Patents
Literature
259 results about "Boiling water reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuclear reactor after the pressurized water reactor (PWR), which is also a type of light water nuclear reactor. The main difference between a BWR and PWR is that in a BWR, the reactor core heats water, which turns to steam and then drives a steam turbine. In a PWR, the reactor core heats water, which does not boil. This hot water then exchanges heat with a lower pressure water system, which turns to steam and drives the turbine. The BWR was developed by the Argonne National Laboratory and General Electric (GE) in the mid-1950s. The main present manufacturer is GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, which specializes in the design and construction of this type of reactor.
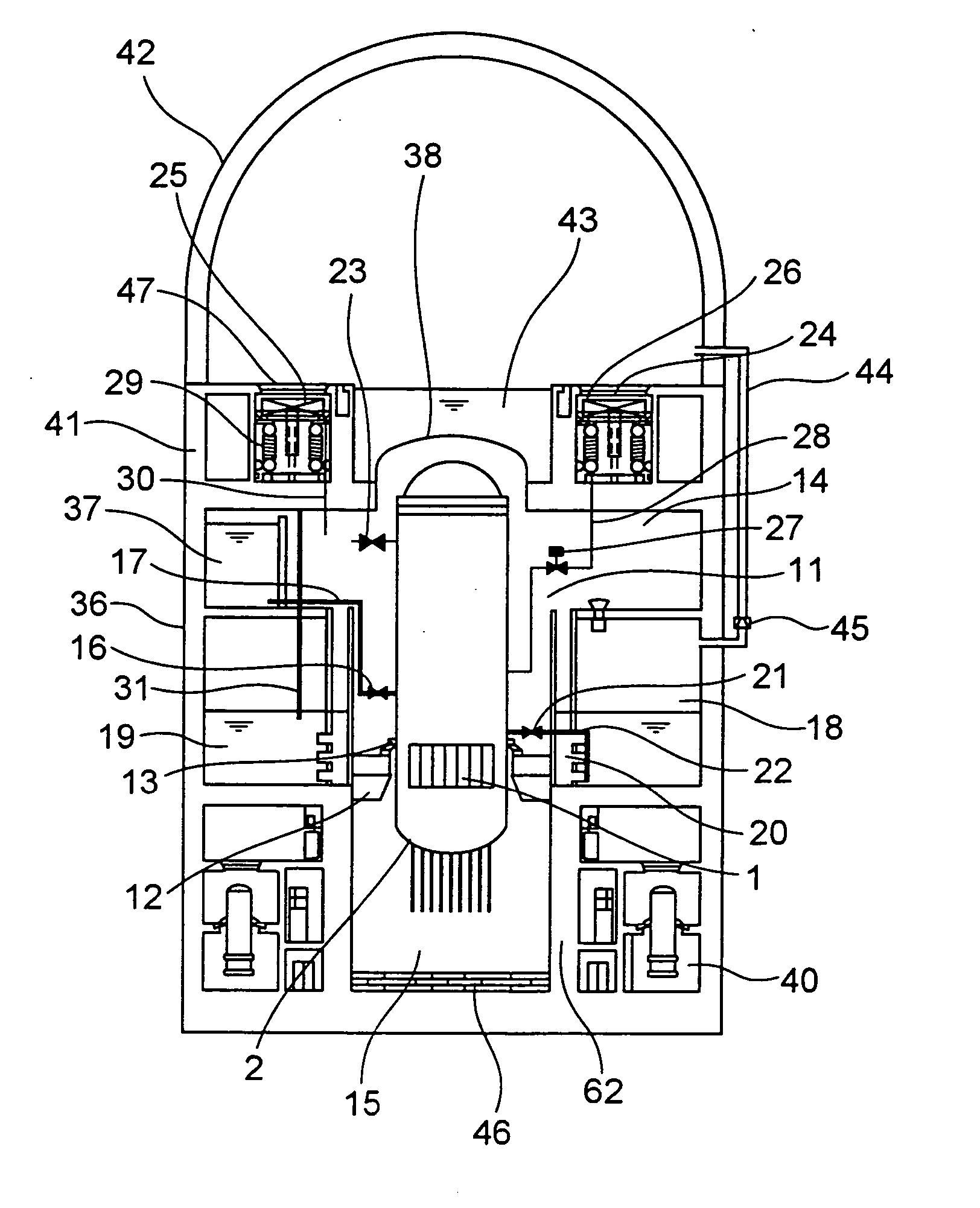
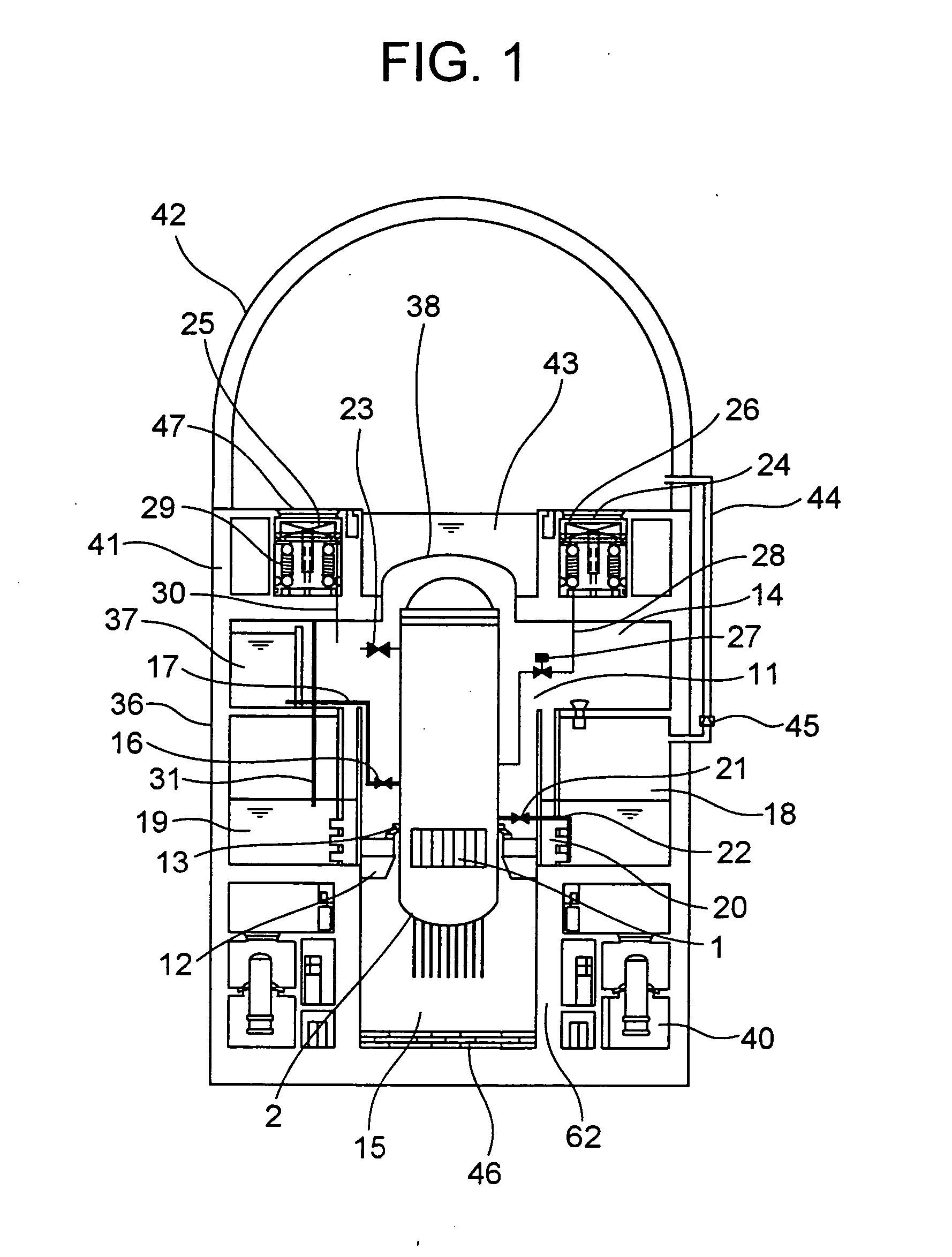
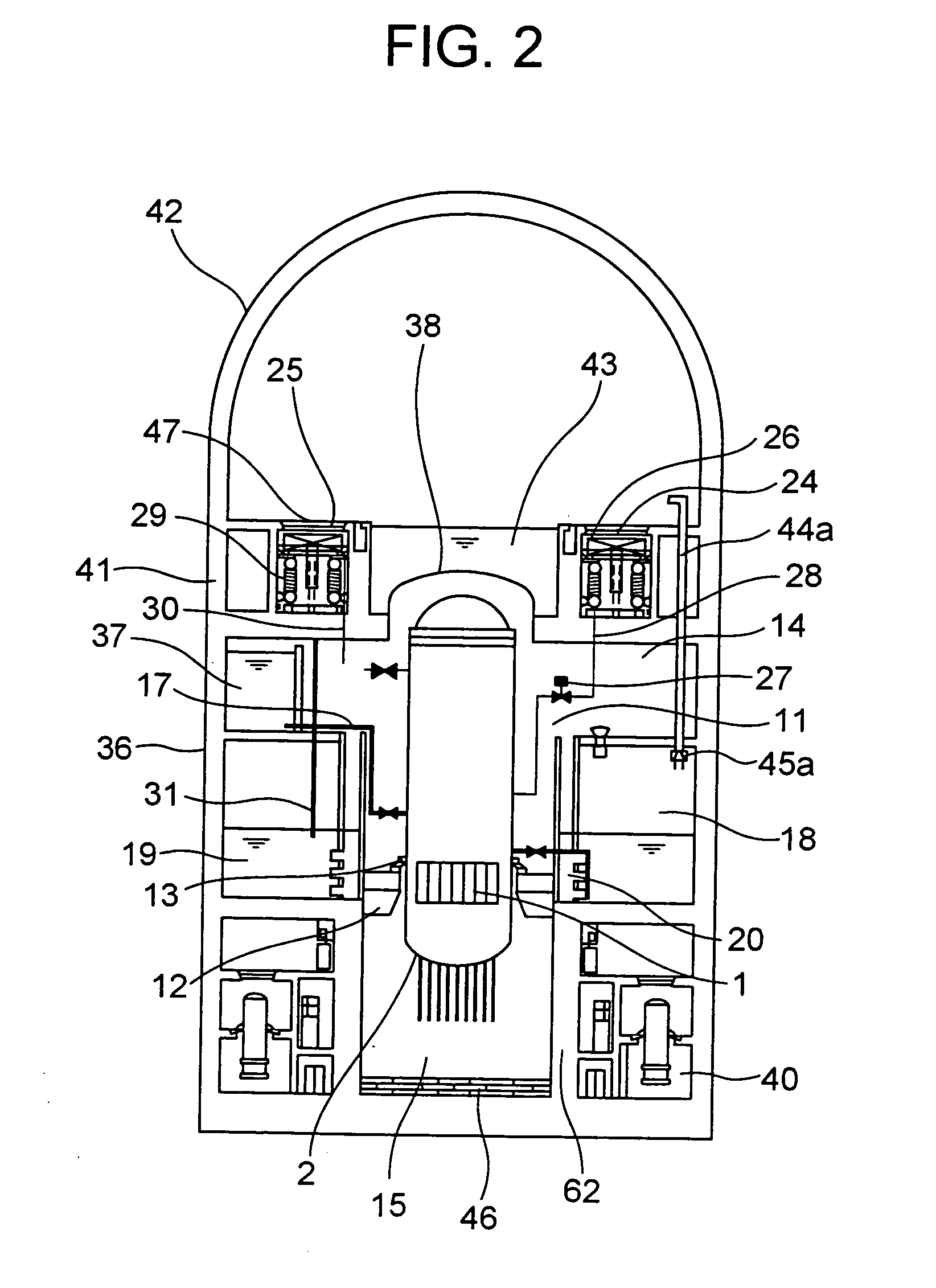
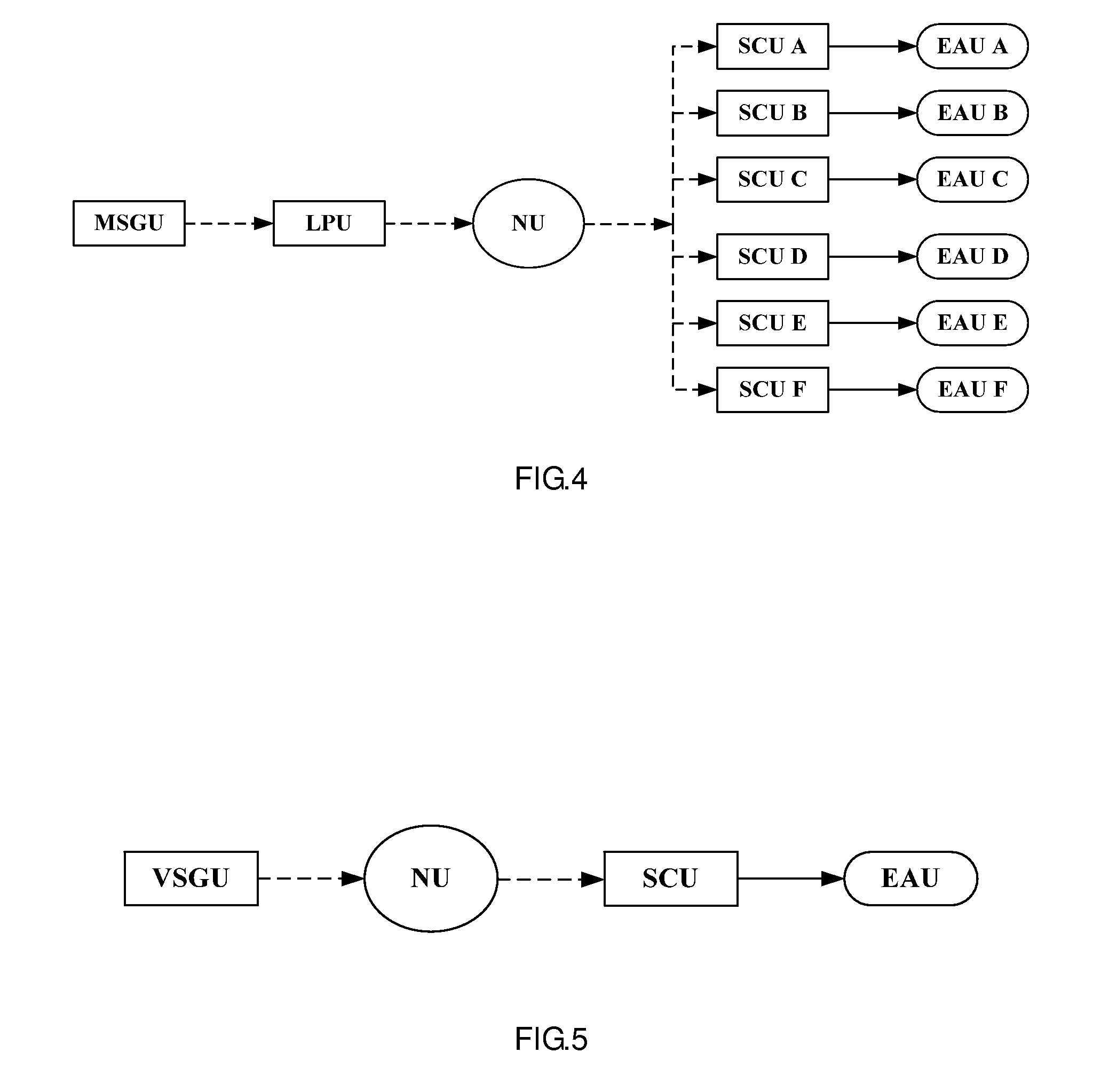
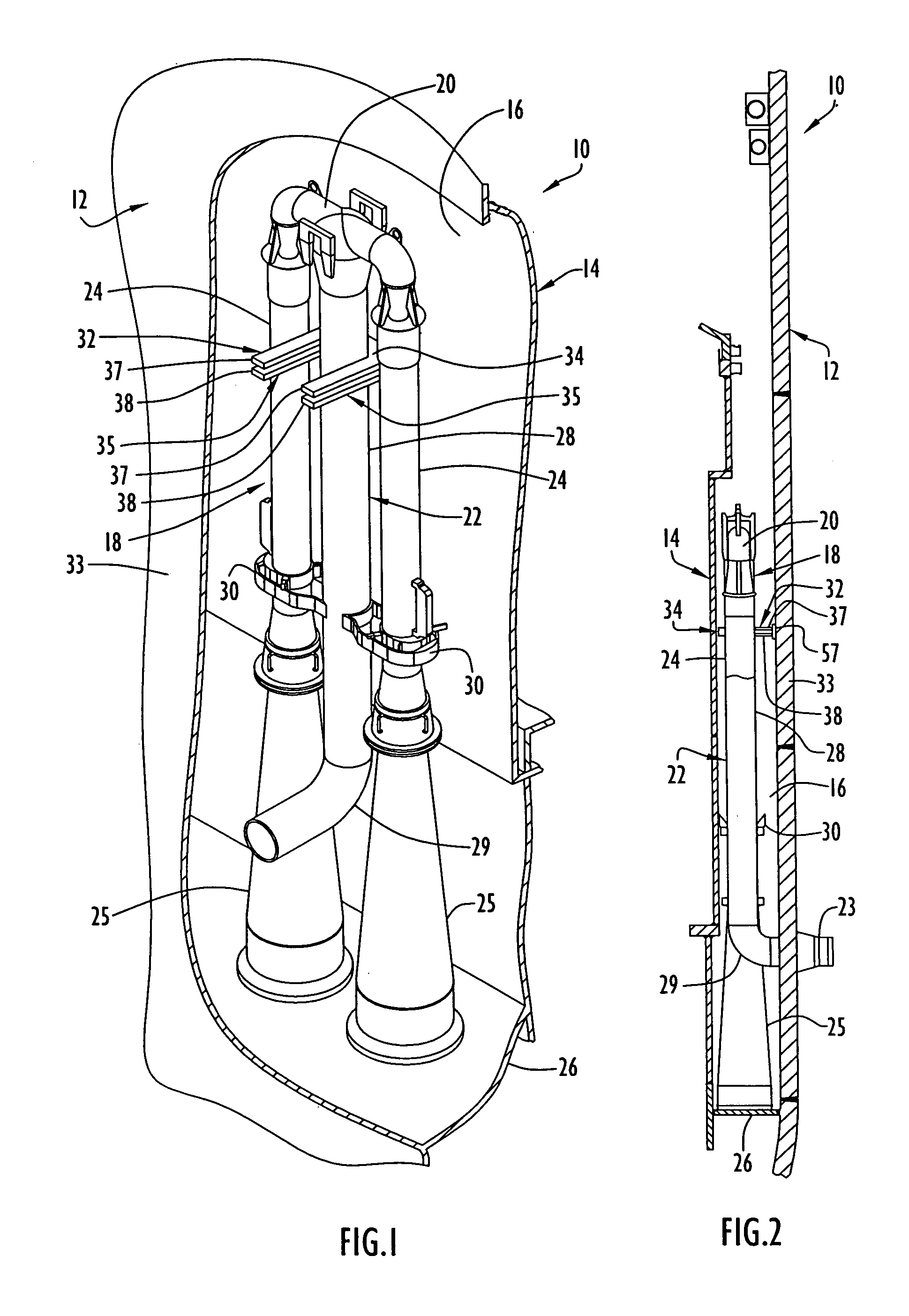
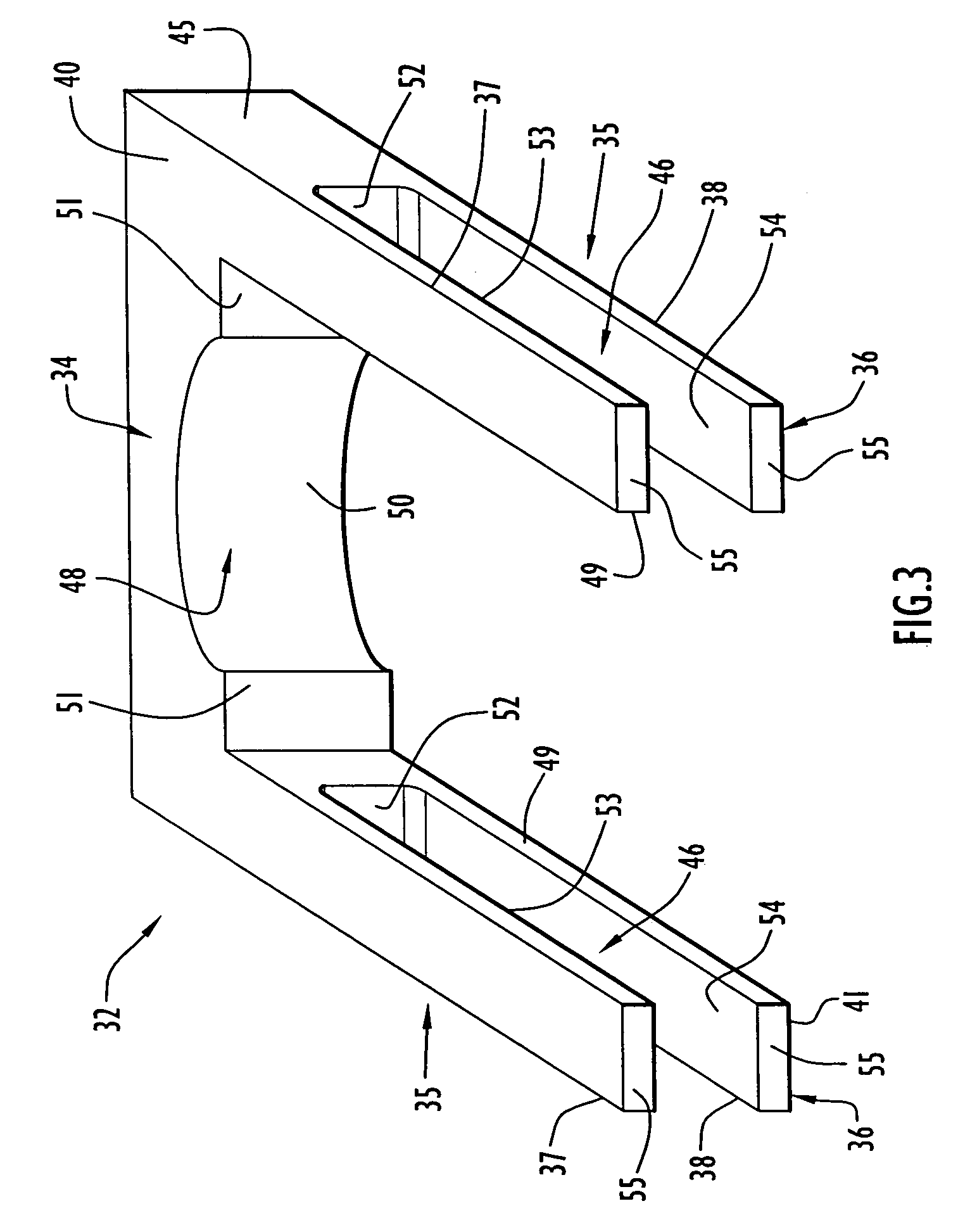
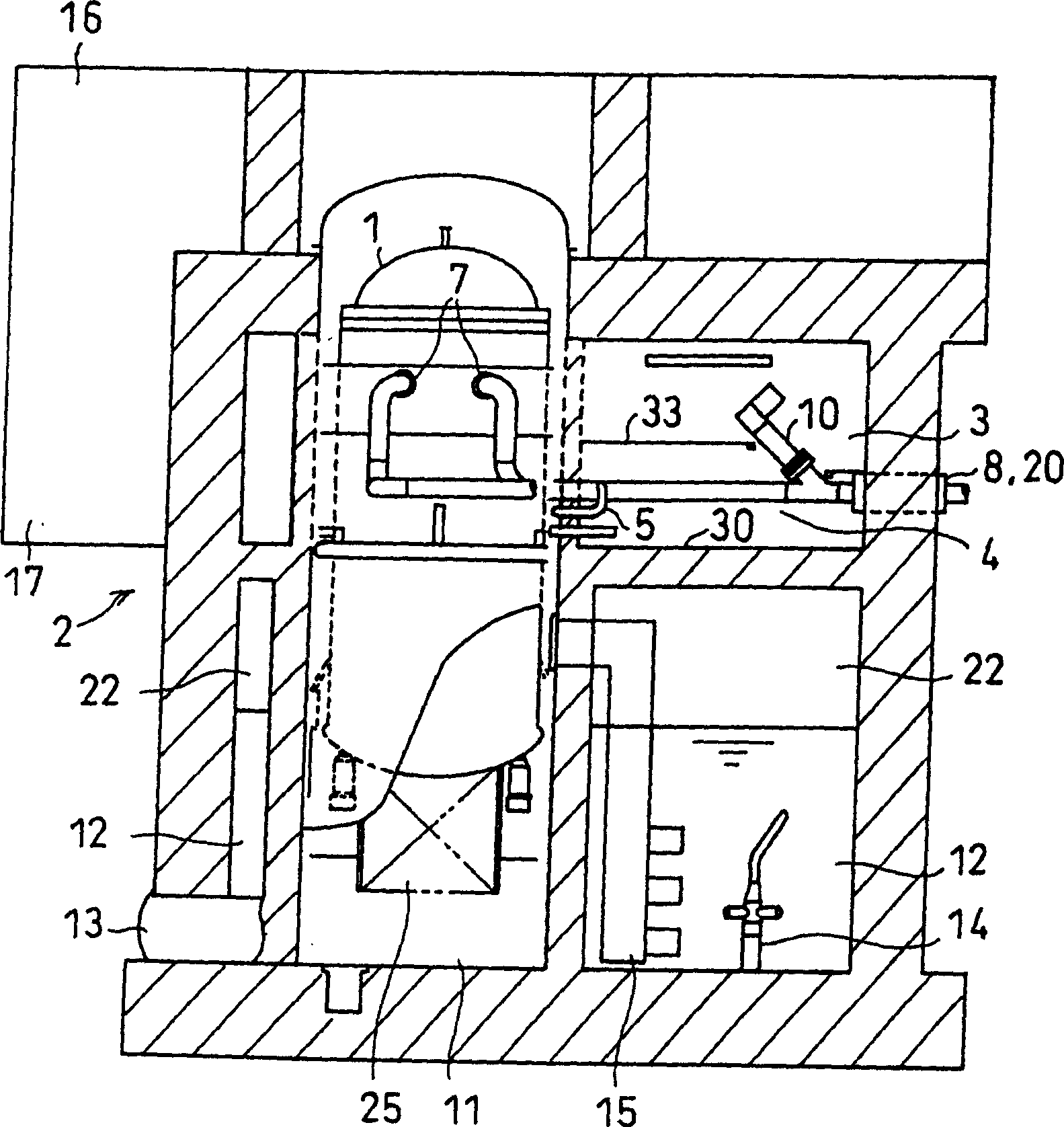
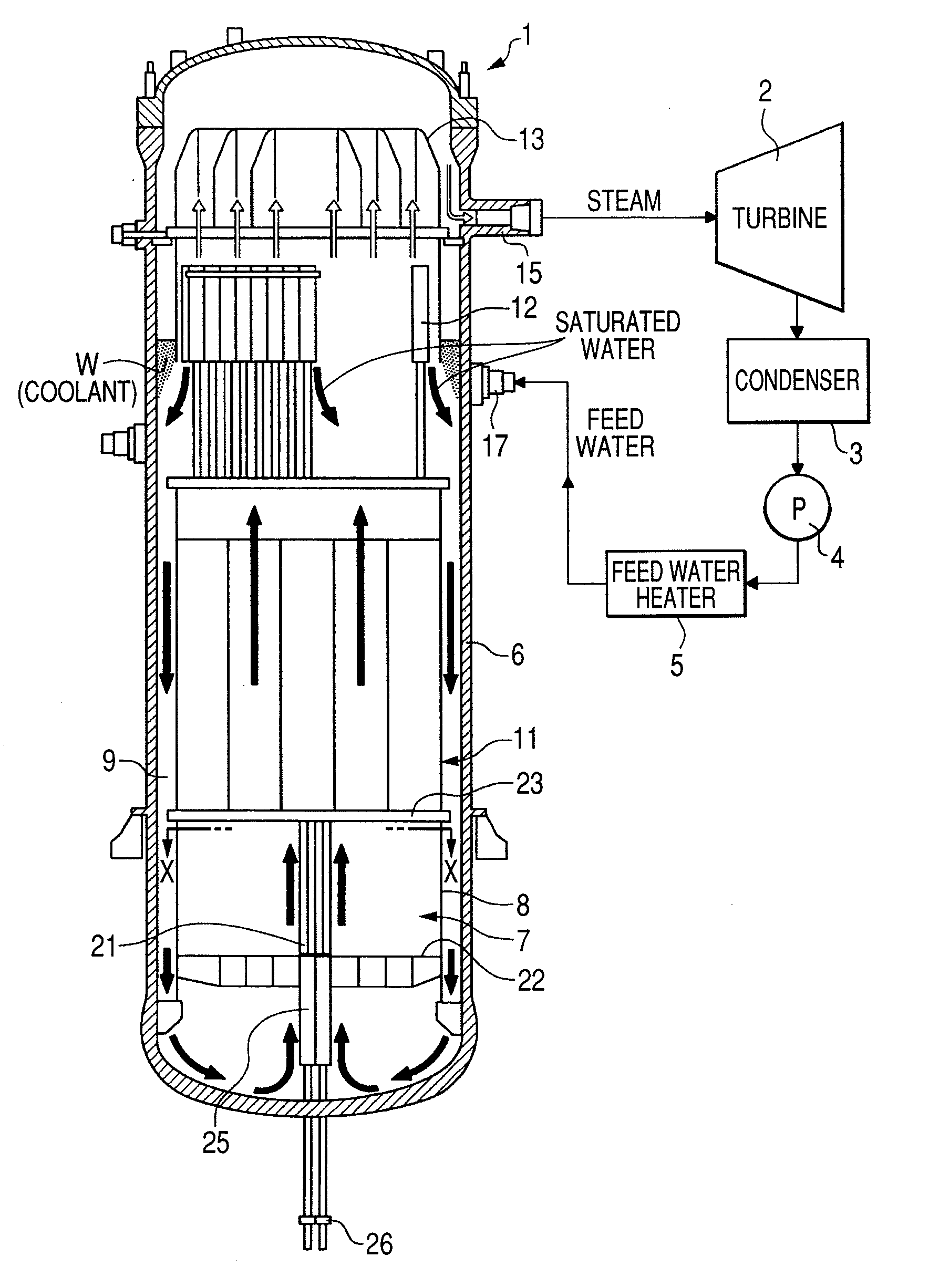
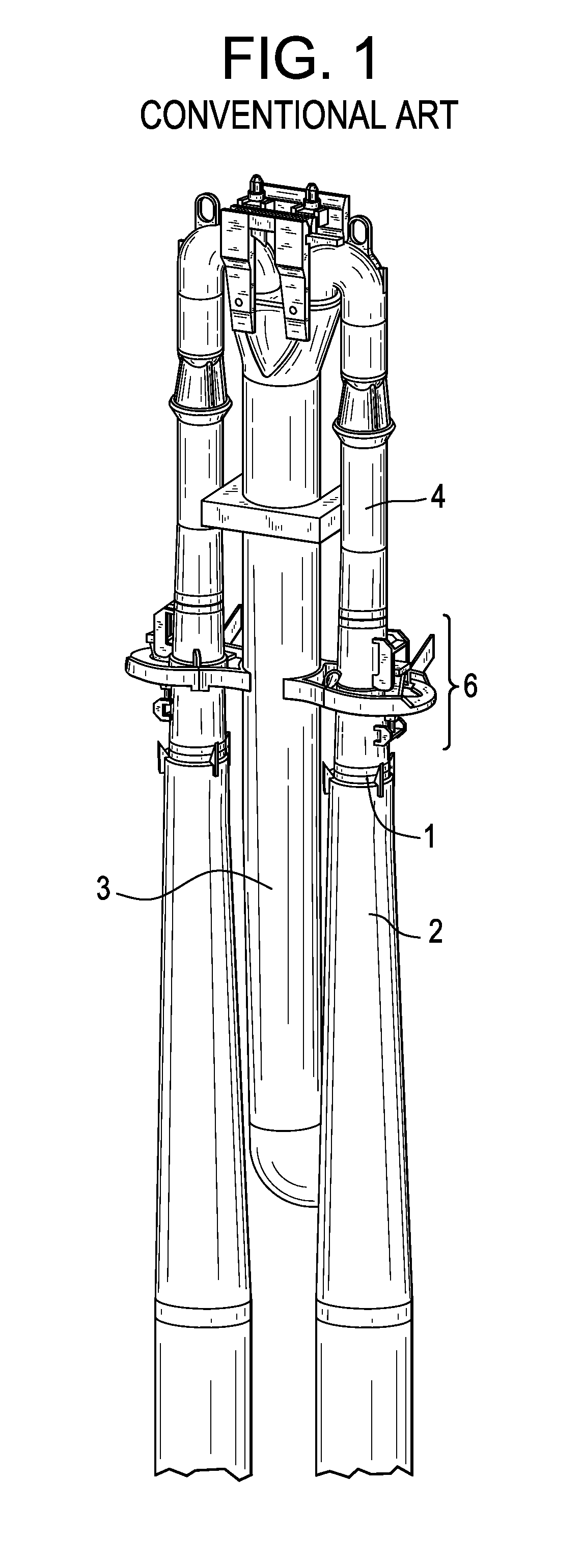
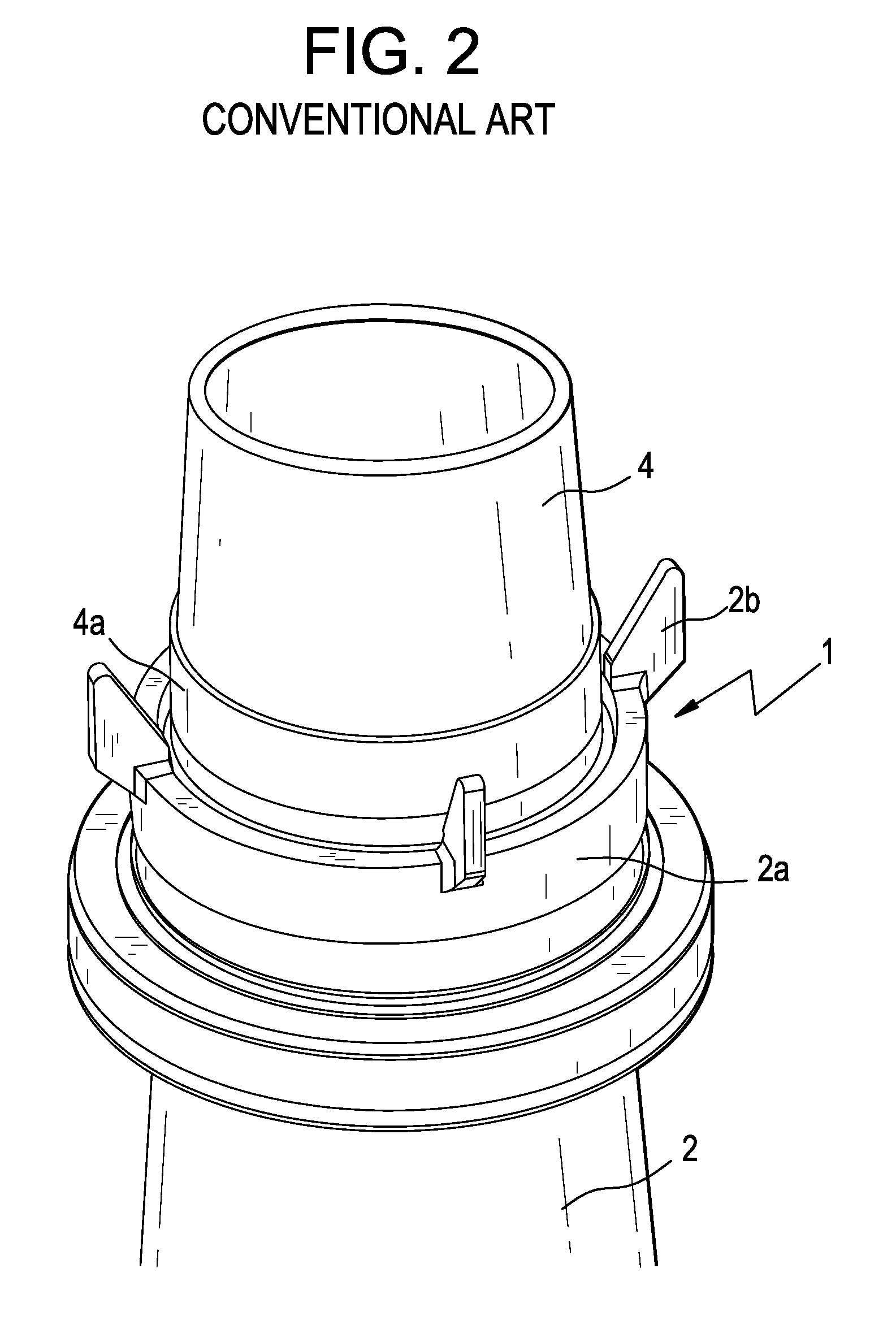
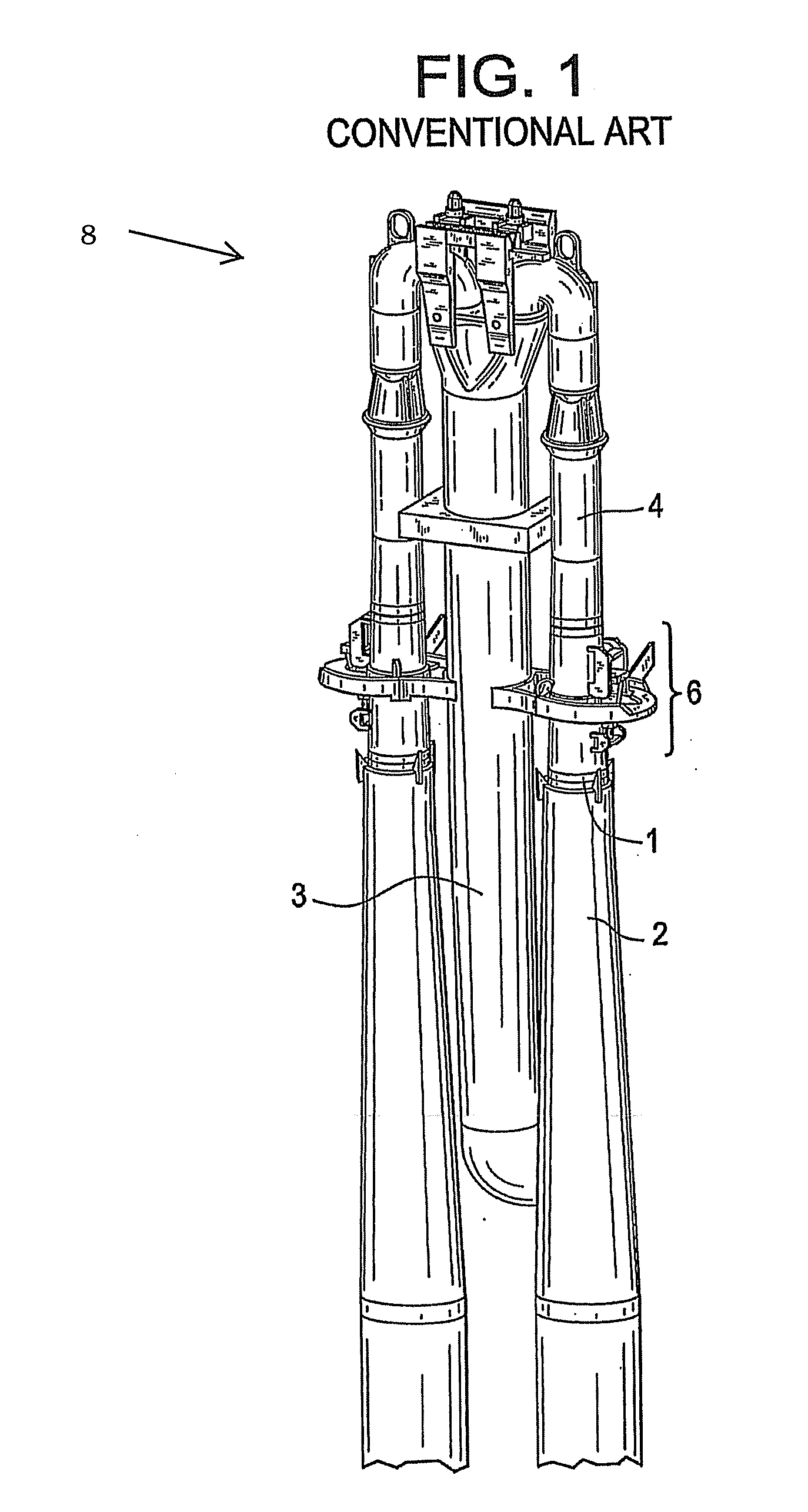
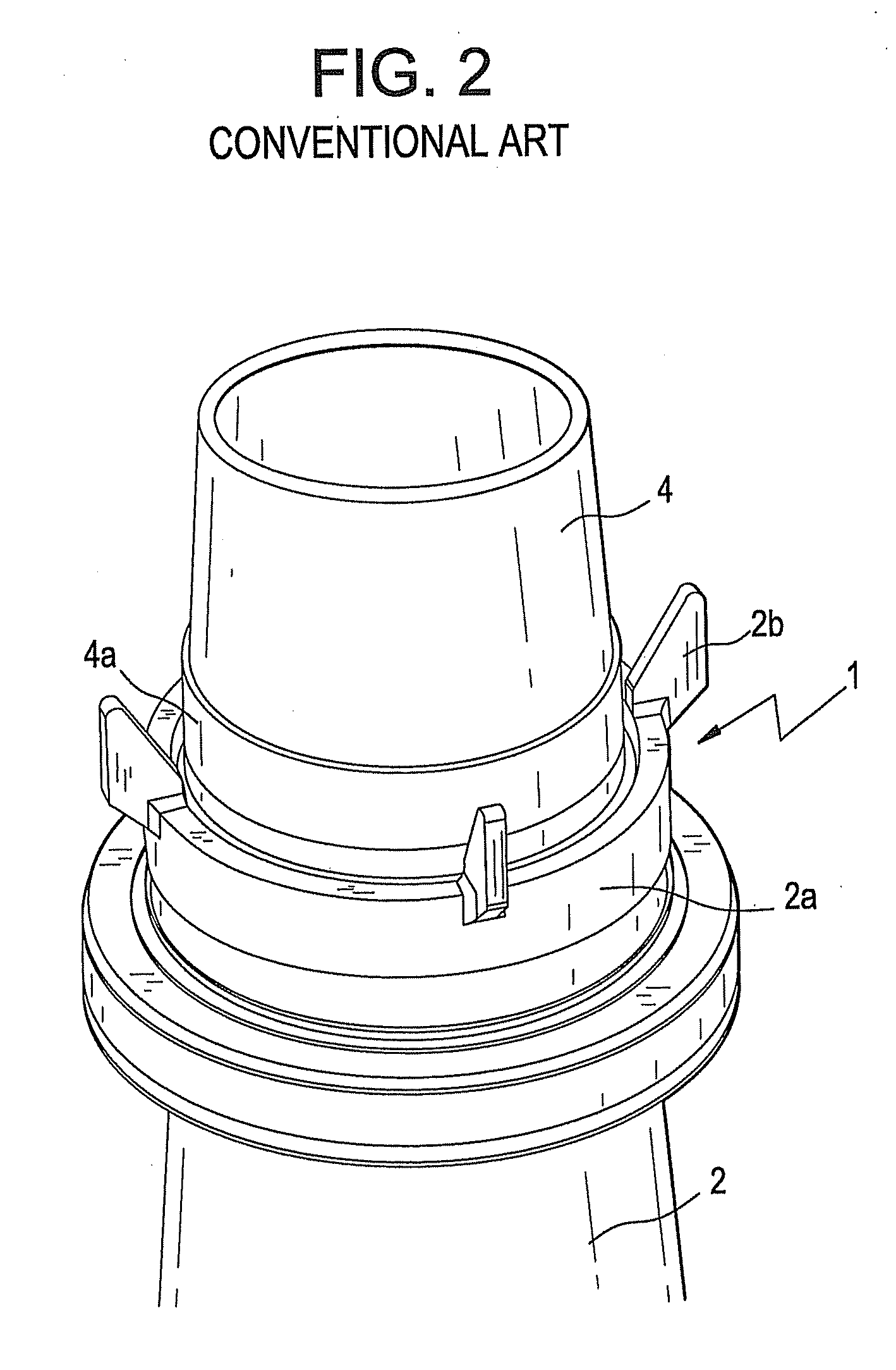
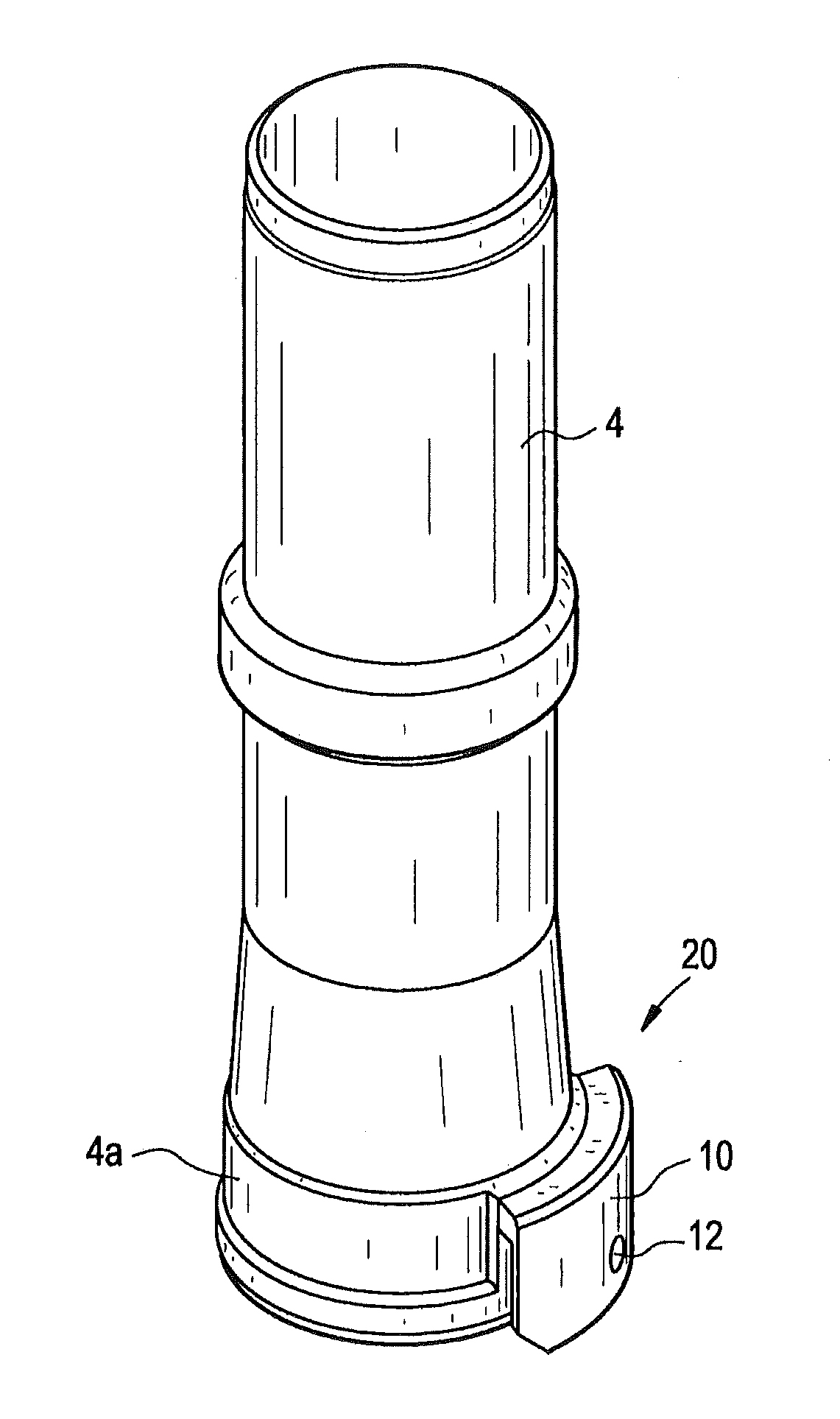
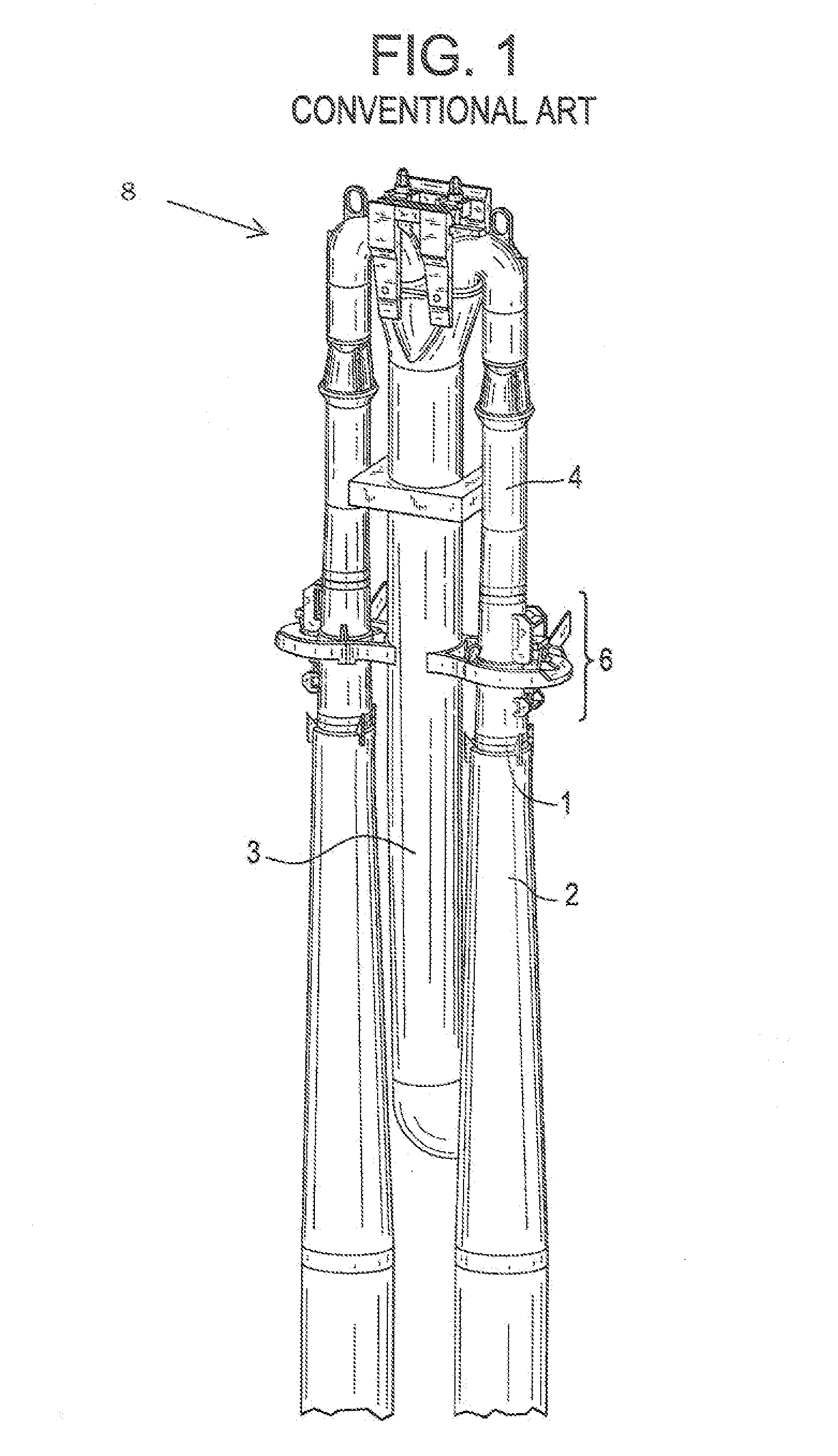
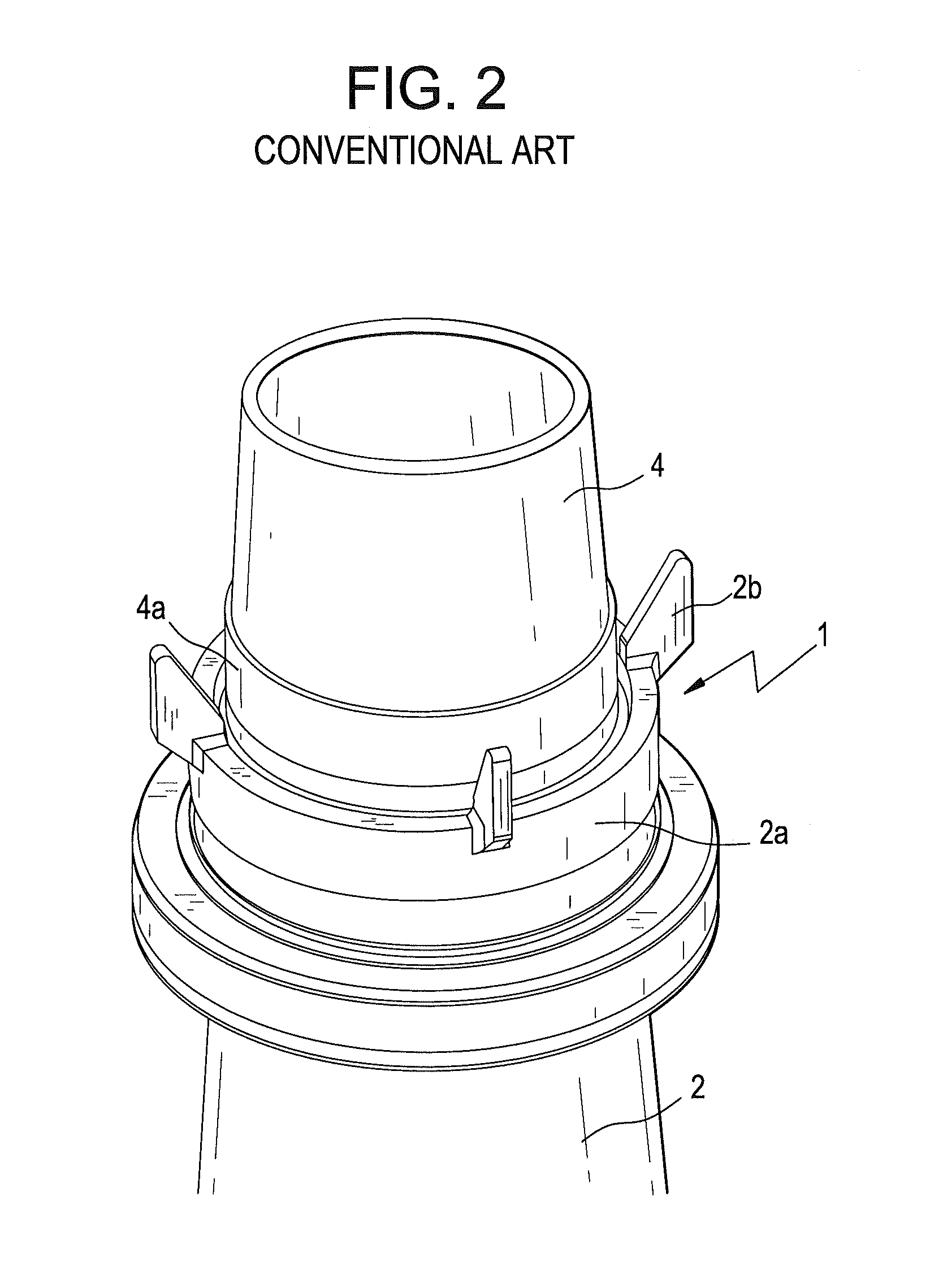
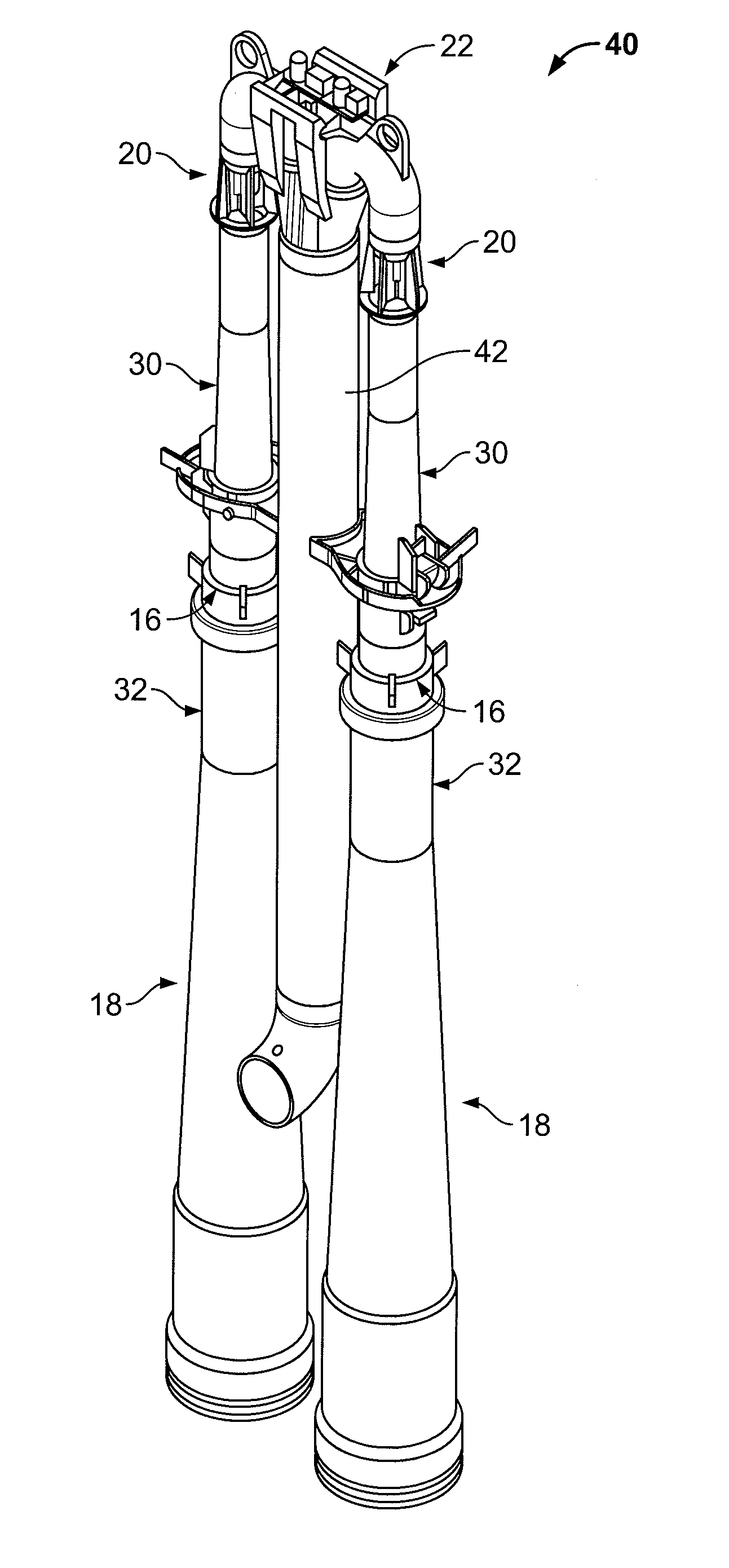
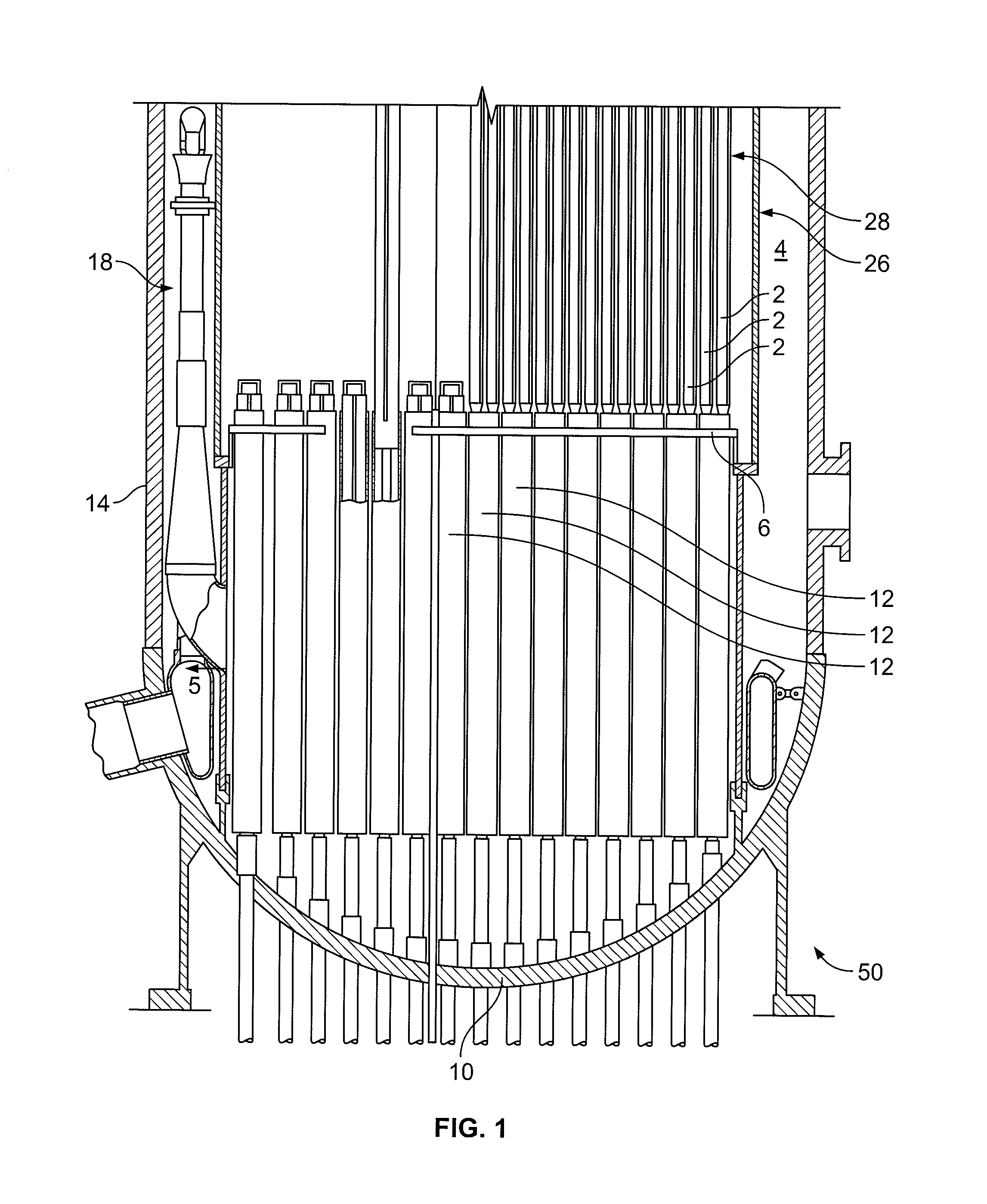
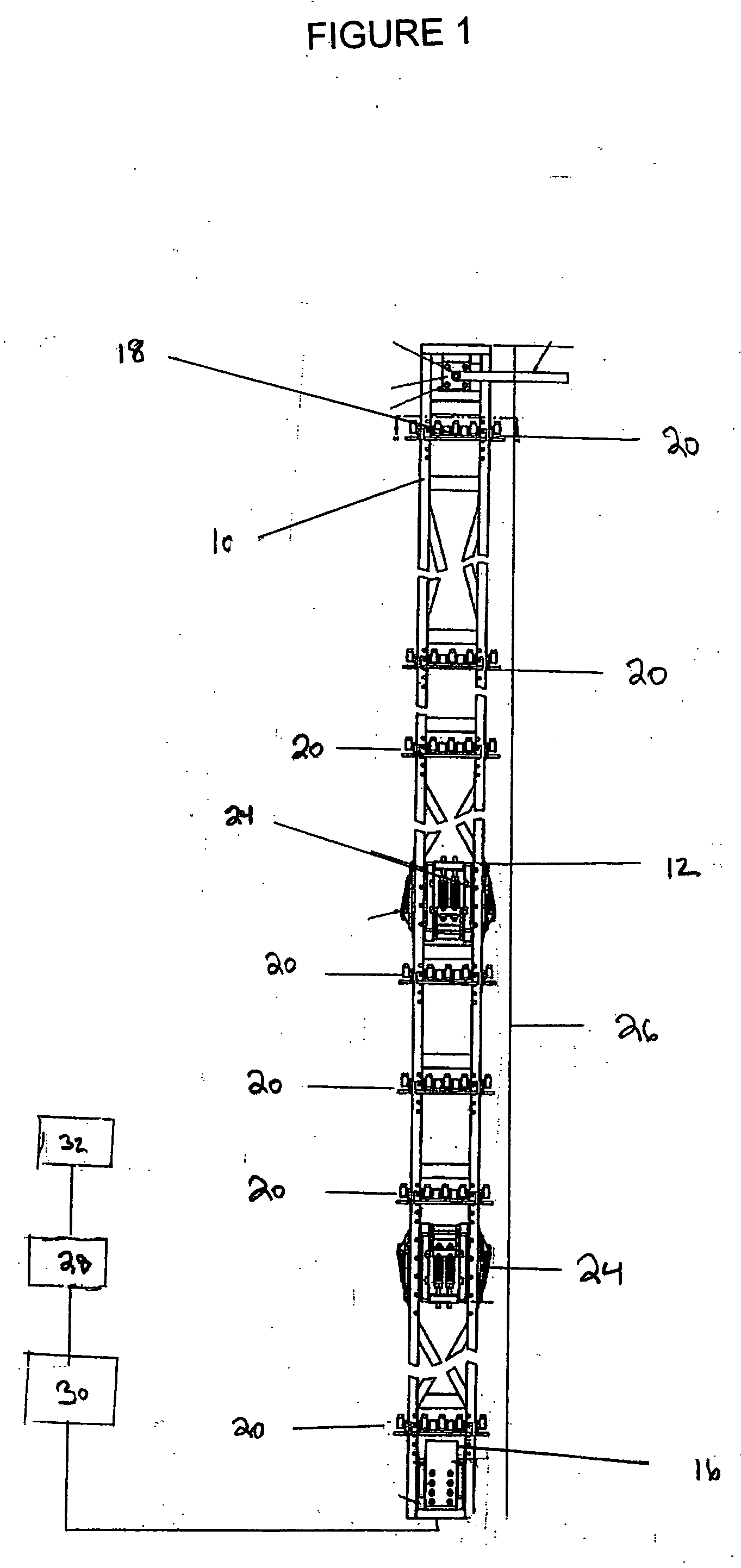
Reactor containment vessel and boiling water reactor power plant
ActiveUS20070092053A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsPower stationReactor pressure vessel
A containment vessel includes a primary containment vessel containing a reactor pressure vessel, an upper secondary containment vessel arranged above the primary containment vessel, and a gas-phase vent pipe linking the primary containment vessel and the upper secondary containment vessel by way of an isolation and connection switching system. The gas-phase vent pipe may be arranged either inside or outside the primary containment vessel and the upper secondary containment vessel. Alternatively, it may be embedded in the wall. An igniter may be arranged in the upper secondary containment vessel. The air in the upper secondary containment vessel may be replaced by nitrogen. A gravity-driven flooding system pool may be arranged in the upper secondary containment vessel and cooling water may be led from the inside of the pool to the inside of the primary containment vessel.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
