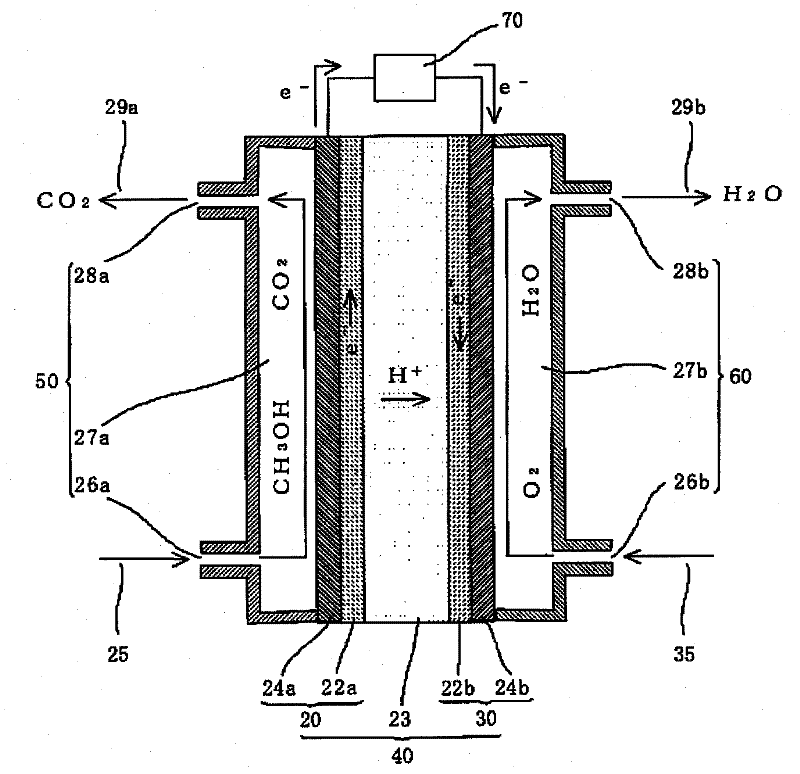
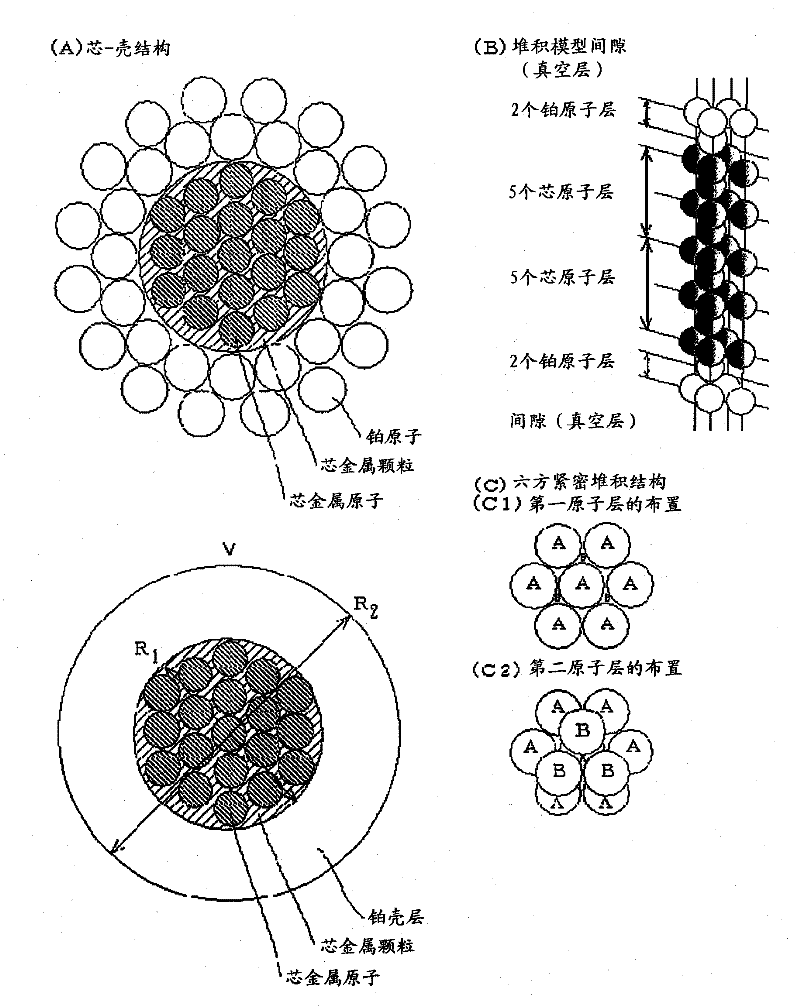
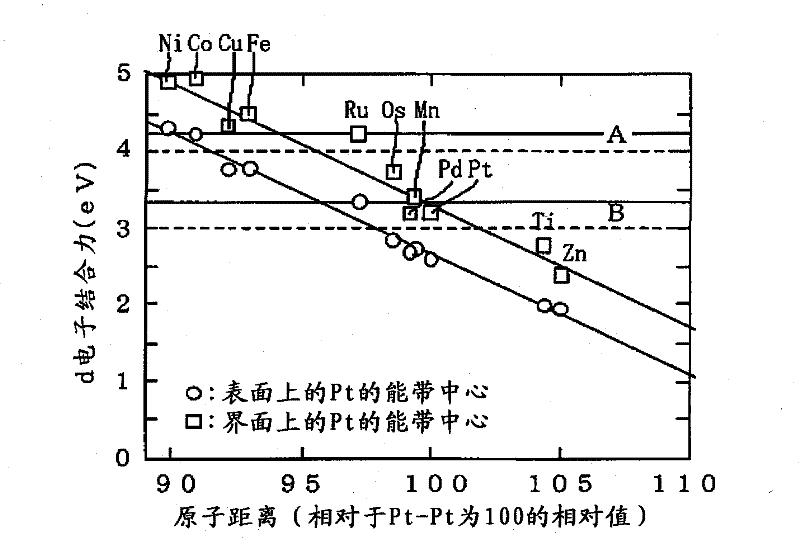
Platinum-containing catalyst, process for producing the platinum-containing catalyst, electrode, and electrochemical device
A platinum catalyst and electrochemical technology, which is applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of reduced catalytic activity and achieve large output density, high toxicity, and high durability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0367]
[0368] Platinum-containing catalyst core particles were prepared in the following manner. Ruthenium(III) chloride hydrate (RuCl 3 ·nH 2 O) was dissolved in ethylene glycol to prepare 190 mL of a solution in which ruthenium (III) ions were dissolved at a concentration of 0.1 mol / L. Then, 10 mL of 0.5-mol / L sodium hydroxide (NaOH) aqueous solution was added to the solution, and while the solution was sufficiently stirred, the temperature of the solution was raised to 170° C. for 1 minute using a microwave heating device, and then the The temperature of the solution was maintained at 170° C. for 1 hour; thus, ruthenium(III) ions were reduced by ethylene glycol, and a dispersion liquid containing dark brown ruthenium nanoparticles was prepared.
[0369]
[0370] 2.88 g of carbon black was added as a carrier to the above dispersion liquid, the dispersion liquid was sufficiently stirred to disperse the carbon black, 100 mL of 0.5-mol / L sulfuric acid was added to the d...
Embodiment 2
