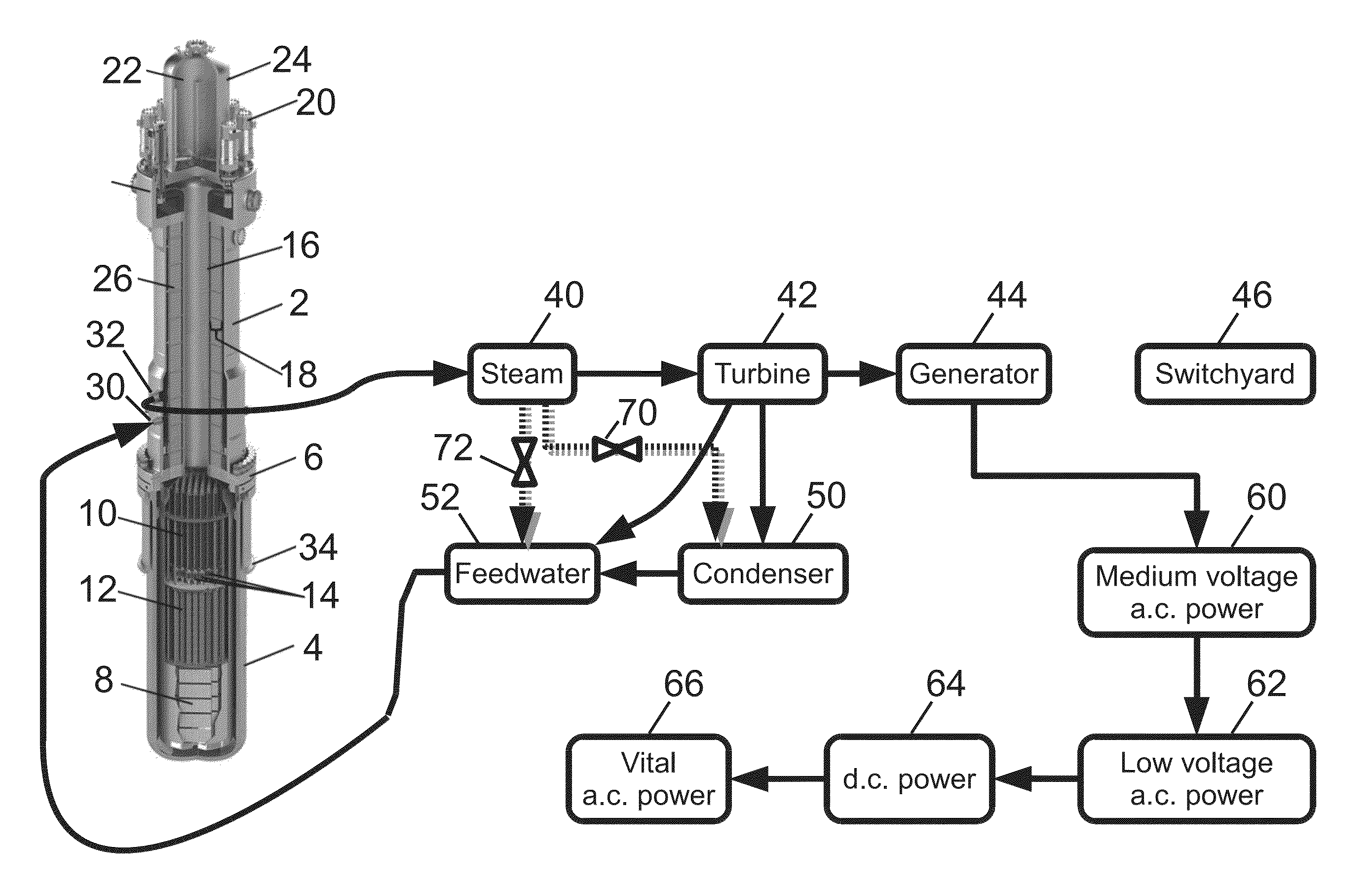
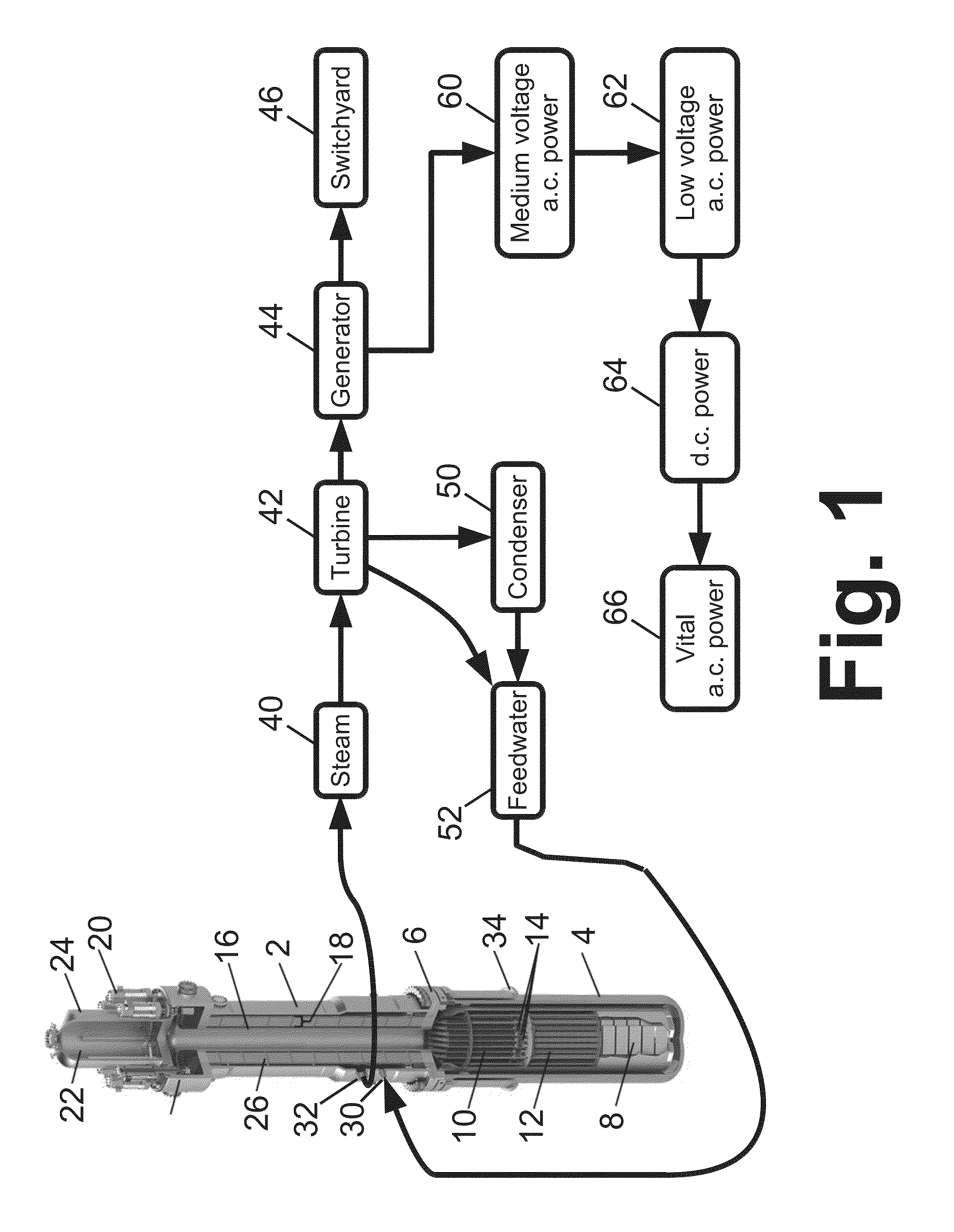
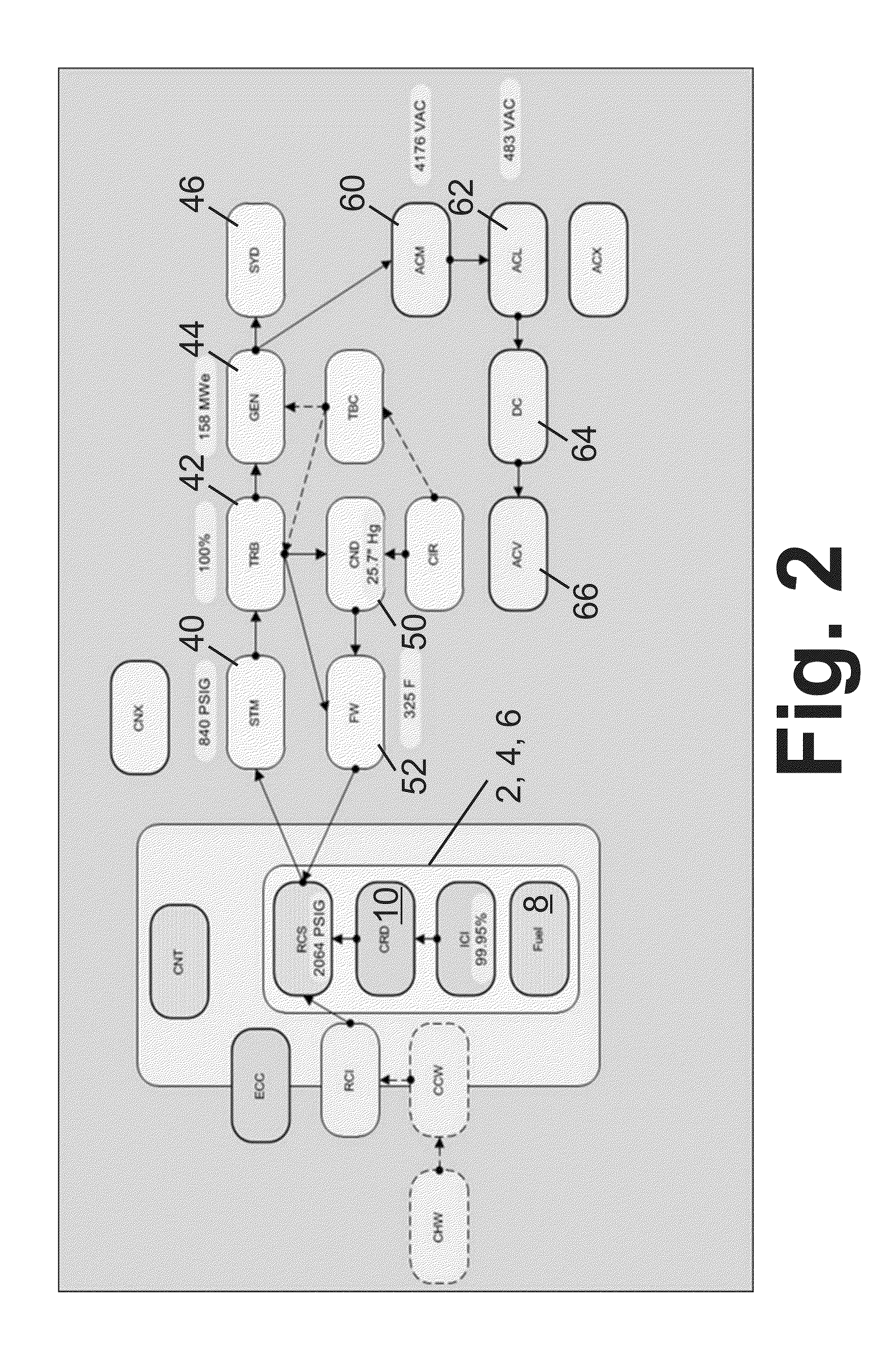
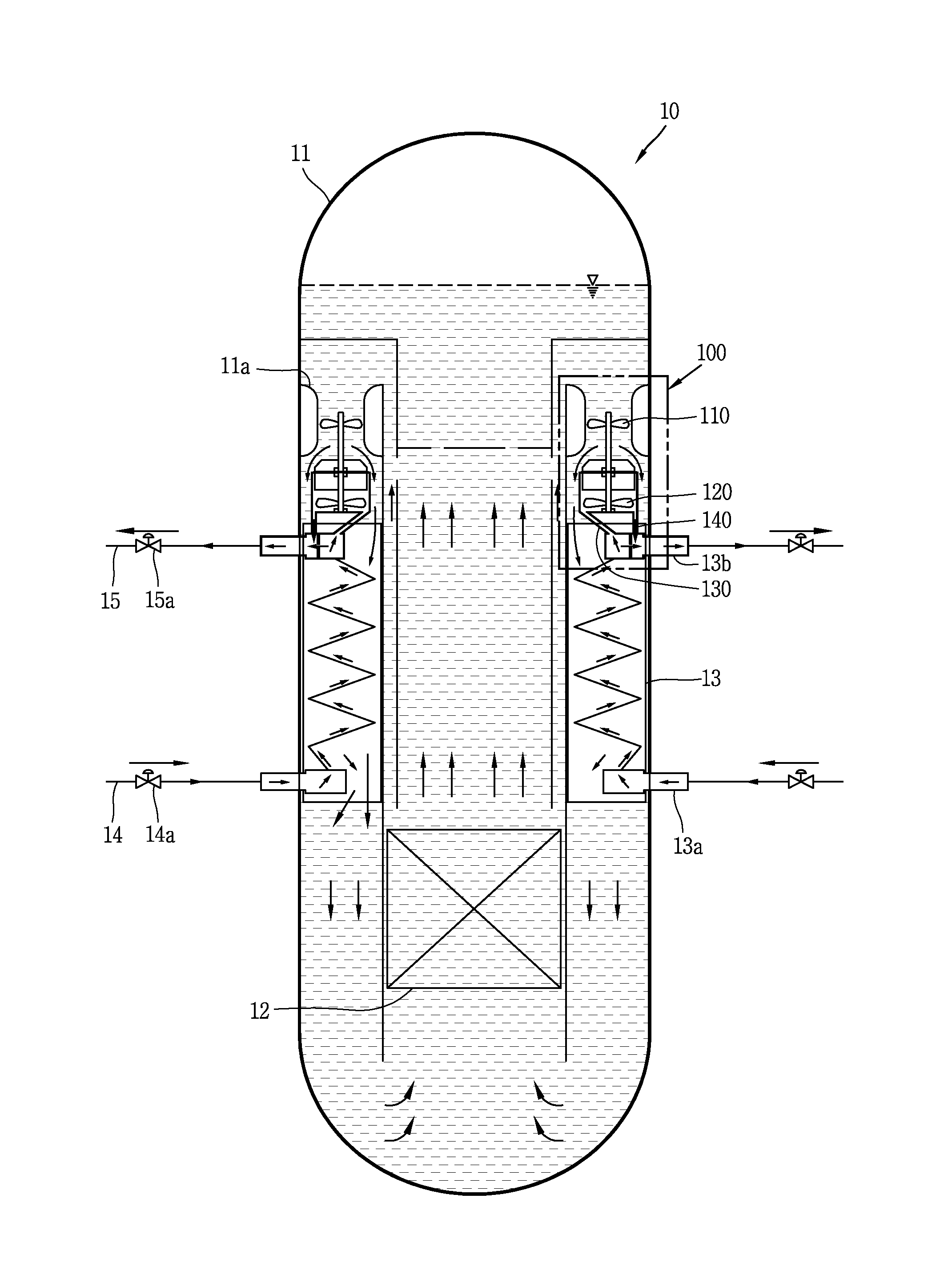
Patents
Literature
1931 results about "Nuclear plant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
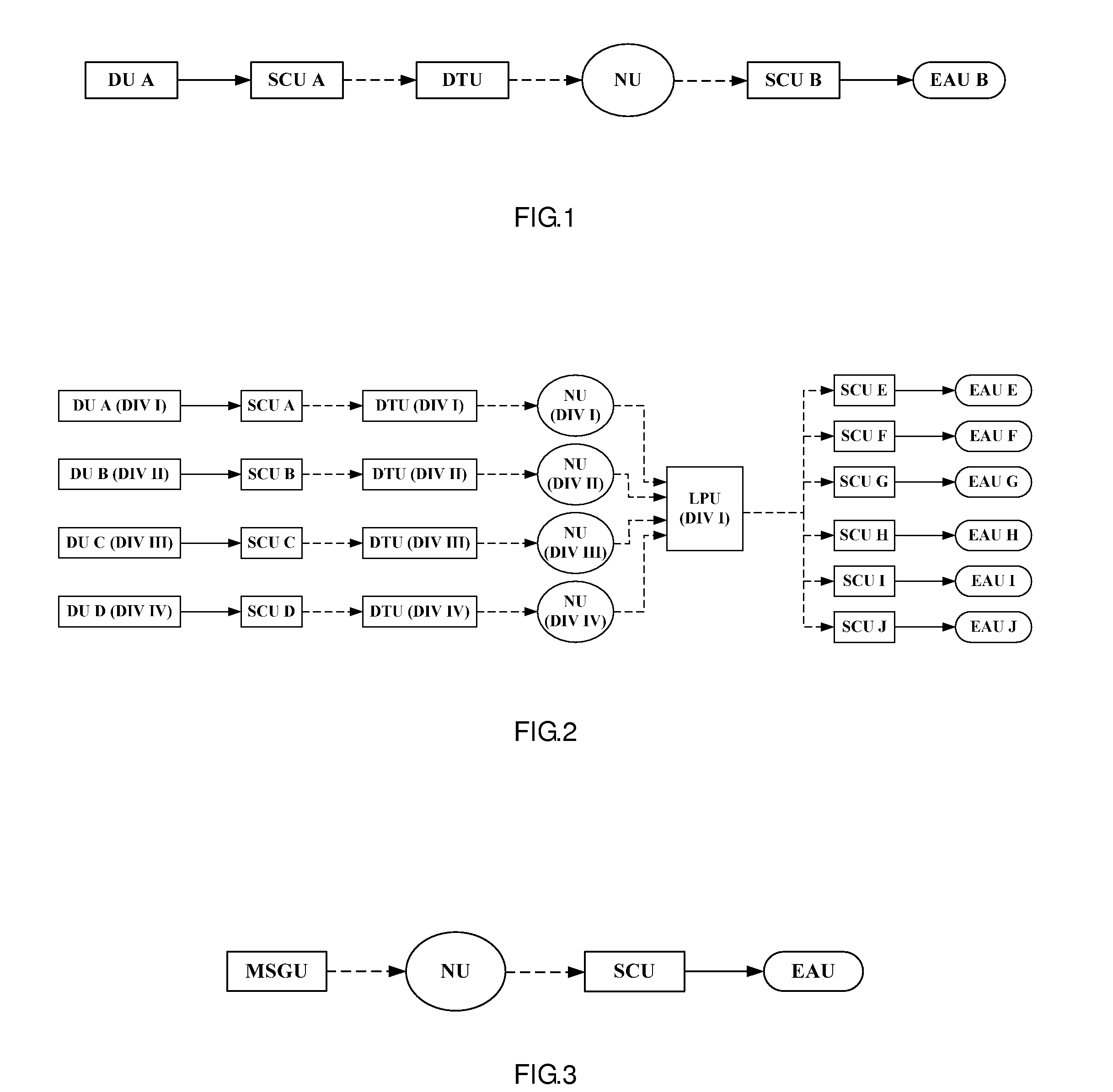
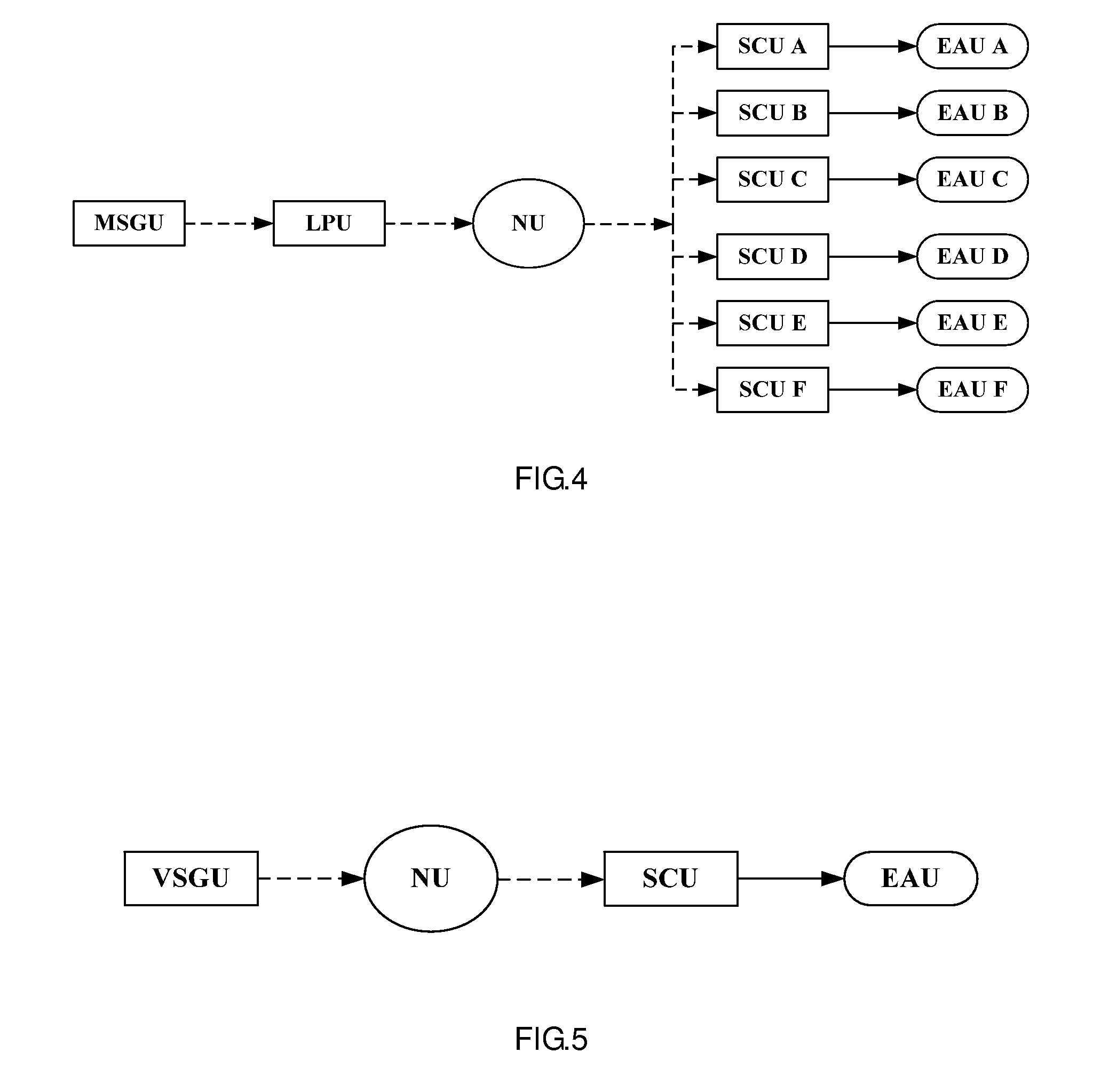
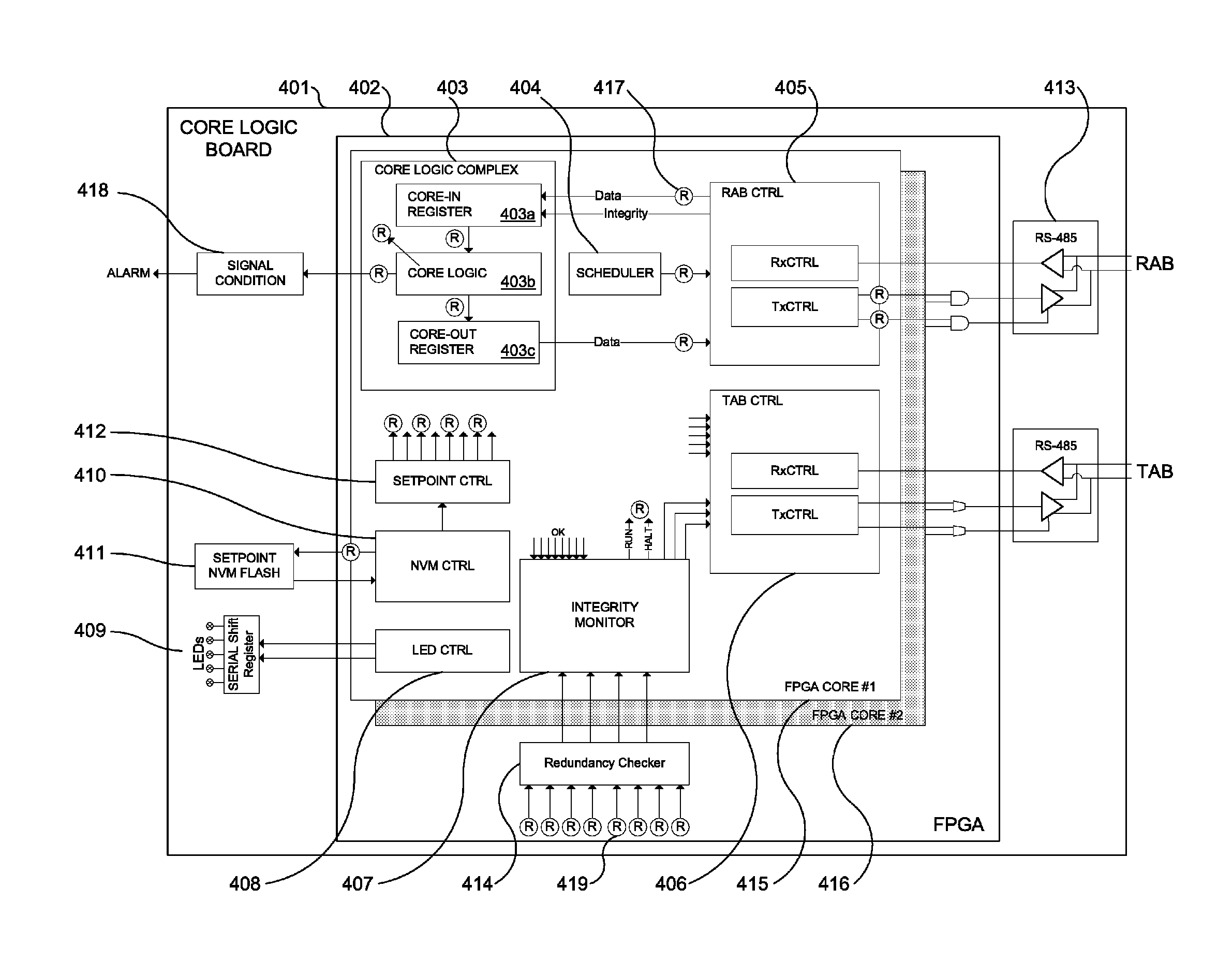
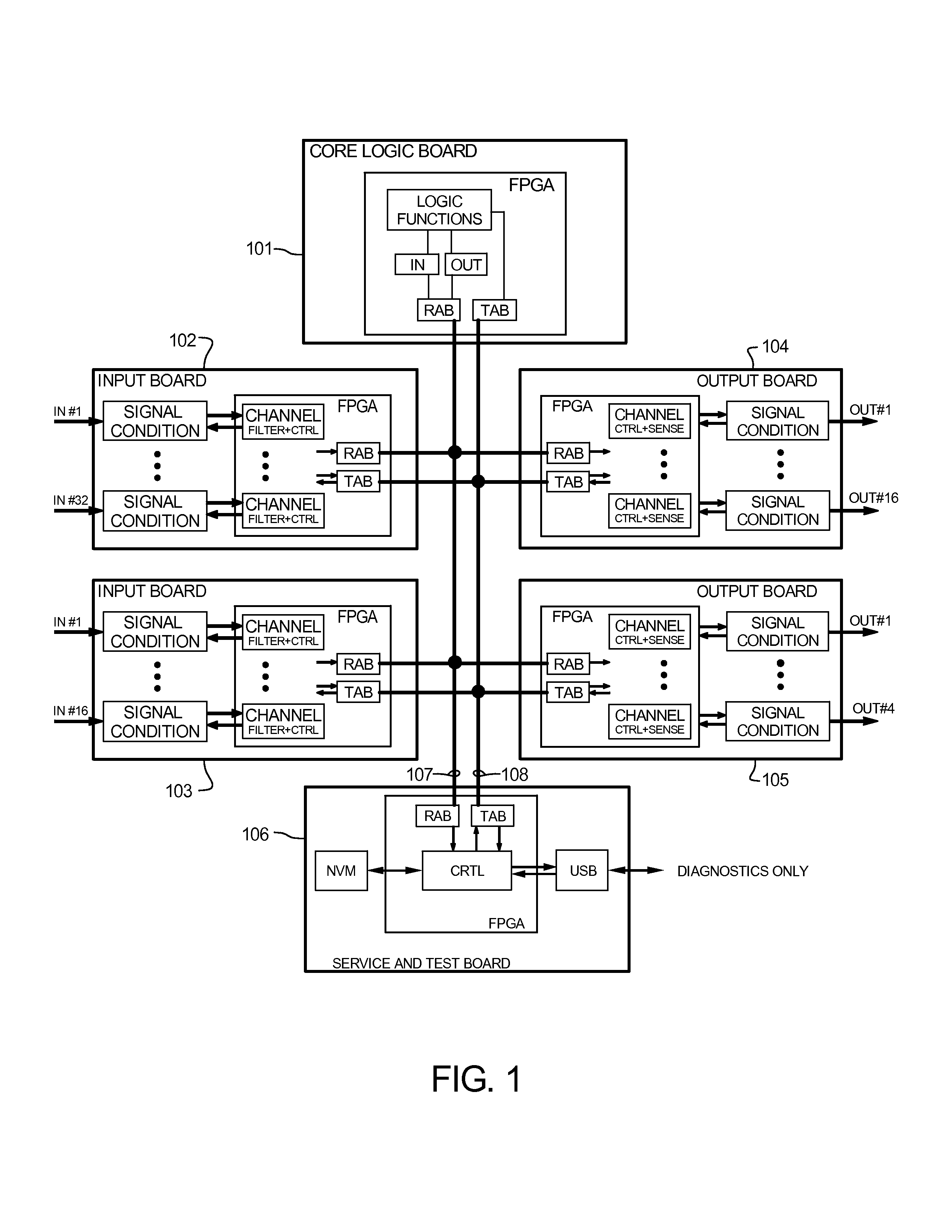
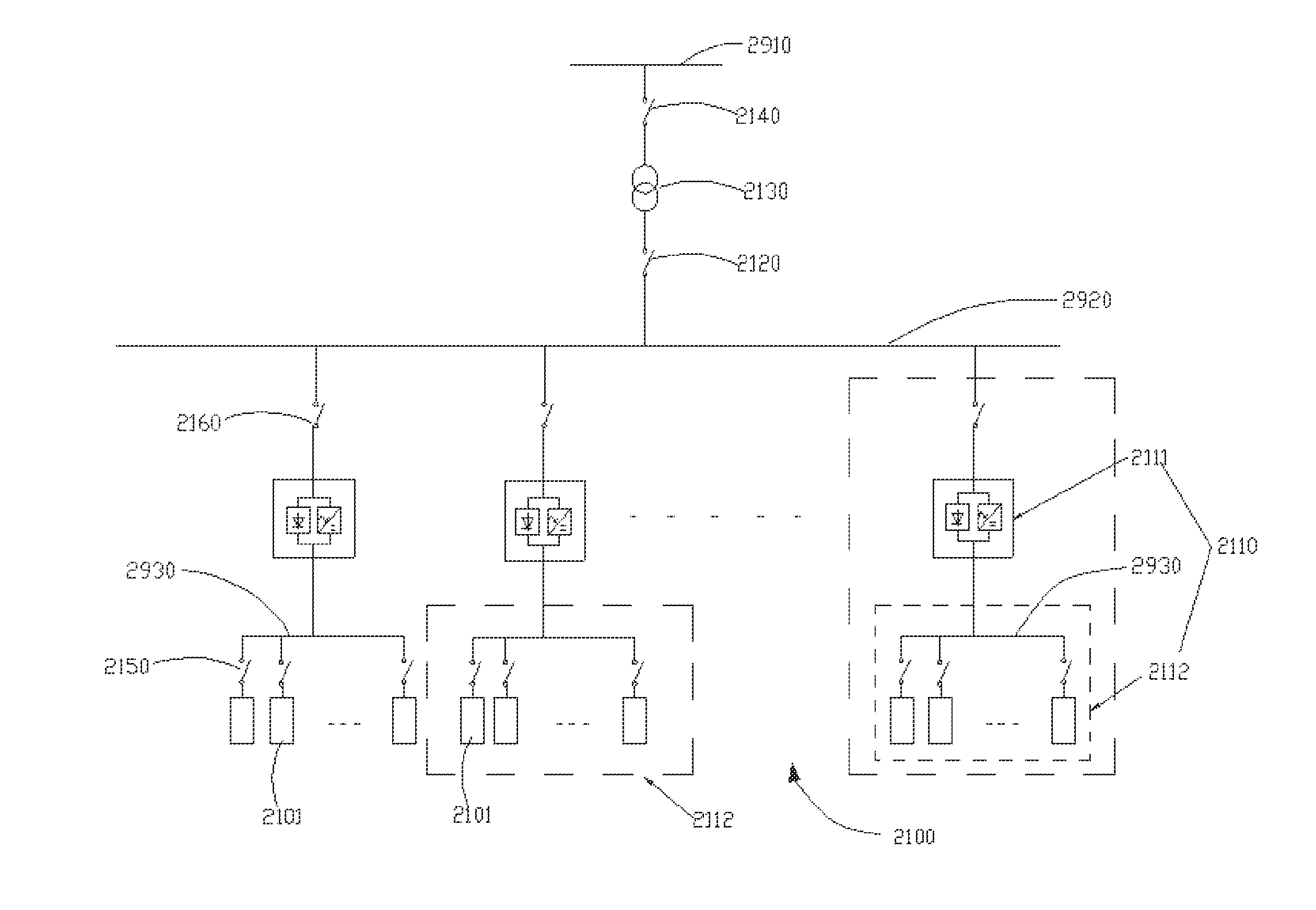
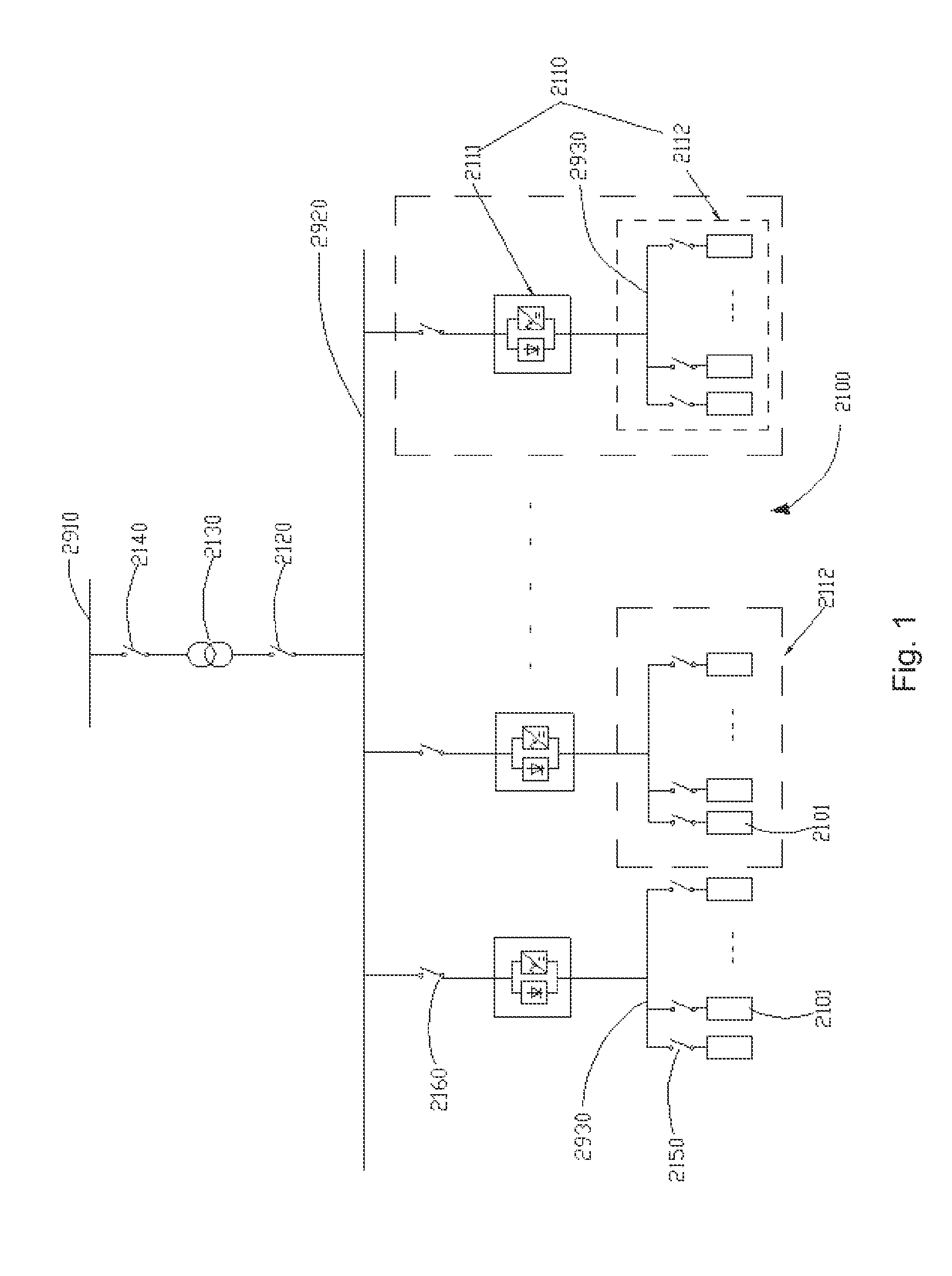
Advanced logic system
ActiveUS7870299B1Improve reliabilityImprove maintainabilityProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsNuclear plantCommon mode failure
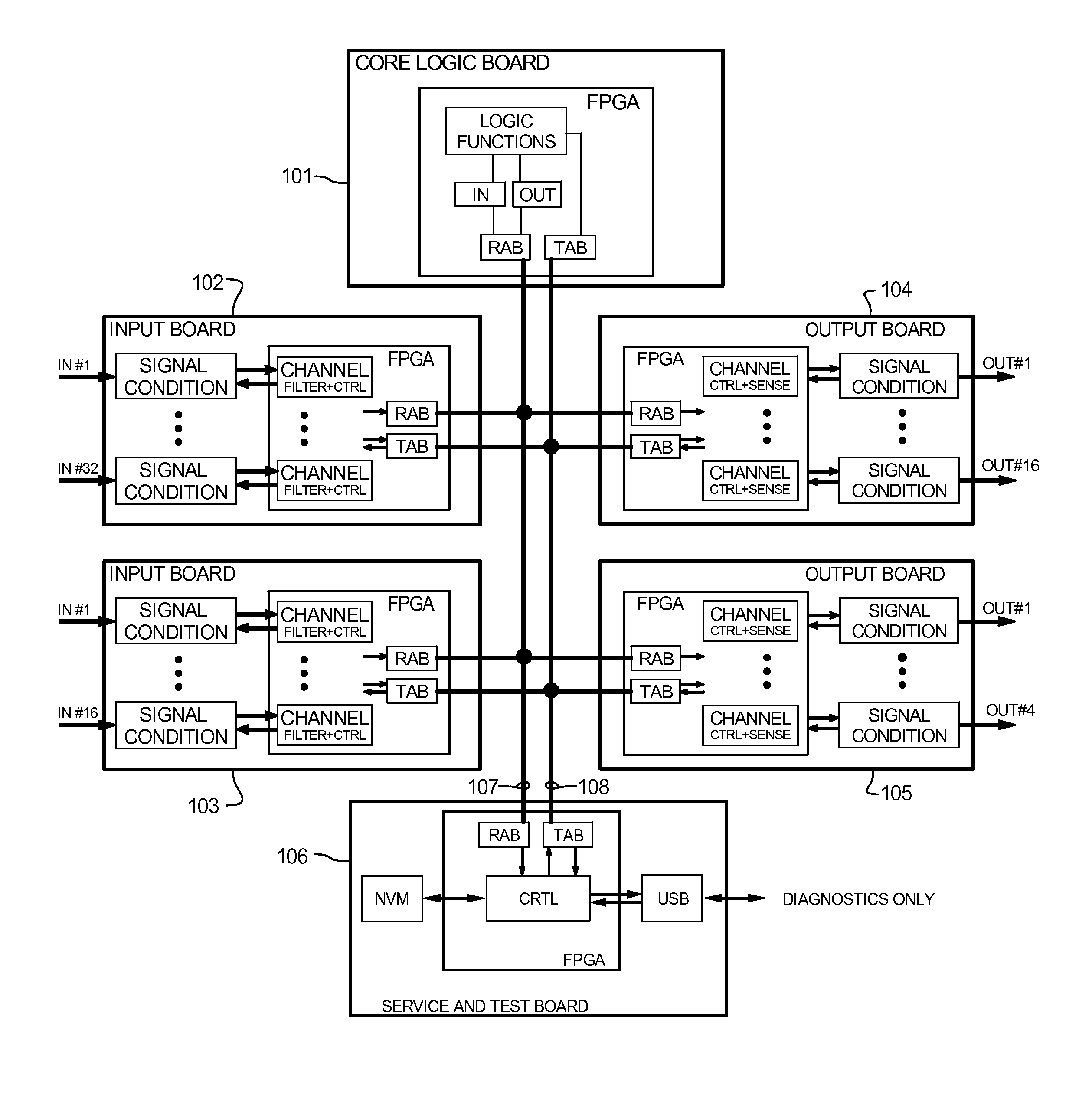
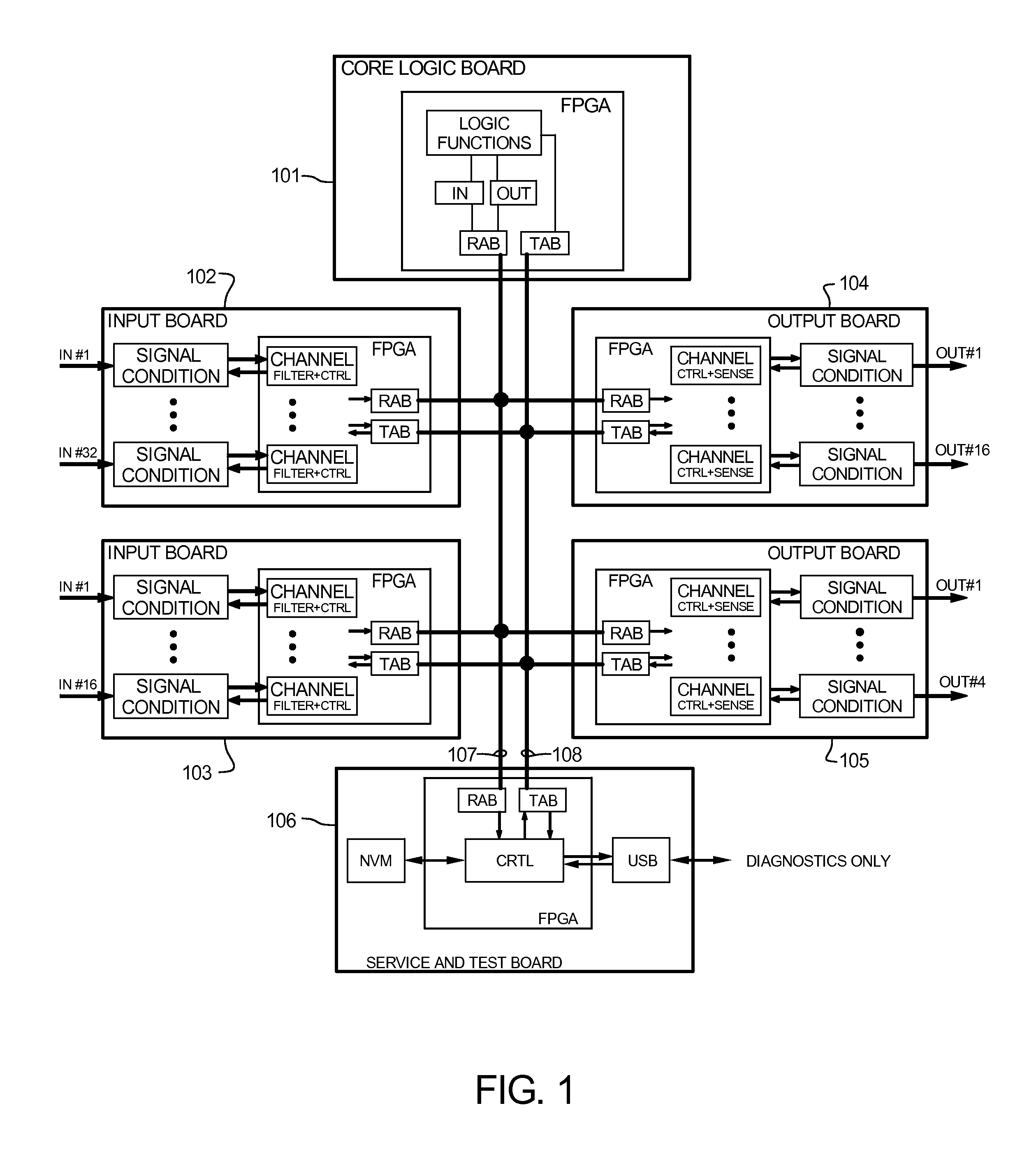
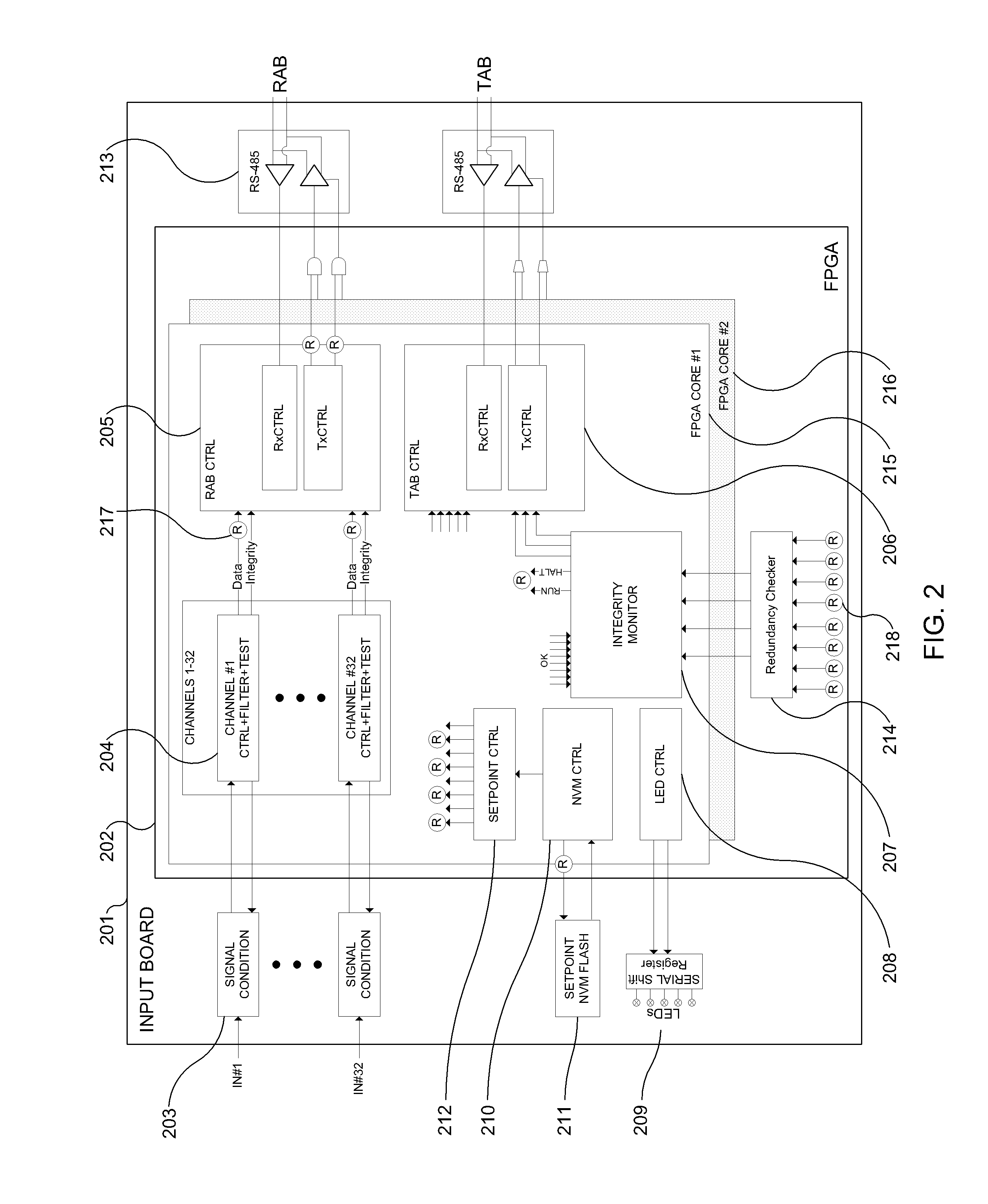
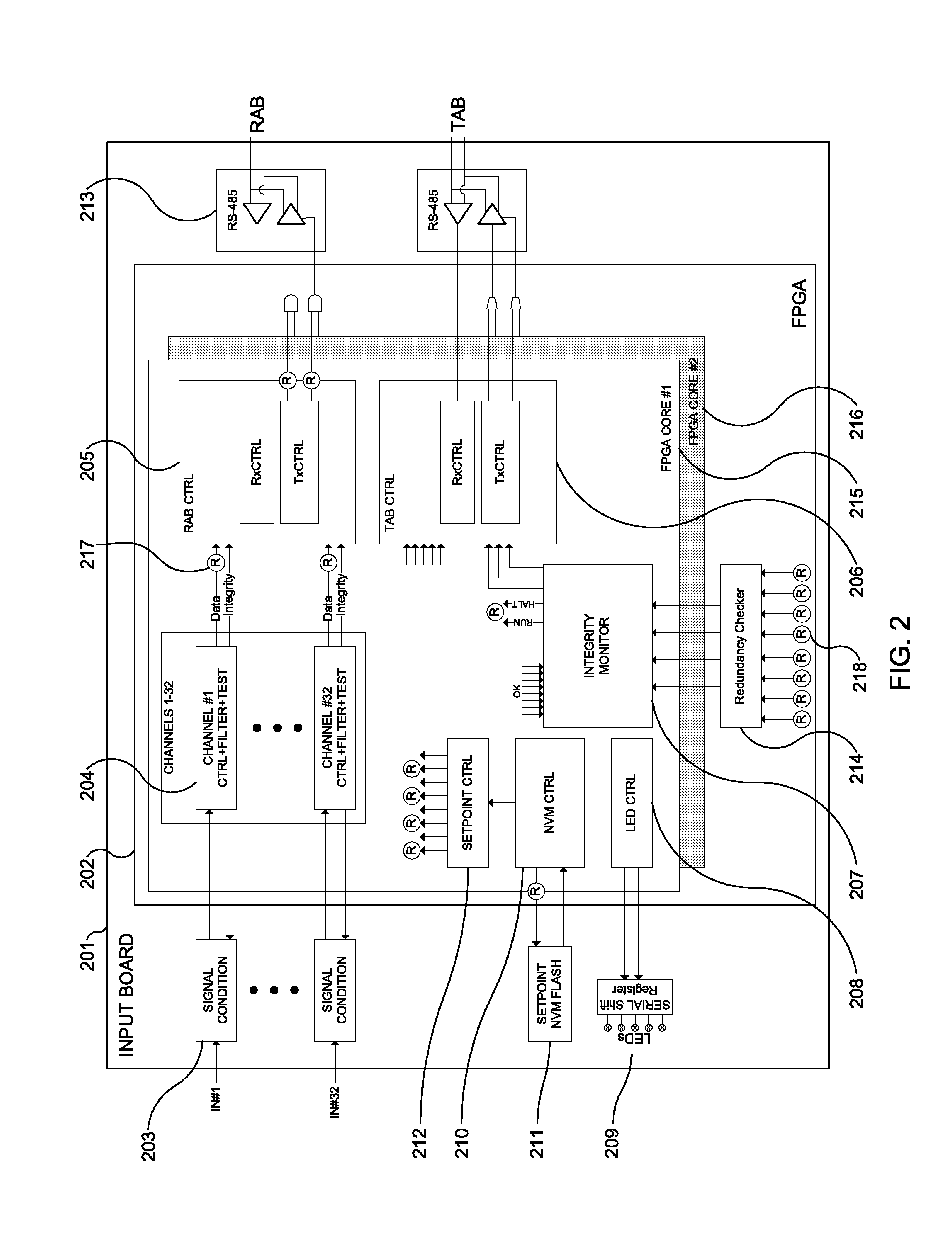
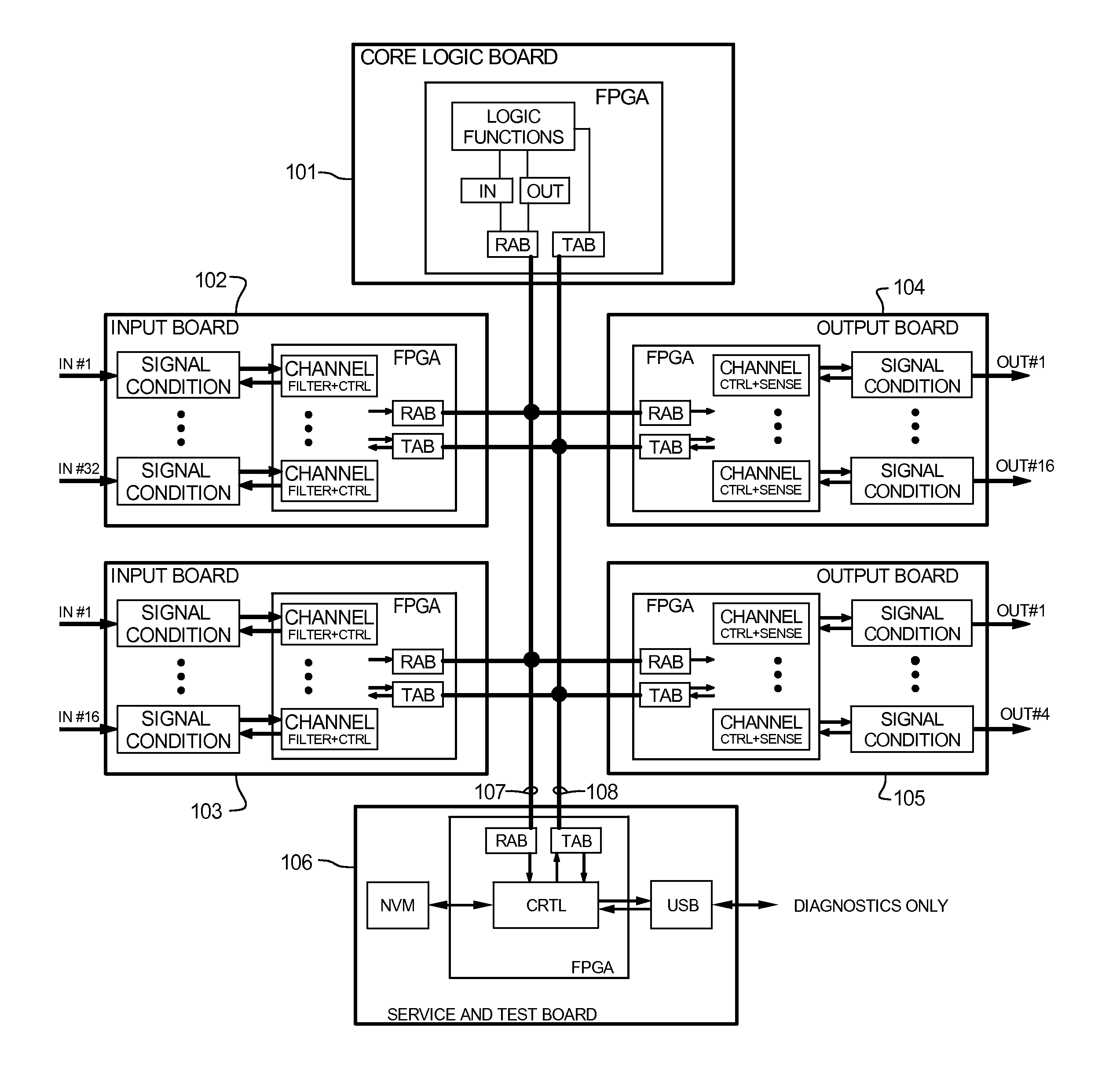
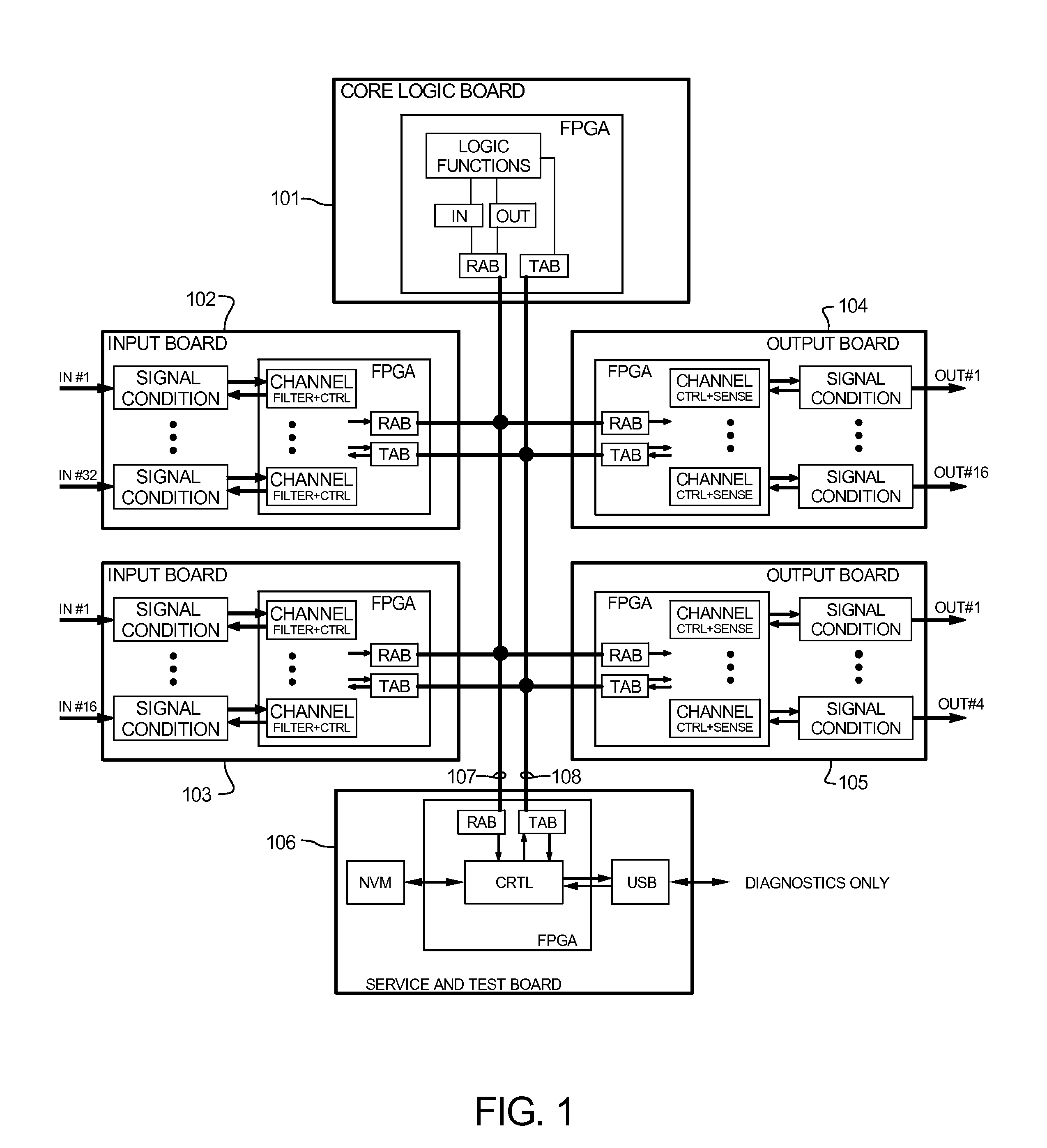
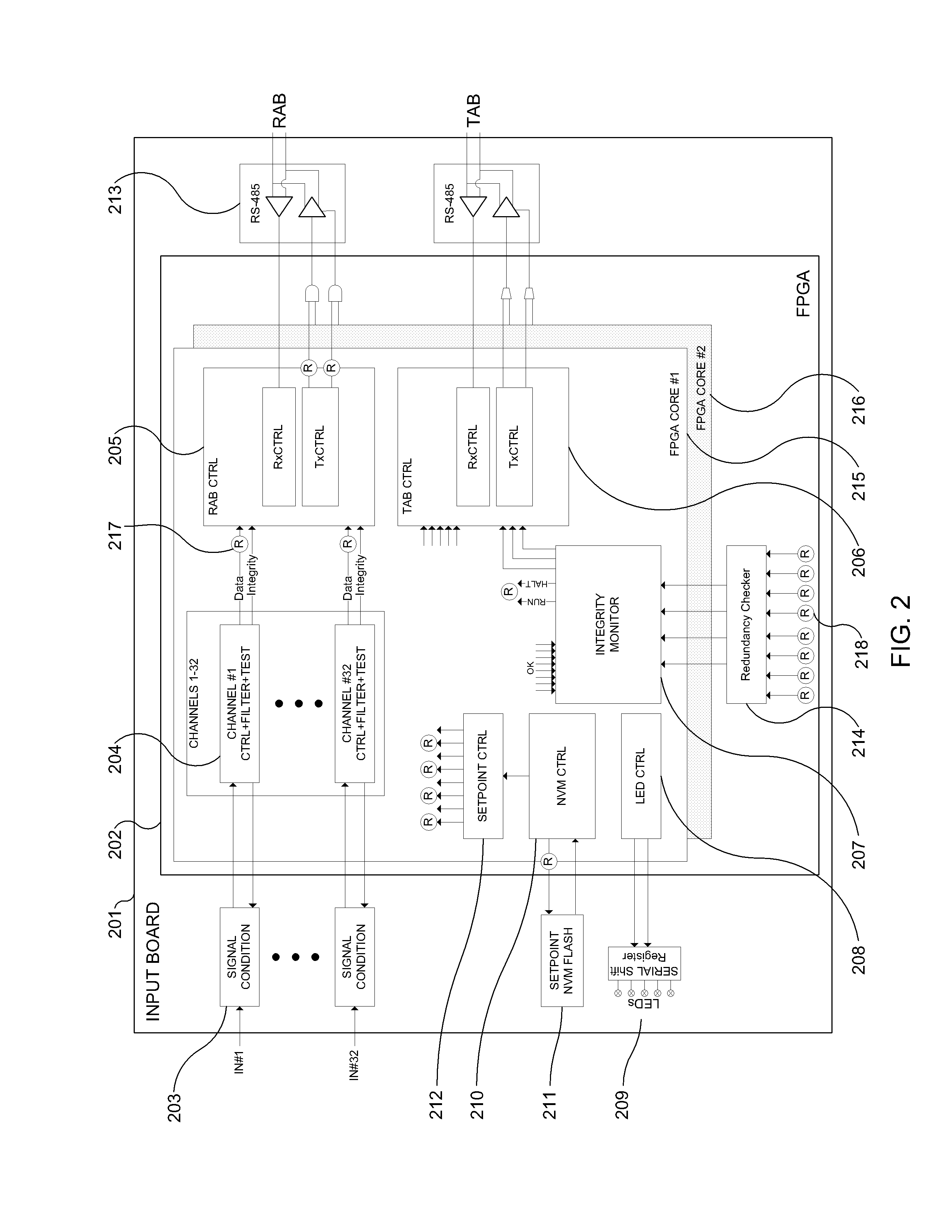
The Advanced Logic System (ALS) is a complete control system architecture, based on a hardware platform rather than a software-based microprocessor system. It is significantly different from other PLC-type control system architectures, by implementing a FPGA in the central control unit. Standard FPGA logic circuits are used rather than a software-based microprocessor which eliminate problems with software based microprocessor systems, such as software common-mode failures. It provides a highly reliable system suitable for safety critical control systems, including nuclear plant protection systems. The system samples process inputs, provides for digital bus communications, applies a control logic function, and provides for controlled outputs. The architecture incorporates advanced features such as diagnostics, testability, and redundancy on multiple levels. It additionally provides significant improvements in failure detection, isolation, and mitigation for the highest level of integrity and reliability.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
A Modeling Method for the Third Generation Pressurized Water Reactor Nuclear Power Unit
ActiveCN102279901ASolving Co-SimulationHas engineering application valueSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a modeling method for a third generation pressurized water reactor nuclear power generating unit. The modeling method comprises the following steps of: 1, decomposing a nuclear power generating unit system into a plurality of subsystem models; 2, establishing the subsystem models in the step 1 according to heat engineering and energy transfer and conversion rules; 3, combining the subsystem models obtained in the step 2 into a nuclear power generating unit full system model, and connecting the nuclear power generating unit full system model with a power system model toobtain a combined model of a nuclear power generating unit and the power system; and 4, establishing a customized model of the third generation pressurized water reactor nuclear power generating uniton the basis of the combined model of the nuclear power generating unit and the power system, and simulating the performance of the nuclear power generating unit and machine-grid interaction according to the customized model. The method effectively solves combined emulation of the nuclear power generating unit and a power unit, can be applied to machine-grid coordination analysis of a nuclear power plant and a power grid, and has high practicability.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
System for comprehensive utilization of three industrial wastes
InactiveCN101618292AAchieve energy saving and emission reductionReduce manufacturing costDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatmentElectric powerToxic industrial waste