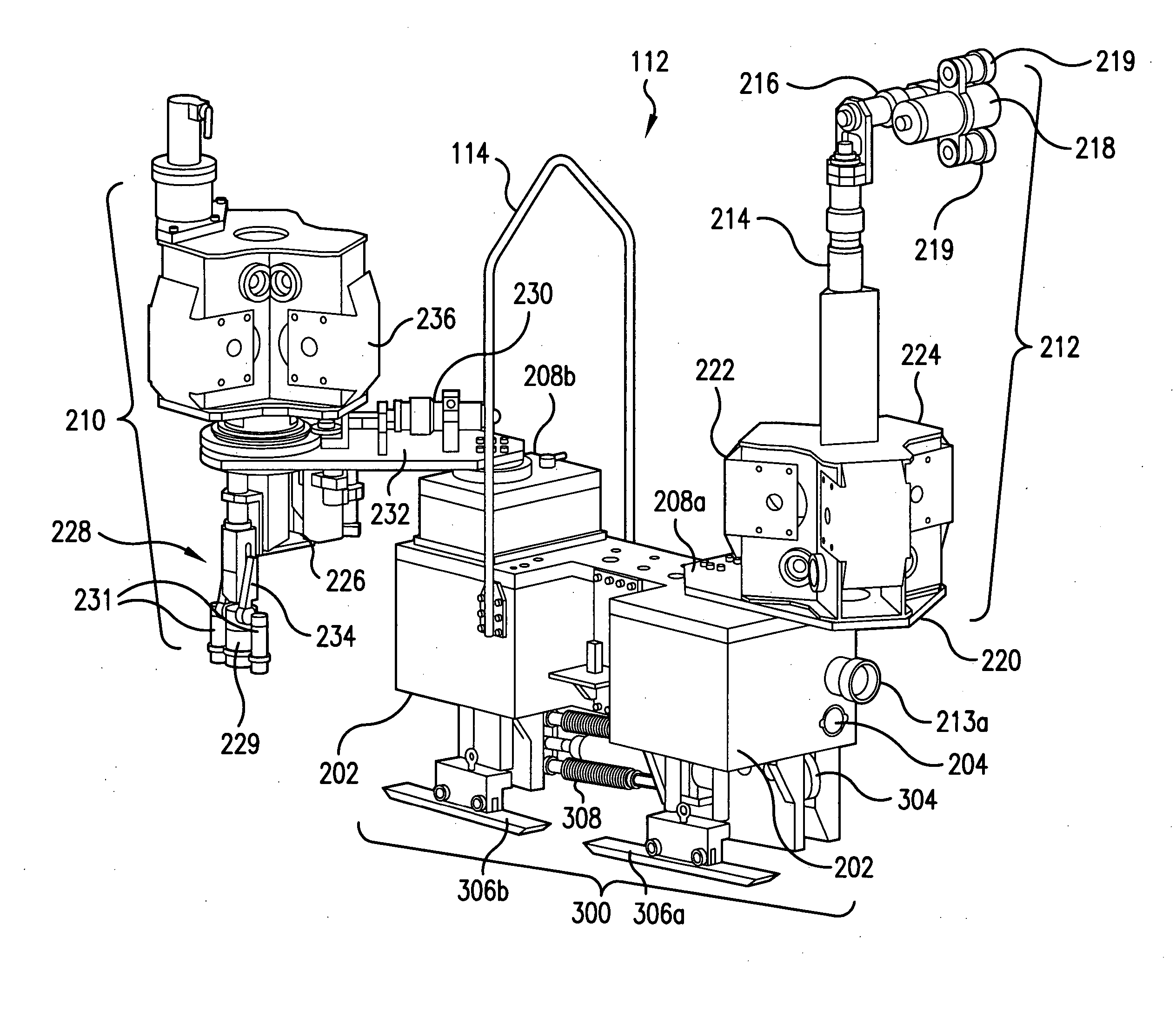
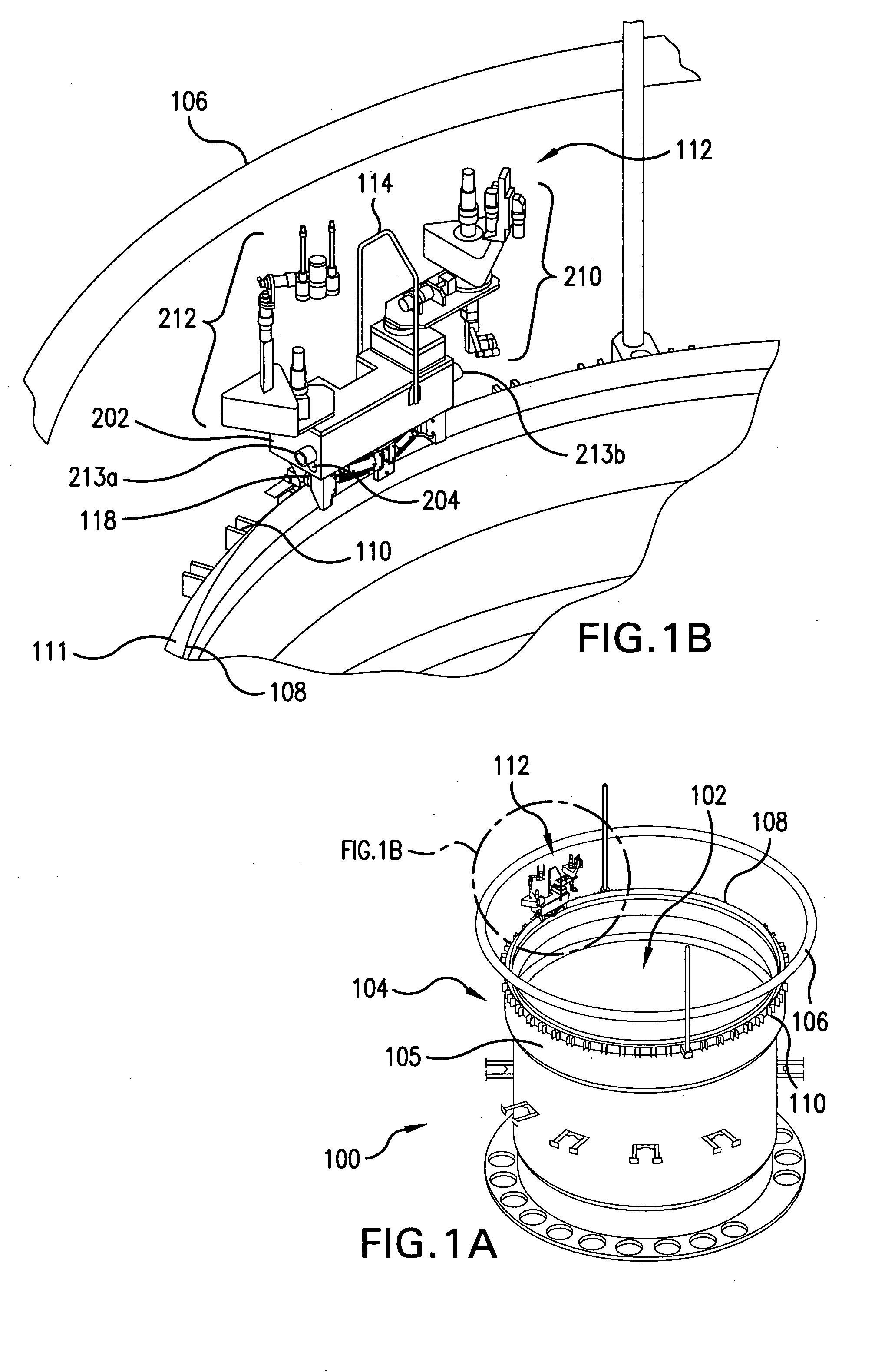
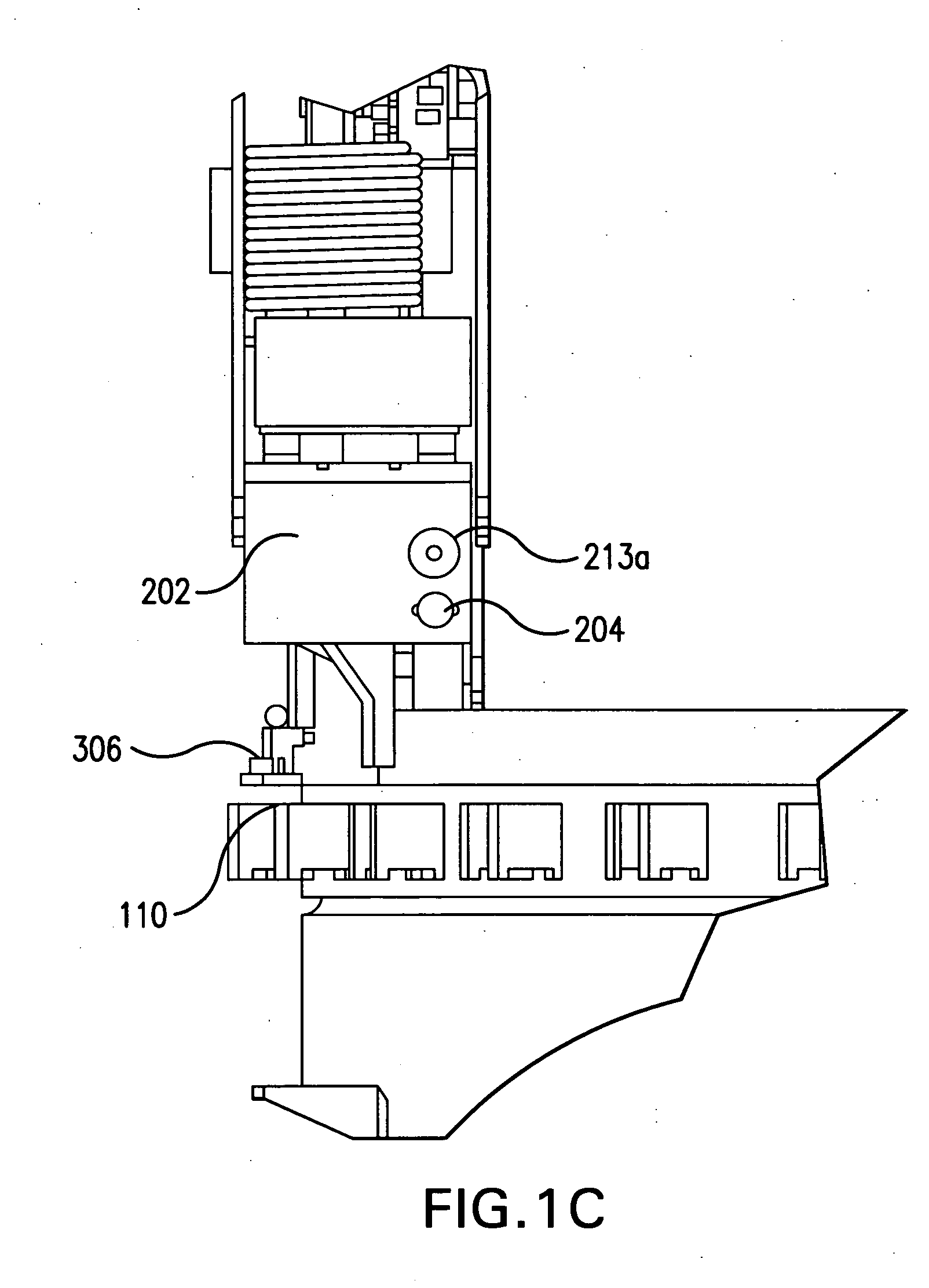
Apparatus and method for inspecting areas surrounding nuclear boiling water reactor core and annulus regions
InactiveUS20070146480A1Shorten the construction periodConserve costNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringElectrical controlEngineering
A remotely controlled apparatus (112) for inspecting the core (102) and annulus (104) areas of nuclear boiling water reactors (100) includes a circumferential drive mechanism for propelling the apparatus (112) on the steam dam (108) of the reactor (100). The inspection apparatus (112) uses a set of driver rollers (314) that grip the side of the steam dam (108) and provide propulsion for the apparatus. A pinch-roller assembly with high-tension springs (308) and pneumatic air cylinders (310) is utilized for removably securing a set of pinch rollers (312) to the side of the steam dam opposite the side of the driver rollers (314). A set of rollers (304) are adapted to rest on top of the steam dam (108), supporting the weight of the apparatus (112) and enabling the apparatus to move around the steam dam (108). Two positioning guide rails (306) aid in the balance of the apparatus (112), especially when it is stationary. The apparatus (112) has a watertight main body (202), which houses the electrical control wiring and circuitry. The main body (202) has a front camera (204) and a rear camera (205) used to direct the movements of the apparatus (112). The main body also has two turret-type telescoping mast assemblies (208) with telescoping masts 210 and 212, which are capable of extending at a selected distance above and below the main body (202). The mast assemblies 210 and 212 support inspection equipment such as radiation-shielded EVT-1-capable video cameras and radiation-tolerant fiberscopes. The apparatus (112) and its inspection tools are remotely controlled via control consoles with video monitors from a low-dose, non-contaminated enclosure located remotely from a boiling water reactor.
