Patents
Literature
514 results about "Microprocessor system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Precision illumination methods and systems
Owner:PHILIPS LIGHTING NORTH AMERICA CORPORATION
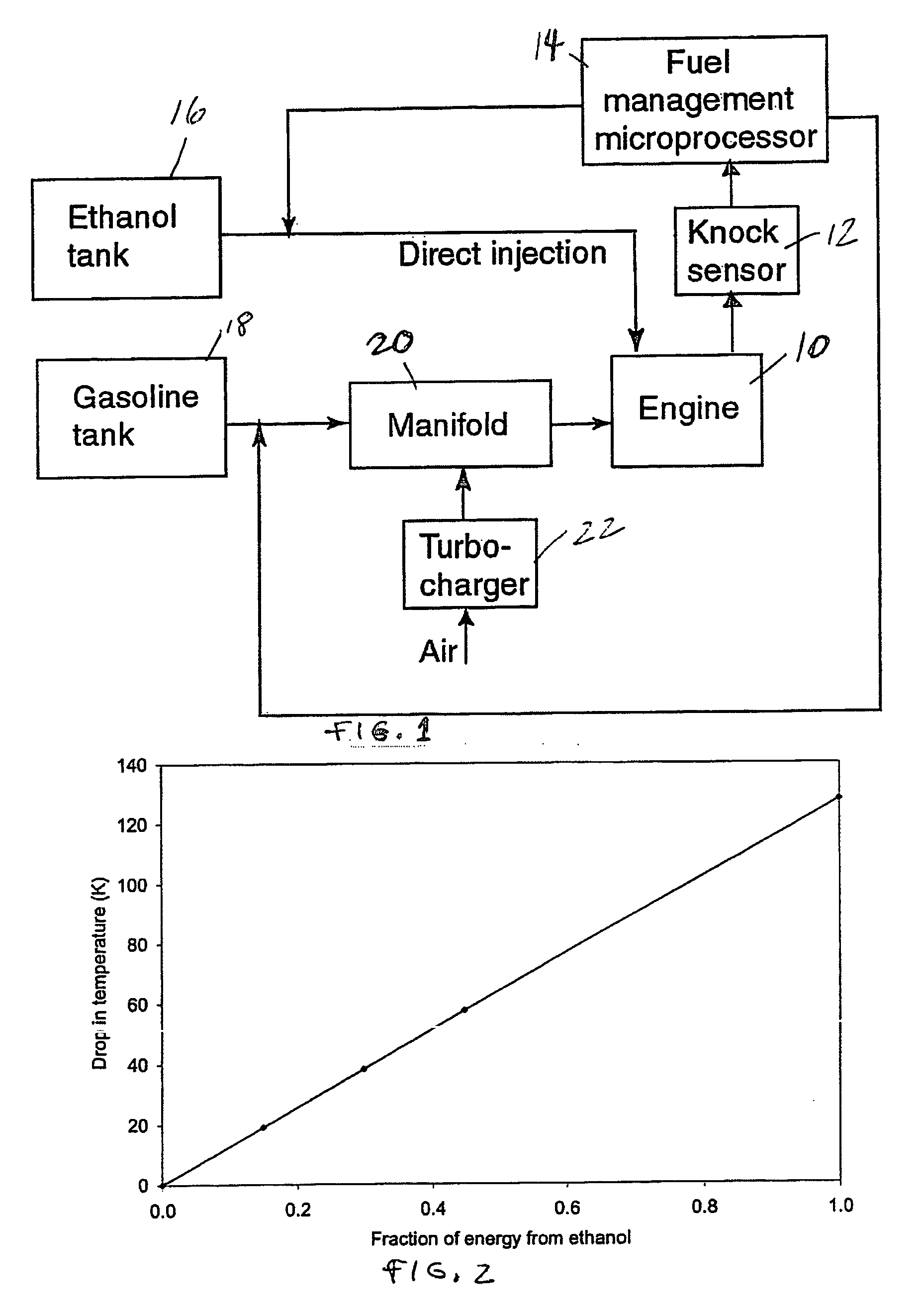
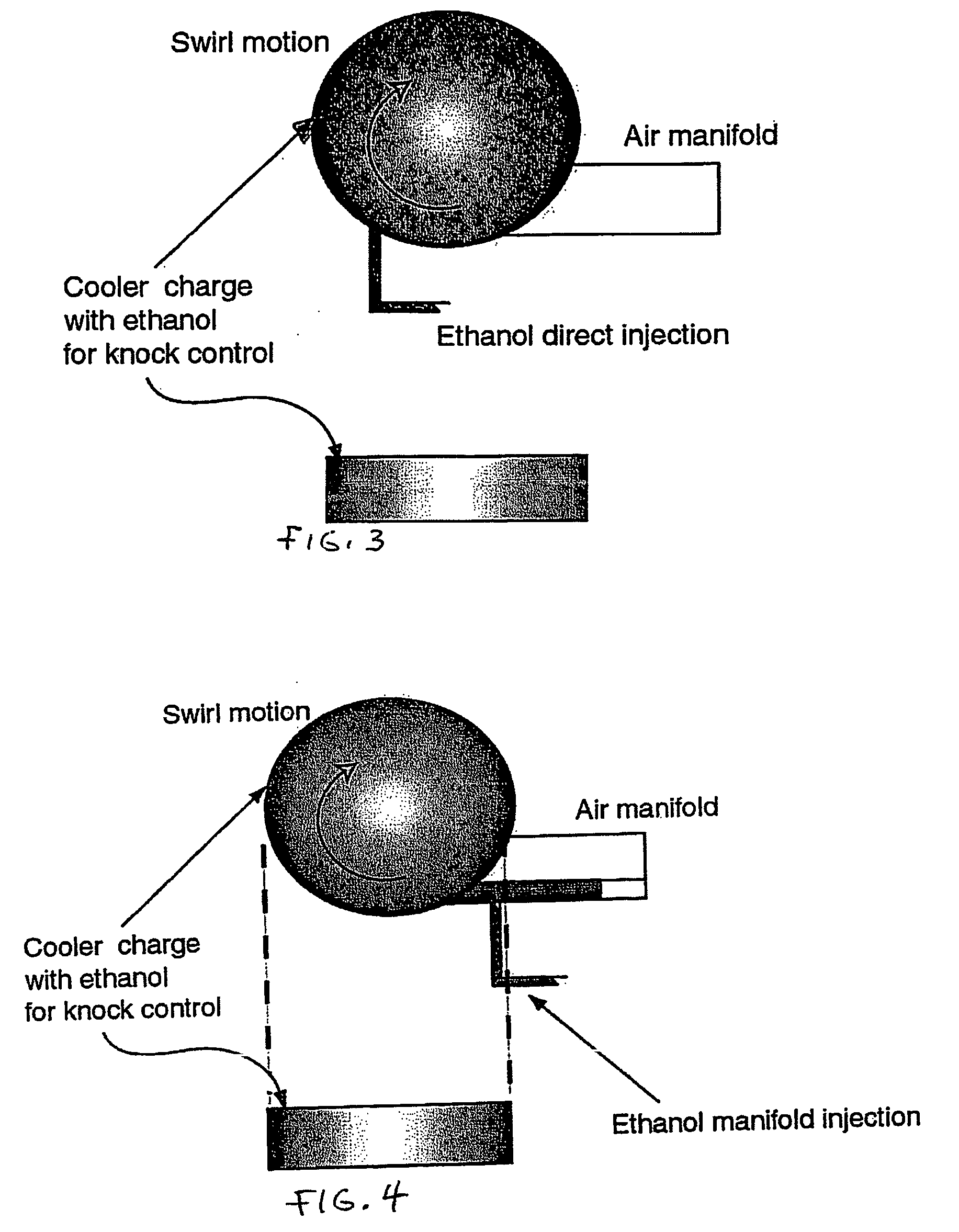
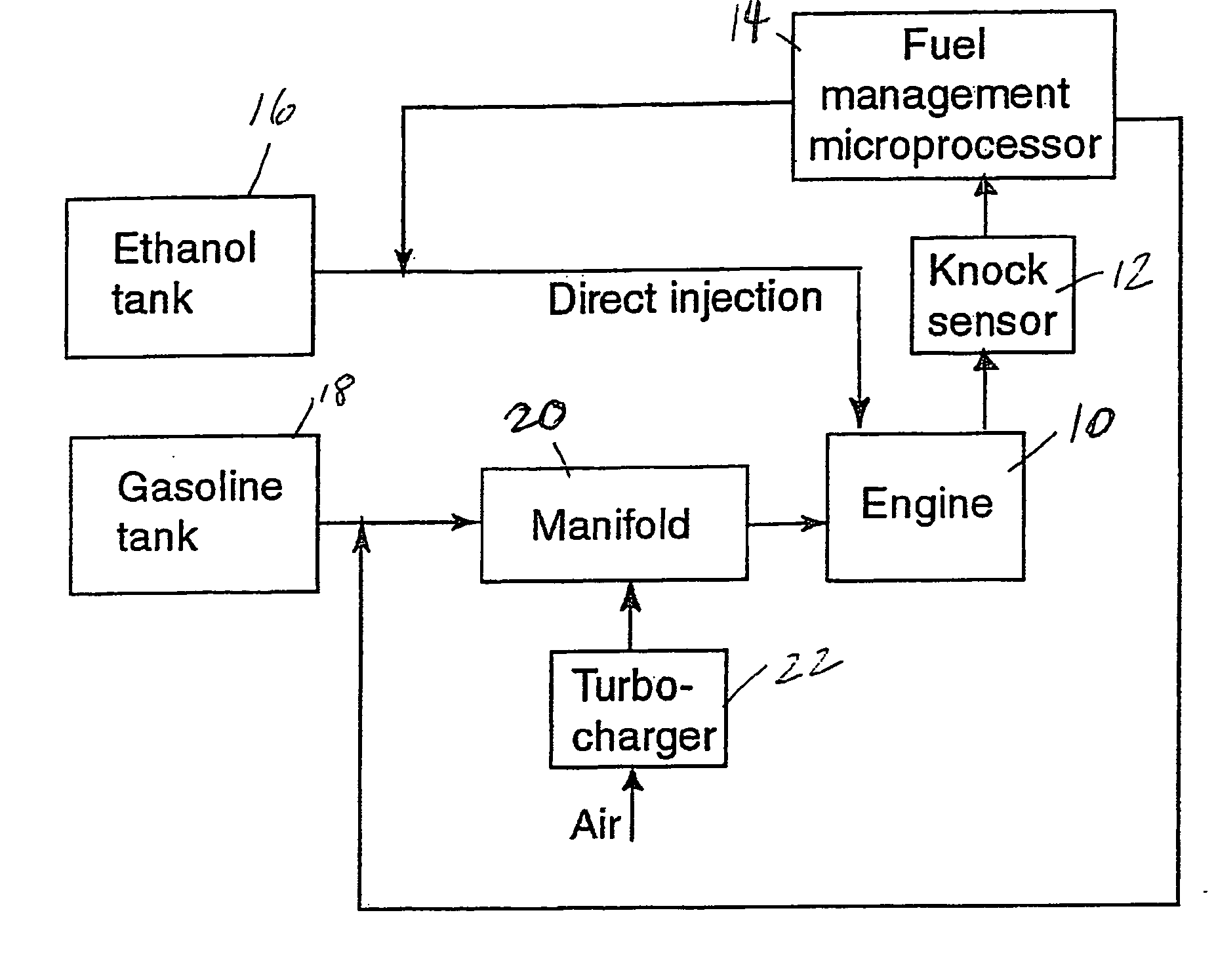
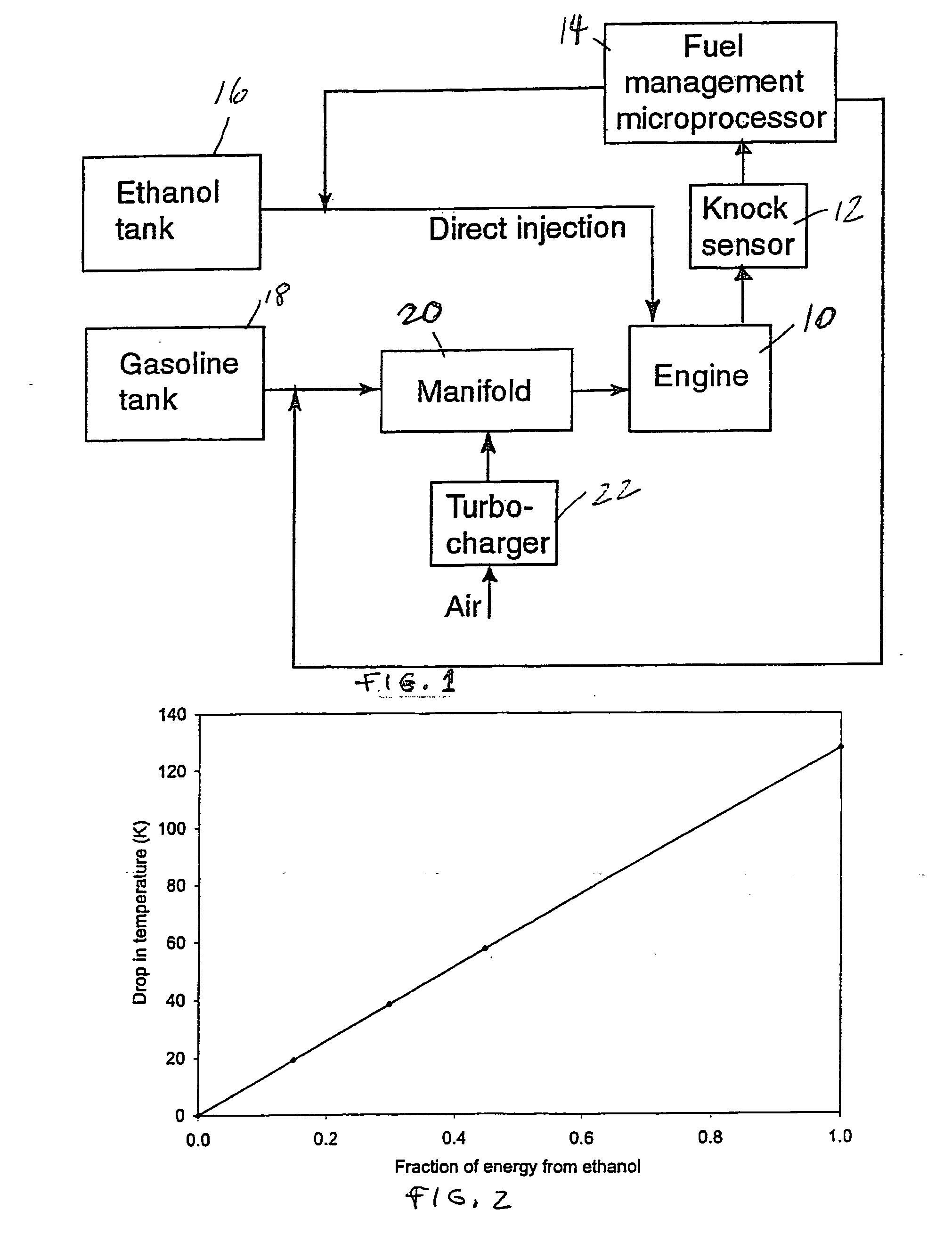
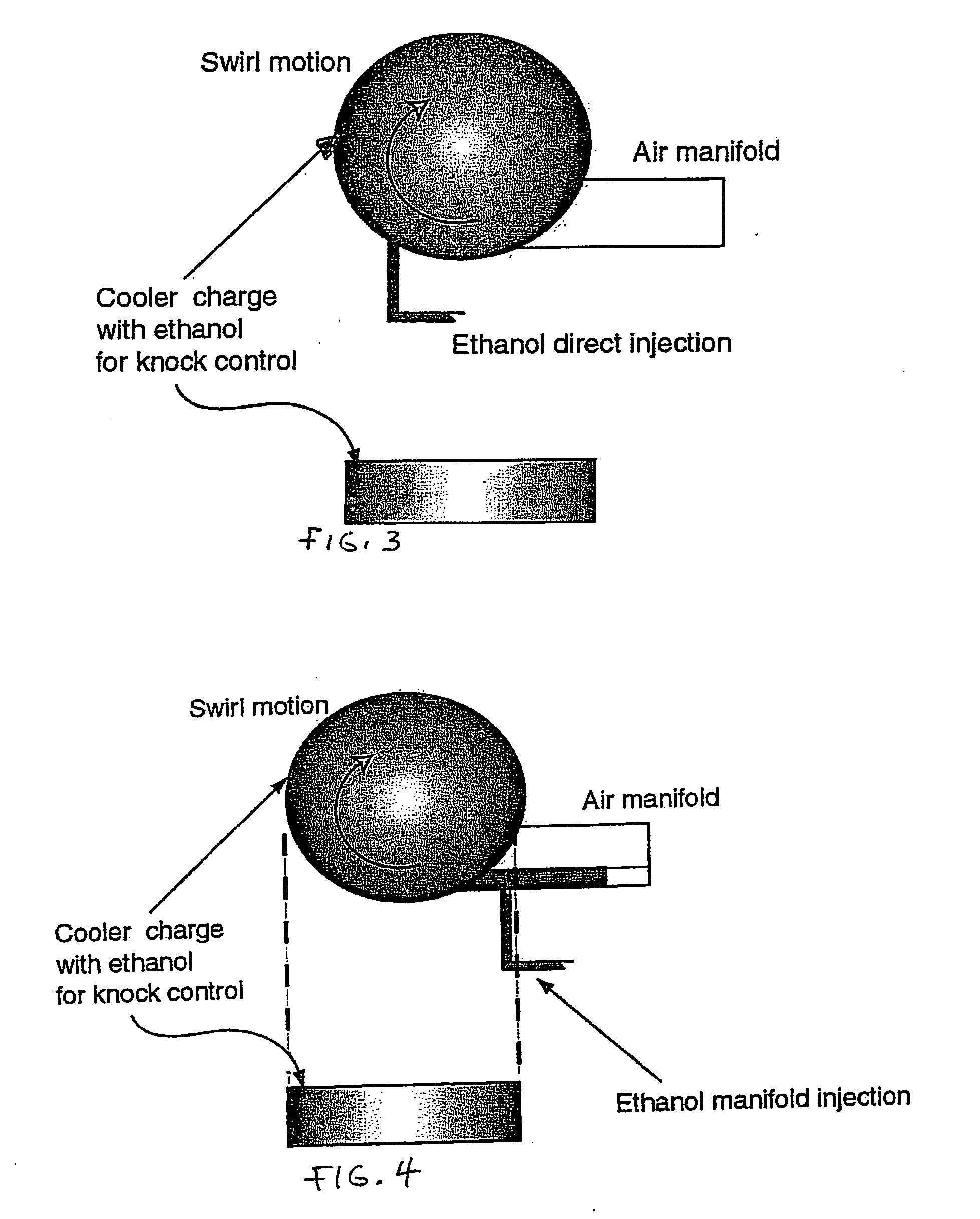
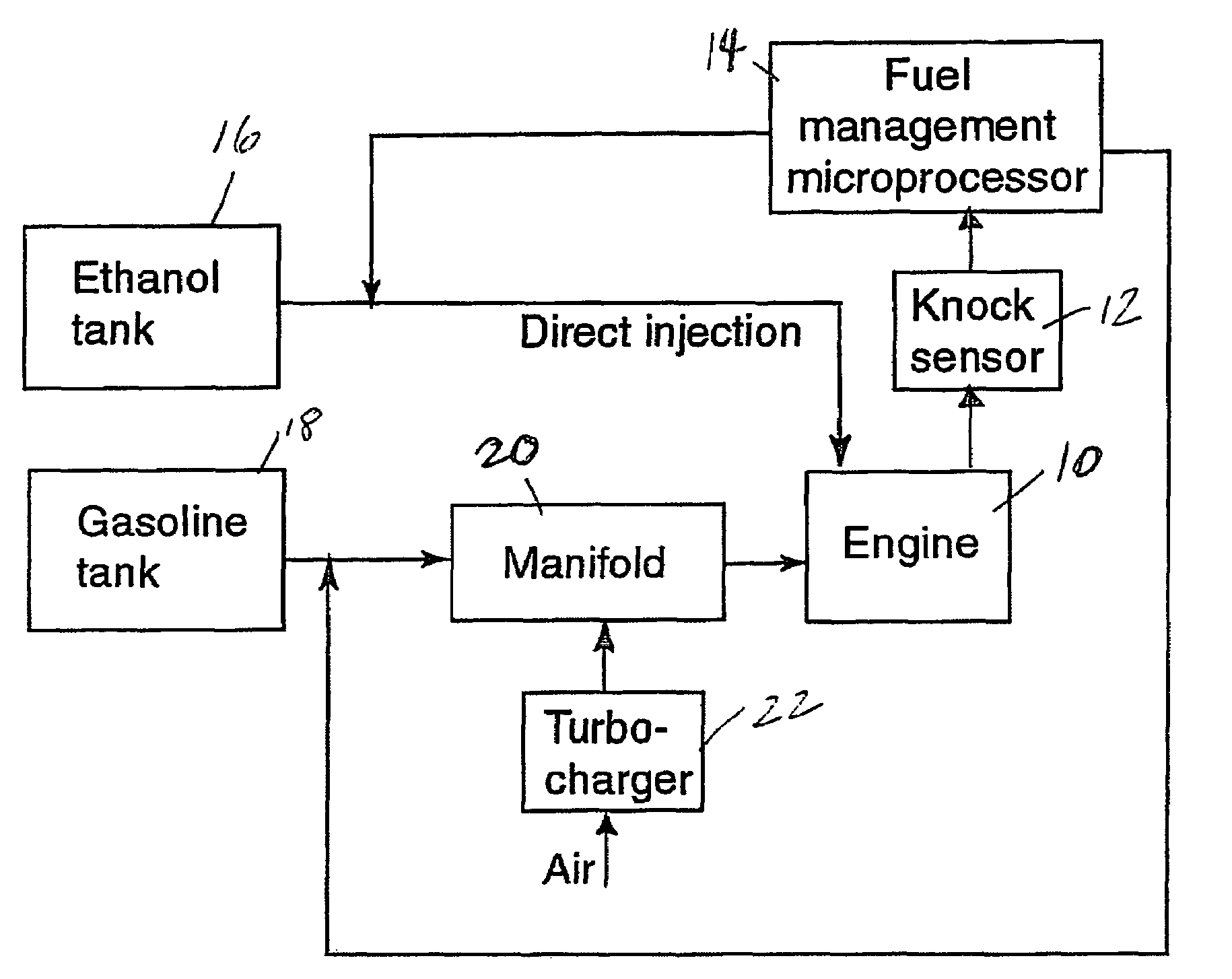
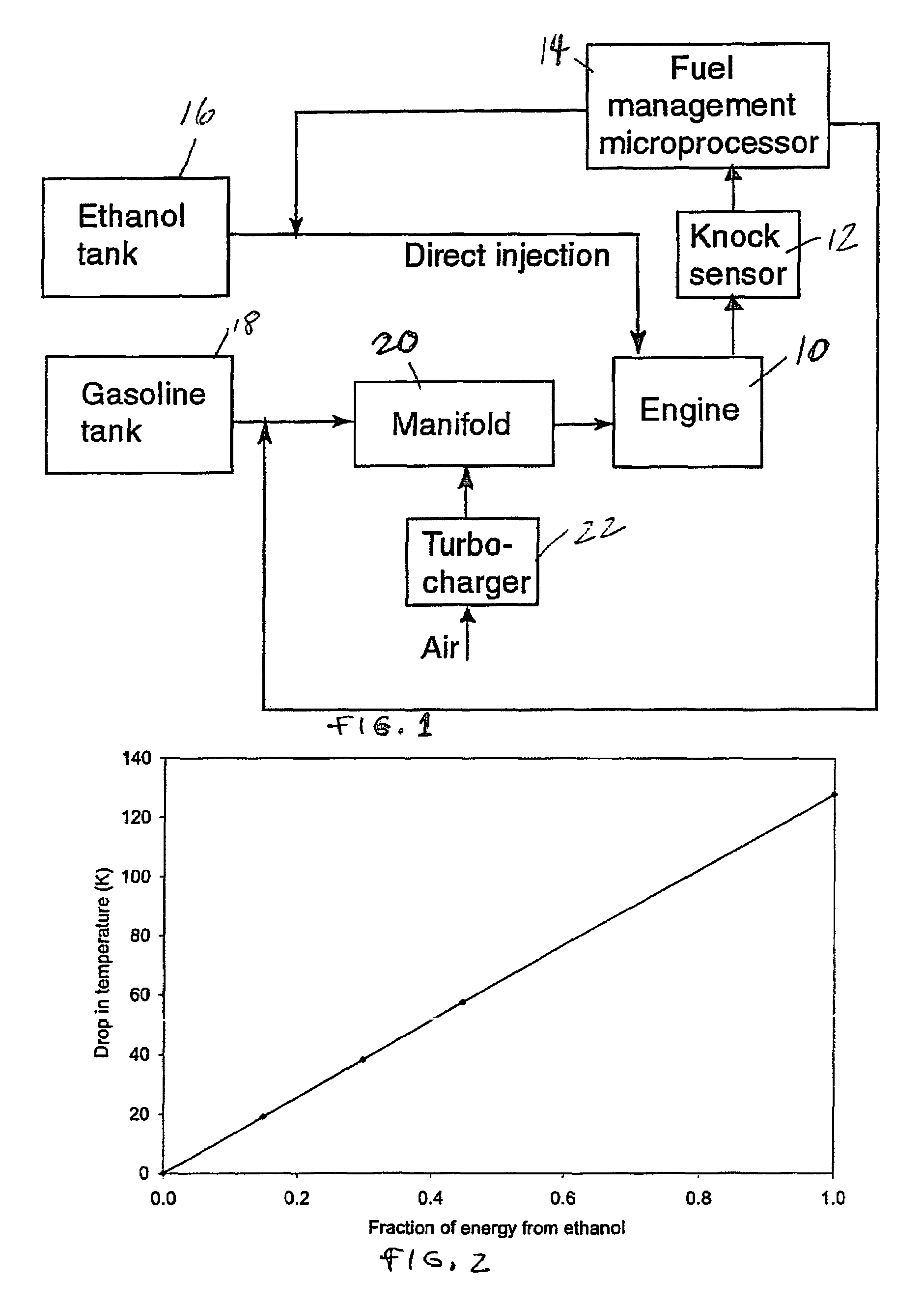
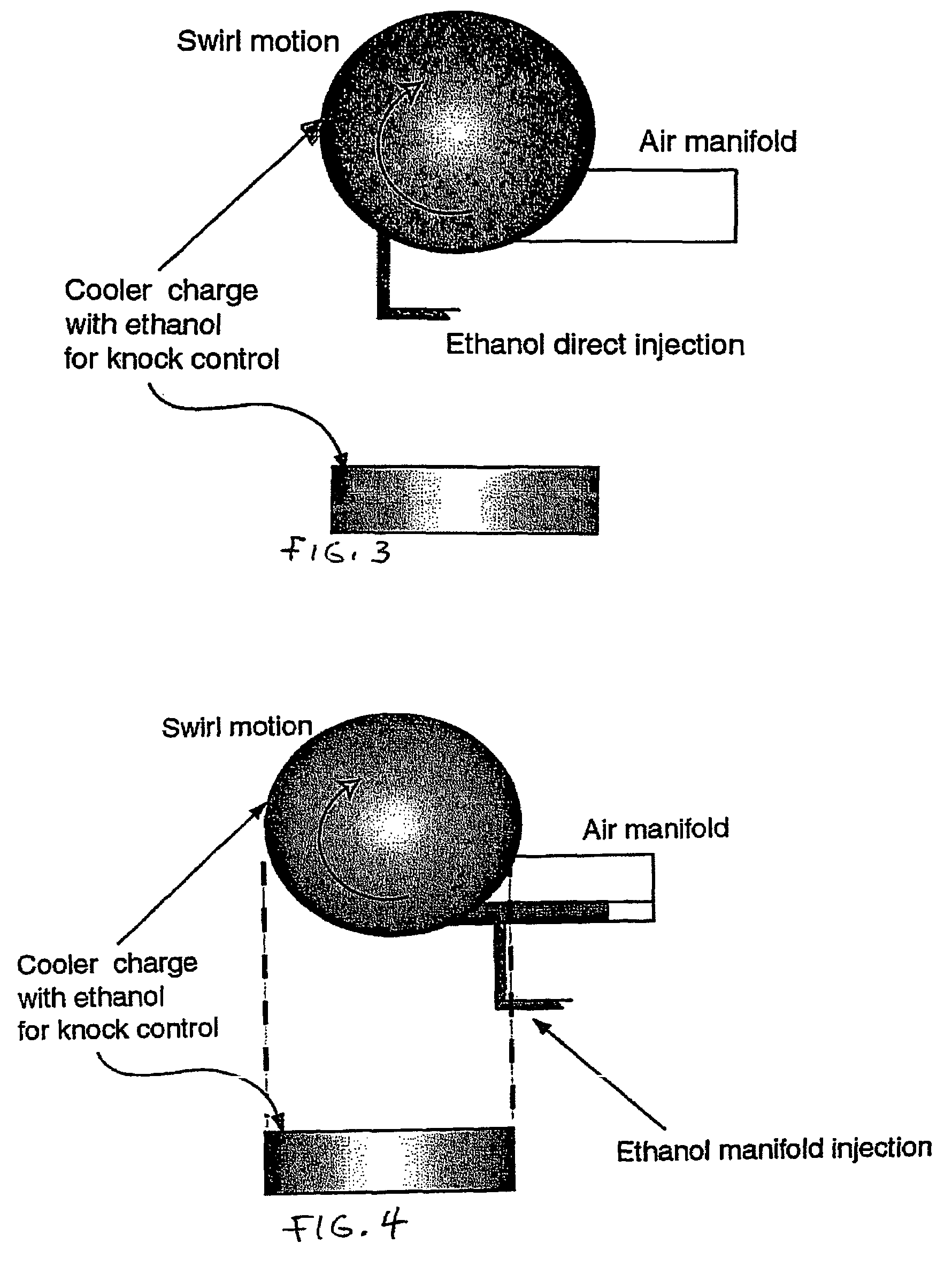
Fuel management system for variable ethanol octane enhancehment of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102145A1Increase heatMeet cutting requirementsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
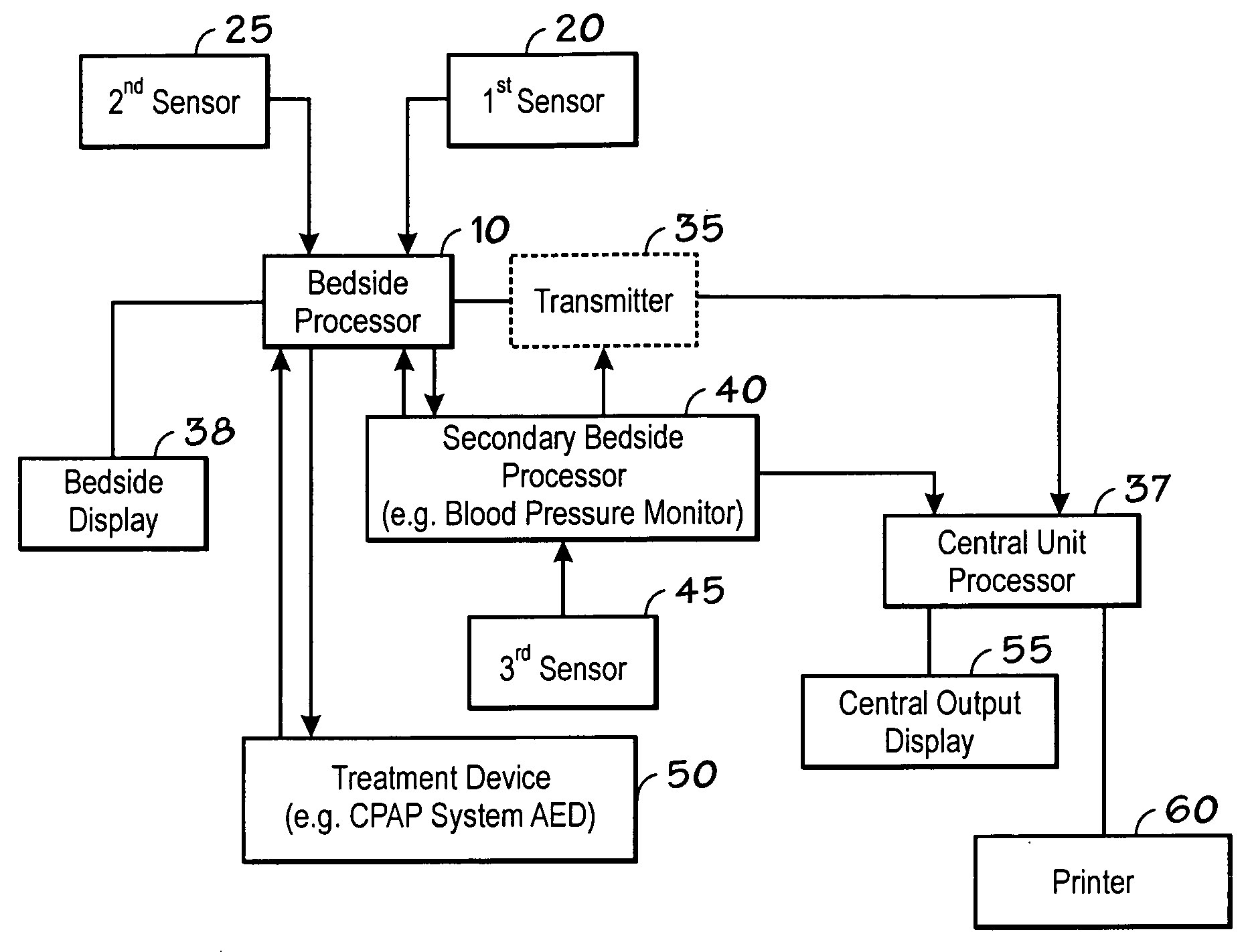
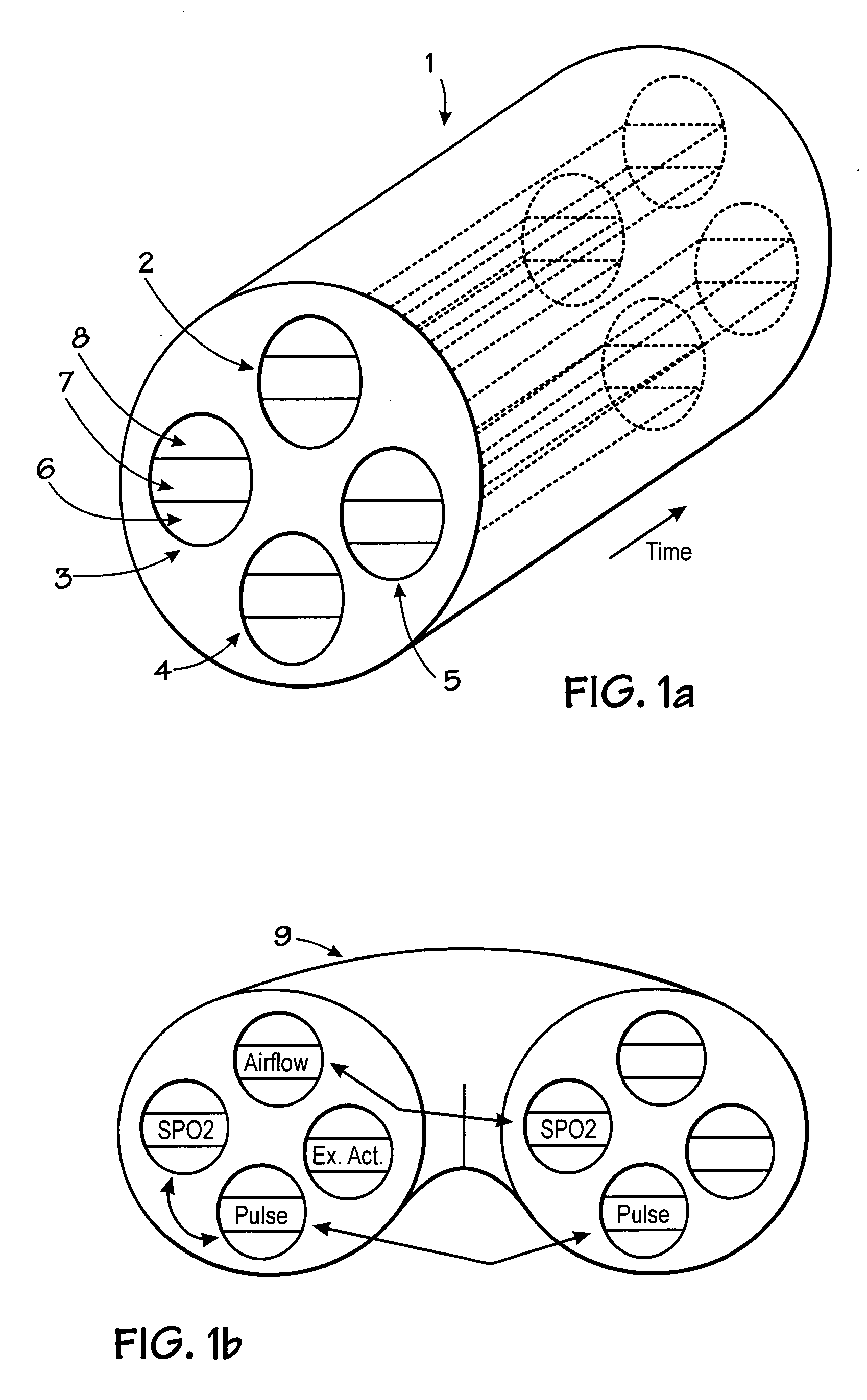
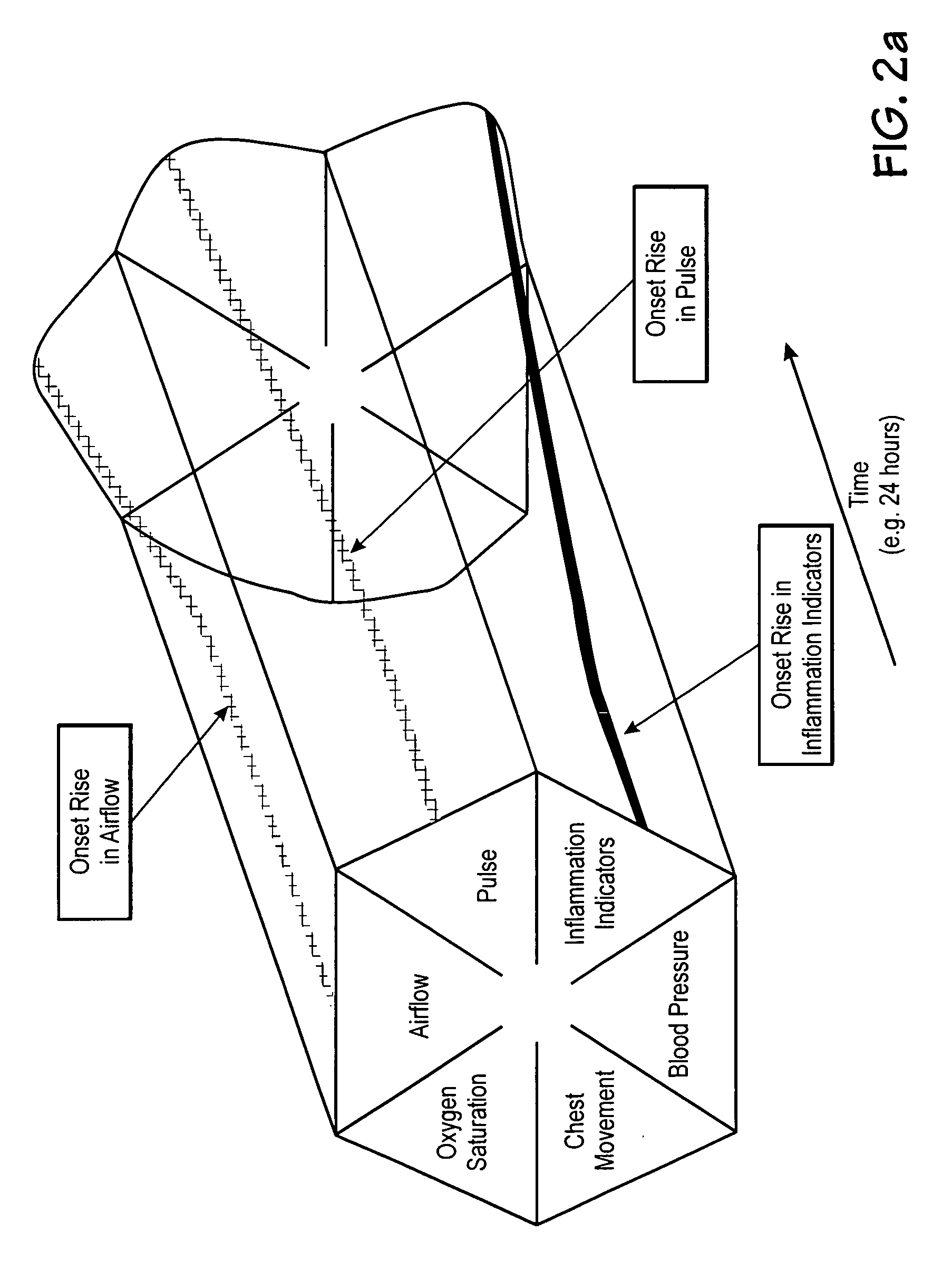
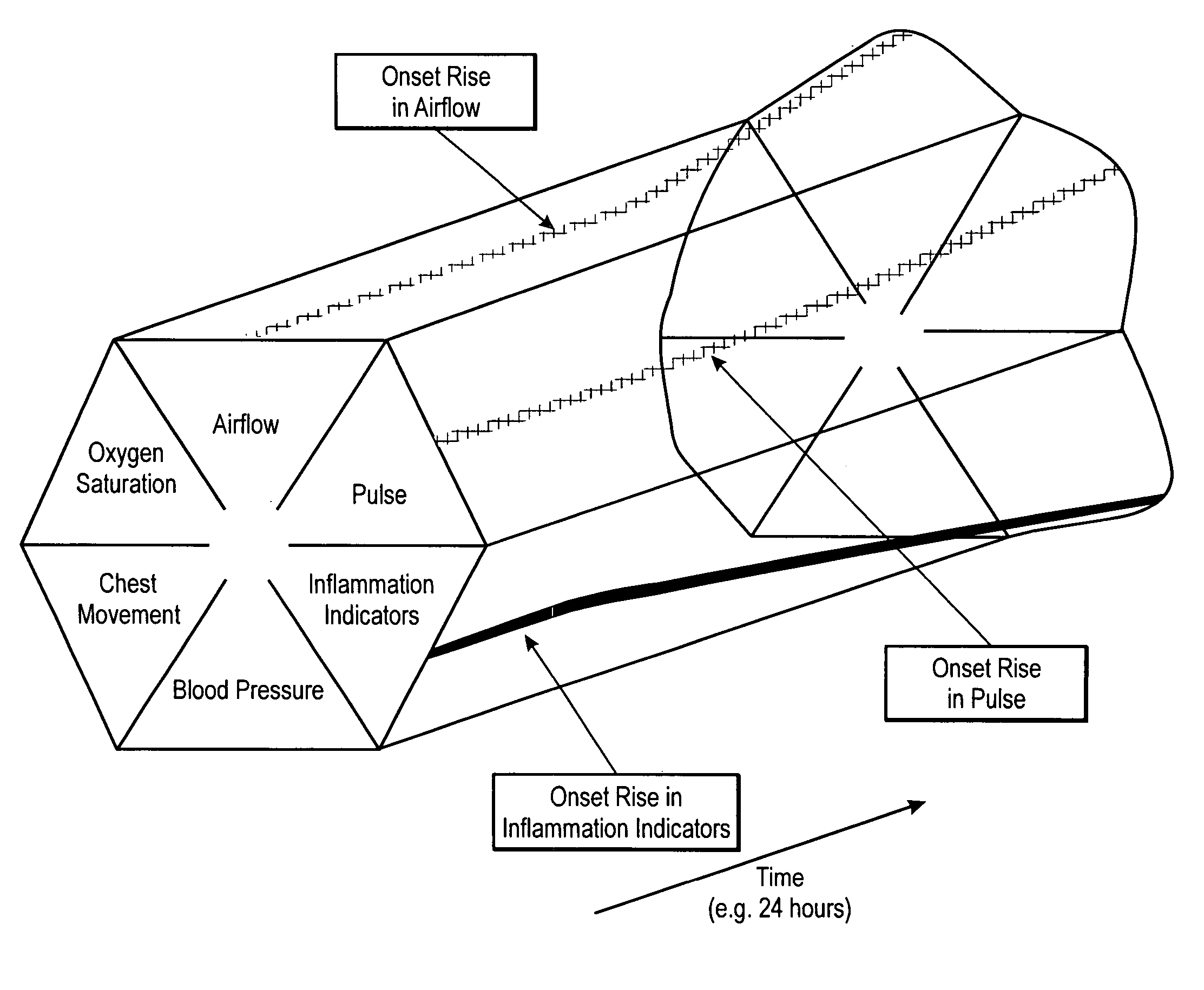
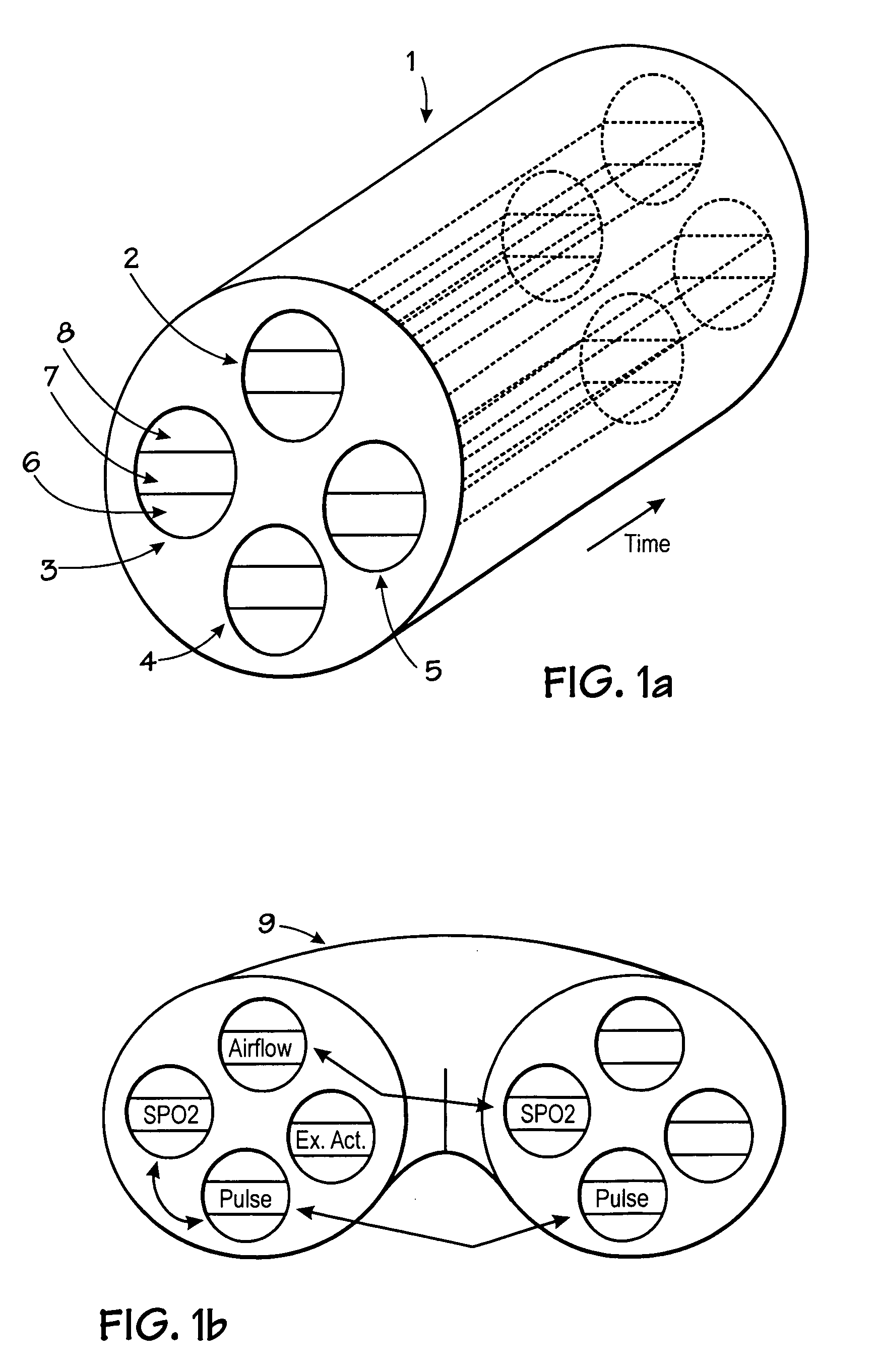
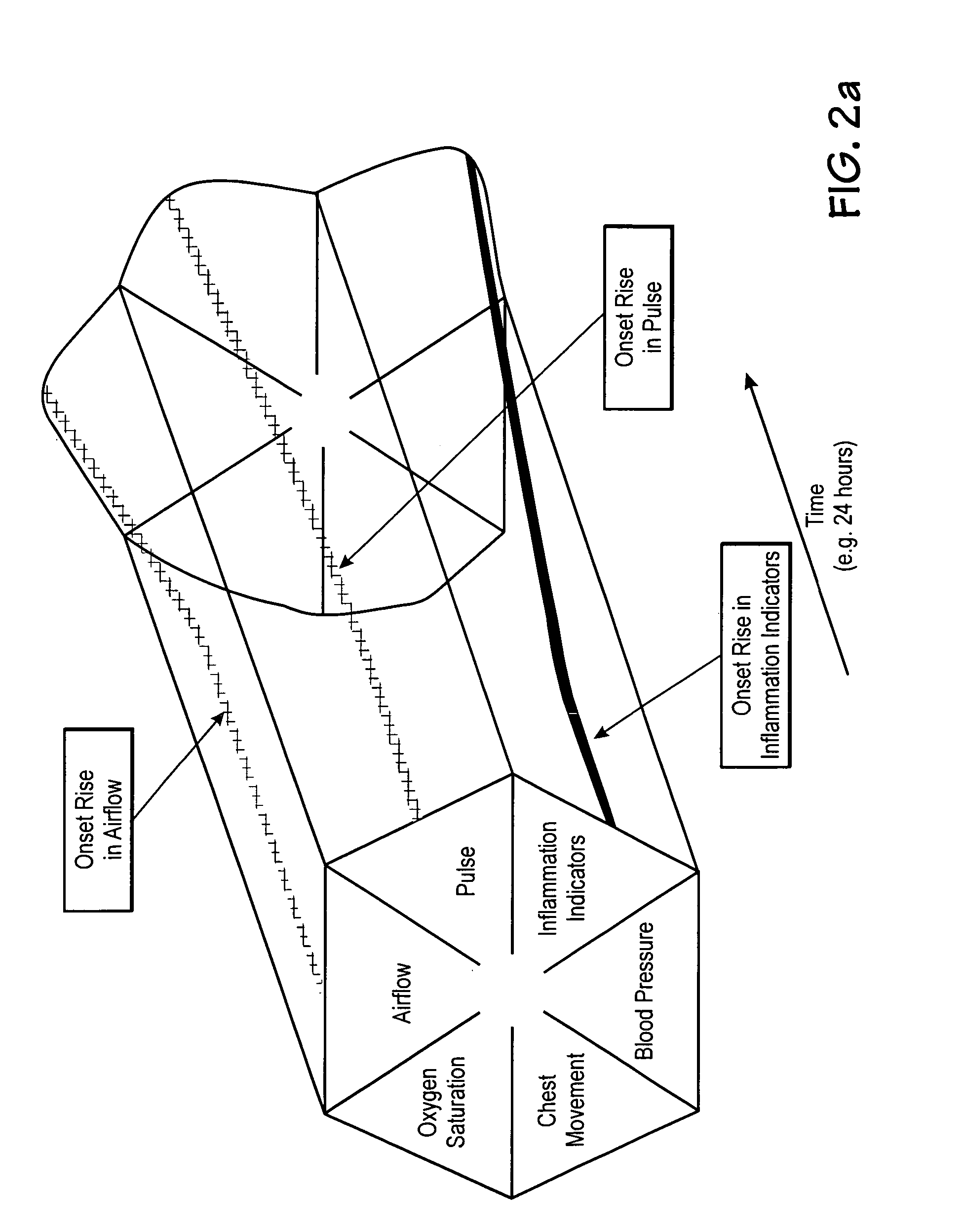
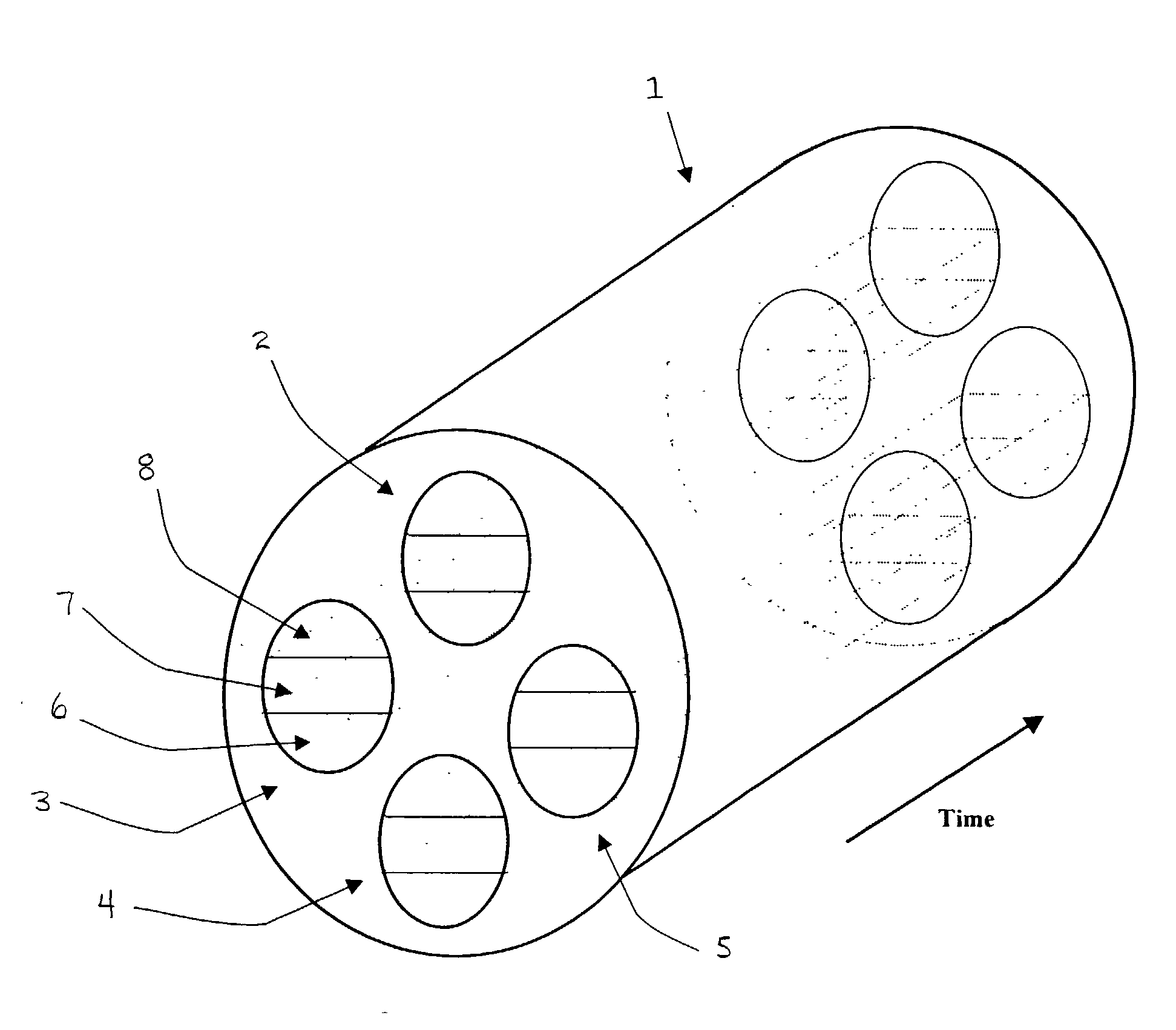
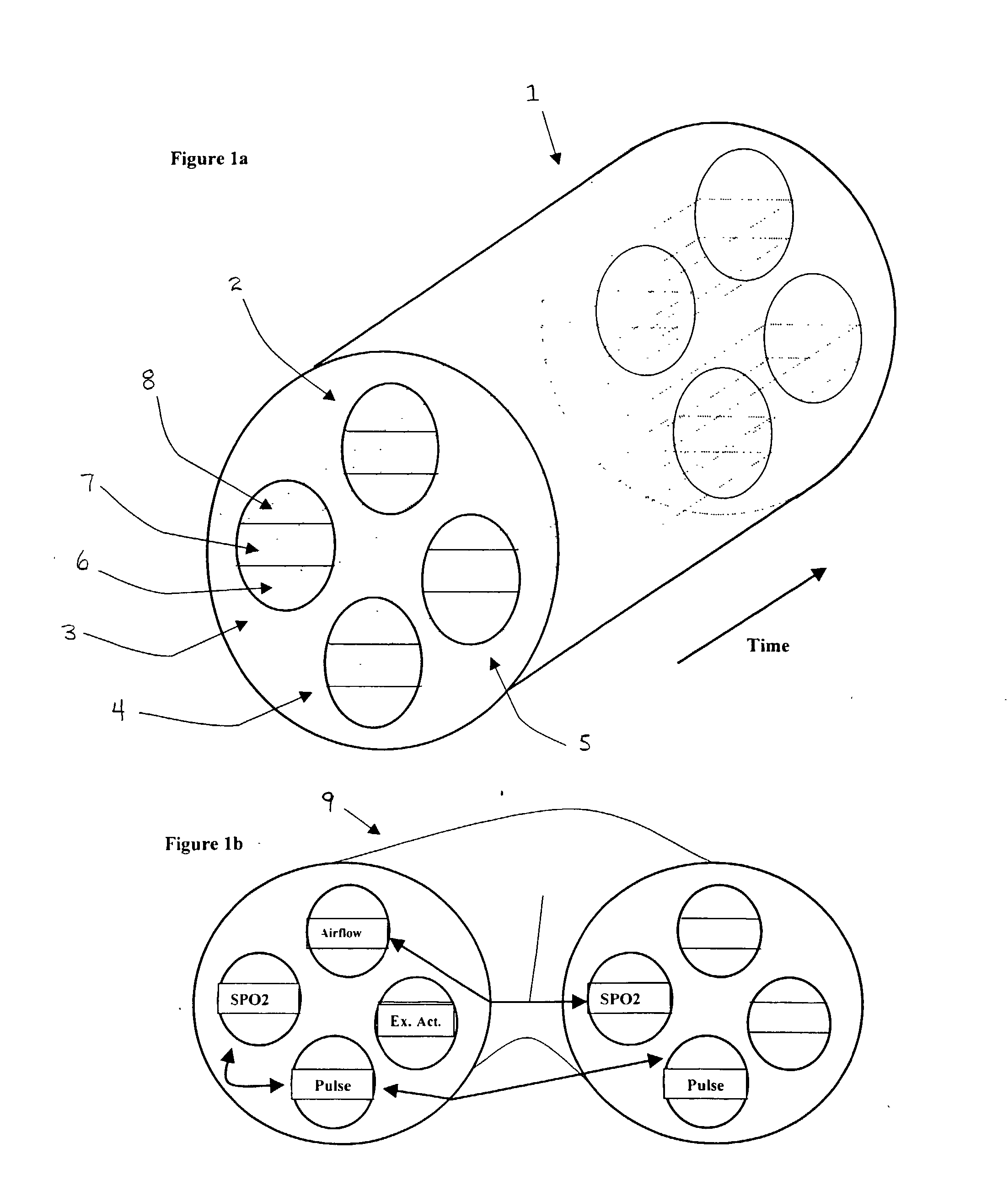
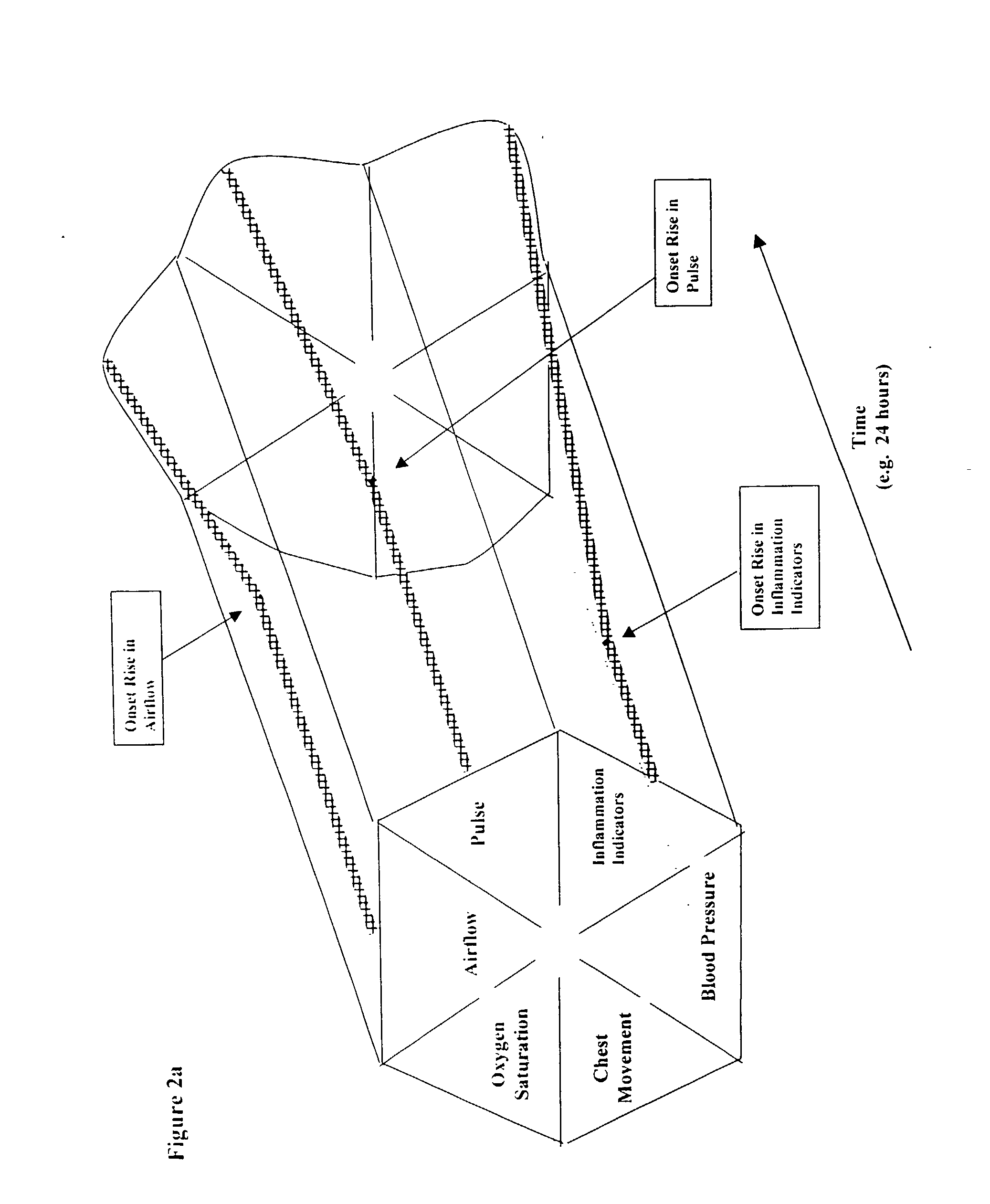
Microprocessor system for the analysis of physiologic and financial datasets
ActiveUS20070149860A1Delay is so severeAvoid delayMedical data miningEvaluation of blood vesselsTime domainObject based
A system and method for organization and analysis of complex and dynamically interactive time series is disclosed. One example comprises a processor based system for relational analysis of physiologic signals for providing early recognition of catastrophic and pathologic events such as pathophysiologic divergence. The processor is programmed to identify pathophysiologic divergence of at least one of first and second physiologic parameters in relationship to the other and to output an indication of the divergence. An object-based method of iterative relational processing waveform fragments in the time domain is described wherein each more complex waveform object inherits the characteristics of the waveform objects from which it is derived. The first physiologic parameter can be the amplitude and frequency of the variation in chest wall impedance or nasal pressure and the second parameter can be a measure or indication of the arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:LYNN LAWRENCE A +1
