Patents
Literature
704 results about "Turbomachinery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
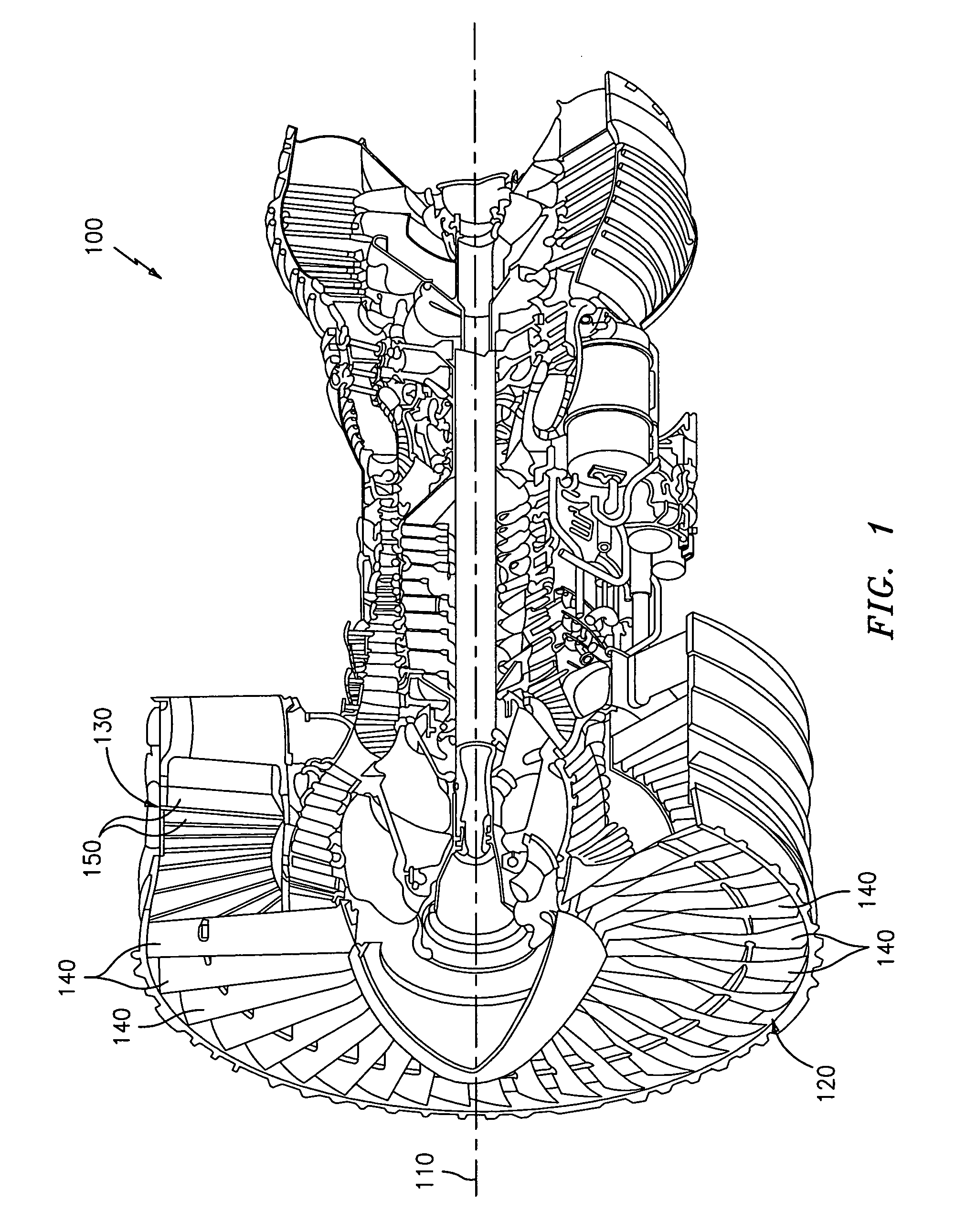
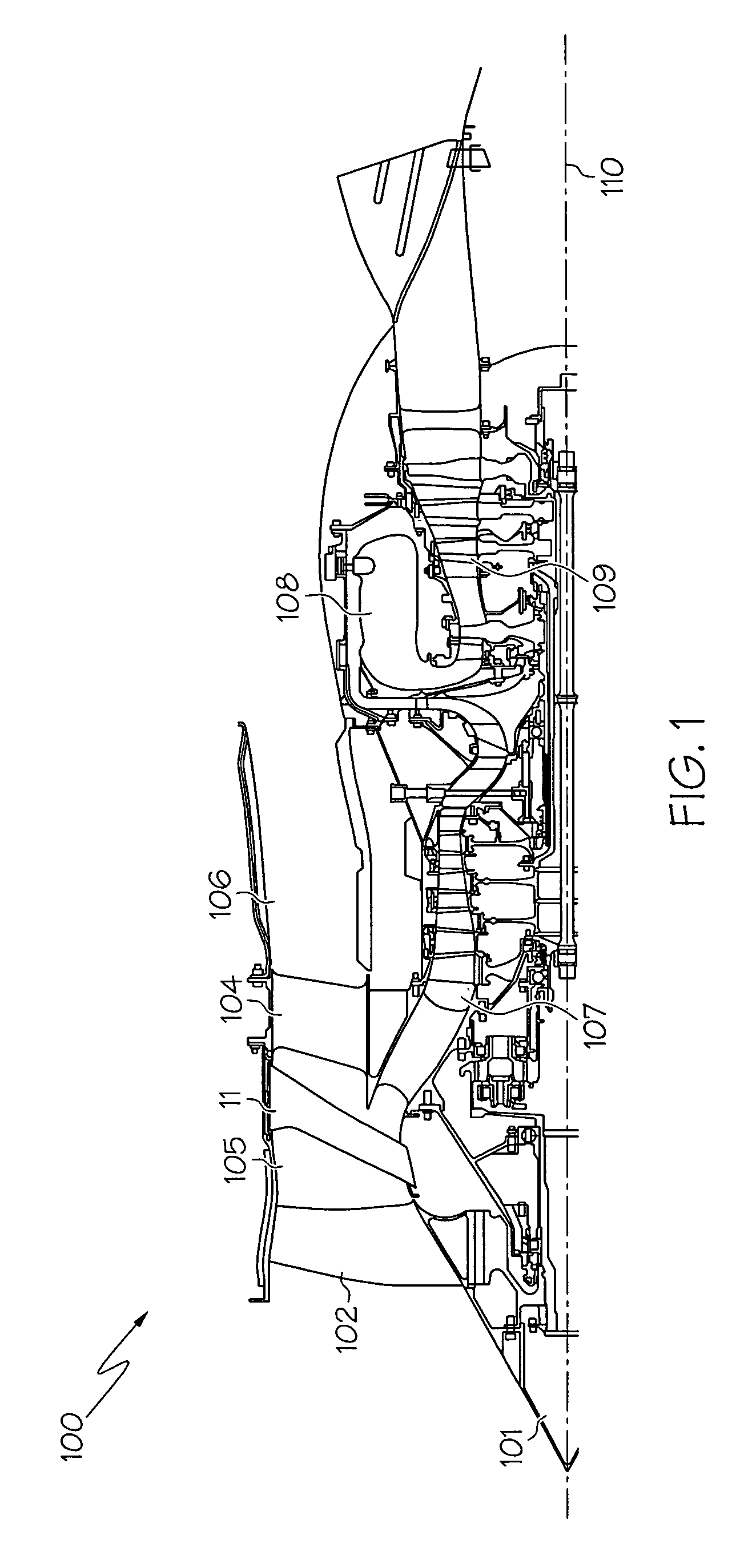
Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid.
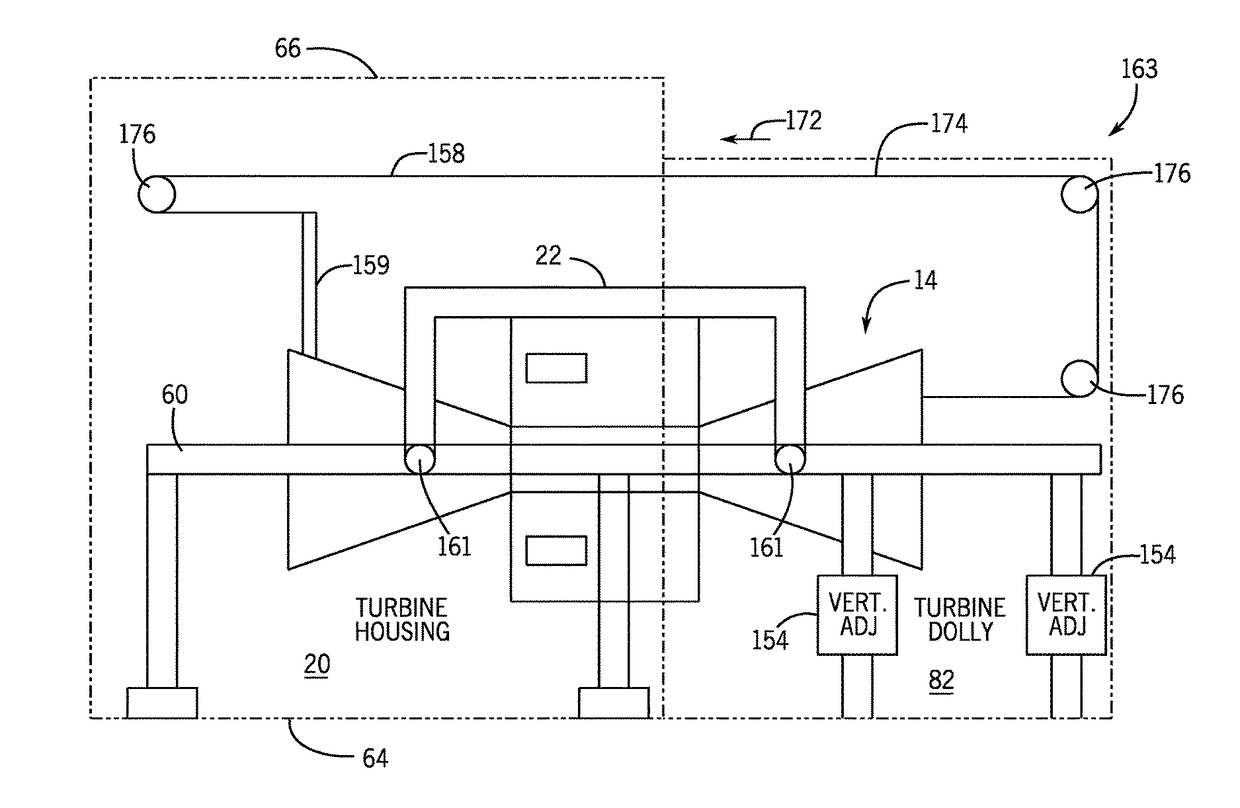
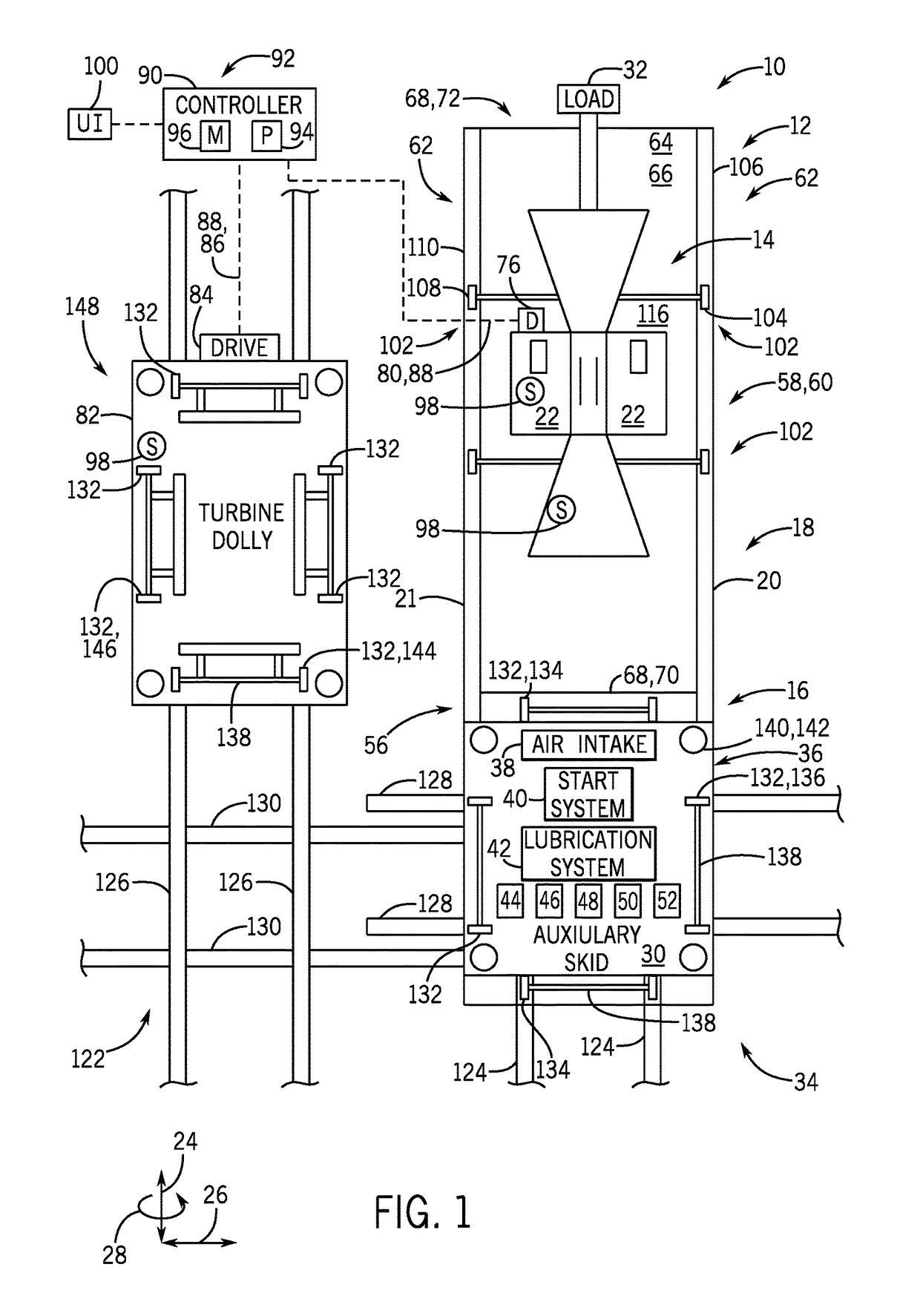
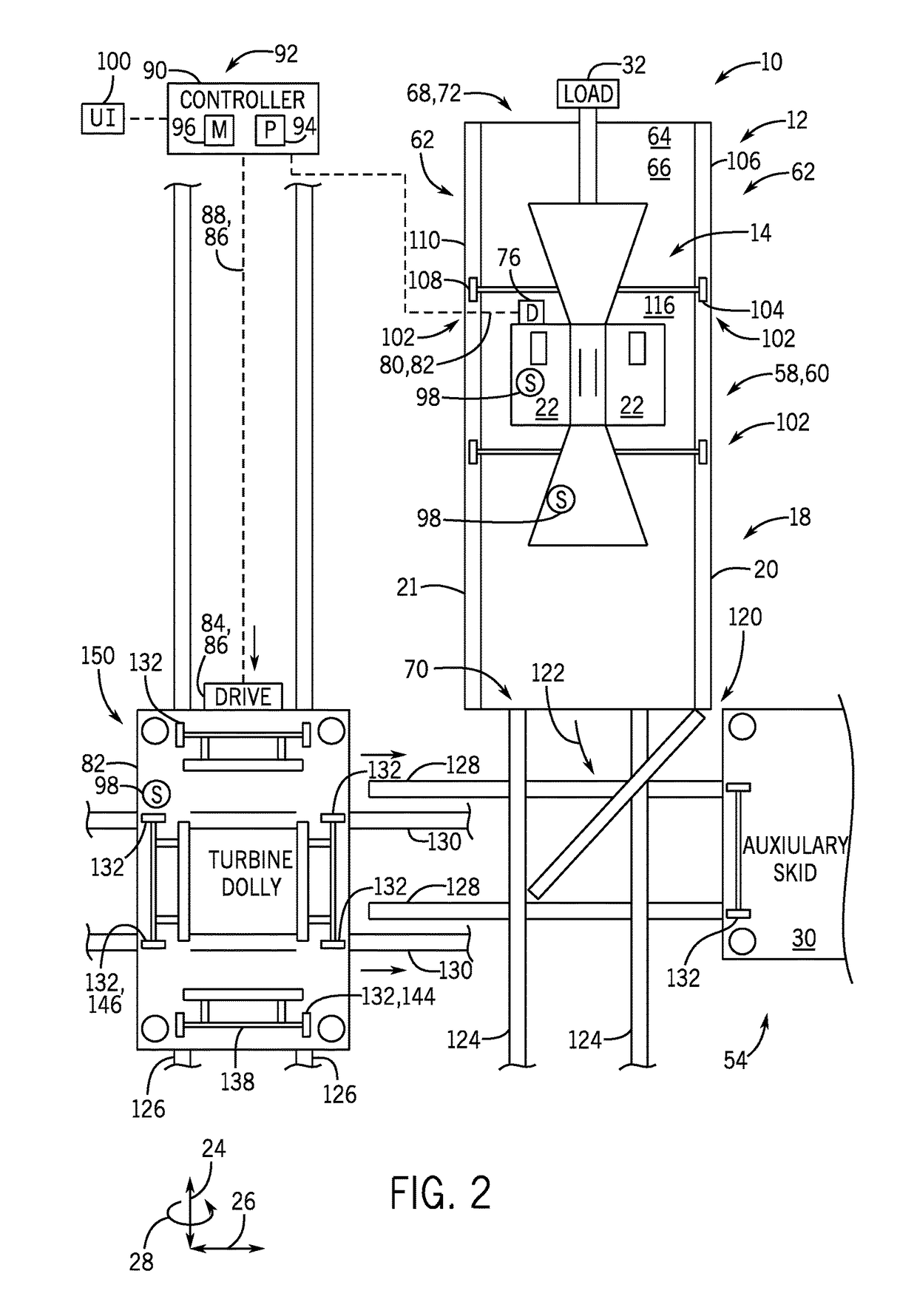
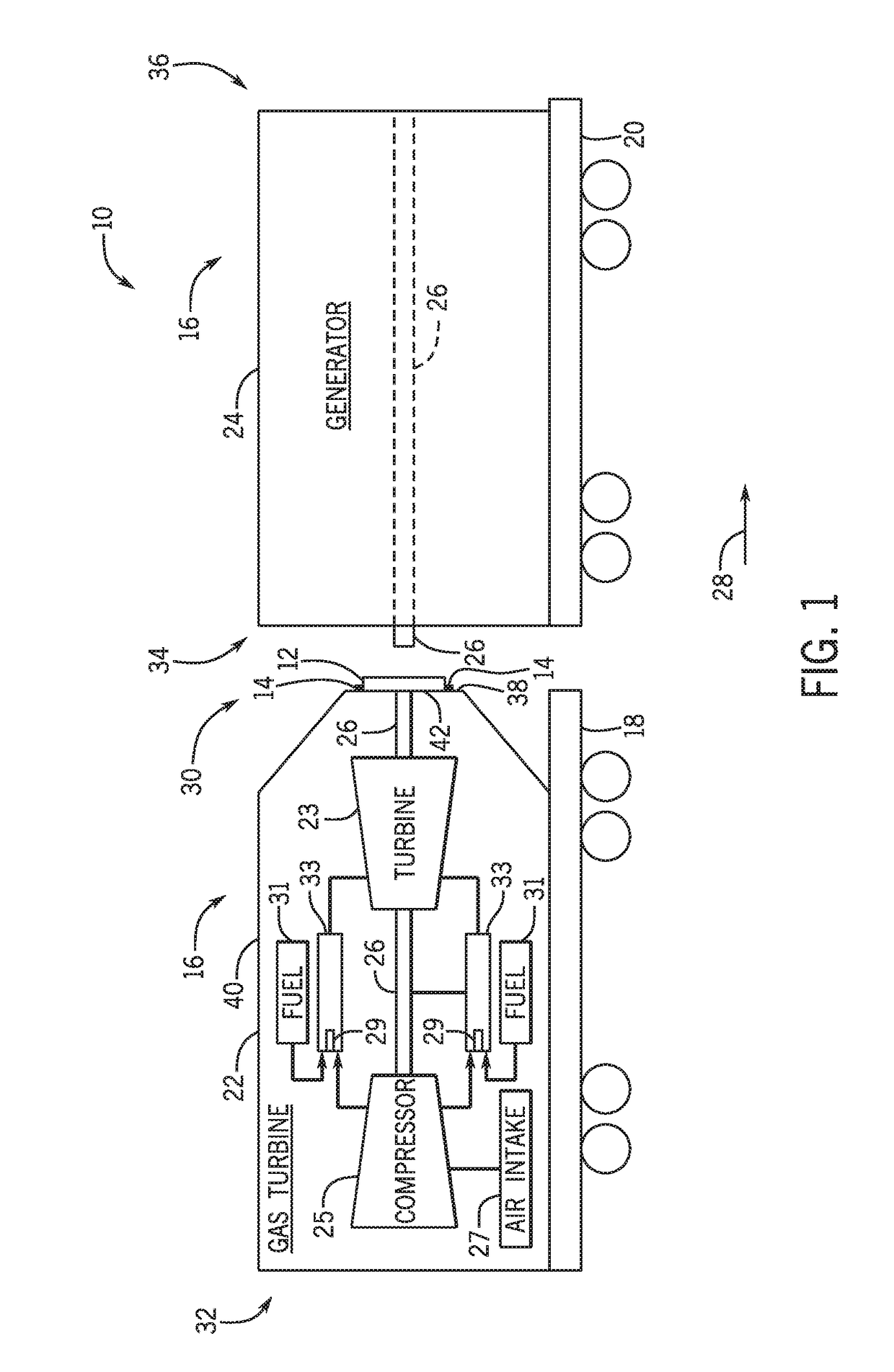
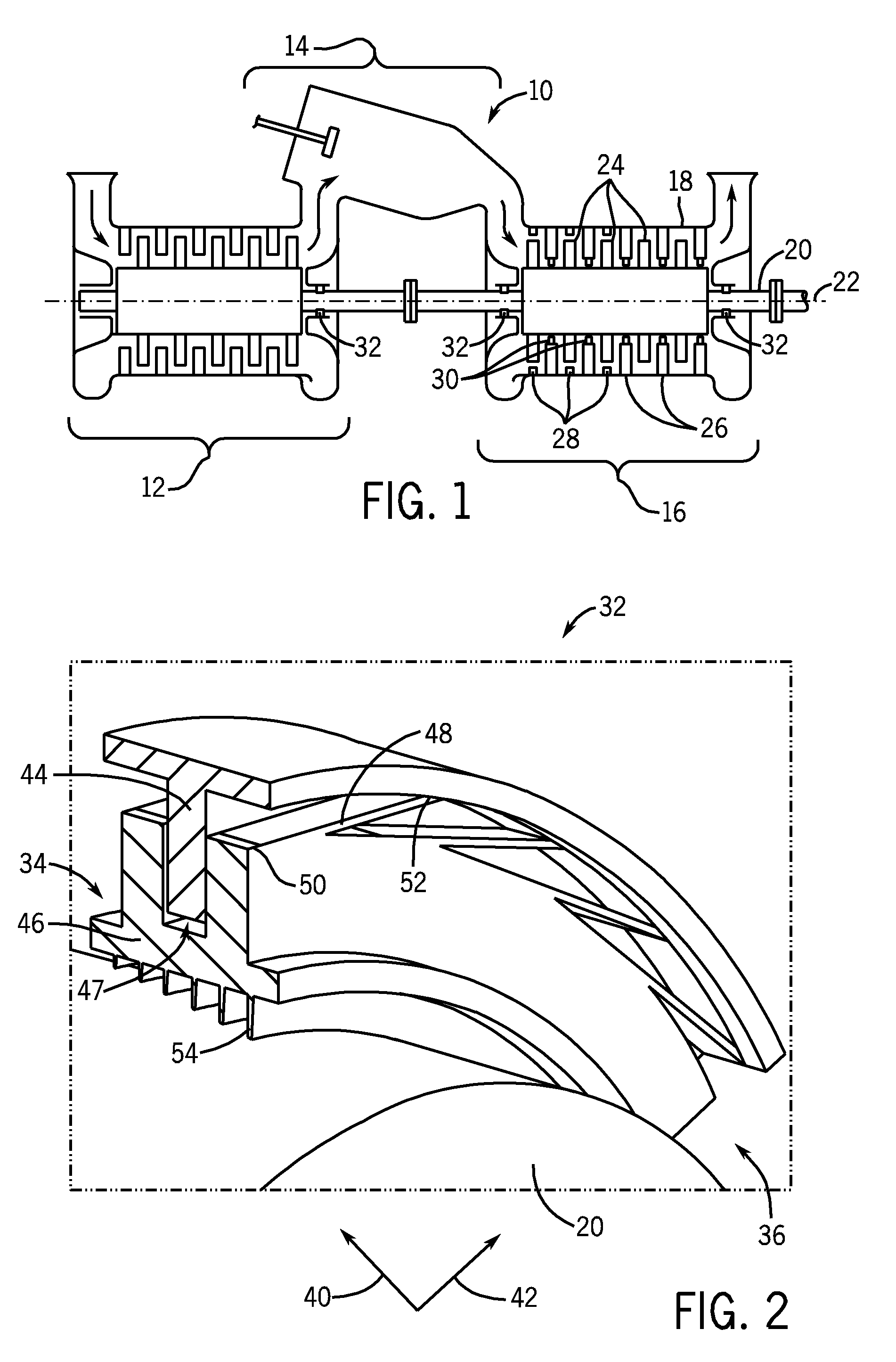
System and method to move turbomachinery
A system includes a turbine housing, a turbine mount disposed in the turbine housing, and a turbine moving machine disposed at least partially within the turbine housing. The turbine moving machine includes a turbine support configured to couple to a turbine and a first translational portion coupled to the turbine support. The turbine moving machine is configured to move the turbine lengthwise along the first translational portion between a first turbine position within the turbine housing and a second turbine position outside of the turbine housing. The turbine moving machine includes a vertical adjustment assembly configured to raise and lower the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
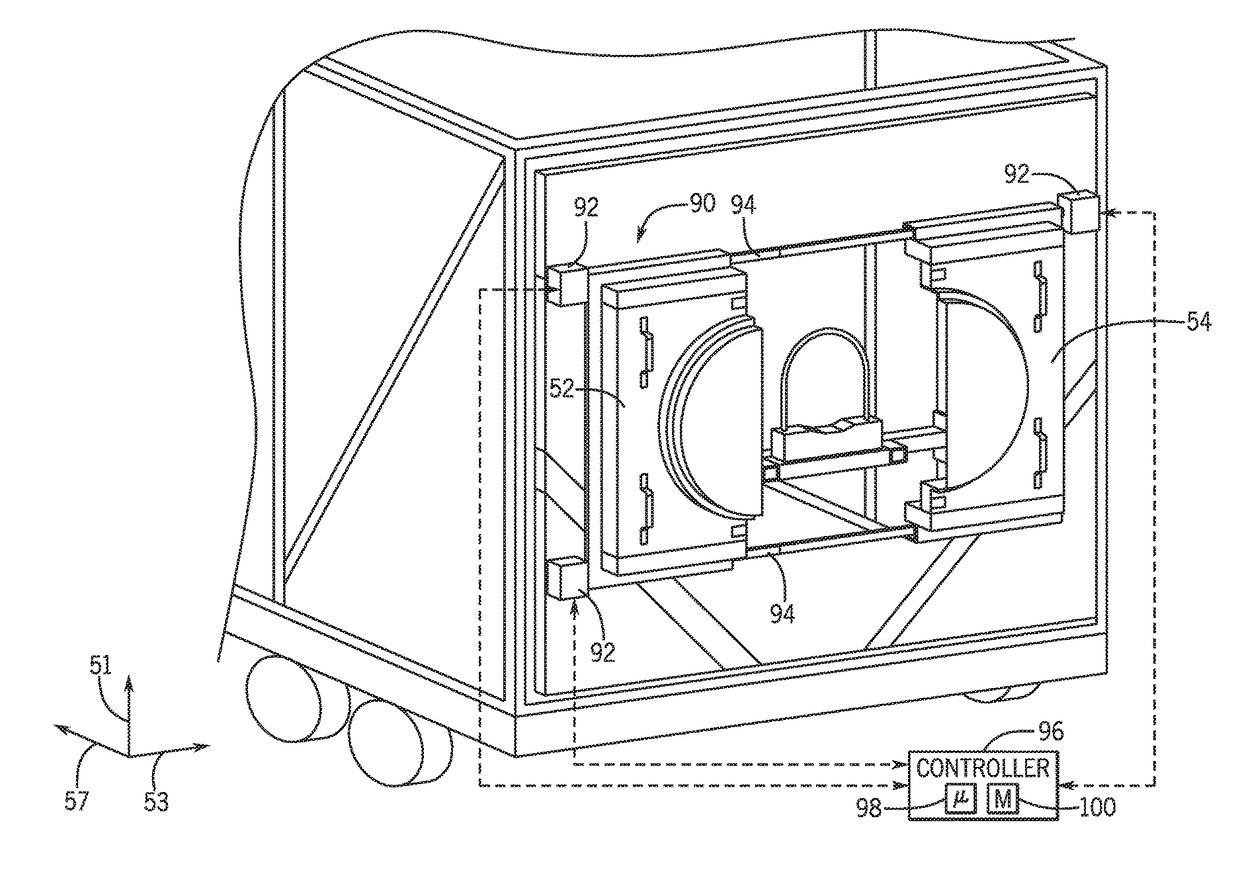
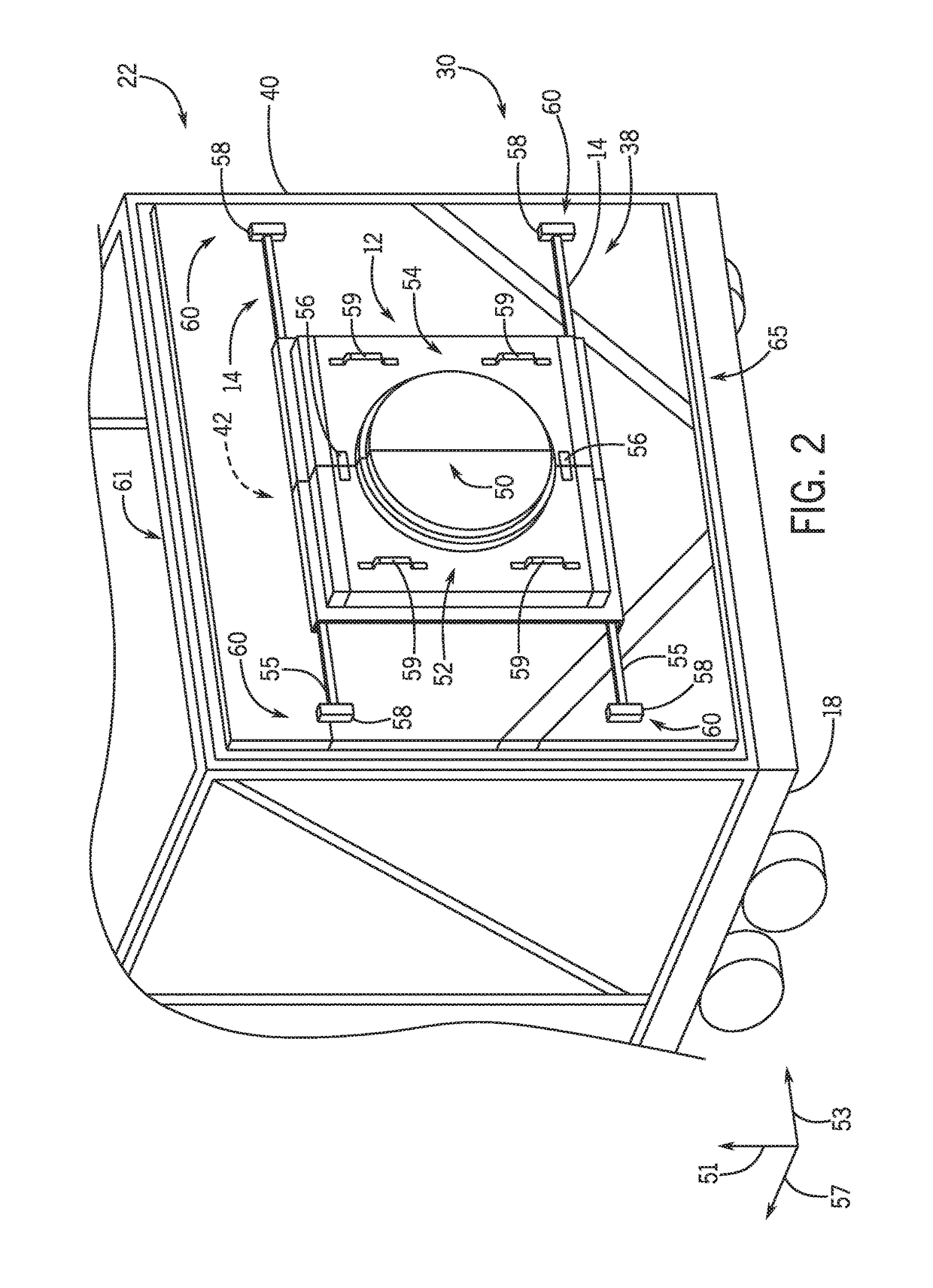
Sliding coupling system for trailer mounted turbomachinery
A system includes a turbine mounted on a first mobile unit and a turbine enclosure configured to enclose the turbine mounted on the first mobile unit. The system also includes a coupling system disposed on the turbine enclosure. The coupling system includes a first component and a second component configured to separate in opposite directions via a sliding system to expose an opening within the turbine enclosure. The turbine couples with a generator through the opening within the turbine enclosure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
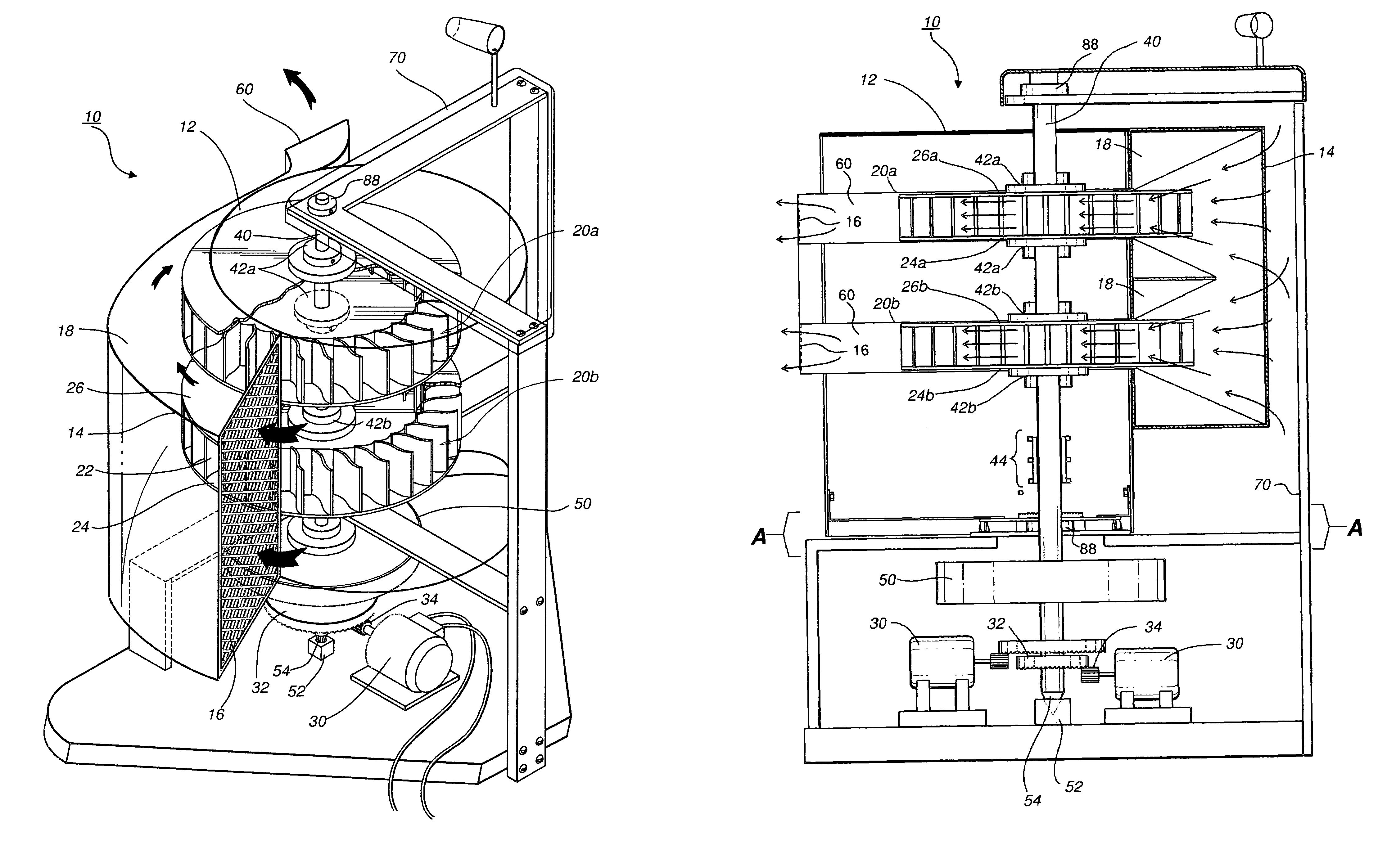
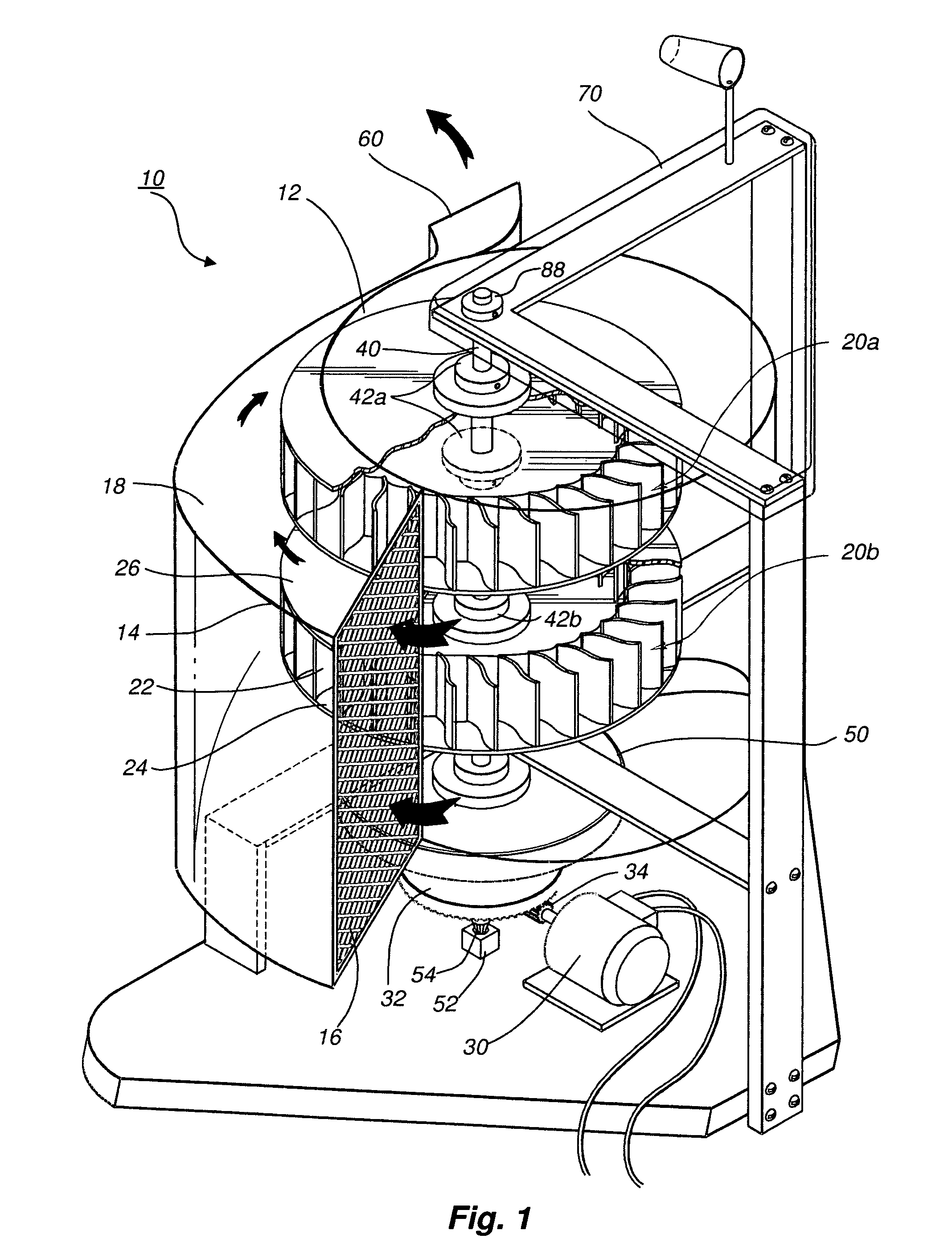
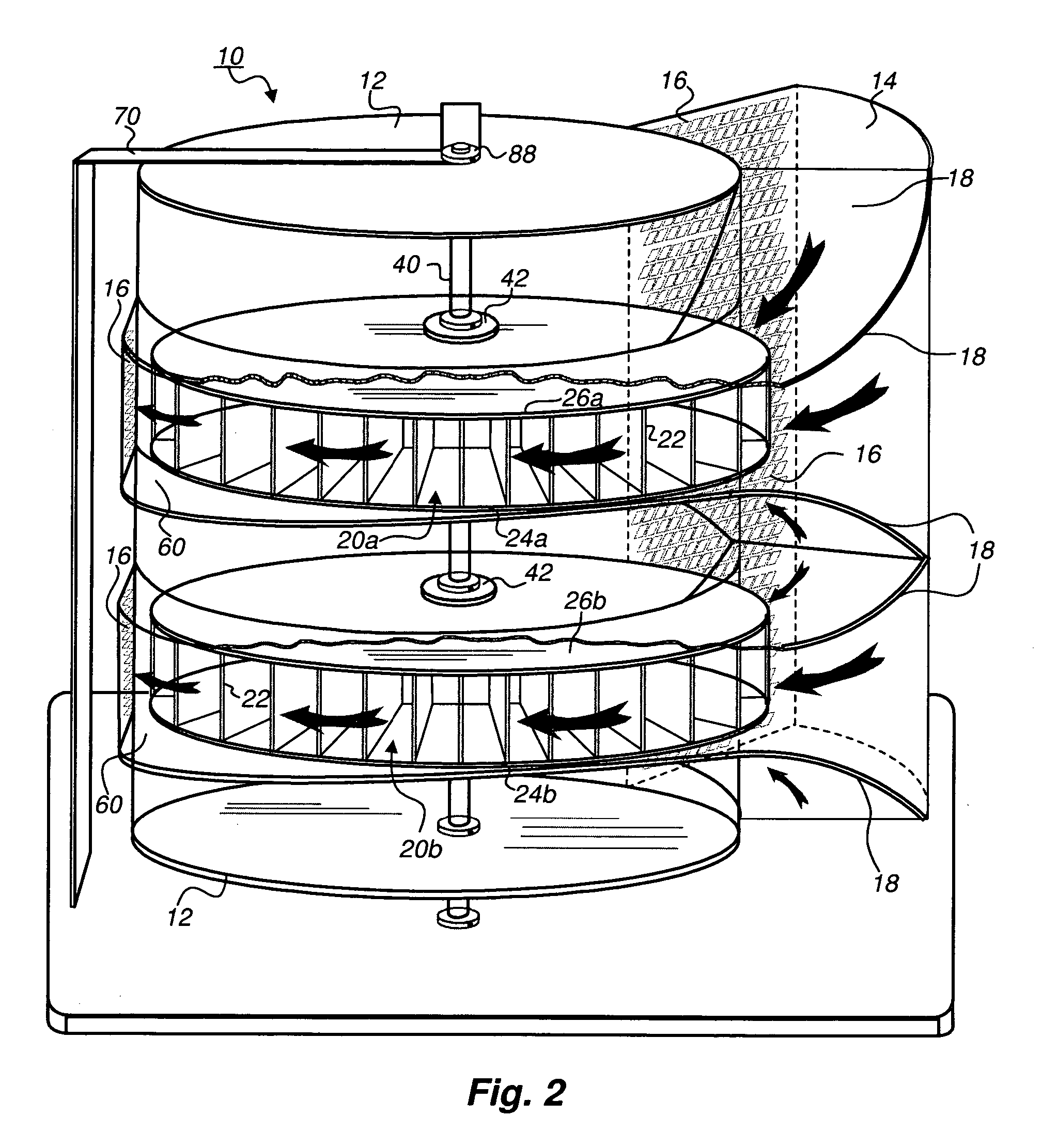
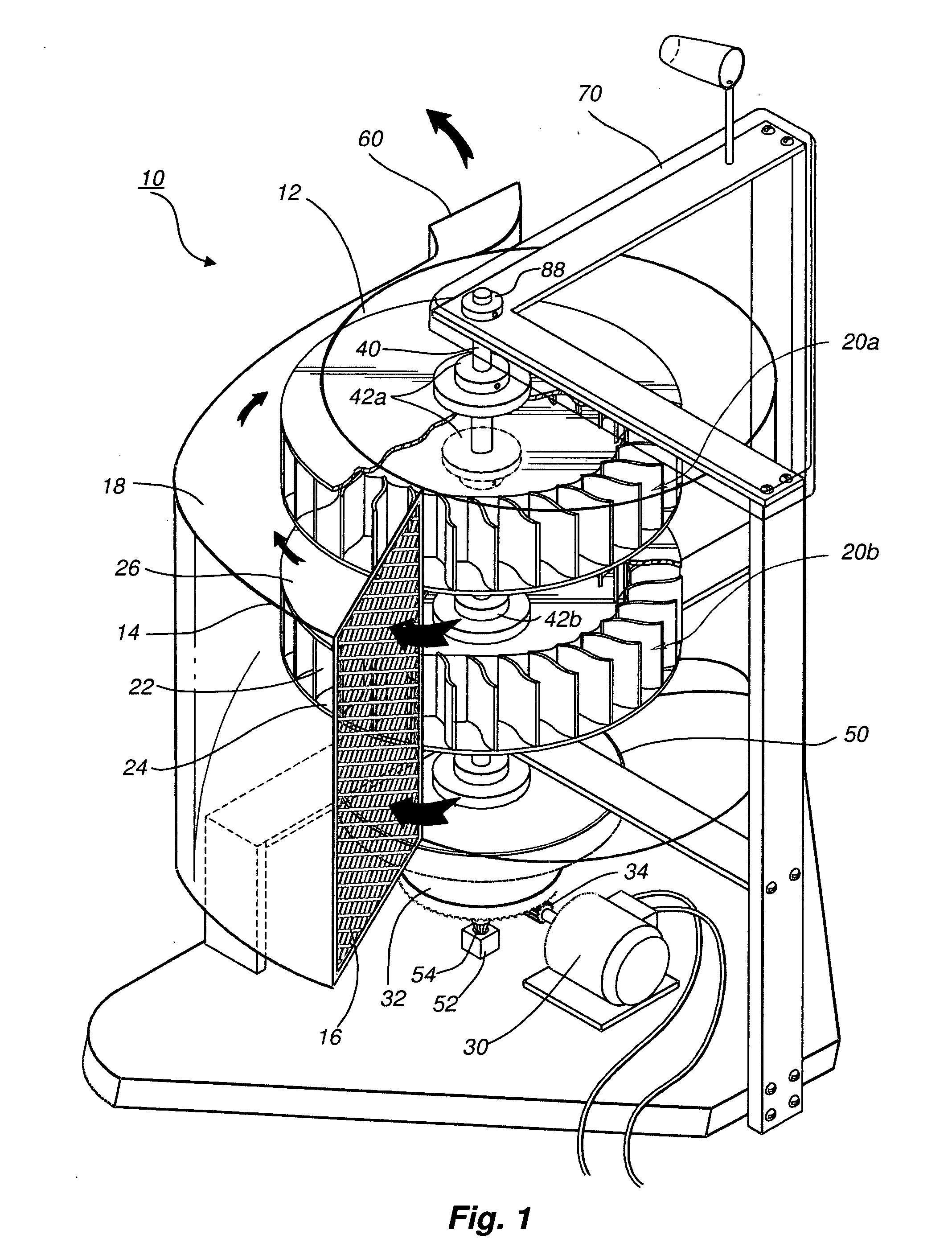
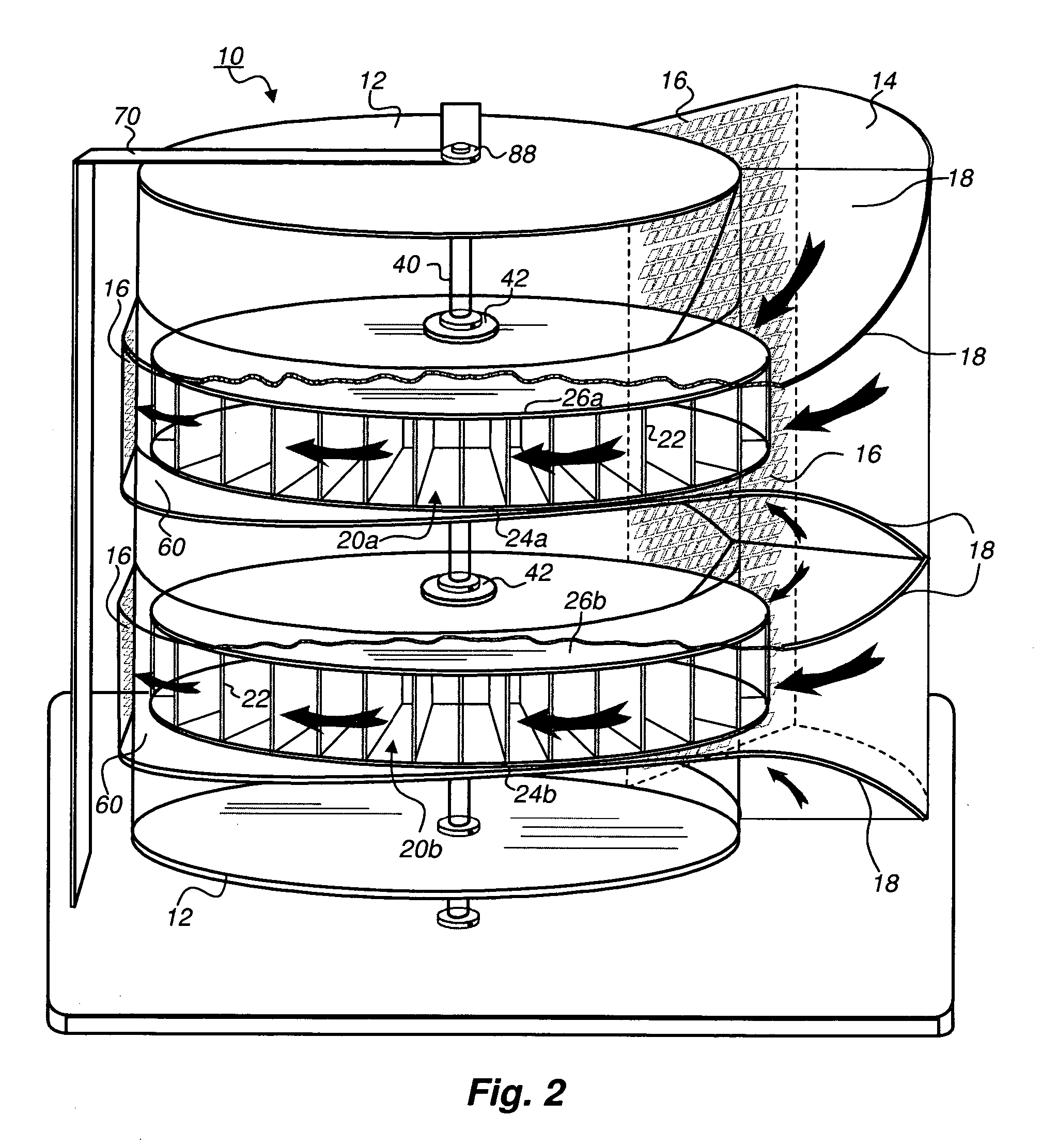
Protective wind energy conversion chamber
ActiveUS7215037B2Improve efficiencyWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesHorizontal axisVertical axis wind turbine
A protective wind energy conversion chamber provides a protected multiple turbine mechanism axially aligned to convert kinetic energy of a moving fluid (e.g., wind) into rotational mechanical power by the reaction of the moving fluid with the turbine. The conversion chamber may either be configured as a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) or horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT). The conversion chamber repositions an intake windward to collect and concentrate the wind prior to converting the wind into energy via the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism. The remaining wind is released via a leeward-facing exhaust. Completely enclosed by the protective wind energy conversion chamber, the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism avoids interference by birds and other outside objects.
Owner:SCALZI SAVERIO
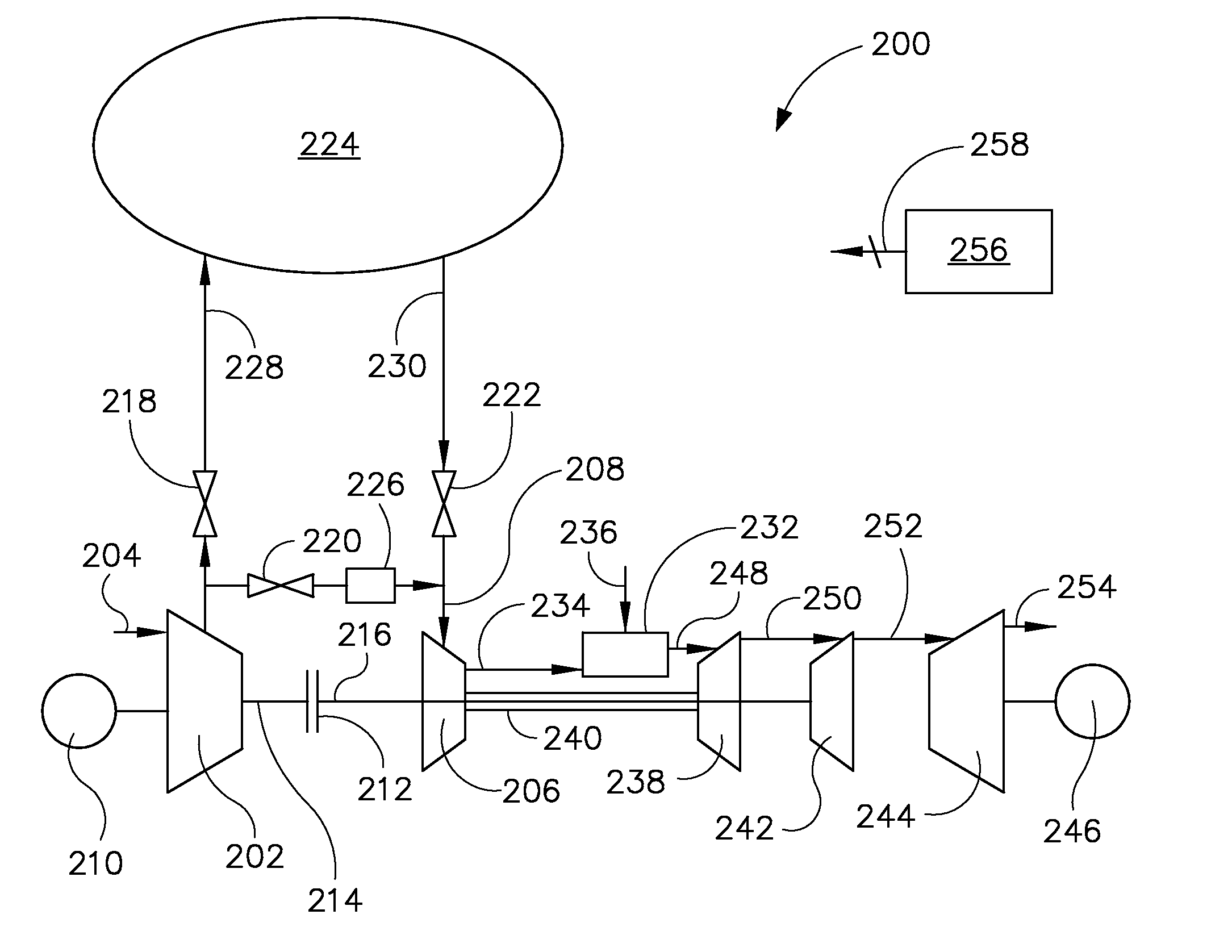
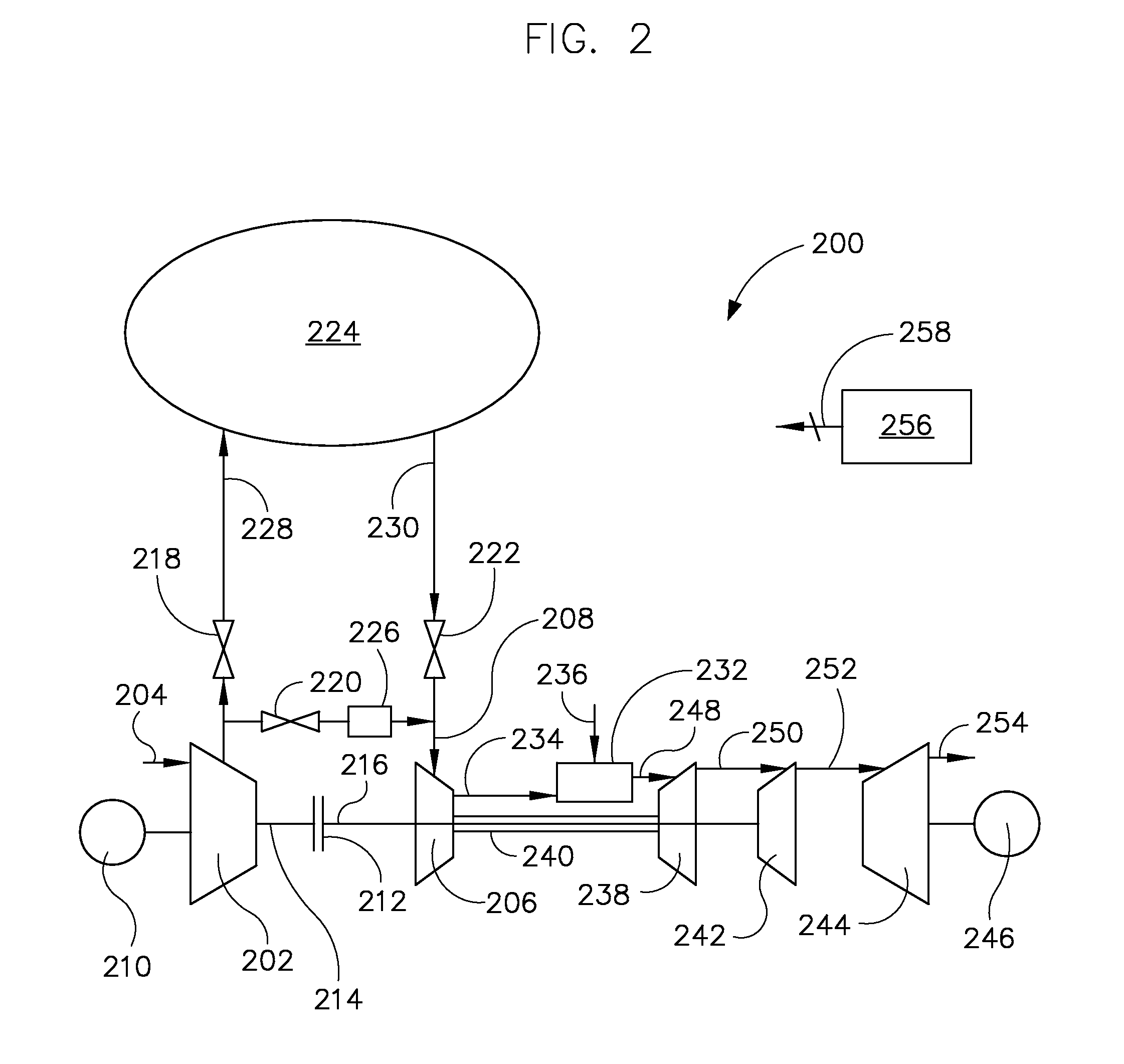