The invention provides a system for comprehensive utilization of three industrial wastes, mainly relating to the field of energy conservation and emission reduction, in particular to the comprehensive utilization of the three industrial wastes; to realize the objective of energy conservation and emission reduction required by the recycle economy, a system technology targeted at comprehensive utilization of the three industrial wastes of factories is adopted; in the invention, the reactor in the nuclear plant, the boiler in the coal-fired power plant and other types of supercritical boilers are utilized to provide a new cooling and turbine drive mode to solve the issue of industrial discharge of greenhouse gas and other polluting gases; in addition, collected emissions are utilized to produce nuclear fuel, compound chemical fertilizer or feedstuff and other chemical raw materials; moreover, to realize recycling of resources and sustainable utilization of energy, the original three wastes are innovatively applied to nuclear electric power generation. The system is characterized by comprising 10 major links and the beneficial effect thereof lies in utilizing new methods to realize energy conservation and emission reduction and production cost in the late stage of production can be reduced.
Owner:李元胜
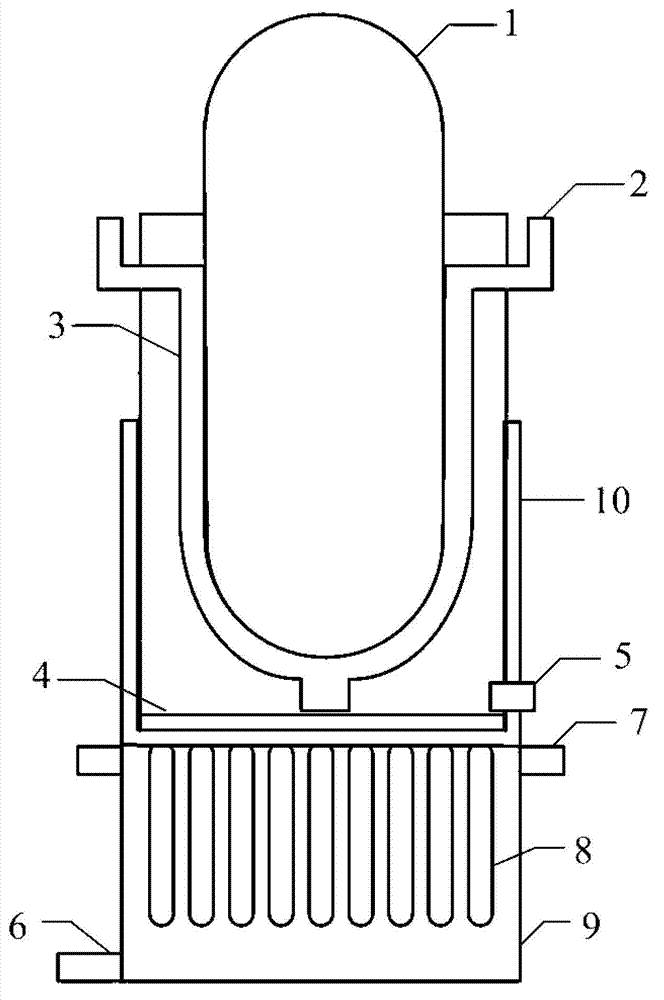
Large-scale passive nuclear plant reactor core catcher with bottom water injection and external cooling
InactiveCN103177778AImplement off-heap retentionImprove securityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear plantCore catcher
The invention provides a large-scale passive nuclear plant reactor core catcher with bottom water injection and external cooling. The catcher comprises a reactor cavity coating the lower middle part of a reactor pressure vessel, and a reactor cavity concrete soleplate is formed at the bottom of the reactor cavity; a refractory layer is formed on the side surface of the reactor cavity and the bottom of the reactor cavity concrete soleplate; a steel cylinder is sleeved outside the refractory layer; an external cooling passage is formed at the bottom of the steel cylinder, and a cooling passage inlet and a cooling passage outlet are respectively formed at the two outward-extending ends of the external cooling passage; and dozens of nozzles are fixed at the bottom of the steel cylinder, and the upper ends of the nozzles extend into the reactor cavity concrete soleplate while the lower ends of the nozzles extend into the external cooling passage. According to the invention, the dilution and the temperature reduction of a melt are implemented through the melting of concrete by adopting the reactor cavity concrete soleplate as a sacrificial material. A reactor core melt is collected in the refractory layer after the reactor cavity concrete soleplate is molten through, so that the security and the reliability of a nuclear plant are further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
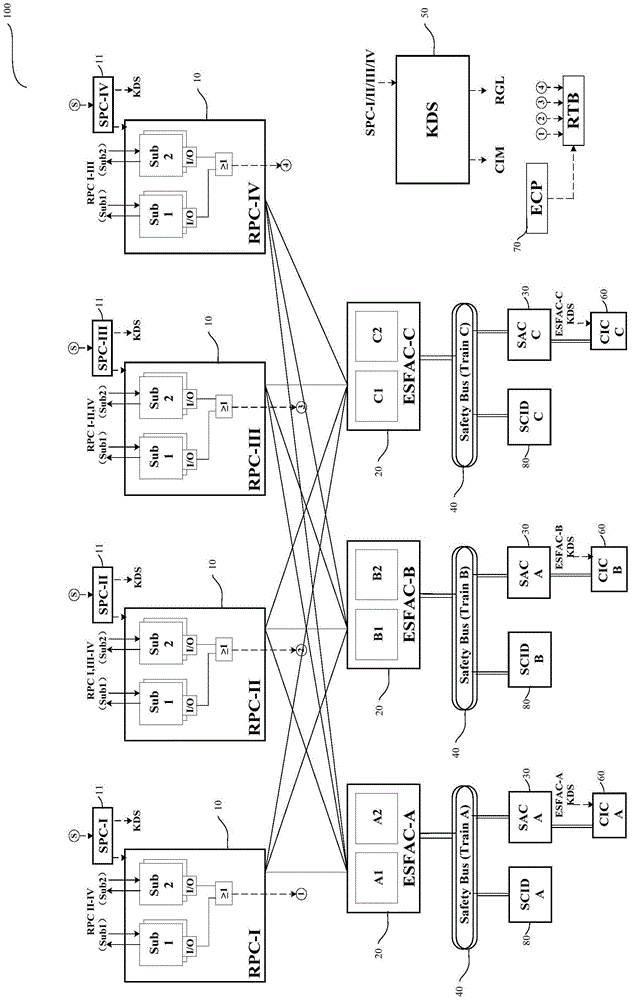
Fault Tree Analysis System for the Instrument Control Process for Nuclear Power Plant with Advanced Boiling Water Reactor Background
InactiveUS20100100251A1Fast and accurate to establishLevel controlAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsProbabilistic risk assessmentBiology
The invention relates to the fault tree analysis system for a nuclear power plant with advanced boiling water reactor. The full digital instrument control system uses six different modes to simulate the transmission of the digital signals and the analog signals from the detection units. It is to develop the fault tree for various signal transmission modes to support the nuclear power plant in probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) and meet requirements for simulated signal detection, transmission, logic operation and equipment actuation. Thus, the digital instrument control flow process can fit into PRA model and properly reflect its importance in risk assessment.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher
InactiveCN103177779AImprove securityImprove reliabilityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear plantCore catcher
