Patents
Literature
64 results about "Nuclear reactor coolant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A nuclear reactor coolant is a coolant in a nuclear reactor used to remove heat from the nuclear reactor core and transfer it to electrical generators and the environment. Frequently, a chain of two coolant loops are used because the primary coolant loop takes on short-term radioactivity from the reactor.
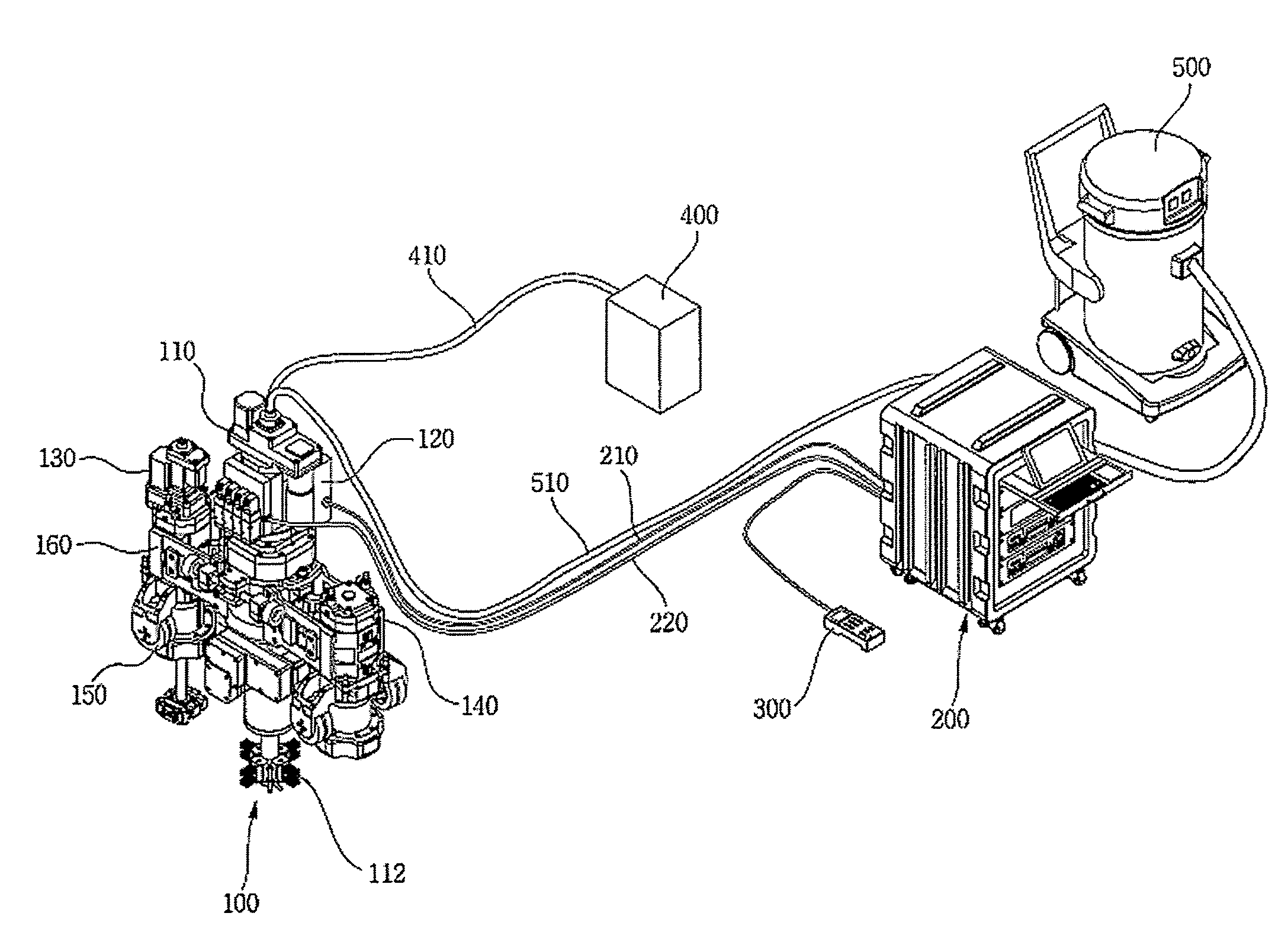
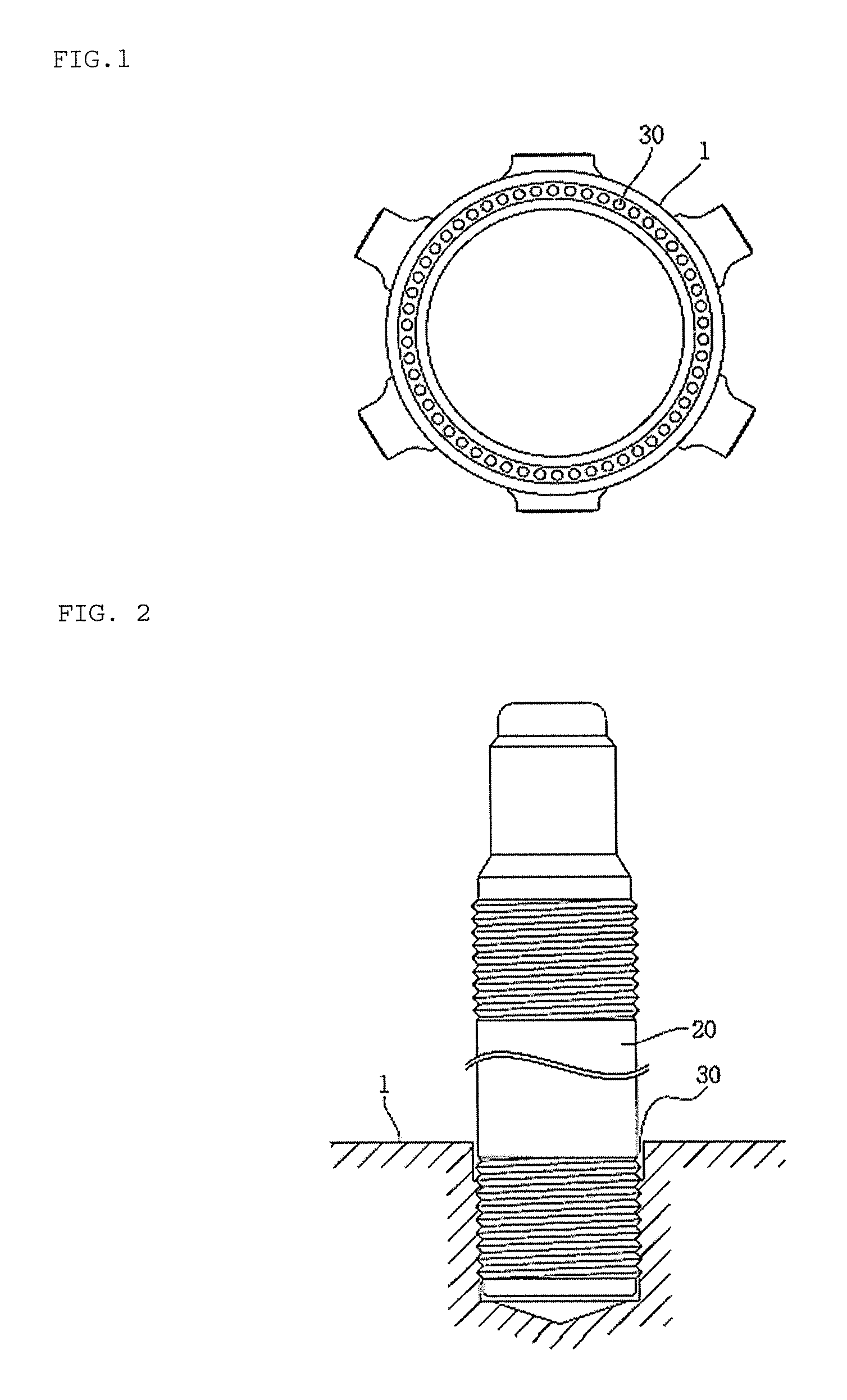
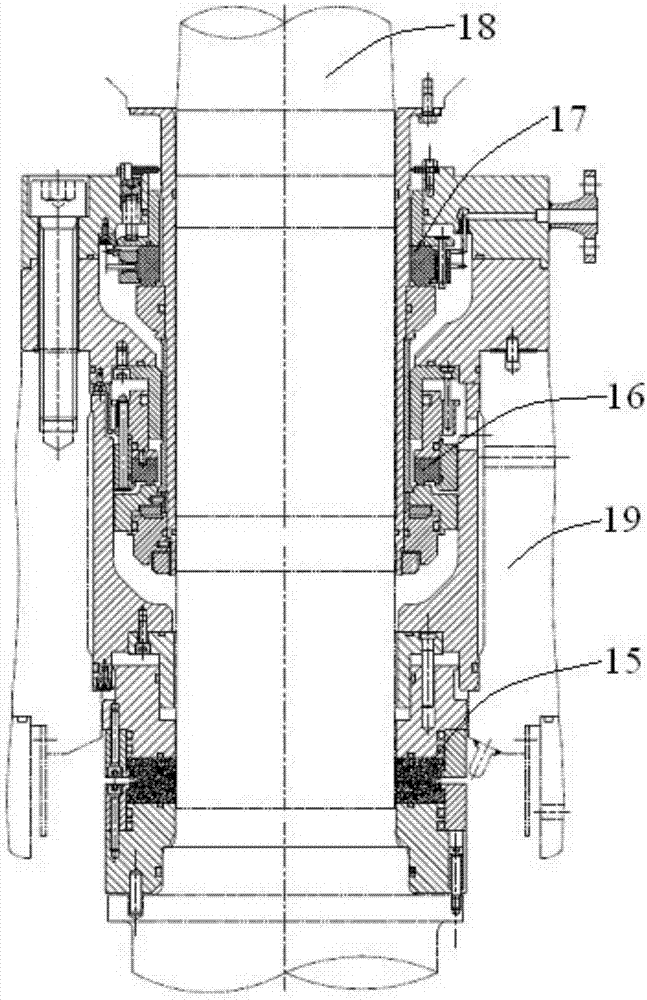
Nuclear reactor coolant pump and nuclear power plant having same
ActiveUS20160260509A1Energy lossElectrical degradationIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreImpeller
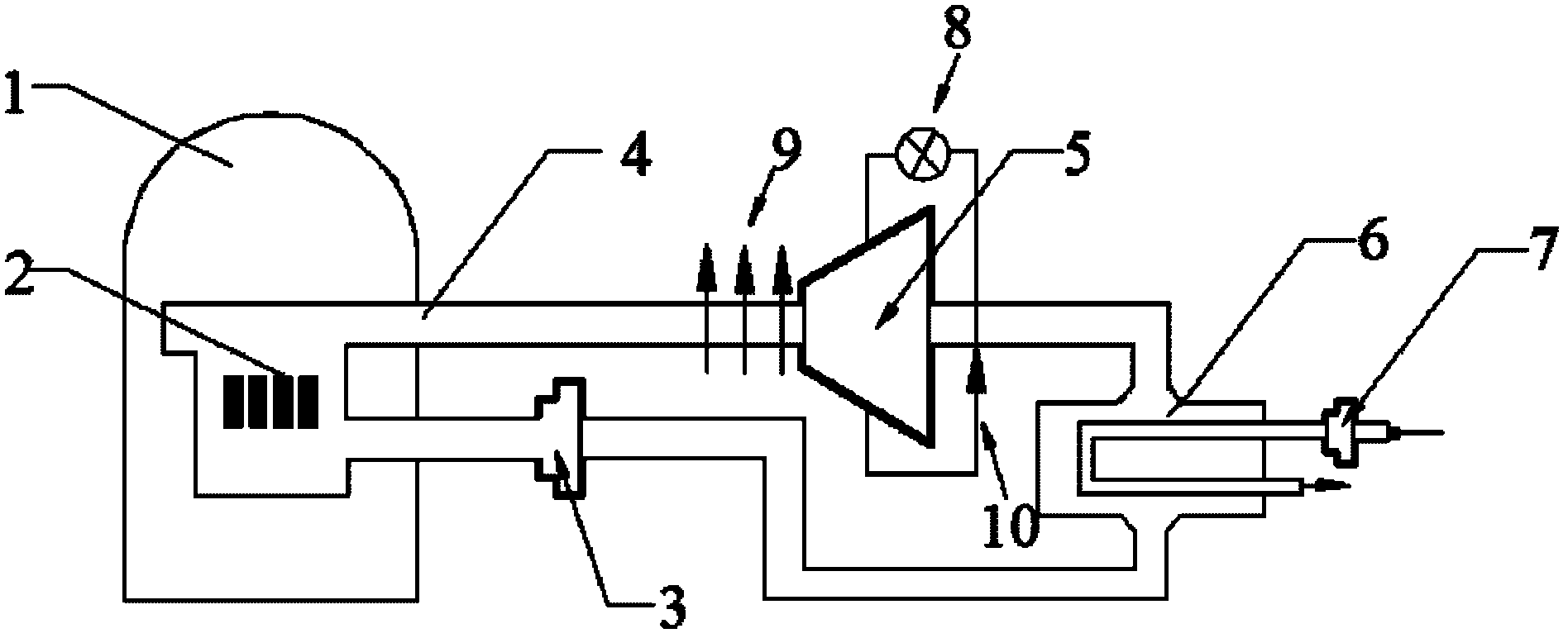
The present invention discloses a nuclear reactor coolant pump that does not rely on an electric motor, but is operated by means of driving force generated inside a nuclear power plant, so a to be capable of maintaining the safety of the nuclear reactor when the nuclear reactor is operating normally and also in the event of an accident in the nuclear reactor. The nuclear reactor coolant pump comprises: a pump impeller rotatably installed in a first fluid passage of a nuclear reactor coolant system to circulate a first fluid inside the nuclear reactor coolant system; a drive unit receiving steam from a steam generator to generate driving force to rotate the pump impeller, and rotating about the same rotating shaft as the pump impeller to transfer the generated driving force to the pump impeller; and a steam supplying unit forming a passage between the steam generator and the drive unit to supply at least a portion of the steam released from the steam generator to the drive unit.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
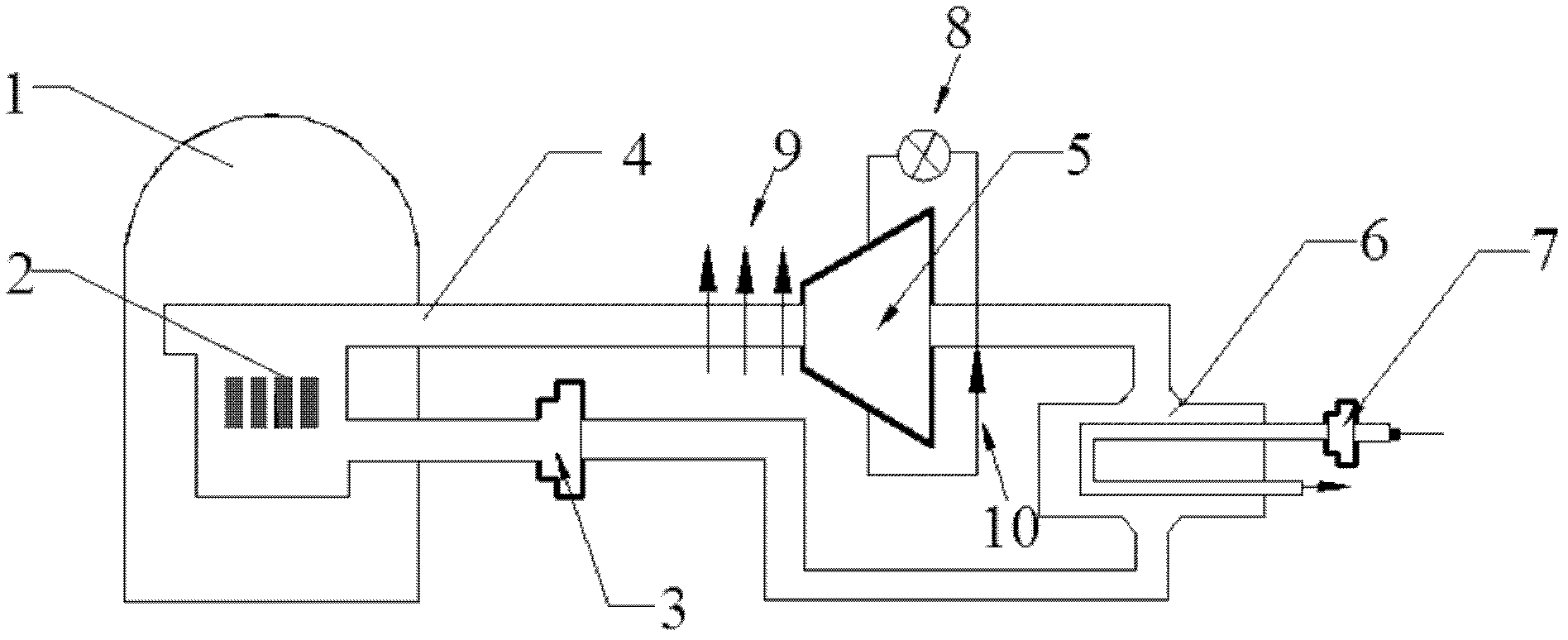
Nuclear energy power generation system using liquid metal magnetofluid as working medium
InactiveCN102592693AImprove efficiencyImprove economyNuclear energy generationEnergy production using magneto-hydrodynamic generatorsWorking fluidNuclear power
The invention discloses a nuclear energy power generation system using a liquid metal magnetofluid as a working medium, belonging to the technical field of nuclear energy and magnetofluid power generation. The nuclear energy power generation system mainly uses a magnetofluid nuclear reactor coolant as the working medium of a magnetofluid power generator simultaneously to take away the heat generated by a reactor core; and according to the nuclear energy power generation system, power generation is realized based on a direct cycle manner, so that a steam turbine-power generation part of a nuclear power station is saved, therefore the power generation efficiency of the nuclear power station is effectively improved. Moreover, no mechanical motion components are arranged in the power generation channel of the magnetofluid power generator, so that the design becomes easier, the cost of the system is reduced, and the stability is increased; the dependence and waste of water resource are avoided; and a liquid metal fluid is used as a coolant, so that environmental pollutions, such as CO2 emission, are prevented.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
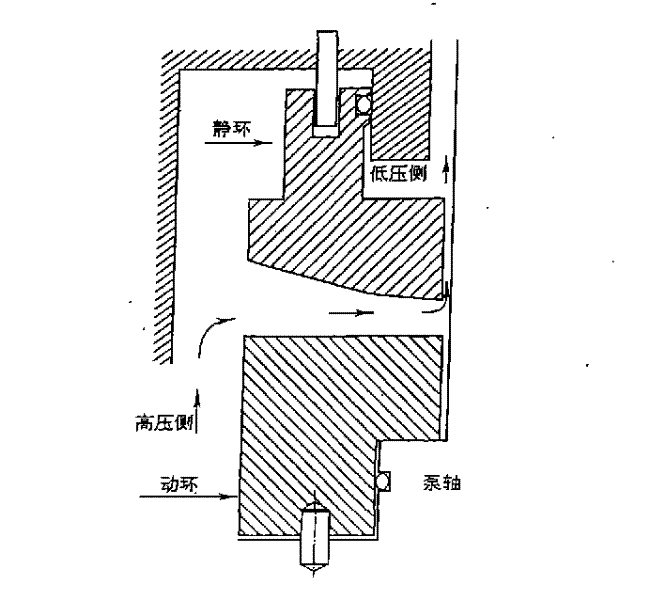
Nuclear reactors cooling agent pump mechanical sealing leakage amount abnormity quick processing method
InactiveCN101211674ALow costReduce the burden onPower plant safety arrangementNuclear energy generationRapid processingNormal range
The invention is a rapid processing method for mechanically sealing leakage exception of refrigerant pump in the nuclear reactor, which comprises the prior detecting method. When the leakage exception of a shaft gland component is detected, the method adjusts the filled water temperature of the shaft gland component within the temperature allowing range of the filling water in the shaft gland component, thus recovering the leakage of the shaft gland component to a normal range. The method can process the exceptional leakage of sealing leakage of the refrigerant pump in the nuclear reactor timely and rapidly, adjust the leakage of the sealing component, and control the leakage in the original normal standard, thus guaranteeing the normal operation of the reactor.
Owner:DAYA BAY NUCLEAR POWER OPERATIONS & MANAGEMENT
Method for preventing abnormity of mechanical seal leakage rate of nuclear reactor coolant pump
ActiveCN102456418AExtend your lifeImprove sealingNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringEngineeringCoolant pump
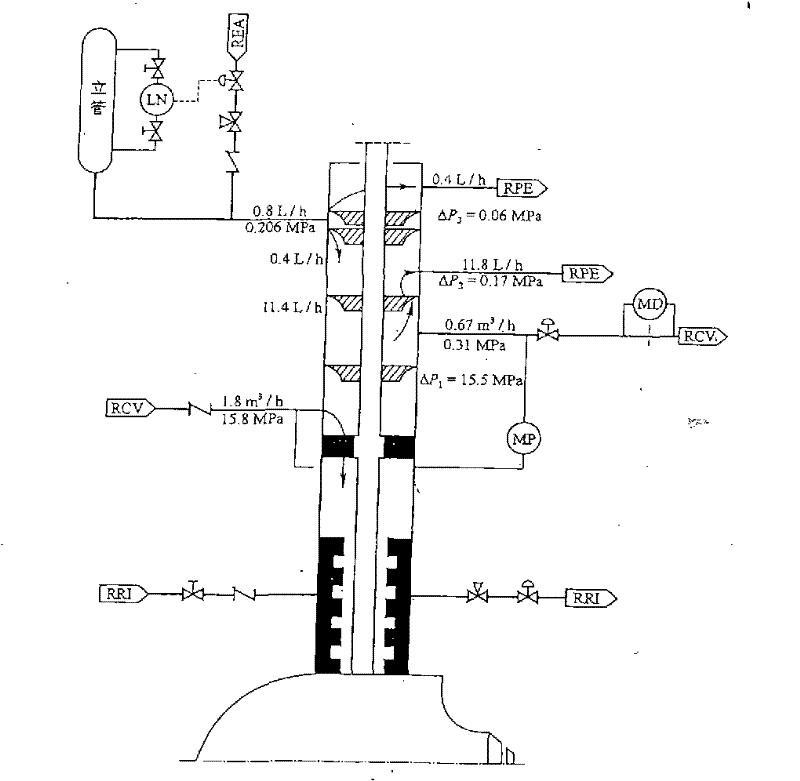
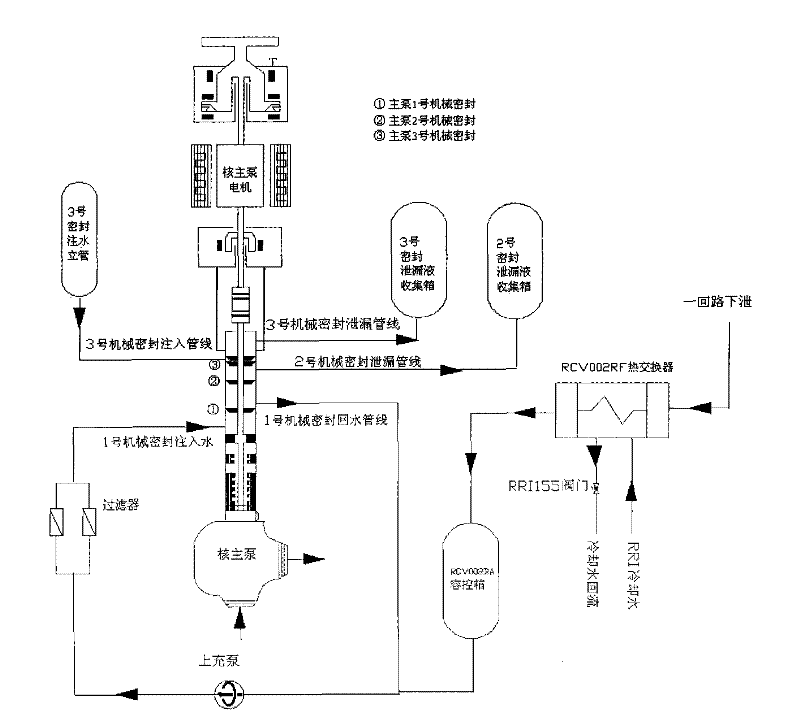
The invention relates to a method for preventing abnormity of mechanical seal leakage rate of a nuclear reactor coolant pump. An injection water loop of a No. 1 shaft seal of a coolant pump is provided with two parallel columns of filters; one row of the filters are operating on the line, and the other column of filters are for standby. The preventive method comprises the following steps: S1. detecting a boron concentration of a loop; S2. comparing the boron concentration of the loop with that of the row of filters for standby; and S3. when a difference between the boron concentration of the standby row and that of the loop exceeds a preset value, switching the standby column of filters to on-line operation, and switching the on-line operating row of filters into a standby state. In the preventive method of the invention, when the difference between the boron concentration of the standby column and that of the loop exceeds the preset value, filter switching is carried out; and a sealing surface of the No. 1 shaft seal can be flushed timely by shaft seal injection water with a relative high boron concentration in the standby column of filters, so as to improve a seal status of the sealing surface of the No. 1 shaft seal timely and effectively.
