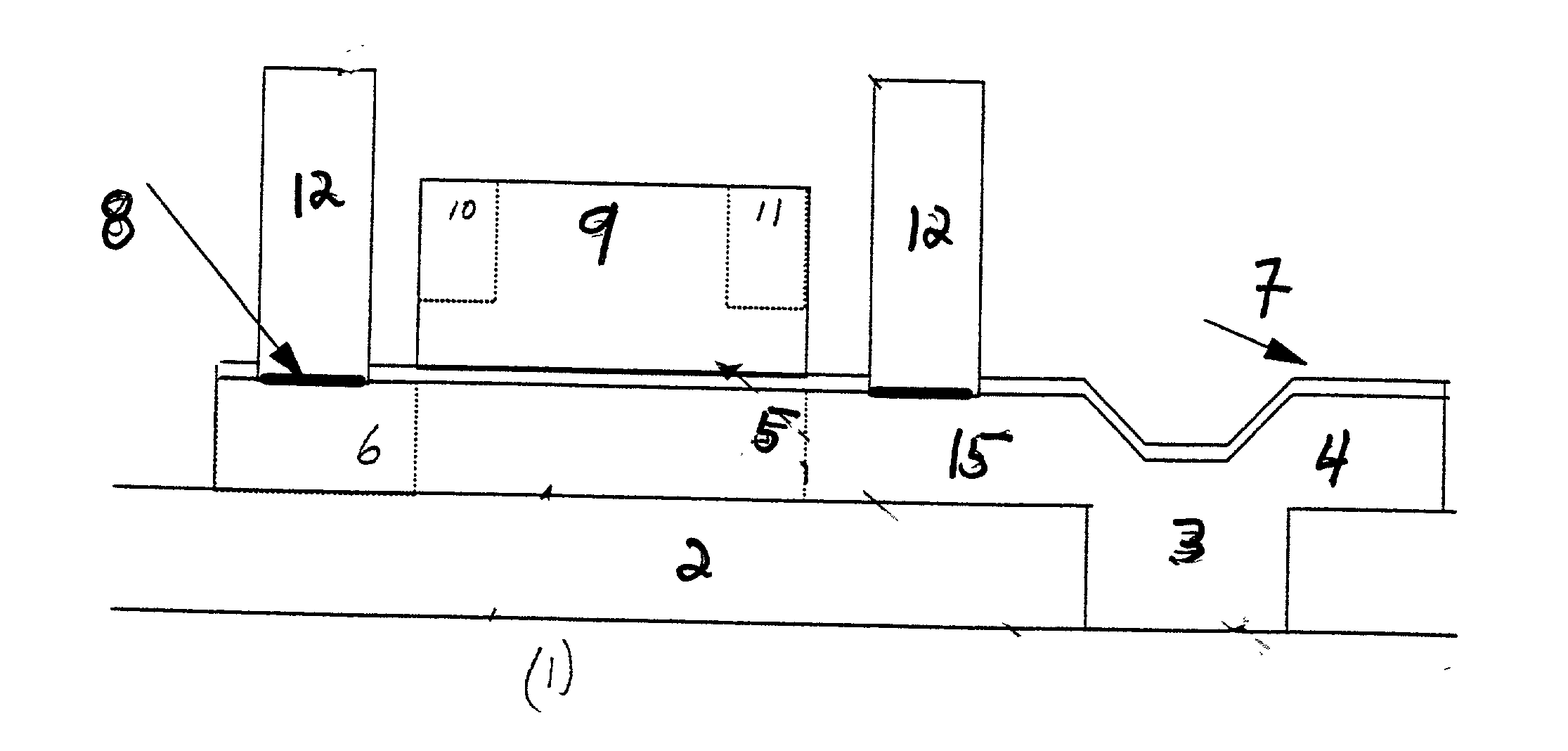
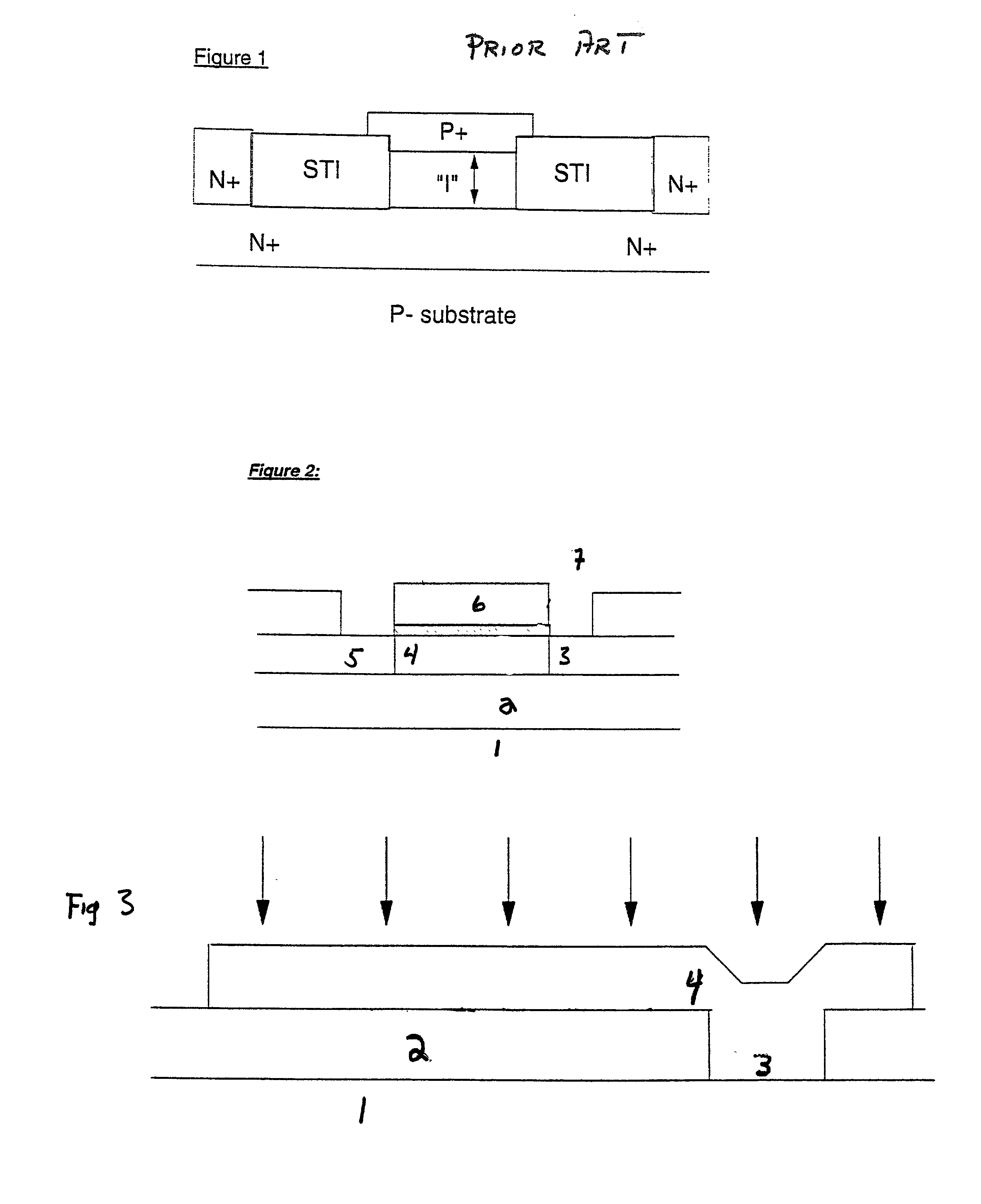
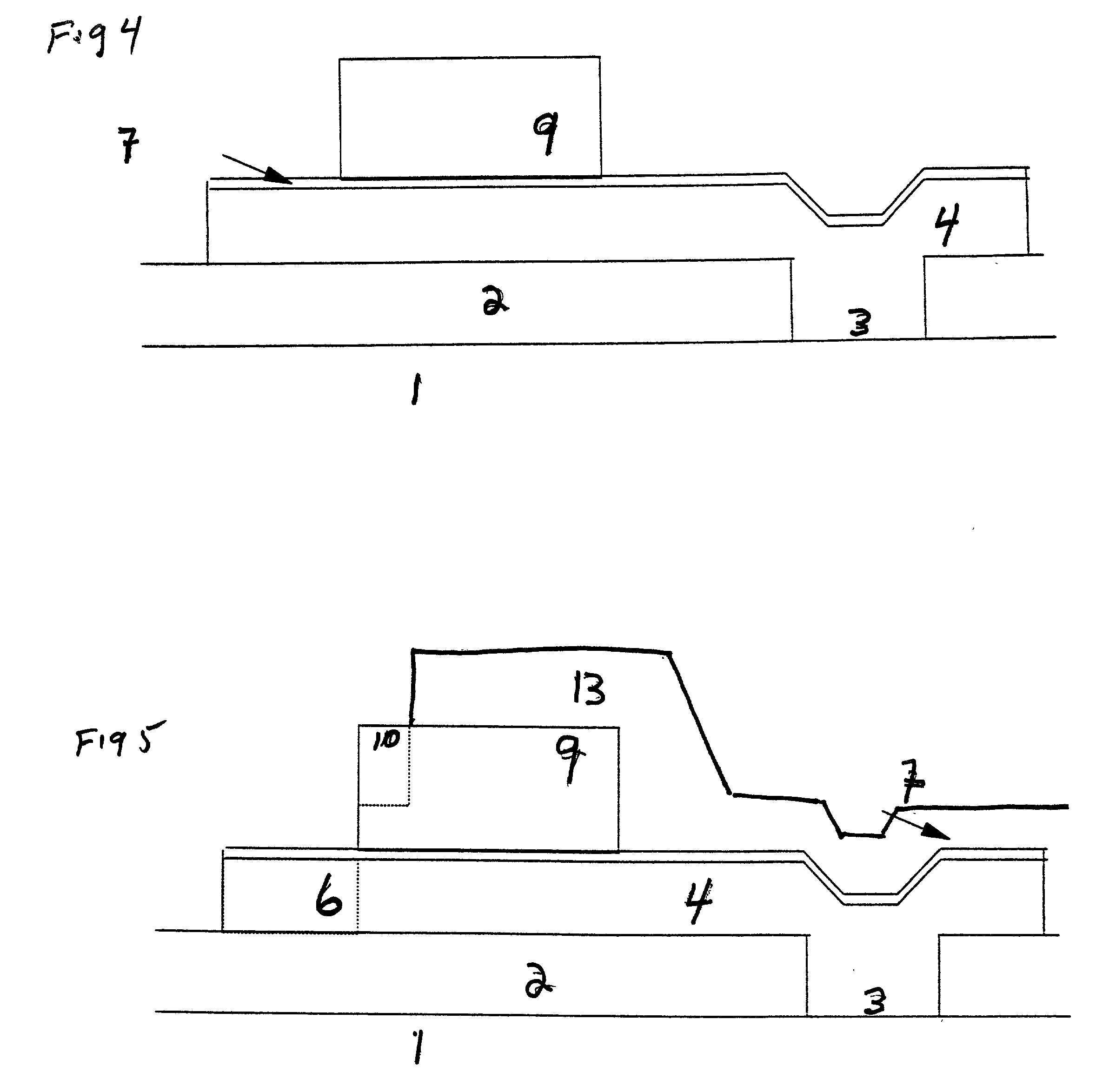
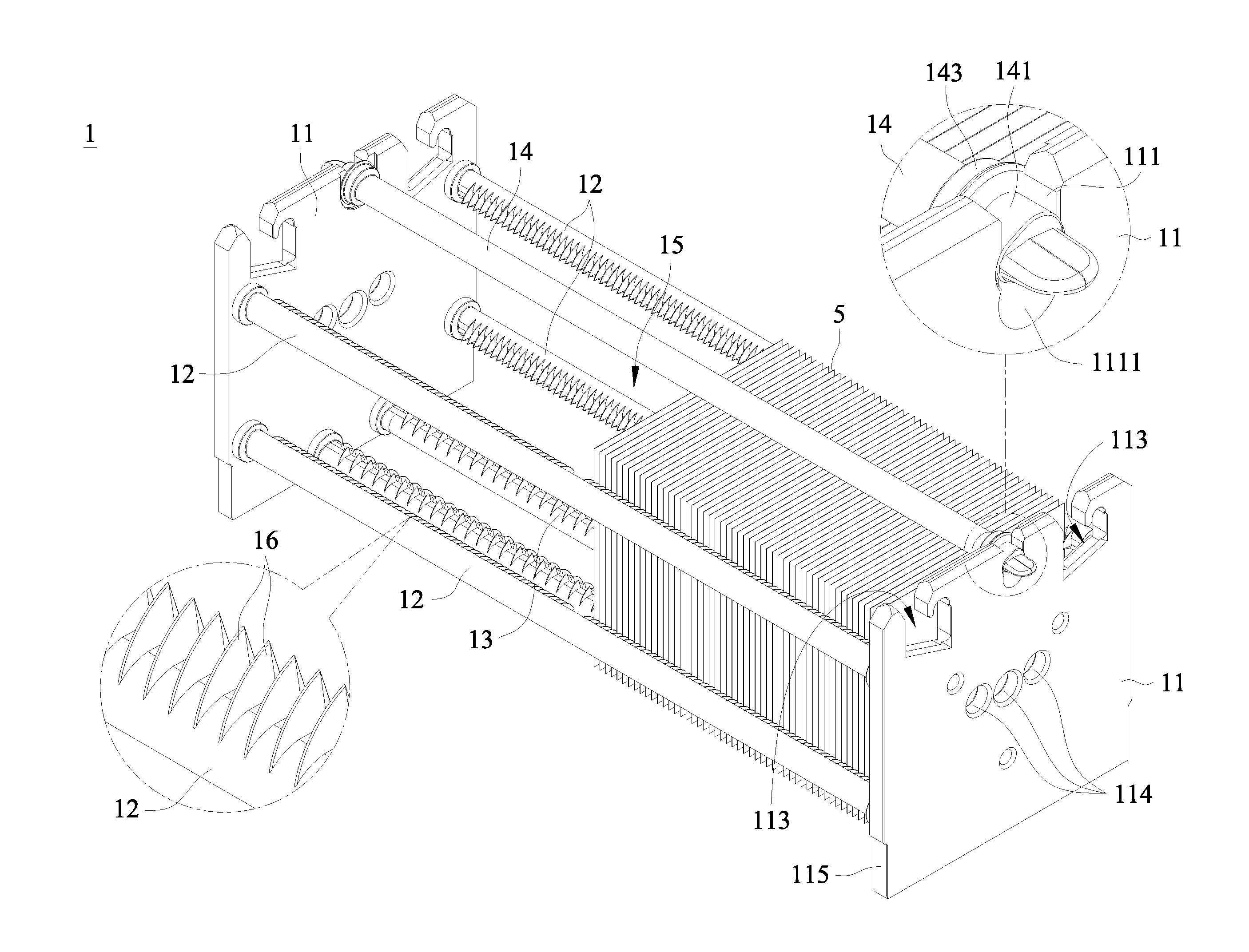
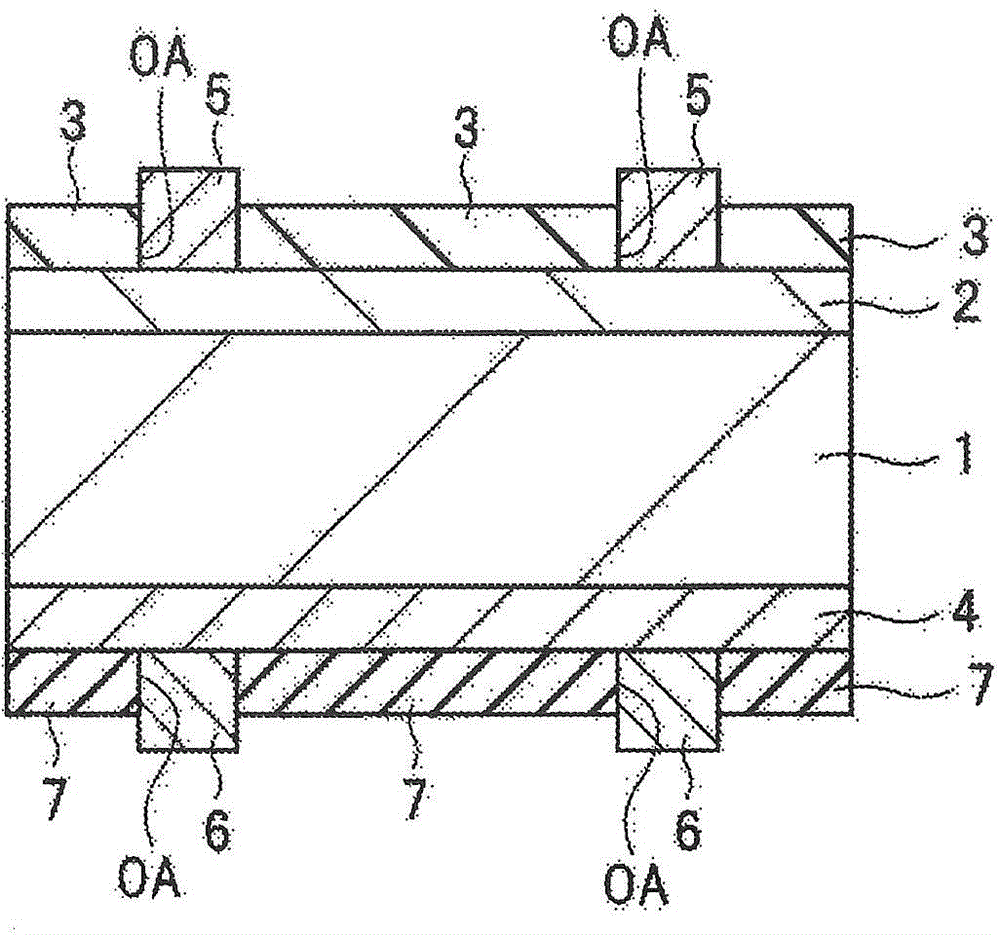
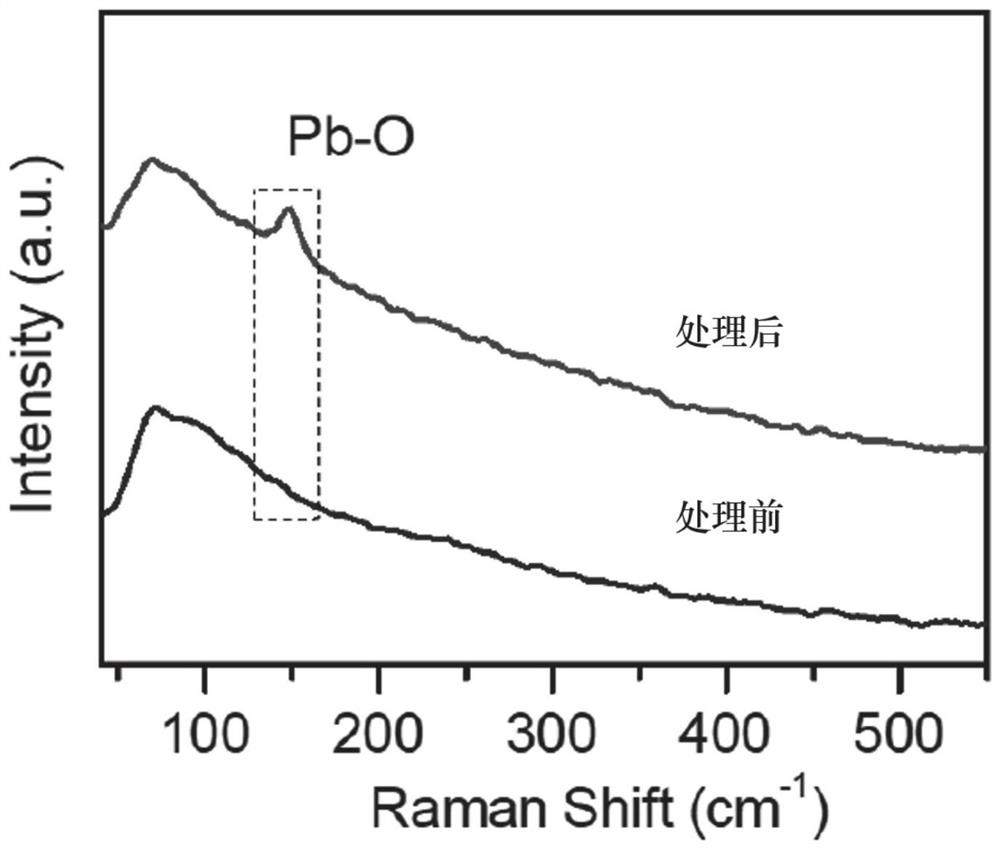
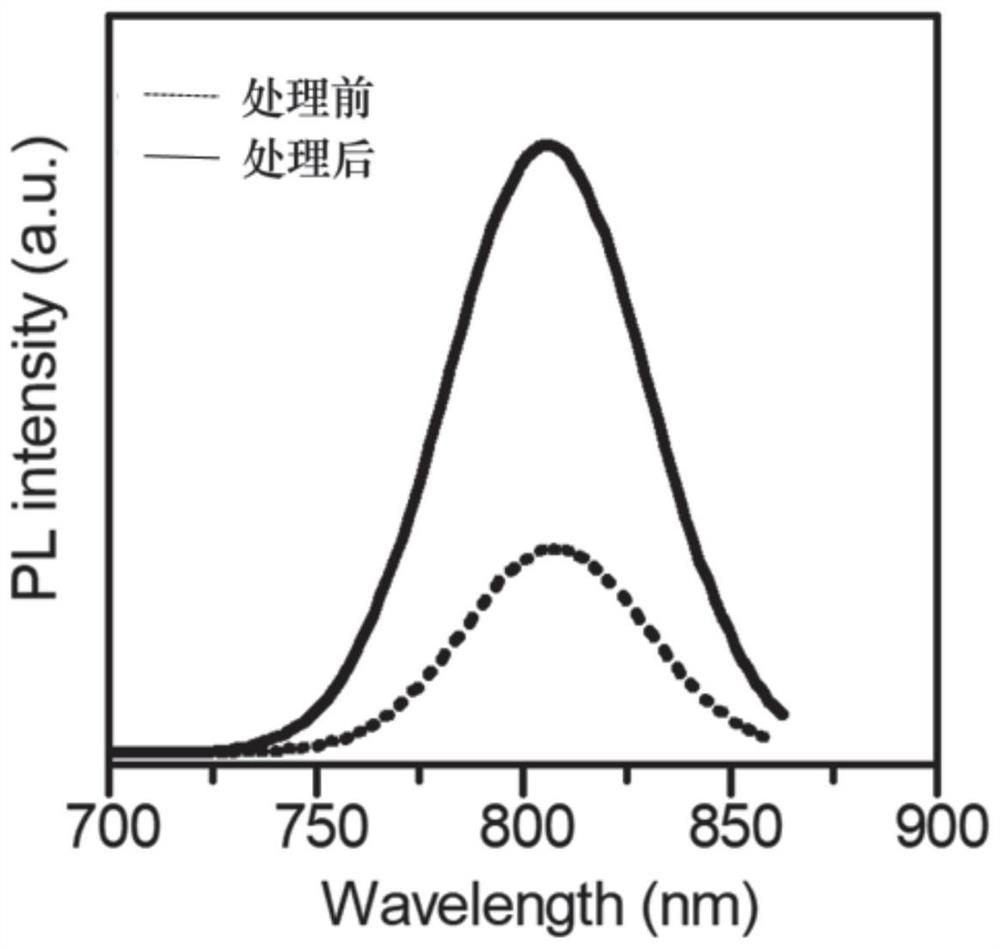
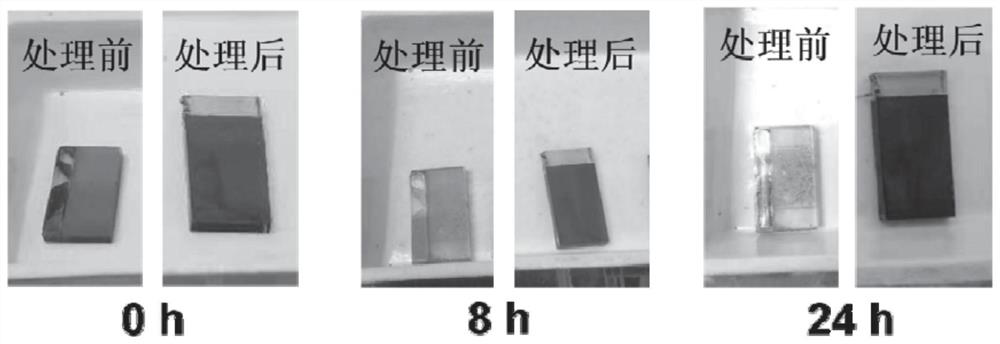
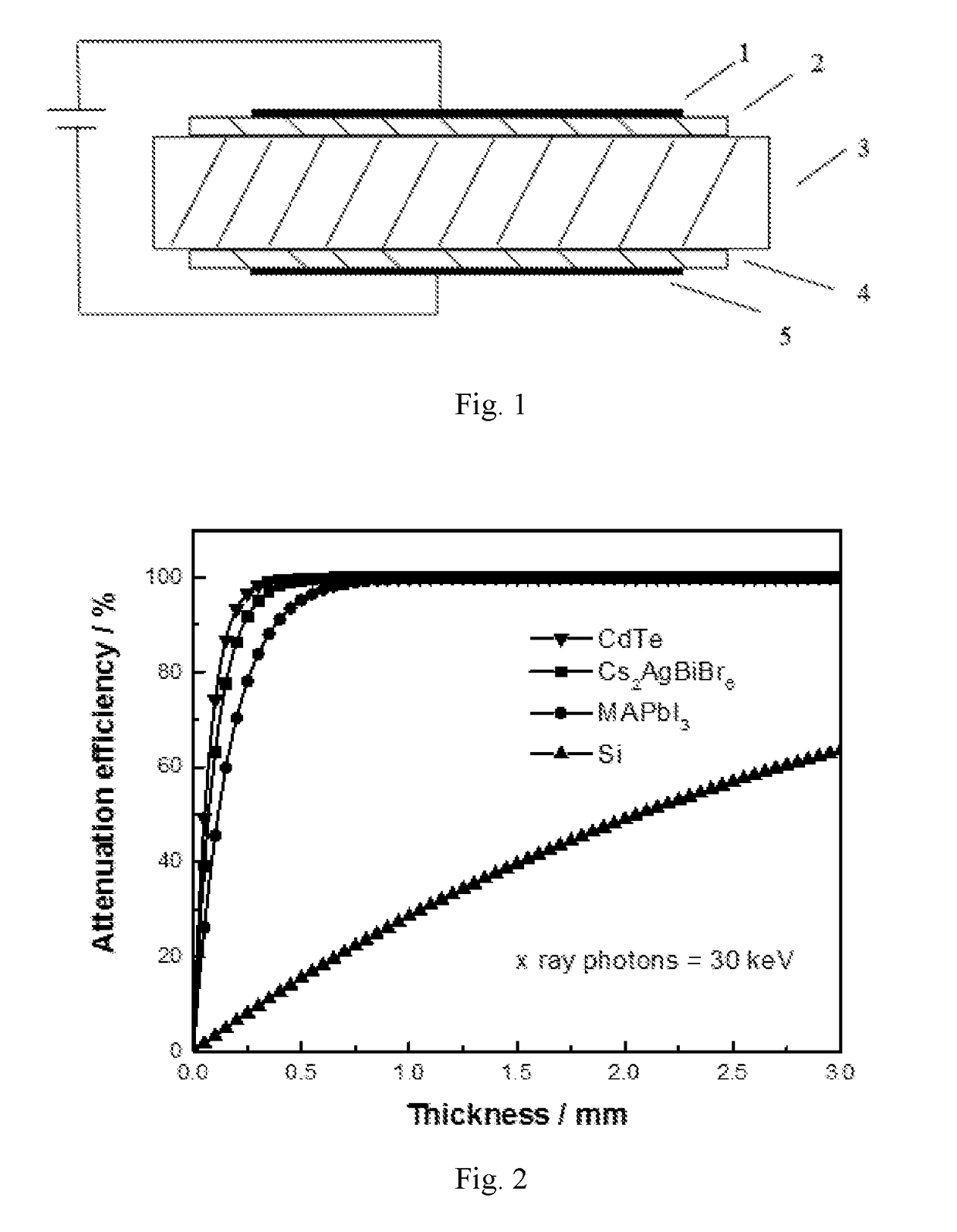
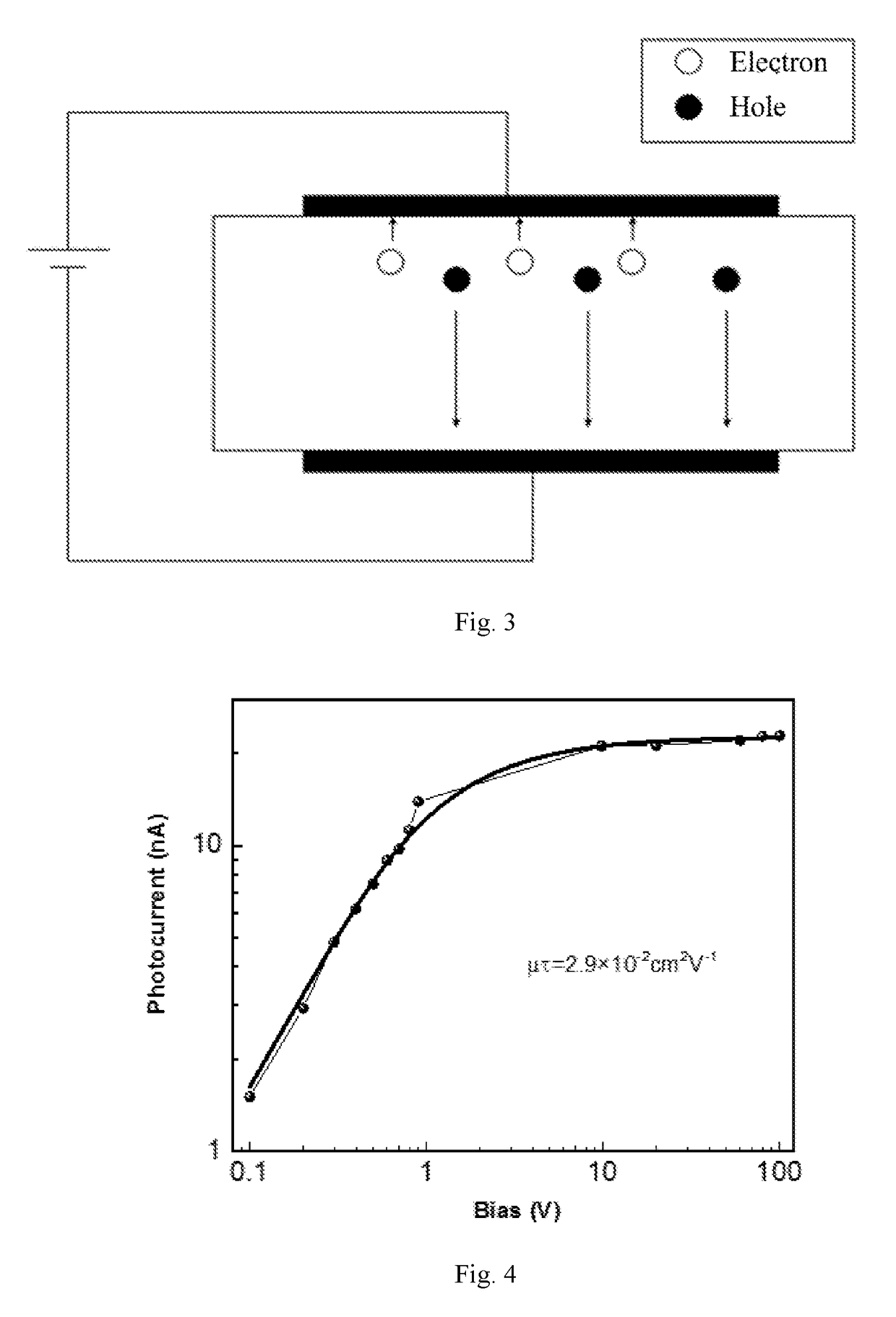
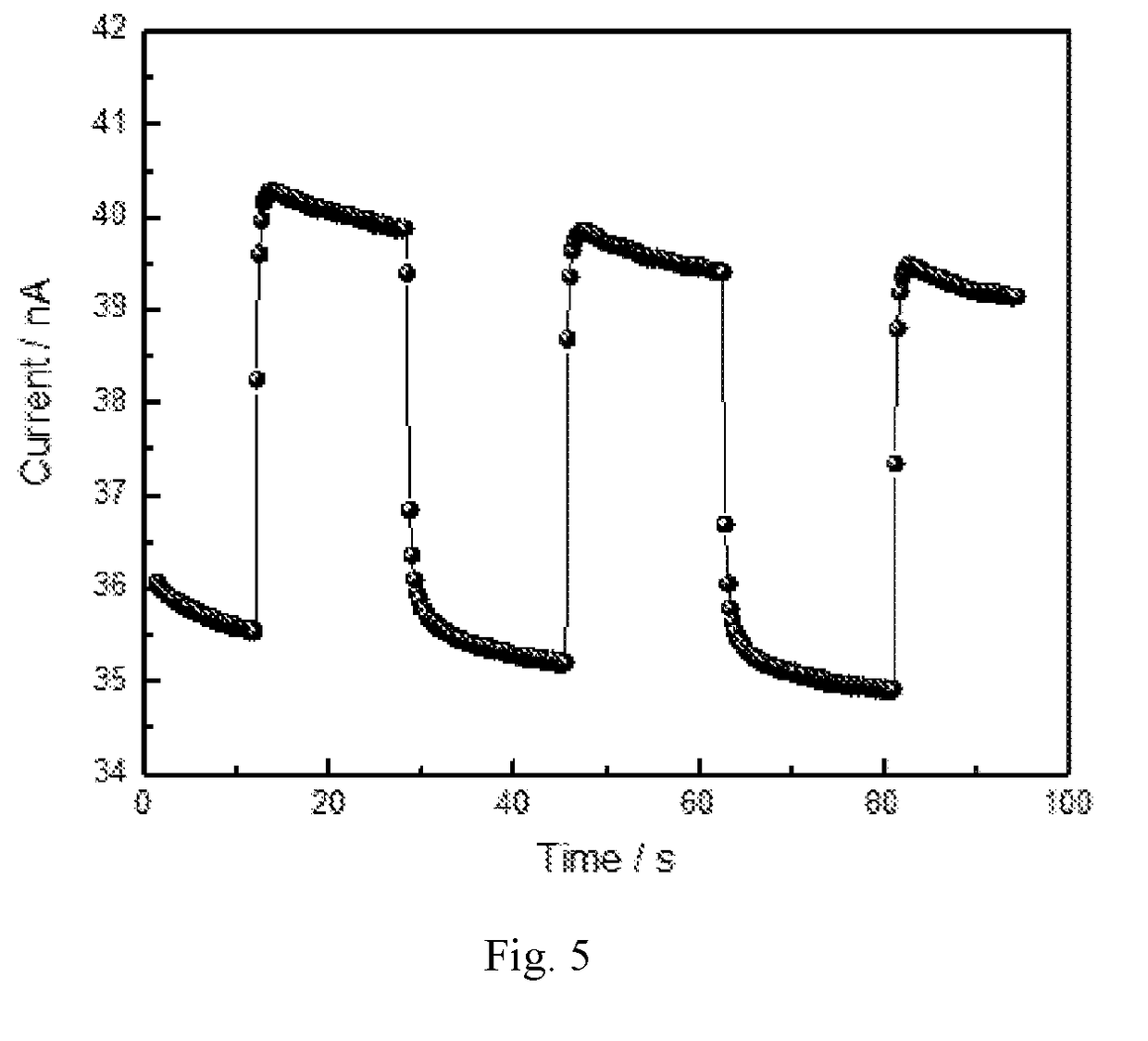
Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Improve carrier lifetime" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
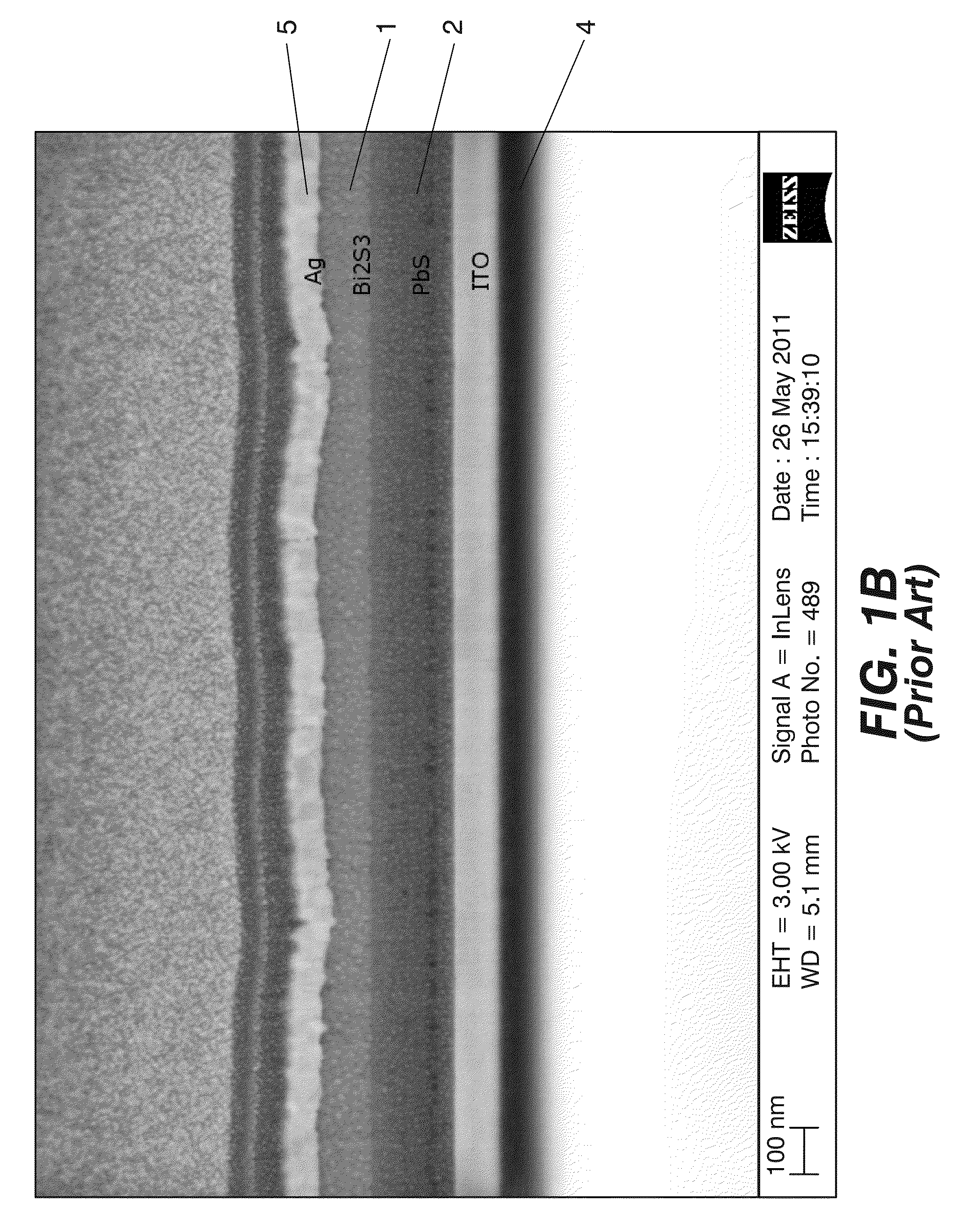
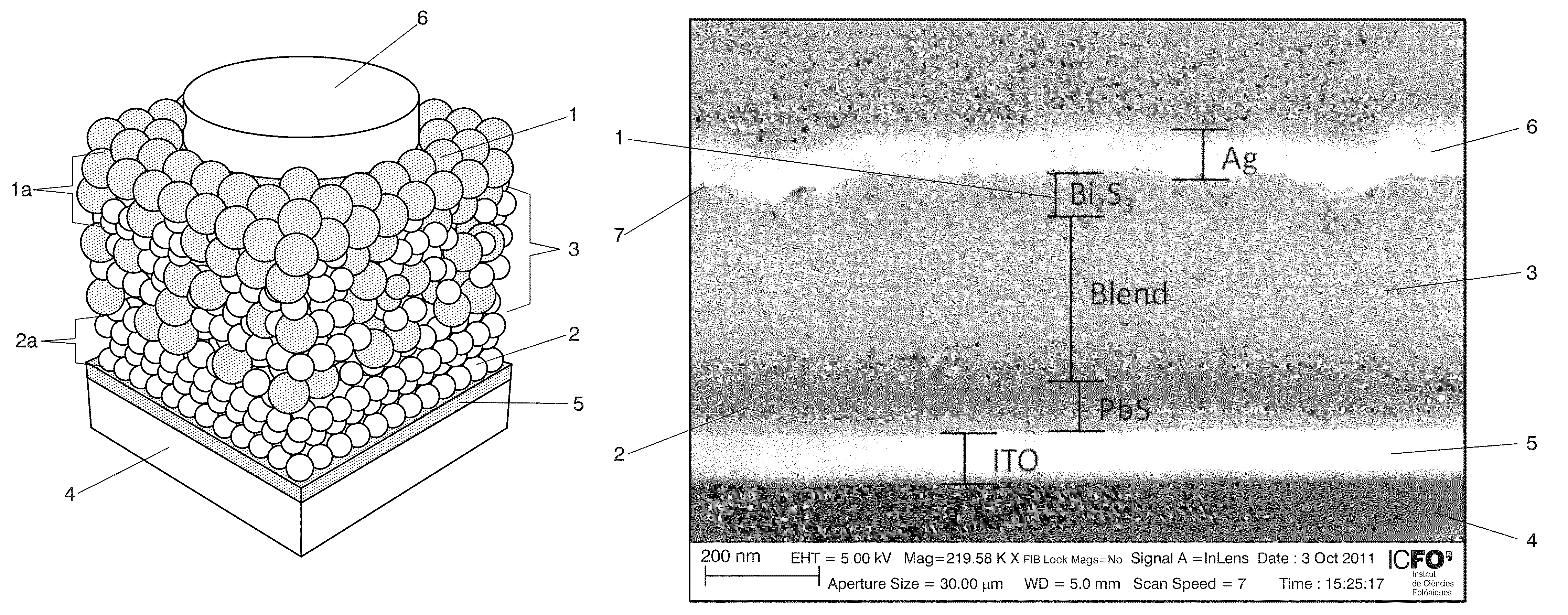
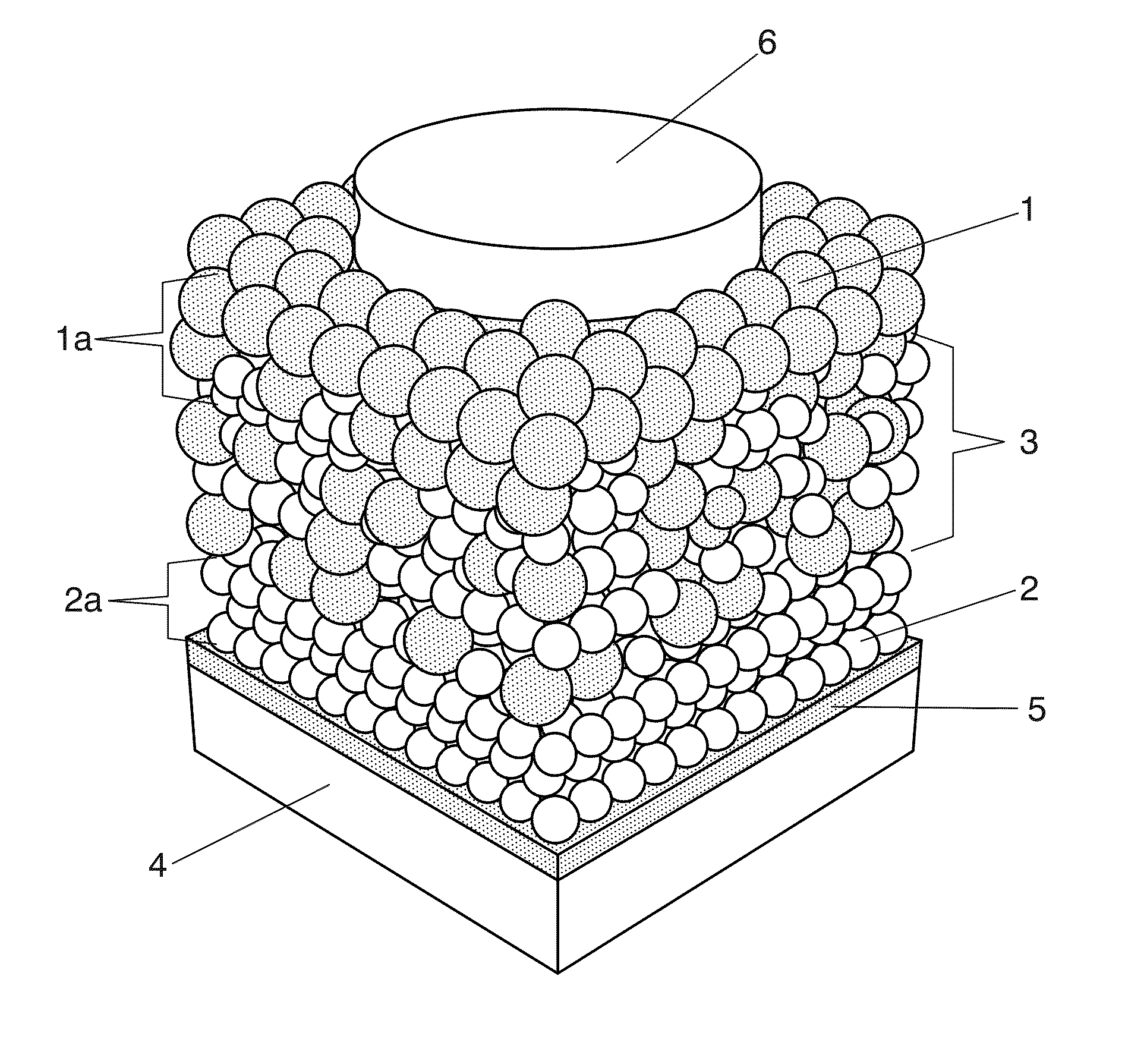
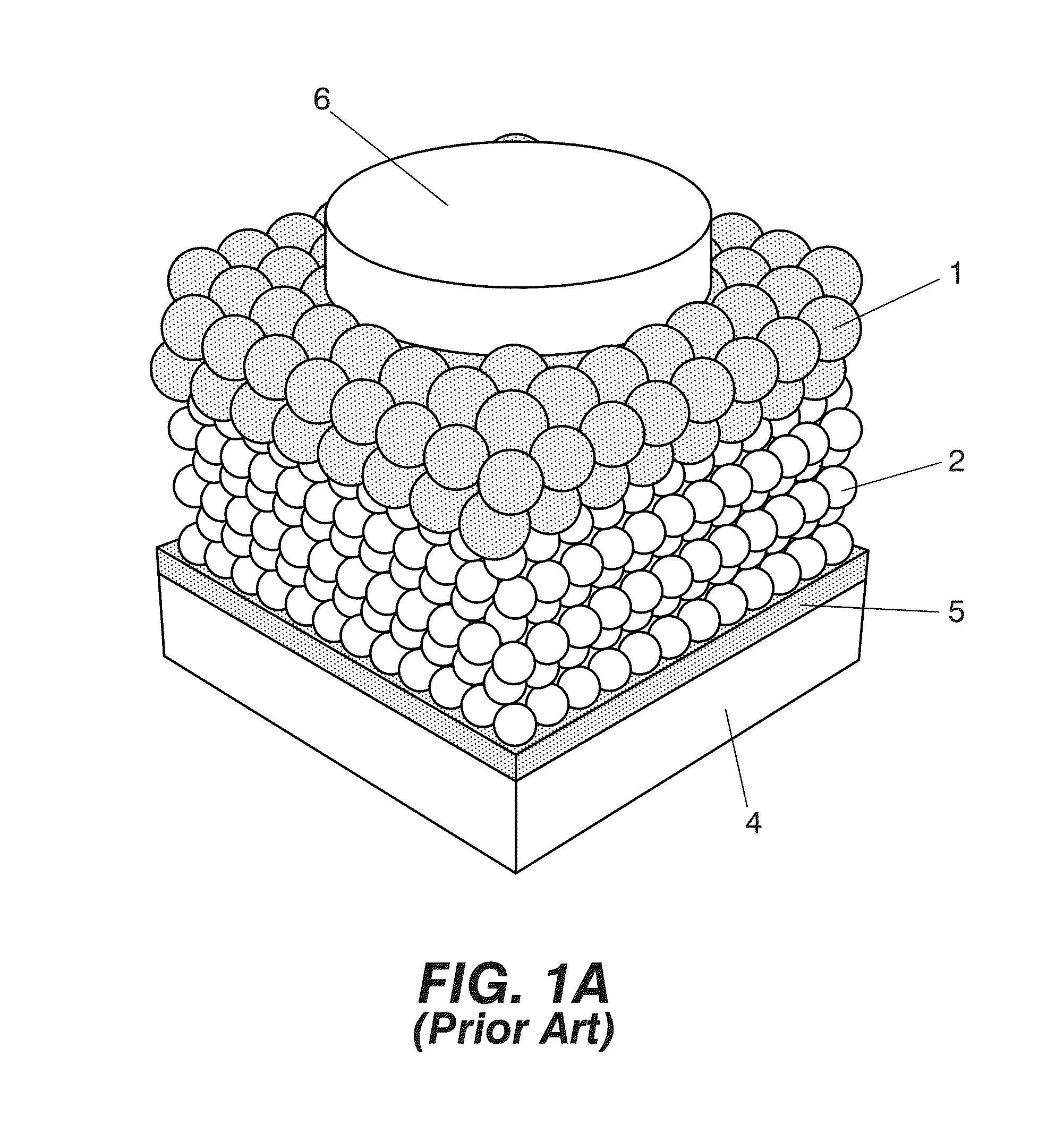
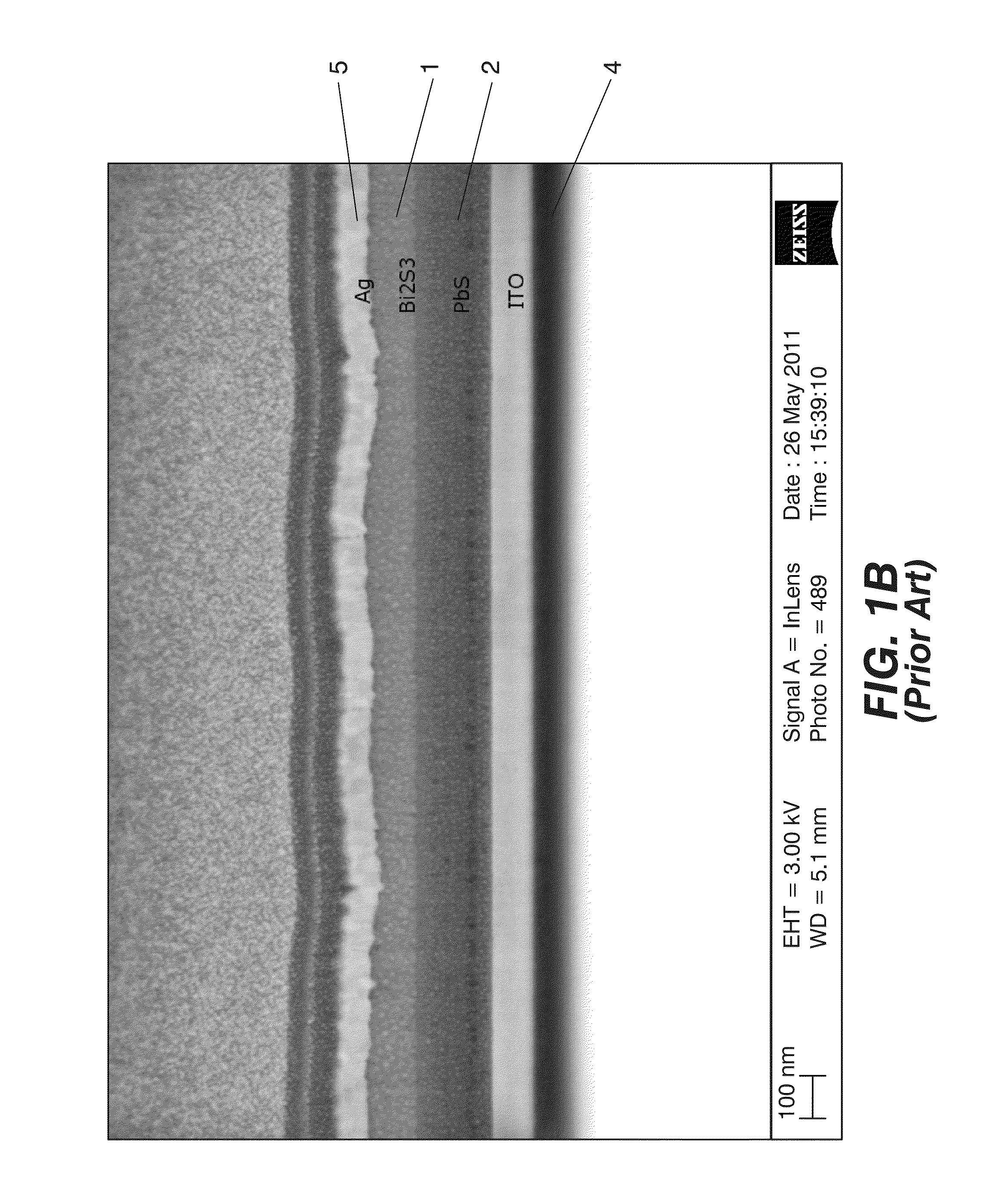
Photovoltaic nanocomposite comprising solution processed inorganic bulk nano-heterojunctions, solar cell and photodiode devices comprising the nanocomposite
ActiveUS20130263918A1Improve carrier lifetimeEfficient separationMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
Photovoltaic nanocomposite and solar cell device including the photovoltaic nanocomposite, where the photovoltaic nanocomposite includes a film of solution processed semiconductor materials having an n-type material selected from n-type quantum dots and n-type nanocrystals, and a p-type material selected from p-type quantum dots and p-type nanocrystals, and where the n-type material has a conduction band level at least equal, compared to vacuum level, to that of the p-type