Fuel management system for variable anti-knock agent octane enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102146A1Increase heatReduces octane requirementElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
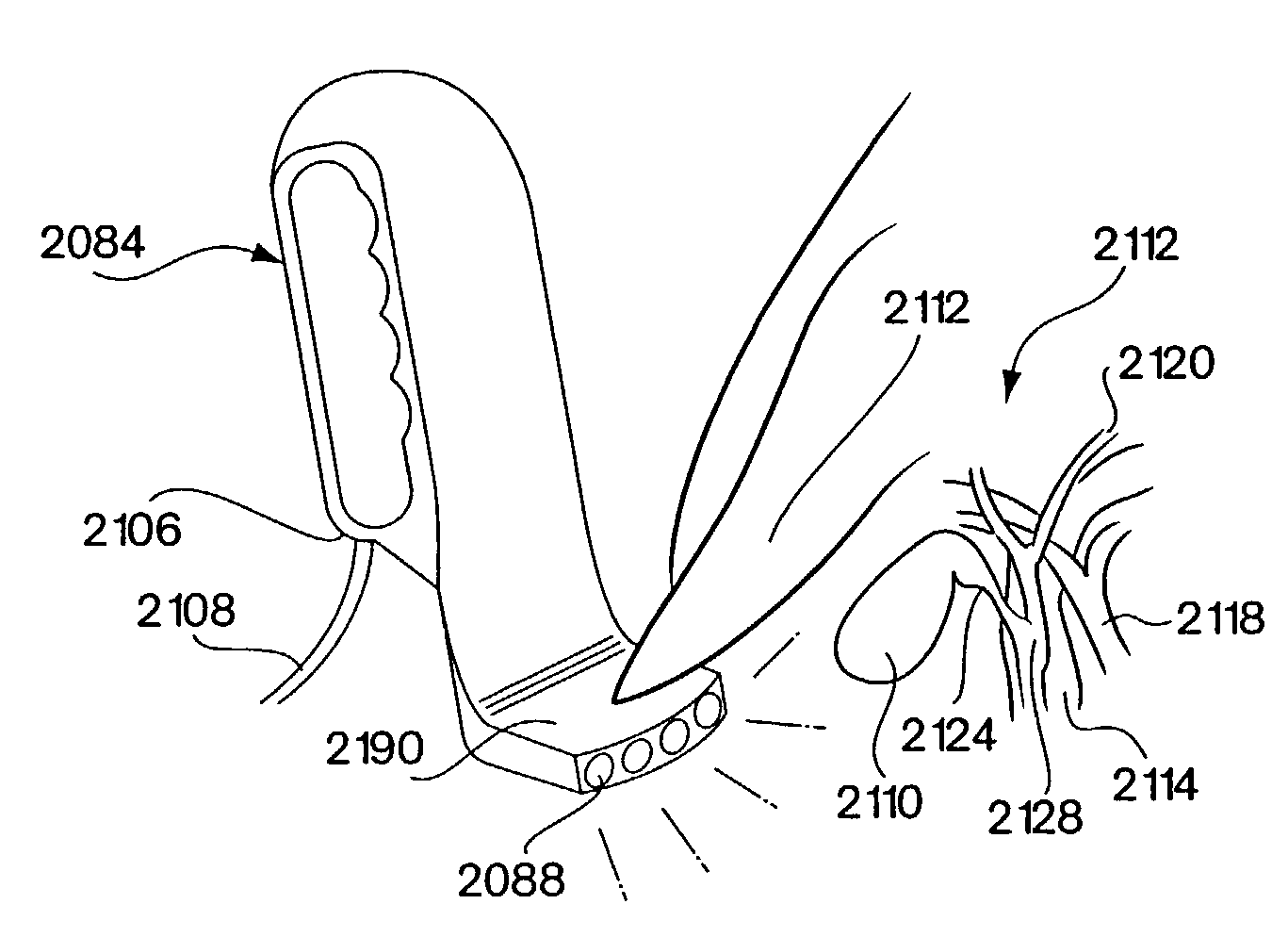
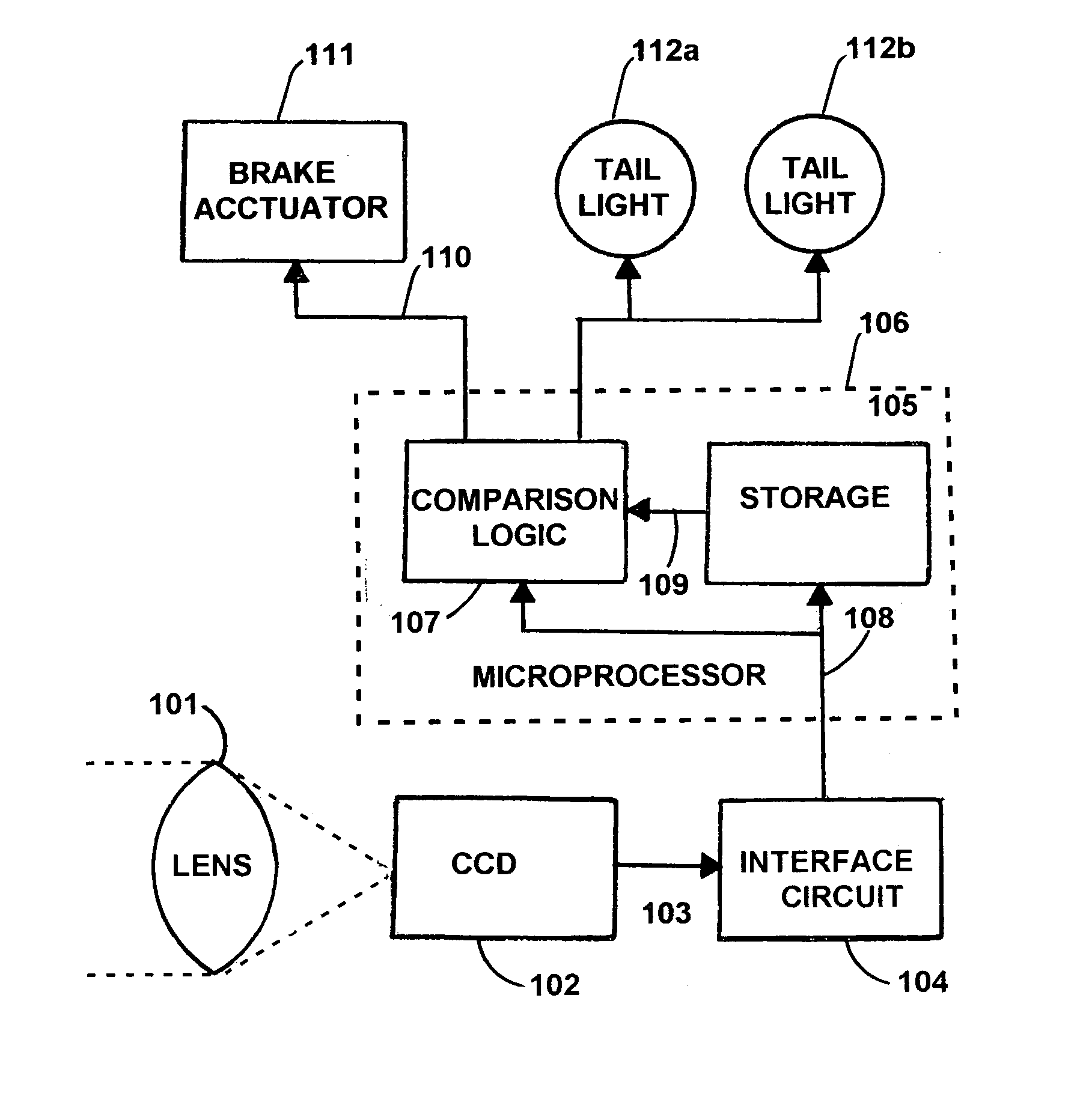
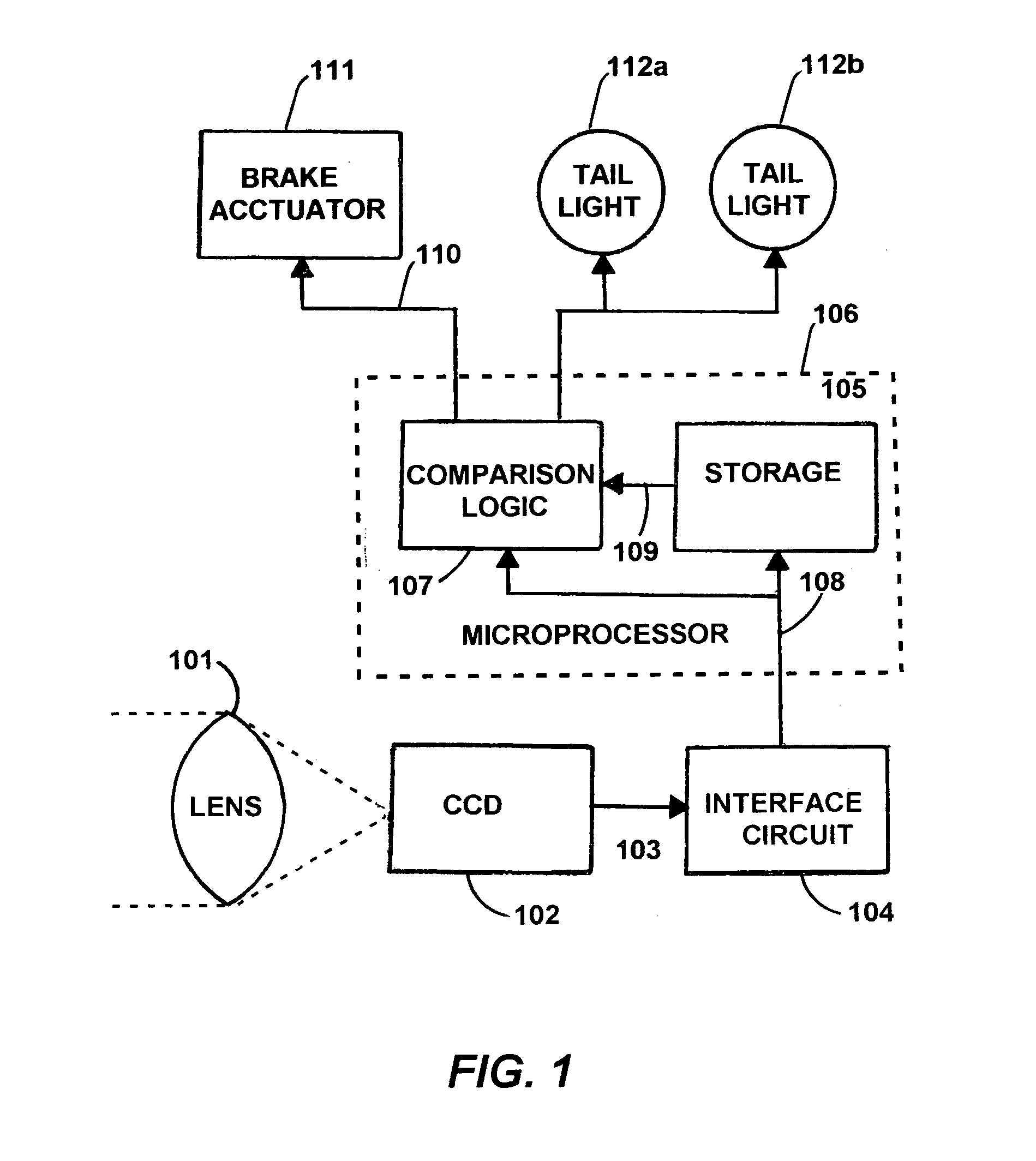
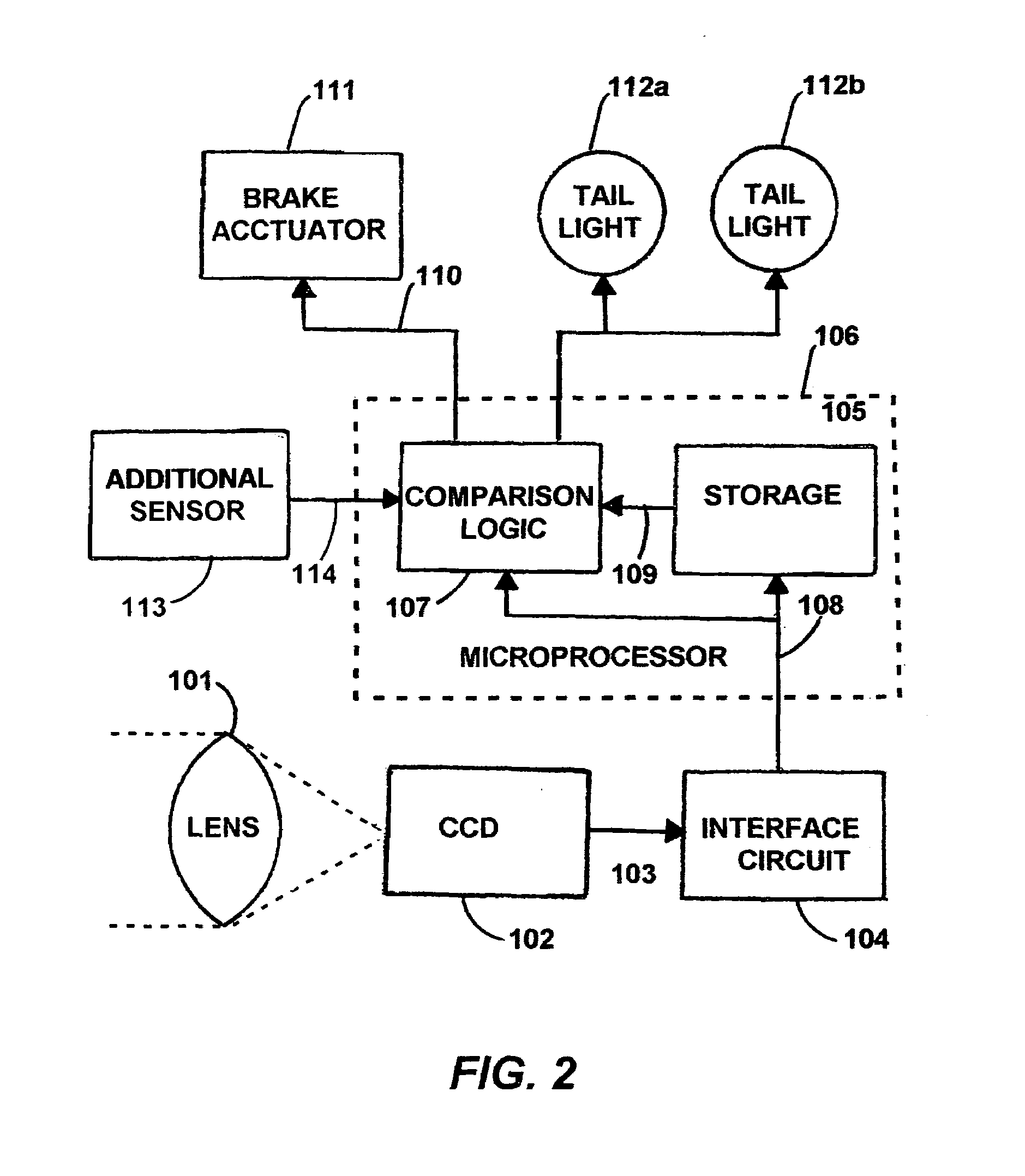
Activating a vehicle's own brake lights and/or brakes when brake lights are sensed in front of the vehicle, including responsively to the proximity of, and/or rate of closure with, a forward vehicle
InactiveUS7365769B1Efficient activationEffective and efficient and flexible and relatively economicalColor television detailsScene recognitionRear-end collisionDriver/operator
Any presence of brake light emissions of another vehicle to the forward of a subject vehicle is sensed in a color camera and microprocessor system that detects (i) red light(s) illuminations in excess of other colors, that are any of (ii) appropriately sized, (iii) appropriately located, (iv) simultaneously occurring, (v) spaced apart in separation, (vi) substantially horizontal, and / or (vii) of approximately of equal intensity, as would be appropriate to a single brake light, or to a pair of brake lights, as the case may be. The brake lights of the subject vehicle are preferably applied either during (i) the persistence of any detection of the brake light(s) of any other vehicle(s) to the forward, or (ii) normal application of the subject vehicle's own brakes. The forward-sensed rearward-propagated brake light signal is preferably delayed in propagation, limiting any propagation of minor perturbations in traffic. Optional application of the vehicle's own brakes may be conditioned upon (i) proximity to and / or rate of closure with a forward emission source as is preferably determined by angles, and / or upon (ii) rate of closure, speed or deceleration G force of the subject vehicle. The brake light signal, whether simple or sophisticated in either its development and / or presentation, beneficially alerts drivers to the rear of impending or actual slowing, thus deterring rear end collisions and promoting fuel economy.