Owner:EXELON CORP
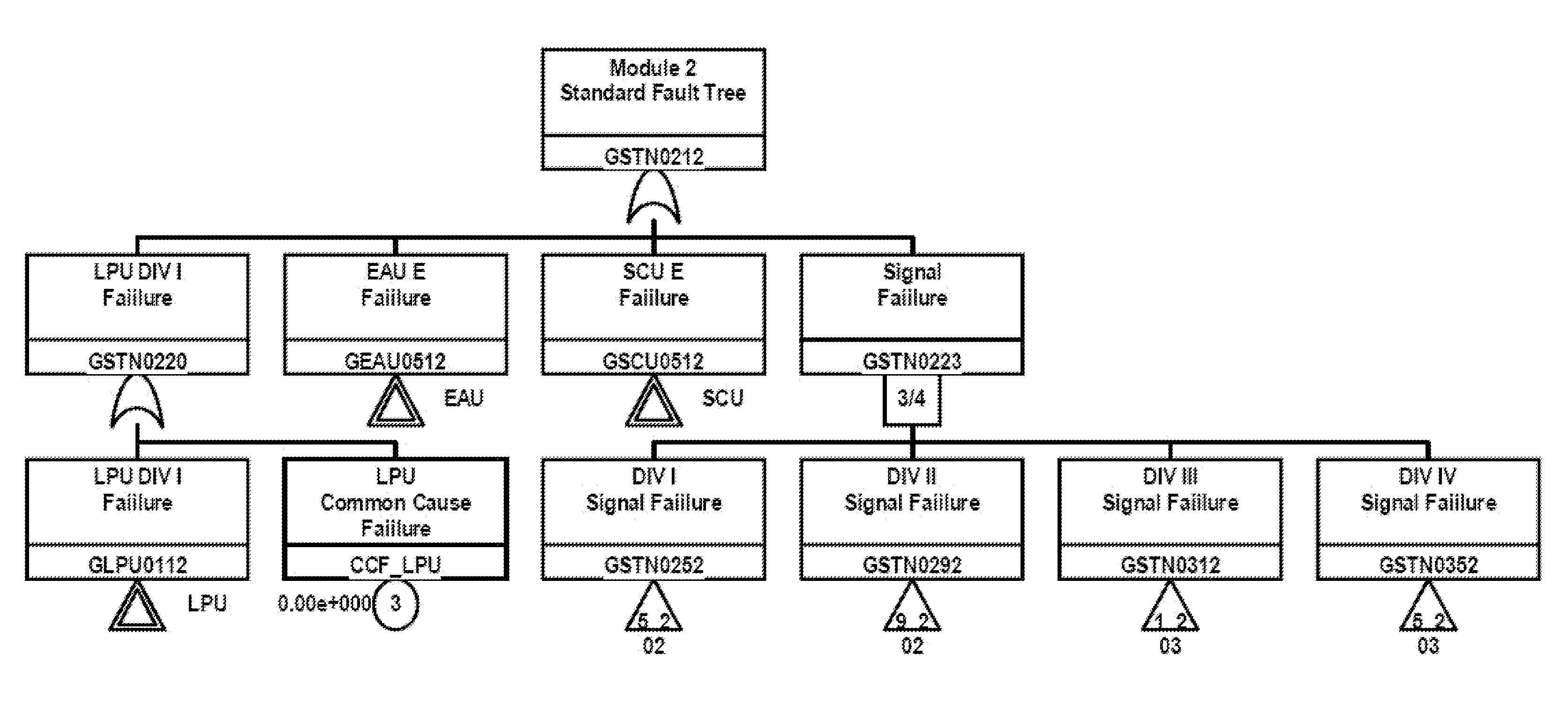
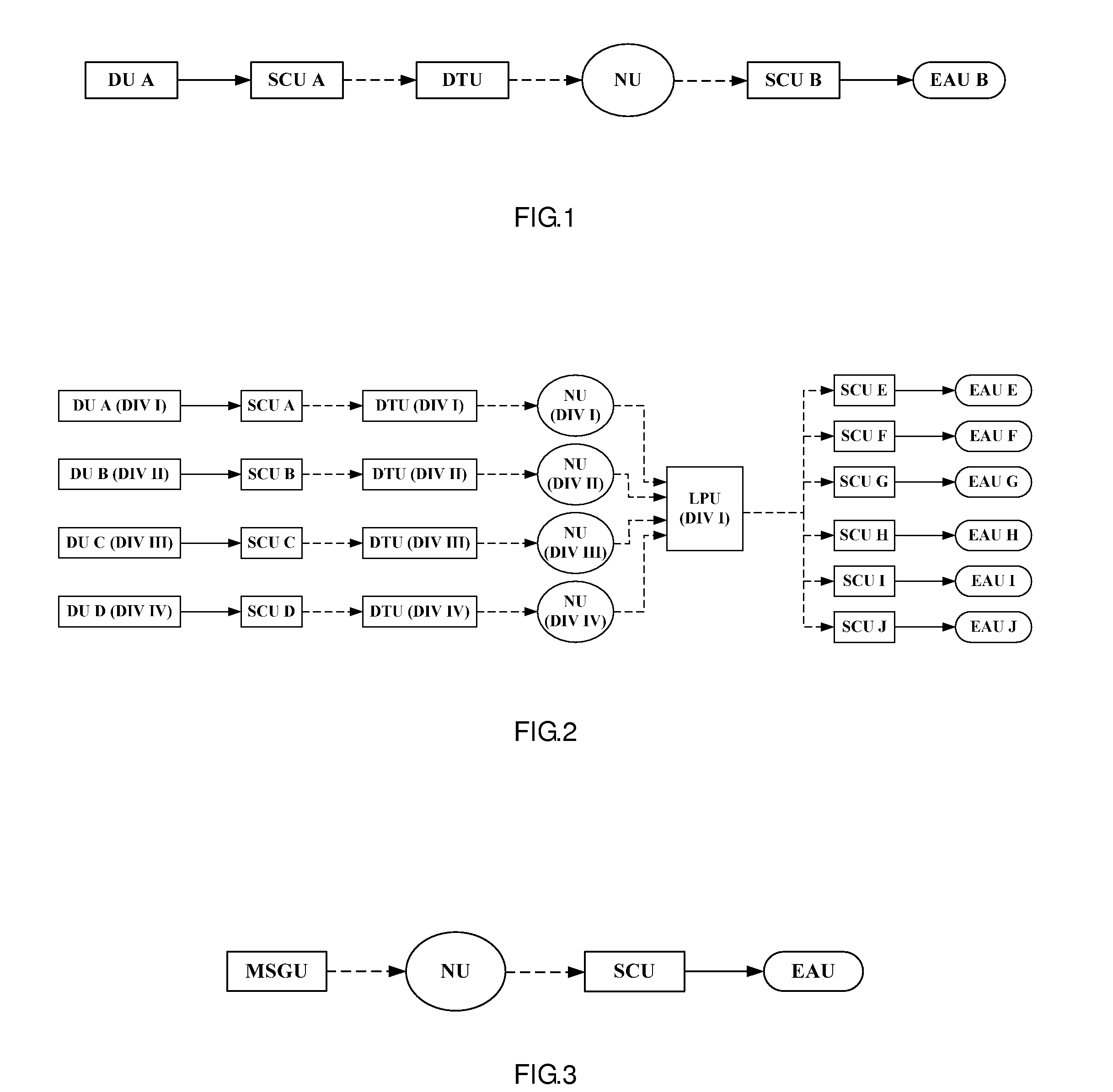
Fault Tree Analysis System for the Instrument Control Process for Nuclear Power Plant with Advanced Boiling Water Reactor Background
InactiveUS20100100251A1Fast and accurate to establishLevel controlAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsProbabilistic risk assessmentBiology
The invention relates to the fault tree analysis system for a nuclear power plant with advanced boiling water reactor. The full digital instrument control system uses six different modes to simulate the transmission of the digital signals and the analog signals from the detection units. It is to develop the fault tree for various signal transmission modes to support the nuclear power plant in probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) and meet requirements for simulated signal detection, transmission, logic operation and equipment actuation. Thus, the digital instrument control flow process can fit into PRA model and properly reflect its importance in risk assessment.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
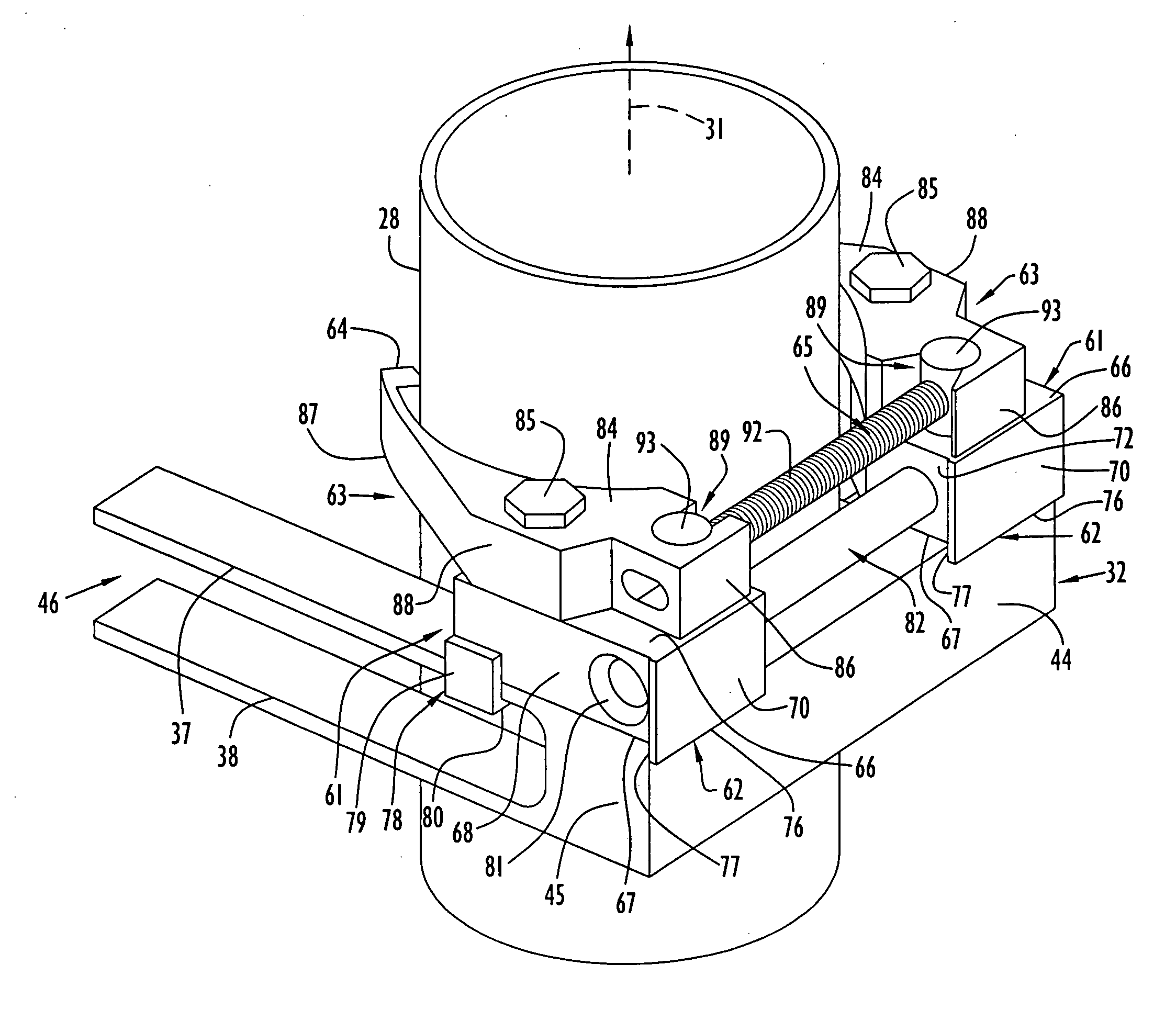
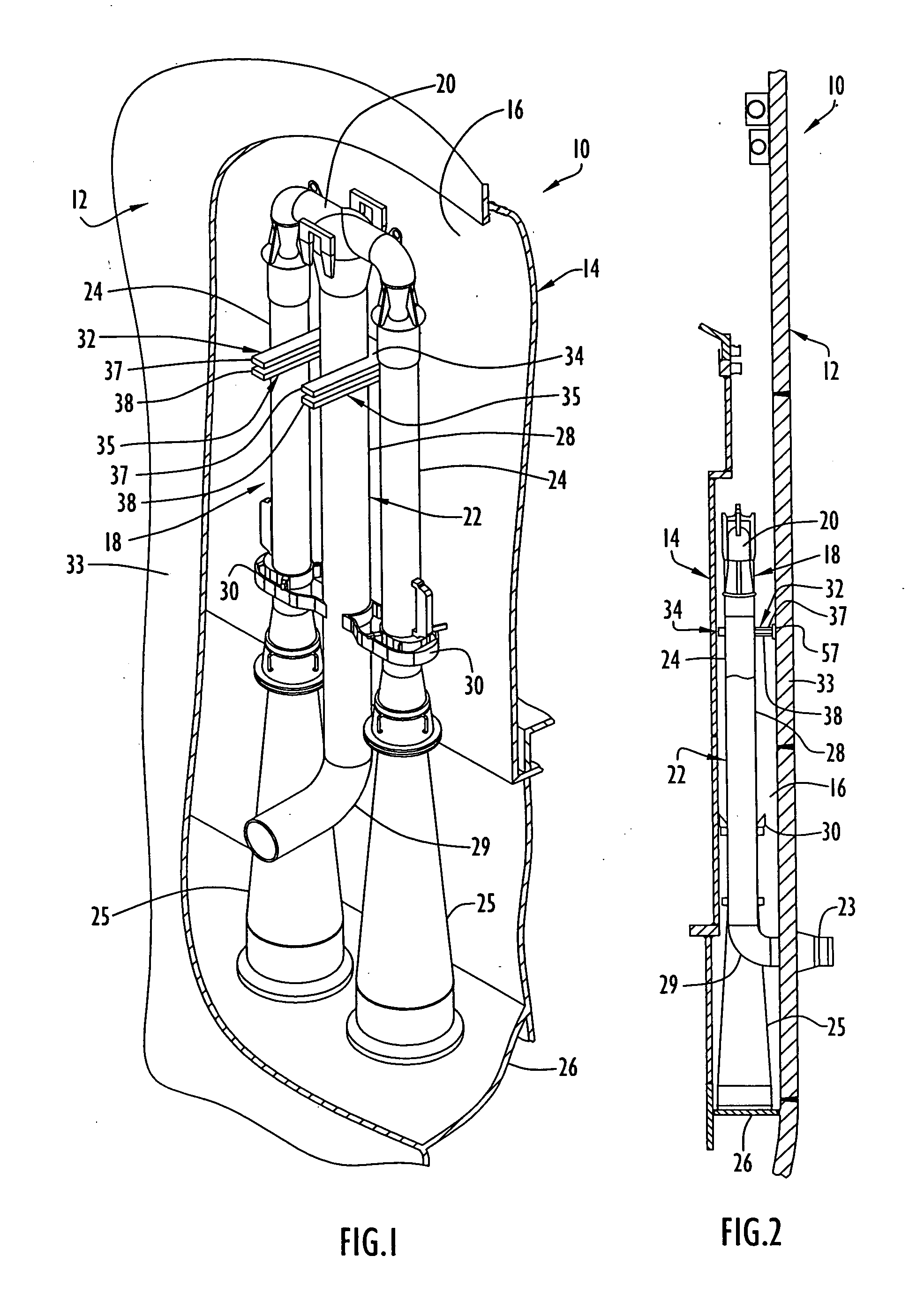
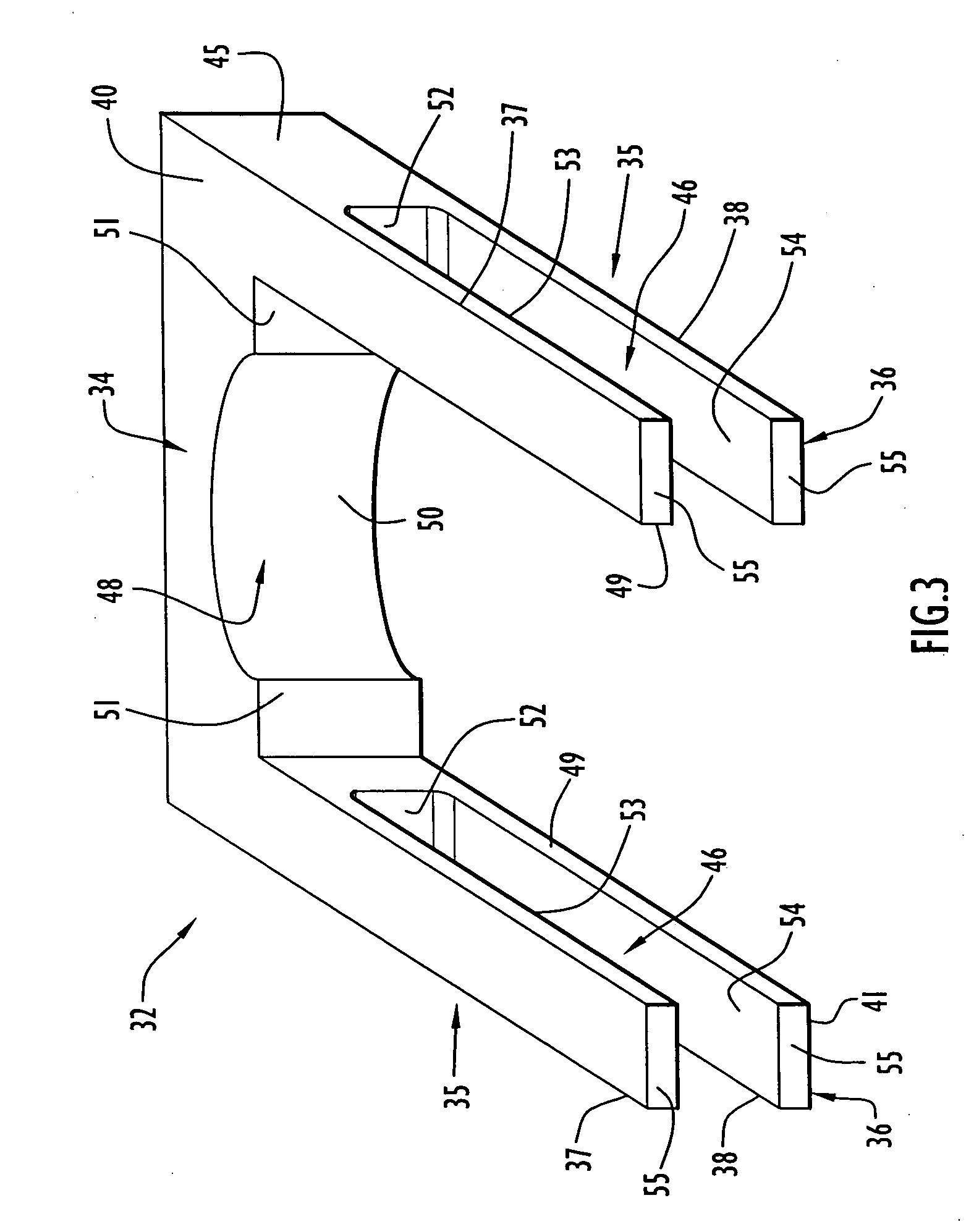
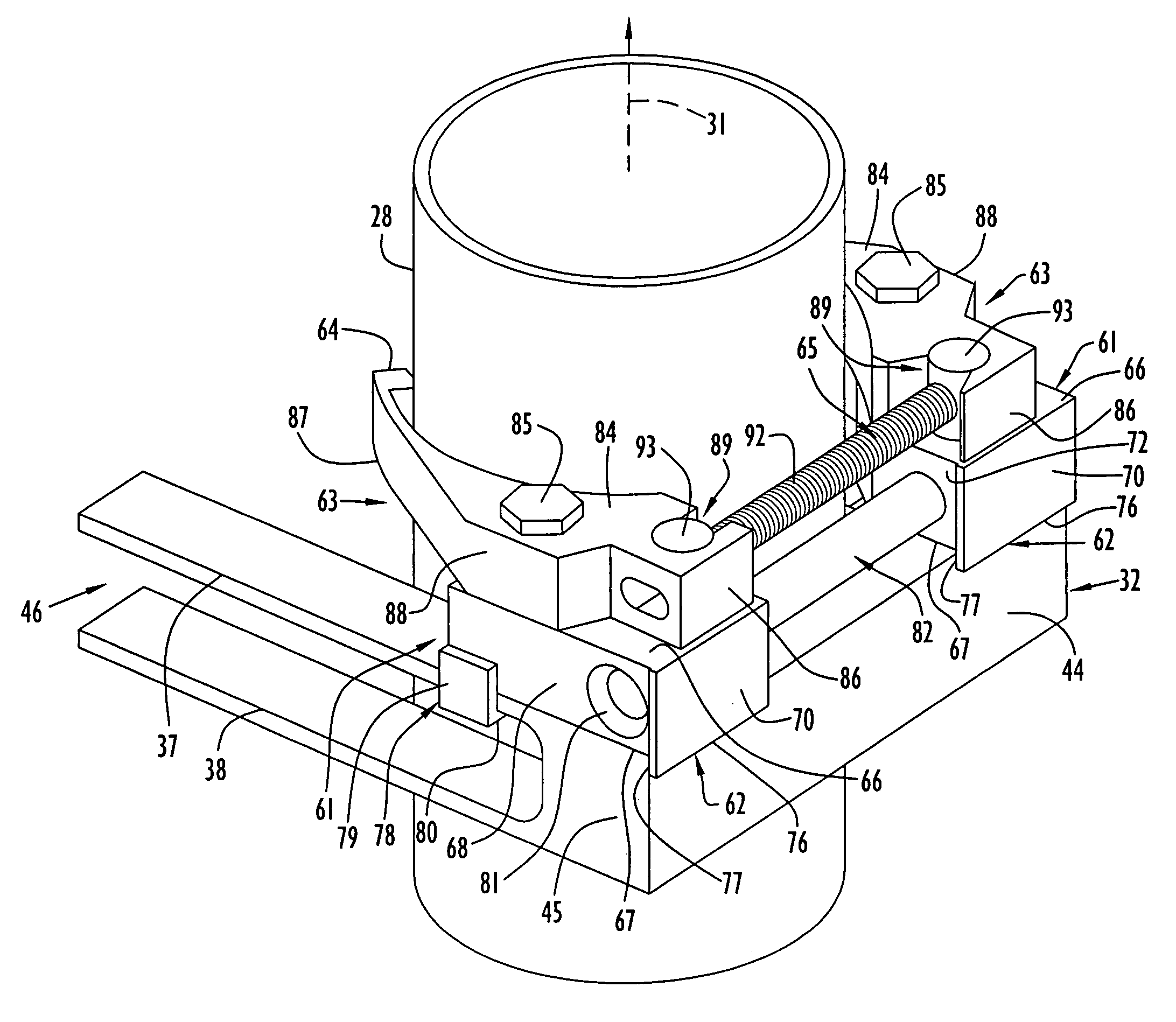
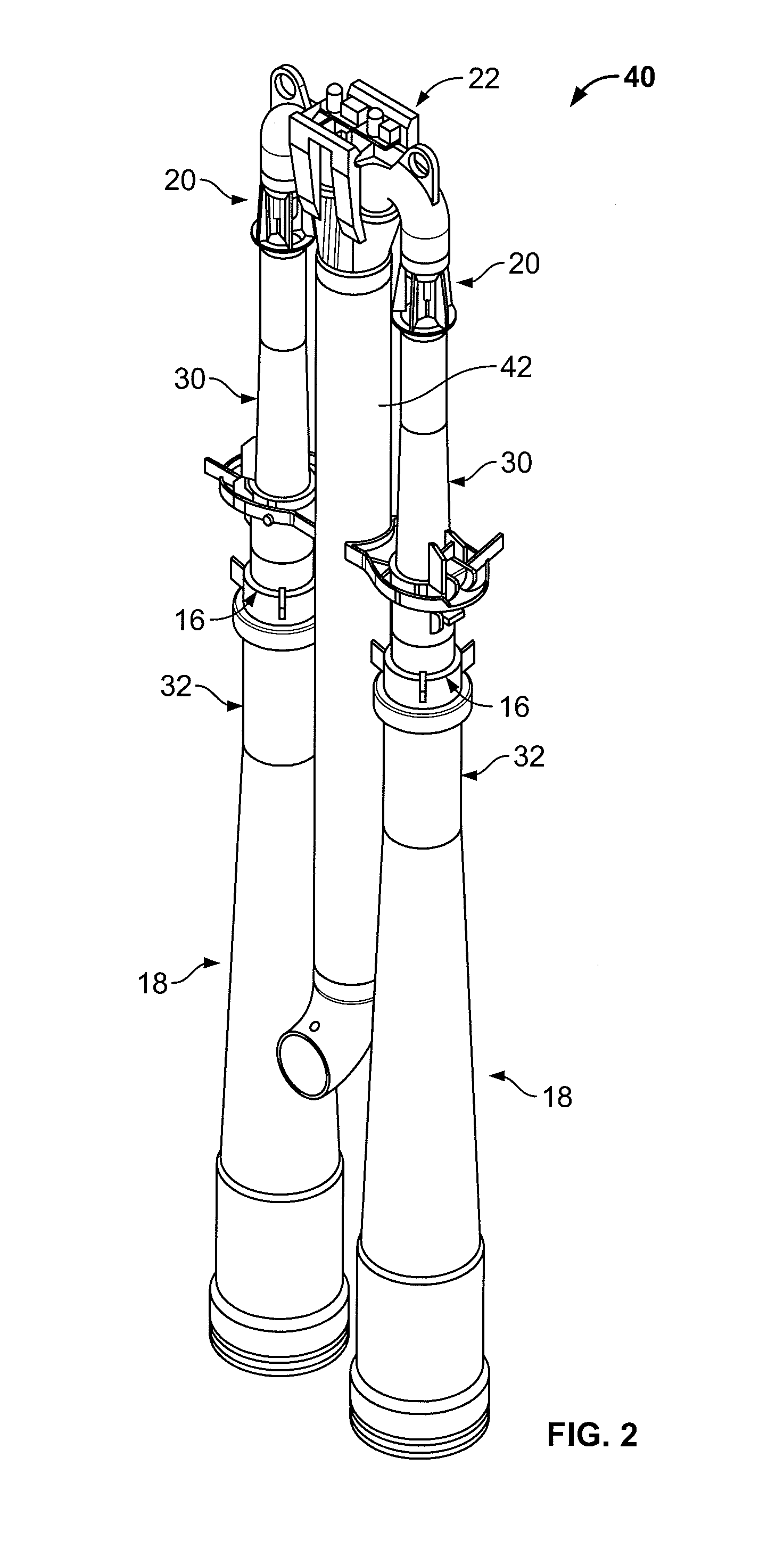
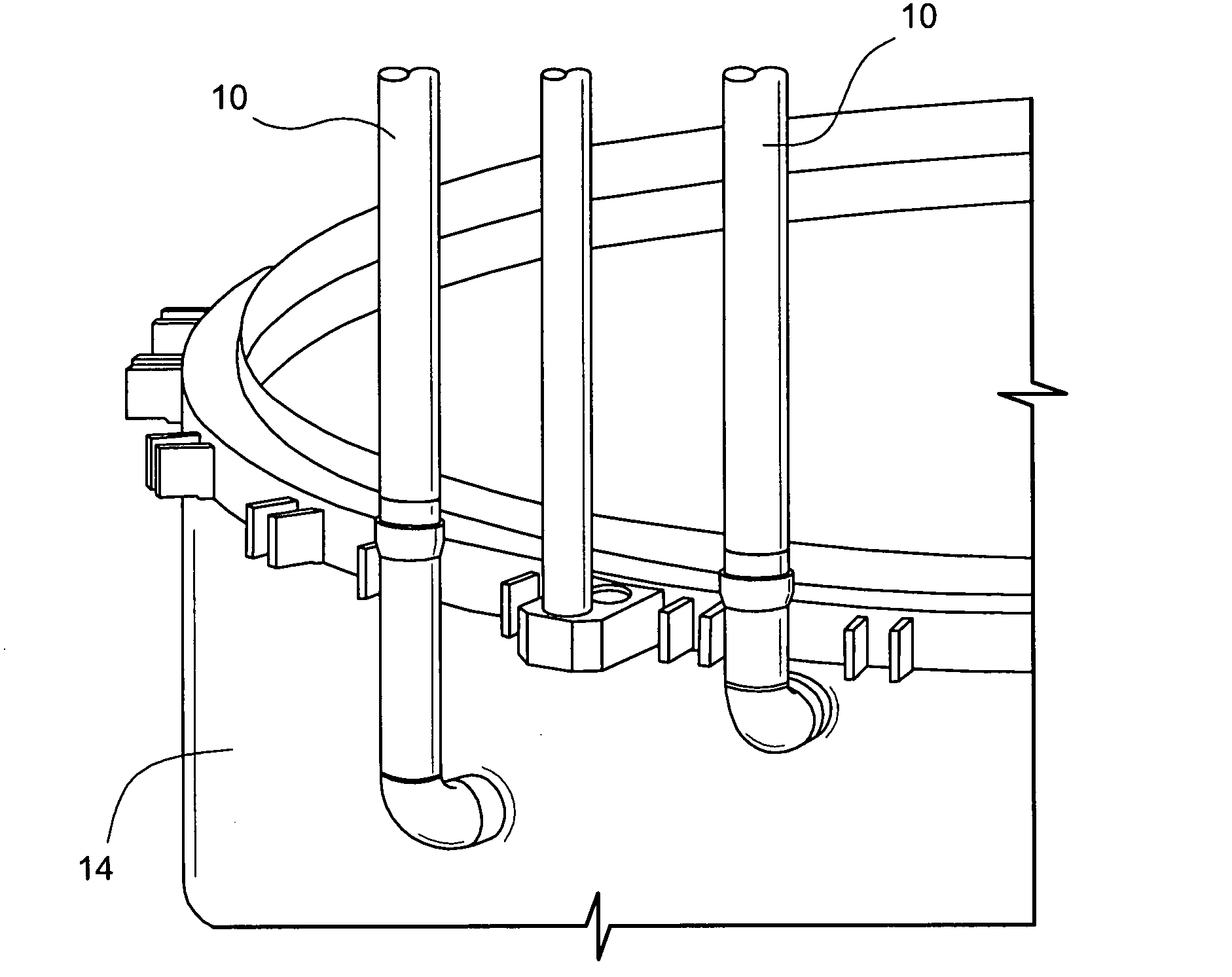
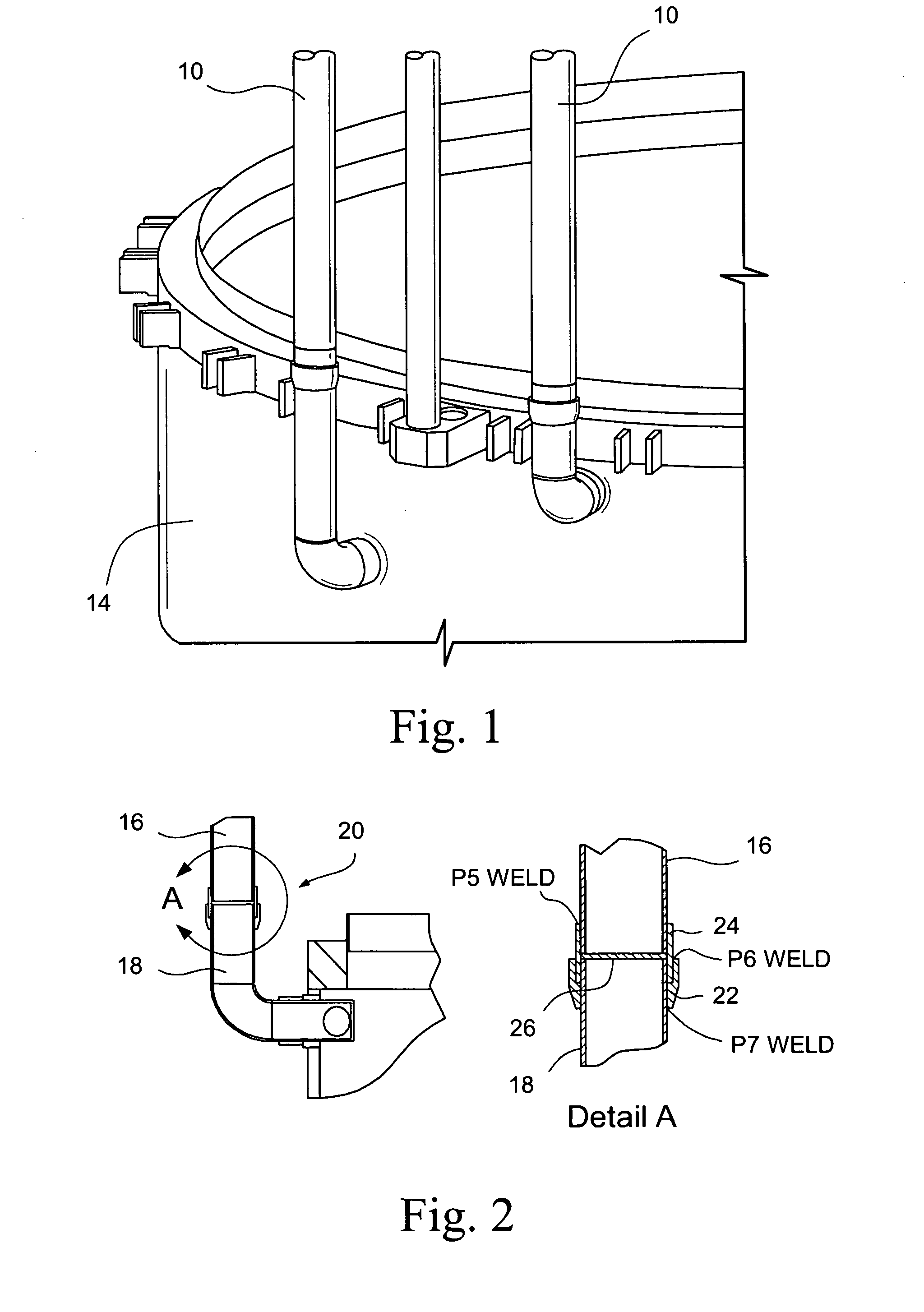
Apparatus and method for mechanically reinforcing the welds between riser pipes and riser braces in boiling water reactors
ActiveUS20050247754A1Overcome problemsLow costNuclear energy generationWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus and method for mechanically reinforcing the weld between a riser pipe and riser brace of a jet pump assembly are characterized by first and second attachment members for attachment on a riser brace of the jet pump assembly, and first and second clamp bodies respectively pivotally mounted on the attachment members for movement to a clamping position. In the clamping position, respective abutment surfaces of the clamp bodies are forced against a riser pipe that is attached to a yoke of the riser brace. The abutment surfaces apply radial forces to the riser pipe, and the radial forces are reacted by forces applied against the yoke by respective engagement elements of the attachment members whereby the riser pipe and riser brace are clamped together between the abutment surfaces and the engagement elements.