material, the p-type material has a valence band at the most equal, compared to vacuum level, to that of the n-type material. at least a portion of the n-type material and at least a portion of the p-type material are present in a bulk nano-heterojunction binary nanocomposite layer having a blend of the n-type material and the p-type material.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE CIENCIES FOT NIQUES
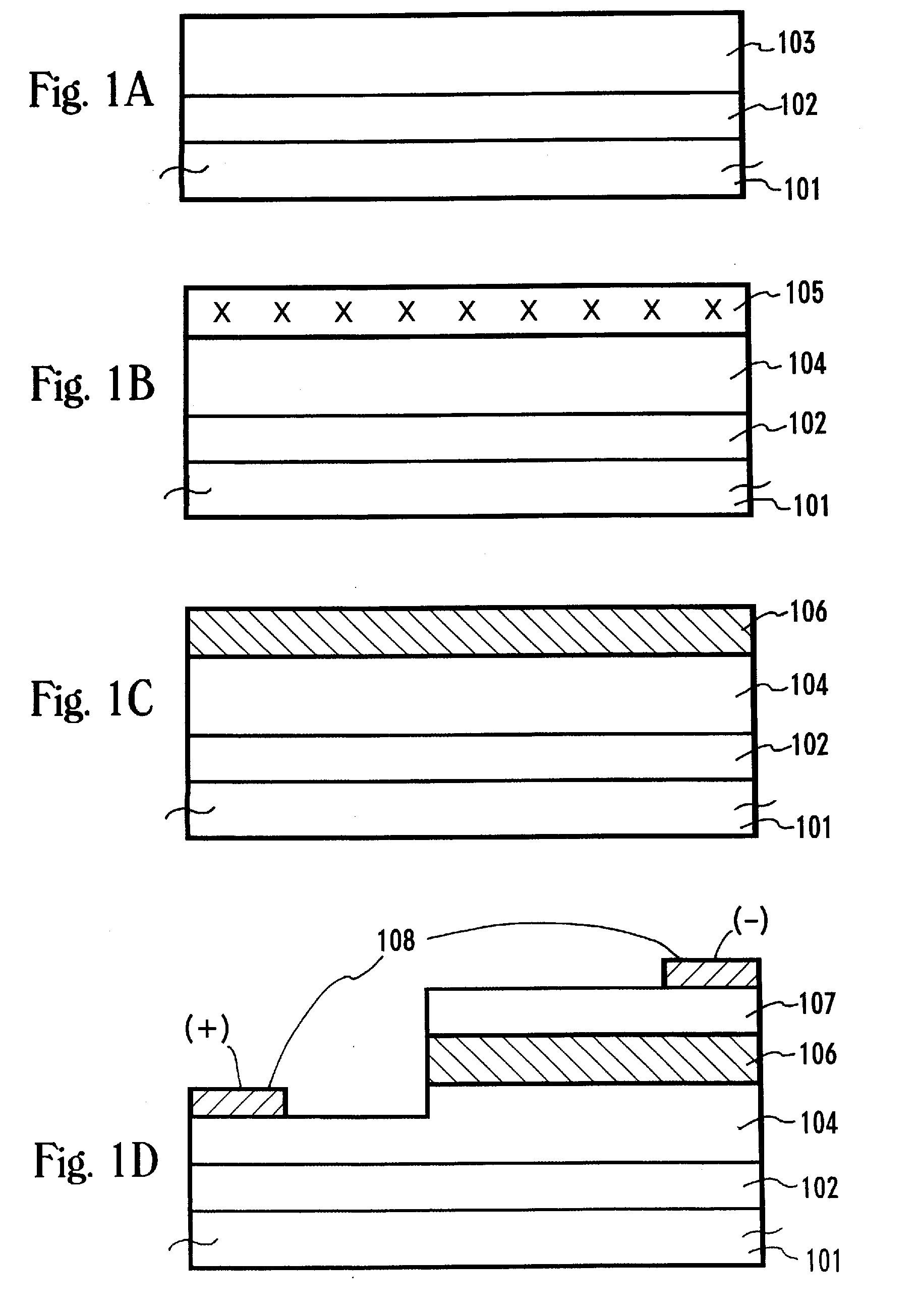
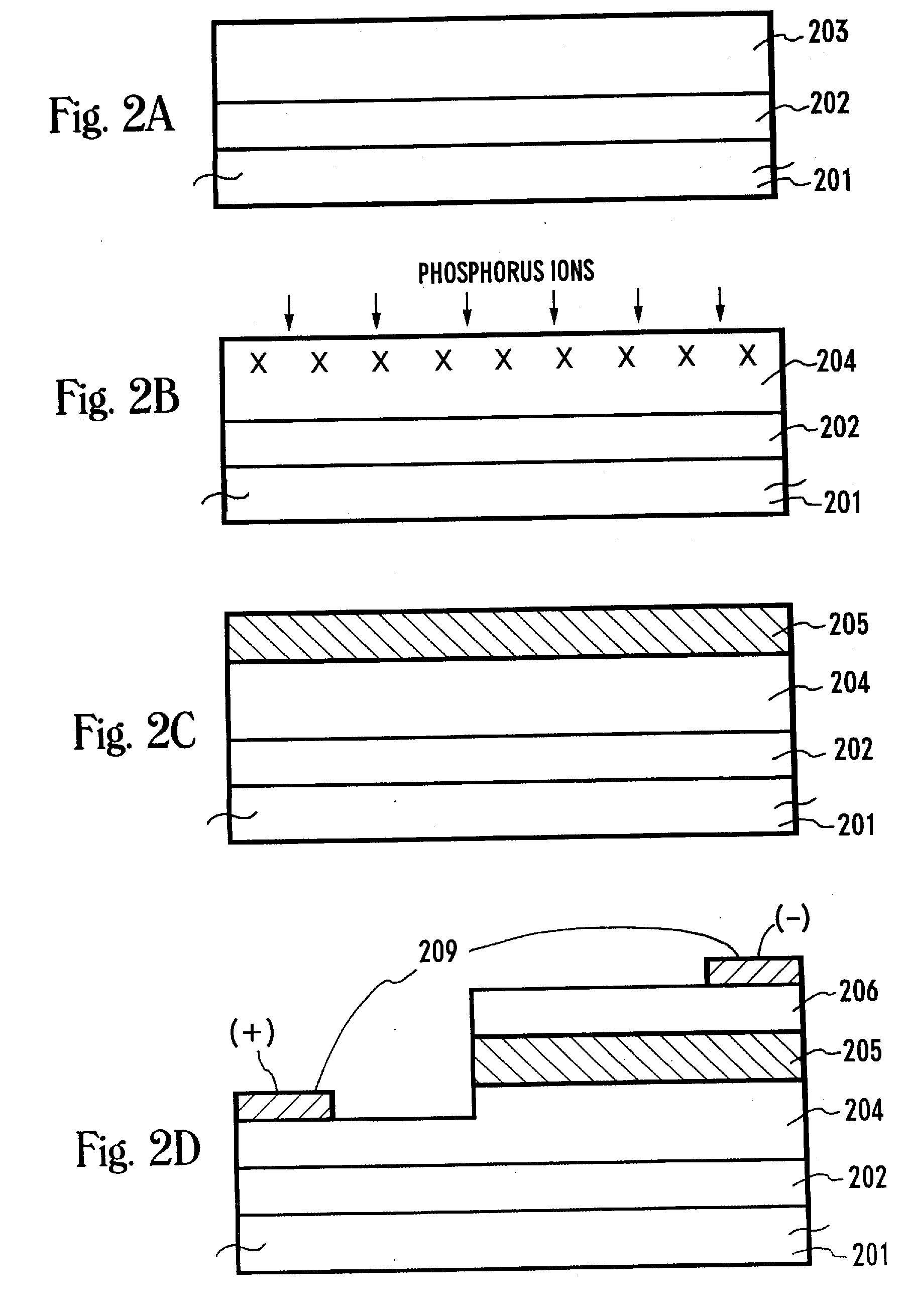
Electrical passivation of silicon-containing surfaces using organic layers
InactiveUS7491642B2Improve electrical performanceImprove electronic efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsElectrical devices
Electrical structures and devices may be formed and include an organic passivating layer that is chemically bonded to a silicon-containing semiconductor material to improve the electrical properties of electrical devices. In different embodiments, the organic passivating layer may remain within finished devices to reduce dangling bonds, improve carrier lifetimes, decrease surface recombination velocities, increase electronic efficiencies, or the like. In other embodiments, the organic passivating layer may be used as a protective sacrificial layer and reduce contact resistance or reduce resistance of doped regions. The organic passivation layer may be formed without the need for high-temperature processing.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Organic photovoltaic cell and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20080083455A1Low costLow cost manufacturingFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsChemical structureCounting Number