Owner:BRAKE
Microprocessor system for the analysis of physiologic and financial datasets
InactiveUS20070093721A1Increase variabilityLittle varianceData visualisationEvaluation of blood vesselsTime domainData set
A system and method for organization and analysis of complex and dynamically interactive time series is disclosed. One example comprises a processor based system for relational analysis of physiologic signals for providing early recognition of catastrophic and pathologic events such as pathophysiologic divergence. The processor is programmed to identify pathophysiologic divergence of at least one of first and second physiologic parameters in relationship to the other and to output an indication of the divergence. An object-based method of iterative relational processing waveform fragments in the time domain is described wherein each more complex waveform object inherits the characteristics of the waveform objects from which it is derived. The first physiologic parameter can be the amplitude and frequency of the variation in chest wall impedance or nasal pressure and the second parameter can be a measure or indication of the arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:LYNN LAWRENCE A +1
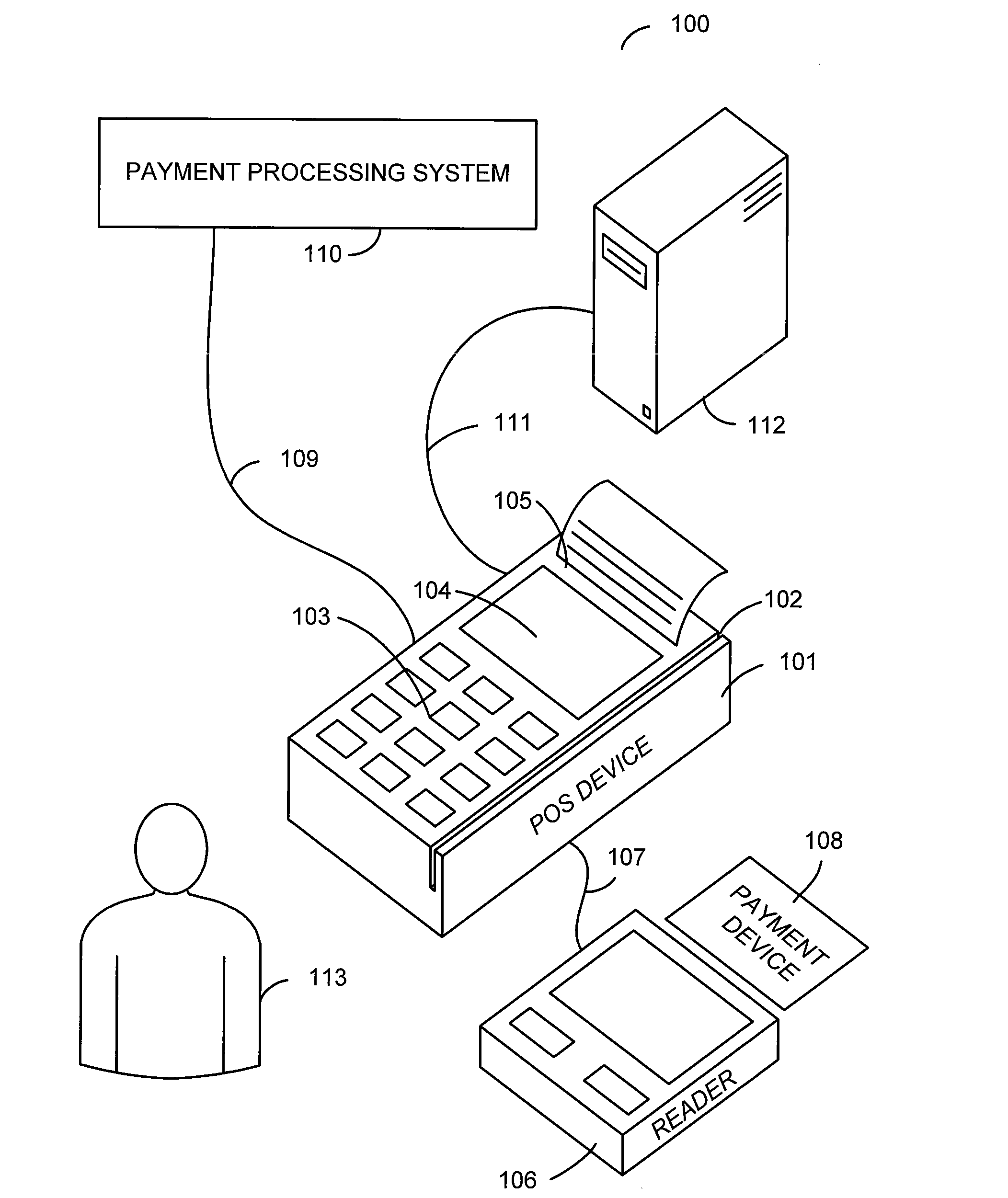
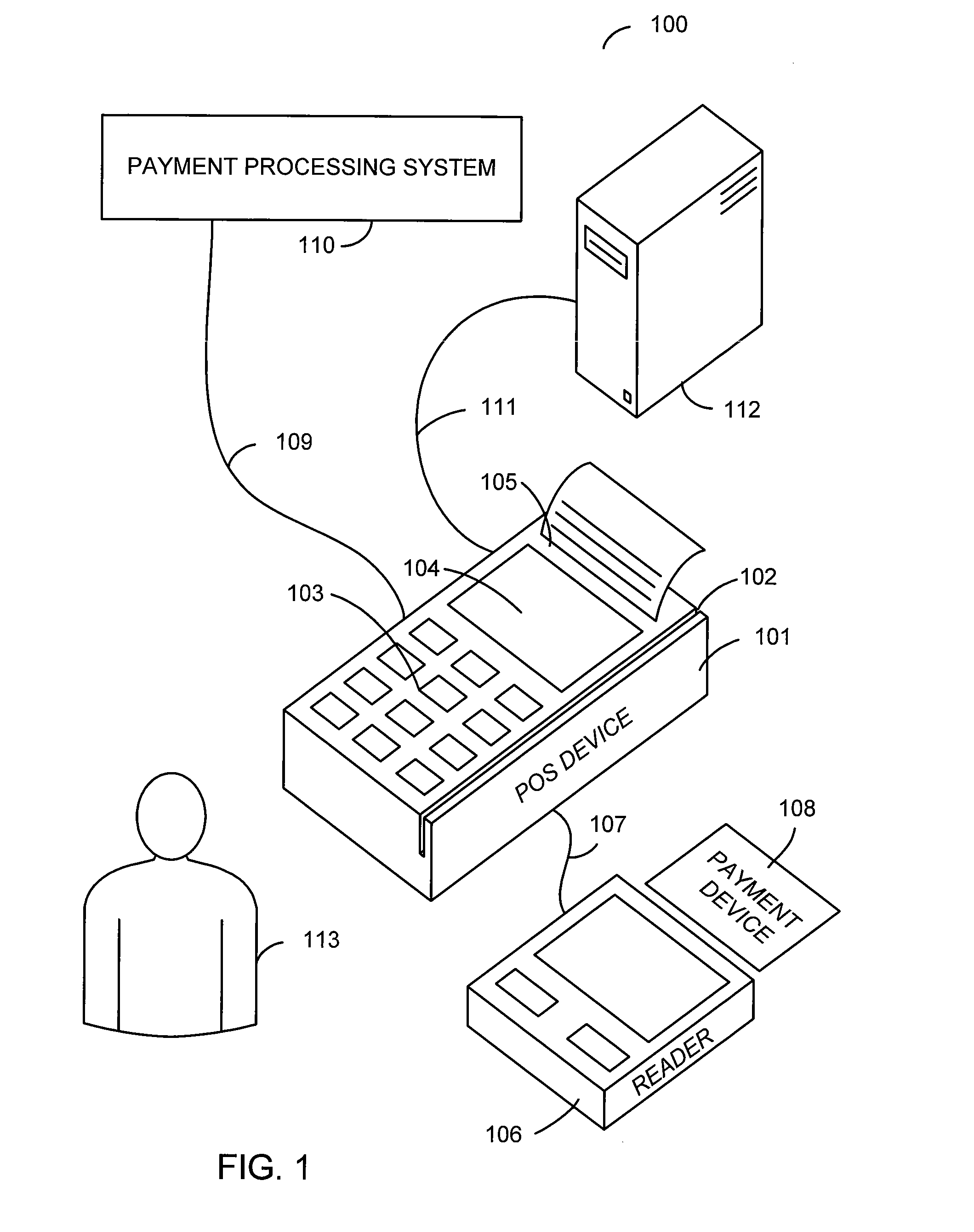
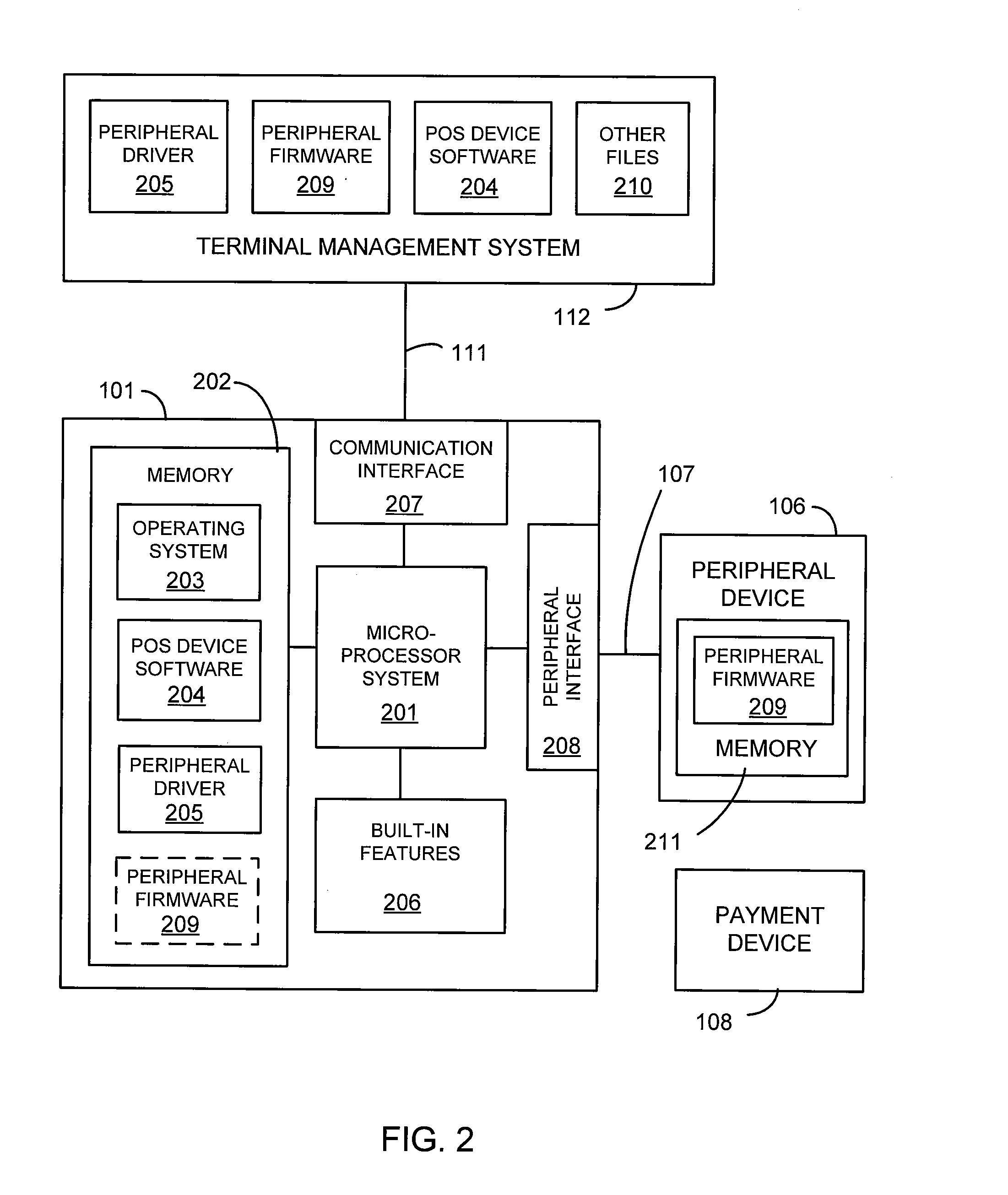
Point of sale system with ability to remotely update firmware
A point of sale system comprises a microprocessor system, a peripheral interface, and a communication interface. The point of sale system is configured to receive, through the communication interface, an update to peripheral operation software associated with a peripheral device that may be connected to the peripheral interface. The peripheral device may be a contactless reader. The updated software may be received from a terminal management system connected to the point of sale device through the communication interface. The updated software may comprise a peripheral driver that is stored in memory comprised in the point of sale device. The updated software may comprise peripheral firmware that is stored in memory comprised in the peripheral device.
Owner:FIRST DATA
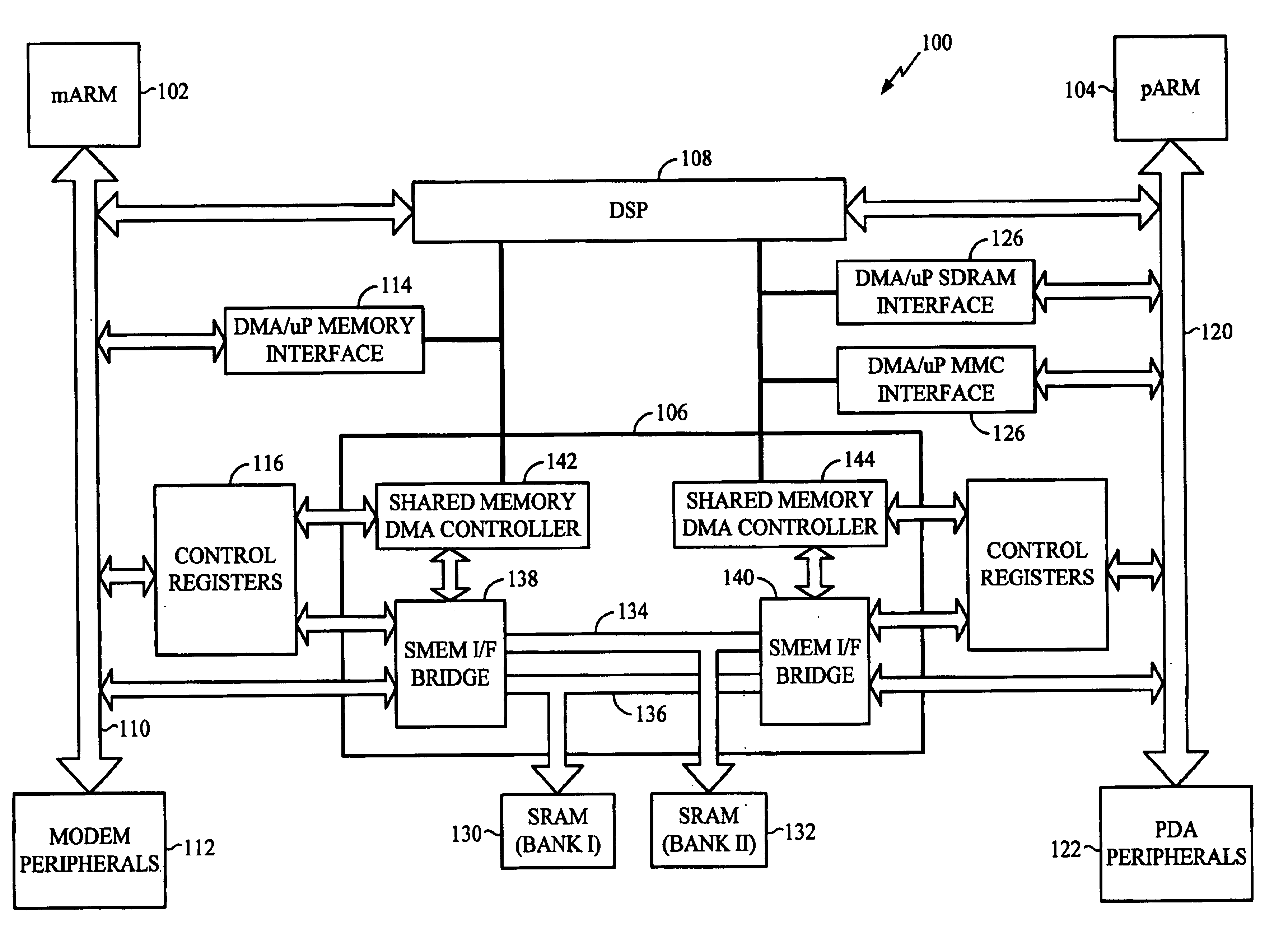
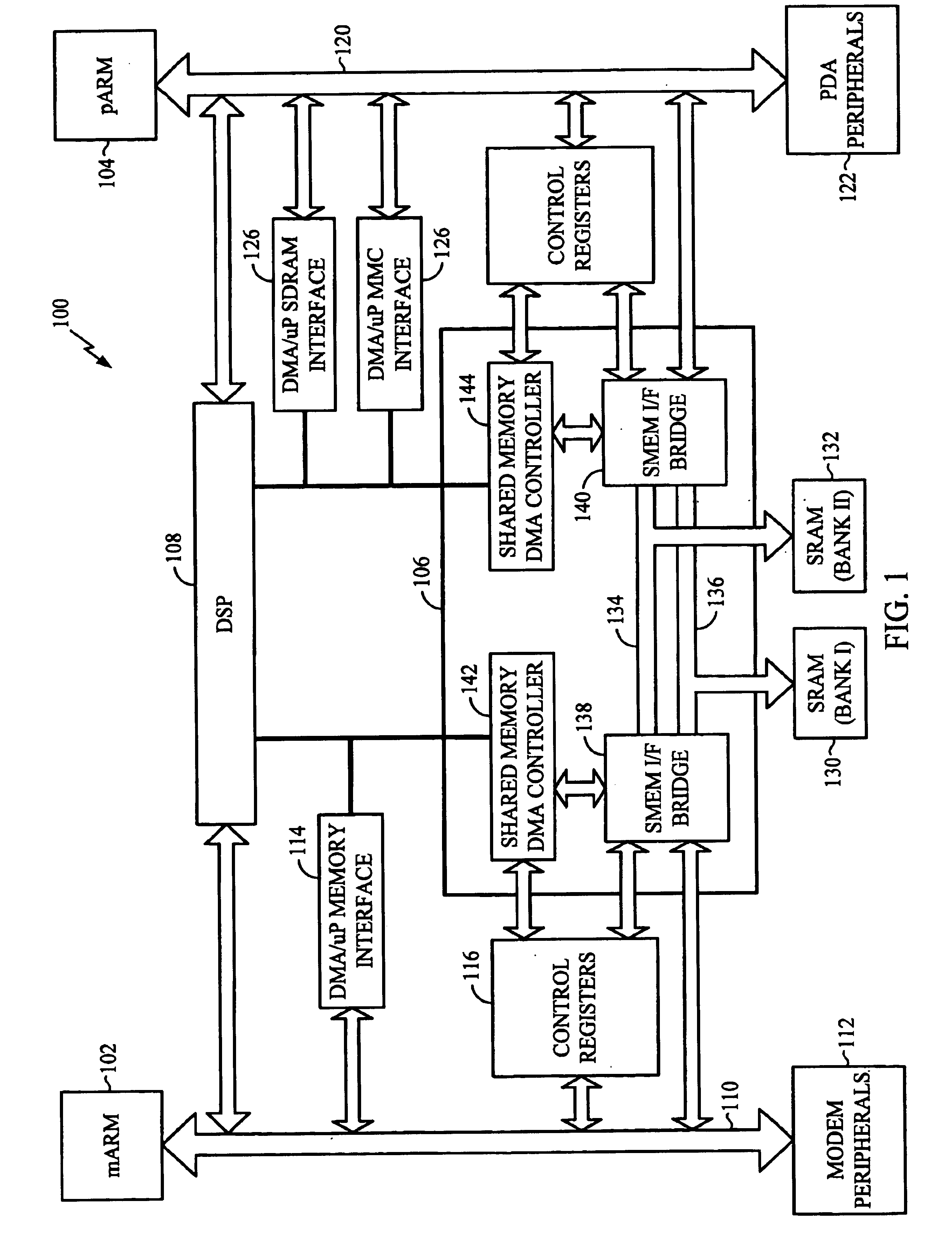
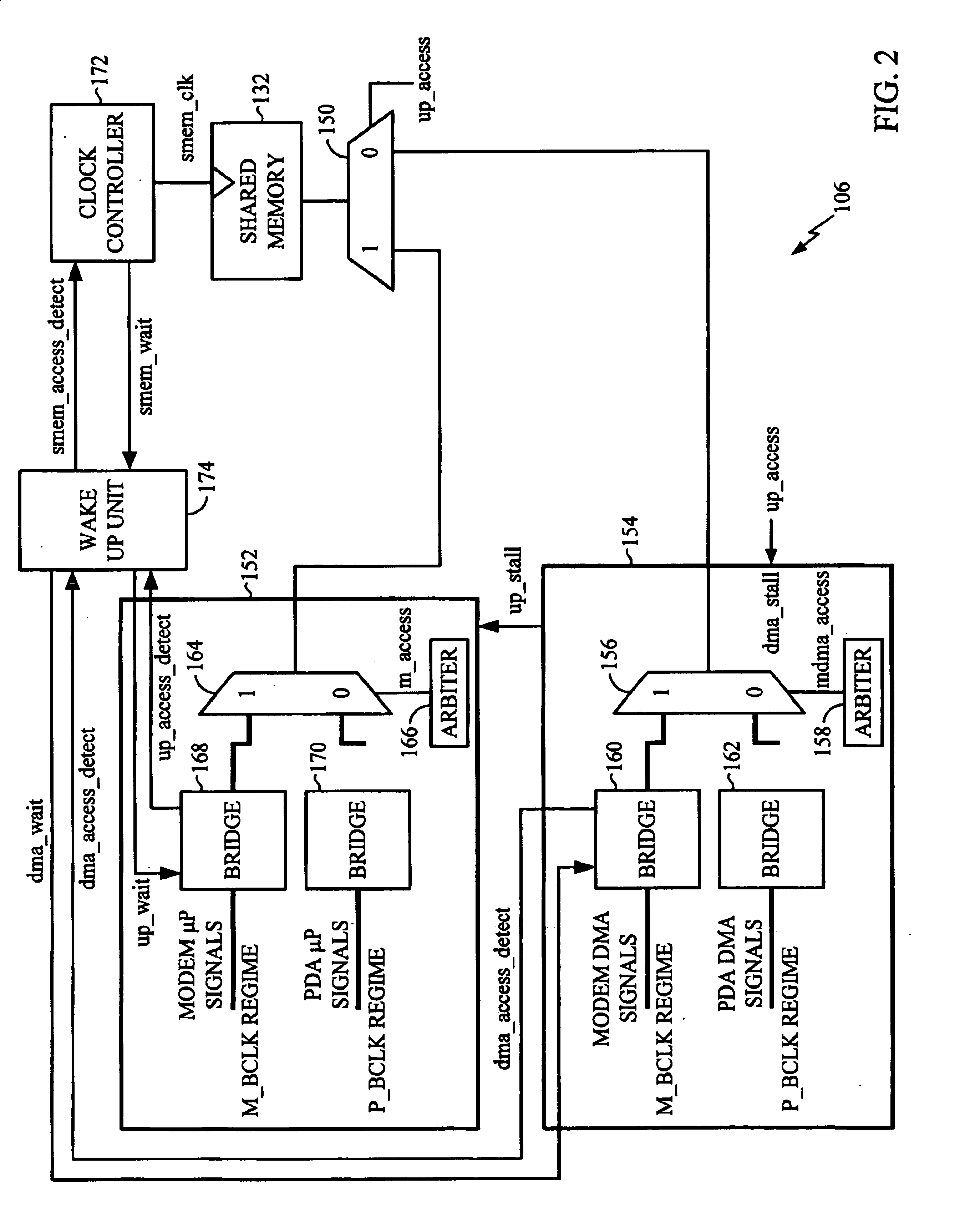
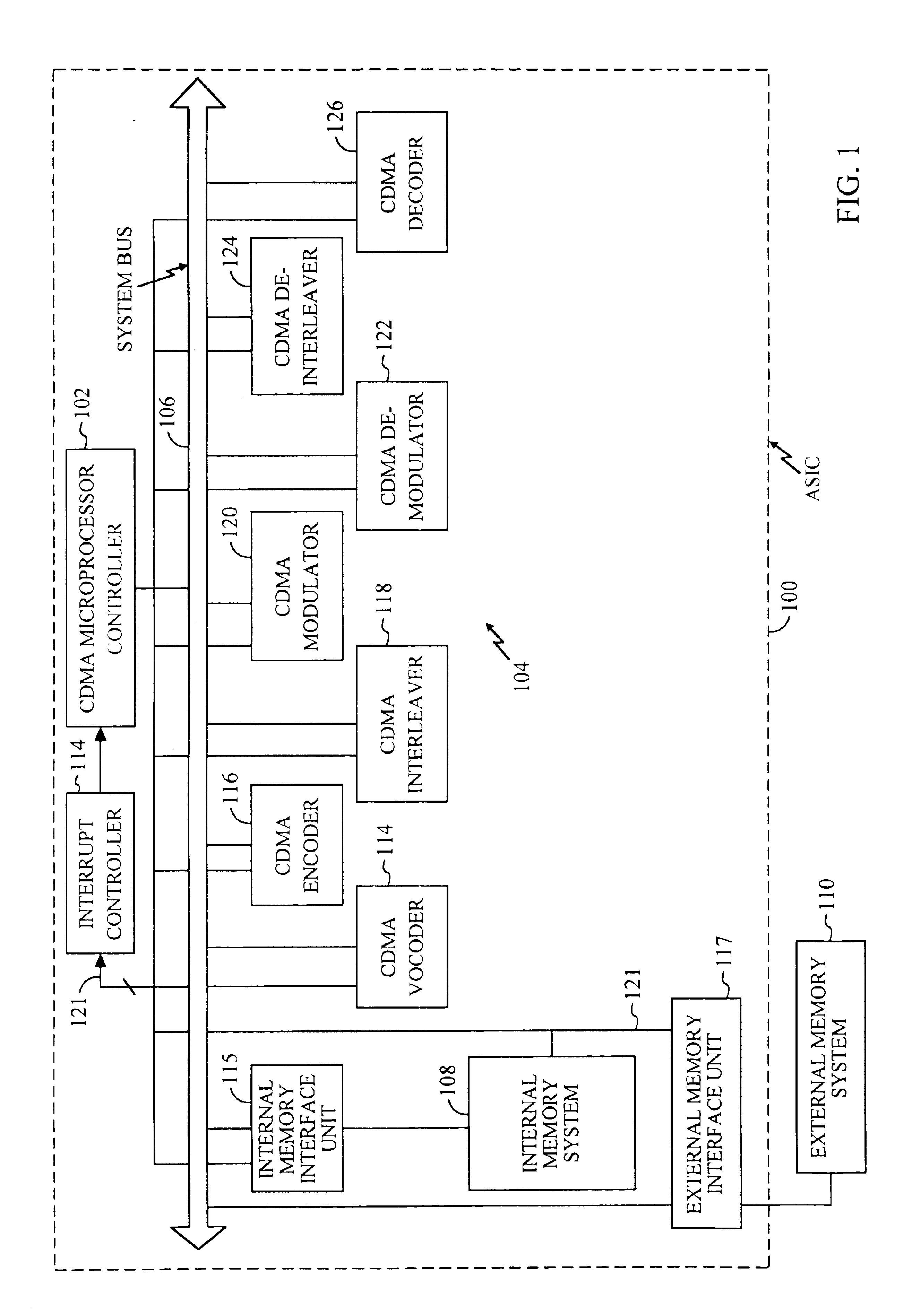
Mobile communication device having dual micro processor architecture with shared digital signal processor and shared memory
The dual microprocessor system includes one microprocessor configured to perform wireless telephony functions and another configured to perform personal digital assistant (PDA) functions and other non-telephony functions. A memory system and a digital signal processor (DSP) are shared by the microprocessors. By providing a shared memory system, data required by both data microprocessors is conveniently available to both of the microprocessors and their peripheral components thereby eliminating the need to provide separate memory subsystems and further eliminating the need to transfer data back and forth between the separate memory subsystems. By providing a shared DSP, separate DSP devices need not be provided, yet both microprocessors can take advantage of the processing power of the DSP. In a specific example described herein, the microprocessors selectively program the DSP to perform, for example, vocoder functions, voice recognition functions, handwriting recognition functions, and the like.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
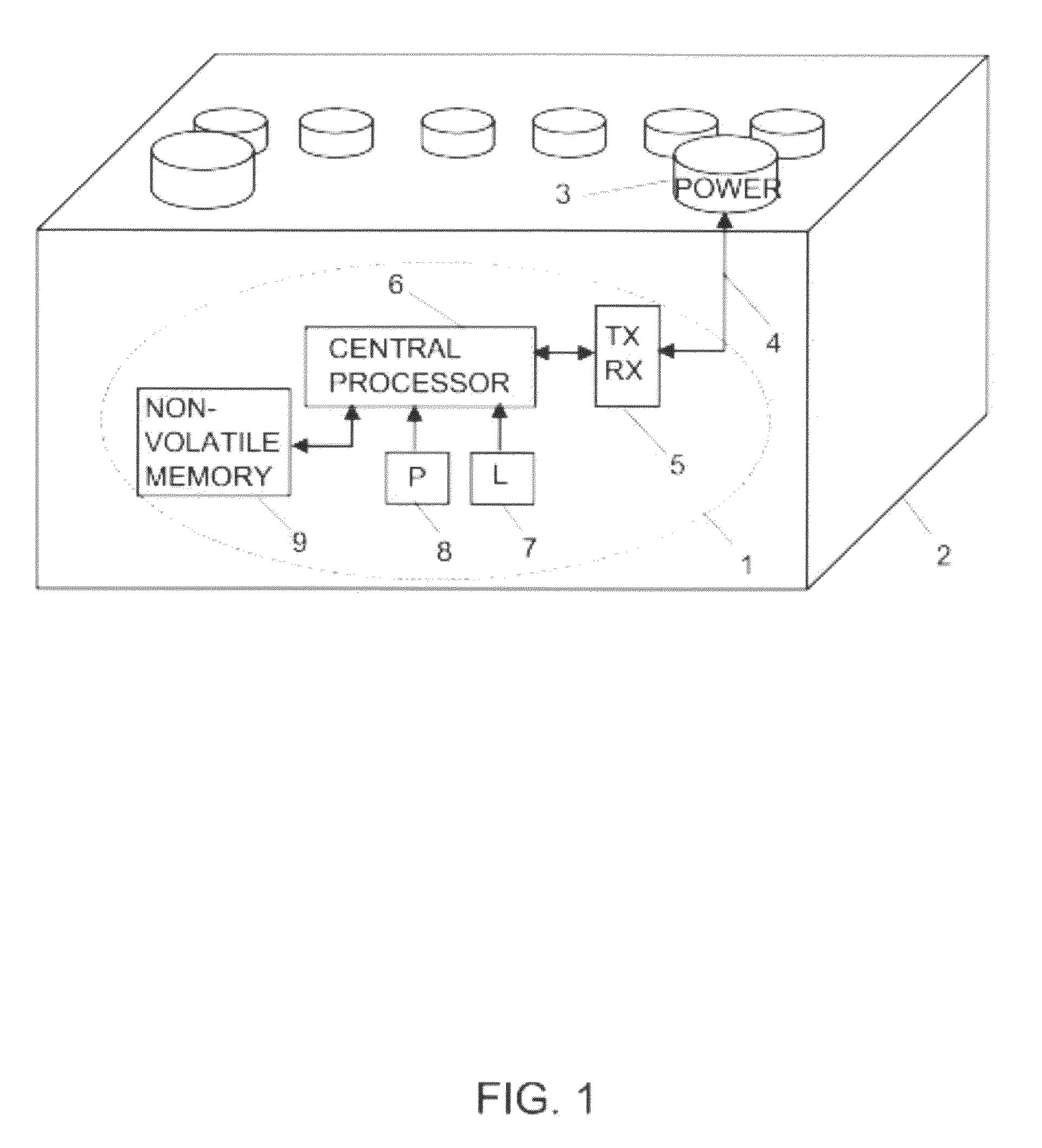
Embedded microprocessor system for vehicular batteries
InactiveUS20100217551A1Batteries circuit arrangementsError detection/correctionElectrical batteryComputerized system
A computer system embedded inside a starter or deep cycle battery that includes manufacturing data, the means to monitor battery pressure, the means to monitor electrolyte level and the means to transfer information to an external device.
