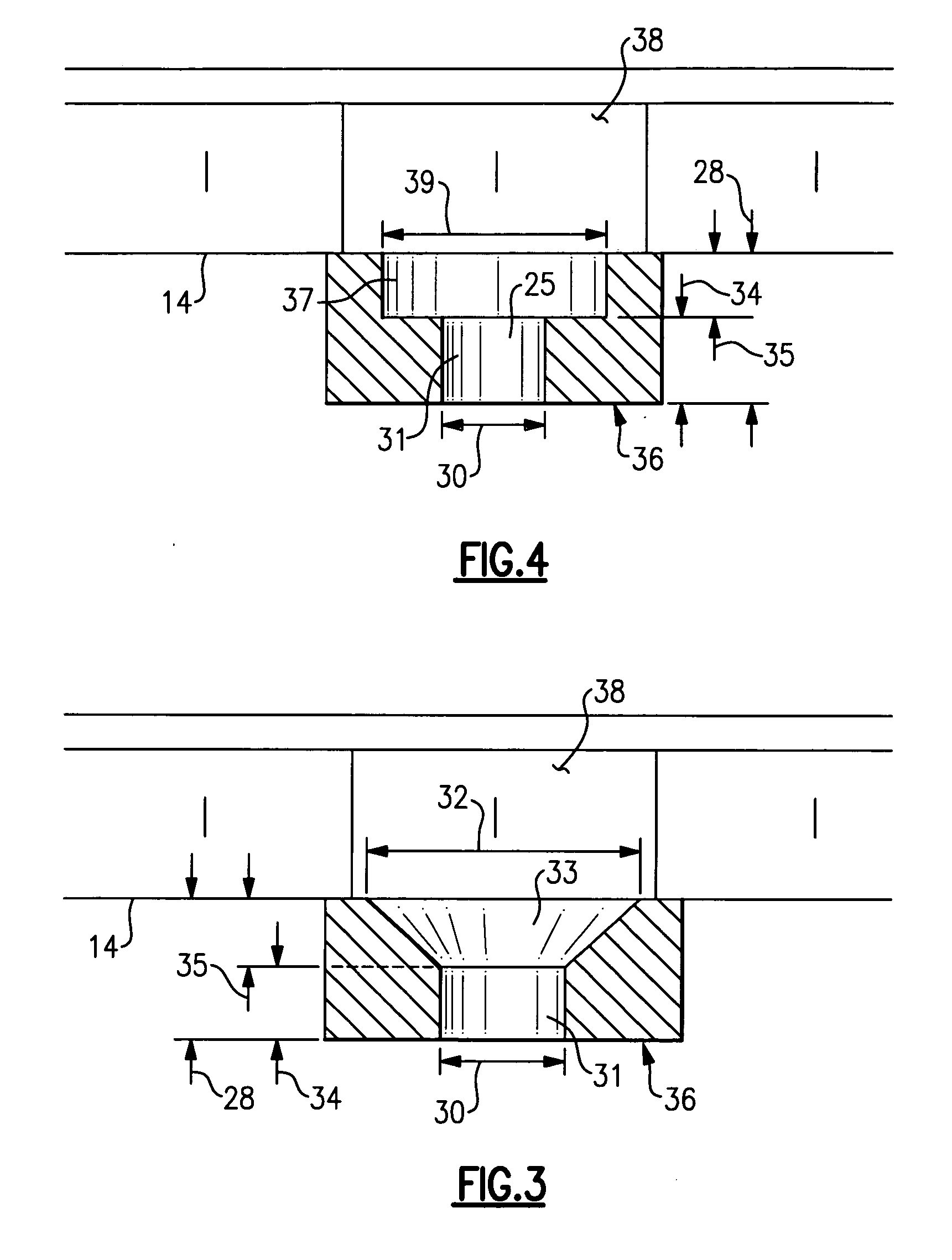
Impact resistance acoustic treatment
InactiveUS20070012508A1Reduce restrictionsNoise reduction installationsEngine fuctionsForeign object damageSound energy
A liner assembly for a duct includes noise attenuation panel for dissipating sound energy generated within the duct. A damage resistant acoustic panel for installation in high velocity impact prone locations includes a plurality of openings for communicating noise signals to the noise attenuation panel. At lease some of the openings includes a first diameter that extends a depth into the acoustic panel. The depth is no greater than the first diameter. A second portion extends the remainder of the thickness into the acoustic panel and includes a diameter greater than the first diameter. The increased area provided by the second diameter reduces restriction to the transmission of sound energy to the noise attenuation panel within an acoustic panel thickness required for protecting against foreign object damage.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Cmc blade with pressurized internal cavity for erosion control
ActiveUS20130330189A1Increased longevityImproves Structural IntegrityPropellersPump componentsForeign object damageLeading edge
A ceramic matrix composite blade for use in a gas turbine engine having an airfoil with leading and trailing edges and pressure and suction side surfaces, a blade shank secured to the lower end of each airfoil, one or more interior fluid cavities within the airfoil having inlet flow passages at the lower end which are in fluid communication with the blade shank, one or more passageways in the blade shank corresponding to each one of the interior fluid cavities and a fluid pump (or compressor) that provides pressurized fluid (nominally cool, dry air) to each one of the interior fluid cavities in each airfoil. The fluid (e.g., air) is sufficient in pressure and volume to maintain a minimum fluid flow to each of the interior fluid cavities in the event of a breach due to foreign object damage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fan blade with segmented fan blade cover