Owner:GUANGDONG NUCLEAR POWER JOINT VENTURE +1
Nuclear main pump mechanical seal system with active and passive shutdown sealing
The invention discloses a nuclear main pump mechanical seal system with active and passive shutdown sealing. A shutdown sealing structure is added above a third-stage contact type seal, after a shutdown sealing active system control valve and a shutdown sealing passive system control valve are connected in parallel, one end is connected with a high-pressure air source, and the other end is connected with an air supply pipeline providing power for a movable ring through a high-pressure air channel. When a first-stage fluid static seal, a second-stage contact type seal and the third contact type seal are ineffective, or a main pump shuts down, the shutdown sealing has an effect through opening of the active system control valve, so that the shutdown sealing becomes the final shield for preventing reactor coolants from leakage; when severe faults, such as a SBO working condition, happen on a nuclear power station, the shutdown sealing has an effect through the passive system control valve, the reactor coolants are prevented from leakage under the condition, time is saved for further dealing with related problems, and losses of the nuclear power station and environmental pollution possibly caused are reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Experimental device and method for studying failure behavior of fuel elements in severe nuclear reactor accidents
ActiveCN110867263AFlexible control of internal pressureVersatileNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringCooling chamberTensile testing
The invention provides an experimental device and method for studying failure behavior of fuel elements in severe nuclear reactor accidents. The experimental device includes an upper electrode coolingchamber, a middle cylinder, a lower electrode cooling chamber, a simulated fuel rod and a tensile testing machine; and the middle cylinder contains multiple thermal shielding equipment, and claddingcan be heated to 2200 DEG C or more to carry out research of severe accident conditions caused by nuclear reactor coolant loss accidents, reactive introduction accidents and the like and the failure behavior of a single fuel rod or fuel rod beams under accident mitigation measures such as reactor core water injection. The invention also provides the experimental method. Experiments on the failurebehavior of fuel elements in the severe nuclear reactor accidents are carried out to reveal the failure mechanism of the fuel elements, and the device and method have important guiding significance for the safety design of nuclear reactors.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
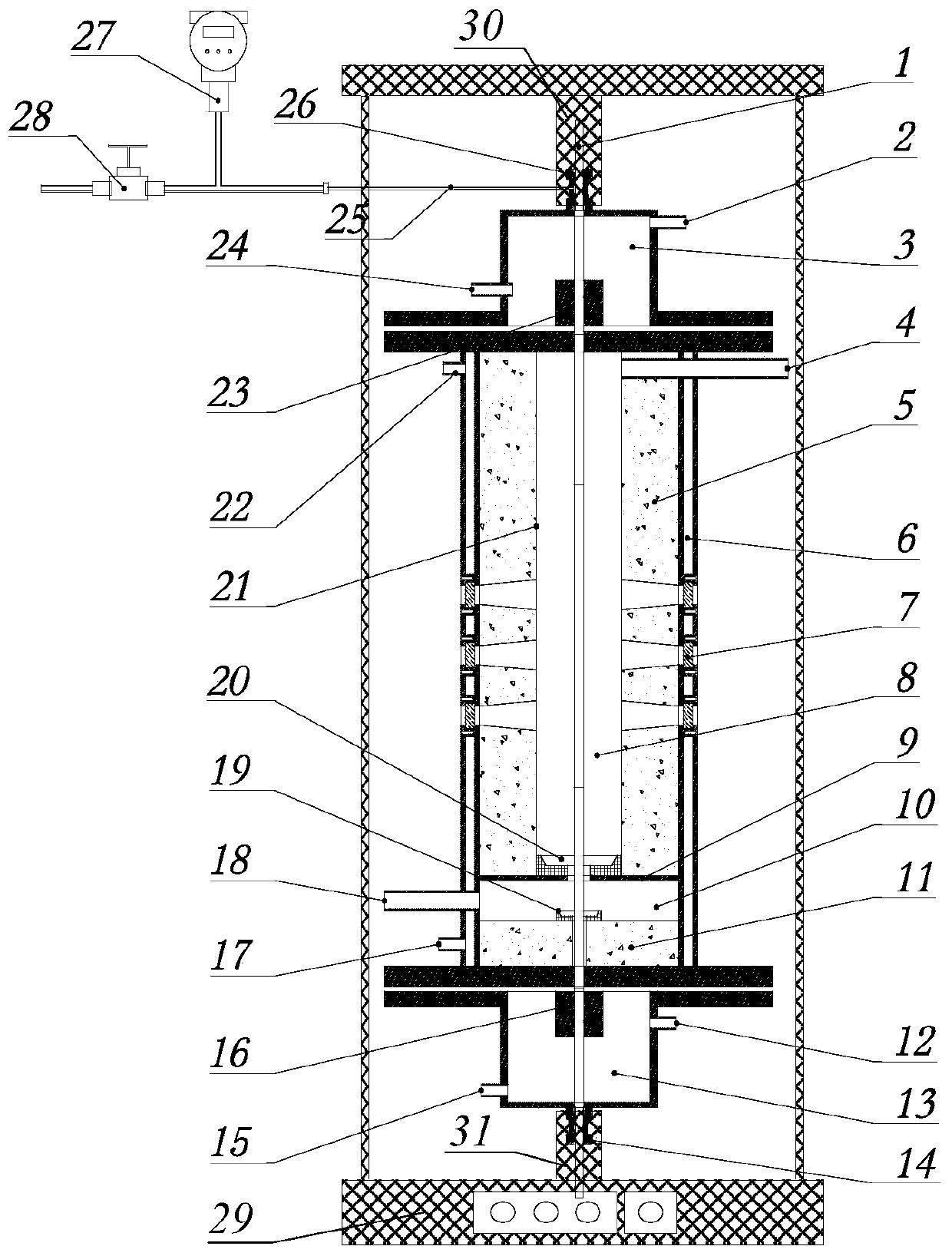
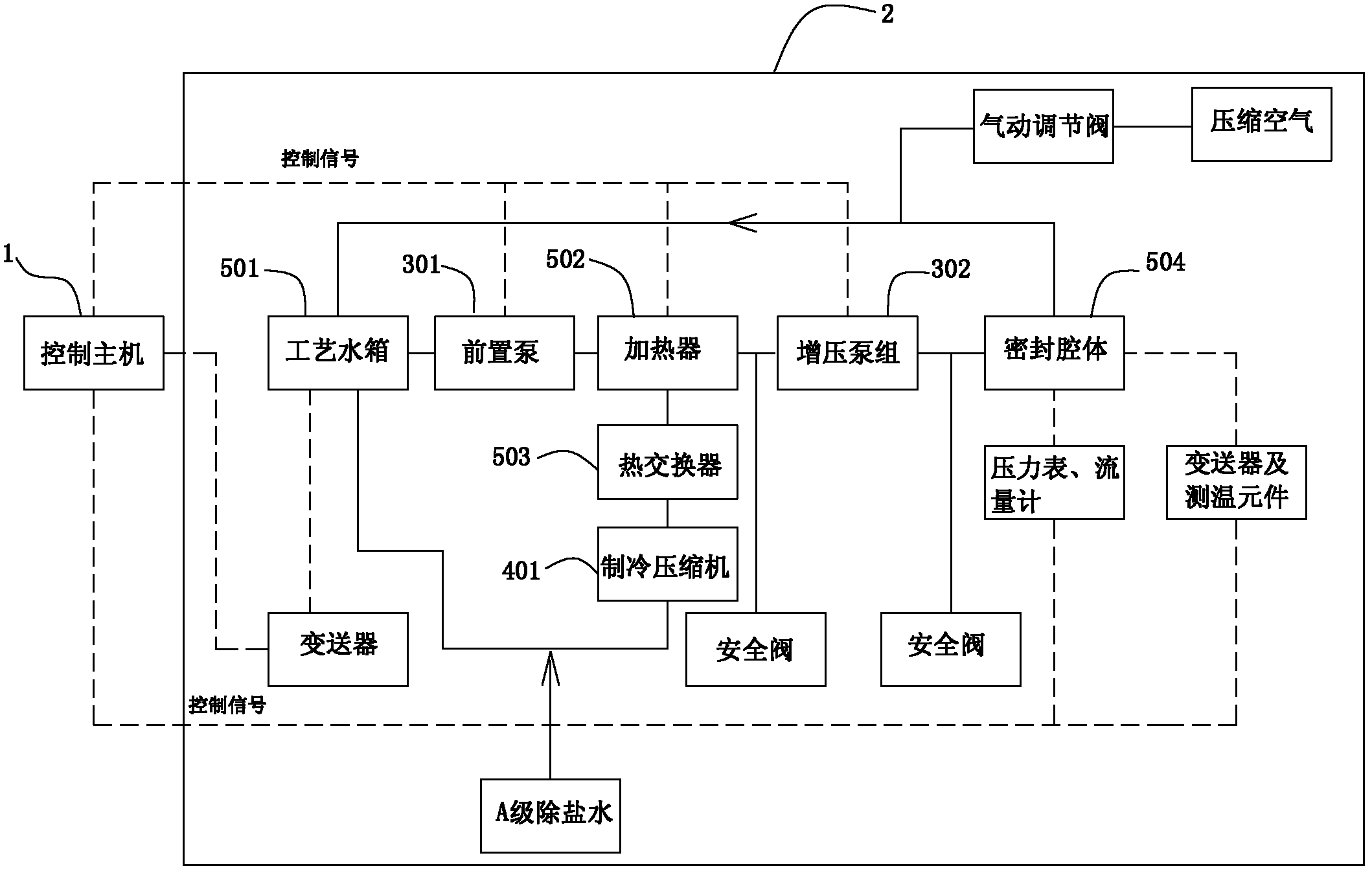
Appraisal platform and method for mechanical seals of reactor coolant pumps in mega-kilowatt nuclear power plants
ActiveCN102278302AImprove sealingImprove analytical performancePump testingPositive-displacement liquid enginesHysteresisEngineering
