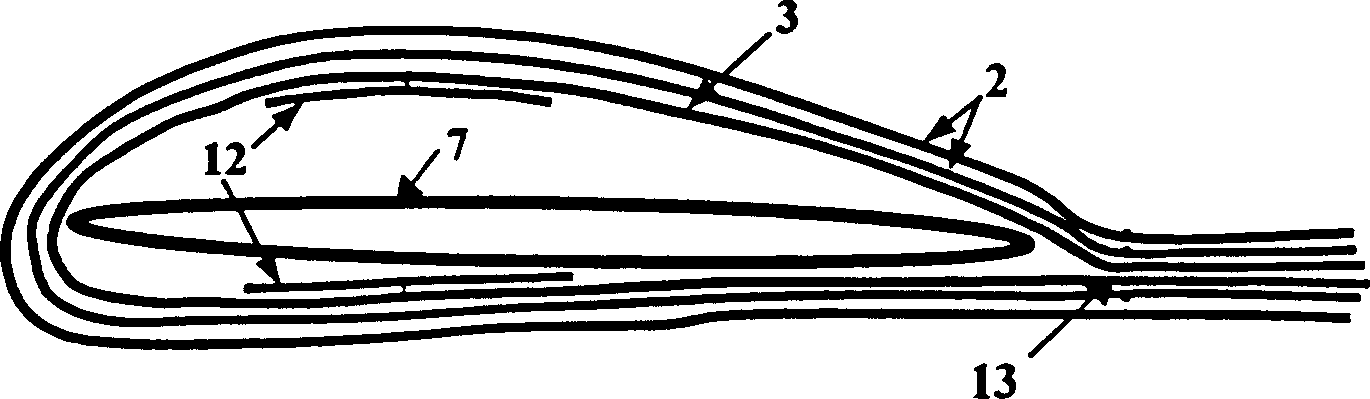Patents
Literature
258 results about "Composite blade" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
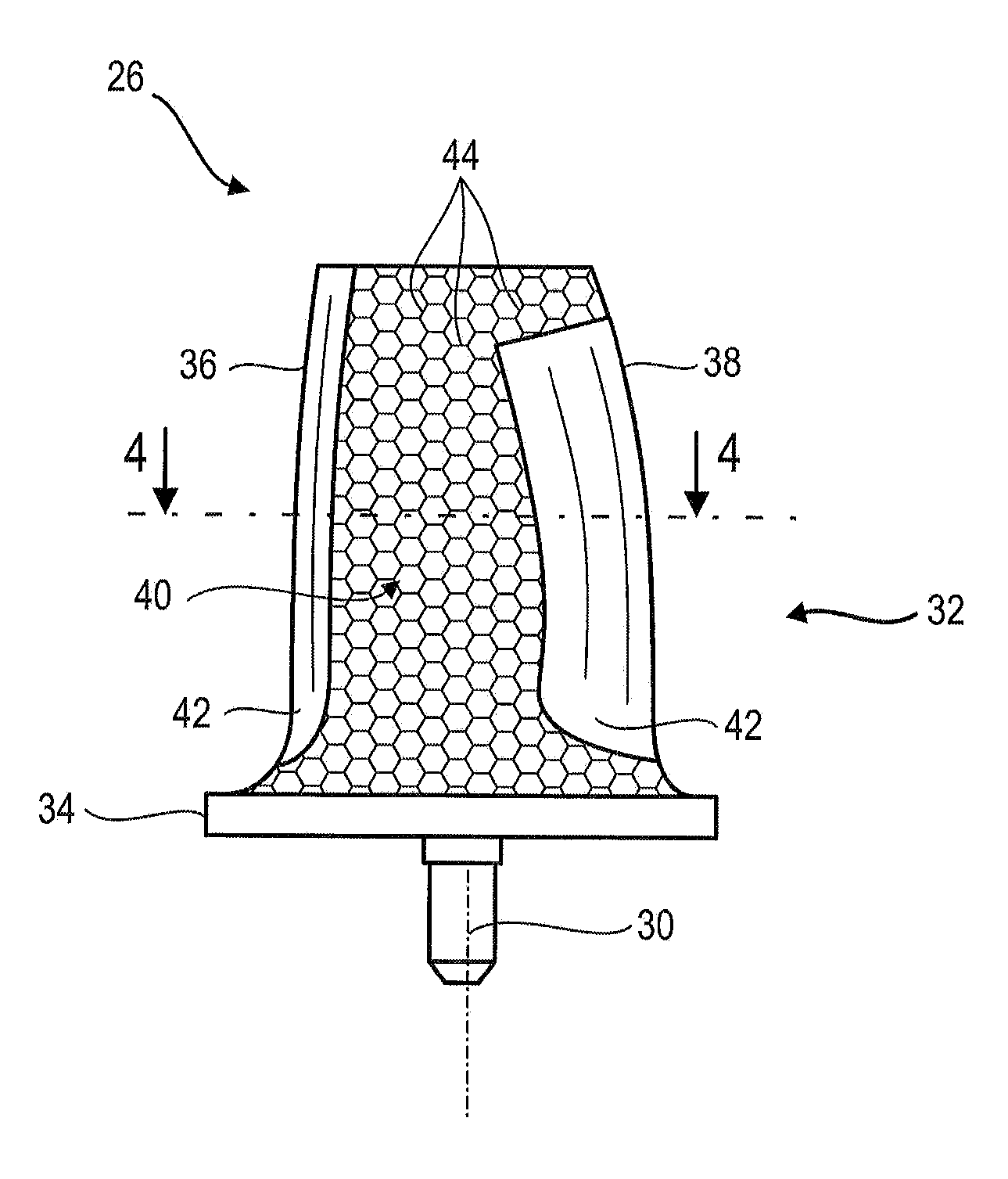
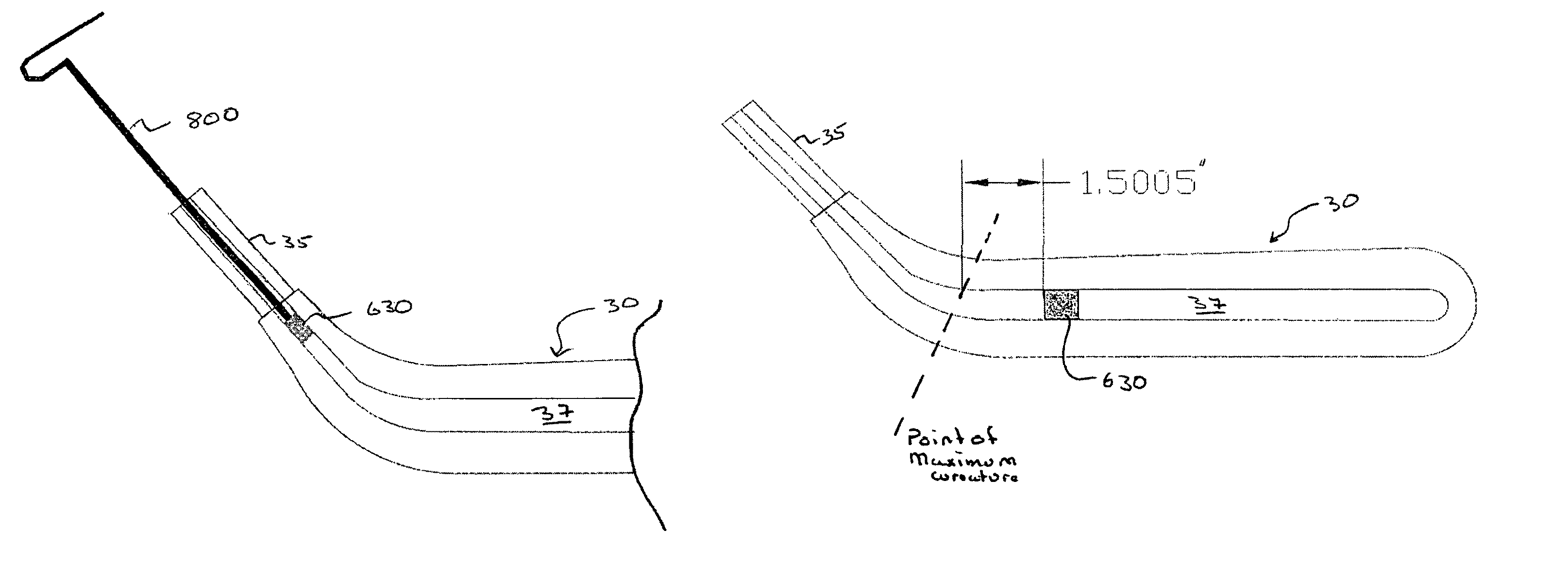
Co-cured sheath for composite blade
A method of forming a composite blade having a sheath on a portion of the blade by placing the dry composite blade and sheath in a mold, adding a resin, and curing the resin to integrally bond the blade to the metal sheath. The portion of the blade having the sheath bonded thereto may be at least one of the leading edge, the tip and the trailing edge of the blade.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
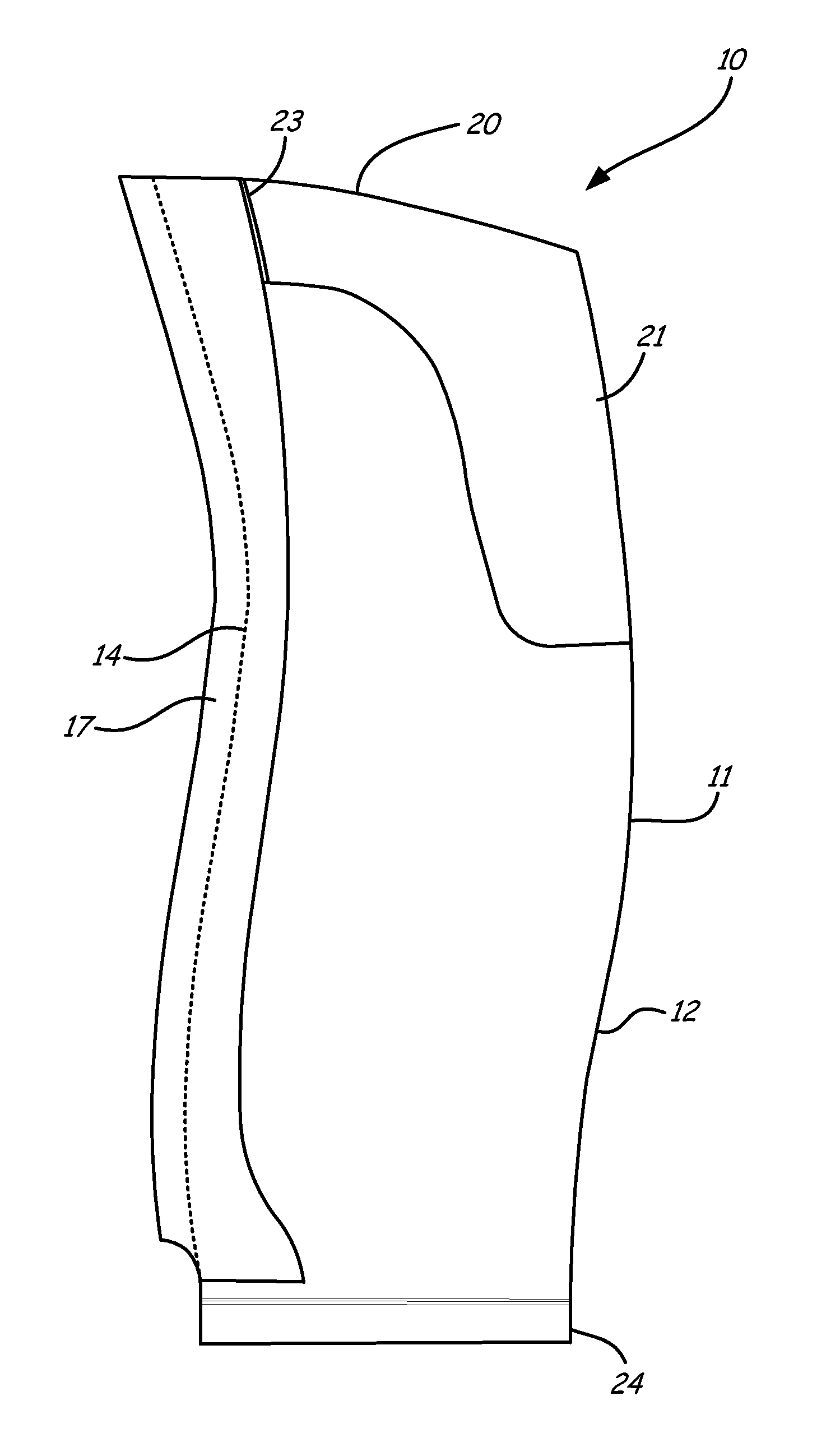
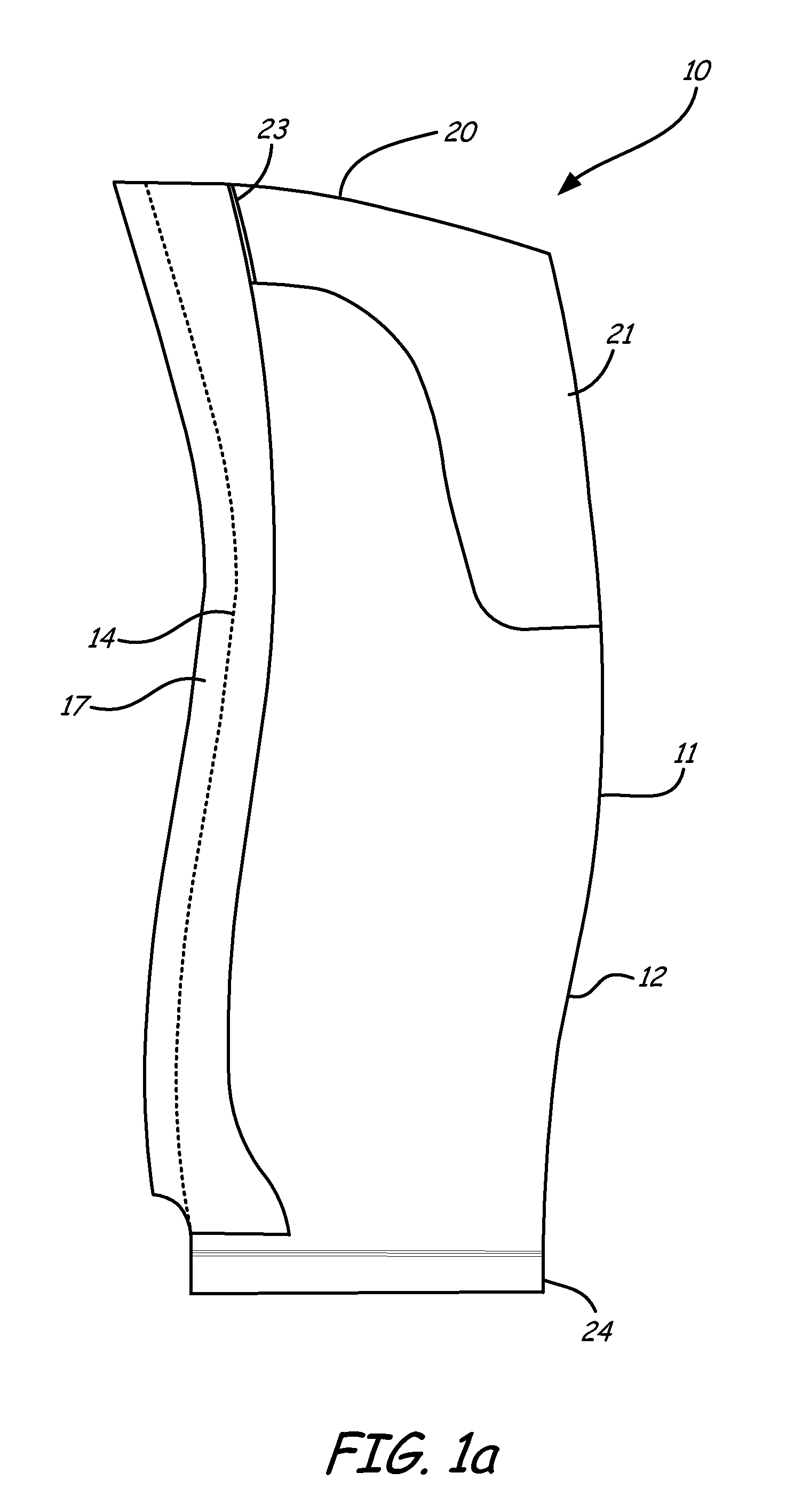
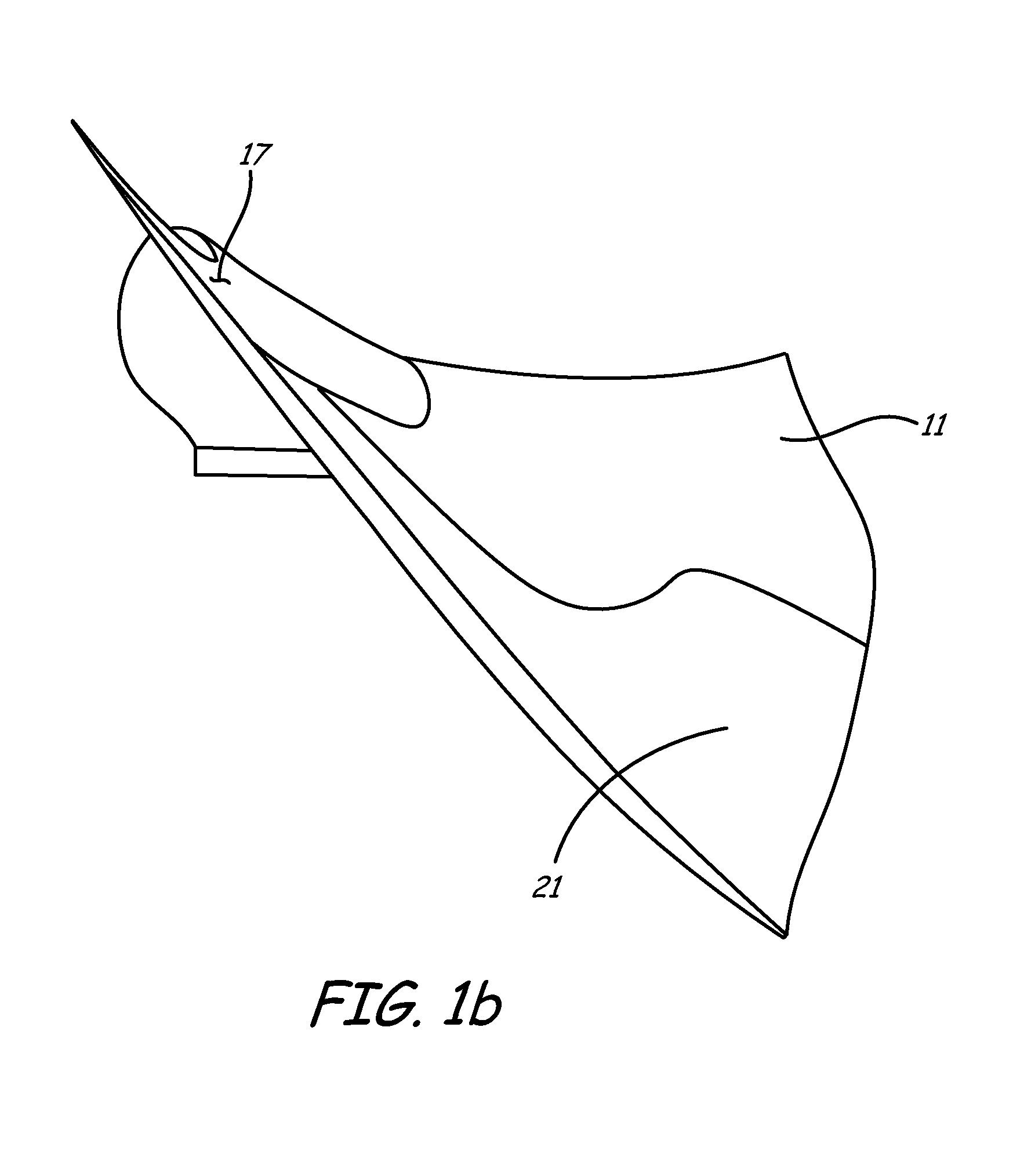
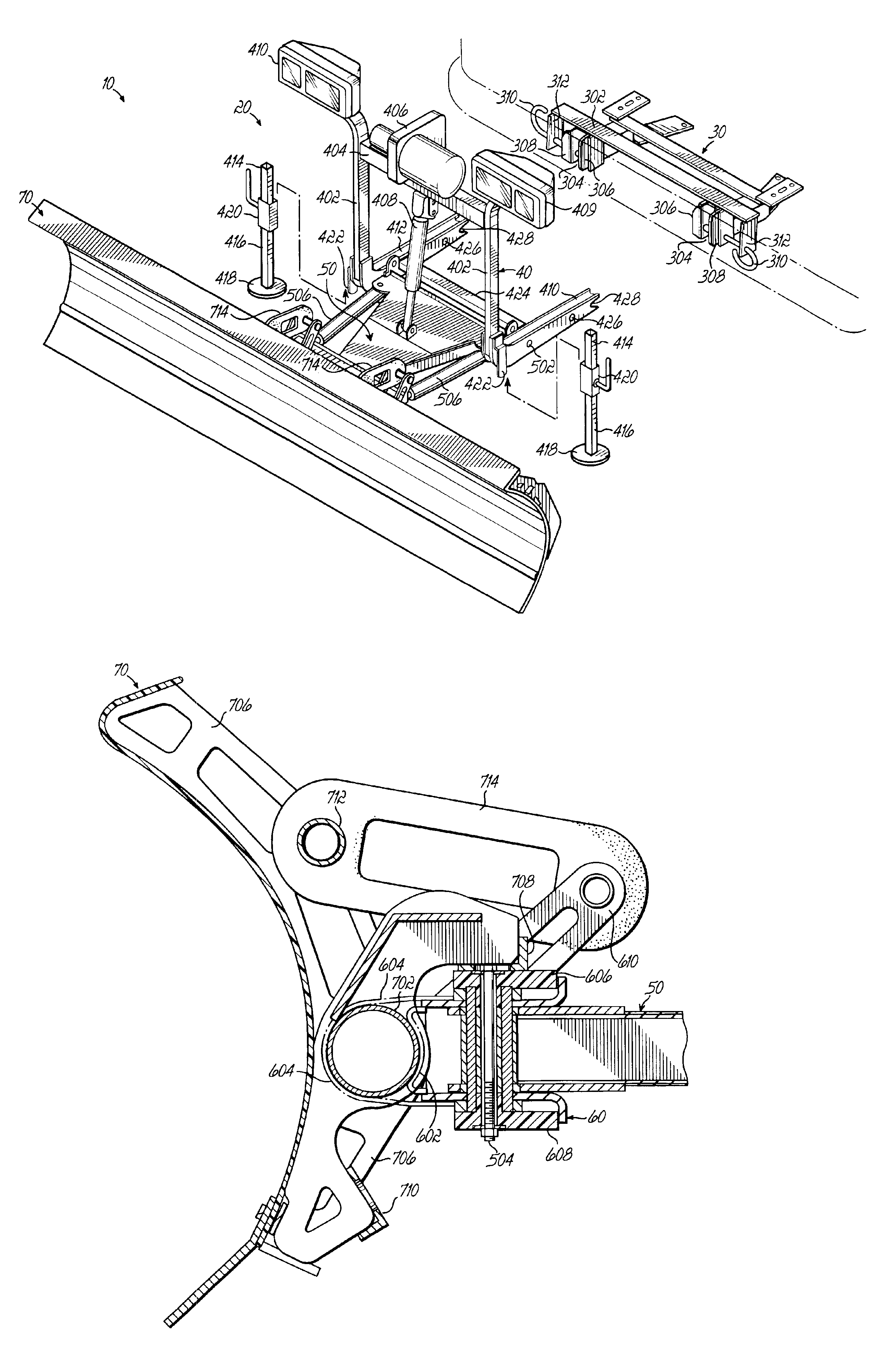
Snowplow assembly
A snowplow assembly comprises a lift frame and A-frame operably pivotally connected together and an actuator operably connected between the lift frame and A-frame for effecting relative pivotal movement between the lift frame and A-frame. A plow blade includes a blade frame. The blade frame includes a tube of circular cross section which is operably pivotally connected to the A-frame. The tube is pivotally received by a quadrant, which is operably connected to the A-frame. A resilient element is operable between the blade frame and A-frame normally biasing a lower edge of the plow blade forwardly. The resilient element is an elastomeric loop. The pivotal connection of the plow blade to the A-frame in combination with the resilient element provides a trip function of the plow blade. The plow blade is a composite. The circular tube of the blade frame provides torsional stiffness to the composite blade.