ActiveUS20170023009A1Minimize risk of damageMinimize damagePump componentsBlade accessoriesForeign object damageEngineering
A lightweight fan blade for use in turbofan gas turbine engines is disclosed. The fan blade includes a metallic body having a pressure side and a suction side. The suction side of the body includes one or more cavities. A cover is then attached to the suction side of the body to cover or enclose the one or more cavities. The cover includes one or more transverse weakened areas, such as a transverse slit so that the cover separates into one or more smaller segments in the event of a foreign object damage (FOD) or fan blade out (FBO) event occurs. The smaller segments of the cover are less likely to do damage to downstream components such as the low and high-pressure compressors. A single smaller segment of the cover may allow for continued operation of the engine because the imbalance created by the event may be tolerated by the engine.
Owner:RTX CORP
Low foreign object damage (FOD) weighted nose decoy flare
ActiveUS20110036260A1Increase burning/explosive forceEasy to igniteAmmunition projectilesFirework flares/torchesForeign matterDecoy
The present invention discloses a low foreign object damage nose weight for affixing to a either a standard or kinematic decoy flare comprising a thin walled nose cup having a closed end, an open end, an internal cavity, and at least one sidewall attached to said closed end and surrounding said internal cavity; and a metal powder disposed within the internal cavity for weighing down the forward end of the decoy flare, said nose cup capable of being affixed to a forward end of a decoy flare such that said powder is jettisoned from said nose cup upon burn out of a flare pellet subassembly of said decoy flare thereby reducing the weight of the nose cup and the possibility of foreign object damage to aircraft, ground troops, ground equipment and buildings resulting from the falling nose weight.
