Method for observing in-situ morphologies of nonmetallic inclusions in steel
A technology for observing non-metallic inclusions and steel is applied in the field of observing the in-situ morphology of non-metallic inclusions in steel, which can solve the problems of fast analysis speed, few standard samples and large sampling volume, and achieves fast analysis speed and sample preparation. Simple, complete appearance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
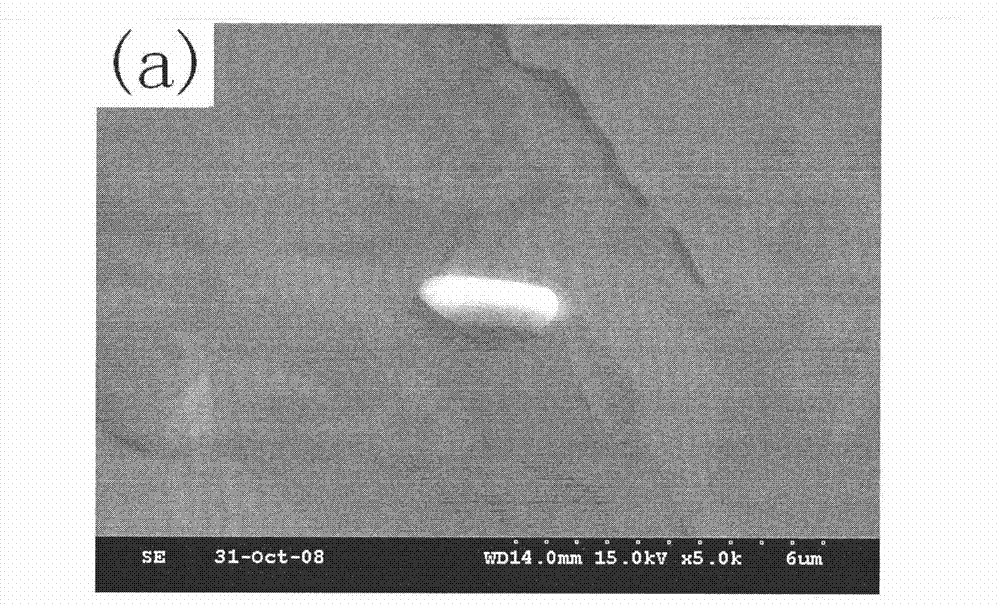
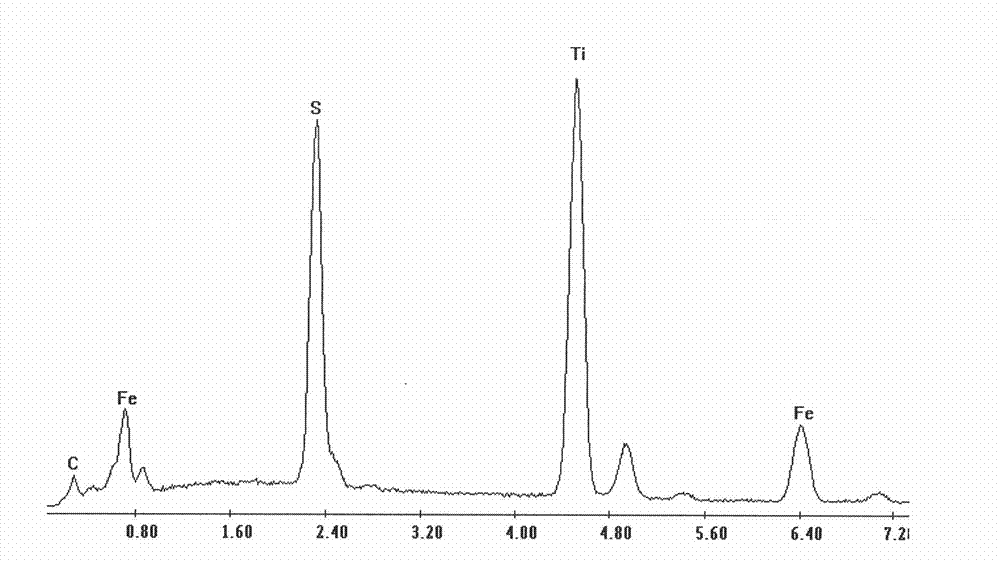
[0017] Adopt the technical scheme of the present invention, the 00Ni14Cr3Mo3Ti maraging steel 00Ni14Cr3Mo3Ti maraging steel smelted in the small furnace is sampled and analyzed, the steel sample is taken and processed into a size of 10mm * 10mm * 10mm, and the surface to be observed of the sample is used 240#, 400#, 600#, 800#, 1000# sandpapers are polished separately and then polished into a mirror surface. Electrolytic polishing is carried out using a Struers LectroPol-5 electrolytic polishing instrument. The electrolyte is 5% (v / v) HCl+5% (v / v) glycerin+1 % (v / v) citric acid methanol solution, current density = 0.05A / cm 2 , Electrolysis temperature: -10℃~-8℃, electrolysis time: 30s, after electropolishing, gently wipe off the corrosion products on the electropolishing surface with a rubber stick, dry the surface of the sample with a hair dryer, non-metallic inclusions will be highlighted come out.