The invention discloses a large passive pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant crucible-type reactor core catcher which comprises a reactor cavity concrete bottom plate (4), a crucible cooling system water filling nozzle (6), a crucible cooling system water vapor outlet (7), a crucible component (8), a crucible cooling system cavity (9) and a melt collector (10). The reactor core catcher is organically combined with an interactive voice response (IVR) system, the safety of the nuclear power plant can be further improved, and the reliability of the system is higher due to the crucible design.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
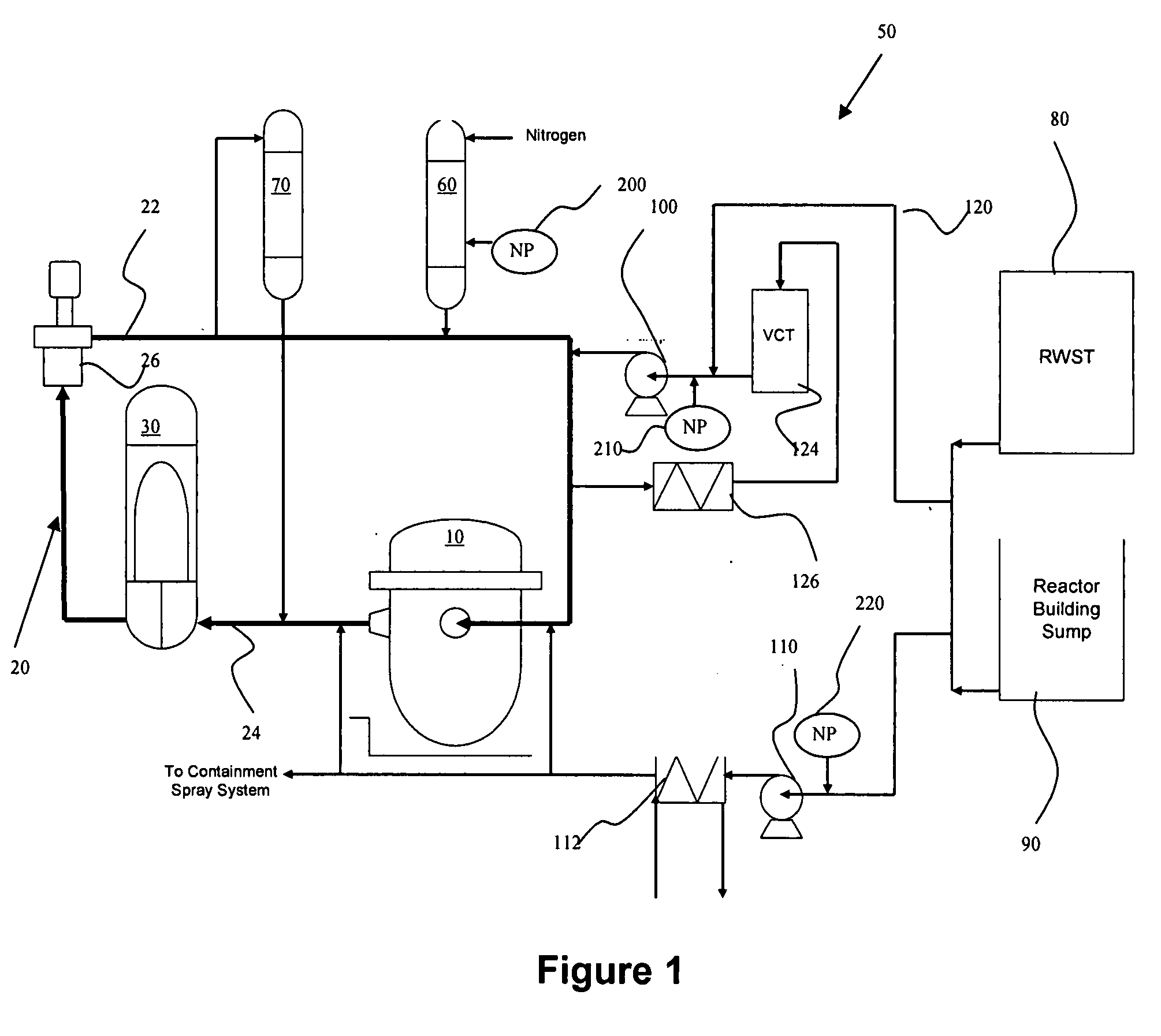
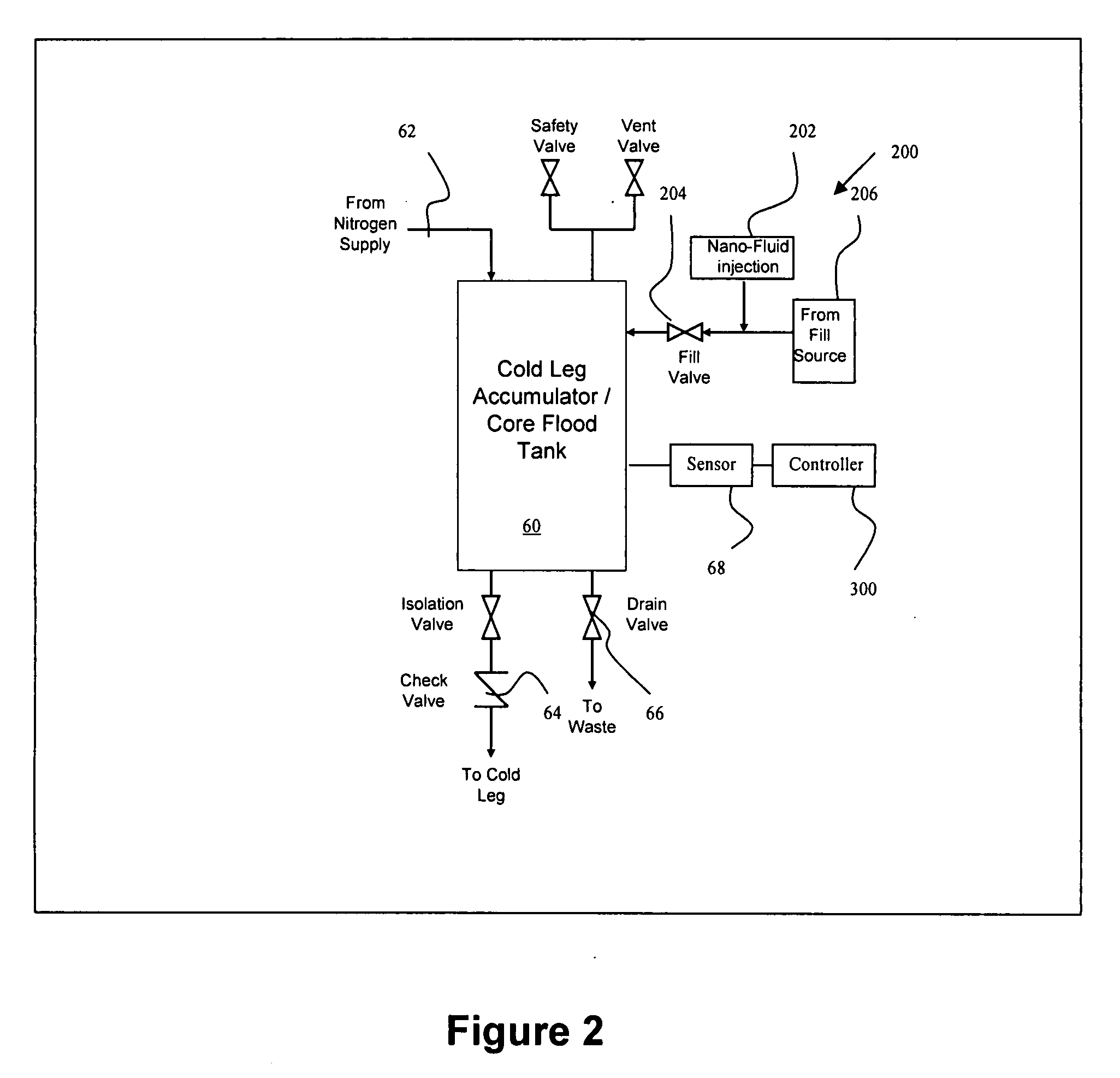
Nuclear power plant using nanoparticles in emergency systems and related method
InactiveUS20080212733A1Improve heat transfer performanceNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsNuclear plantMotor drive
A nuclear power plant with an improved cooling system using nanoparticles in solid or fluid form is provided. The nanoparticles are delivered in locations such as the cold leg accumulator and high and low pressure pumps of an emergency core cooling system. Motor driven valves and pressurization can aid in the delivery. Methods for providing the nanoparticles are also provided.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
Advanced logic system diagnostics and monitoring
ActiveUS8554953B1Improve reliabilityImprove maintainabilityStethoscopeDiagnostic recording/measuringNuclear plantCommon mode failure
The Advanced Logic System (ALS) is a complete control system architecture, based on a hardware platform rather than a software-based microprocessor system. It is significantly different from other PLC-type control system architectures, by implementing a FPGA in the central control unit. Standard FPGA logic circuits are used rather than a software-based microprocessor which eliminate problems with software based microprocessor systems, such as software common-mode failures. It provides a highly reliable system suitable for safety critical control systems, including nuclear plant protection systems. The system samples process inputs, provides for digital bus communications, applies a control logic function, and provides for controlled outputs. The architecture incorporates advanced features such as diagnostics, testability, and redundancy on multiple levels. It additionally provides significant improvements in failure detection, isolation, and mitigation for the highest level of integrity and reliability.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Advanced logic system
ActiveUS8156251B1Improve reliabilityImprove maintainabilityProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsNuclear plantCommon mode failure
The Advanced Logic System (ALS) is a complete control system architecture, based on a hardware platform rather than a software-based microprocessor system. It is significantly different from other PLC-type control system architectures, by implementing a FPGA in the central control unit. Standard FPGA logic circuits are used rather than a software-based microprocessor which eliminate problems with software based microprocessor systems, such as software common-mode failures. It provides a highly reliable system suitable for safety critical control systems, including nuclear plant protection systems. The system samples process inputs, provides for digital bus communications, applies a control logic function, and provides for controlled outputs. The architecture incorporates advanced features such as diagnostics, testability, and redundancy on multiple levels. It additionally provides significant improvements in failure detection, isolation, and mitigation for the highest level of integrity and reliability.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
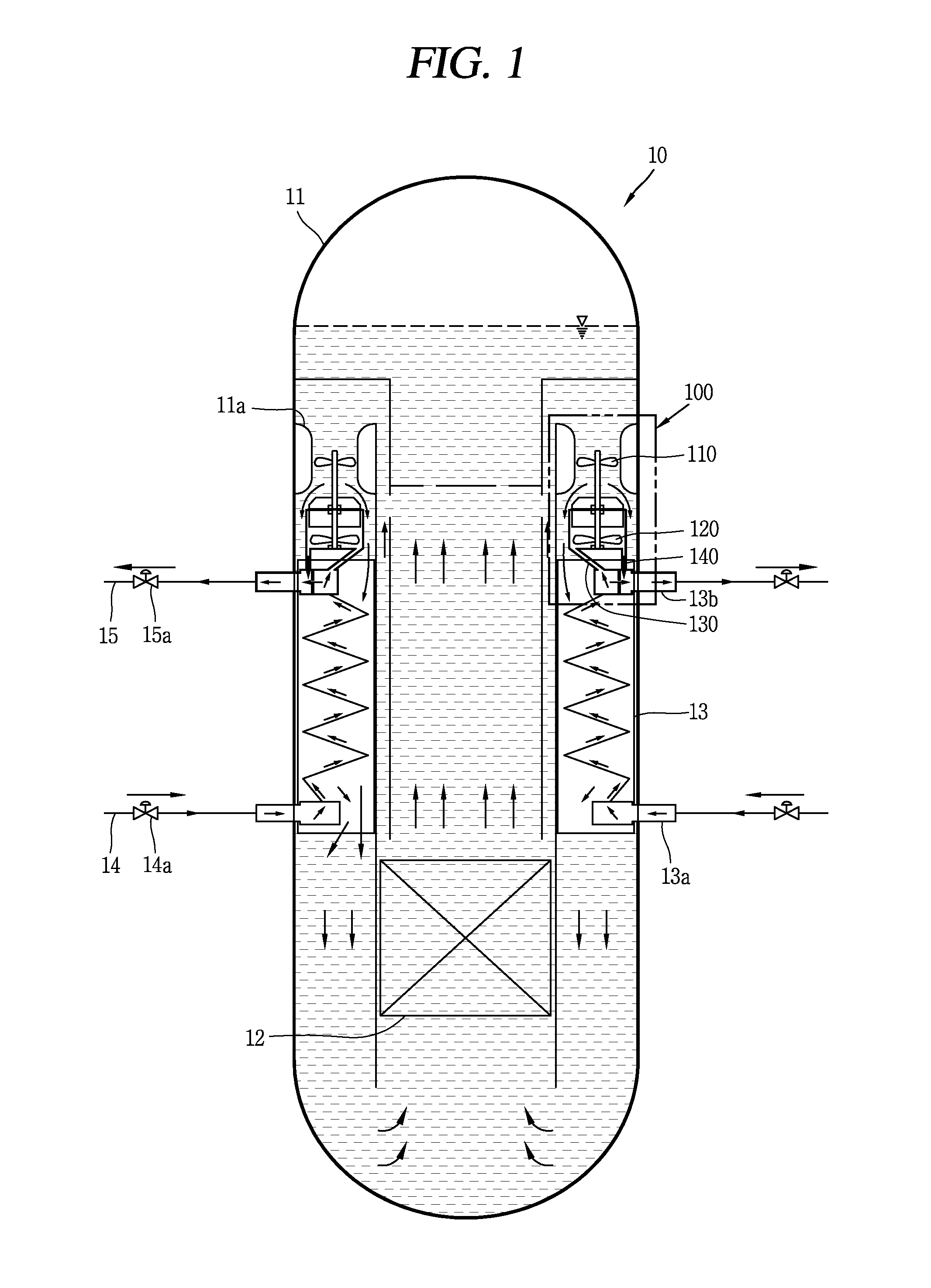
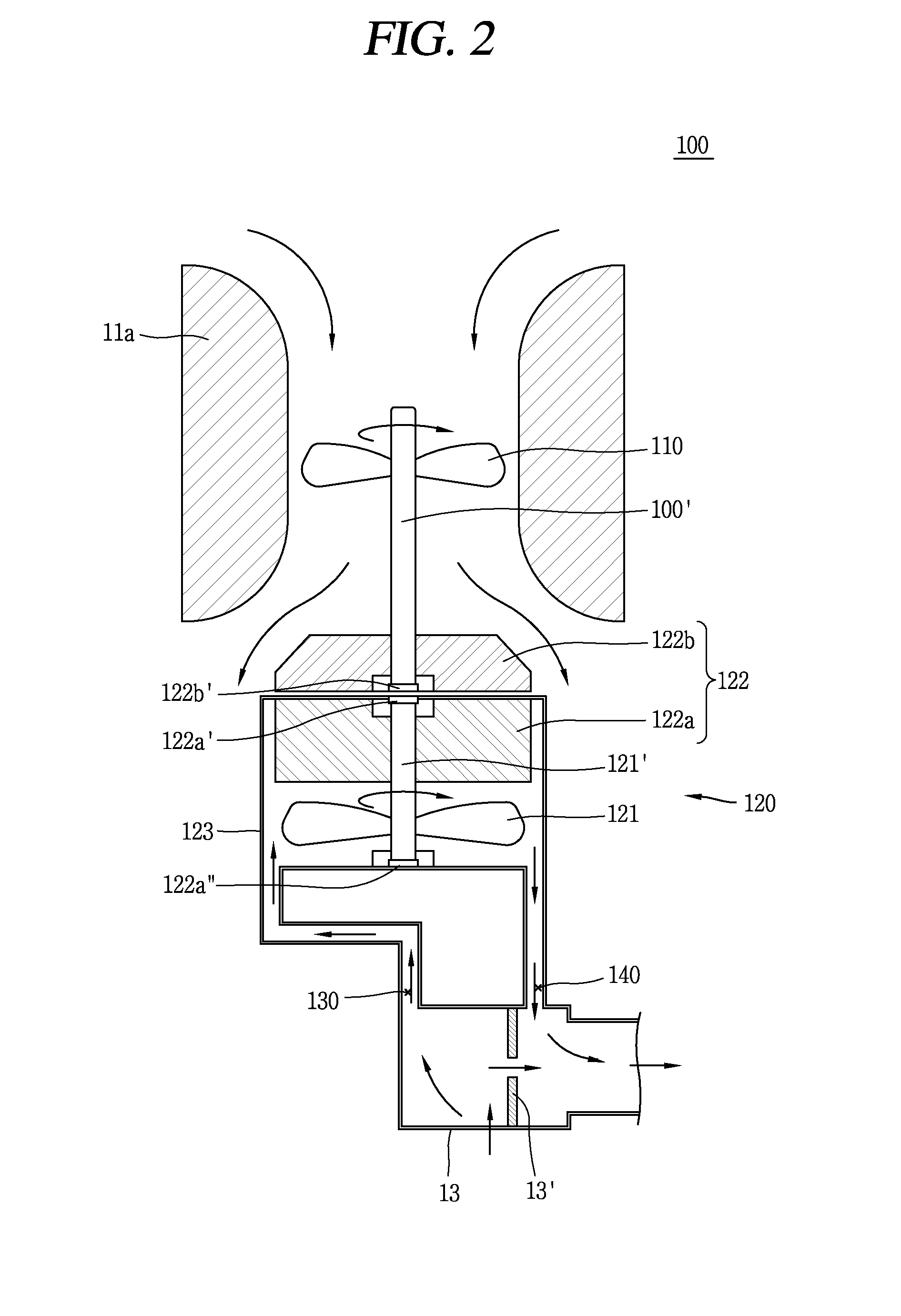
Reactor core and method for operating nuclear reactor
InactiveUS6925138B2Continuous operationShorten the durationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNuclear plantNuclear reactor core
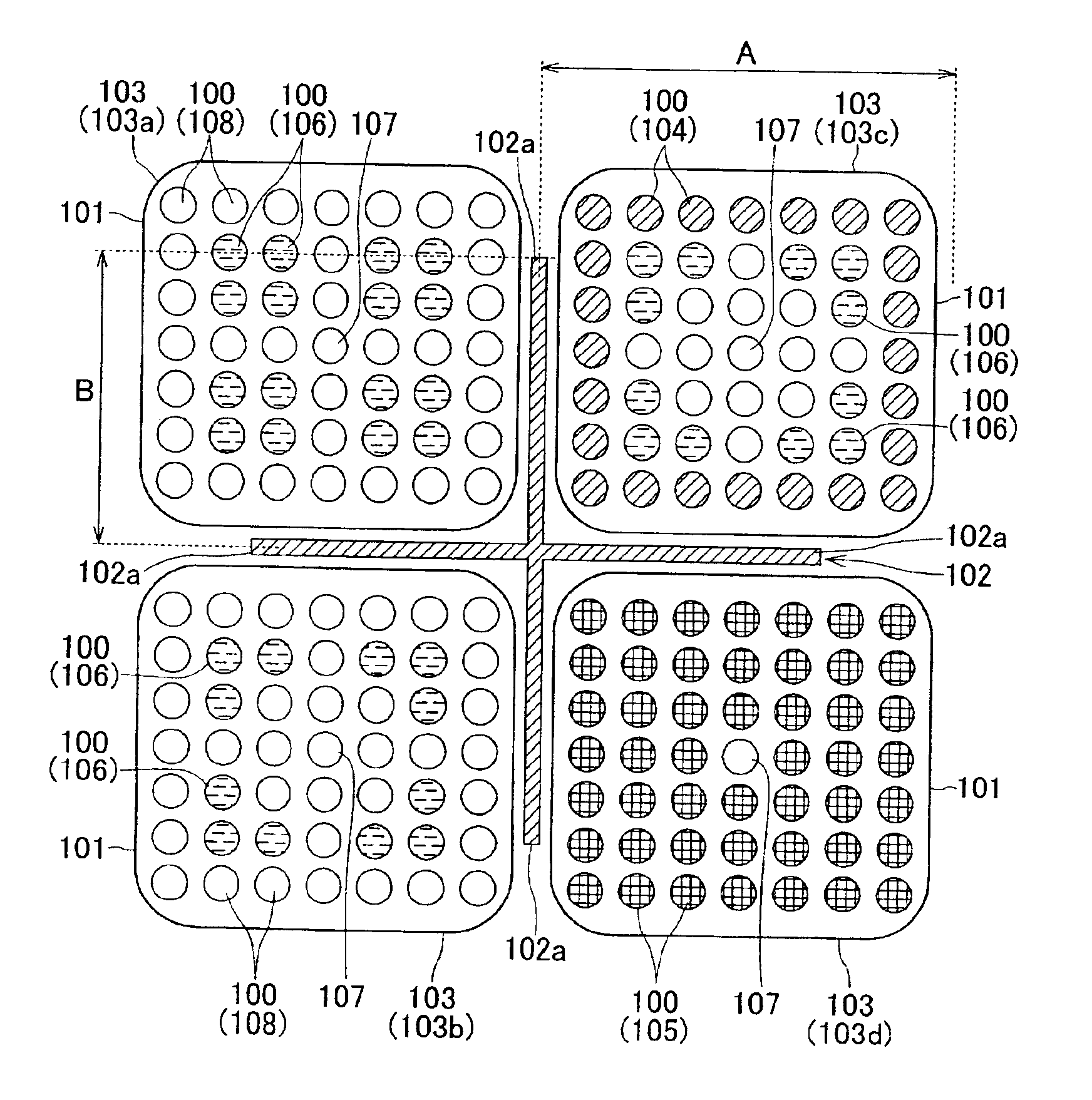
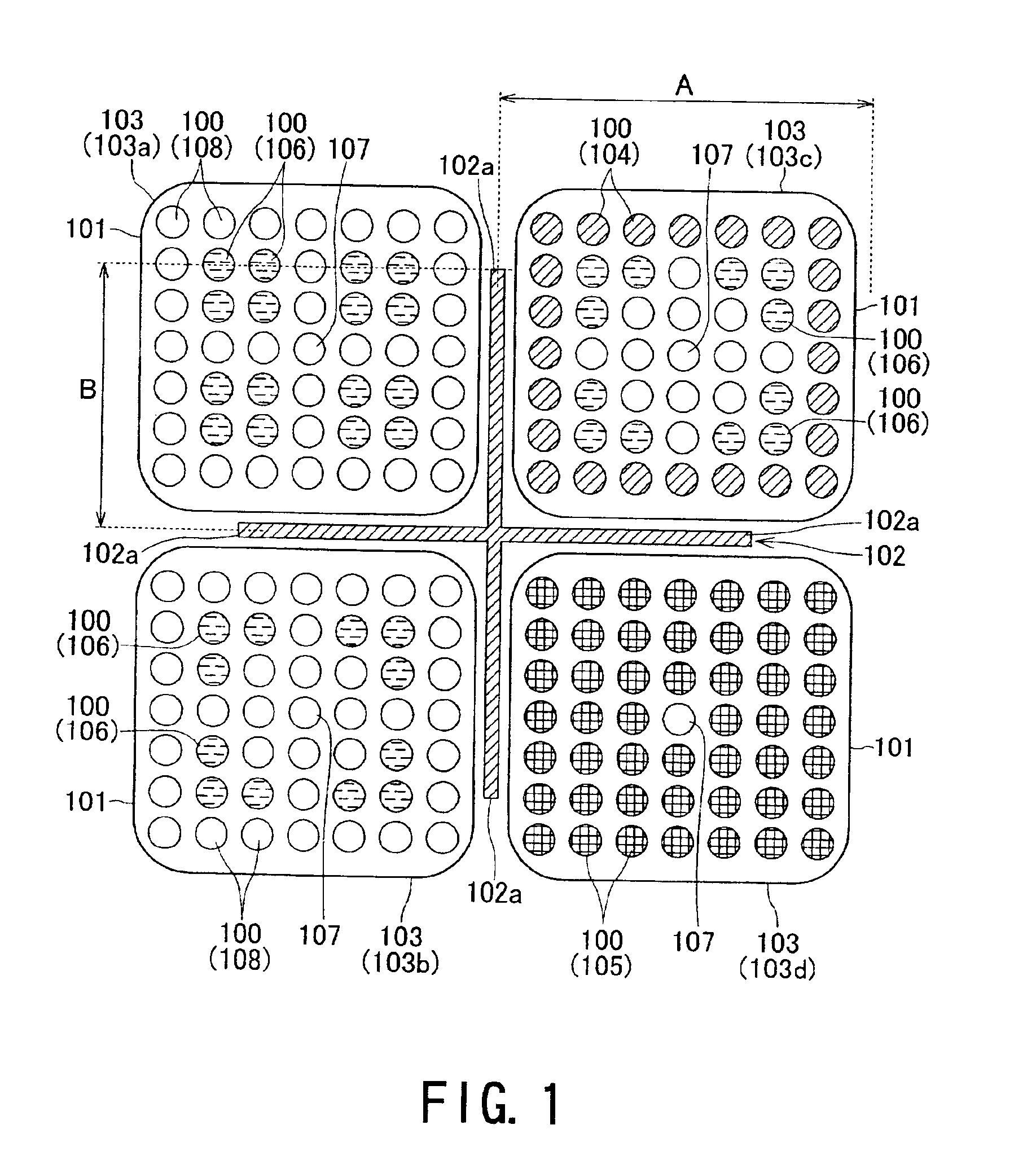