The invention discloses a mechanical seal appraisal platform and method for a reactor coolant pump of a million-kilowatt nuclear power plant. The appraisal platform includes a seal appraisal test bench and a control host for controlling the seal appraisal test bench; the seal appraisal test bench includes A pump unit module, a refrigeration unit module and a sealing test module, the sealing test module is used to measure the stable working condition sealing characteristics, high temperature sealing leakage characteristics, cold state characteristics, pressure hysteresis transient characteristics and static sealing characteristics of the mechanical seal. The identification method includes the step of replacing the O-ring in the mechanical seal and several characteristic determination steps: stable working condition seal, high temperature seal leakage, pressure hysteresis transient, cold state and static seal. The ability of fault diagnosis and analysis of reactor coolant pump mechanical seal is improved, which not only saves cost, but also can carry out theoretical research work on various characteristics of seal under various working conditions, so as to facilitate safe production.
Owner:GUANGDONG NUCLEAR POWER JOINT VENTURE +3
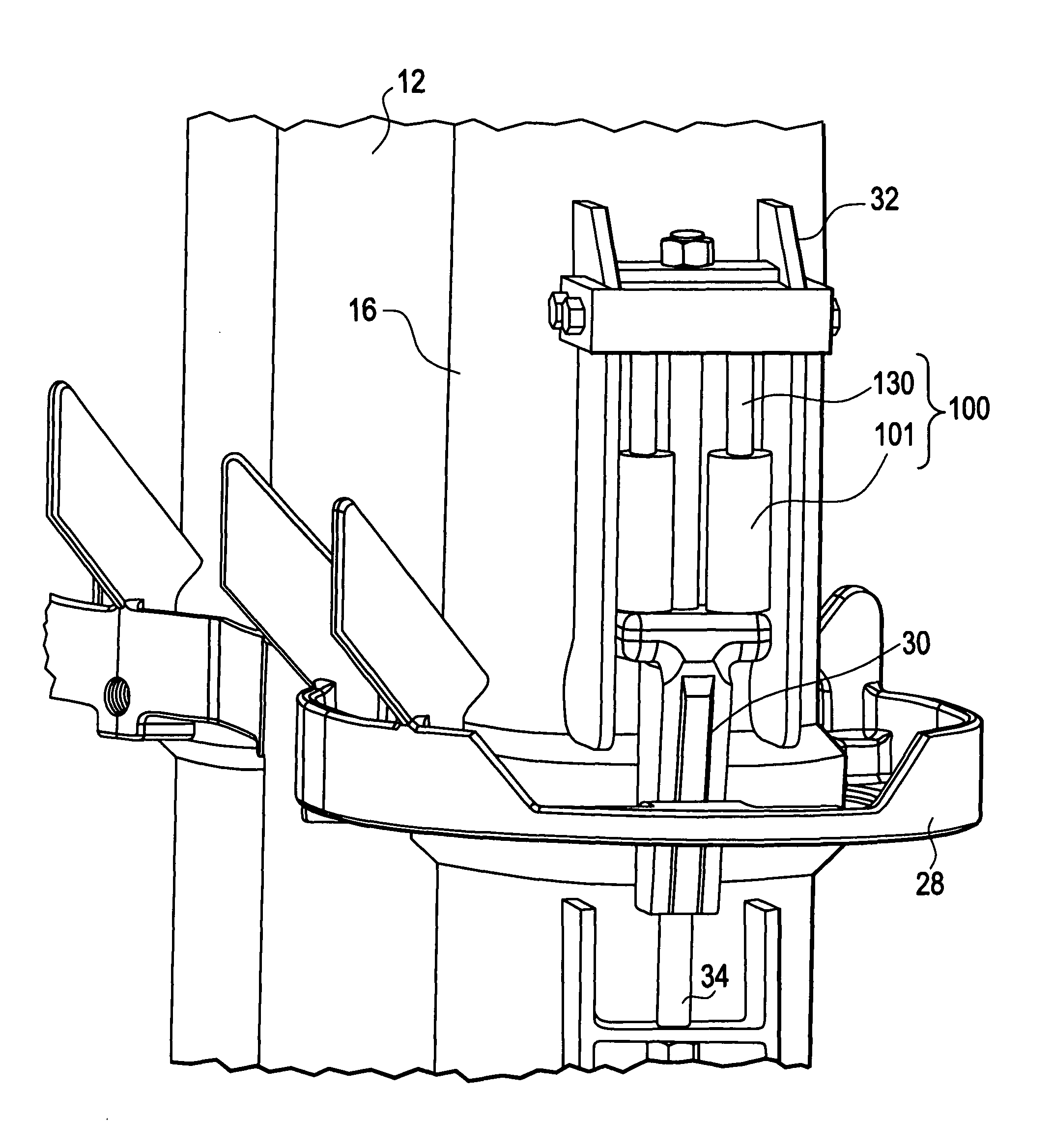
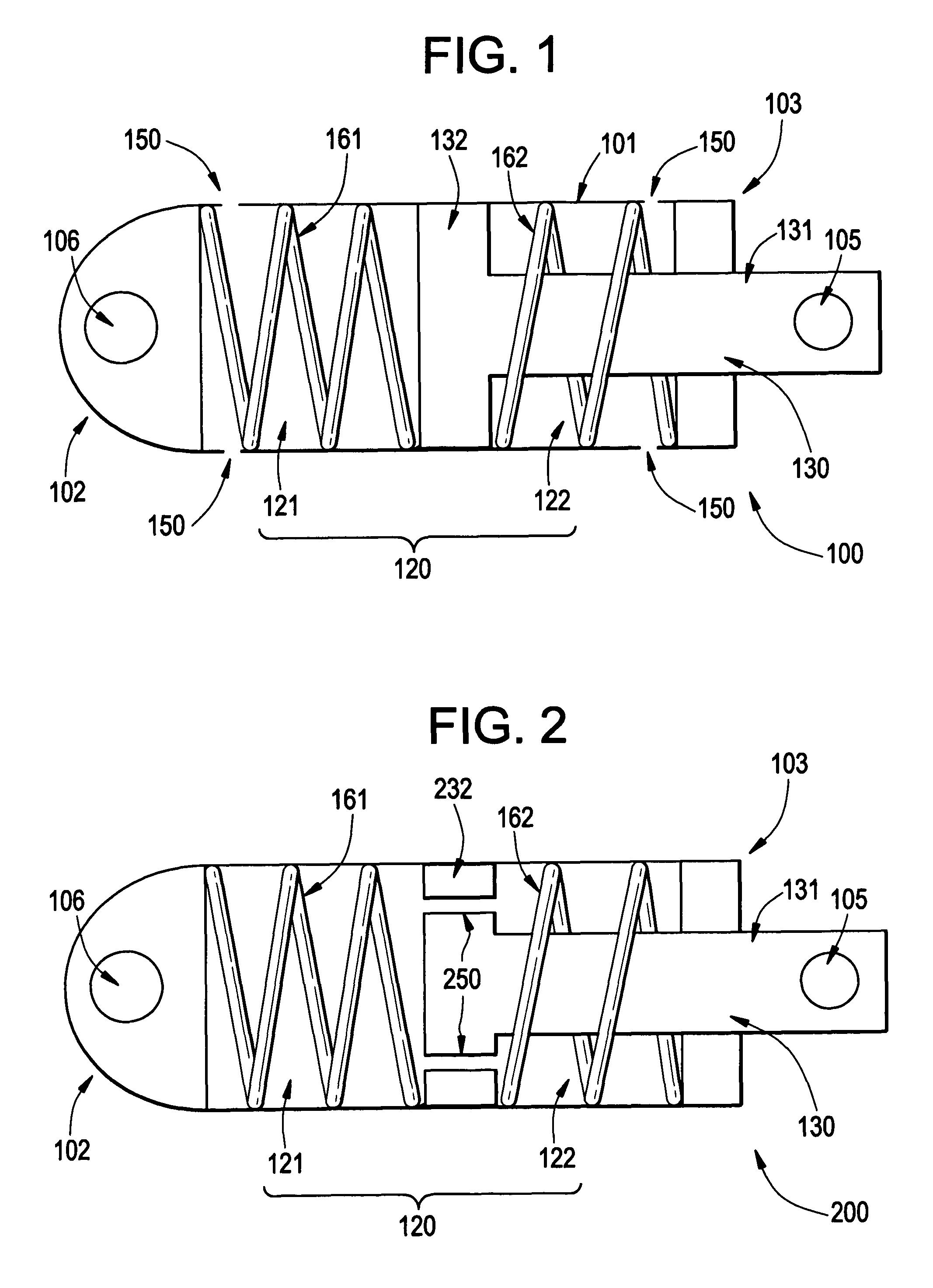
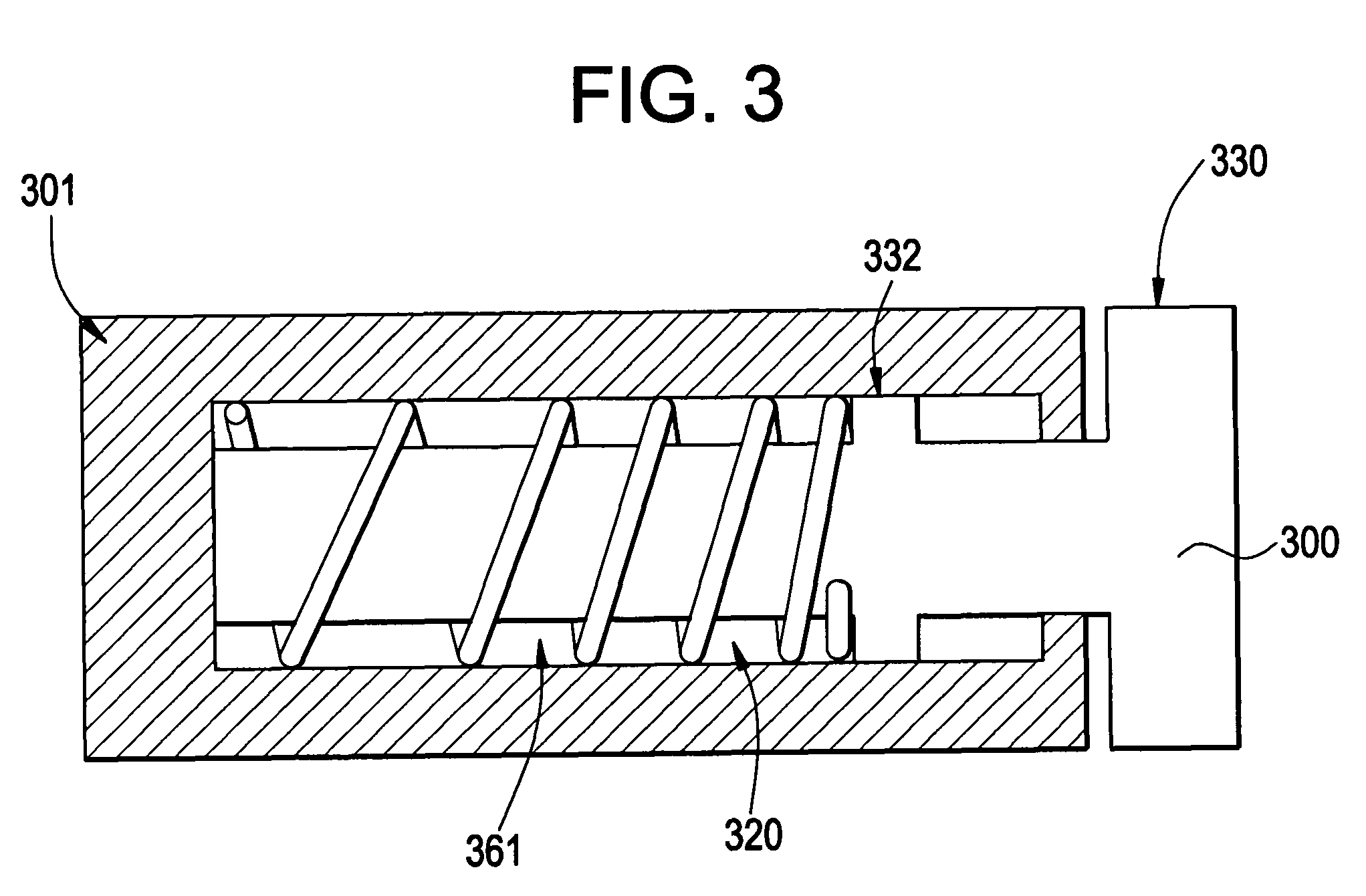
Apparatuses and methods for damping nuclear reactor components
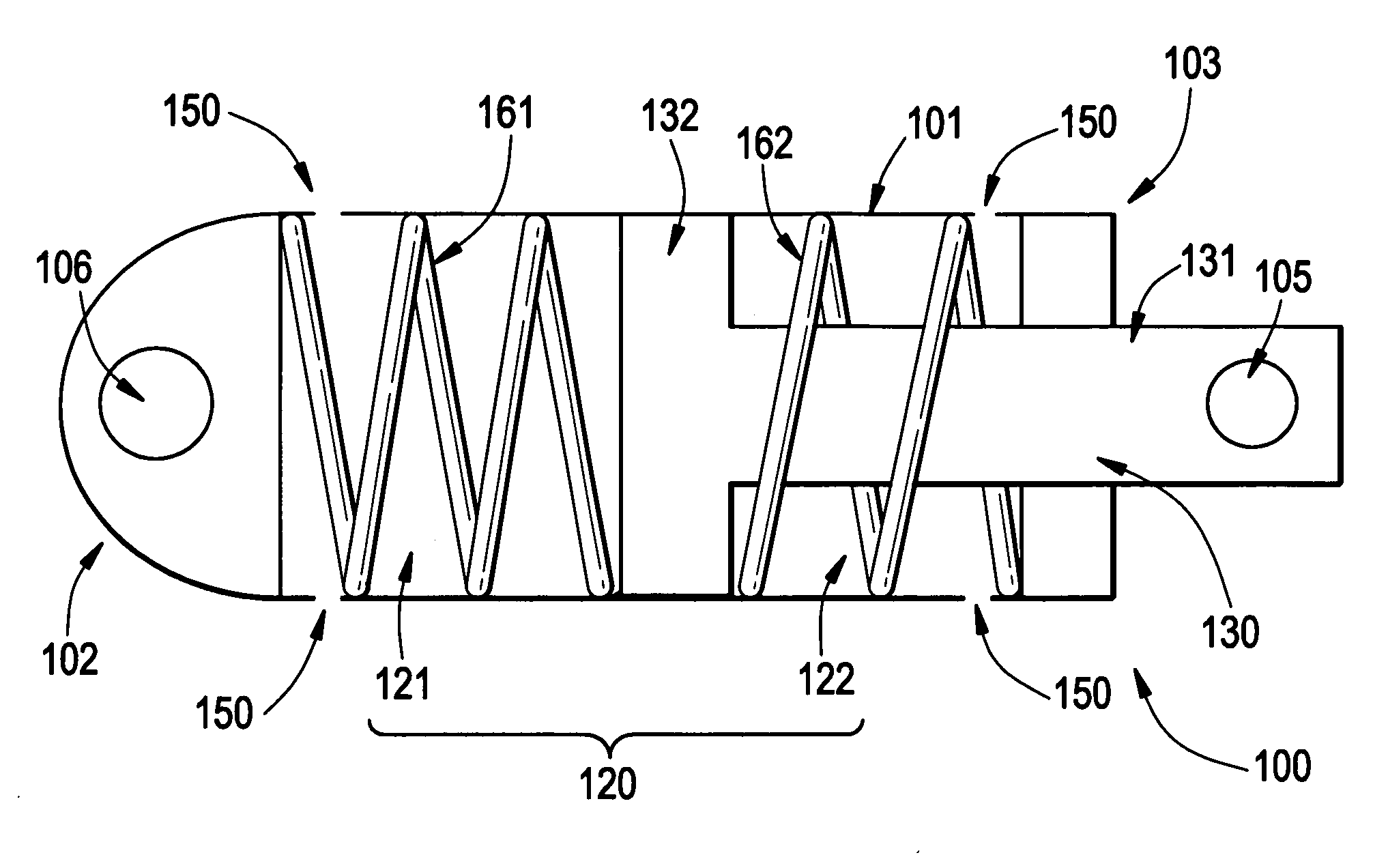
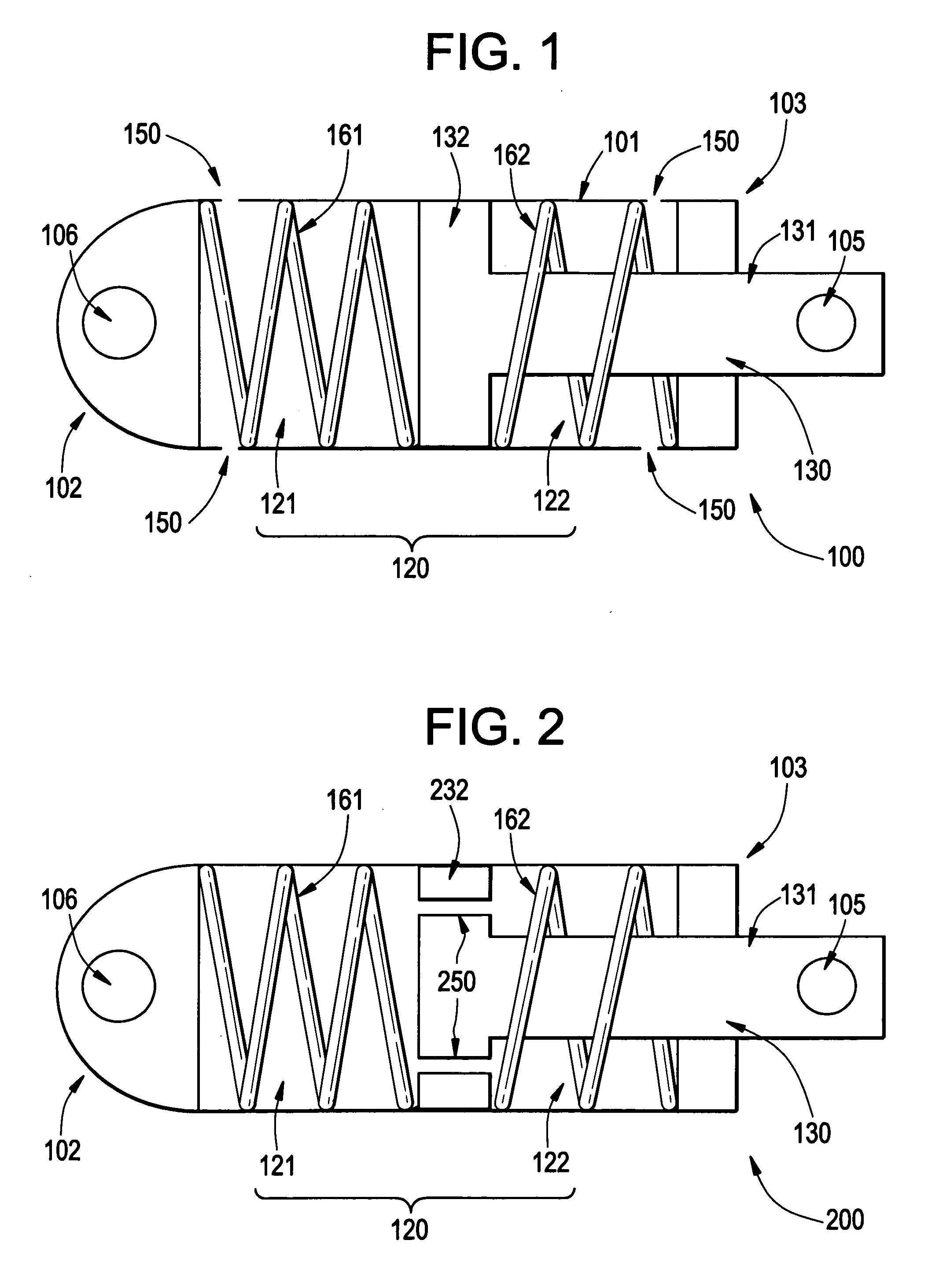
Example embodiment damping devices may include a housing capturing a piston. The housing may be filled and / or able to be filled with a damping fluid compatible with the nuclear reactor coolant, so that a leak from the housing or coolant passing into the housing does not damage the reactor or example embodiment devices. Example embodiments may further include one or more springs that provide an elastic force opposing movement between the piston and housing. A shaft of the piston and an end of the housing may be connected to two nuclear reactor components with relative motion or vibration to be damped. Example methods may use example embodiment damping devices to reduce and / or prevent relative motion and vibration among components of a nuclear reactor.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
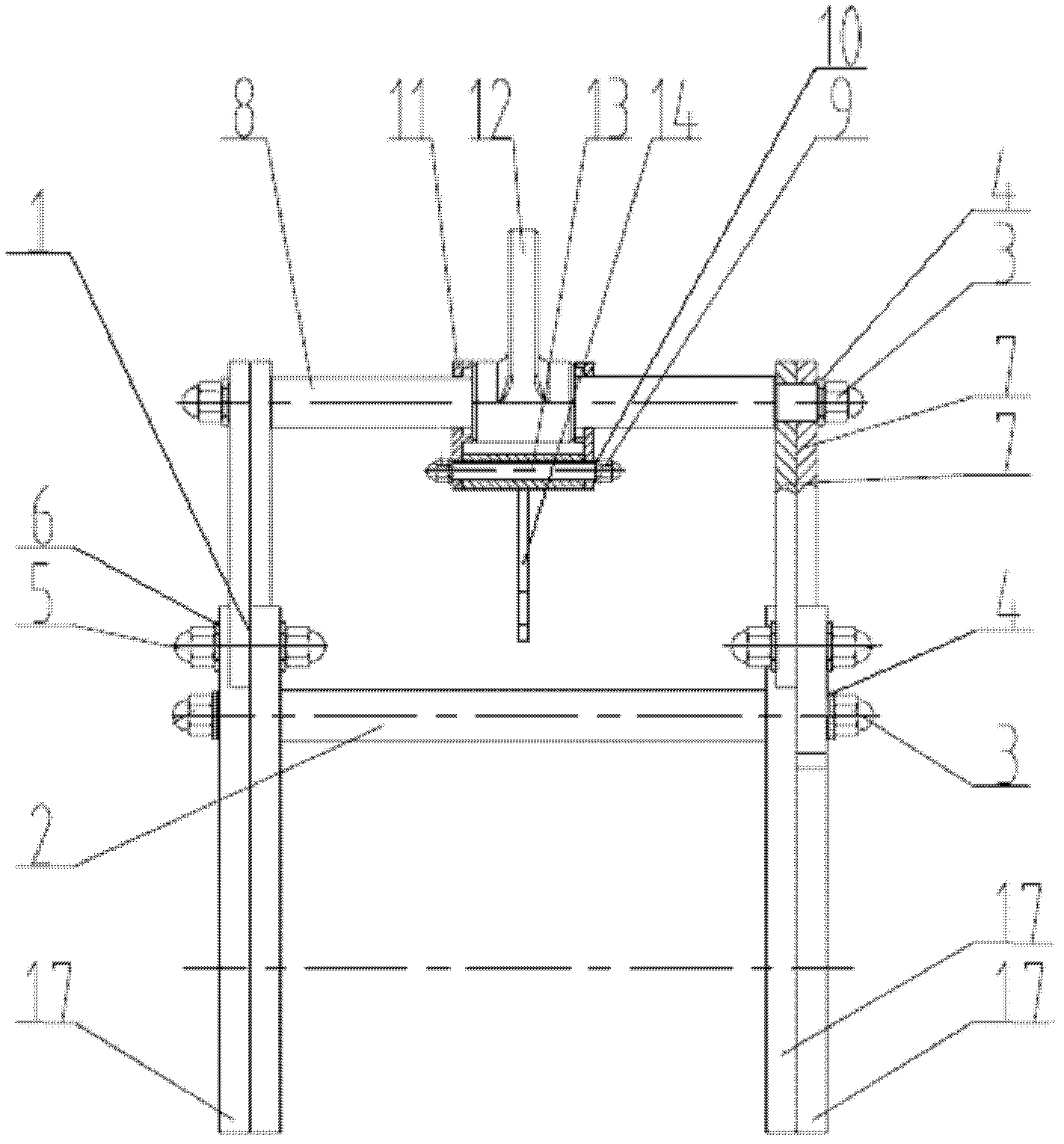
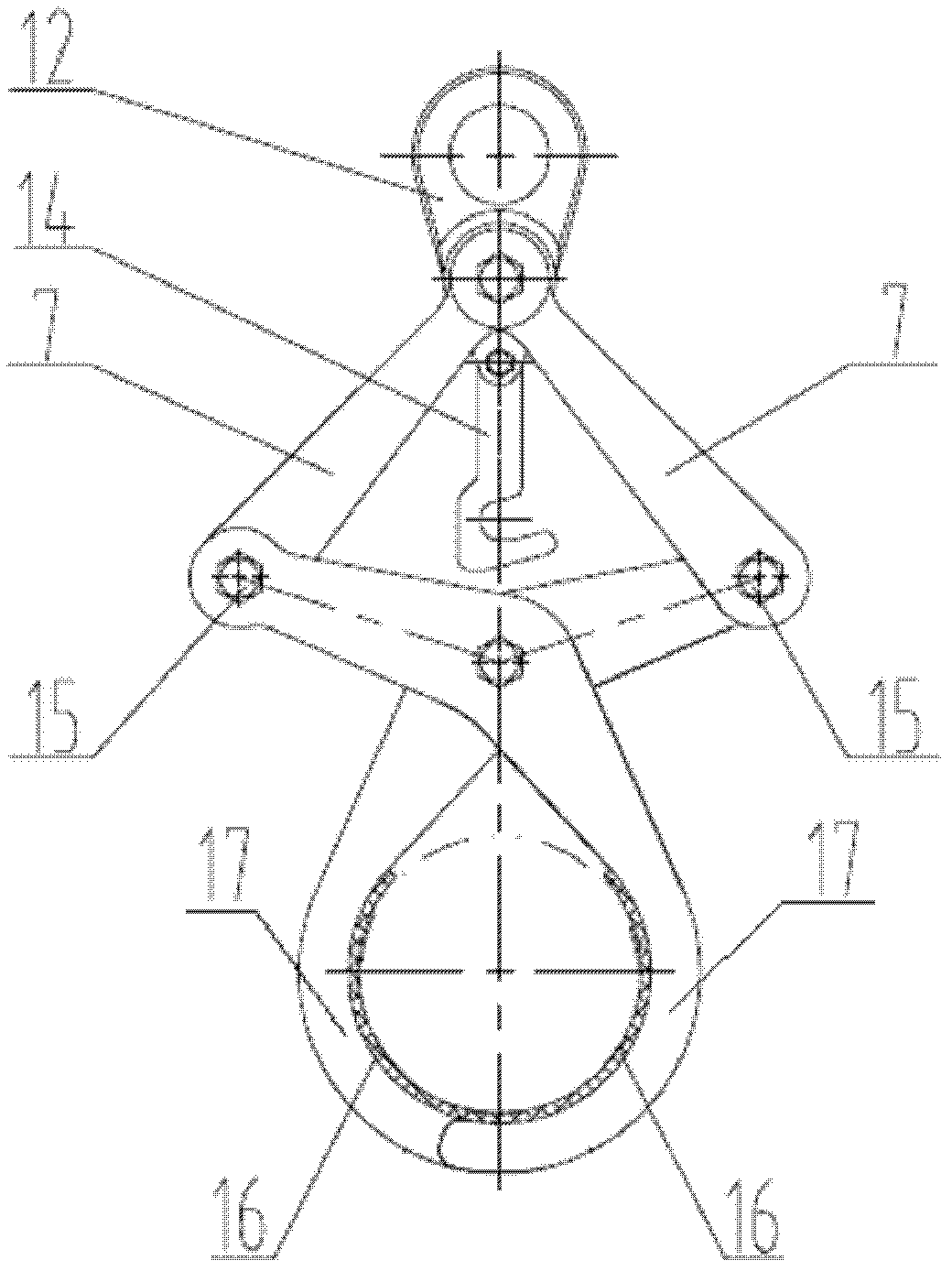
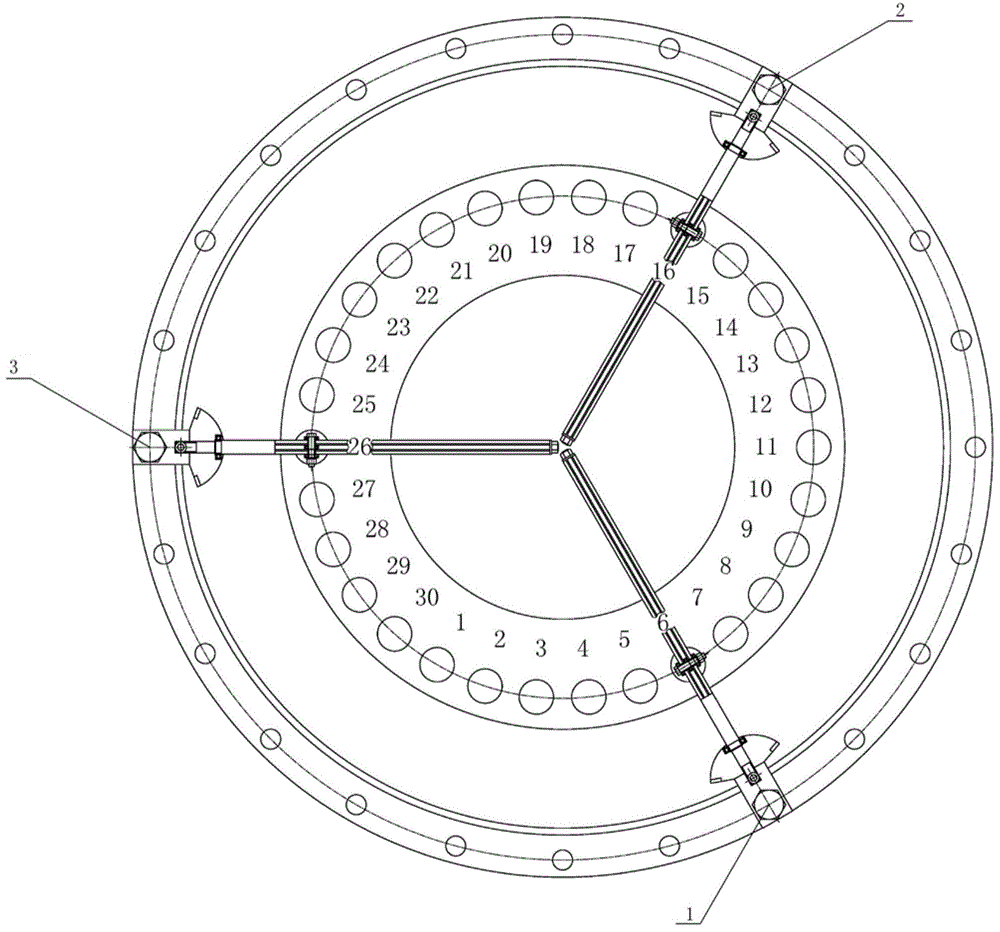
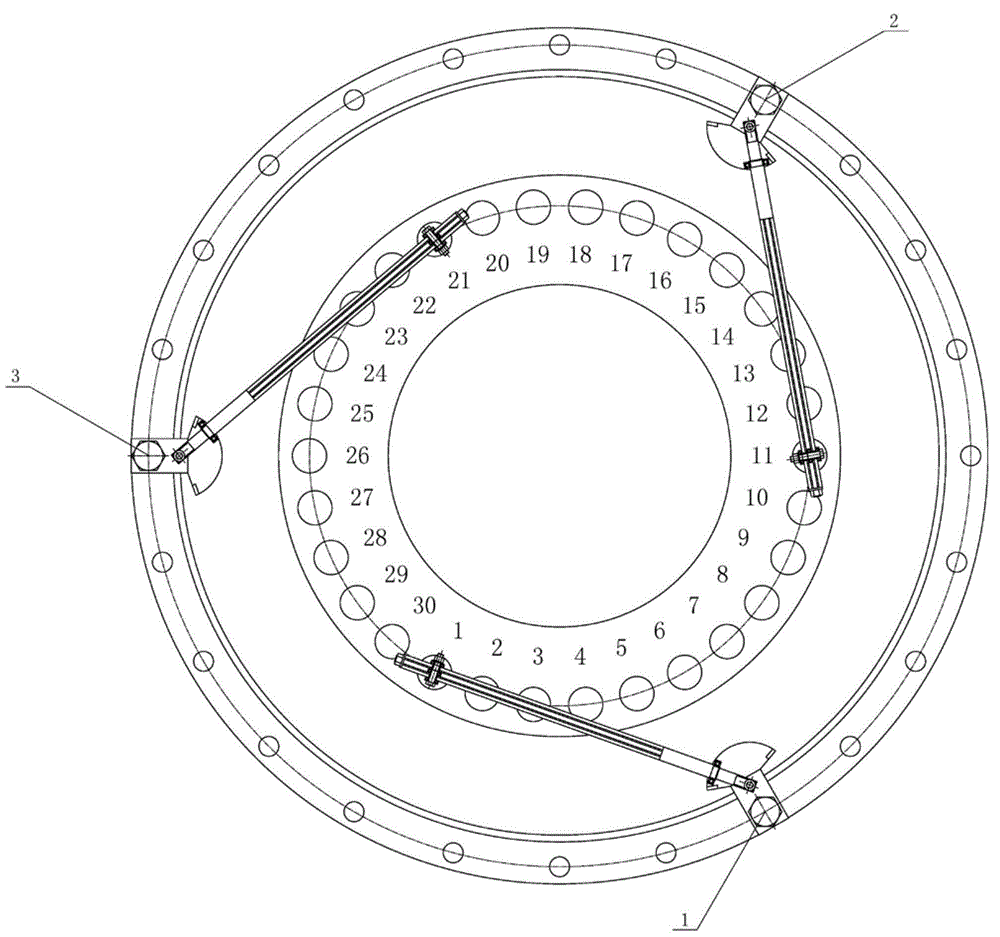
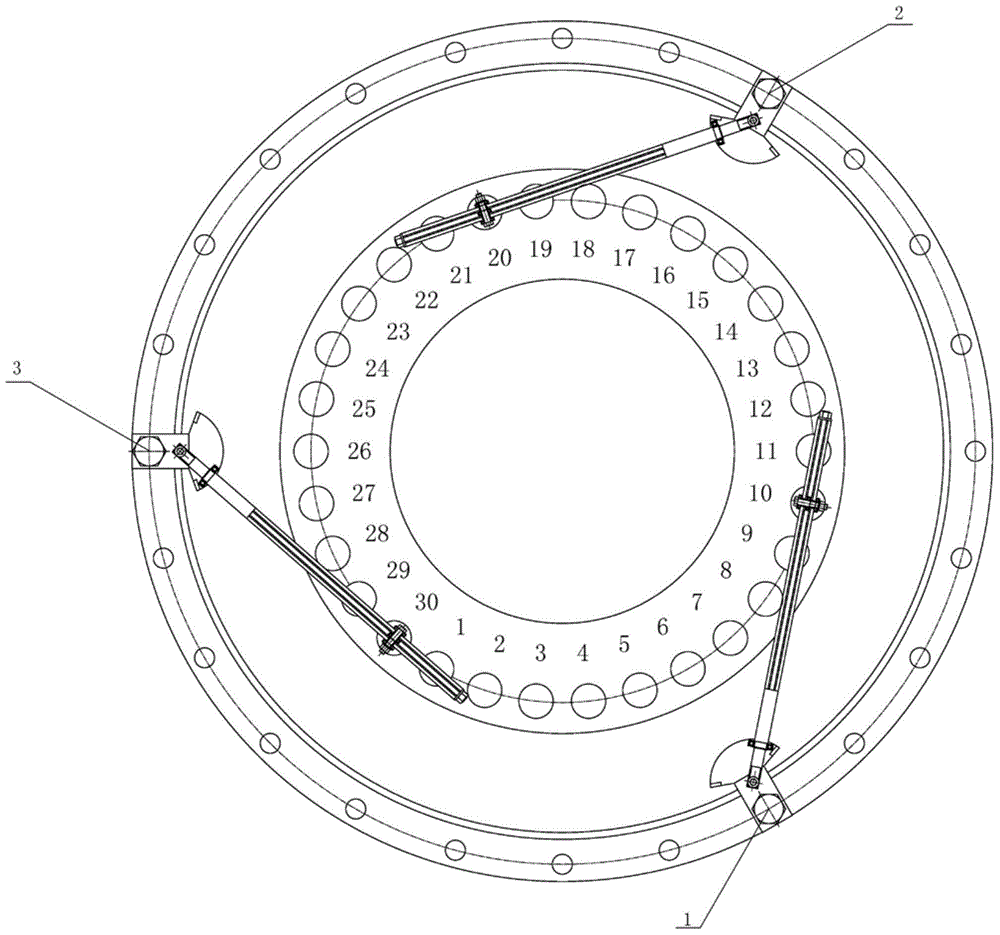
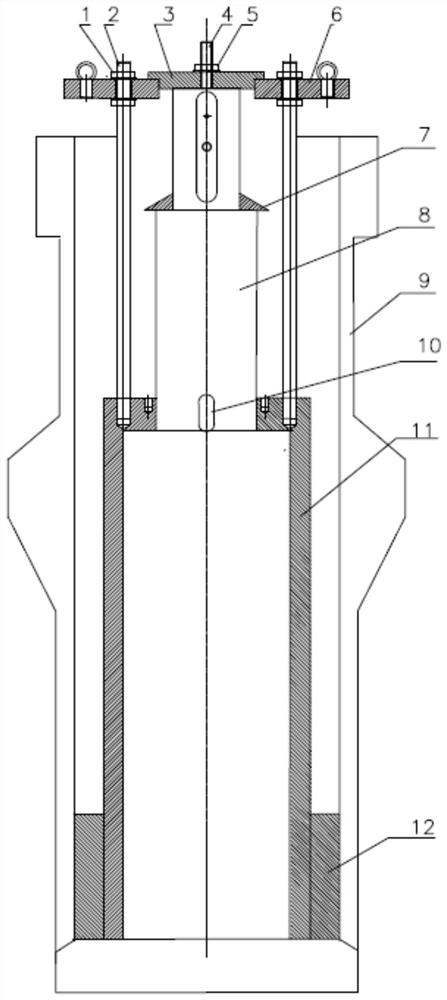
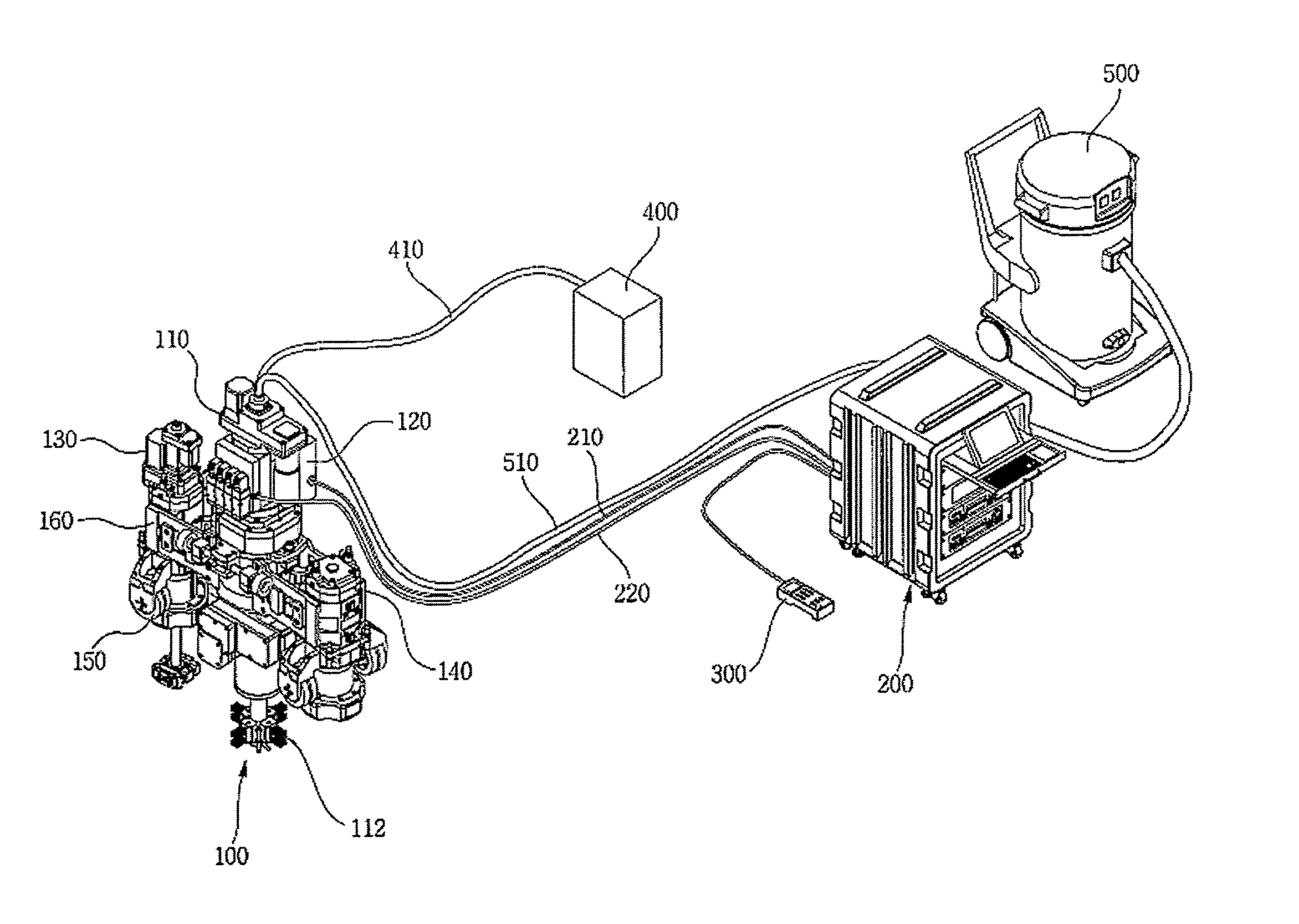
Hoisting clamp specially used for reactor coolant pump main flange bolt
The invention relates to a hoisting clamp specially used for a reactor coolant pump main flange bolt, which comprises a hoisting ring, clamping jaw assemblies, a hoisting rod, an intermediate rod located below the hoisting rod parallelly to the hoisting rod, two sets of clamping jaw assemblies which are respectively arranged at two ends of the hoisting rod and the intermediate rod symmetrically; the hoisting ring is fixed at the center of the hoisting rod; each set of clamping jaw assemblies comprises two hook-shaped bodies and two connecting rods; the hook-shaped body has a one-piece structure comprising a hook body and a hook handle; the two hook bodies are arranged symmetrically and intersect with each other, and round holes are disposed at the intersecting parts; the hook handle end of each of the two hook-shaped body is respectively and movably connected with one end of each of the two connecting rods, and the other end of each of the two connecting rods is movably connected with one end of the hoisting rod; two ends of the intermediate rod pass through the round holes of the two sets of clamping jaw assemblies respectively, and are movably connected with the two sets of clamping jaw assemblies. The invention realizes rapid, convenient, and safe hoisting of a reactor coolant pump main flange bolt, and improves the cleaning efficiency and the automation level of hoisting equipment.
