Optical method for additive manufacturing of complex metallic shapes using a gaseous medium
a technology of additive manufacturing and gaseous medium, which is applied in the direction of liquid/solution decomposition chemical coating, solid-state diffusion coating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of significant waste of material, and achieve the effects of high density, high strength and high quality nickel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
I. A General Explanation of the Invention and How to Practice It
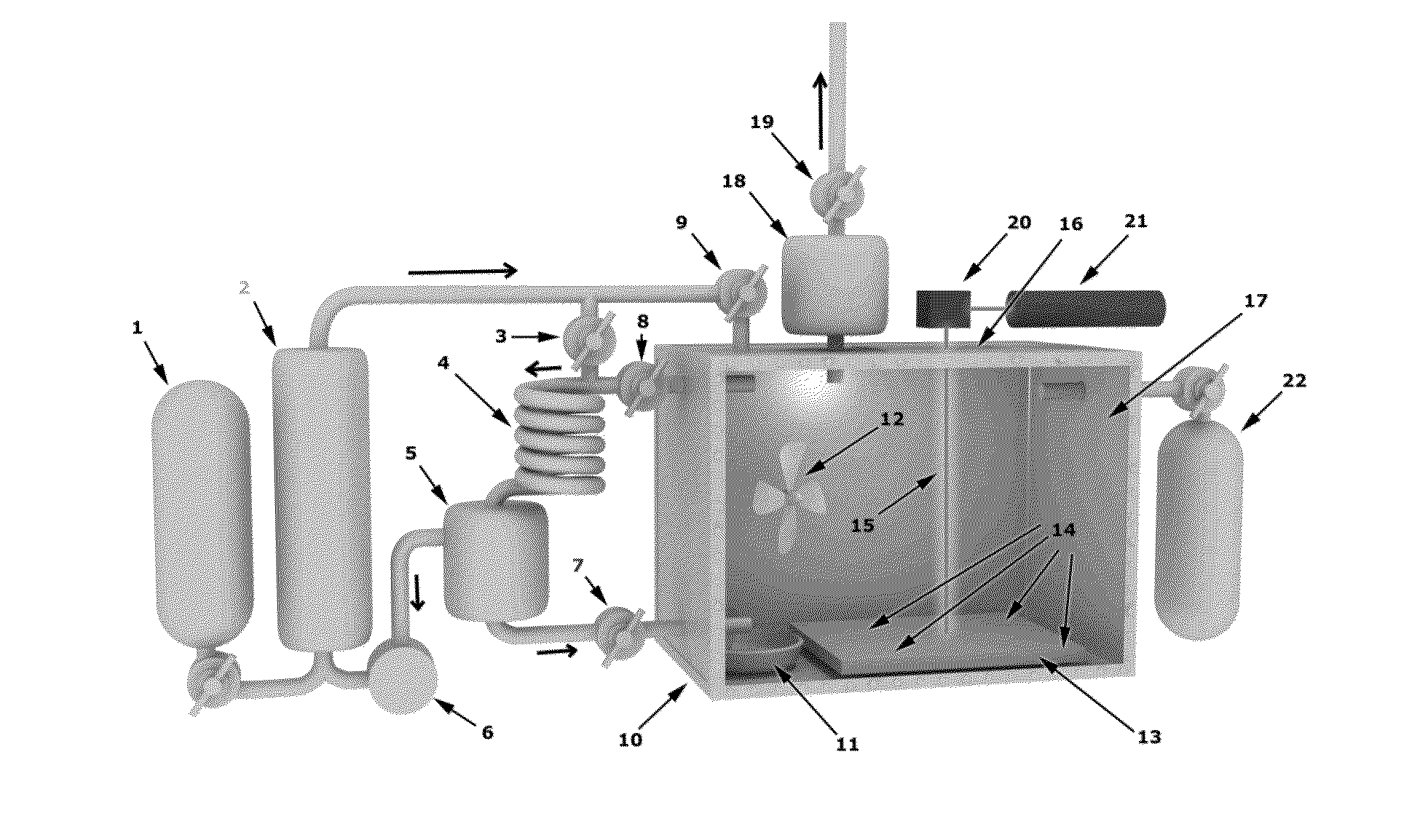
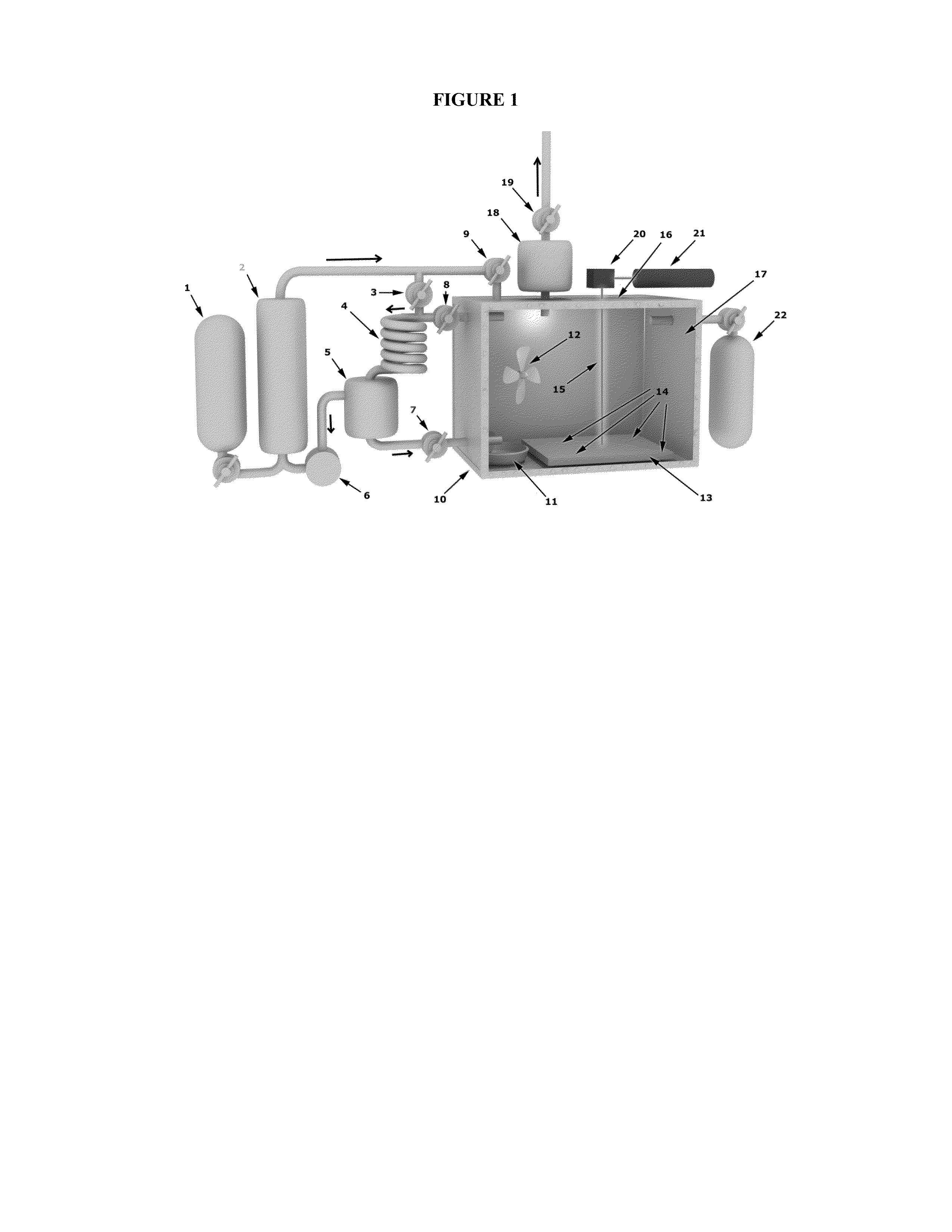
[0028]The present invention is a new method for an additive manufacturing process of complex metallic shapes utilizing advanced computer assisted design. The process of the present invention deposits metal from a vapor in a precise 3d shape. Using a metal source feedstock, a unique laser (or other optical patterning method) to metal carbonyl (or other gas) vapor process allows for a new method of 3d printing. The metal deposition on a cold substrate is mediated directed by laser raster (or other optical) heating (or energy deposit) to build a free form object using a CAD design process to measure and observe the process.
[0029]The present invention seeks to create a unique additive manufacturing capability utilizing common metallic feedstock which is then sublimated by conversion to carbonyl gas and then subsequently deposited by using modifications of known 3d printing processes. By utilizing metal carbonyl vapor (or ot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com