The present invention is an organic photovoltaic cell that can be manufactured by using an organic solvent having a low environmental load and high safety, such as xylene, and a manufacturing method therefor. The organic photovoltaic cell according to the present invention has a pair of electrodes and an organic thin film for photoelectric conversion provided between the electrodes, and the organic thin film is formed from an organic material which has a chemical structure of: where R1-R5 are hydrogen, alkyl group, alkoxy group, or aryl group, and may include oxygen, nitrogen, silicon, phosphorus or sulfur, and wherein and m are counting numbers in the range of 1 to 10000.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Thin-film photoelectric conversion device and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060213550A1Improve featuresImprove carrier lifetimeFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationAmorphous siliconPhotoelectric conversion
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
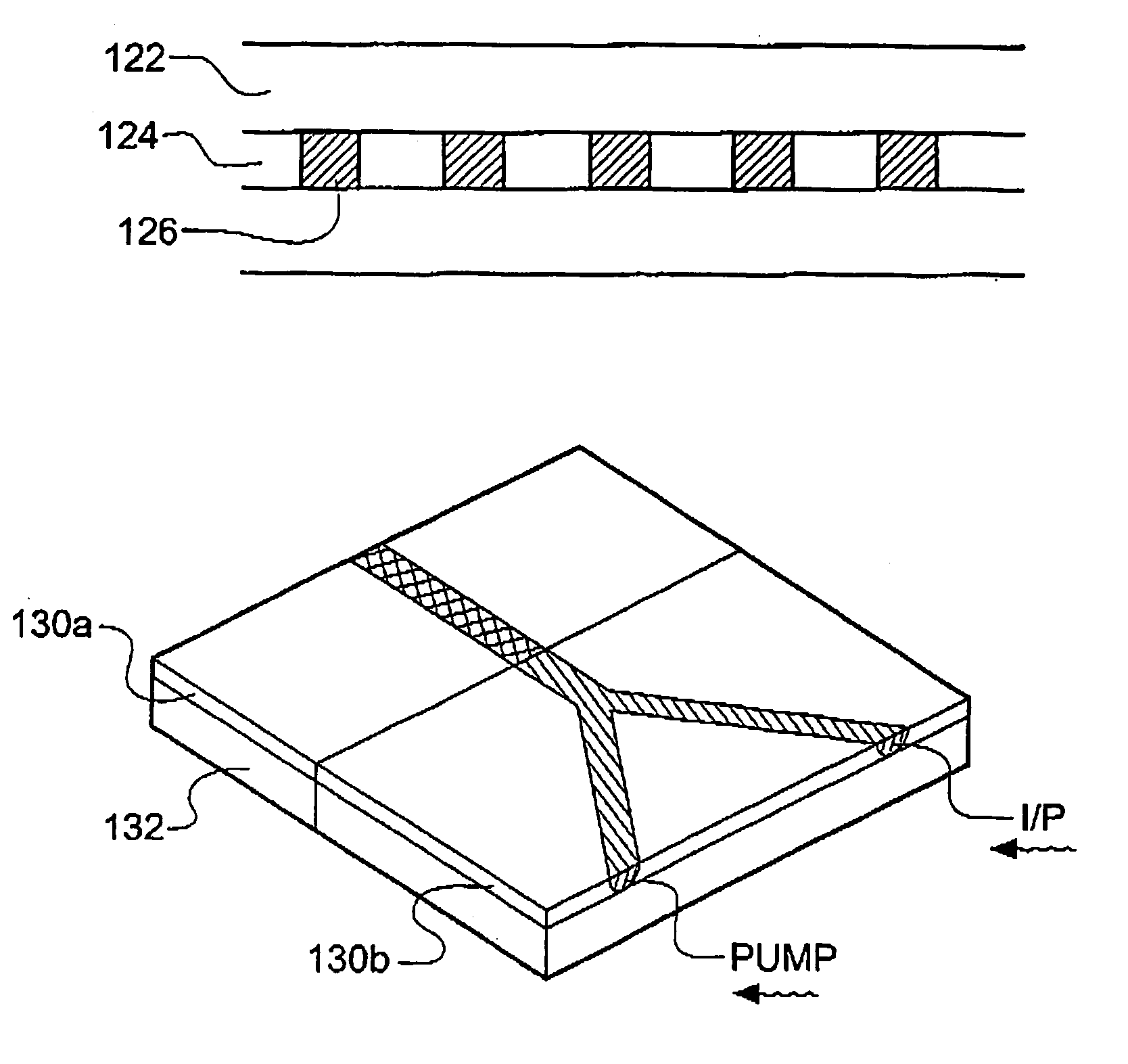
Method for annealing photovoltaic cells
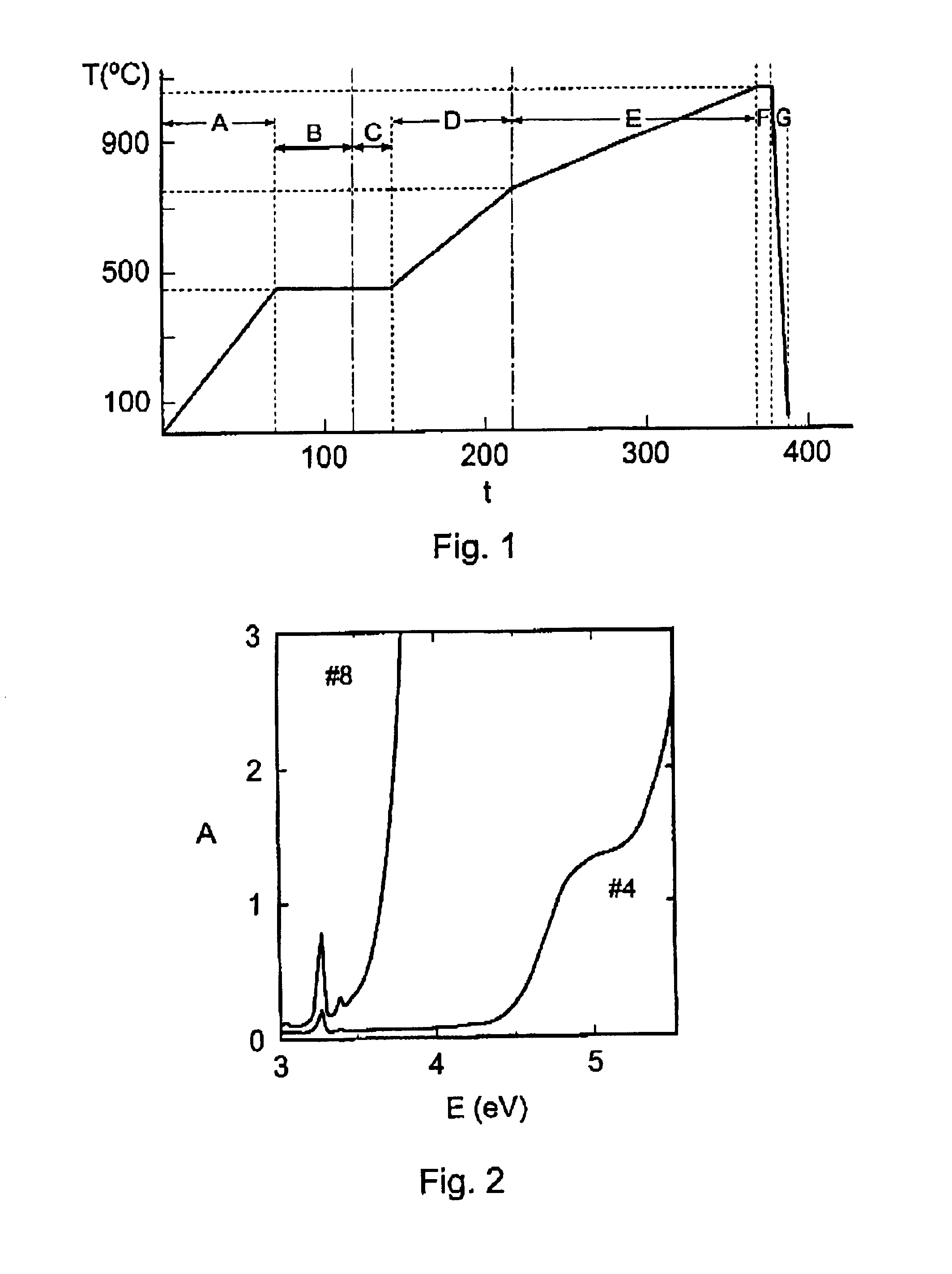
ActiveUS20080075840A1Improve photovoltaic conversion efficiencyImprove carrier lifetimeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenElectrical battery