Owner:KILGORE FLARES
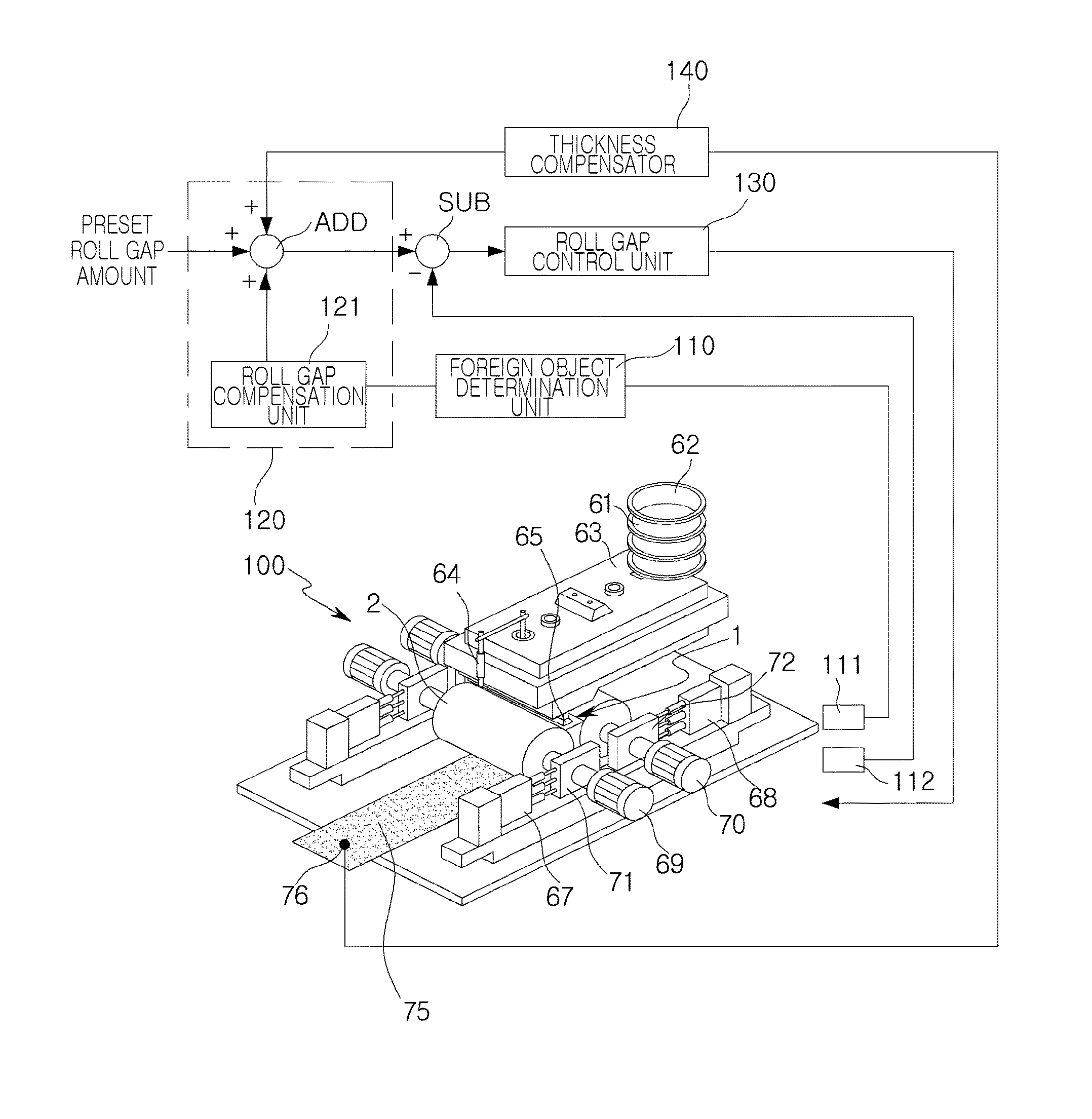
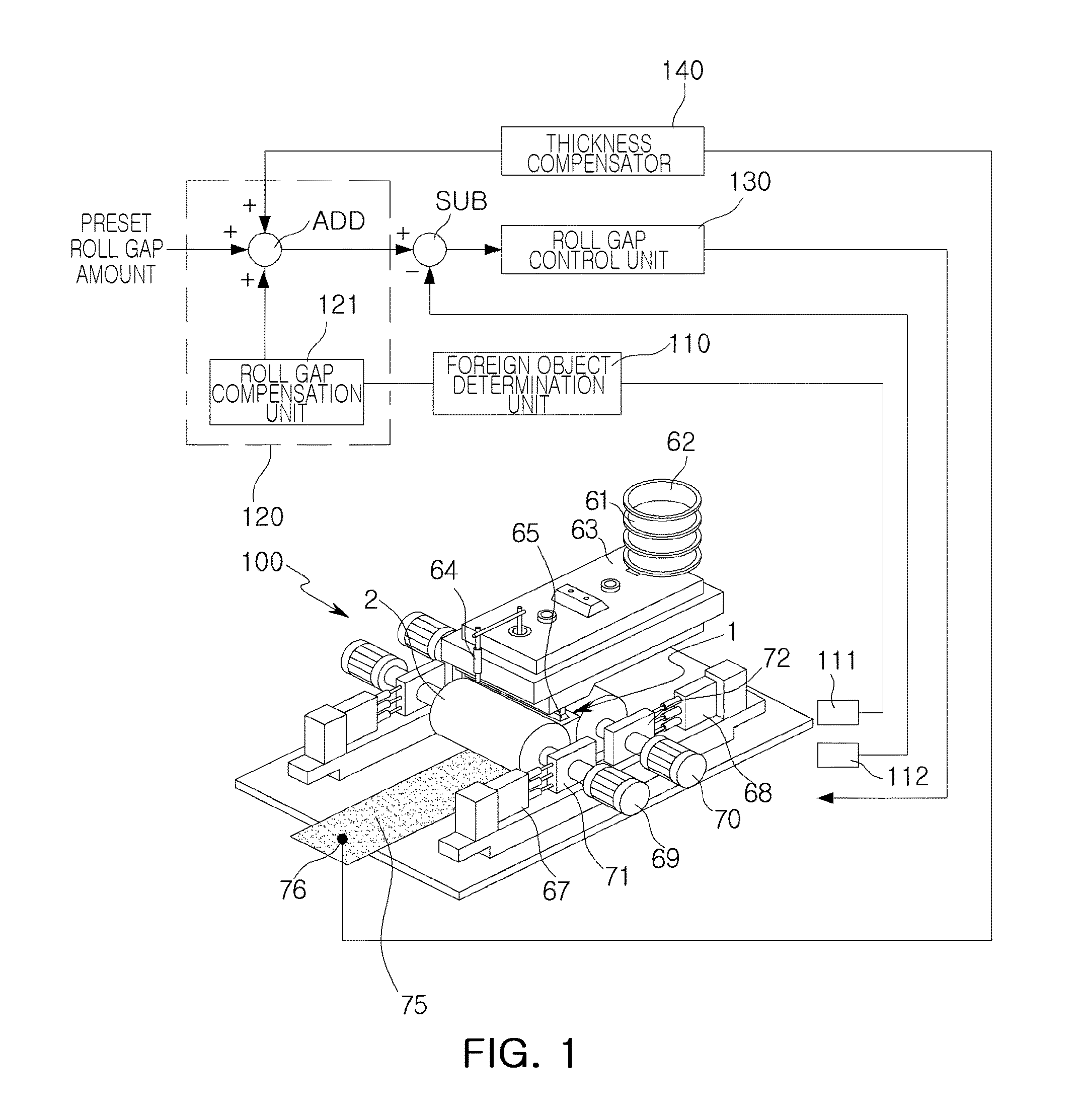
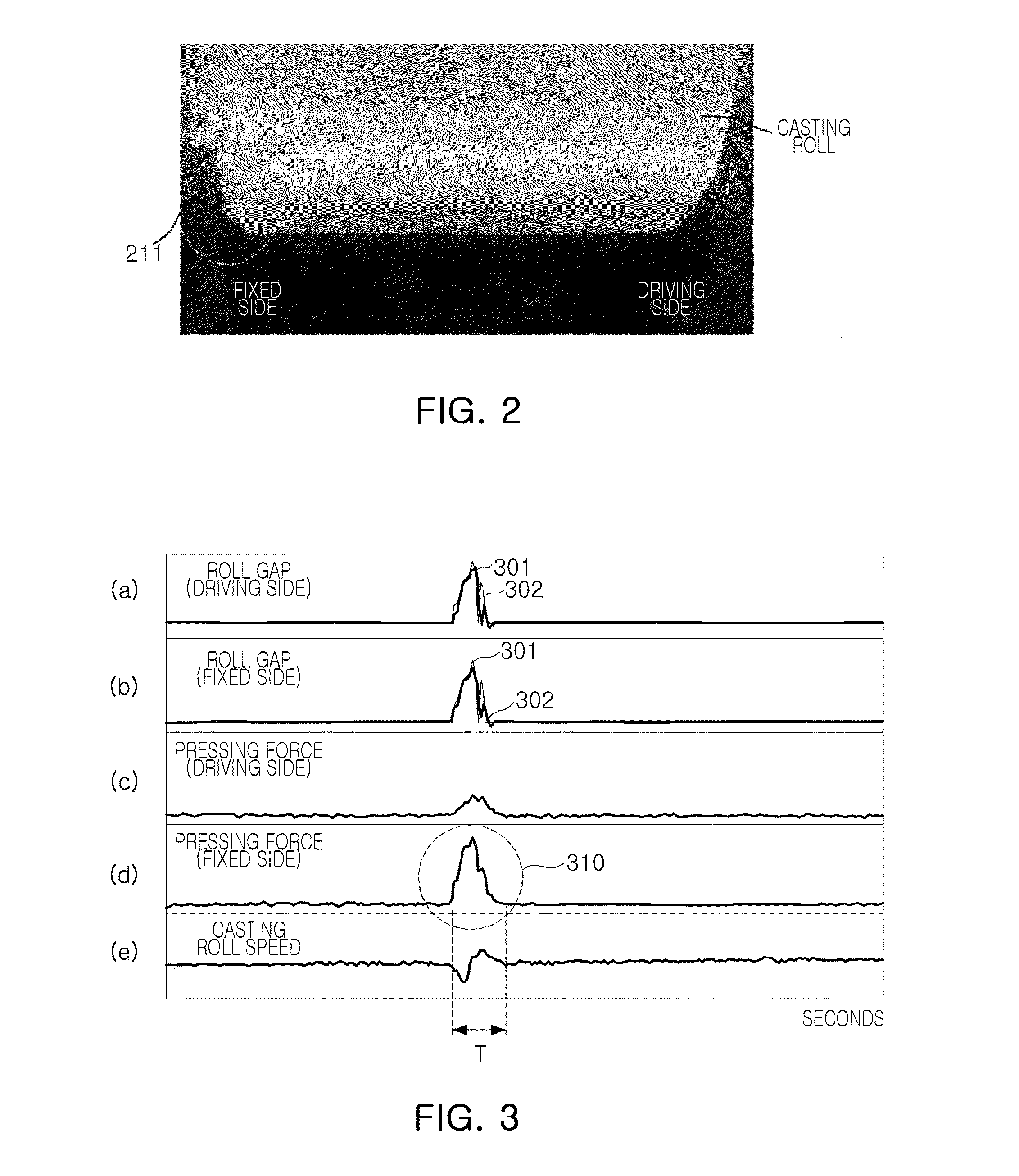
Apparatus For Preventing Damage To Casting Rolls In Strip Casting Machine
ActiveUS20150174651A1Decrease damage to surfaceImprove processing yieldCasting safety devicesMould controlling devicesForeign matterStrip casting
The apparatus for preventing damage to casting rolls includes: a roll pressing force detection unit measuring a roll pressing force applied to the casting rolls; a foreign object determination unit