Owner:MPR ASSOC
Apparatus and method for mechanically reinforcing the welds between riser pipes and riser braces in boiling water reactors
ActiveUS7185798B2Low costEasy to installNuclear energy generationWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:MPR ASSOC
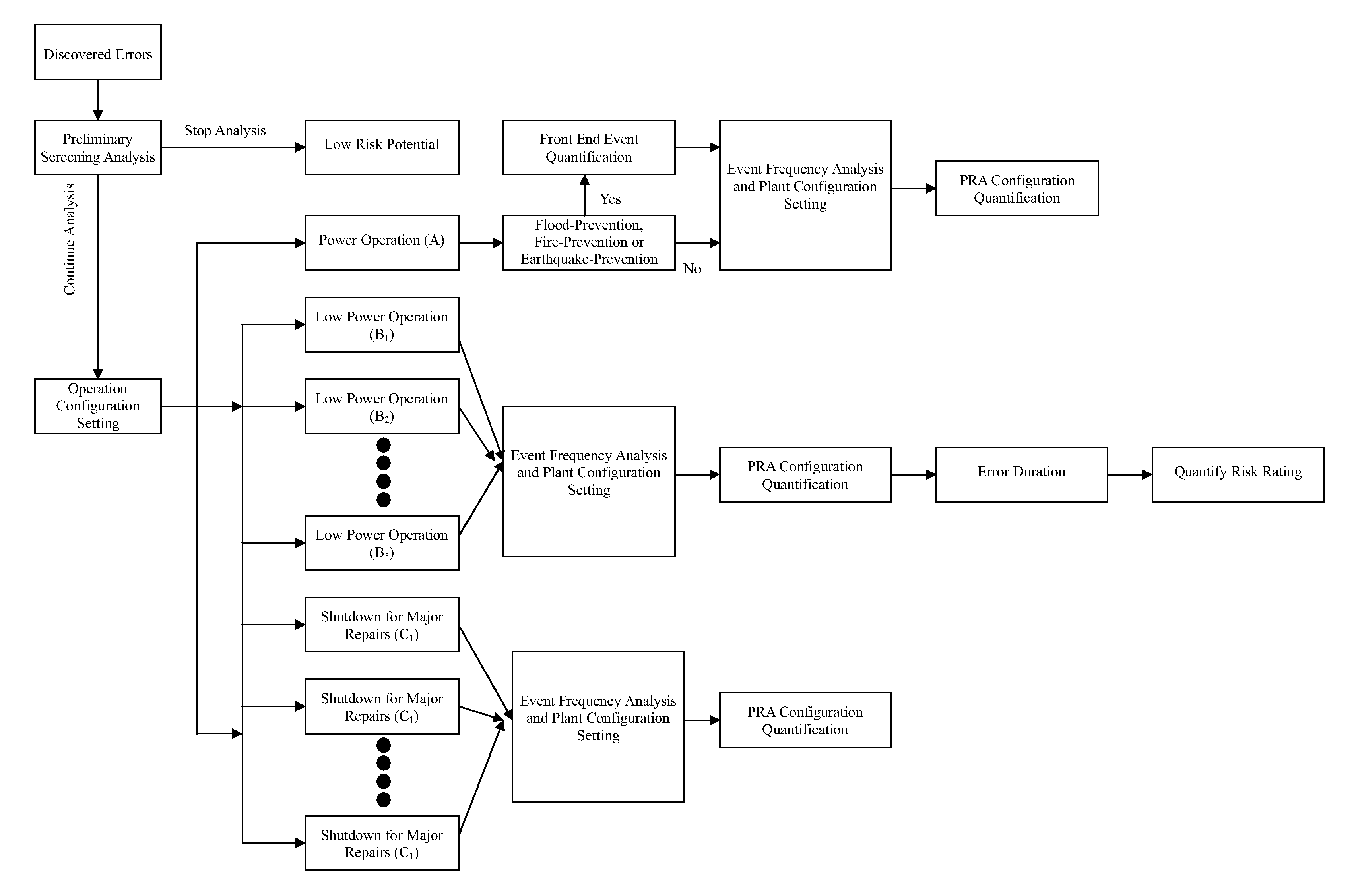
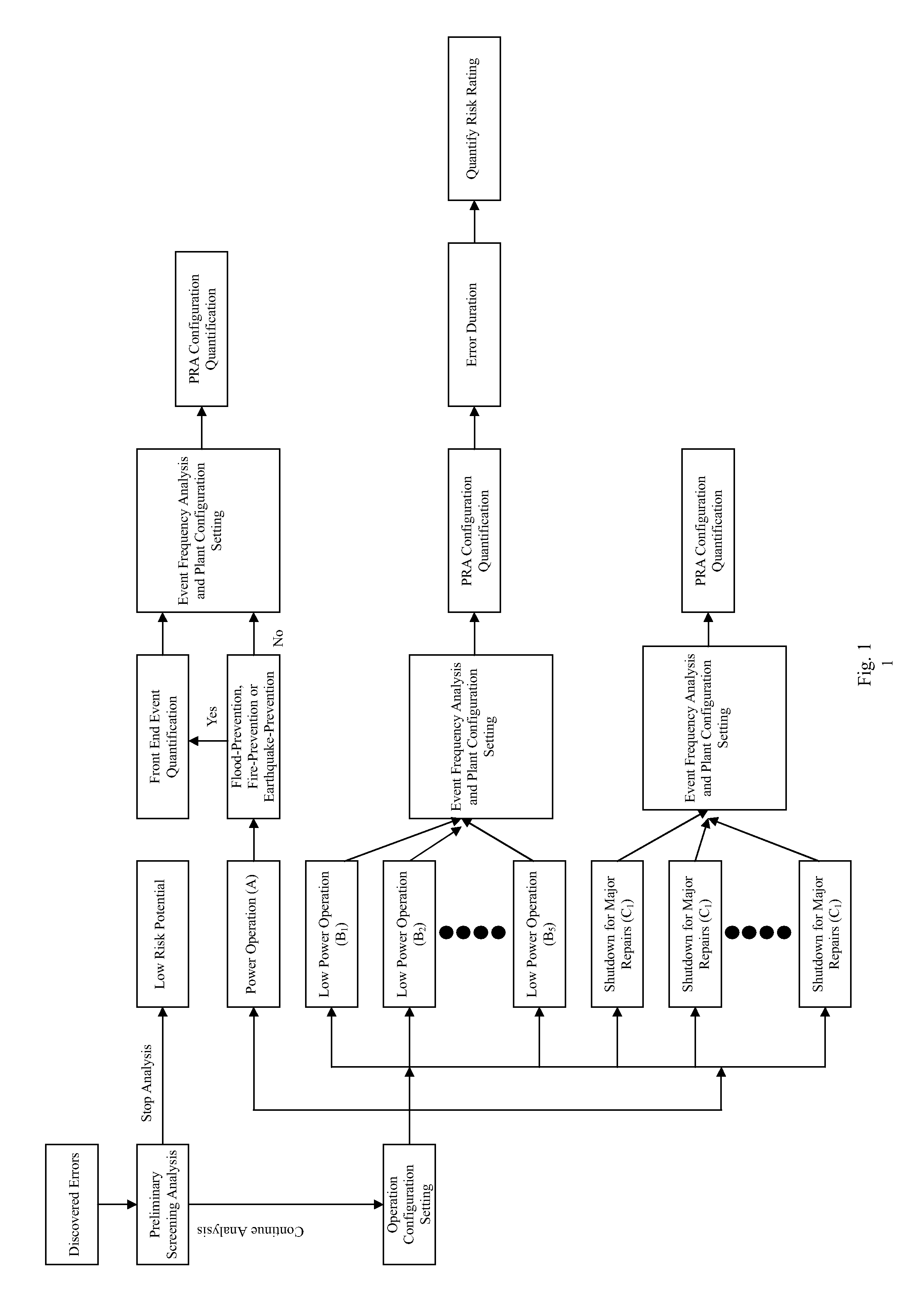
All aspect quantification system for the risk rating of operating errors for an advanced boiling water reactor
InactiveUS20100138253A1Improve consistencyFail to accuratelyFinanceClimate change adaptationProbabilistic risk assessmentRisk effect
Based on the discovered operating errors under all basic operating mode s for advanced boiling water reactor, a suitable quantification analytical model is employed to fast assess the risk situation for the discovered operating errors and quantified results are used to differentiate the risk rating for the operating errors. This is used to determine the necessity and urgency for the corrective measures to respond to the errors. The adopted quantification analytical model is the safety assessment (Probabilistic Risk Assessment, PRA) model for all basic operating mode s for advanced boiling water reactor, including power operation, low power operation and shutdown for major repairs. For the discovered operating error during power operation period, the invention uses the specifically developed safety assessment model for plant event, earthquake, flood and fire to determine risk effect for the discovered operating error on different event to manifest the risk characteristics for the discovered operating error and match the quantification results to existing plant design, operation and maintenance conditions.
Owner:CHAO CHUN CHANG +1
Emergency core cooling system
InactiveUS20080317193A1Improve securityPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationHigh pressureDiesel generator
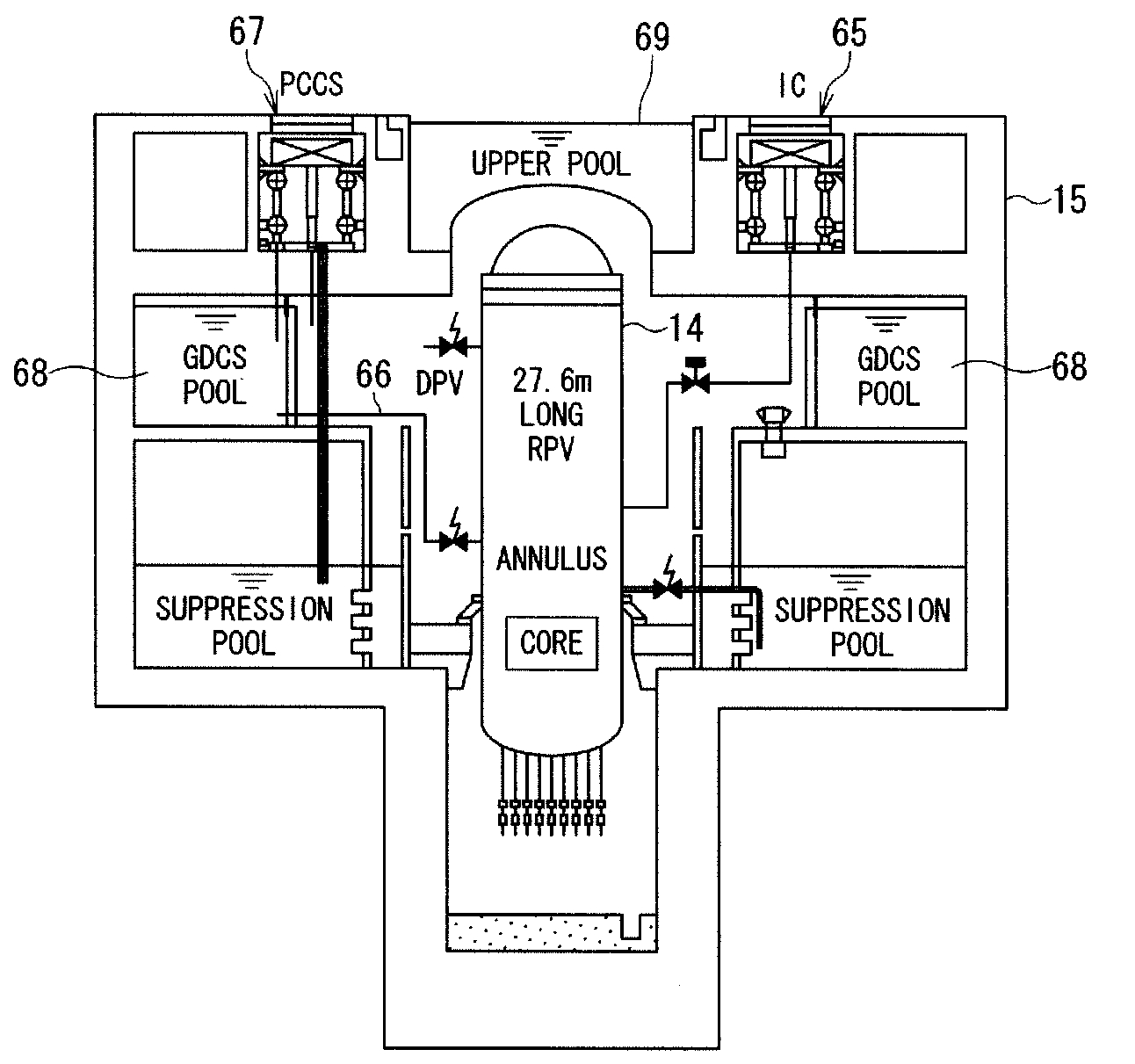
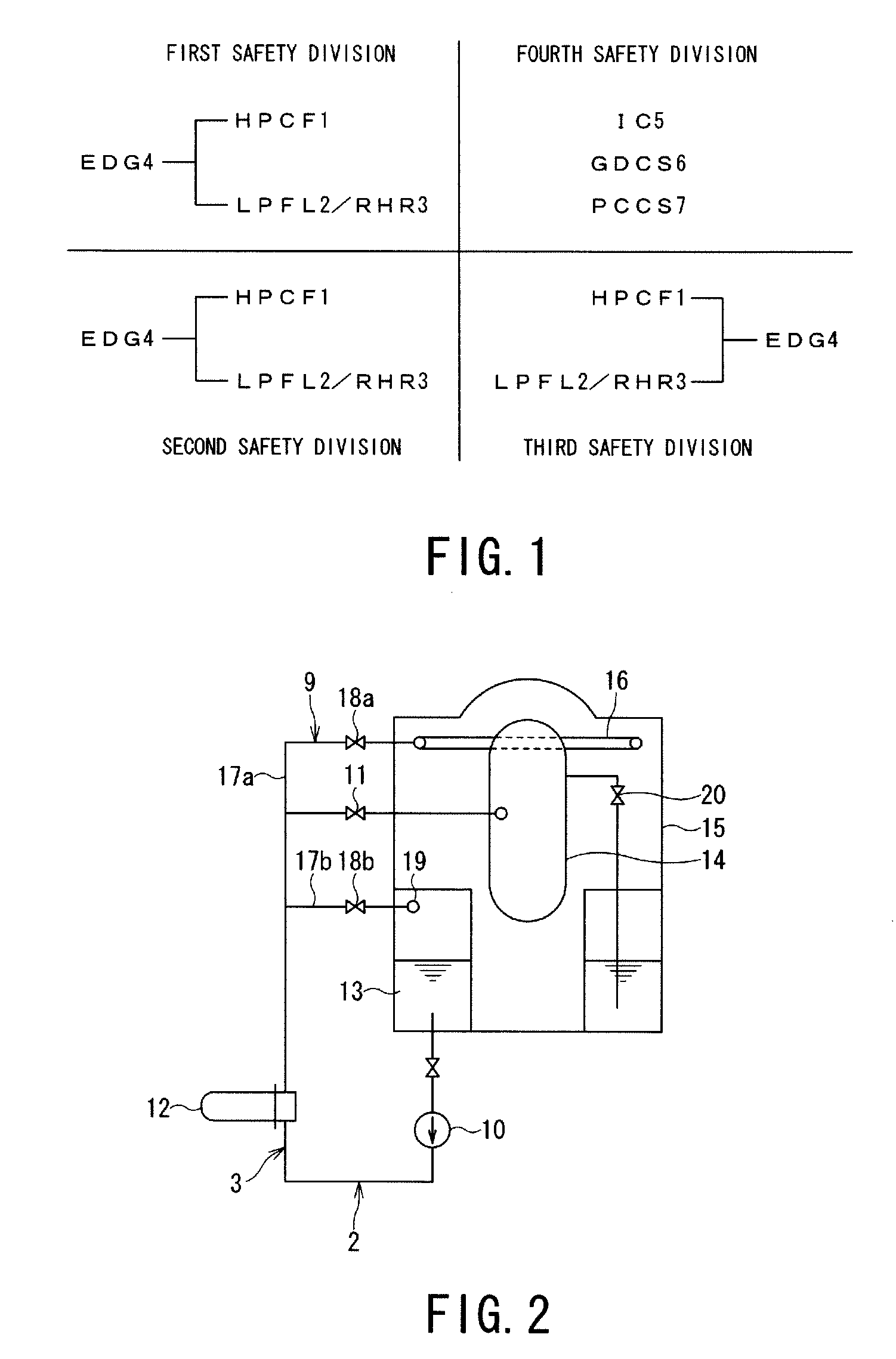
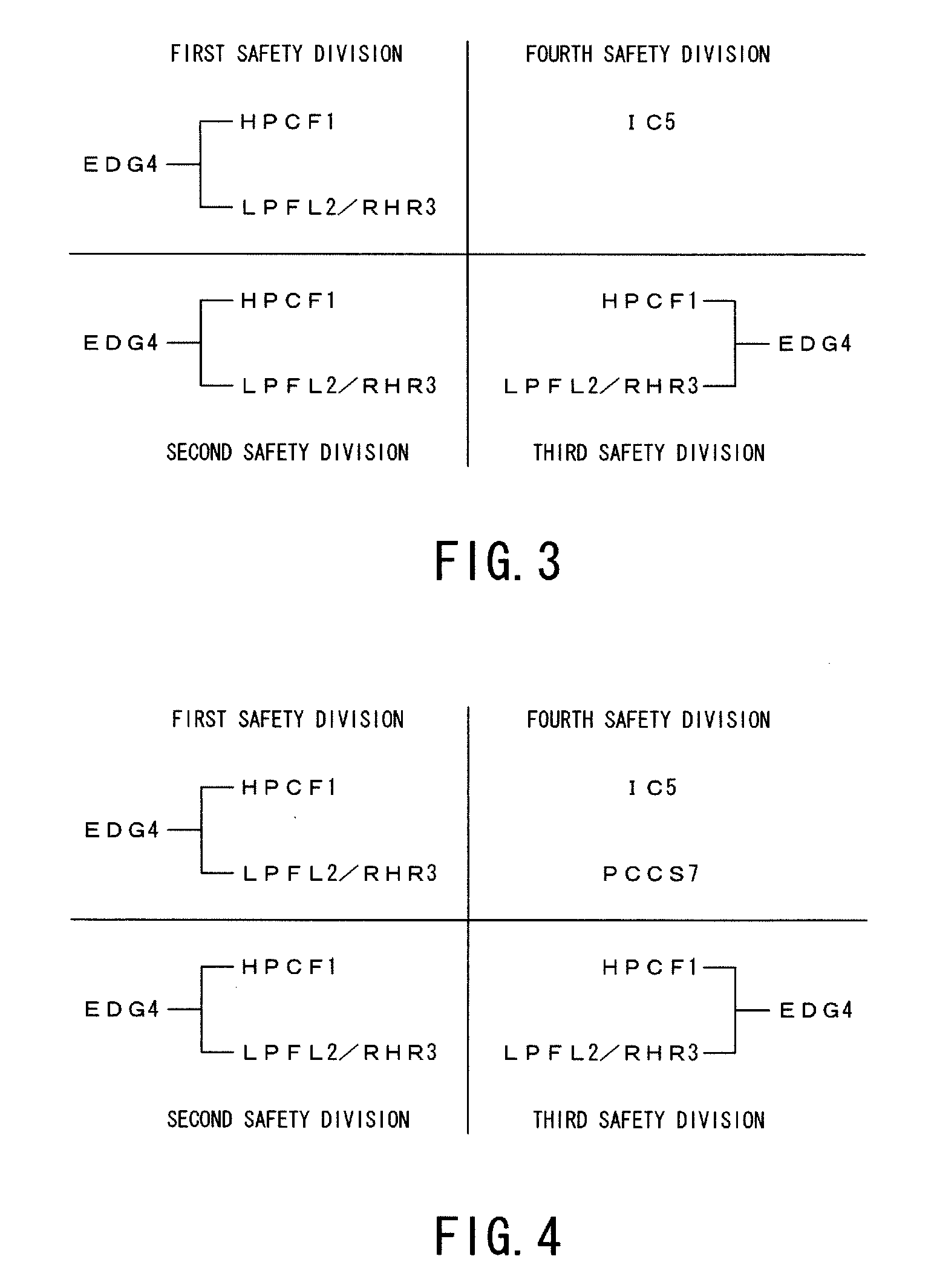
An emergency core cooling system is provided with a hybrid safety system composed of an active safety system and a static safety system for ensuring the safety against a severe natural phenomenon such as a giant earthquake and a mega hurricane. An emergency core cooling system for a boiling water reactor includes four safety divisions in total: three safety divisions for an active safety system having a high pressure reactor core cooling system, a low pressure reactor core cooling system, a residual heat removal system, and an emergency diesel generator; and one safety division for a static safety system having an isolation condenser, a gravity drop reactor core cooling system, and a static containment vessel cooling system.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
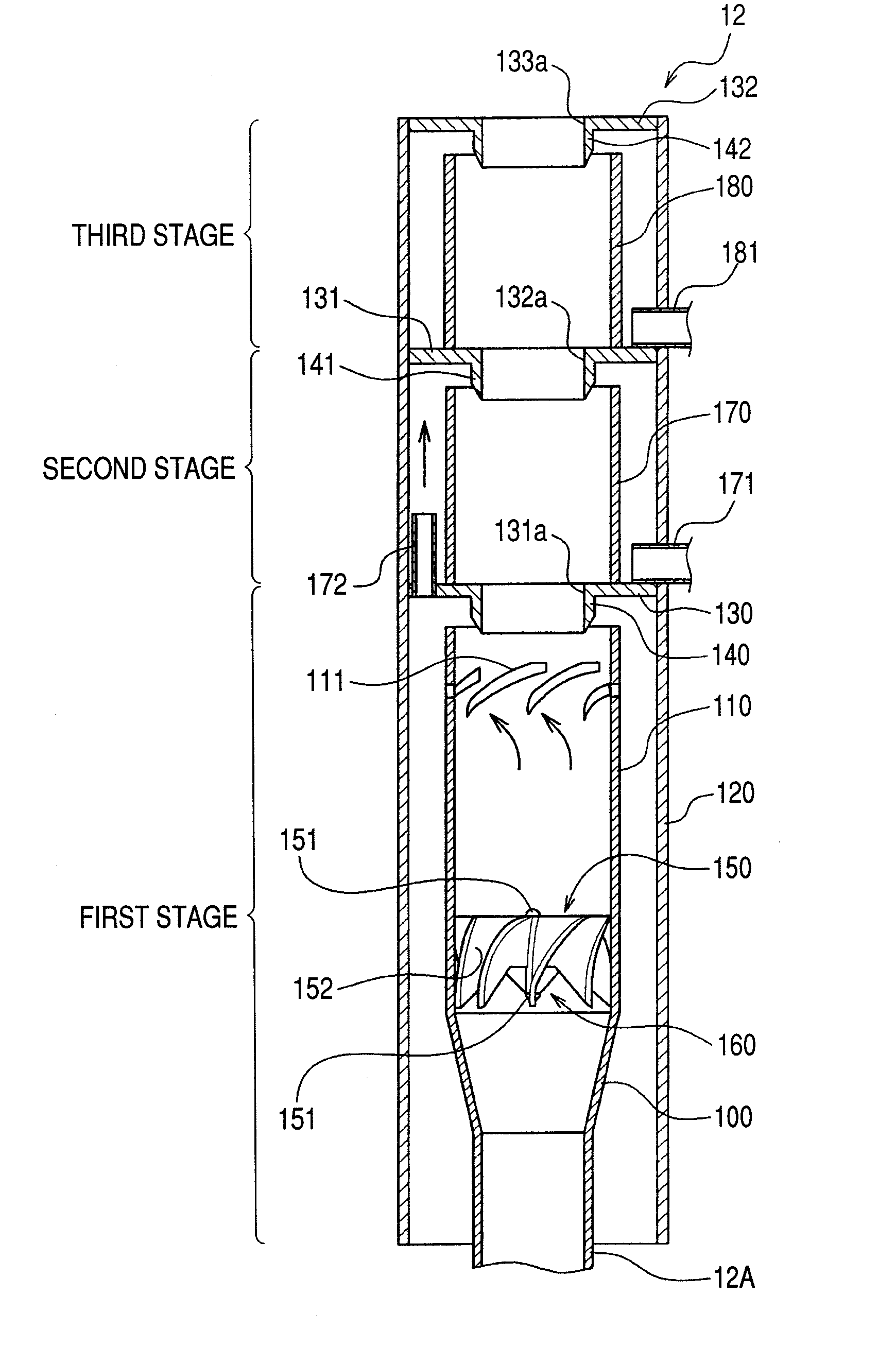
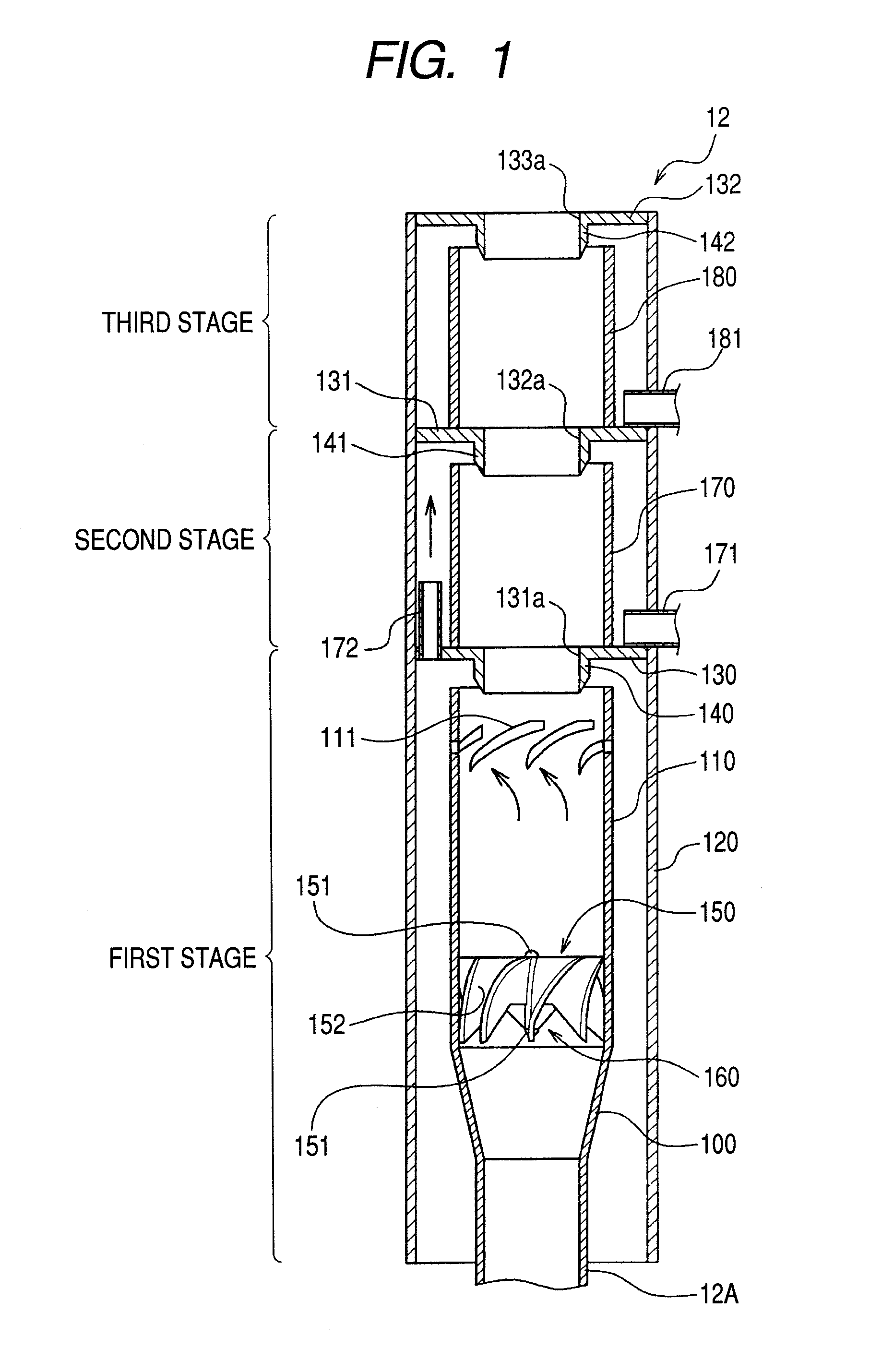
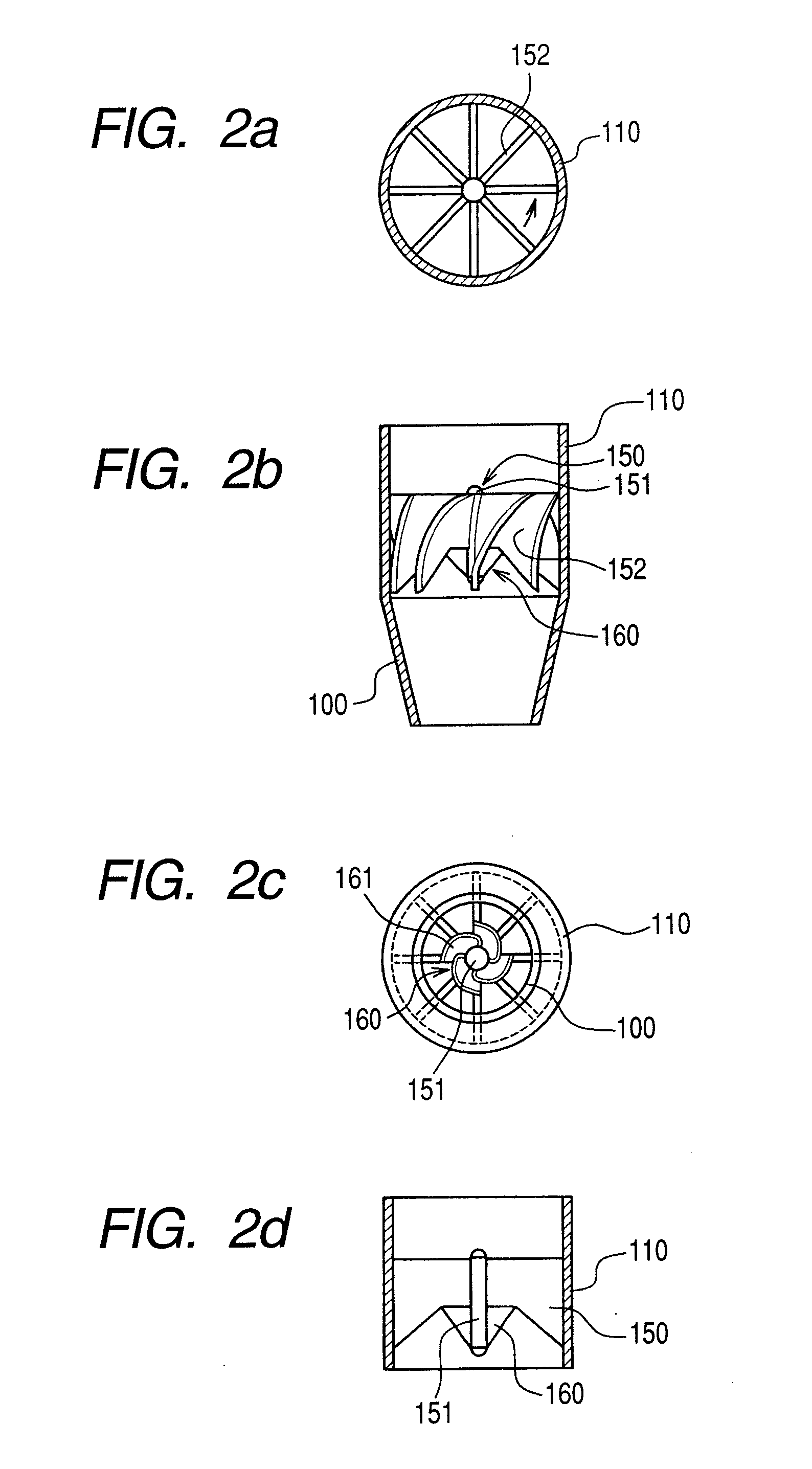
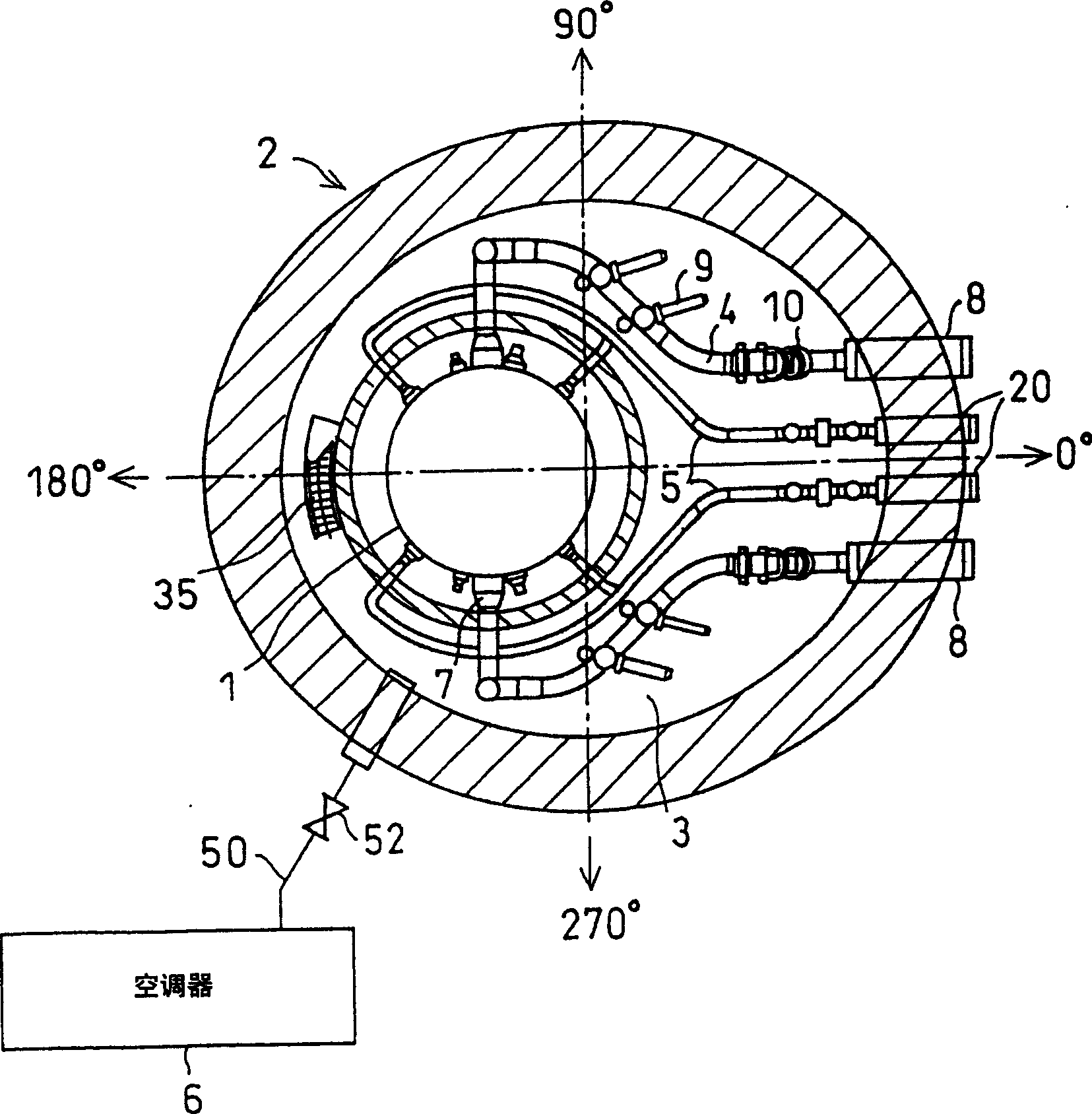
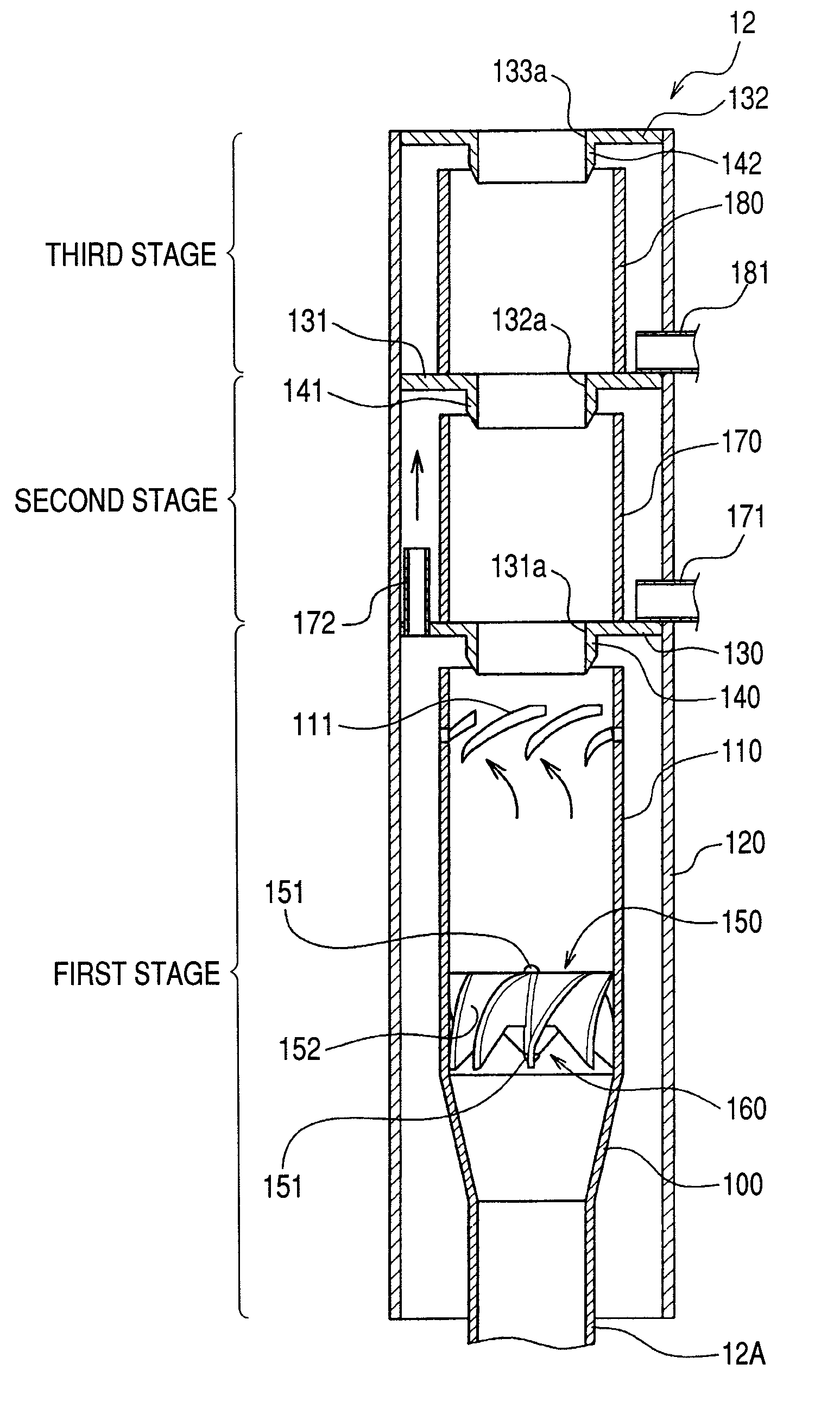
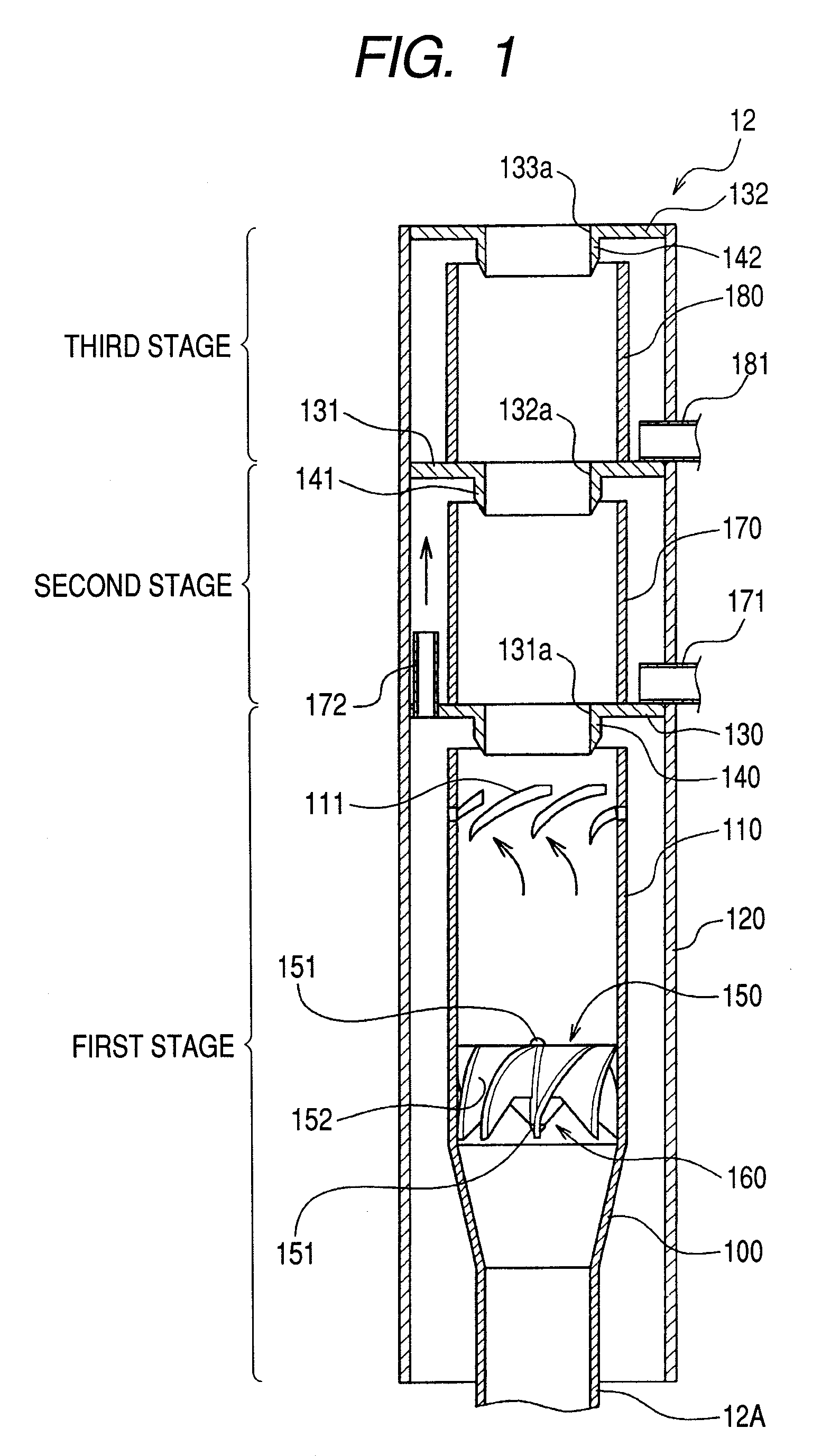
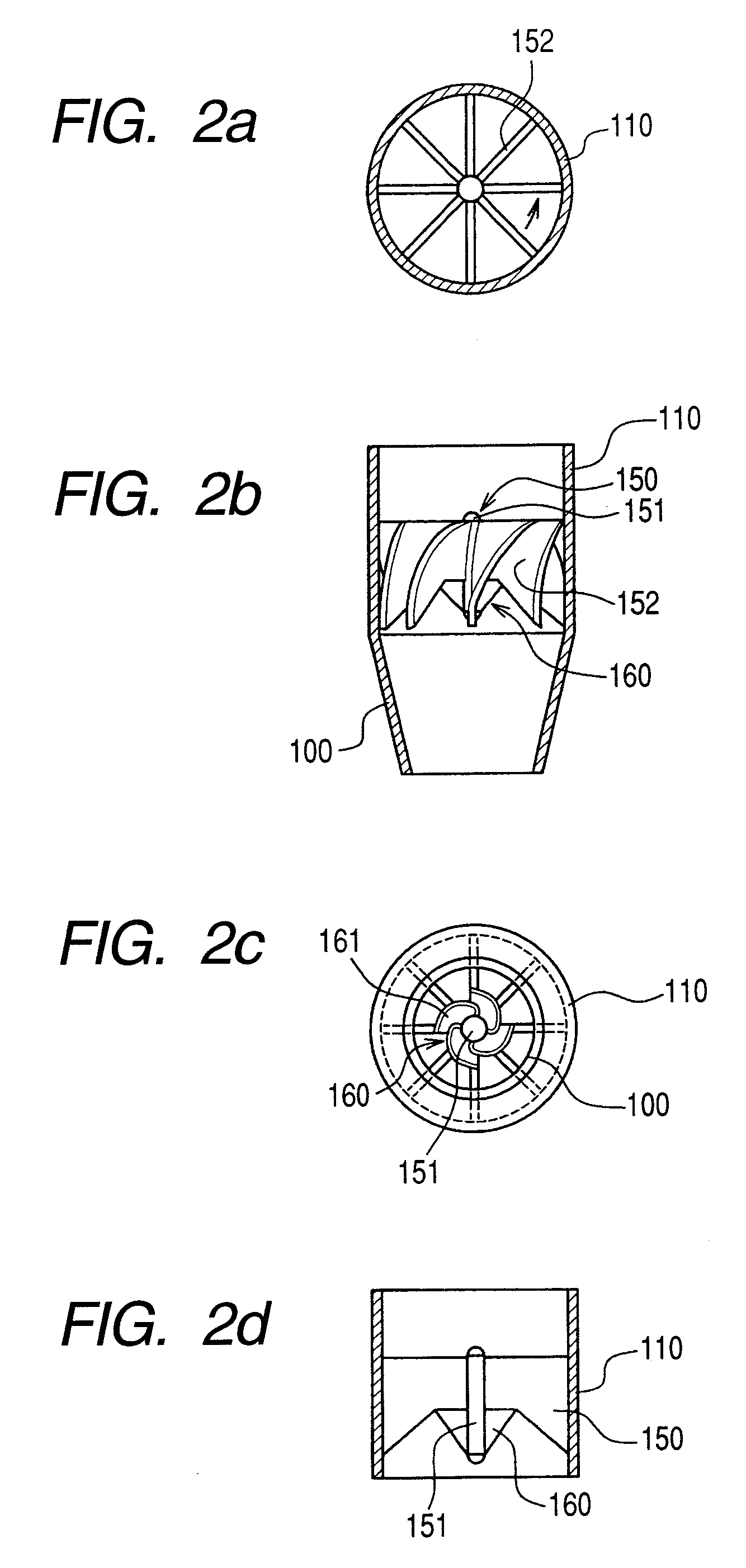
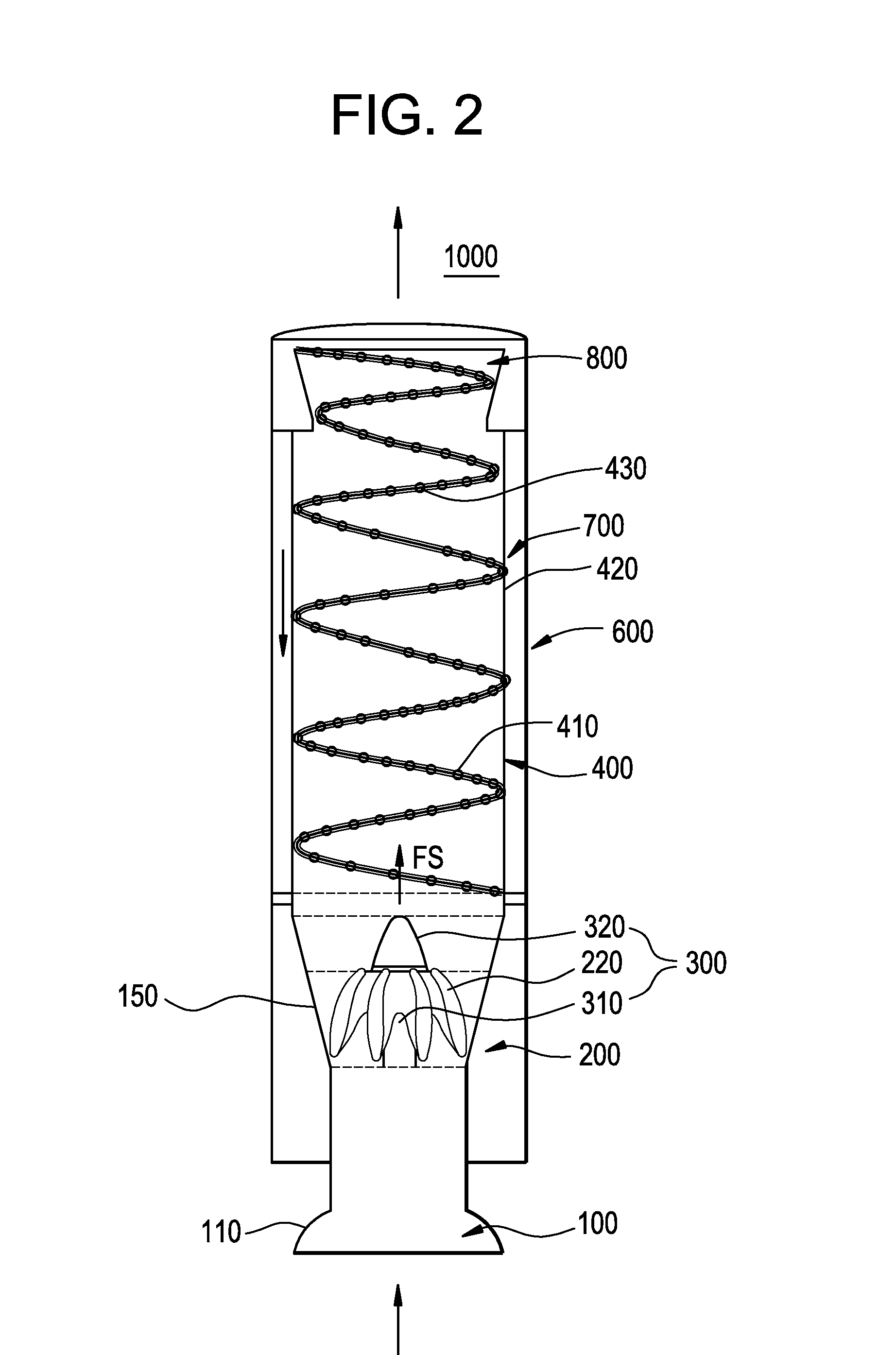
Steam separator, boiling water reactor and swirler assembly
ActiveUS20070201604A1Easy to separateSmall pressure lossNuclear energy generationDispersed particle separationEngineeringCentrifugal force
A steam separator comprises an outer main swirler and an inner auxiliary swirler which is smaller than the main swirler. The swirlers are provided so as to be concentric on the inner wall at the lower side of the first stage inner cylinder. In the steam separator, when the gas-liquid two-phase flow which flows in the vicinity of the axial center of the first stage inner cylinder passes the auxiliary swirler, it is separated into steam and water by the centrifugal force. The separated water (droplets) is introduced into the main swirler. When the separated water (droplets) passes the main swirler, it is separated at the inner wall side of the first stage inner cylinder by the centrifugal force.Pressure loss in a steam separator is reduced and steam separation capability is increased without increasing the moisture from the steam separator.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Nuclear reactor safety casing