Owner:4 PEAKS TECH
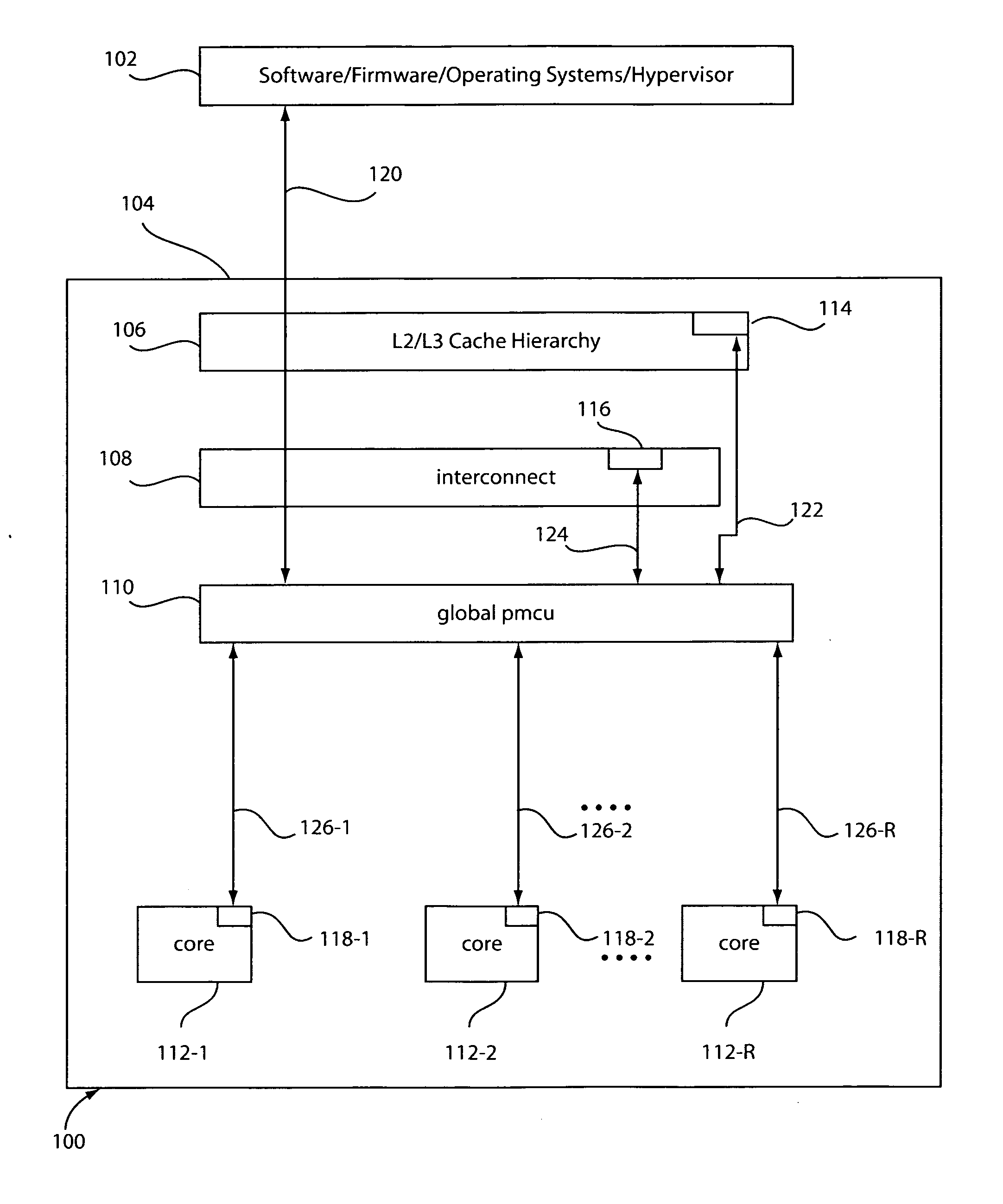
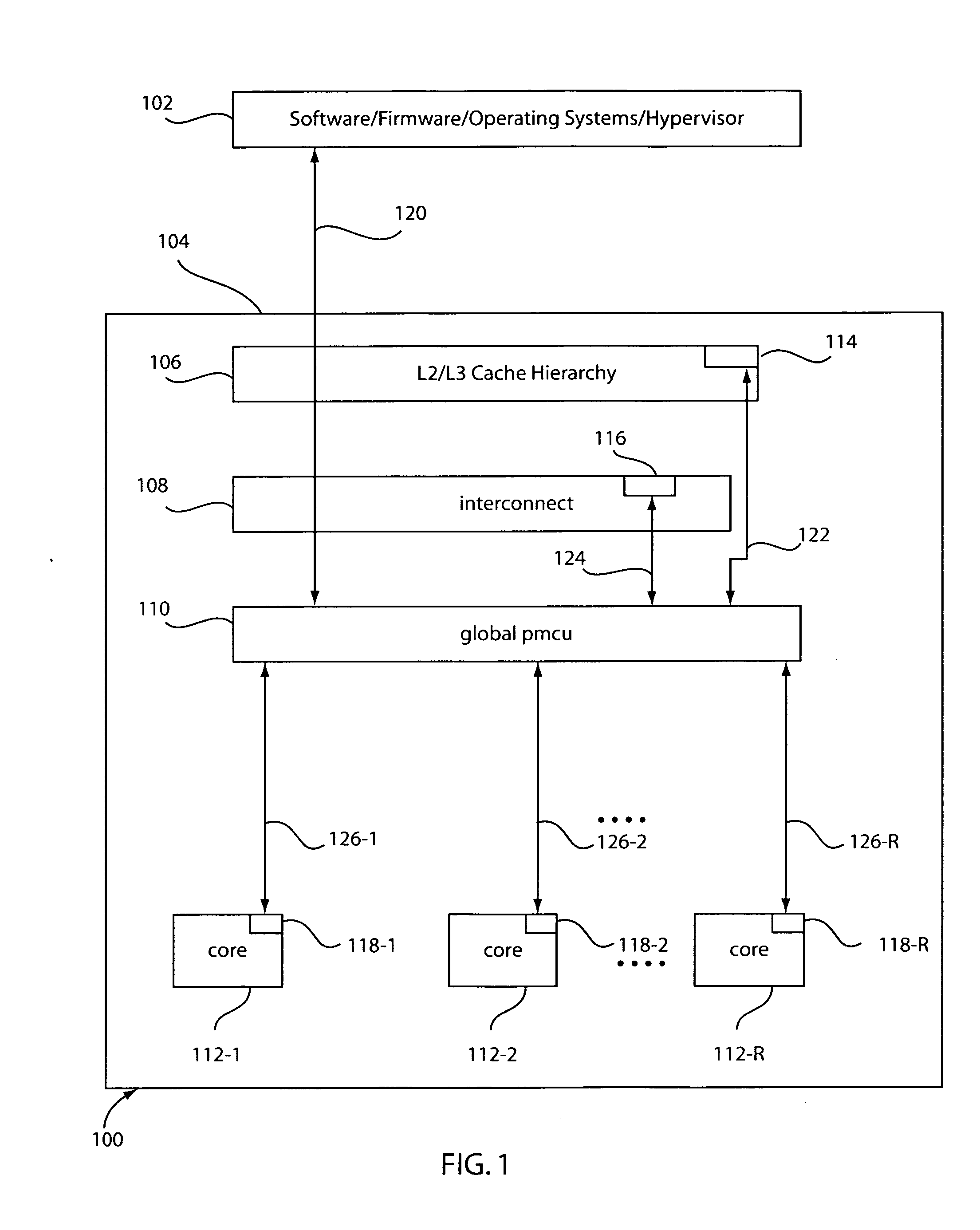
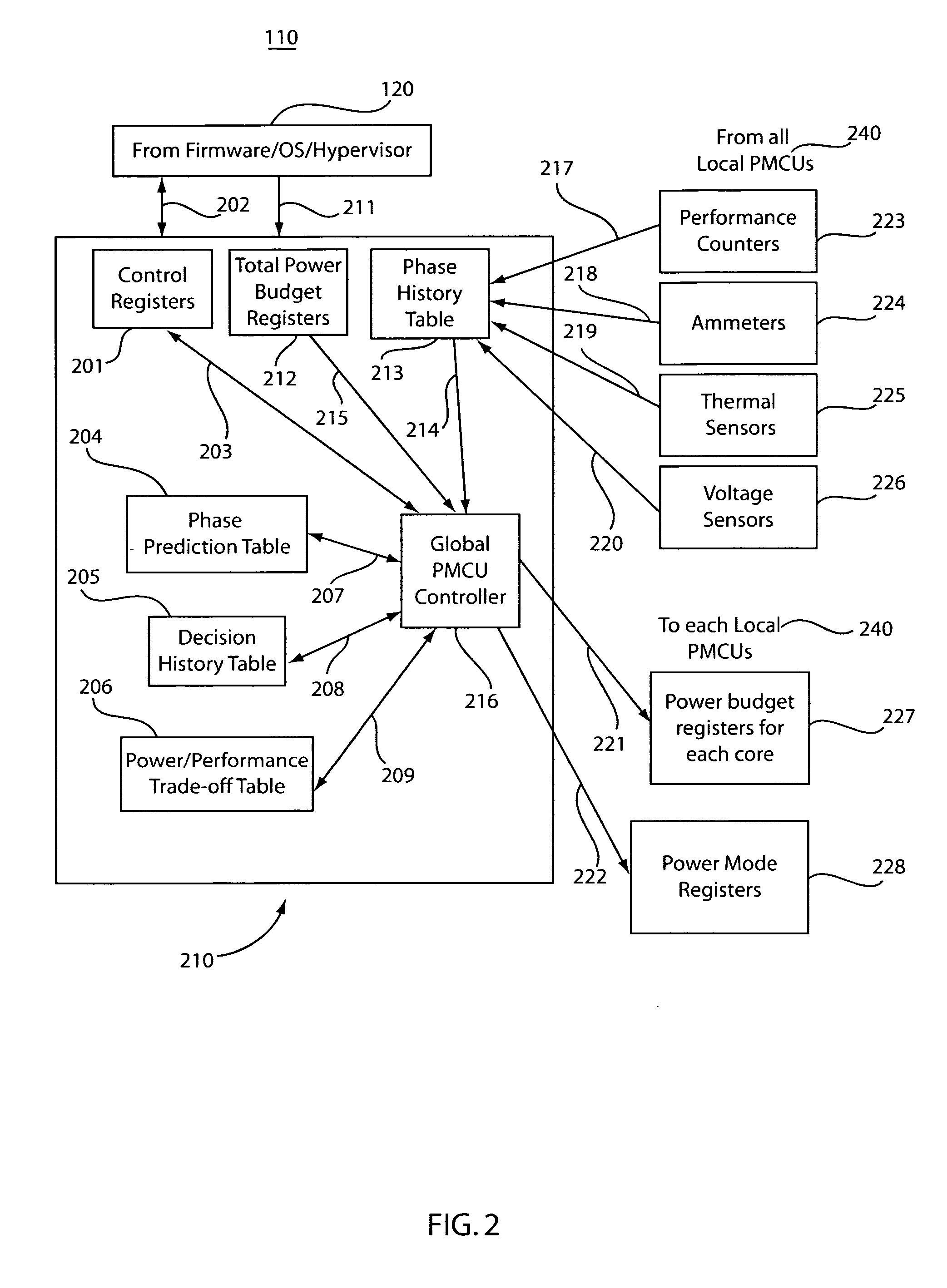
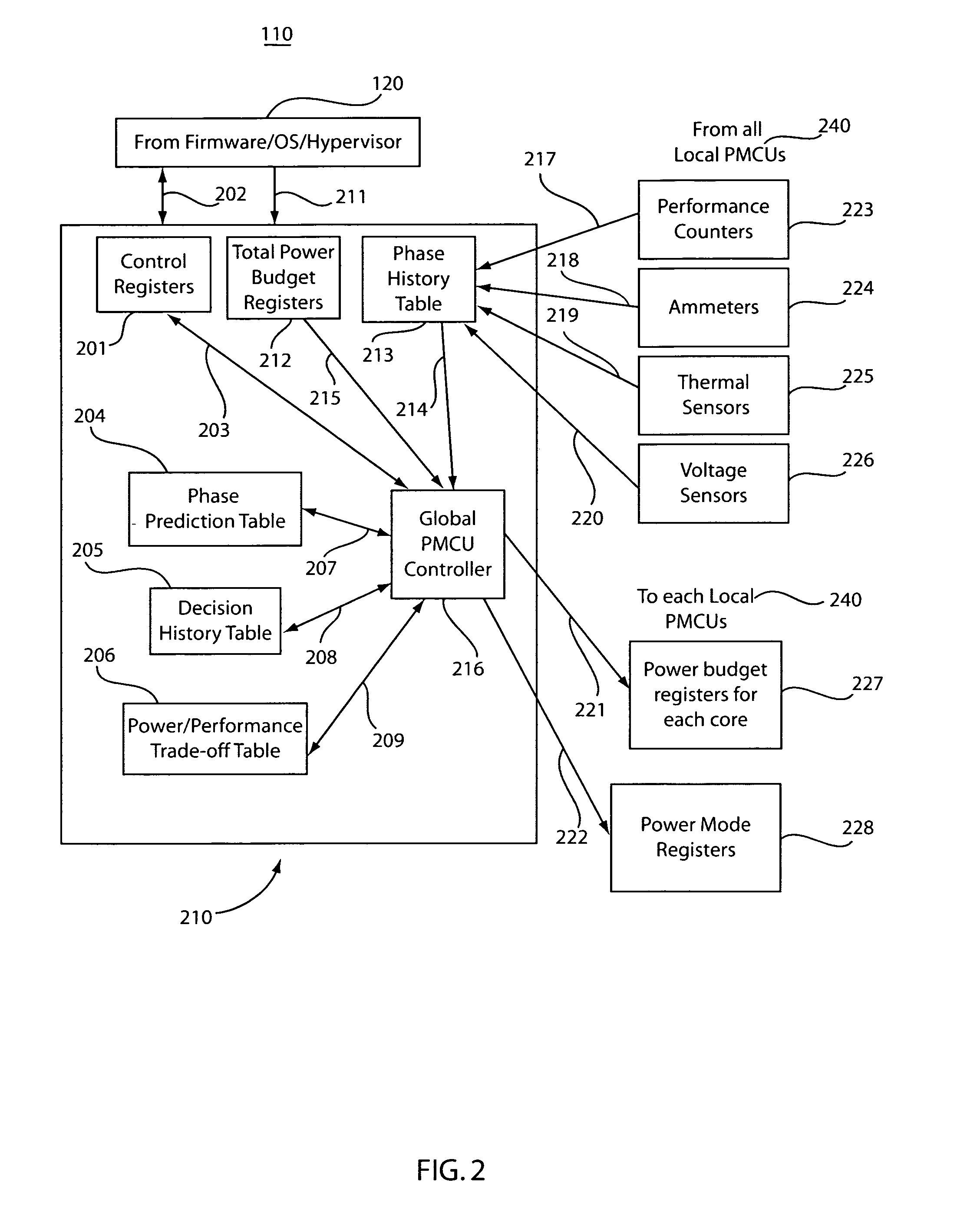
Method and system for controlling power in a chip through a power-performance monitor and control unit
ActiveUS20070198863A1Improve performancePerformance maximizationEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementControl powerControl system
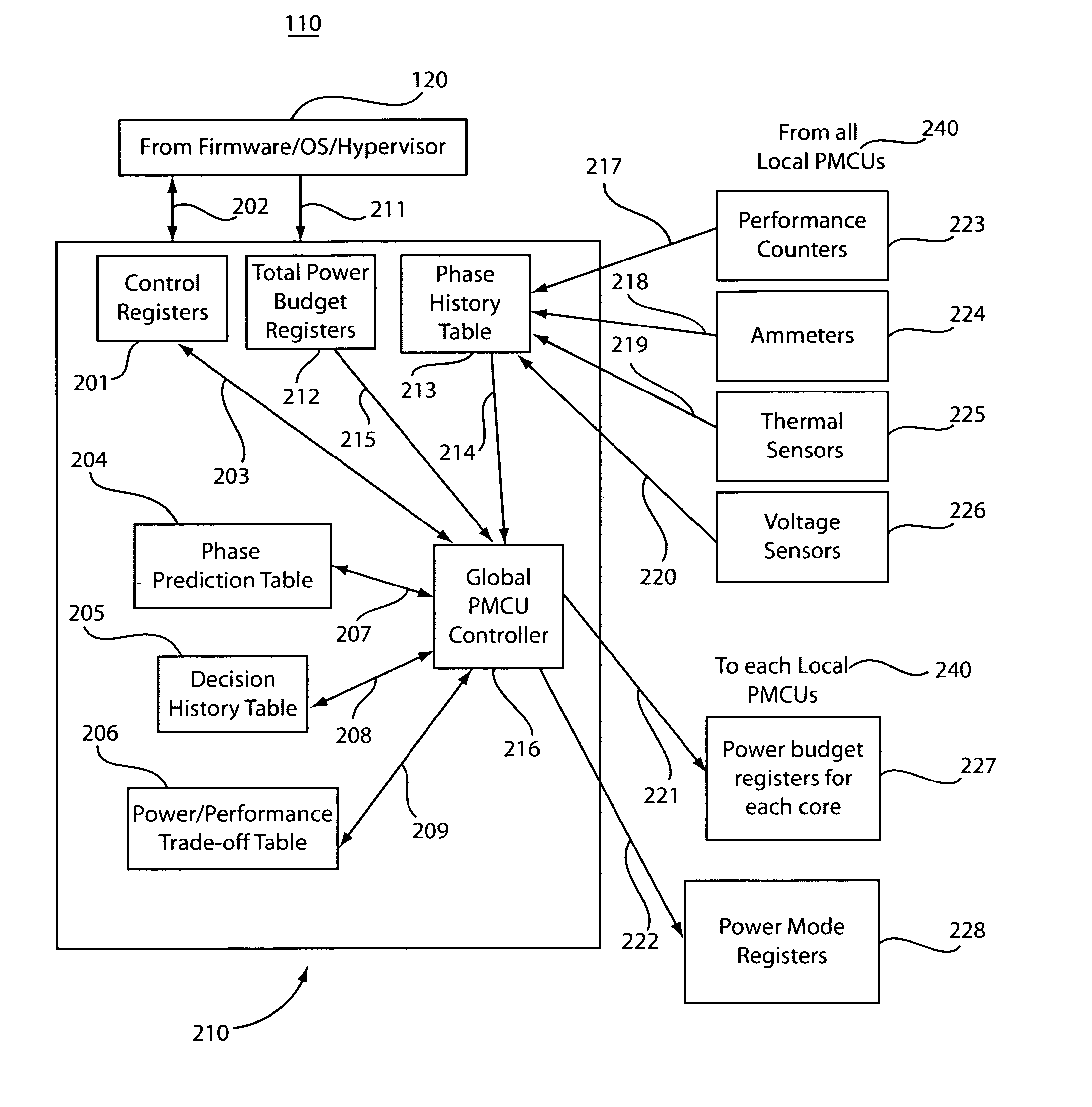
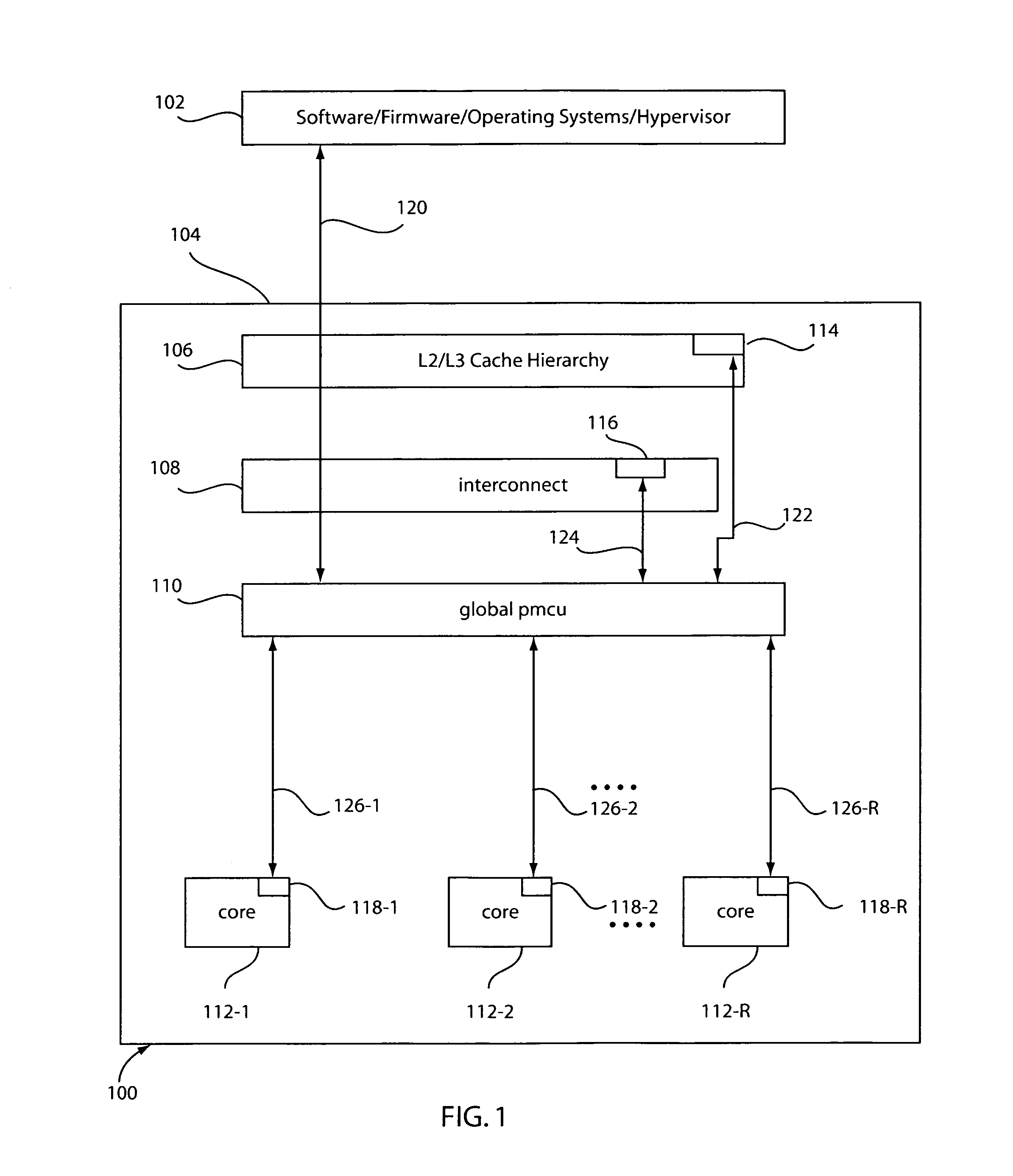
A system and method for controlling power and performance in a microprocessor system includes a monitoring and control system integrated into a microprocessor system. The monitoring and control system includes a hierarchical architecture having a plurality of layers. Each layer in the hierarchal architecture is responsive to commands from a higher level, and the commands provide instructions on operations and power distribution, such that the higher levels provide modes of operation and budgets to lower levels and the lower levels provide feedback to the higher levels to control and manage power usage in the microprocessor system both globally and locally.
Owner:IBM CORP
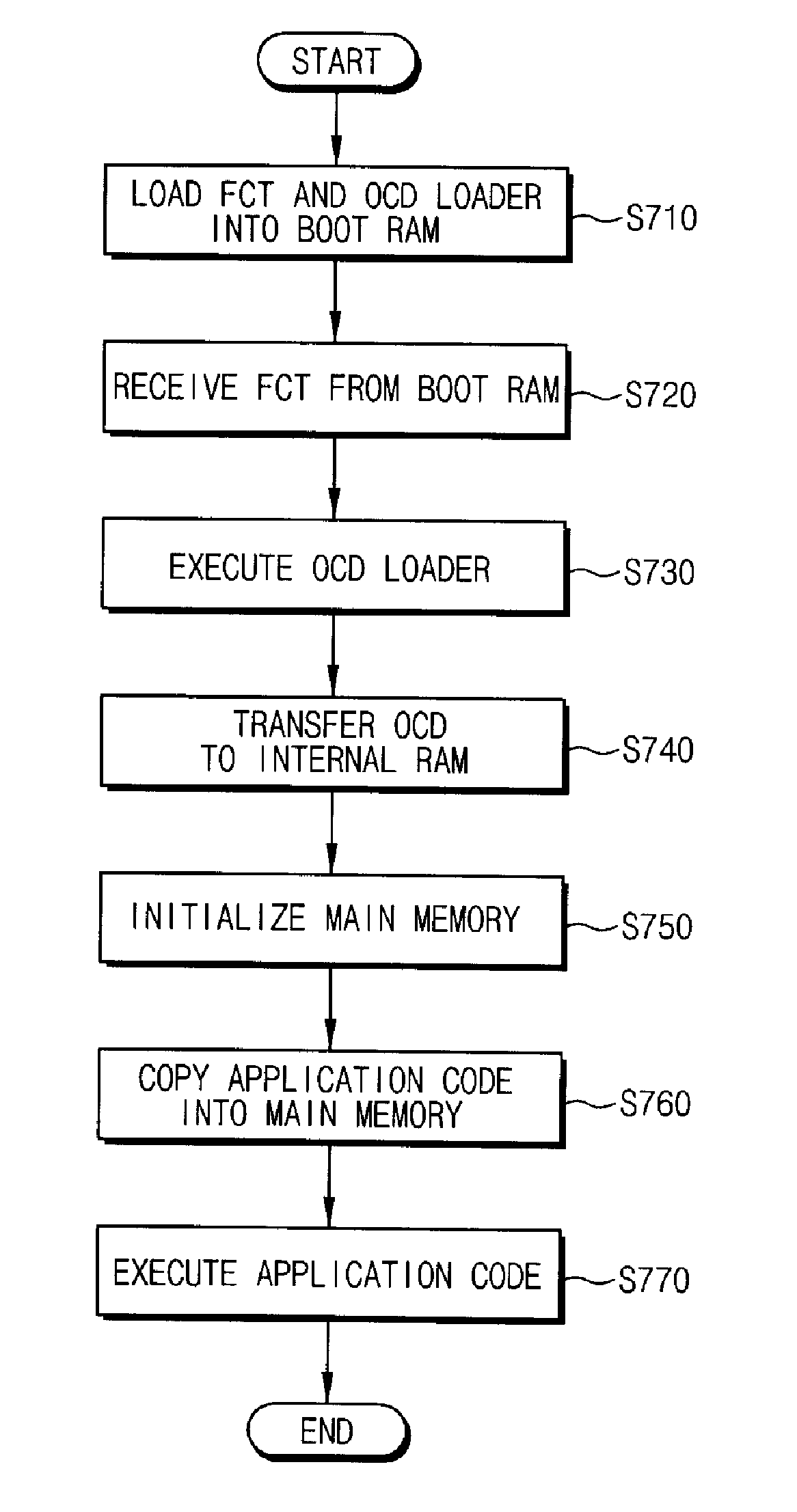
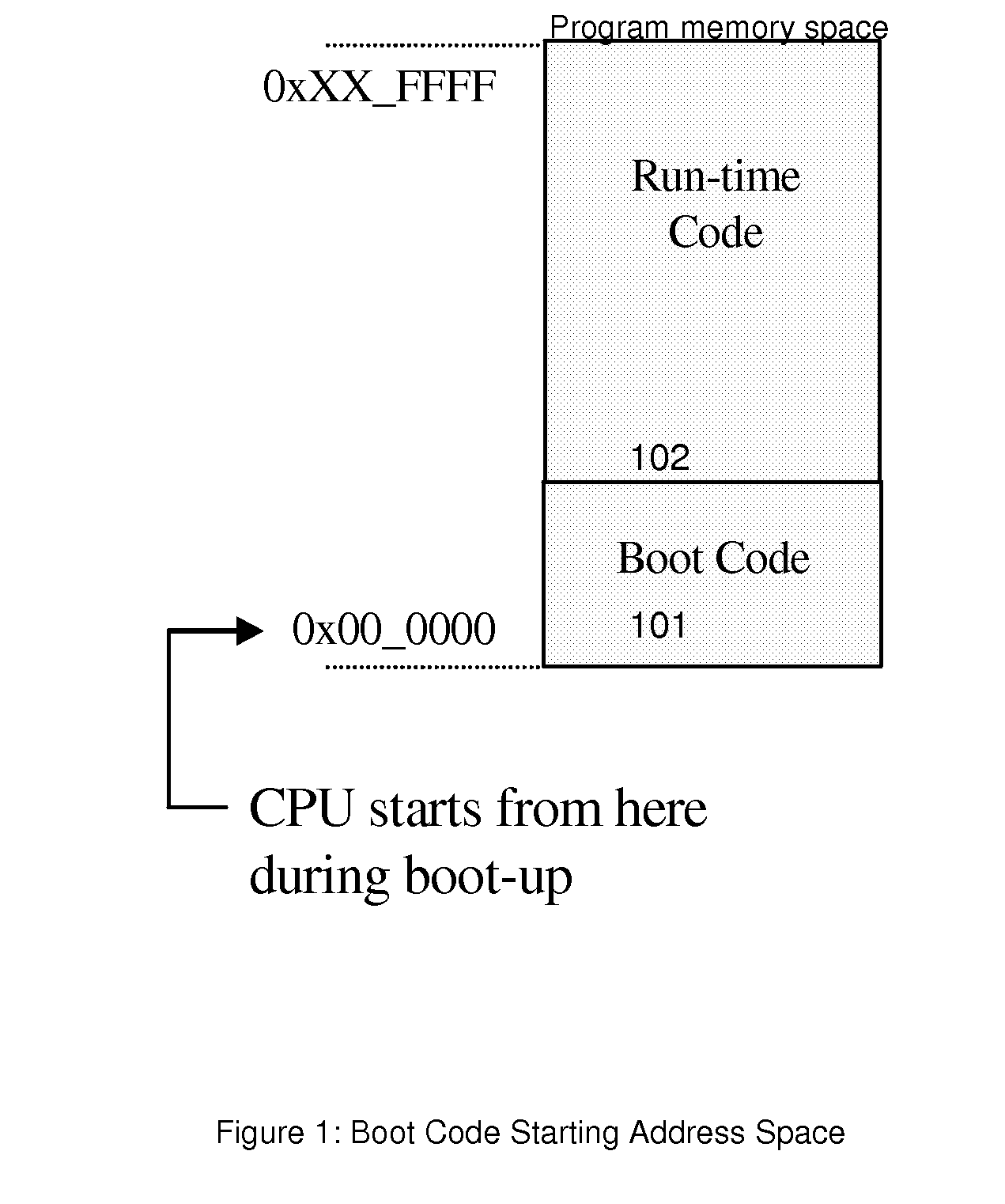
Method and apparatus for booting a microprocessor system using boot code stored on a serial flash memory array having a random-access interface
ActiveUS20070113067A1Ensure flexibilityLow costDigital computer detailsData resettingRead-only memoryProgram code
A method and apparatus for booting a microprocessor system using a serial (e.g., NAND-type) flash memory array having a random-access (parallel, e.g., NOR-flash type) interface. The method includes loading a boot code loader stored in the serial (e.g., NAND-type) flash memory array into a RAM when power is turned on, according to a routine of a read-only memory (ROM) of the microprocessor; loading boot code stored in the serial flash memory into an internal or external (main) RAM of the microprocessor according to the boot code loader; loading application code stored in the serial flash memory into the main (RAM) memory according to the boot is code; and executing the application code. The system may be manufactured at a low cost compared to NOR-Flash based systems, while ensuring flexibility of a microprocessor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Fuel management system for variable ethanol octane enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS7314033B2Increase heatMeet cutting requirementsElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringAntiknock agent