determining whether foreign objects have been introduced to the casting rolls based on the measured roll pressing force; a roll gap instruction value generation unit generating a roll gap instruction value by adding a preset roll gap amount to the set roll gap if it is determined that foreign objects have been introduced to the casting rolls; and a roll gap control unit controlling a roll gap between the casting rolls based on the roll gap instruction value. Therefore, surfaces of the casting rolls may be less damaged by foreign objects.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
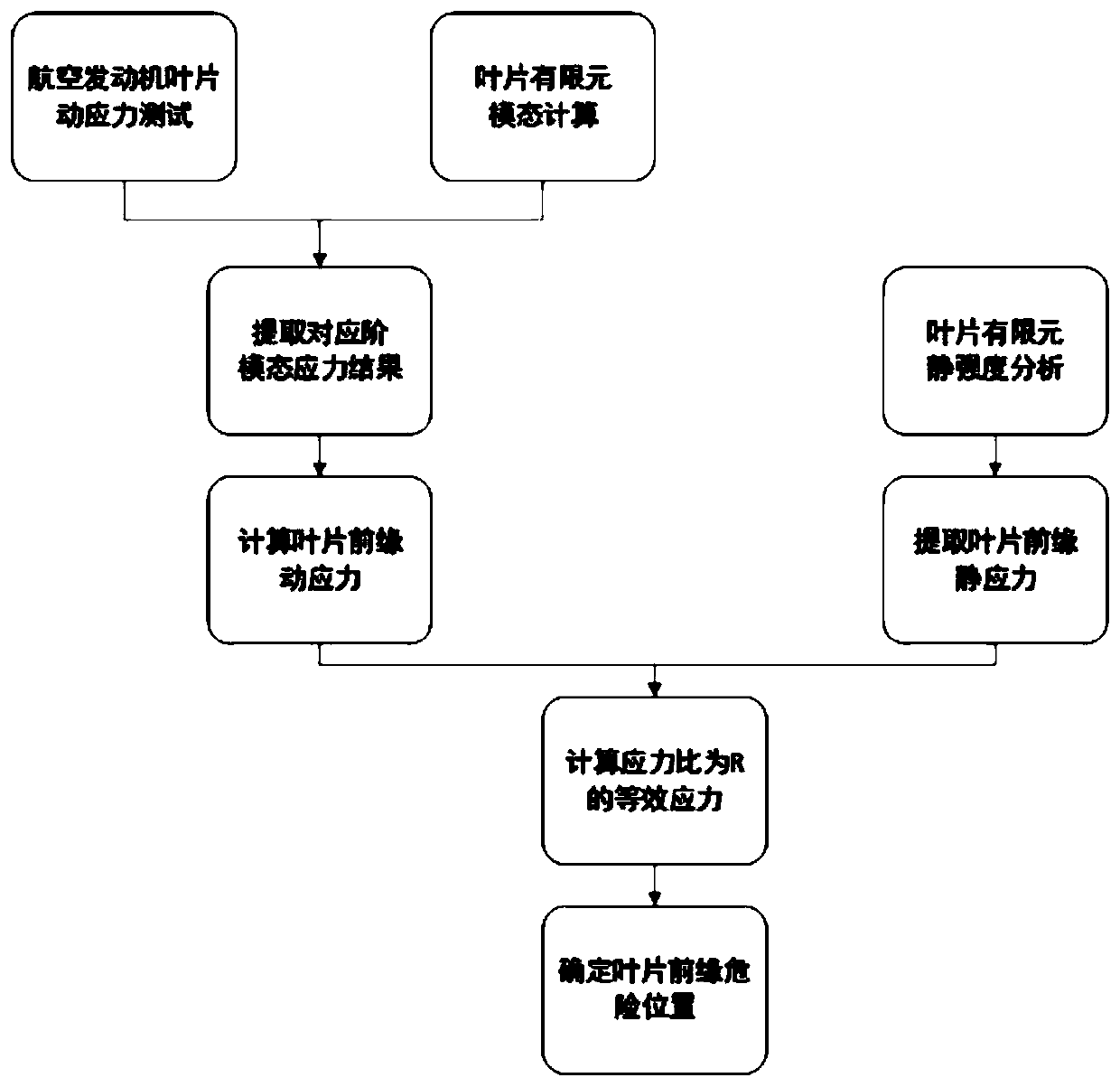
Method for detecting dangerous part at front edge of aero-engine blade
ActiveCN110134990AExact lesion sizeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAviationForeign object damage
The invention discloses a method for detecting a dangerous part at the front edge of an aero-engine blade. The method comprises the steps of carrying out a dynamic stress test in an aero-engine working state test run, carrying out finite element modal calculation on blades, extracting a vibration stress simulation result under a modal corresponding to a dynamic stress test result, and the like. The stress level of each part of the front edge of the aero-engine blade under the working load can be detected, the dangerous part of the front edge of the aero-engine blade and the possible damage size during service can be accurately obtained, and data support can be provided for design of foreign object damage resistance of the aero-engine blade and formulation of a foreign object damage repairprinciple.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com