Owner:RES INST OF NUCLEAR POWER OPERATION +1
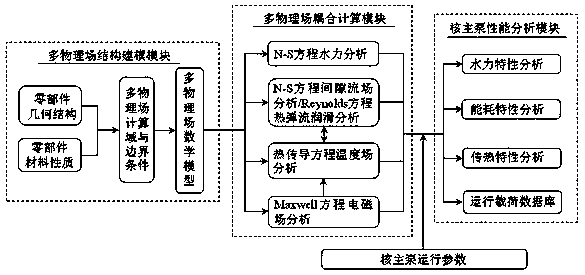
Method for constructing shielded nuclear main pump digital prototype through multi-physical field coupling
ActiveCN110598317AMeet performance simulation needsAccurately analyze energy consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsMultiphysics couplingPhysical field
The invention discloses a method for constructing a shielded nuclear main pump digital prototype through multi-physical-field coupling, and belongs to design and manufacturing of nuclear reactor coolant pumps. The method comprises the following construction steps: 1, according to a flow field, a temperature field and an electromagnetic field associated with a nuclear main pump part, considering geometric and material properties of the part, determining calculation domains and boundary conditions of all physical fields, establishing mathematical models of all the physical fields, obtaining entity models of multiple physical fields through finite element discretization, and generating a multi-physical-field structure modeling module; 2, based on the passive physical process of the nuclear main pump, performing coupling calculation on the multiple physical fields by adopting a partial iteration method to generate a multi-physical-field coupling calculation module, and constructing a three-dimensional digital prototype of the nuclear main pump on the solid model; and 3, receiving the three-dimensional digital prototype through a nuclear main pump performance analysis module, calling multi-physical field coupling calculation data under nuclear main pump operation parameters as input, and outputting simulation results of a nuclear main pump hydraulic characteristic database, an energy consumption characteristic database, a heat transfer characteristic database and an operation load database. The method has the advantage of accurate analysis of working characteristics and performance of the nuclear main pump.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