A reactor containment vessel of a boiling water reactor configured to contain a reactor pressure vessel. The reactor pressure vessel is connected to at least one main steam pipe which penetrates the reactor containment vessel at a main-steam-line penetration point. The main-steam-line penetration point is disposed on a first side of the reactor containment vessel. Distance between outer surface of the reactor pressure vessel and inner surface of the reactor containment vessel on the first side is longer than the distance on a second side which is opposite to the first side.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
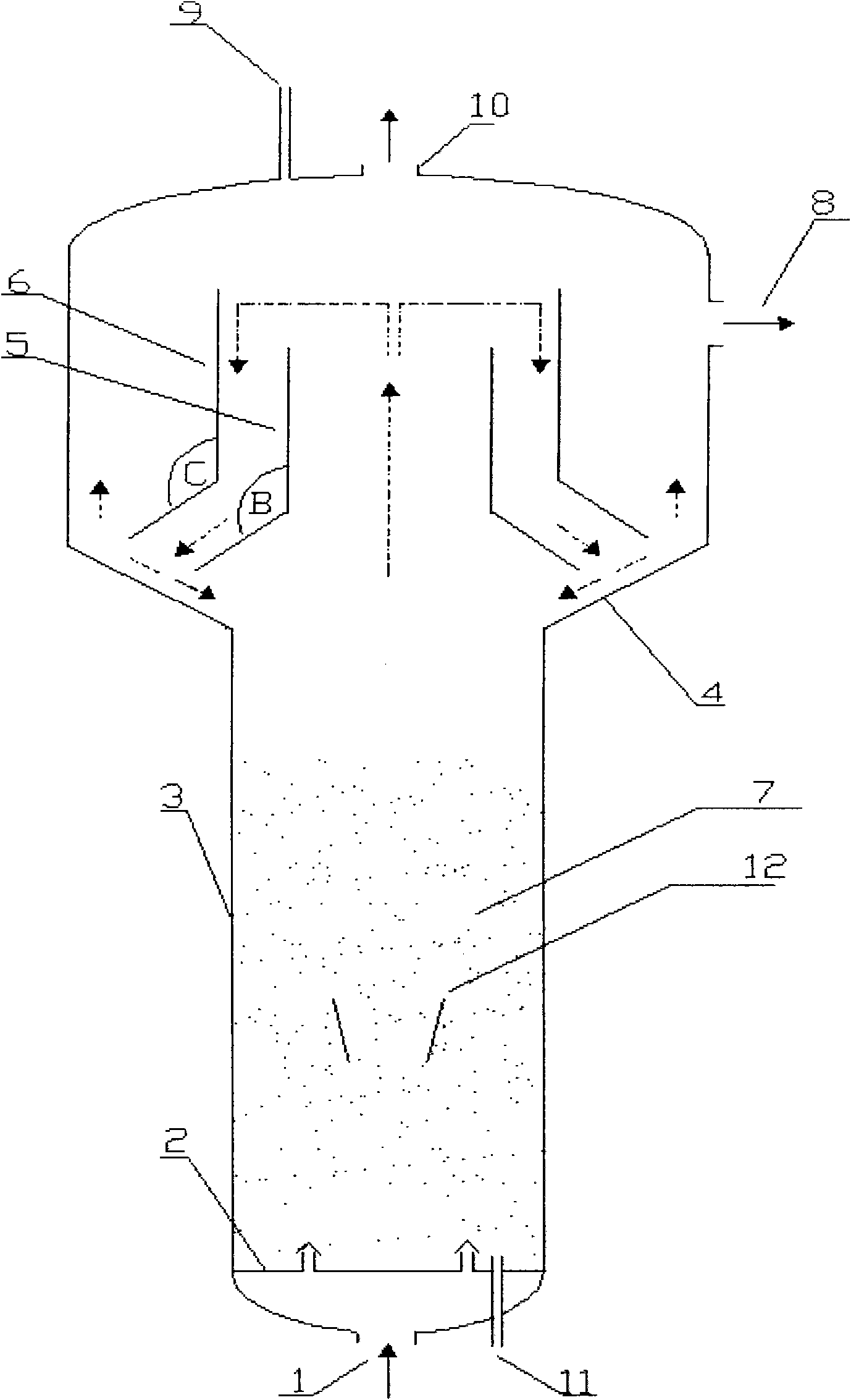
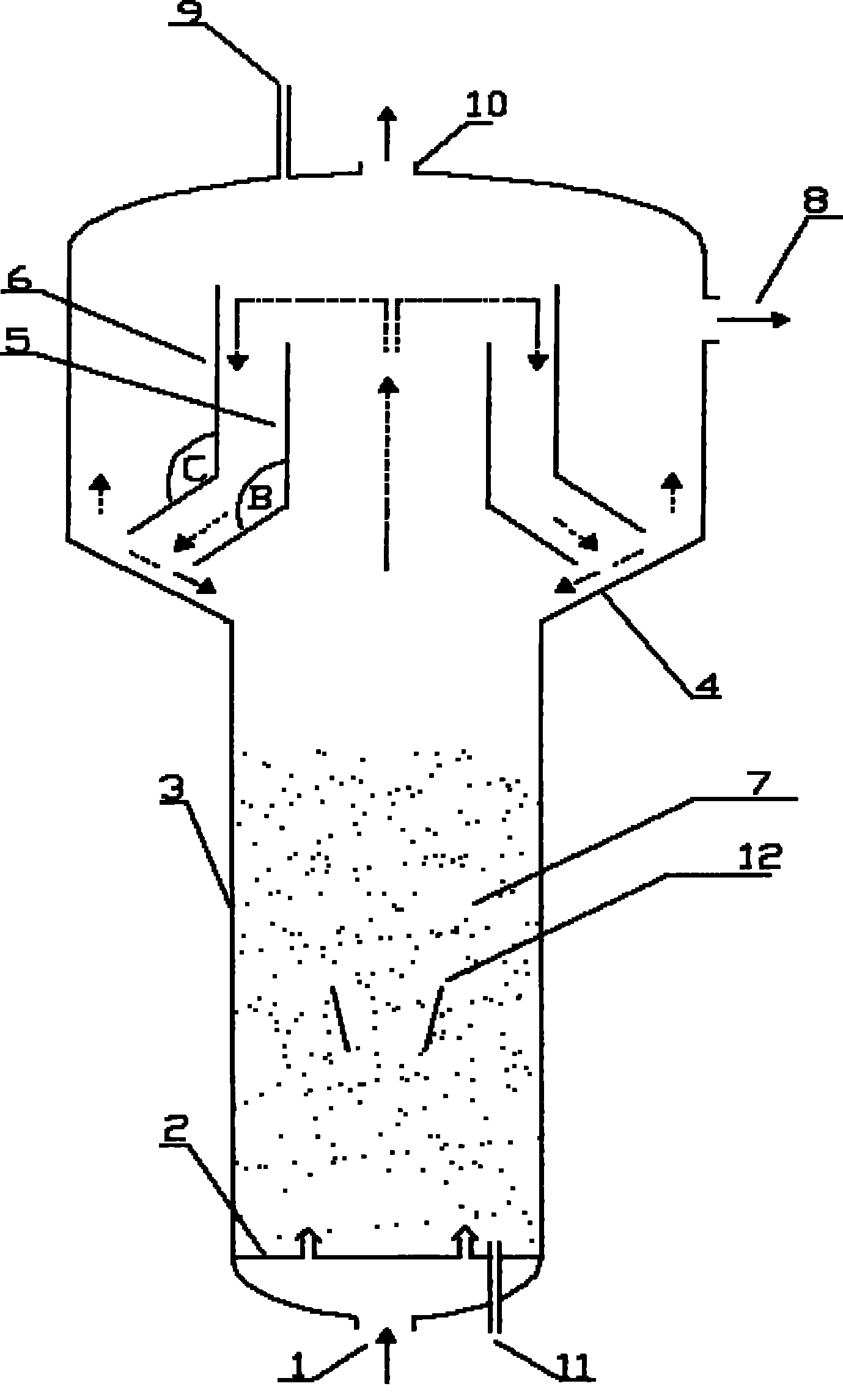
Three-phase boiling bed reactor
InactiveCN102463077AGreat operating flexibilityReduce carryoverChemical/physical processesChemical reactionStraight tube
The invention discloses a three-phase boiling bed reactor, which comprises a reactor casing and a three-phase separator, wherein the three-phase separator is positioned at the upper part in the reactor casing and comprises two homocentric round tubes with different inner diameters: an inner tube and an outer tube, the upper ends and the lower ends of the inner tube and the outer tube are all open, and the inner tube and the outer tube respectively comprise a straight tube section and a diffusion section. The three-phase boiling bed reactor is characterized in that the diameter of the straight tube section of the inner tube of the three-phase separator is 0.6 to 0.9 time of the diameter of the reactor casing. Through analyzing the speed distribution rule of liquid in the boiling bed reactor in the radial direction positions, the structure of the three-phase separator is reasonably set, so the operation elasticity of the three-phase separator is increased, and the efficient separation of the three-phase separator is ensured. The reactor is mainly applicable to the chemical reaction taken by different kinds of liquid and gas substances under the condition of being contacted with solid particles, and the reactor has the advantages that the catalyst inventory is large, the utilization rate of the reactor is high, the structure is simple, the operation is easy, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Nuclear fuel assembly end cap arrangement
InactiveUS20060018422A1Restrict movementLoose materialNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesDry storageNuclear fuel
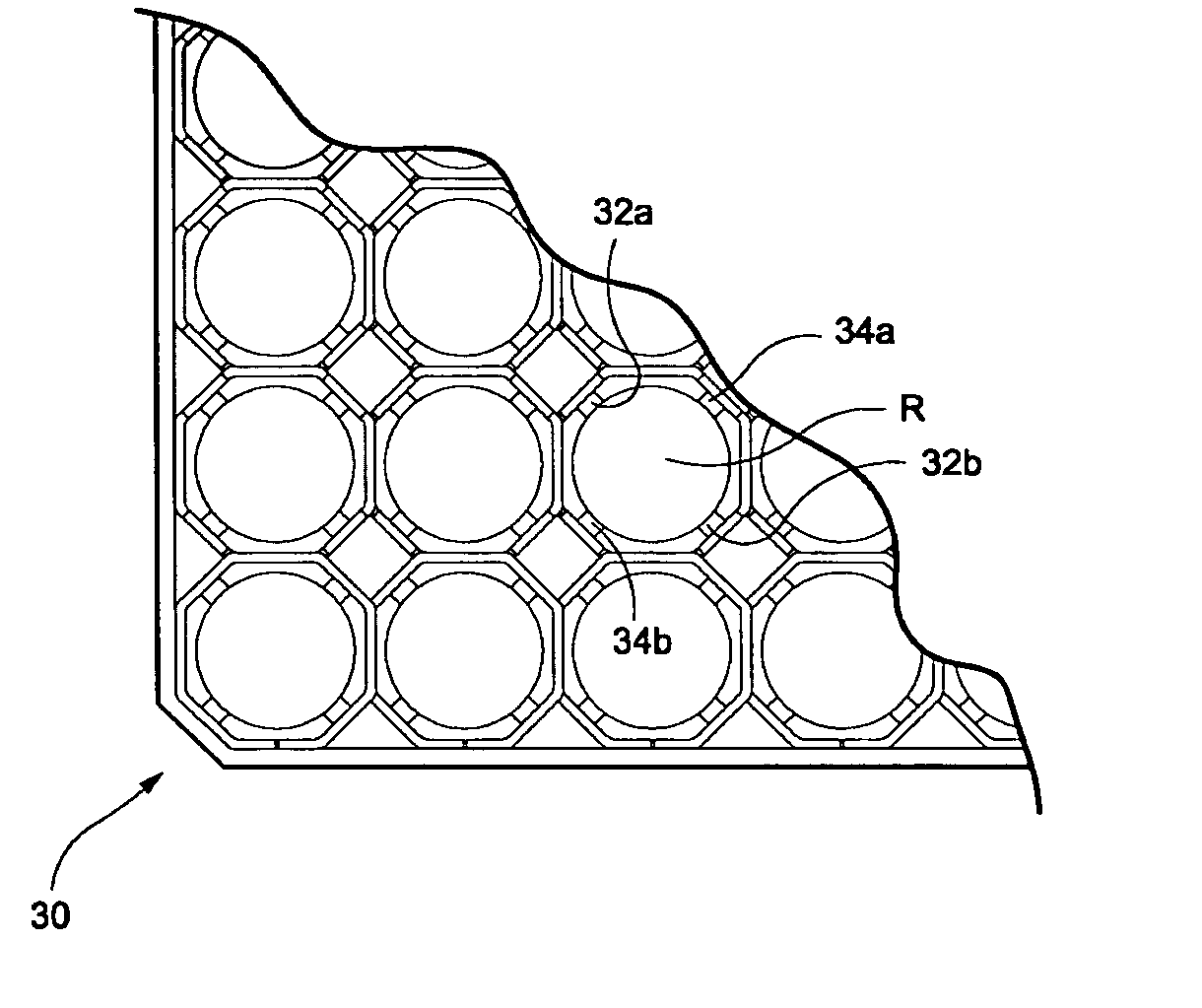
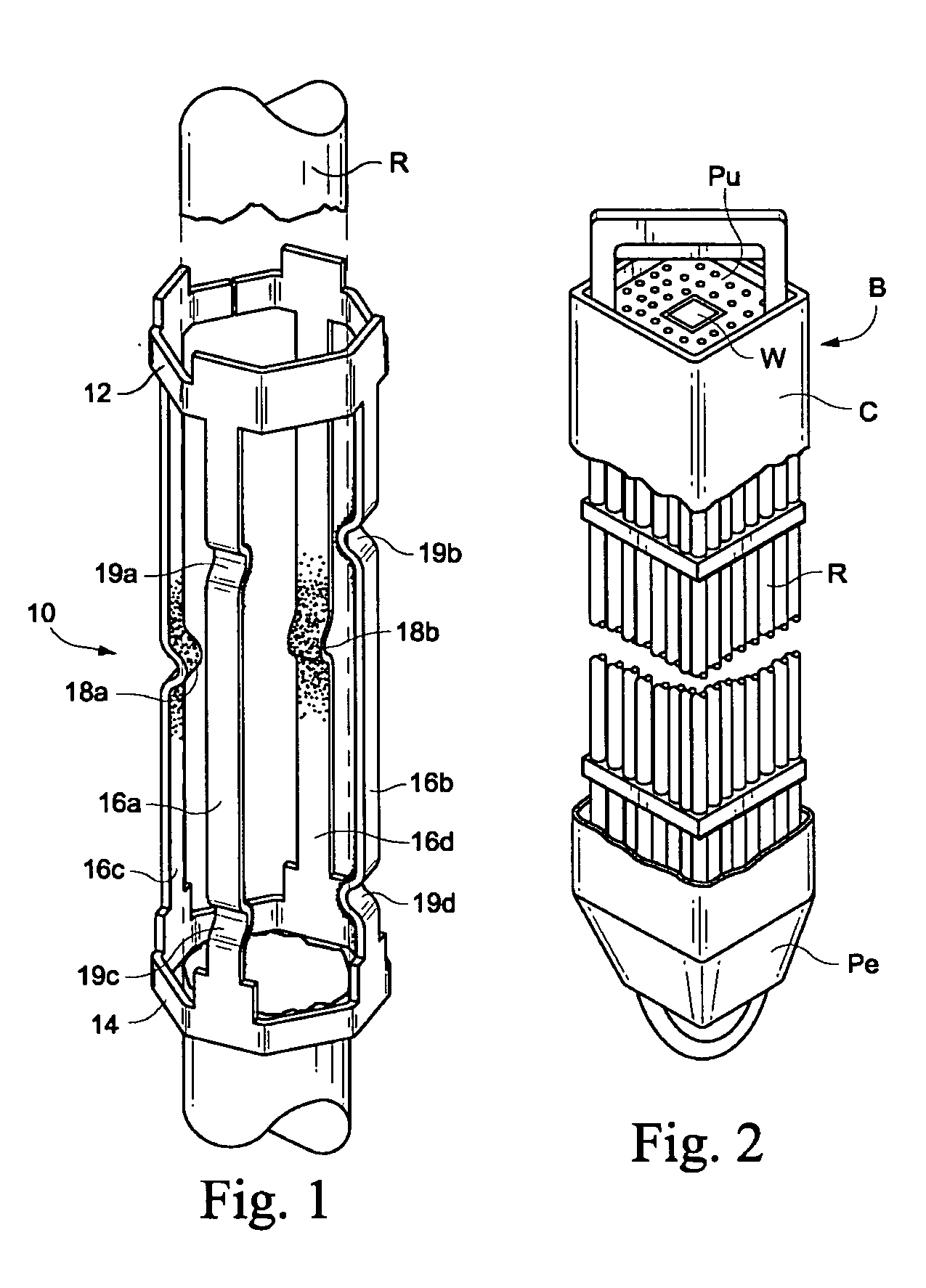
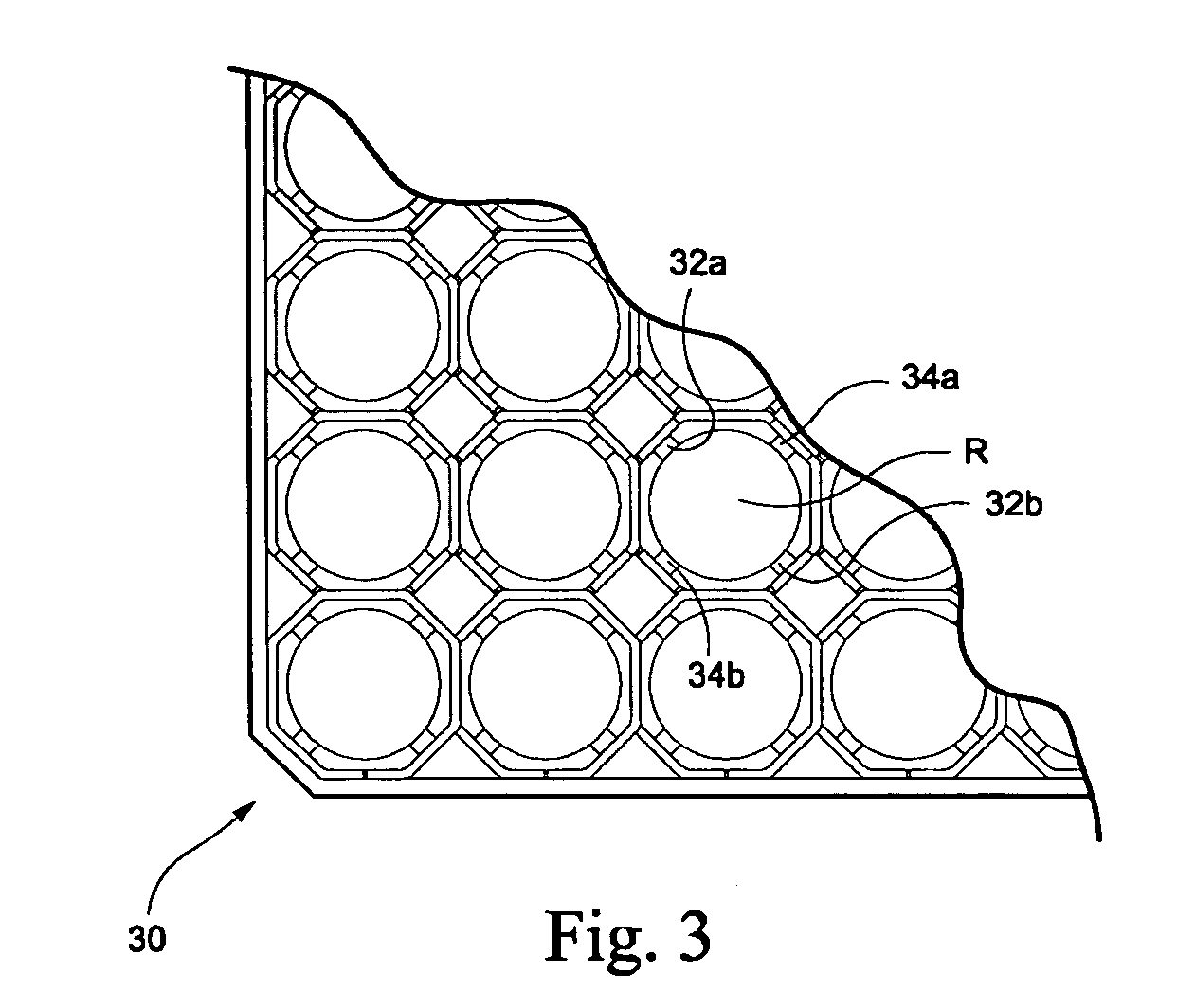
A method and arrangement to control fuel material debris originating from a fuel assembly for a dry storage system wherein the method includes providing a damaged boiling water reactor nuclear fuel assembly, providing a bottom end cap configured to fit on a bottom of a boiling water reactor nuclear fuel assembly, inserting the bottom end cap into the damaged boiling water reactor nuclear fuel assembly such that the bottom end cap prevents debris from inside the damaged nuclear fuel assembly from leaving the bottom of the fuel assembly, providing a top end cap configured to fit on a top of the boiling water reactor nuclear fuel assembly, and inserting the top end cap into the top of the damaged boiling water reactor nuclear fuel assembly such that the top end cap prevents debris from inside the damaged nuclear fuel assembly from leaving the top of the fuel assembly.