The present invention is to provide a reactor core that allows a nuclear plant to continuously operate for a long term period, for example 15 years or longer, without requiring any fuel exchange, reduces the duration and number of maintenance steps involved in regular plant inspections, markedly improves plant availability and economic efficiency, and is effective in terms of nuclear nonproliferation.A plurality of fuel assemblies 103, themselves obtained by arranging fuel rods 100 and water rods 107 in square lattices, are arranged in a square lattice at a certain pitch. The blades 102a of a cross-shaped (cruciform) control rod 102 in a cross section are inserted into four adjacent spaces formed by four fuel assemblies 100 facing each other. A value of 0.06 cm−1 or greater is selected for the ratio (B / S) of the width (B) of each blade on the cruciform control rod 102 and the surface (S) of the fuel lattice defined by the surface area of a square whose side is equal to the pitch between the fuel assemblies 103.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and system for supplying emergency power to nuclear power plant
ActiveUS20140001863A1Improve securityReduce probabilityPower plant safety arrangementBatteries circuit arrangementsPressurized water reactorNuclear power
Method and system for supplying emergency power to nuclear power plant, wherein the method includes, providing accumulator battery system, connected to emergency bus, the accumulator battery system is monitored by online monitoring system; in case of power loss of electrical devices of the nuclear power plant, the online monitoring system starts the accumulator battery system to provide power supply to the electrical devices of the nuclear power plant via the emergency bus. The present application is adapt to the key technologies and battery management technologies of million kilowatt-class advanced pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant, facilitating to improve the safety of the nuclear power plant in case of serious natural disasters beyond design working conditions.
Owner:DAYA BAY NUCLEAR POWER OPERATIONS & MANAGEMENT +1
Nuclear power station reactor protection system and safety control method therein
ActiveCN105575448AReduce complexityPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear engineeringAutonomation
The invention provides a nuclear power station reactor protection system and a safety control method therein, and relates to the field of a nuclear power station, for reducing the complexity of a protection system maintenance and regular test scheme. The protection system is provided with an emergency shutdown system dividing into N protection channels, wherein each protection channel obtains protection parameters from a signal preprocessing system and carries out a threshold comparison; a special driving system which is connected with the N protection channels, receives threshold comparison results, performs special driving logic processing according to the threshold comparison results and outputs first special driving instructions for driving an execution mechanism needing to be operated before a reactor reaches a controllable state after a nuclear power plant design reference accident takes place; and a safety automation system which is connected with the special driving system through a safety-grade ring network and generates first equipment-grade control instructions for controlling the execution mechanism needing to be operated when the state of the reactor is converted from the controllable state to a safe shutdown state after the nuclear power plant design reference accident takes place.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
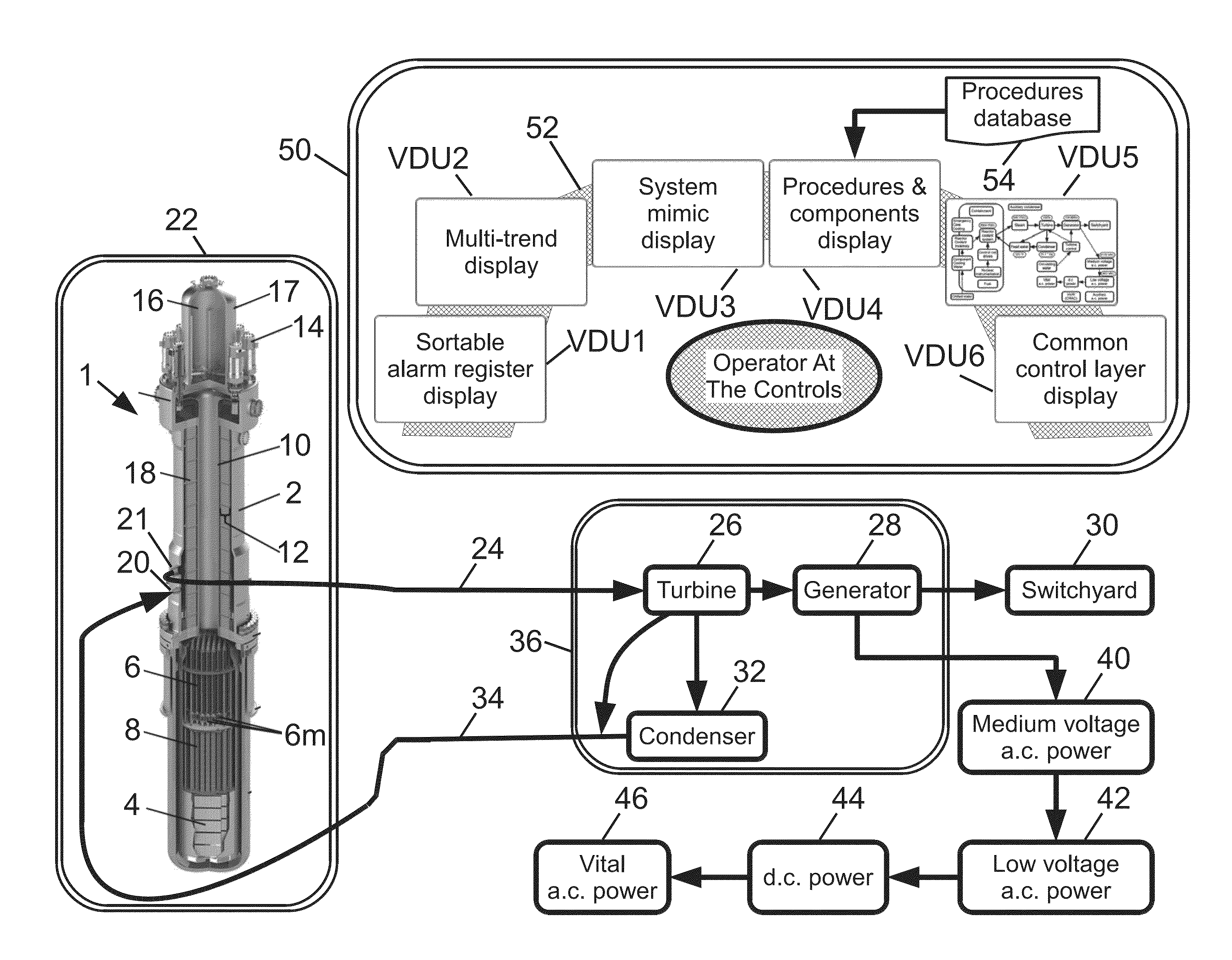
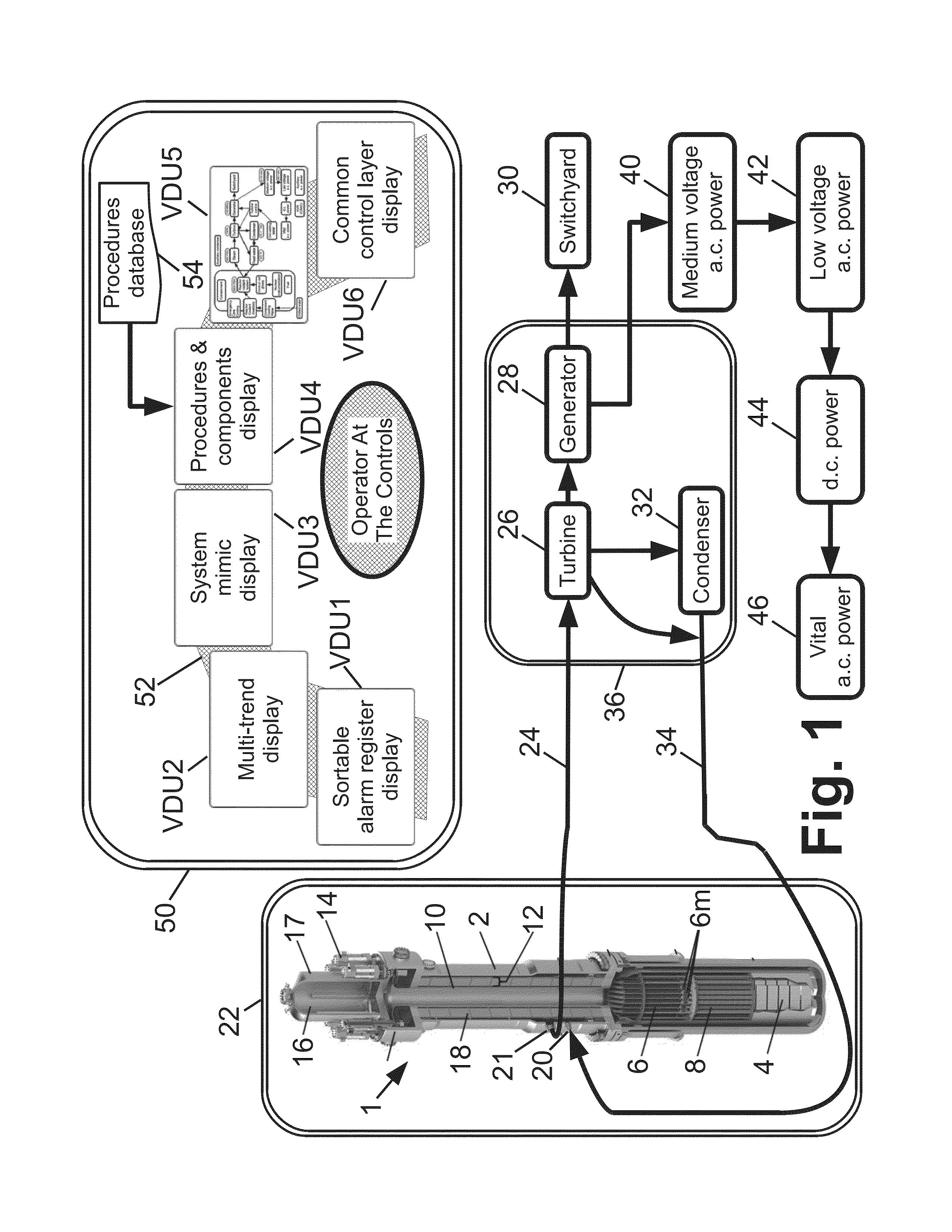
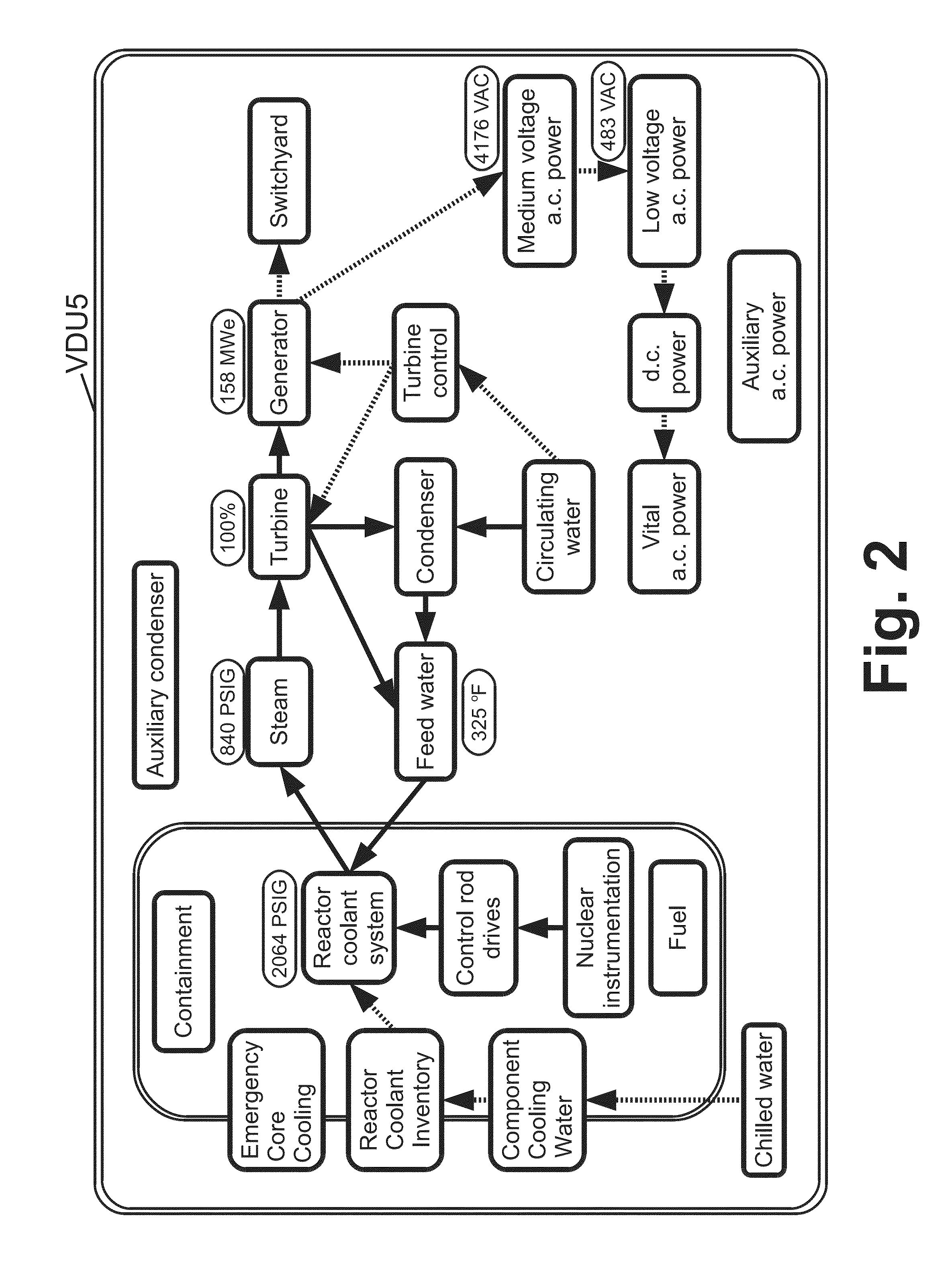
Control room for nuclear power plant
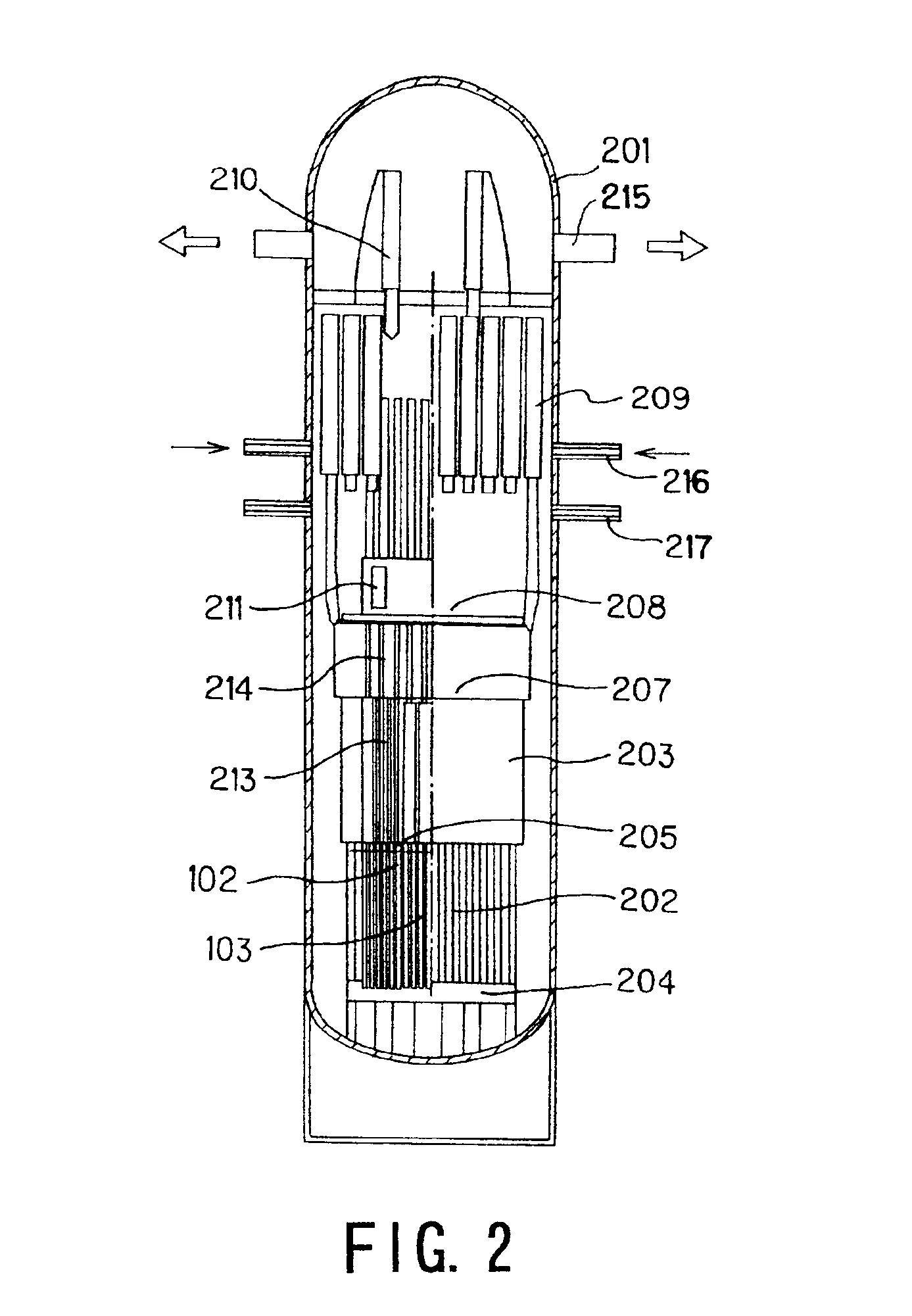