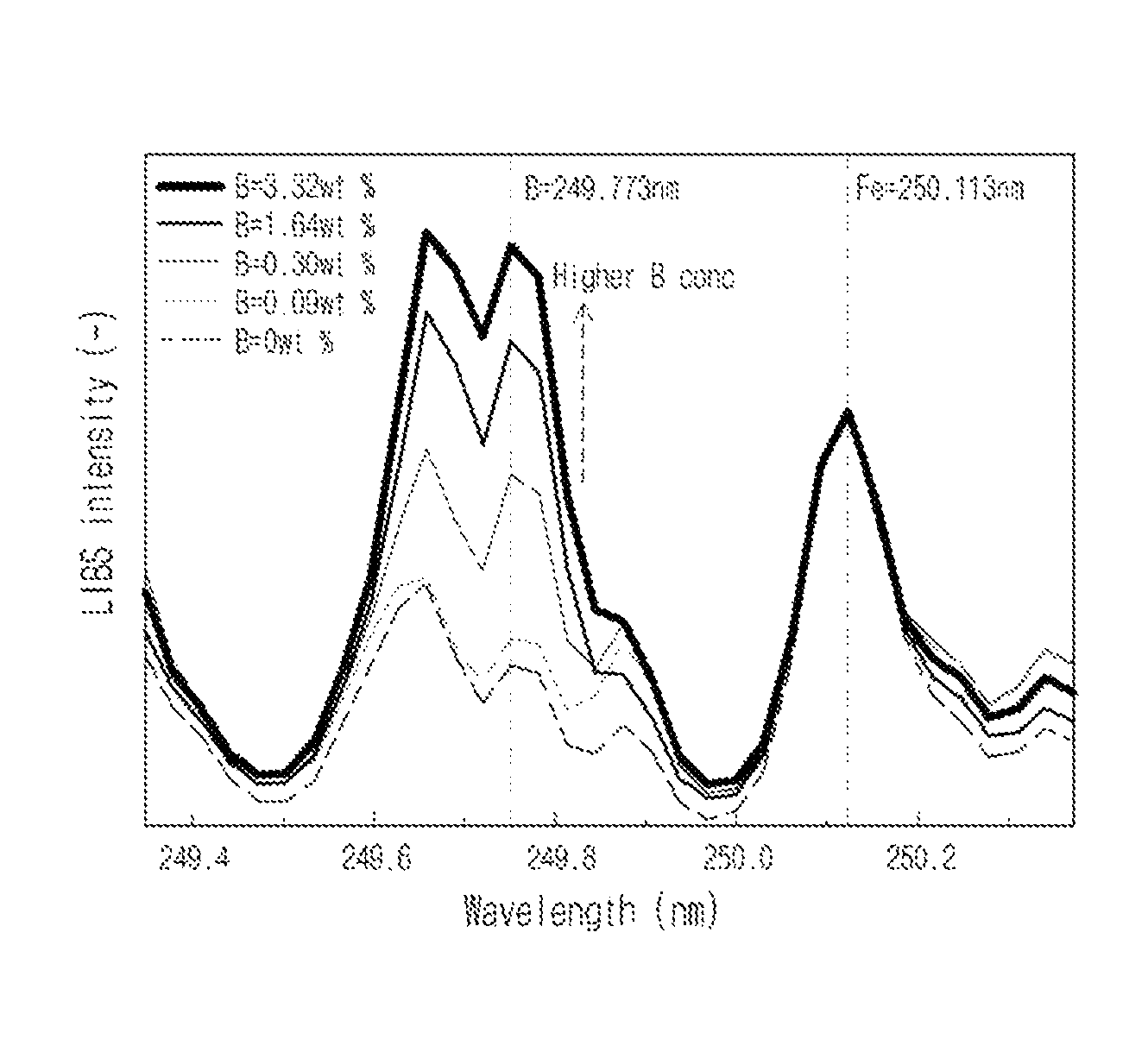
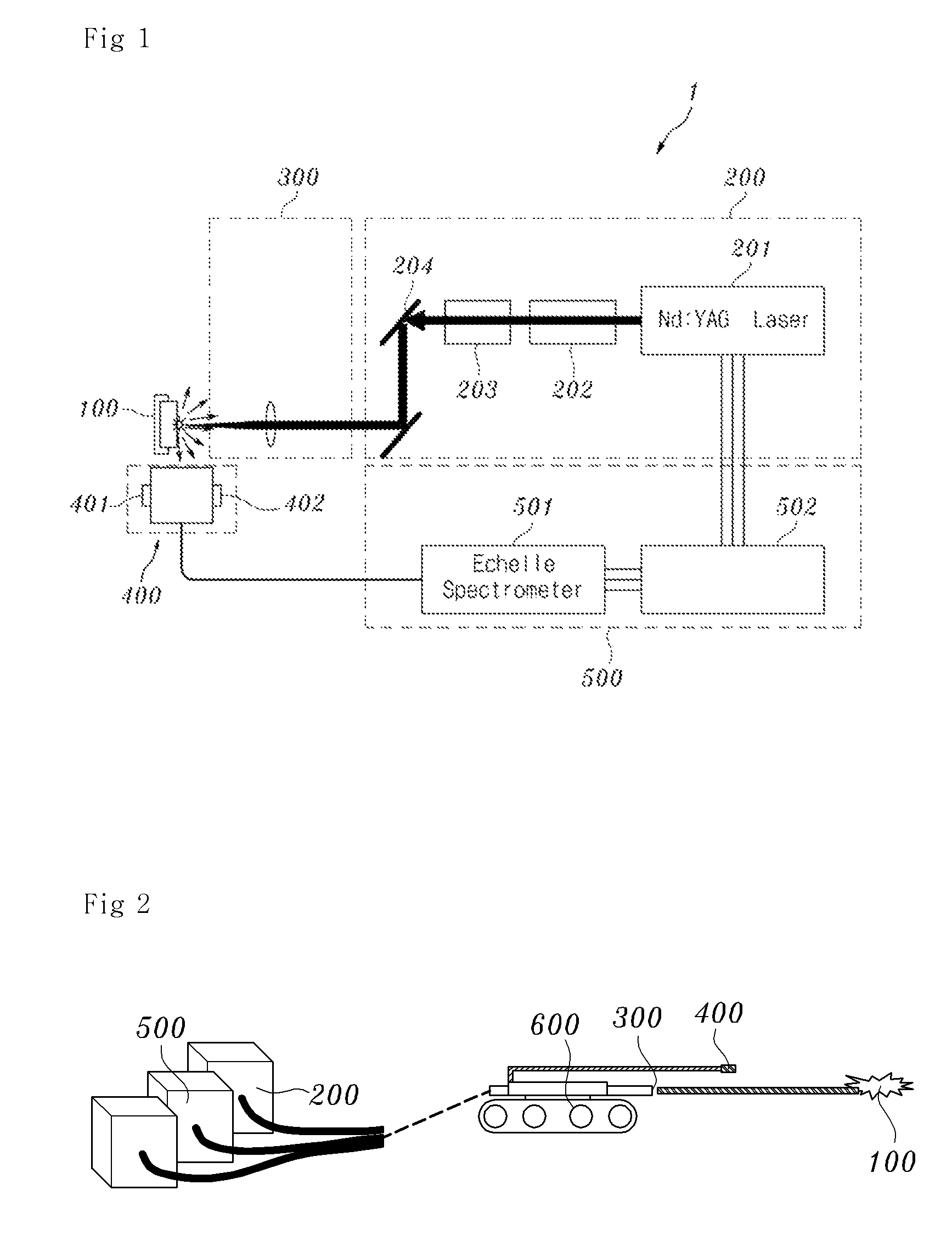
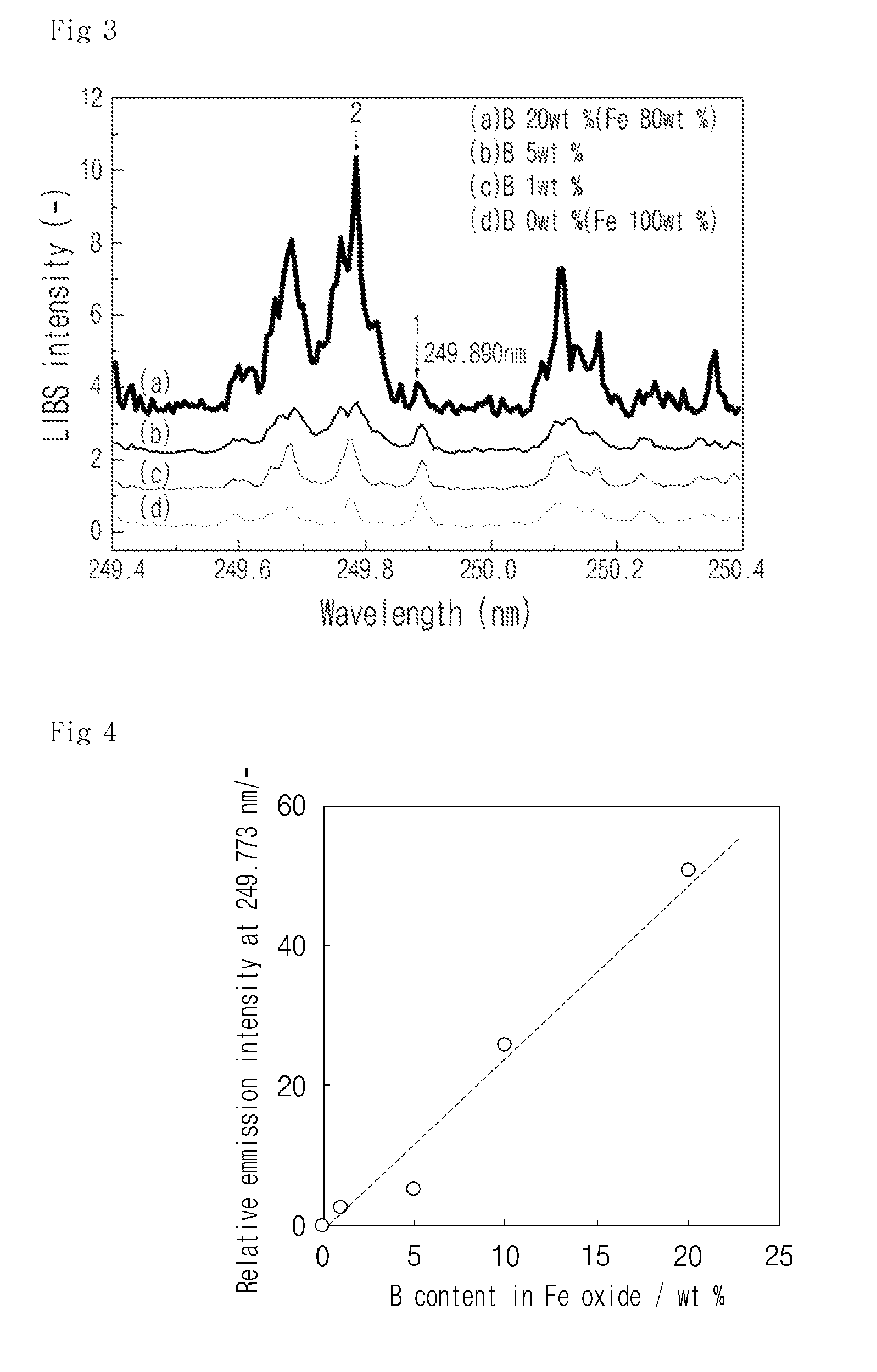
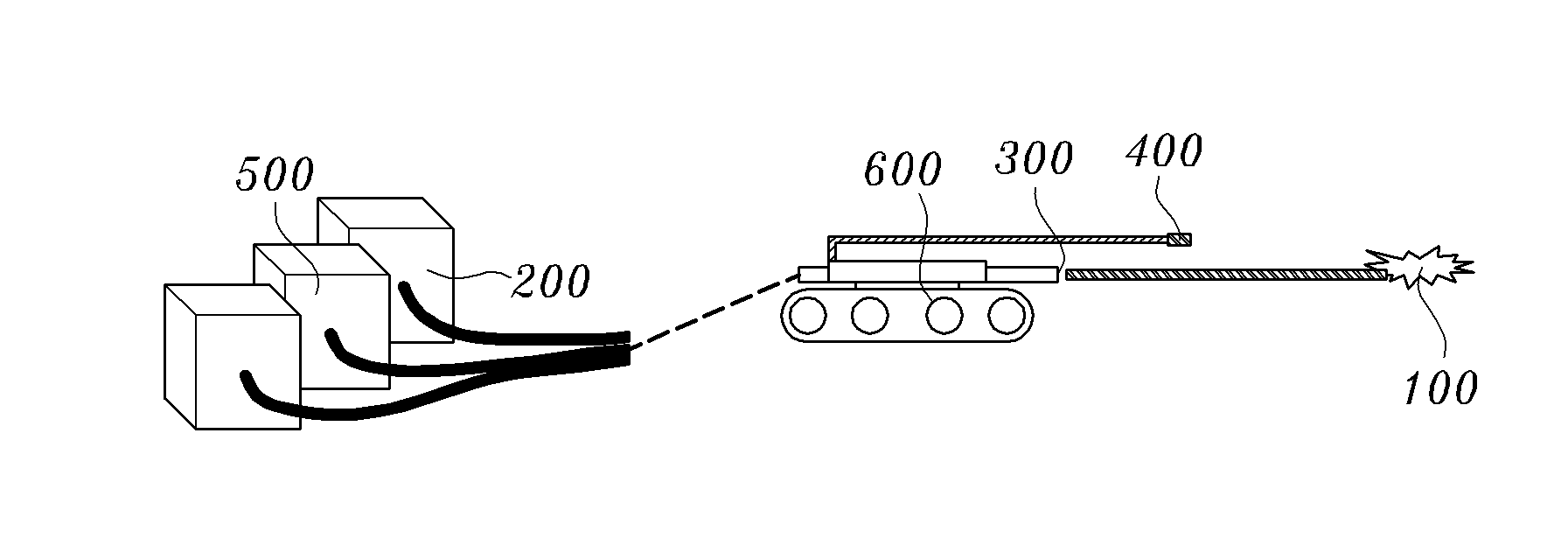
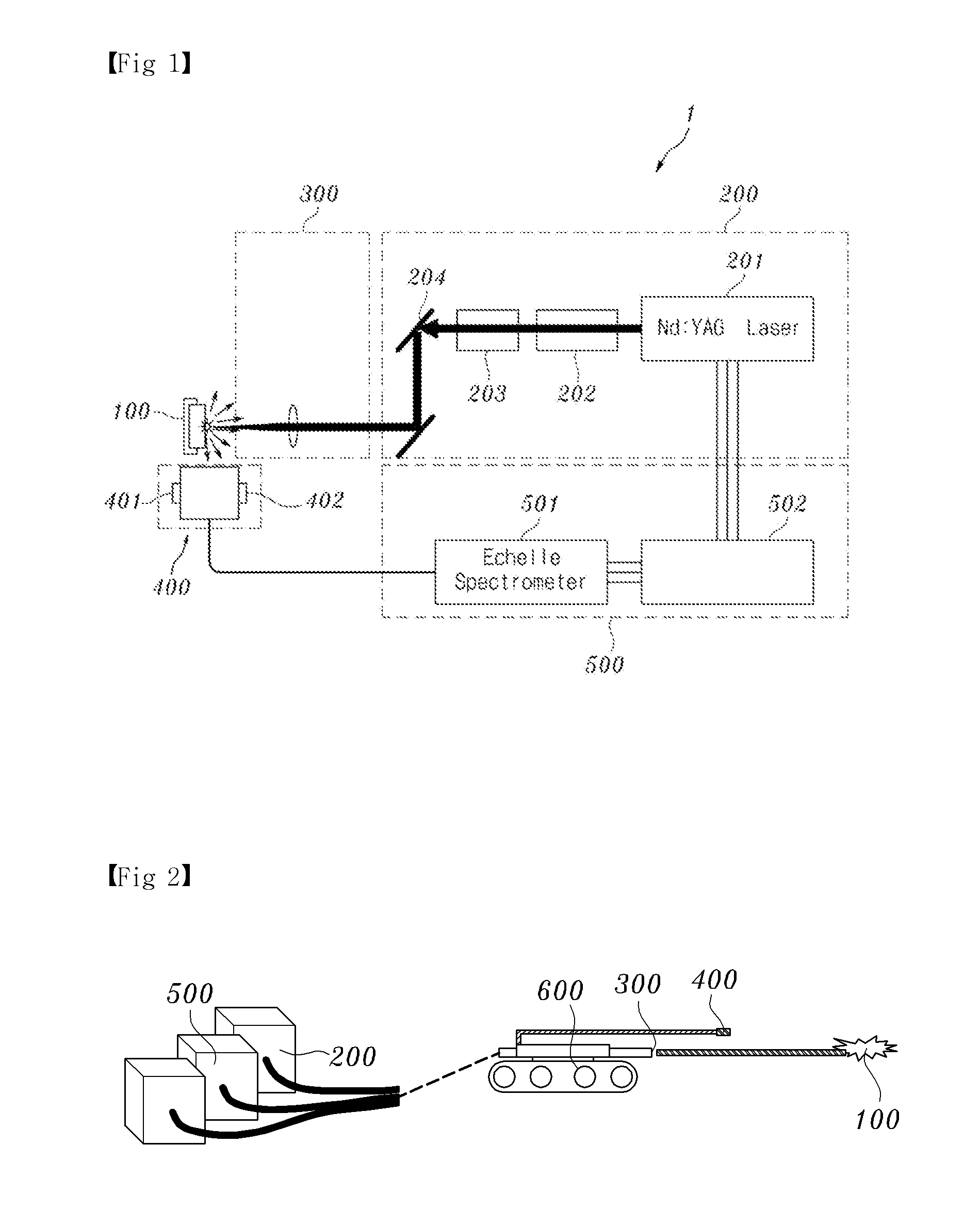
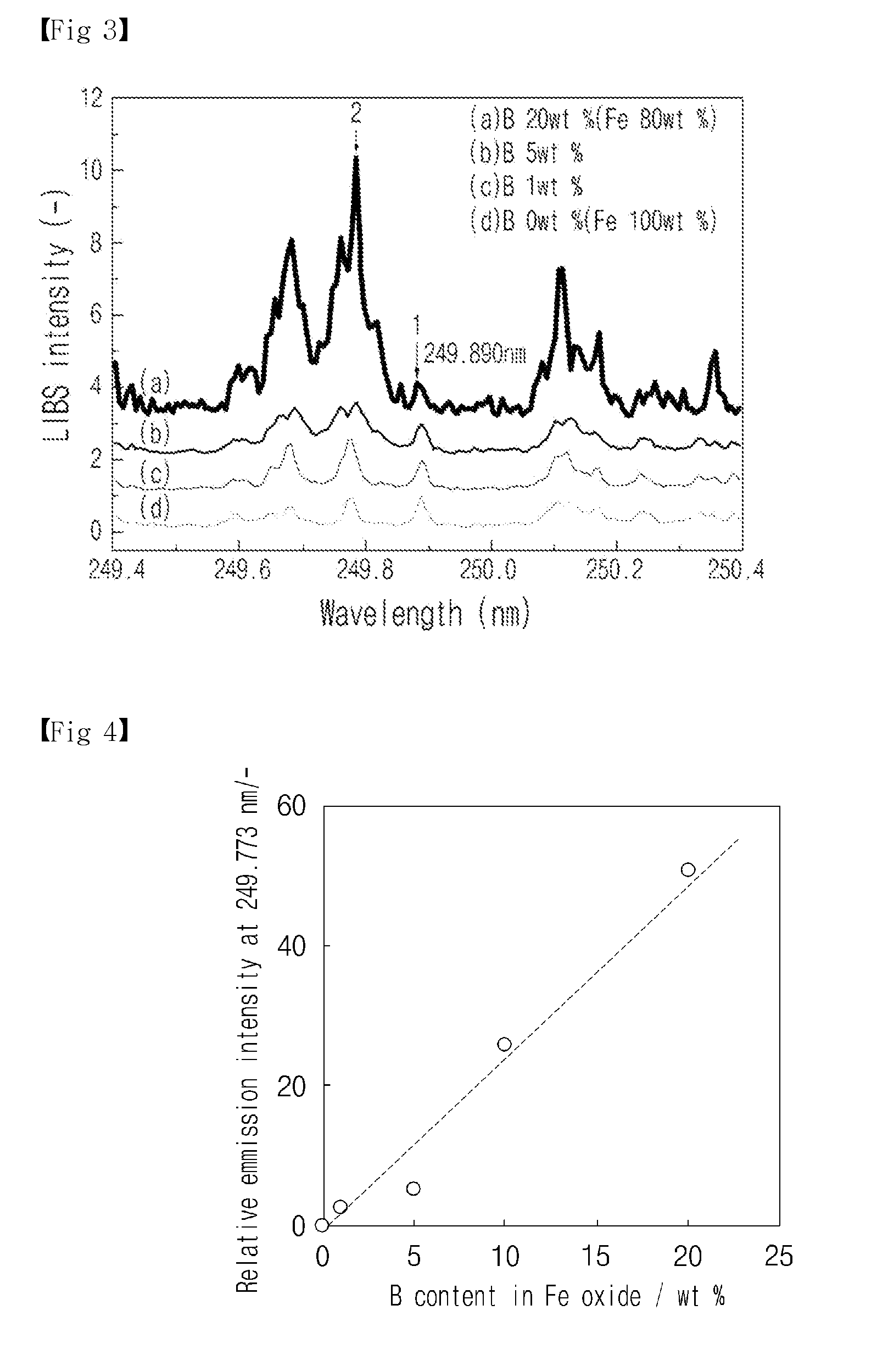
System and method for detecting leakage of nuclear reactor coolant using laser induced emission spectrum
InactiveUS8855259B2Reduce impurityEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryNuclear reactor coreSpectroscopy
System and method for detecting and / or predicting in a field the leakage of nuclear reactor coolant that may occur at the pressure boundary of the primary system of a nuclear reactor. The system and method for detecting the leakage of nuclear reactor coolant uses a laser induced emission spectrum. The leakage of coolant is detected by detecting boron (B), a main component of the coolant, in corrosive products generated at the nuclear reactor pressure boundary on the basis of laser spectroscopy. An embodiment of the system for detecting leakage of nuclear reactor coolant may include a laser generator, a laser focusing lens, an emission collector, and emission spectrum analyzer.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
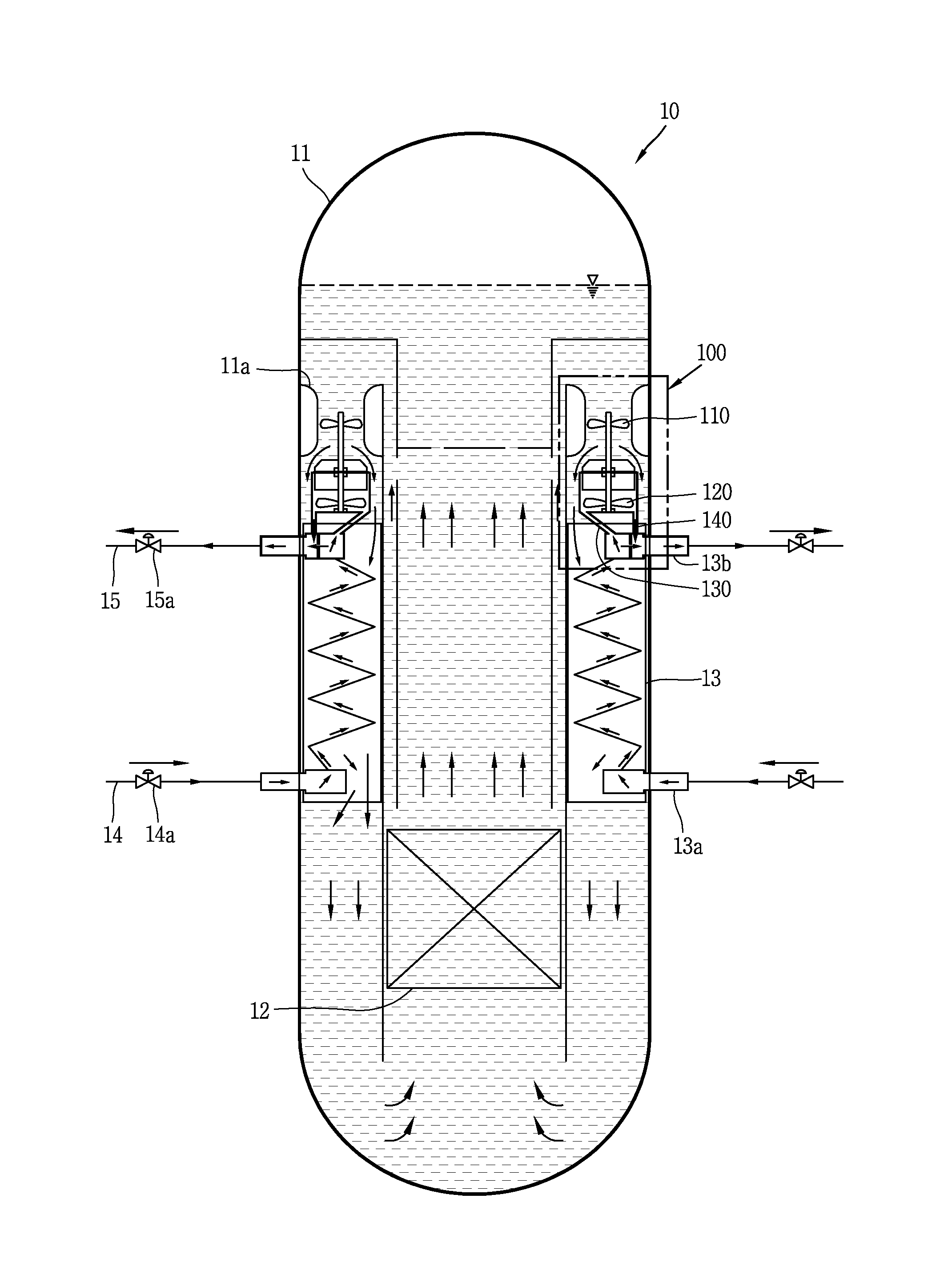
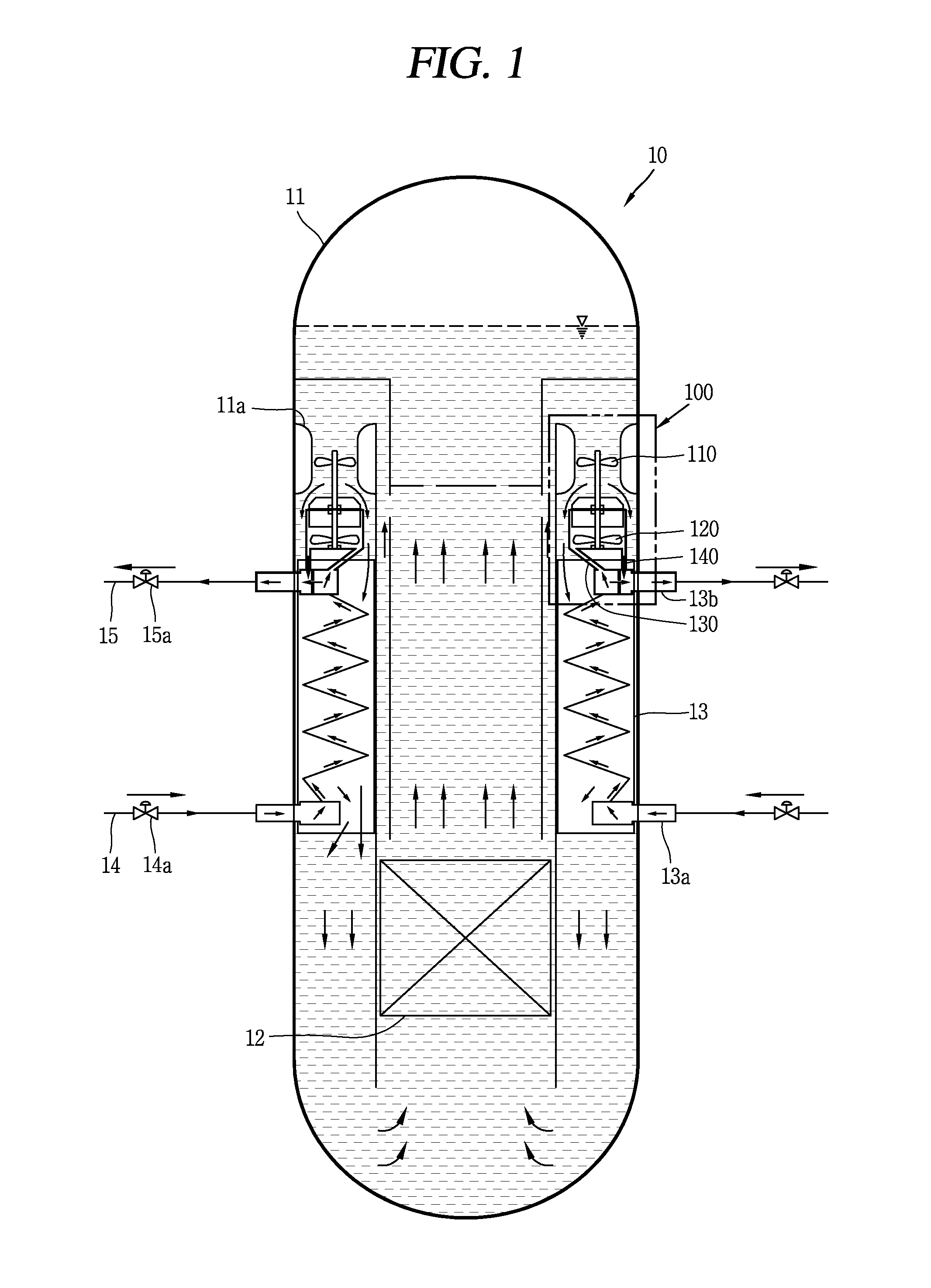
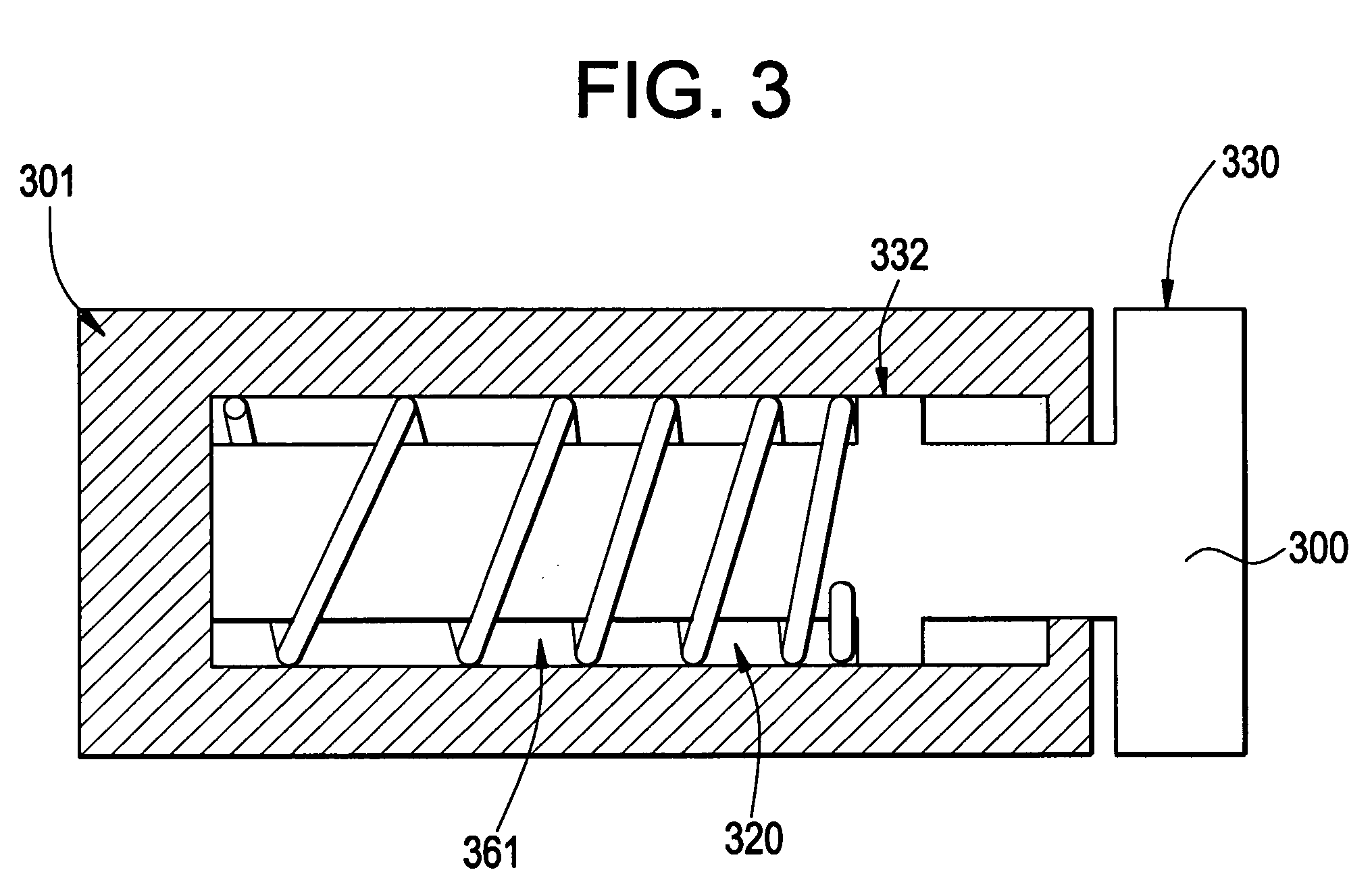
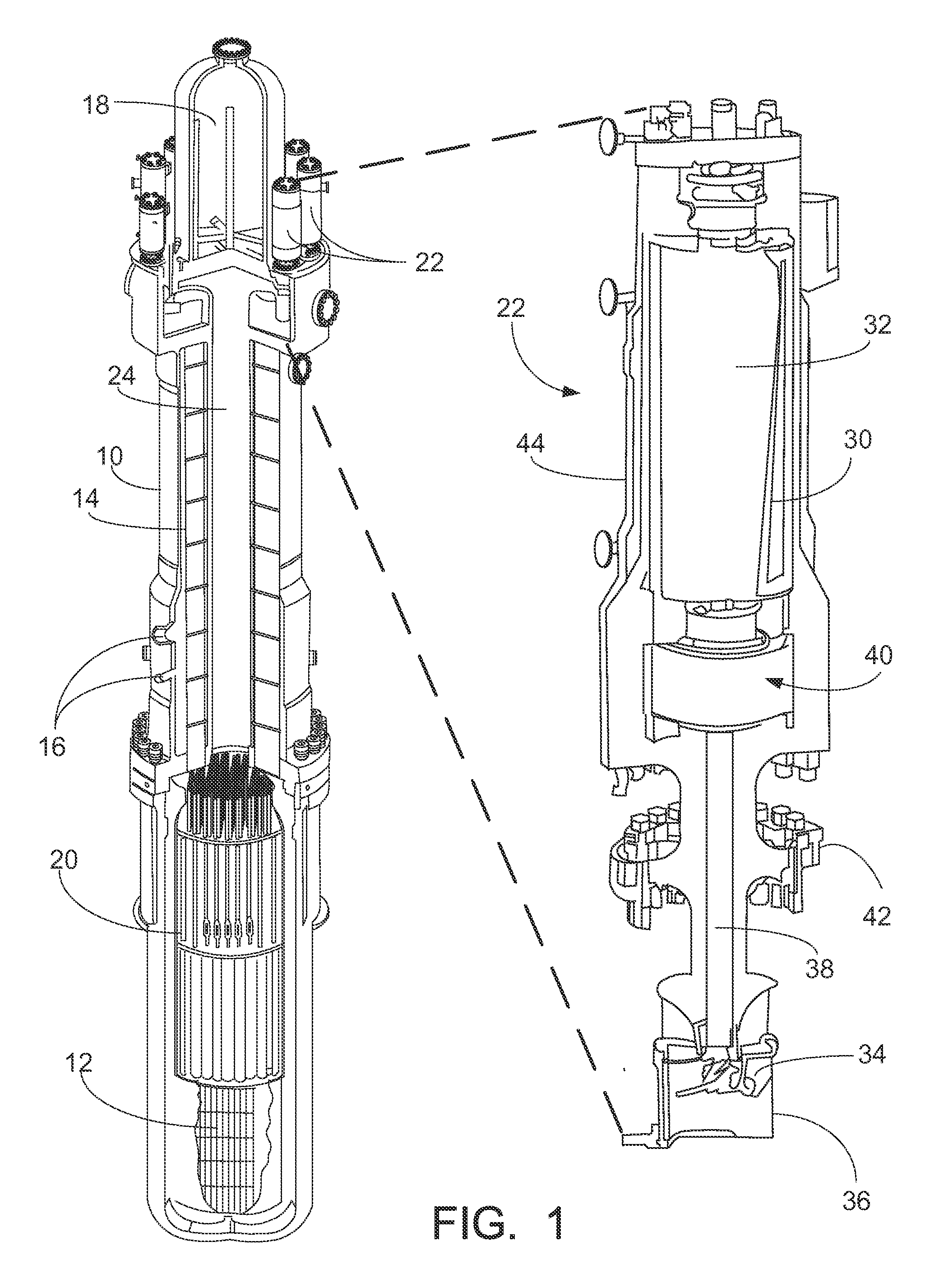
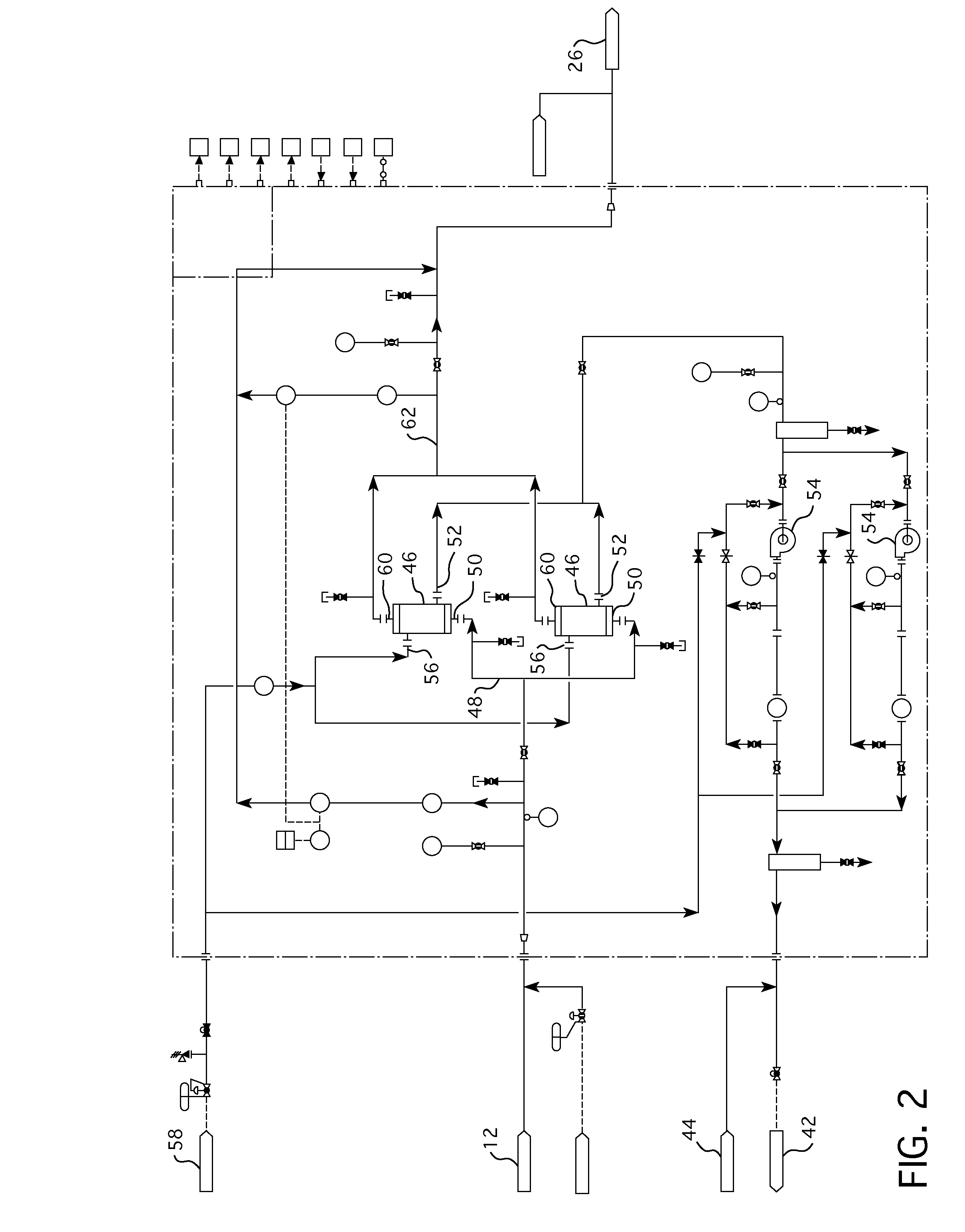
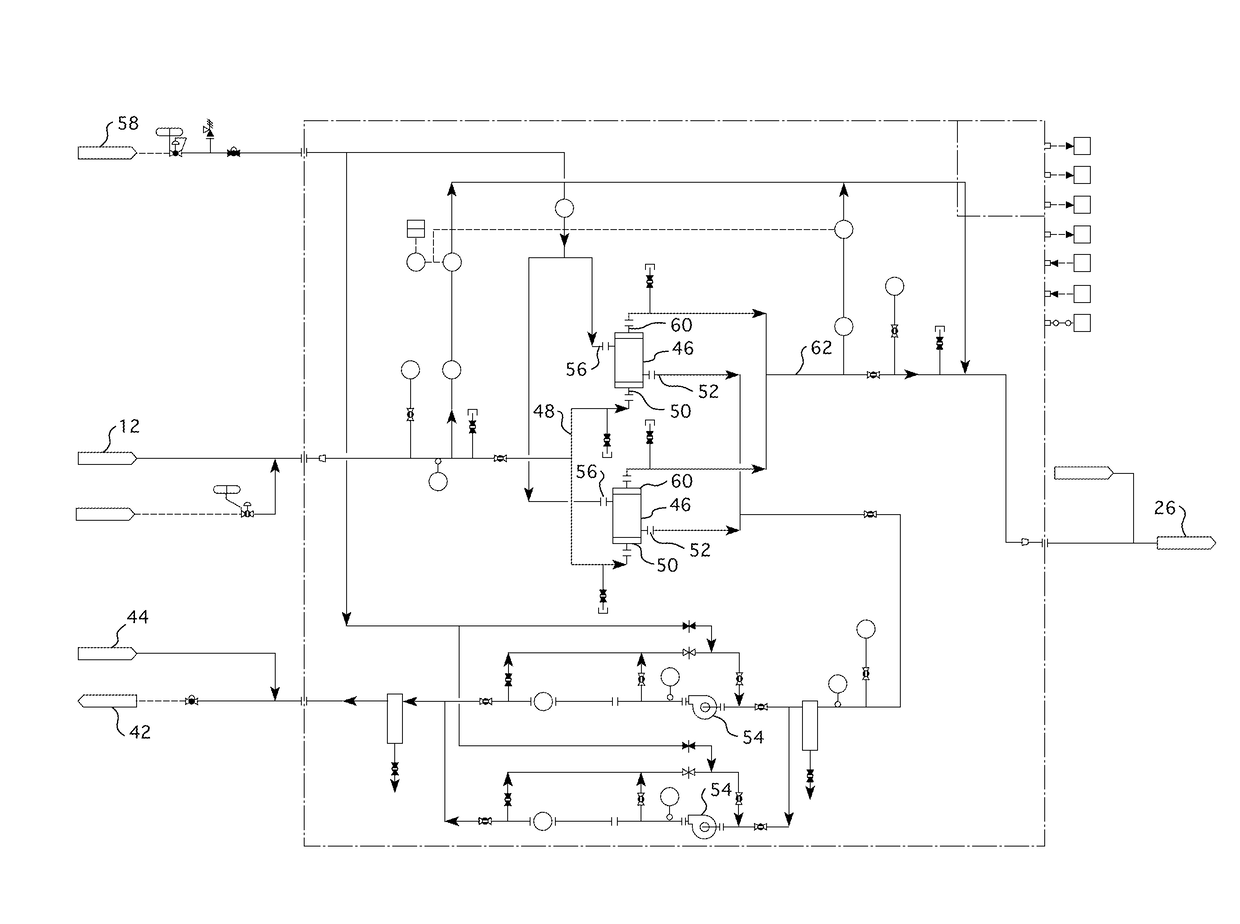
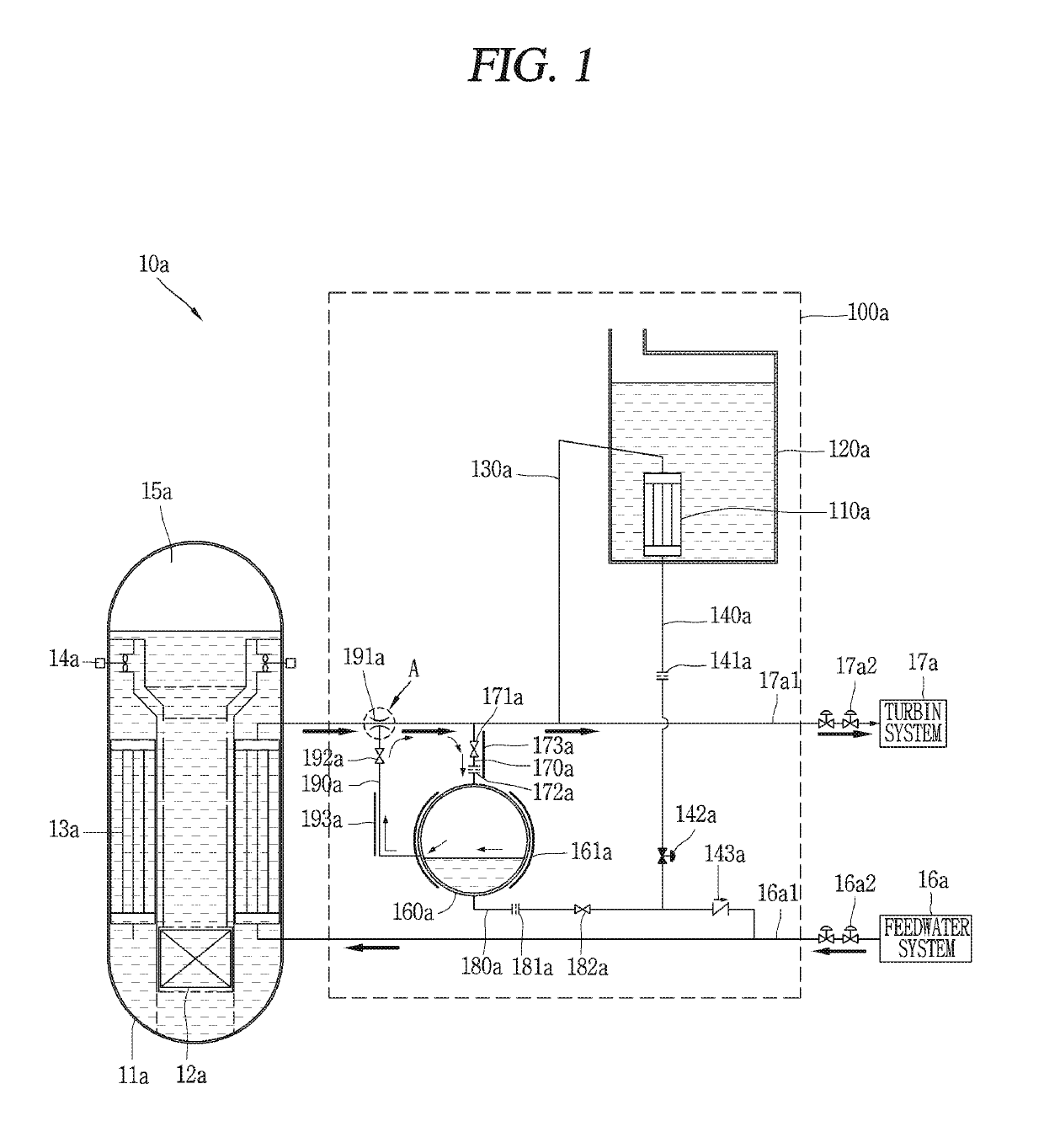
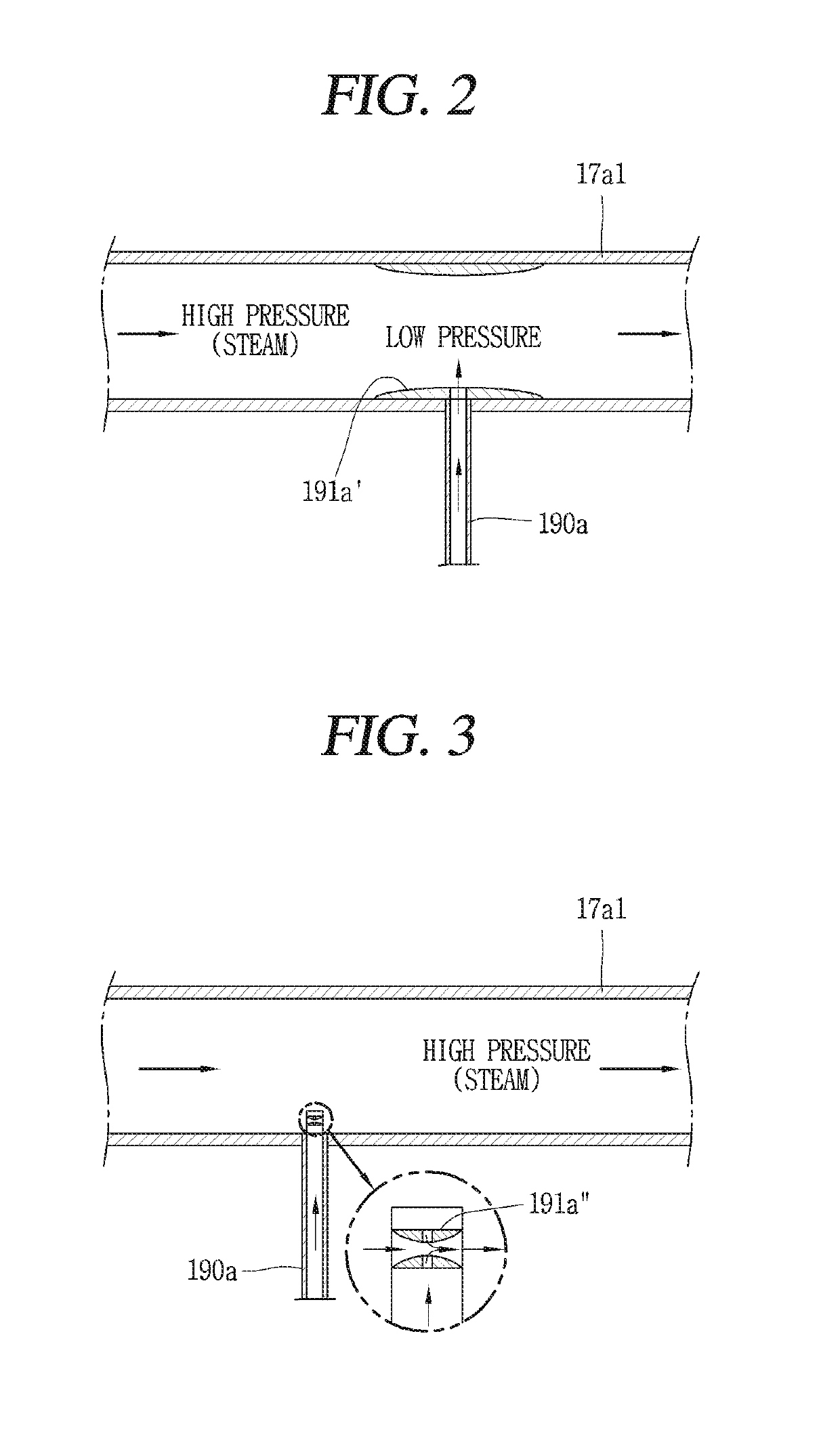
Nuclear reactor primary circuit
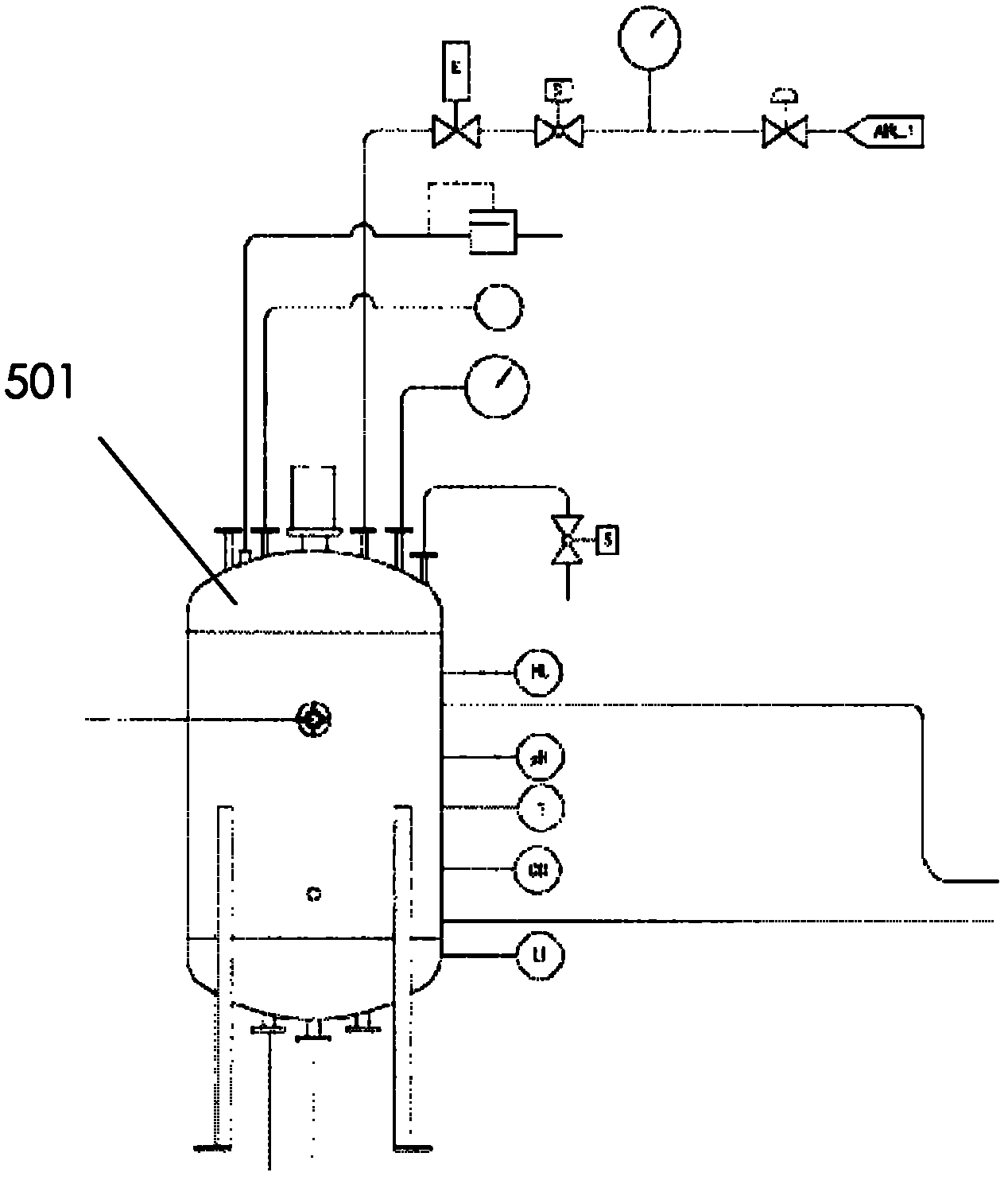
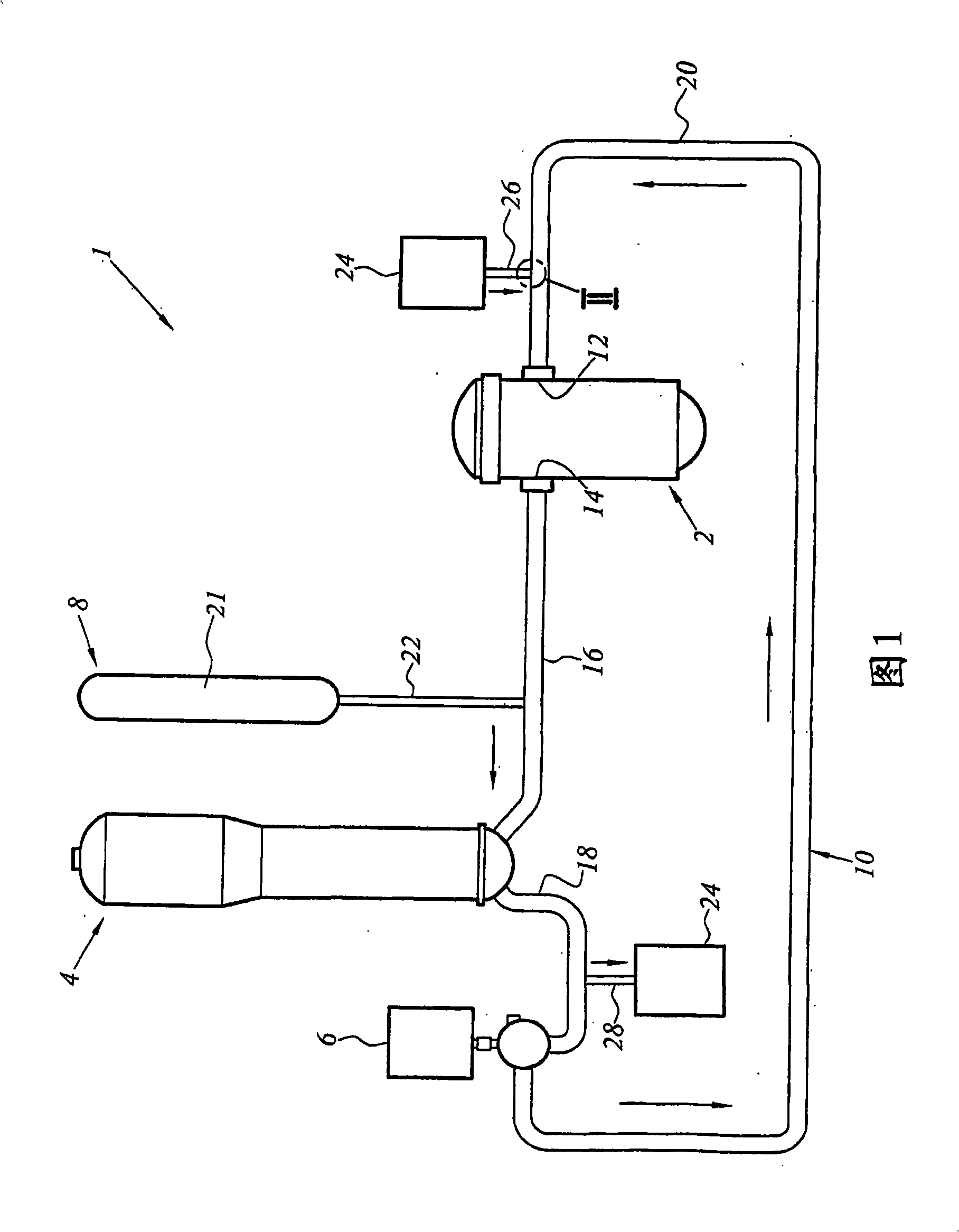
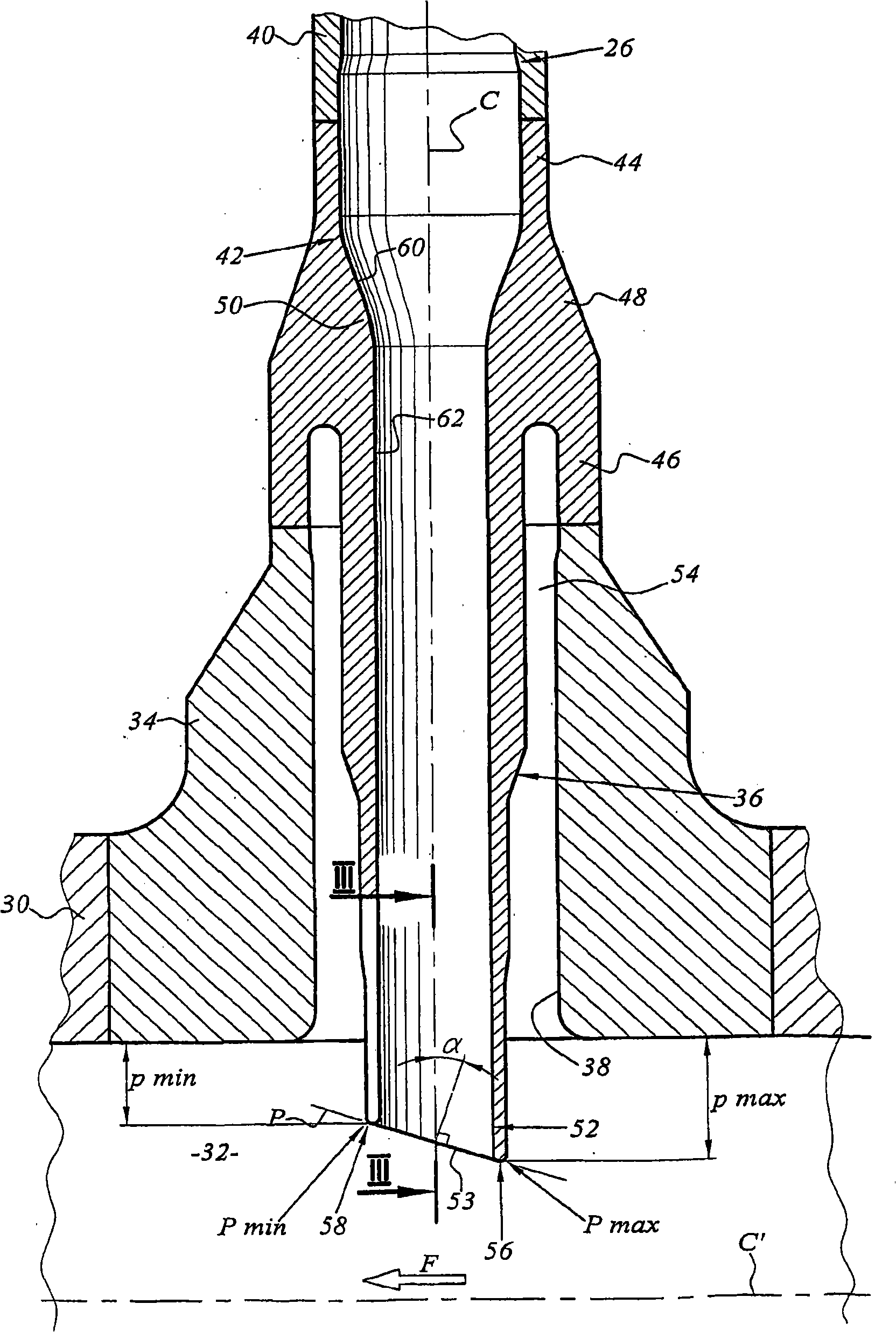
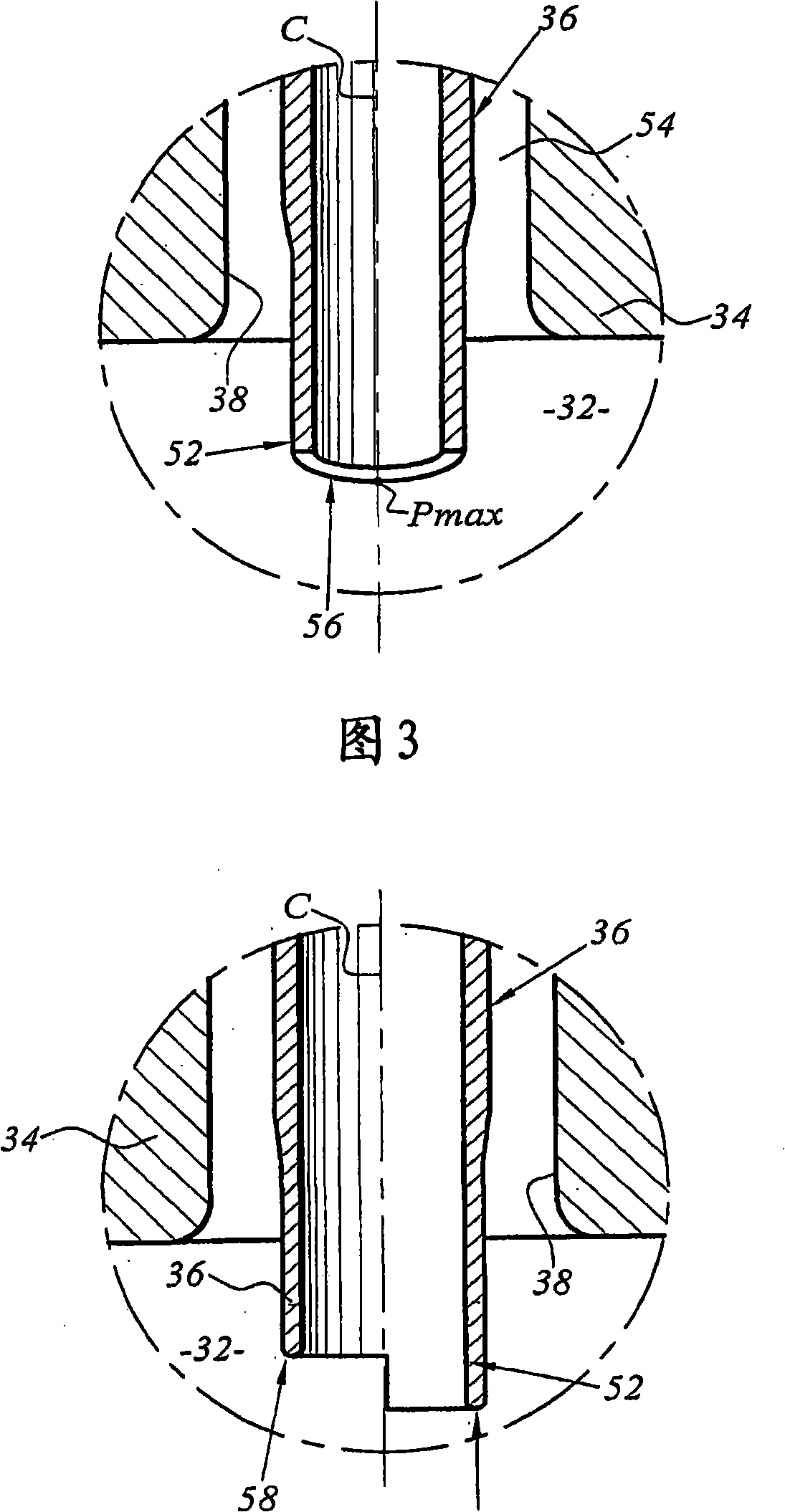
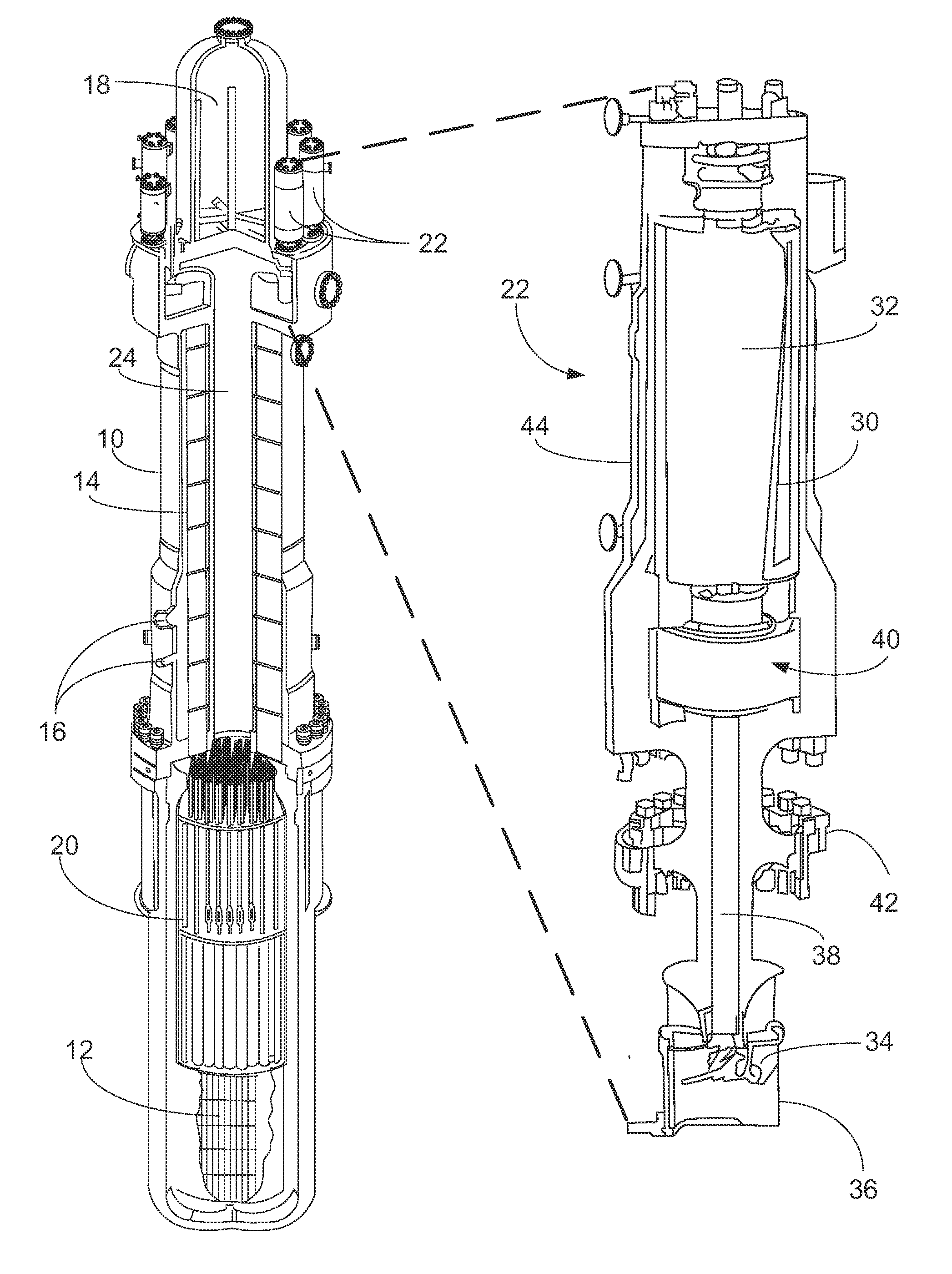