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
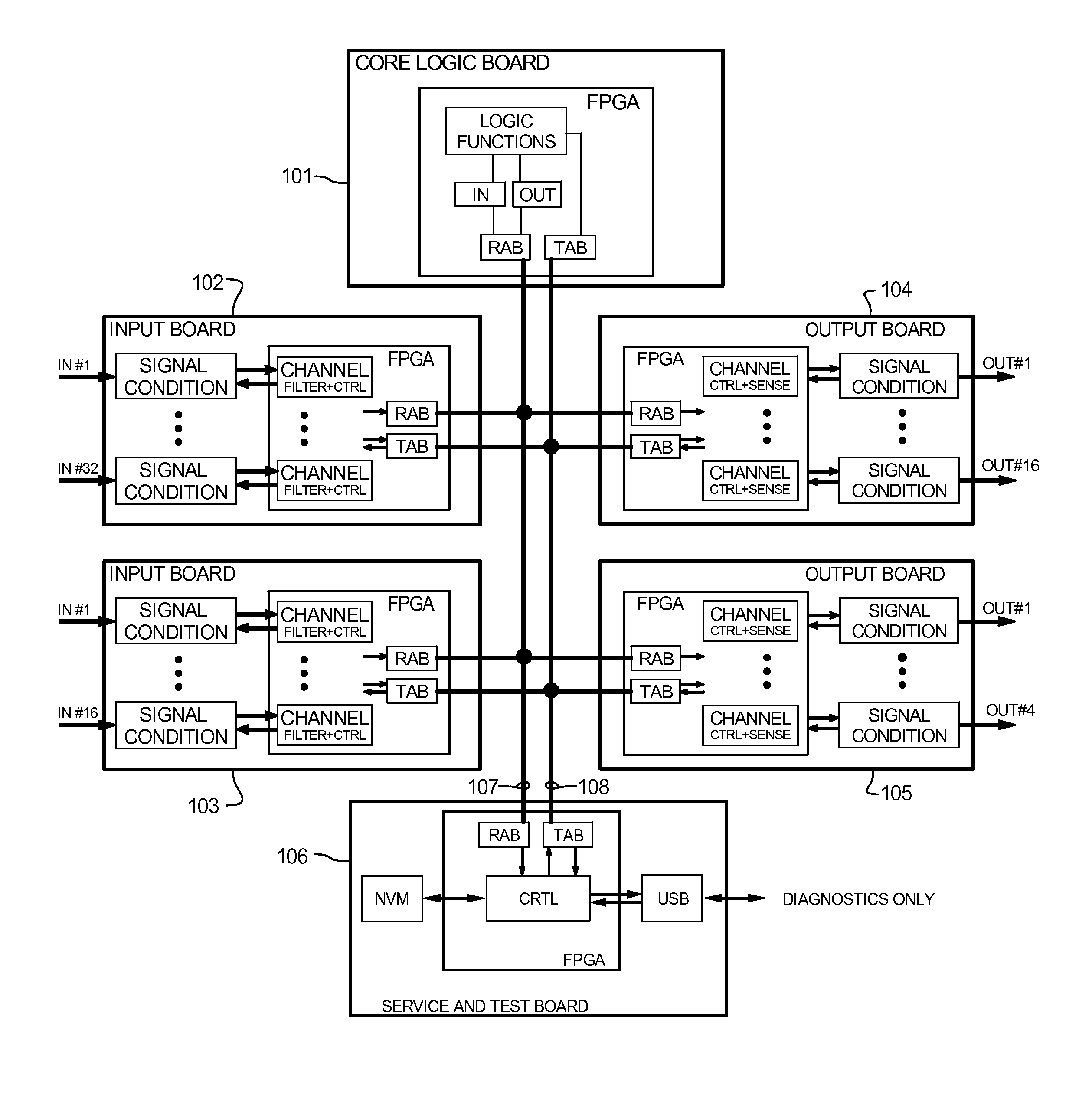
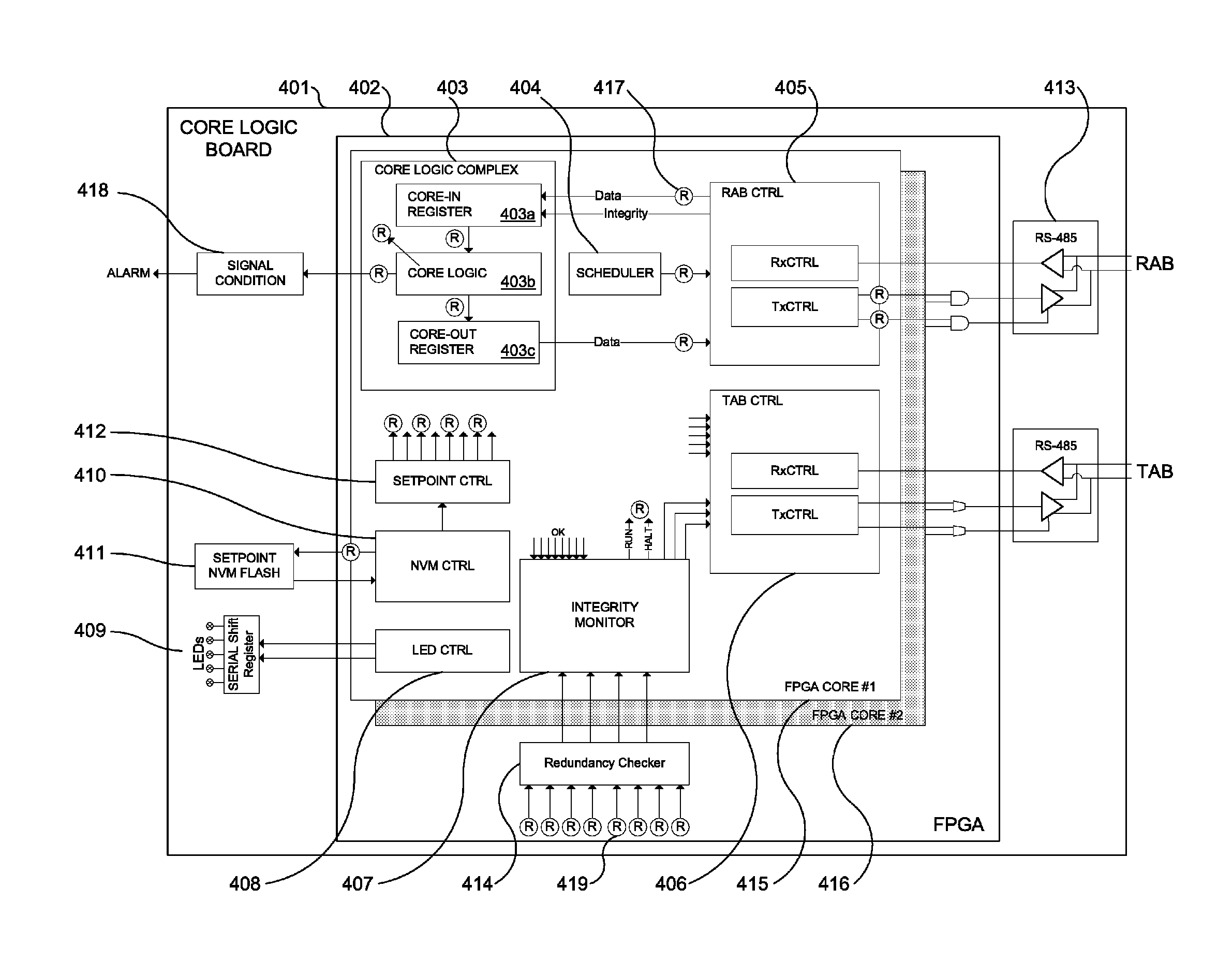
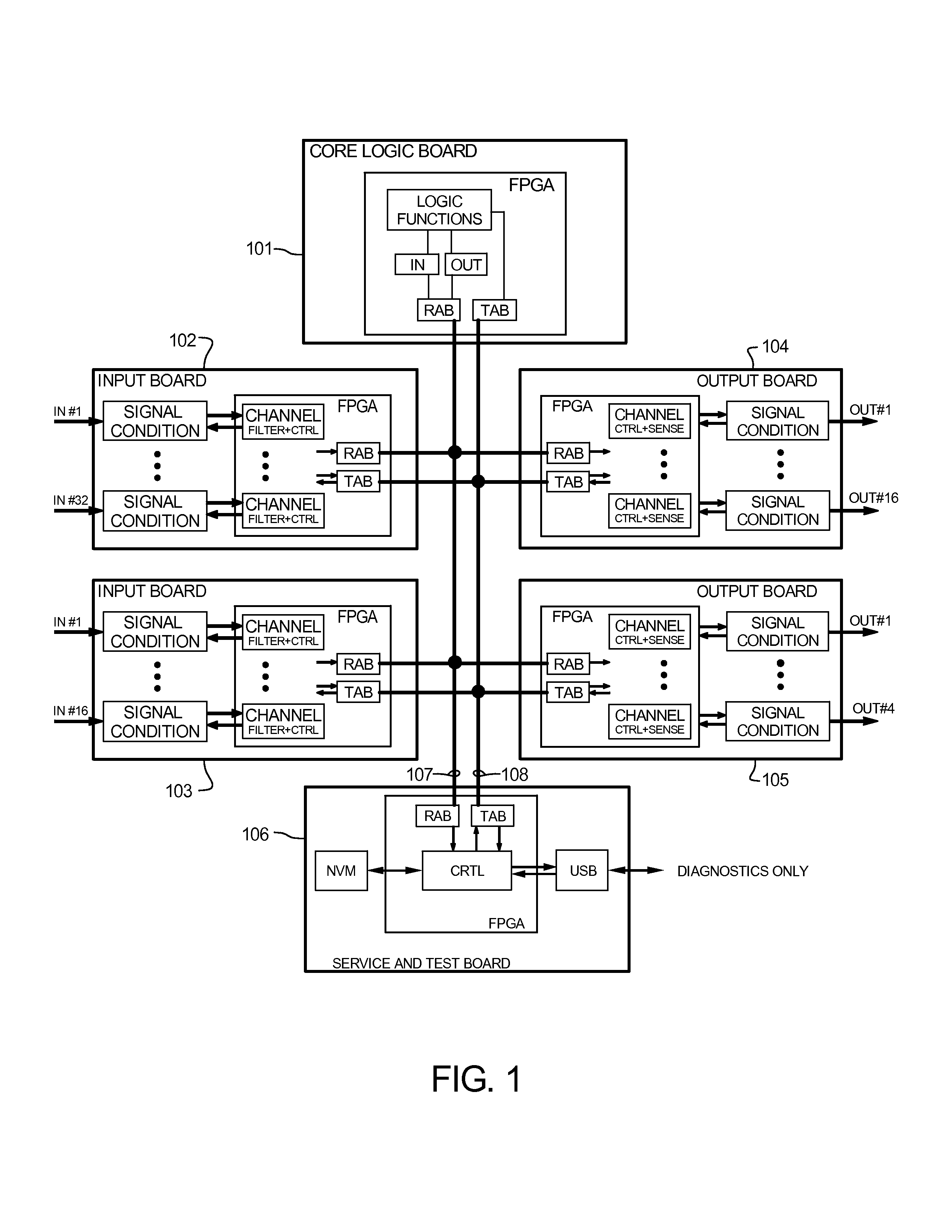
Advanced logic system
ActiveUS7870299B1Improve reliabilityImprove maintainabilityProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsNuclear plantCommon mode failure
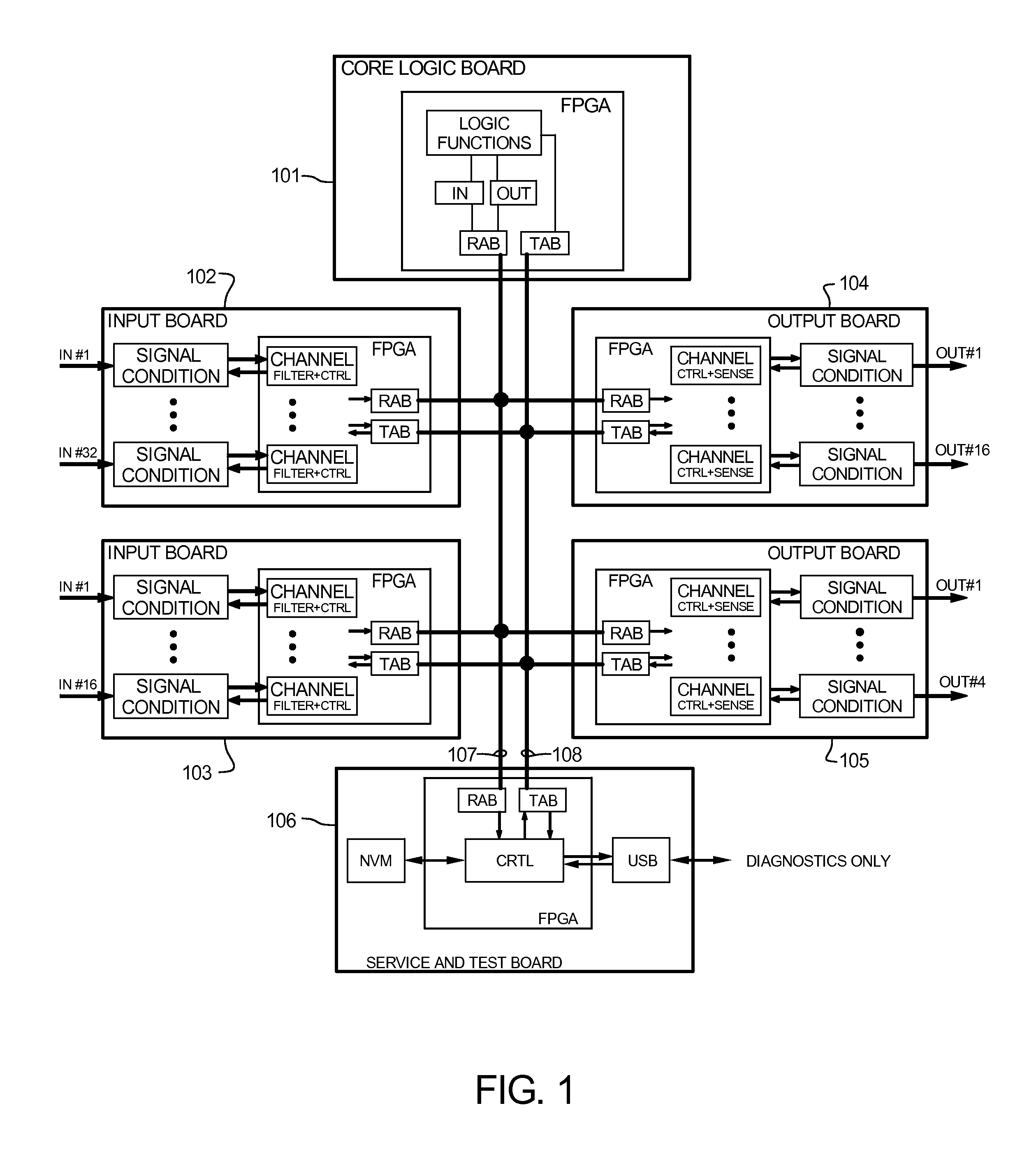
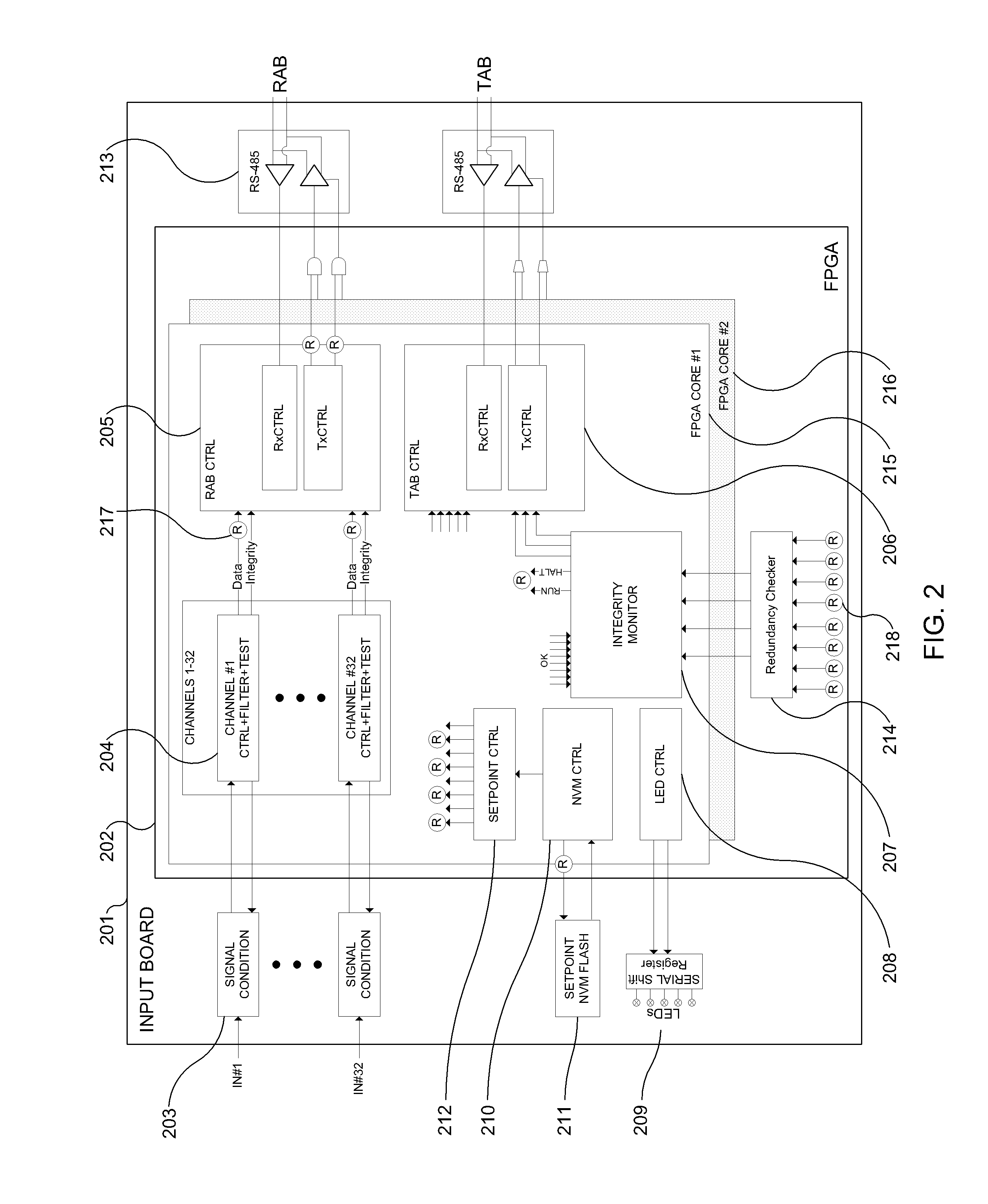
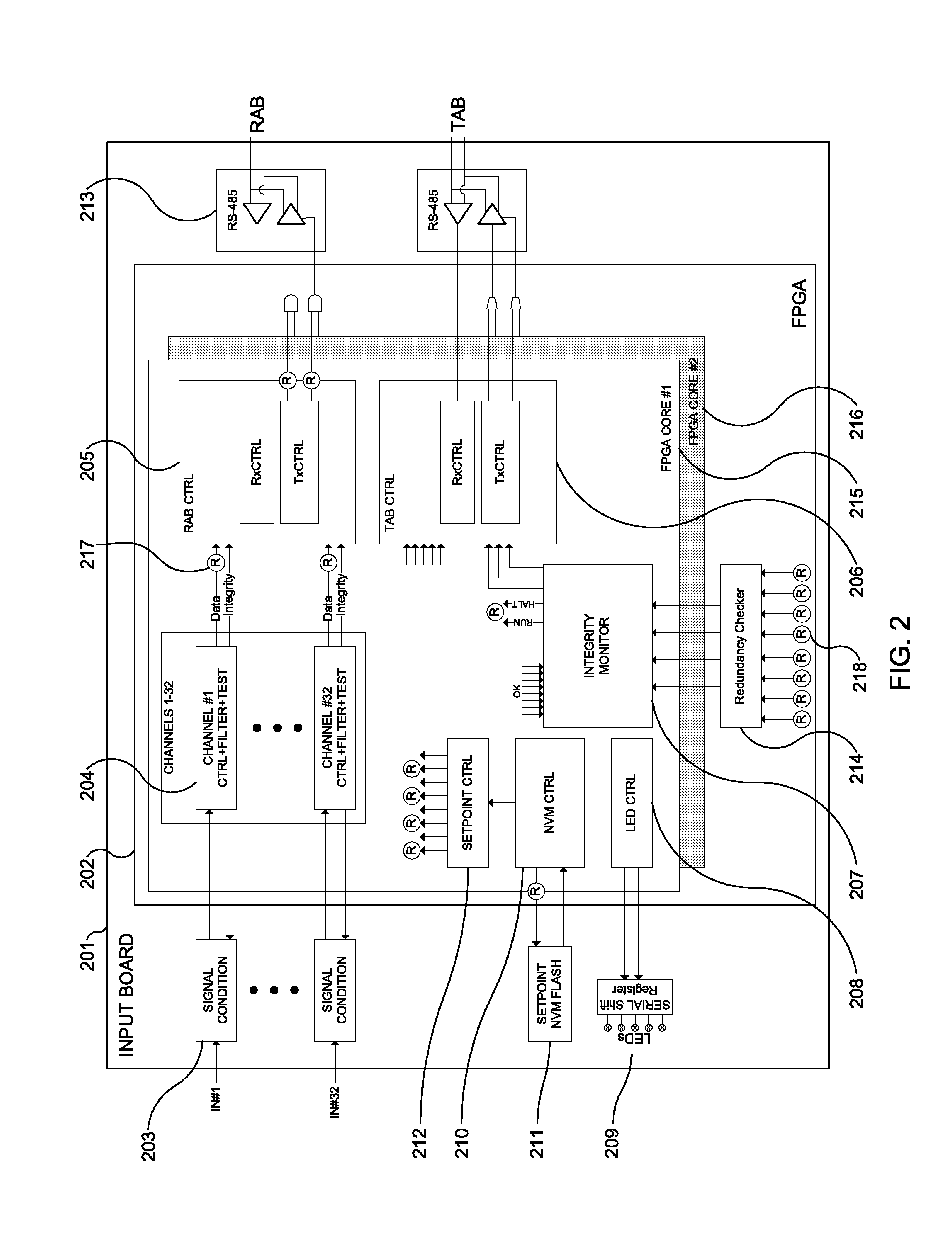
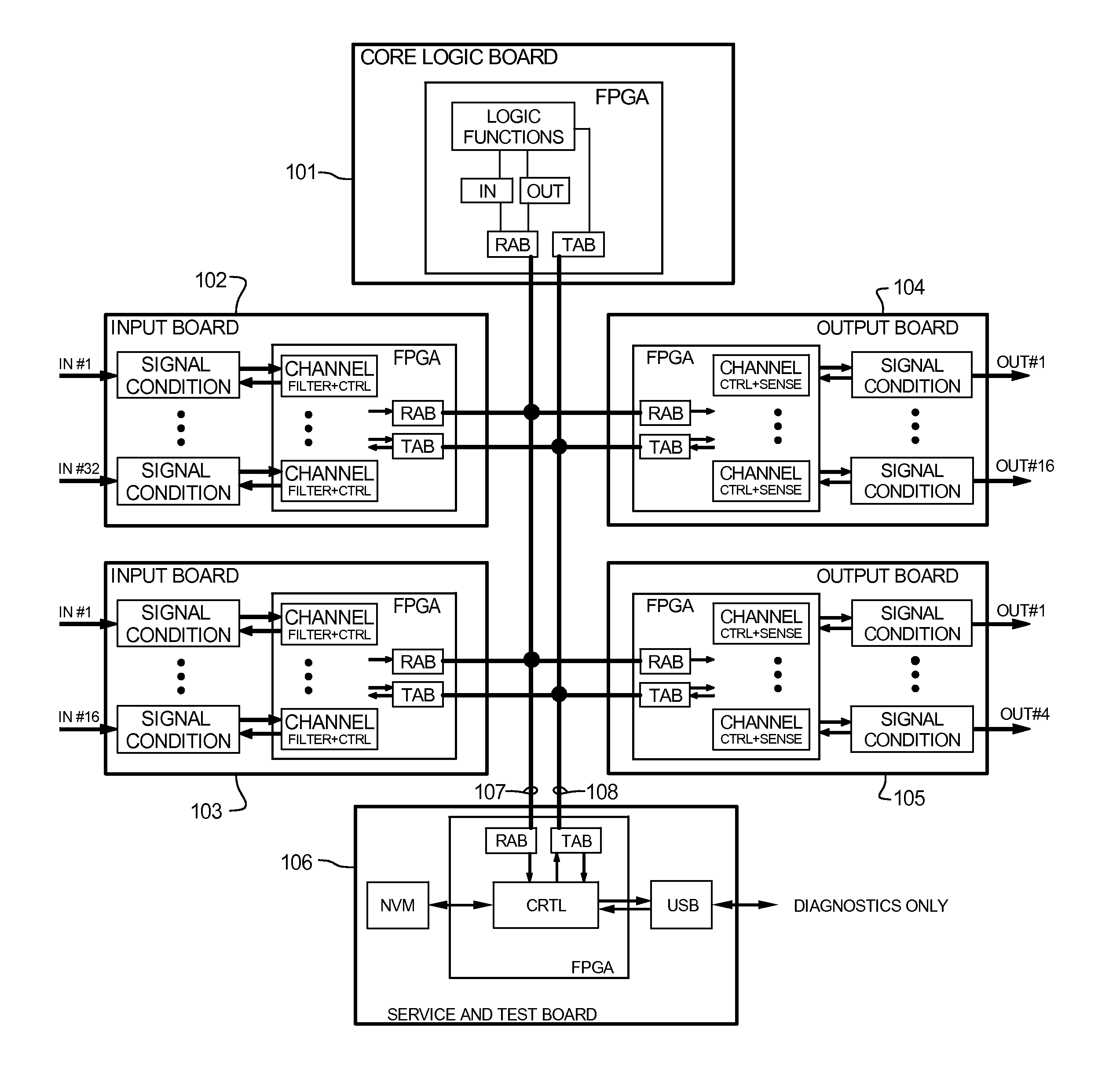
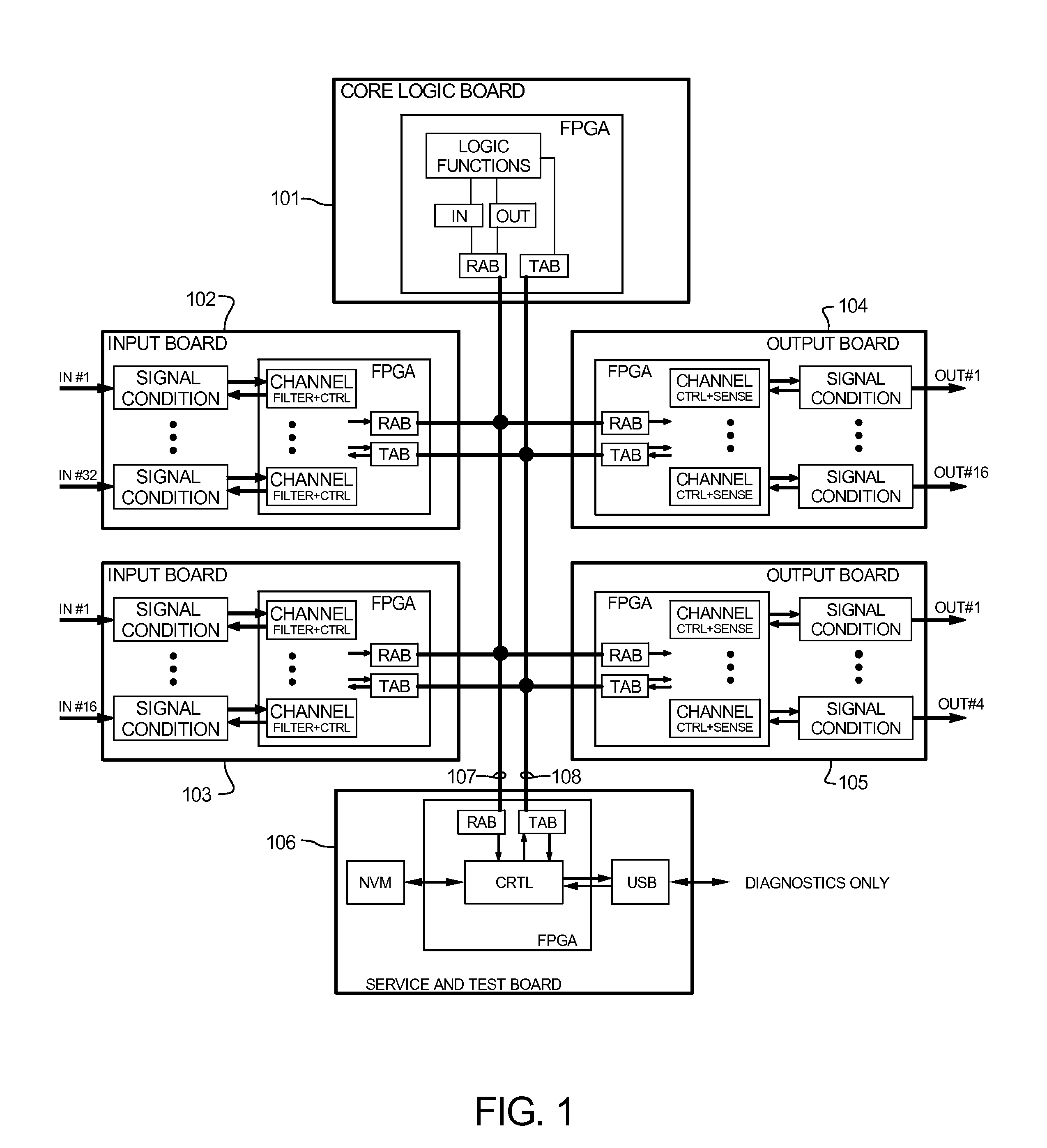
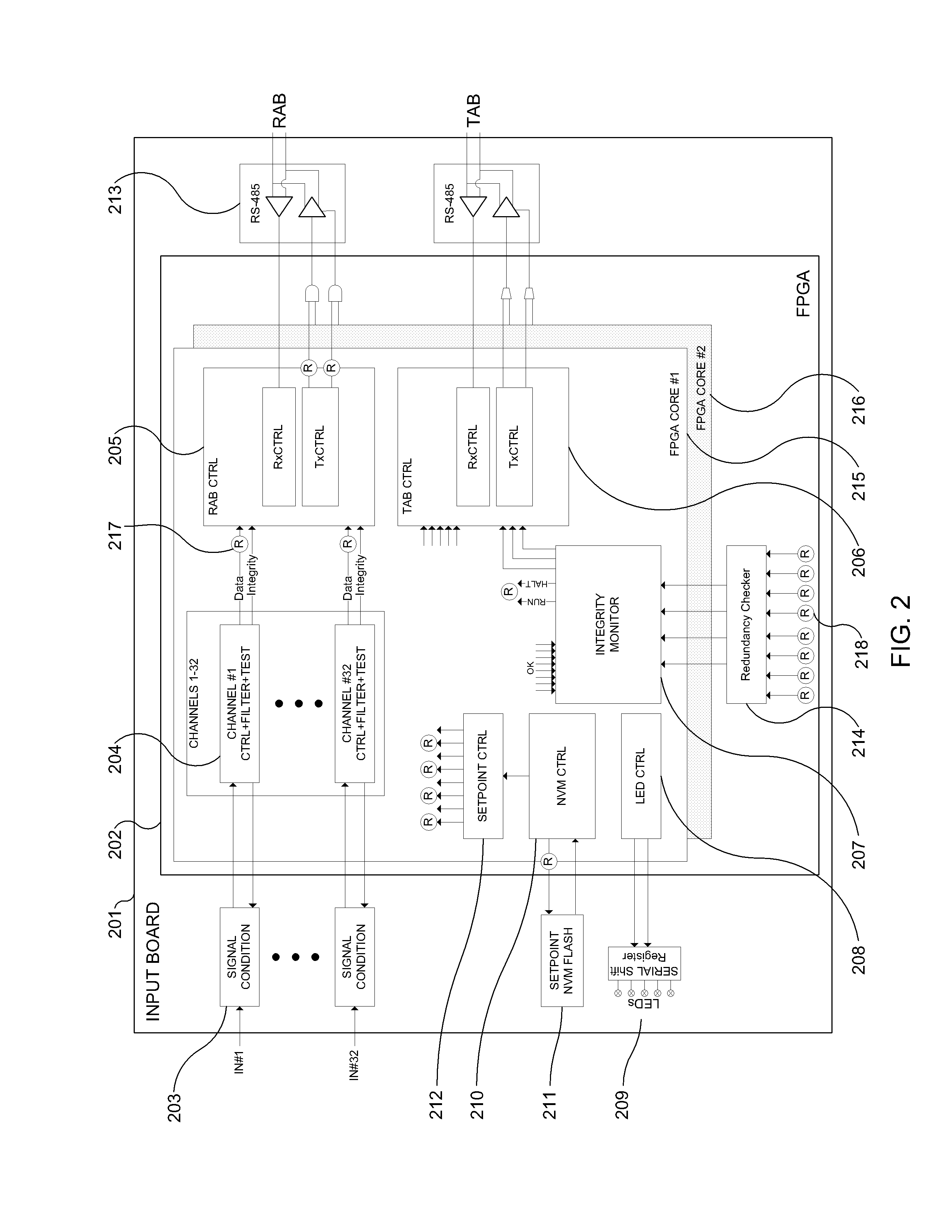
The Advanced Logic System (ALS) is a complete control system architecture, based on a hardware platform rather than a software-based microprocessor system. It is significantly different from other PLC-type control system architectures, by implementing a FPGA in the central control unit. Standard FPGA logic circuits are used rather than a software-based microprocessor which eliminate problems with software based microprocessor systems, such as software common-mode failures. It provides a highly reliable system suitable for safety critical control systems, including nuclear plant protection systems. The system samples process inputs, provides for digital bus communications, applies a control logic function, and provides for controlled outputs. The architecture incorporates advanced features such as diagnostics, testability, and redundancy on multiple levels. It additionally provides significant improvements in failure detection, isolation, and mitigation for the highest level of integrity and reliability.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Method and system for controlling power in a chip through a power-performance monitor and control unit
ActiveUS7421601B2Performance maximizationImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementControl powerControl system
A system and method for controlling power and performance in a microprocessor system includes a monitoring and control system integrated into a microprocessor system. The monitoring and control system includes a hierarchical architecture having a plurality of layers. Each layer in the hierarchical architecture is responsive to commands from a higher level, and the commands provide instructions on operations and power distribution, such that the higher levels provide modes of operation and budgets to lower levels and the lower levels provide feedback to the higher levels to control and manage power usage in the microprocessor system both globally and locally.