Owner:DOUGLAS DYNAMICS
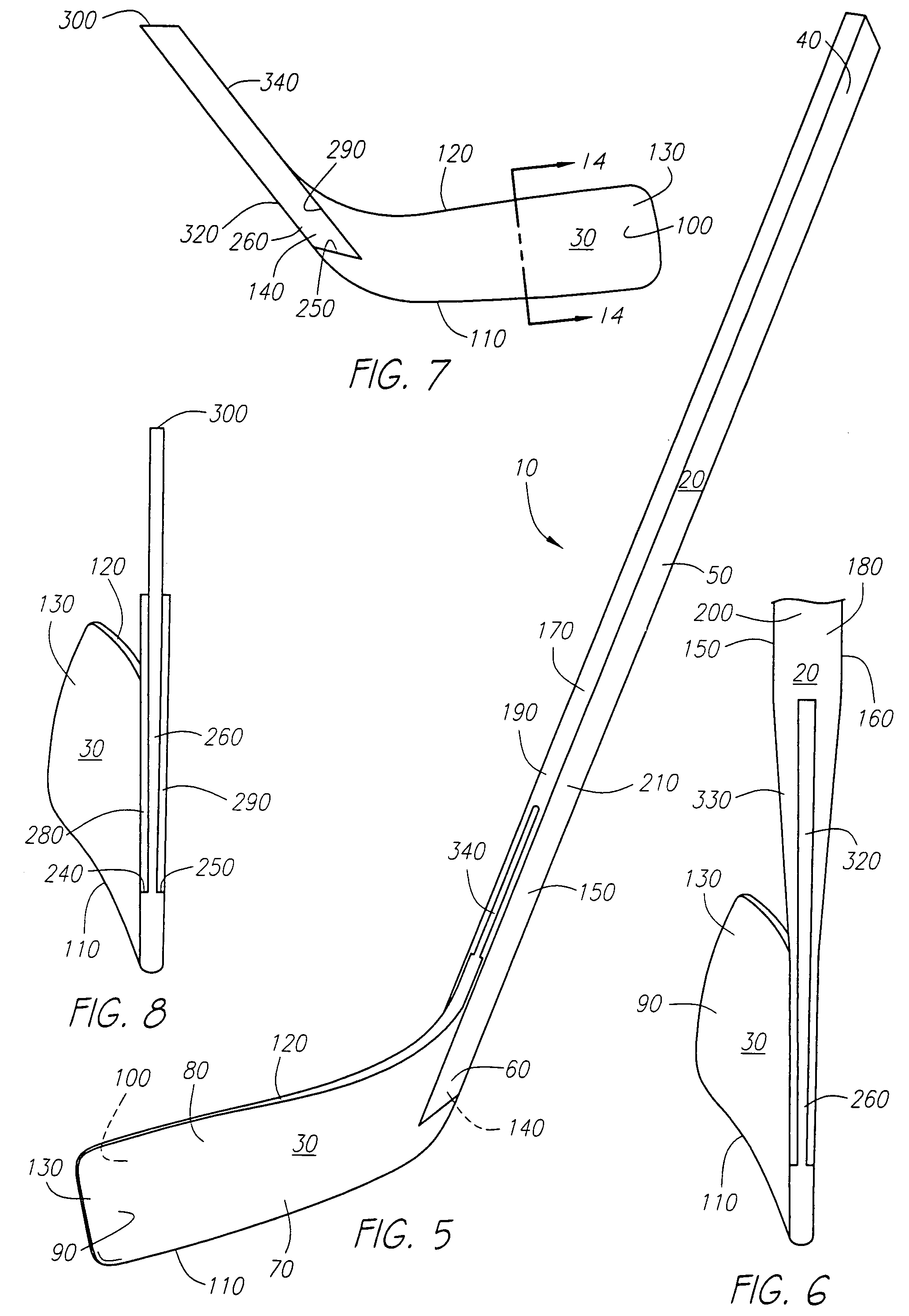
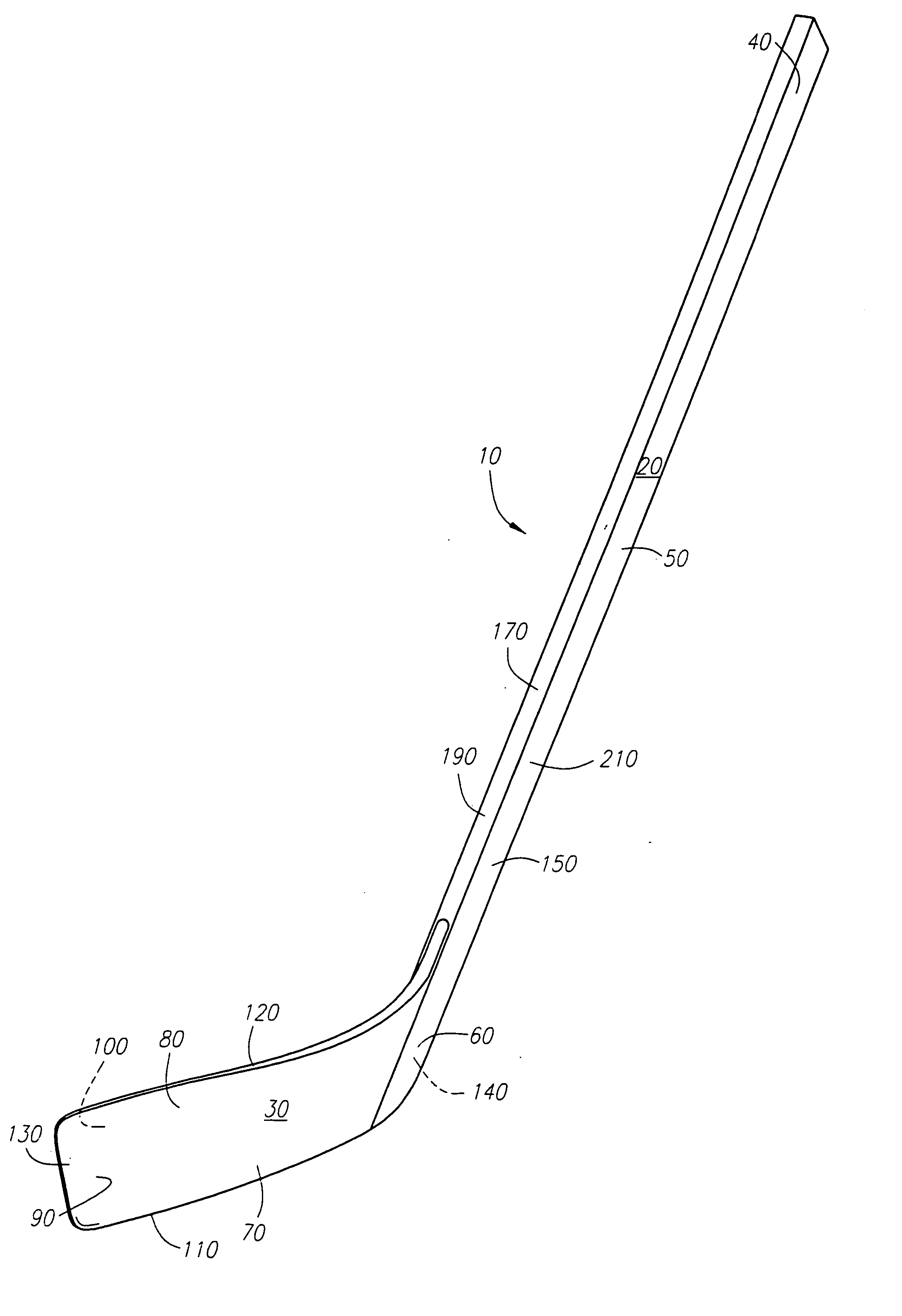
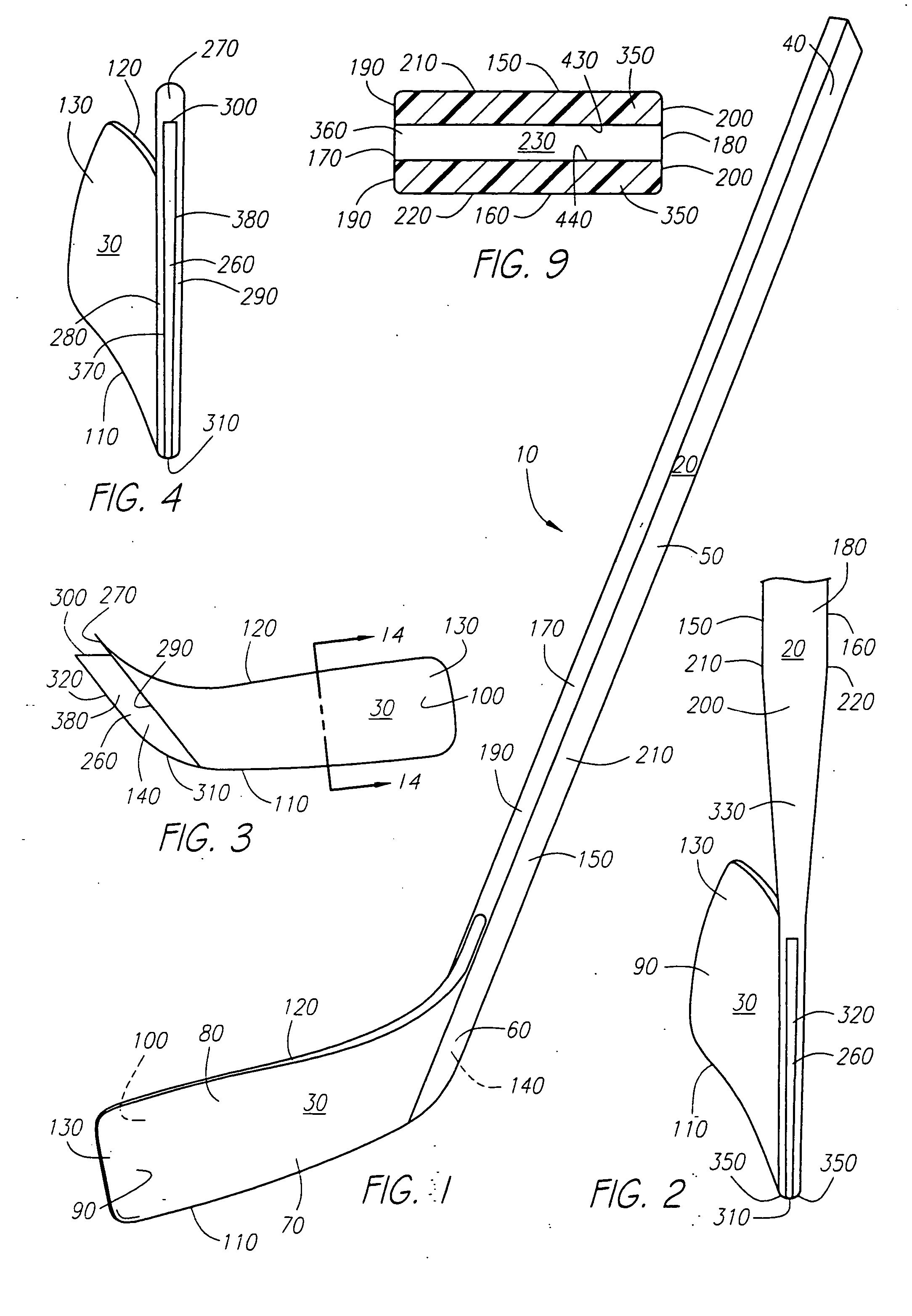
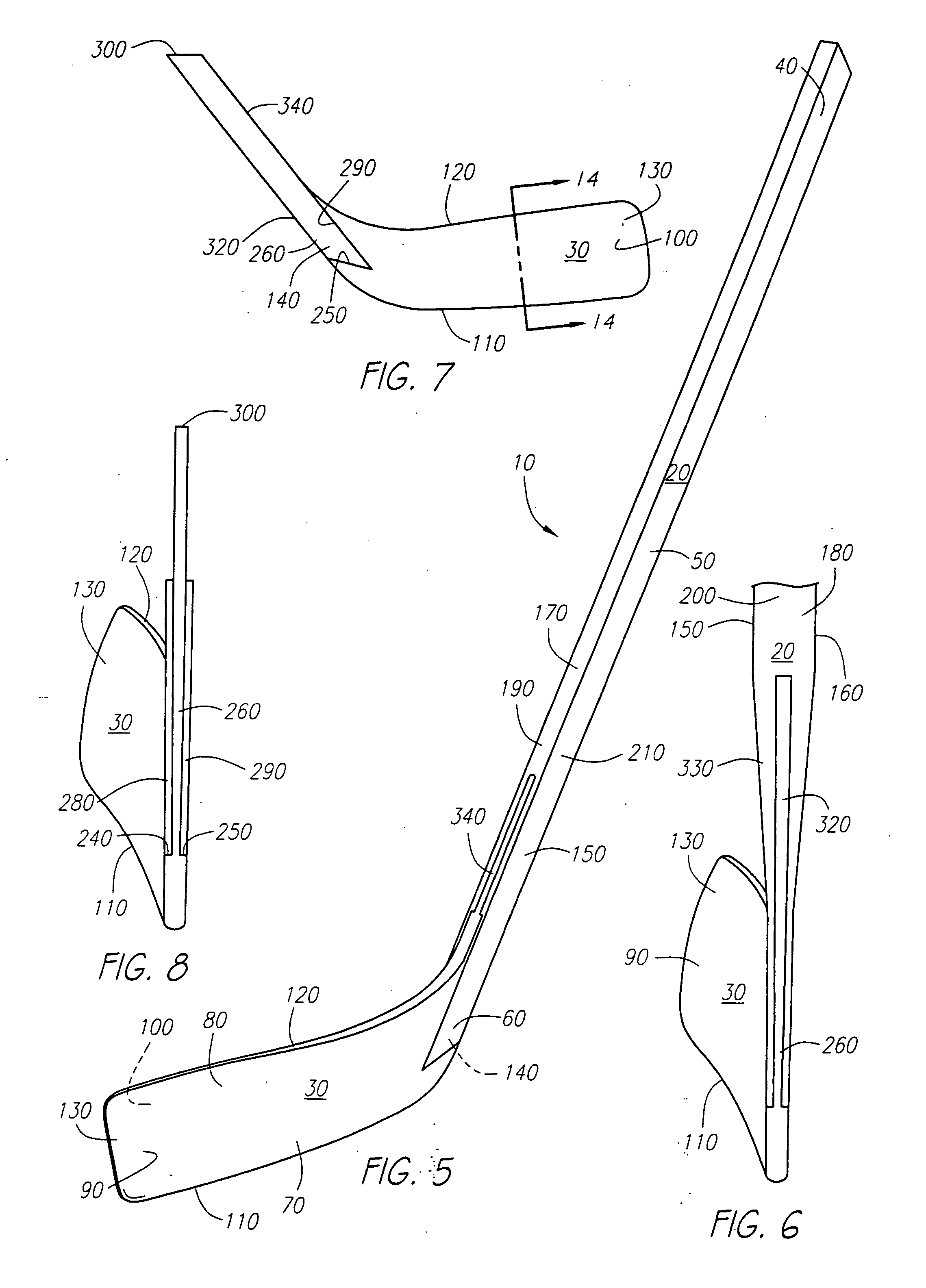
Hockey stick
InactiveUS7097577B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationFiberComposite blade
A hockey stick having a composite blade and a shaft is disclosed. The composite blade includes a heel section that is recessed relative to the front and back faces of the blade. The recessed heel section is configured to be received by a hockey stick shaft or an adapter member configured to connect the blade to the shaft. The composite blade preferably comprise a foam inner core overlaid preferably with substantially continuous fibers disposed in a matrix material and may include an internal bridge structure extending from one side of the blade to the other. The blade may also be preferably comprised of a core comprising non-continuous fibers disposed within a matrix material. In another aspect, processes for manufacturing the previously described hockey stick blade(s) are described.
Owner:BAUER HOCKEY LLC
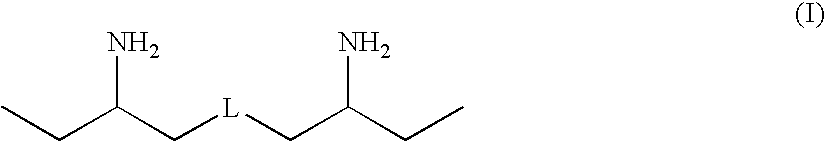
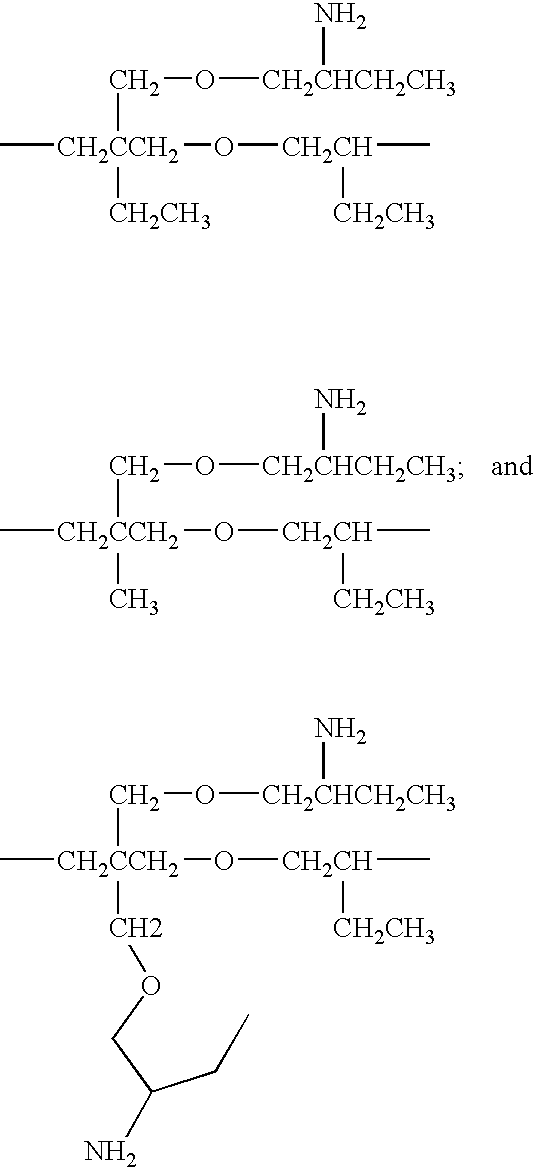
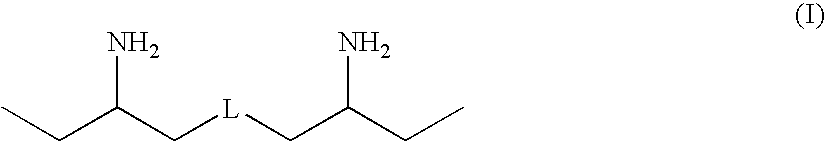
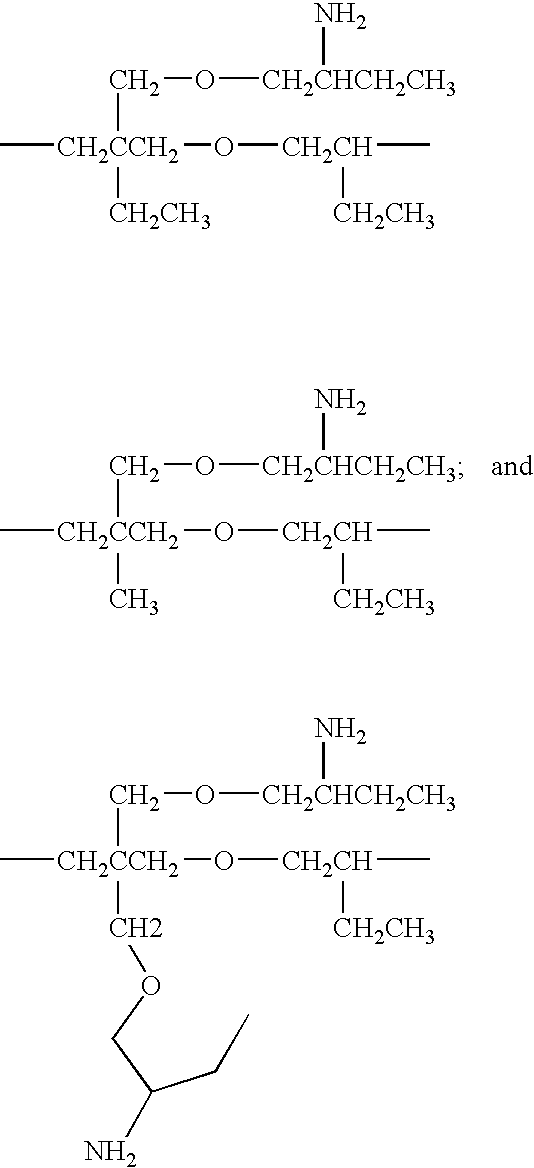
Polyether polyamine agents and mixtures therefor
Provided herein are polyamine precursors useful in the manufacture of epoxy resins. Use of a polyamine precursor according to the invention provides an epoxy resin formulation having an increased working time over prior art amines used for curing epoxies. Increased working times translate to the ability to manufacture composites which could not be made using conventional epoxy curing agents, such as composite blades for wind-driven turbines. Such polyamines are also useful in polyurea formulations for lengthening reaction time, thus allowing more flow of applied polyurea coatings prior to gellation.
Owner:HUNTSMAN PETROCHEMICAL LLC +1
Method and apparatus for fabricating variable gauge, contoured composite stiffeners
ActiveUS8465613B2Low costShorten the timeMechanical working/deformationMetal-working apparatusEngineeringComposite blade
Tooling apparatus for forming a composite charge into a contoured composite blade stringer includes an elongate punch and an elongate die flexible along their lengths. The charge is press formed by using the punch to drive the charge into the die. The punch and the die are mounted between a pair of flexible plates. A press coupled with the plates contours the charge by bending the plates into a desired contour.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
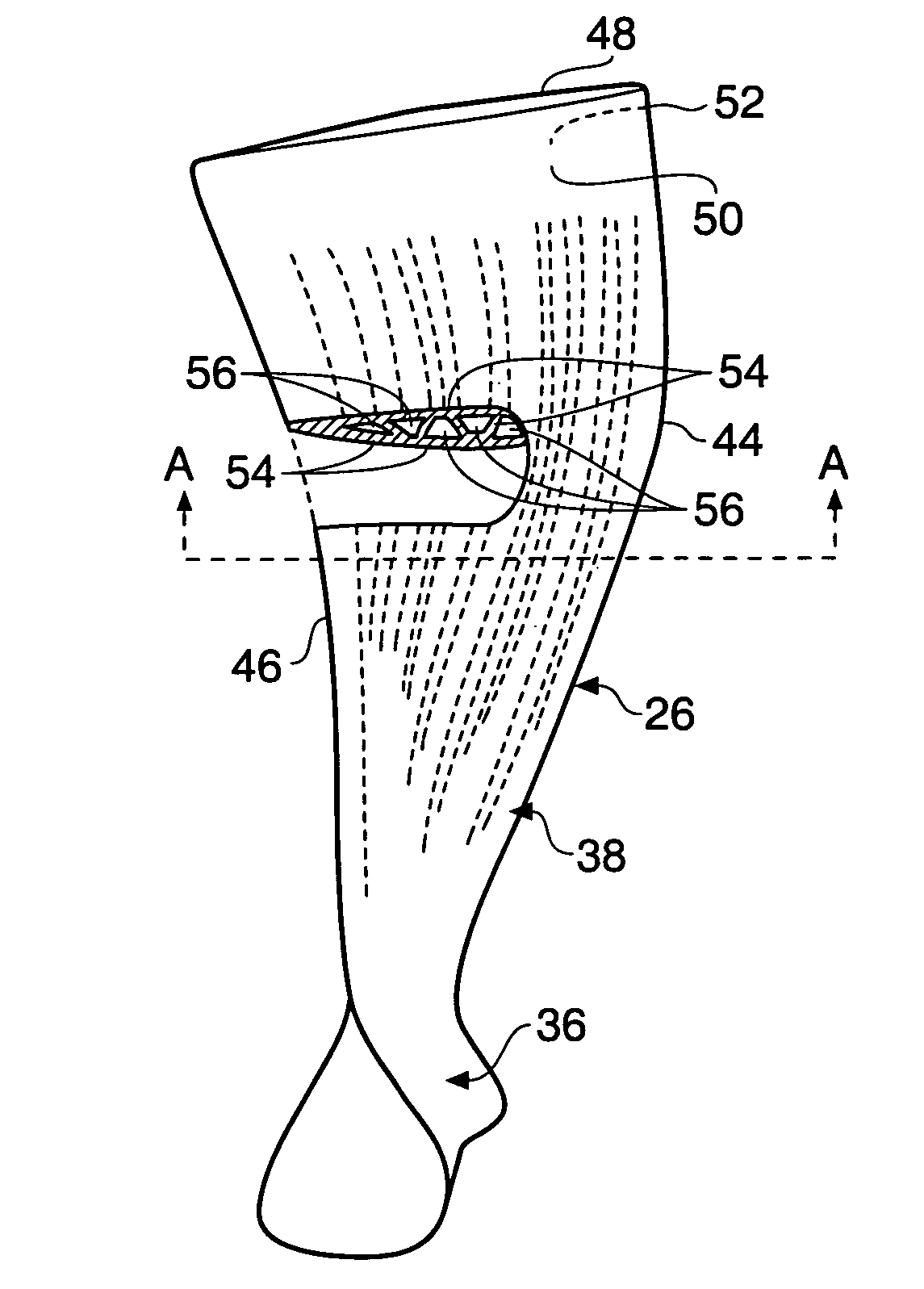
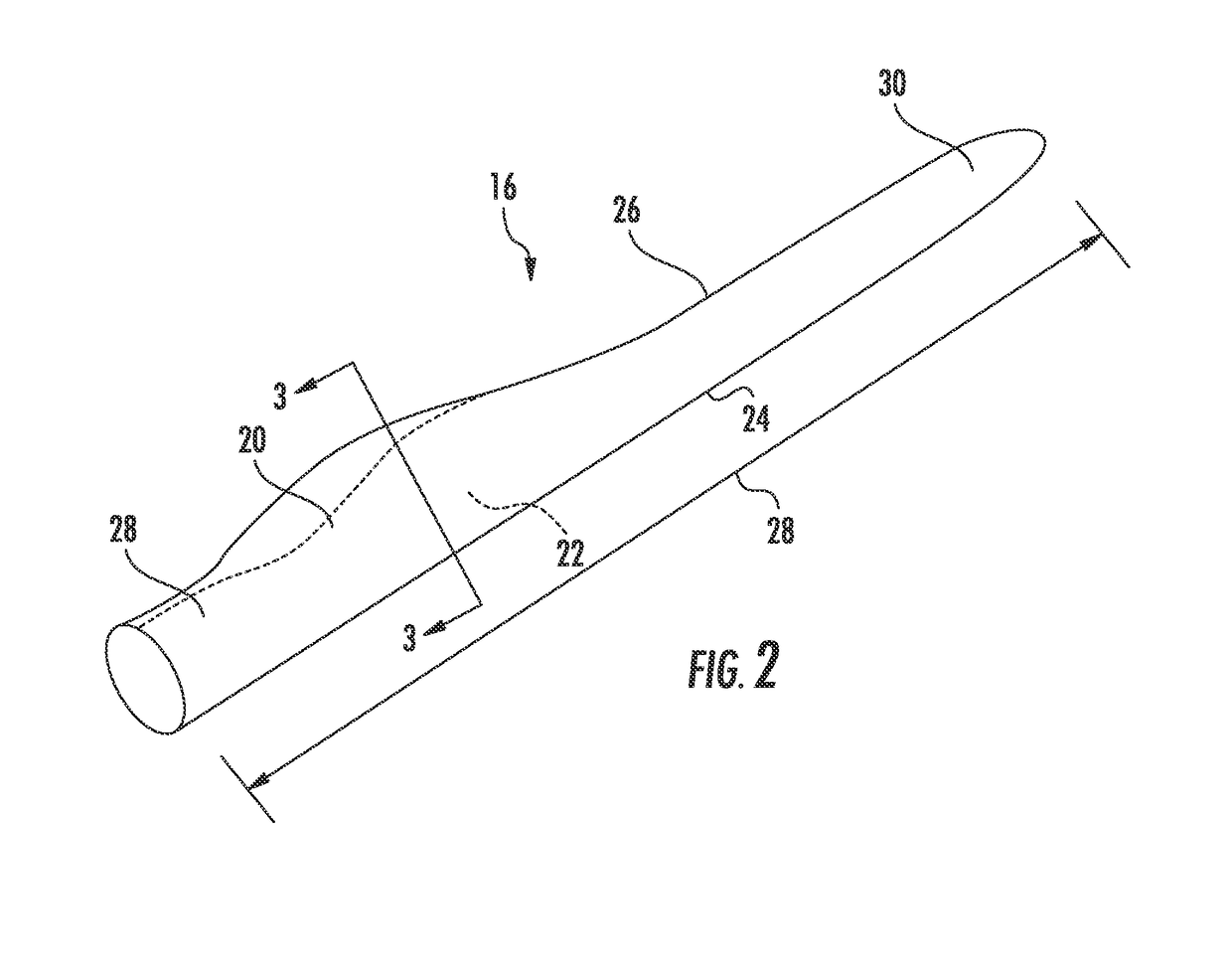
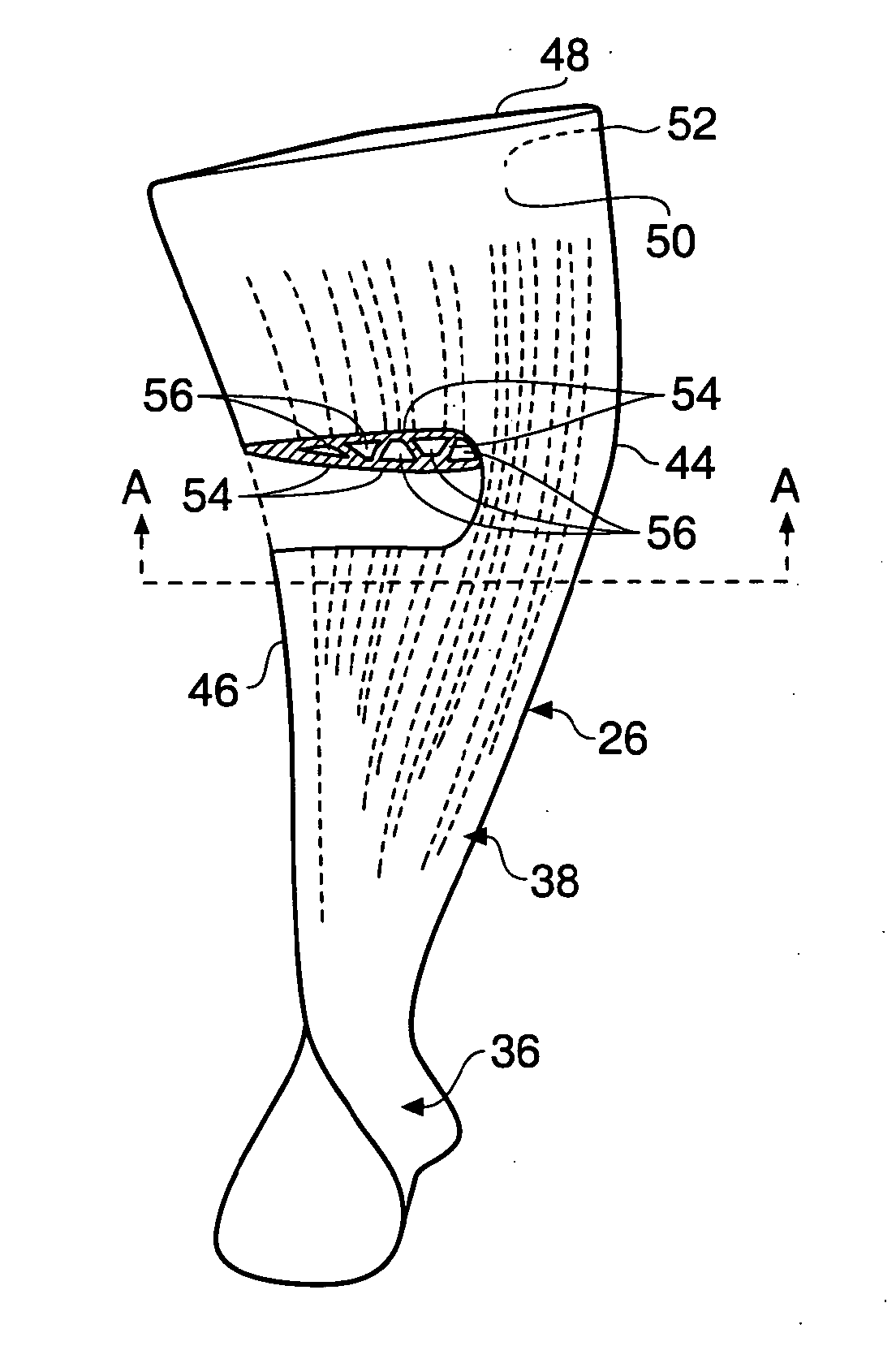
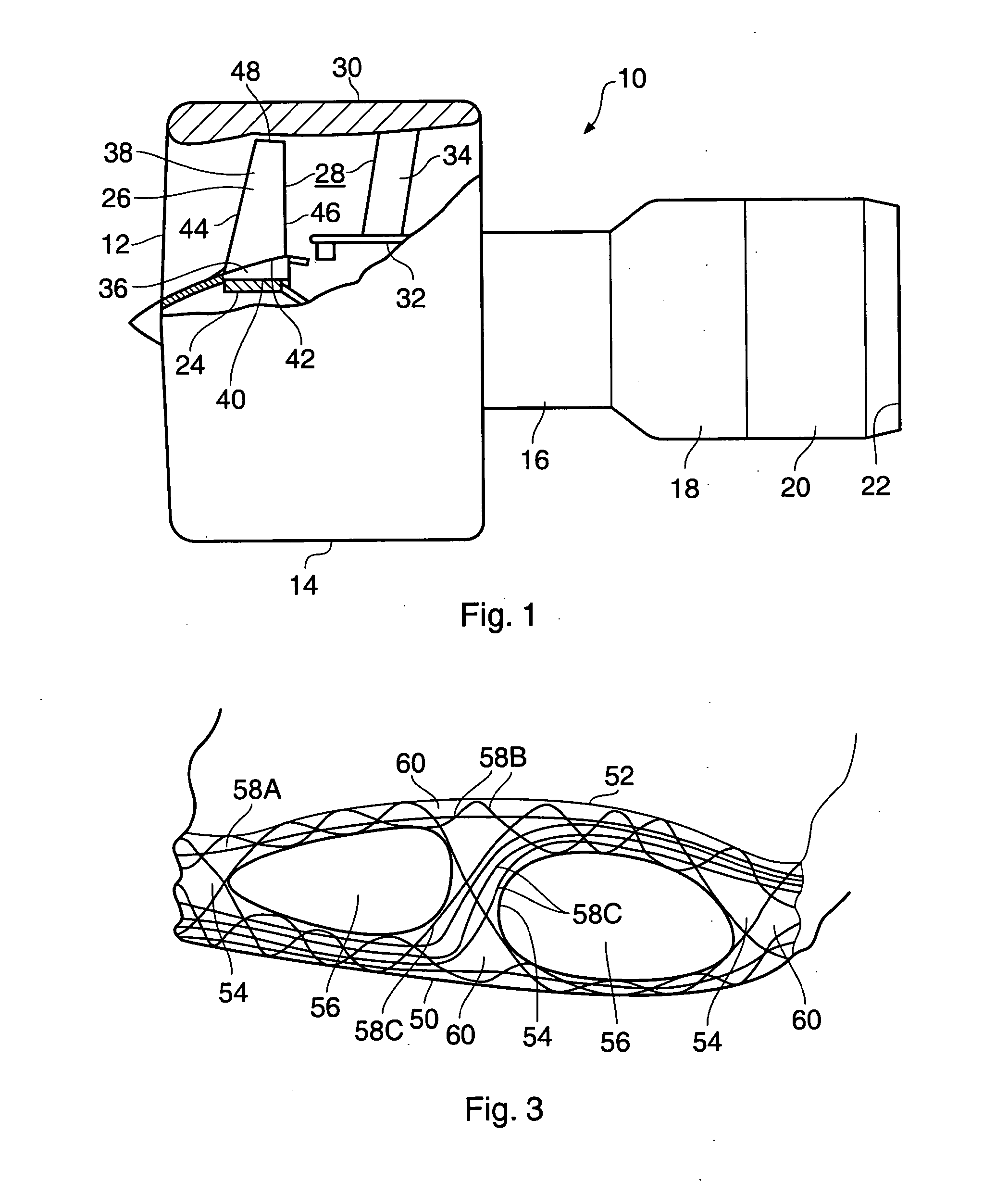
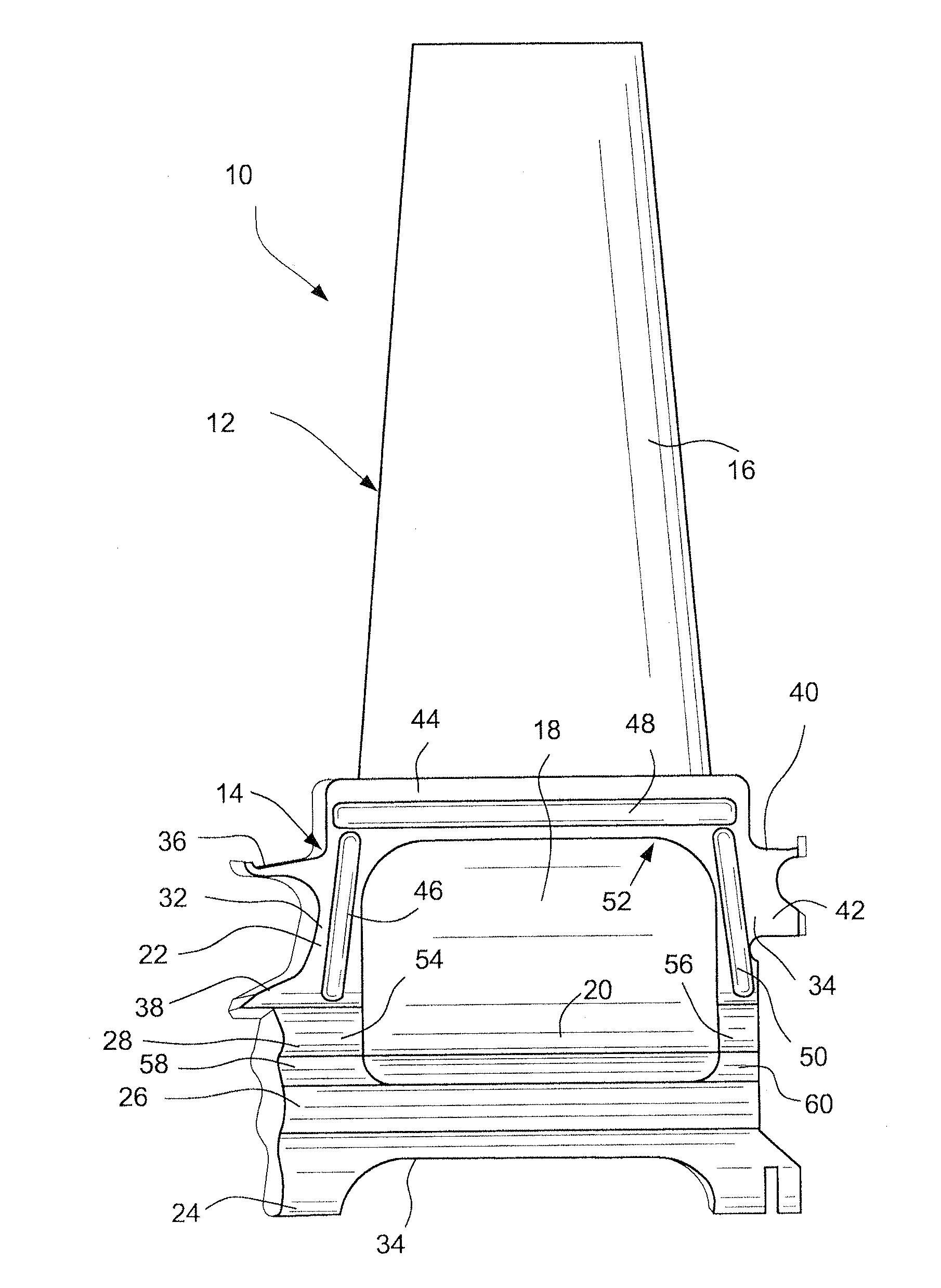
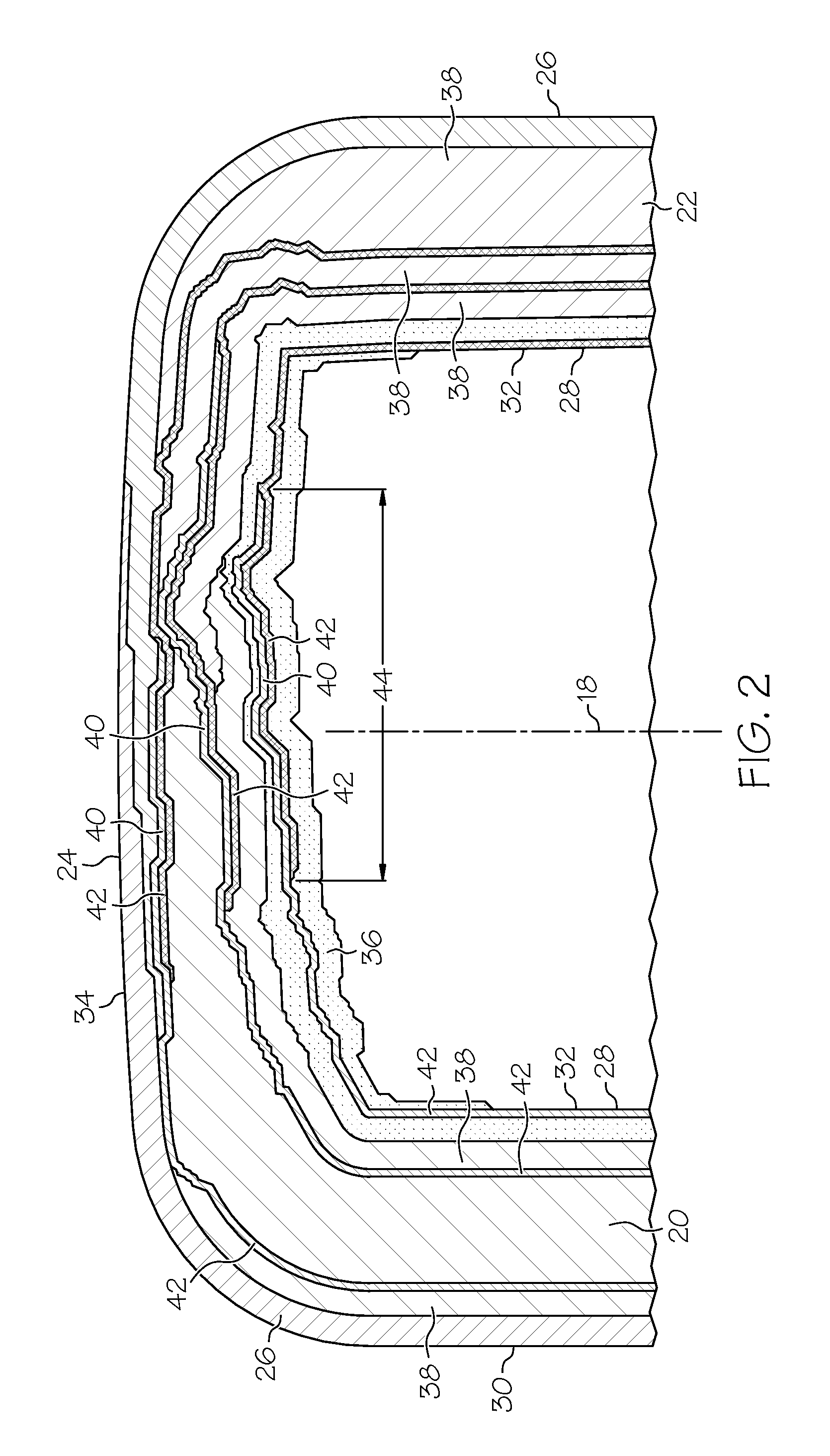
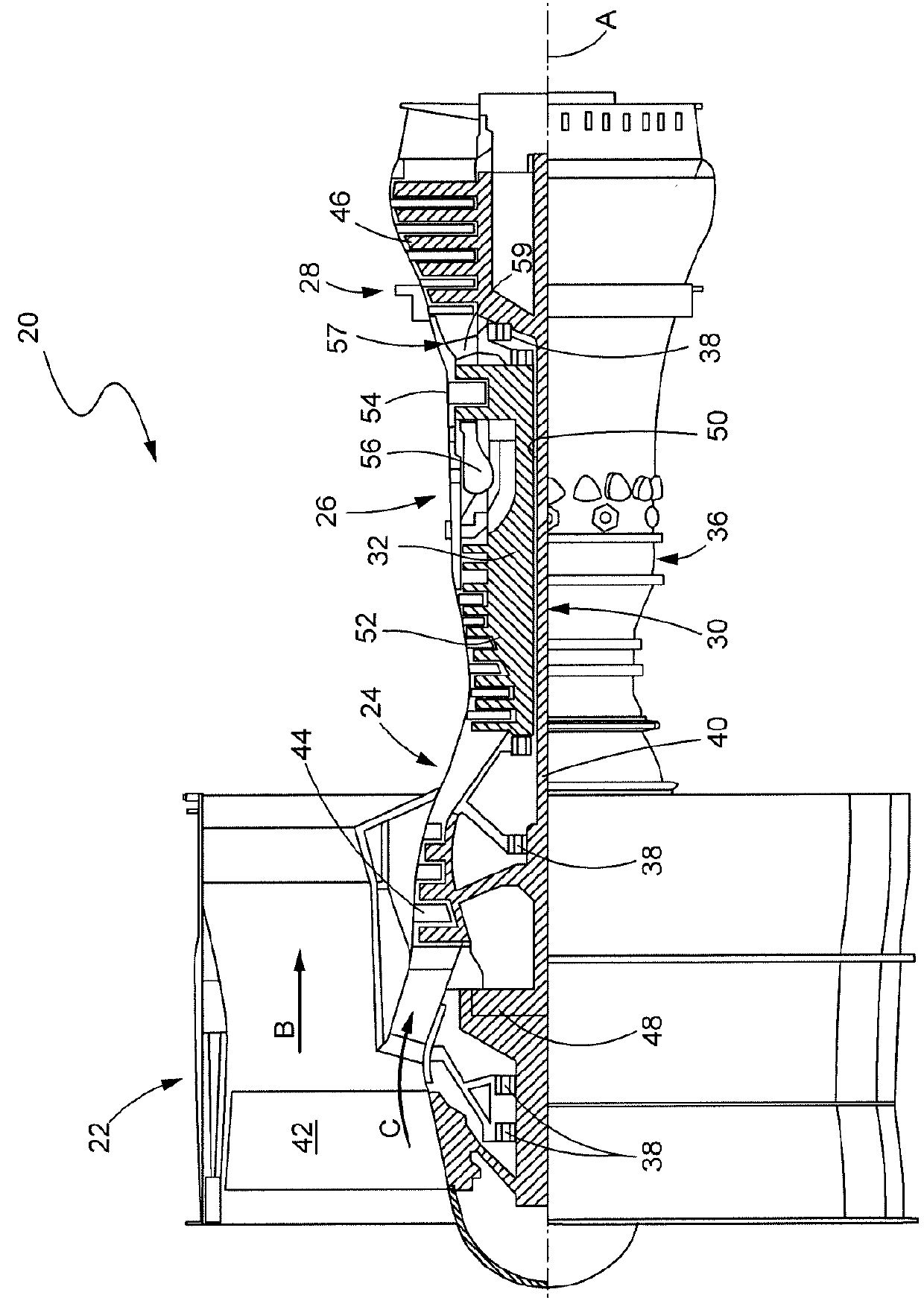
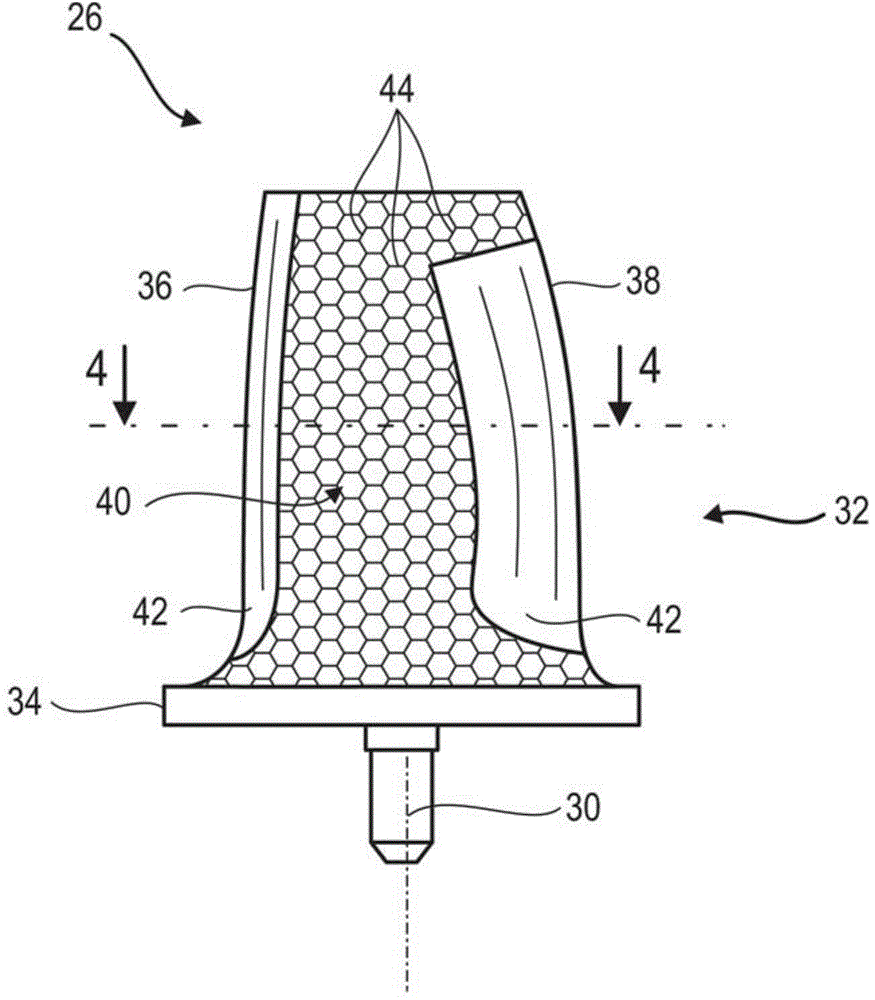
Composite blade
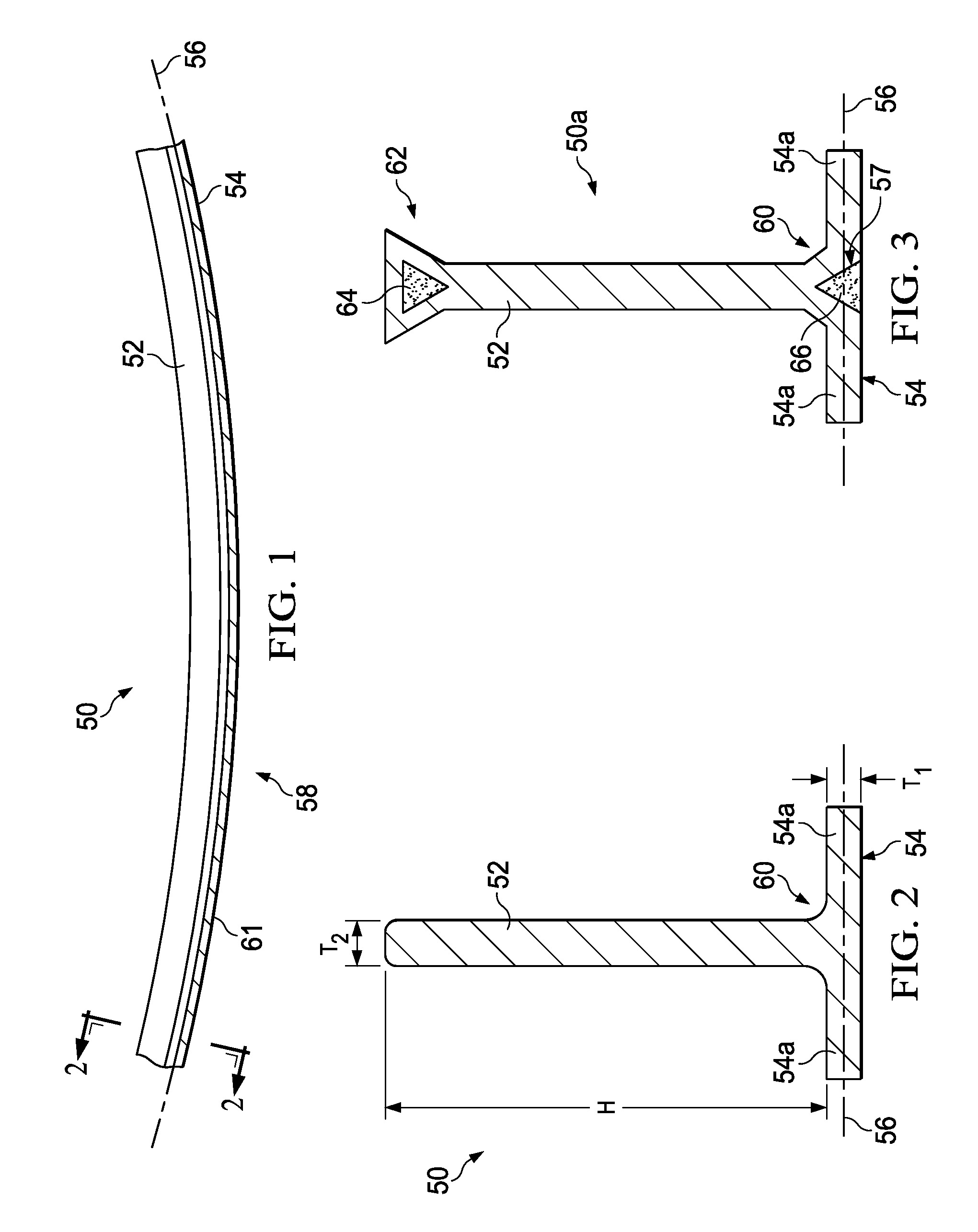
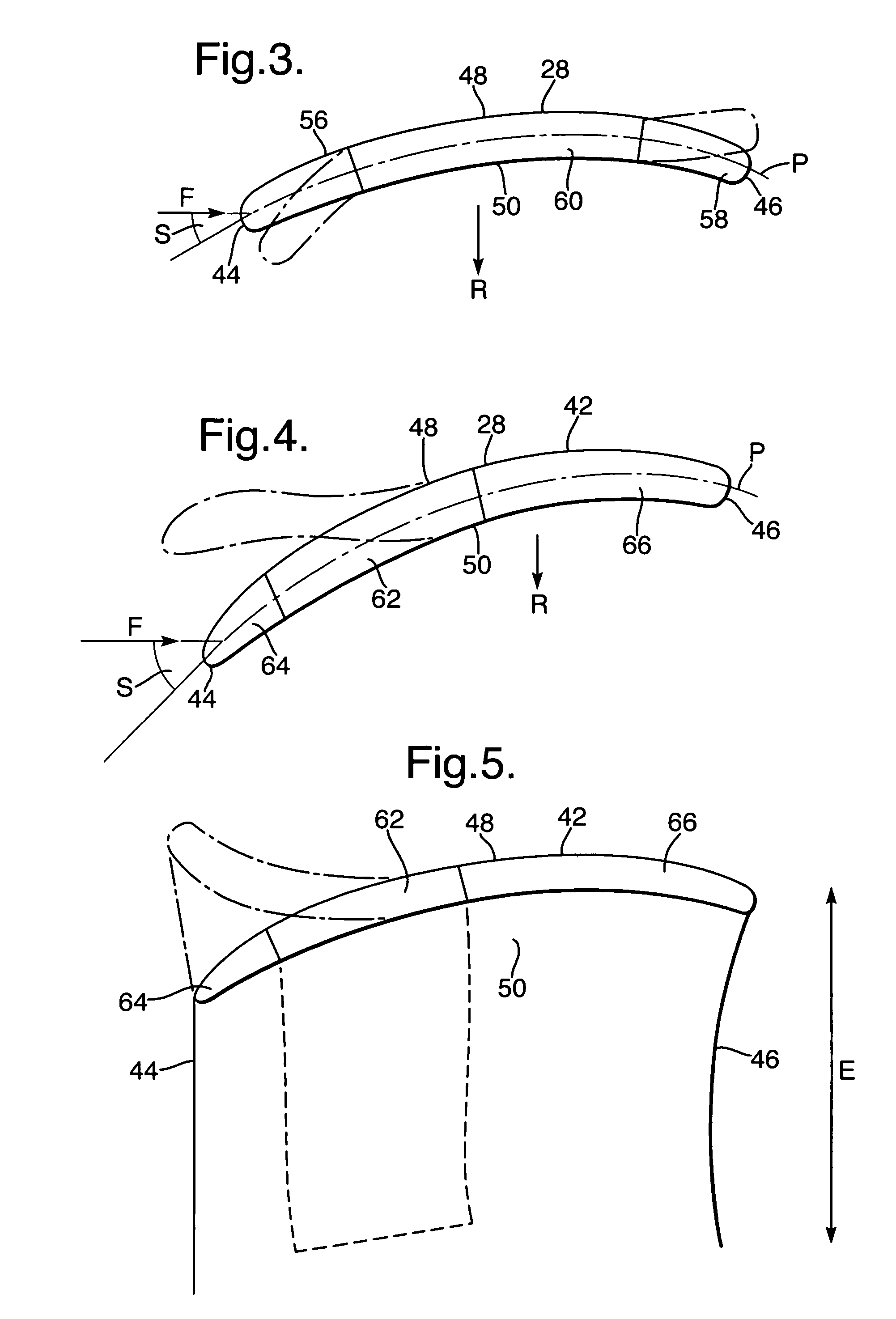
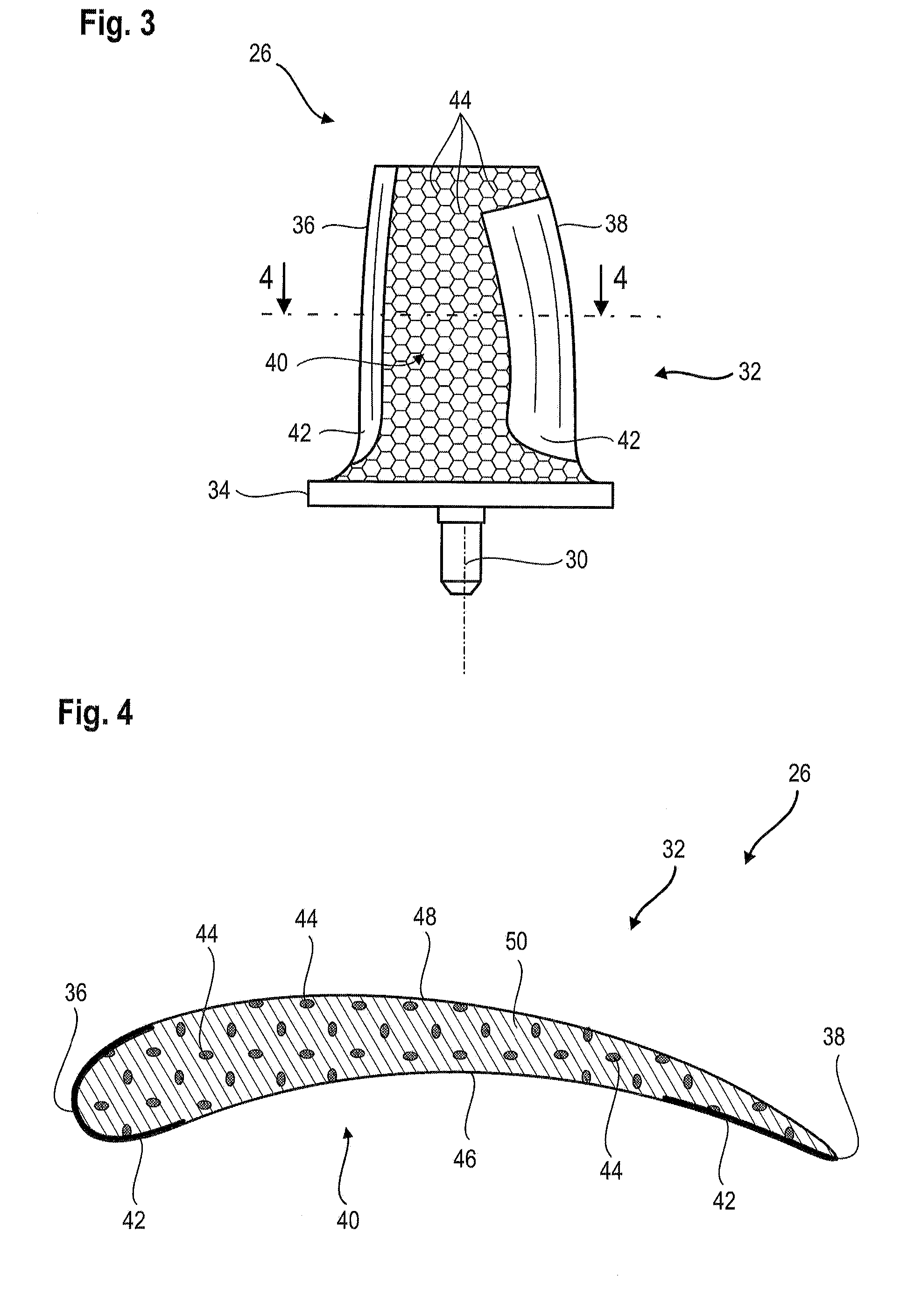
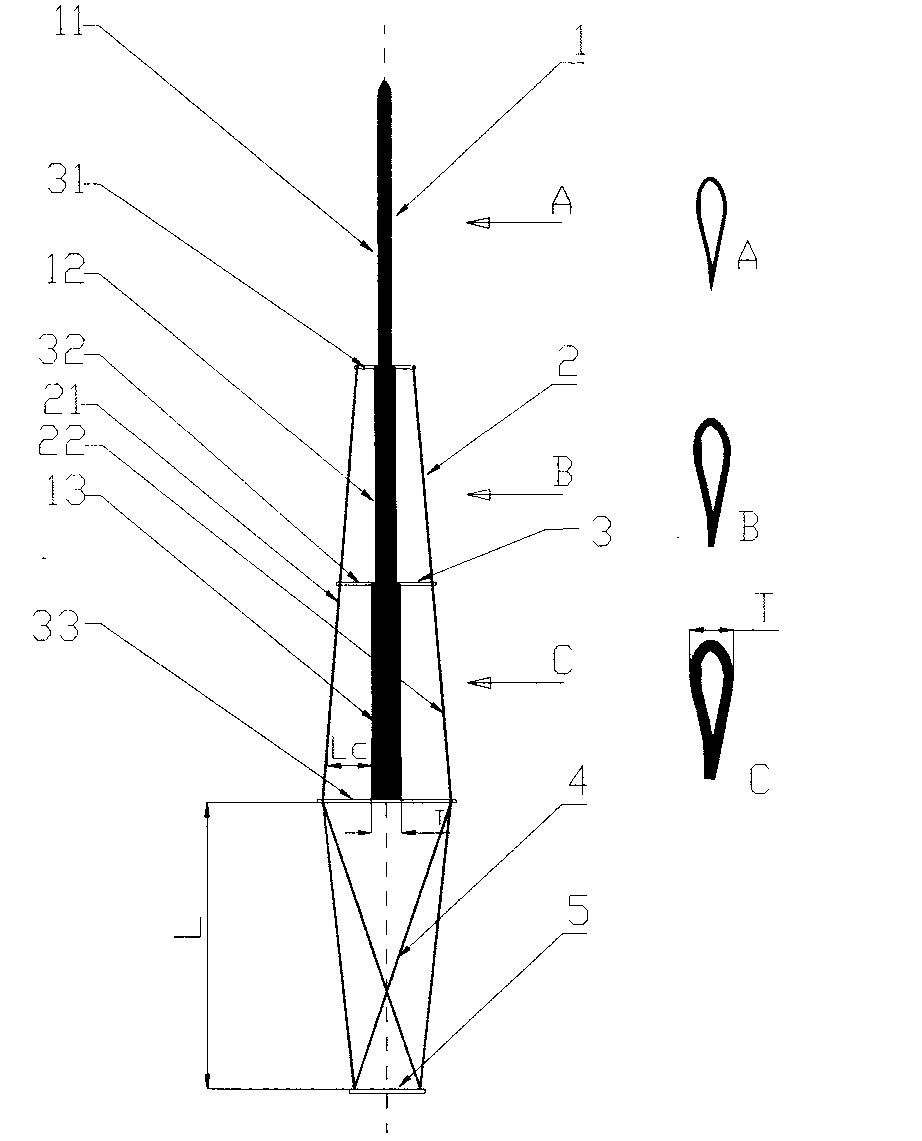
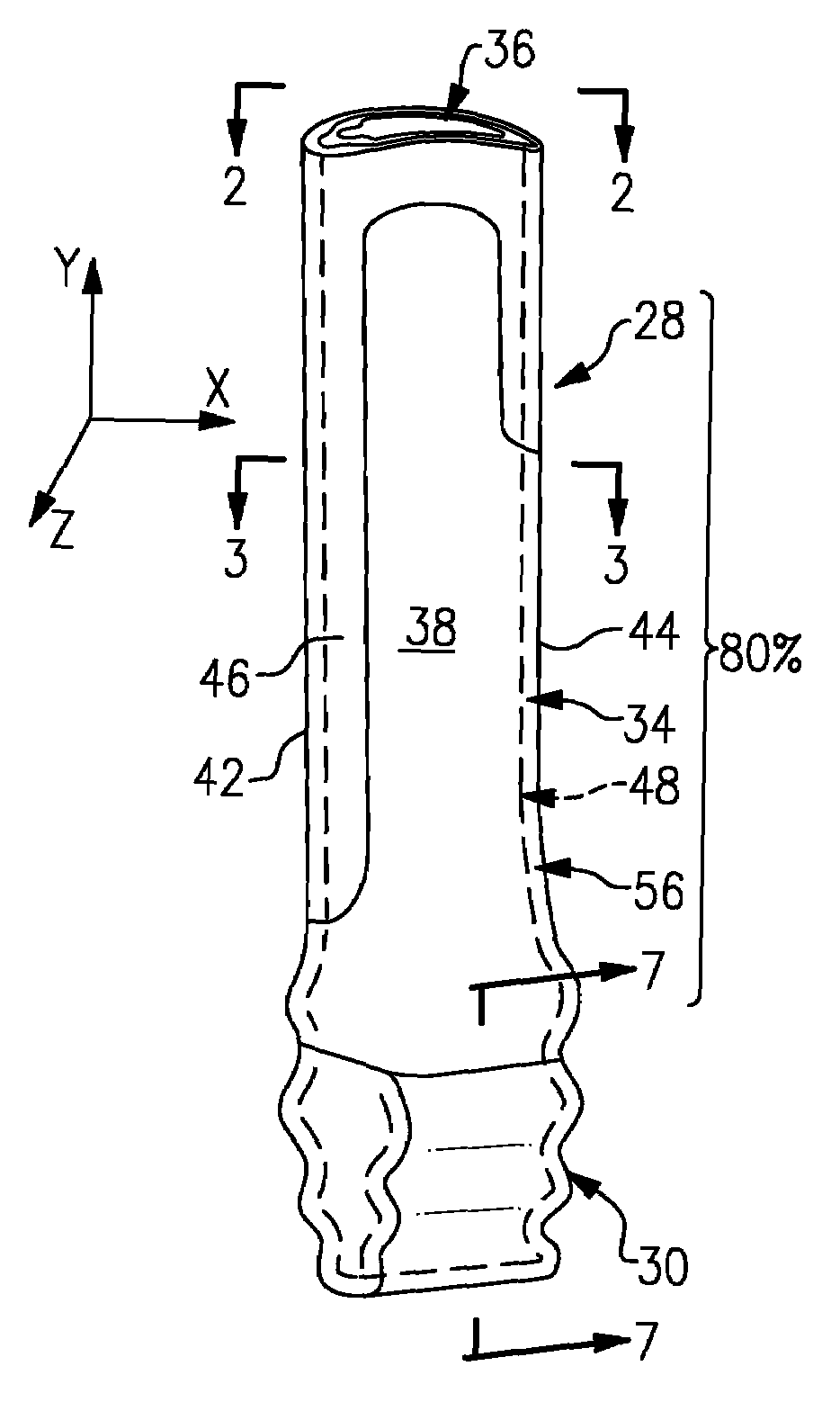
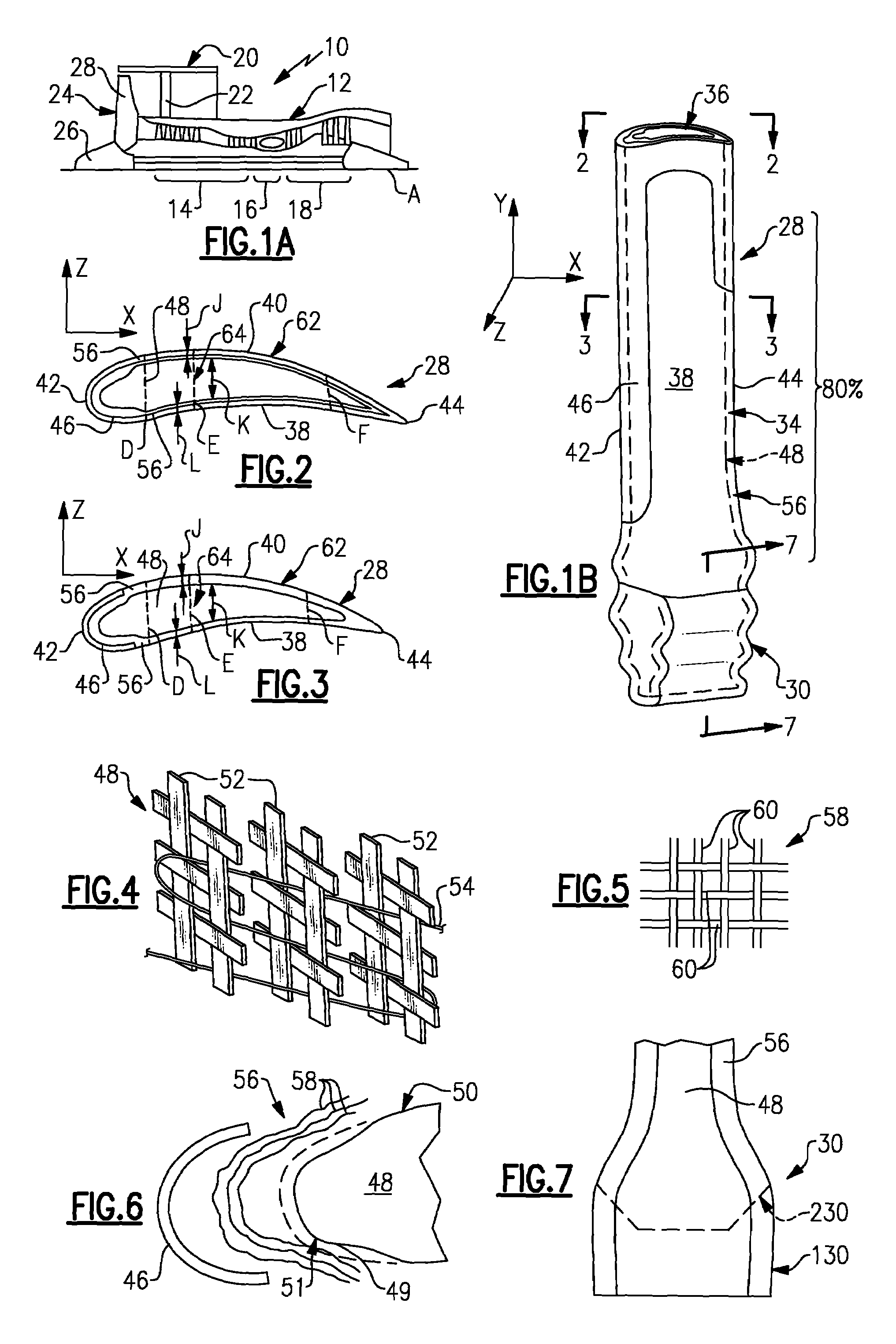