[0018] The three-dimensional morphology of non-metallic inclusions was obs...
Embodiment 2
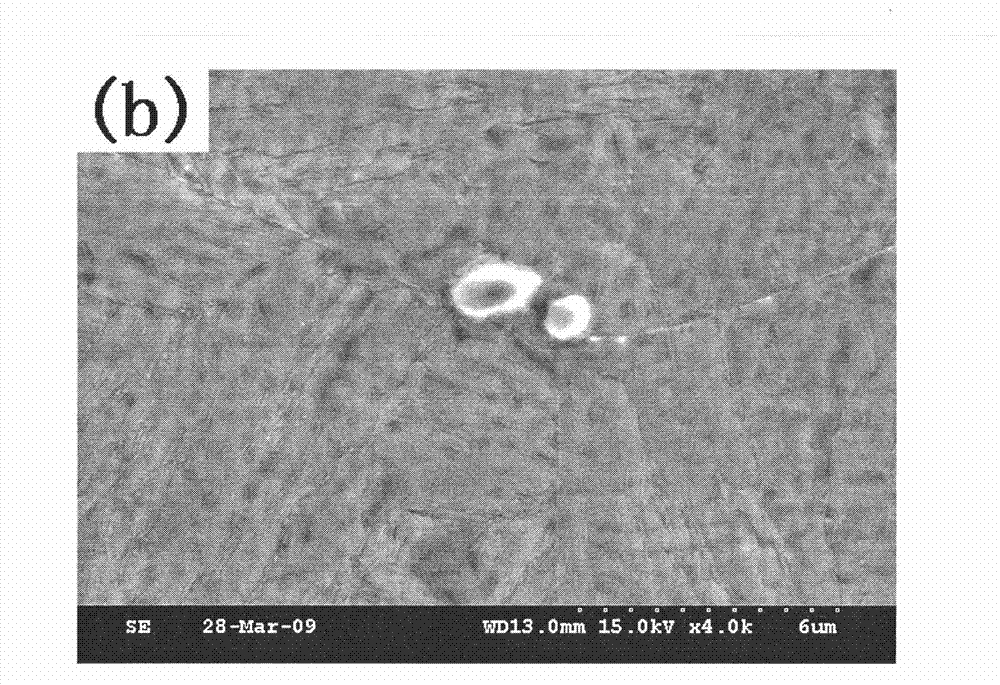
[0020] Adopt the technical scheme of the present invention, the 00Ni13Cr9MoTi maraging steel 00Ni13Cr9MoTi maraging steel smelted in the small furnace is sampled and analyzed, the steel sample is taken and processed into a size of 10mm * 10mm * 10mm, and the surface to be observed of the sample is used 240#, 400#, 600#, 800#, 1000# sandpapers are polished separately and then polished into a mirror surface. Electrolytic polishing is carried out using a Struers LectroPo1-5 electrolytic polishing instrument. The electrolyte is 5% (v / v) HCl+5% (v / v) glycerin+1 % (v / v) methanol solution of citric acid, current density = 0.10A / cm 2 , Electrolysis temperature: -8℃~-5℃, electrolysis time: 20s, after electropolishing, gently wipe off the corrosion products on the electropolishing surface with a rubber stick, dry the surface of the sample with a hair dryer, non-metallic inclusions will be highlighted come out.
[0021] The three-dimensional morphology of non-metallic inclusions was obs...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com