Owner:IBM CORP
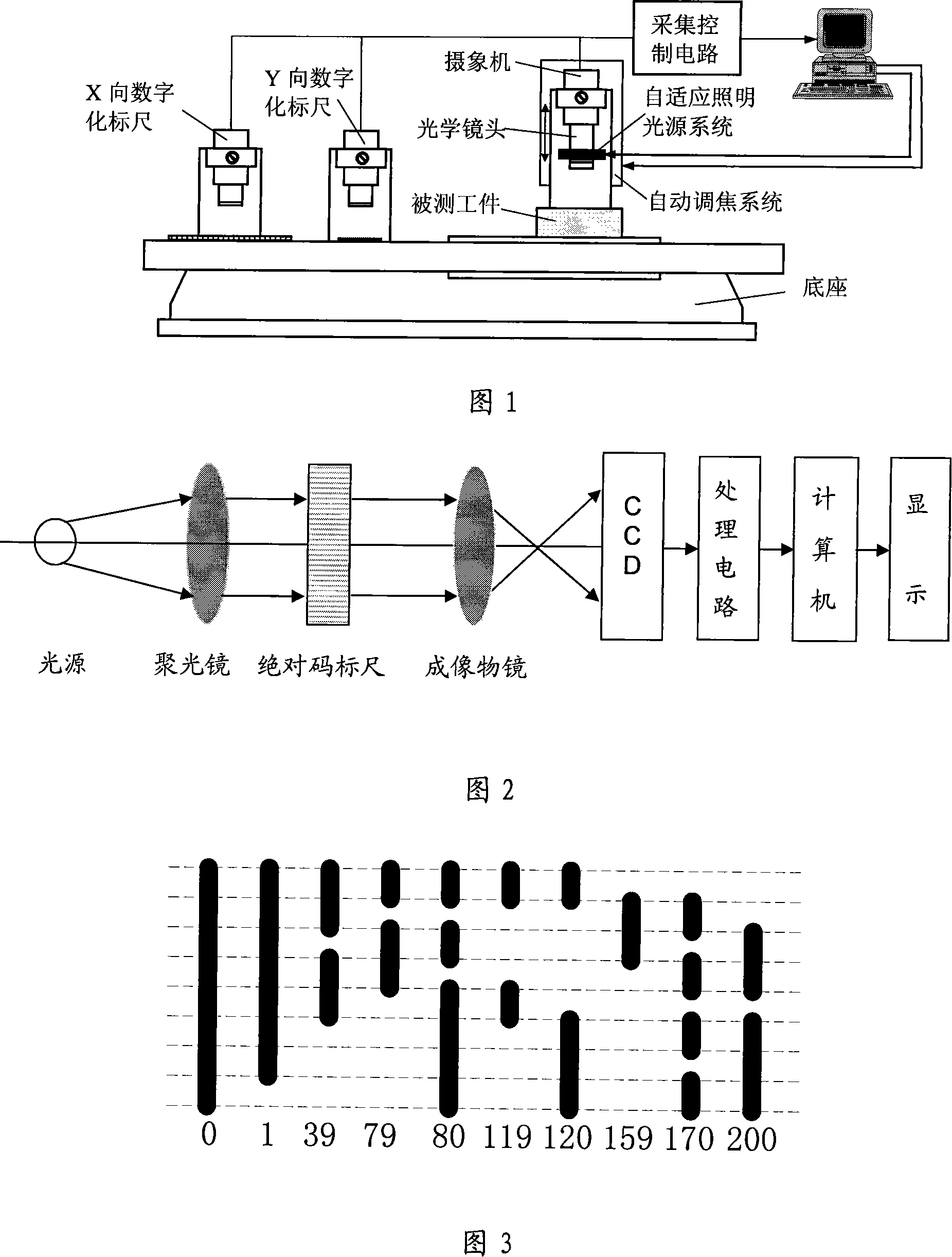
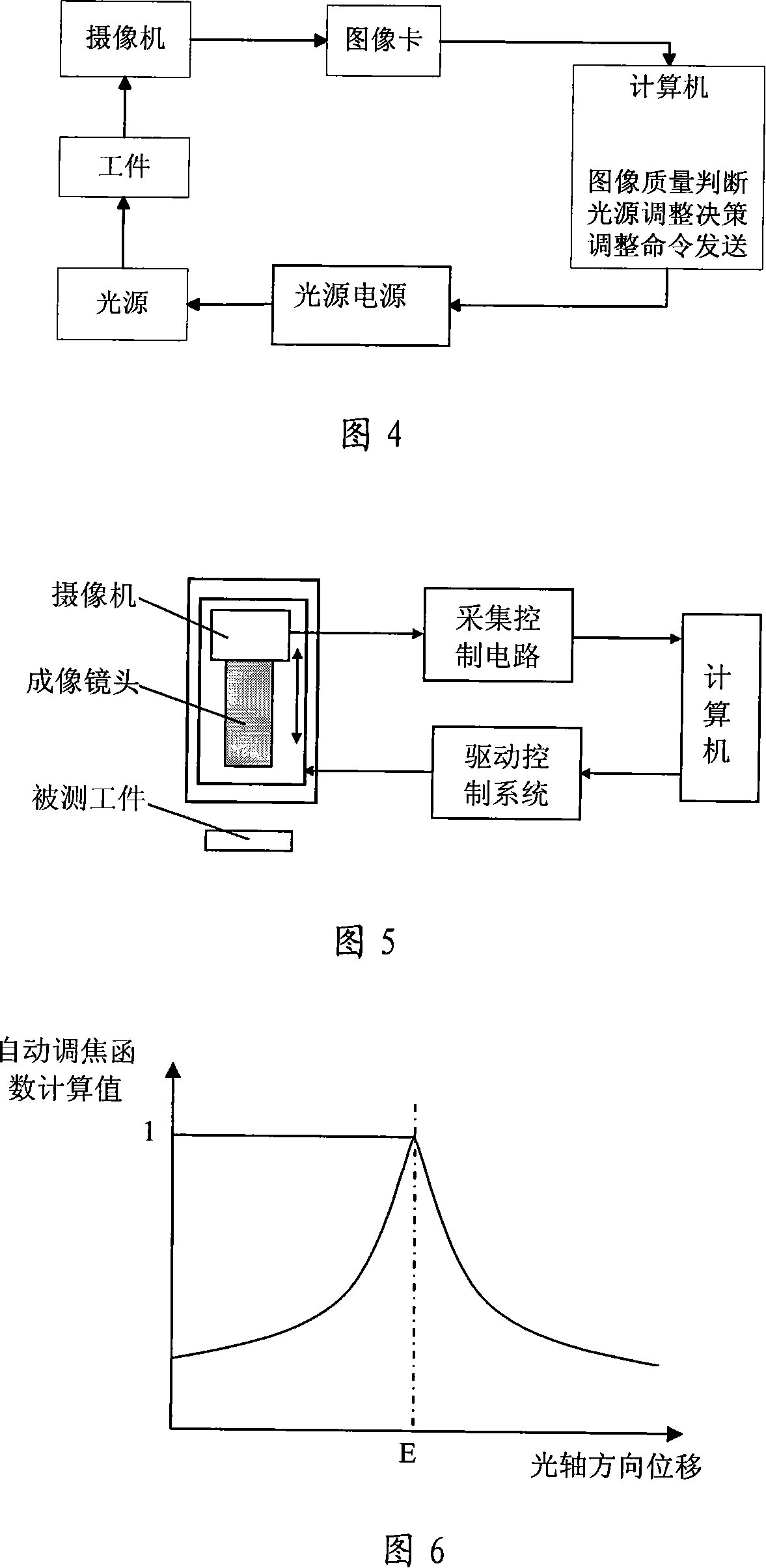
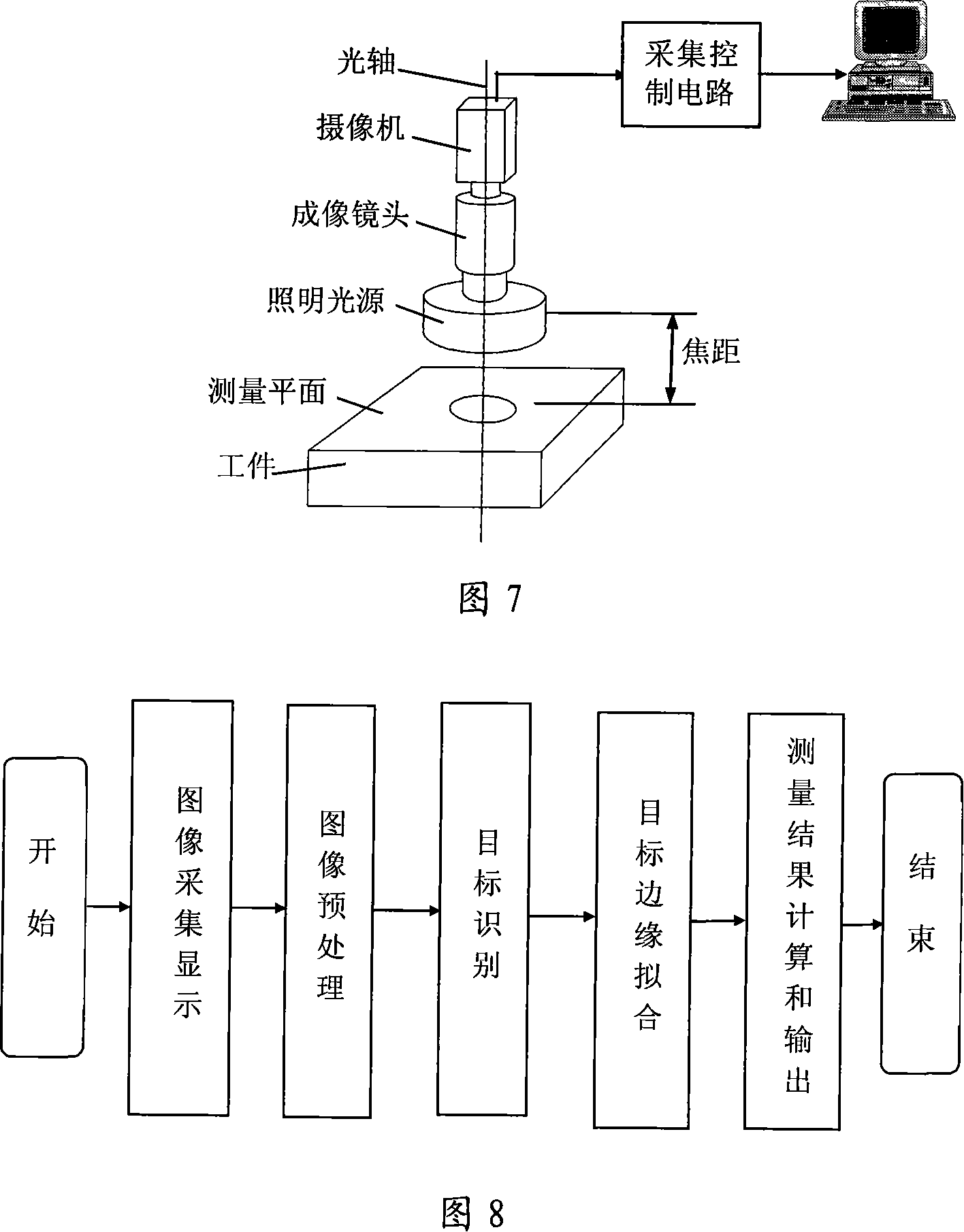
High accuracy vision detection system
InactiveCN101149254ARealize automatic pickingRealize SegmentationUsing optical meansFocusing aidsCamera lensImaging quality
The high precision vision detection system includes the digital staff guage system, the illuminating system with adaptive adjusting optical intensity, the auto focus system, the optical image system, the vision detection software, the foundation, the computer or microprocessor system. The digital staff guage system is used to provide the high precision length detection base in large scale; the illuminating system is used to adjust the optical intensity according to the different of the detection distance, detection angle and the surface reflectivity of detected workpiece to provide the uniform and stable illuminating intensity to pledge the image quality and the detection precision; the auto focus system is used to adjust the working distance of the detection system to pledge the image has the good quality and constant amplification ratio and pledge the repeatability and detection precision of the detection system; the optical image system is the main part of the detection system, which is used to transform the geometry outlook of detected workpiece to the computer or processor through the optical lens image, the vidicon photoelectricity switch and collecting control circuit; the vision detection software is used to process the image and get the detection result; the foundation is the supporting frame of vision detection system, which is used to fix, support and move every part of system; the computer or microprocessor system is the core part of the whole vision detection system, which is used to coordinate and control every system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
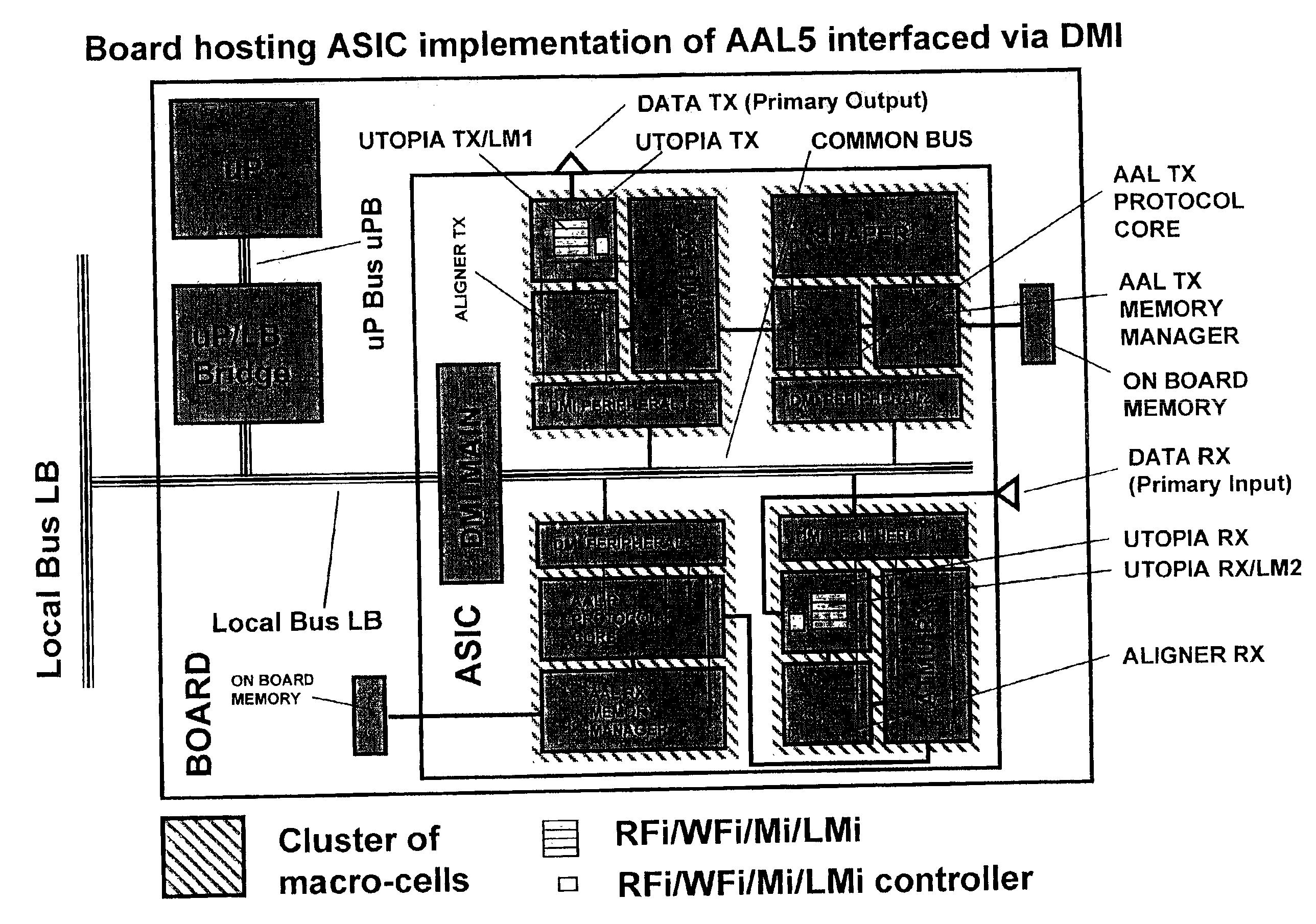
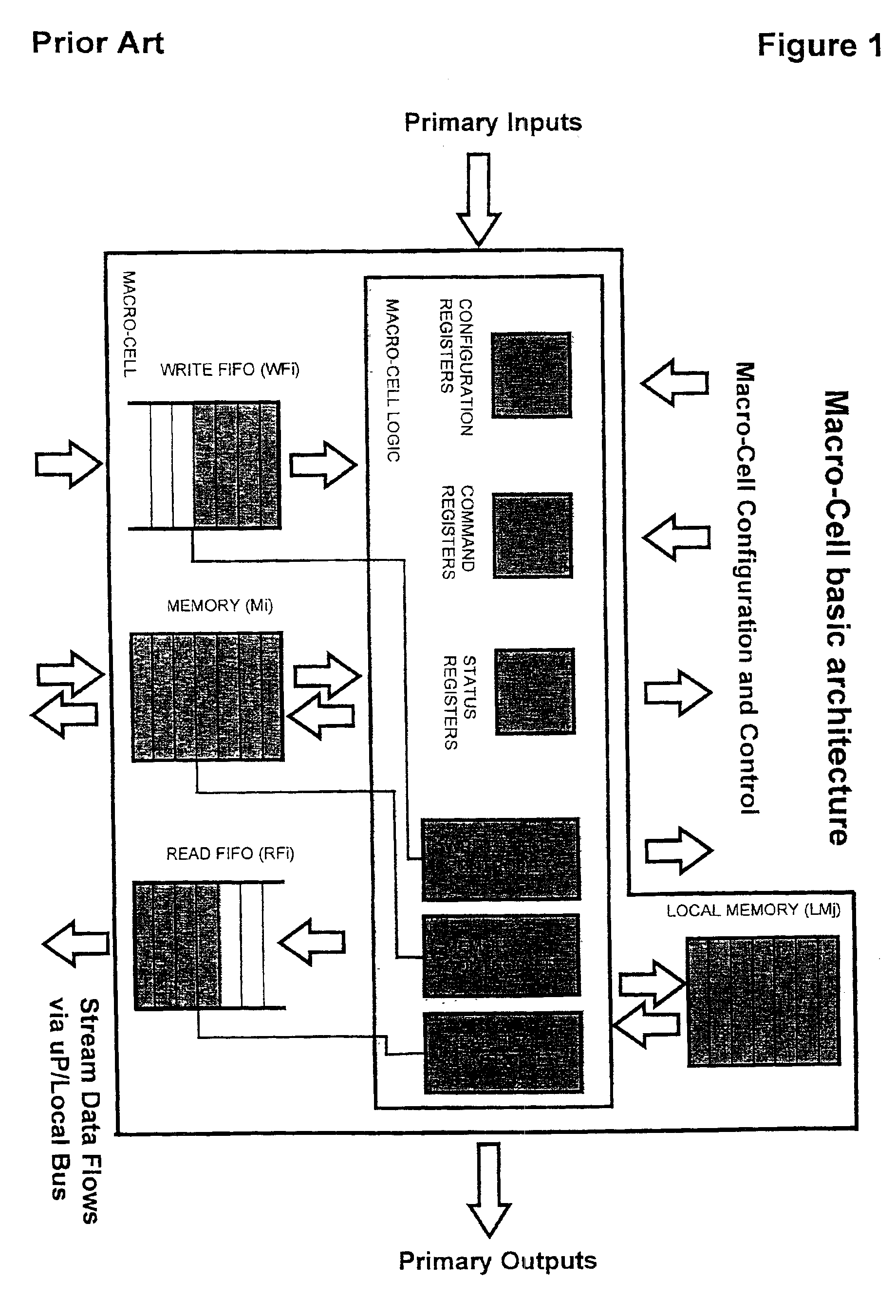
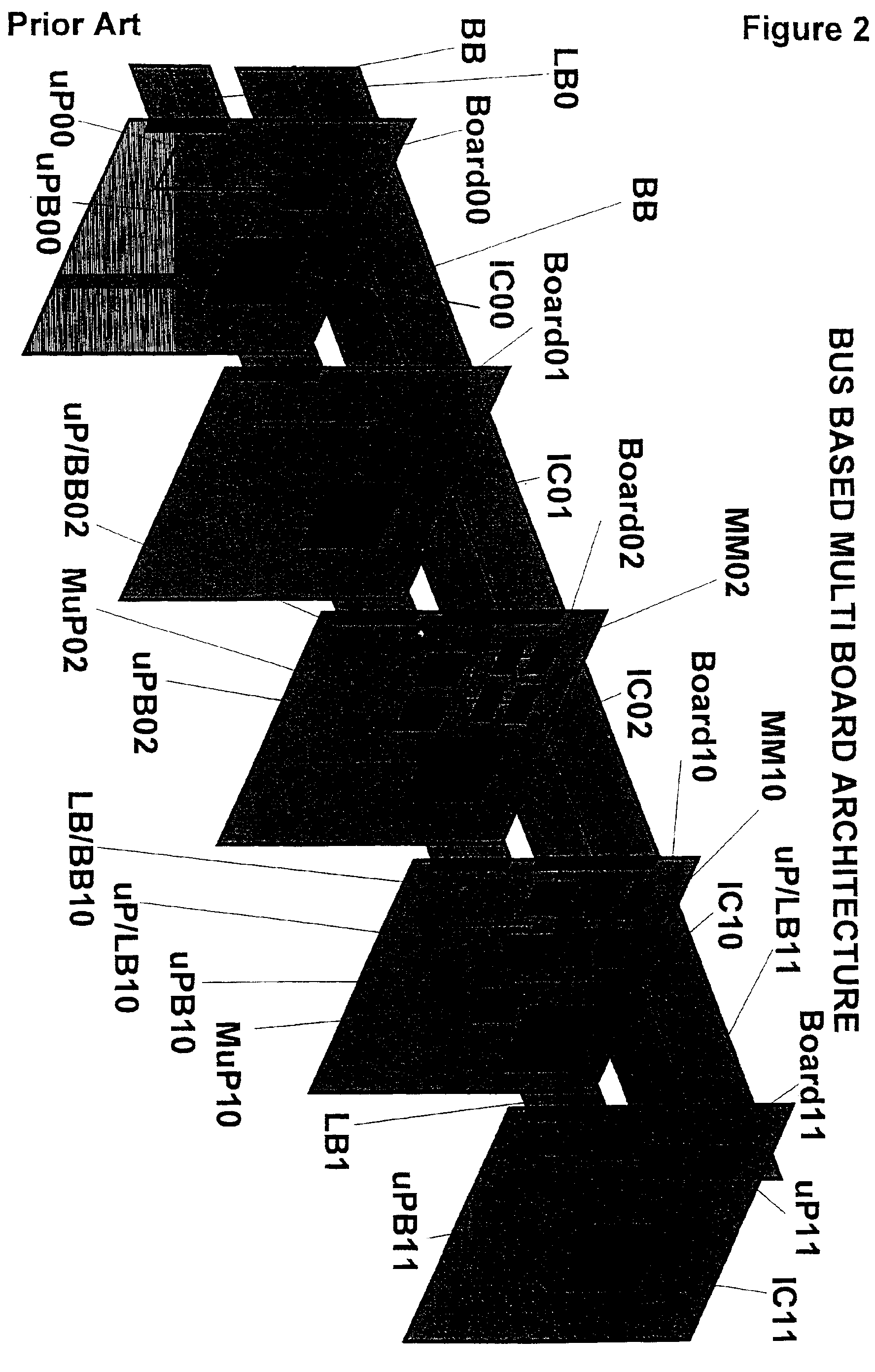
System of distributed microprocessor interfaces toward macro-cell based designs implemented as ASIC or FPGA bread boarding and relative common bus protocol
InactiveUS6970966B2Easy to implementImprove developmentDigital computer detailsData resettingMultiple pointMacrocell
A distributed interface between a microprocessor or a standard bus and user macro-cells belonging to an ASIC, or FPGA, or similar silicon devices includes a main module connected to the microprocessor bus on one side and to a COMMON-BUS inside the interface on which a cluster of peripheral modules is appended on the other side. Peripheral modules are also connected to the user macro-cells through as multiple point-to-point buses to transfer signals two directions. A set of hardware and firmware resources such as registers, counters, synchronizers, dual port memories (e.g. RAM, FIFO) either synchronous or asynchronous with respect to macro-cells clock is encompassed in each peripheral module. Subsets of the standard resources are diversely configured in each peripheral module in accordance with specific needs of the user macro-cells.
Owner:ITALTEL SPA
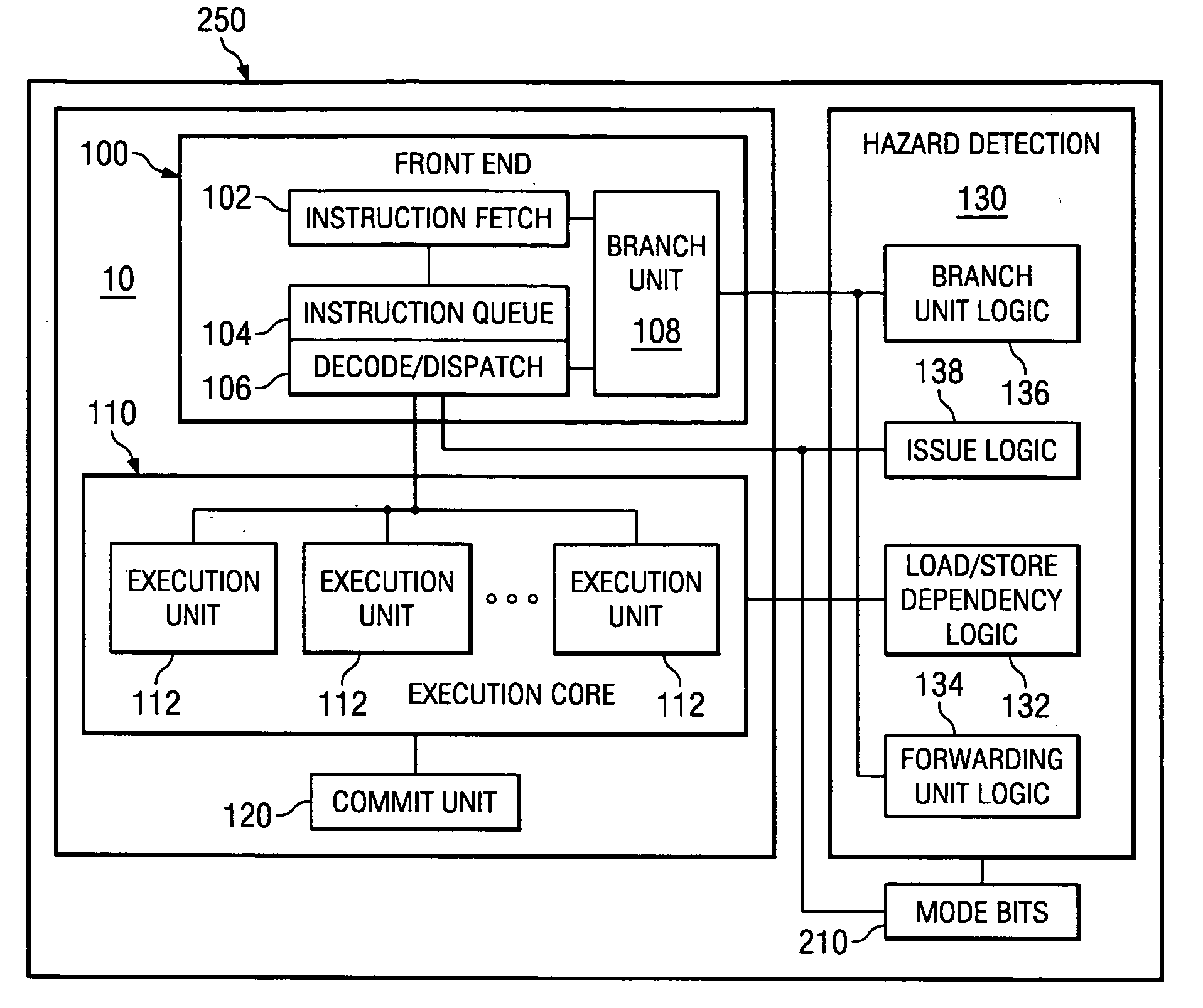
Method and system for an enhanced microprocessor
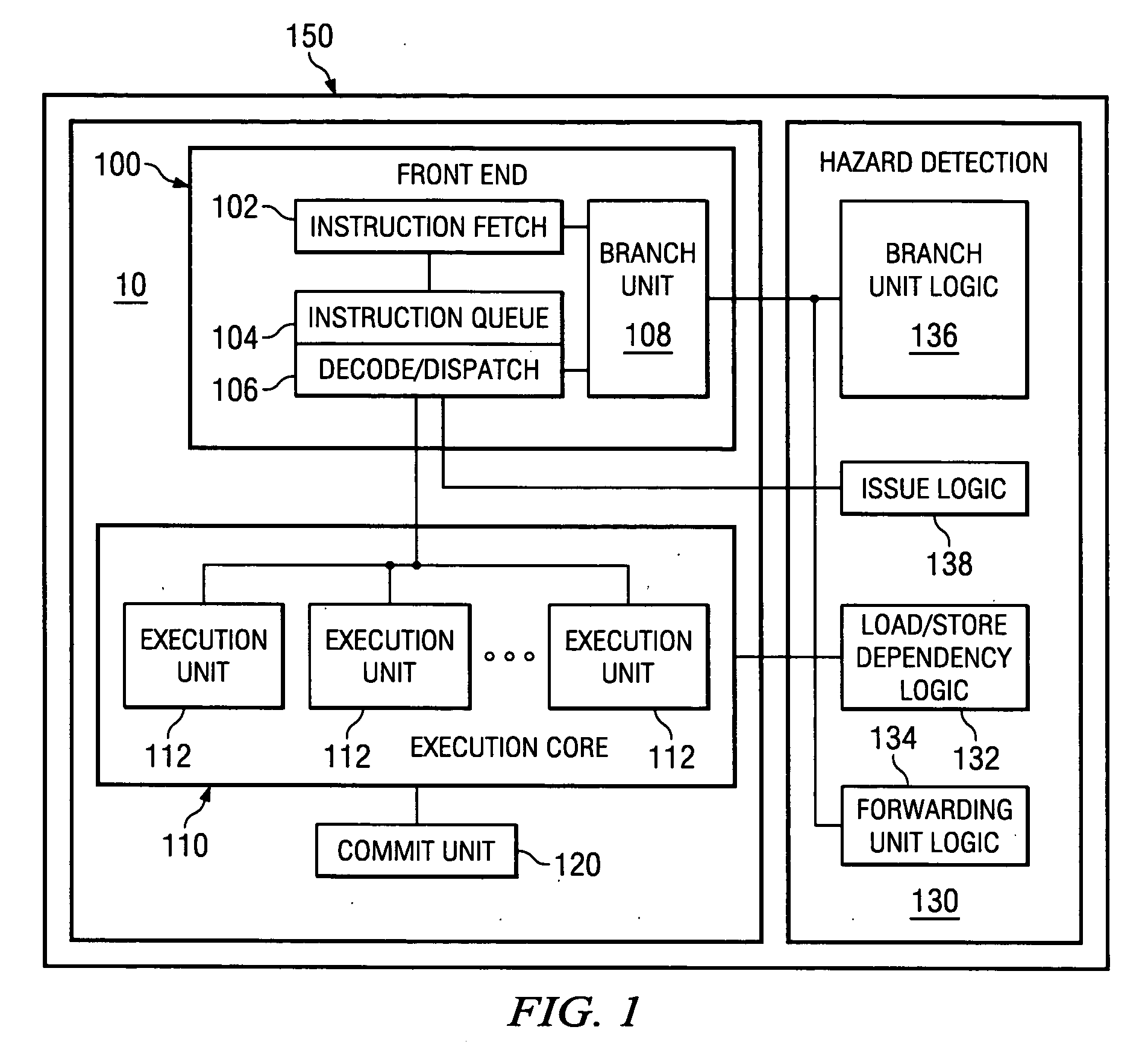
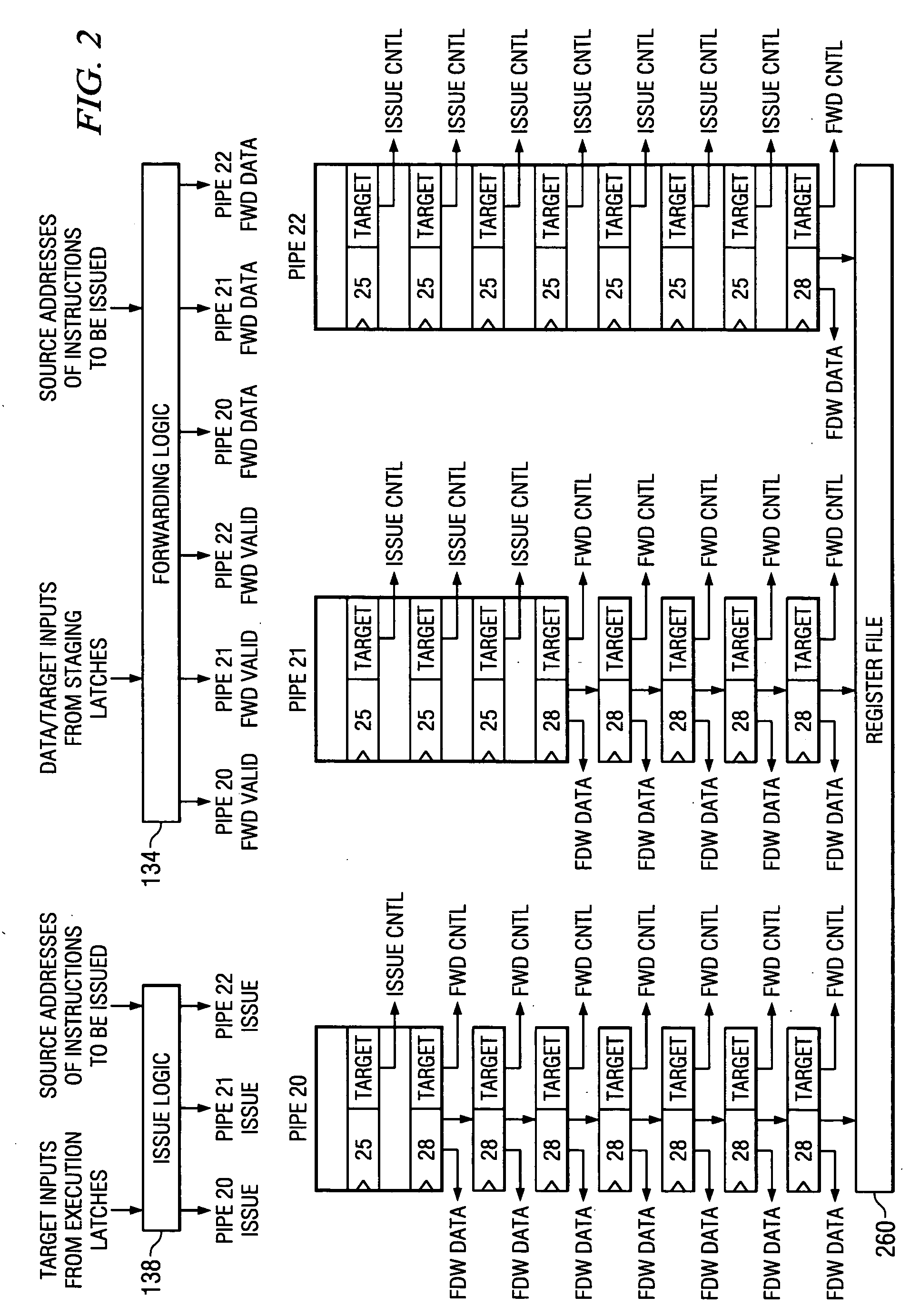
InactiveUS20070022277A1High-speed executionLess powerDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsCombined useComputer science
Systems and methods for modes of operation for processing data are disclosed. While executing a program in one mode the hazard checking logic present in the microprocessor system may be utilized to check or ameliorate the hazards caused by the execution of this program. However, when a program does not need this hazard checking, the microprocessor may execute this program in a mode where some portion of the hazard checking logic of the microprocessor may not be utilized in conjunction with the execution of this program. This allows the higher speed execution of these types of programs by eliminating checking for dependencies, the detection of false load / store dependencies, the insertion of unnecessary stalls into the execution pipeline of the microprocessor or other hardware operations. Furthermore, by reducing the use of hazard detection logic a decrease in power consumption may also be effectuated.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
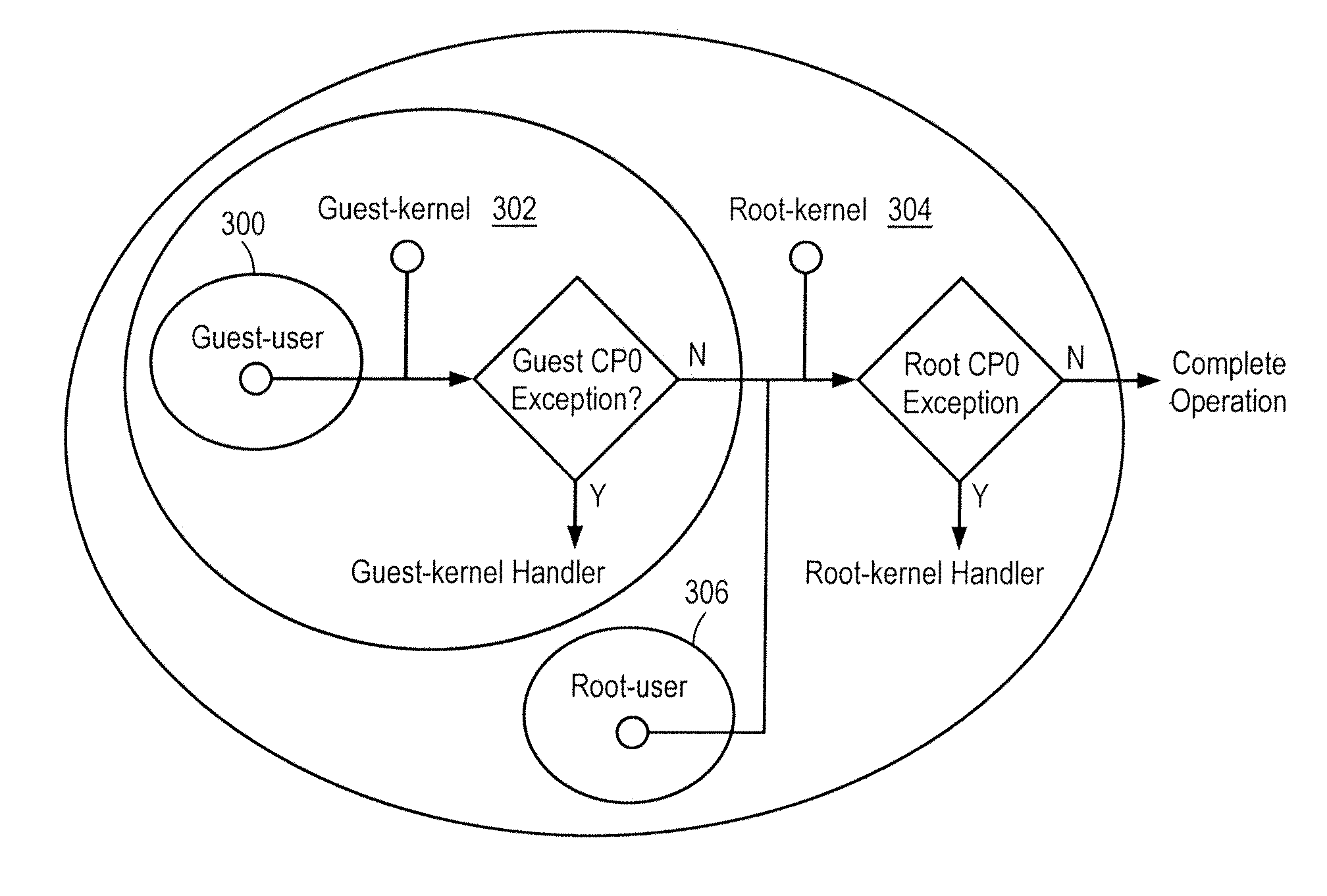
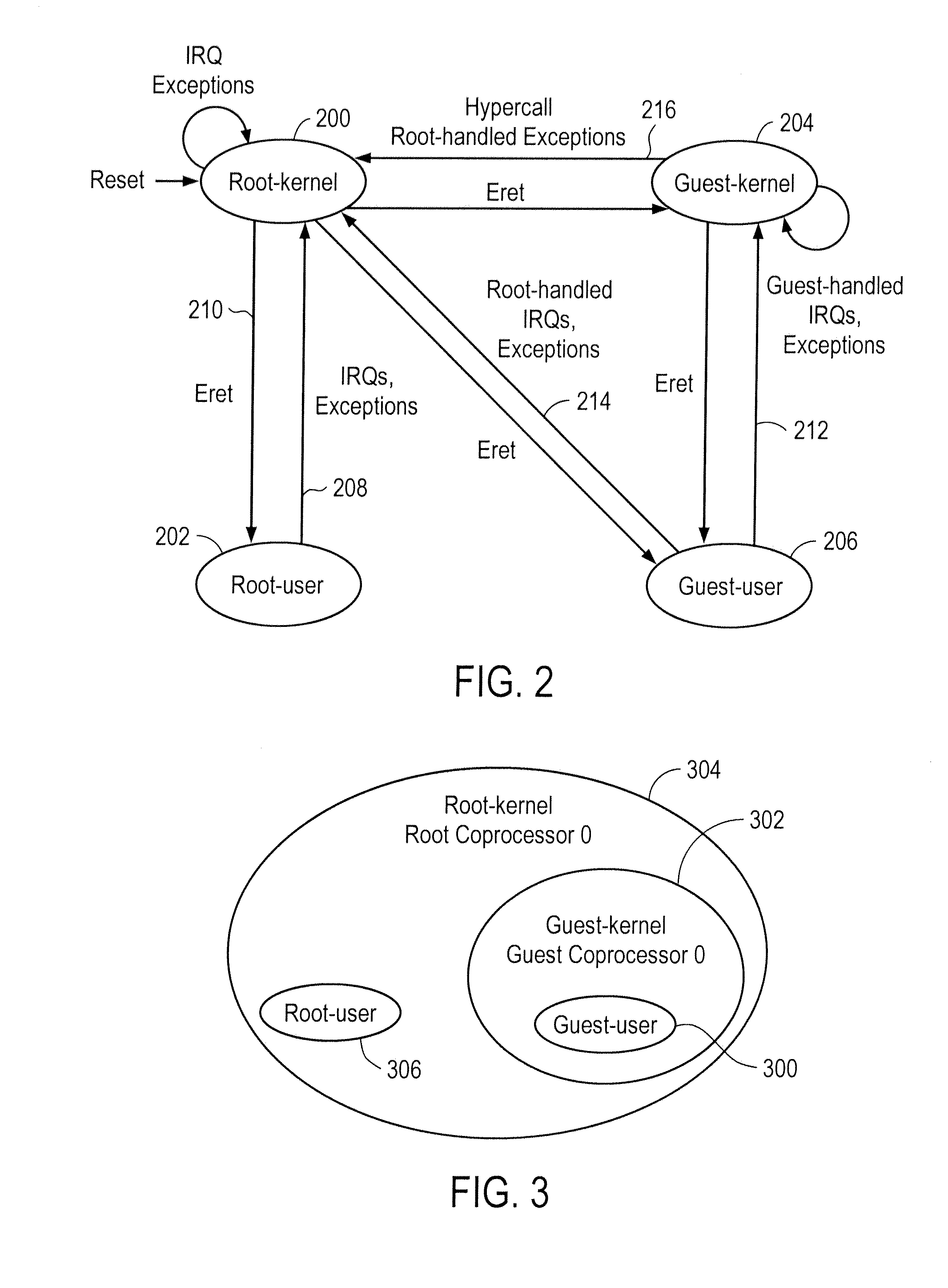
Microprocessor system for virtual machine execution
ActiveUS20120079479A1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsVirtualizationMode control
A processor includes guest mode control registers supporting guest mode operating behavior defined by guest context specified in the guest mode control registers. Root mode control registers support root mode operating behavior defined by root context specified in the root mode control registers. The guest context and the root context are simultaneously active to support virtualization of hardware resources such that multiple operating systems supporting multiple applications are executed by the hardware resources.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
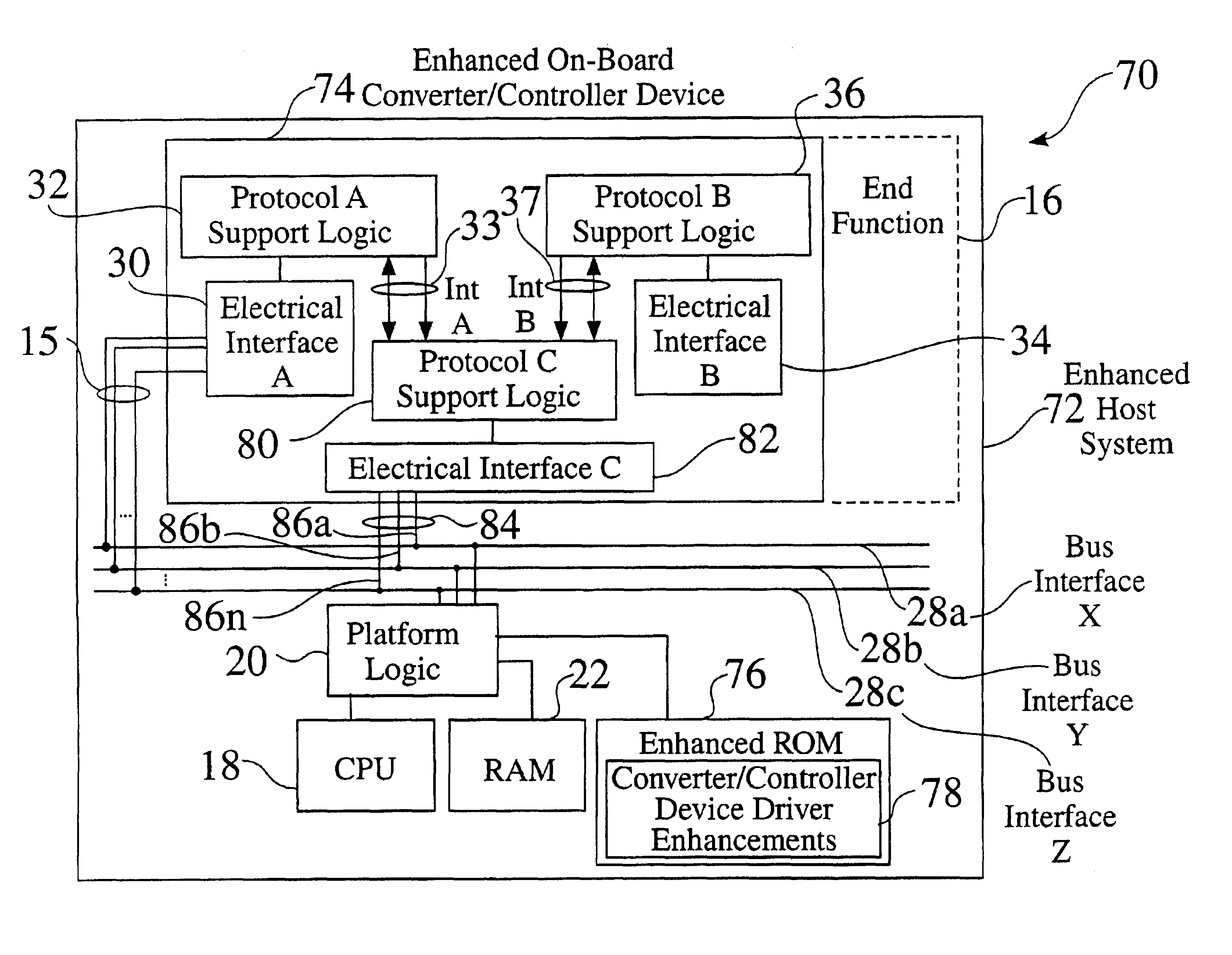
System and method capable of offloading converter/controller-specific tasks to a system microprocessor
Systems are provided for the offloading of protocol control and conversion information within microprocessor-based systems. A converter controller comprises a first interface and protocol, as well as a second interface and protocol. An intermediate protocol and interface is interconnected to both the first protocol and the second protocol, and forwards or offloads protocol information to the system CPU, which comprises device driver information for protocol conversion and / or control. The CPU acts upon the received protocol information, performs protocol conversion as necessary, and forwards the converted protocol information back to the converter controller through the intermediate interface. Some embodiments of the offloading protocol conversion system comprise a SDIO controller within a USB-based device.