System and method of using a compressed air storage system with a gas turbine
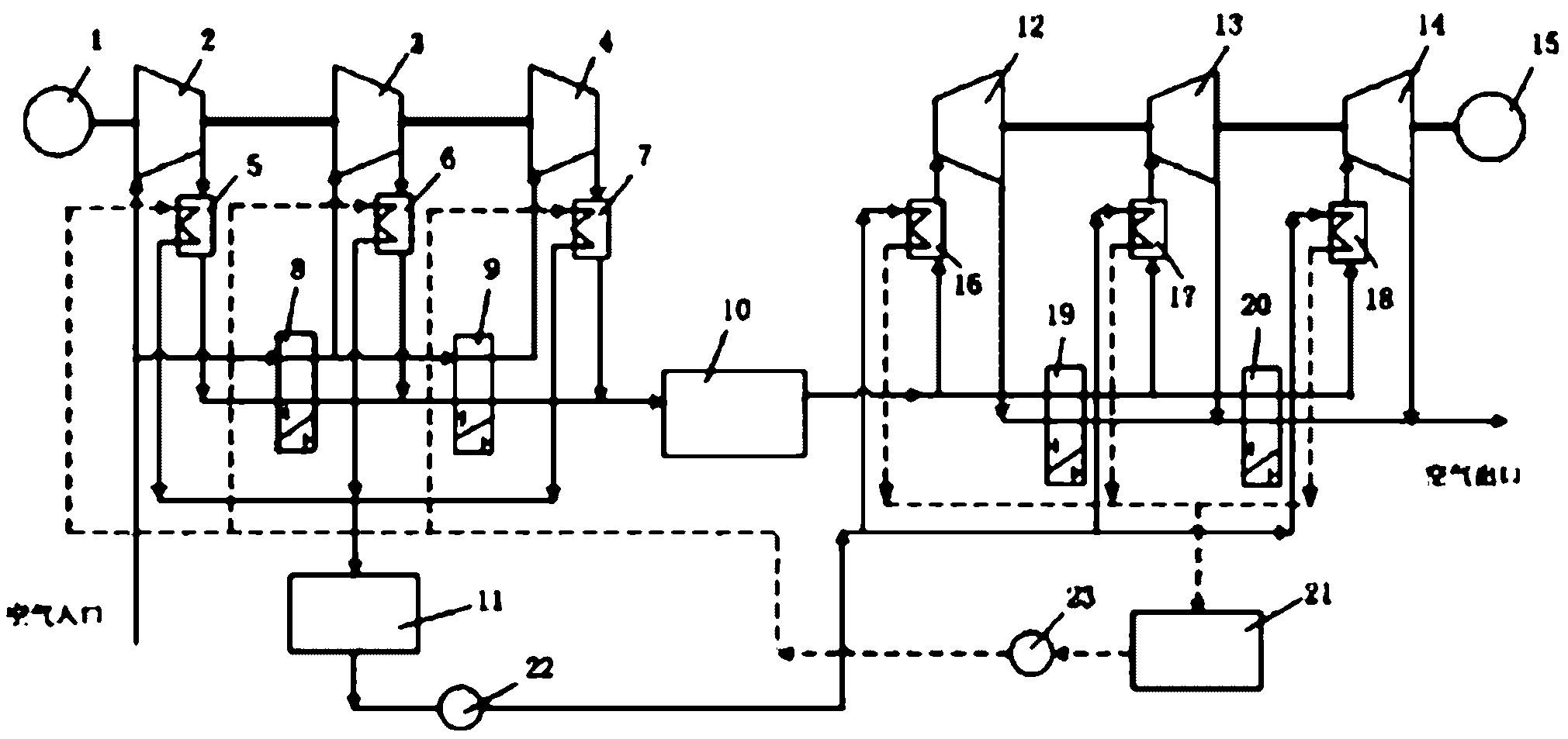
A power generation system includes a first compressor, a second compressor, a combustor configured to receive compressed air from the second compressor to produce an exhaust stream, a first turbine, and a power turbine. The first turbine is configured to receive the exhaust stream, generate a rotational power from the exhaust stream, output the rotational power to a second compressor, and output the exhaust stream. The system includes a coupling device configured to couple and decouple the first compressor to / from a second turbine, an electrical generator coupled to an output of the power turbine and configured to output electrical power, and a controller configured to cause the coupling device to mechanically decouple the second turbine from the first compressor, and cause the coupling device to direct compressed air from an air storage cavern to an inlet of the second compressor.
Owner:NUOVO PIGNONE TECH SRL
Energy efficiency improvements for turbomachinery
InactiveUS20160052621A1Reduce resistanceGood effectInfluencers by generating vorticesEngine manufactureProcess engineeringEnergy analysis
A method and apparatus are disclosed that allow Conformal Vortex Generator art to improve energy efficiency and control capabilities at many points in a turbomachine or device processing aero / hydrodynamic Newtonian fluid-flows.
Owner:IRELAND PETER +1
Nonlinearly stacked low noise turbofan stator
The present invention provides a nonlinearly stacked low noise turbofan stator vane. The stator is in an axial fan or compressor turbomachinery stage that is comprised of a collection of vanes whose highly three-dimensional shape is selected to reduce rotor-stator and rotor-strut interaction noise while maintaining the aerodynamic and mechanical performance of the vane. The nonlinearly stacked low noise turbofan stator vane reduces noise associated with the fan stage of turbomachinery to improve environmental compatibility. The stator vane has a characteristic curve that is characterized by a nonlinear sweep and a nonlinear lean.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Protective wind energy conversion chamber
ActiveUS20060108809A1Improve efficiencyImprove environmental safetyMachines/enginesWind motor combinationsHorizontal axisVertical axis wind turbine
A protective wind energy conversion chamber provides a protected multiple turbine mechanism axially aligned to convert kinetic energy of a moving fluid (e.g., wind) into rotational mechanical power by the reaction of the moving fluid with the turbine. The conversion chamber may either be configured as a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) or horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT). The conversion chamber repositions an intake windward to collect and concentrate the wind prior to converting the wind into energy via the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism. The remaining wind is released via a leeward-facing exhaust. Completely enclosed by the protective wind energy conversion chamber, the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism avoids interference by birds and other outside objects.