A composite blade (26) comprises a root portion (36) and an aerofoil portion (38). The aerofoil portion (38) has a tip (42), a chord (C), a leading edge (44), a trailing edge (46), a suction surface (48) extending from the leading edge (44) to the trailing edge (46) and a pressure surface extending from the leading edge (44) to the trailing edge (46). The composite blade (26) comprises reinforcing fibres (52) in a matrix material (54). The aerofoil portion (38) adjacent the root portion (36) has regions (56, 58) at least at the leading edge (44) and trailing edge (46) comprising an asymmetric lay up of reinforcing fibres (52) and the aerofoil portion (38) adjacent the tip (42) having at least a region (62) at the mid-chord comprising an asymmetric lay up of reinforcing fibres (52).
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Composite Blade Made by Additive Manufacturing
ActiveUS20150064015A1Improve robustnessEnhance a composite bladeAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlade accessoriesLeading edgeTurbine blade
The present application relates to a blade of a rectifier of a low pressure compressor of an axial turbomachine. The blade can also be a rotor and / or turbine blade. The blade includes a composite material with a matrix and a reinforcement comprising a mesh with rods. The rods of the reinforcement are connected to each other and are distributed throughout the volume between the pressure side surface and the suction side surface of the blade. The mesh forms a three-dimensional structure extending over the majority of the thickness of the blade between the pressure side surface and the suction side surface and / or the majority of the length of the blade between the leading edge and the trailing edge. The present application also relates to an iterative method for manufacturing a blade composite where the reinforcement is formed by additive layer manufacturing based on titanium powder and then placed in an injection mold.
Owner:TECHSPACE AERO
Hockey stick
ActiveUS7914403B2High densityWeight increaseGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A composite hockey stick having a tubular hollow shaft and a blade is disclosed. The shaft includes a region of focused weight in the form of an overlay coating that is applied on top if the internal surfaces of the cured shaft using a coating plug. The blade includes a focused weight region that is inserted into a cavity within the cured composite blade. Methods and suitable materials for constructions of the various components of the blade and shaft are also disclosed.
Owner:BAUER HOCKEY LLC
Method for manufacturing ultra-hard composite blade
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a super-hard composite cutting blade. Firstly, carbide alloy or high-speed steel sheets prepared to be a base body of the cutting blade is cut into the needed size and shape. Secondly, the cutting tip portion is cut down, and the lateral surface of base body is manufactured with curve lines. Thirdly, the manufactured and formed base body of the cutting blade is placed inside a corresponding sintering mold, super-hard materials and composite powder are added into the missing cutting tip portion, and the super-hard materials and composite powder are transformed into super-hard polycrystalline materials and are fixedly combined with the base body of the cutting blade after being sintered under high temperature and high pressure. Fourthly, the super-hard polycrystalline cutting blade is made through the procedures of abrasive fabrication and blade-opening. The invention resolves problems of un-solid welding, easy peeling and high manufacture cost of an integral tool-holder super-hard cutter of the existing super-hard composite cutting blade. The invention not only increases the rigidity of the composite super-hard cutters, but also greatly reduces the using amount of super-hard material powder, and lowers the manufacture cost.