A reactor control interface includes a home screen video display unit (VDU) displaying blocks representing functional components of a nuclear power plant and connecting arrows that connect blocks that are providing the current heat sinking path for the nuclear power plant. Directions of the connecting arrows represent the direction of heat flow along the current heat sinking path. If the current heat flow path of the plant changes, the connecting arrows are updated accordingly. Additional VDUs include: a mimic VDU displaying a mimic of a plant component; a procedures VDU displaying a stored procedure executable by the plant; a multi-trend VDU trending various plant data; and an alarms VDU displaying side-by-side alarms registries sorted by time and priority respectively. If a VDU fails, the displays are shifted to free up one VDU to present the display of the failed VDU, and one display is shifted to an additional VDU.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
Stable and passive decay heat removal system for liquid metal reactor
InactiveUS20070253520A1Eliminate heat decayNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsNuclear plantIntermediate heat exchanger
A decay heat removal system for a liquid metal reactor, in which a decay heat exchanger (DHX) is installed concentrically with an intermediate heat-exchanger (IHX) in the same cylinder which separates the DHX and IHX from the reactor pool fluid, and serves to remove the reactor core decay heat. The cylinder surrounds the IHX and the DHX, and has an opened top portion protruded out of the level of the fluid in a hot pool, a bottom portion connected to a cold pool and a guide pipe for allowing the passage of the fluid from the hot pool into the IHX. The decay heat removal system can remove decay heat immediately after occurrence of an accident, thereby improves the safety of a nuclear plant.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
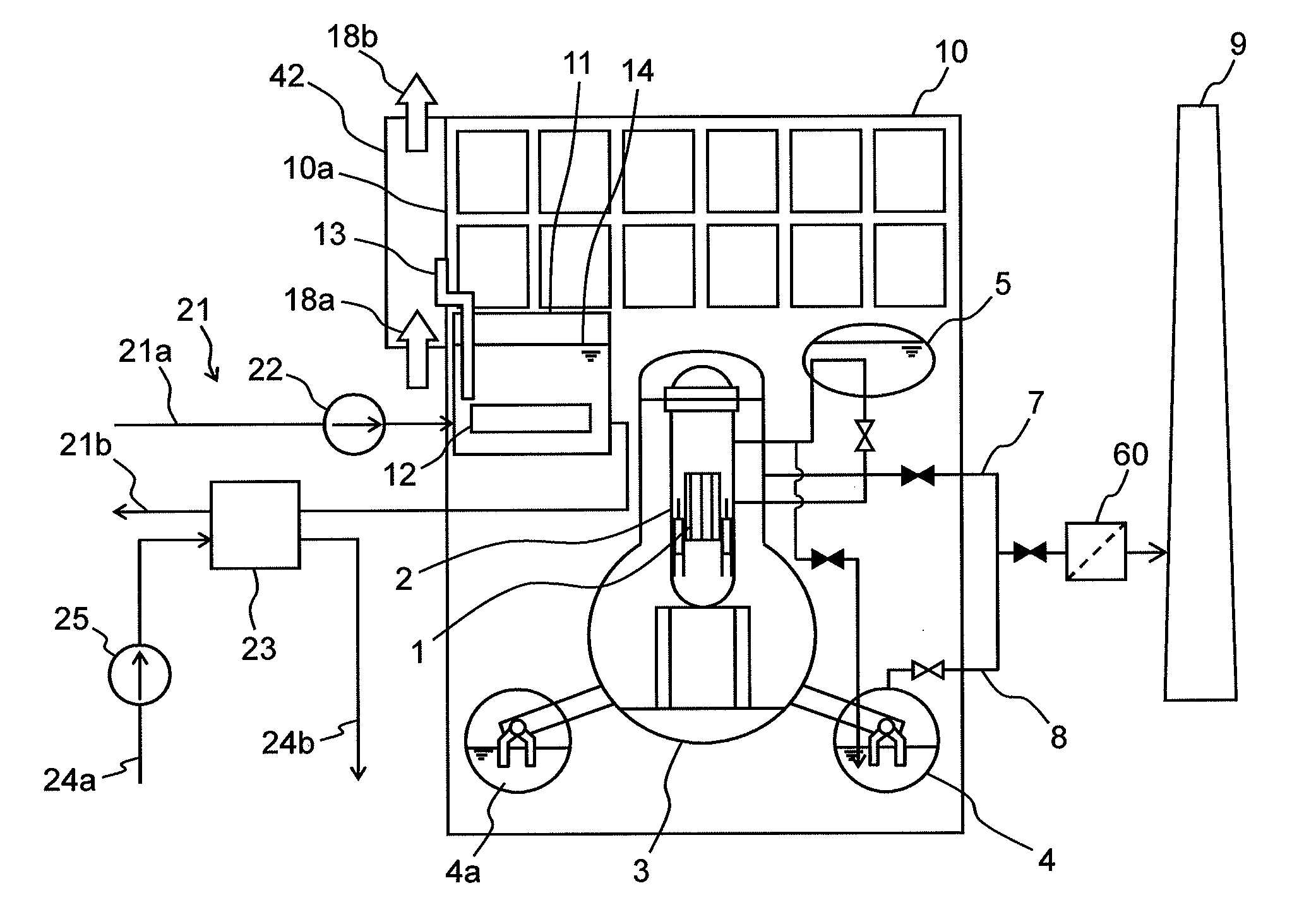
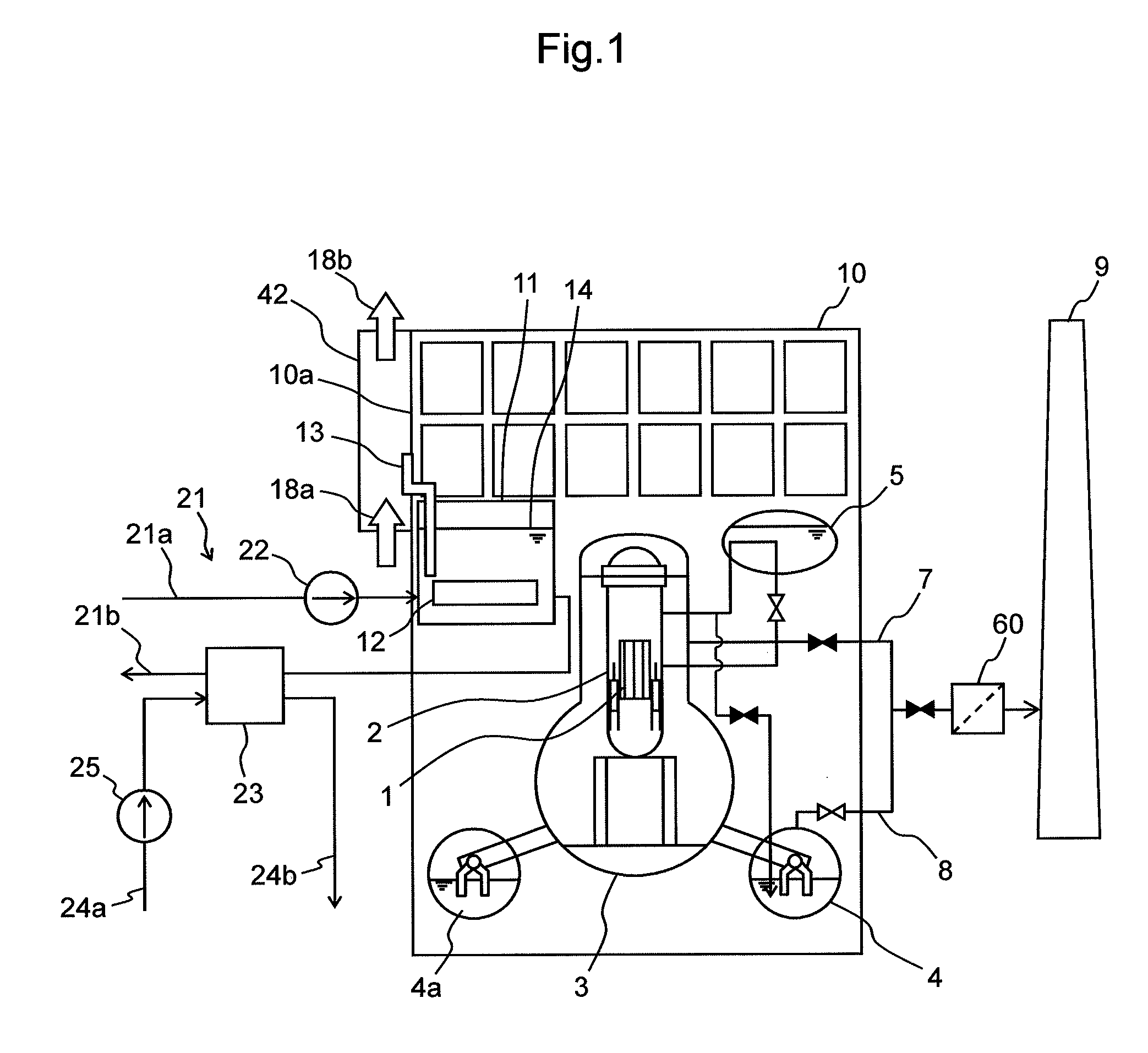
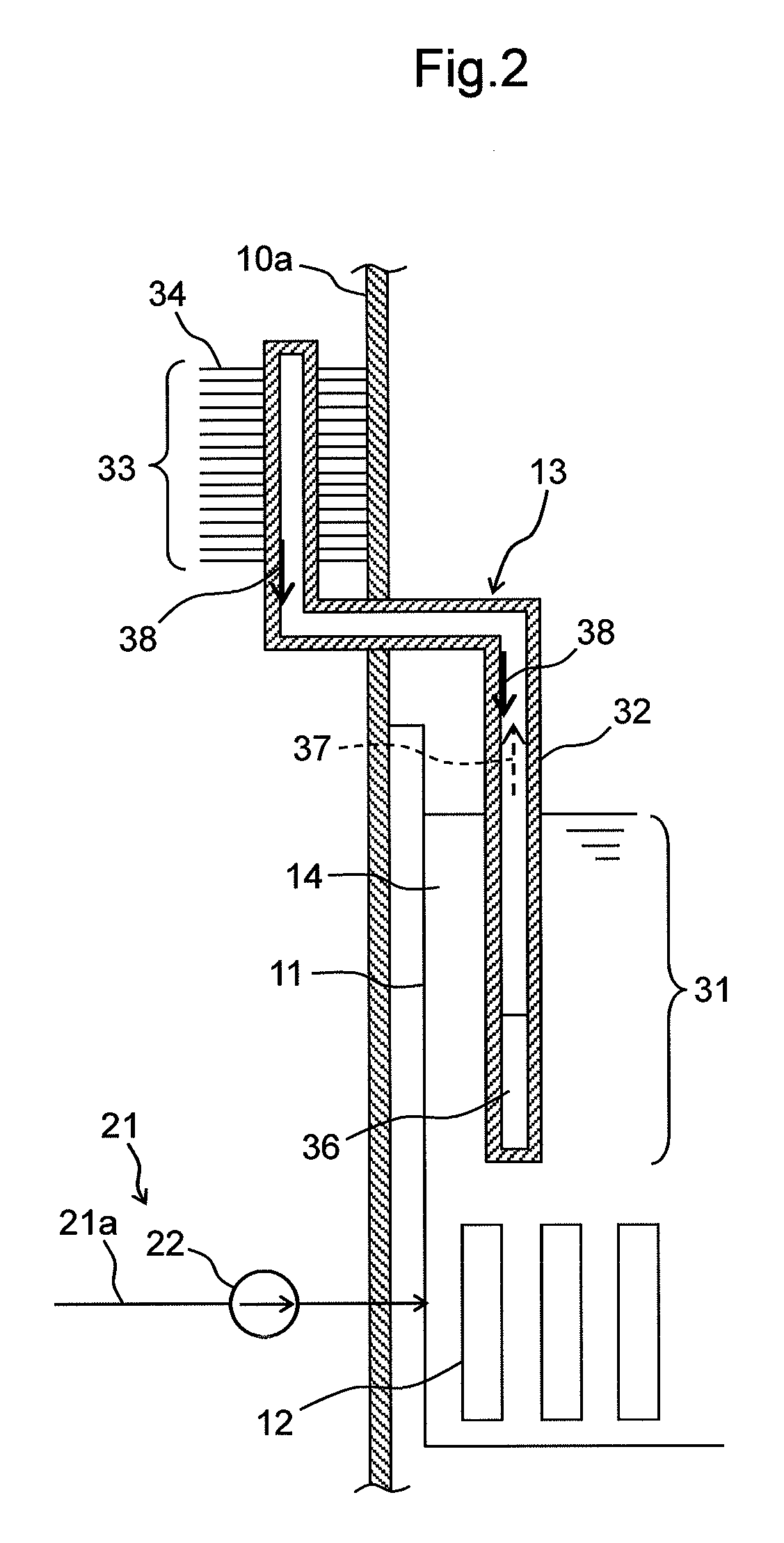
Nuclear Power Plant, Fuel Pool Water Cooling Facility and Method Thereof
InactiveUS20120294407A1Lower Level RequirementsPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear plantReactor pressure vessel
A nuclear power plant and a fuel pool water cooling facility and method are provided that can suppress the decrease of a water level in a fuel pool with no power supply at the time of malfunction of a circulating water system.The nuclear power plant includes a reactor pressure vessel 2 that encompasses a reactor 1 containing nuclear fuel; a containment vessel 3 for housing the reactor pressure vessel 2; a fuel pool 11 for storing spent fuel 12; a reactor building 10 that houses the reactor pressure vessel 2, the containment vessel 3 and the fuel pool 11; a circulating water system 21 adapted to forced-circulating-cool the fuel pool water 14 in the fuel pool 11; and at least one heat pipe 13 for transferring heat of the fuel pool water 14 in the fuel pool 11 and discharging the heat to the atmosphere.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
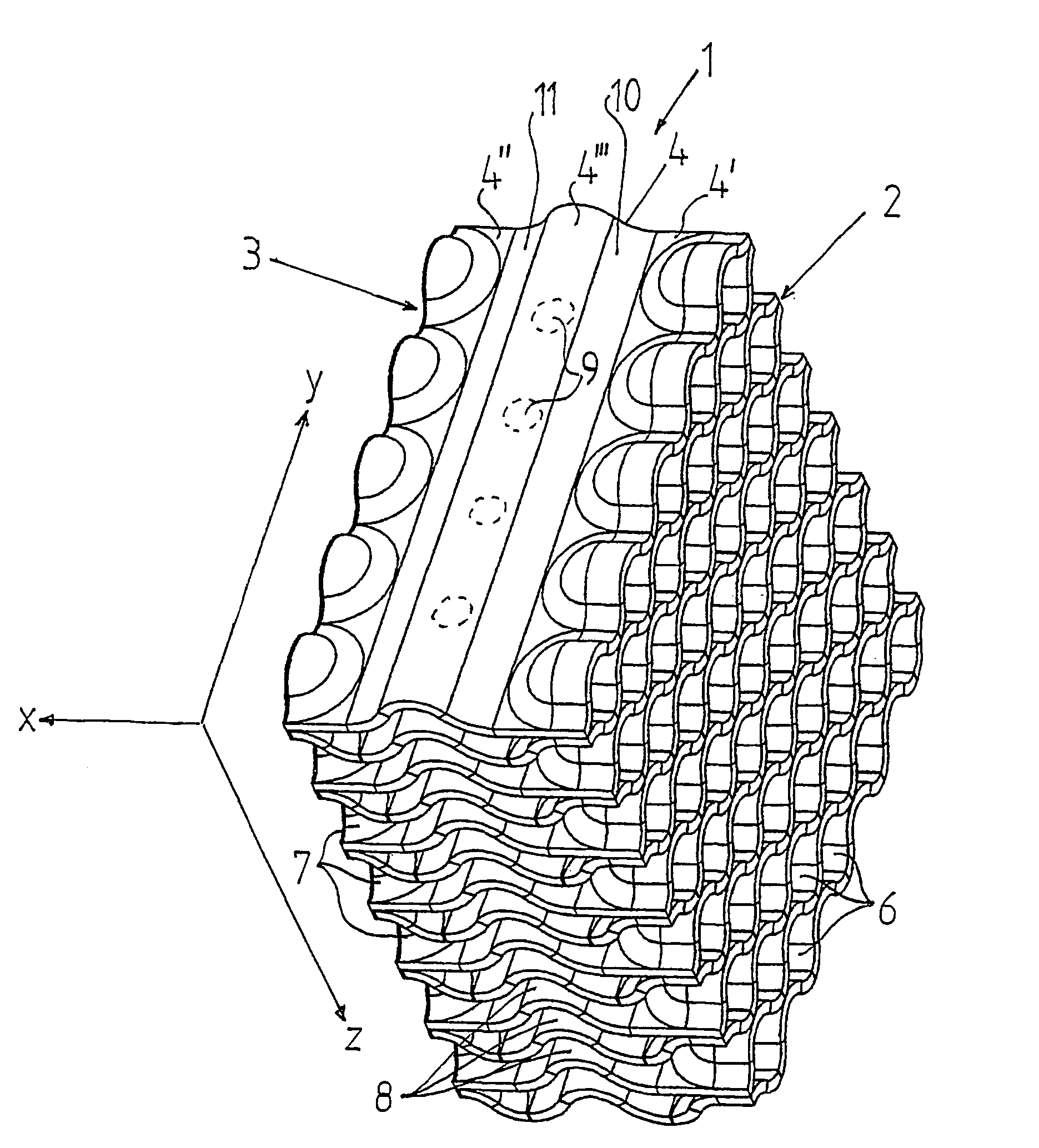
Filter for cooling water in a light water cooled nuclear reactor
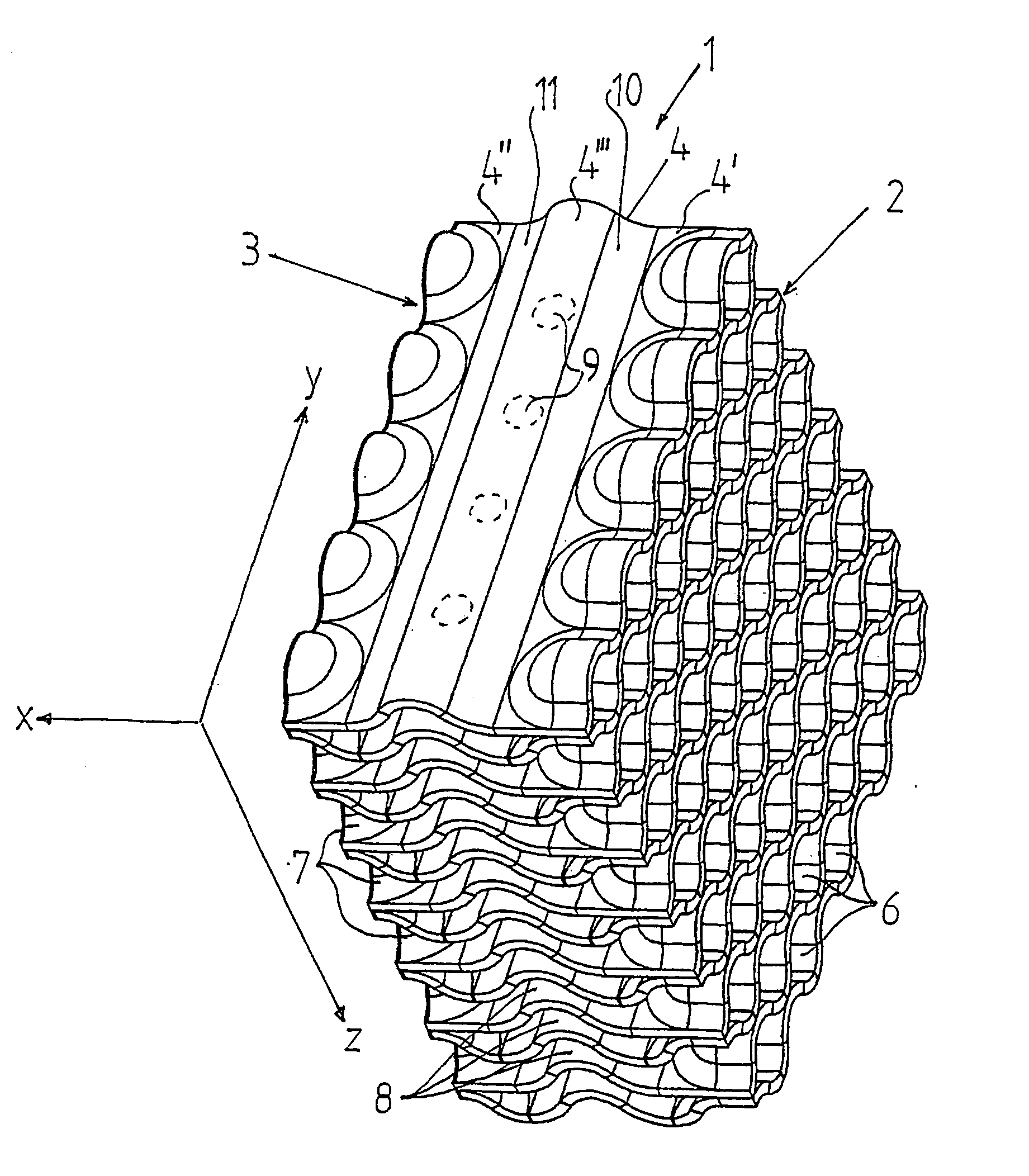
InactiveUS7149272B2Lower overall flow resistanceLow costNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesNuclear reactor coreNuclear plant
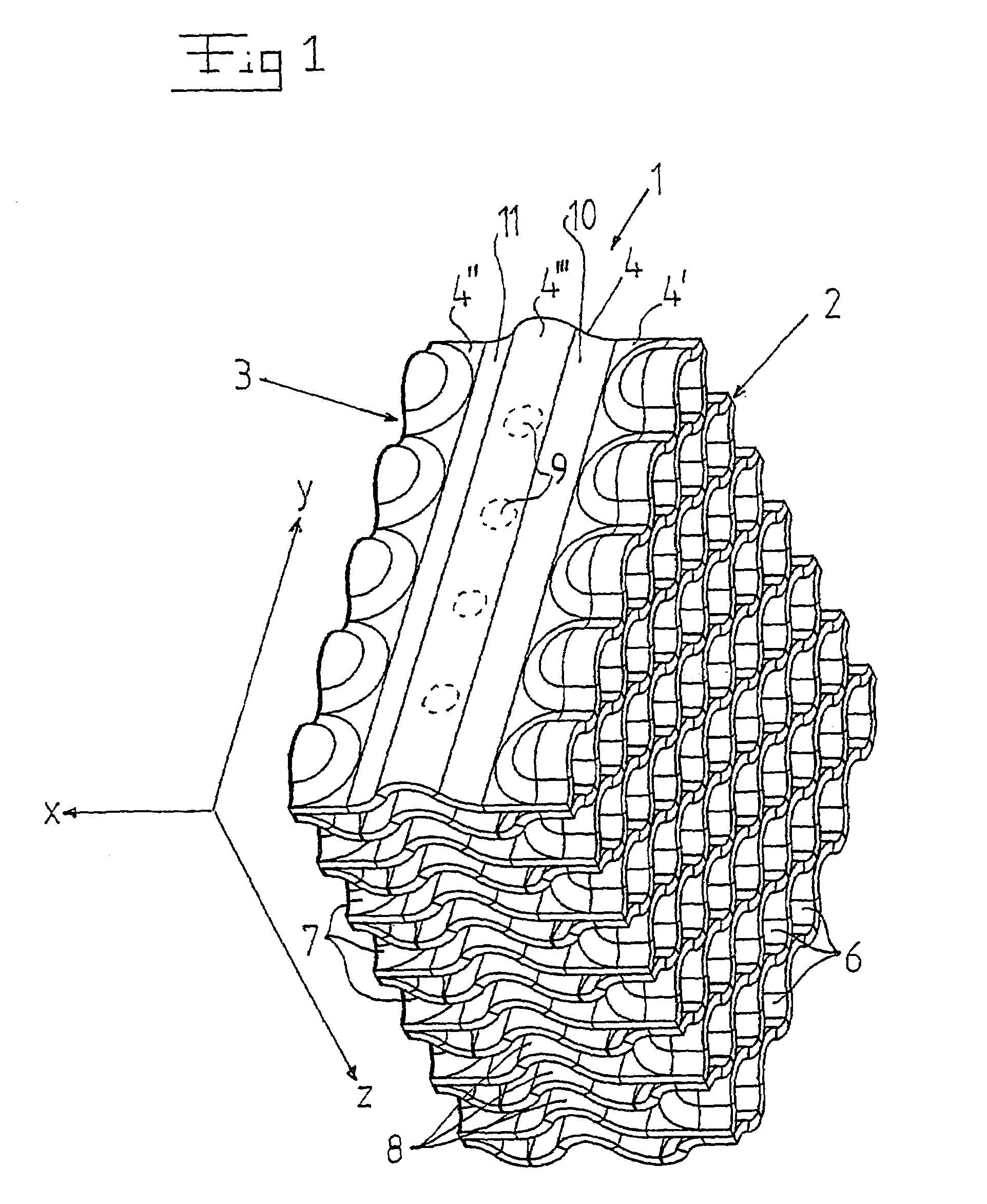
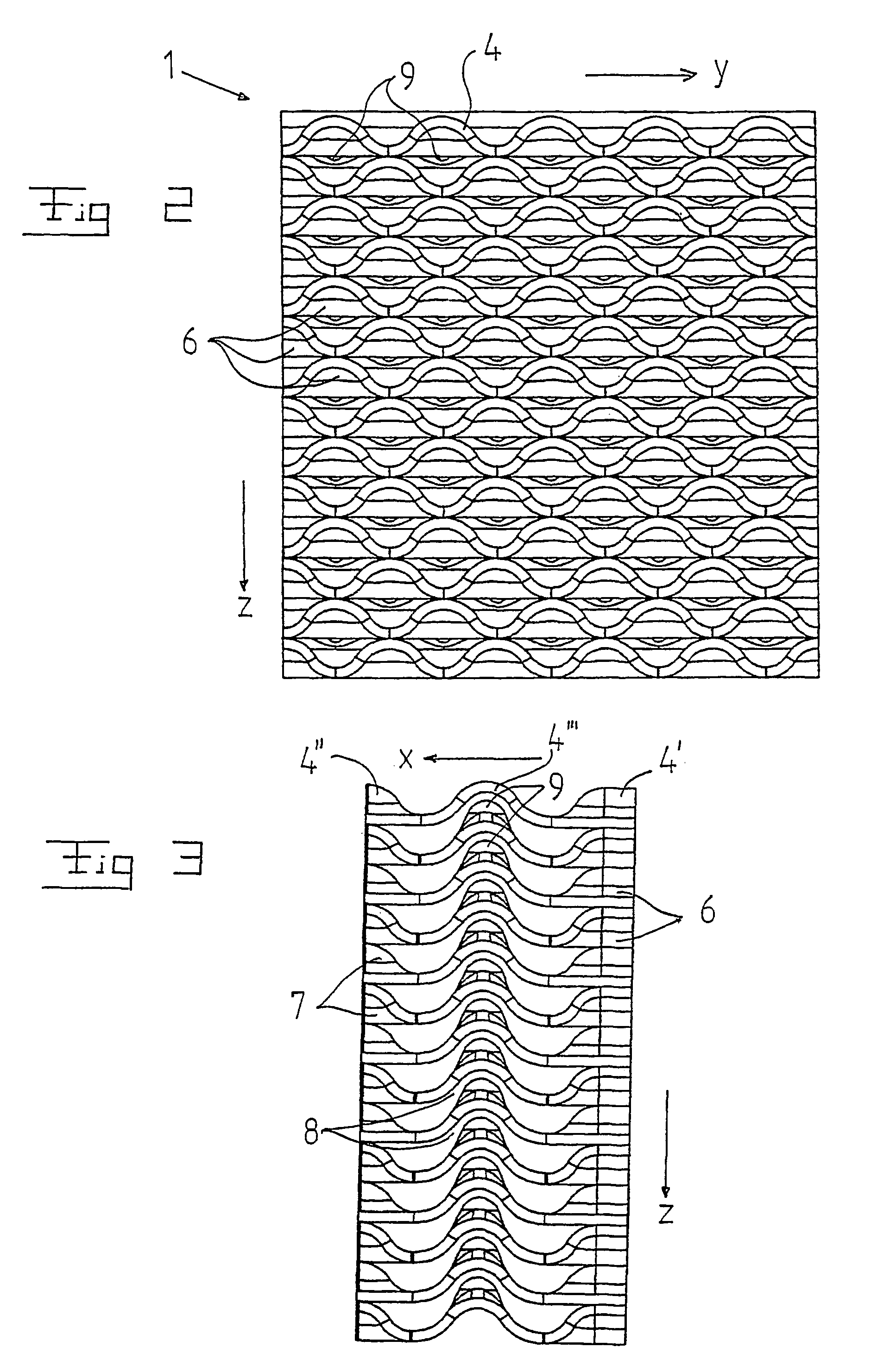
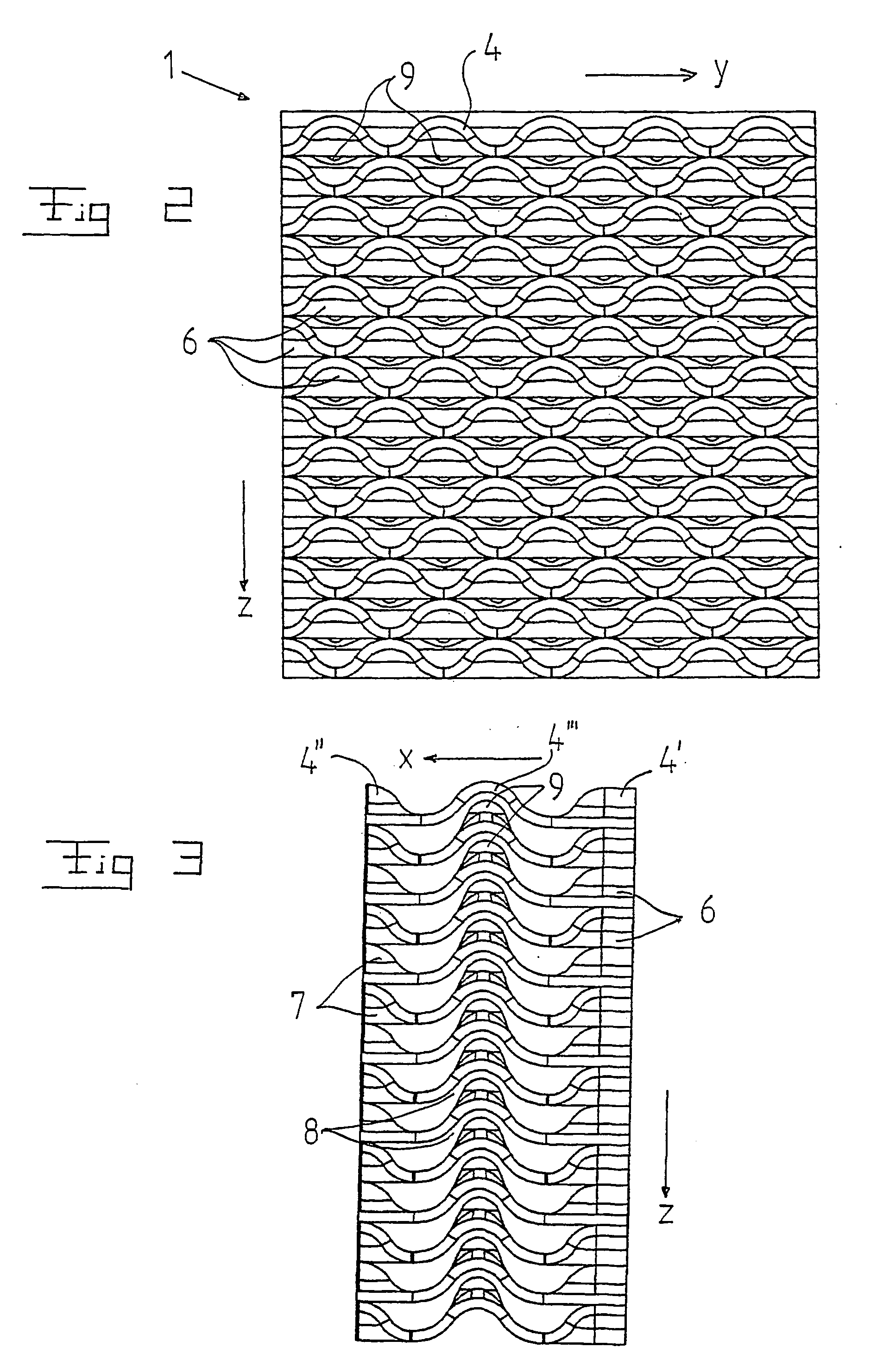
The invention refers to a filter (1) for separating particle from cooling water in a nuclear plant, and a fuel assembly with such a filter. The filter has an inlet end (2) and an outlet end (3) and permits through-flow of the cooling water in a main flow direction (x). The filter includes a number of sheets (4) extending in the flow direction from the inlet end to the outlet end. The sheets are arranged beside each other and form passages for the cooling water. The sheets include a first portion (4′) extending from the inlet end (2), a second portion (4″) extending from the outlet end (3), and a third portion (4′″) extending between the first portion (4′) and the second portion (4″). The sheets (4) have along the first portion continuous wave-shape extending in a direction (y) transversally to the flow direction (x) and along the third portion a continuous wave-shape extending in the flow direction (x).