Owner:SCALZI SAVERIO
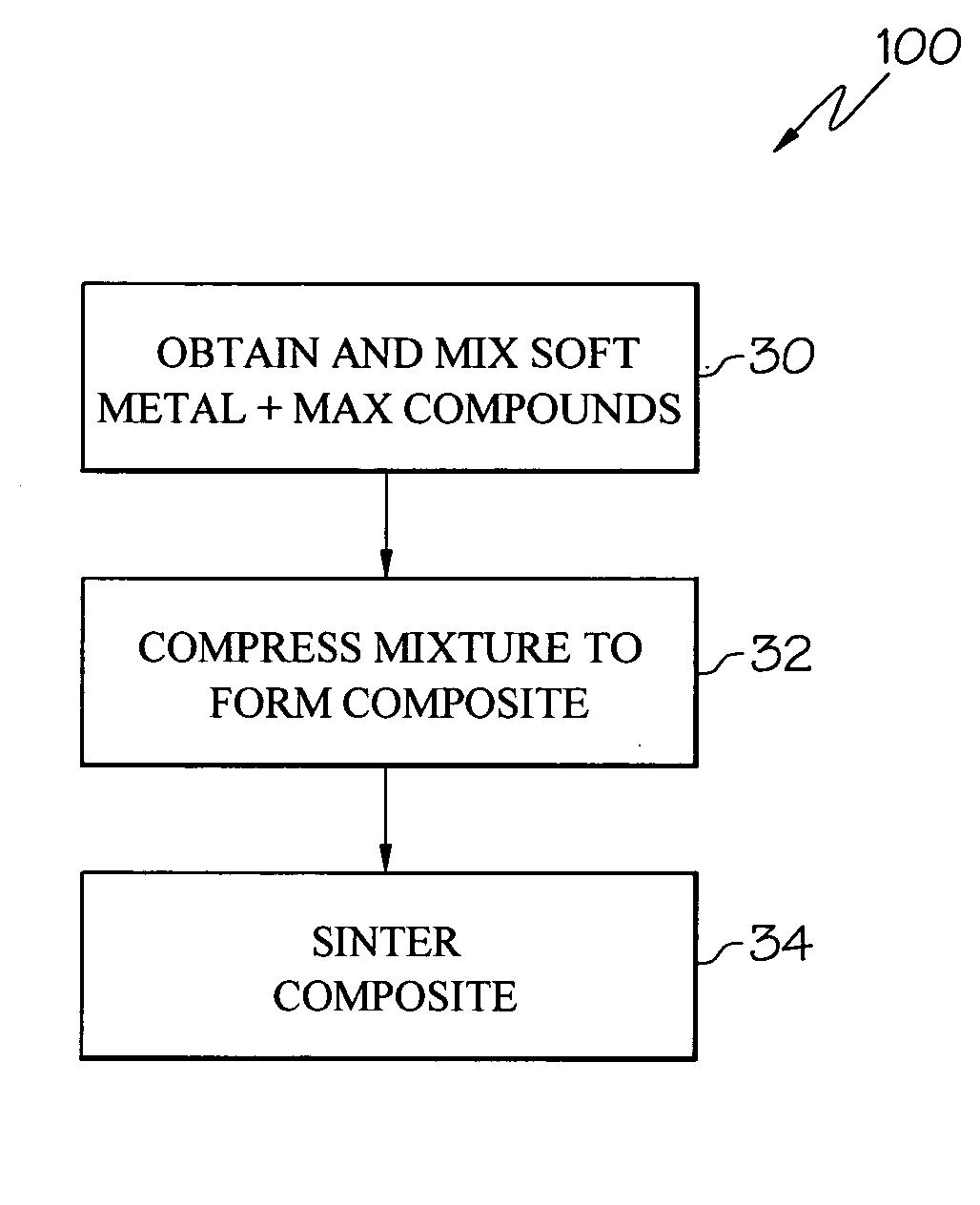
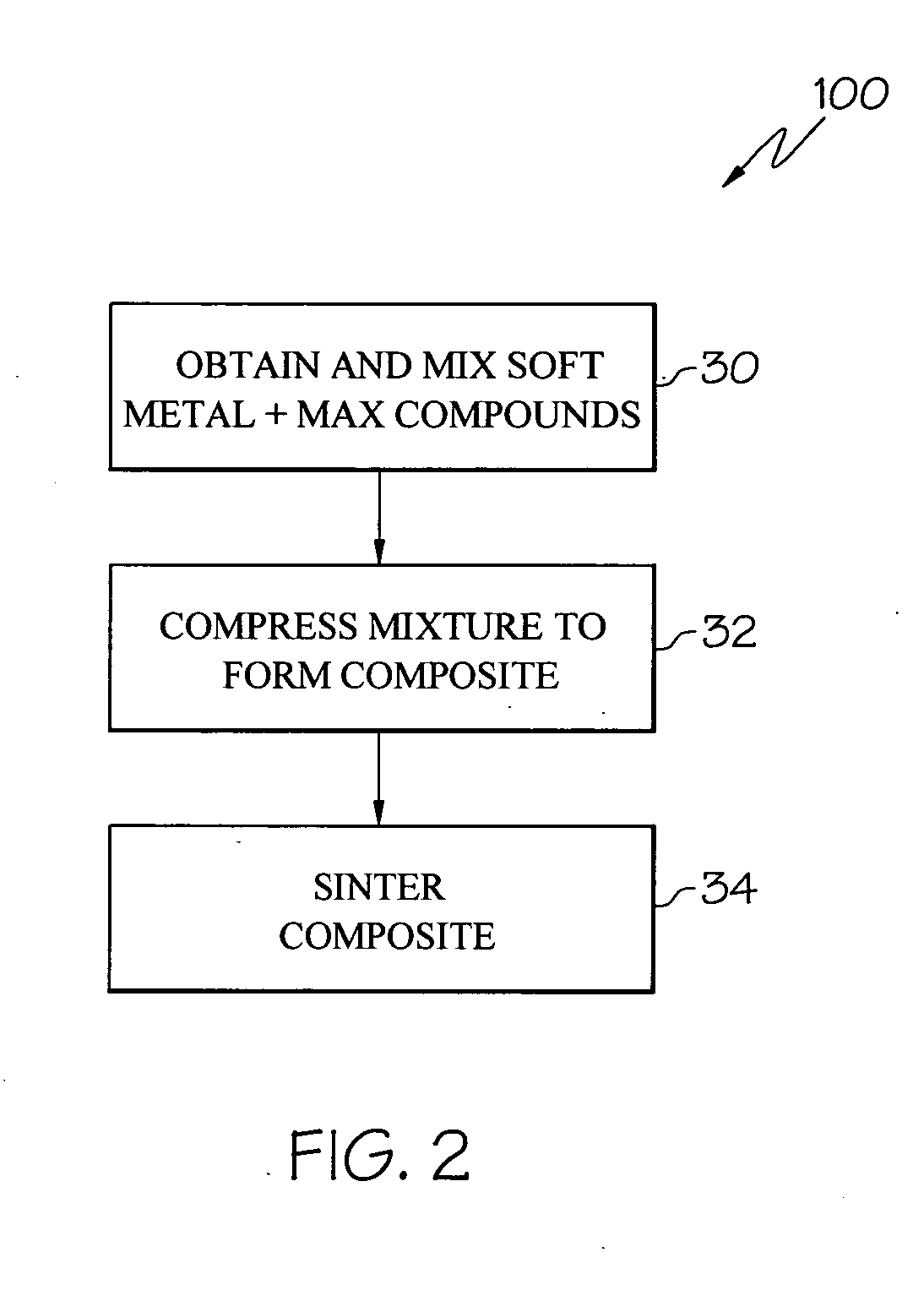
Ternary carbide and nitride composites having tribological applications and methods of making same
A turbomachinery component includes a substrate having a surface, the surface consisting essentially of at least one composite of at least one metal and at least one compound having the chemical formula Mn+1AXn, wherein M is at least one early transition metal selected from groups IIIB, IVB, VB, and VIB, A is at least one element selected from groups IIIA, IVA, VA, VIA, and VIIA, X is one or both of carbon and nitrogen, and n is an integer between 1 and 3. The component is made by compressing a powdered material to form a substrate that consists essentially of the composite and sintering the substrate, or by coating a substrate with the composite.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC +1
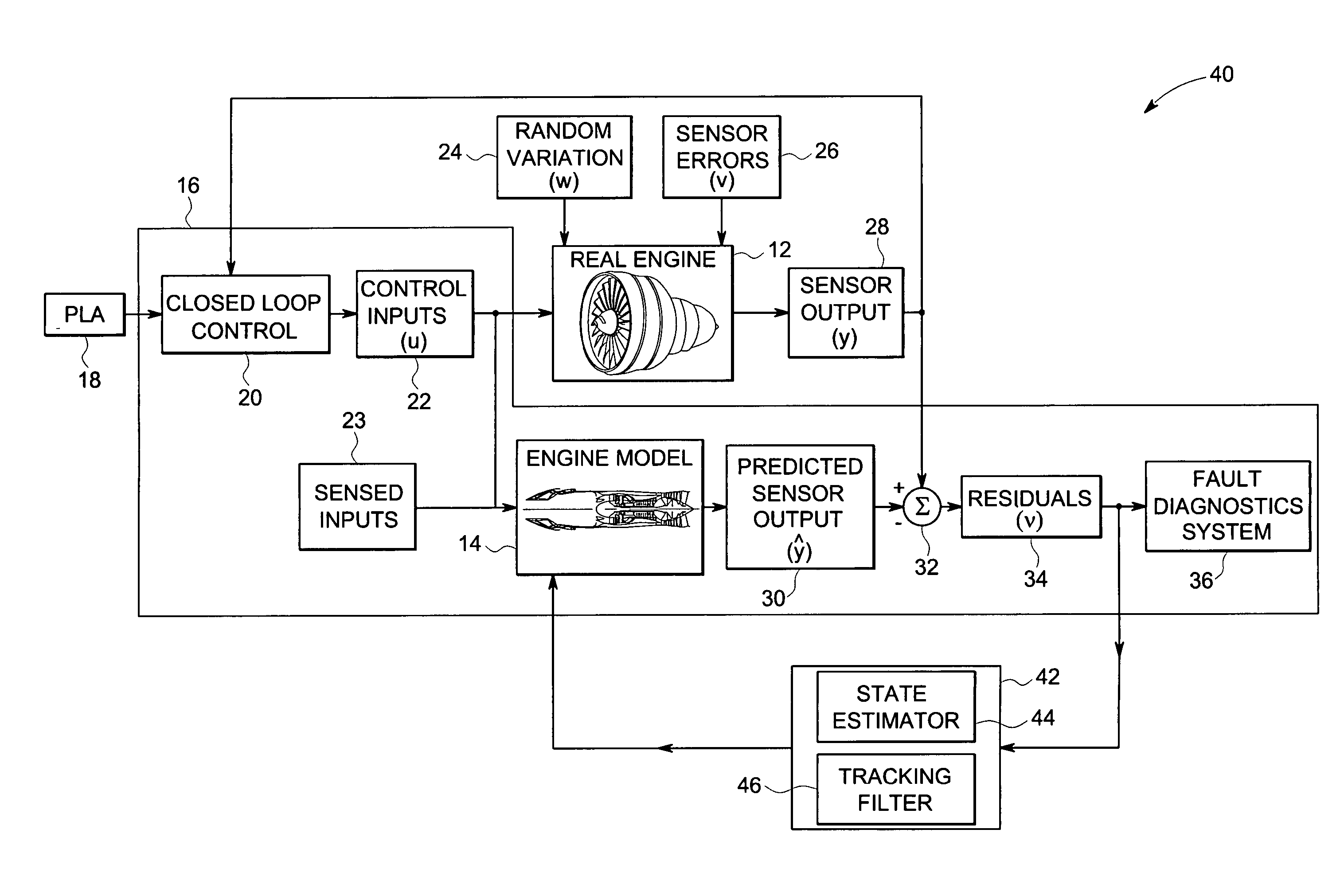
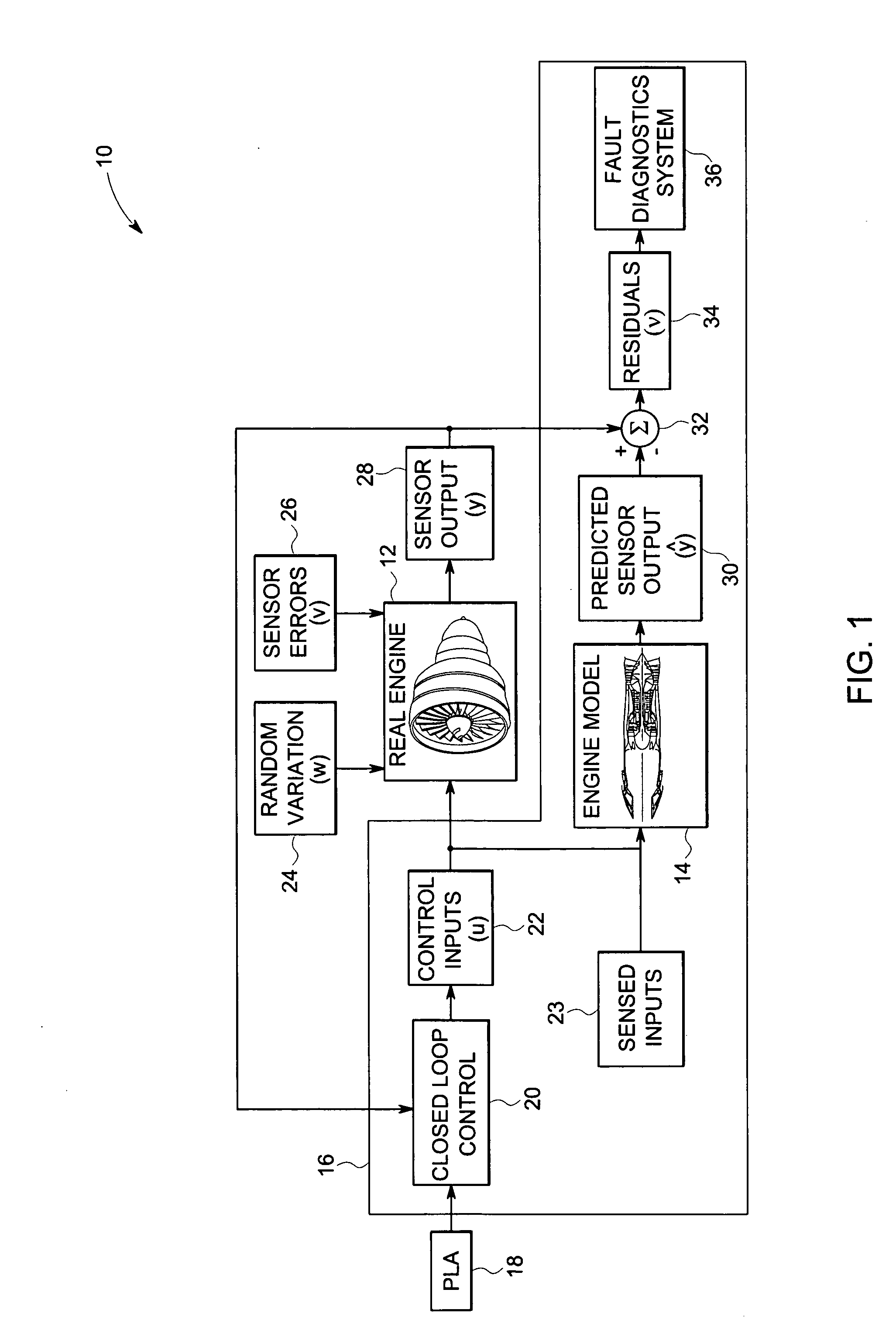
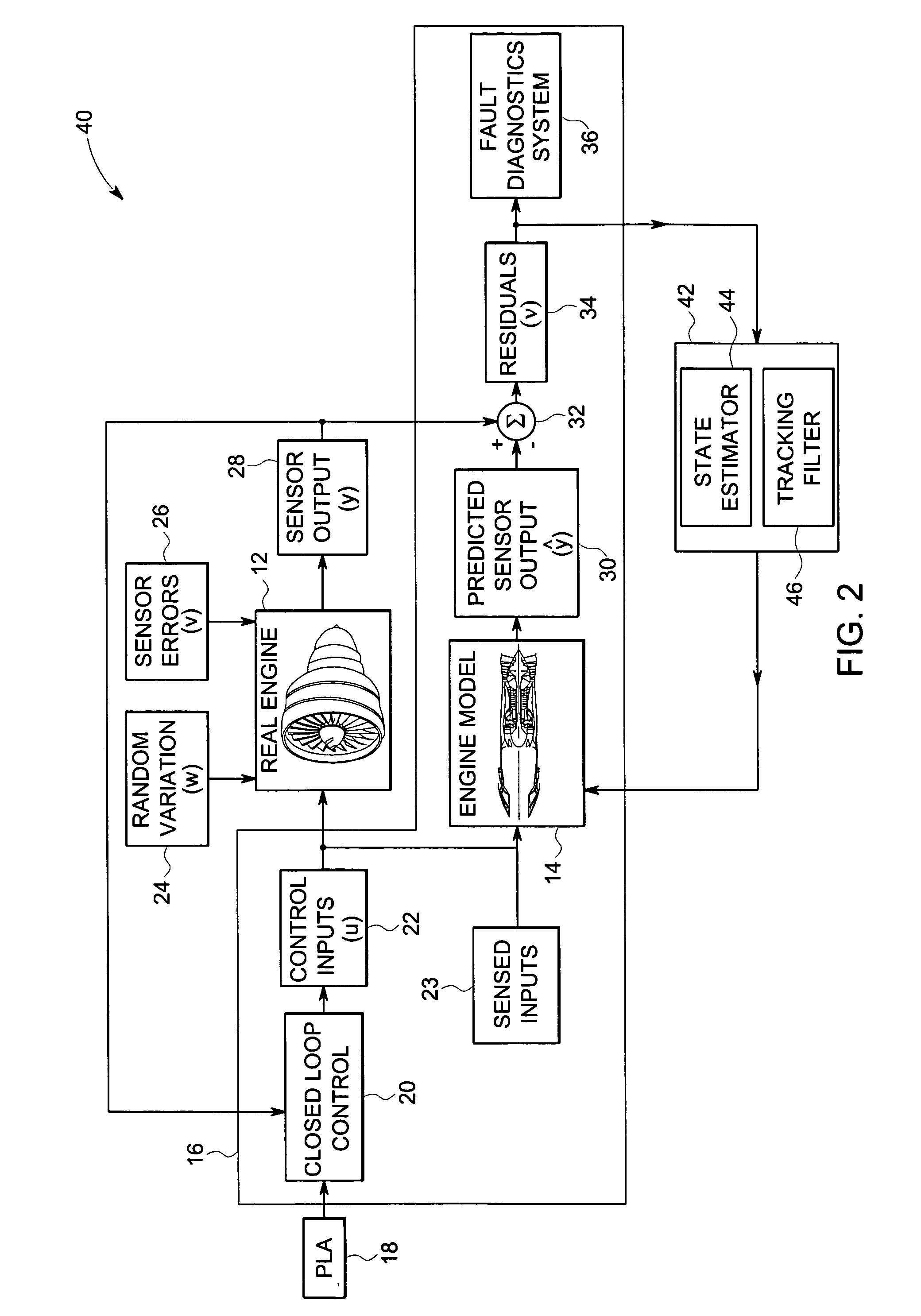
System and method for system-specific analysis of turbomachinery
InactiveUS20060212281A1Residue reductionGeometric CADRegistering/indicating working of machinesAutomotive engineeringTurbomachinery
A method for system-specific analysis of an engine includes applying control inputs to the engine and an engine model and estimating outputs from the engine model based upon the control inputs. The method includes sensing outputs from the engine and analyzing residuals between estimated and sensed outputs. The method also includes customizing the engine model to reduce residuals for a particular engine and detecting the faults in the engine based upon the residuals for the particular engine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
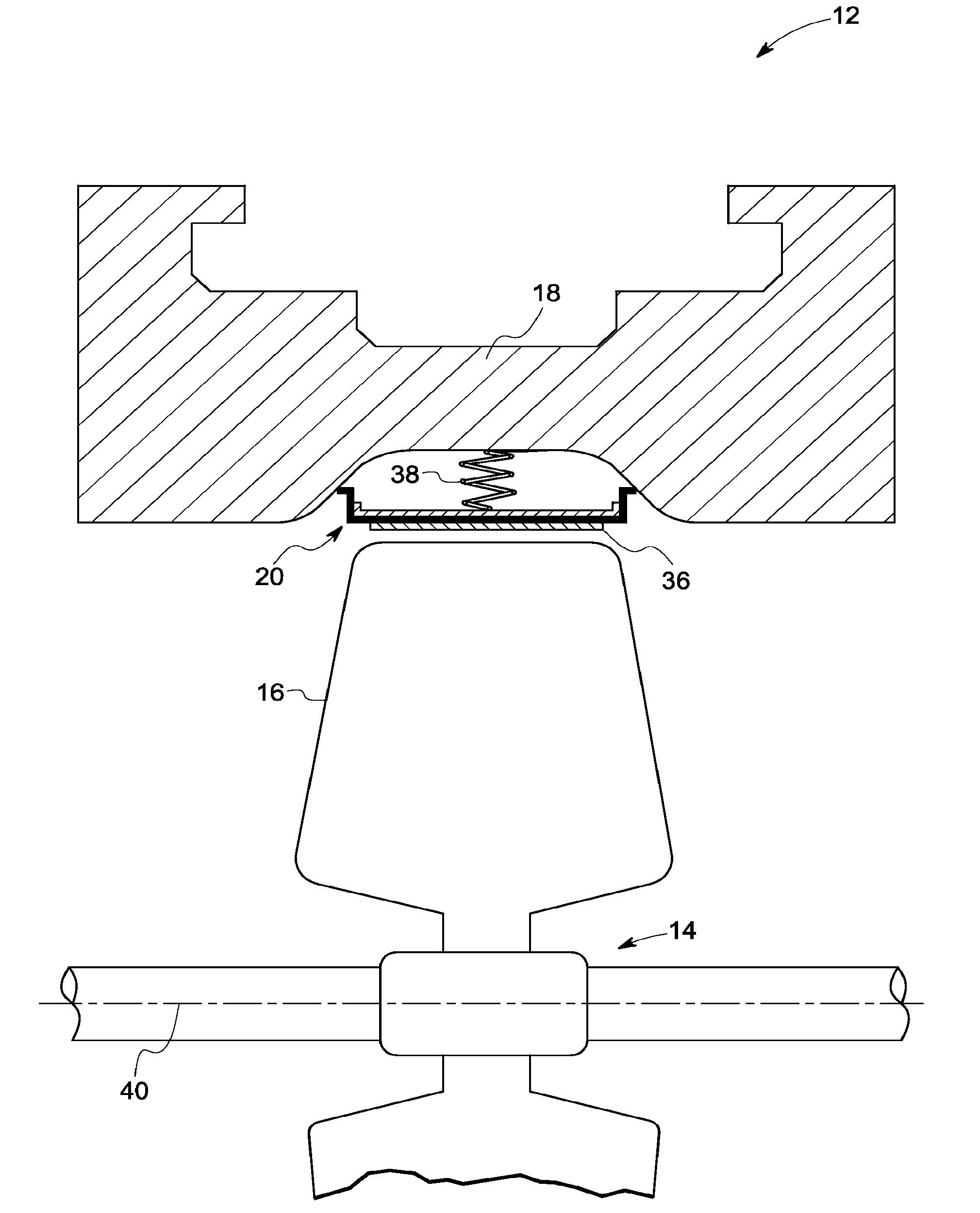
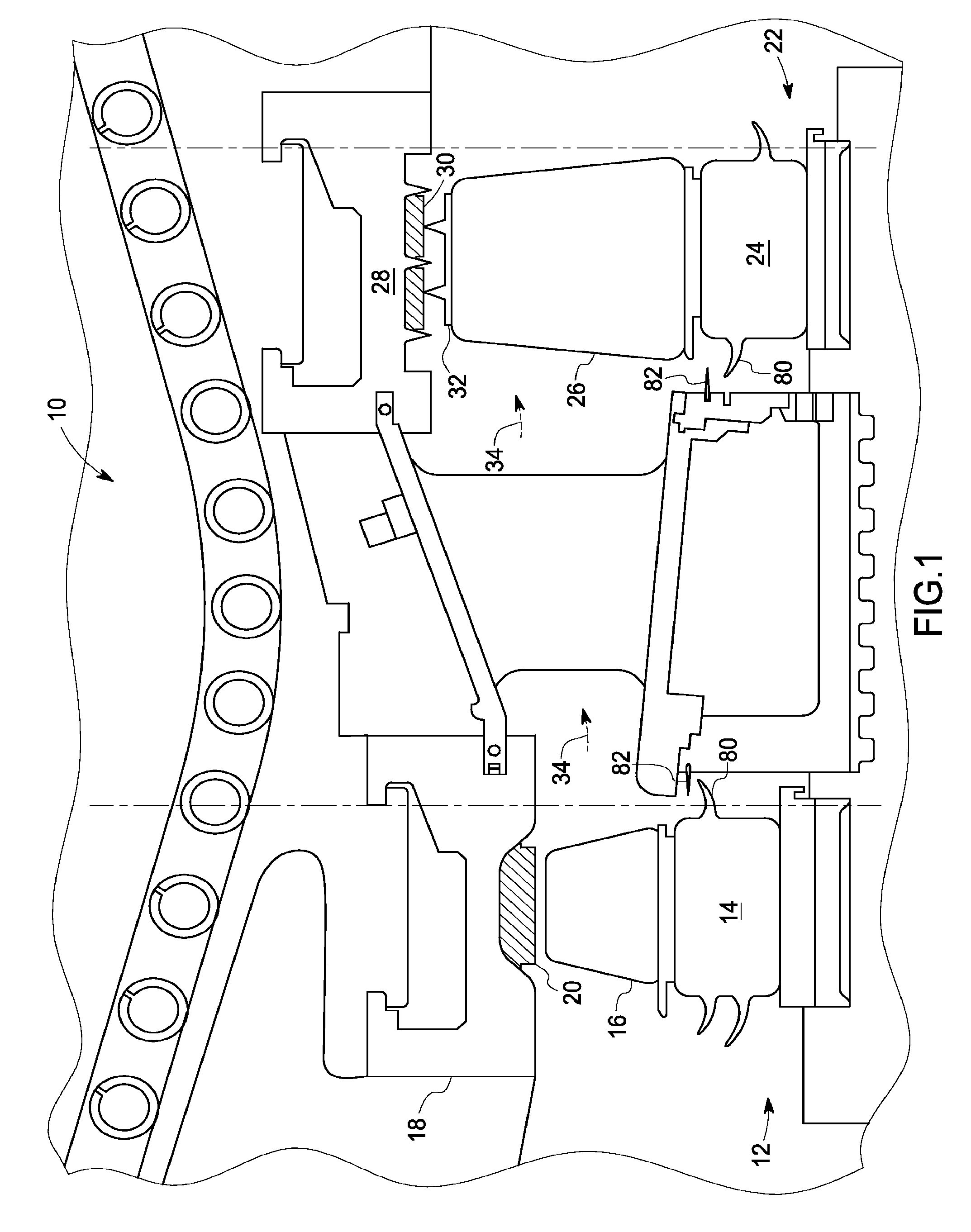
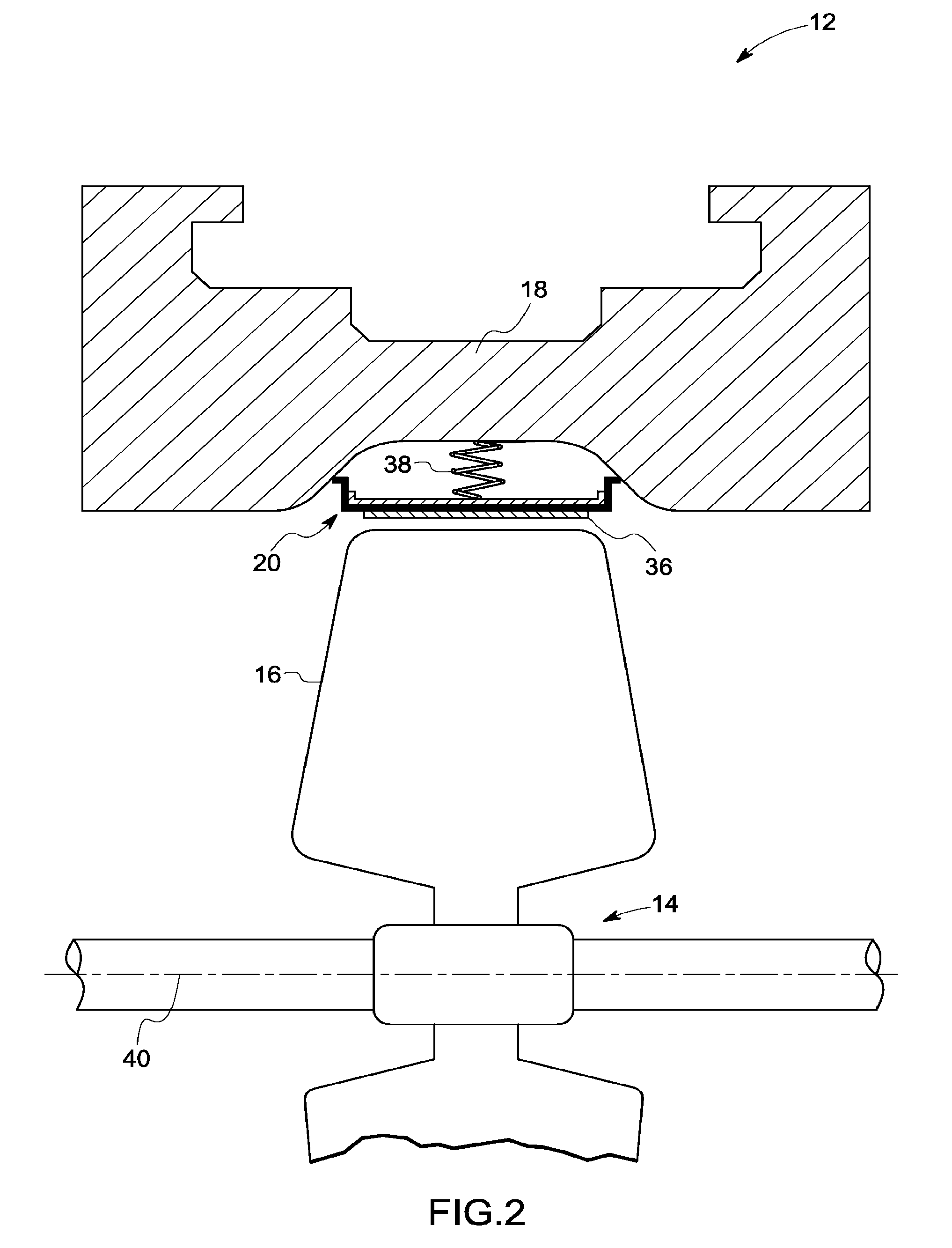
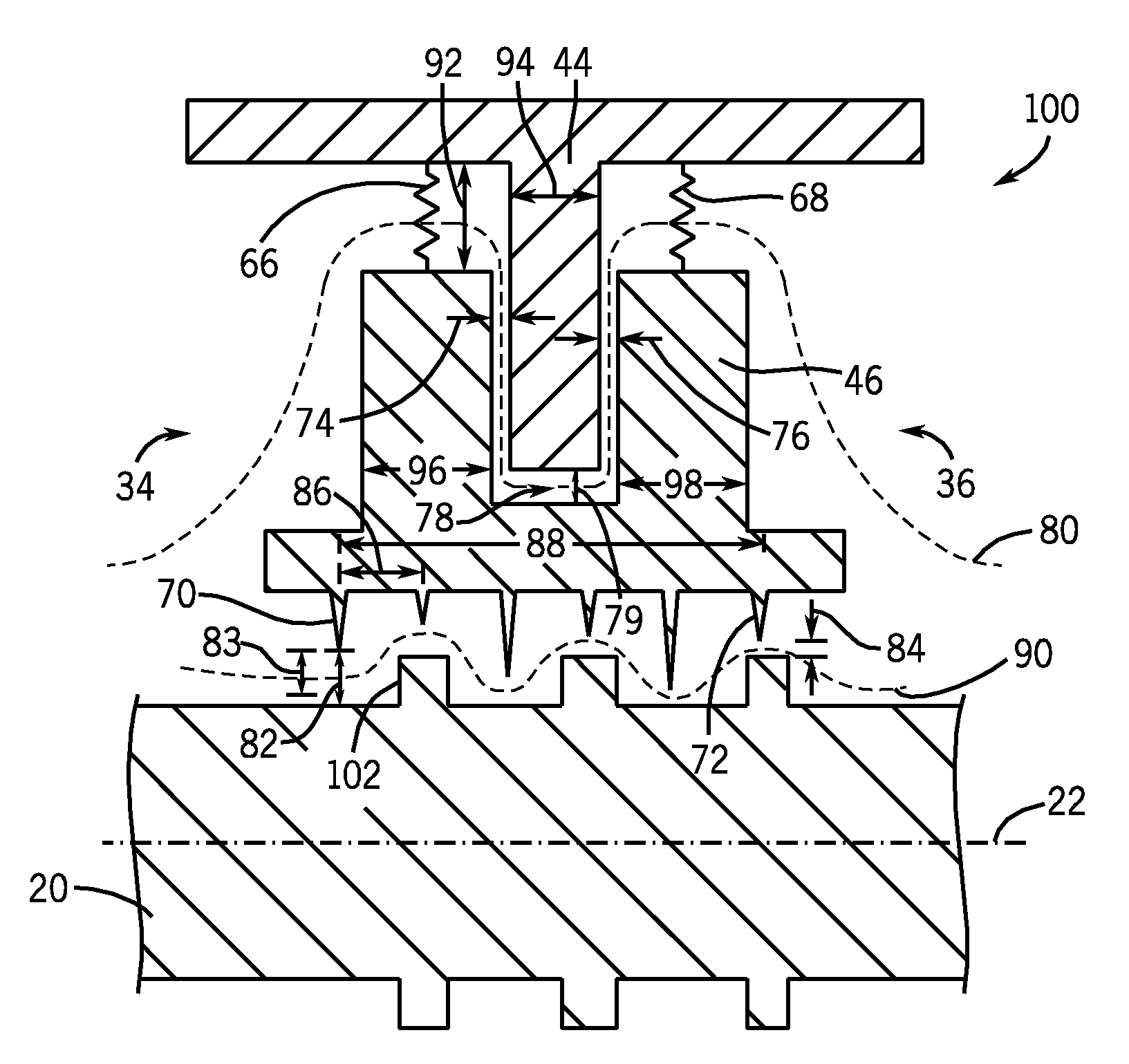
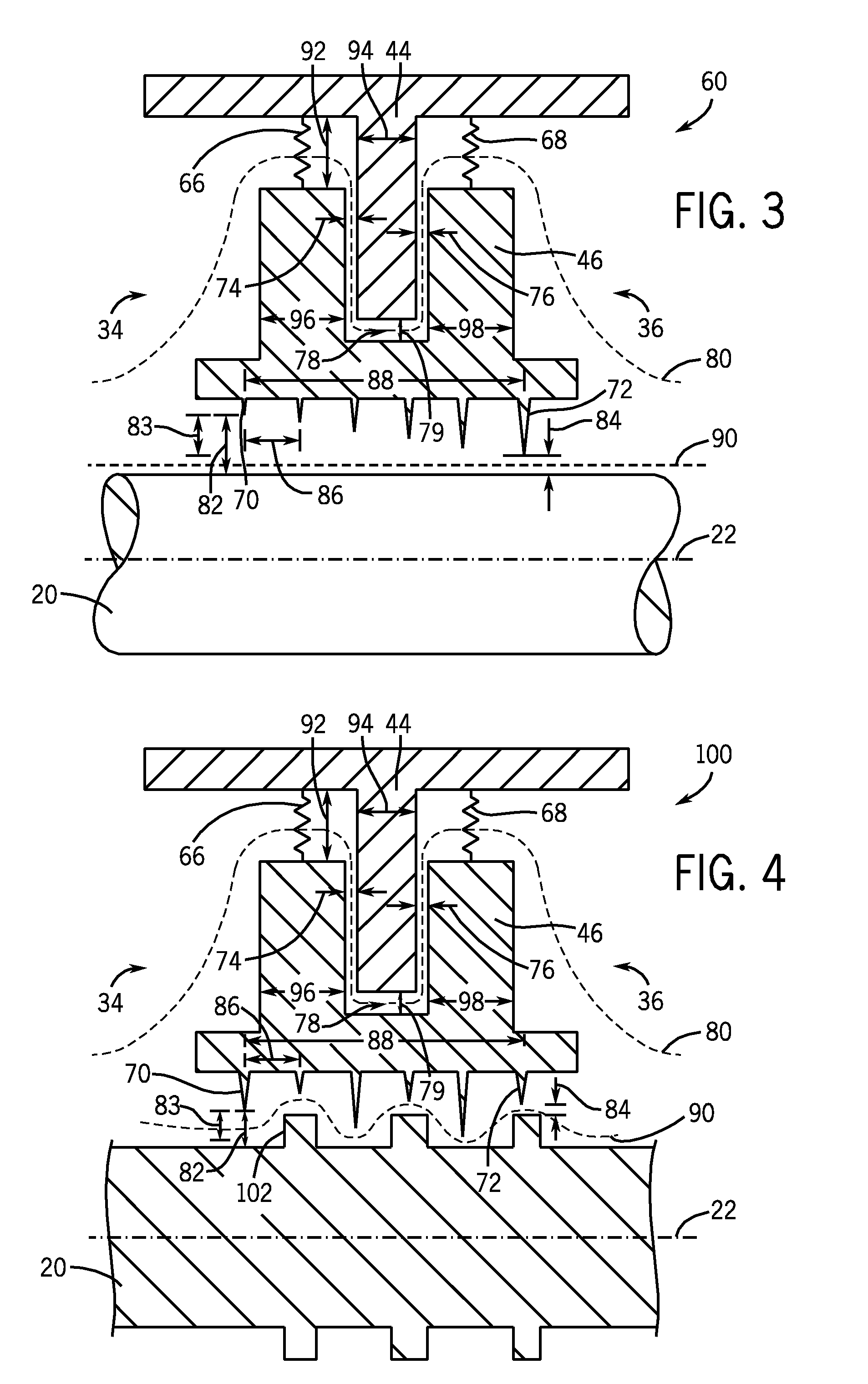
Sealing device and method for turbomachinery
A compliant seal for use between rotating blades and a static shroud surrounding the rotating blades in a steam or gas turbine is disclosed. The seal includes a tip surface, substantially resistant to wear due to rubbing by the tip of the rotating blades, and an elastic biasing member, comprising a biasing element. The wear-resistant surface is thus biased against the tips of the rotating blades to seal a gas path between the rotating blades and the static shroud.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
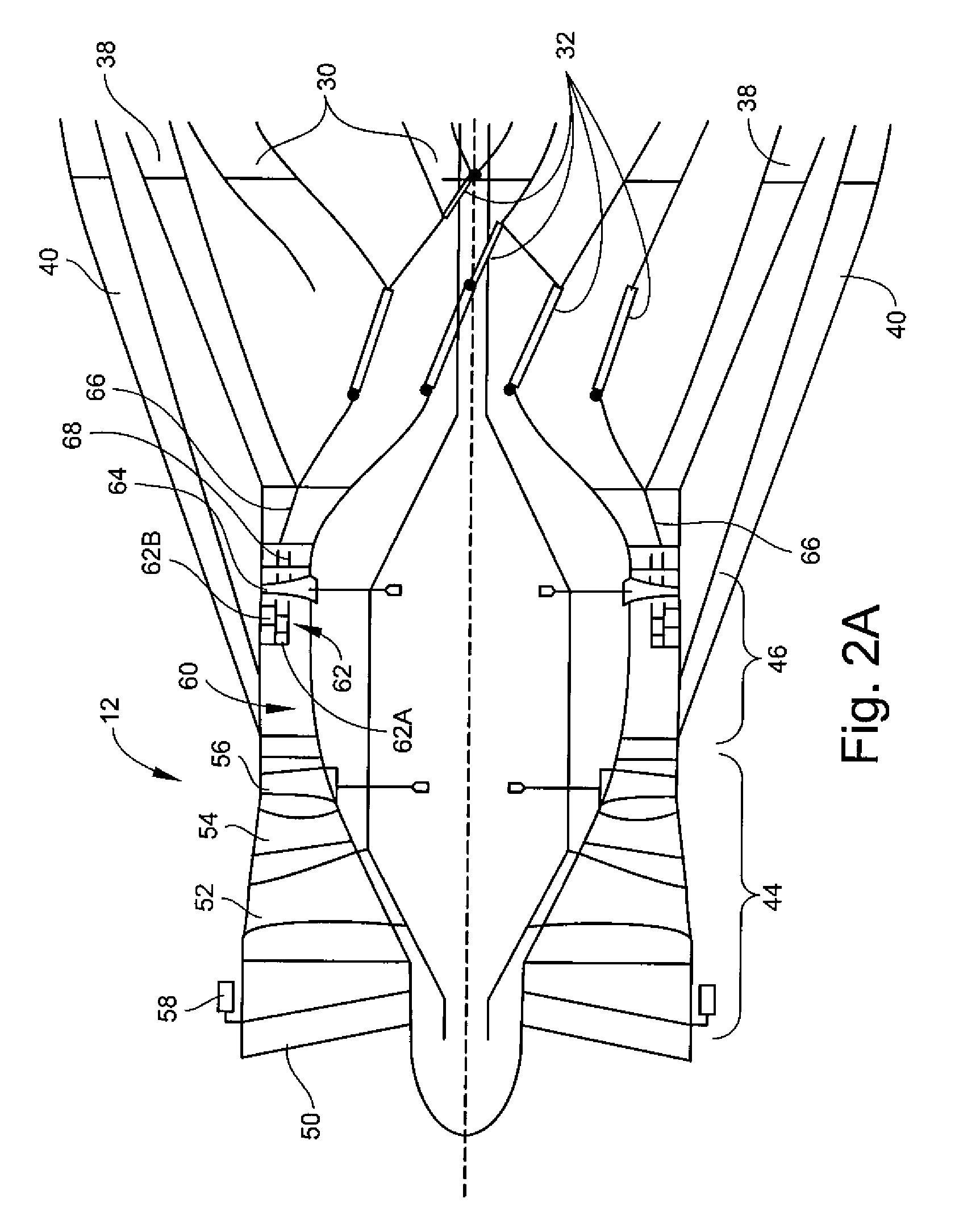
Airfoil embodying mixed loading conventions
A high-lift airfoil embodying a combination of loading conventions in a single design specifically to reduce and control total pressure losses that occur in the flow channels between airfoils employed in turbomachinery applications is disclosed herein. The mixed-loading high-lift airfoil designs embody and exhibit the best total profile and secondary loss characteristics possessed by both aft-loaded airfoil and front-loaded airfoil conventions through controlling the development and interaction of boundary layers forming along the surfaces of the airfoils and the endwalls in such applications. The mixed-loading high-lift airfoil may be utilized in both rotating and non-rotating turbomachinery applications.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
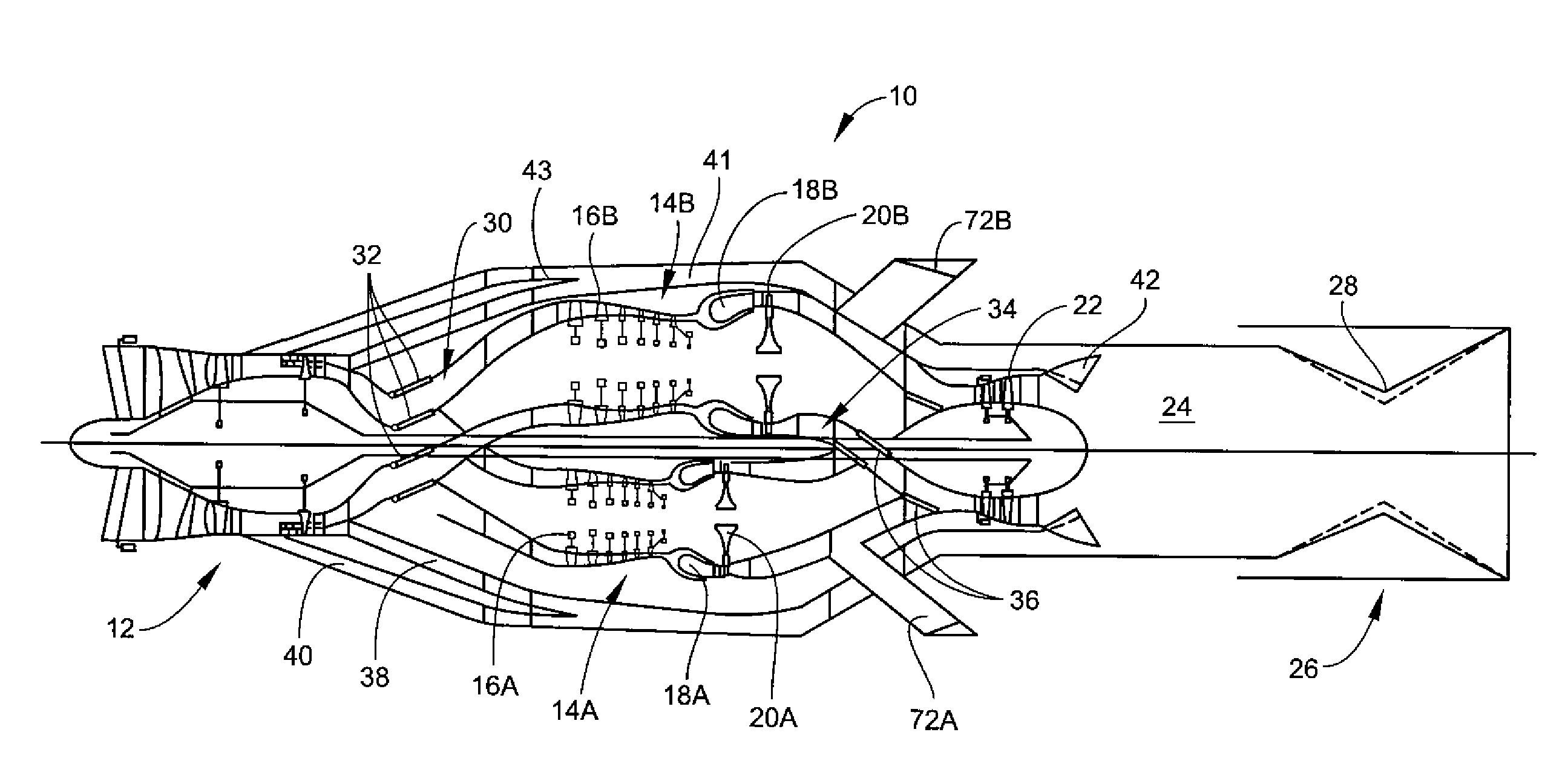
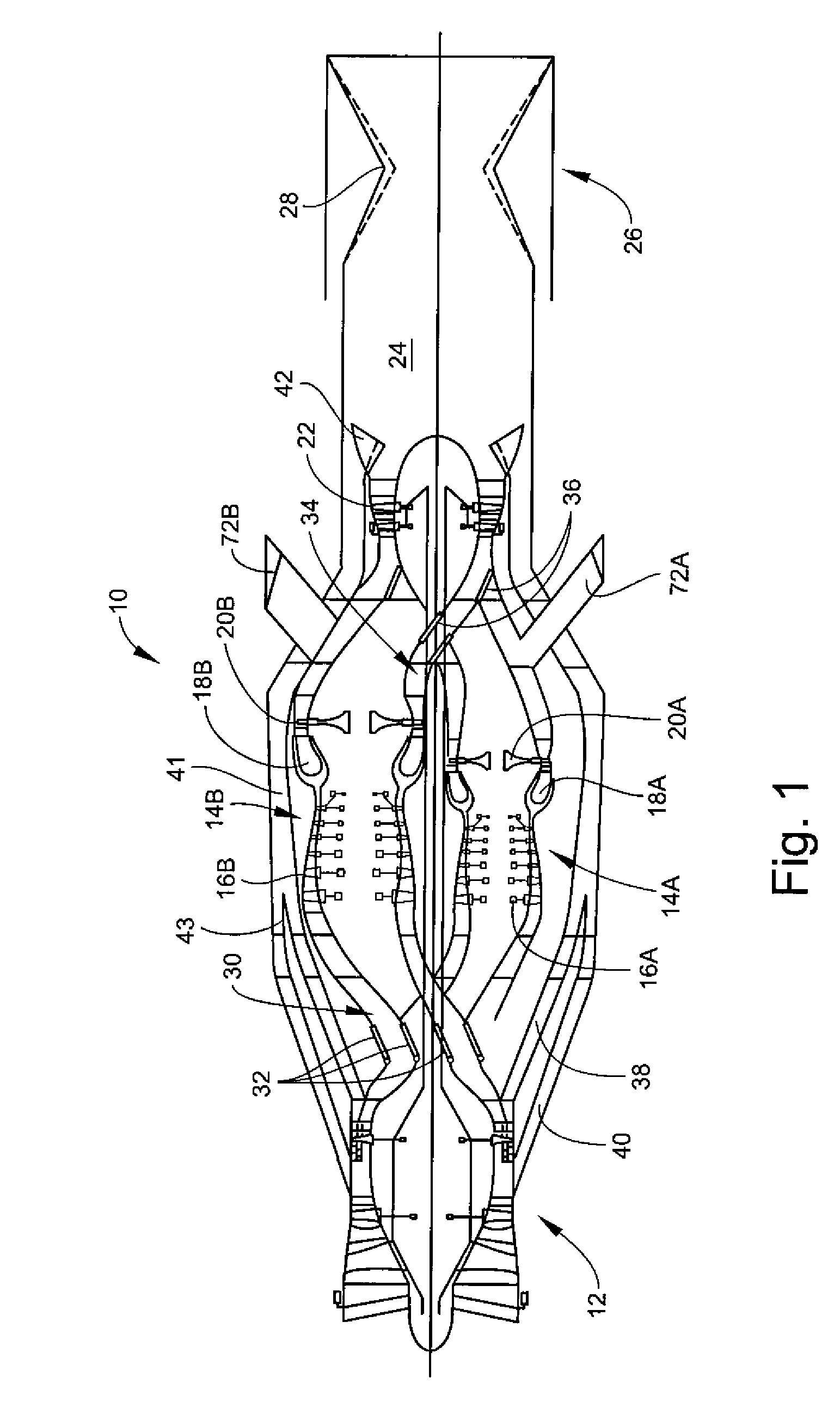
Convertible gas turbine engine
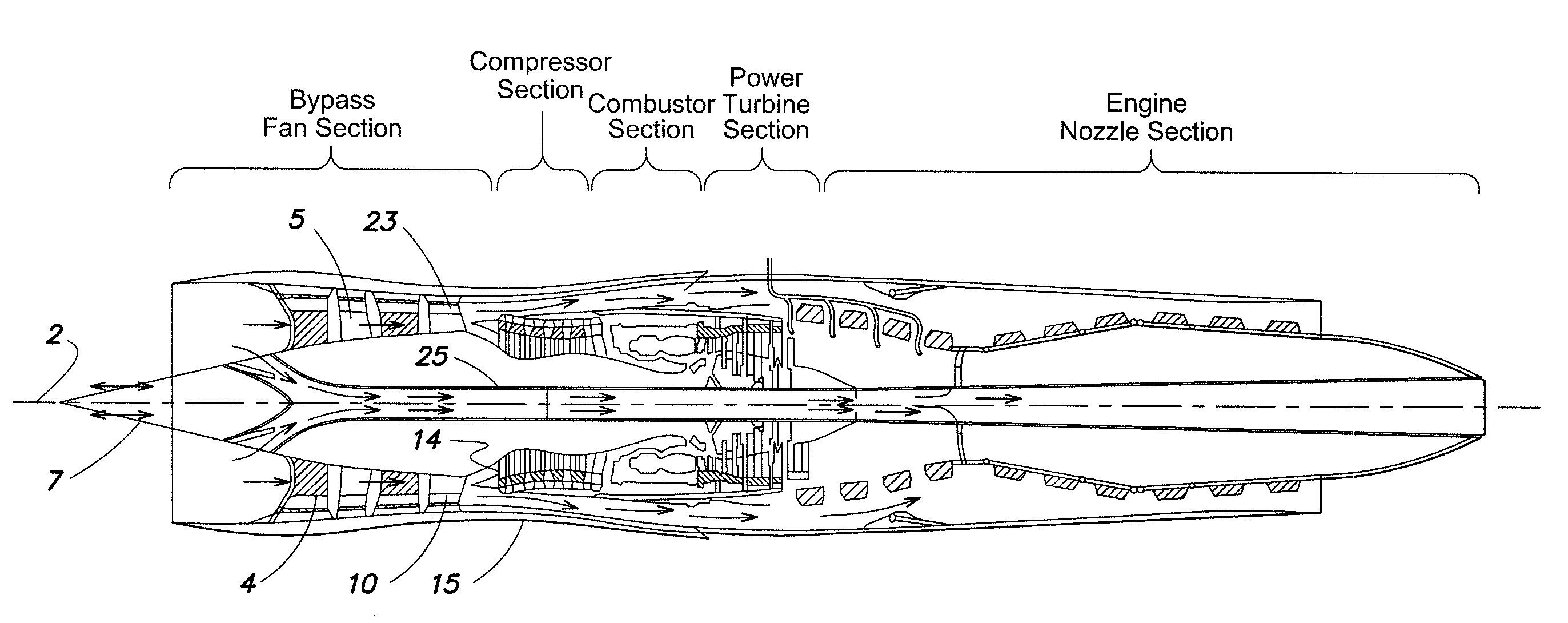