Owner:FUNIK ULTRAHARD MATERIAL
Method and Apparatus for Fabricating Variable Gauge, Contoured Composite Stiffeners
Method and tooling apparatus for forming a composite charge into a contoured composite blade stringer including an elongate punch and an elongate die flexible along their lengths. The charge is press formed by using the punch to drive the charge into the die. The punch and the die are mounted between a pair of flexible plates. A press coupled with the plates contours the charge by bending the plates into a desired contour. The stringer is allowed to cool down to room temperature while being constrained, before withdrawing the stringer from the tooling apparatus in order to reduce wrinkling.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Wind machine's laminae made from composite material and preparation method
InactiveCN1687586AReduce weightImprove qualityFinal product manufactureMachines/enginesWinding machineFiber
The invention is the blade of composite wind mill and its manufacturing method. It is characterized in that the composite blade is closed die forming, which adopts the flexible core, the core heating and solidifying, the fiber closed along the section and the fixing of the connective device and the blade root. The blade is composed of the reinforcing fiber cloth, the resin base, the connective parts and the filling core. One half of the fiber cloth is spread at the root end of the formed die of the blade, and is put into the stretch core bag with heating equipment, and the connective parts are set at the fiber place of the blade root. The other half of the fiber cloth coats the stretch core bag and the connective parts. Die composition, die locking, vacuuming, resin injection and liquid pumping to the stretch bag to form the sealed head squeezing of the bag and the die chamber, and heat the liquid and solidify the blade under the medium temperature; remove the die chamber and the core bag, and inject poly resin materials into the hollow blade shell to bubble and fill to get the composite wind mill blades.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Polyether polyamine agents and mixtures therefor
Owner:HUNTSMAN PETROCHEMICAL LLC +1
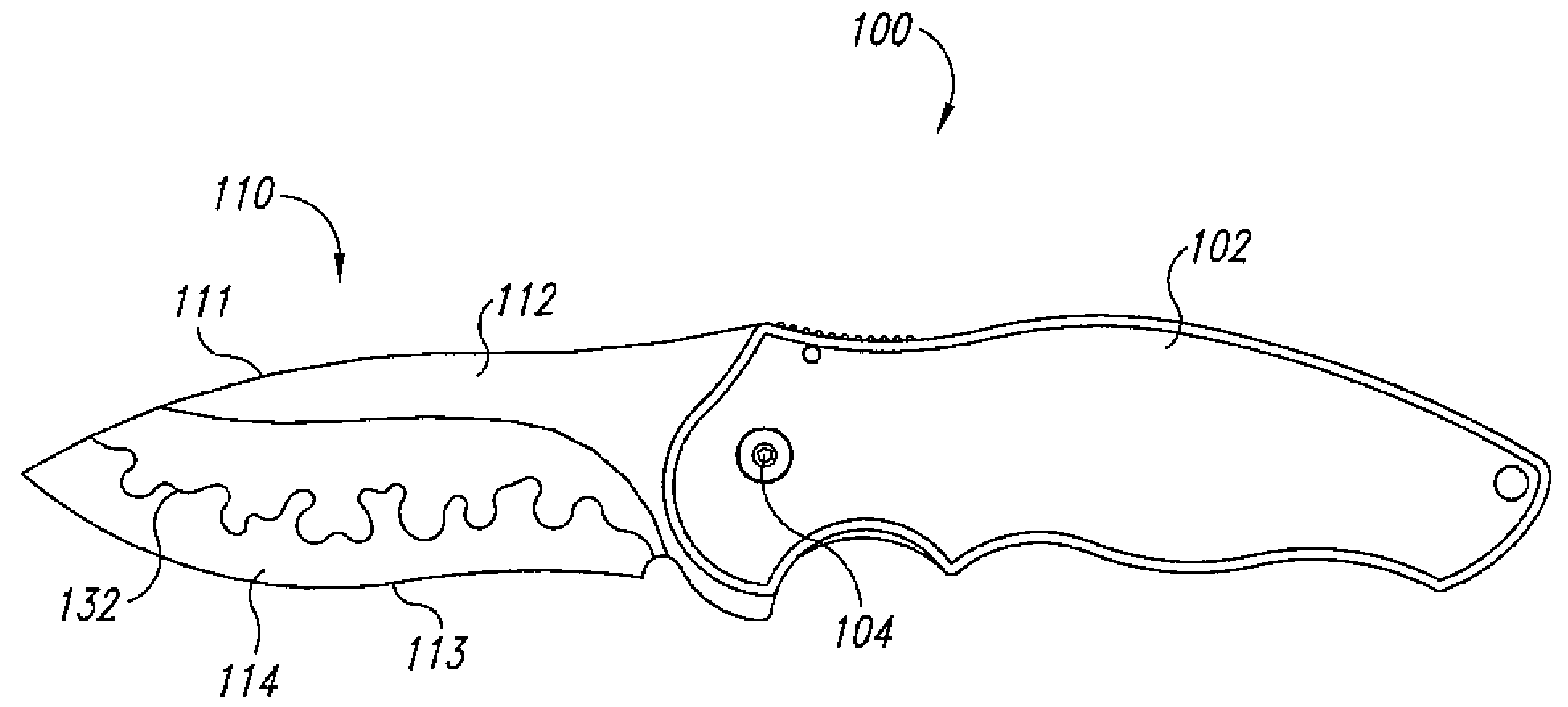
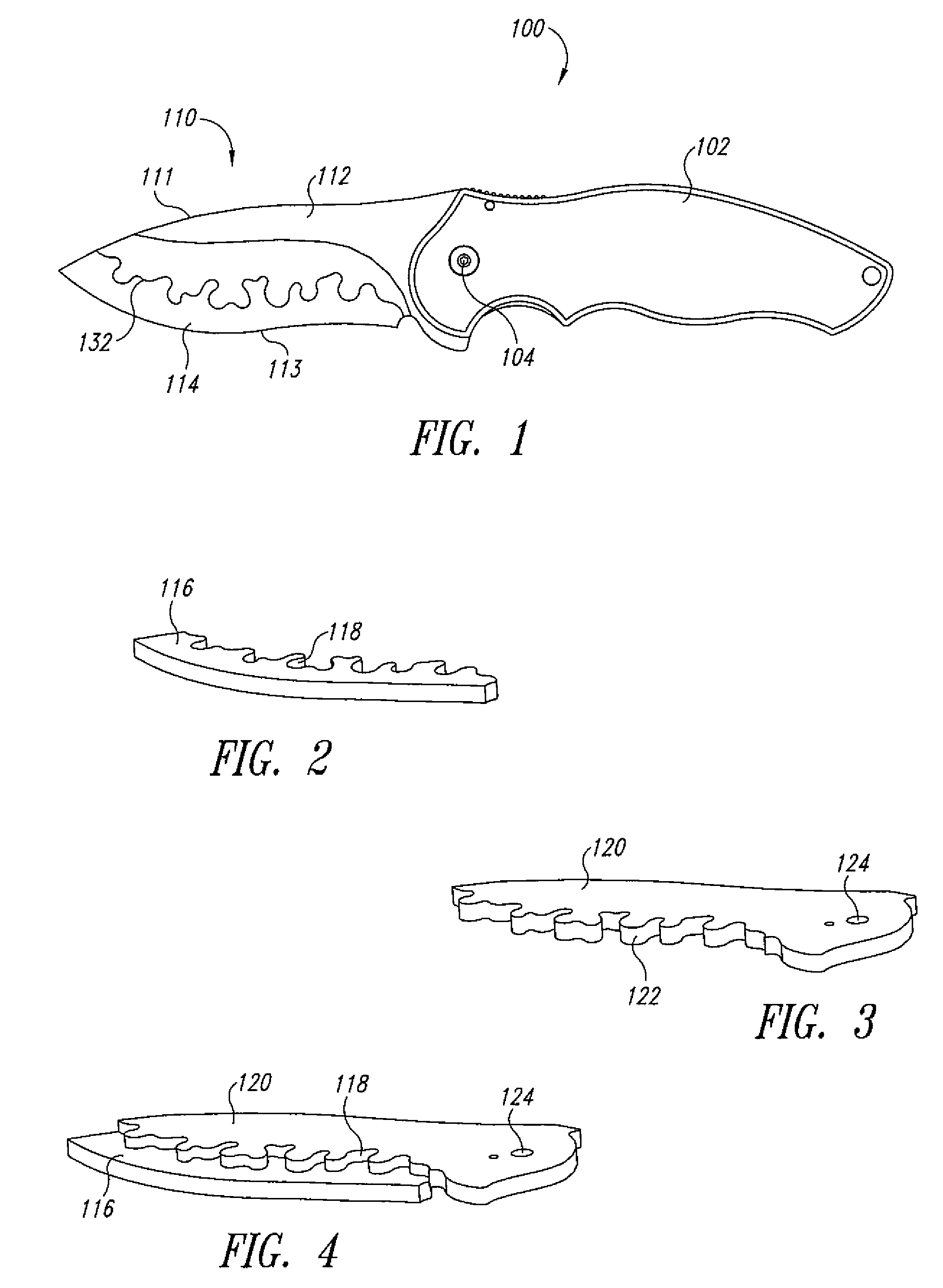
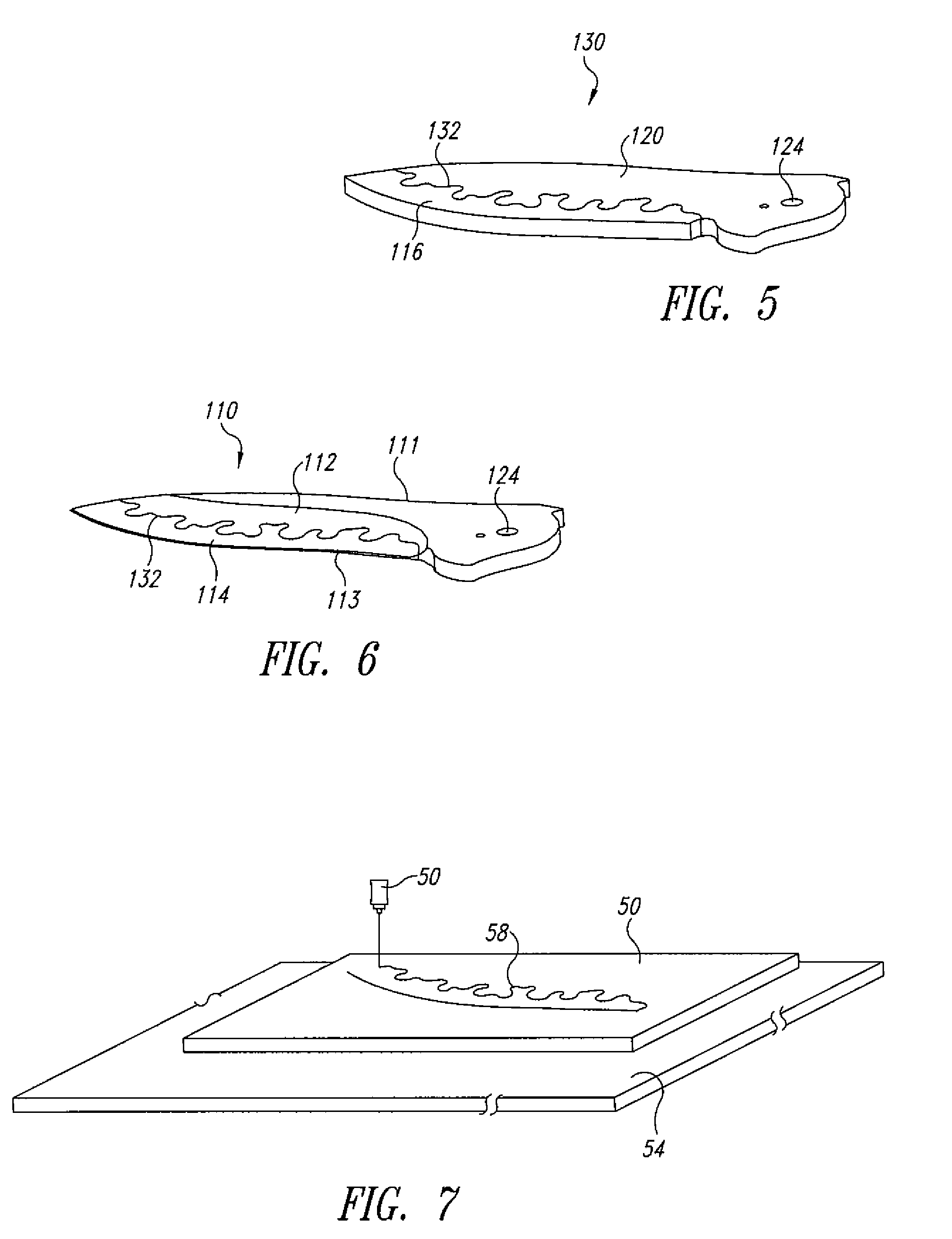
Composite knife blade
InactiveUS20080250656A1High mechanical strengthHigh Rockwell hardness valueMetal working apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusAlloyHardness
A composite knife blade includes a cutting-edge piece of a first alloy, a back piece of a second alloy different from the first alloy, the cutting-edge piece and the back piece are brazed together at a serpentine joint. The cutting-edge piece has a high Rockwell hardness value, as compared to a hardness of the back piece. A method of manufacture of the knife blade includes fine blanking the back piece of from a sheet of the first alloy, laser cutting the cutting-edge piece from a sheet of the second alloy, and brazing the first piece to the second piece to form a composite blade. The composite blade is then cooled from the brazing temperature to an austenizing temperature of the cutting-edge piece, and quenched, to harden the cutting-edge piece.