Owner:MAISHI ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) LTD
Microprocessor system for the analysis of physiologic and financial datasets
InactiveUS20060276695A9Increase variabilityLittle varianceMedical data miningEvaluation of blood vesselsTime domainObject based
A system and method for organization and analysis of complex and dynamically interactive time series is disclosed. One example comprises a processor based system for relational analysis of physiologic signals for providing early recognition of catastrophic and pathologic events such as pathophysiologic divergence. The processor is programmed to identify pathophysiologic divergence of at least one of first and second physiologic parameters in relationship to the other and to output an indication of the divergence. An object-based method of iterative relational processing waveform fragments in the time domain is described wherein each more complex waveform object inherits the characteristics of the waveform objects from which it is derived. The first physiologic parameter can be the amplitude and frequency of the variation in chest wall impedance or nasal pressure and the second parameter can be a measure or indication of the arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:LYNN LAWRENCE ALLAN
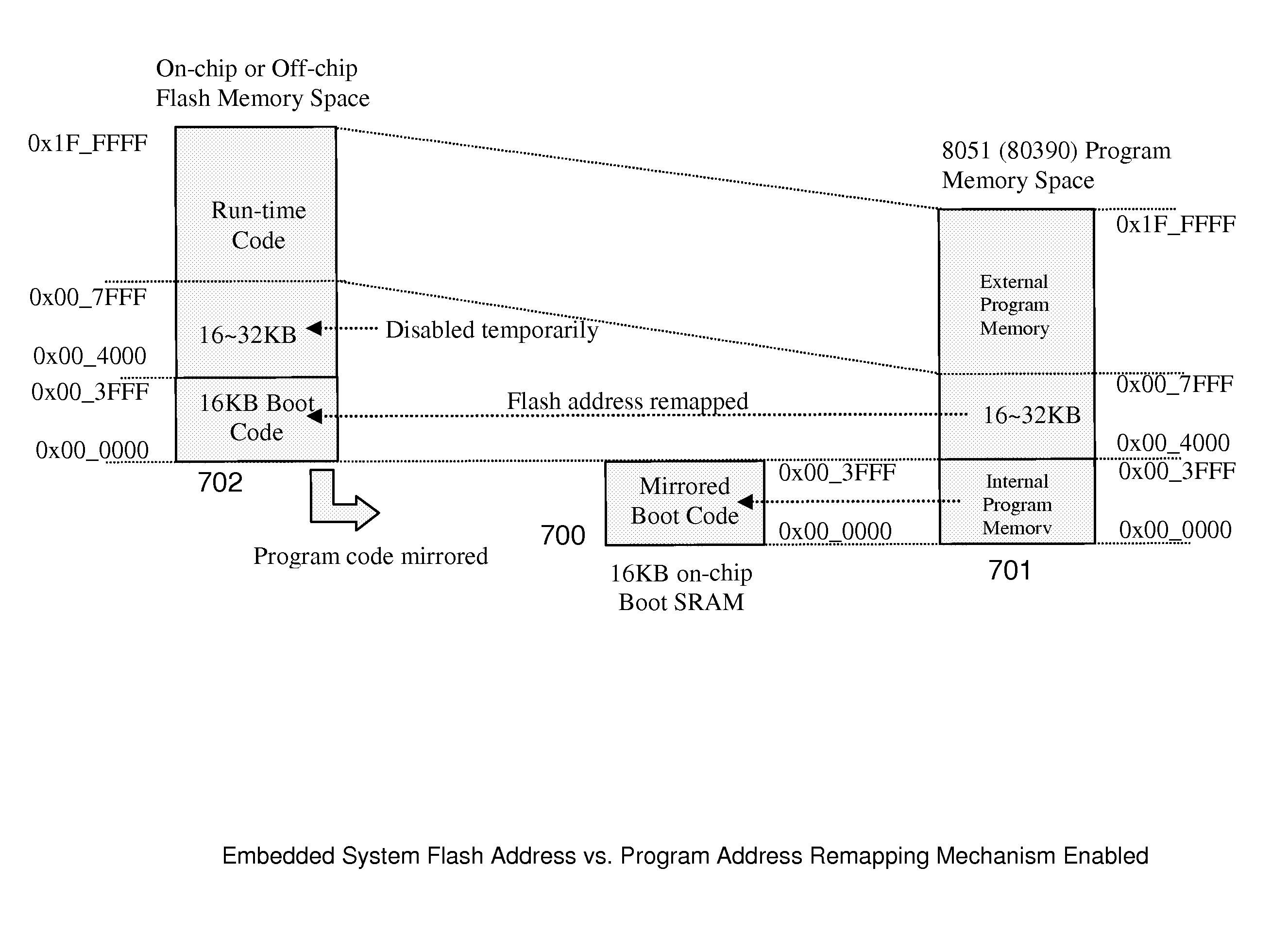
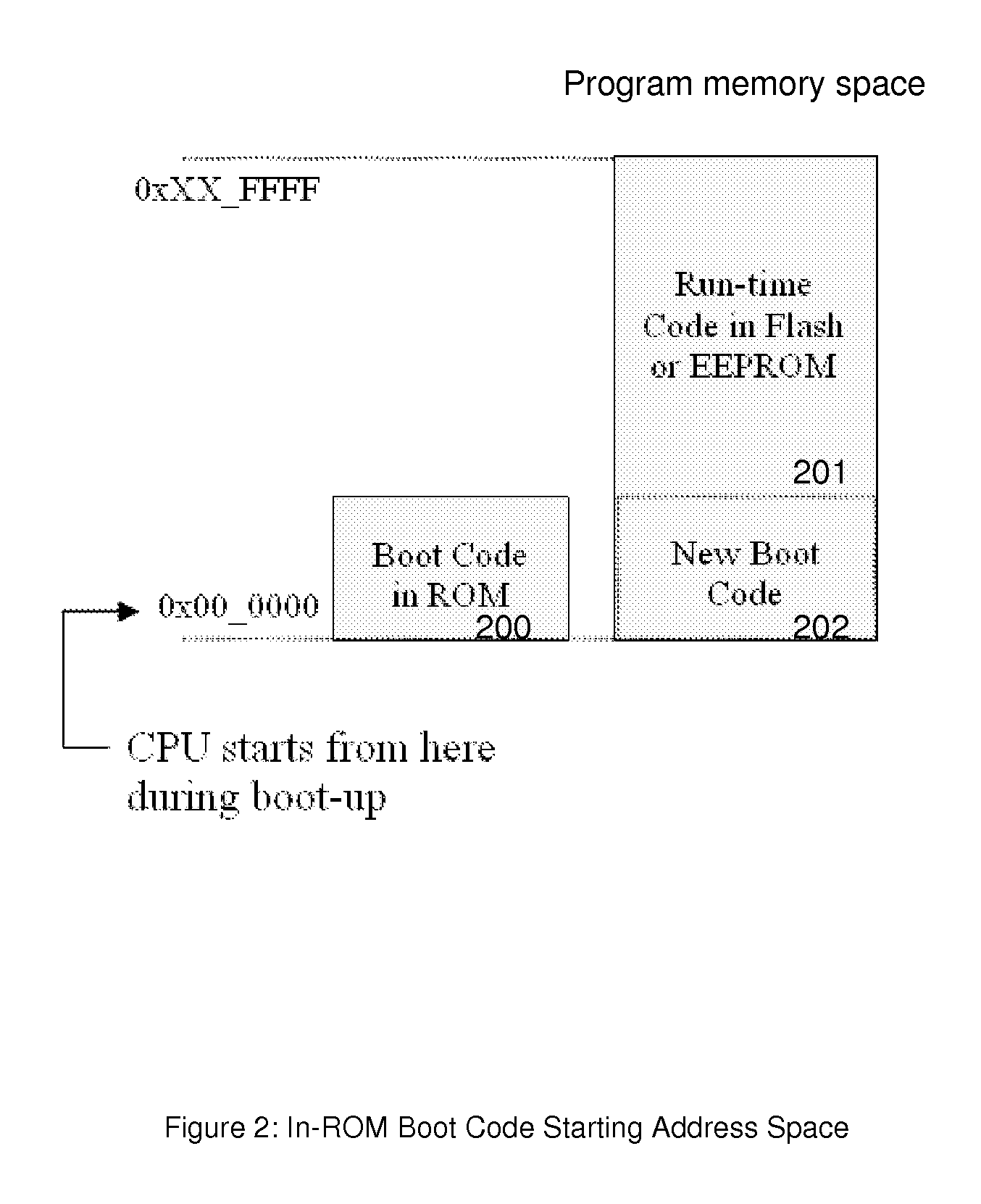
Method and systems for advanced reprogrammable boot codes and in-application programming of embedded microprocessor systems
InactiveUS20090113196A1Increase flexibilitySoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsIn-system programmingApplication programming interface
This invention relates to an advanced system and method of reprogrammable boot codes and In Application Programming (IAP) of embedded systems by booting up with boot loader to shadow program codes on to an internal high speed SRAM and extending contiguously to external higher space memory for runtime applications, and supporting on-line IAP to update run-time firmware or boot loader driver through network communication by utilizing advanced address remapping scheme as well as supporting In System Programming (ISP) to program initial Flash memory via ISP adaptor.
Owner:ASIX ELECTRONICS
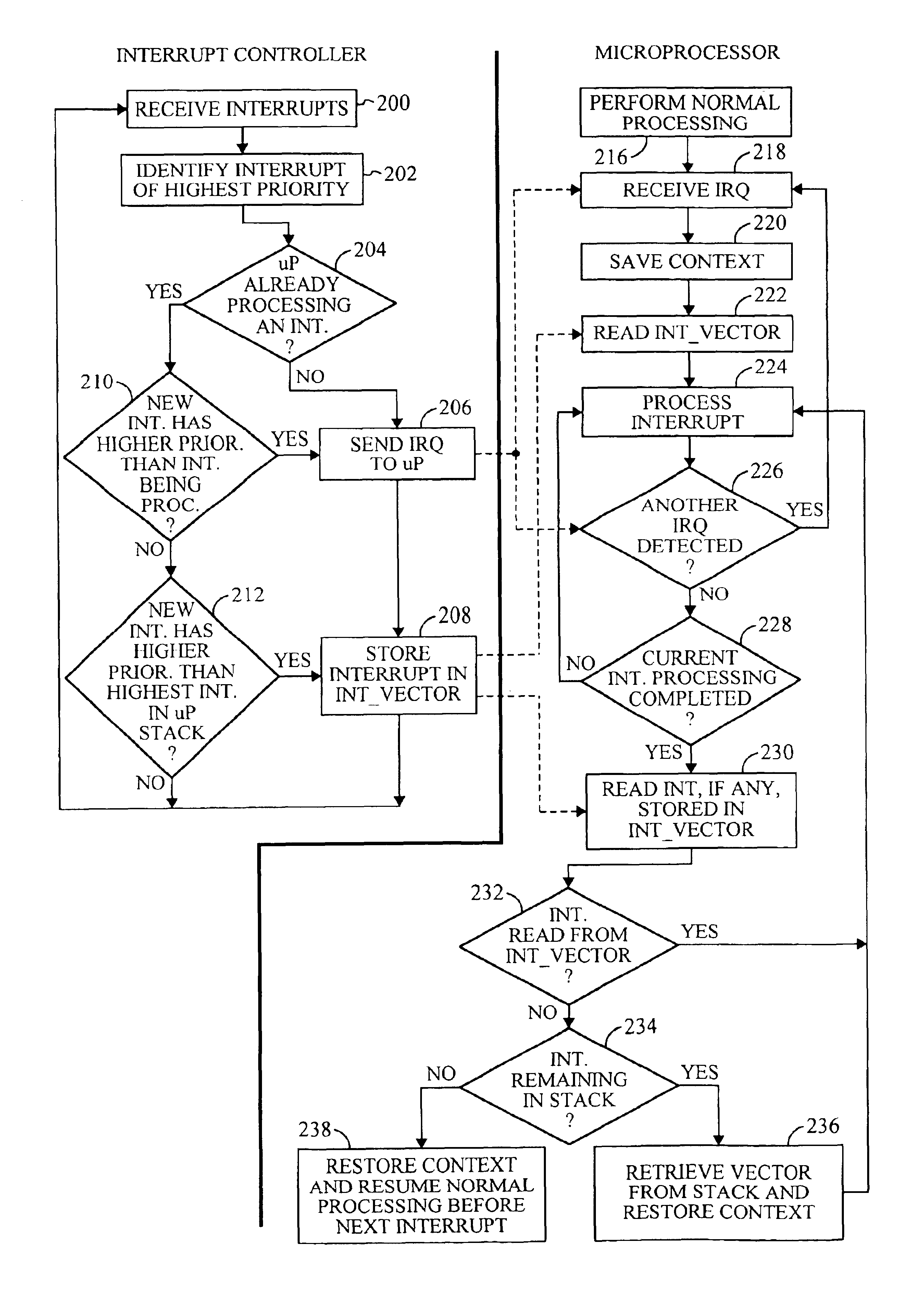
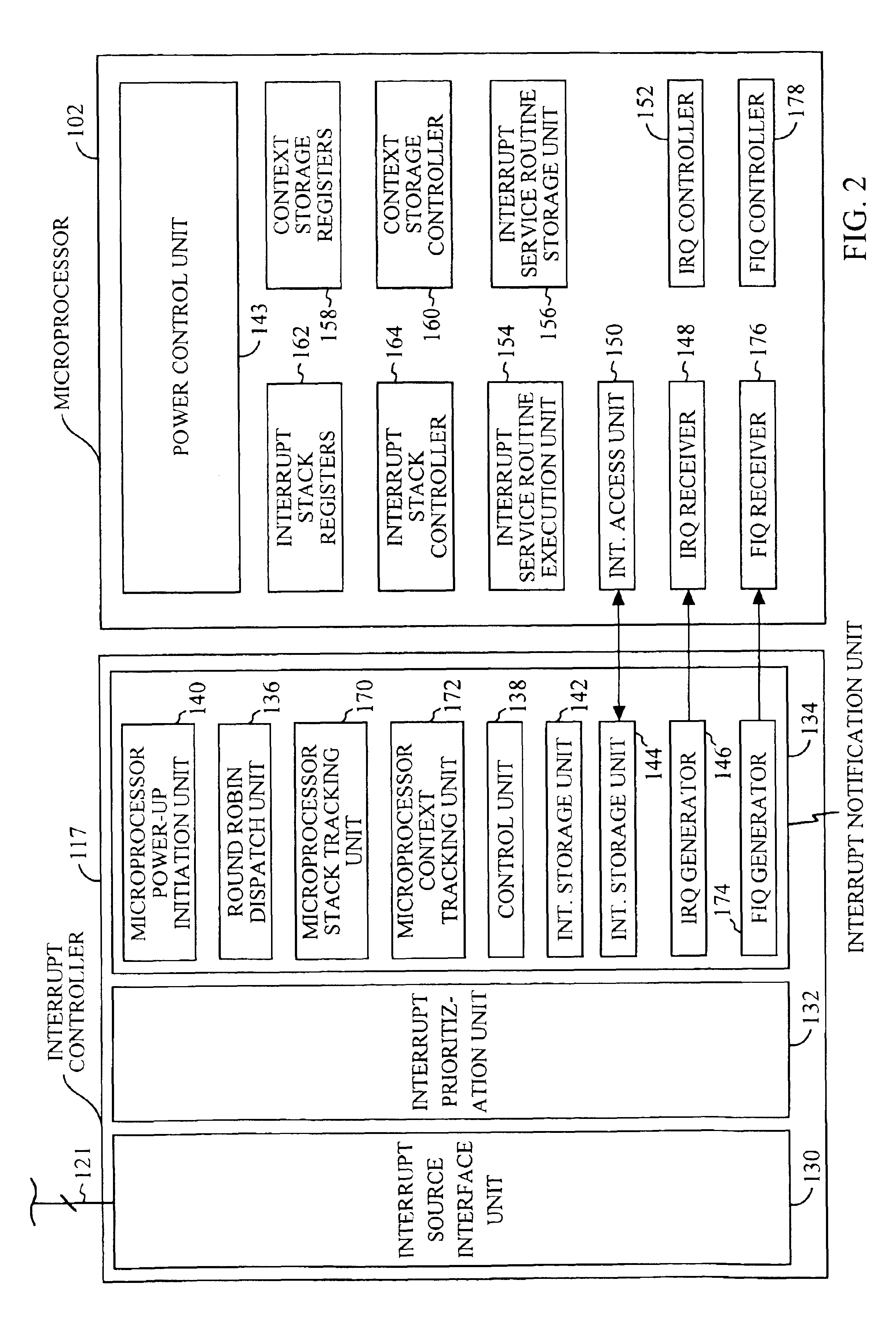
Mobile communication device having a prioritized interrupt controller
InactiveUS6807595B2Energy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingProgrammable Interrupt ControllerComputer science
A microprocessor system having an interrupt controller is provided for use in a mobile communications device. Peripheral processing units generate interrupt requests for sending to the microprocessor. The microprocessor has components for responding to interrupt requests by interrupting current processing and performing an interrupt service routine associated with the interrupt request. The interrupt controller receives interrupt requests directed to the microprocessor from the peripheral processing units and for prioritizes the interrupt requests on behalf of the microprocessor. By providing an interrupt controller for prioritizing interrupt requests on behalf of the microprocessor, the microprocessor therefore need not devote significant internal resources to prioritizing the interrupt request signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
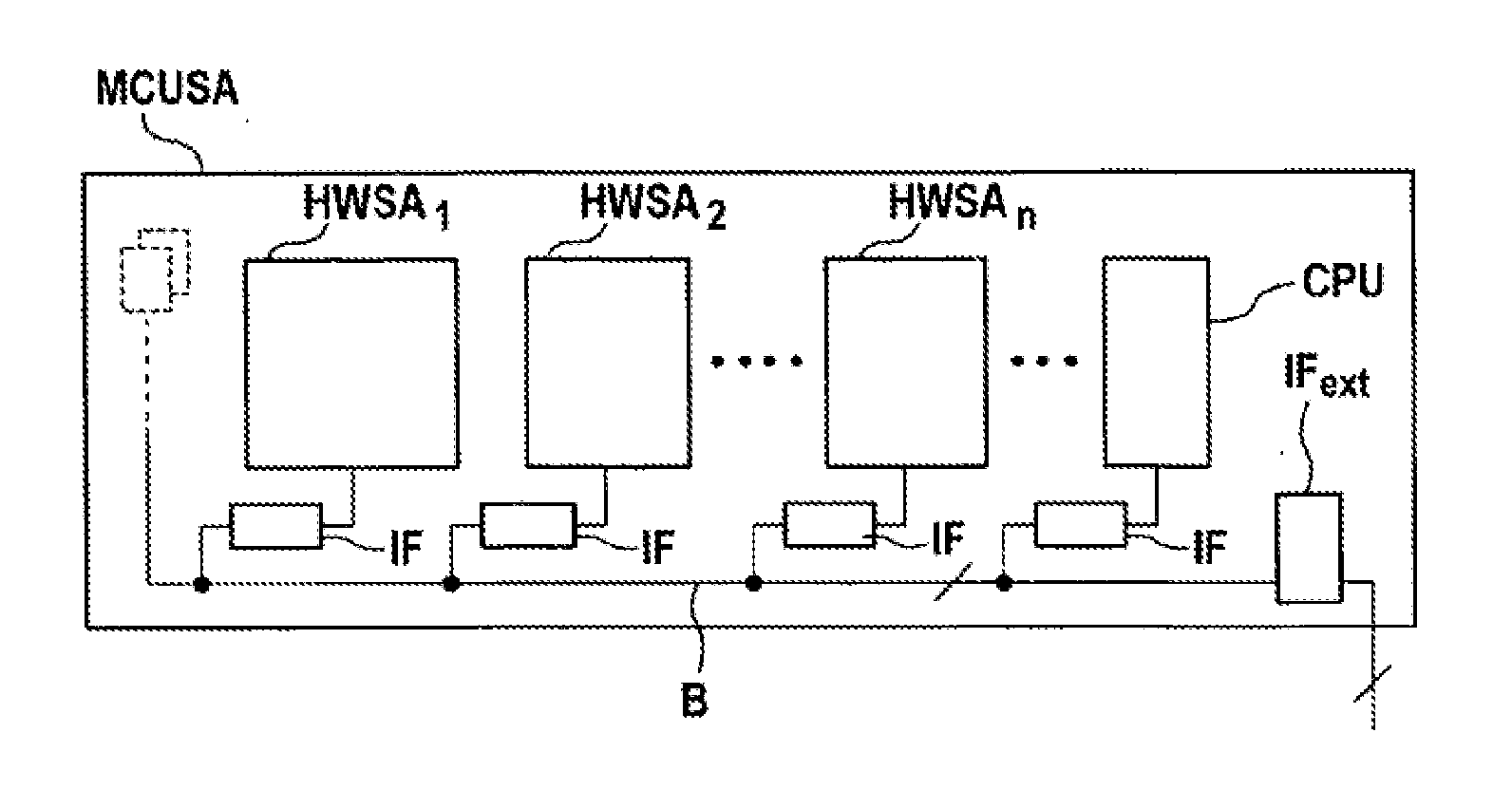
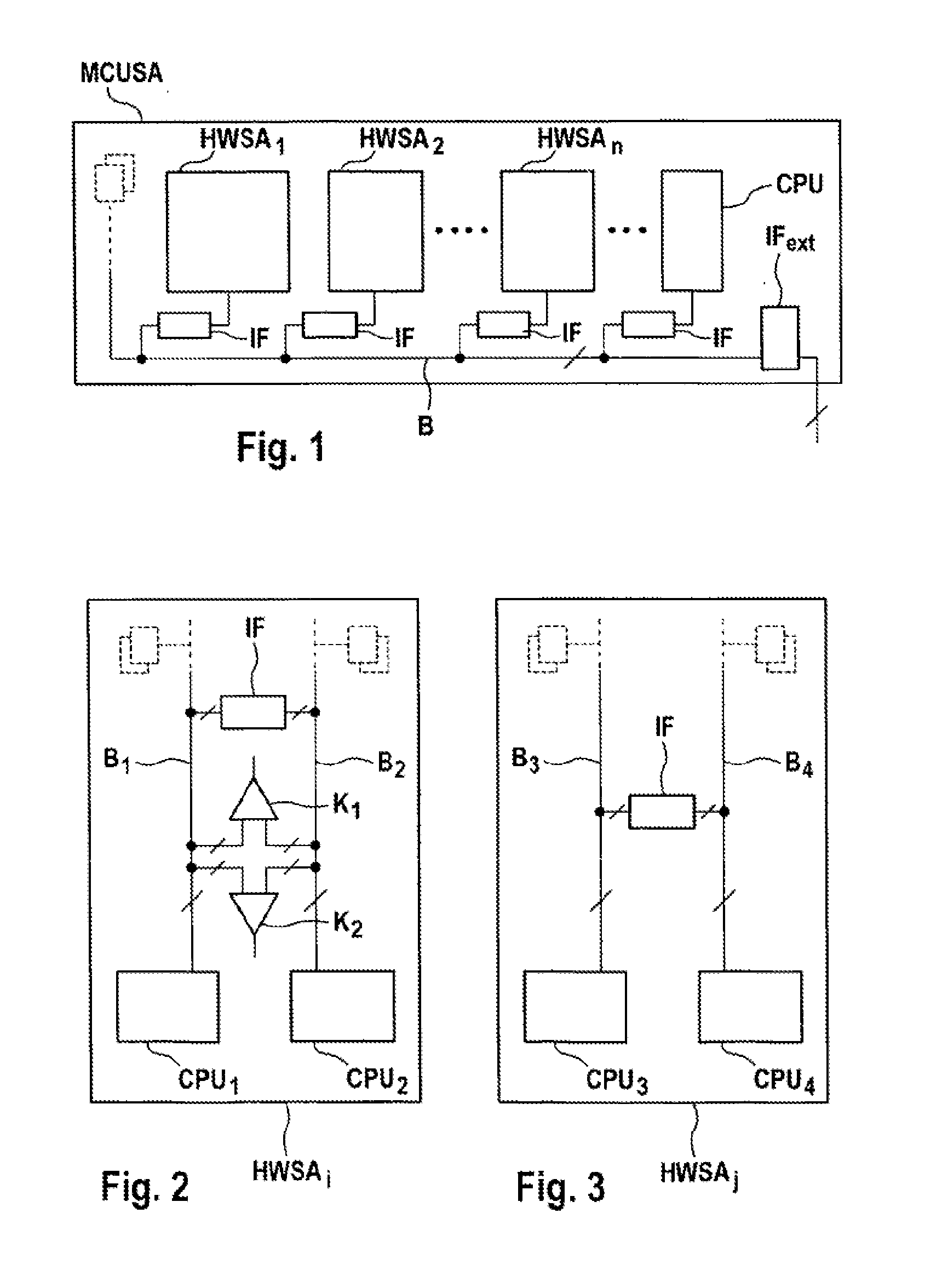
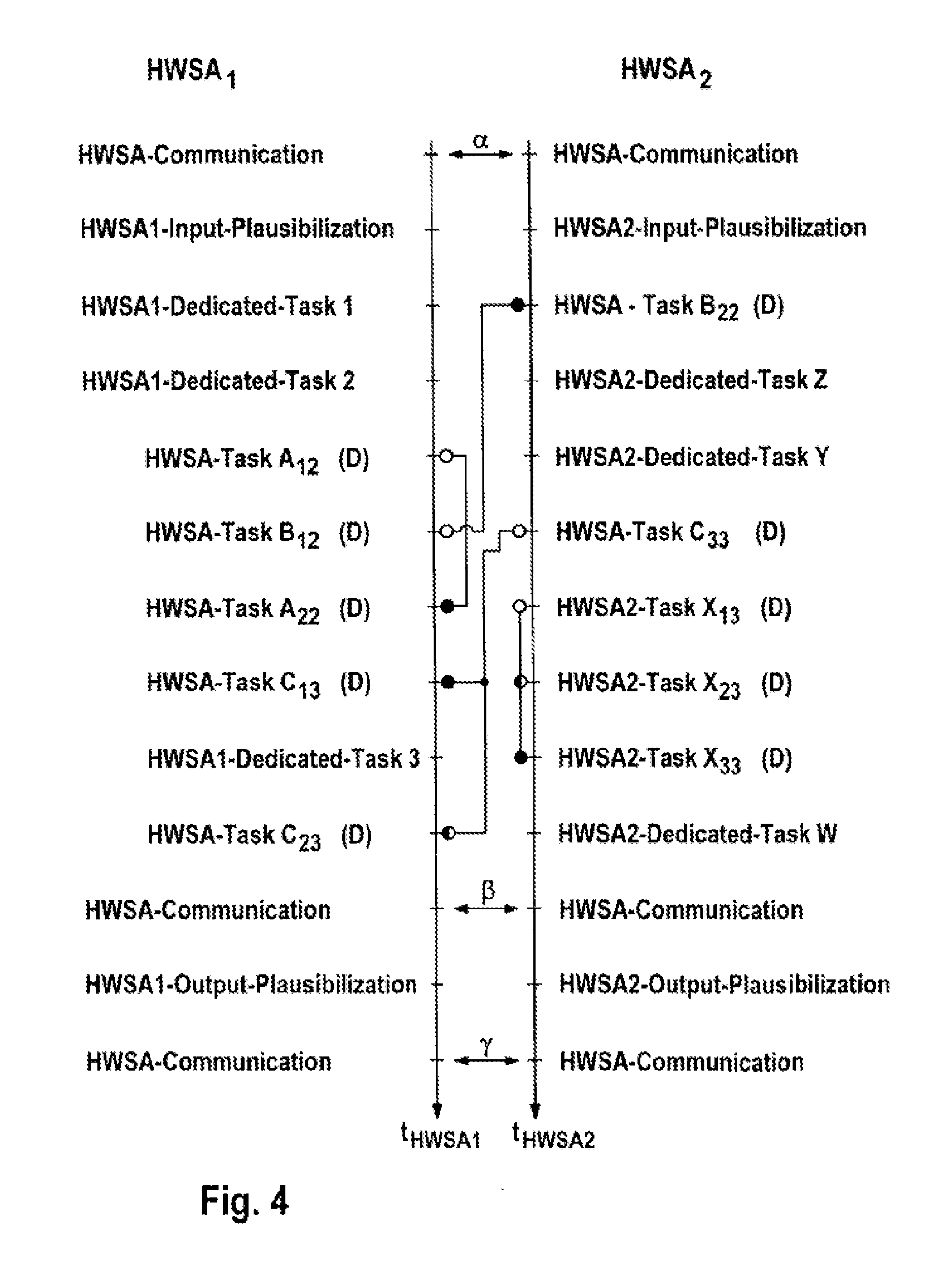
Microprocessor System Having Fault-Tolerant Architecture
InactiveUS20130268798A1Improve robustnessFurther-increased robustnessSafety arrangmentsError avoidanceFault tolerant architectureIntrinsic safety
The invention relates to a microprocessor system for executing software modules, at least some of which are security critical, within the scope of controlling functions or tasks assigned to the software modules, comprising an intrinsically safe microprocessor module having at least two microprocessor cores. At least one further intrinsically safe microprocessor module having at least two microprocessor cores is provided. At least two microprocessor modules are connected via a bus system, at least two software modules are provided which execute functions, at least some of which overlap, the software modules having at least partially overlapping functions are distributed on a microprocessor module or n at least two microprocessor modules, and means for comparing or arbitrating events generated with the software modules for the identical functions are provided in order to detect software or hardware faults.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
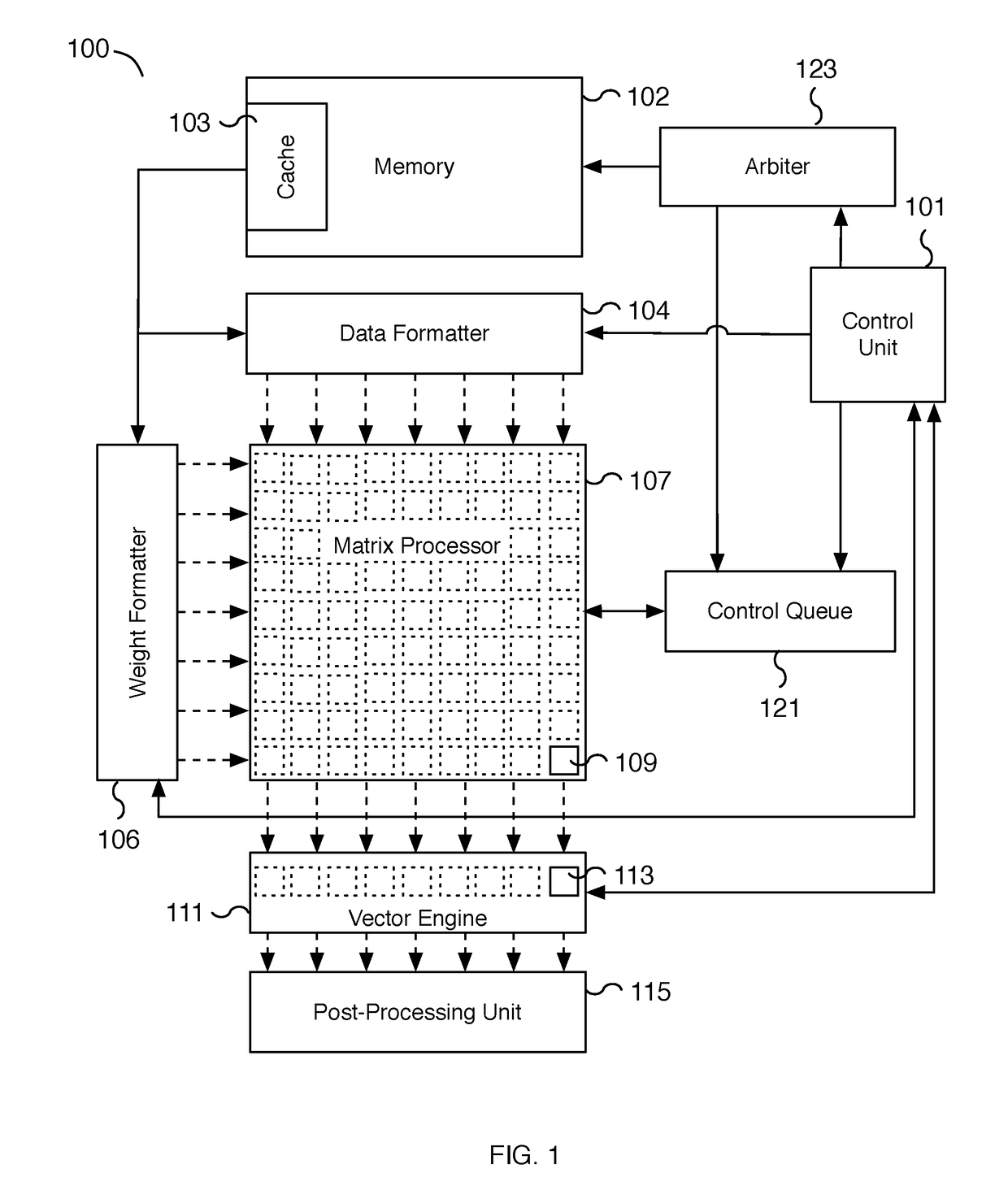
Computational array microprocessor system with variable latency memory access
ActiveUS20190026237A1Input/output to record carriersSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsControl signalParallel computing
A microprocessor system comprises a computational array and a hardware arbiter. The computational array includes a plurality of computation units. Each of the plurality of computation units operates on a corresponding value addressed from memory. The hardware arbiter is configured to control issuing of at least one memory request for one or more of the corresponding values addressed from the memory for the computation units. The hardware arbiter is also configured to schedule a control signal to be issued based on the issuing of the memory requests.