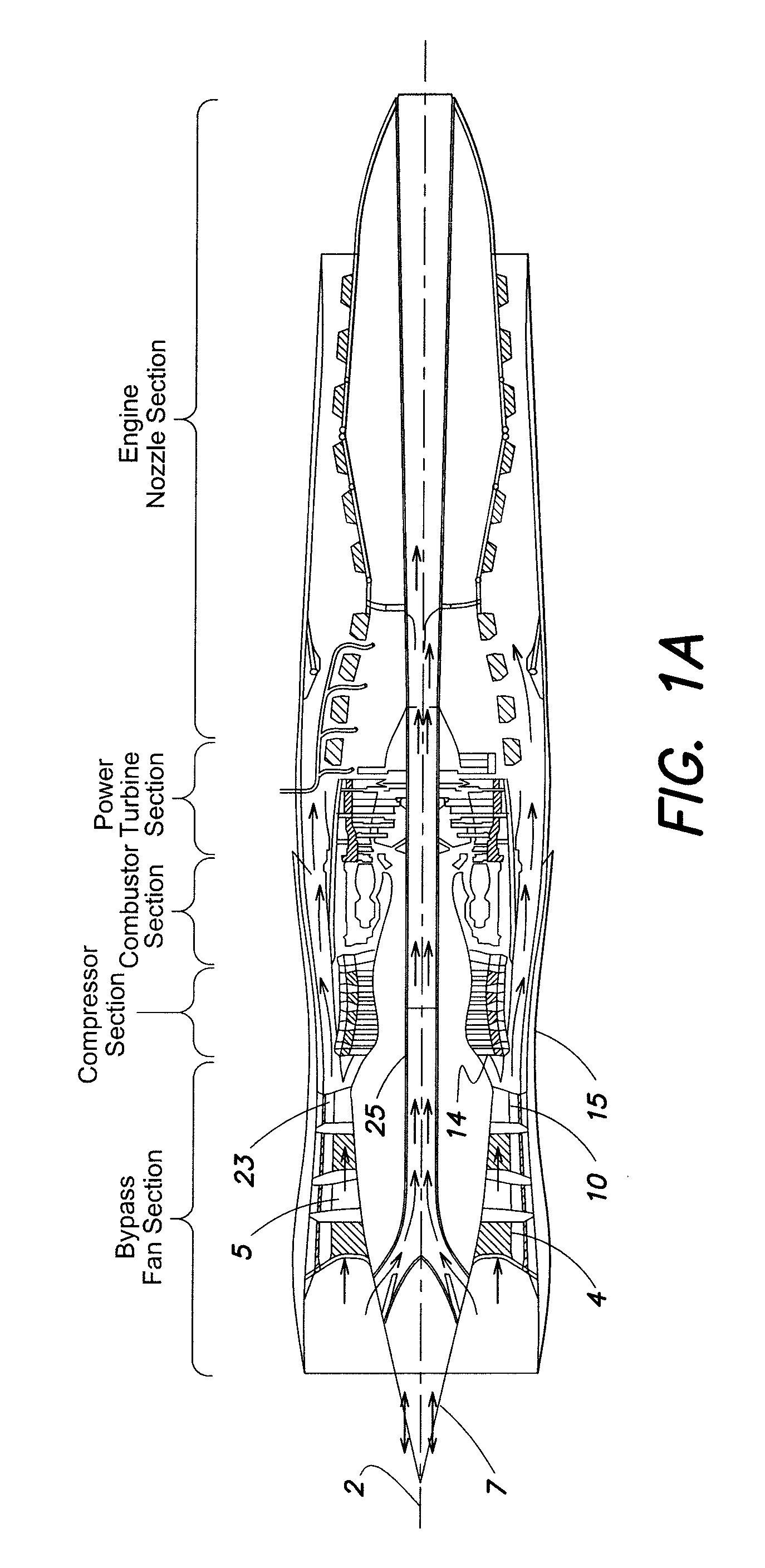
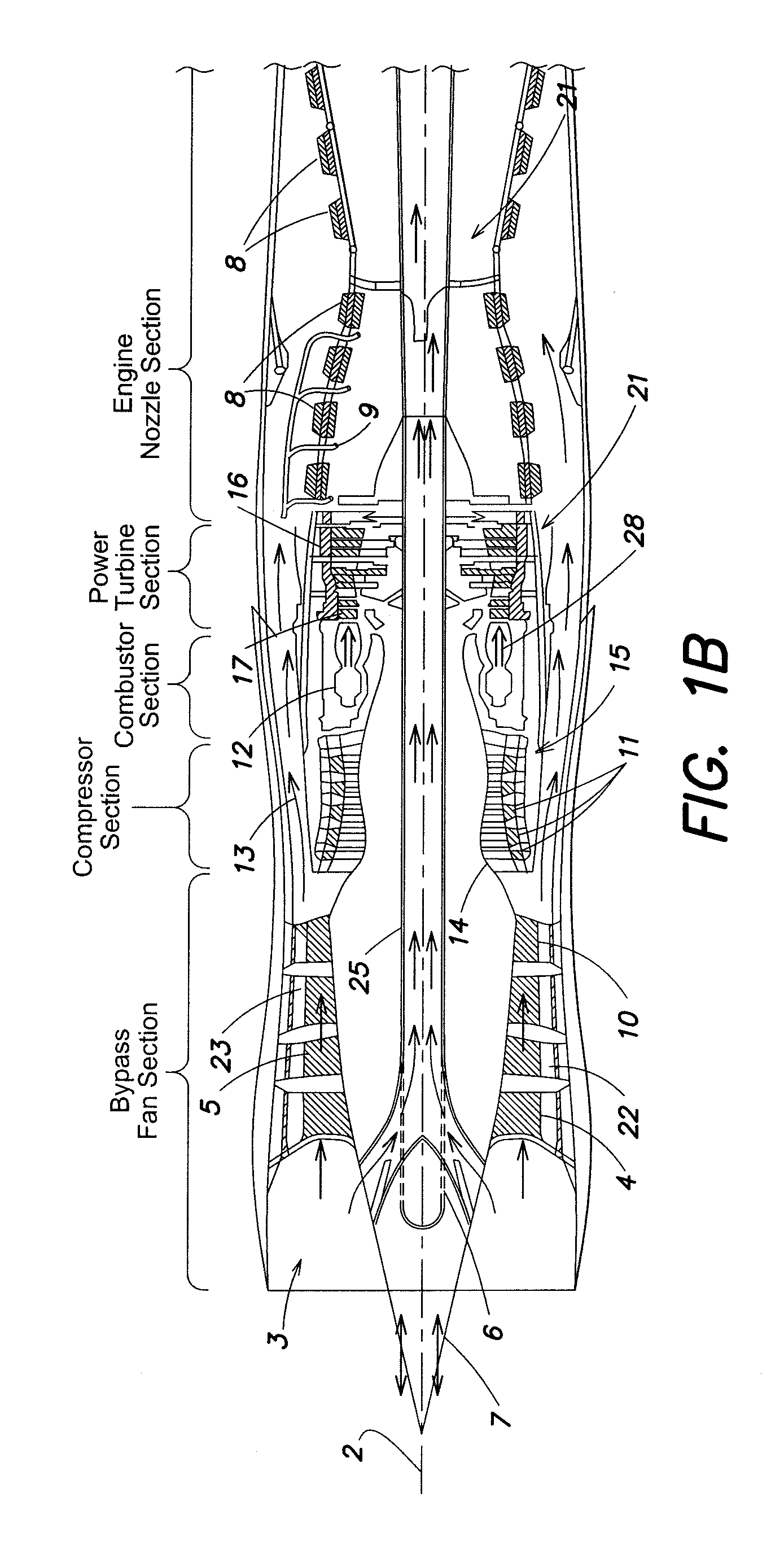
A gas turbine engine includes a turbomachinery core operable to generate a flow of pressurized combustion gases at a variable flow rate, while maintaining a substantially constant core pressure ratio; a rotating fan disposed upstream of the core, the fan adapted to extract energy from the core and generate a first flow of air which is compressed at a first pressure ratio; and at least a first bypass duct surrounding the core downstream of the fan adapted to selectively receive at least a first selected portion of the first flow which is compressed at a second pressure ratio lower than the first pressure ratio, and to bypass the first selected portion around the core, thereby varying a bypass ratio of the engine. The fan is adapted to maintain a flow rate of the first flow substantially constant, independent of the bypass ratio.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for predicting turbomachinery failure events employing genetic algorithm
ActiveUS20090100293A1Increase valueFault responseTesting/monitoring control systemsComputer scienceFitness function
A method for predicting or detecting an event in turbomachinery includes the steps of obtaining operational data from at least one machine and at least one peer machine. The operational data comprises a plurality of performance metrics. A genetic algorithm (GA) analyzes the operational data, and generates a plurality of clauses, which are used to characterize the operational data. The clauses are evaluated as being either “true” or “false”. A fitness function identifies a fitness value for each of the clauses. A perturbation is applied to selected clauses to create additional clauses, which are then added to the clauses group. The steps of applying a fitness function, selecting a plurality of clauses, and applying a perturbation can be repeated until a predetermined fitness value is reached. The selected clauses are then applied to the operational data from the machine to detect or predict a past, present or future event.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
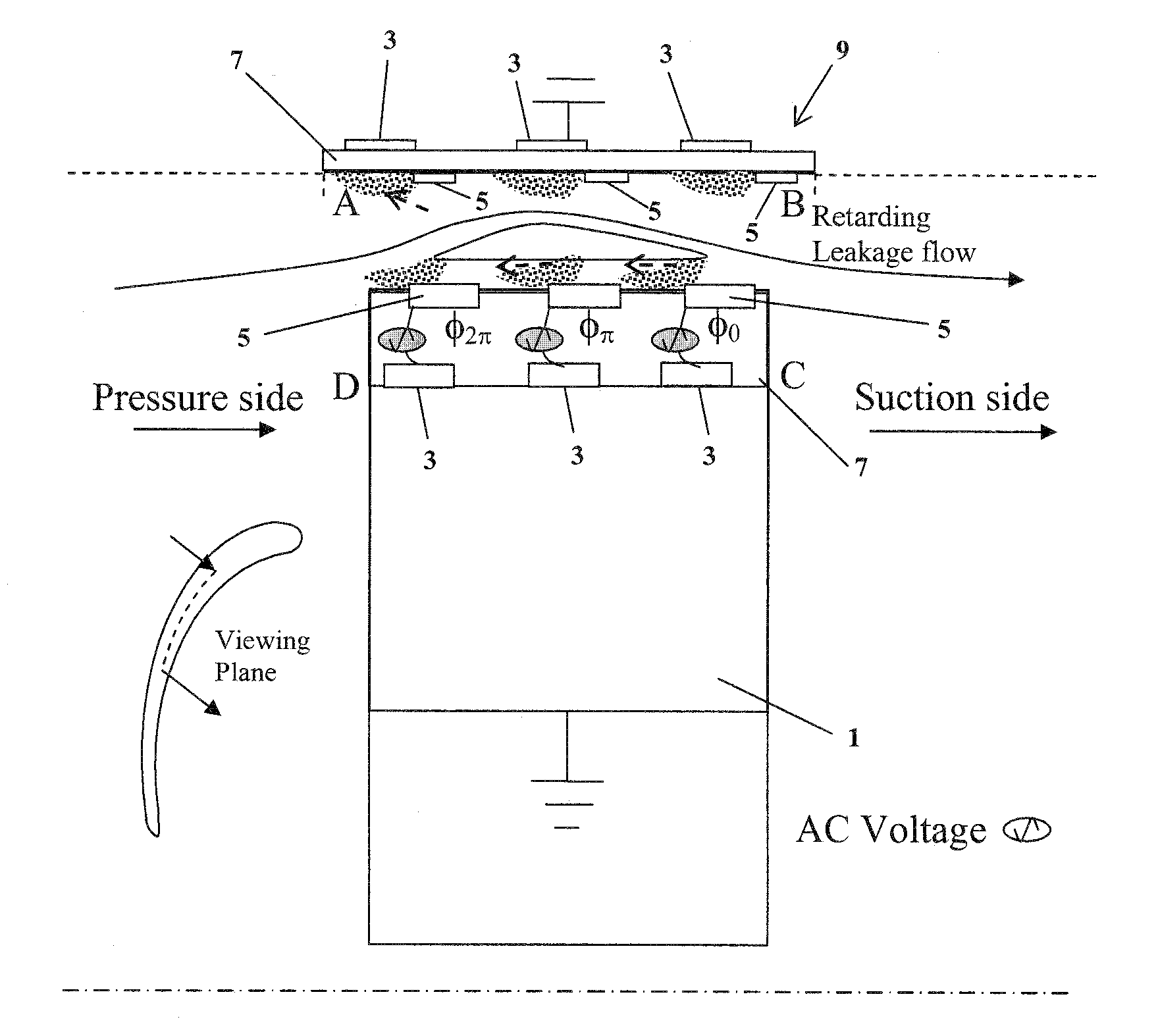
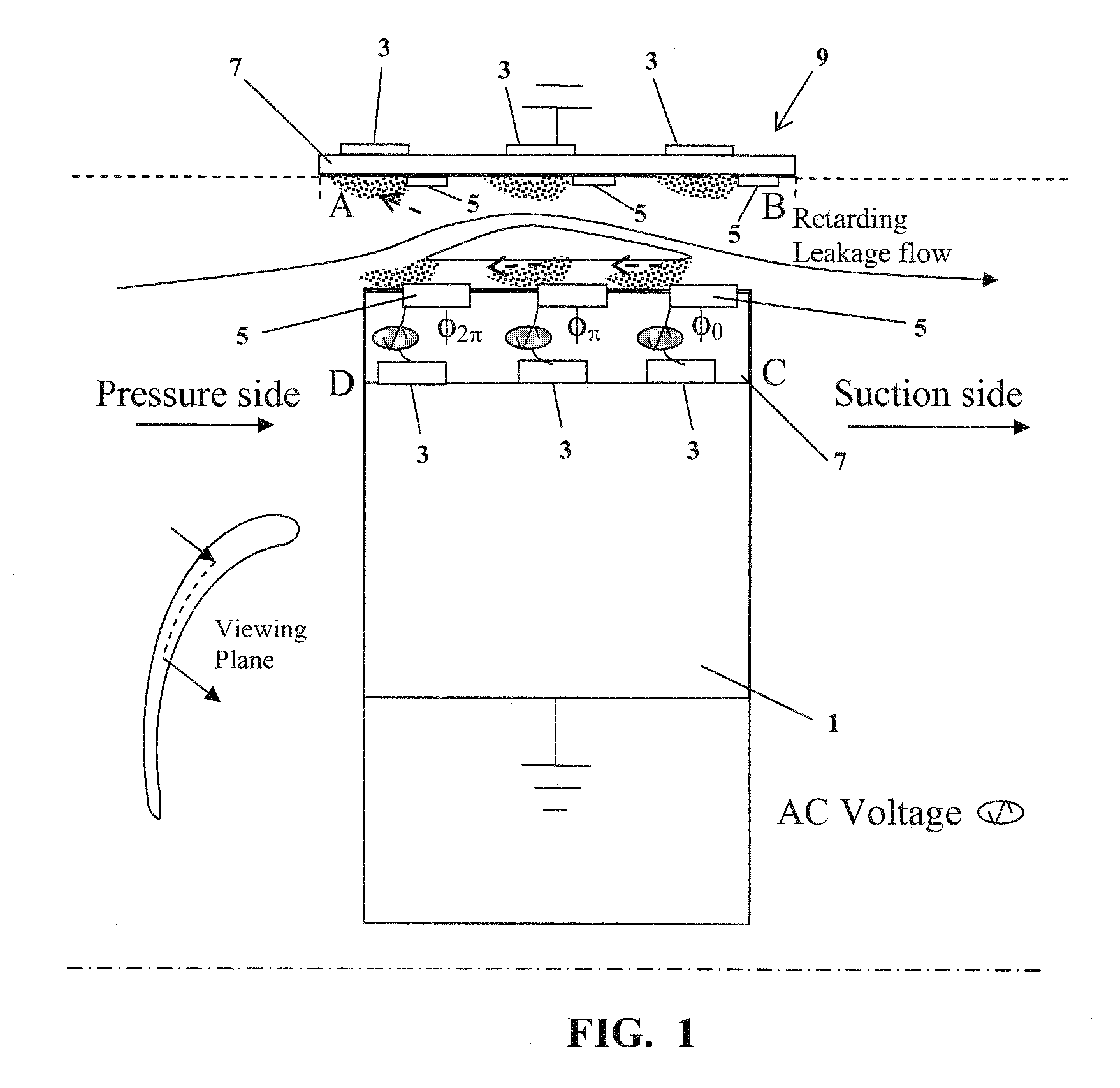
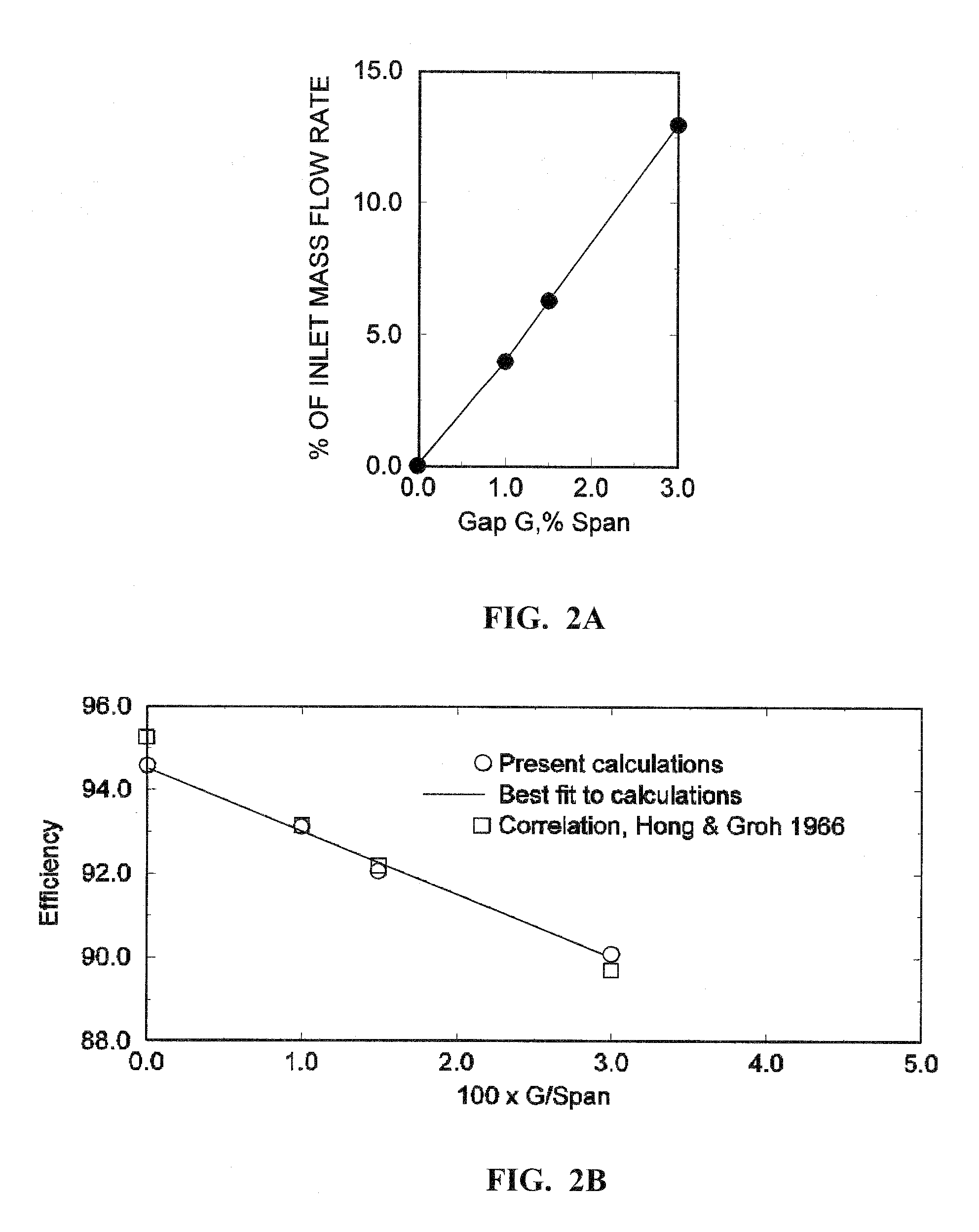
Electrodynamic Control of Blade Clearance Leakage Loss in Turbomachinery Applications
Electrodynamic control of fluid leakage loss is provided. Embodiments utilize electrohydrodynamic (EHD) principles to control and / or reduce leakage flow in turbomachinery. Electrodes can be used to provide a flow actuation mechanism inside the clearance gap for generating discharge. The electrodes can be positioned to have geometric asymmetry. Embodiments provide the electrodes on a turbine blade. The blade can have a DC power that can function as a square pulsed DC wave with the duty cycle equal to the blade passing frequency and the stator can be grounded. In an embodiment, the stator can have the actuator of the electrode-insulator assembly attached to the inside. In one embodiment, the actuators can be arranged just on the stator or casing. The phase and power supply to individual electrodes can be adapted as needed. In one embodiment, the phase can be lagged for accurate control of leakage flow. The control of the power supply to the electrodes can involve a closed control loop that monitors tip gap size.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Nonlinearly stacked low noise turbofan stator