The invention relates to a nuclear reactor primary circuit comprising a primary pipeline (30), which defines an internal volume (32) and in which a primary nuclear reactor coolant downwardly runs, an additional pipeline (26) which is branched to the primary pipeline (30) and defines an internal volume communicating with the internal volume (32) of the primary pipeline (30) and a cuff (36) whose first end (50) is connected to the additional pipeline (26) and the second free end (52) is positioned in the internal volume (32) of the primary pipeline (30). According to said invention, the second end (52) is delimited by a free peripherial edge (53) comprising at least one upstream and downstream sections (56, 58) which are oriented towards the upstream, wherein the upstream section (56) penetrates into the internal volume (32) deeper from the primary pipeline (30) than the downstream section (58).
Owner:FRAMATOME ANP
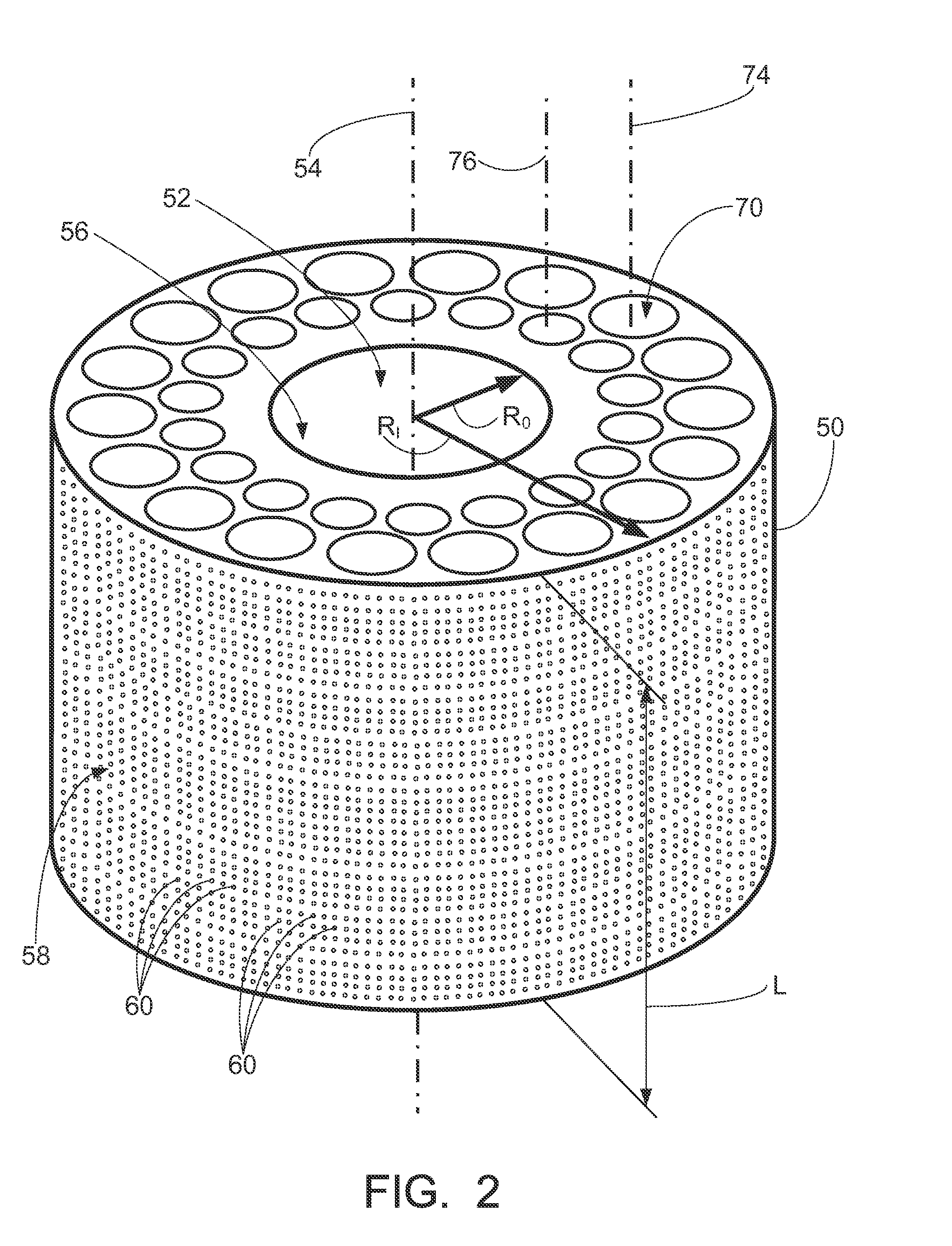
Nuclear reactor coolant pump with high density composite flywheel
A nuclear reactor coolant pump (RCP) comprises a stator and a rotating assembly including a rotor, an impeller, and a flywheel configured to rotate about an axis of rotation in response to the stator being electrically energized. The flywheel comprises a first material (such as stainless steel) and has a plurality of mutually parallel tubular openings filled with a second material that is denser than the first material (such as tungsten or tungsten alloy). In some embodiments the mutually parallel tubular openings are cylindrical openings, and are filled with the second material comprising cylindrical rods. In a nuclear reactor including a reactor pressure vessel and a nuclear reactor core comprising fissile 235U disposed in the reactor pressure vessel, the RCP is suitably disposed on or in the reactor pressure vessel with the impeller of the RCP arranged to engage coolant water disposed in the reactor pressure vessel.