Owner:TESLA INC
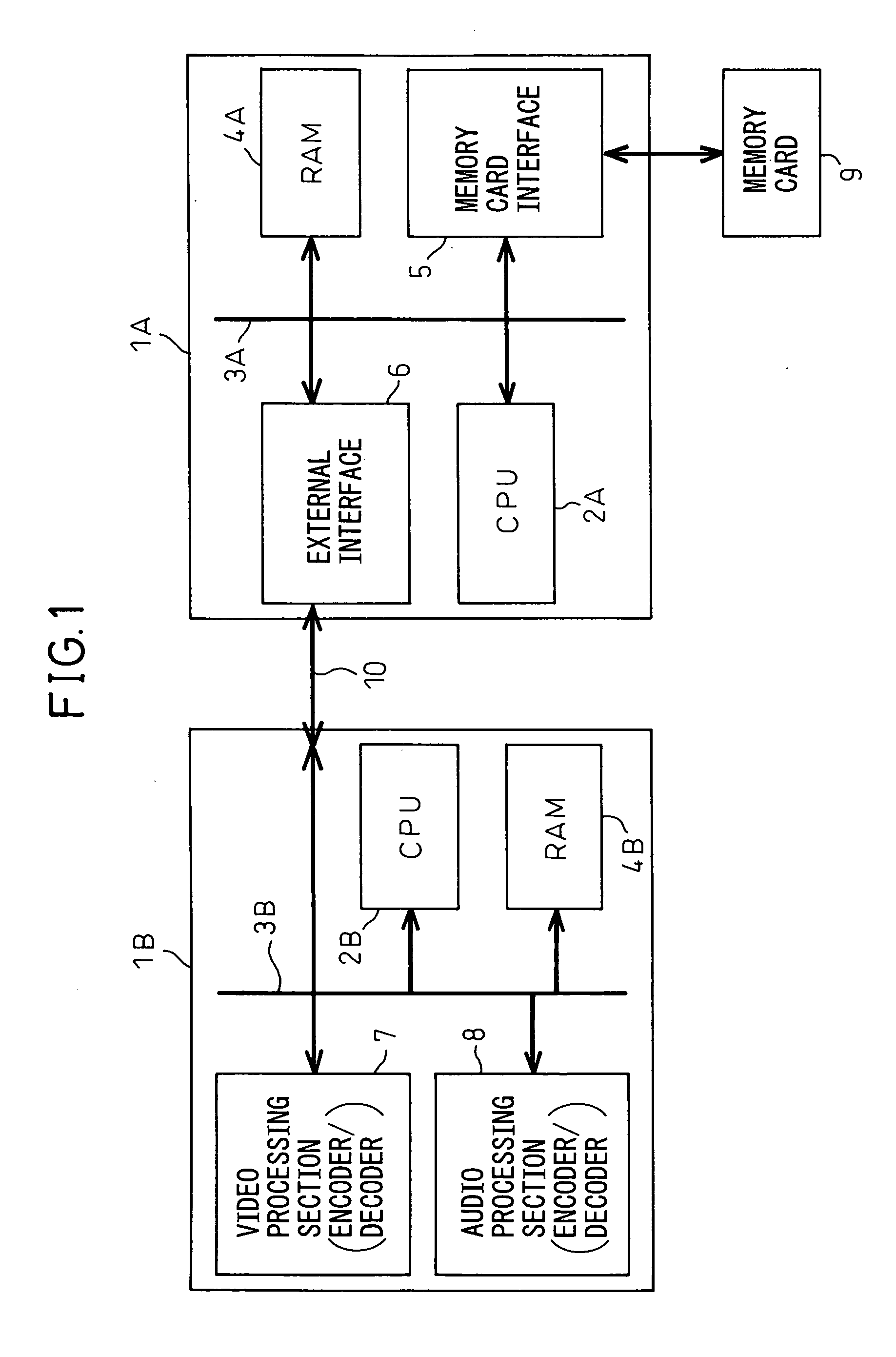
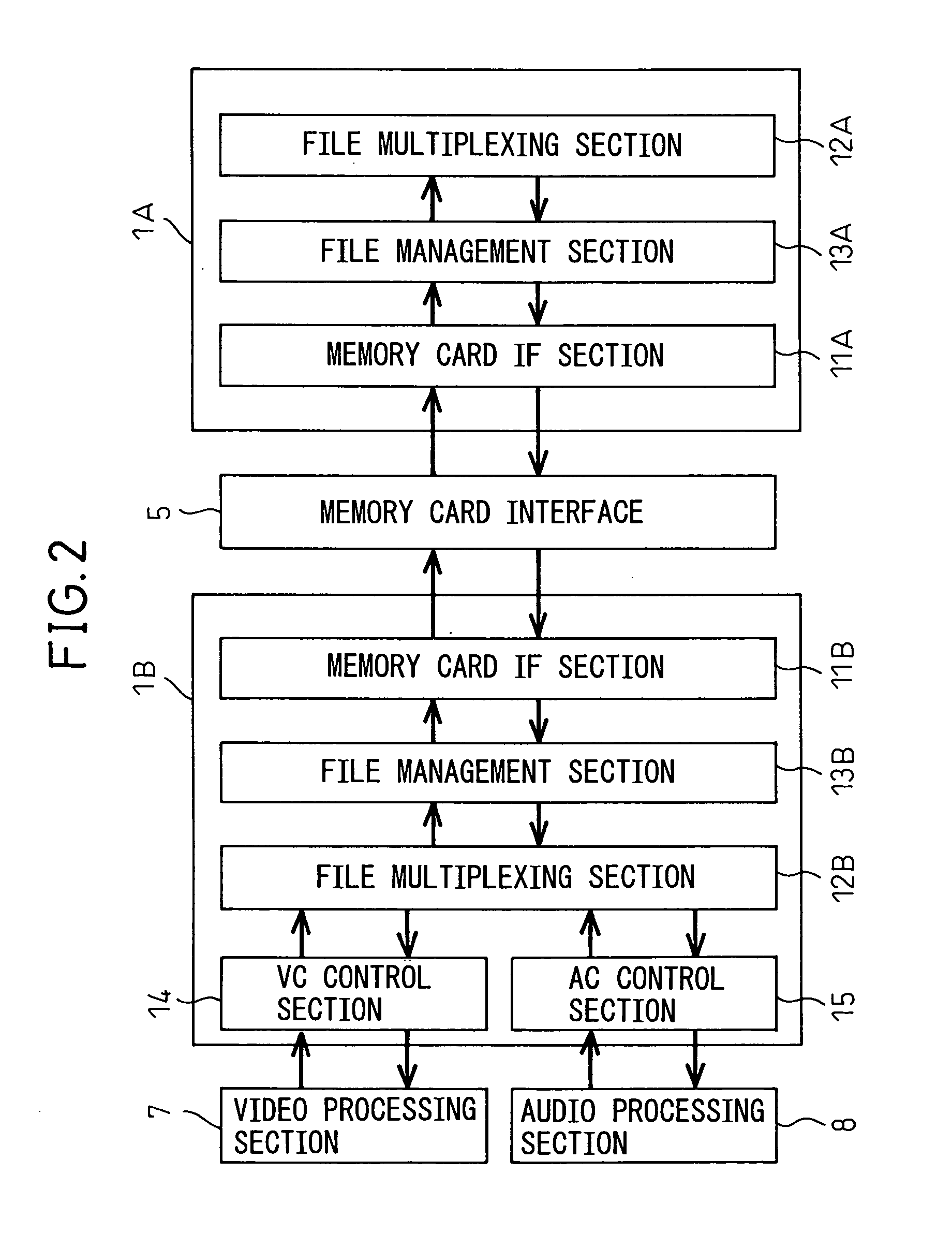
Microprocessor system
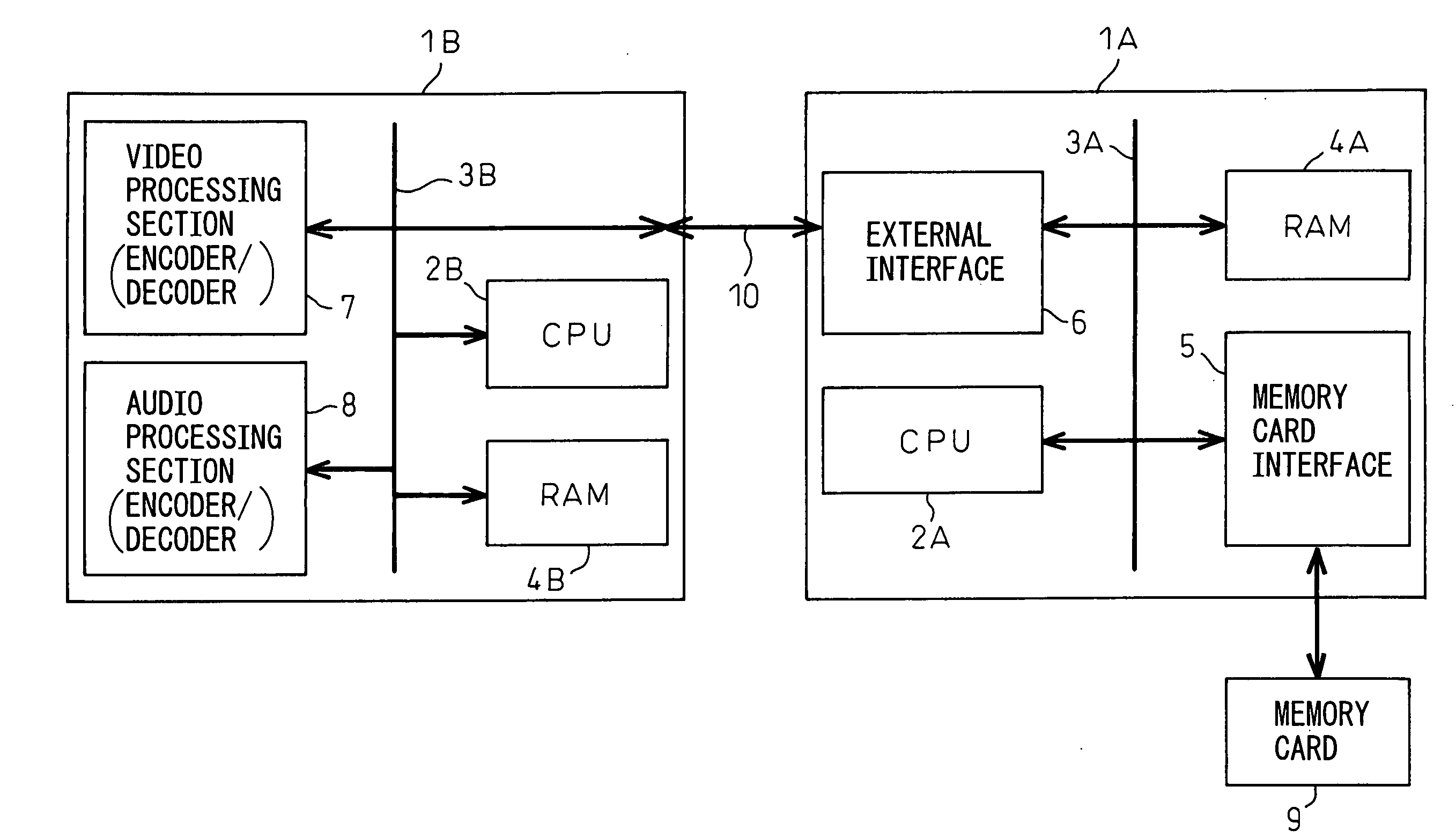
InactiveUS20070260784A1Easy accessReduce and adjust loadElectric digital data processingCommunication interfaceMulti processor
A multiprocessor system, in which a memory card can be easily accessed from a data processor other than a data processor to which the memory card is connected without impeding processing, has been disclosed. The multiprocessor system comprises data processors wherein a first data processor comprises a memory card interface, a first communication interface, and a first buffer, and another data processor comprises a second communication interface, and when the other data processor reads data from the memory card, the first data processor transmits data after reading the data of the memory card in accordance with the condition of processing and storing the data temporarily in the first buffer and, when the other data processor writes data to the memory card, the first data processor stores the data from the other data processor in the first buffer irrespective of the condition of processing of the first data processor and writes the data to the memory card in accordance with the condition of processing.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Advanced logic system diagnostics and monitoring
ActiveUS8554953B1Improve reliabilityImprove maintainabilityStethoscopeDiagnostic recording/measuringNuclear plantCommon mode failure
The Advanced Logic System (ALS) is a complete control system architecture, based on a hardware platform rather than a software-based microprocessor system. It is significantly different from other PLC-type control system architectures, by implementing a FPGA in the central control unit. Standard FPGA logic circuits are used rather than a software-based microprocessor which eliminate problems with software based microprocessor systems, such as software common-mode failures. It provides a highly reliable system suitable for safety critical control systems, including nuclear plant protection systems. The system samples process inputs, provides for digital bus communications, applies a control logic function, and provides for controlled outputs. The architecture incorporates advanced features such as diagnostics, testability, and redundancy on multiple levels. It additionally provides significant improvements in failure detection, isolation, and mitigation for the highest level of integrity and reliability.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Advanced logic system
ActiveUS8156251B1Improve reliabilityImprove maintainabilityProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsNuclear plantCommon mode failure
The Advanced Logic System (ALS) is a complete control system architecture, based on a hardware platform rather than a software-based microprocessor system. It is significantly different from other PLC-type control system architectures, by implementing a FPGA in the central control unit. Standard FPGA logic circuits are used rather than a software-based microprocessor which eliminate problems with software based microprocessor systems, such as software common-mode failures. It provides a highly reliable system suitable for safety critical control systems, including nuclear plant protection systems. The system samples process inputs, provides for digital bus communications, applies a control logic function, and provides for controlled outputs. The architecture incorporates advanced features such as diagnostics, testability, and redundancy on multiple levels. It additionally provides significant improvements in failure detection, isolation, and mitigation for the highest level of integrity and reliability.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
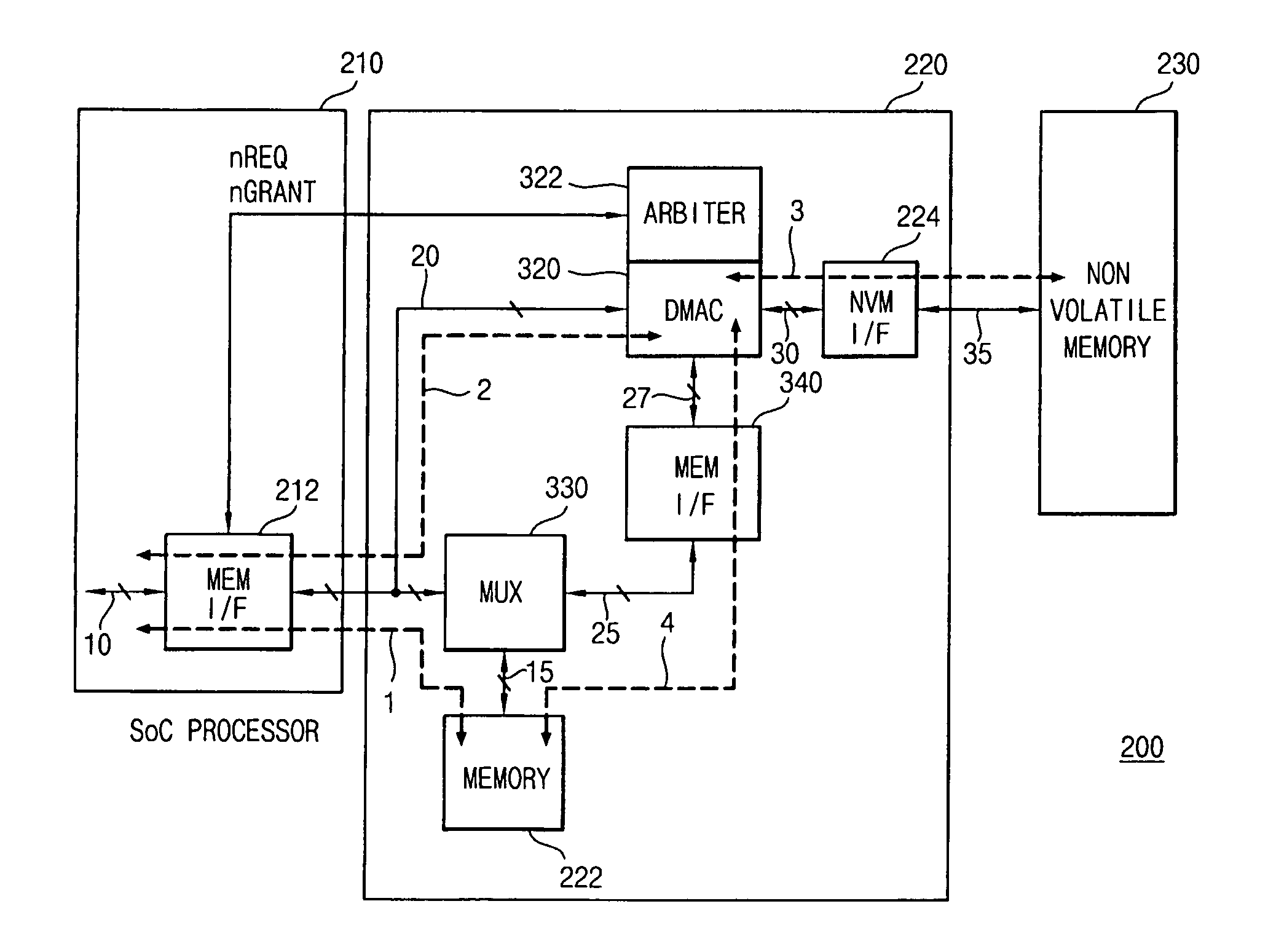
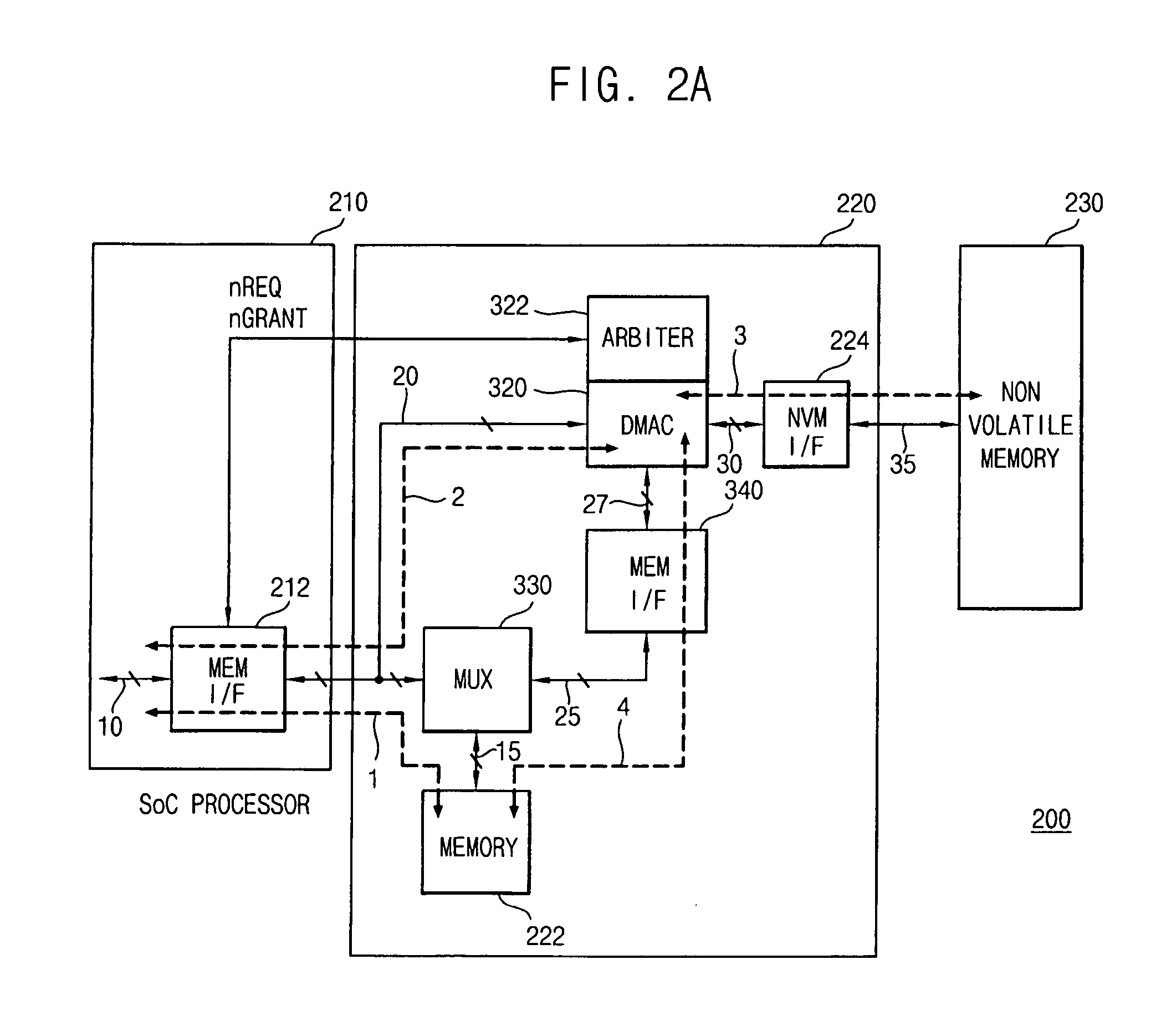
Microprocessor system with memory device including a DMAC, and a bus for DMA transfer of data between memory devices
InactiveUS20060090017A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageDirect memory accessExternal storage
A processor system having a memory device including a (RAM) memory and a direct memory access controller (DMAC) and an internal bus switchably connected between the memory and the DMAC. A Bus Switch (multiplexer) within the memory device alternately establishes a first data transmission path over the system bus between the memory and an external processor, and a second data transmission path over the internal bus between the memory and the DMAC. The first data transmission path, when established through the Bus Switch, supports random access of the memory by the external processor. The second data transmission path, when established through the Bus Switch, supports a Direct Memory Access (DMA) between the RAM and an external storage device, e.g., a Nonvolatile Memory (NVM), connected to the DMAC while the processor has full and exclusive use of the system bus.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
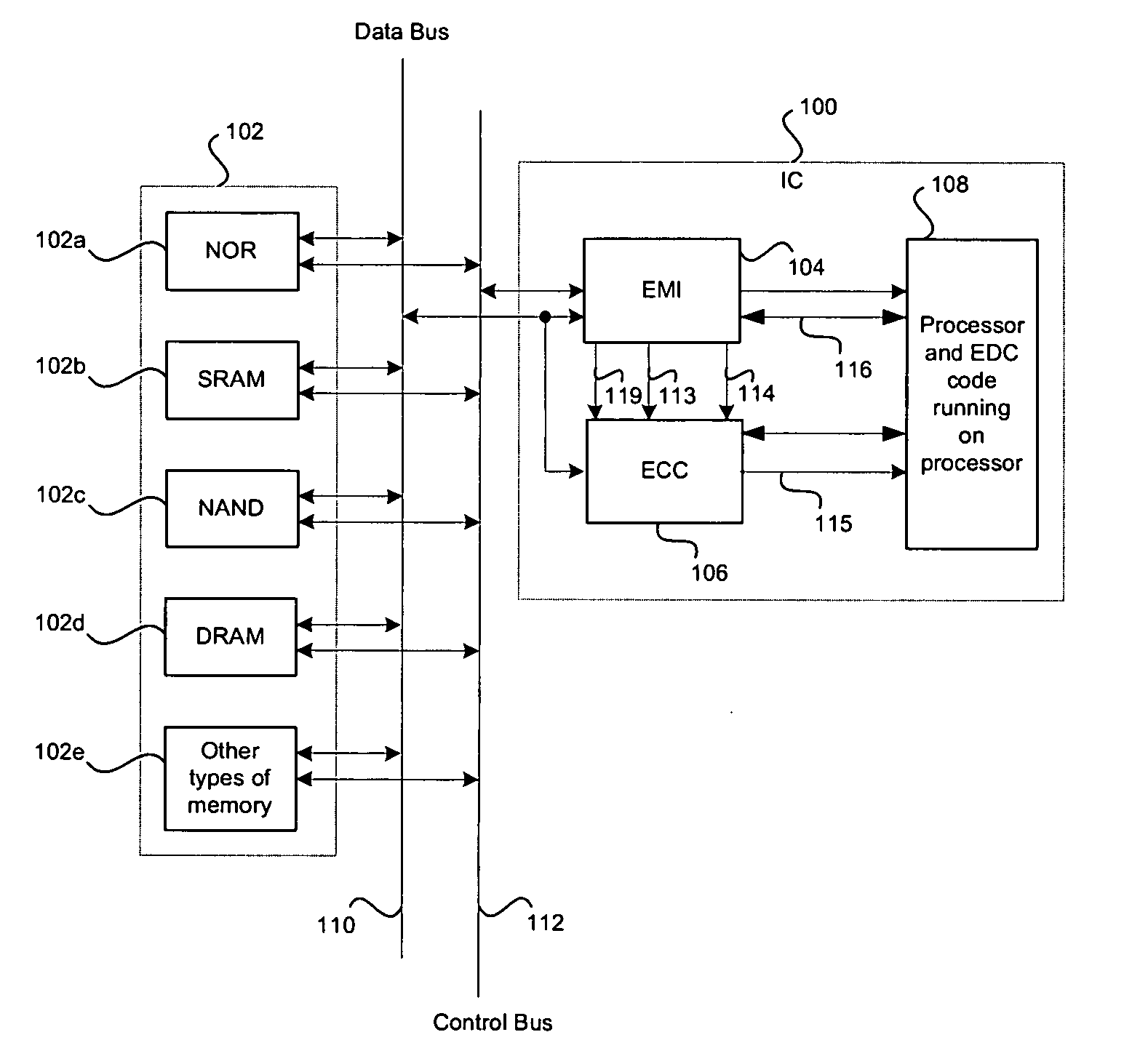
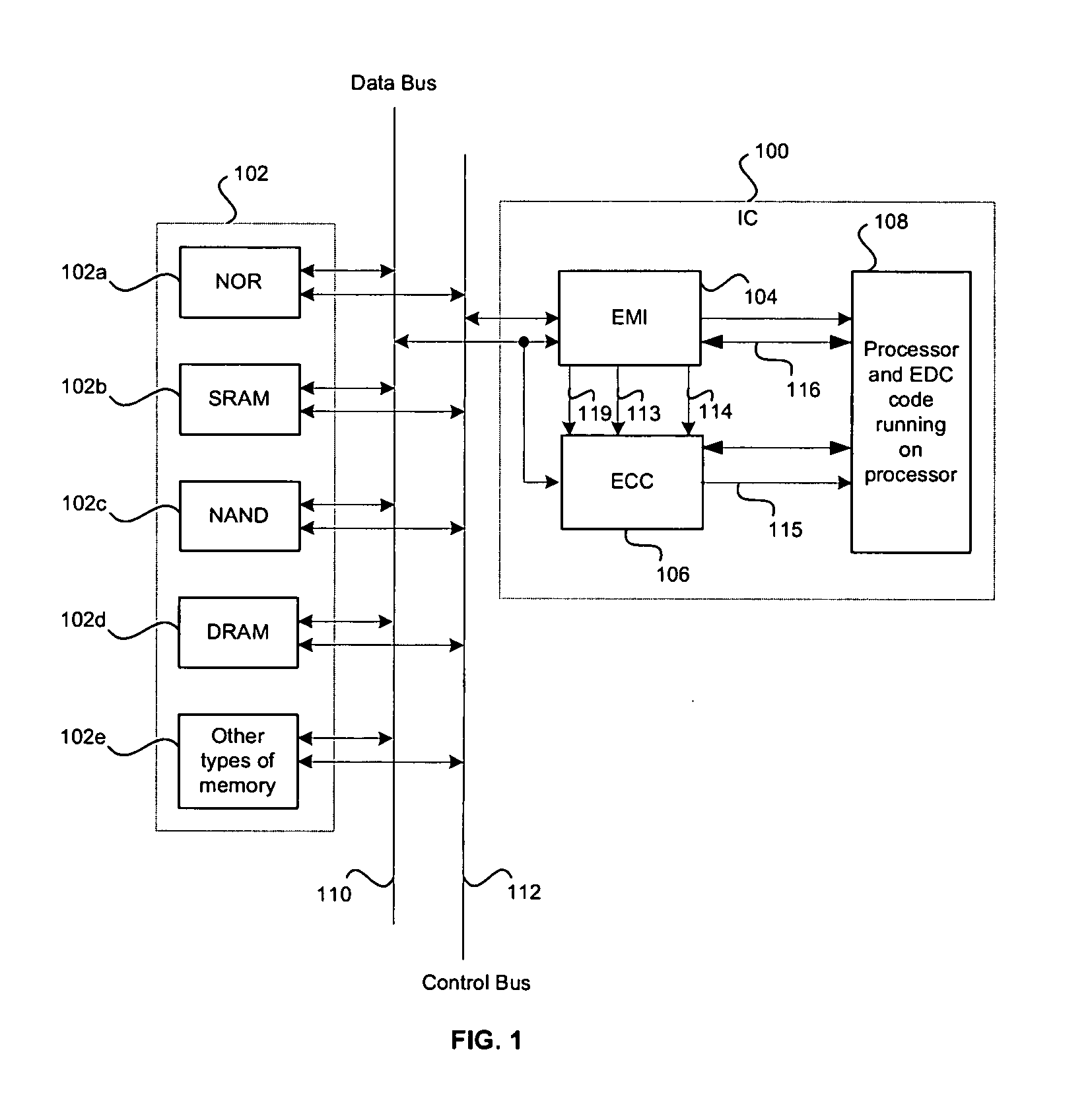
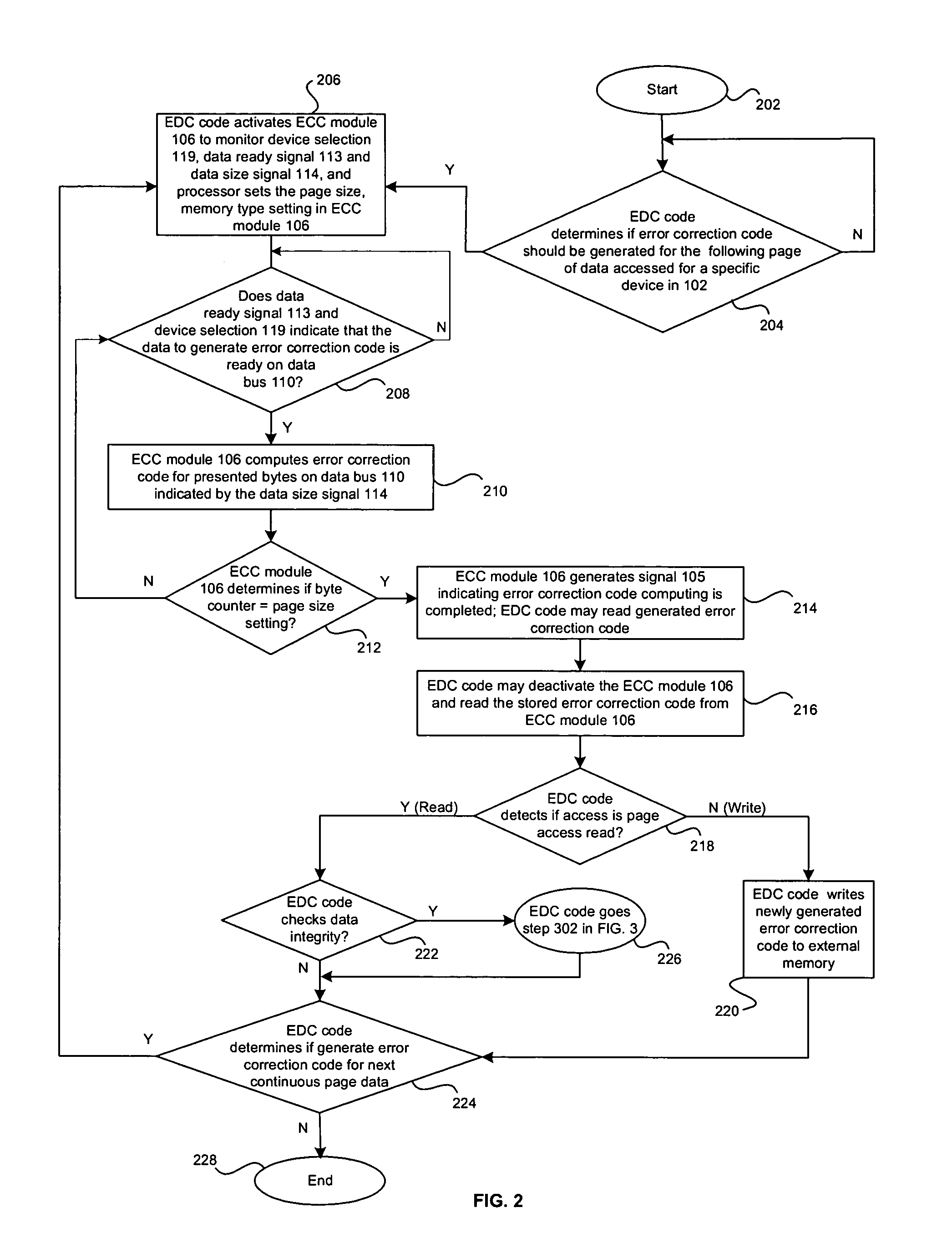
Method and system for detecting and correcting errors while accessing memory devices in microprocessor systems
InactiveUS20050283650A1Ensure data integrityError detection/correctionStatic storageData processing systemData integrity
A method and system for ensuring data integrity in a data processing system may comprise monitoring when data for a specified device is available for error correction code generation, and receiving a first indication of the specified device, a second indication of the data, and a third indication of a size of the data during the monitoring. A new error correction code may be generated in hardware for the data based on the indicated size of the data and an indication may be provided to signal when generation of the new error correction code for a specified number of accesses for at least a portion of the data is complete. Detected errors may be corrected in software based on the newly generated error correction code. The first indication may be a device selection signal and the error correction code generation may be enabled or disabled via an enable signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
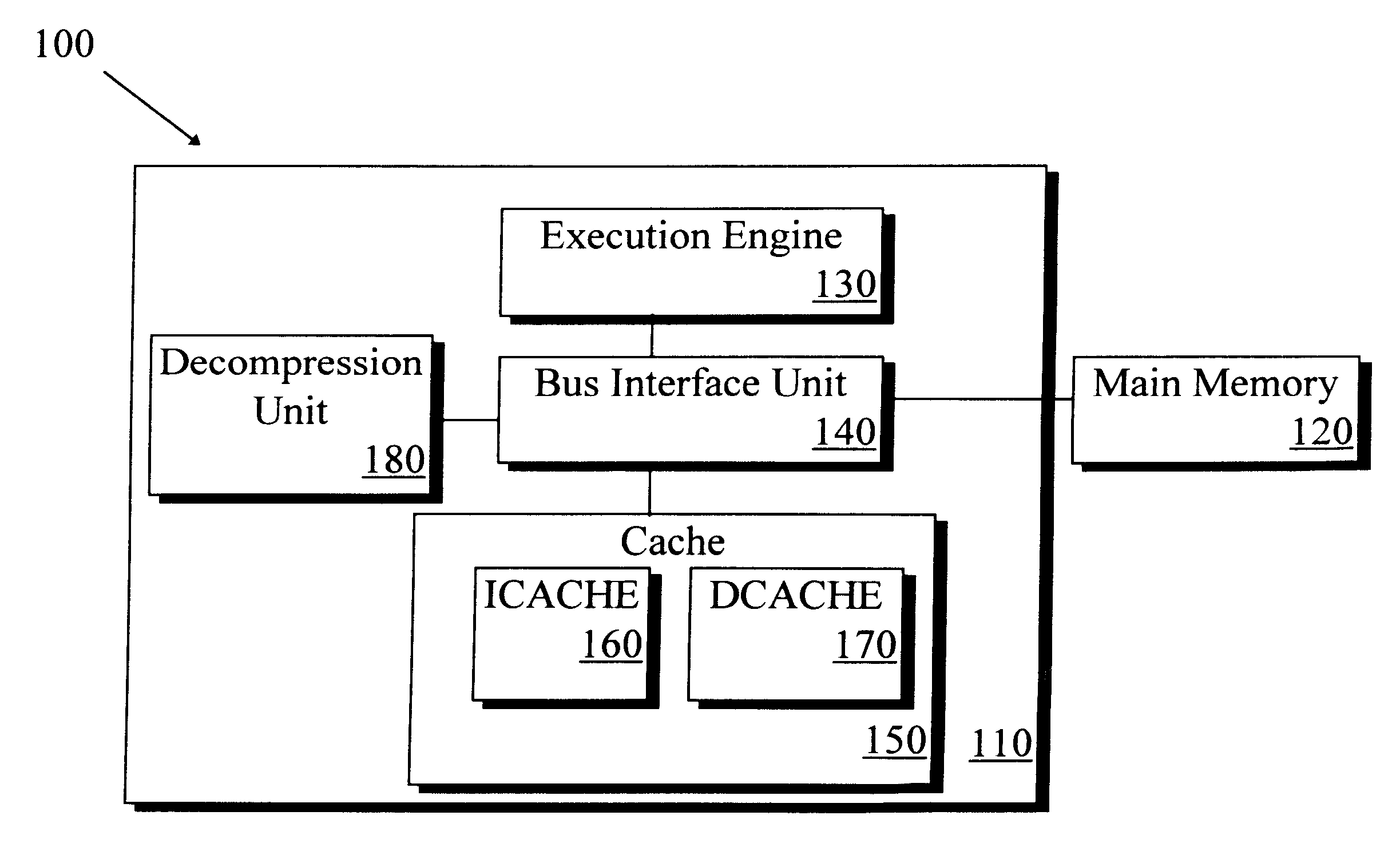
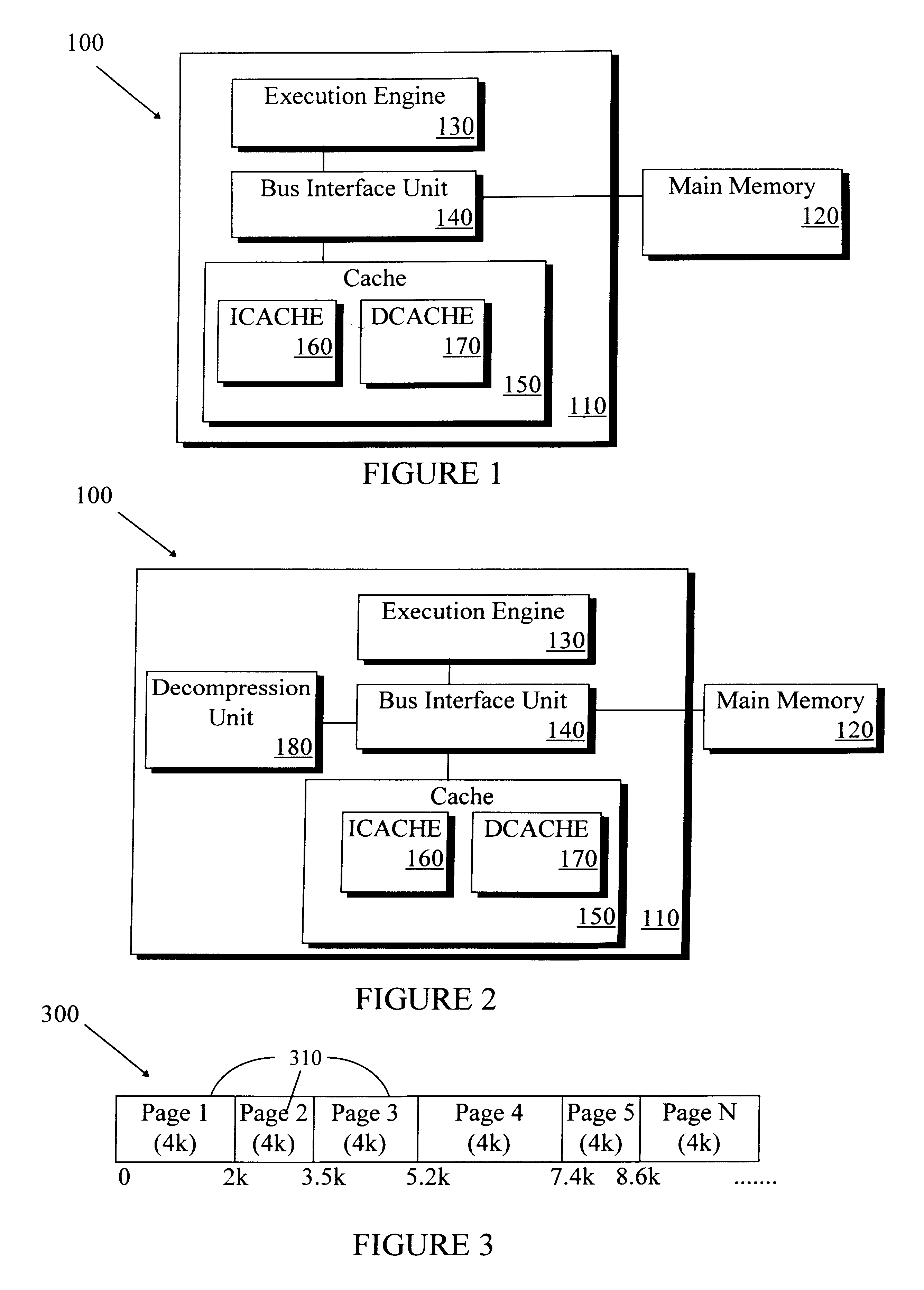
Microprocessor system and method for increasing memory Bandwidth for data transfers between a cache and main memory utilizing data compression
InactiveUS6175896B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData compressionParallel computing
A microprocessor includes a cache memory, a bus interface unit, and an execution engine. The bus interface unit is connected to the cache memory and adapted to receive compressed data from a main memory. The execution engine is connected to the bus interface unit and adapted to receive the compressed data from the bus interface unit. The execution engine decompresses the compressed data into uncompressed data and transmits the uncompressed data to the bus interface unit. The bus interface unit is further adapted to transmit the uncompressed data to the cache memory. The microprocessor may be used in a microprocessor system having a main memory capable of storing compressed data, where the bus interface unit transfers compressed data from the main memory to the cache memory in the microprocessor. A method is also provided for increasing memory bandwidth in a microprocessor system including a microprocessor having a cache memory. The method comprises receiving compressed data into the microprocessor; decompressing the compressed data into uncompressed data; and transmitting the uncompressed data to the cache memory. The method includes the handling of page boundaries between the compressed and uncompressed data.The compressed data may comprise pages of data, and may include an index table containing address information related to the pages. The index table may define upper and lower boundary addresses for each page, and a fault condition may be generated if a requested address is not contained within the cache memory. The compressed data may also comprise encrypted compressed data, and the execution engine may decrypt and decompress the encrypted compressed data into uncompressed data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com