A nonlinearly stacked low noise turbofan stator vane having a characteristic curve that is characterized by a nonlinear sweep and a nonlinear lean is provided. The stator is in an axial fan or compressor turbomachinery stage that is comprised of a collection of vanes whose highly three-dimensional shape is selected to reduce rotor-stator and rotor-strut interaction noise while maintaining the aerodynamic and mechanical performance of the vane. The nonlinearly stacked low noise turbofan stator vane reduces noise associated with the fan stage of turbomachinery to improve environmental compatibility
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
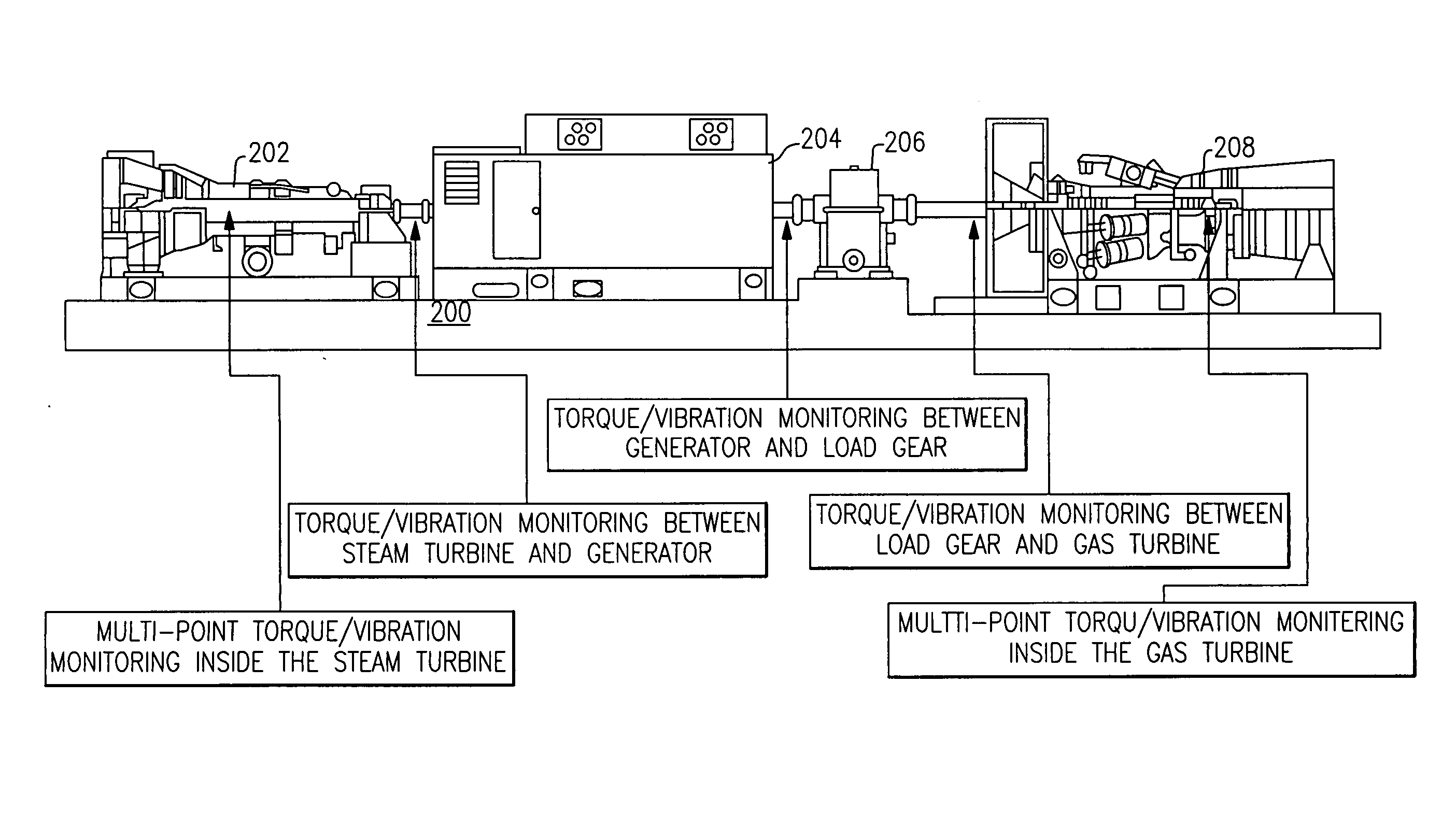
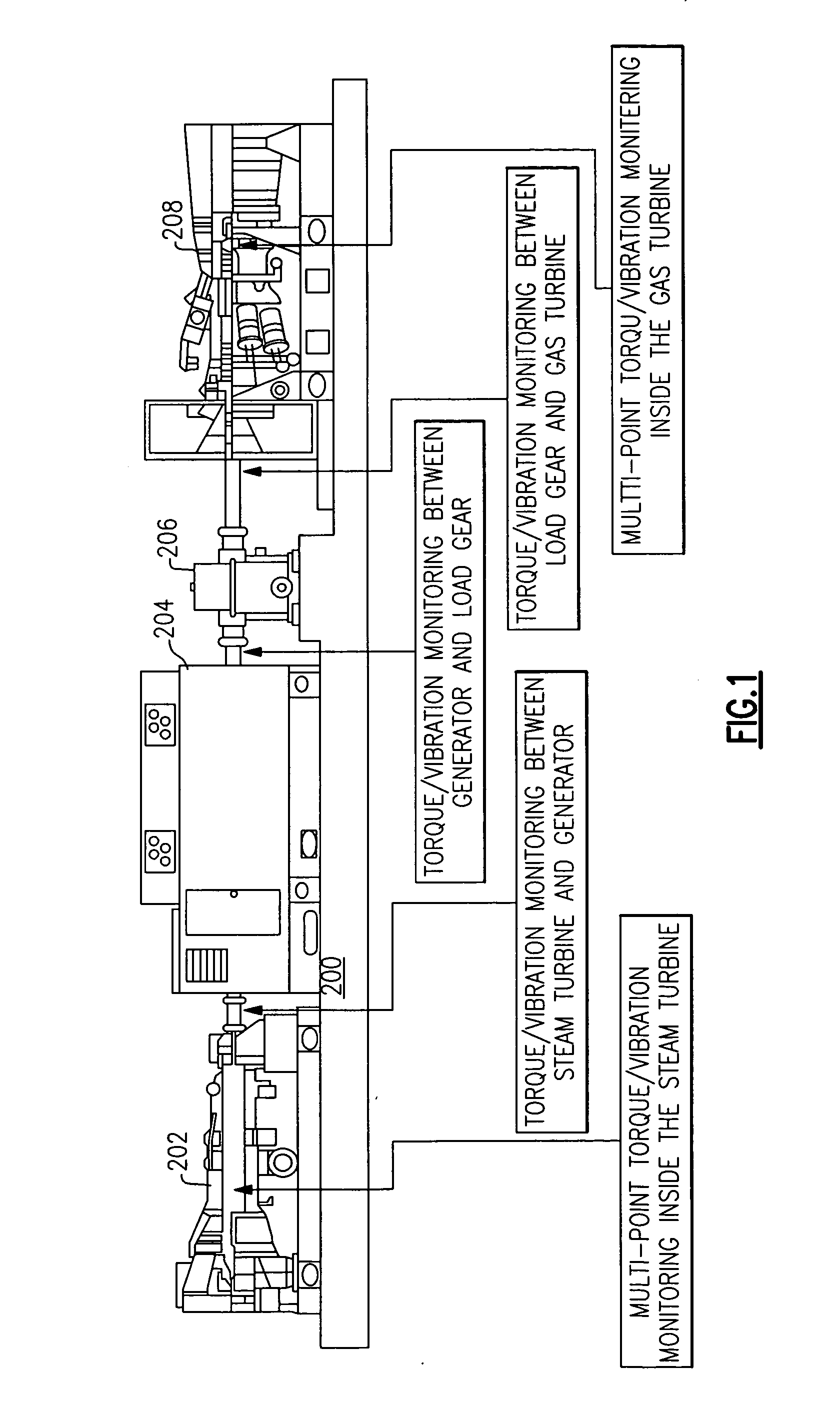
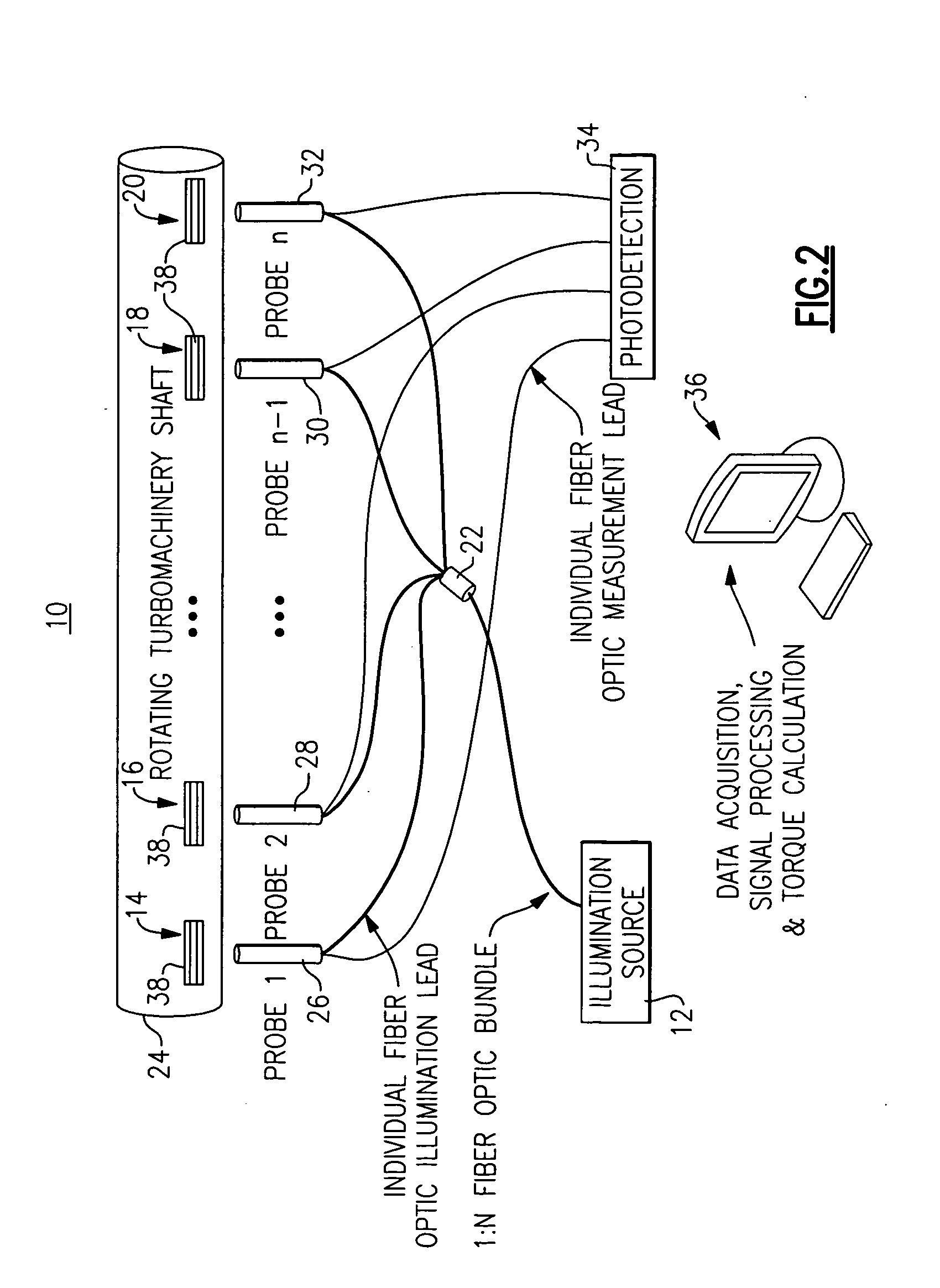
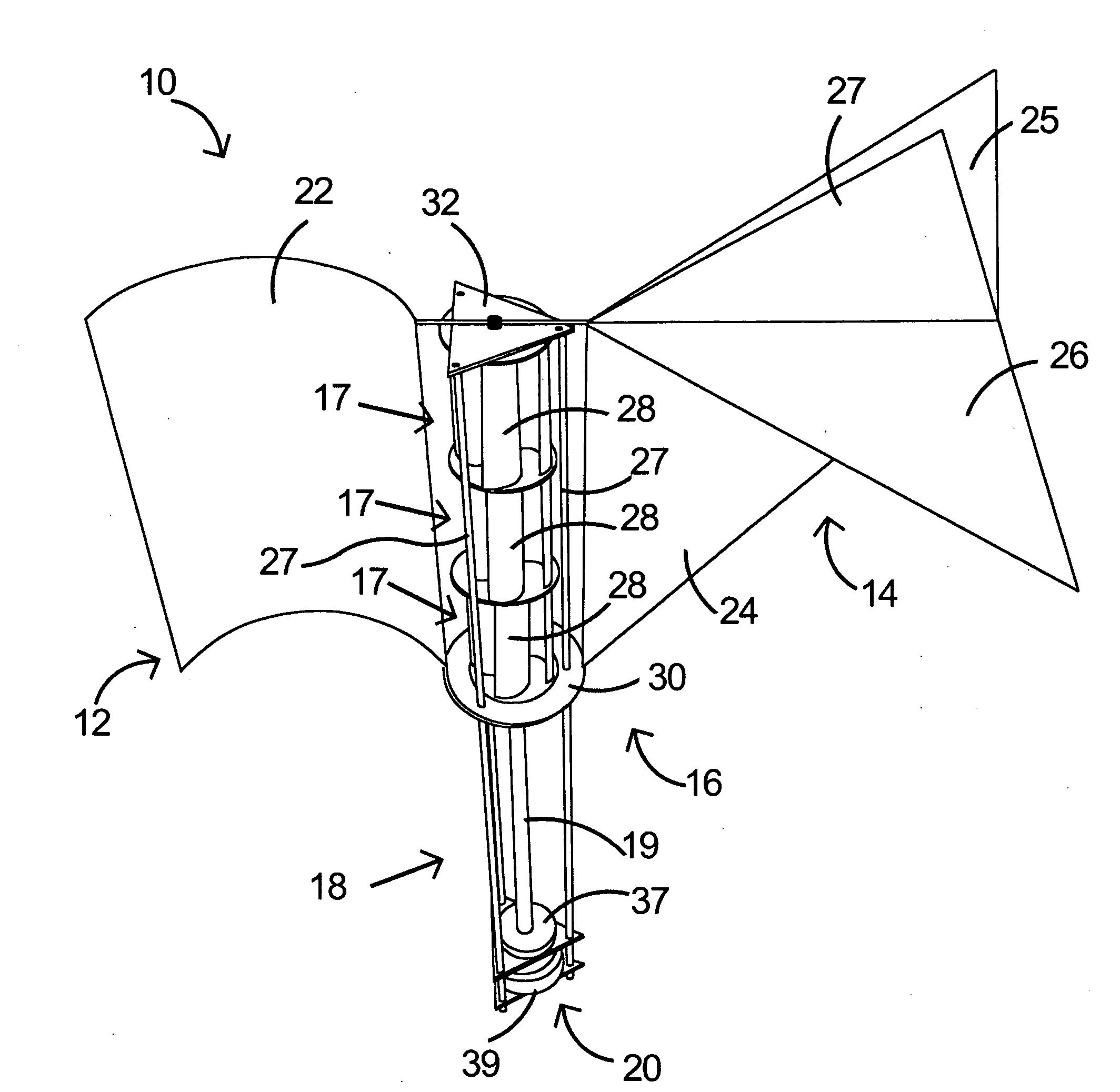
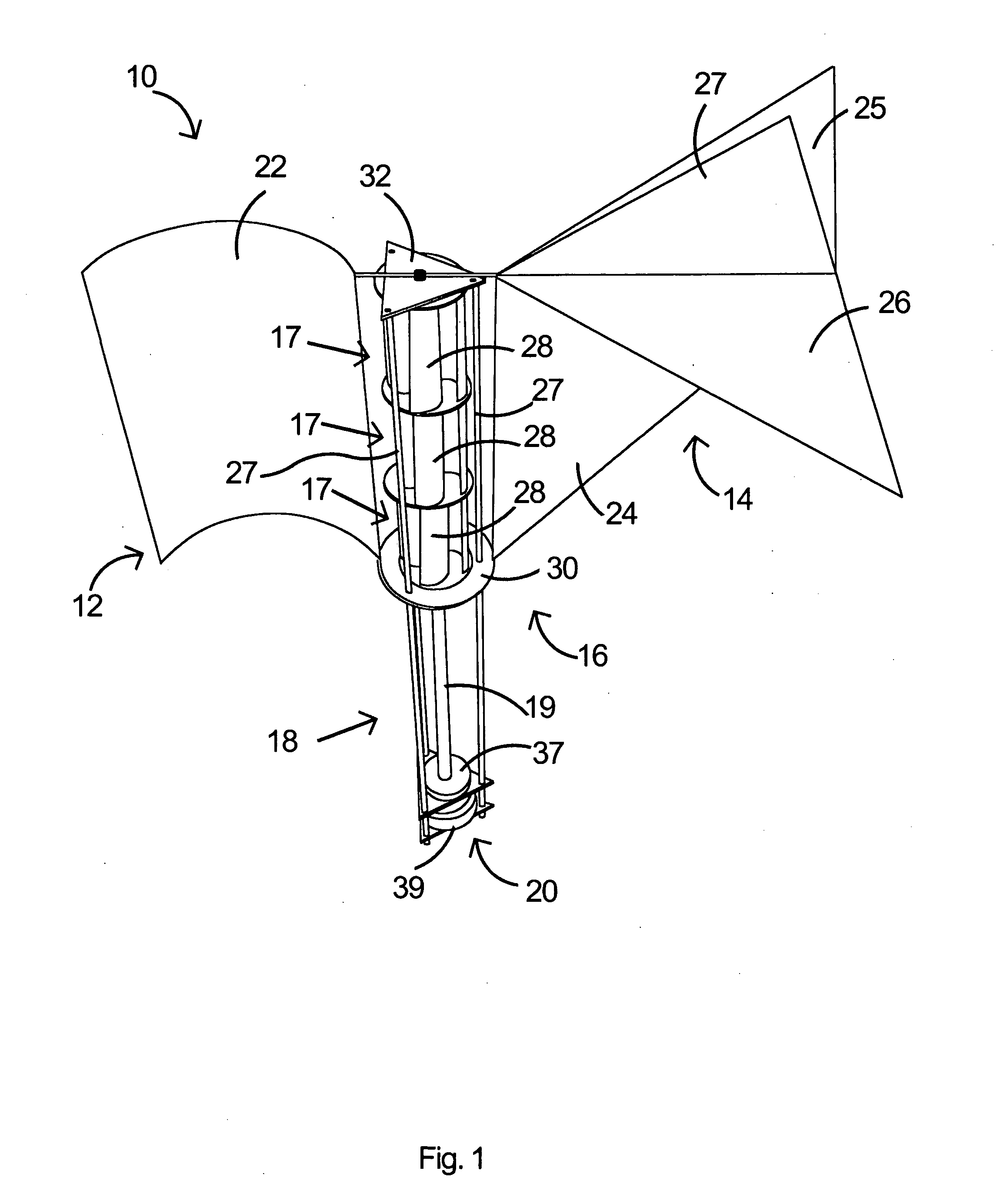
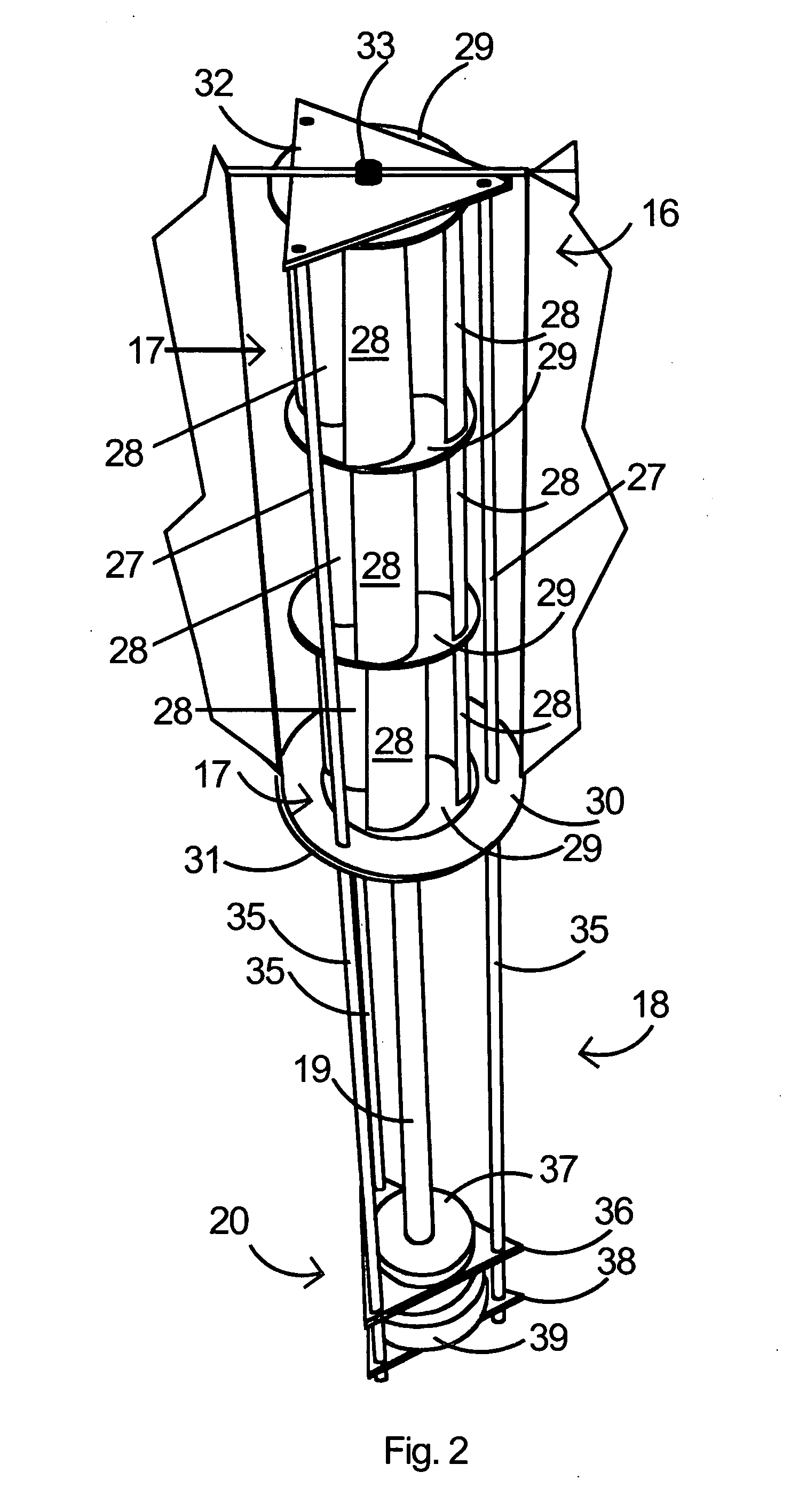
Turbomachinery system fiberoptic multi-parameter sensing system and method
ActiveUS20090320609A1High torque loadVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringReflectivity
A fiberoptic multi-parameter sensing system for monitoring turbomachinery system shaft static and dynamic torques, vibration modes and associated operation status includes a multi-furcated fiber bundle based optical splitter configured to transmit light to a surface of at least one turbomachinery system shaft through a plurality of optical fiber bundles disposed at a plurality of locations in proximity to the surface of the at least one shaft, in which the plurality of locations together are arranged in a substantially axial direction between the ends of the at least one shaft. The system further includes an array of high-temperature bifurcated fiber bundle based reflectance probes to receive reflectance signals from the shaft surface and send to an array of photosensitive detectors, configured to detect dynamic light reflected from the at least one turbomachinery system shaft surface in response to the transmitted light during rotation of at least one turbomachinery system shaft and generate dynamic reflected light signals there from. A sensing mechanism is configured to determine a torque or vibration on at least one turbomachinery system shaft in response to the dynamic reflected light signal signatures based on time-domain and frequency-domain signal processes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-Axis Wind Turbine With Power Concentrator Sail
InactiveUS20090191057A1Effective and reliableAvoid disruptionPropellersPump componentsVisibilityAir movement
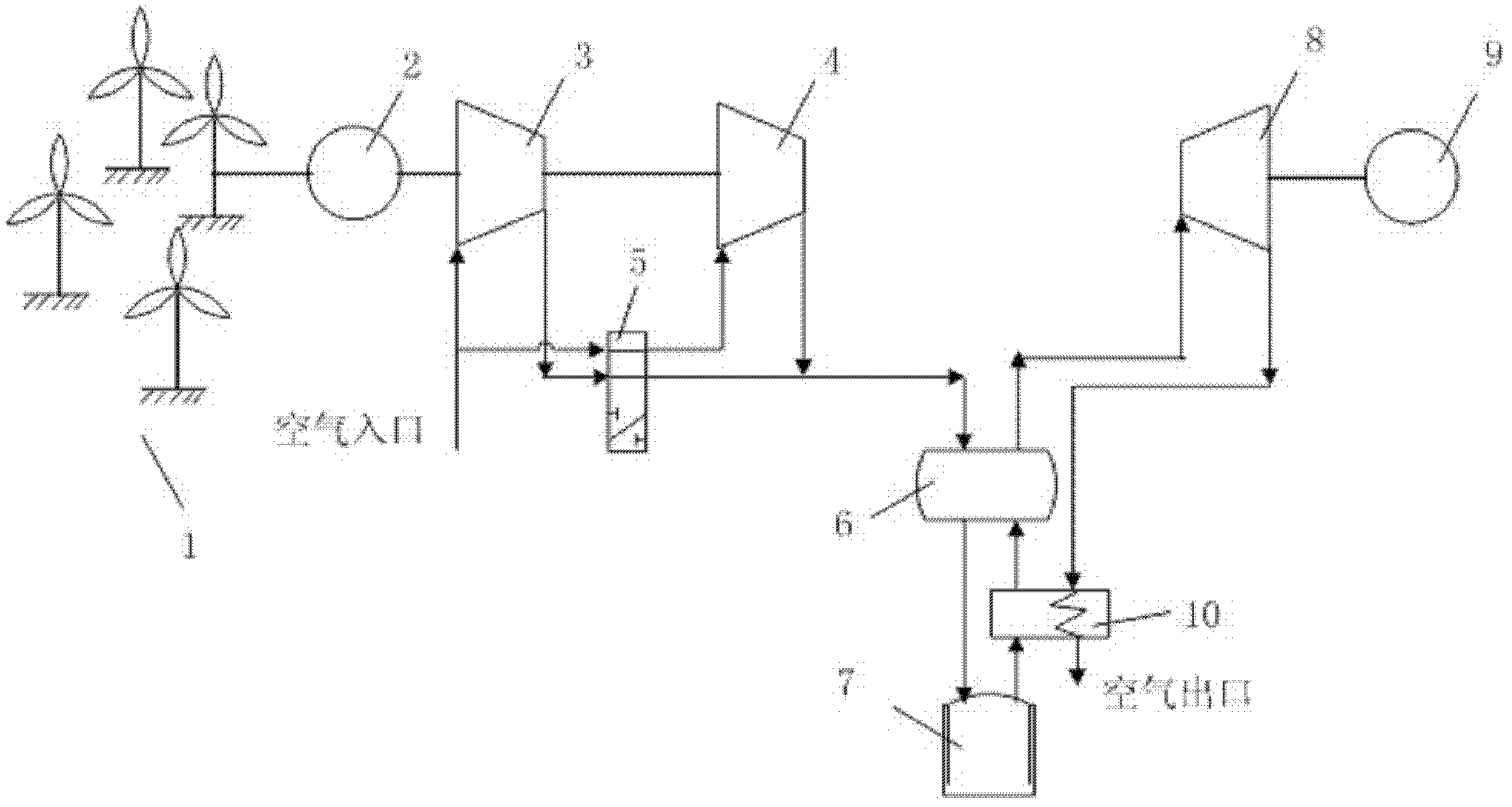
A wind energy to electrical power conversion device provides a protected multiple turbine mechanism axially aligned to convert kinetic energy of air movement, i.e. wind (or other moving fluid such as water), into rotational mechanical power to directly create electrical energy by the reaction of the wind with the turbine. The present wind energy to electrical power conversion device may either be configured as a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) or horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT). An associated wind gathering sail automatically repositions itself to maximize wind intake and to collect and concentrate the wind prior to converting the wind into energy via the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism into electrical energy. The remaining wind is released via a leeward-facing exhaust. The present axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism avoids interference by birds and other outside objects due to its inherent structural visibility.