Owner:FRAMATOME ANP RICHLAND
Natural circulation boiling water reactor
InactiveUS20070201605A1Thermal margin in the core is reducedReduced responseNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsReactor pressure vesselPressure vessel
A core disposed in a reactor pressure vessel includes one layer (an outermost region) at an outermost side of the core, two-three layers (an outer region) inside the outermost region and other layers (an inner region) inside the outer region. Fuel assemblies arranged in the core are supported by fuel supports having orifice. Orifice pressure loss coefficient of the orifice in the outermost region is set to be maximum and the orifice pressure loss coefficient of the orifice in the outer region is set to be minimum such that the flow rate of the coolant W for each fuel assembly in the outermost region is lowest and that for each fuel assembly in the outer region is highest. In the core of the natural circulation boiling water reactor, the reactor power distribution in a radial direction is flattened, and it is possible to increase the thermal margin.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Zirconium alloy resistant to corrosion in drop shadows for a fuel assembly component for a boiling water reactor, component produced using said alloy, fuel assembly, and use of same
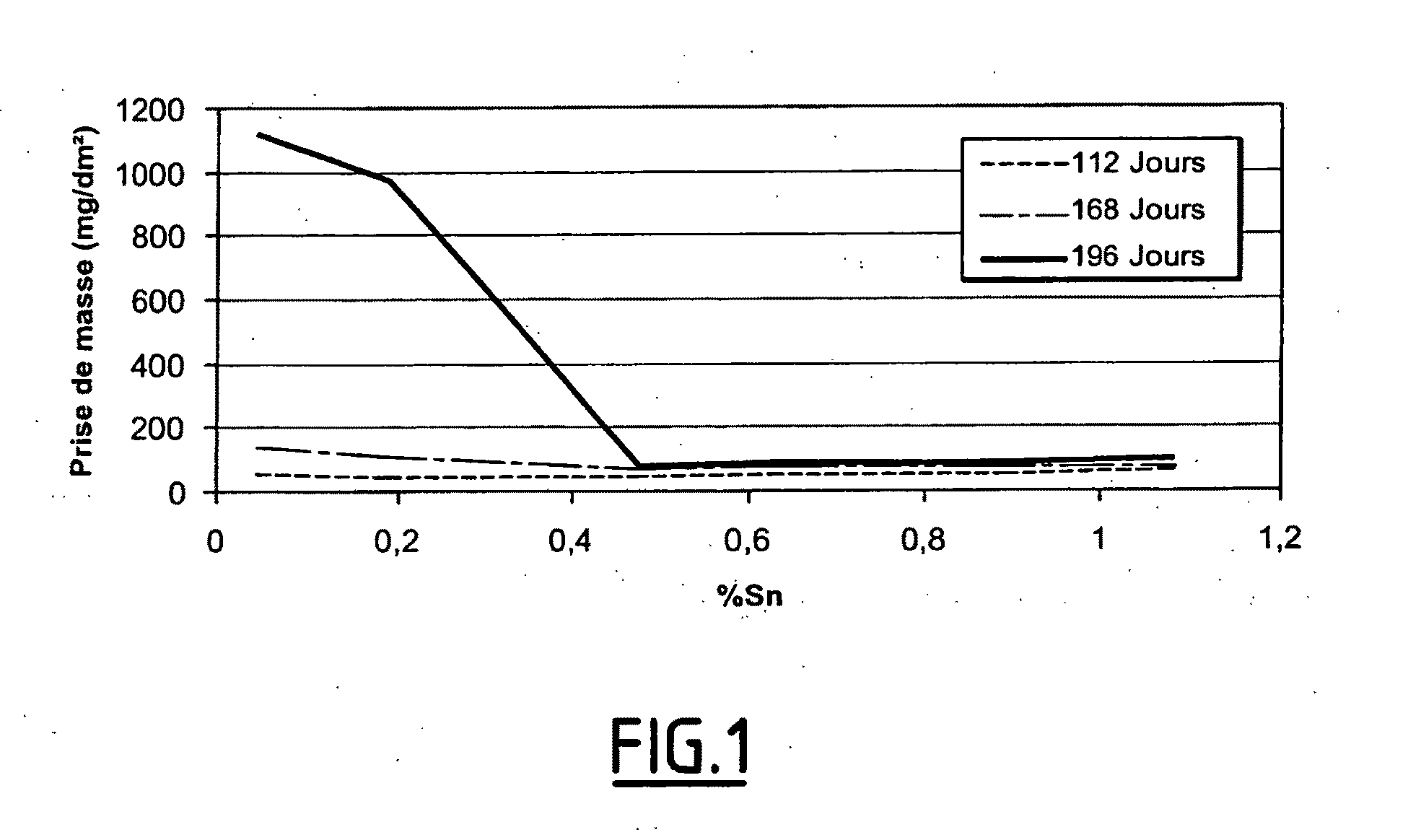
ActiveUS20100126636A1Satisfactory propertyReducing corrosion potentialNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsZirconium alloyDrop shadow
A zirconium alloy that is resistant to shadow corrosion for a boiling water nuclear reactor fuel assembly component, the alloy being characterized in that:its composition in percentages by weight is as follows:Nb=0.4%-4.5%Sn=0.20%-1.7%Fe=0.05%-0.45%Fe+Cr+Ni+V=0.05%-0.45%, with Nb≦9×[0.5−(Fe+Cr+V+Ni)]S=traces-400 ppmC=traces-200 ppmSi=traces-120 ppmO=600 ppm-1800 ppmthe balance being Zr and impurities from processing;in that, during fabrication, after its last hot deformation, it is subjected to one or more heat treatments lying in the range 450° C. to 610° C. for a total duration of at least 4 h, with at least one cold rolling operation with a rolling ratio of at least 25%; andin that a final heat treatment operation is performed at a temperature in the range 450° C. to 610° C. for 1 minute to 20 hours.A fuel assembly component made of the alloy, a fuel assembly including the component, and the use thereof.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
Method and apparatus for a jet pump slip joint internal seal
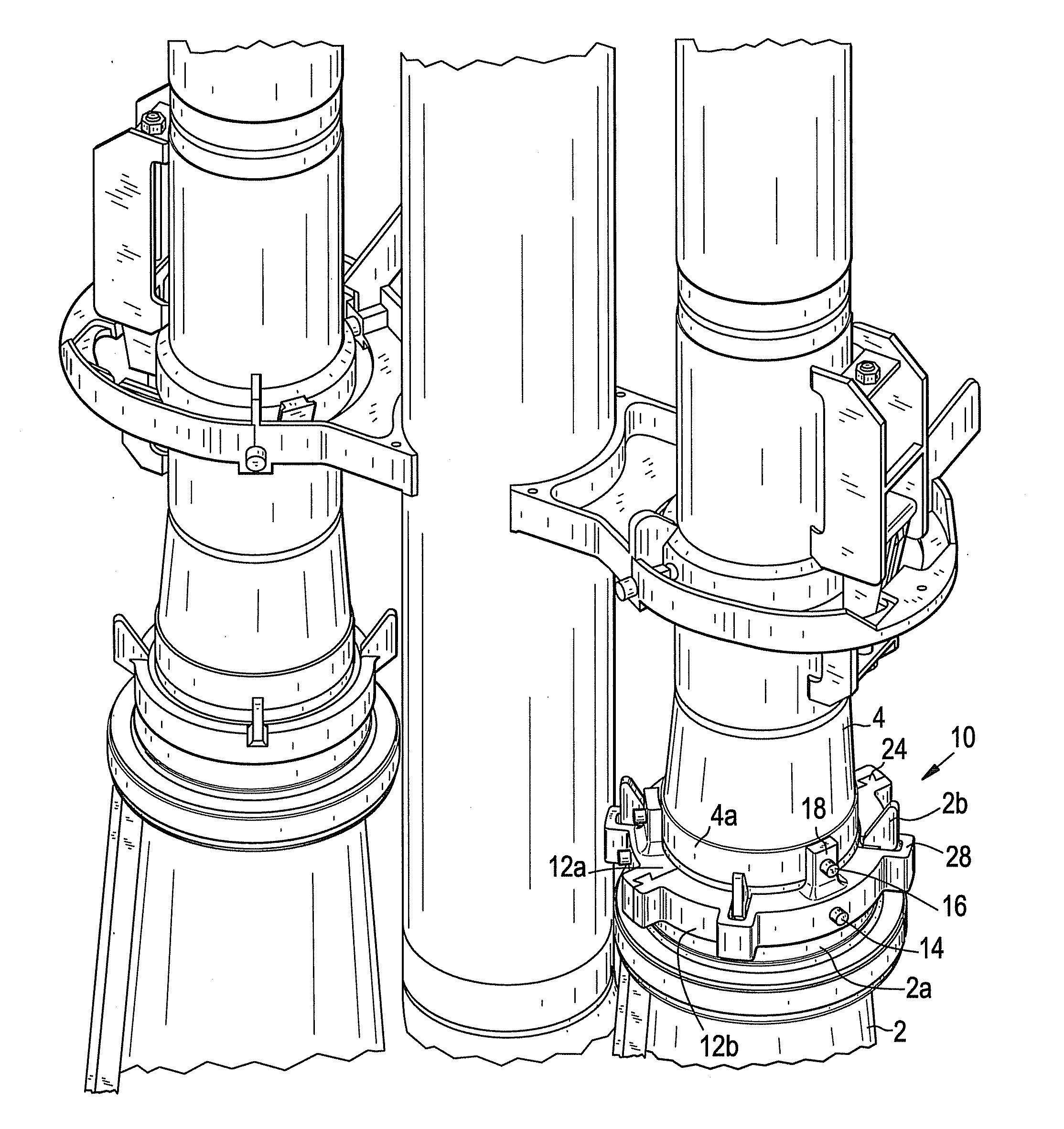
A method and apparatus for providing a Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) jet pump slip joint internal seal in the interface between an inlet mixer and a diffuser of a jet pump assembly. The internal seal provides an effective means of mitigating leakage and slip joint flow induced vibration (FIV) between the inlet mixer and diffuser to reduce damage to many of the jet pump assembly components that may otherwise be damaged by FIV. A metallic seal of the slip joint internal seal flares out to conform the internal seal to a range of gap sizes, and may be compressed or spring back to nominal dimensions as thermal expansion and contraction occurs. The internal seal is also self-expanding / self-tightening, as the internal seal flares further outward as a result of the internal pressure caused by flowing fluids in an operating jet pump assembly.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
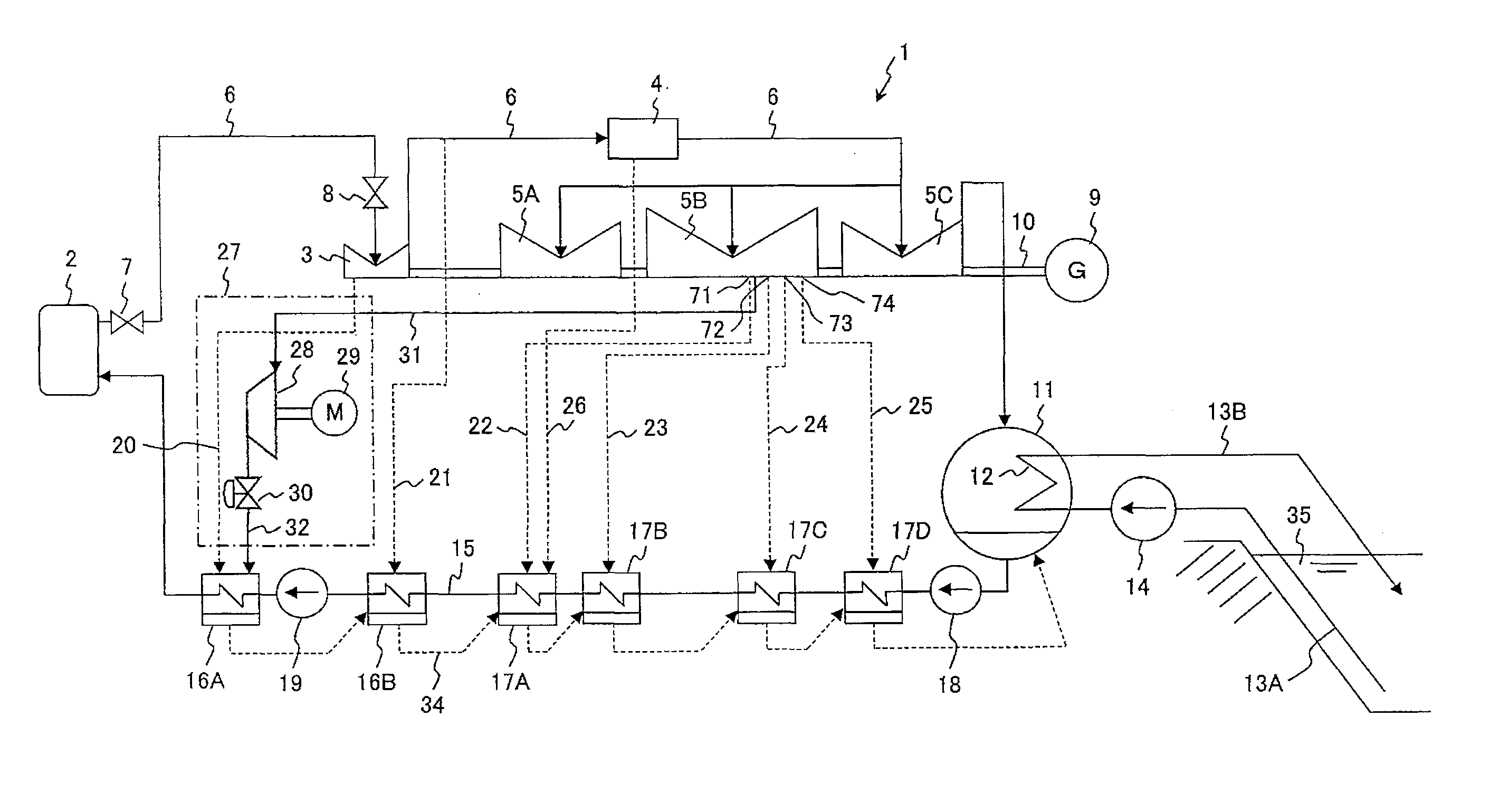
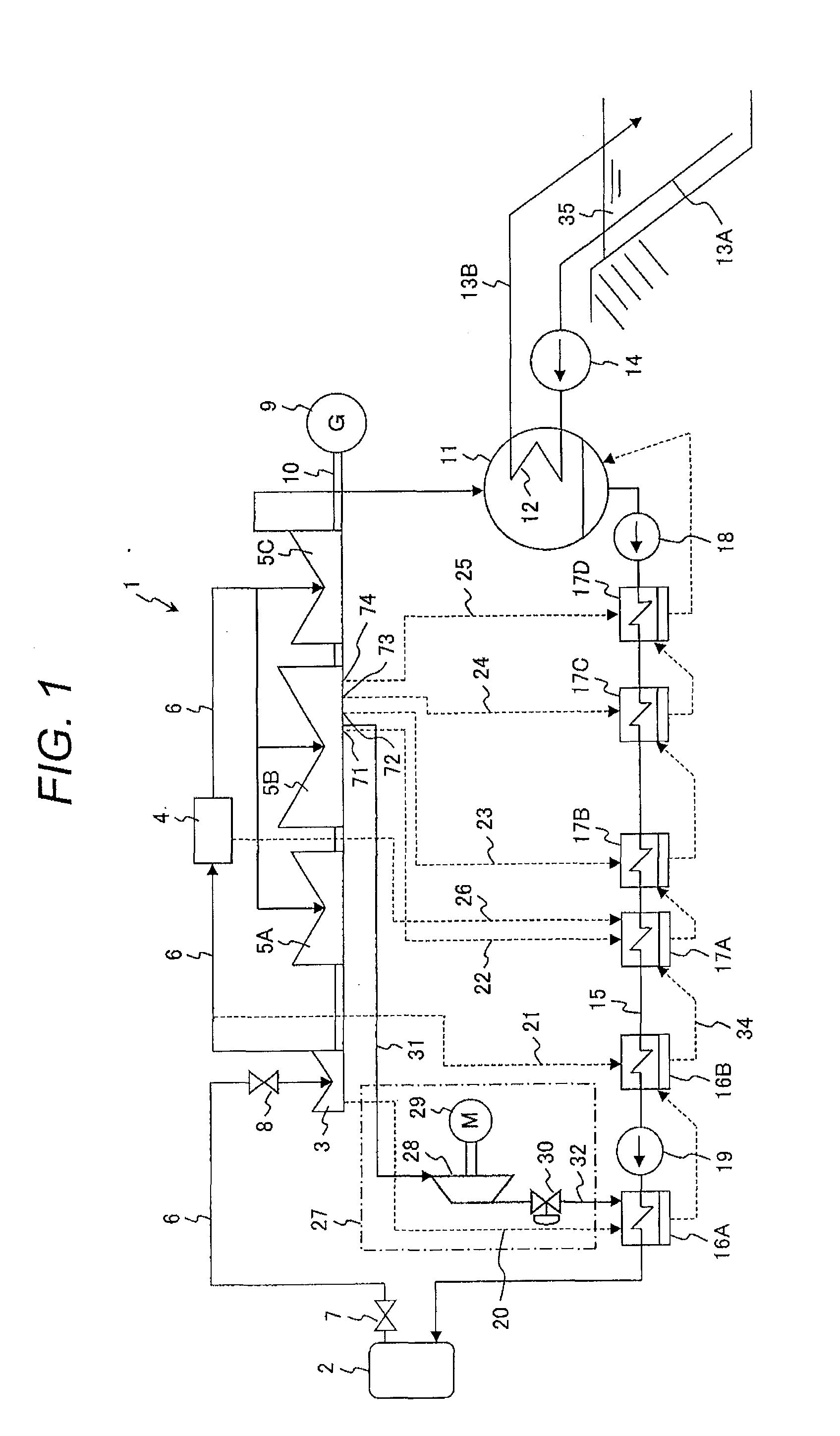
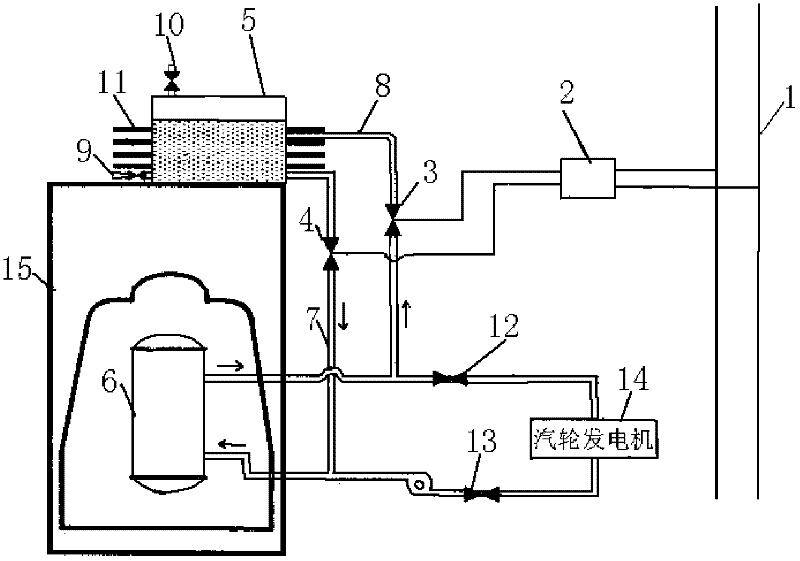
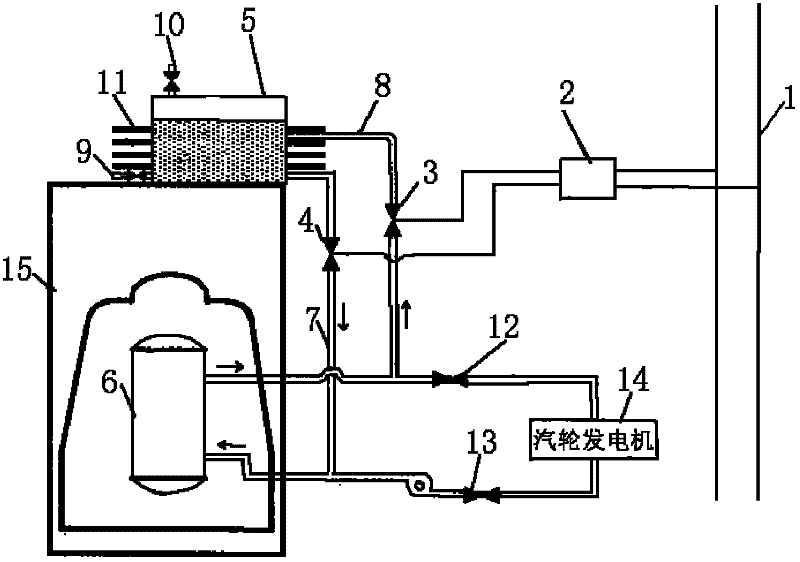
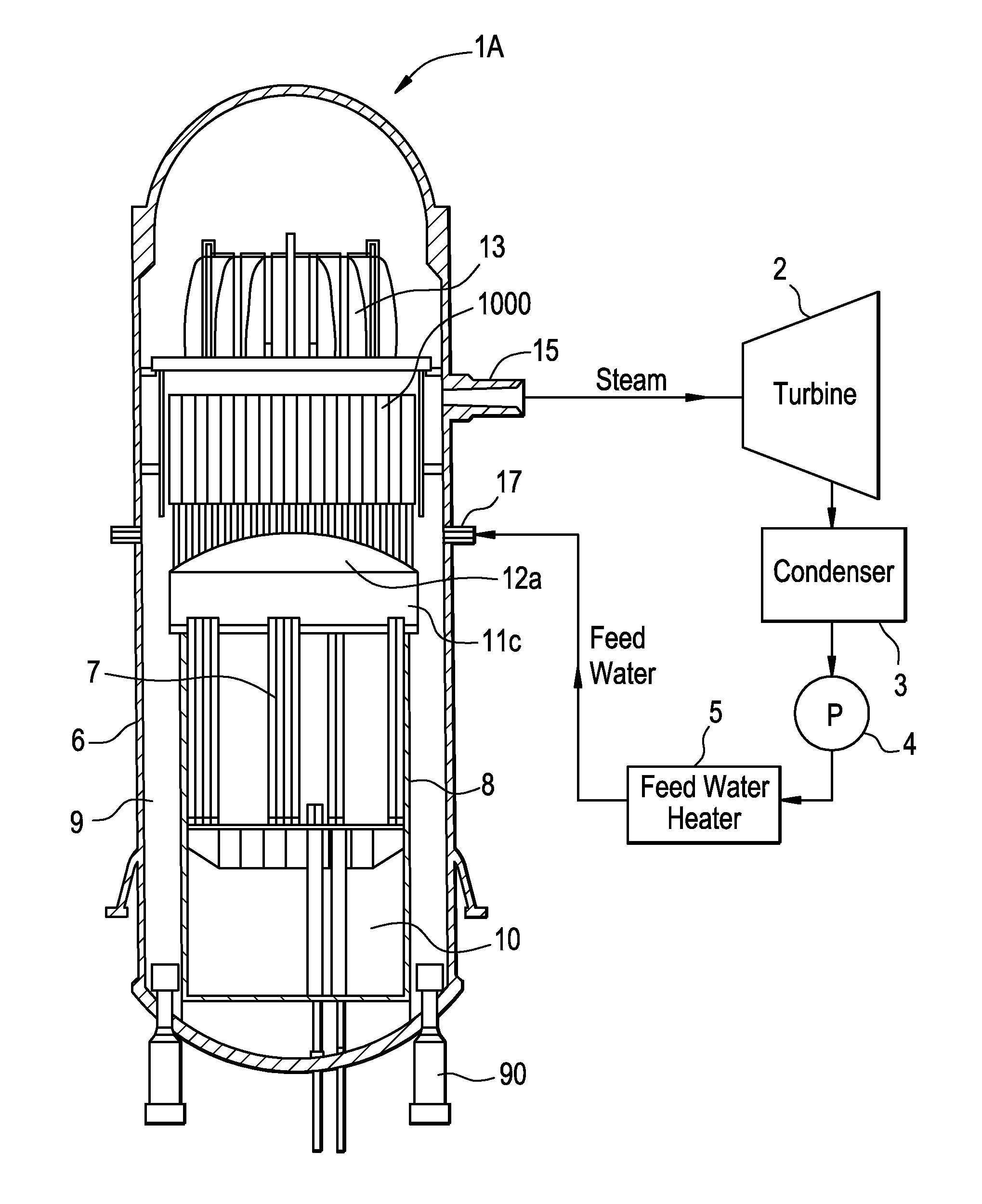
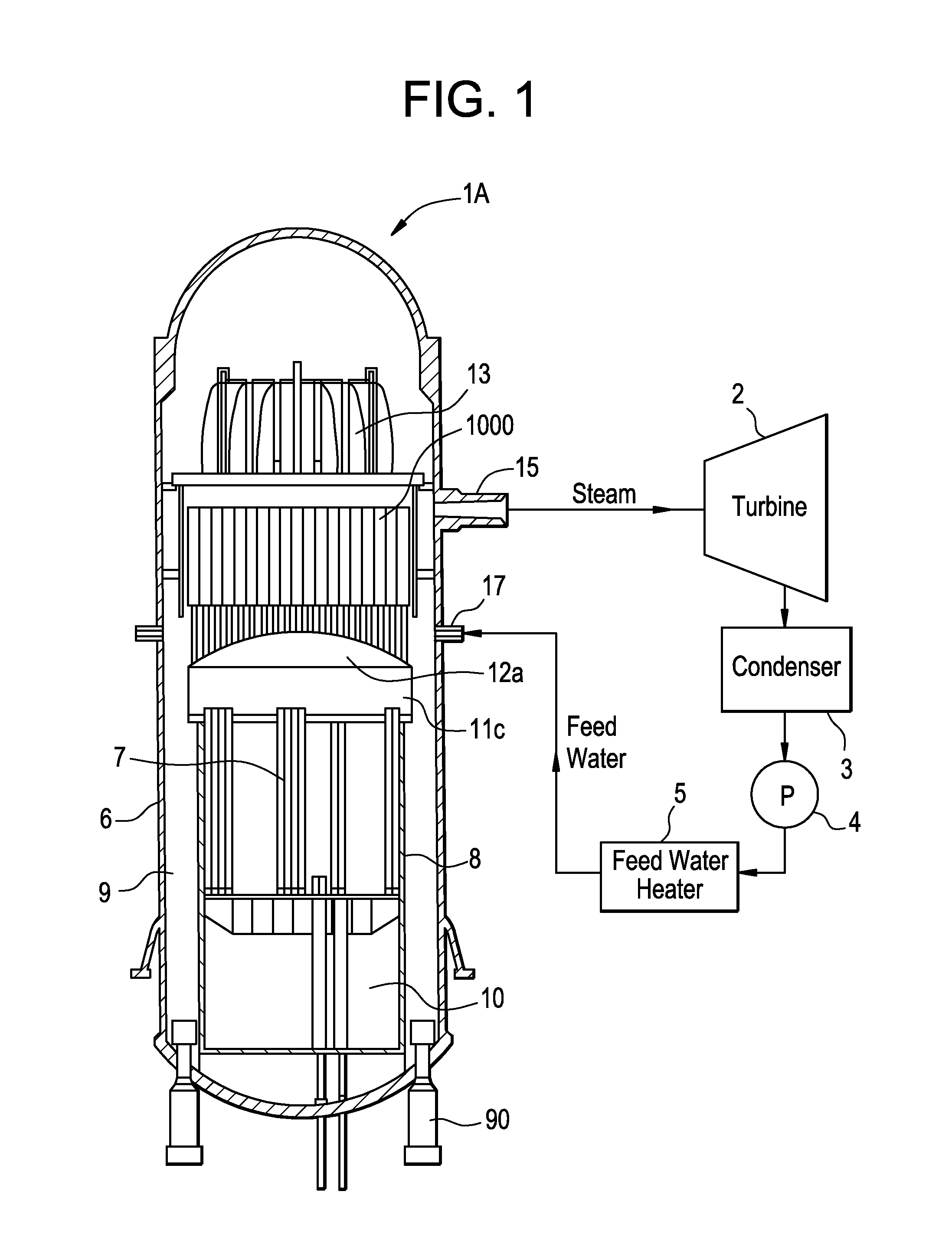
Electric Power Plant, and Method for Running Electric Power Plant
ActiveUS20110005225A1Improve thermal efficiencyHigh power outputSteam useReactor heat to mechanical energyWater flowHigh pressure
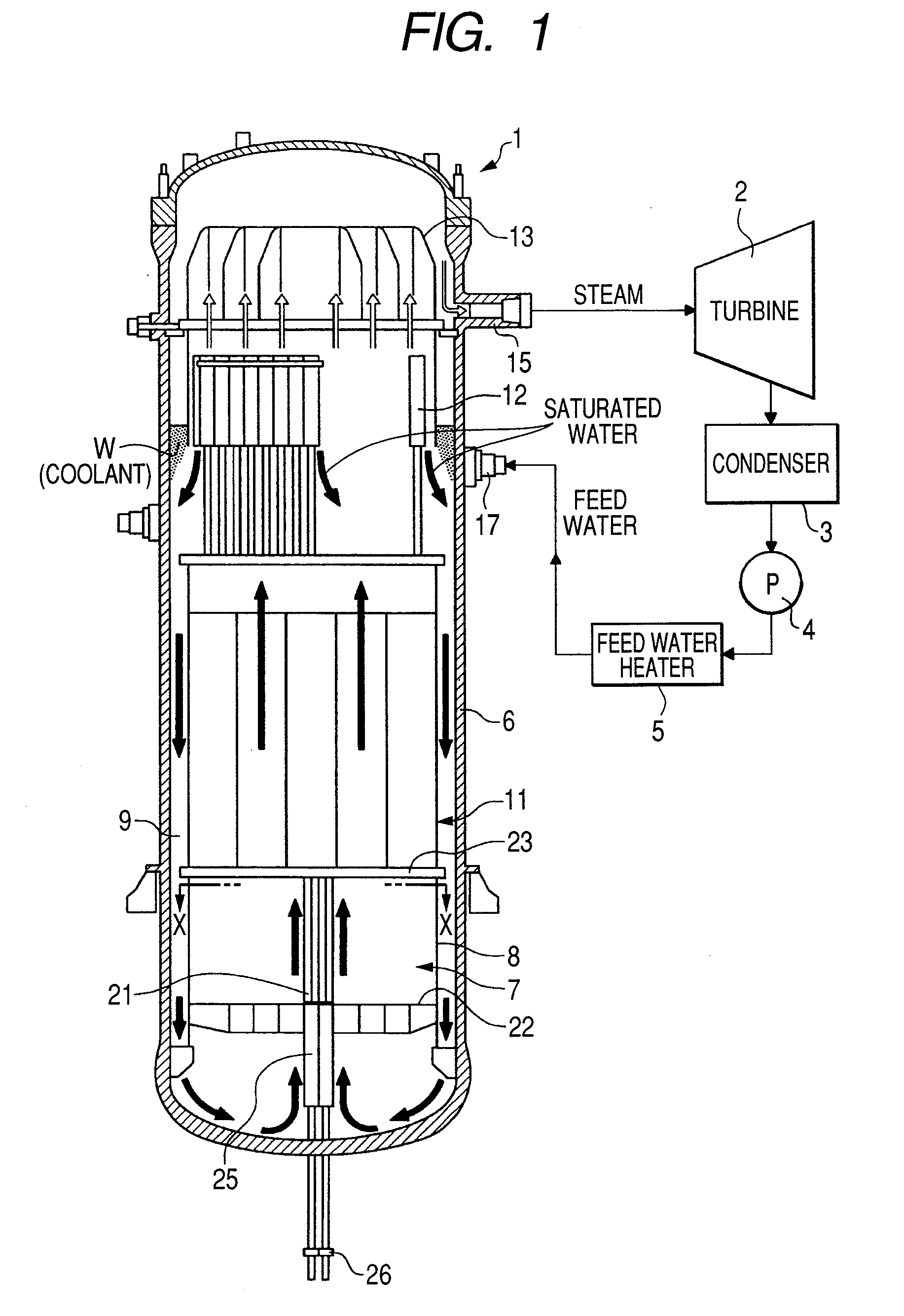
An electric power plant, e.g., a boiling water reactor nuclear power plant supplies steam generated in a nuclear reactor to a high-pressure turbine and a low-pressure turbine. The steam discharged from the low-pressure turbine is condensed with a condenser. Water generated with the condenser, used as feed water, flows through a feed water pipe, is heated with a low-pressure feed water heater and a high-pressure feed water heater, and then supplied to the nuclear reactor. The steam extracted from the high-pressure turbine is supplied to the high-pressure feed water heater. The steam extracted from the low-pressure turbine is compressed with a steam compressor, and the steam whose temperature has been increased is then supplied to the high-pressure feed water heater. The feed water to be directed to the nuclear reactor is heated in the high-pressure feed water heater by both the steam extracted from the high-pressure turbine and the steam compressed with the steam compressor. Because the feed water is heated by both the extracted steam and the compressed steam in the high-pressure feed water heater, the amount of plant service power consumed by the steam compressor can be reduced. Therefore, it is possible to increase thermal efficiency in the electric power plant when increasing the power output.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Method and apparatus for a fret resistant fuel rod for a light water reactor (LWR) nuclear fuel bundle