Method for annealing at least one photovoltaic cell comprising a substrate based on silicon with a first type of conductivity, a layer doped with a second type of conductivity produced in the substrate and forming a front face of the substrate, an antireflection layer produced on the front face of the substrate and forming a front face of the photovoltaic cell, at least one metallization on the front face of the cell and at least on metallization on a rear face of the substrate. This method comprises at least the steps of:a) a first annealing of the photovoltaic cell at a temperature between around 700° C. and 900° C.,b) a second annealing of the photovoltaic cell at a temperature between around 200° C. and 500° C., at ambient pressure and in ambient air,with hydrogen being diffused in the substrate during the process.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
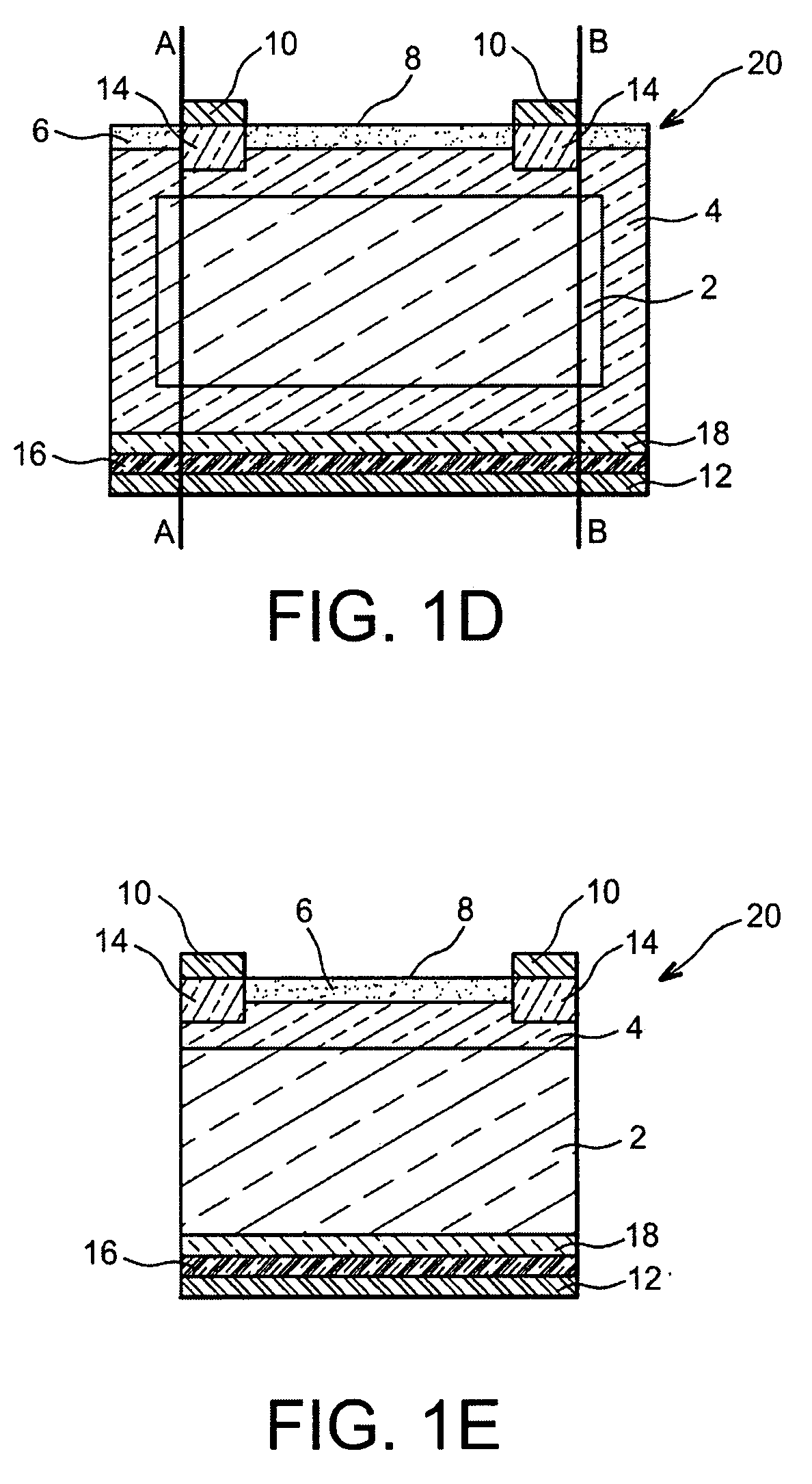
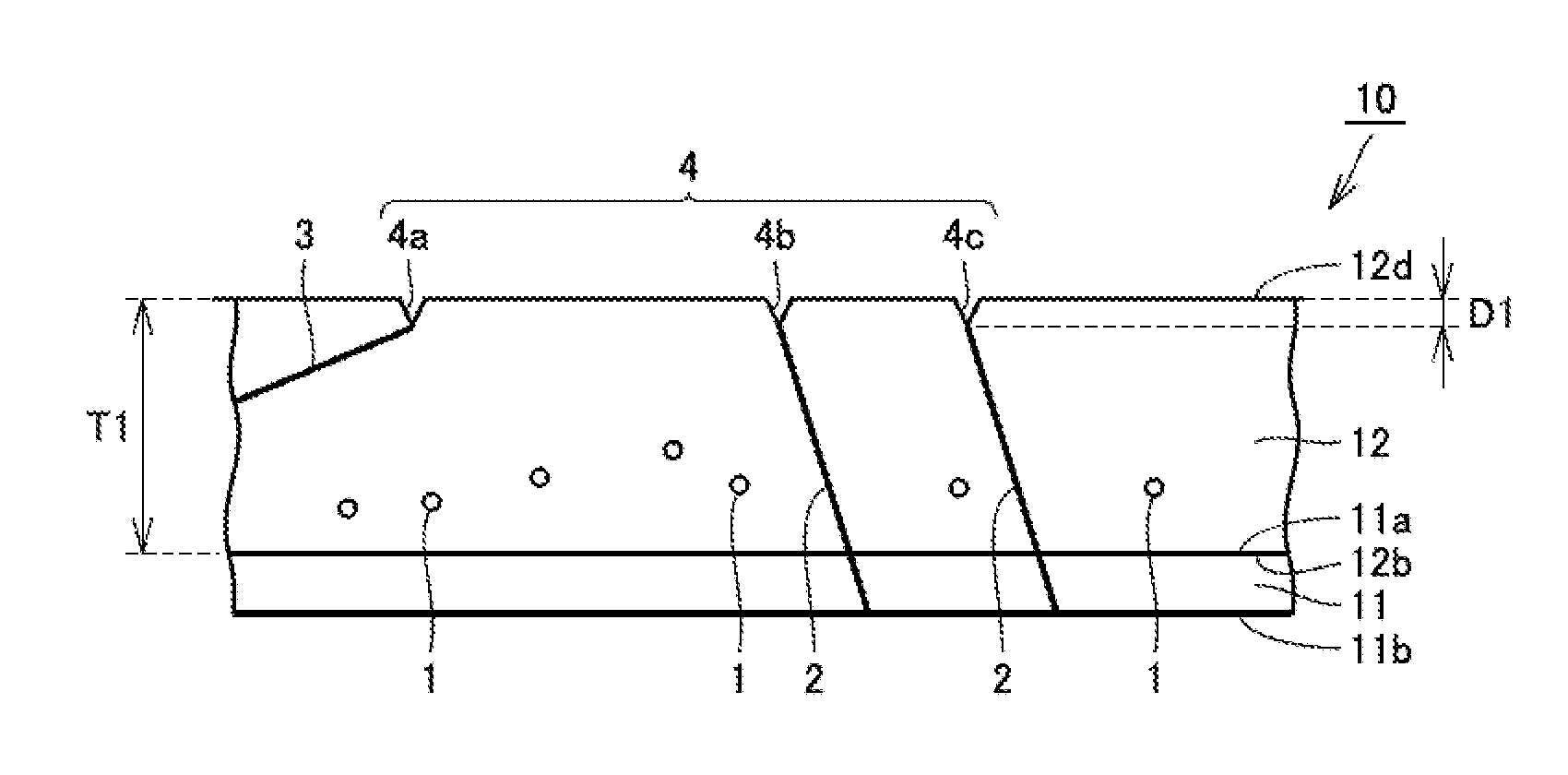
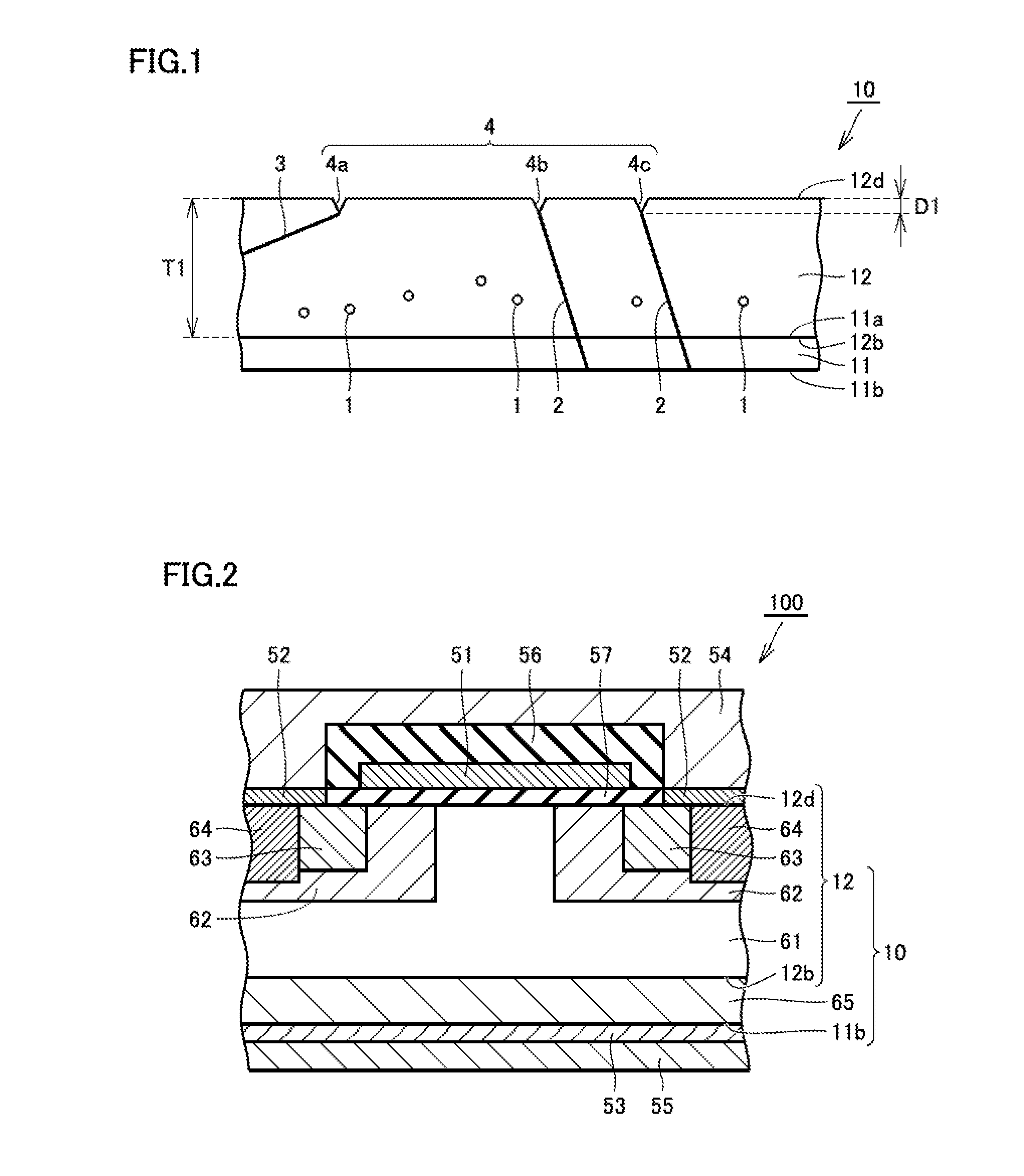
Silicon carbide substrate, silicon carbide semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing silicon carbide substrate
InactiveUS20160197155A1Improve carrier lifetimeLevel of become deepSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMaximum depthDislocation
A silicon carbide substrate has a silicon carbide epitaxial layer. The silicon carbide epitaxial layer has a first main surface and a second main surface opposite to the first main surface. The silicon carbide epitaxial layer has a thickness of not less than 50 μm in a direction perpendicular to the second main surface. Z1 / 2 centers are in the silicon carbide epitaxial layer at a density of not more than 1×1012 cm−3. A pit has a maximum depth of not more than 5 nm, the pit originating from a threading dislocation or a basal plane dislocation and having an opening at the second main surface.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Lateral polysilicon pin diode and method for so fabricating
InactiveUS20020070388A1Extending charge storage areaIncrease storage areaSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringBicmos process
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Substrate Carrier For Solar Cells
InactiveUS20160322253A1Improve carrier lifetimeImprove hydrophobicitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingEngineering
A substrate carrier for solar cells, utilized in a wet etching process, comprising: two side plates; at least a side rod, connected respectively to an outer portion on each side of the two side plates; at least a bottom rod, connected respectively to a lower portion on each side of the two side plates; at least a press rod, connected respectively to an upper portion on each side of the two side plates. Wherein, a space formed by formed by the two side plates, the side rod, the bottom rod, and press rod, is used to receive at least a solar cell substrate. Wherein, a plurality of first teeth are arranged axially along axes of the side rod and the press rod, such that each of the first teeth maintains a point-to-point contact with each of the solar cell substrates.