Owner:KNUTSON ROGER C
Gas turbine engine lockout reduction
ActiveUS8776530B2Shorten the overall cycleShorten the timeLeakage preventionGas turbine plantsCombustorTurbine
A method is provided of reducing lockout time of a gas turbine engine which includes: an inlet, a compressor, a combustor, a turbine, and an exhaust duct, where the compressor and the turbine are carried on a turbomachinery rotor and each include an array of blades mounted for rotation inside a casing of the engine. The method includes: operating the engine at a first power output; shutting down operation of the engine without substantially reducing the power output beforehand, wherein thermomechanical changes occur in the engine subsequent to shutdown that tend to reduce a radial clearance between at least one of the blades and the casing; and subsequent to shutting down the engine, (1) heating the casing and / or (2) pumping an airflow of ambient air into the inlet and through the casing, past the rotor, and out the exhaust duct, so as to reverse at least partially the thermomechanical changes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
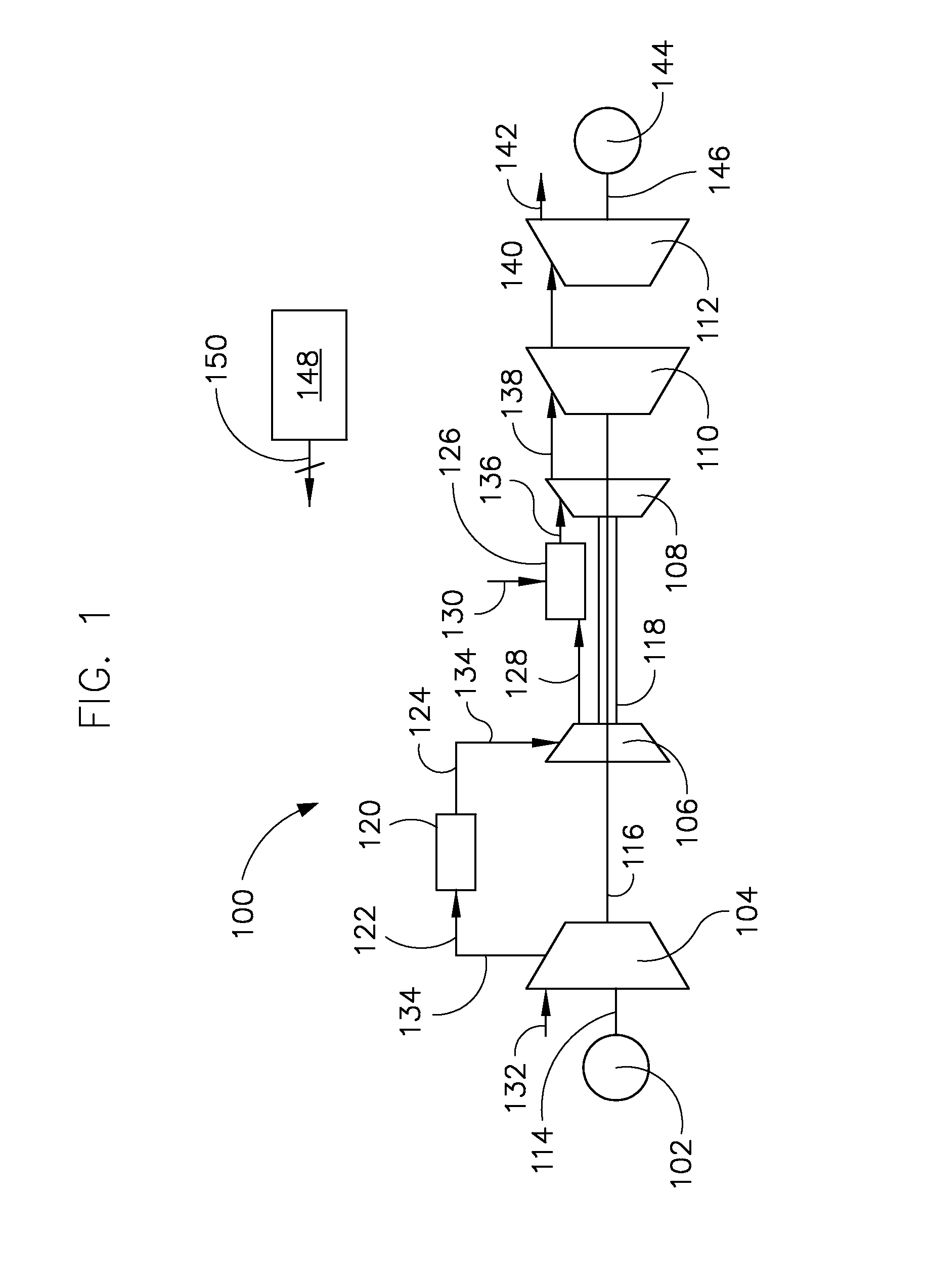
Compressed-air energy-storage system
ActiveCN102213113AIncrease flexibilityChange flowFrom solar energyWind energy with garvitational potential energyPower stationFour-way valve
The invention relates to a compressed-air energy-storage system. A three-position four-way valve is arranged in a pipeline of a compression part and an expansion part of the system and the flowing condition of air in the system is changed by utilizing the feature of change of a turn-on state of the three-position four-way valve, thus the variation of the manners of serial-connection and parallel-connection between a gas compressor and a turbine is realized, and the overall working efficiency is increased. With the adoption of the three-position four-way valve, on one hand, the overall flexibility of the compressed-air energy-storage system is improved, so that the operating of the system is more targeted, and the use of the compressed-air energy-storage system matched with various types of power stations is facilitated; and on the other hand, the service condition of turbomachinery is improved, and the optimized configuration of the turbomachinery according to the needs of energy storage and power generation can be realized.
Owner:中科国风科技有限公司
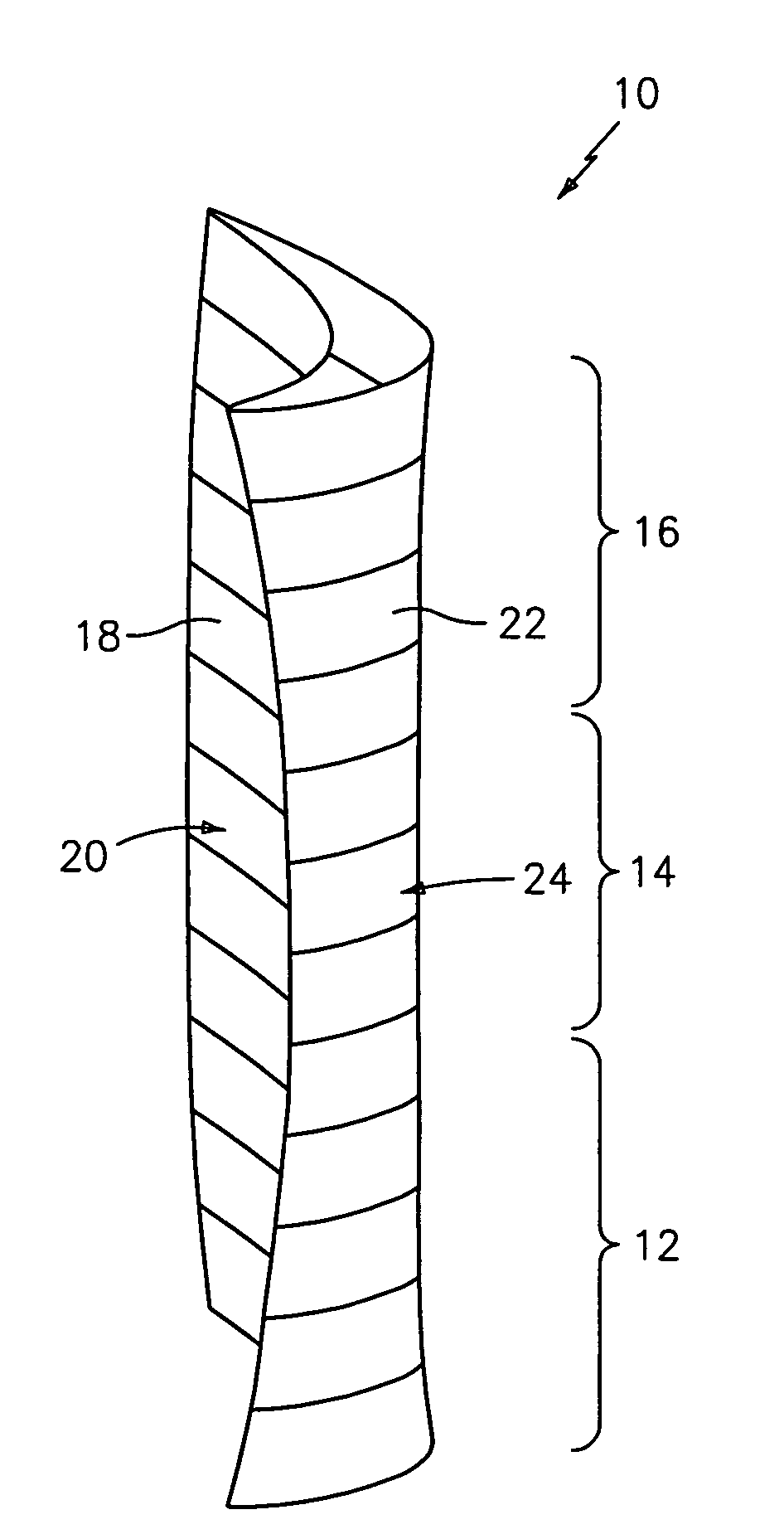
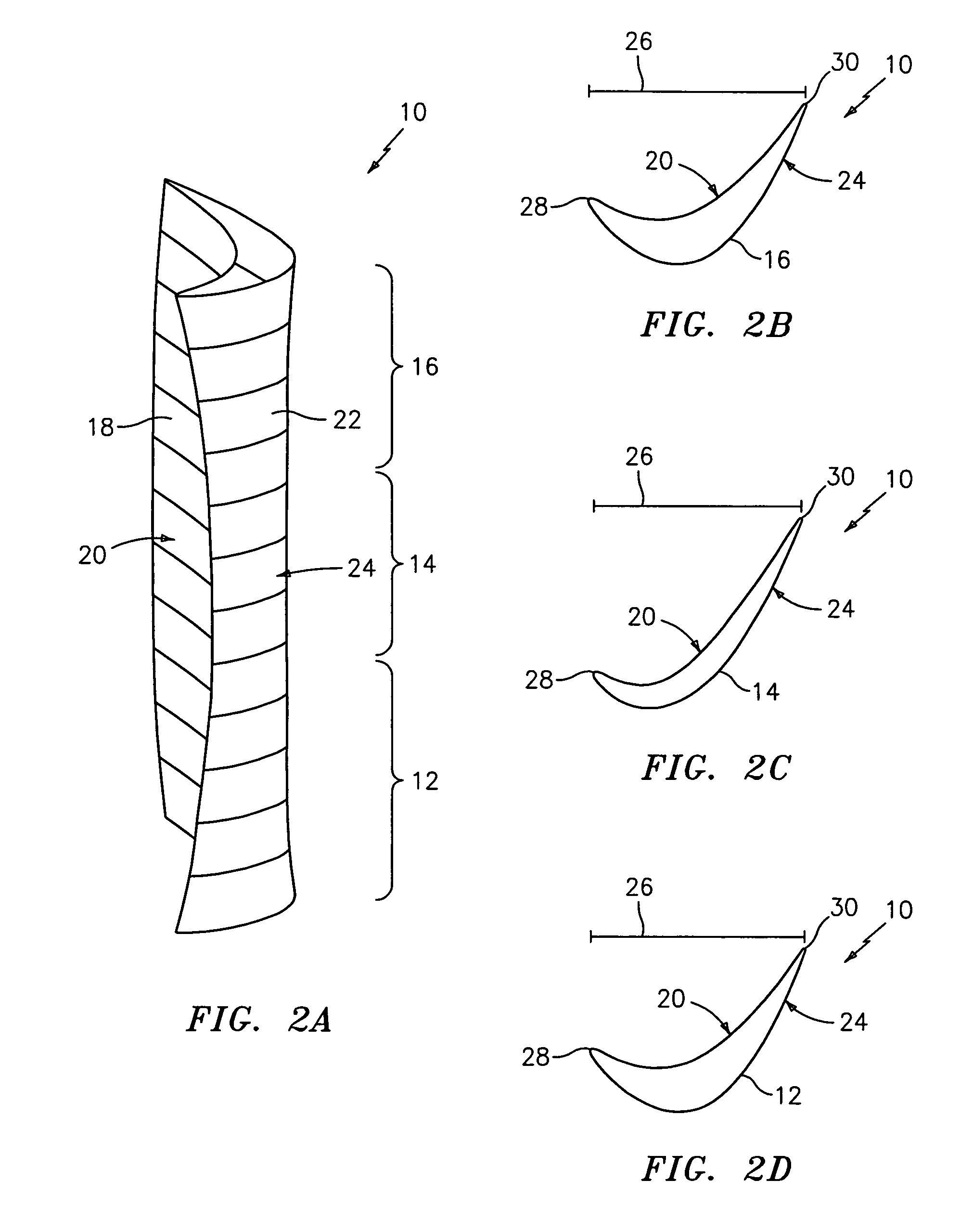
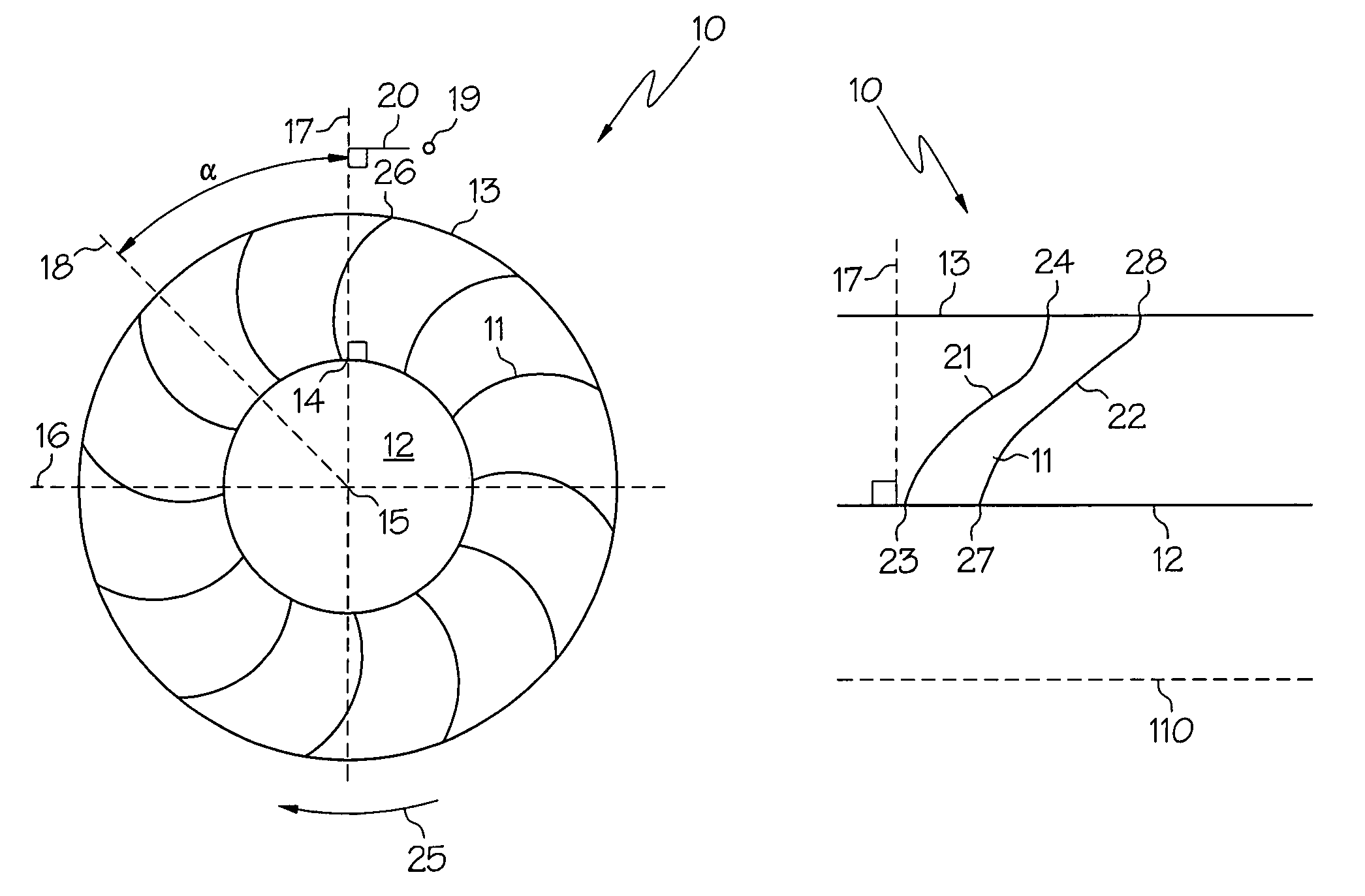
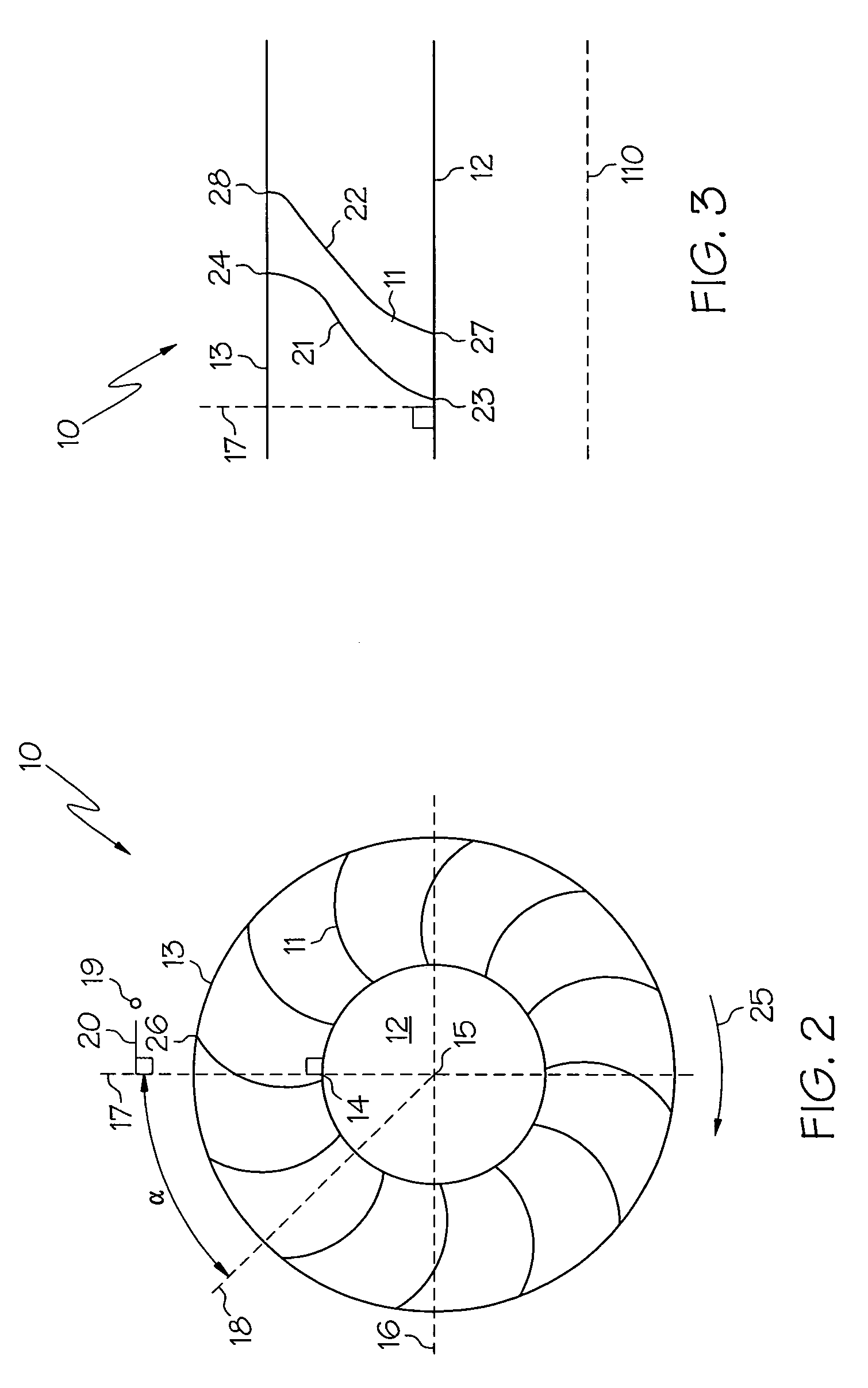
Swept turbomachinery blade
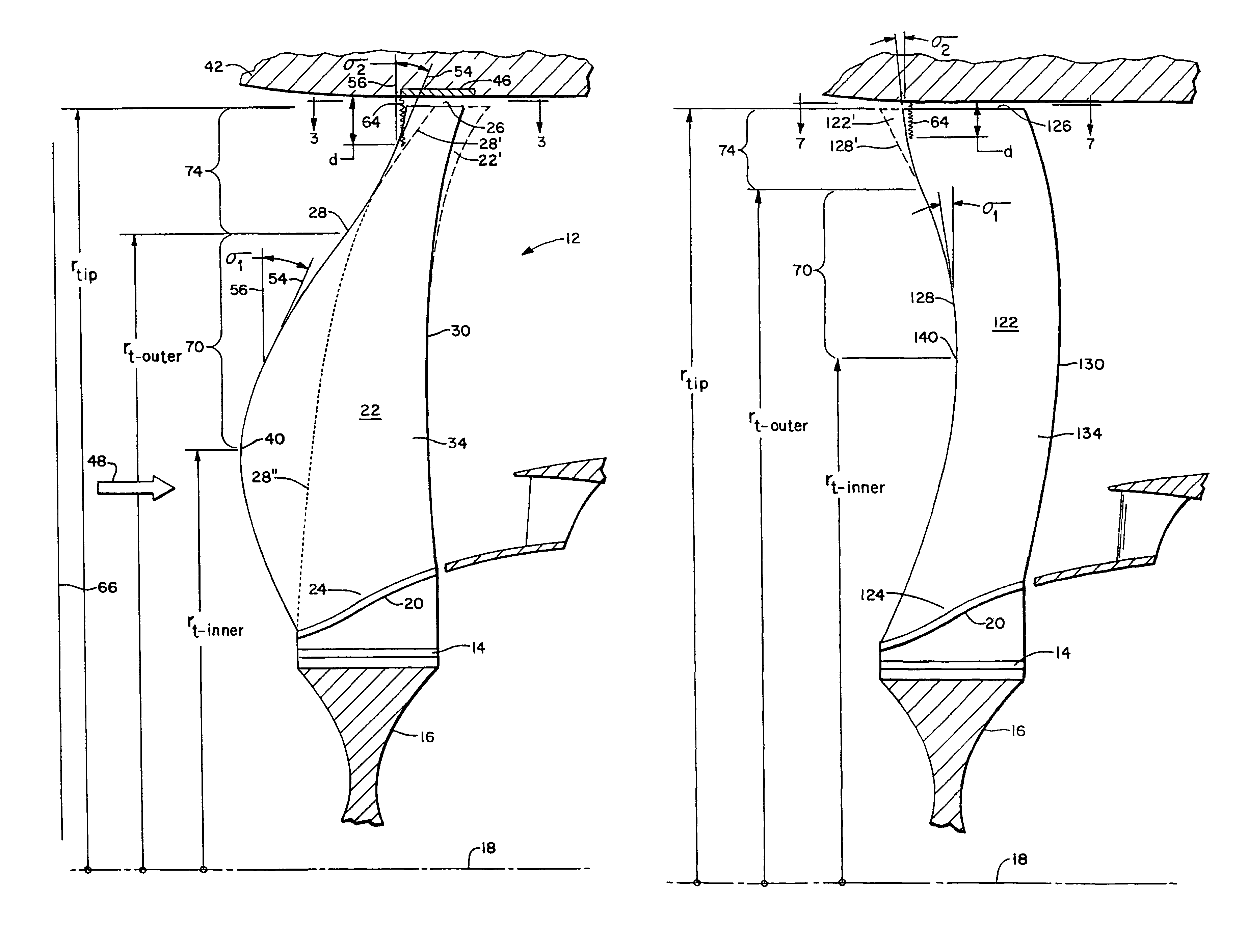
InactiveUSRE38040E1Maximize engine efficiencyReduce in quantityPropellersSupersonic fluid pumpsEngineeringTransition point
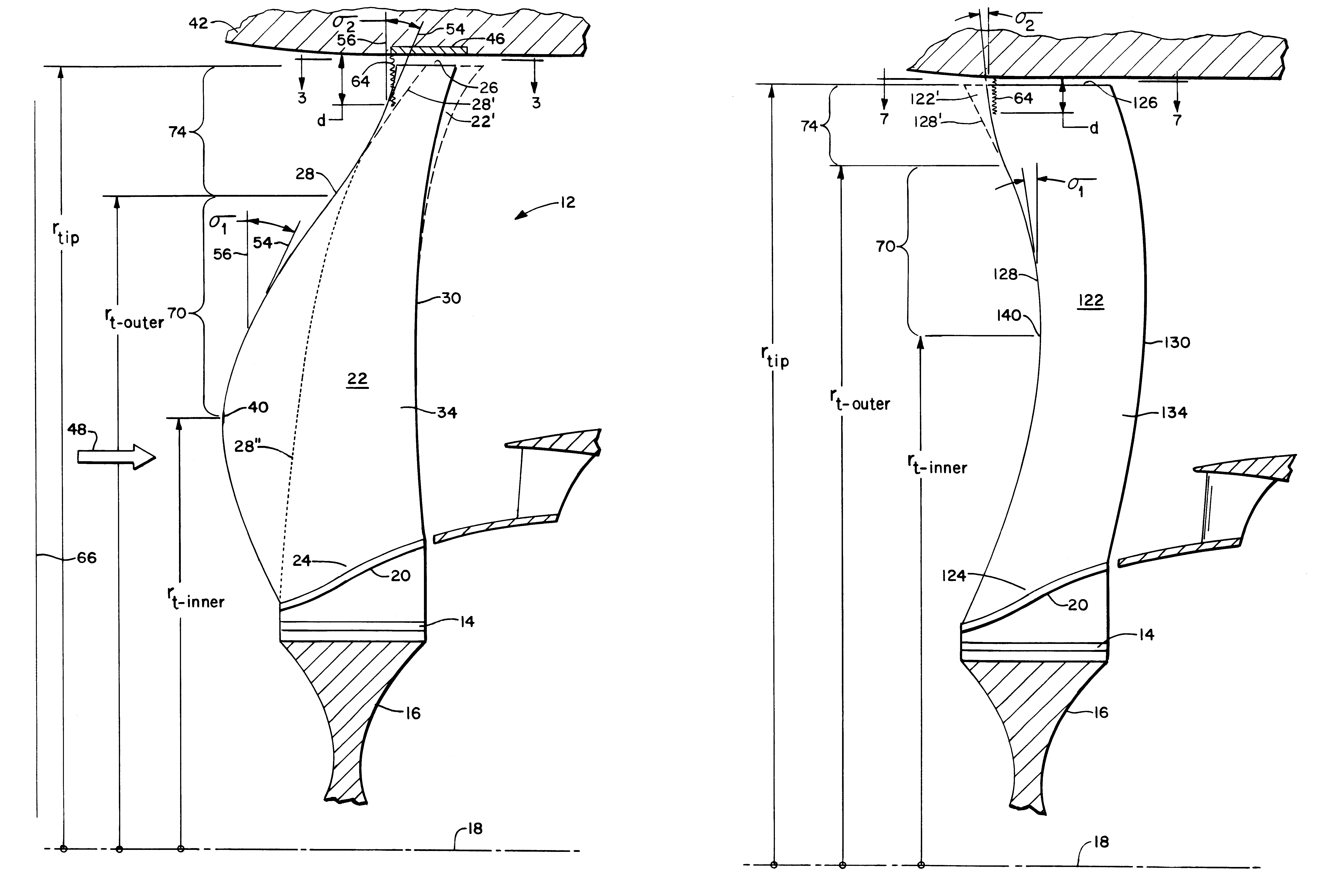
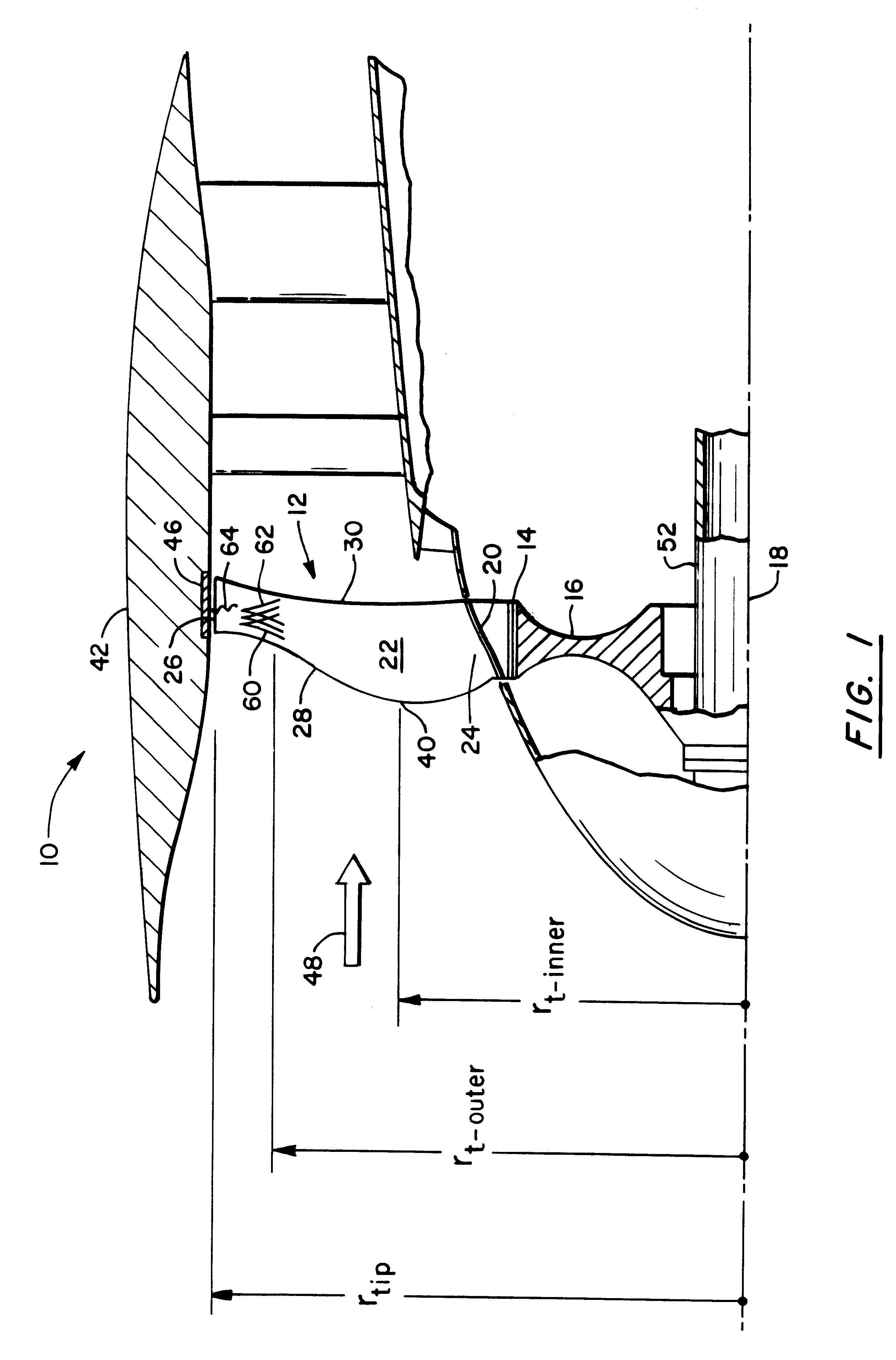
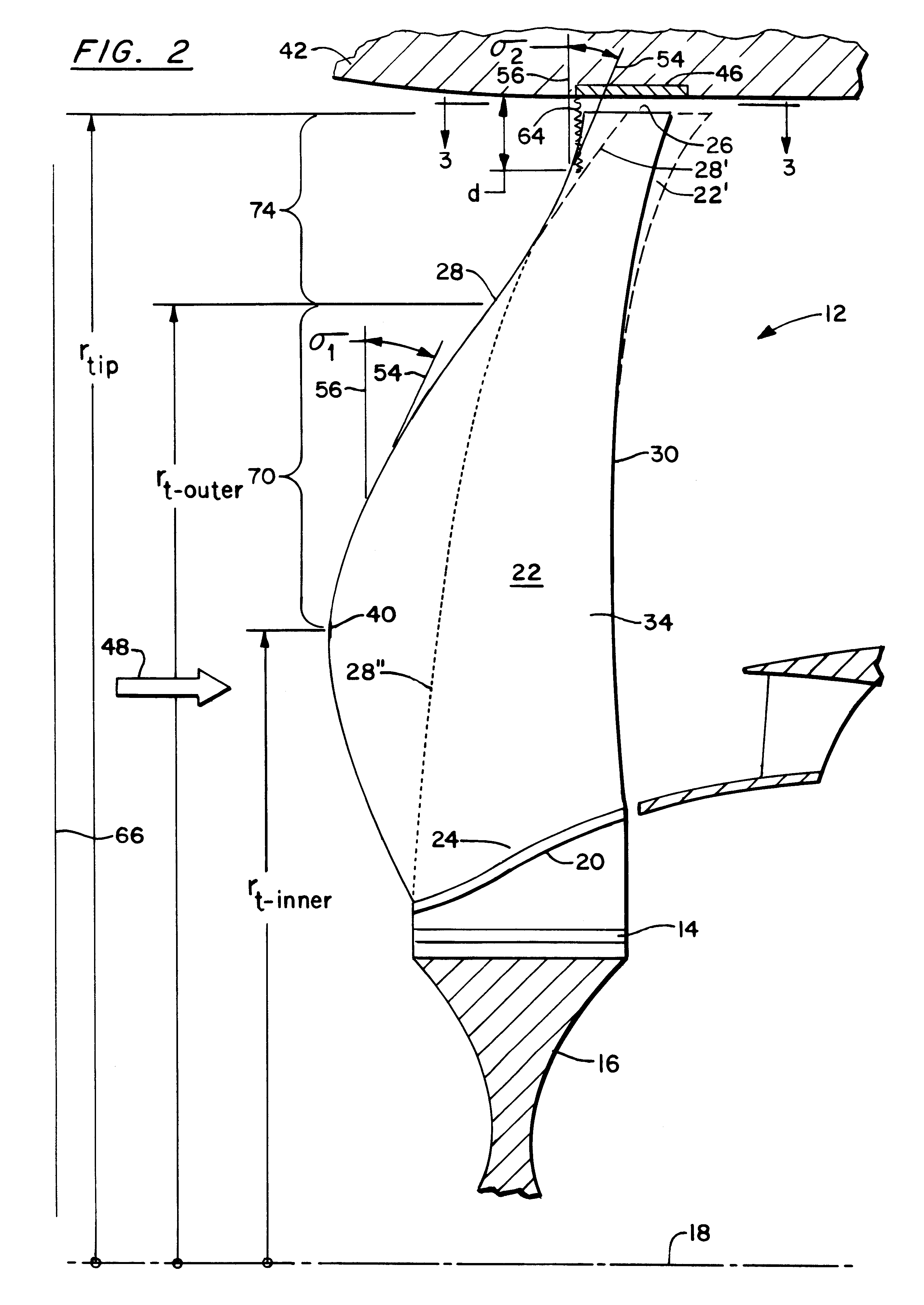
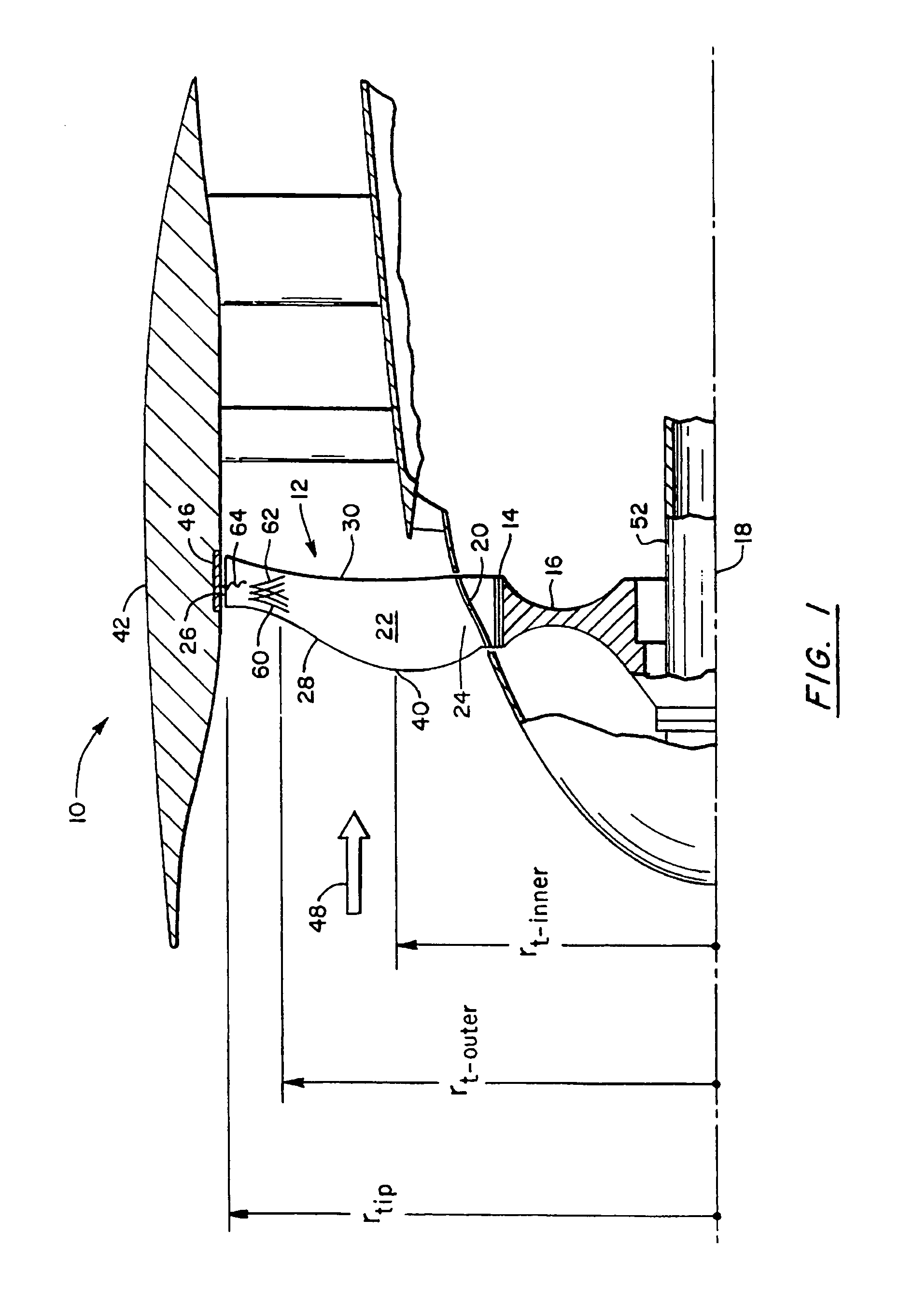
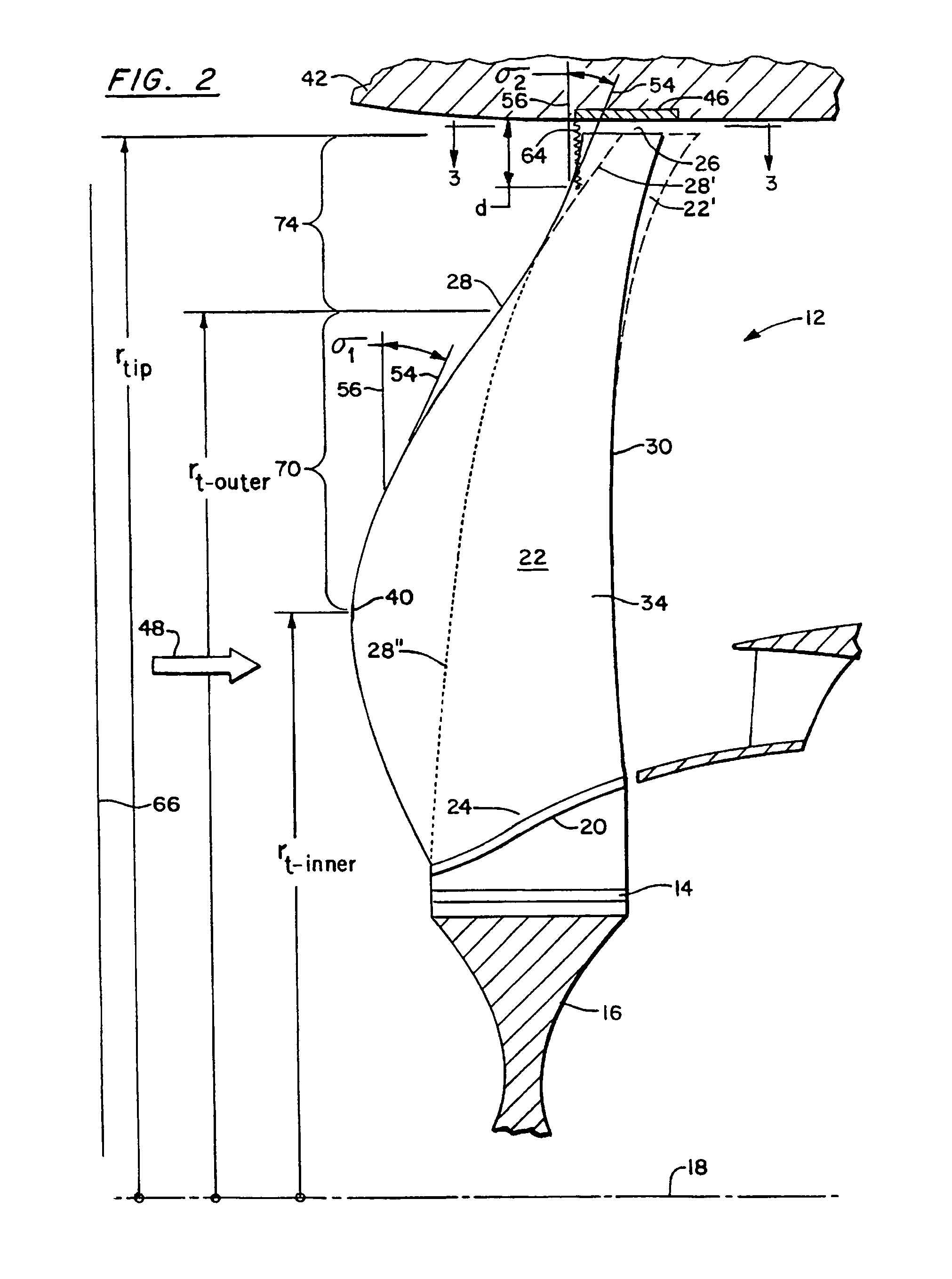
A swept turbomachinery blade for use in a cascade of such blades is disclosed. The blade (12) has an airfoil (22) uniquely swept so that an endwall shock (64) of limited radial extent and a passage shock (66) are coincident and a working medium (48) flowing through interblade passages (50) is subjected to a single coincident shock rather than the individual shocks. In one embodiment of the invention the forwardmost extremity of the airfoil defines an inner transition point (40) located at an inner transition radius rt-inner. The sweep angle of the airfoil is nondecreasing with increasing radius from the inner transition radius to an outer transition radius rt-outer, radially inward of the airfoil tip (26), and is nonincreasing with increasing radius between the outer transition radius and the airfoil tip.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Low shock strength inlet
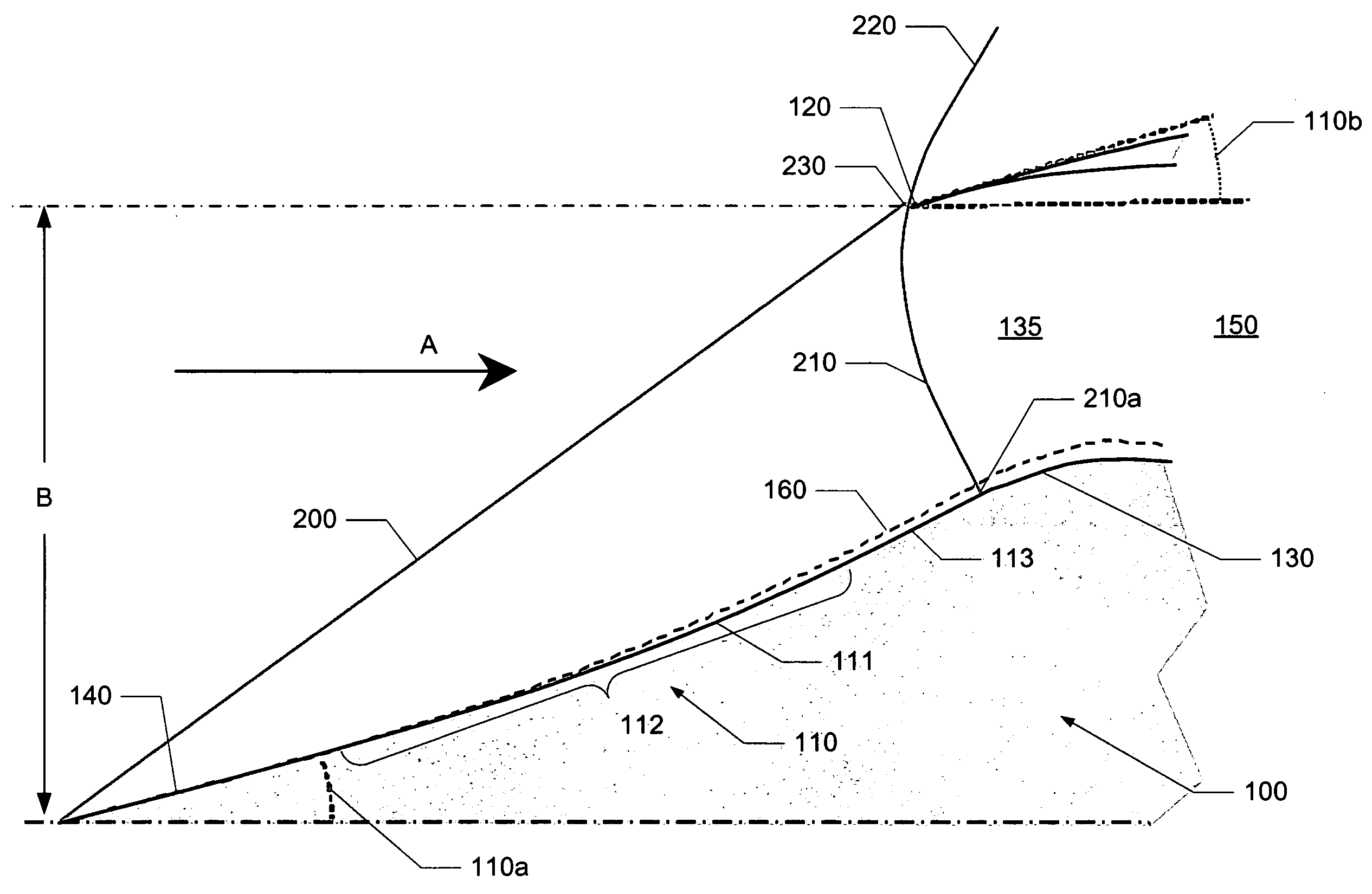
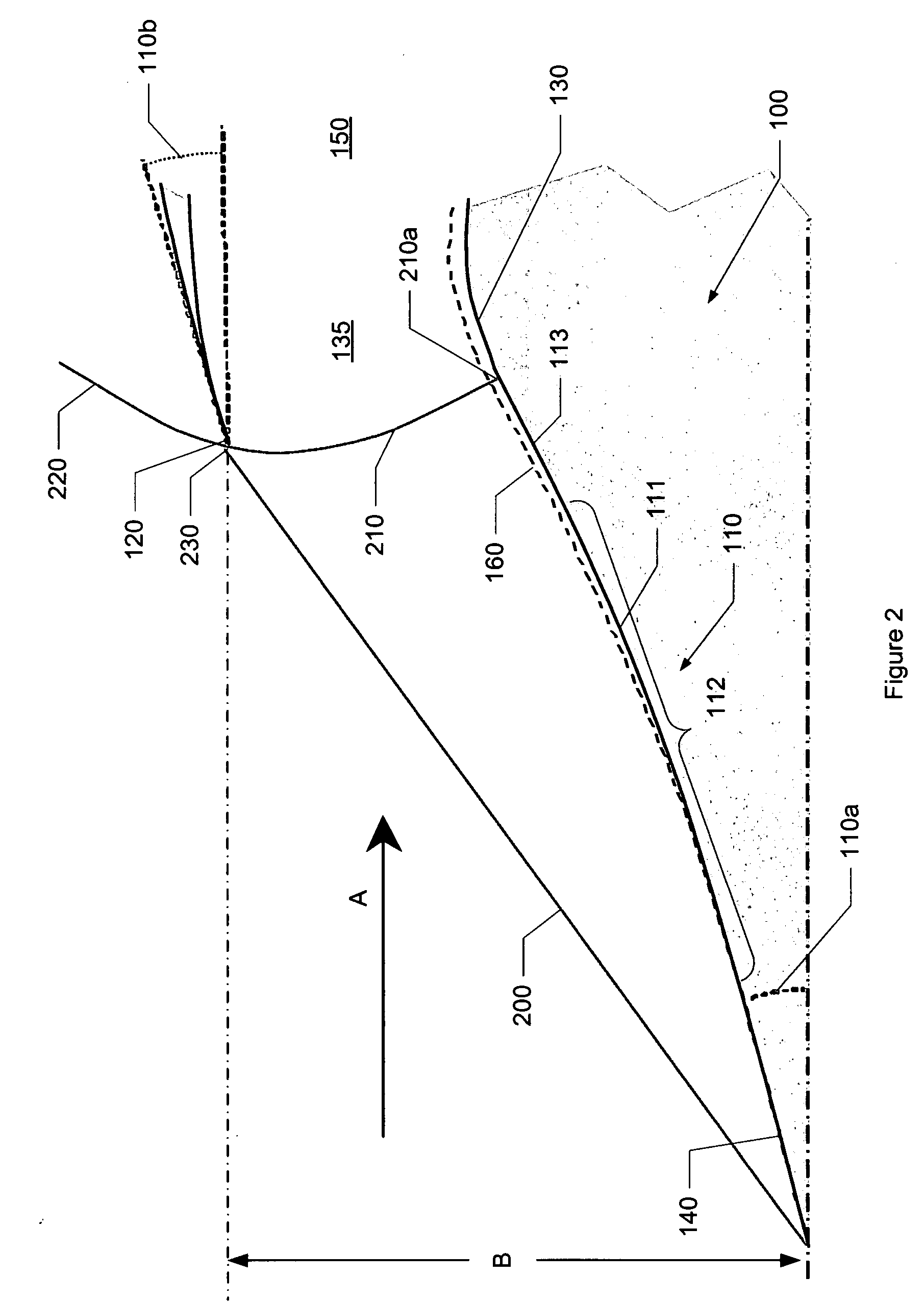
ActiveUS20090107557A1Power plant exhaust arrangementsAircraft power plant componentsNacelleUltimate tensile strength
Embodiments of the invention relate to a supersonic inlet having a cowl lip configured to capture the conic shock and exhibit a zero or substantially zero cowl angle. The inlet may be configured to employ a relaxed isentropic compression surface and an internal bypass. The nacelle bypass may prevent flow distortions, introduced by the capture of the conic shock, from reaching the turbomachinery, thereby allowing the cowl angle to be reduced to zero or substantially zero. Such a cowl angle may reduce the inlet's contribution to the overall sonic boom signature for a supersonic aircraft while allowing for an increase in engine pressure recovery and a subsequent improvement in generated thrust by the engine.
Owner:GULFSTREAM AEROSPACE CORP
Magnetic advanced generation jet electric turbine
ActiveUS8365510B2Maximizes propulsion efficiencyImprove combustionGas turbine plantsEnergy production using magneto-hydrodynamic generatorsAviationElectric power system