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC SWEDEN
Main machine hall group arrangement method of nuclear power plant
ActiveCN103850483AImprove waterproof performanceImprove seismic performanceIndustrial buildingsNuclear plantNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a main machine hall group arrangement method of a nuclear power plant and relates to the technical field of nuclear power, and the main machine hall group arrangement method is used for solving the problem that an compact and efficient arrangement method capable of meeting enabling and non-enabling safety facility arrangement requirements, which is used for solving the reasonable equipment arrangement of a nuclear island plant does not exist in the prior art. The scheme provided by the invention is as follows: according to the main machine hall group arrangement method of the nuclear power plant, a main machine hall group comprises a nuclear island and a conventional island, and a nuclear island machine hall group comprises a reactor machine hall with a double-layer safety shell, an electric machine hall, a safety machine plant, a fuel machine hall, a nuclear auxiliary machine hall, a nuclear waste machine hall, an operation service machine hall, an emergency diesel generator machine hall and a nuclear-island fire-fighting water machine hall. According to the nuclear-island machine hall group arrangement method, a novel nuclear power plant single-pile arrangement structure is adopted and comprises an enabling and non-enabling combined safety system, has stronger capability of resisting severe external events, meets the requirement of a third-generation nuclear power technology, is beneficial to improvement on the safety of the whole nuclear power plant, and can be used for enhancing the nuclear safety acceptability of the public.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
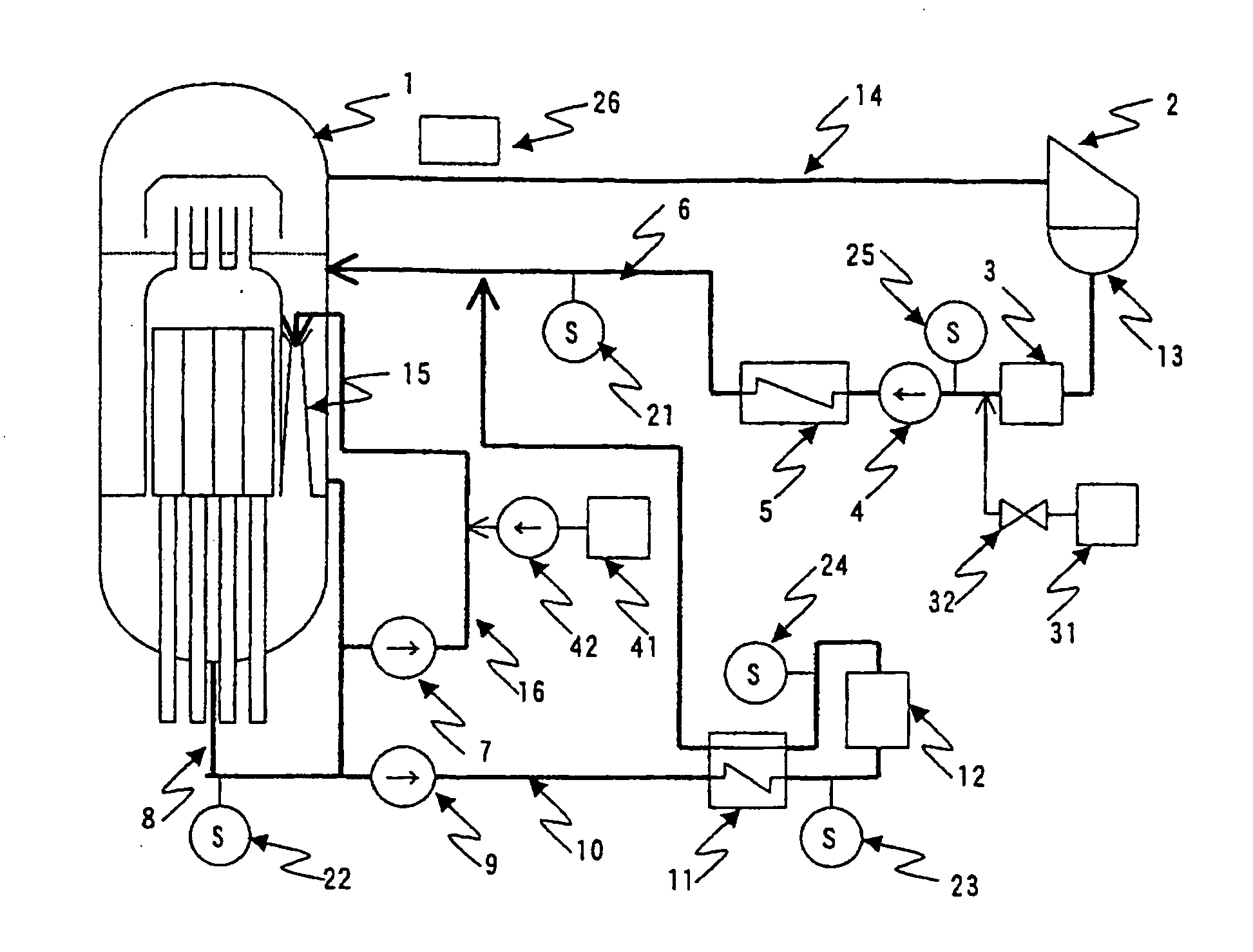
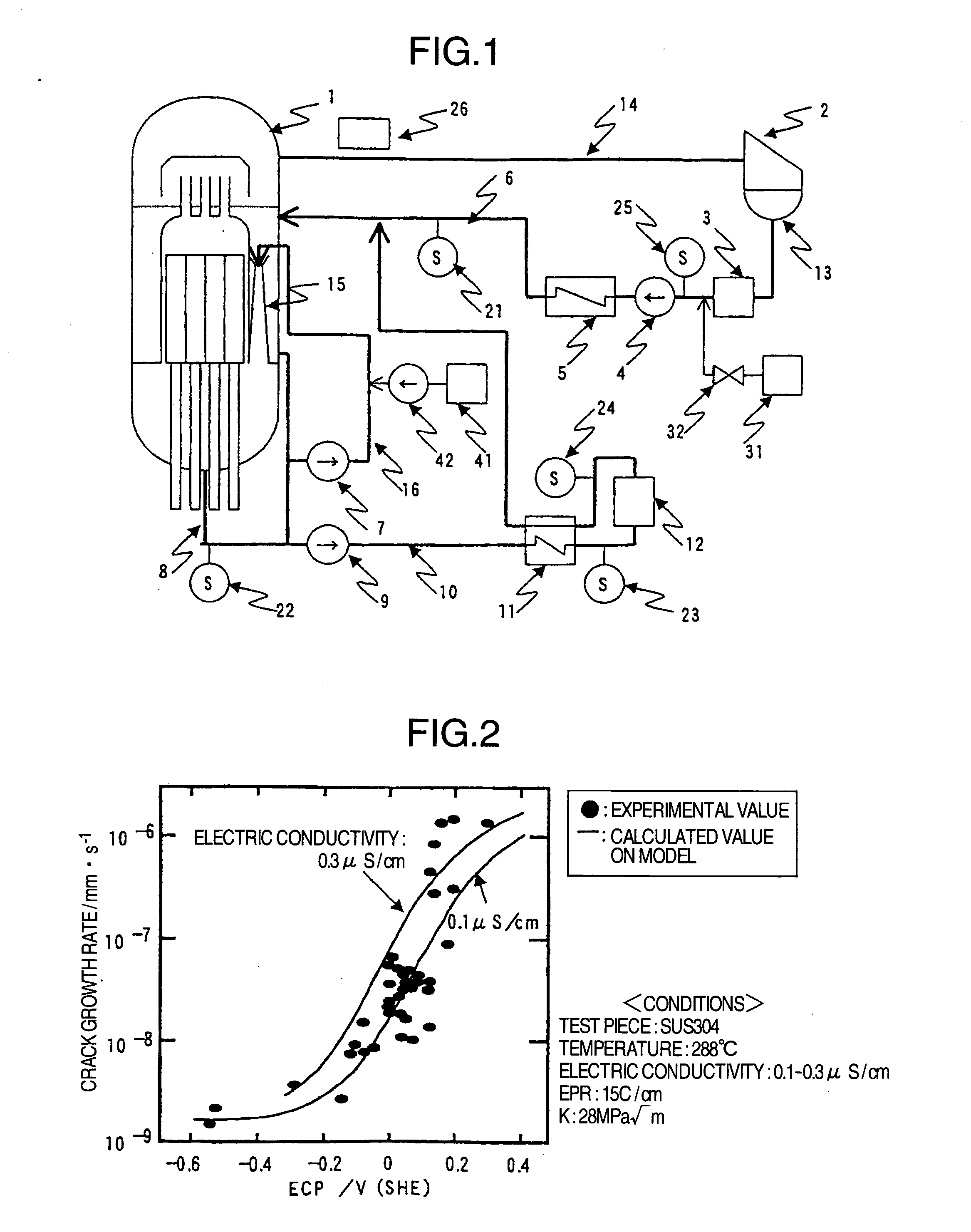
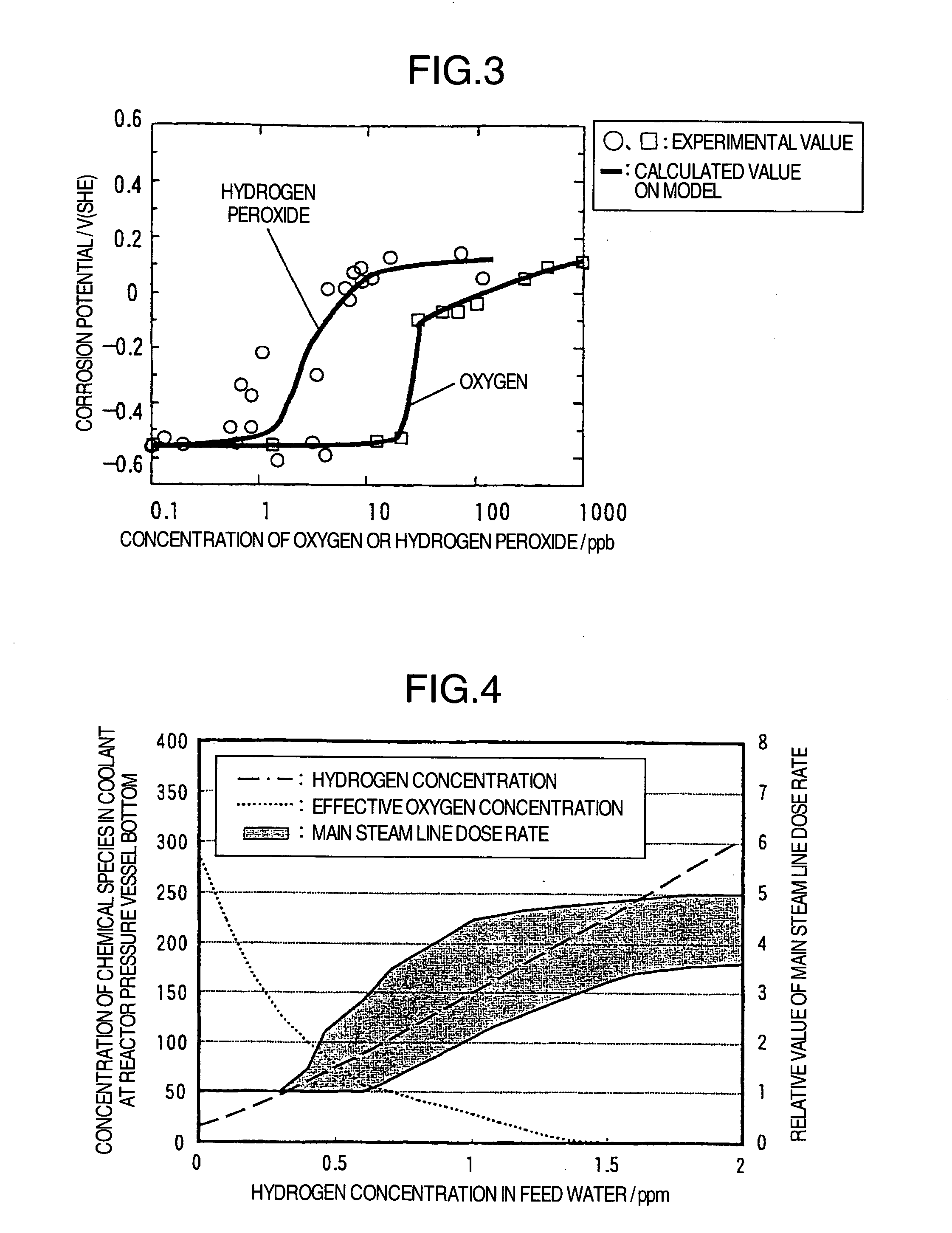
Method of stress corrosion cracking mitigation for nuclear power plant structural materials
InactiveUS20050018805A1Reduce stress corrosion crackingReduce stressPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationDose rateHydrazine compound
The object of this invention is to provide a method for mitigating a stress corrosion cracking of reactor structural material which makes it possible to suppress the rise in the main steam line dose rate without secondary effects such as a rise in the concentration of radioactive cobalt-60, etc. in the reactor water. Hydrogen and a reductive nitrogen compound containing nitrogen having a negative oxidation number (for example, hydrazine) are injected into the core water of boiling water nuclear power plant. By injecting the reductive nitrogen compound containing nitrogen having a negative oxidation number into the core water, the stress corrosion cracking of structural material of reactor can be mitigated without side reactions such as a rise in the concentration of cobalt-60, etc.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
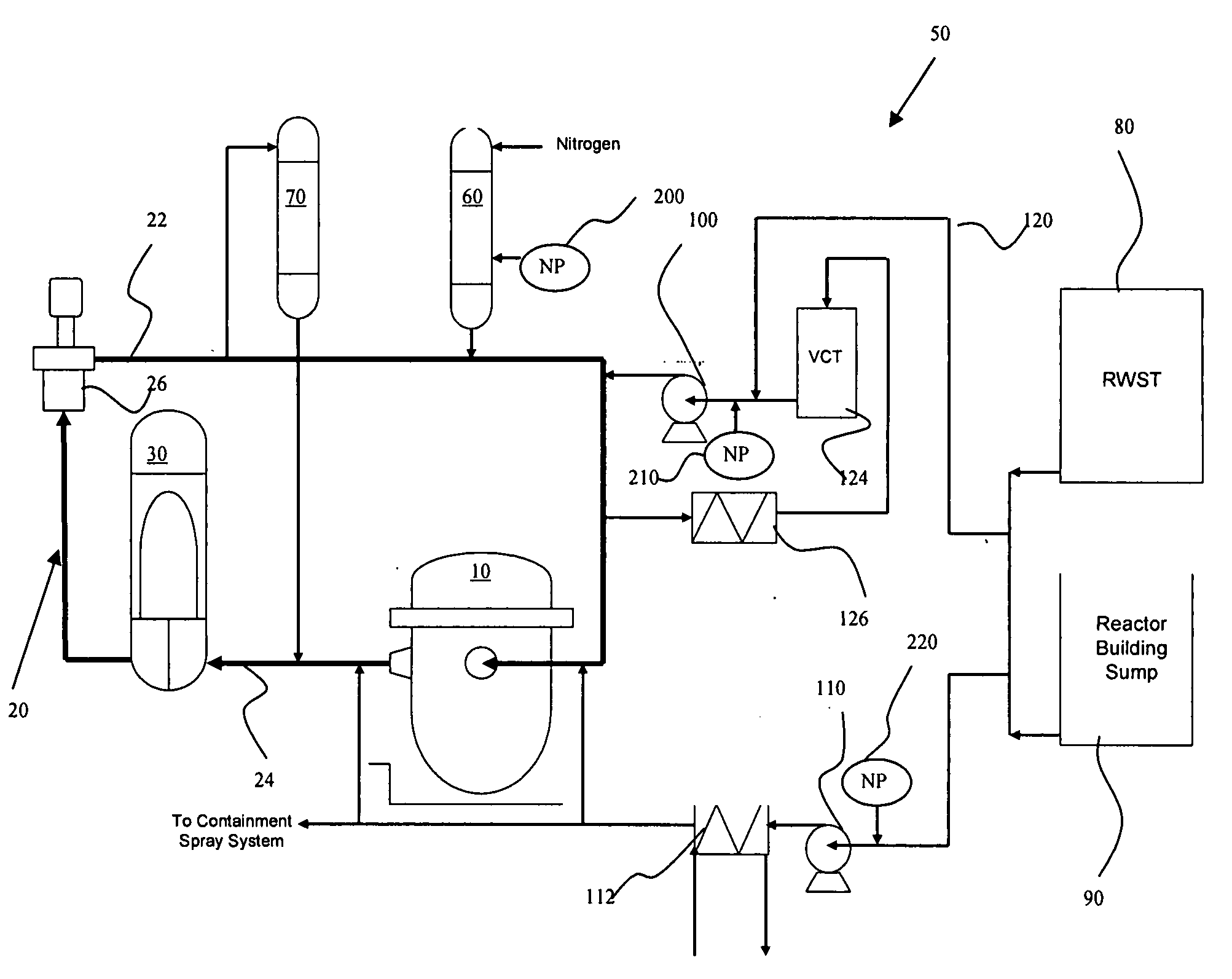
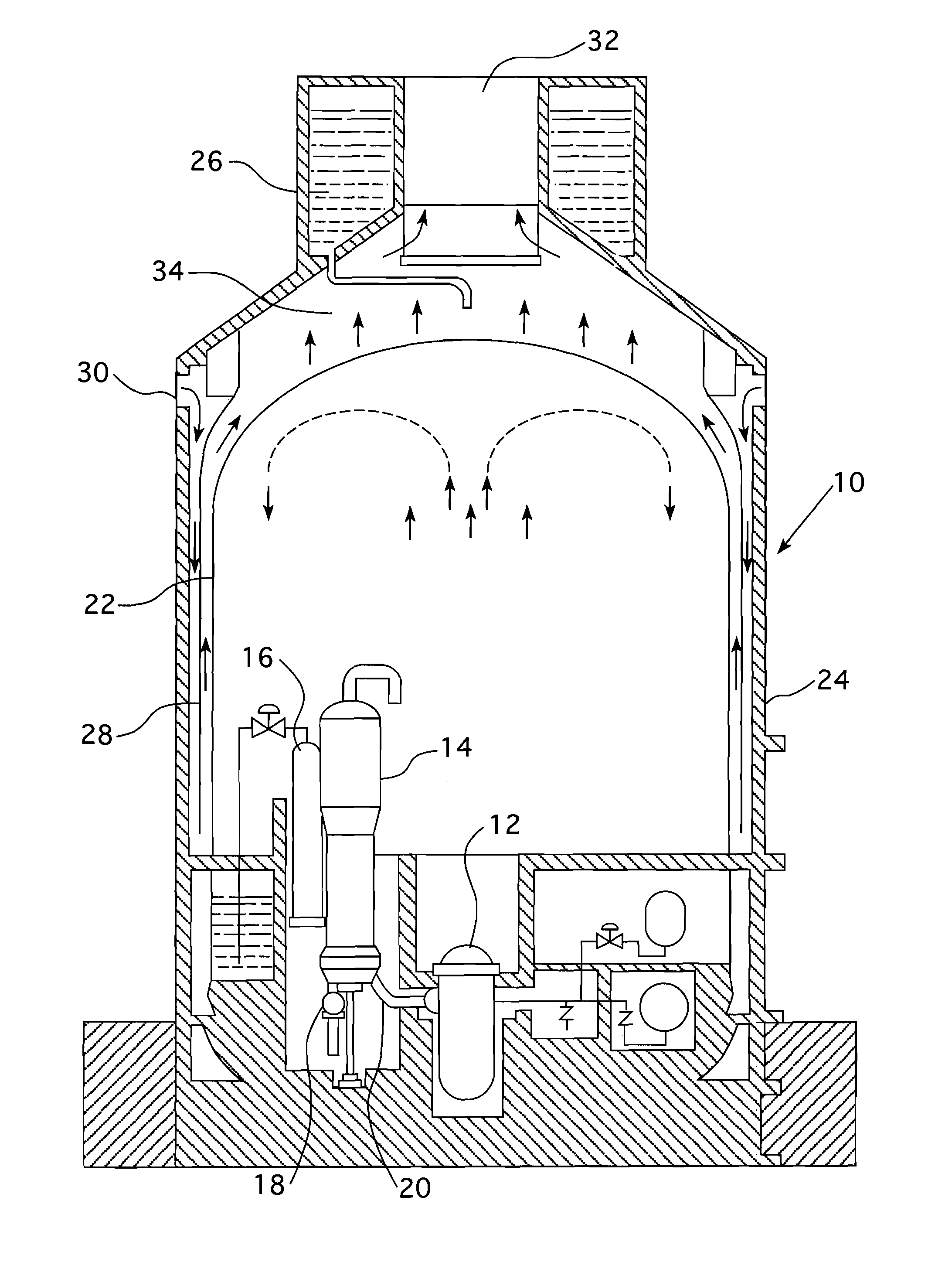
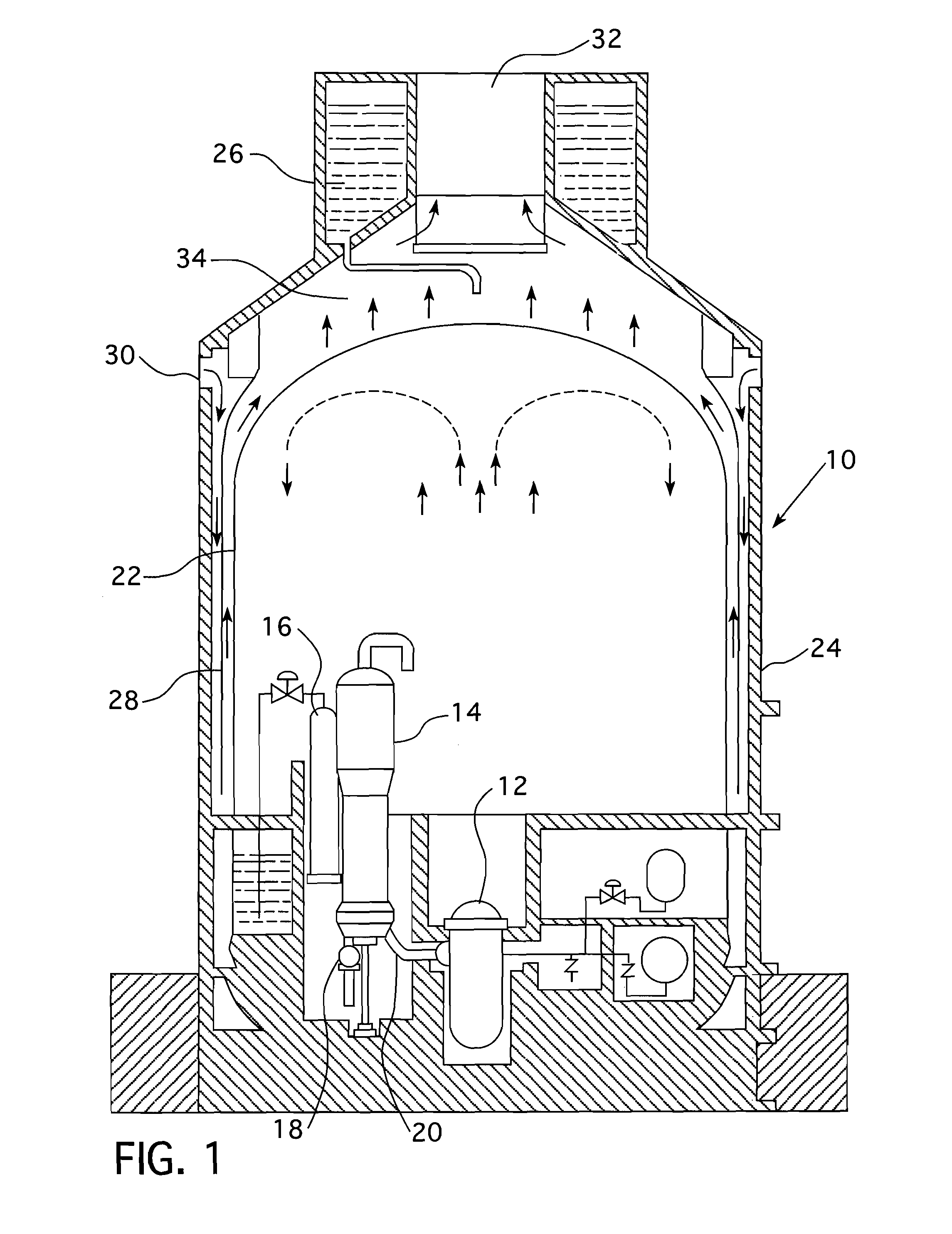
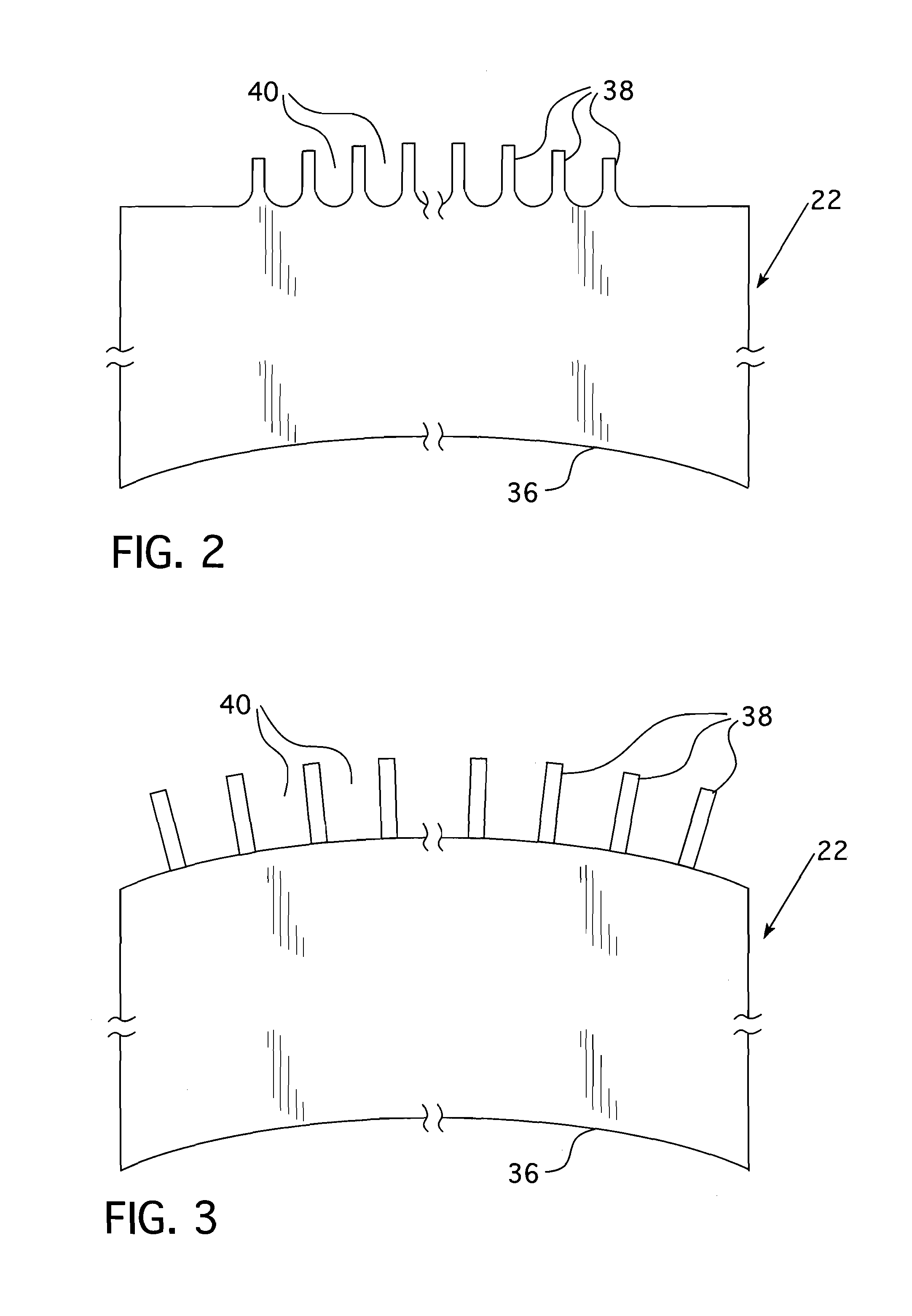
Passive containment air cooling for nuclear power plants
InactiveUS20130272474A1Power plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationNuclear plantNuclear engineering
An enhanced passive containment air cooling system for a nuclear power plant that increases the heat transfer surface on the exterior of the nuclear plant's containment vessel. The increased surface area is created by forming a tortuous path in or on at least a substantial part of the exterior surface of the containment vessel over which a cooling fluid can flow and follow the tortuous path. The tortuous path is formed from a series of indentations and protrusions in or on the exterior surface that form a circuitous path for the cooling fluid.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
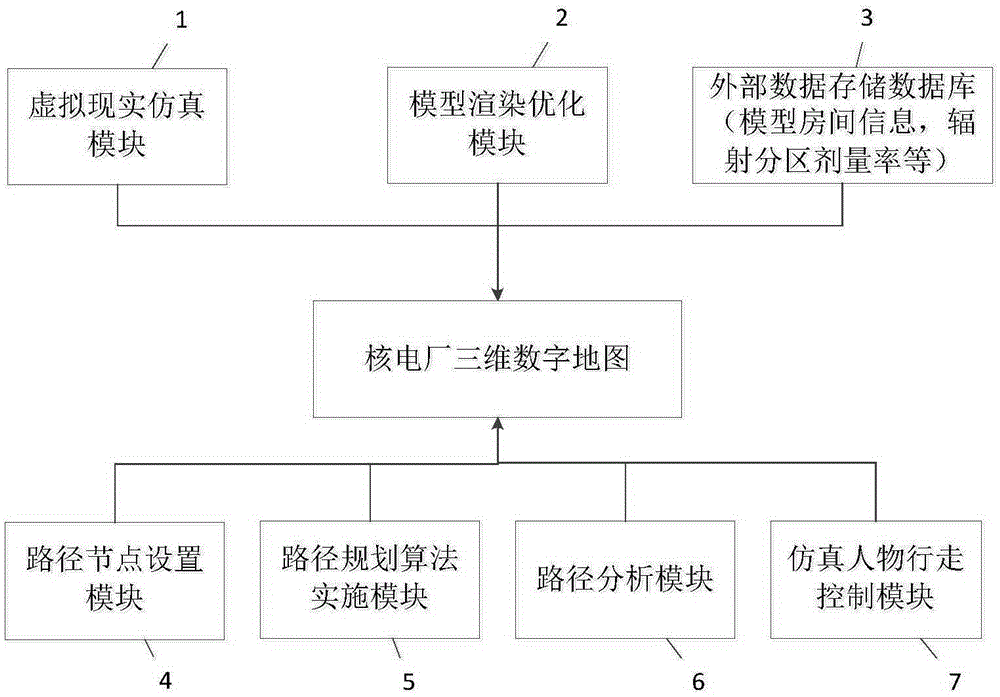
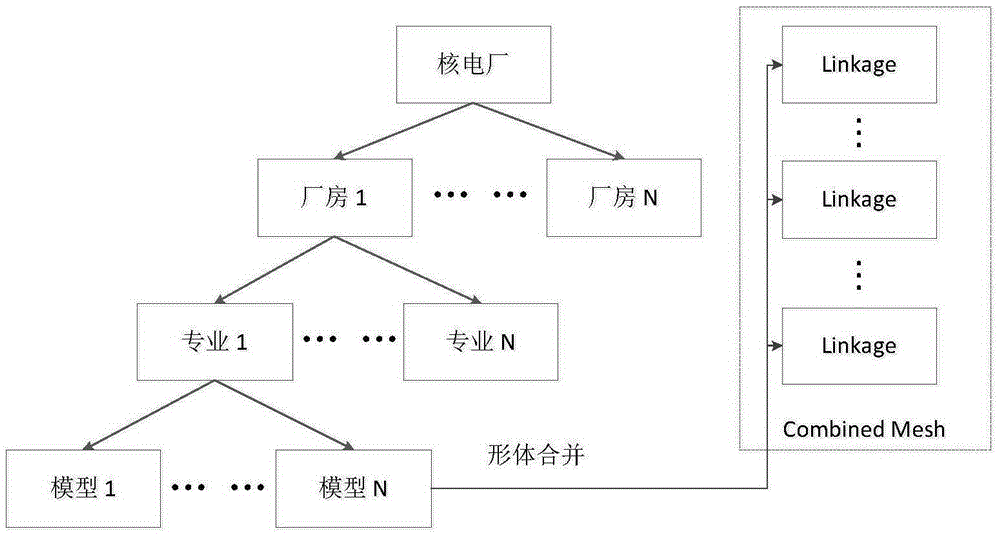
System and method for realizing nuclear plant three-dimensional digital map
InactiveCN105354393AEasy to set upEfficient executionForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsNuclear plantNuclear power