A method and apparatus for a fret resistant fuel rod for a Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) nuclear fuel bundle. An applied material entrained with fret resistant particles is melted or otherwise fused to a melted, thin layer of the fuel rod cladding. The applied material is made of a material that is chemically compatible with the fuel rod cladding, allowing the fret resistant particles to be captured in the thin layer of re-solidified cladding material to produce an effective and resilient fret resistant layer on an outer layer of the cladding.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
Nuclear fuel, a fuel element, a fuel assembly and a method of manufacturing a nuclear fuel
The invention refers to a nuclear fuel, a fuel element, a fuel assembly and a method of manufacturing a nuclear fuel. The nuclear fuel is adapted for use in a water cooled nuclear reactor, including light water reactors LWR, such as Boiling Water Reactors BWR and Pressure Water Reactors PWR. The nuclear fuel comprises an uranium-containing compound consisting of UN. The uranium content of the uranium-containing compound comprises less than 10% by weight of the isotope 235U. The nuclear fuel comprises an additive substantially consisting of at least one element, in elementary form or as a compound, selected from the group consisting of Zr, Mo, Si, Al, Nb and U.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC SWEDEN
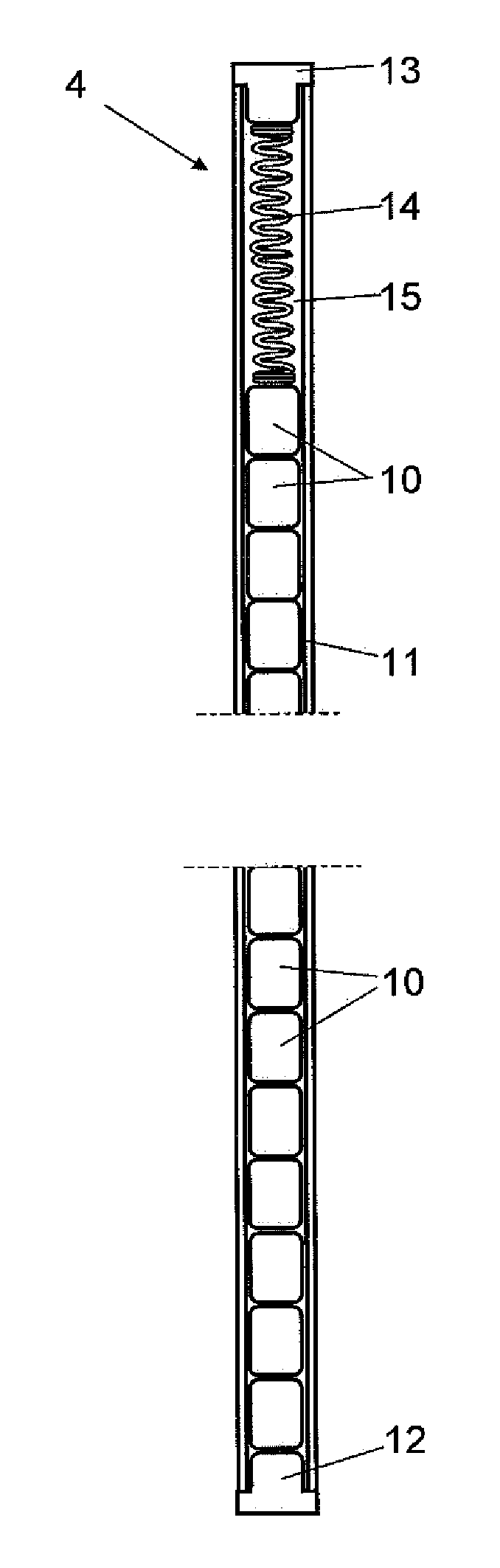
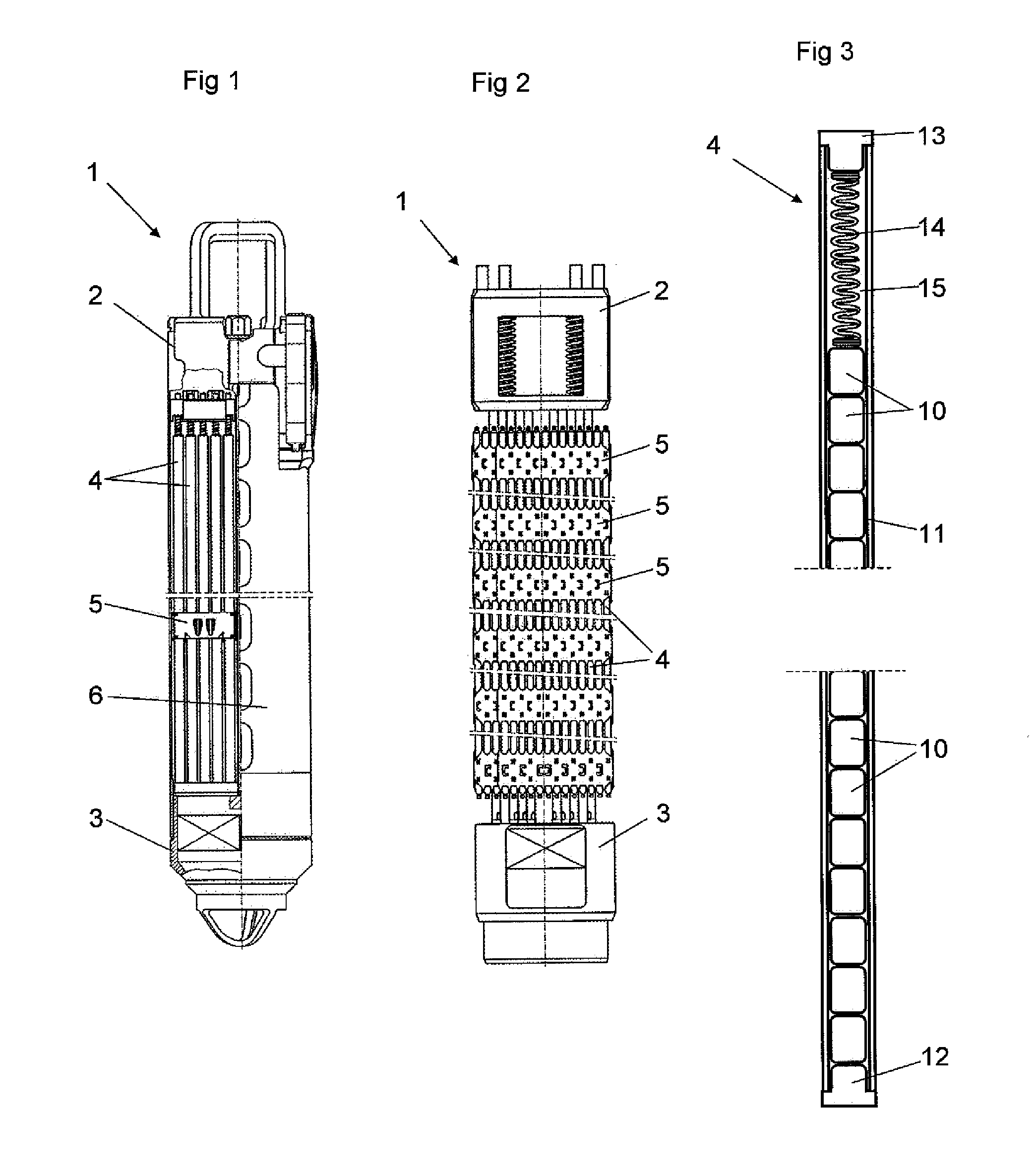
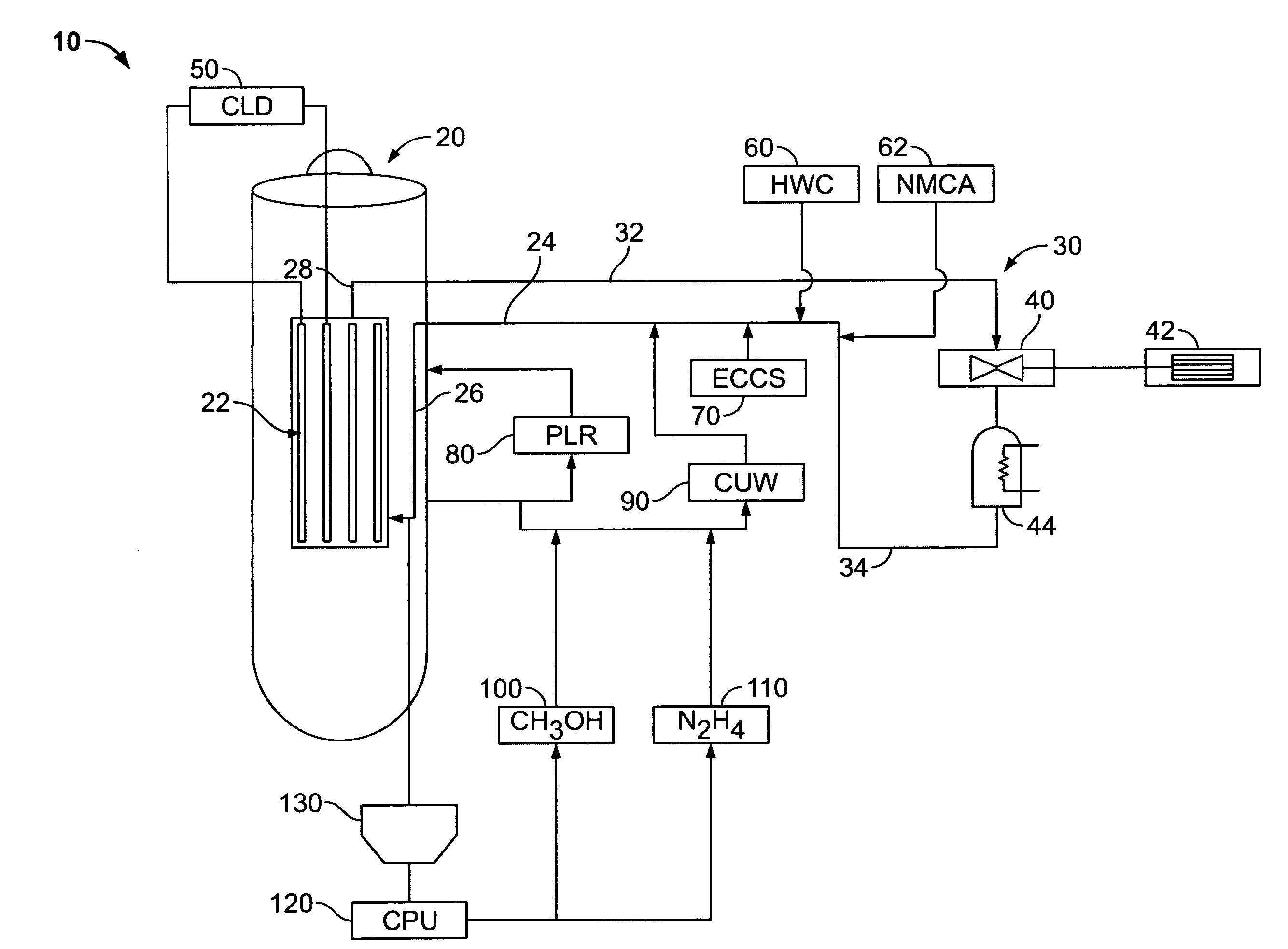
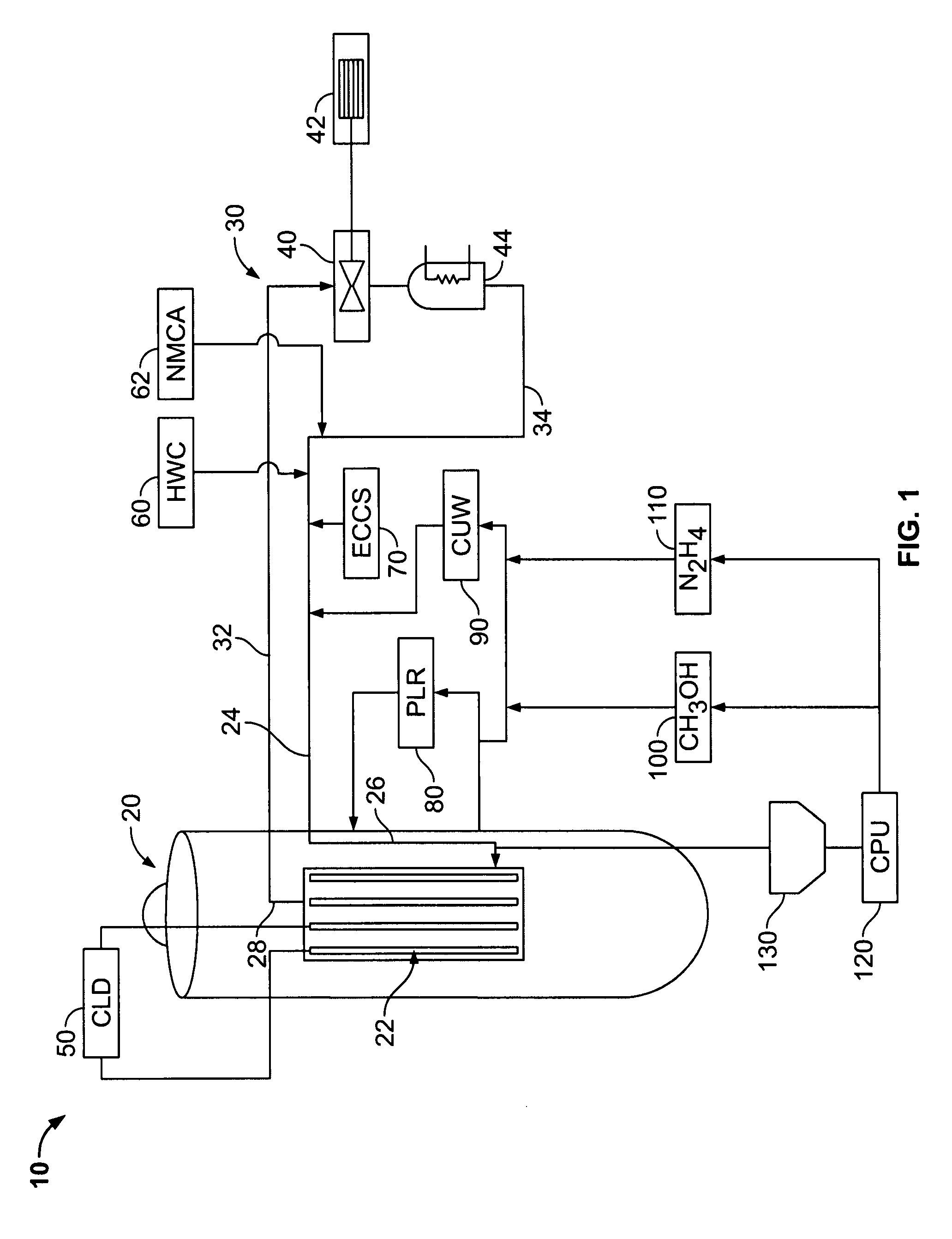
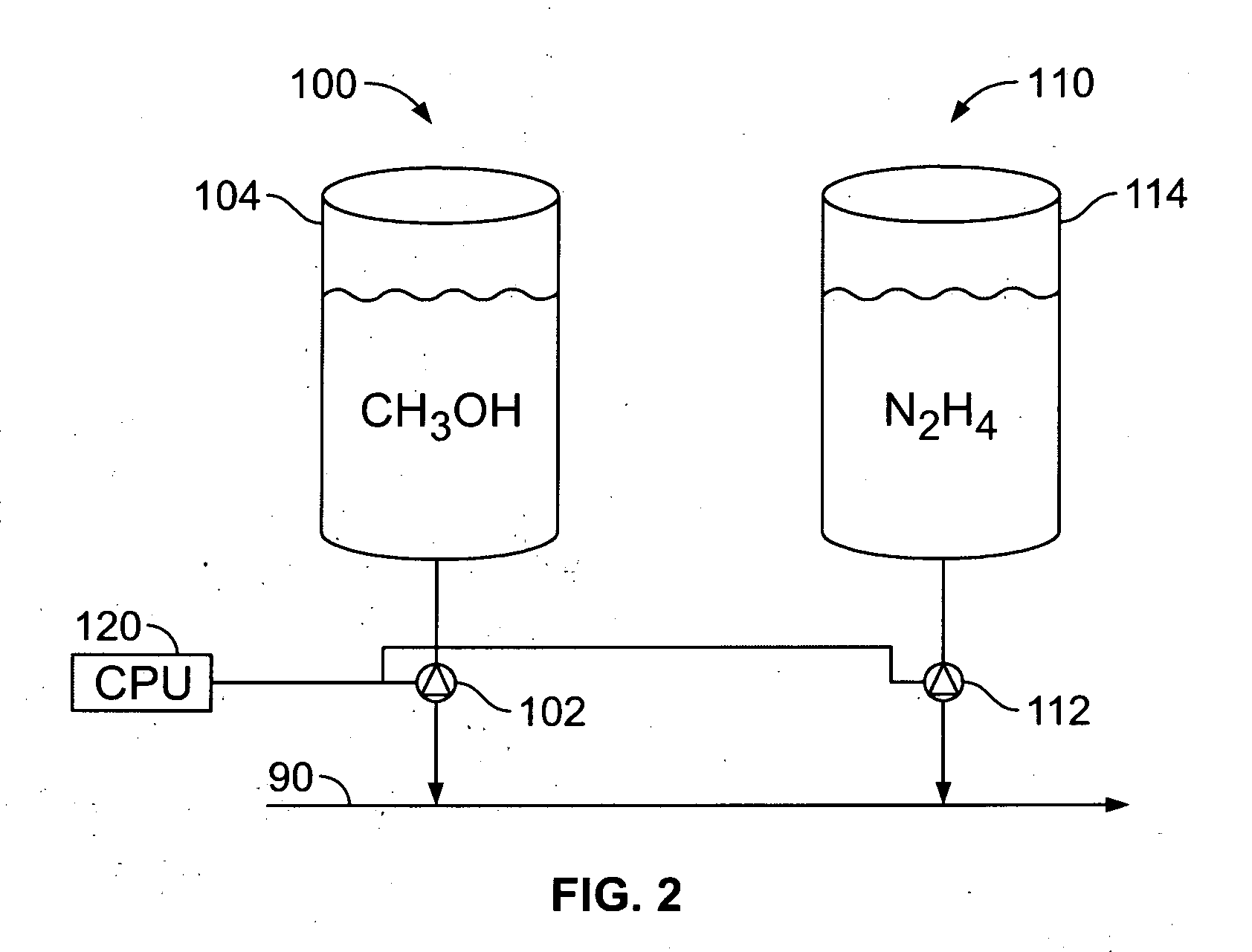
Boiling water reactor nuclear power plant with alcohol injection
ActiveUS20090086878A1Adequate oxidation reductionReduce the amount requiredWater treatment parameter controlPlant parameters regulationAlcoholHydrogen
A nuclear power plant is provided including a BWR, a reactor cooling system cooling the BWR, an HWC hydrogen injection system connected to the reactor cooling system and an alcohol injection system connected to the reactor cooling system. Methods for providing methanol and hydrogen are also provided.
Owner:AREVA GMBH +1
Steam separator, boiling water reactor and swirler assembly
ActiveUS7835483B2Easy to separateSmall pressure lossNuclear energy generationDispersed particle separationEngineeringCentrifugal force
A steam separator comprises an outer main swirler and an inner auxiliary swirler which is smaller than the main swirler. The swirlers are provided so as to be concentric on the inner wall at the lower side of the first stage inner cylinder. In the steam separator, when the gas-liquid two-phase flow which flows in the vicinity of the axial center of the first stage inner cylinder passes the auxiliary swirler, it is separated into steam and water by the centrifugal force. The separated water (droplets) is introduced into the main swirler. When the separated water (droplets) passes the main swirler, it is separated at the inner wall side of the first stage inner cylinder by the centrifugal force.Pressure loss in a steam separator is reduced and steam separation capability is increased without increasing the moisture from the steam separator.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
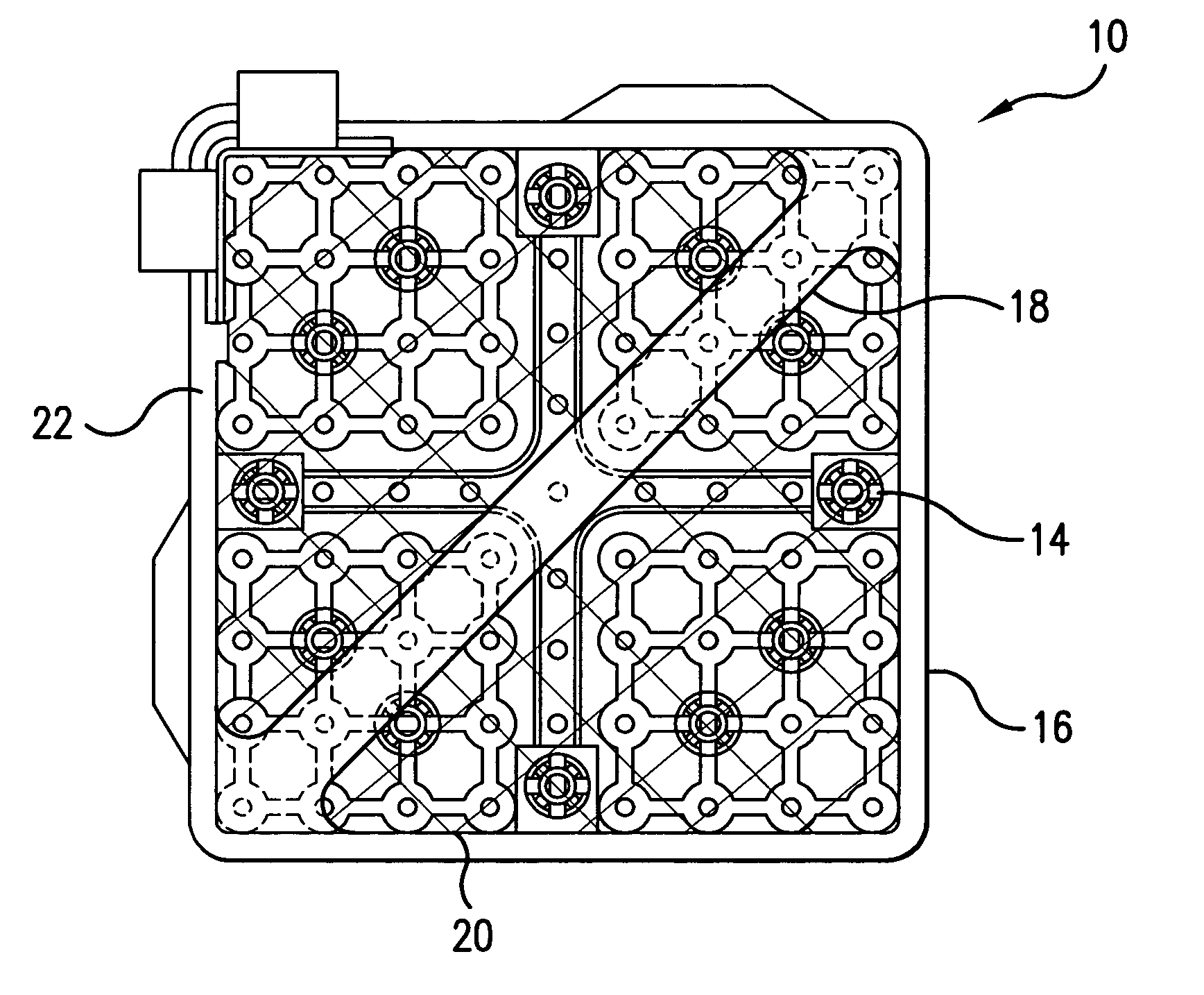
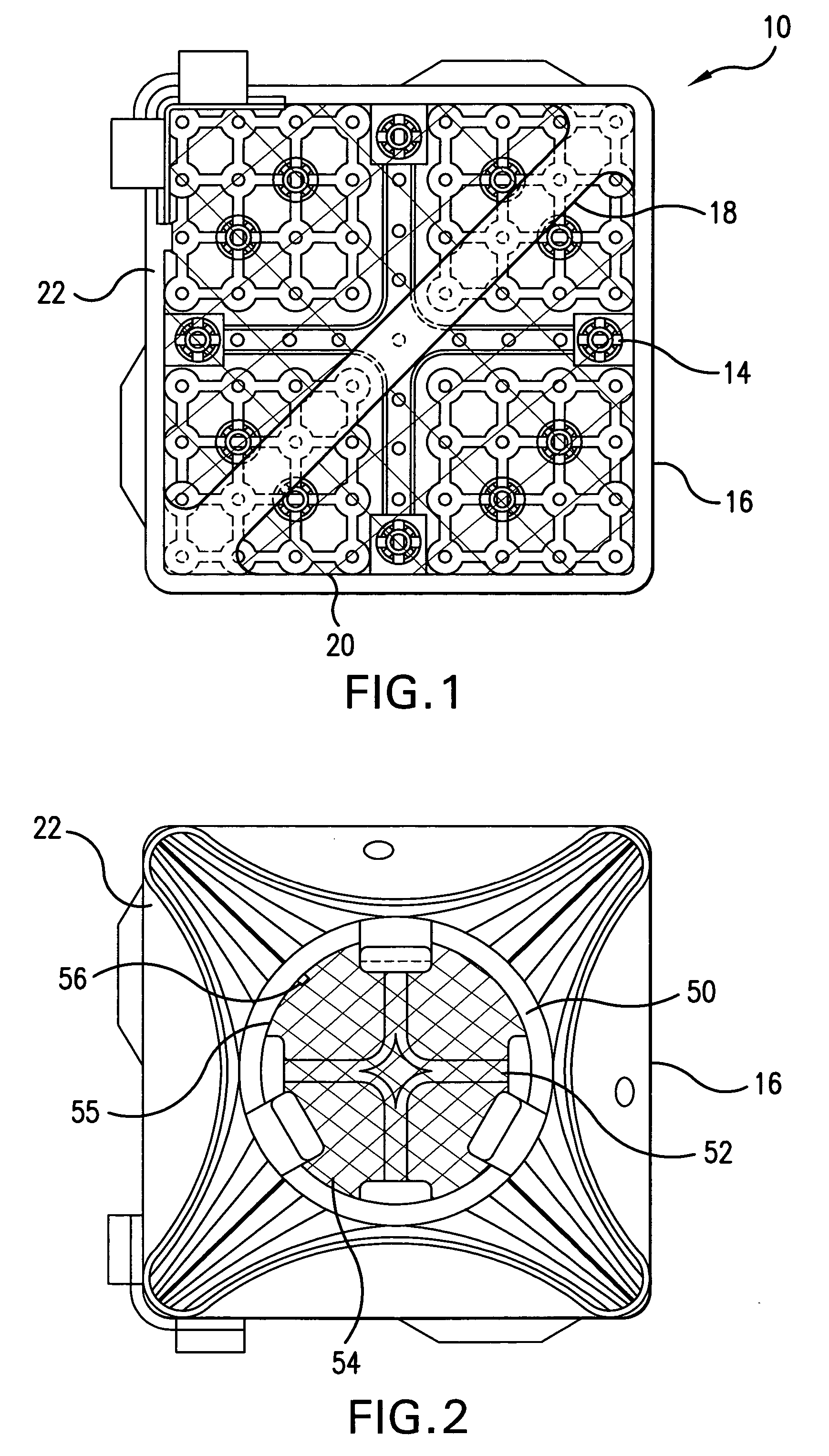
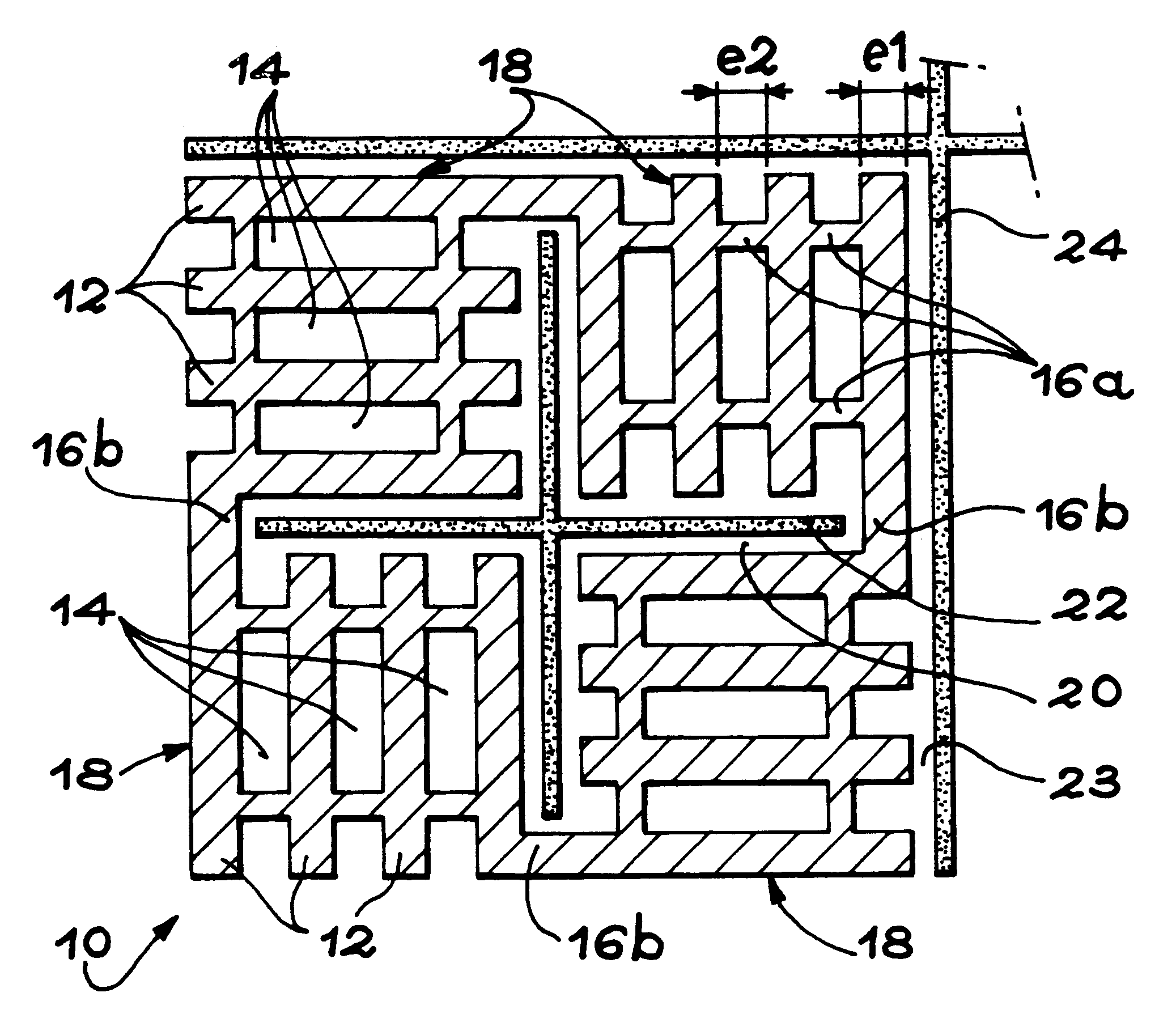
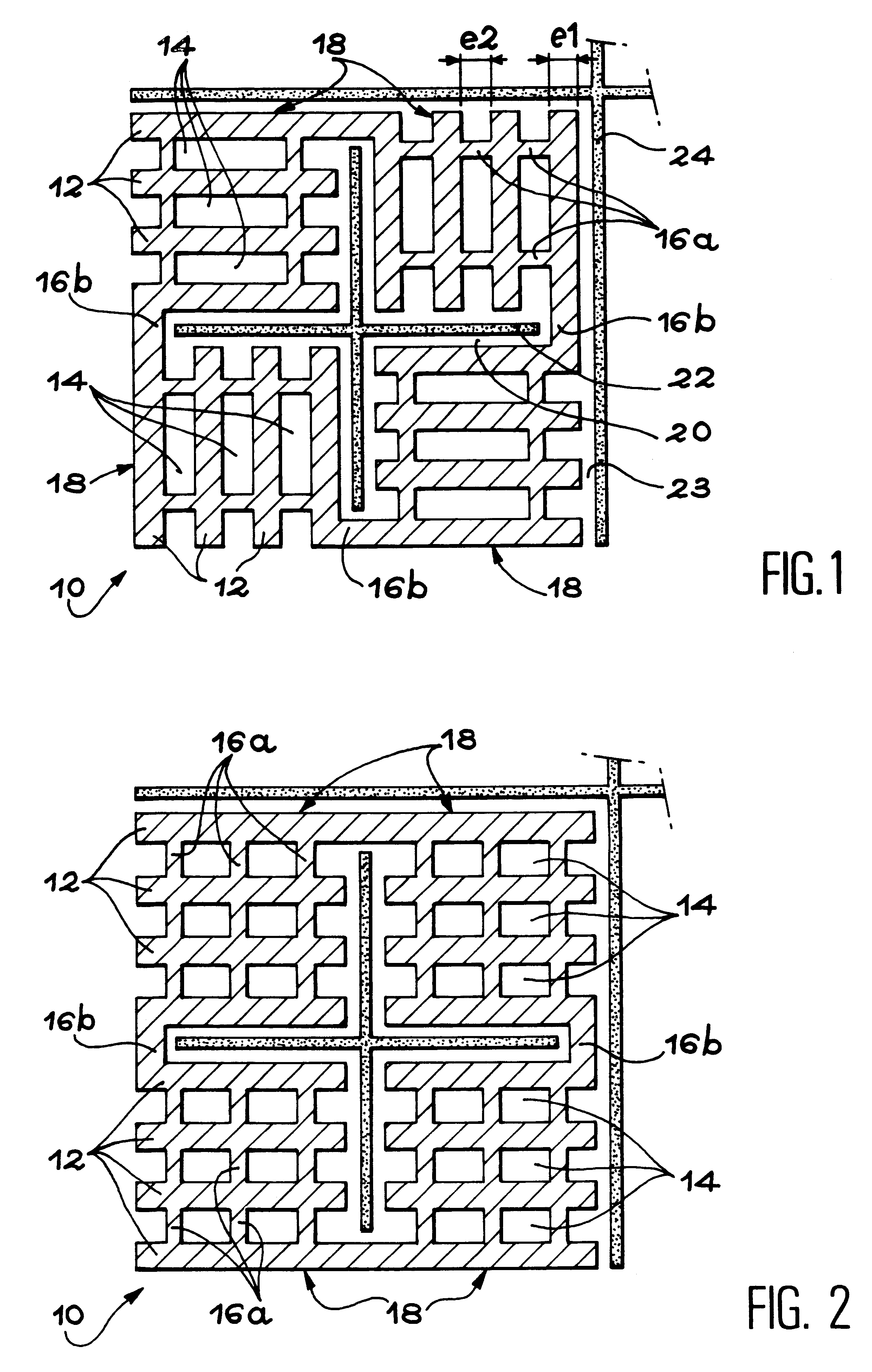
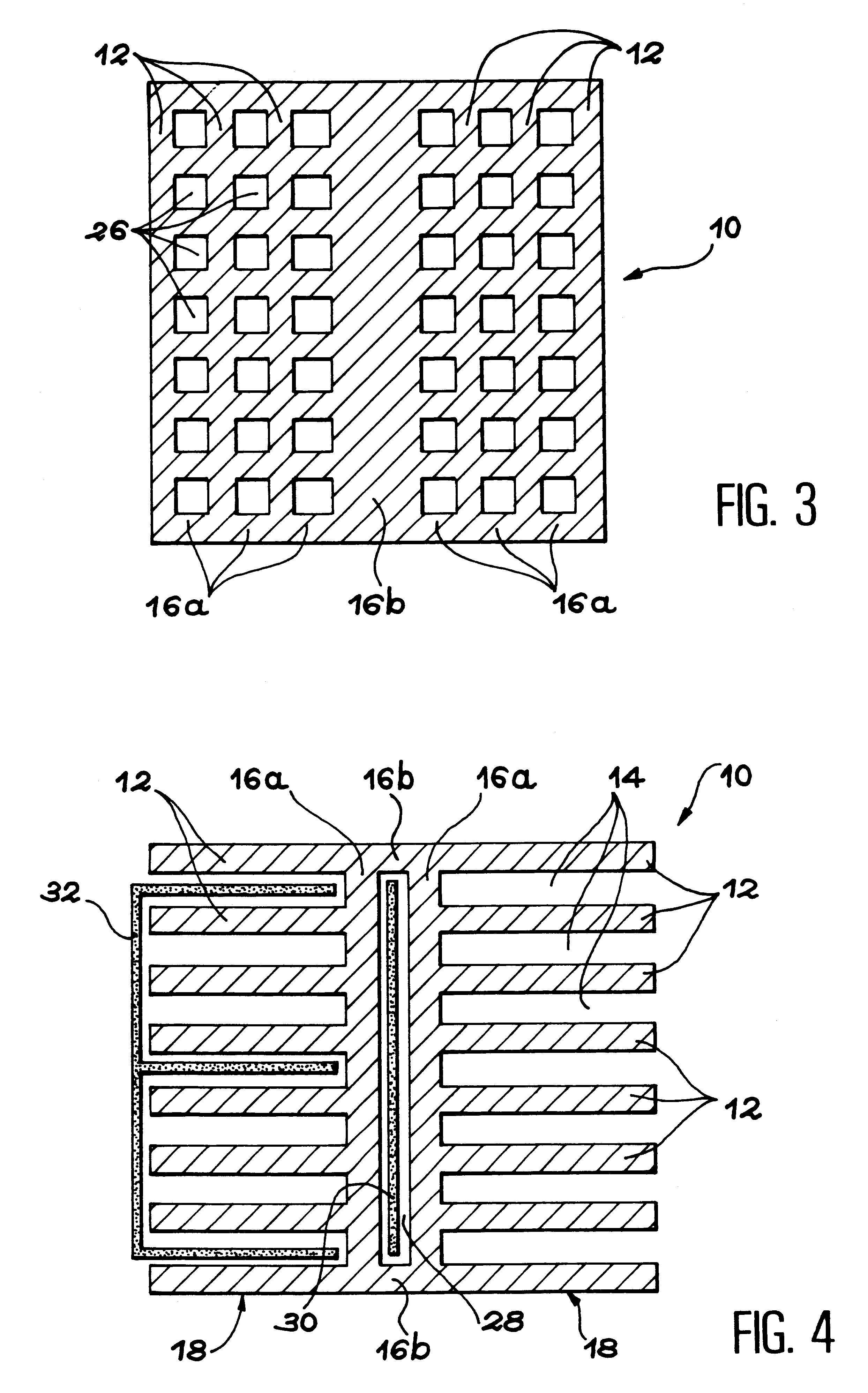
Non shadow forming spacers and hardware for a BWR fuel assembly
InactiveUS20060045232A1Improve corrosion resistanceReduces and eliminates shadow formationNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesInconelNickel alloy
A new type of coated component for use in boiling water reactor (“BWR”) fuel assemblies, particularly Zircaloy spacers, having protective coatings applied to selected surfaces of the spacers in order to prevent the formation and propagation of “shadow corrosion” on adjacent zirconium alloy structures. In its broader aspects, the coating material is applied to those surfaces of the BWR components having electro-chemical characteristics that differ from zirconium alloys, such as Inconel spacers or springs. The new coatings impart an electro-chemical potential to the surfaces of the components that is substantially similar to the adjacent zirconium alloy, thereby preventing or significantly inhibiting shadow corrosion.