Supersonic Magnetic Advanced Generation Jet Electric Turbine (S-MAGJET) described herein, and a subsonic derivative, MAGJET, integrate a gas power turbine, superconducting electric power and propulsion generation, and magnetic power flux field systems along with an ion plasma annular injection combustor which utilizes alternative petroleum-based fuel and combustion cycles to create a hybrid turbine turbomachine for aerospace propulsion. The propulsion unit is able to achieve a dramatic increase in horsepower, combustion and propulsion efficiency, and weight reduction. In addition, the turbomachinery structures may be disposed within an exo-skeleton architecture that achieves an increase in thrust to weight ratio with a concomitant increase in fuel efficiency and power generation over traditional gas turbine technology today. The engine continuously adjusts the temperature, pressure and mass airflow requirements using an electromagnetic power management system architecture. Engine performance may be controlled across the entire desired flight envelope, whether subsonic, transonic or supersonic flight conditions.
Owner:SONIC BLUE AEROSPACE
Swept turbomachinery blade
InactiveUSRE43710E1Minimize the aerodynamic losses and efficiency degradationMaximize efficiencyPropellersSupersonic fluid pumpsEngineeringTransition point
A swept turbomachinery blade for use in a cascade of such blades is disclosed. The blade (12) has an airfoil (22) uniquely swept so that an endwall shock (64) of limited radial extent and a passage shock (66) are coincident and a working medium (48) flowing through interblade passages (50) is subjected to a single coincident shock rather than the individual shocks. In one embodiment of the invention the forwardmost extremity of the airfoil defines an inner transition point (40) located at an inner transition radius rt-inner. The sweep angle of the airfoil is nondecreasing with increasing radius from the inner transition radius to an outer transition radius rt-outer, radially inward of the airfoil tip (26), and is nonincreasing with increasing radius between the outer transition radius and the airfoil tip.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
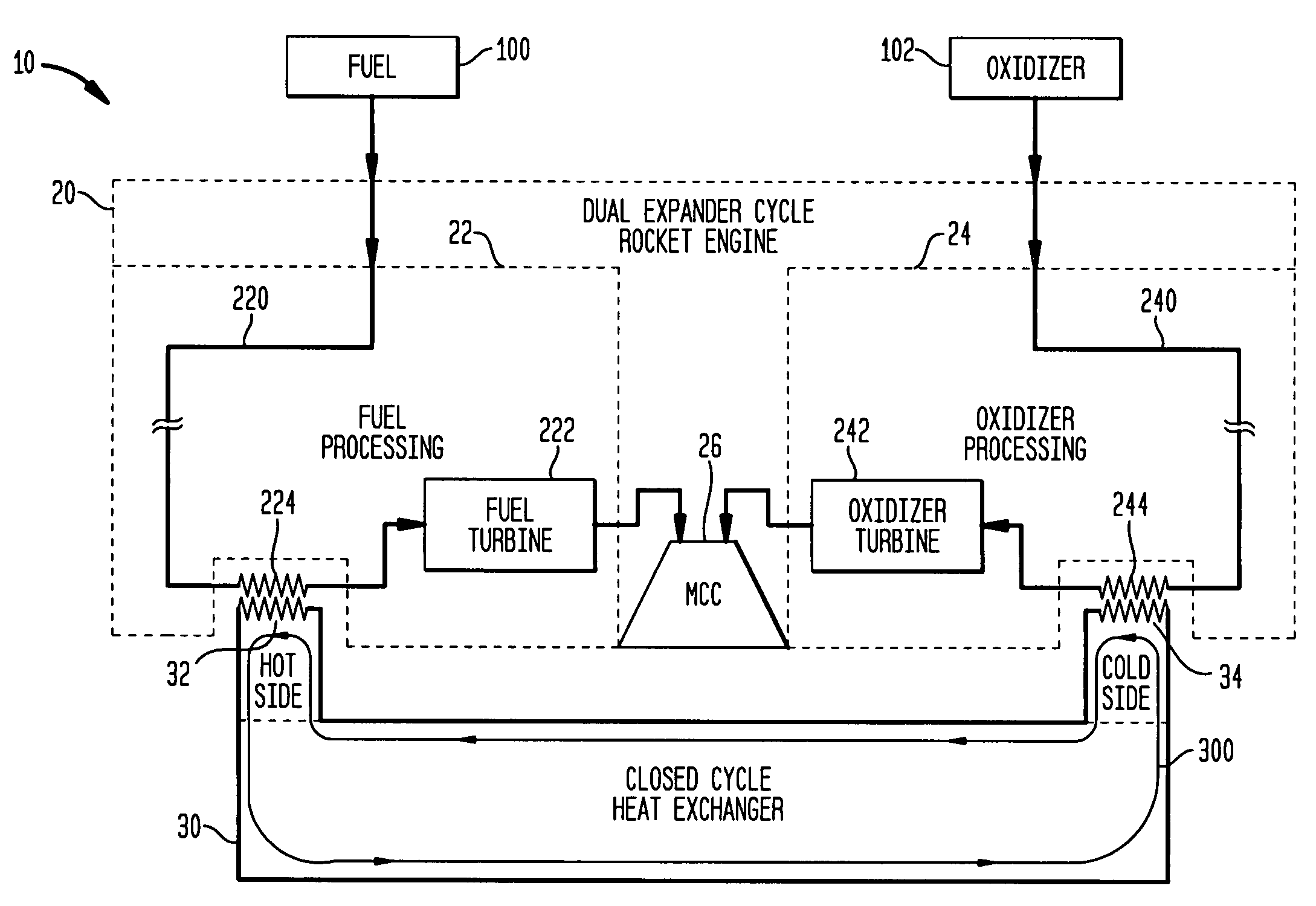
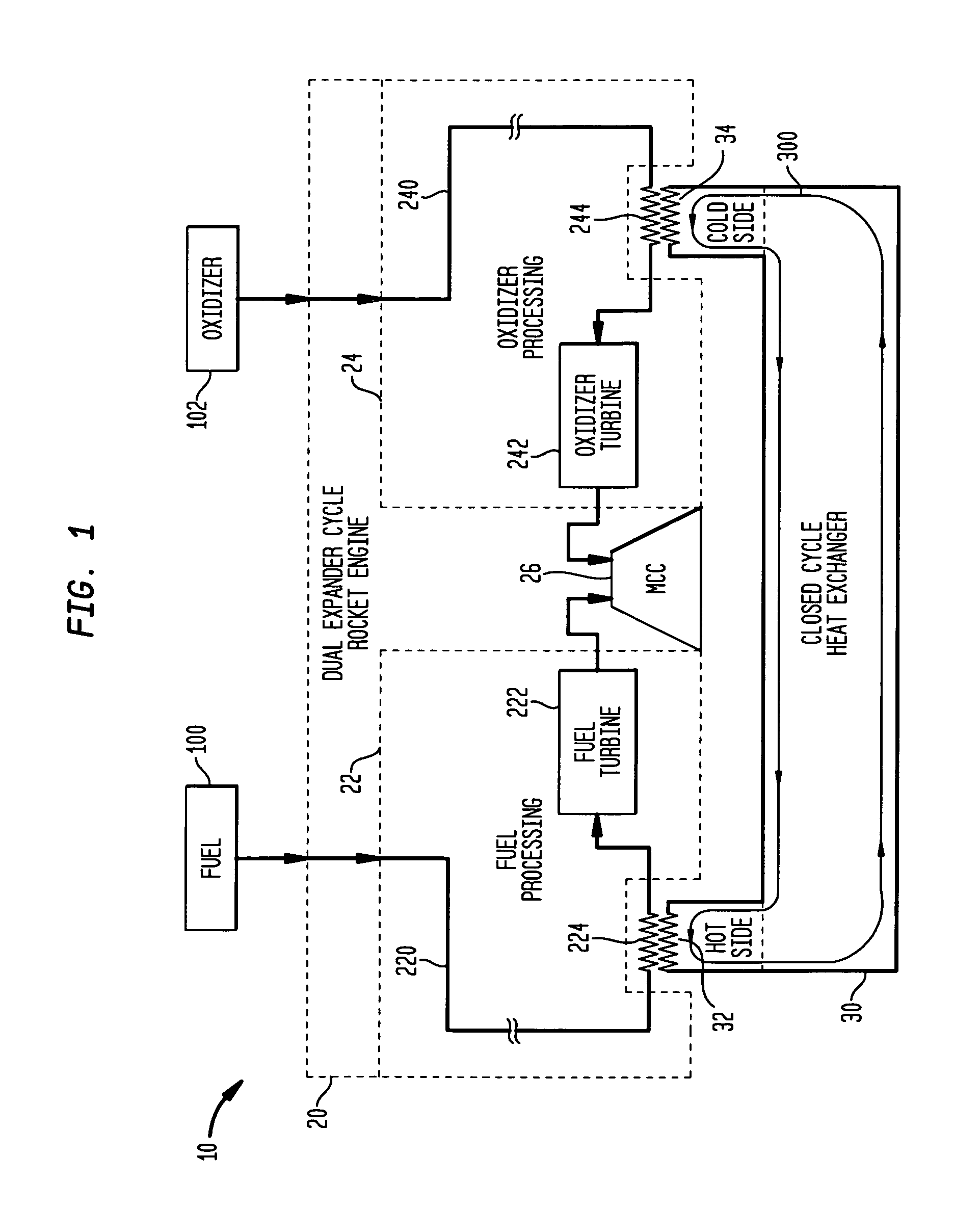
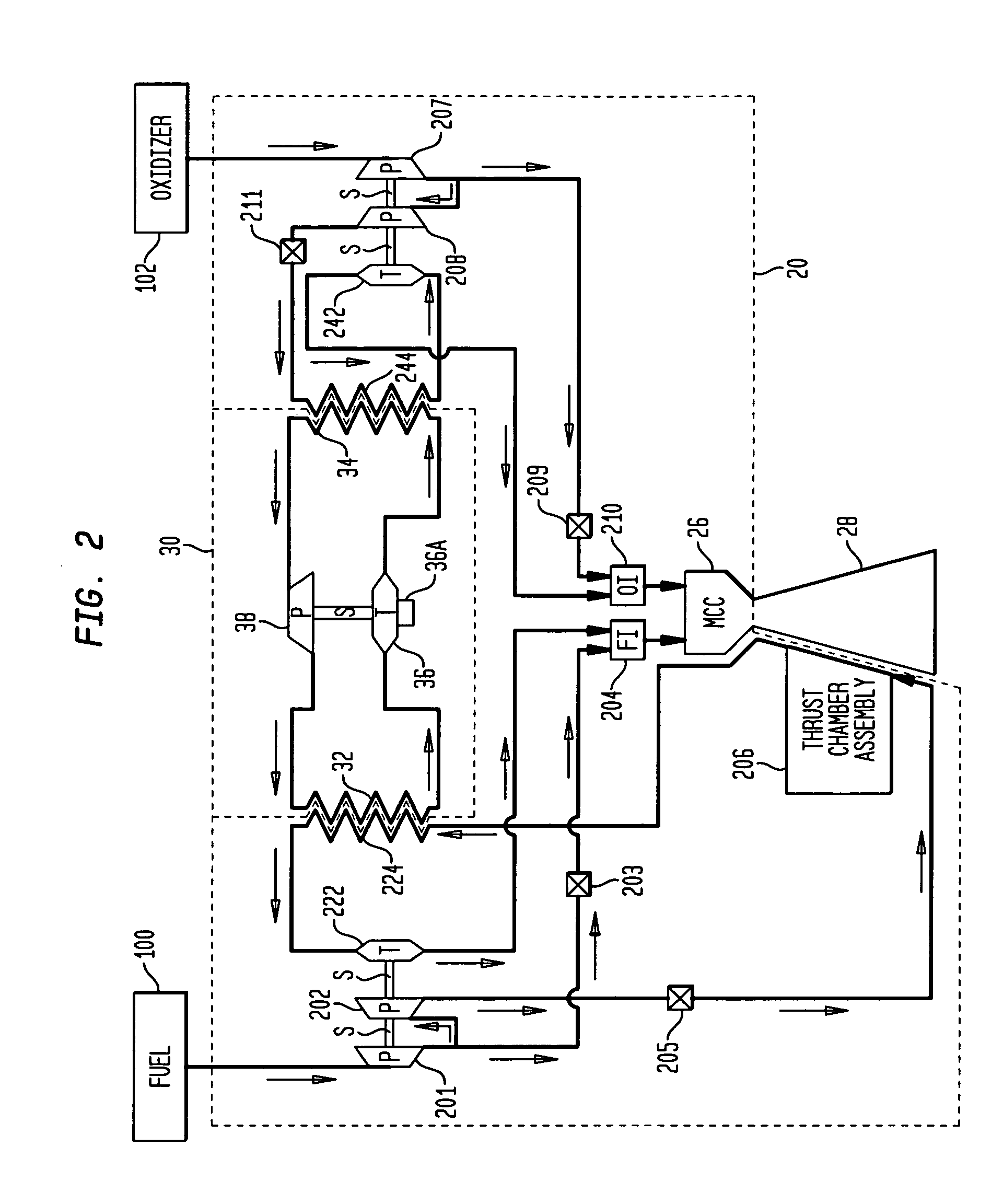
Dual expander cycle rocket engine with an intermediate, closed-cycle heat exchanger
InactiveUS7418814B1Efficient and safe and reliableSafe, reliable and efficient operationCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusMotor fuelHeat exchanger
A dual expander cycle (DEC) rocket engine with an intermediate closed-cycle heat exchanger is provided. A conventional DEC rocket engine has a closed-cycle heat exchanger terhamlly coupled thereto. The heat exchanger utilizes heat extracted from the engine's fuel circuit to drive the engine's oxidizer turbomachinery.
Owner:ADMINISTATOR OF THE NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS RERESENTED BY
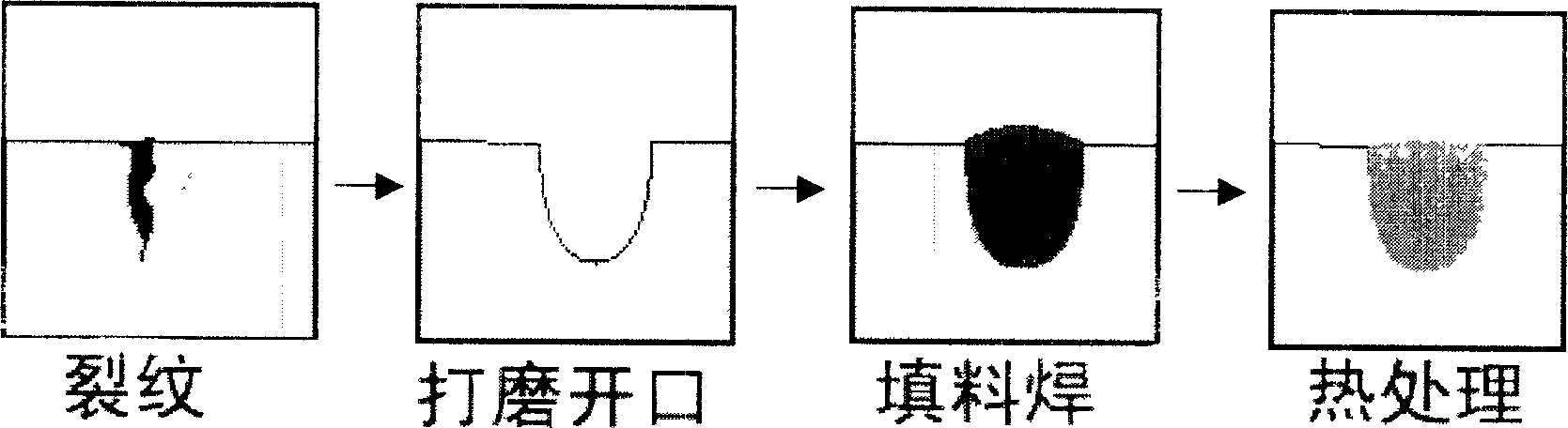
Crack repair process for high-pressure turbine blade tip in gas turbine
The present invention belongs to the metal surface crack repairing method, meaning the tip crack repairing method of a gas-turbine engine high-pressure turbine blade. The method comprises polishing apertures for complete crack removal based on the crack conditions of the gas-turbine engine high-pressure turbine blade tip, carrying out surfacing welding in the repair welding zone using low-heat input welding technology and implementing heat treatment process to the repaired blade. The present invention has the virtues of simple process, needing no vacuum or preheating, small damage to blade base materials, realizing loss-free repair to the high-pressure turbine blade tip cracks and reducing repair cost. The invention can be used to repair both the gas-turbine engine high-pressure turbine blade tip cracks and steam turbine, smoke turbine and other turbine mechanisms high-pressure or low-pressure blade tip cracks. And the aircraft engine high-pressure turbine blade repaired with the method has passes 368h long-term bench trial check.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Centrifugal separator having a rotor and driving means thereof
InactiveUS7022150B2Available spaceEfficient use ofCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentRotational axisTurbine blade
In a centrifugal separator, the rotor of which is adapted to be driven by means of a gaseous driving fluid, the rotor itself supports a ring of turbine blades extending around the rotational axis of the rotor. A stationary nozzle is adapted to direct a flow of the driving fluid towards the ring of turbine members. After the driving fluid has passed between the turbine blades and has influenced them for driving of the centrifugal rotor, it enters a reversing chamber formed by a stationary reversing member. In the reversing chamber the driving fluid is caused to change its direction and is then conducted again towards the ring of turbine members in order to be utilized a second time for driving of the centrifugal rotor.