Owner:CHUNG KING ENTERPRISE CO LTD
Method for prolonging service life of current carrier of silicon carbide material
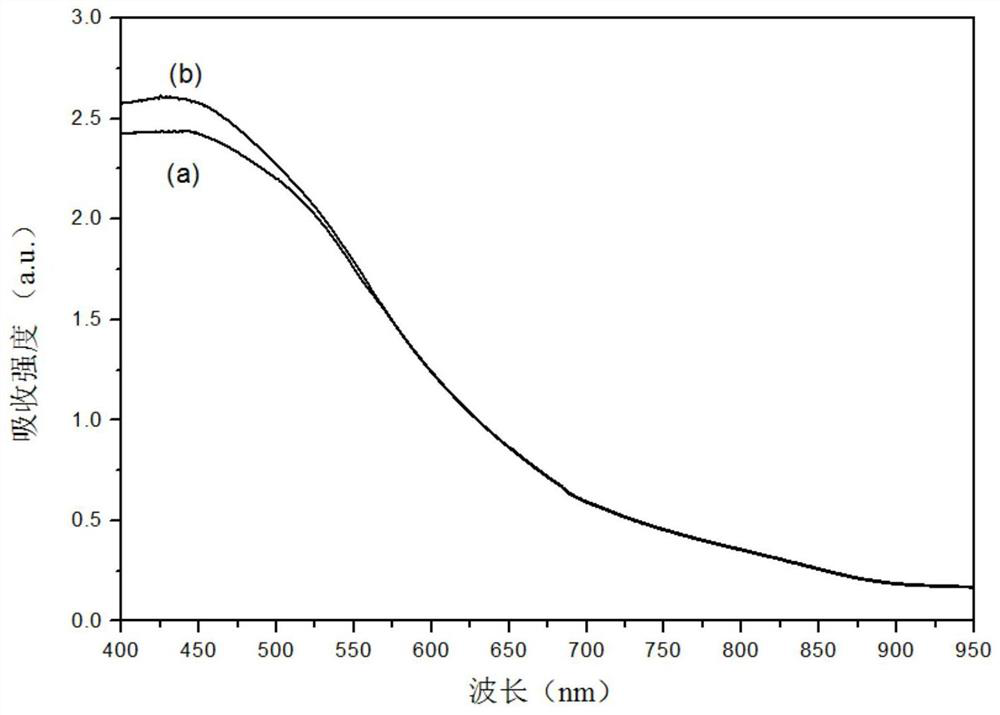
InactiveCN102560673AImprove carrier lifetimeReduce or even eliminate deep level defectsPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCharge carrierCarrier lifetime
The invention relates to a method for prolonging the service life of a current carrier of silicon carbide material, wherein the method comprises the steps as follows: in step (a1), a silicon carbide sacrificial layer rich in carbon or silicon interstitial atoms grows on the surface of grown silicon carbide material; and in step (b1), the structure that is obtained in the step (a1) is processed through high-temperature annealing. The invention further relates to a method for manufacturing silicon carbide crystals, wherein the service life of the current carrier of the silicon carbide crystals is prolonged; the method comprises the steps as follows: in step (a2), silicon carbide crystals grow; in step (b2), the silicon carbide sacrificial layer rich in silicon or carbon interstitial atoms grows on the surfaces of the silicon carbide crystals obtained in the step (a2); and in step (c2), the structure that is obtained in the step (b2) is processed through high-temperature annealing.
Owner:EPIWORLD INT
Method for passivating perovskite and perovskite solar cell
ActiveCN110635039AHigh phase stabilityReduce the density of defect statesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerovskite solar cellCyclic ether
The invention provides a method for passivating perovskite. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a perovskite precursor solution; carrying out annealing on a substrate, wherein the substrate comprises an electron transport layer; coating the perovskite precursor solution on the substrate and carrying out heating to generate a perovskite thin film; and forming a cyclic ether passivation layer on the perovskite thin film to obtain a perovskite thin film modified by the cyclic ether. The method for preparing the perovskite layer through the N-methyl pyrrolidone and passivating andmodifying the perovskite layer through the cyclic ether is simple in process; the solar cell assembled by the perovskite prepared through the method is high in efficiency and good in repeatability; and the stability is obviously improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method of manufacturing semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS20100062588A1Reduce metal pollutionHigh crystallinitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBuried oxideOxide
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor substrate, in which a silicon layer is provided on a buried oxide film, includes preparing a base substrate having a seed layer of the silicon layer on the buried oxide film with a film thickness equal to or more than 1 nm and equal to or less than 100 nm, and epitaxially growing the seed layer at a temperature equal to or more than 1000° C. and equal to or less than 1300° C. so as to form the silicon layer with a film thickness equal to or more than 1 μm and equal to or less than 20 μm.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Ultra long lifetime gallium arsenide
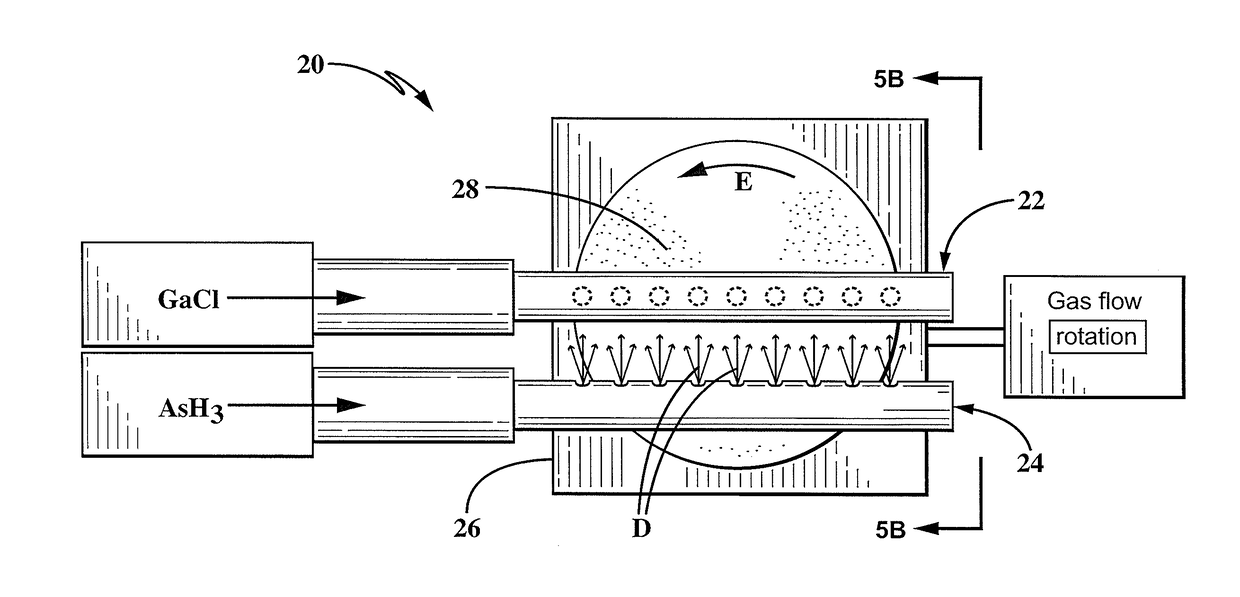
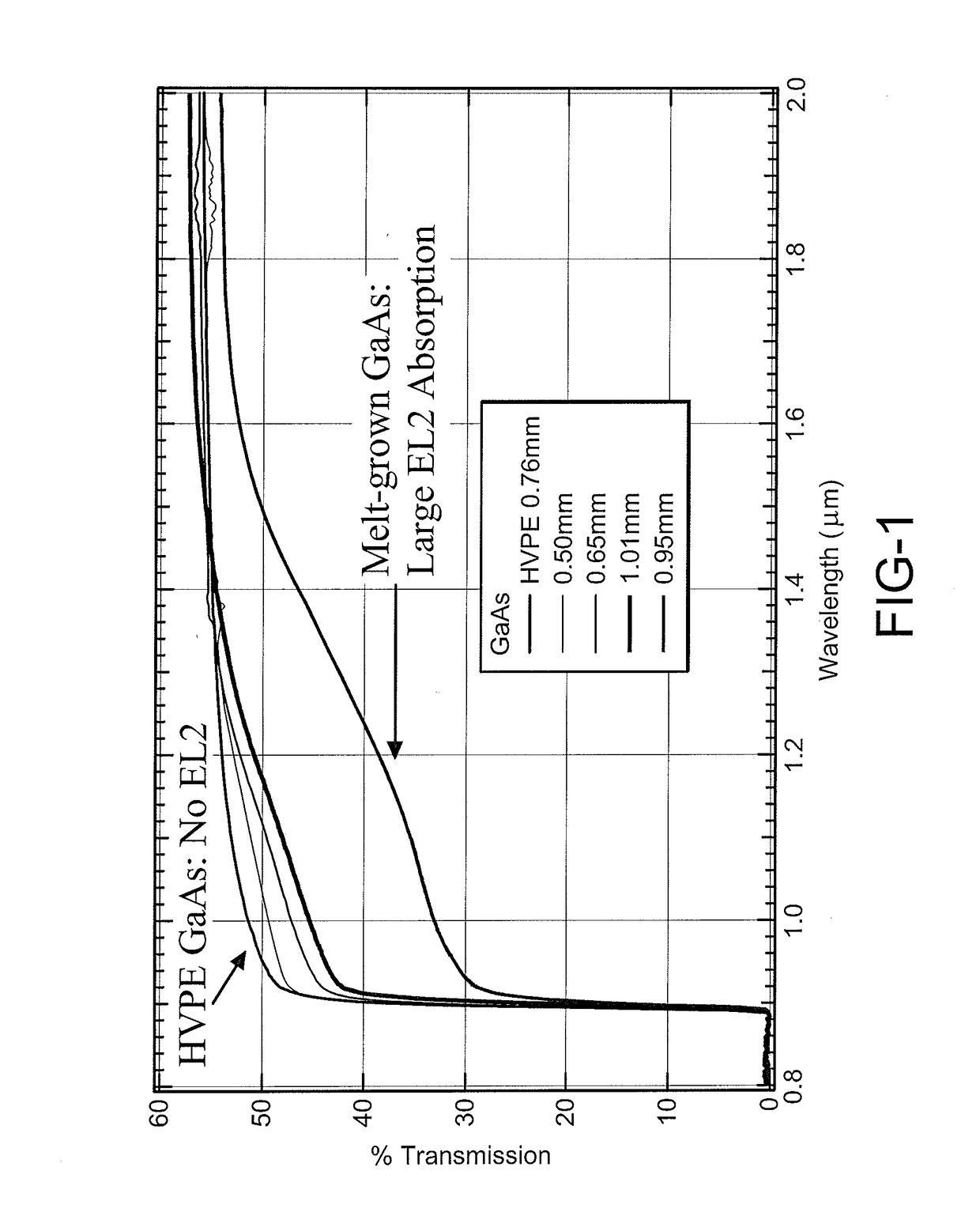
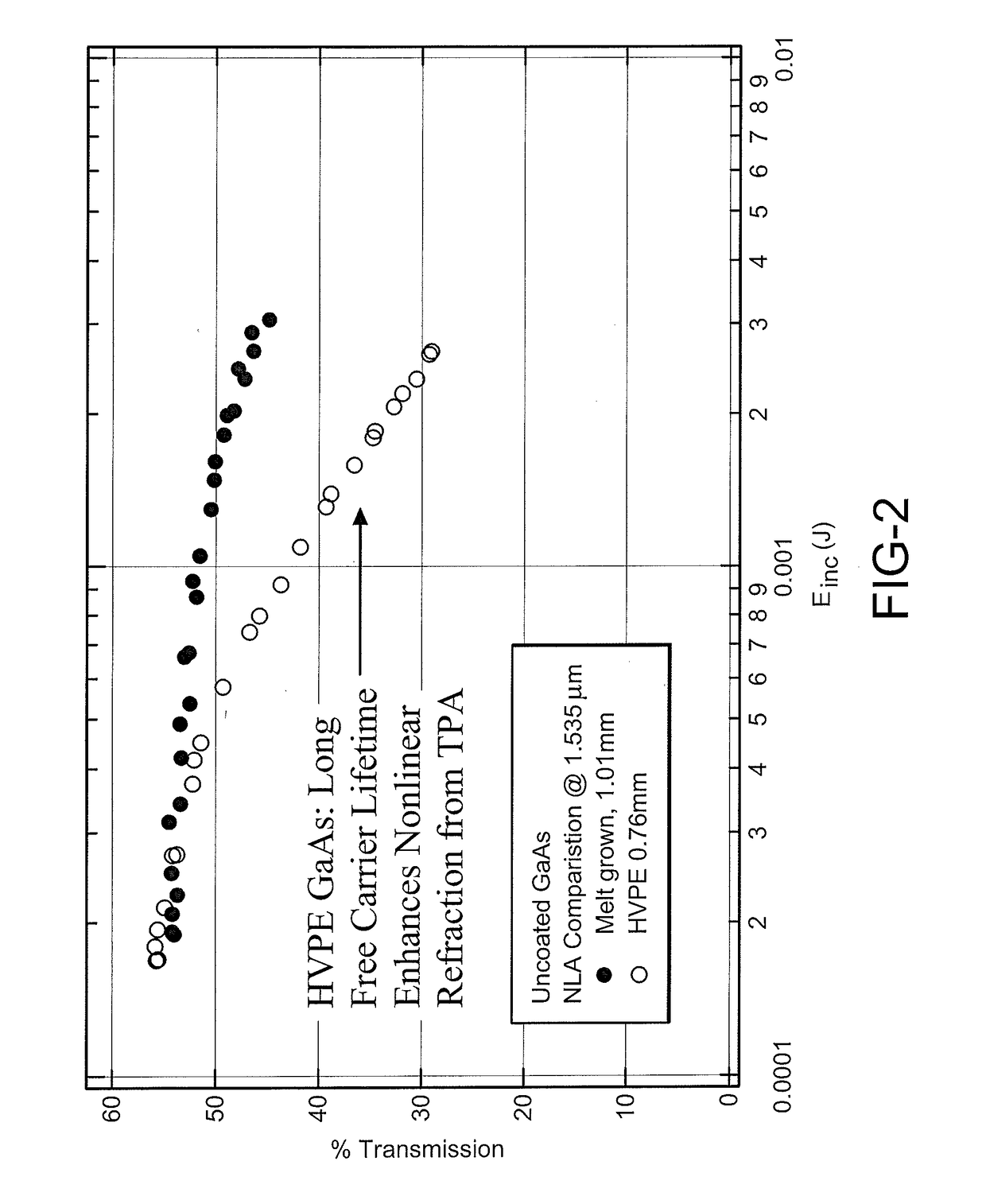
InactiveUS20170204533A1Improve carrier lifetimeReduces back-side impurity vapor transportPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSolar cellImaging Procedures
A system and method for producing bulk GaAs with an increased carrier lifetime of at least 10 microseconds is provided. The system and method of producing the GaAs crystal involves using a technique called low pressure hydride vapor phase epitaxy (LP-HVPE). In this technique, a gas containing Ga (typically GaCl) is reacted with a gas containing As (typically AsH3) at the surface of a GaAs substrate. When grown under the proper conditions, the epitaxial, vapor grown GaAs crystal has ultra-long free carrier lifetimes of at least one order of magnitude greater than that of the previous lifetime of 1 microsecond. This very long free carrier lifetime GaAs will be particularly useful as a semiconductor radiation detector material and is also expected to be useful for many other applications than include medical imaging, solar cells, diode lasers, and optical limiters and other applications.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
N-type substrate silicon solar cell and production method thereof
InactiveCN102403377AImprove carrier lifetimeFew composite defectsFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationTemperature coefficientAluminium
The invention discloses an N-type substrate silicon solar cell and a production method of the N-type substrate silicon solar cell. The N-type substrate silicon solar cell comprises an N-type silicon substrate and is characterized in that an N plus area layer is arranged at one side of the N-type silicon substrate; an antireflection film layer is arranged on the N plus area layer; a positive silver layer is arranged on the antireflection film layer; a P area layer is arranged at the other side of the N-type silicon substrate; and a back electrode layer is arranged on the P area layer and is a metal aluminum layer. The inventionhas the beneficial effects that compared with a P-type substrate silicon solar cell, the N-type substrate silicon solar cell has longer carrier service life, fewer complex defects, small temperature coefficient errors and thin thickness and also has the imponderable advantages in feed; through further improving the process of the N-type substrate silicon solar cell, the conversion efficiency of the solar cell can be more greatly improved, and the electrical property of the solar cell is improved to a large extent; and compared with the P-type substrate silicon solar cell, each N-type substrate silicon solar cell is improved by 0.15W on average, so that the profit on each production line can be greatly increased.