Owner:KAI US
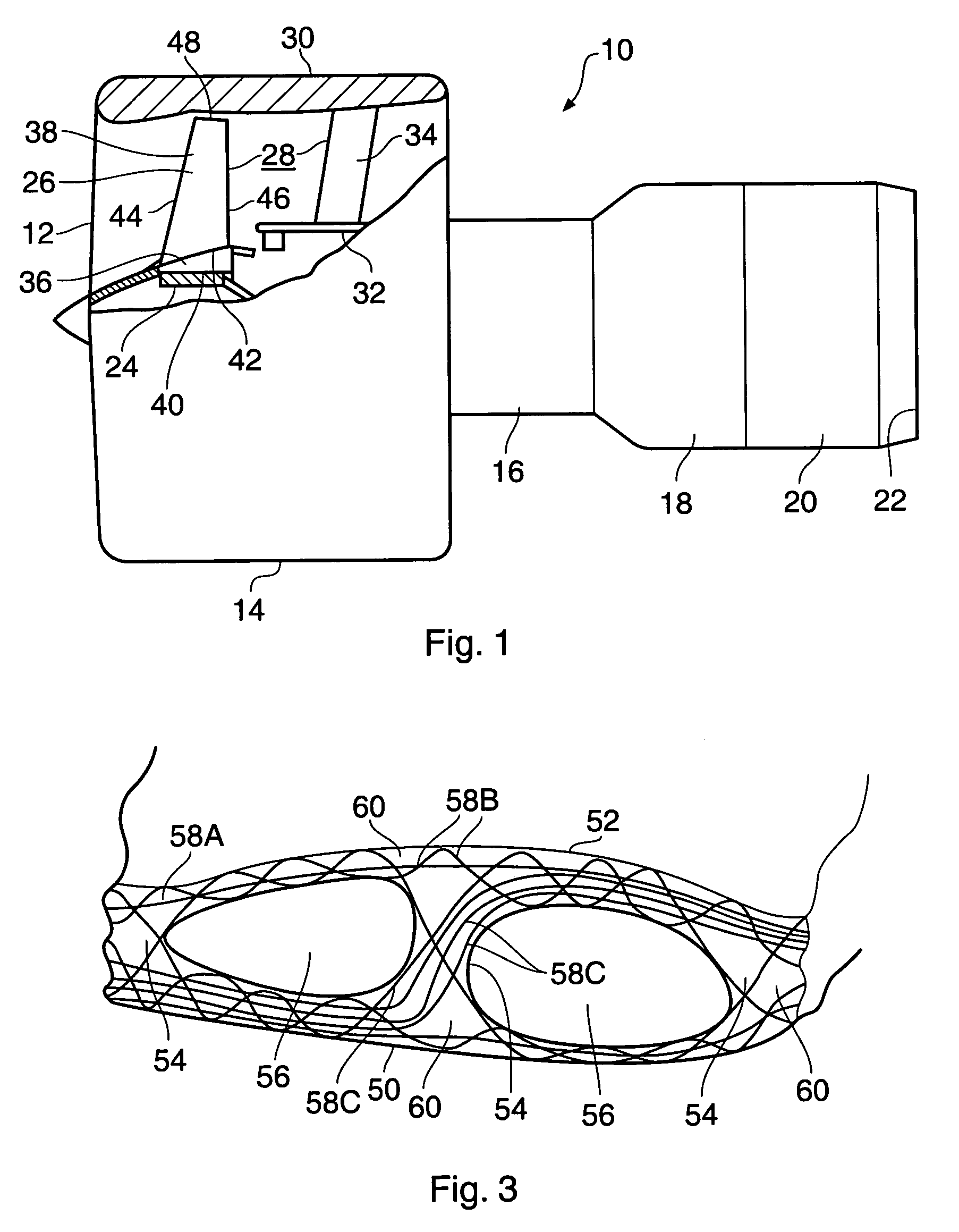
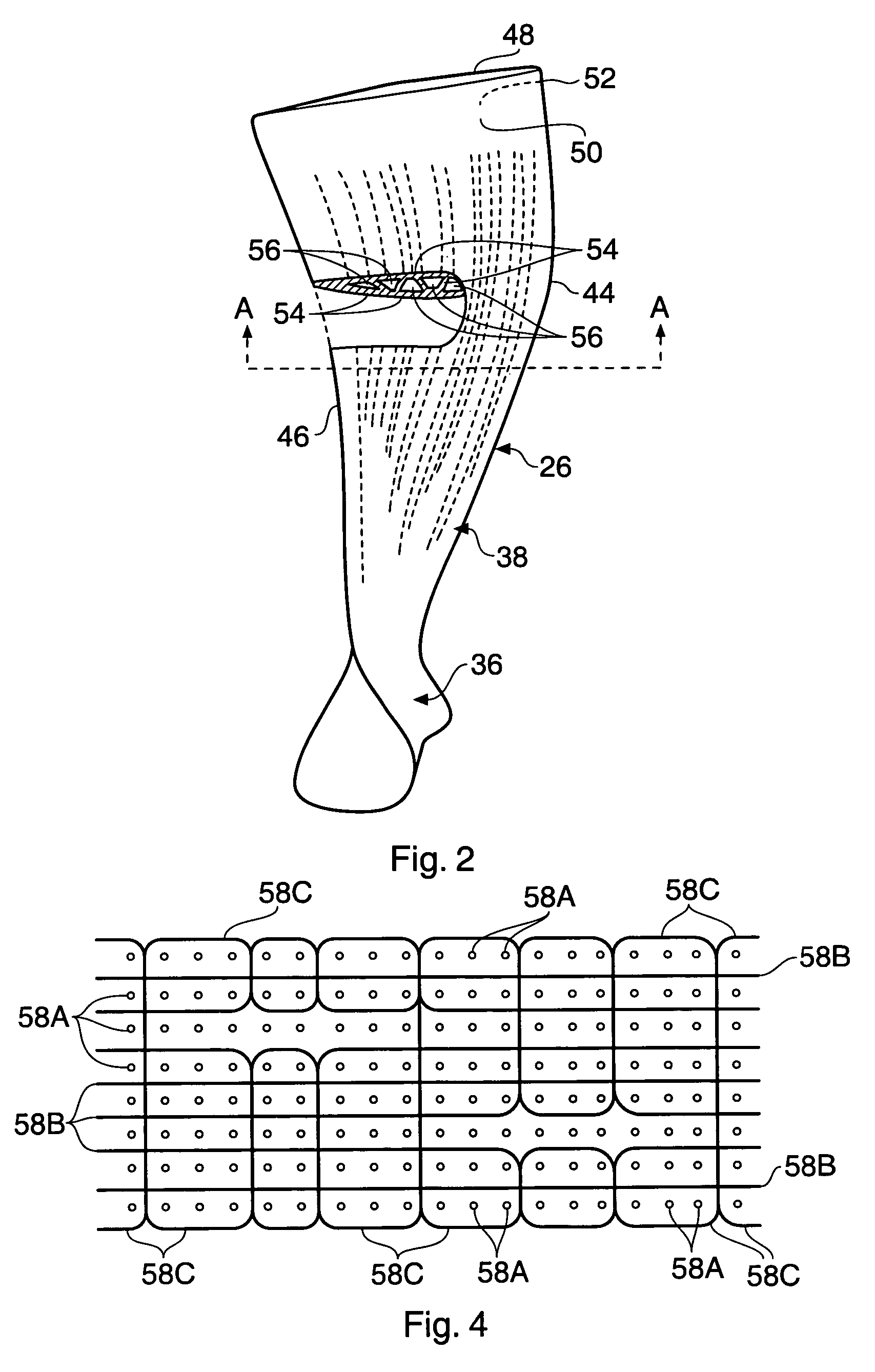
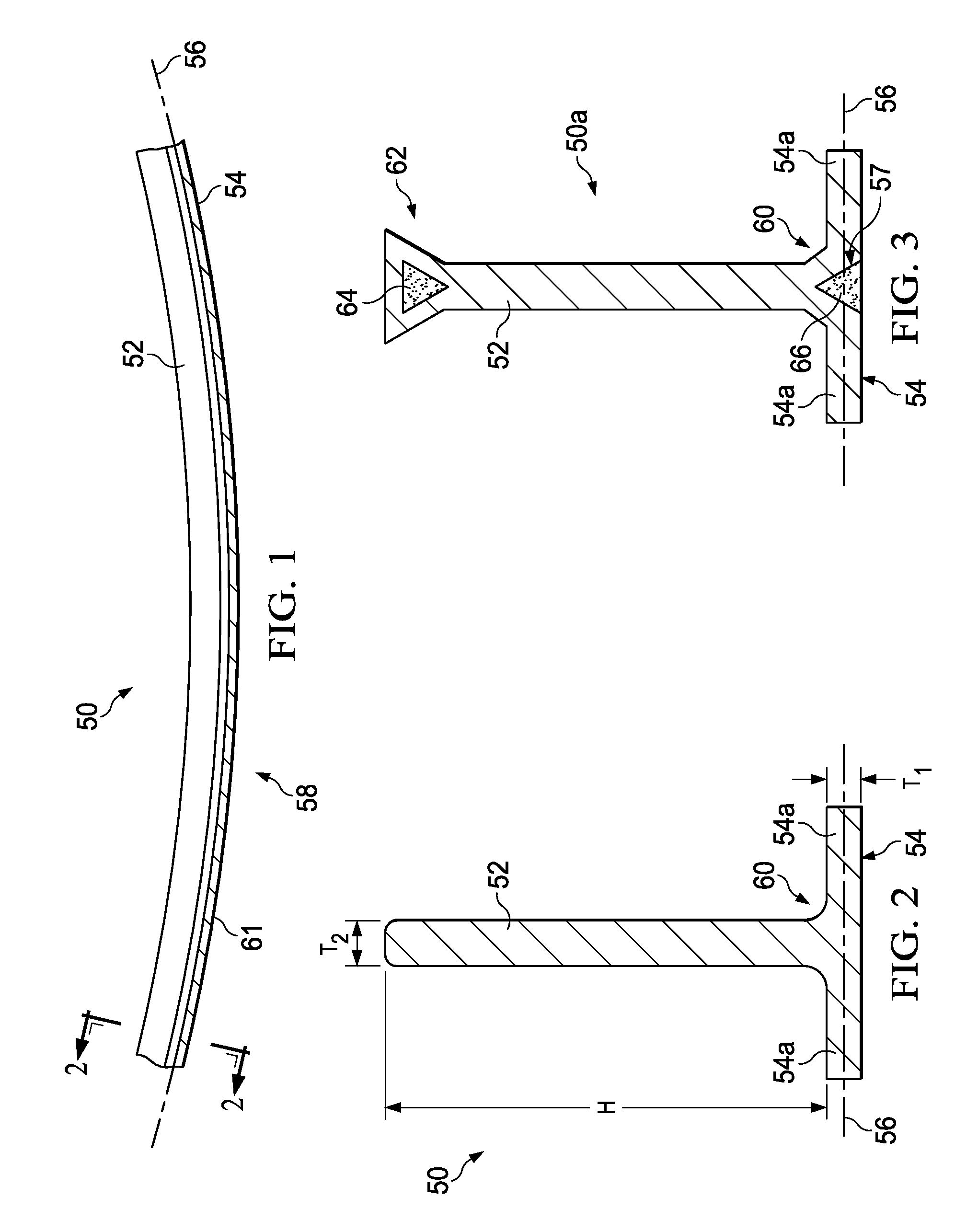
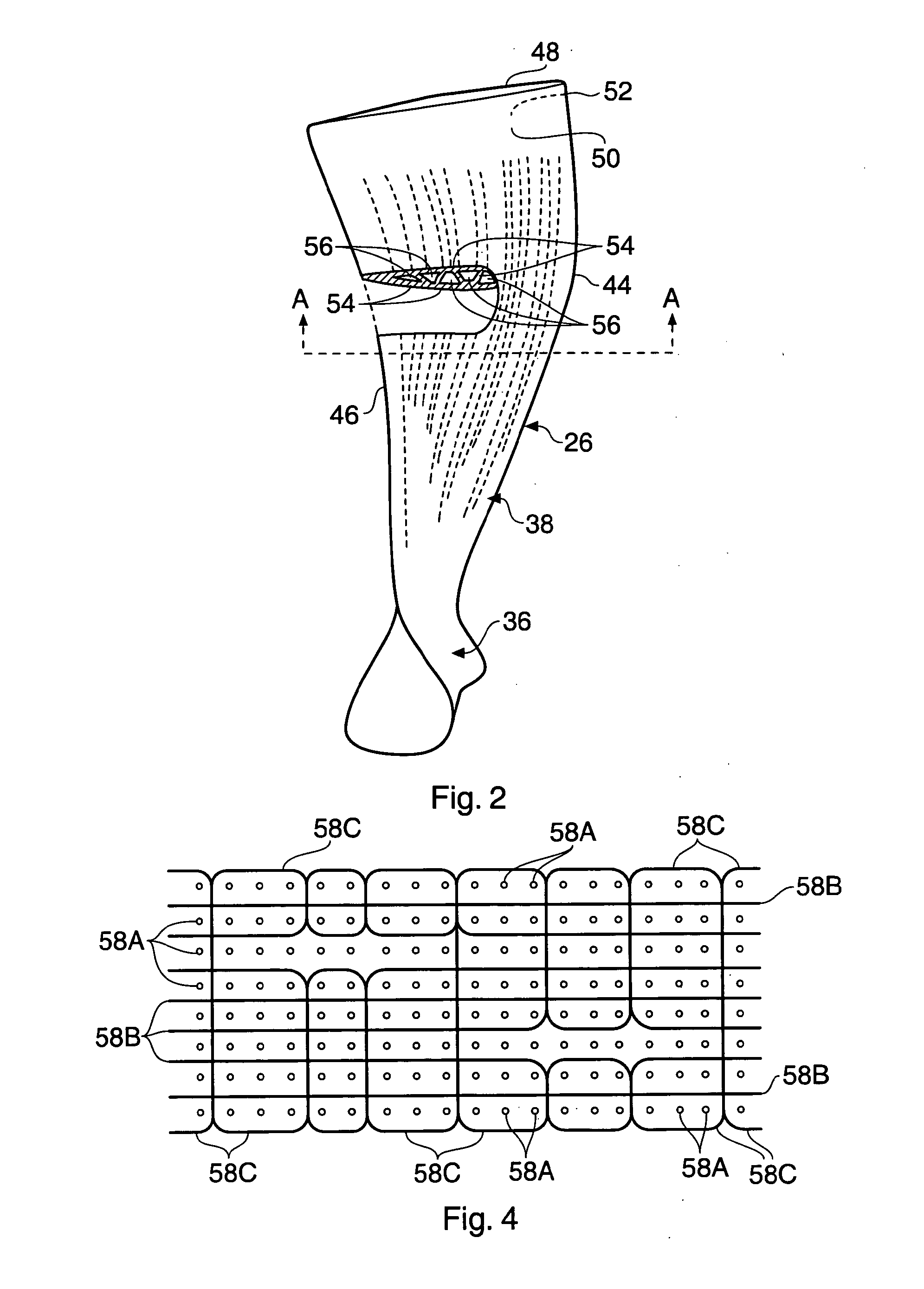
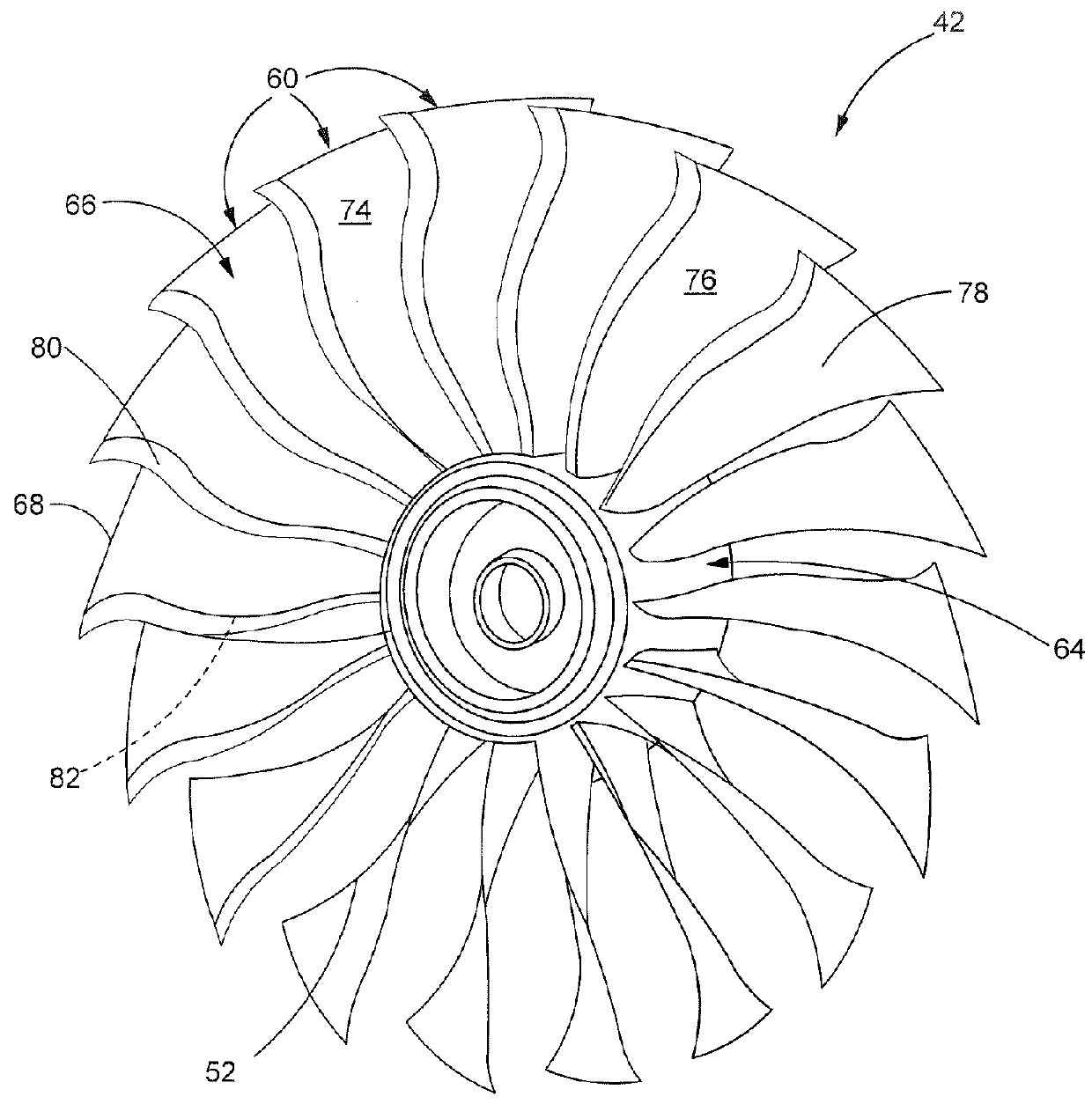
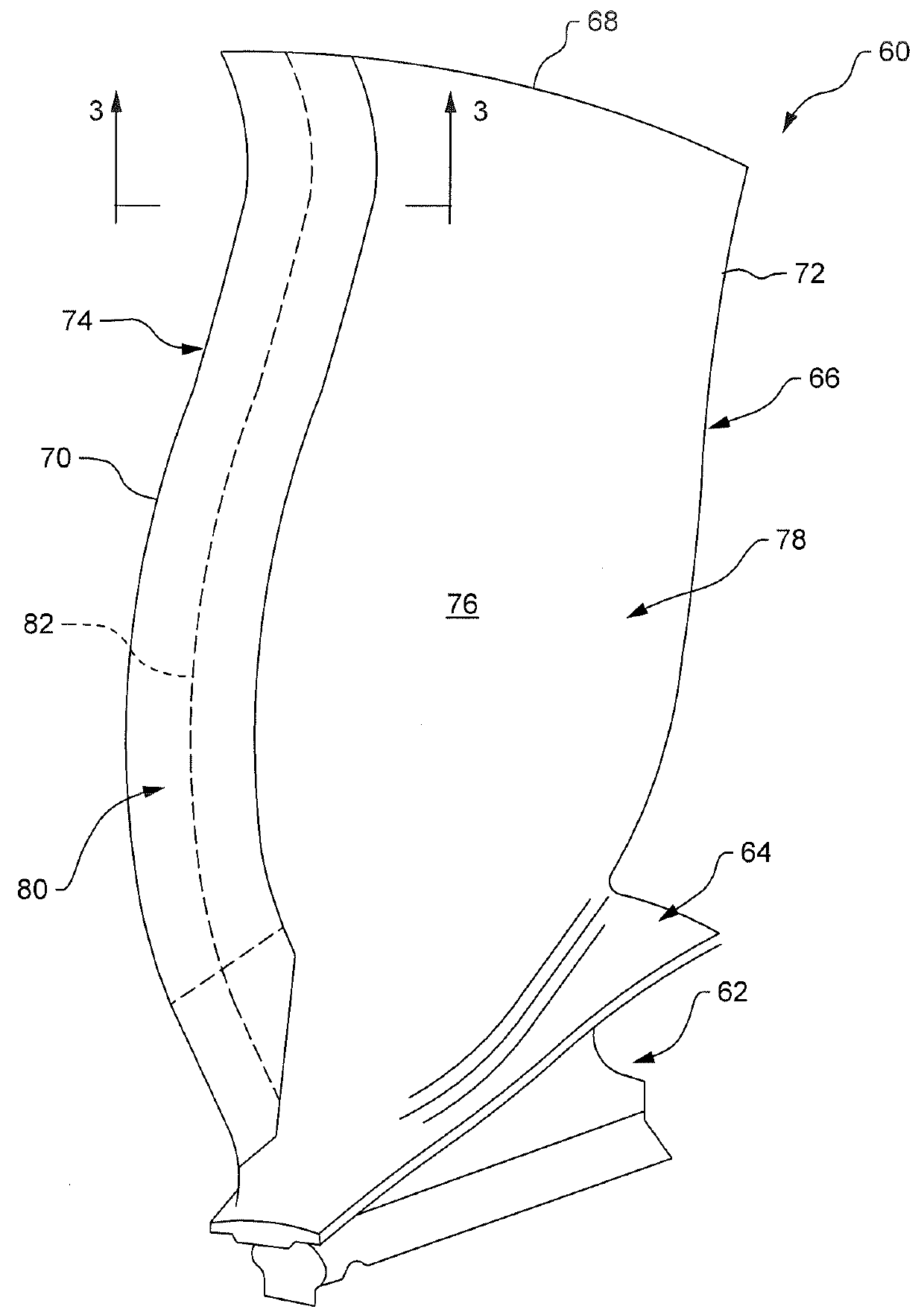
Composite aerofoil
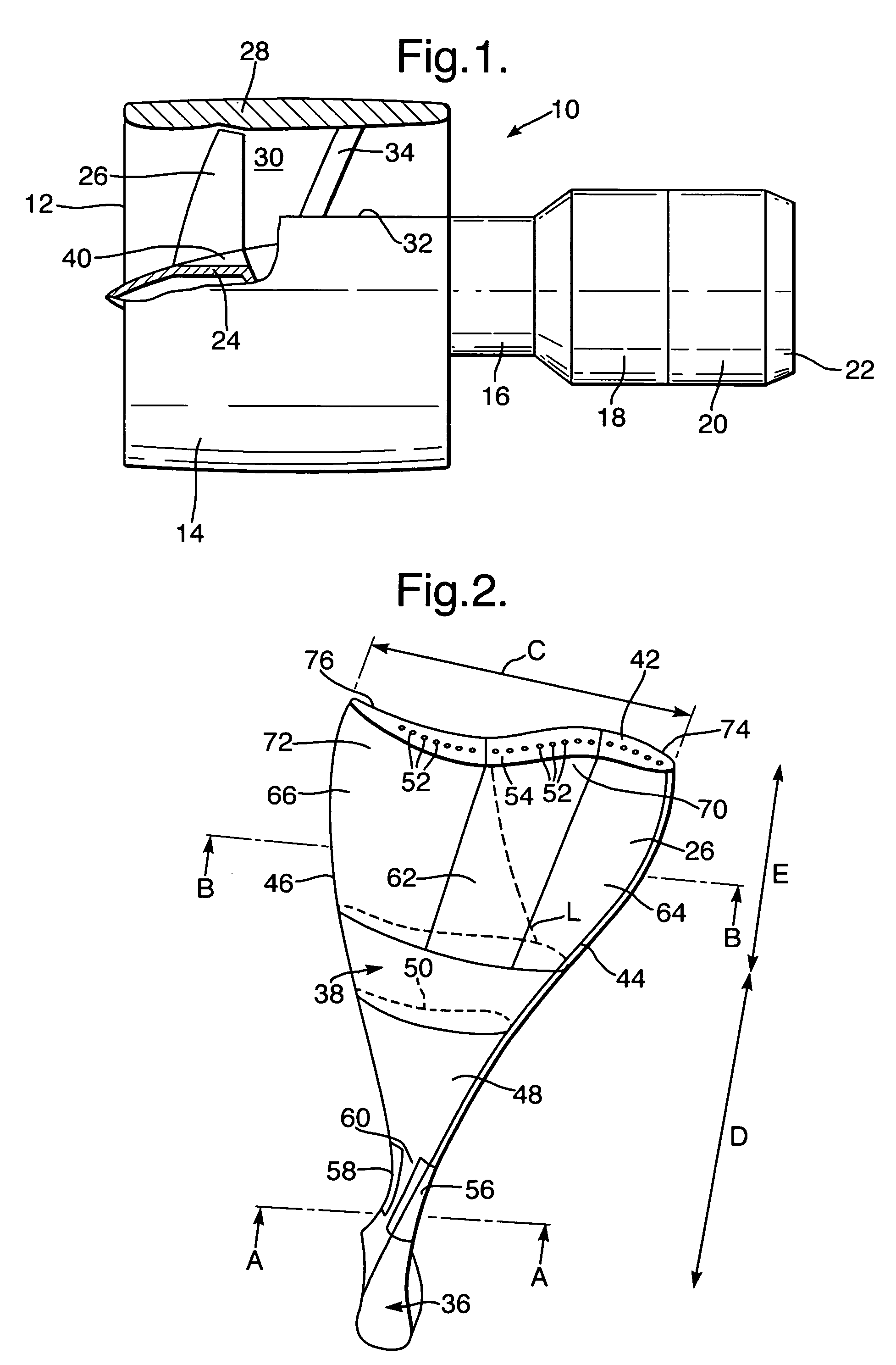
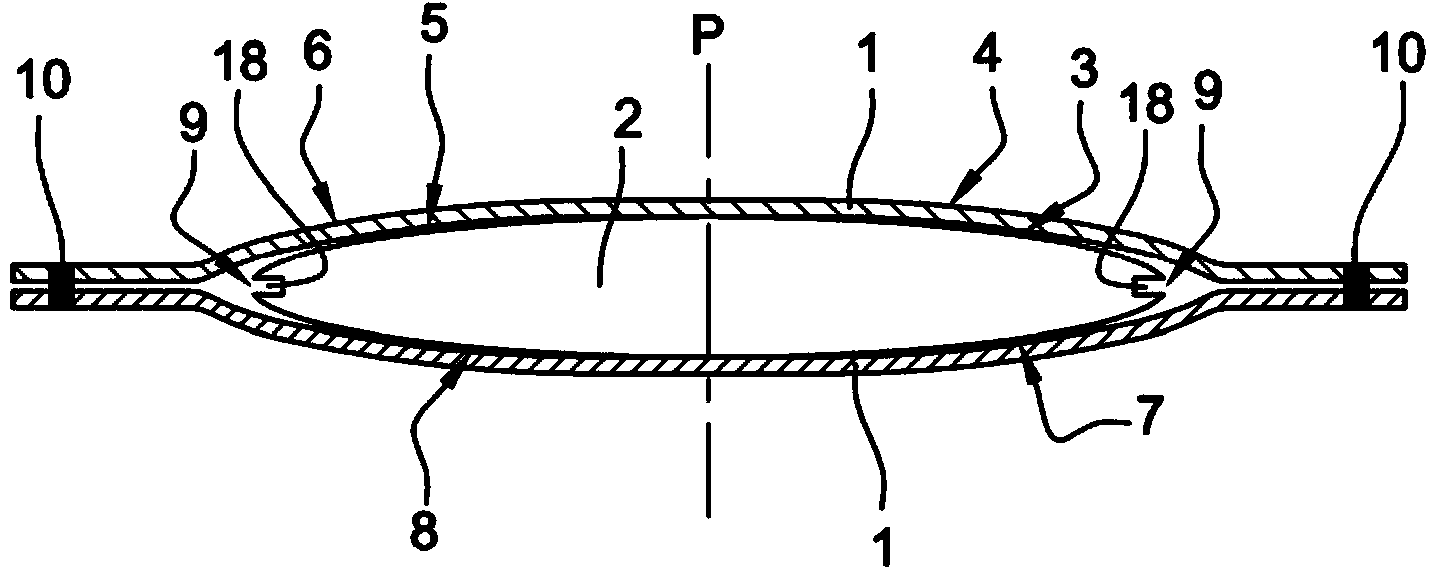
A composite blade (26) comprises a three-dimensional arrangement of reinforcing fibres (58) and a matrix material (60) infiltrated around the three-dimensional arrangement of woven reinforcing fibres (60). The three-dimensional arrangement of woven reinforcing fibres (58) defines a plurality of cavities (56) within the aerofoil (28). The composite blade (26) comprises an aerofoil portion (38) and a root portion (36). The aerofoil portion (38) comprises a leading edge (44), a trailing edge (46), a concave pressure surface wall (50), a convex suction surface wall (52) and a tip (48). The aerofoil portion (36) comprises a plurality of webs (54) extending between, and being secured to, the concave pressure surface wall (50) and the convex suction surface wall (52) to produce a Warren girder structure. The three-dimensional arrangement of woven reinforcing fibres (58) are arranged to produce the concave pressure surface wall (50), the convex suction surface wall (52) and the plurality of webs (54). The matrix material (60) is an organic resin and the reinforcing fibres (58) comprise carbon fibres.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Hockey Stick
InactiveUS20060281592A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationFiberEngineering
A hockey stick having a composite blade and a shaft is disclosed. The composite blade includes a heel section that is recessed relative to the front and back faces of the blade. The recessed heel section is configured to be received by a hockey stick shaft or an adapter member configured to connect the blade to the shaft. The composite blade preferably comprise a foam inner core overlaid preferably with substantially continuous fibers disposed in a matrix material and may include an internal bridge structure extending from one side of the blade to the other. The blade may also be preferably comprised of a core comprising non-continuous fibers disposed within a matrix material. In another aspect, processes for manufacturing the previously described hockey stick blade(s) are described.