The invention provides a system for realizing a nuclear plant three-dimensional digital map. The system comprises a virtual reality simulation module, a model rendering optimization module, a path planning algorithm implementation module, a path planning analysis module, a simulated figure walking control module, a path node arrangement module and an external data storage database. According to the system and method for realizing the nuclear plant three-dimensional digital map, through use of a nuclear power three-dimensional design model and combination of a virtual reality technology and a Dijkstra path planning algorithm, algorithm path nodes are distributed according to escape paths and paths through which staff of the nuclear island plant go into or out of rooms, path node attributes are set according to radiation subarea dosage rate and control information like internal locks, shield gates and so on in the nuclear plant, so that the nuclear plant three-dimensional digital map is created.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Passive waste heat removal system for floating nuclear power plant
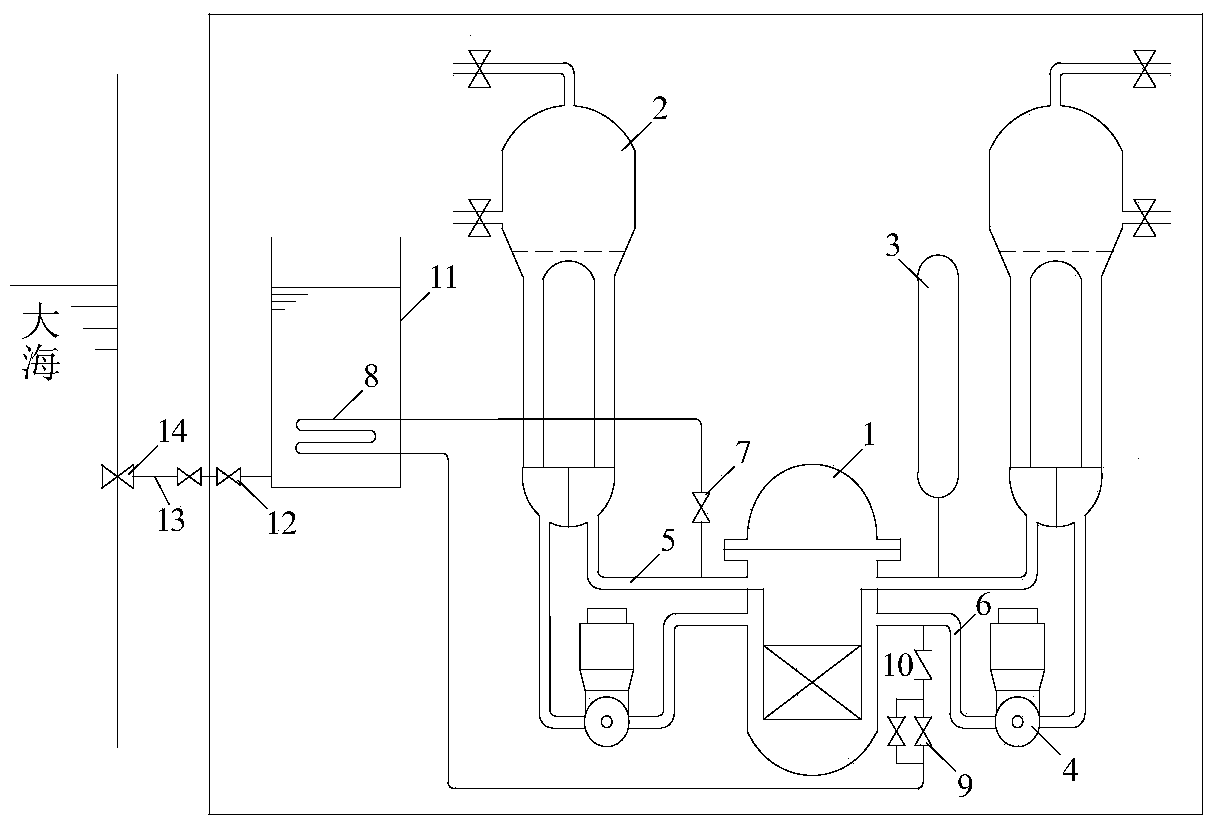
ActiveCN103903659ALow flow resistanceReduce trafficNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementReactor pressure vesselNuclear power
The invention relates to a passive waste heat removal system for a floating nuclear power plant. The system consists of a reactor pressure vessel 1, a passive waste heat removal heat exchanger 8 and a passive emergency cooling water tank 11, wherein the passive waste heat removal heat exchanger 8 is arranged in the emergency cooling water tank 11; an inlet / outlet of the heat exchanger is connected with a loop main coolant pipeline; the emergency cooling water tank 11 is arranged in the pressure vessel; the bottom of the water tank is connected with an ocean through a seawater pipeline; a water level in the water tank is kept consistent with the sea level, and the passive waste heat removal heat exchanger 8 is completely submerged. The passive waste heat removal system is operated under accident conditions, and heat in a loop is finally taken into an atmospheric environment by means of evaporation of water in the water tank. When the water level in the water tank is reduced, seawater automatically enters the water tank through a seawater pipeline, the water level in the water tank is kept, and the reactor is cooled for a long time.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Filter for cooling water in a light water cooled nuclear reactor
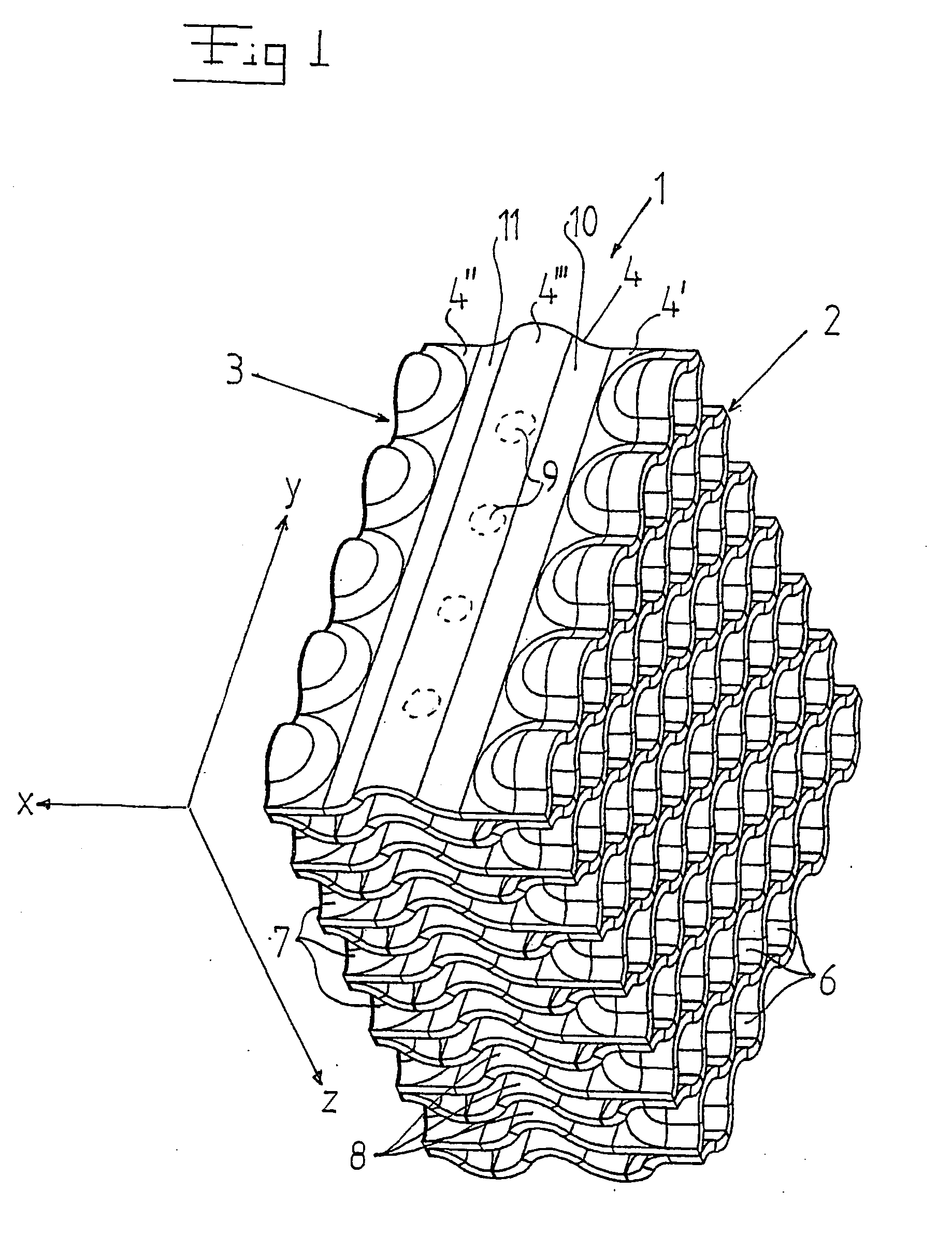
InactiveUS20040076253A1Lower overall flow resistanceEfficient captureNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesNuclear plantNuclear reactor core
The invention refers to a filter (1) for separating particle from cooling water in a nuclear plant, and a fuel assembly with such a filter. The filter has an inlet end (2) and an outlet end (3) and permits through-flow of the cooling water in a main flow direction (x). The filter includes a number of sheets (4) extending in the flow direction from the inlet end to the outlet end. The sheets are arranged beside each other and form passages for the cooling water. The sheets include a first portion (4') extending from the inlet end (2), a second portion (4'') extending from the outlet end (3), and a third portion (4''') extending between the first portion (4') and the second portion (4''). The sheets (4) have along the first portion continuous wave-shape extending in a direction (y) transversally to the flow direction (x) and along the third portion a continuous wave-shape extending in the flow direction (x).
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC SWEDEN
Universal analog quantity plate detection system for nuclear plant and method
ActiveCN103163397AEarly detection of quality defectsImprove accuracyElectrical testingNuclear plantPower equipment
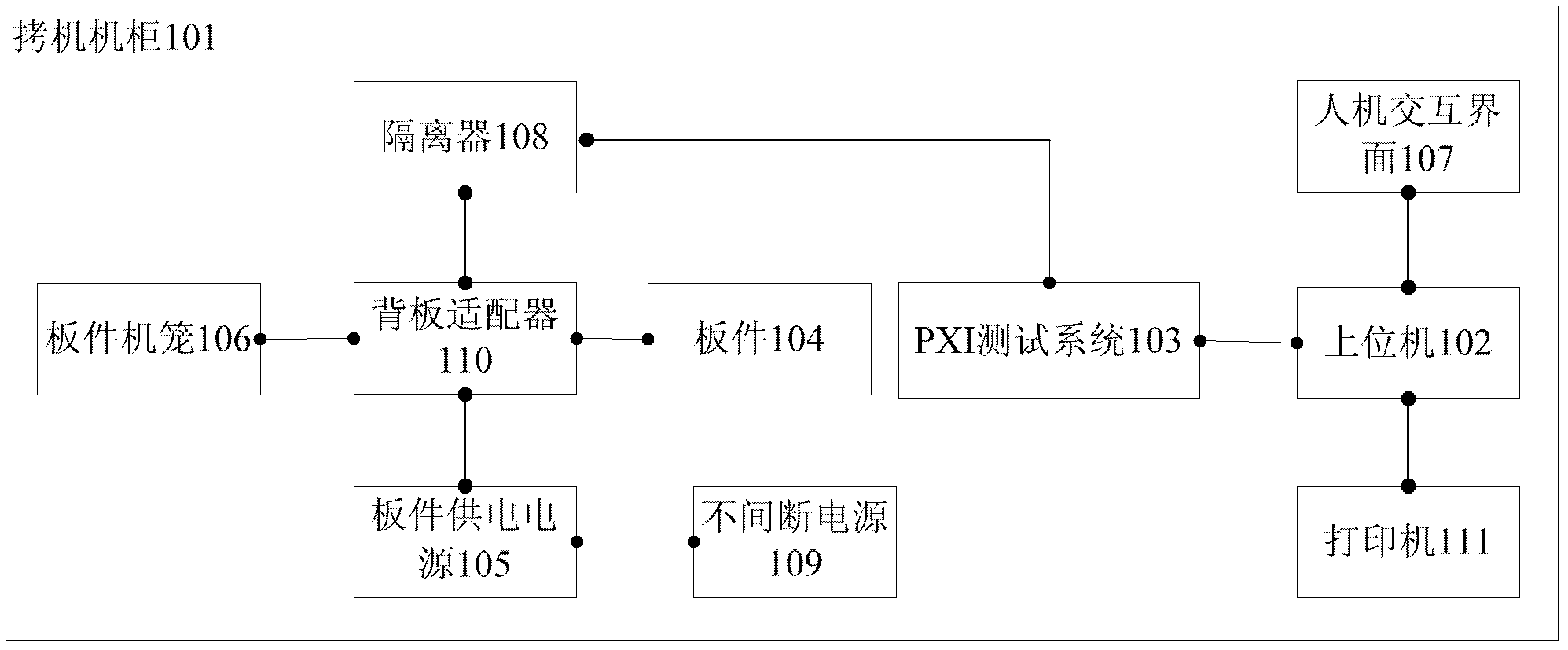
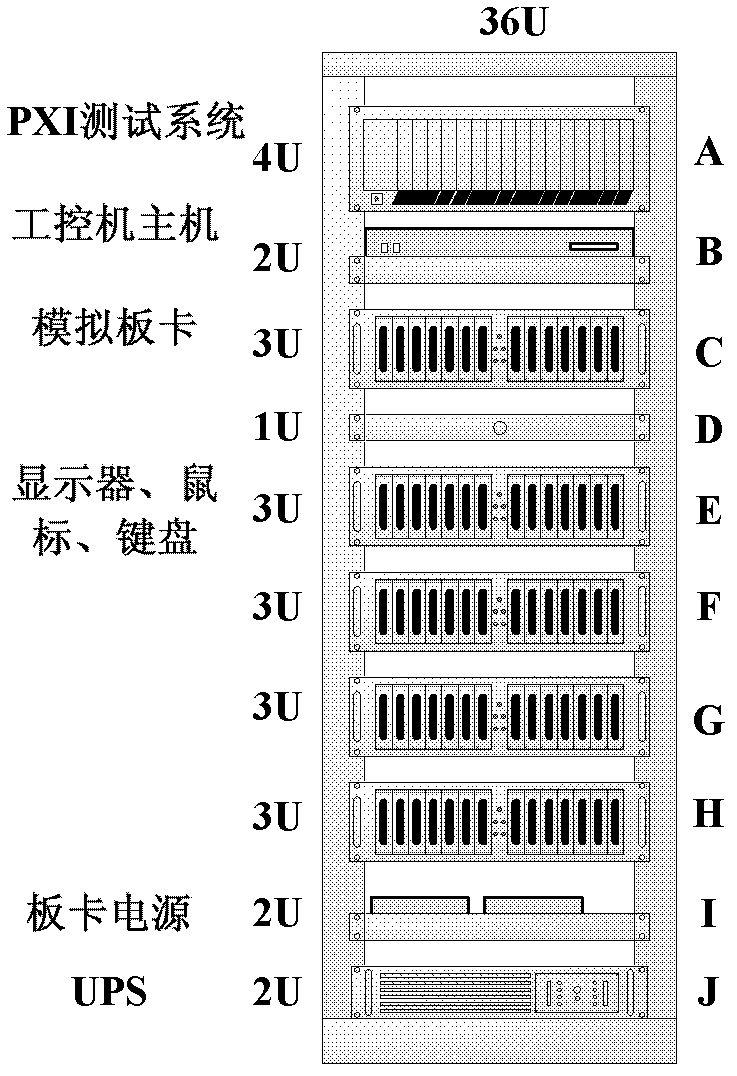
The invention is suitable for a power equipment online digital detection and monitoring technology, belongs to the key technical field of million-kilowatt nuclear plants, and provides a universal analog quantity plate detection system for a nuclear plant and a method. The system comprises a stress test machine cabinet, an upper computer, a peripheral component interconnect (PCI) expansion for instrument (PXI) test system, plates and a plate power supply. The stress test machine cabinet is used for installation of the upper computer, the PXI test system, the plates and the plate power supply. The upper computer is used for sending control commands to the PXI test system and processing test data fed back by the PXI test system. The PXI test system is used for controlling the plate power supply to output current excitation signals and voltage excitation signal to the plates according to a predefined time shaft, collecting test data of the plates, and outputting the test data to the upper computer. The detection system and the method enable people to find quality defects of the plates in an early stage in advance, and improve accuracy of detection of the plates.