Owner:宁波市鑫友光伏有限公司
Quantum cascade detector
ActiveUS20150123076A1Improve carrier lifetimeHigh sensitivitySemiconductor devicesLevel structureCoupling
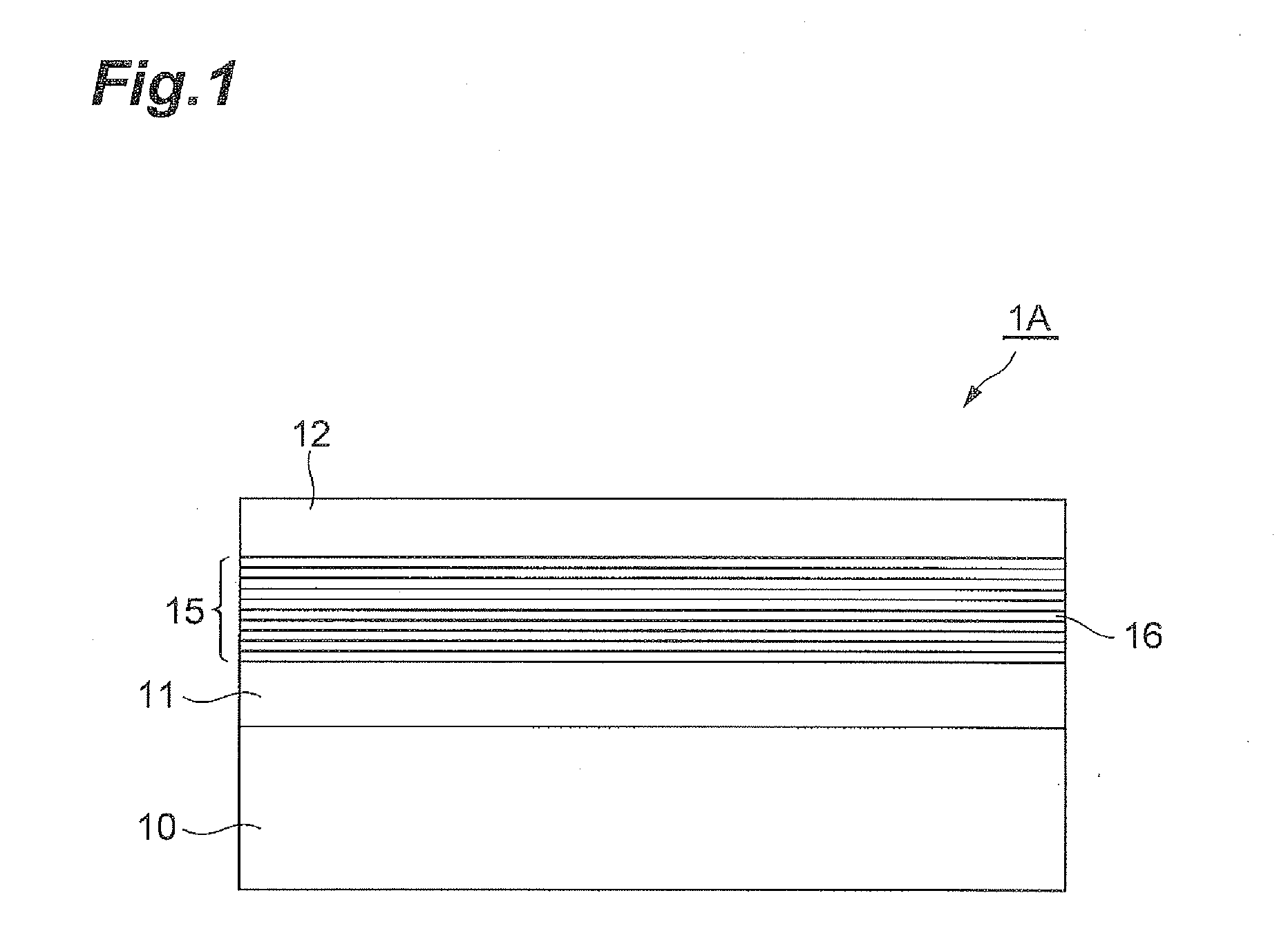
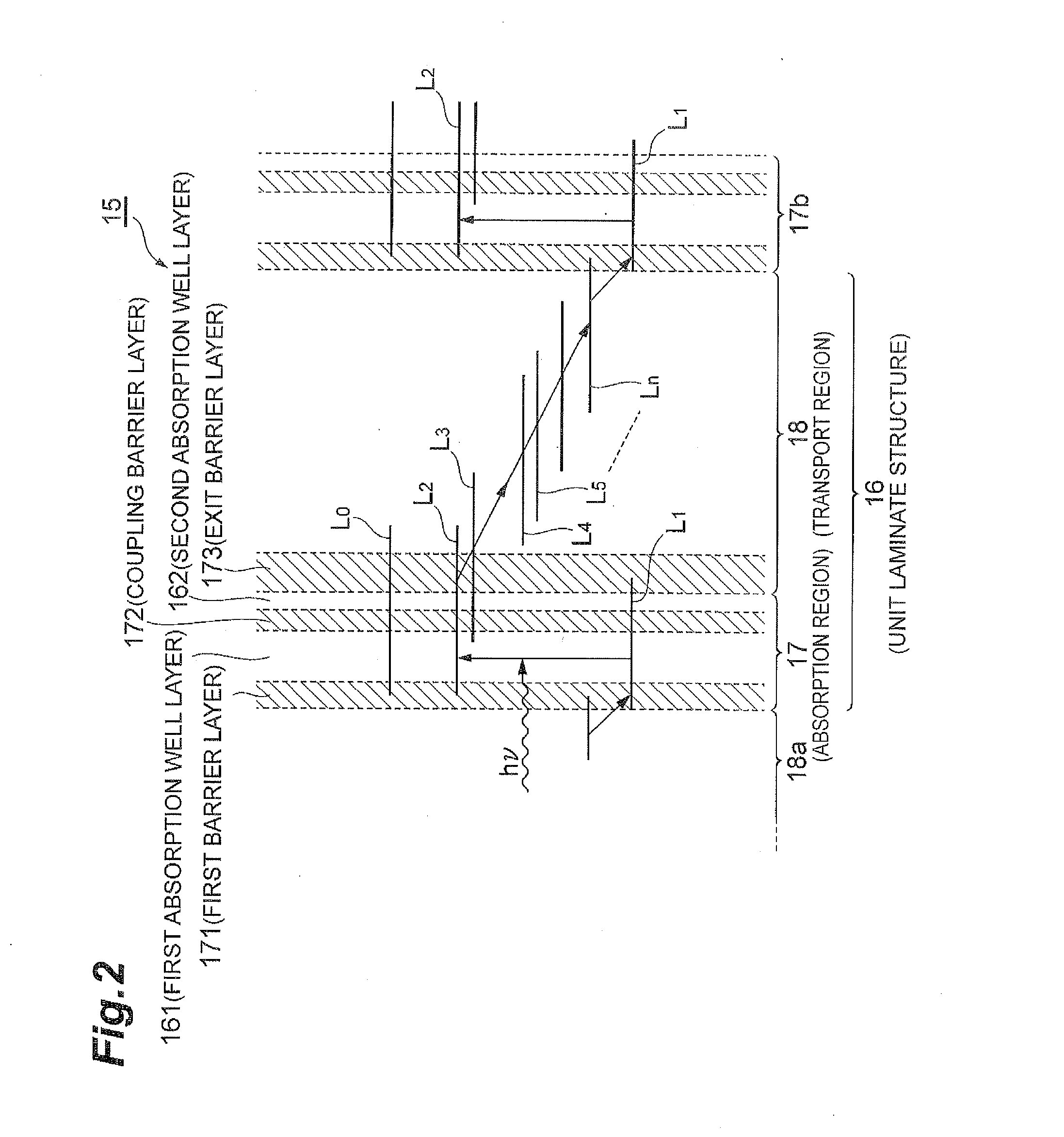
A quantum cascade detector includes a semiconductor substrate, and an active layer formed by laminating unit laminate structures each having an absorption region with a first barrier layer to a second well layer and a transport region with a third barrier layer to an n-th well layer. A second absorption well layer has a layer thickness ½ or less of that of a first absorption well layer thickest in one period, and a coupling barrier layer has a layer thickness smaller than that of an exit barrier layer thickest in one period. The unit laminate structure has a detection lower level arising from a ground level in the first well layer, a detection upper level generated by coupling an excitation level in the first well layer and a ground level in the second well layer, and a transport level structure for electrons.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Elimination of basal plane dislocations in post growth silicon carbide epitaxial layers by high temperature annealing while preserving surface morphology
ActiveUS9129799B2Improve carrier lifetimeImprove activation/incorporationPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsNitrogenGraphite
A method to remove basal plane dislocations in post growth silicon carbide epitaxial layers by capping post growth silicon carbide epilayers with a graphite cap and annealing the capped silicon carbon epilayers at a temperature of 1750° C. or greater with a nitrogen overpressure of 60-110 psi, wherein basal plane dislocations in the epilayers are removed while surface morphology is preserved. Also disclosed is the related silicon carbide substrate material made by this method.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Low phonon energy gain medium and related active devices
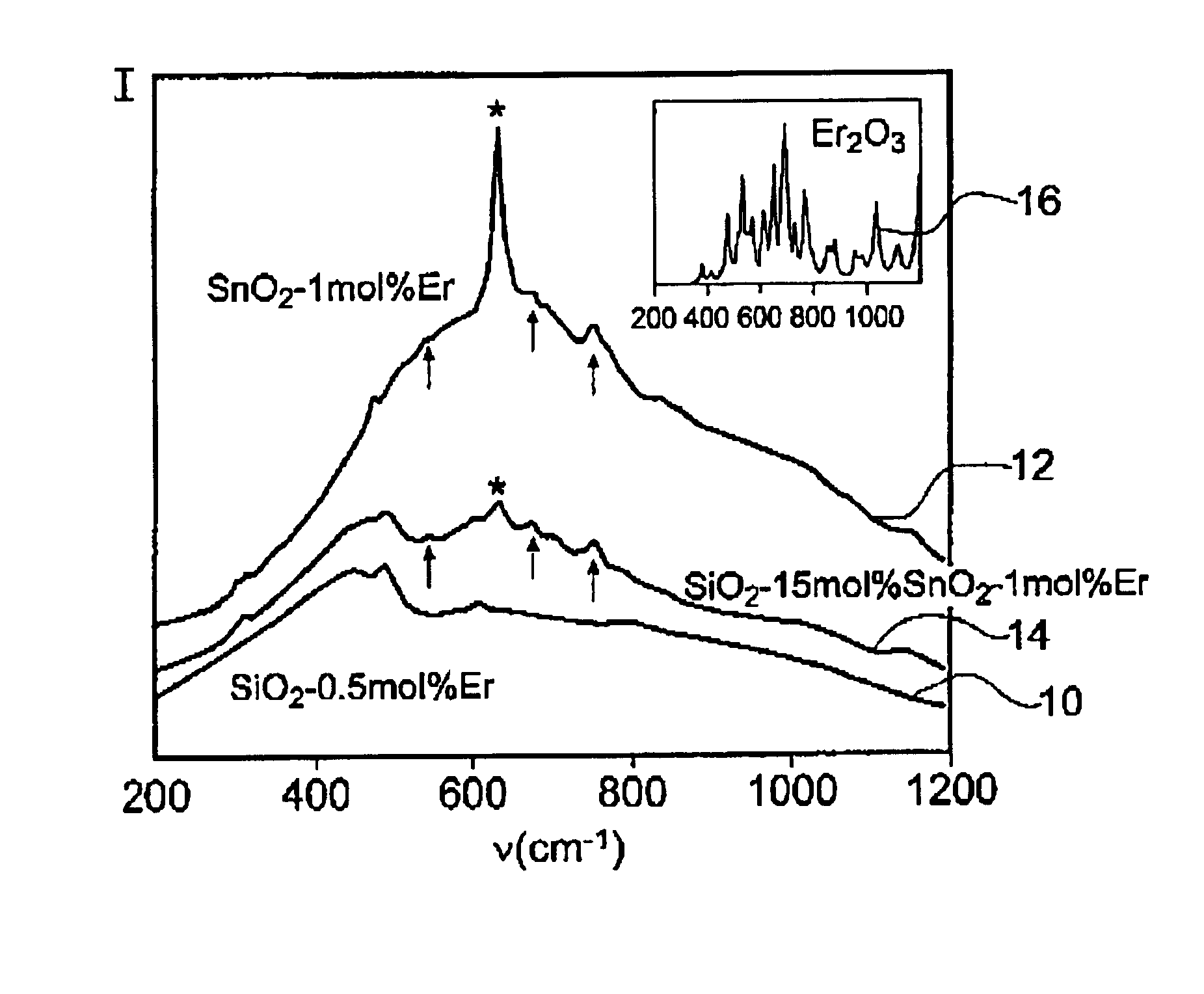
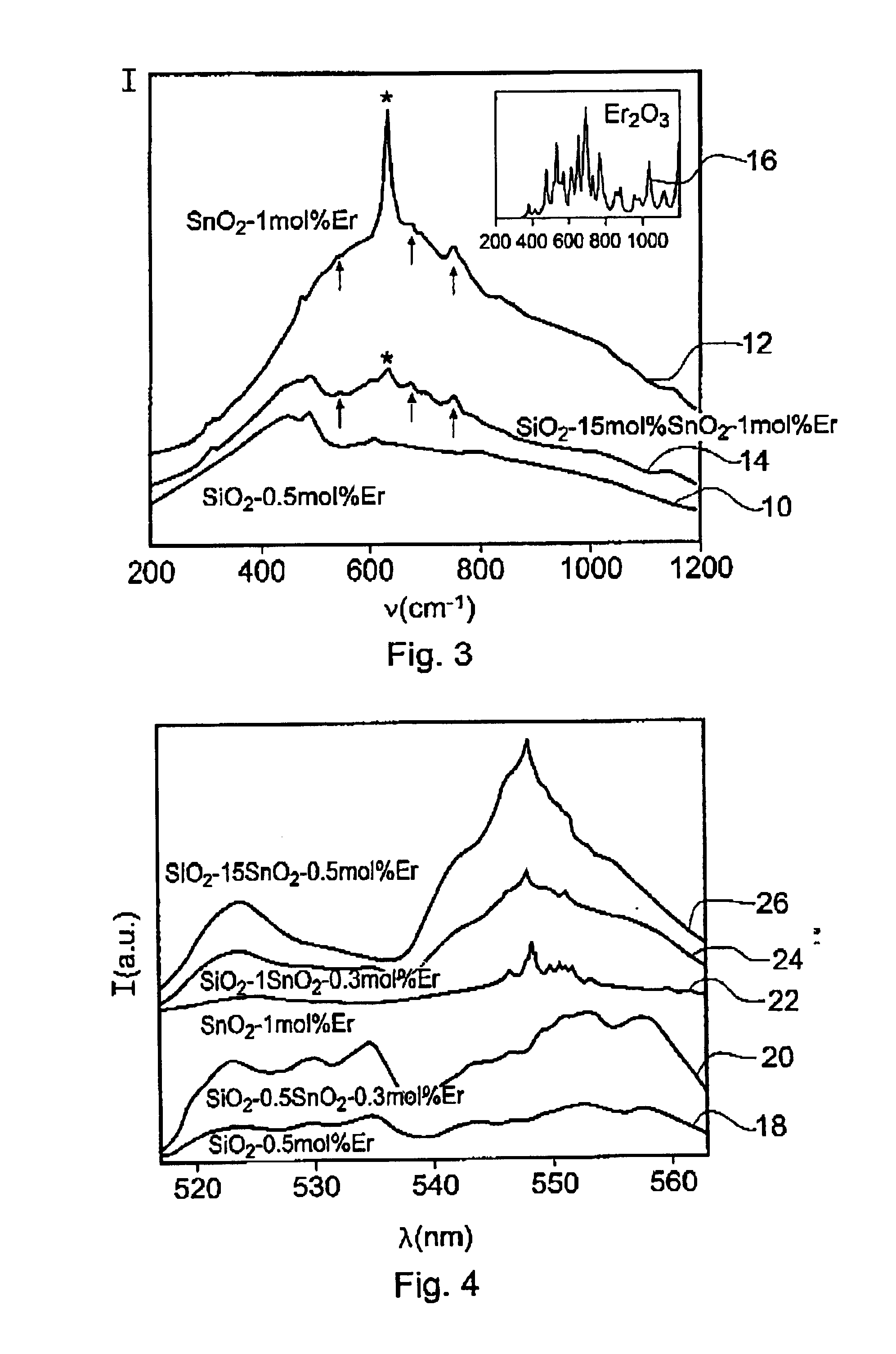
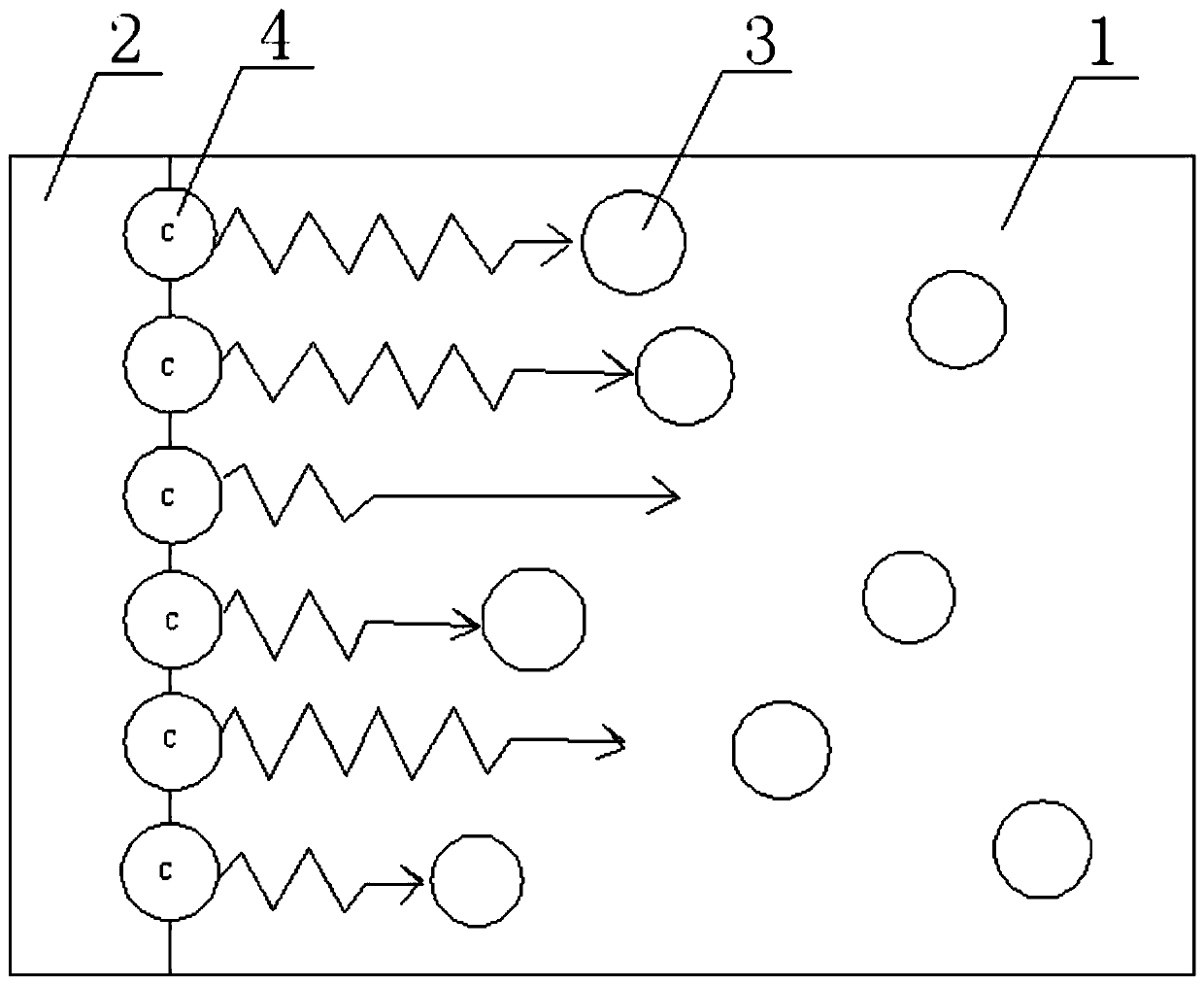
InactiveUS7003981B2Improve carrier lifetimeHigh energyGlass furnace apparatusOptical filtersCrystalline oxideSilicon dioxide
Using sol-gel techniques, an optical gain medium has been fabricated comprising a glass ceramic host material that includes clusters of crystalline oxide material, especially tin oxide, and that is doped with active ions concentrated at the clusters. The active ions are preferentially located at the nanoclusters so that they experience the relatively low phonon energy of the oxide and are insensitive to the phonon energy of the host. A host with a high phonon energy, such as silica, can therefore be used without the usual drawback of reduced carrier lifetimes through enhanced nonradiative decay rates.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Elimination of basal plane dislocations in post growth silicon carbide epitaxial layers by high temperature annealing while preserving surface morphology