Owner:BWXT MPOWER INC
Apparatus for degassing a nuclear reactor coolant system
InactiveUS20160225470A1Improve efficiencyMinimize the numberNuclear energy generationDispersed particle separationNuclear reactor coreProduct gas
An in-line dissolved gas removal membrane-based apparatus for removing dissolved hydrogen and fission gases from the letdown stream from a reactor coolant system.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
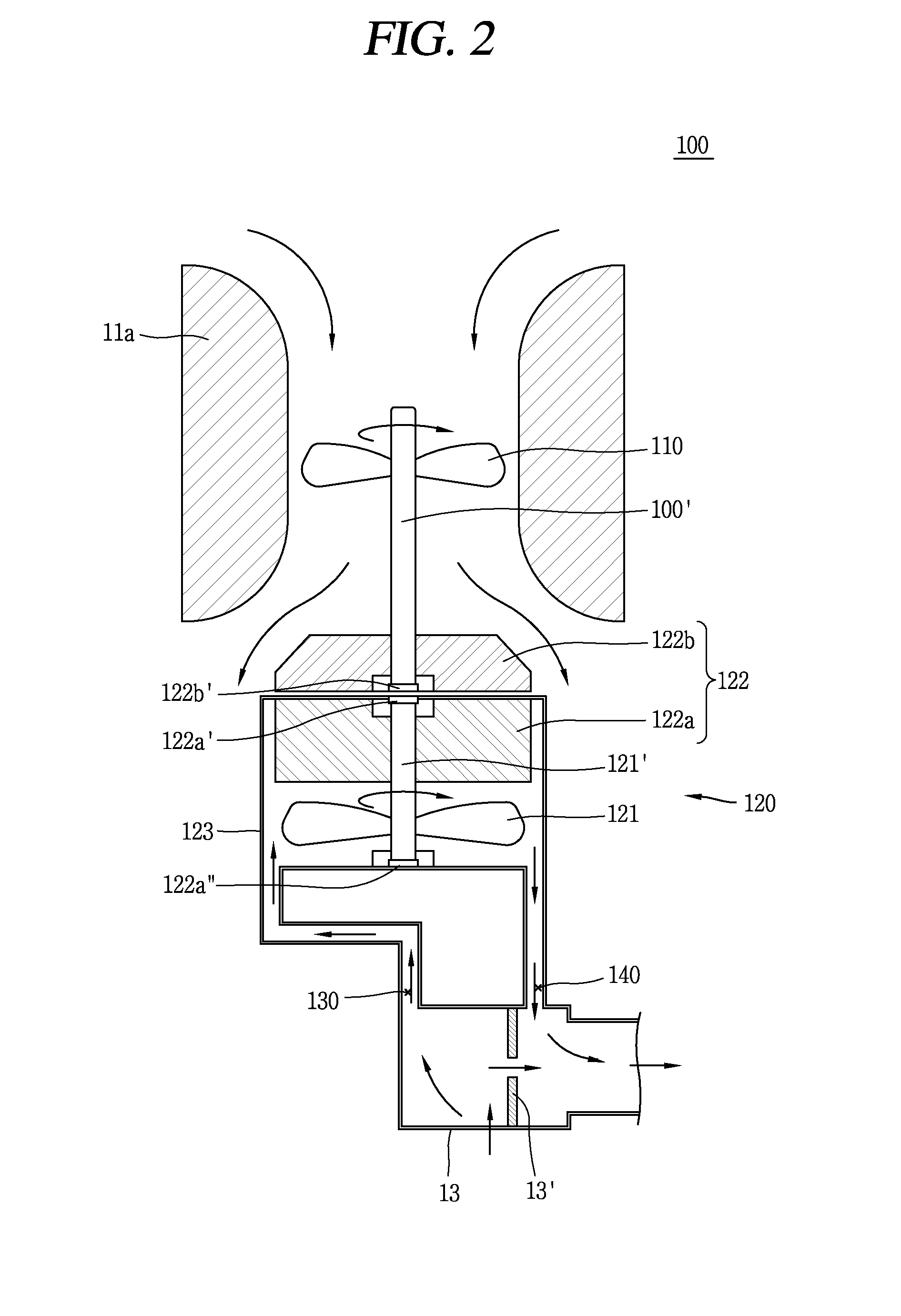
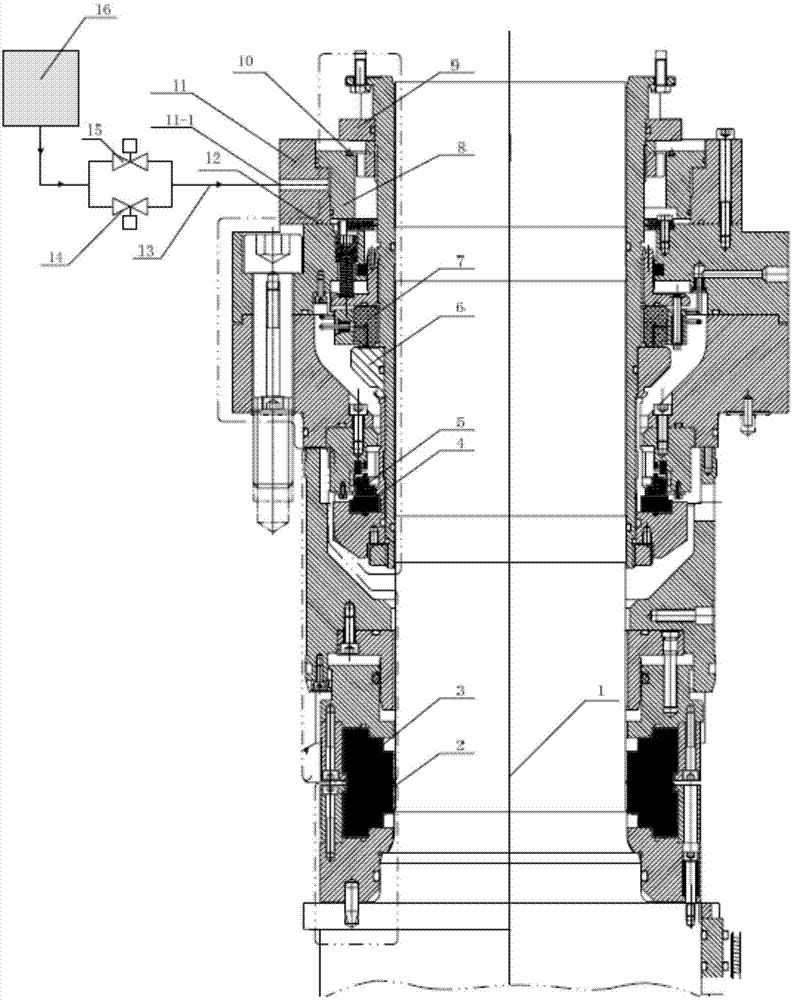
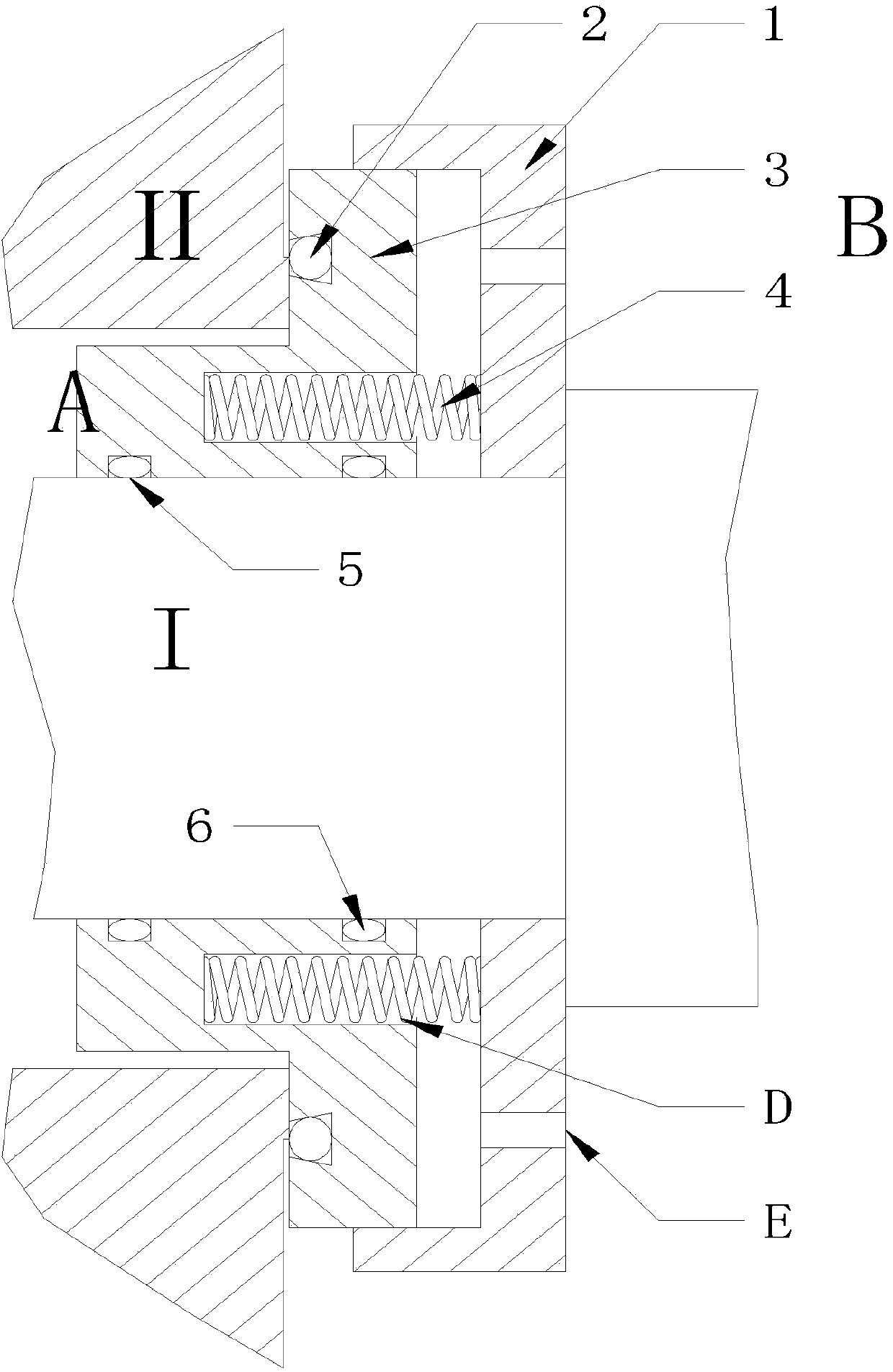
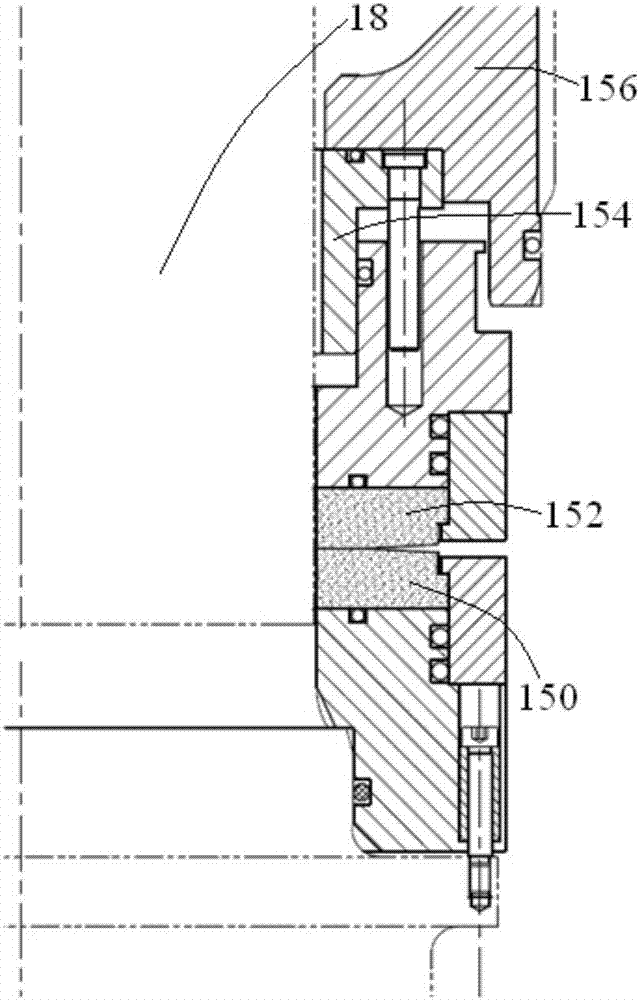
Nuclear reactor coolant pump and passive shutdown sealing device thereof
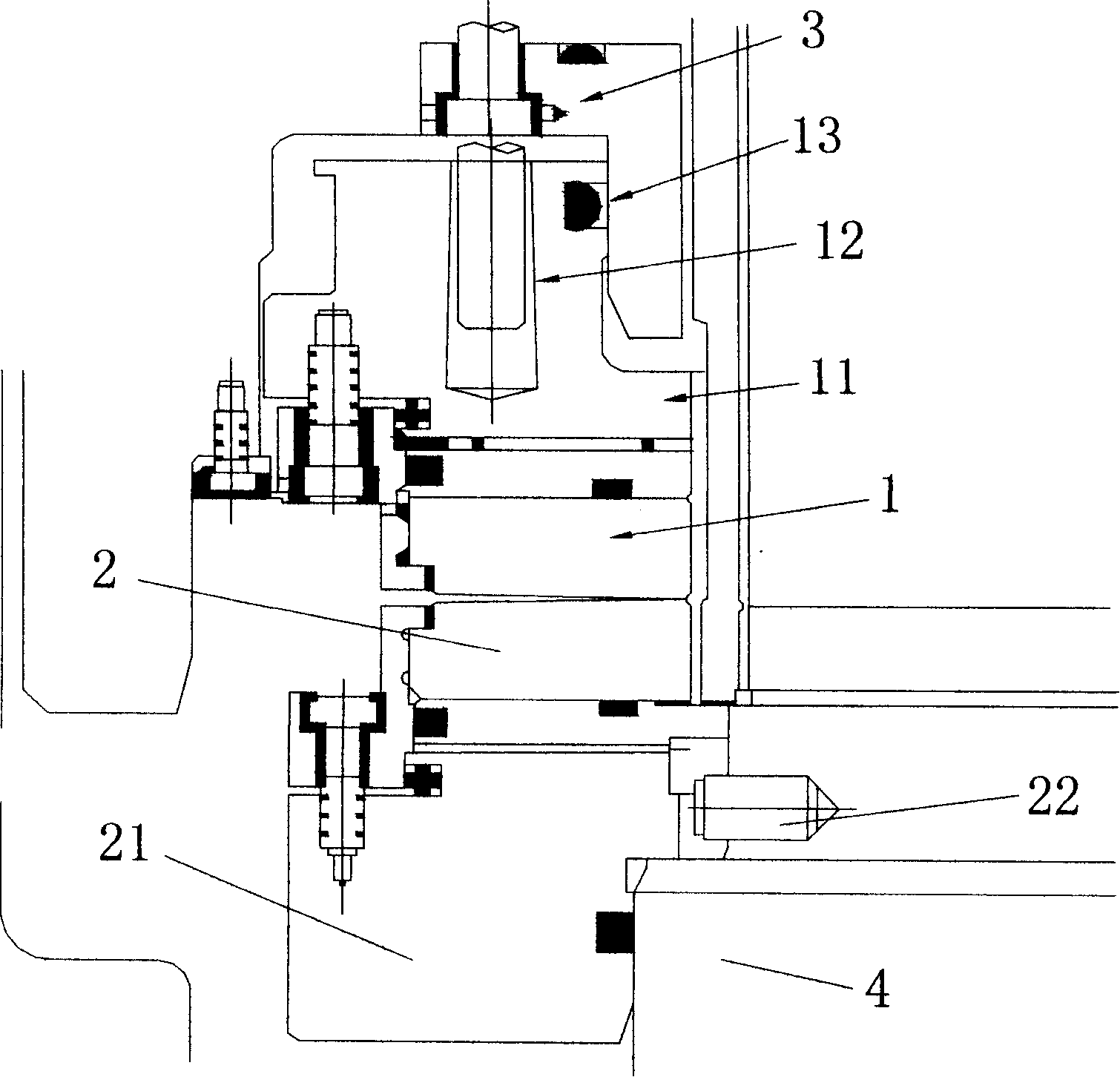
ActiveCN104976150AMeet shaft seal integrity requirementsSimple structurePump componentsPumpsSplit ringNuclear reactor coolant
The invention discloses a nuclear reactor coolant pump and a passive shutdown sealing device thereof. The passive shutdown sealing device comprises a sealing ring, a split ring and a fusible spacer block. The sealing ring is a closed circular ring, the split ring is provided with a longitudinal opening, and the fusible spacer block is a segmental arc having the same cross section as the split ring and is embedded into the longitudinal opening of the split ring so that the fusible spacer block and the opened split ring can form a spliced ring together. Under a normal working condition, the sealing ring and the spliced ring surround a pump shaft of the nuclear reactor coolant pump circumferentially in a spaced mode; under a station blackout working condition, the fusible spacer block is fused and fails, and the split ring is closed to hold the pump shaft tightly under pretightening force. Compared with the prior art, being only provided with the three elements, the passive shutdown sealing device not only can meet the shaft seal completeness requirement under the station blackout working condition without depending on an emergency shaft seal injection system but also has the advantages of being simple in structure and achieving firm double-layer sealing.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
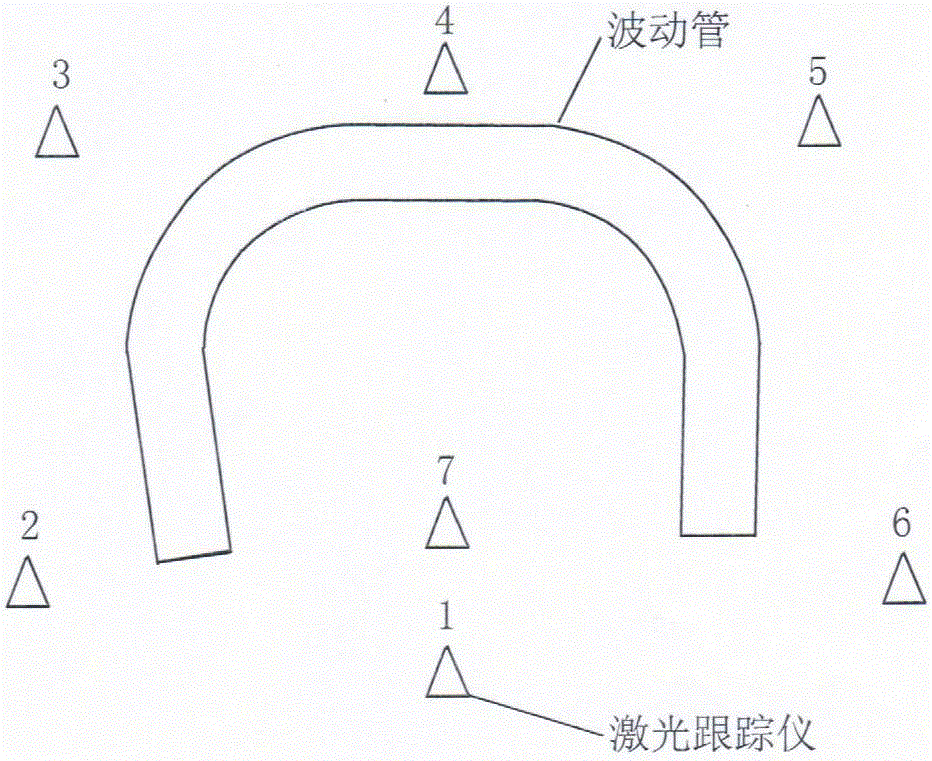
Method for stretching main bolts of coolant pump of nuclear reactor
InactiveCN106271563AReduce labor intensityEasy to implementMetal working apparatusNuclear reactor coreNuclear power
The invention belongs to the technical field of nuclear power projects of nuclear power plants and particularly relates to a method for stretching main bolts of a coolant pump of a nuclear reactor. The method comprises steps as follows: step 1, a plurality of the main bolts are numbered and marked; step 2, a plurality of cantilever type effort-saving manipulators are mounted on upper support frames corresponding to the main bolts in the middle and are fastened; step 3, a plurality of bolt stretching cylinders are mounted on rapid grapplers of the cantilever type effort-saving manipulators respectively; step 4, the plurality of cantilever type effort-saving manipulators are moved above to-be-stretched main bolts respectively and then stretch the main bolts; step 5, after the main bolts are stretched, the cantilever type effort-saving manipulators are moved above other bolts. The method is convenient to implement, the labor intensity of maintenance persons can be effectively reduced, the working efficiency can be improved, and the collective dose value can be reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU NUCLEAR POWER CORP
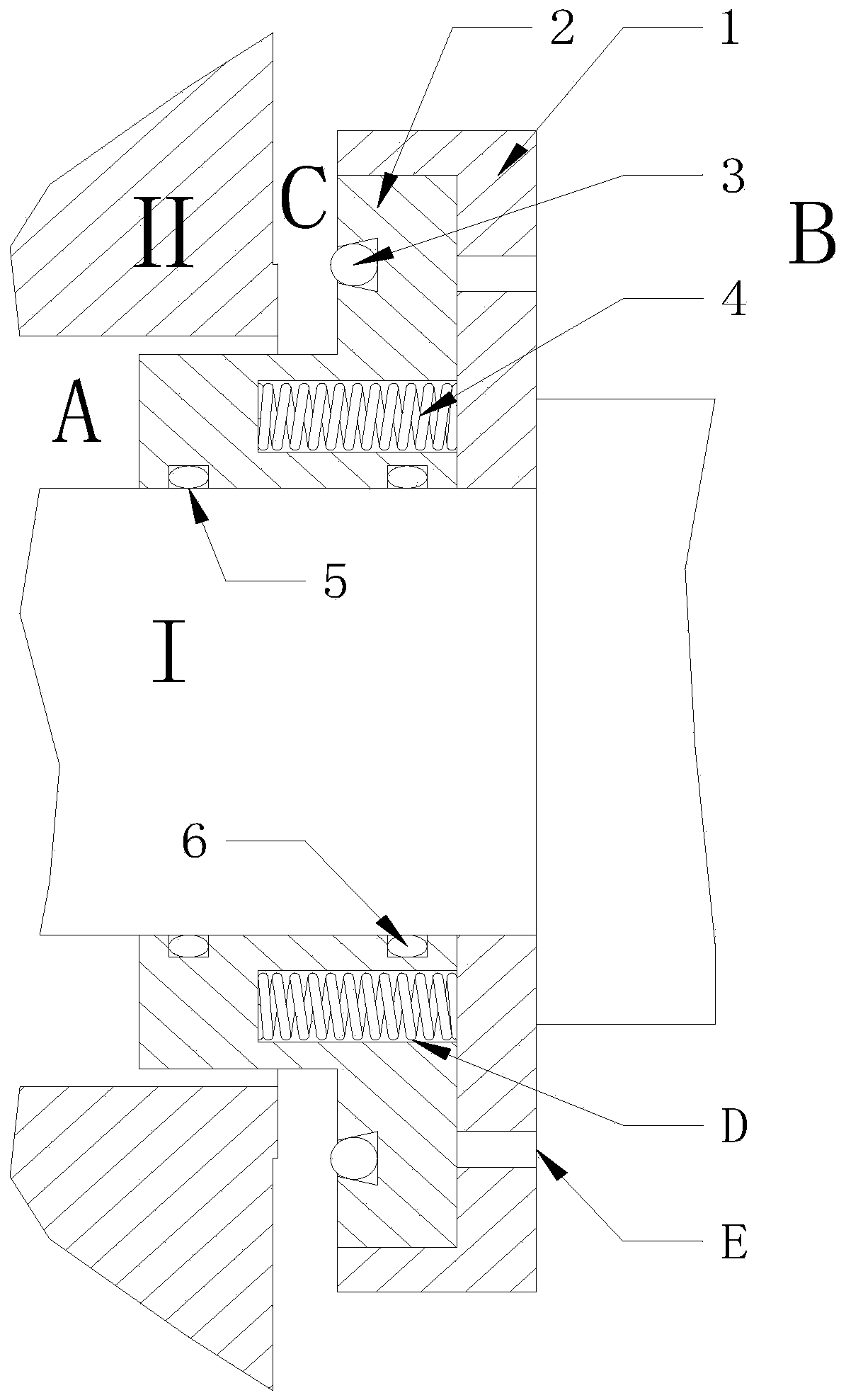
Thermomagnetic sliding bush stop sealing device for nuclear reactor coolant pump
A thermomagnetic sliding bush stop sealing device for a nuclear reactor coolant pump comprises a sliding bush base and a sliding bush. The sliding bush base and a shaft are in interference fit, the sliding bush and the shaft are in clearance fit, the sliding bush is sleeved in the sliding bush base, a first seal ring, a second seal ring and a third seal ring are arranged on the sliding bush which is made of metal materials, and the sliding bush base is made of magnetic materials. The sliding bush is internally provided with two symmetric spring cavities, springs are arranged in the spring cavities, and the sliding bush base is provided with a hole. The sliding bush base and the sliding bush are attracted to compress the springs while the hole is sealed by the sliding bush. When a primary seal of the nuclear reactor coolant pump fails, high-temperature process fluid makes the sliding bush base lose magnetism, magnetic force between the sliding bush and the sliding bush base disappears, the sliding bush moves to the primary seal until being tightly pressed on the wall of a pump cavity under the action of spring force and pressure of the high-temperature fluid in the pump cavity, and the high-temperature process fluid in the pump cavity is prevented from leaking outwards. The thermomagnetic sliding bush stop sealing device is passive and free of external gas supply.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Nuclear reactor coolant pump shaft sleeve installation technology
ActiveCN111637085ASolve technical problems that cannot be accurately positionedTo achieve the expected effect of the installationPump componentsPumpsCircular discRadiochemistry
The invention relates to a nuclear reactor coolant pump shaft sleeve installation technology. A mounting disc capable of being leveled, a long screw rod and a connecting nut are adopted to perform overall levelling and lifting on a shaft sleeve, guide tools are adopted in the bearing falling process for guiding, the position precision in the shaft sleeve falling process is ensured, and the shaft sleeve and a lower pump shaft are prevented from being scratched; and after the shaft sleeve falls by a certain depth, the screw rod and the nut do work on a pressing disc, it is ensured that the shaftsleeve is smoothly assembled to the shaft shoulder position of the lower pump shaft after falling, and the shaft sleeve is smoothly installed and positioned. According to the process, the problems that in the installation process of the nuclear reactor coolant pump shaft sleeve, shaking occurs, two workpieces cannot be ensured to be concentric, the sight is shielded, accurate positioning operation cannot be realized, and scratches and grooves are generated in the assembly process are solved, and the technology can also be applied to the field of installation technologies of other long-cylinder thin-walled parts.