Owner:BAUER HOCKEY LLC
Method and Apparatus for Fabricating Variable Gauge, Contoured Composite Stiffeners
Tooling apparatus for forming a composite charge into a contoured composite blade stringer includes an elongate punch and an elongate die flexible along their lengths. The charge is press formed by using the punch to drive the charge into the die. The punch and the die are mounted between a pair of flexible plates. A press coupled with the plates contours the charge by bending the plates into a desired contour.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
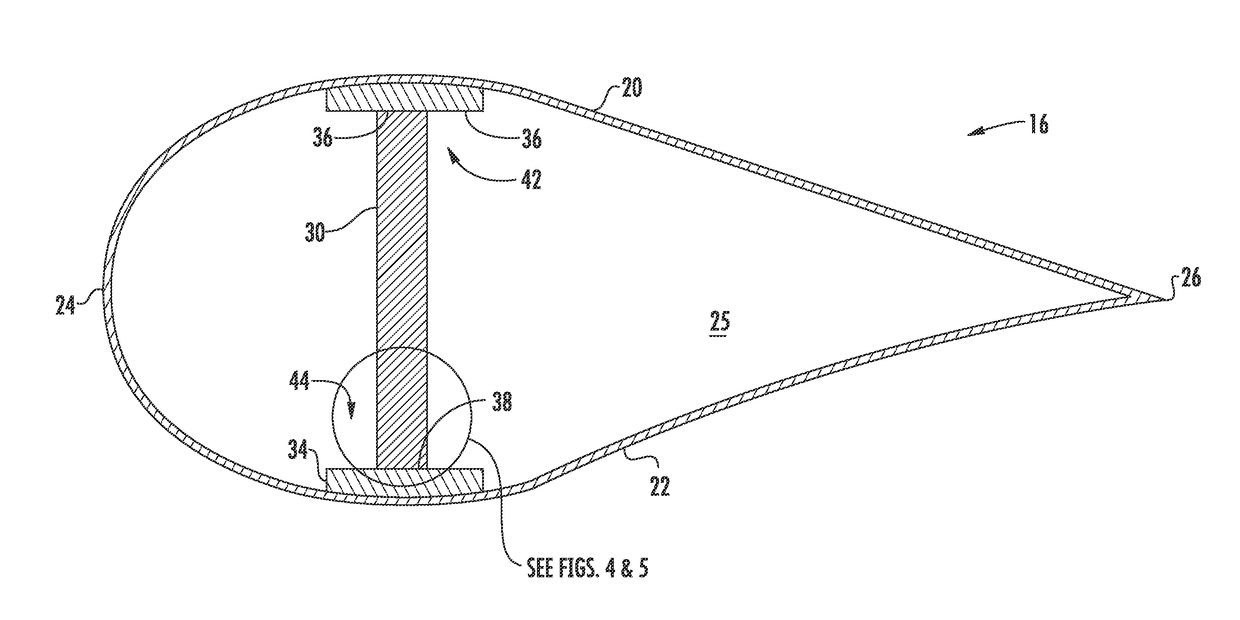
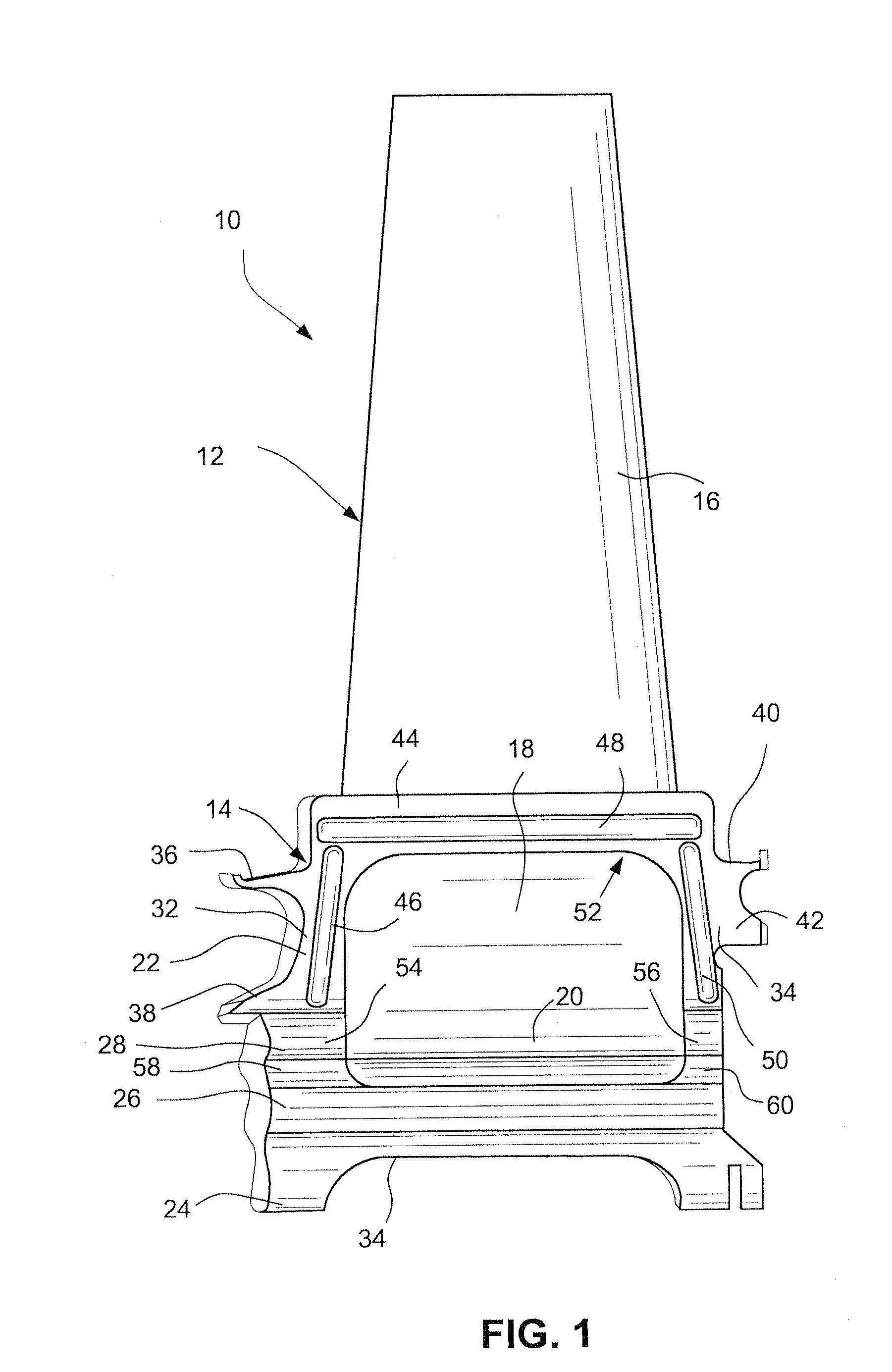
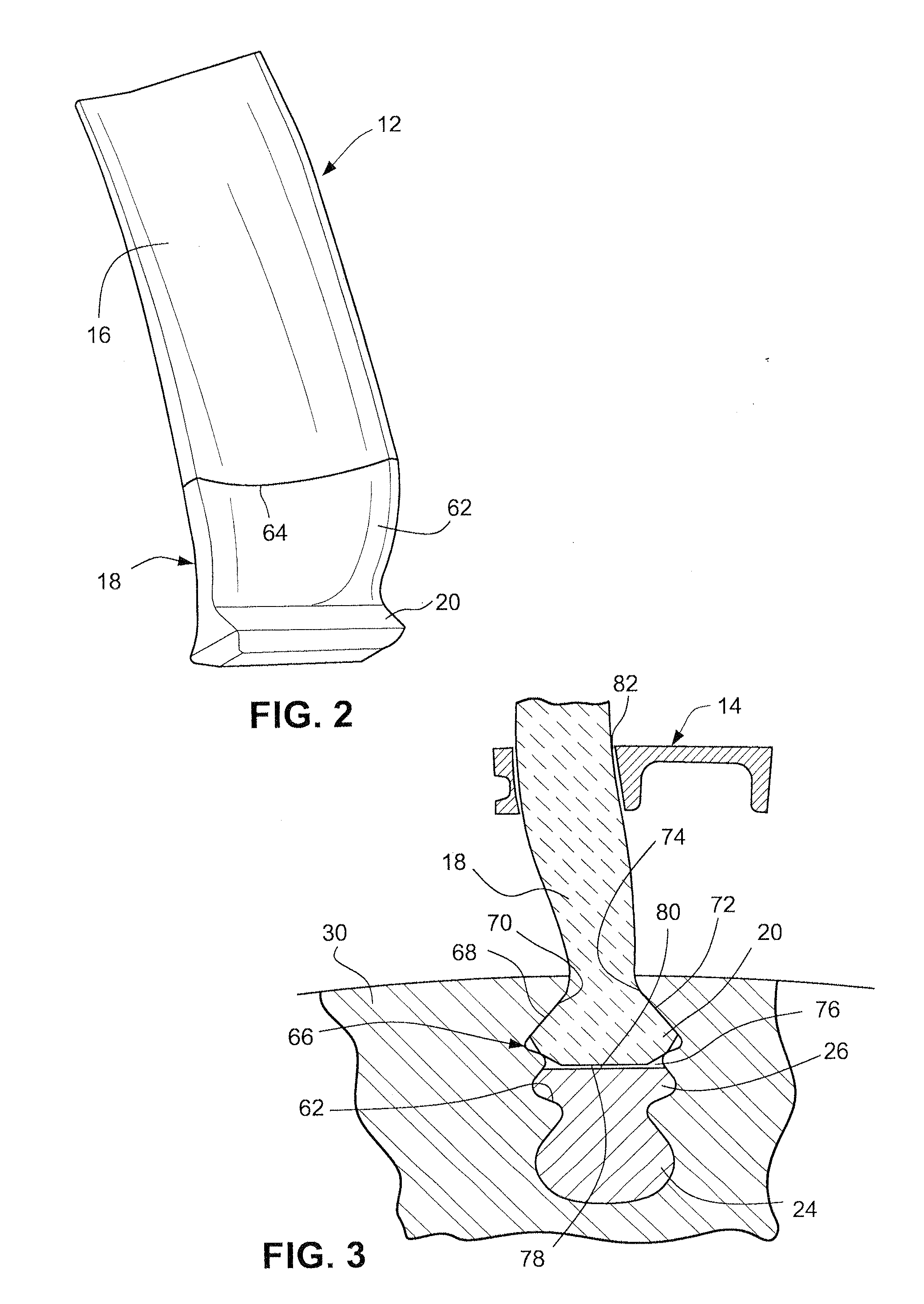
Composite Blade and Method of Manufacture
A method of making a composite blade that is attachable to a rotating shaft using a conventional metal blade attachment. A blade is formed from a composite material with a blade root at one end thereof. A metallic member having an external shape conforming to a conventional metal blade root is shaped with an interior cavity having an opening for receipt of the blade root. Before the composite material is fully cured, a bladder is formed into or is inserted into an end of the blade root and inflated, thereby forcing the composite material into intimate contact with the interior cavity of the metallic member, thereby ensuring a fret-free interface upon final curing of the composite material. The interior cavity of the metallic member may be shaped or surfaced to improve the load carrying capability there between.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
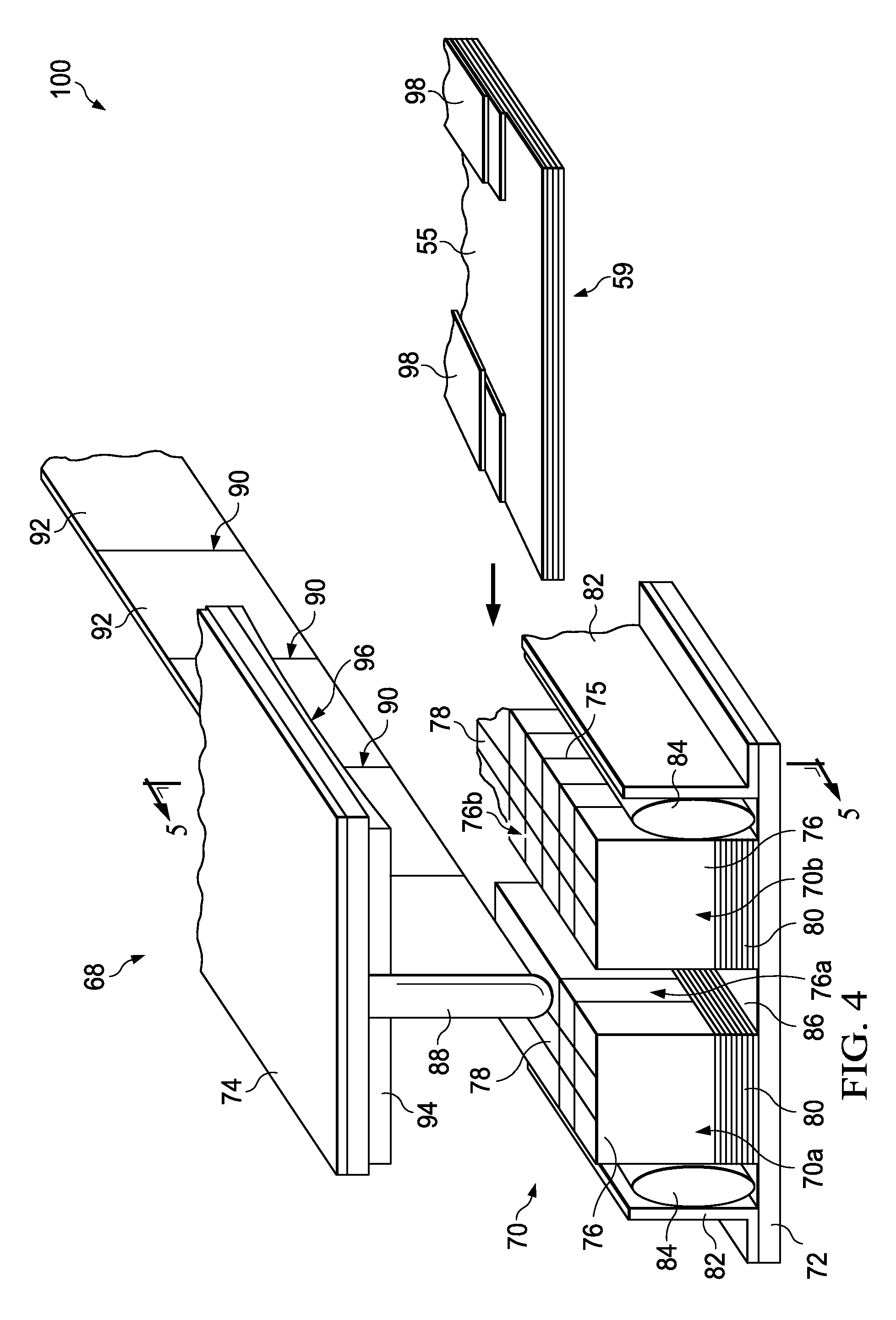
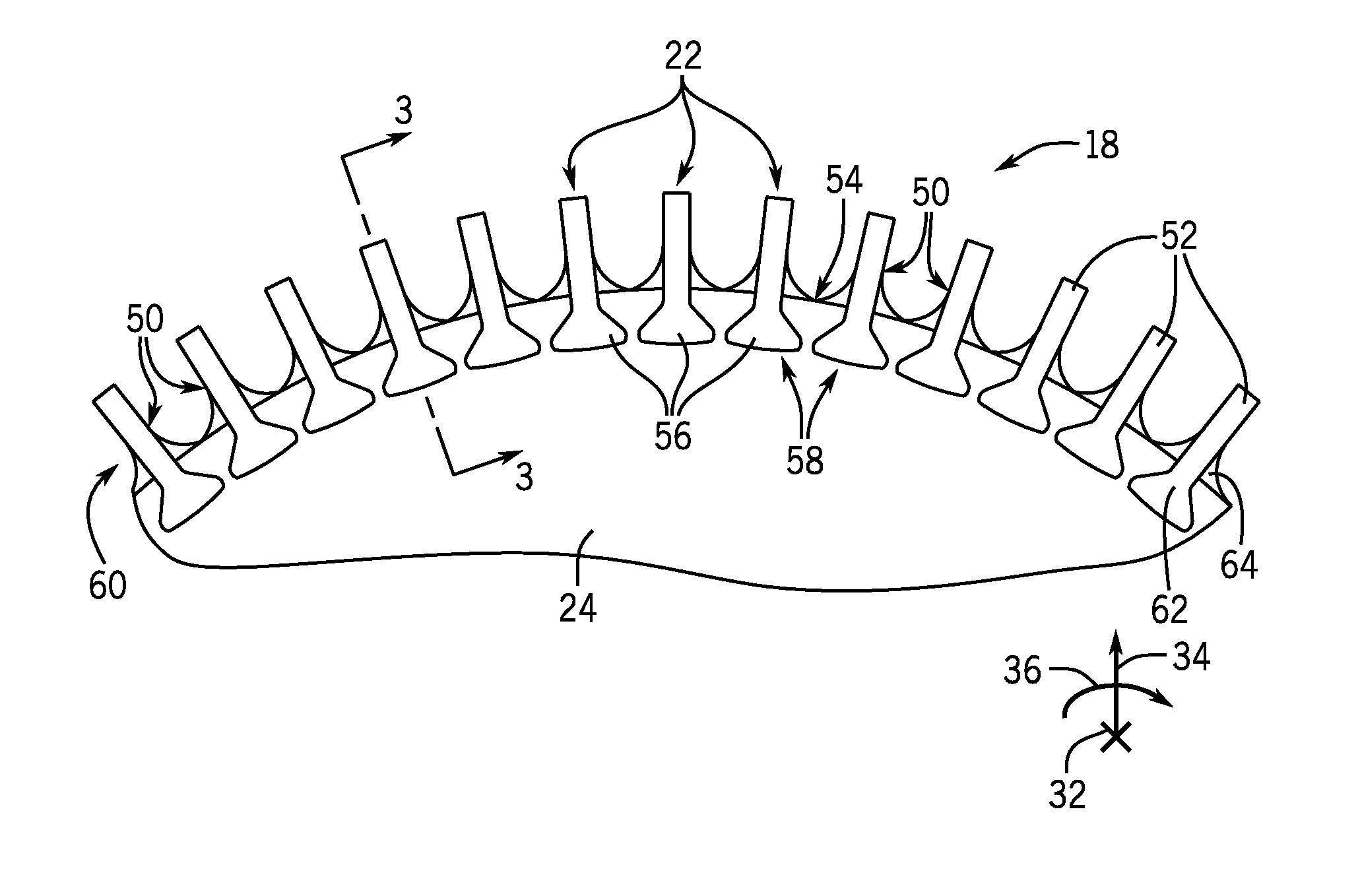
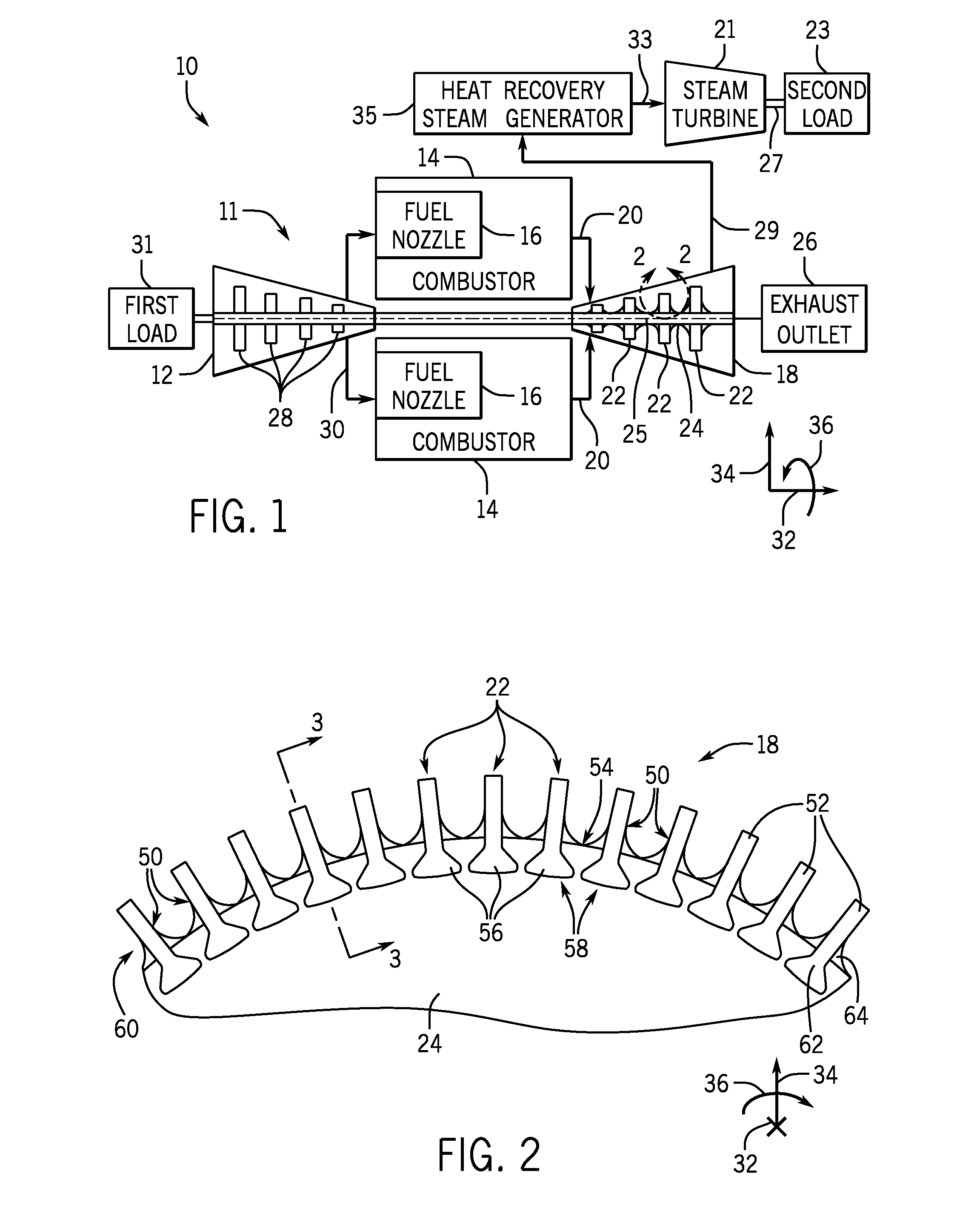
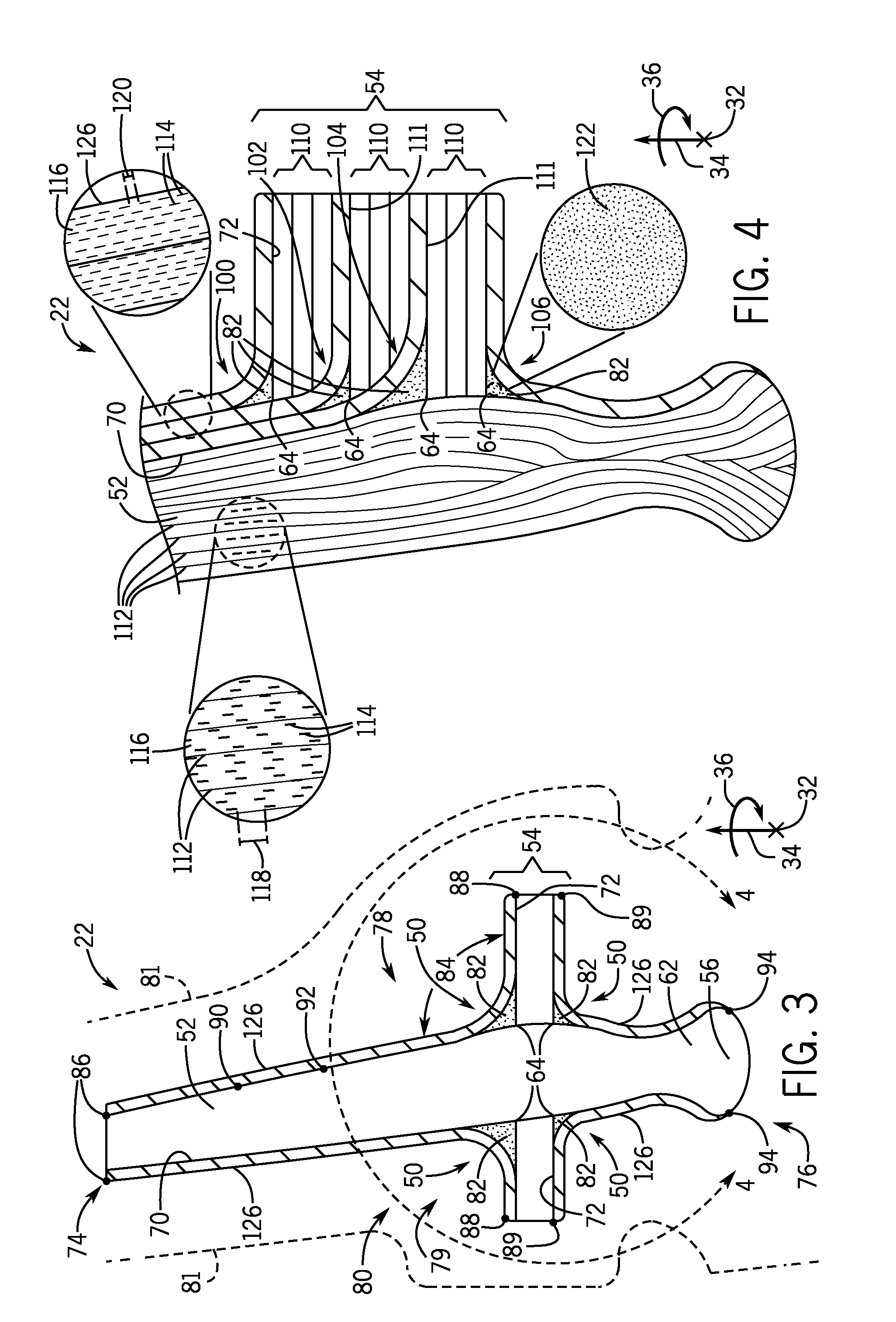
Systems and method for a composite blade with fillet transition
A system includes a turbomachine blade segment including an airfoil with an exterior surface, and a platform coupled to the airfoil having a first side and a second side. The system also includes a concave fillet transition extending between the airfoil and the platform. The concave fillet transition includes one or more interface ply segments extending across the exterior surface of the airfoil and the first or the second side of the platform to form a continuous surface between the airfoil and the platform.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for manufacturing ultra-hard composite blade
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a super-hard composite cutting blade. Firstly, carbide alloy or high-speed steel sheets prepared to be a base seat of the cutting blade is proceeded the treatment of drilling prepared forming openings, thereby prepared forming openings are formed. Secondly, super-hard materials and composite powder are directly added into the inner of the prepared forming openings under the protection of a sintering mold, and the materials installed inside the prepared forming openings are transformed into super-hard polycrystalline materials after being sintered under high temperature and high pressure. Thirdly, the demanded size of the cutting blade is made by cutting along the centre of the prepared forming openings, the super-hard polycrystalline materials installed inside the original prepared forming openings b a cutting tip, and the carbide alloy or high-speed steel sheets mounted between each prepared forming opening is used as a cutting base body. The invention resolves problems of un-solid welding, easy peeling and high manufacture cost of an integral tool-holder super-hard cutter of the existing super-hard composite cutting blade. The invention not only increases the rigidity of the composite super-hard cutters, but also greatly reduces the using amount of super-hard material powder, and lowers the manufacture cost.