Owner:GLOBAL NUCLEAR FUEL -- AMERICAS
Method and apparatus for a jet pump three point slip joint clamp
ActiveUS20120170704A1Reduce loadPrevent leakageNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsEngineeringCantilever
A method and apparatus for providing a Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) jet pump three point slip joint clamp to mitigate sleep joint leakage flow induced vibration of a BWR jet pump assembly. A collar, provided as one seamless component or in separate portions, is installed on the upper crown of a diffuser. The collar includes a lower set of fasteners and an upper set of fasteners that contact the inlet mixer and diffuser, respectively, to horizontally stabilize the inlet mixer in a fixed position inside of the diffuser. The upper fasteners may be anchored by bosses that ensure a light-weight design of the collar. An optional cantilevered seal (including a cantilevered overhang and a lip) may mitigate leakage from the slip joint interface.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Passive residual heat removal system under accident of boiling-water reactor based on characteristics of nanometer fluid
InactiveCN102243897AExport implementationPassiveNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementNuclear powerNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a passive heat removal system of a boiling-water reactor based on the characteristics of a nanometer fluid and belongs to the technical field of equipment and safety of nuclear power stations. The system consists of a valve controller, a water tank, a circulating pipeline, a valve and the like. In the case of unavailability of a station power supply, the quick removal of heat in the boiling-water reactor is realized by using the higher heat transfer characteristic and lower viscosity coefficients of the nanometer fluid and higher natural circulation capacity. The aims of preventing radioactive materials from being discharged and protecting the public and environments are fulfilled. When a severe accident occurs, a safety assurance function is executed and realized. The system is good in backup safety, simple in flow, stable in performance, high in reliability, convenient for implementation and simple to control.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method and apparatus for a jet pump inlet mixer integral slip joint clamp
InactiveUS20120170703A1Reduce vibrationNuclear energy generationHollow article cleaningSlip jointFlange
A method and apparatus for providing a Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) jet pump inlet-mixer integral slip joint clamp to constrain the inlet mixer and diffuser to mitigate inlet mixer flow induced vibration of a BWR jet pump assembly. The slip joint clamp includes horizontally projecting flanges with vertical sidewalls that protrude toward a lowest distal end of the inlet mixer. Fasteners penetrating the flanges provide a biasing load on the diffusers by being tightened to press against an upper crown on the diffuser. One or more flanges may be used. Laterally disposed gaps between the flanges may provide a clearance for guide ears of the diffuser to fit between the flanges.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Vibration reduction techniques for jet pump slip joints
InactiveUS20120219103A1Reduce vibrationImprove stabilityNuclear energy generationJet pumpsEngineeringLeakage flow
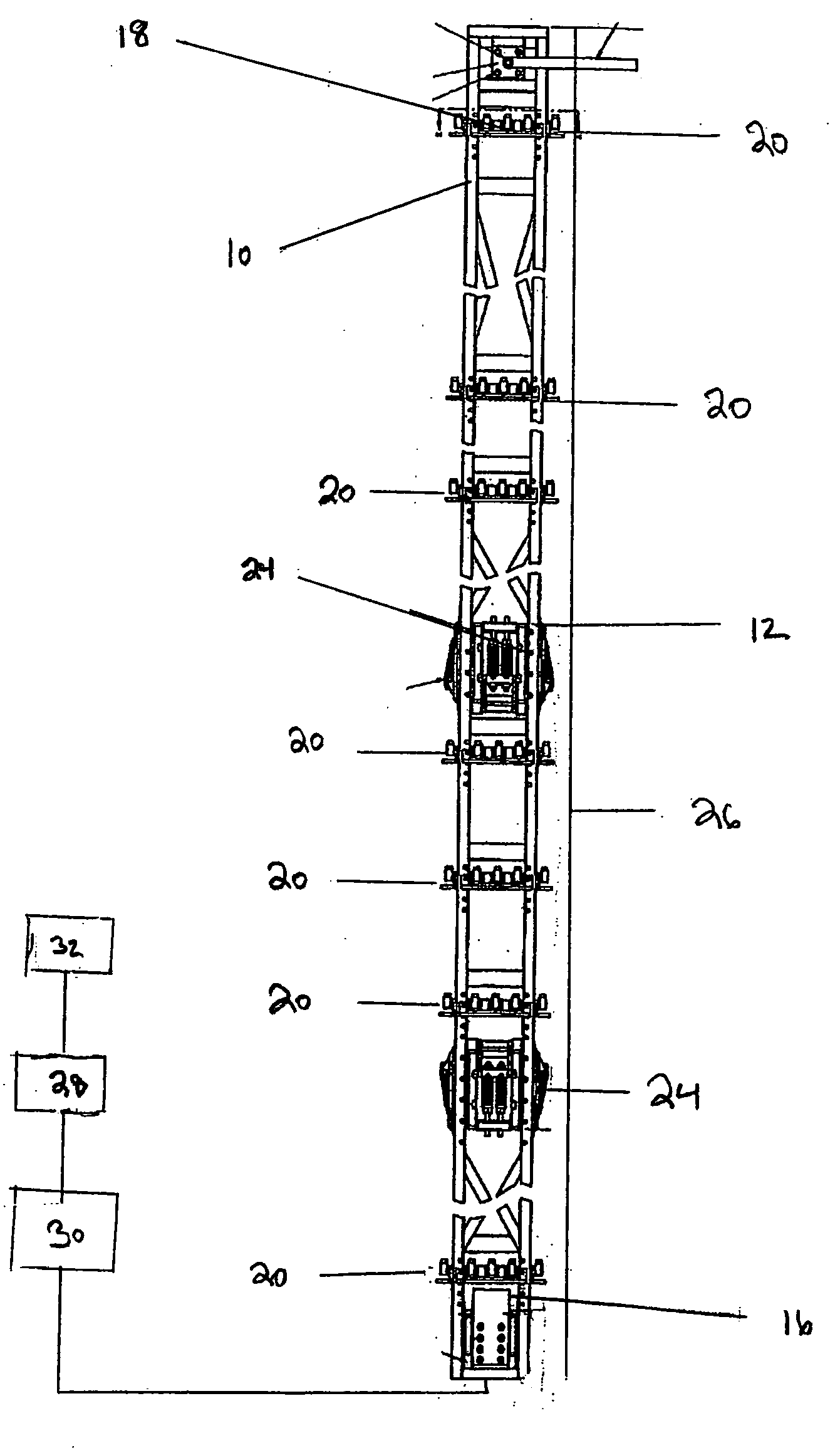
A method for retrofitting a boiling water reactor is provided. The method includes removing a mixing chamber from a slip joint defined by a diffuser and the mixing chamber, the mixing chamber having an inner surface and a bottom edge directing flow to the diffuser such that a recirculation zone at an entrance to the slip joint creates a diverging effective path for the leakage flow entering the slip joint. The method also includes providing a new inner surface and new bottom edge, the new inner surface and the new bottom edge being reshaped to decrease the size of the recirculation zone. A jet pump is also provided.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
Method and apparatus for repairing a core spray downcomer pipe slip joint coupling
A slip joint clamp is disclosed which structurally replaces cracked welded joints in the core spray downcomer slip joint coupling, which is part of the lower portion of internal core spray piping internal to a reactor vessel of a Boiling Water Reactor plant. The internal piping delivers core spray cooling water to the reactor core region. The clamp assembly consists of a primary clamp housing and a secondary clamp housing, which are rotationally joined together by a hinge assembly including a hinge pin. The clamp assembly is installed at a desired elevation relative to the downcomer slip joint, and then secured to the downcomer piping by installing coupling bolts and associated coupling bolt keeper nuts that hold the primary and secondary clamp housings in a facing relationship to one another around the downcomer slip joint.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
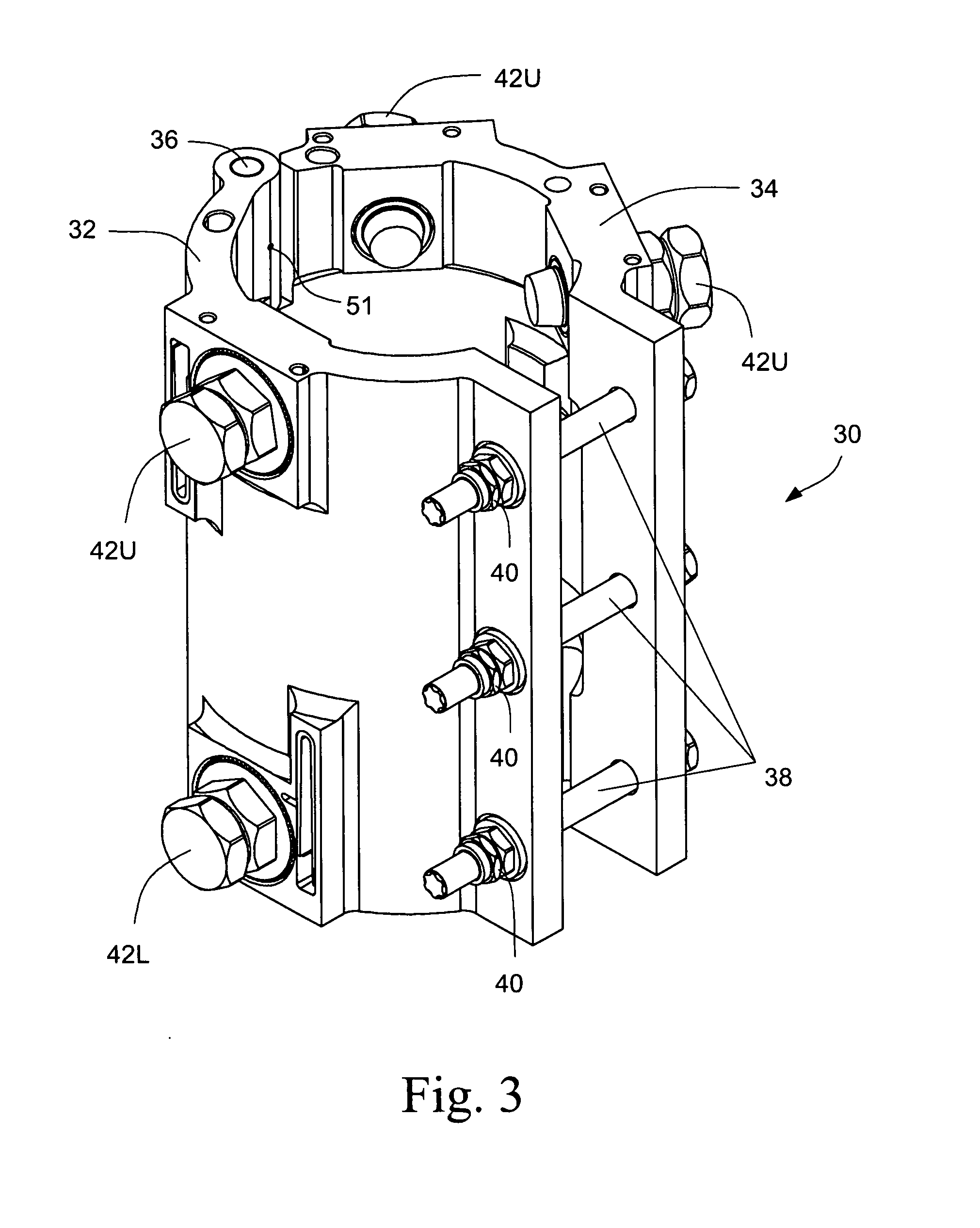
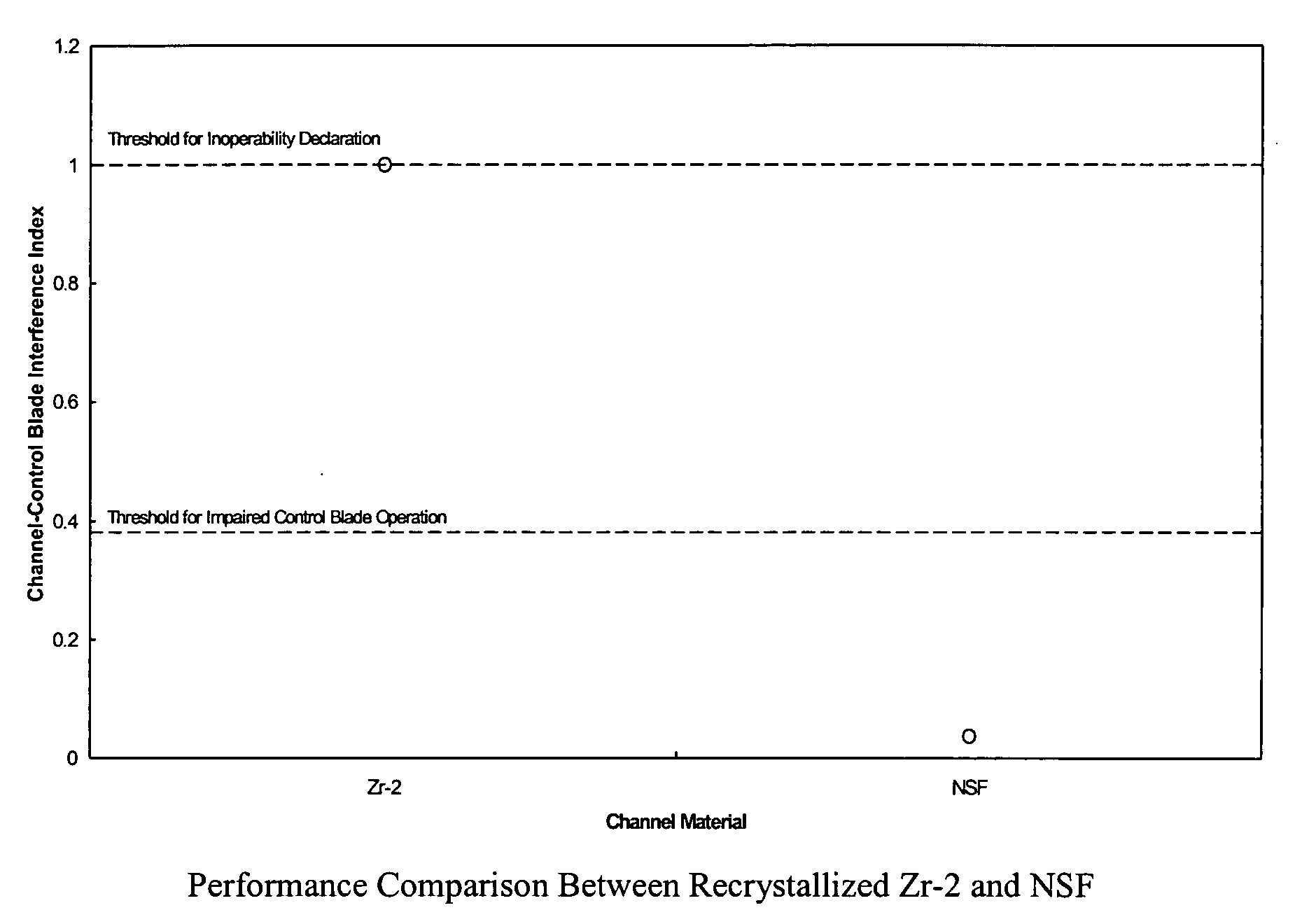
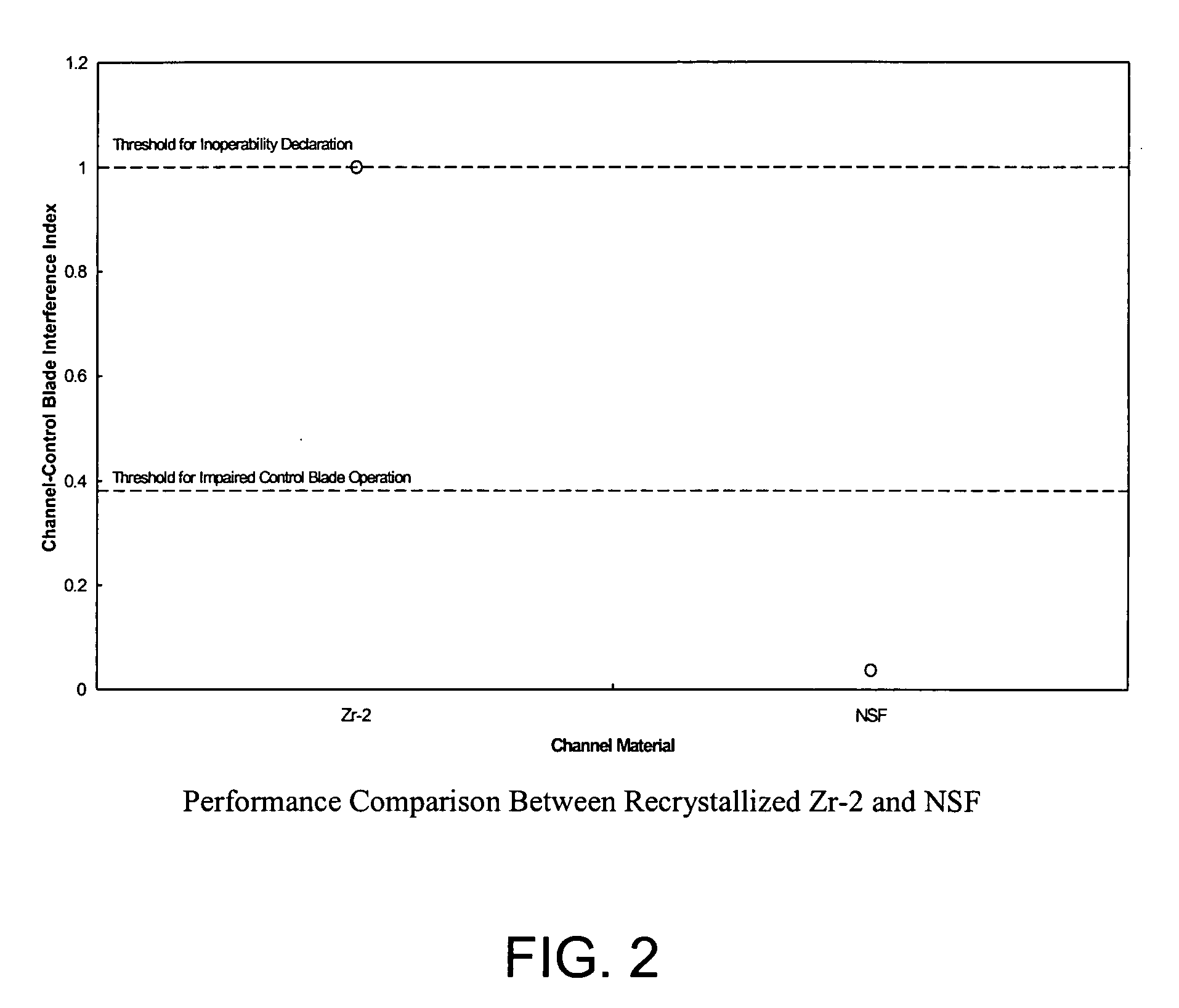
LWR flow channel with reduced susceptibility to deformation and control blade interference under exposure to neutron radiation and corrosion fields
ActiveUS20070153963A1Reduce the possibilityReduce sensitivityNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsRadiation fieldNeutron radiation
A zirconium alloy suitable for forming reactor components that exhibit reduced irradiation growth and improved corrosion resistance during operation of a light water reactor (LWR), for example, a boiling water reactor (BWR). During operation of the reactor, the reactor components will be exposed to a strong, and frequently asymmetrical, radiation fields sufficient to induce or accelerate corrosion of the irradiated alloy surfaces within the reactor core. Reactor components fabricated from the disclosed zirconium alloy will also tend to exhibit an improved tolerance for cold-working during fabrication of the component, thereby simplifying the fabrication of such components by reducing or eliminating subsequent thermal processing, for example, anneals, without unduly degrading the performance of the finished component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Boiling water heater
ActiveUS20170248343A1Easy to controlReduce trafficMechanical apparatusWater heatersWater flowBarrel Shaped
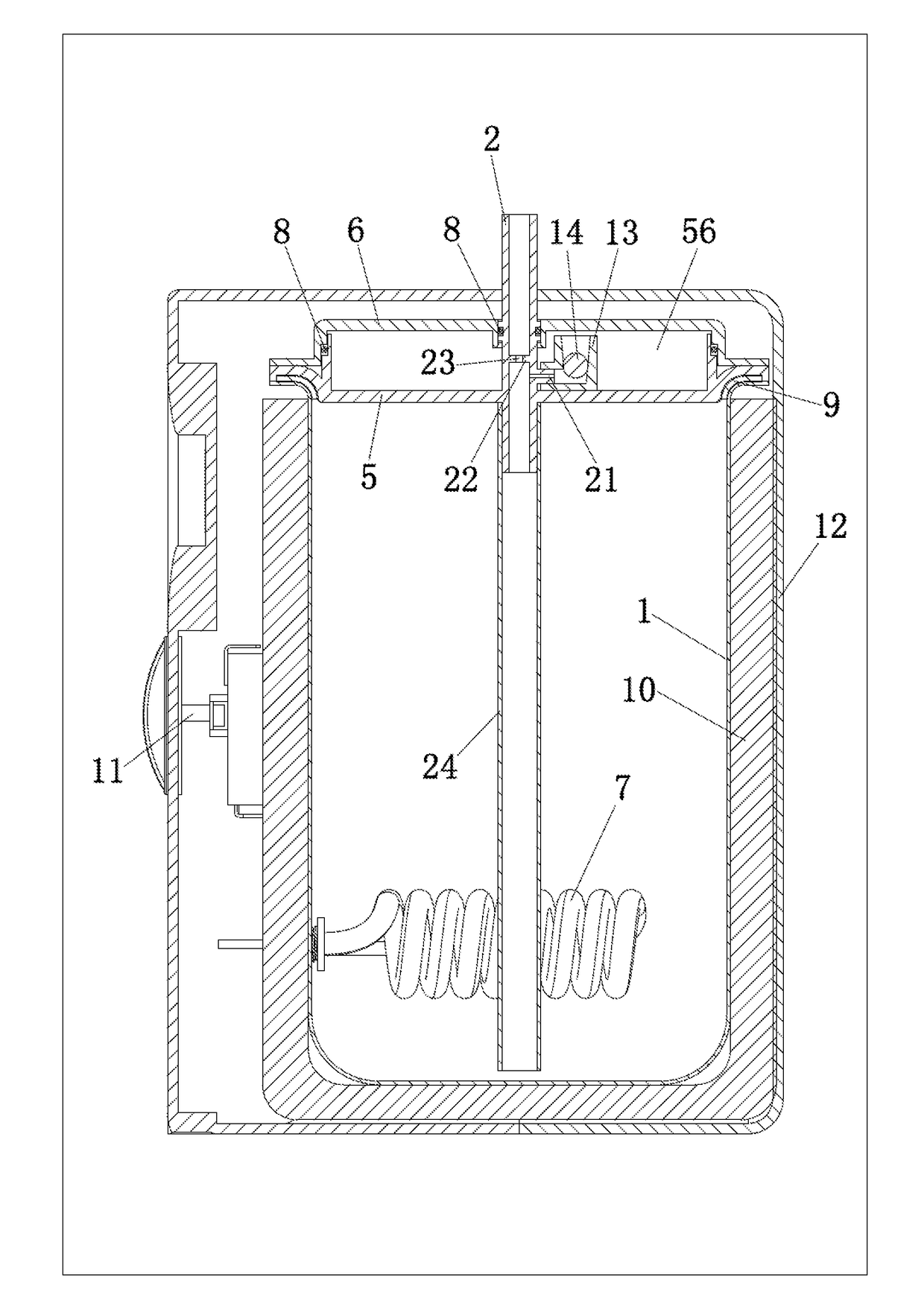
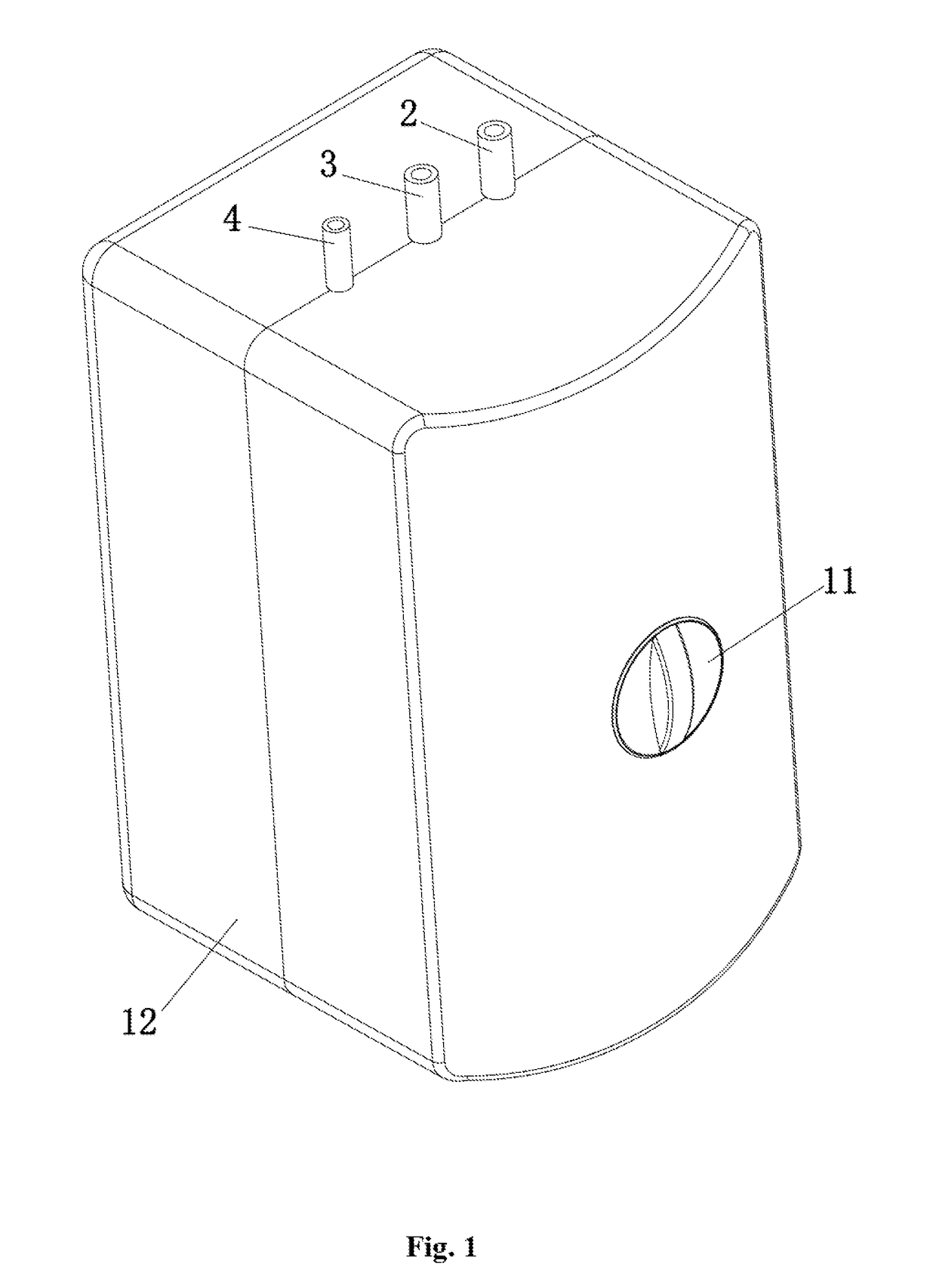
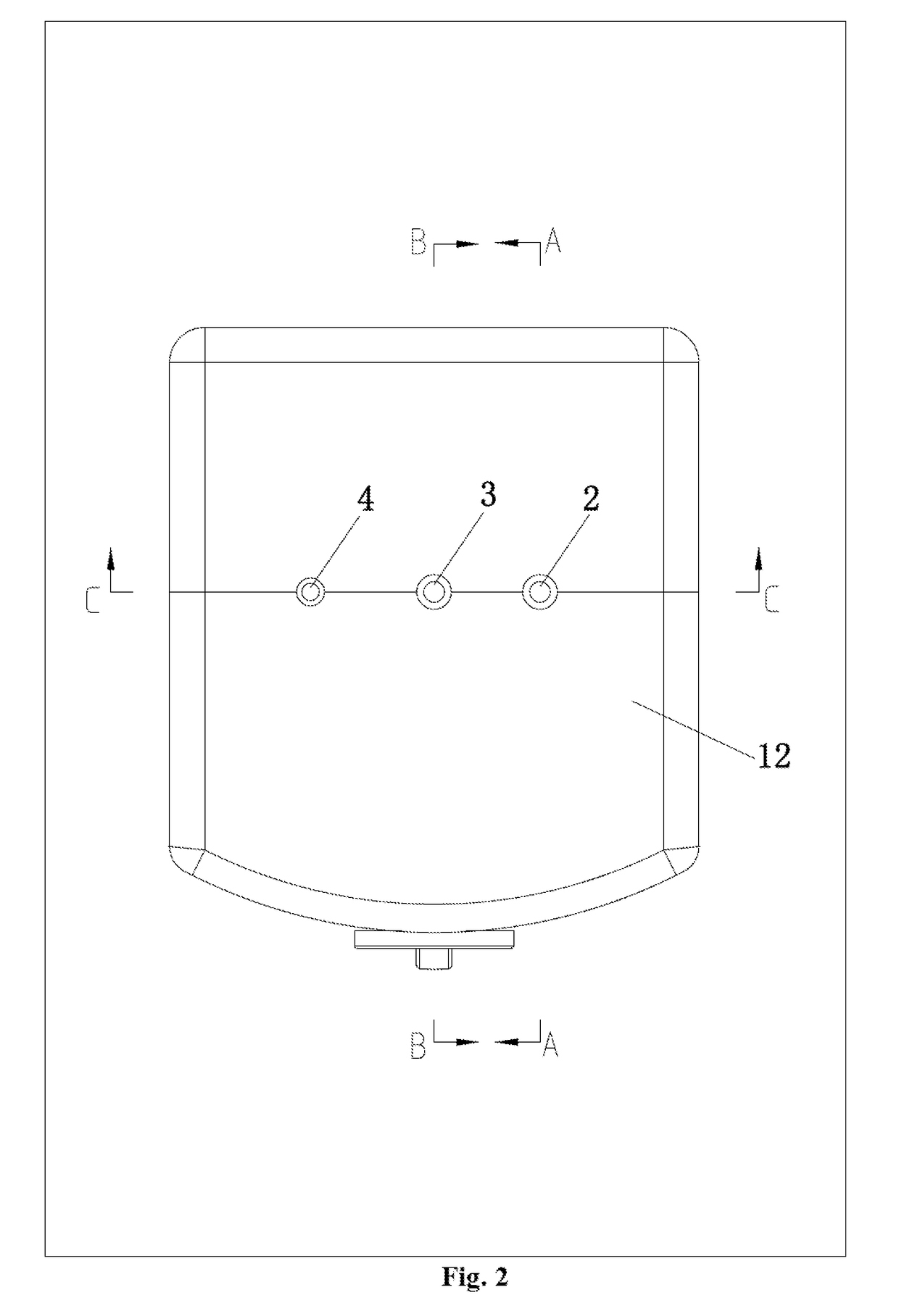
The invention discloses a boiling water heater, which includes a barrel shape internal tank body, a water inlet pipe, a water outlet pipe and a exhaust pipe, the upper end of the tank body, fixedly and hermetically connect to the first upper cover, the first upper cover is fixedly and hermetically connected to the second upper cover. One cavity is formed between the first and second upper covers, water inlet pipe passes through the second upper cover. An exhaust hole is set on the inner wall of water inlet pipe to connect to the cavity, a separation plate extended to the middle which is above the exhaust hole on water inlet pipe's internal wall. The invention has the characteristics of convenient installation and disassembly, convenient cleaning, and can ensure the quality of water flows out, and the production cost is low, and very safe for use.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER YOUYANG TECH CO LTD
Fuel channel characterization method and device
InactiveUS20060291608A1Fast and accurate mannerAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNuclear energy generationUltrasonic sensorEngineering
An apparatus to measure external dimensions of a fuel channel of a boiling water reactor, having a rigid frame which has a lower seat to accept a nozzle of a nuclear fuel assembly, the rigid frame extending an entire length of the nuclear fuel assembly, an inspection arrangement including ultrasonic transducers placed upon the rigid frame, the ultrasonic transducers supported by the rigid frame, the ultrasonic transducers configured to generate and receive ultrasonic signals imparted into a medium and generate an electrical signal upon receipt of the ultrasonic signal, a signal processing arrangement configured to evaluate electrical signals received from the inspection arrangement, and a series of leads connected to the arrangement of ultrasonic transducers, the series of leads taking the electrical signals generated by the inspection arrangement of ultrasonic transducers and transporting the electrical signals from the ultrasonic transducers to the signal processing arrangement.
Owner:DAVIS MICHAEL D +3
Monobloc fuel element and boiling water and fast spectrum nuclear reactor using such elements
InactiveUS6665366B2Increase the exchange surface areaFuel elementsNuclear energy generationParallel plateEngineering
A single piece fuel element and fast spectrum boiling water reactor using such a single piece fuel element. The single piece fuel element is formed from coated fissile particles embedded in a matrix made from a material such as SiC that is inert to all fissile and fertile heavy nuclei and to the coolant fluid circulating in and around this element. Furthermore, the fuel element includes parallel plates delimiting spaces between them. A ratio between the thickness of the plates and the width of the spaces is set so that the fuel element can be put in fast spectrum or thermal spectrum at will. An application of the single piece fuel element to a fast spectrum boiling water nuclear reactor operating with natural circulation in which the above mentioned ratio is approximately equal to 1 enables a high consumption of plutonium.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Steam separator and nuclear boiling water reactor including the same
A steam separation system includes a standpipe configured to receive a gas-liquid two-phase flow stream, a first diffuser configured to receive the gas-liquid two-phase flow stream from the standpipe, the first diffuser including a swirler configured to separate the gas-liquid two-phase flow stream, and a separation barrel configured to receive the gas-liquid two-phase flow stream from the swirler, the separation barrel including a rifled channel having orifices along an inner surface thereof.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com