Owner:CHINA GENERAL NUCLEAR POWER CORP +2
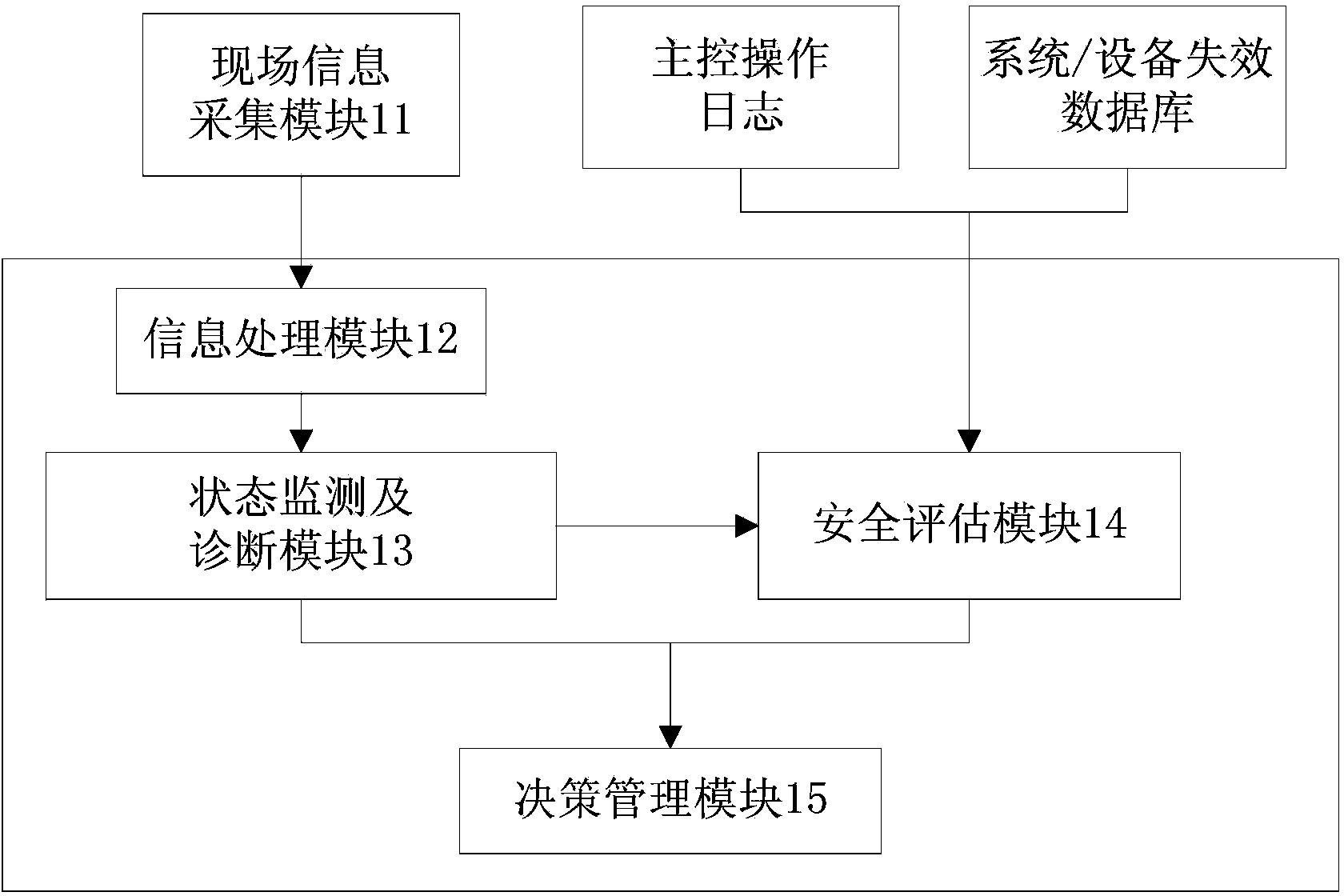
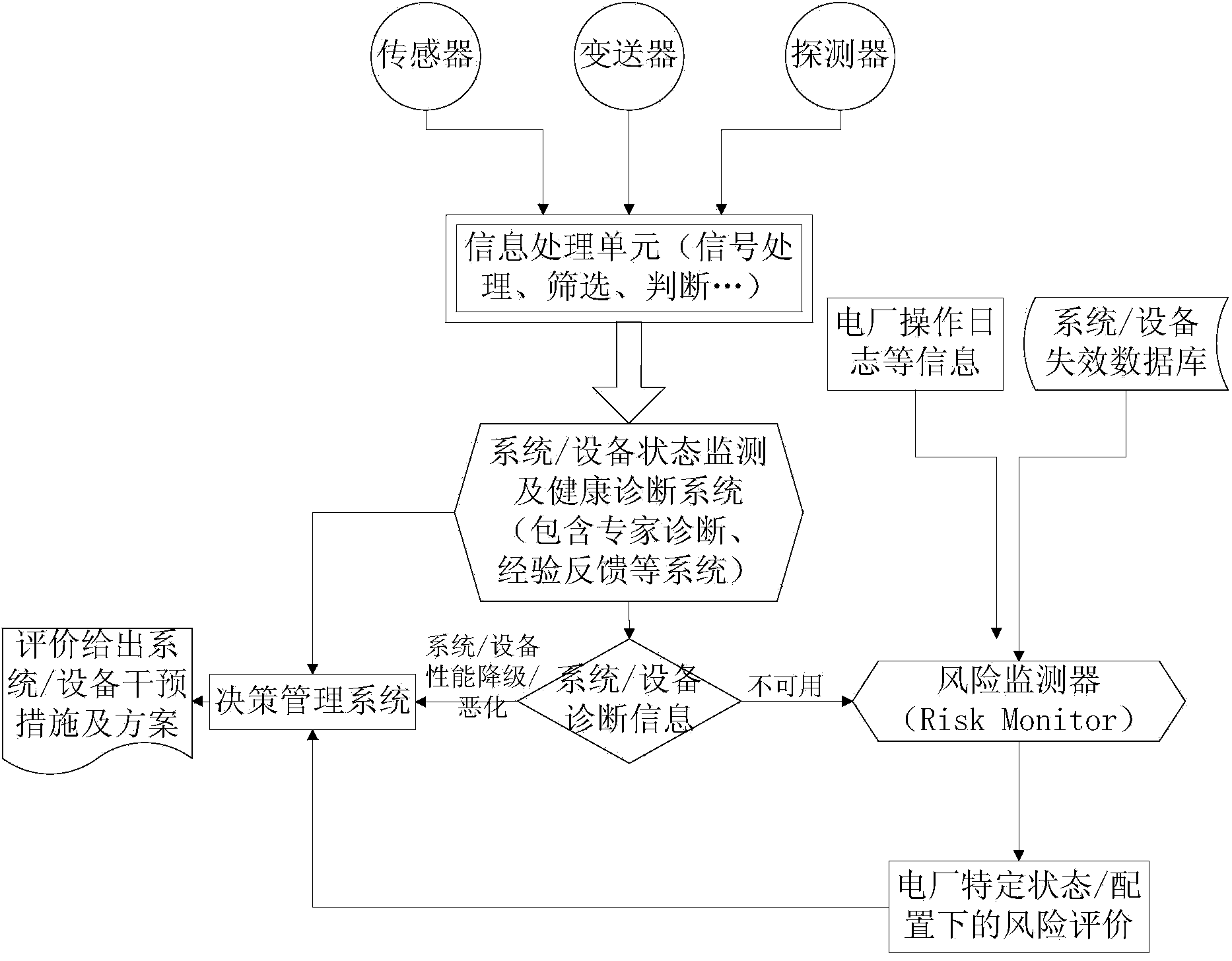
Nuclear plant safety evaluating system and method
InactiveCN103685490ADisadvantages of changing reliance on human operationsImprove availabilityResourcesTransmissionNuclear plantData information
The invention discloses a nuclear plant safety evaluating system and method. Firstly, field data information of a power plant system / equipment is collected through a field information collecting device, and the collected field data information is processed; then the performance state of the power plant equipment is judged according to the processed field data information, and then the safety level of a power plant is evaluated according to the performance state of the power plant system / equipment and power plant system / equipment information recorded in a power plant system / equipment failure database. By means of the nuclear plant safety evaluating system and method, the safety level of the power plant can be evaluated in real time, the defect that a current risk monitor is more relied on personnel operation is overcome, safety of the power plant is ensured, and the availability ratio and the economical efficiency of the power plant are improved effectively.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
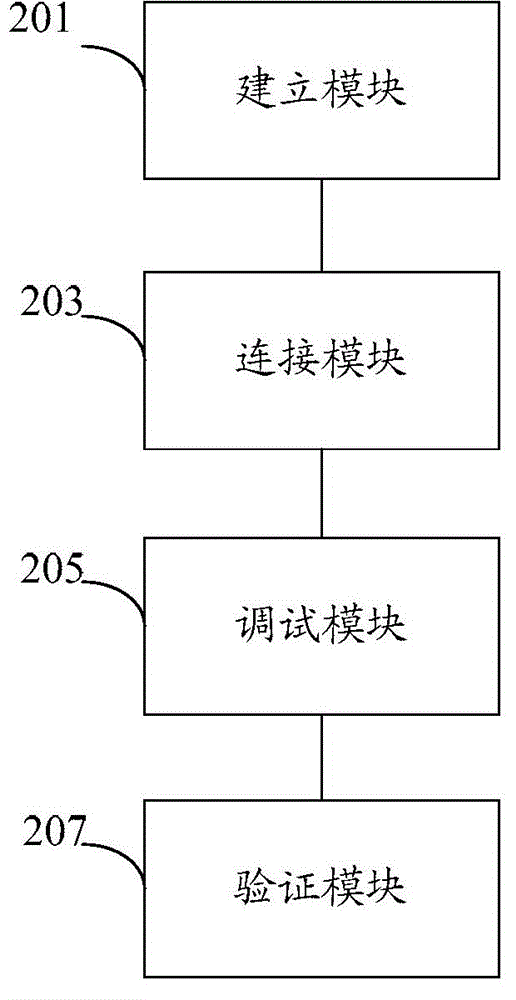
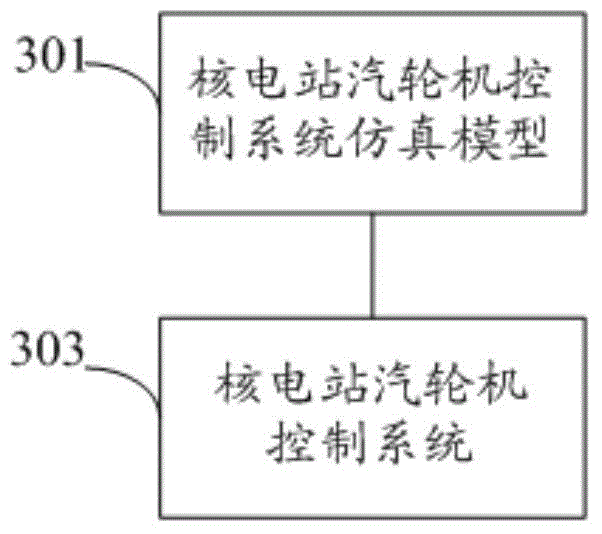
Debugging method, device and system of nuclear power station steam turbine control system
ActiveCN103559924AReduce riskEfficient test design functionPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNuclear plantControl system
The invention discloses a debugging method of a nuclear power station steam turbine control system. The method comprises the steps that a nuclear power station steam turbine control system simulation model is established, the simulation model at least comprises a simulation debugging device; the nuclear power station steam turbine control system is connected with the simulation model, the nuclear power station steam turbine control system at least comprises one of a steam turbine adjusting subsystem, a steam turbine protecting subsystem, a steam turbine monitoring subsystem (GME) and a steam turbine shaft seal subsystem, each subsystem is subjected to simulation debugging through the simulation debugging device, and according to the simulation debugging results, the functions of the subsystems are verified. According to the debugging method of the nuclear power station steam turbine control system, the simulation model is used for being connected with the steam turbine control system, system function verifying is carried out in advance, nuclear power plant debugging scheme optimizing is achieved, the debugging period is shortened, and the risk of steam turbine unexpected halt and the risk of reactor unexpected tripping after a nuclear power unit is started are lowered. In addition, the invention further discloses a debugging device and system of the nuclear power station steam turbine control system.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Island mode for nuclear power plant
ActiveUS20130272471A1Reducing thermal power outputReduce outputPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationPressurized water reactorNuclear engineering
A nuclear power plant comprises a pressurized water reactor (PWR) and a steam generator driving a turbine driving an electric generator. A condenser condenses steam after flowing through the turbine. Responsive to a station blackout, the nuclear power plant is electrically isolated and a bypass valve is opened to convey bypass steam flow from the steam generator to the condenser without flowing through the turbine. The thermal power output of the PWR is gradually reduced over the transition time interval. After opening, the bypass valve is gradually closed over the transition time interval. A supplemental bypass valve may also be opened responsive to the station blackout to convey supplemental bypass steam flow from the steam generator to a feedwater system supplying secondary coolant feedwater to the steam generator. The supplemental bypass steam flow does not flow through the turbine and does not flow through the condenser.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
Nuclear reactor coolant pump and nuclear power plant having same
ActiveUS20160260509A1Energy lossElectrical degradationIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreImpeller
The present invention discloses a nuclear reactor coolant pump that does not rely on an electric motor, but is operated by means of driving force generated inside a nuclear power plant, so a to be capable of maintaining the safety of the nuclear reactor when the nuclear reactor is operating normally and also in the event of an accident in the nuclear reactor. The nuclear reactor coolant pump comprises: a pump impeller rotatably installed in a first fluid passage of a nuclear reactor coolant system to circulate a first fluid inside the nuclear reactor coolant system; a drive unit receiving steam from a steam generator to generate driving force to rotate the pump impeller, and rotating about the same rotating shaft as the pump impeller to transfer the generated driving force to the pump impeller; and a steam supplying unit forming a passage between the steam generator and the drive unit to supply at least a portion of the steam released from the steam generator to the drive unit.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
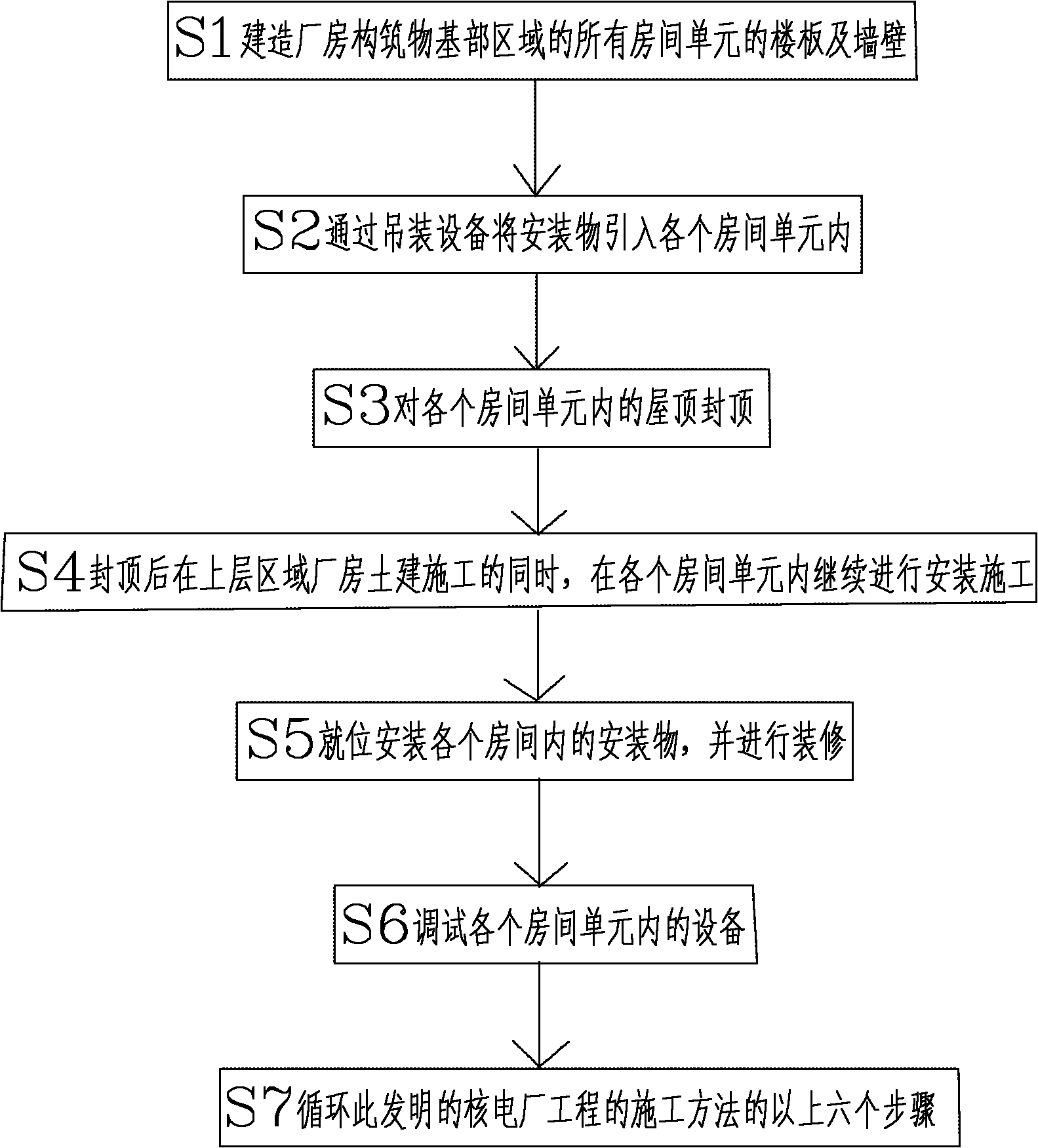
Construction method of nuclear power plant project
ActiveCN101864842AShorten the construction periodSolve the problem of introducing difficultiesBuilding material handlingIndustrial buildingsNuclear plantFloor slab
The invention discloses a construction method of a nuclear power plant project, which comprises the following steps that: S1. building the floor slabs and walls of all room units in the base area of a plant structure; S2. leading installation objects into all the room units through hoisting equipment; S3. sealing the roofs of all the room units; S4. after sealing the roofs, continuing to carry out installation construction in the room units while carrying out the civil engineering construction of the plant in an upper area; S5. installing the installation objects in all rooms in place, and decorating; S6. debugging the equipment in all the room units; and S7. repeating the six steps of the construction of the nuclear power plant project. The nuclear power plant project construction method sets the construction modes of a civil engineering project and a mechanical and electronic installation project into parallel, thereby not only greatly shortening the construction period of the nuclear power plant project but also solving the problems that some large equipment is difficult to lead in and the utilization of large special hoisting equipment, so as to reduce the installation difficulty of the equipment, improve the installation quality and reduce the construction cost of the nuclear power plant.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Nuclear reactor containment vessel and nuclear power plant using same
InactiveCN102483963ANuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsNuclear reactor coreReactor pressure vessel
A nuclear reactor containment vessel (8) comprises a nuclear reactor's primary containment vessel (3) which contains a nuclear reactor pressure vessel (2), a nuclear reactor's secondary containment vessel (4) which is disposed outside the nuclear reactor's primary containment vessel (3) and which has the pressure resistant properties and the air-tightness which are equivalent to those of the nuclear reactor's primary containment vessel (3), an airbag (5) which is disposed within the nuclear reactor's secondary containment vessel (4) and which, when a failure occurs in the nuclear reactor's primary containment vessel (3), expands while receiving and encapsulating a high-pressure gas discharged from the inside of the nuclear reactor's primary containment vessel (3), and a gas phase vent pipe (6) which connects the nuclear reactor's primary containment vessel (3) and the airbag (5).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Supersafe and simply- / easily-decommissionable nuclear power plant
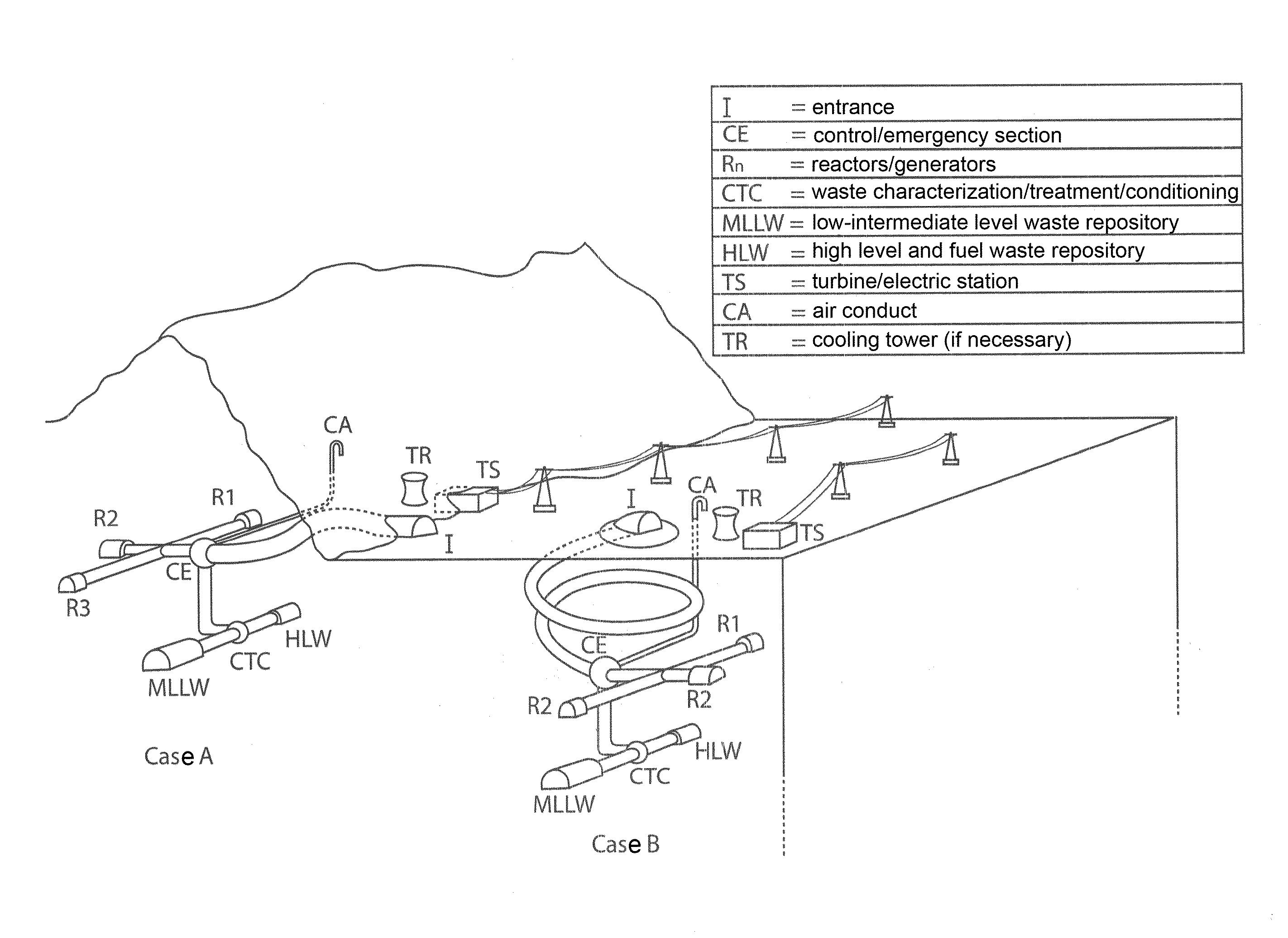
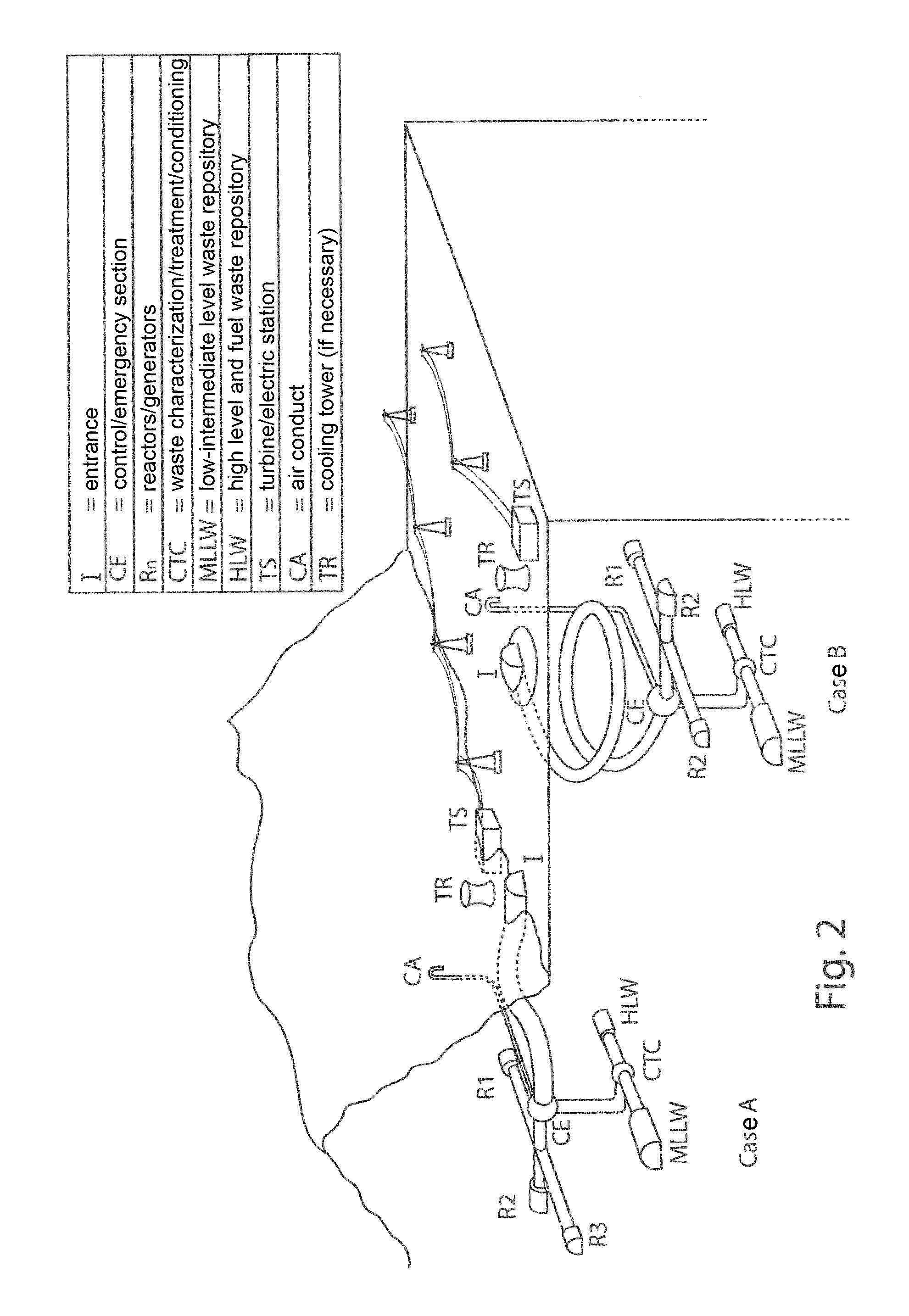
The invention relates to an inexpensively- / easily-decommissionable nuclear power plant, where a nuclear isle of one or more nuclear power-stations is installed in caverns, and further, side by side with them, a centre for characterising, treating and conditioning radioactive wastes and two repositories are installed in suitable caverns, with a final repository being adapted to store low-intermediate level nuclear wastes and a temporary repository being adapted to store spent fuel, high-level long-life radioactive materials and, in case, spare nuclear rods for reactor refueling.
Owner:SERGIO DOFFIZI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com