Owner:FUNIK ULTRAHARD MATERIAL
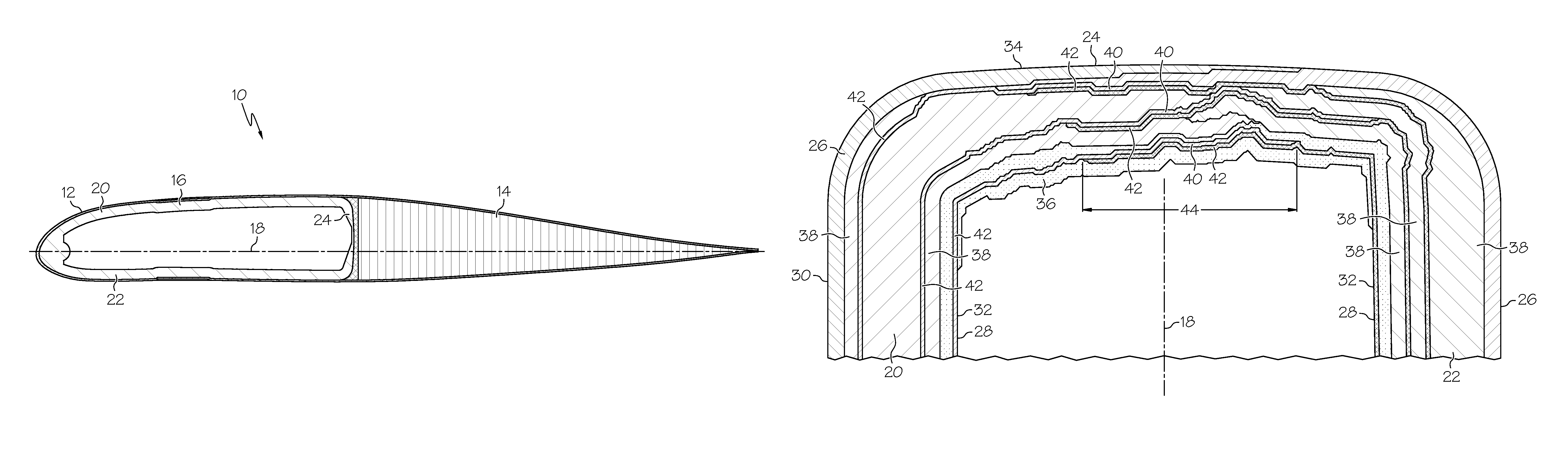
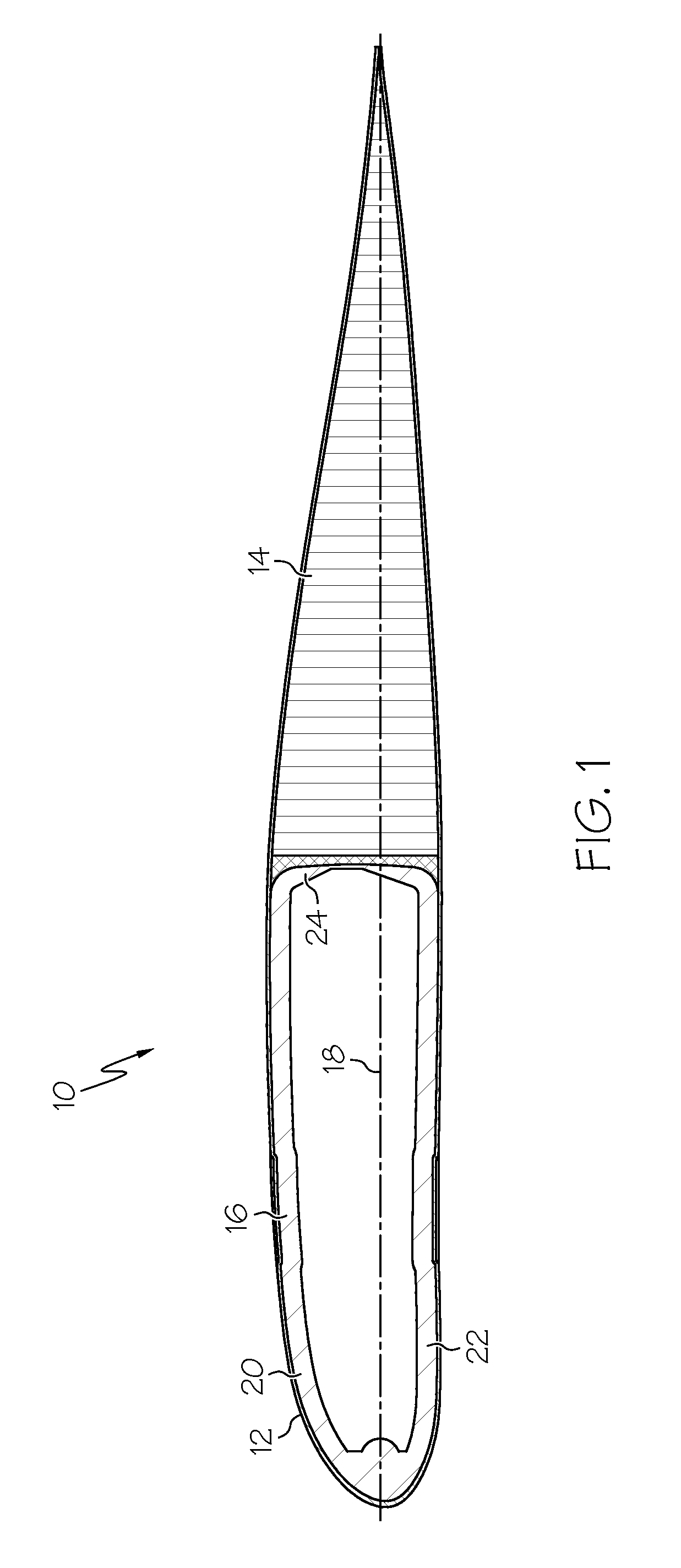
Damping device for a composite blade
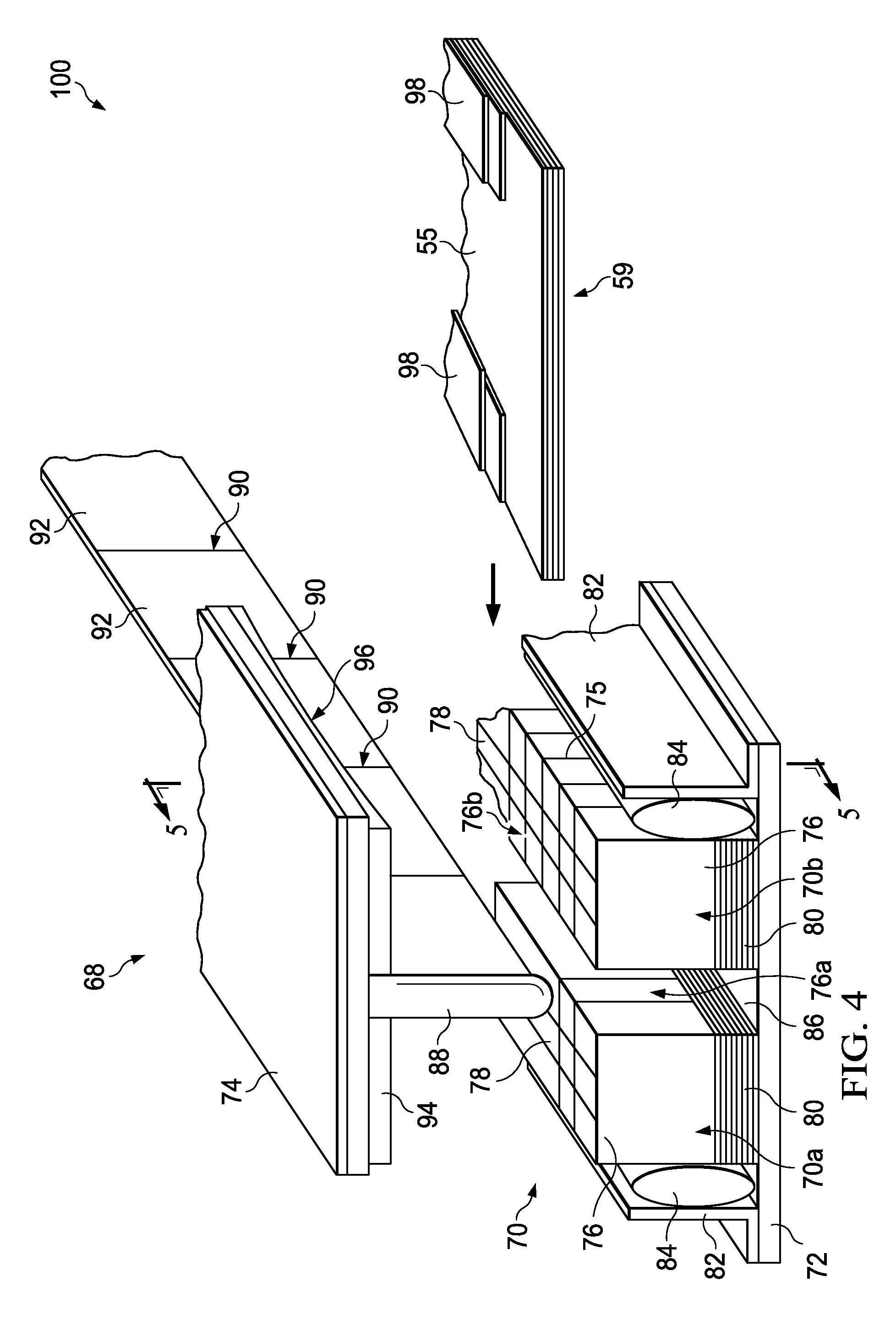
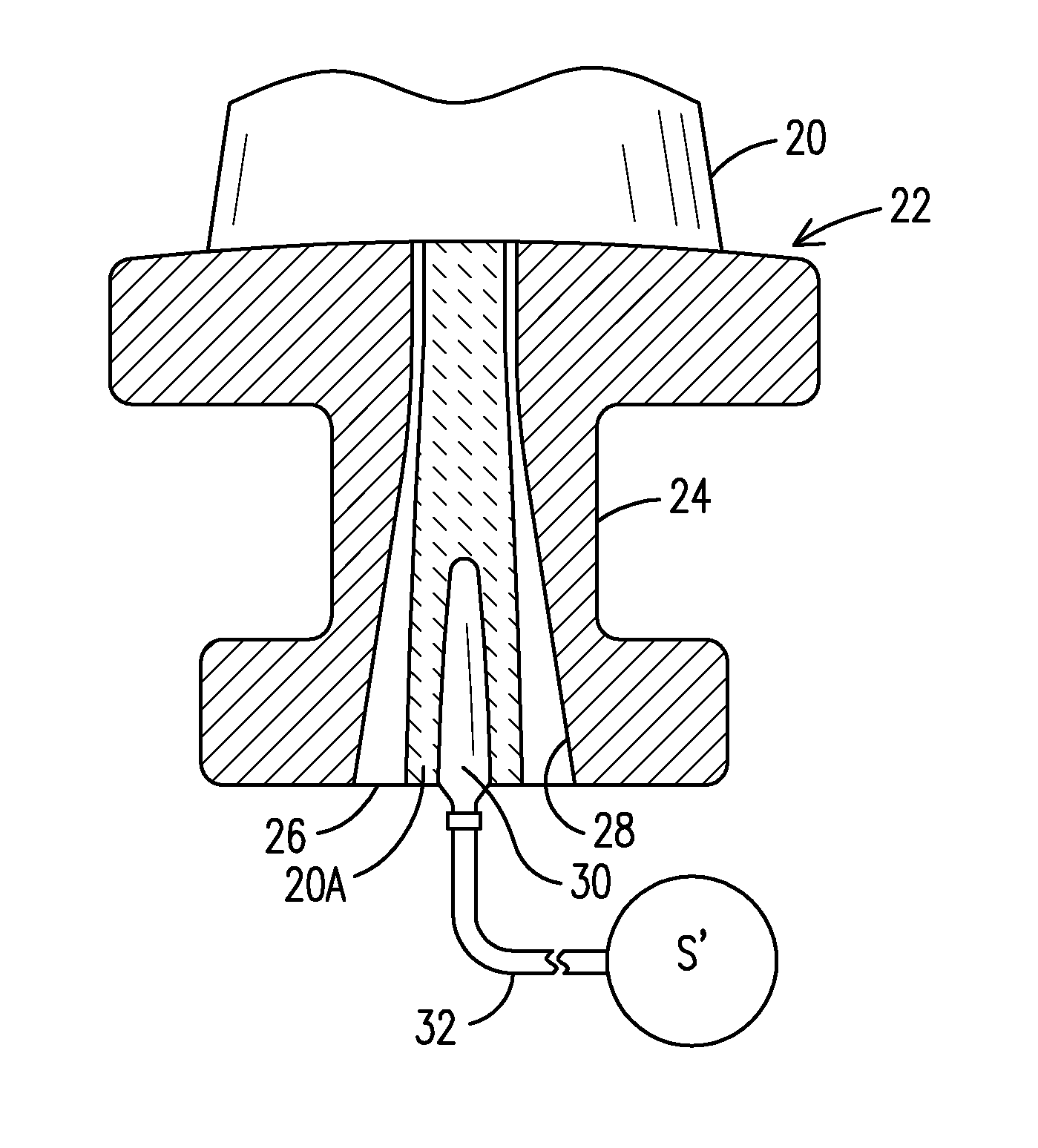
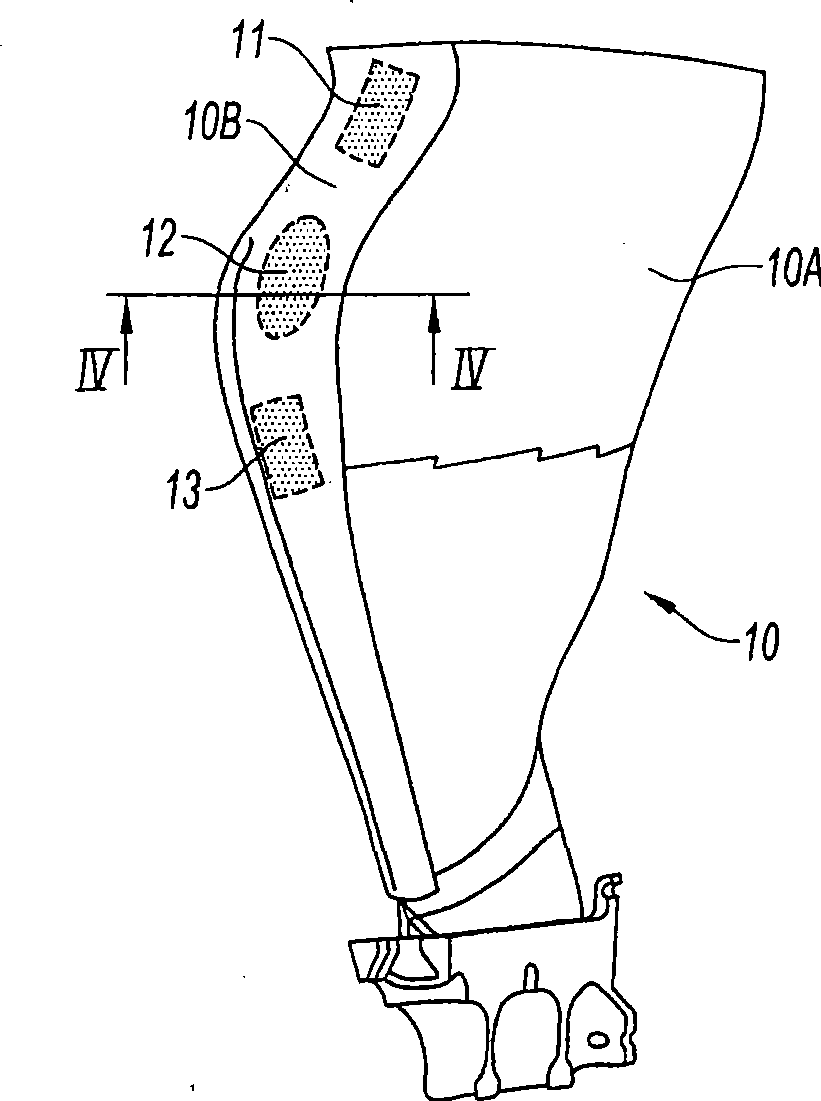
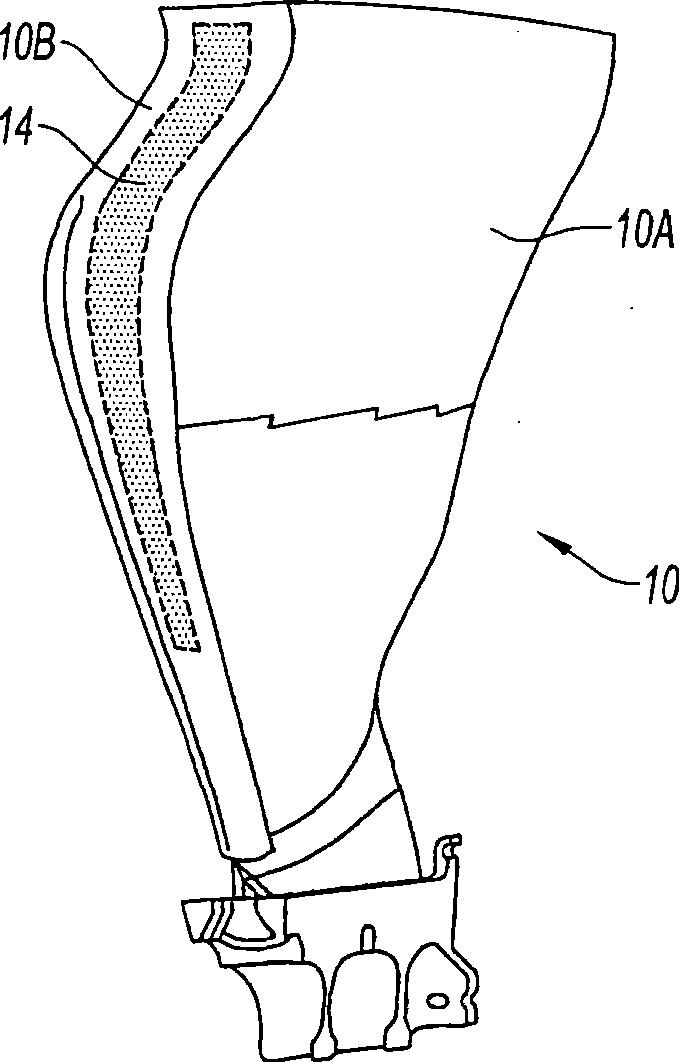
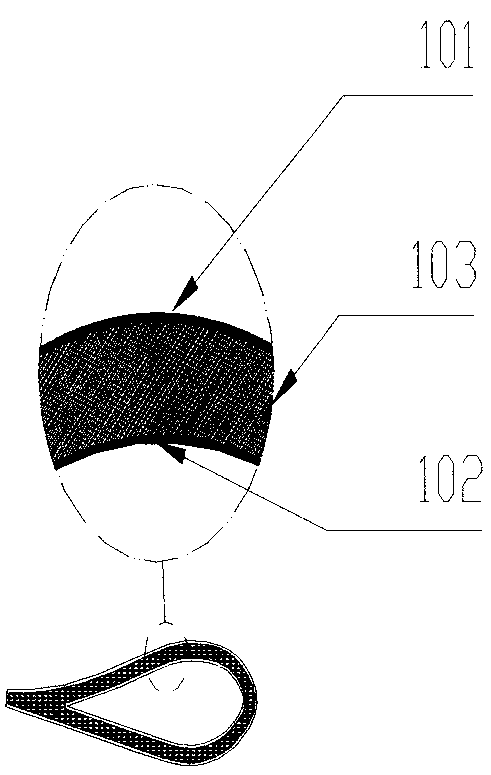
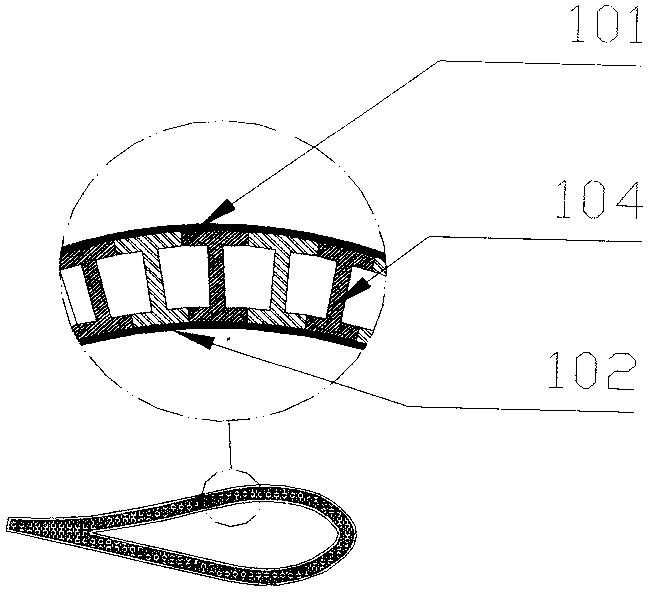
ActiveCN101387205AFirmly connectedLow costPump componentsOther chemical processesLeading edgeComposite blade
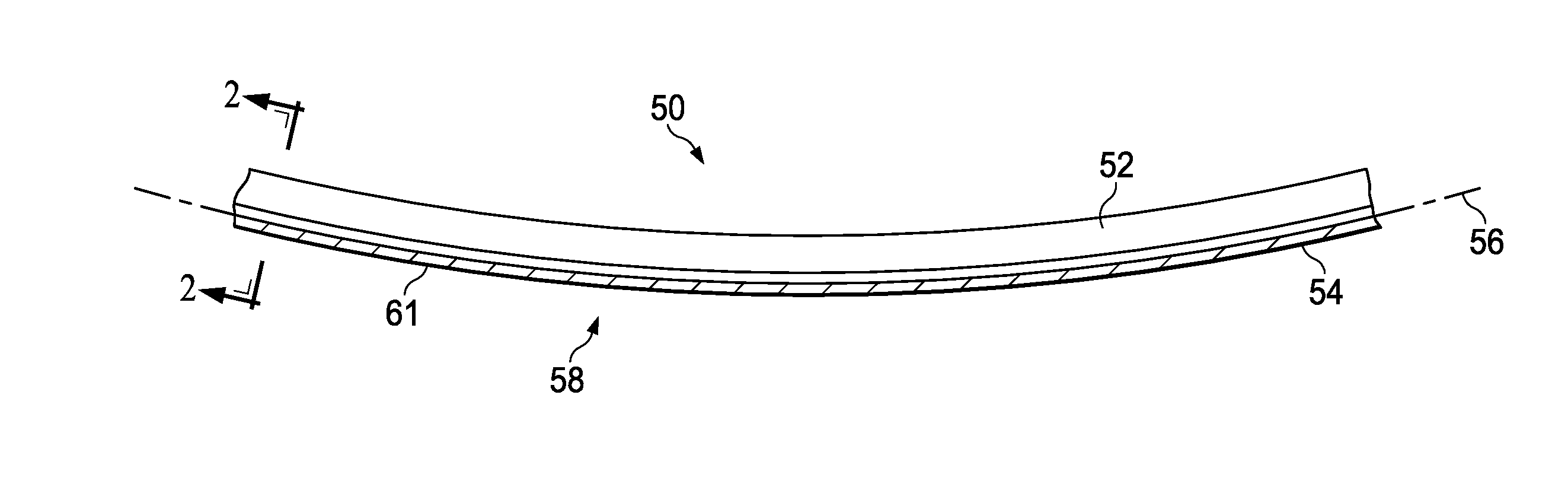
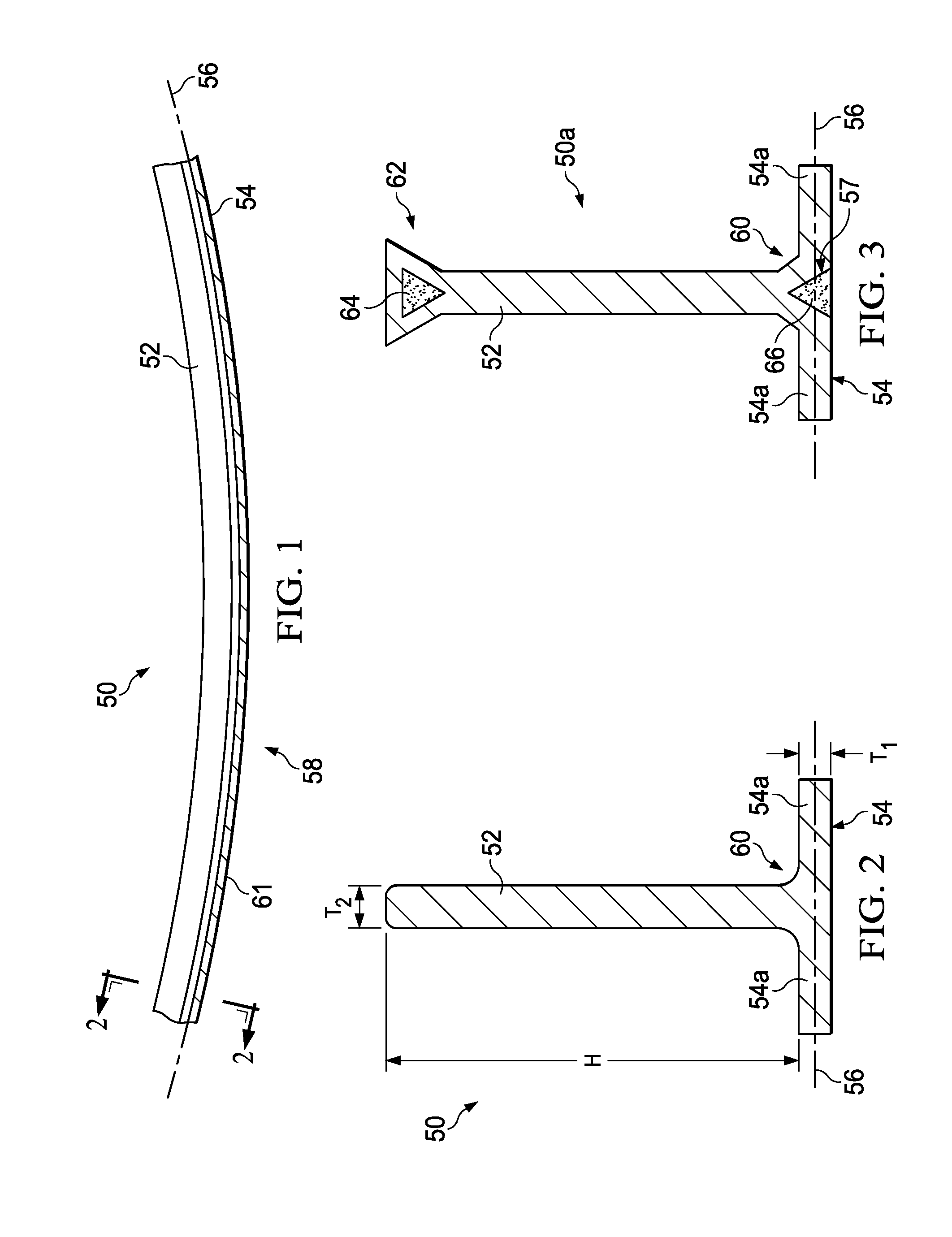
The present invention relates to a blade made of composite, comprising a vane (10A) formed of woven filaments impregnated with a thermosetting resin with a protective element (10B) in the region of the leading edge of the vane comprising a part in the form of a rigid strip, said strip being secured to the vane. The blade is characterized in that at least one layer of a viscoelastic material (20, 21) is at least partially interposed between said rigid strip (10Bi, 10Be) and the vane (10A) so as to form, with the protective element, a means of damping the vibrations (11, 12, 13) of the vane.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Method of producing a metal reinforcement for a turbine engine blade
ActiveCN104364031AAvoid using effectsAvoid the disadvantages from itsTurbinesPropellersLeading edgeMetal sheet
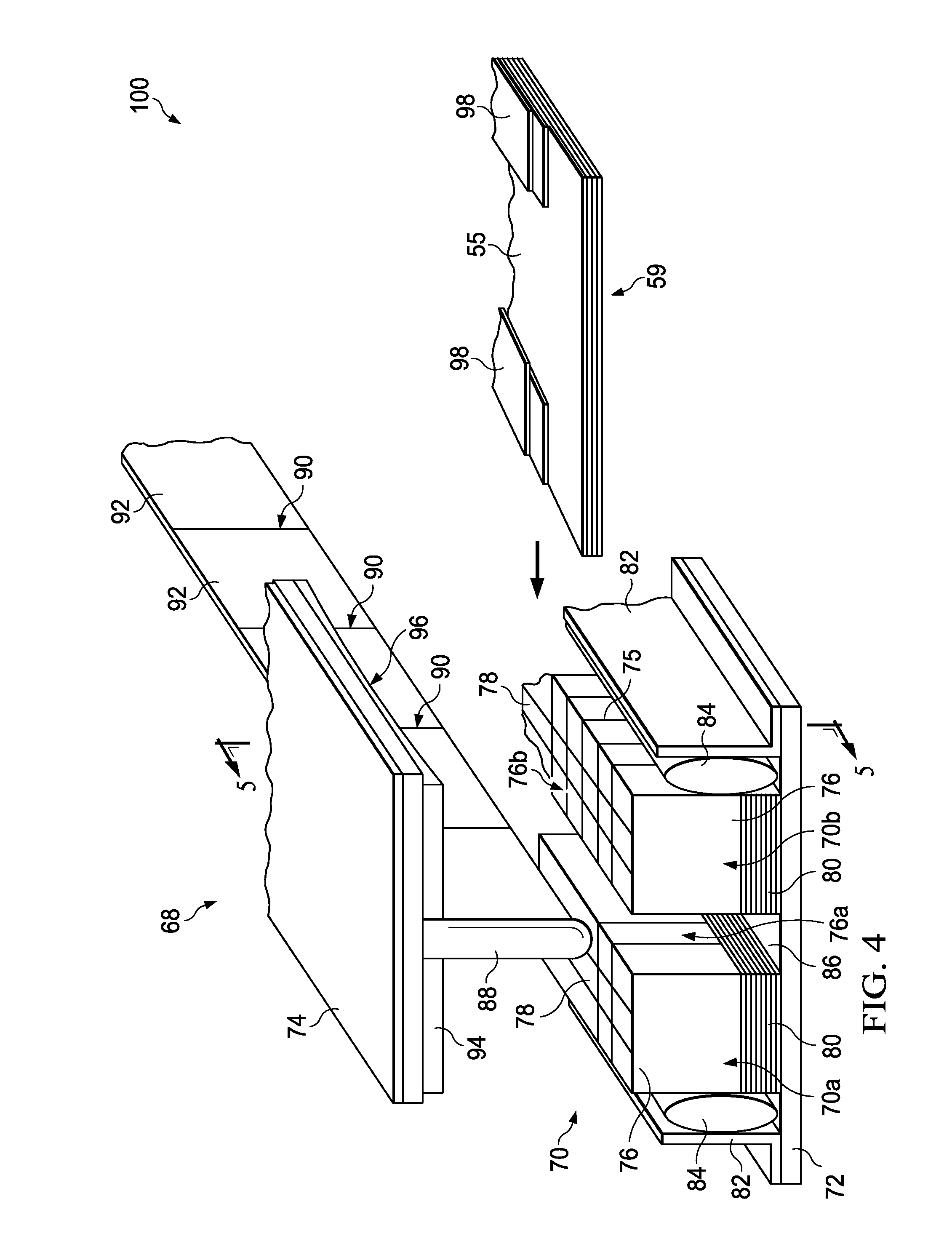
The invention concerns a method of producing a metal reinforcement (4, 6) intended to be mounted on the leading edge (23) or trailing edge of a composite blade of a turbine engine, consisting of shaping two metal sheets (1), positioning them on each side of a core (2) comprising at least one recess intended to form a cavity for a wedge (19) for positioning the reinforcement (4, 6), assembling them under vacuum, shaping them on the core (2) by hot isostatic pressing, and cutting them to separate the reinforcement (4, 6) and release the core (2).
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
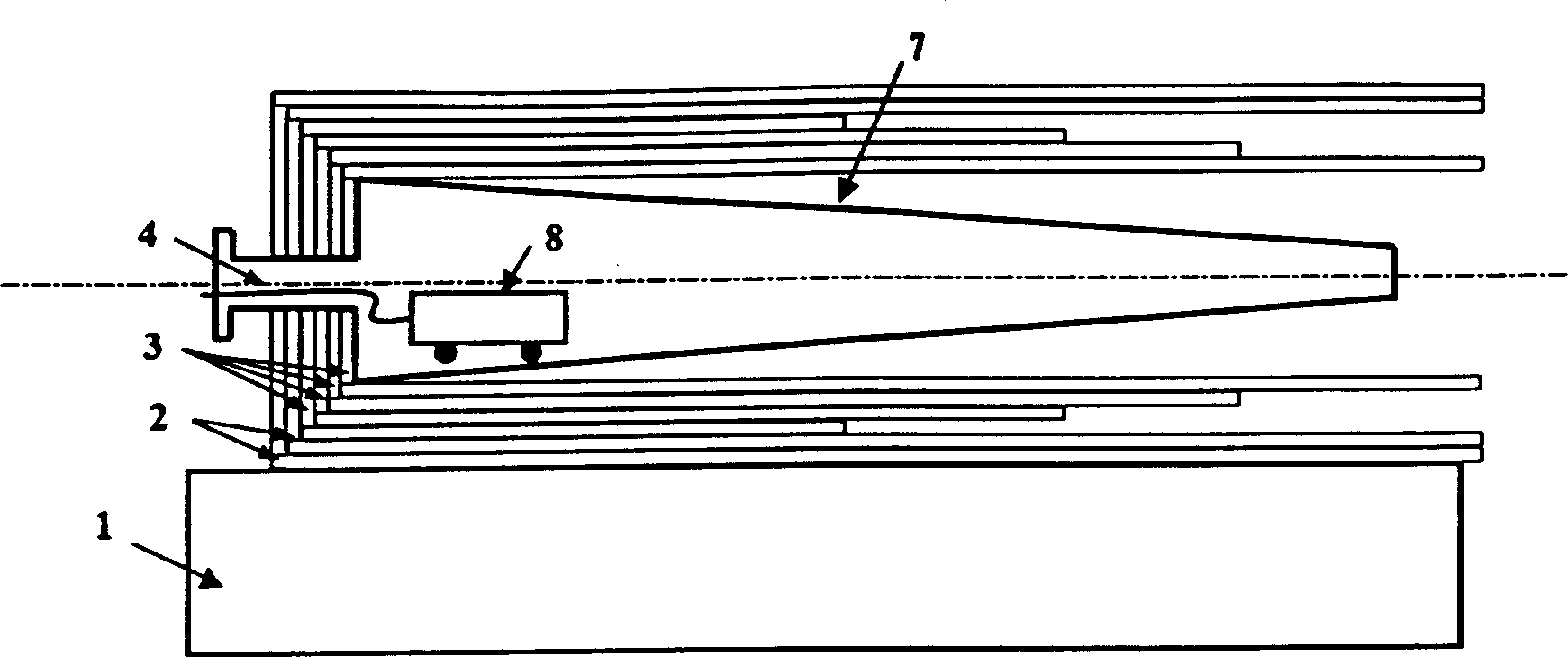
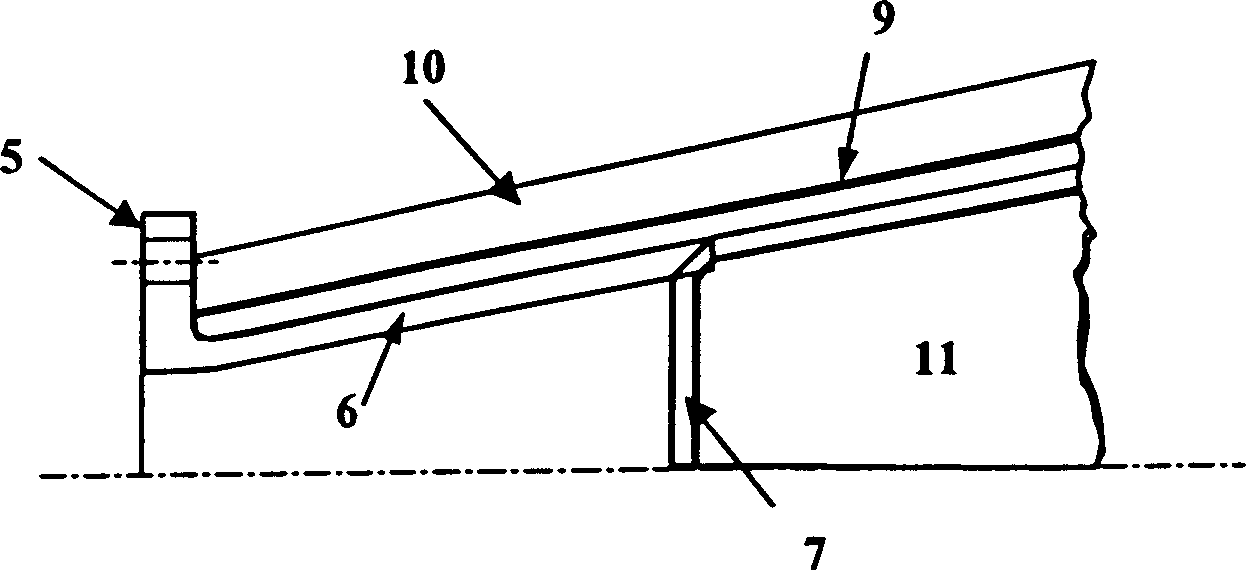
Blade of horizontal axis WTGS and forming method and equipment thereof
The invention discloses a composite blade of a horizontal axis WTGS (wind turbine generator system). A pneumatic functional part and a bearing structure part of the blade are separated from each other according to the design, particularly, external longitudinal beams are distributed on a front side surface and a rear side surface of the section surface of a pneumatic wing section and keep enough pneumatic clearance distances from the pneumatic wing section, and a section of truss structure is introduced at a blade stalk part of the blade, therefore, on the premise of guaranteeing the pneumatic power, the blade manufacture cost and transportation cost can be greatly lowered in comparison with the prior art. A horizontal axis fan formed on the basis of the pultrusion technology enhances the resin composite blade through using uniform-section fibers, a casing of the blade is divided into a stressed-skin construction layer and a core material construction layer which bear blade horizontal and longitudinal loads respectively, the core material part is made of preformed continuous-pultrusion sectional material, and the stressed-skin part is finished in the second pultrusion process. The method for manufacturing the full fiber composite blade by adopting the second pultrusion technology gives full play to the blade structure, material performance and technology advantages reasonably.
Owner:张向增
Composite layers for bonding components of a wind turbine rotor blade
ActiveUS20170067439A1Broaden applicationEasy to unrollFinal product manufactureMachines/enginesComposite bladeTurbine rotor
The present disclosure is directed to a method for bonding composite blade components of a rotor blade of a wind turbine. The method includes providing a first blade component being constructed of a first composite material. The method also includes providing a second blade component being constructed of a second composite material. Further, the method includes arranging the first and second blade components together at an interface. Another step includes placing one or more layers of a wetted composite material between the first and second blade components at the interface. The method also includes allowing the one or more layers of the wetted composite material at the interface to cure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
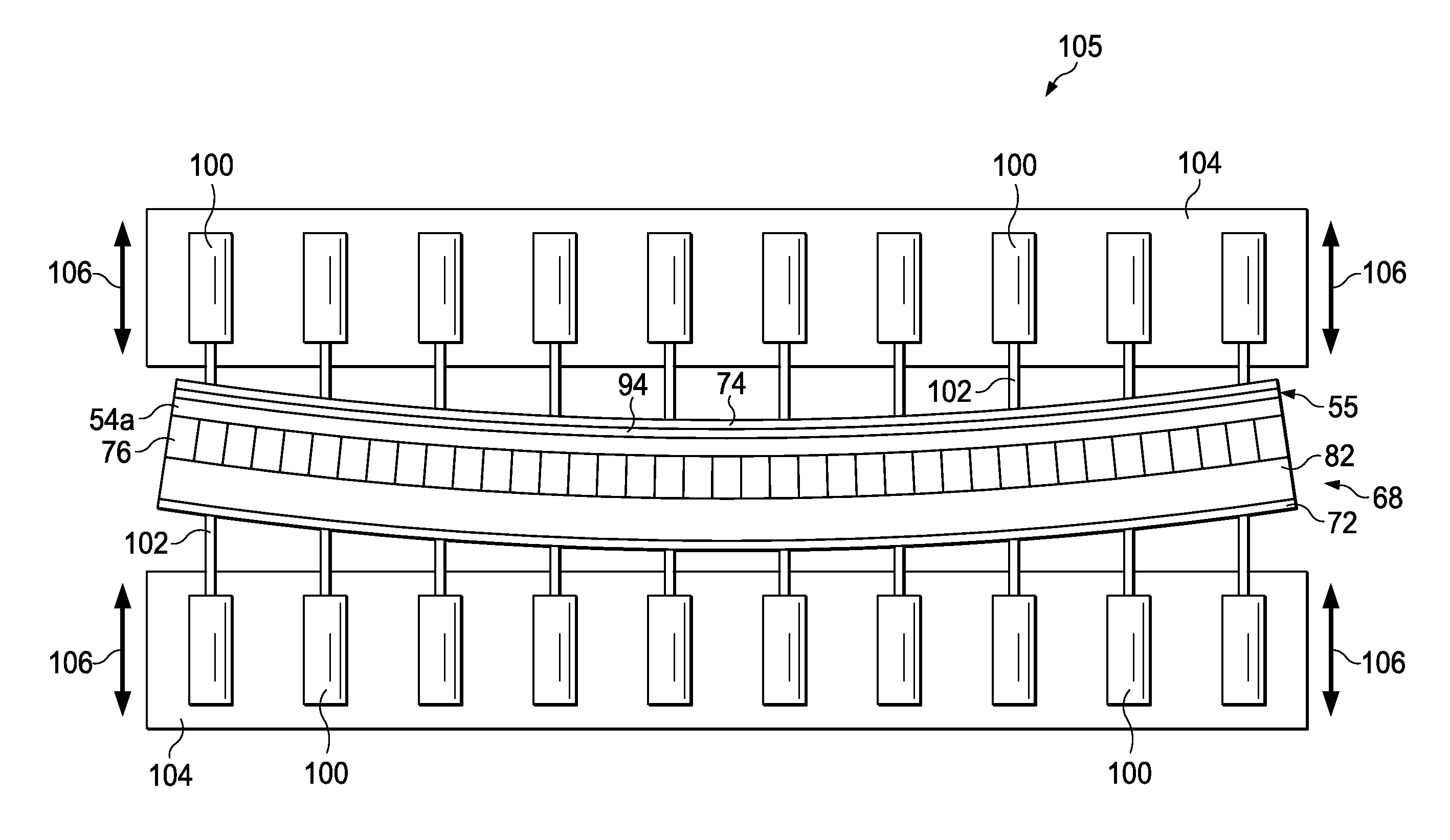
Ultrasonic detection method for different technical stages of composite blade ring
ActiveCN105806946AAchieve quality controlRealize automatic imagingAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFocus ultrasoundTitanium matrix composites