Owner:ALFA LAVAL CORP AB
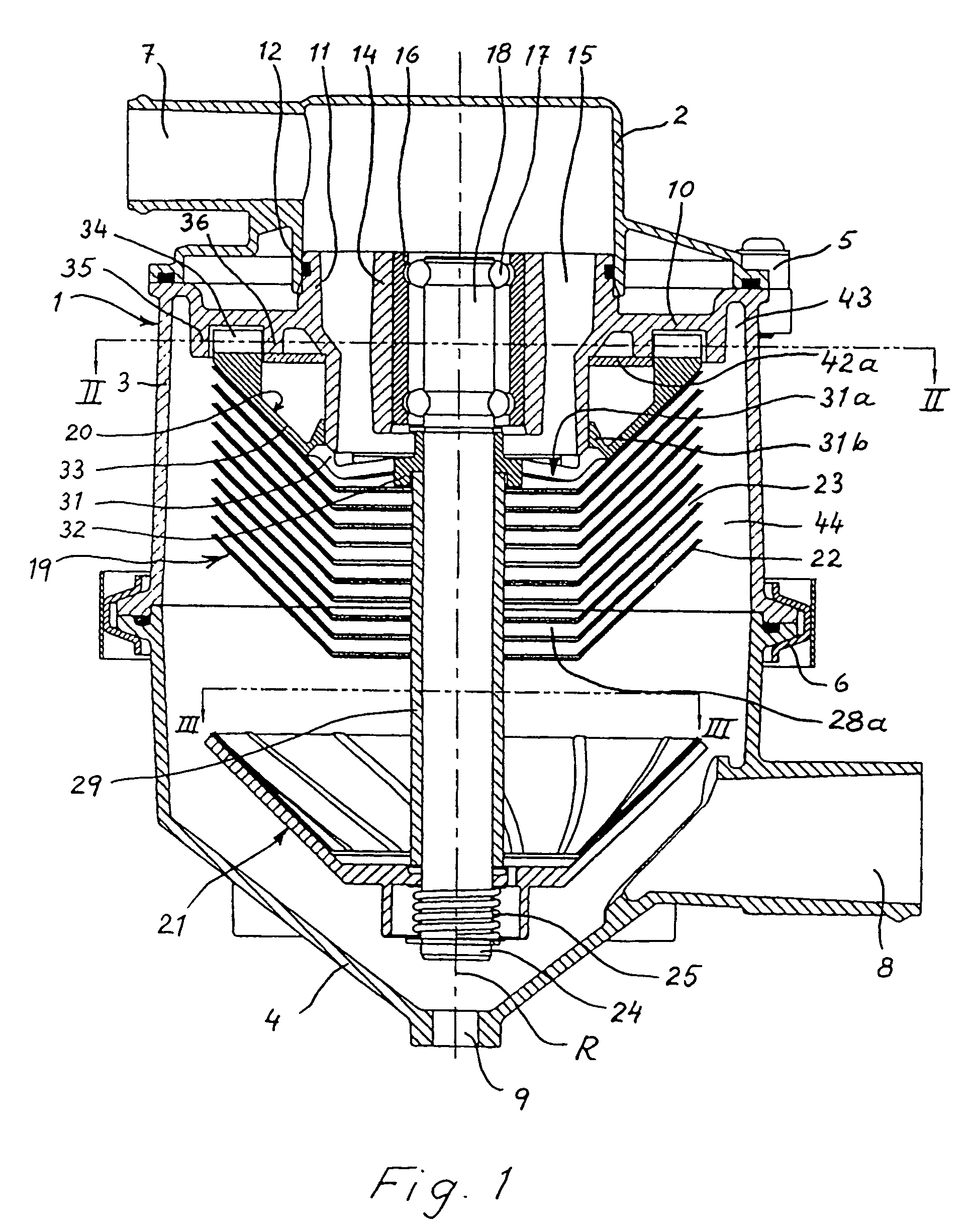
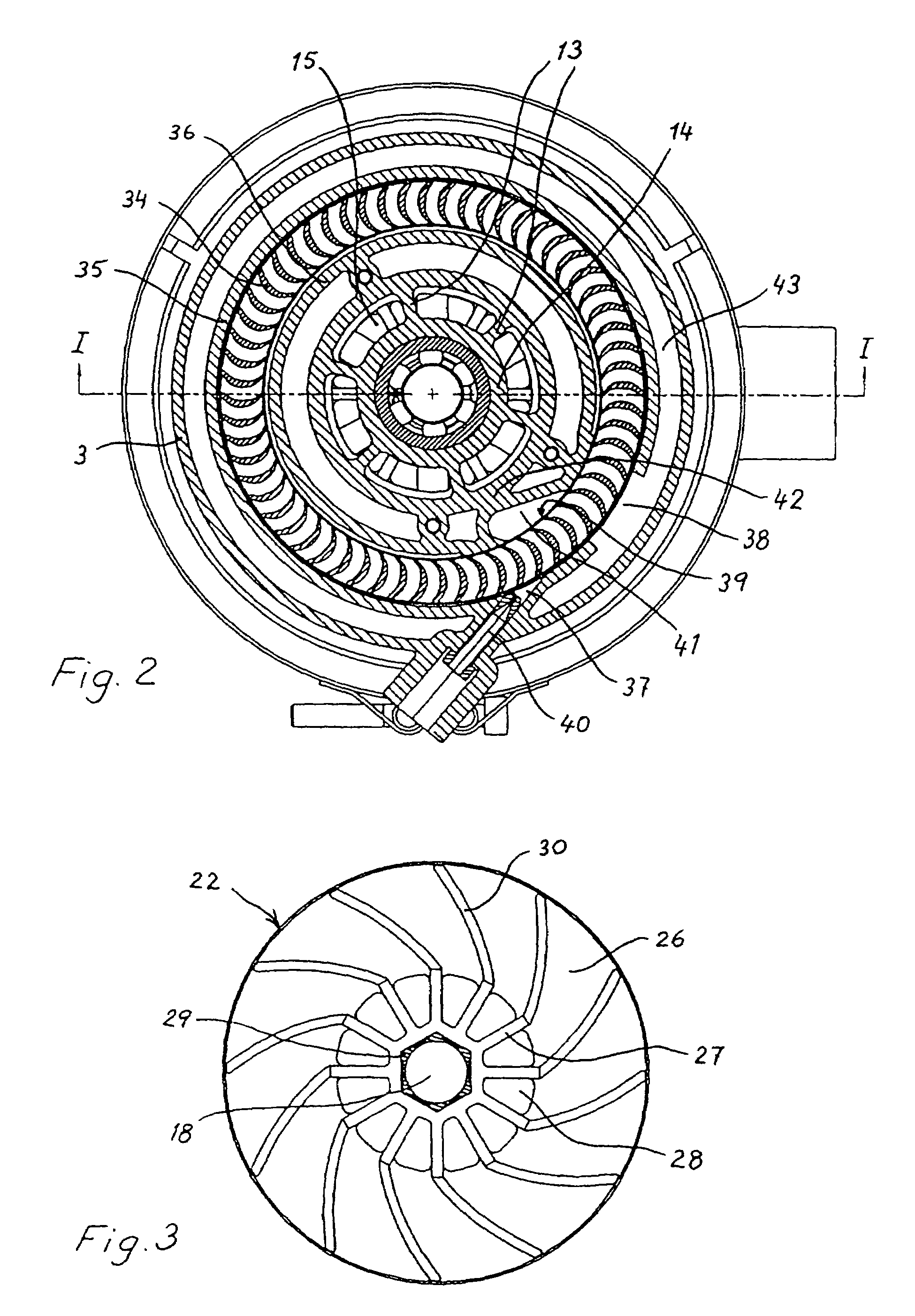
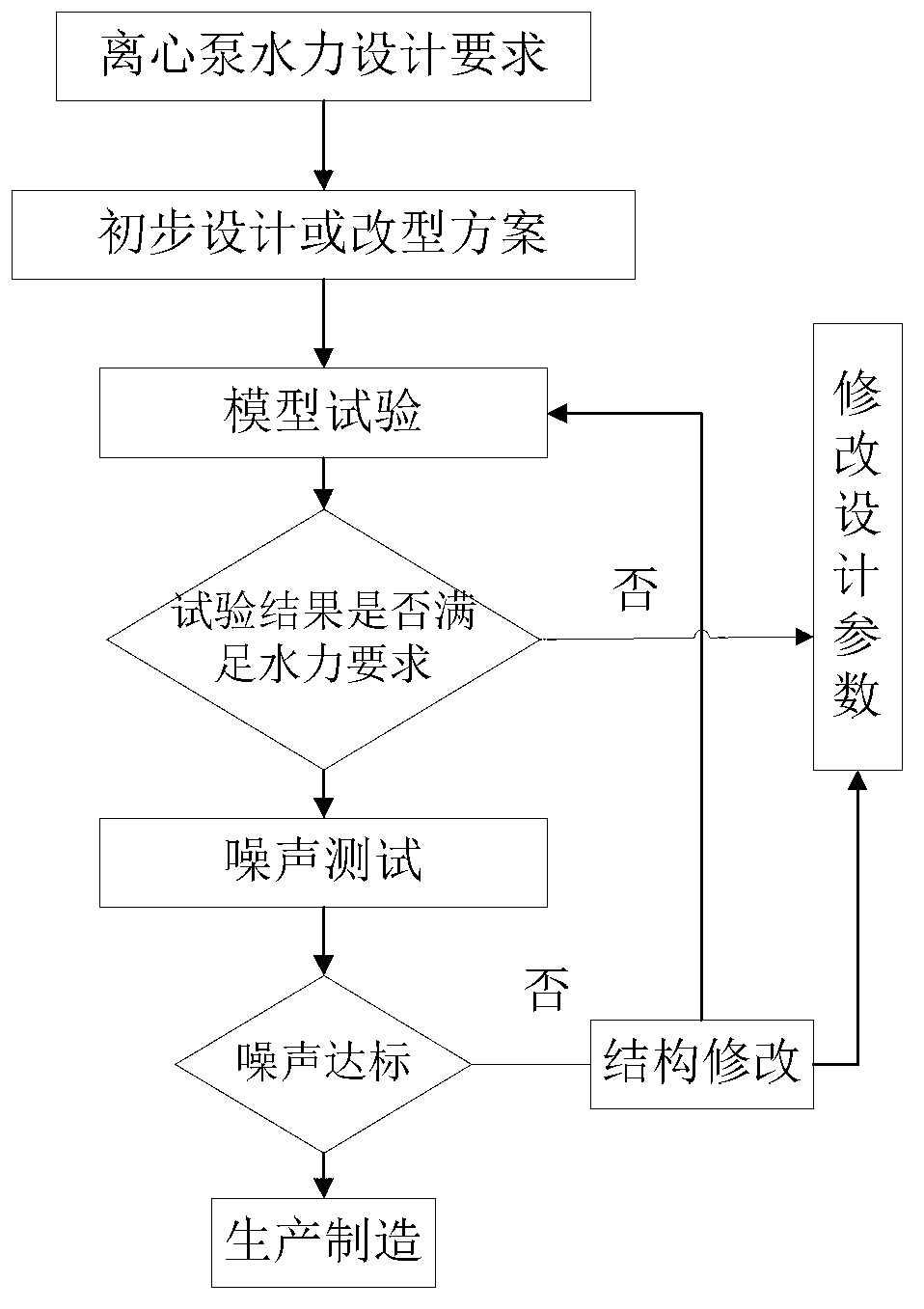
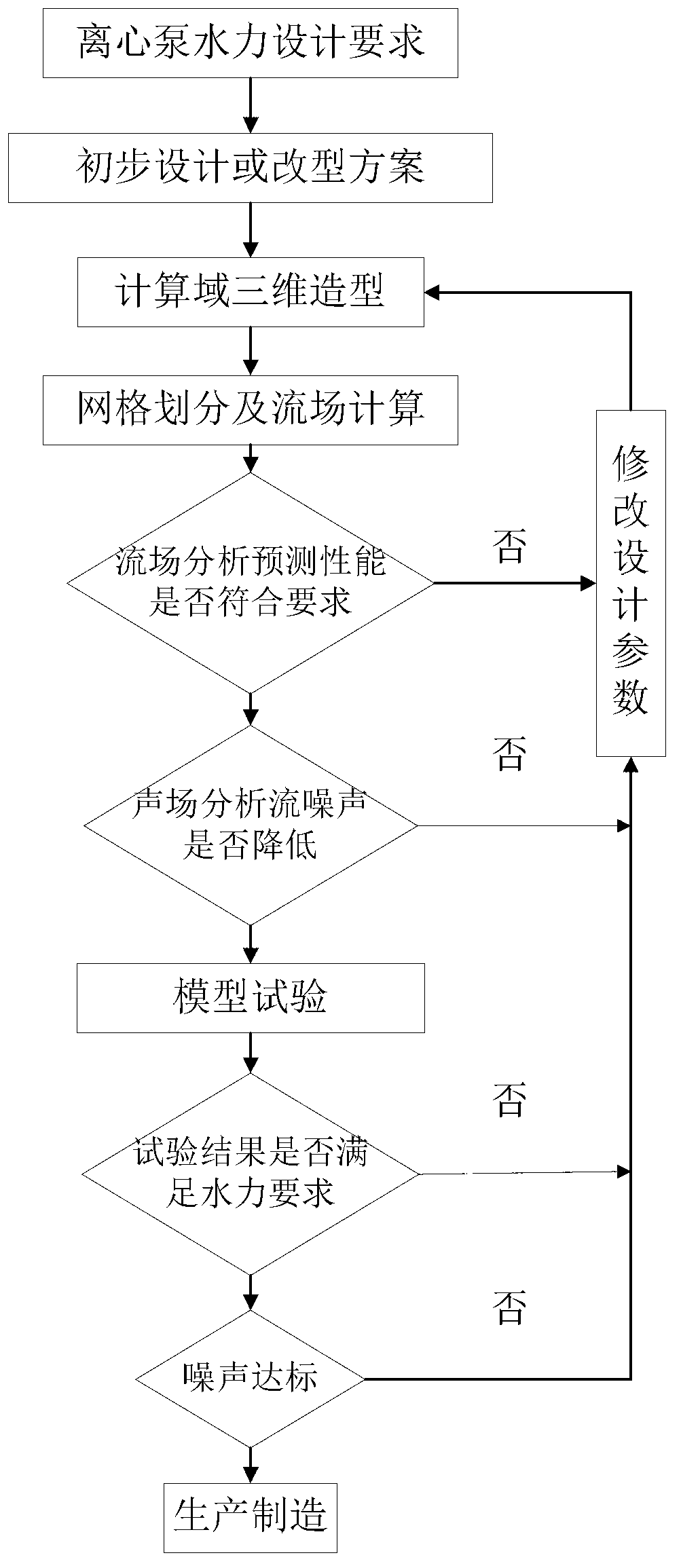
Low-noise hydraulic design method of centrifugal pump with low specific speed
ActiveCN103306985AImprove design qualityImprove machine performancePump componentsSpecial data processing applicationsLow noiseComputational acoustics
The invention discloses a low-noise design method of a centrifugal pump with low specific speed, and relates to an active control method of flow noise of turbomachinery. The design method comprises the steps that firstly, main structural dimensions of a centrifugal pump impeller and a helical pumping chamber (volute) are obtained by the traditional low-specific-speed pump design method; secondly, an internal flow field of the pump is computed by a computational fluid mechanics method; the performance of the pump is predicted whether to meet a design requirement; an optimum design improvement is performed by analyzing a stationary flow field; thirdly, flow induction noise of the pump with low specific speed is predicted by a computational acoustics method; if a flow noise index is qualified, the design is accomplished; if the flow noise index is disqualified, subsequent steps are performed; fourthly, the diameter of the impeller basically meeting a performance requirement in the design is adjusted to allow a gap between the impeller and a volute tongue to be increased continuously to 20%; splitter blades are added in the middles of blades to increase the lift, control the flow situation, and ensure the efficiency; and finally, the pump subjected to the impeller improvement design is subjected to noise prediction; if the flow noise index is qualified, the design is accomplished; and if the flow noise index is disqualified, the beginning step is repeated. The design method shortens the research and development period, saves the development cost, effectively improves the design quality of the centrifugal pump, can simultaneously meet low-noise requirements of the lift and the efficiency, and realizes optimization of the performance of the complete centrifugal pump with low specific speed.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
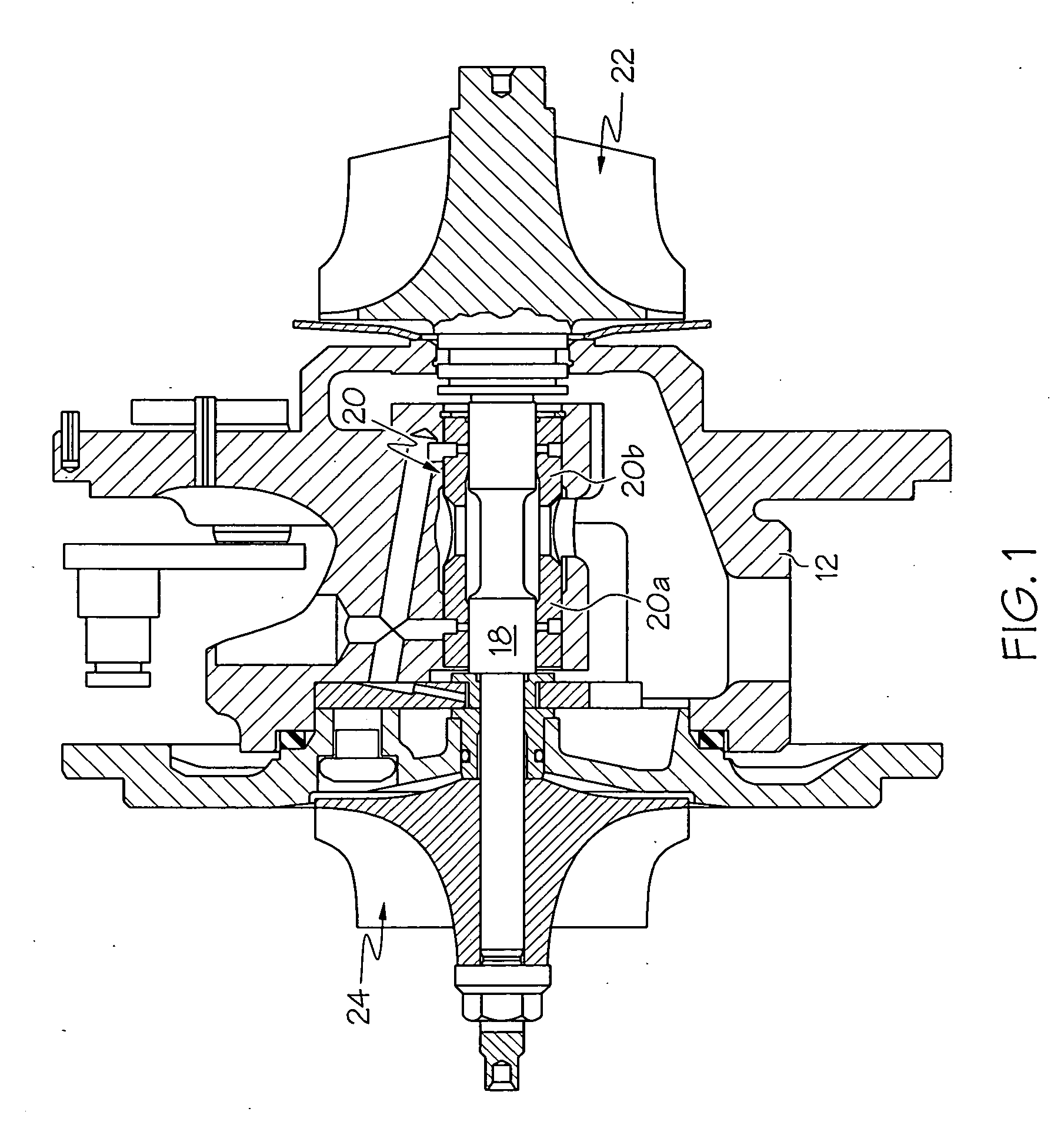
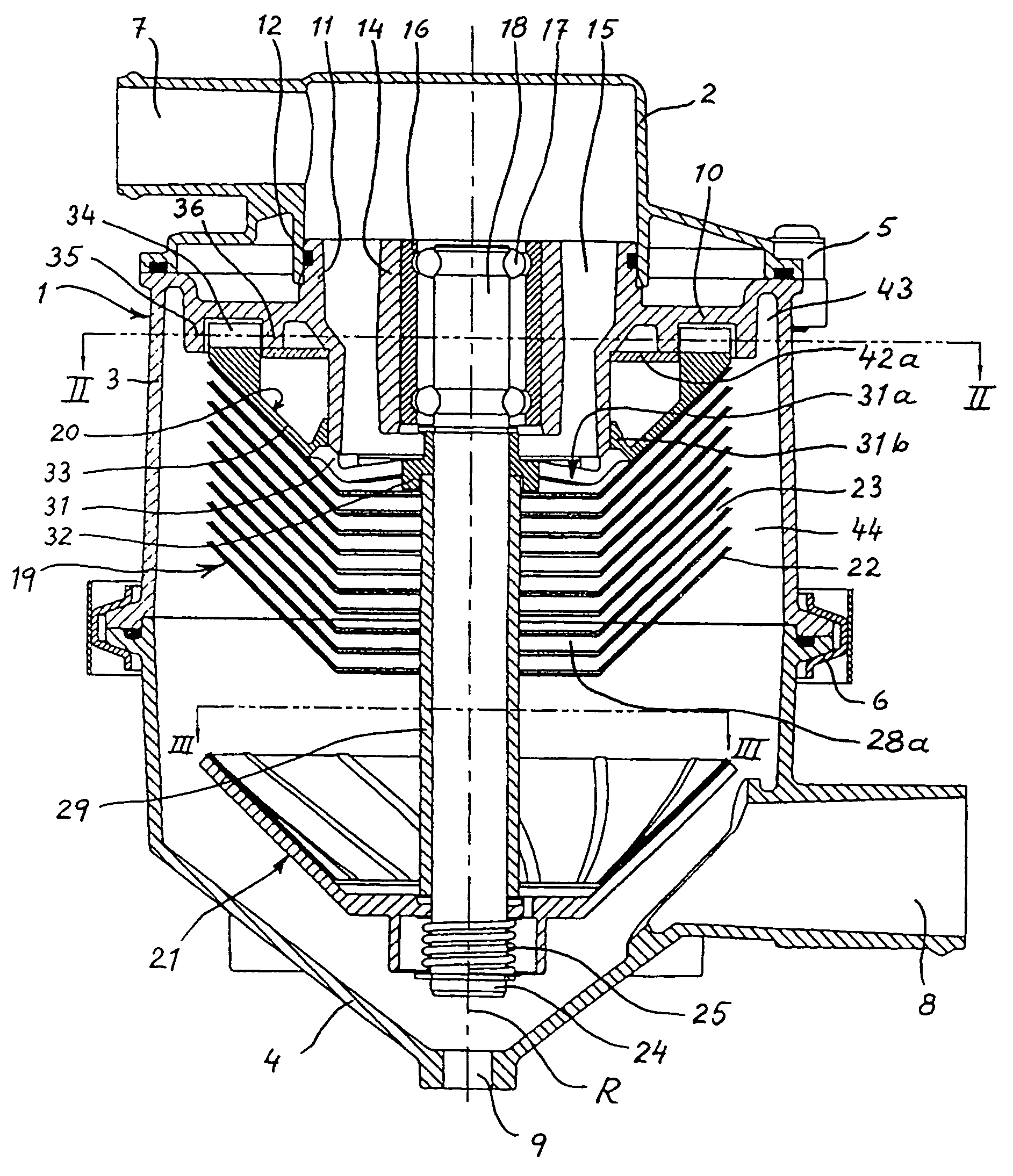
Method and appartus for labyrinth seal packing rings
A seal assembly for a turbomachine may include at least one arcuate plate coupled to an interior surface of a stationary housing; a circumferentially-segmented packing ring disposed intermediate to a rotor and the plate; a plurality of arcuate teeth disposed intermediate to the ring and the rotor, wherein a clearance of each tooth decreases progressively going from an upstream side of the turbomachinery to a downstream side; wherein the progressive decrease in the clearances of the teeth creates a passive feedback, such that as a tip clearance decreases, outward radial forces cause the packing ring to move away from the rotor and as the tip clearance increases, inward radial forces cause the packing ring to move toward the rotor; and a biasing member disposed intermediate to the arcuate plate and the ring and coupled to both.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Convertible gas turbine engine
A gas turbine engine includes a turbomachinery core operable to generate a flow of pressurized combustion gases at a variable flow rate, while maintaining a substantially constant core pressure ratio; a rotating fan disposed upstream of the core, the fan adapted to extract energy from the core and generate a first flow of air which is compressed at a first pressure ratio; and at least a first bypass duct surrounding the core downstream of the fan adapted to selectively receive at least a first selected portion of the first flow which is compressed at a second pressure ratio lower than the first pressure ratio, and to bypass the first selected portion around the core, thereby varying a bypass ratio of the engine. The fan is adapted to maintain a flow rate of the first flow substantially constant, independent of the bypass ratio.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
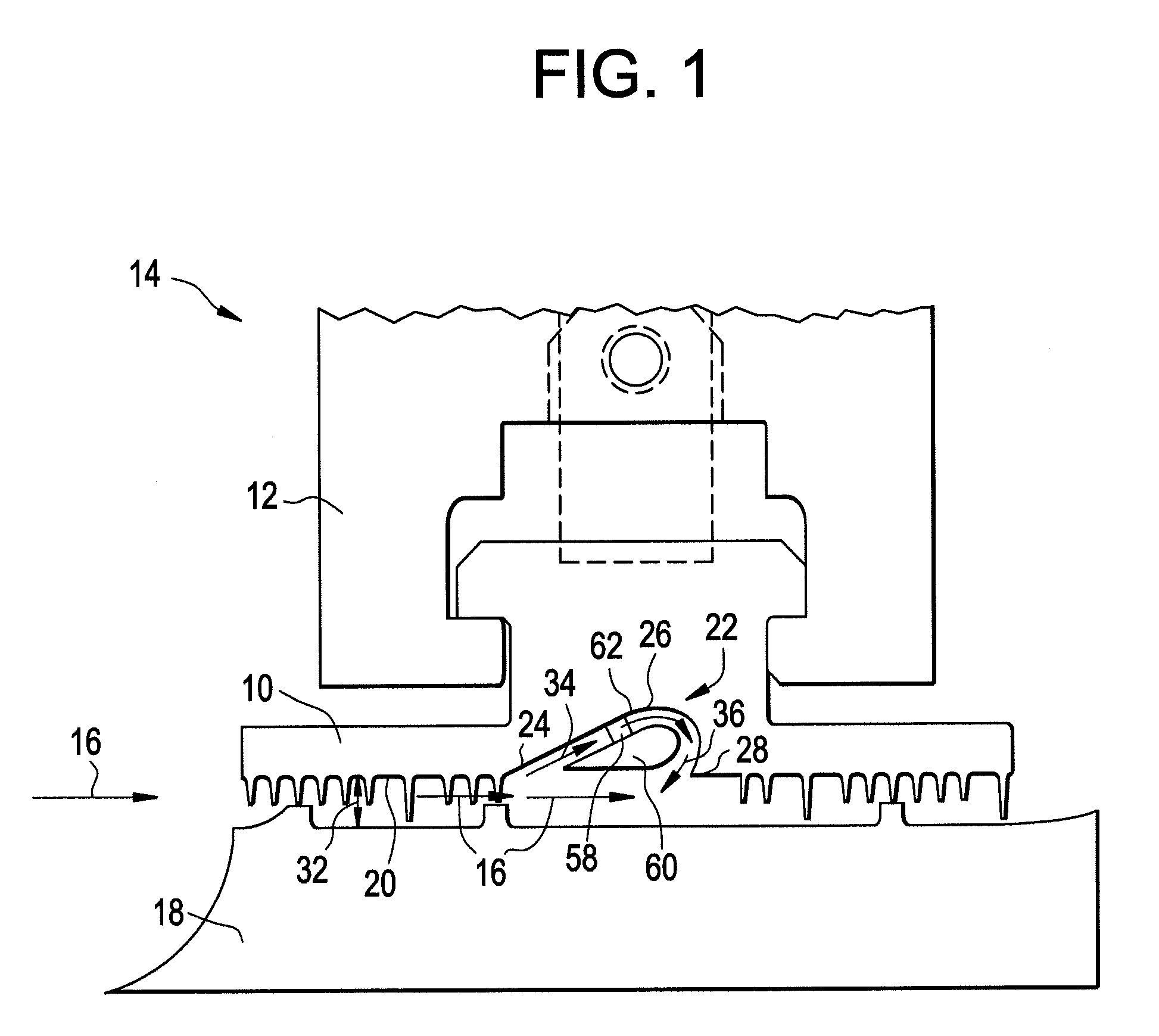
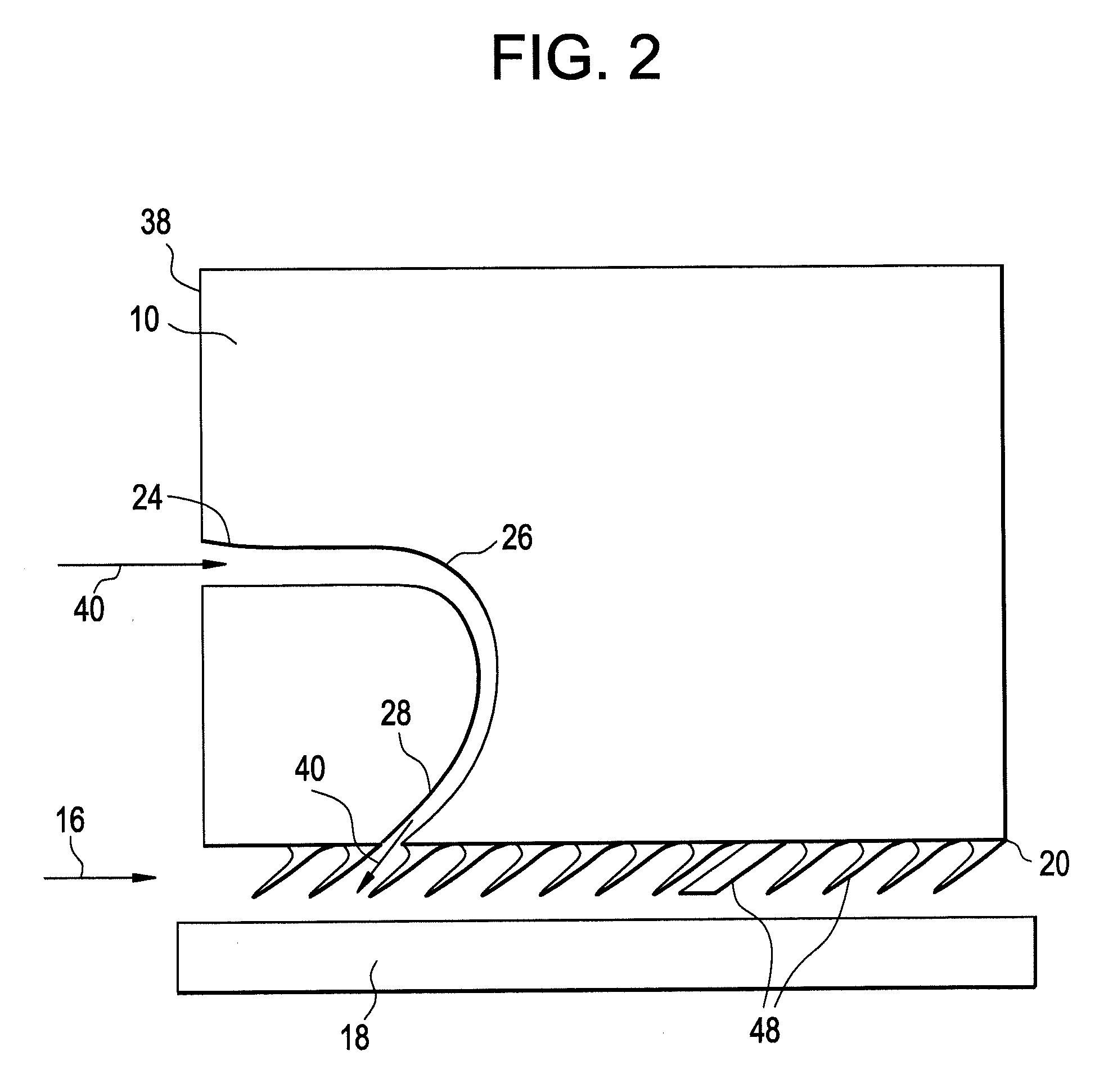
Fluidic sealing for turbomachinery
Disclosed is a seal for turbomachinery including a seal face locatable between a first turbomachinery component and a second turbomachinery component. At least one fluid channel extends through the seal. The at least one fluid channel is capable of injecting fluid flow between the first turbomachinery component and the second turbomachinery component at the seal face thereby disrupting a leakage flow between the first turbomachinery component and the second turbomachinery component. Further disclosed is a turbomachine utilizing the seal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com