Owner:HARBIN ELECTRIC POWER EQUIP
System for automatically cleaning and inspecting stud bolt holes, and managing histories of the stud bolt holes
ActiveUS20070251045A1Improve securityImprove performanceNuclear energy generationSuction cleanersPump headPressure vessel
A system for cleaning and inspecting stud bolt holes, and managing damage histories of the stud bolt holes is disclosed. The system allows an operator to clean stud bolt holes to inspect the stud bolt holes with the naked eye, and manage damage histories of the stud bolt holes. The stud bolt holes fix a nuclear reactor, a nuclear reactor coolant pump head and a pressure vessel main body thereto.
Owner:KOREA PLANT SERVICE & ENG CO LTD
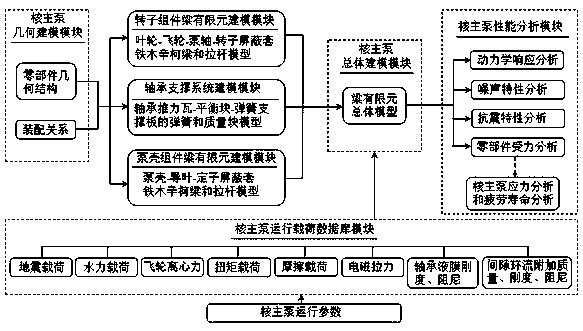
Nuclear reactor coolant circuit fluctuation tube measuring method
InactiveCN105180803ASolve the problem that the installation cannot be effectively connectedUsing optical meansStraight tubeNuclear engineering
The present invention provides a nuclear reactor coolant circuit fluctuation tube measuring method. Firstly, a straight tube section and a circular section are measured and then the data processing is carried out. According to the method, the AP1000 nuclear reactor coolant circuit fluctuation tube 3D space actual state can be reproduced in SA software, and the problem that the data generated by a conventional measurement data and the installation of a post fluctuation tube can not be effectively connected is solved. The method is suitable for the method application of nuclear reactor coolant circuit fluctuation tube measurement.
Owner:BOHAI SHIP HEAVY IND CO LTD
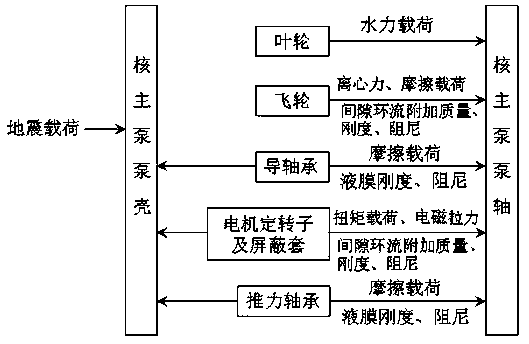
Method for constructing shielded nuclear main pump digital prototype based on beam finite element model
ActiveCN110598316AMeet performance simulation needsAccurate assessment of kinetic responseSpecial data processing applicationsSupporting systemInformation support
The invention discloses a method for constructing a shielded nuclear main pump digital prototype based on a beam finite element model, and belongs to nuclear reactor coolant pump design and manufacturing. The method comprises the following construction steps: 1, generating a nuclear main pump geometric modeling module according to a nuclear main pump part geometry and assembly relationship; 2, onthe basis of the nuclear main pump geometric model, generating a rotor assembly beam finite element modeling module, a bearing support system modeling module and a pump shell assembly beam finite element modeling module; 3, integrating a rotor assembly model, a bearing support system model and a pump shell assembly model, establishing a beam finite element overall model, generating a nuclear mainpump overall modeling module, and constructing a nuclear main pump three-dimensional digital prototype by taking an operation load database module under nuclear main pump operation parameters as information support; and 4, the nuclear main pump performance analysis module receiving the three-dimensional digital prototype, calling beam finite element overall model calculation data as input, and outputting simulation results of nuclear main pump dynamic response and noise analysis, anti-seismic analysis and part stress analysis. The method has the advantage of accurate analysis of nuclear main pump dynamic characteristics.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
System for automatically cleaning and inspecting stud bolt holes, and managing histories of the stud bolt holes
ActiveUS7574770B2Improve securityImprove performanceNuclear energy generationSuction cleanersPump headPressure vessel
A system for cleaning and inspecting stud bolt holes, and managing damage histories of the stud bolt holes is disclosed. The system allows an operator to clean stud bolt holes to inspect the stud bolt holes with the naked eye, and manage damage histories of the stud bolt holes. The stud bolt holes fix a nuclear reactor, a nuclear reactor coolant pump head and a pressure vessel main body thereto.
Owner:KOREA PLANT SERVICE & ENG CO LTD
Apparatus for Degassing a Nuclear Reactor Coolant System
ActiveUS20170229201A1Improve efficiencyMinimize the numberNuclear energy generationDispersed particle separationDissolved hydrogenChemistry
An in-line dissolved gas removal membrane-based apparatus for removing dissolved hydrogen and fission gases from the letdown stream from a reactor coolant system.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Coolant recirculation equipment for nuclear reactor
InactiveUS20060050834A1Improve workabilityReduce in quantityNuclear energy generationNuclear engineering problemsReactor pressure vesselSupply current
A nuclear reactor coolant recirculation equipment includes a plurality of internal pumps which are installed around a bottom portion of a reactor pressure vessel of a boiling-light-water reactor, power-supply sections for supplying current to the internal pumps, an internal pump cooling system, for cooling the internal pumps, including cooling water pipes and heat exchangers connected to the cooling water pipes, and auxiliary cooling water pumps for supplying the cooling water to the heat exchangers, respectively. The positions are set as internal pump installation positions at substantially same interval in a circumferential direction around a central portion of the bottom portion of the reactor pressure vessel, and nine or less and four or more numbers of the internal pumps are installed at the ten internal pump installation positions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Real-time reactor coolant system boron concentration monitor utilizing an ultrasonic spectroscpopy system
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatuses and methods for damping nuclear reactor components
Example embodiment damping devices may include a housing capturing a piston. The housing may be filled and / or able to be filled with a damping fluid compatible with the nuclear reactor coolant, so that a leak from the housing or coolant passing into the housing does not damage the reactor or example embodiment devices. Example embodiments may further include one or more springs that provide an elastic force opposing movement between the piston and housing. A shaft of the piston and an end of the housing may be connected to two nuclear reactor components with relative motion or vibration to be damped. Example methods may use example embodiment damping devices to reduce and / or prevent relative motion and vibration among components of a nuclear reactor.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
Nuclear reactor coolant pump and passive power-off sealing device thereof
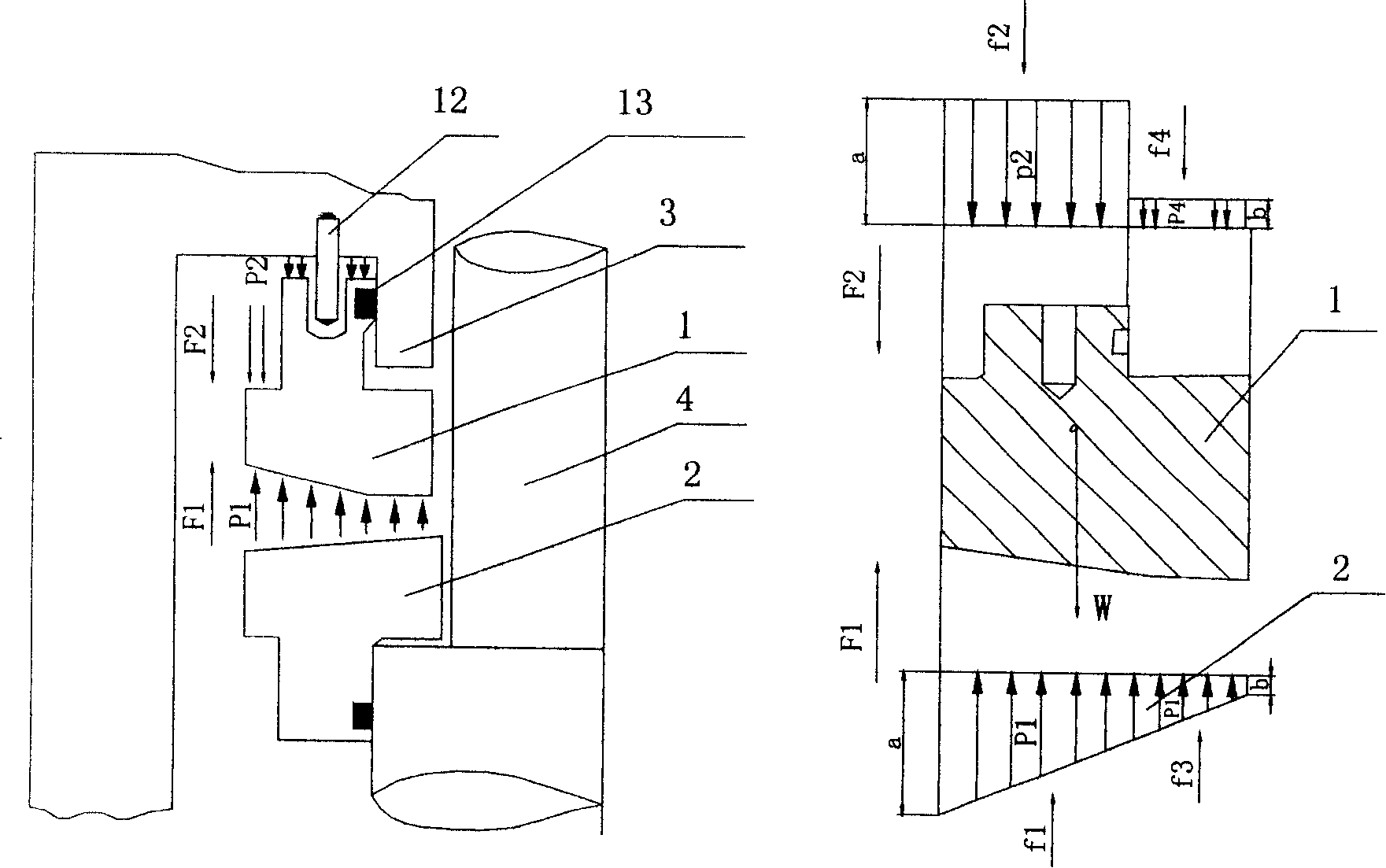
ActiveCN107100882ASimple structureImprove sealingPump componentsPump installationsElectrical and Electronics engineeringNuclear reactor coolant
The invention discloses a passive power-off sealing device of a nuclear reactor coolant pump. The passive power-off sealing device comprises a complete sealing ring and a complete limiting ring, wherein the complete sealing ring can be at a starting position and a non-starting position, and the complete limiting ring can be softened when the state conversion temperature is reached; when the temperature of the limiting ring is below the state conversion temperature, the sealing ring surrounds a pump shaft of the nuclear reactor coolant pump in the circumferential direction and keeps a clearance from the pump shaft under the supporting action of the limiting ring; and when the temperature of the limiting ring is equal to the state conversion temperature or above the state conversion temperature, the limiting ring is softened or melted, the sealing ring loses the support of the limiting ring and holds the pump shaft tightly, and therefore a reactor coolant can be prevented from flowing along the pump shaft. Compared with the prior art, the passive power-off sealing device of the nuclear reactor coolant pump has the advantages that only the two elements, namely, the sealing ring with the sealing function and the limiting ring with the limiting function are arranged, the sealing ring does not depend on the external force from the non-starting position to the starting position, in the whole sealing process, the structure is simple, and sealing is reliable.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Passive heat removal system for nuclear power plant
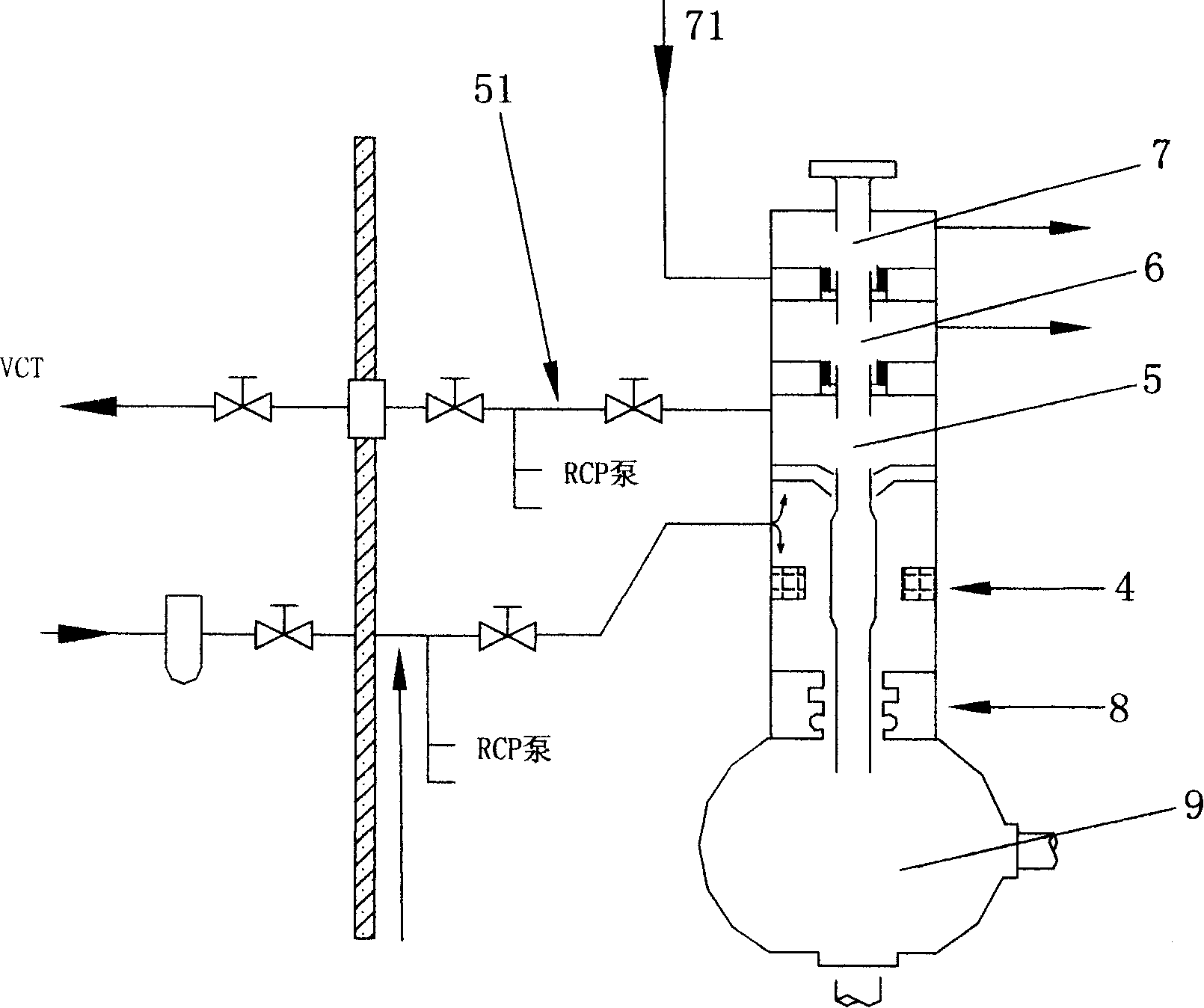
ActiveUS10325688B2Avoid dysfunctionAlleviate performance degradation and prediction uncertaintyIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationNuclear powerCooling fluid
The present invention relates to a passive heat removal system which circulates cooling fluid to a steam generator via a main water supply line connected to the lower inlet of the steam generator, and a main steam pipe connected to the top outlet of the steam generator, to remove sensible heat of a nuclear reactor coolant system and residual heat of a core. The heat removal system comprises supplementary equipment for receiving surplus cooling fluid or for supplying supplementary cooling fluid in order to maintain the flow rate of the cooling fluid within a predetermined range. The supplementary equipment comprises: a supplementary tank, installed at a height between the lower inlet and the top outlet of the steam generator; a first connection pipe, connected to the main steam pipe and the supplementary tank; and a second connection pipe, connected to the supplementary tank and the main water supply pipe.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
System and method for detecting leakage of nuclear reactor coolant using laser induced emission spectrum
InactiveUS20110164715A1Reduce impurityEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryNuclear reactor coreSpectroscopy
System and method for detecting and / or predicting in a field the leakage of nuclear reactor coolant that may occur at the pressure boundary of the primary system of a nuclear reactor. The system and method for detecting the leakage of nuclear reactor coolant uses a laser induced emission spectrum. The leakage of coolant is detected by detecting boron (B), a main component of the coolant, in corrosive products generated at the nuclear reactor pressure boundary on the basis of laser spectroscopy. An embodiment of the system for detecting leakage of nuclear reactor coolant may include a laser generator, a laser focusing lens, an emission collector, and emission spectrum analyzer.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Device and method for removing particles in nuclear reactor coolant
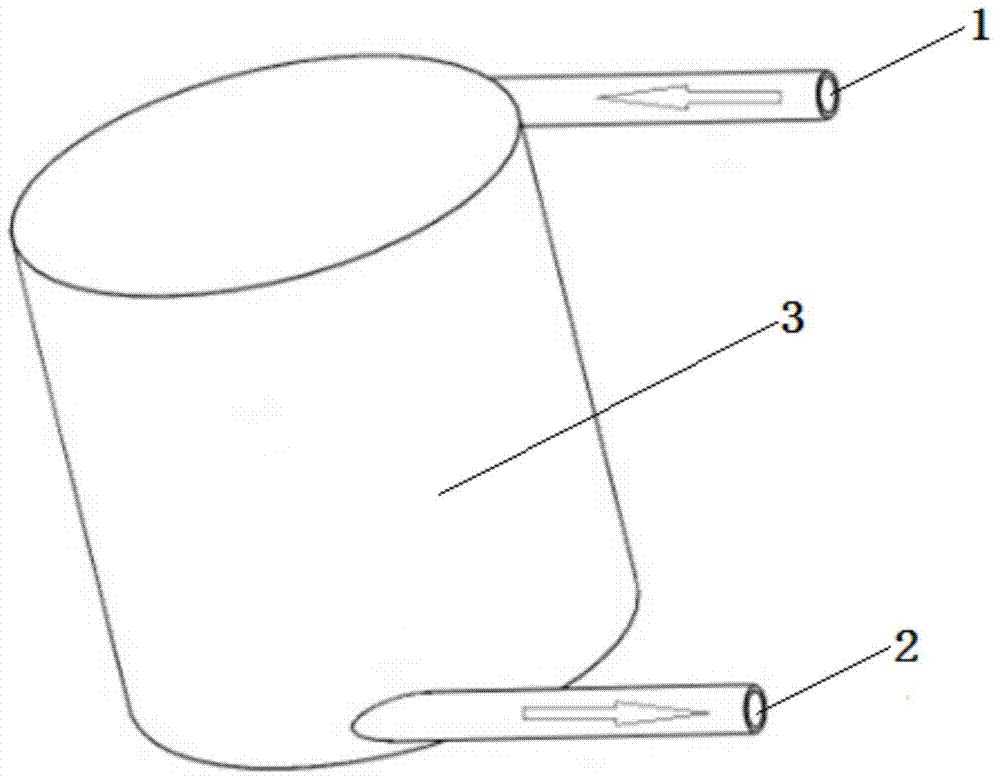
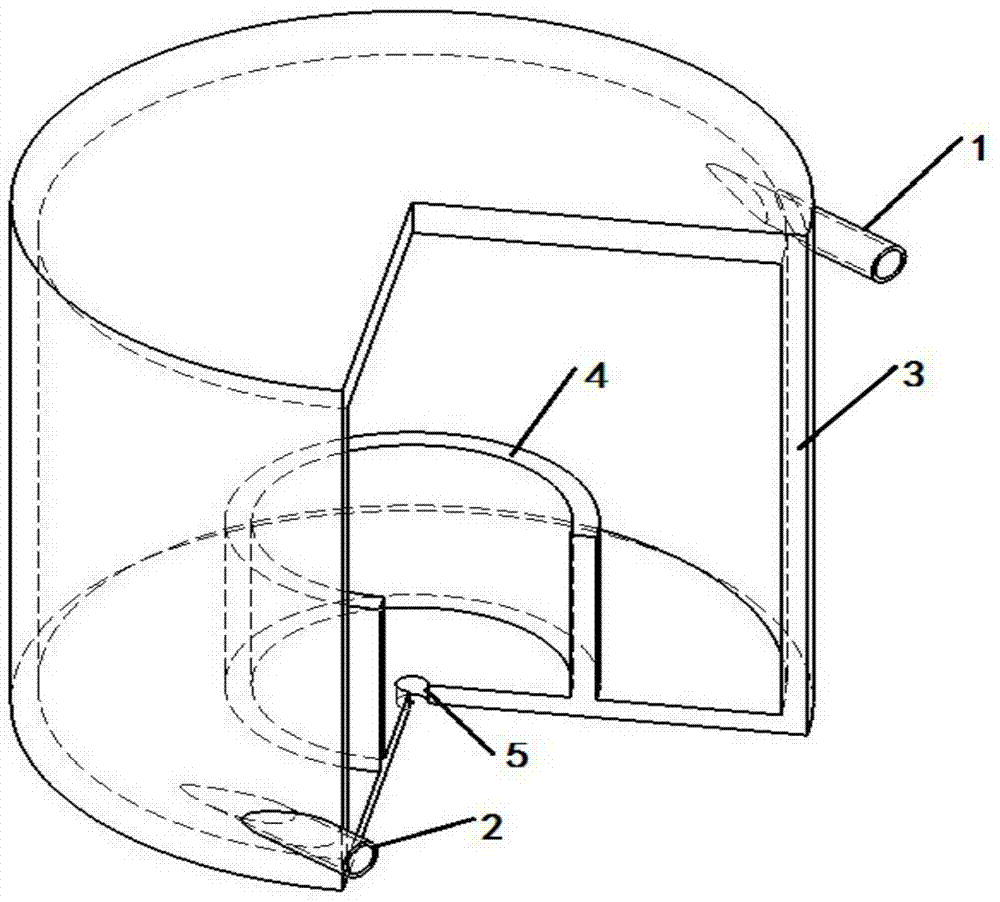
InactiveCN104766644ASimple structureLow costRadioactive decontaminationParticulatesNuclear reactor core
The invention discloses a device for removing particles in a nuclear reactor coolant. The device comprises an outer barrel body, an inner barrel body, a liquid inlet pipeline, a liquid outlet pipeline, and a central hole formed in the bottom part of the inner barrel body, wherein the liquid inlet pipeline and the liquid outlet pipeline are arranged on the outer barrel body; the feeding speed and direction of liquid are basically consistent with the tangential line direction of the wall surface of the outer barrel body through the liquid inlet pipeline; liquid generates secondary flow while spirally moves; fine particles in the liquid can be continuously collected to the middle part of the outer barrel body under the effect of the secondary flow and can be deposited in the inner barrel body under the effects of turbulent flow and gravity; a discharging pipeline is arranged at the bottom part of the inner barrel body; when the fine particles are deposited to reach a certain of volume, a valve is opened to remove the deposited fine particles through the pipeline. The device has the characteristics of being safe, efficient, and safe in design and to control.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com