[0399] A platinum layer is formed so that the surface of the ruthenium nanoparticles is covered with the platinum layer, and the molar ratio of platinum and ruthenium reaches a set molar ratio (feeding molar ratio) of 4:1 in the platinum-containing catalyst to be prepared. Other than that, as in Working Example 1, a platinum-containing catalyst was synthesized, refined, and dried, and performance evaluation of the platinum-containing catalyst was performed. The platinum-containing catalyst particles supported by carbon black were observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). From the TEM observation image, the average particle diameter of the platinum-containing catalyst particles was 2.5 nm (standard deviation: ±0.5 nm). Therefore, the average thickness of the platinum layer is 0.55 nm (=2.5-1.4 / 2), corresponding to 2.4 (=0.55 / 0.2265) platinum atomic layers.
Embodiment 3
[0401] A platinum layer was formed so that the surface of the ruthenium nanoparticles was covered with the platinum layer, and the molar ratio of platinum and ruthenium reached a set molar ratio (feeding molar ratio) of 7:1 in the platinum-containing catalyst to be prepared. Other than that, as in Working Example 1, a platinum-containing catalyst was synthesized, refined, and dried, and performance evaluation of the platinum-containing catalyst was performed. The platinum-containing catalyst particles supported by carbon black were observed by transmission electron microscopy. From the TEM observation image, the average particle diameter of the platinum-containing catalyst particles was 2.9 nm (standard deviation: ±0.5 nm). Therefore, the average thickness of the platinum layer is 0.75 nm (=(2.9-1.4) / 2), which corresponds to 3.3 (=0.75 / 0.2265) platinum atomic layers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com