The invention relates to an ultrasonic detection method for different technical stages of a composite blade ring. A pulse echo type water-leaching focused ultrasound C scan method is adopted for performing ultrasonic detection on the whole blade ring. The ultrasonic detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, respectively performing water-leaching focused ultrasound C scan detection on interior defects of a titanium alloy inner ring and outer ring forge piece to be used for making the whole blade ring; detecting a joint interface in an integrally formed blade ring after being subjected to cellosilk winding and inner and outer ring hot isostatic pressure, namely with a 5-10MHz water-leaching focused probe, respectively performing C scan imaging on an interface signal and a bottom wave signal; and detecting the bonding quality of a metal / metal interface between the inner and outer rings of titanium alloy and a metal / fiber interface between titanium alloy and silicon carbide cellosilk. The ultrasonic detection method can be adopted for comprehensively controlling the inner quality and interface bonding quality of the whole blade ring of silicon carbide fiber enhanced Ti-based composite and has the advantages of strong operability, high detection sensitivity and direct detection result.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Composite aerofoil
A composite blade (26) comprises a three-dimensional arrangement of reinforcing fibres (58) and a matrix material (60) infiltrated around the three-dimensional arrangement of woven reinforcing fibres (60). The three-dimensional arrangement of woven reinforcing fibres (58) defines a plurality of cavities (56) within the aerofoil (28). The composite blade (26) comprises an aerofoil portion (38) and a root portion (36). The aerofoil portion (38) comprises a leading edge (44), a trailing edge (46), a concave pressure surface wall (50), a convex suction surface wall (52) and a tip (48). The aerofoil portion (36) comprises a plurality of webs (54) extending between, and being secured to, the concave pressure surface wall (50) and the convex suction surface wall (52) to produce a Warren girder structure. The three-dimensional arrangement of woven reinforcing fibres (58) are arranged to produce the concave pressure surface wall (50), the convex suction surface wall (52) and the plurality of webs (54). The matrix material (60) is an organic resin and the reinforcing fibres (58) comprise carbon fibres.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Composite airfoil assembly
A composite blade assembly for mounting on a turbine wheel includes a ceramic airfoil and an airfoil platform. The ceramic airfoil is formed with an airfoil portion, a blade shank portion and a blade dovetail tang. The metal platform includes a platform shank and a radially inner platform dovetail. The ceramic airfoil is captured within the metal platform, such that in use, the ceramic airfoil is held within the turbine wheel independent of the metal platform.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Helicopter composite blade spar and method
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Composite Fan Blade
A composite fan blade for a gas turbine engine is disclosed. The fan blade may include a core being made of a first material and a shell enclosing the core. The shell may be made of a second material and the second material may have less plasticity than the first material.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Gas turbine engine composite blade
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Composite Blade Made by Additive Manufacturing
ActiveCN104420890AUniform resistanceImprove sturdinessTurbinesAdditive manufacturing apparatusLeading edgeTurbine blade
The present application relates to a blade of a rectifier of a low pressure compressor of an axial turbomachine. The blade can also be a rotor and / or turbine blade. The blade includes a composite material with a matrix and a reinforcement comprising a mesh with rods. The rods of the reinforcement are connected to each other and are distributed throughout the volume between the pressure side surface and the suction side surface of the blade. The mesh forms a three-dimensional structure extending over the majority of the thickness of the blade between the pressure side surface and the suction side surface and / or the majority of the length of the blade between the leading edge and the trailing edge. The present application also relates to an iterative method for manufacturing a blade composite where the reinforcement is formed by additive layer manufacturing based on titanium powder and then placed in an injection mold.
Owner:SAFRAN AERO BOOSTERS SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com