ActiveUS20150155166A1Improve carrier lifetimeImprove activation/incorporationPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsNitrogenGraphite
A method to remove basal plane dislocations in post growth silicon carbide epitaxial layers by capping post growth silicon carbide epilayers with a graphite cap and annealing the capped silicon carbon epilayers at a temperature of 1750° C. or greater with a nitrogen overpressure of 60-110 psi, wherein basal plane dislocations in the epilayers are removed while surface morphology is preserved. Also disclosed is the related silicon carbide substrate material made by this method.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
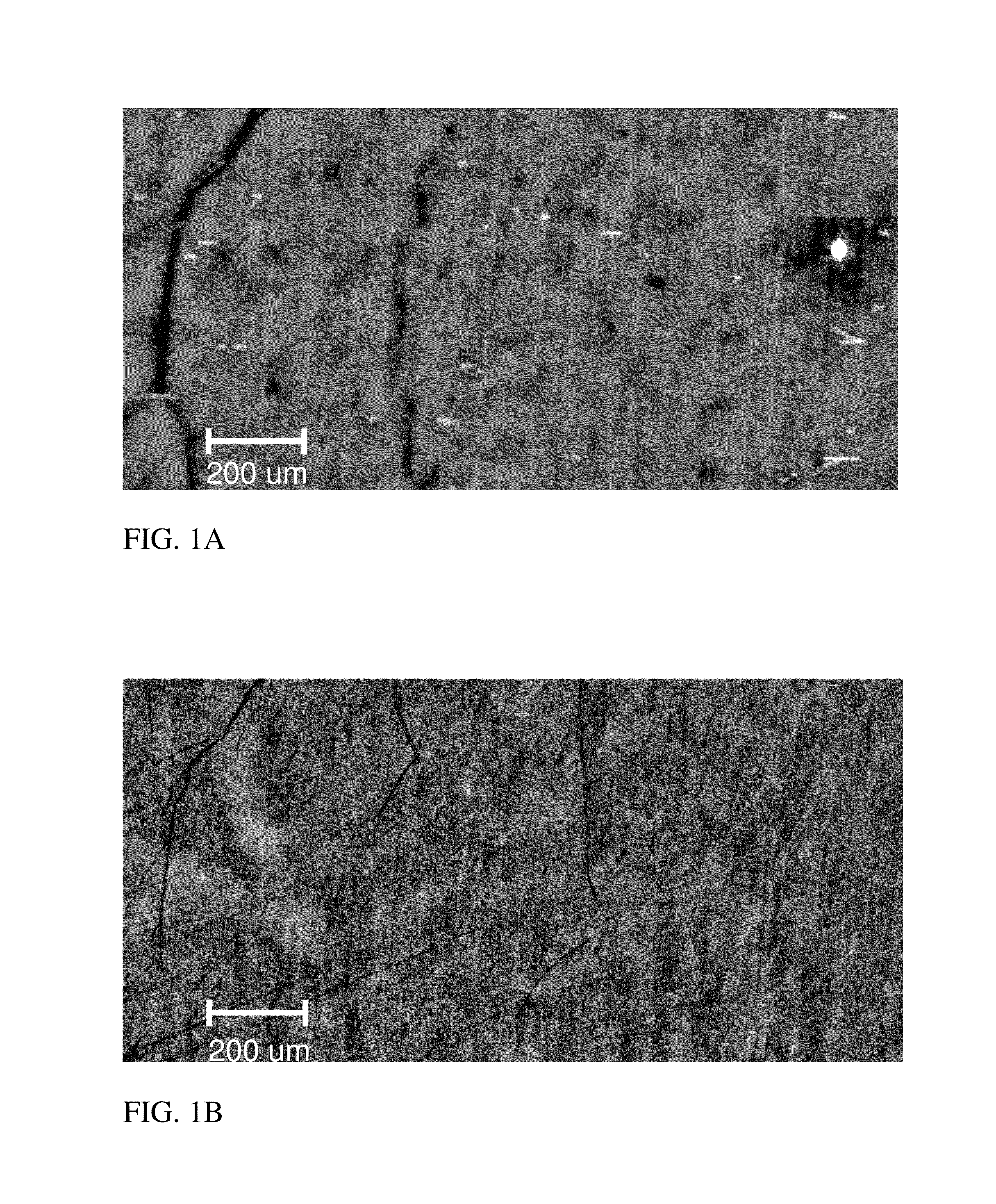
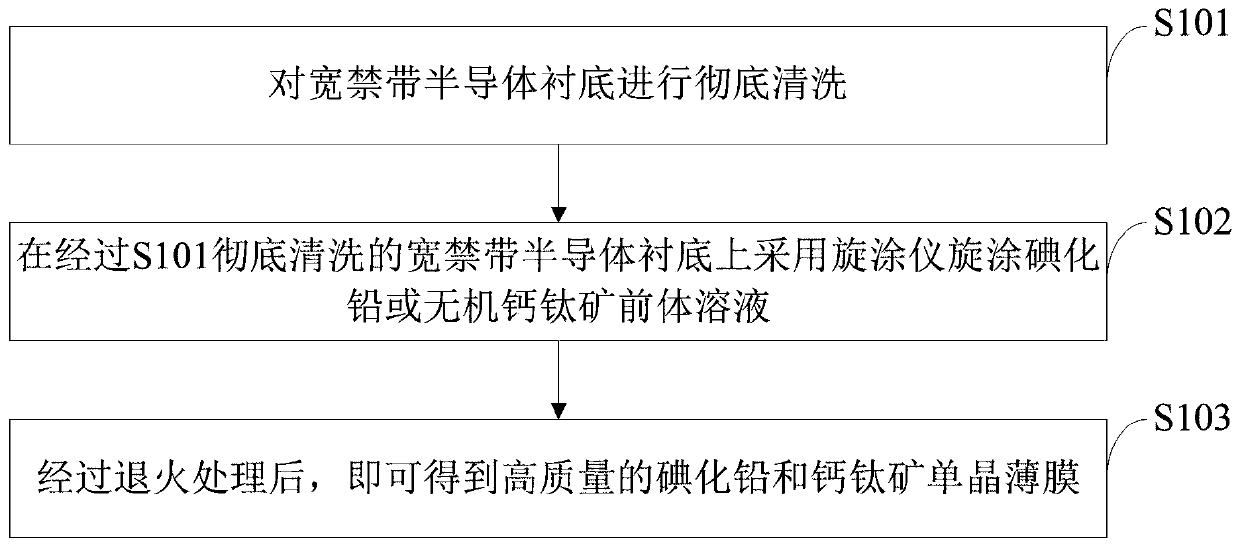
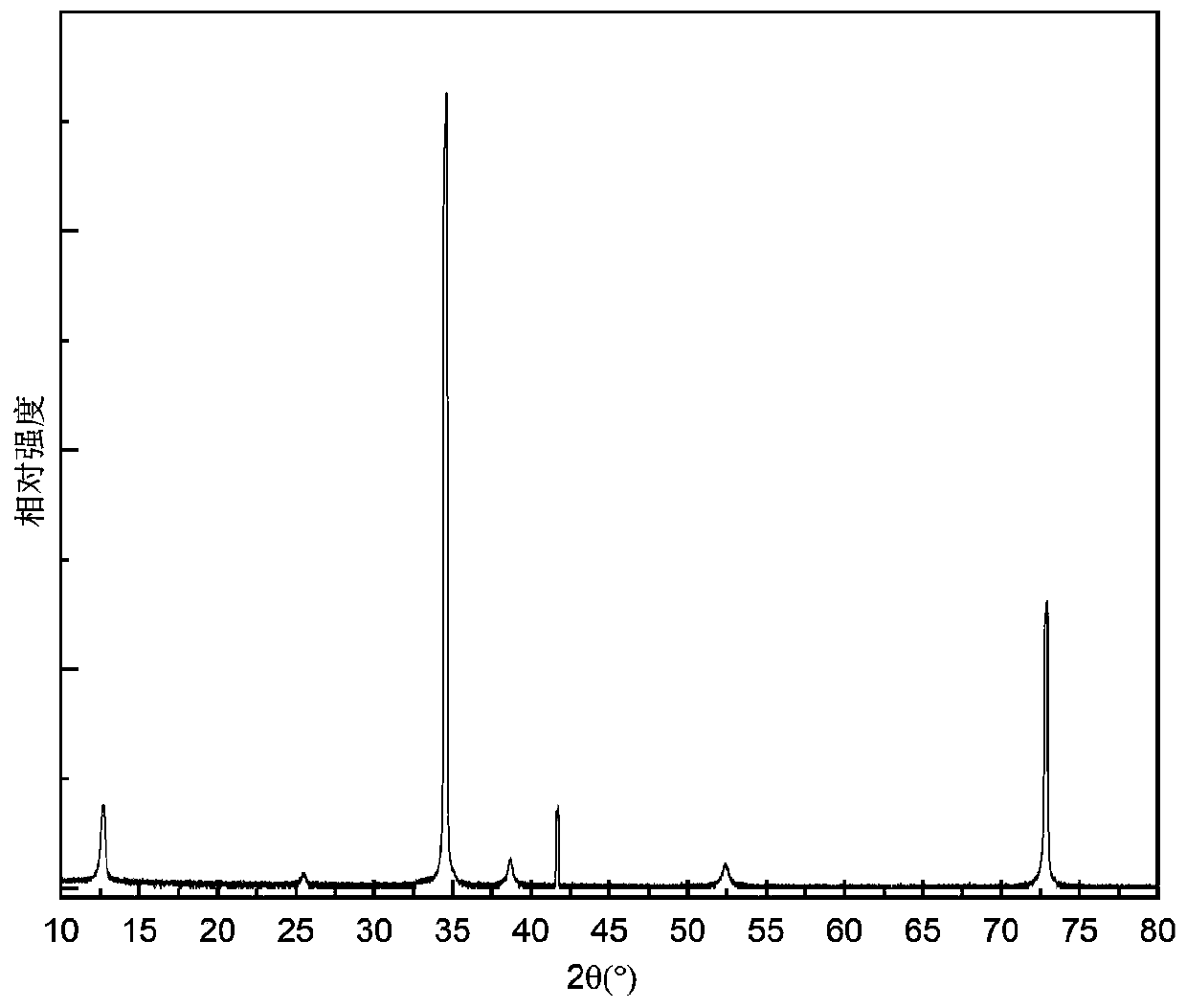
Growth method for spin-coating single crystal on wide bandgap semiconductor substrate
PendingCN111235635AQuality improvementImprove crystal qualityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthUltravioletSingle crystal
The invention belongs to the technical field of perovskite solar cells, photoelectric detectors and wide bandgap semiconductor photoelectric materials and devices, and discloses a growth method for spin-coating single crystal on a wide bandgap semiconductor substrate. The growth method comprises the following steps: respectively cleaning the wide bandgap semiconductor substrate for 30 minutes by using isopropanol, ethanol and deionized water in an ultrasonic cleaning machine, treating the substrate for 15 minutes by using ultraviolet ozone, and thoroughly cleaning the wide bandgap semiconductor substrate; spin-coating lead iodide or an inorganic perovskite precursor solution on the thoroughly cleaned wide bandgap semiconductor substrate by using a spin coater; and carrying out annealing treatment to obtain the high-quality lead iodide and perovskite single crystal film. The invention discloses a technology for growing a high-quality lead iodide and perovskite single crystal thin film by adopting a spin-coating process. By optimizing the proportion of a precursor solution and the growth temperature of the film, lead iodide or a perovskite material grows on the wide bandgap semiconductor substrate by using the spin-coating process, and a high-quality epitaxial single crystal film is obtained and is applied to manufacturing of an efficient photoelectric detector or a solar cell.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
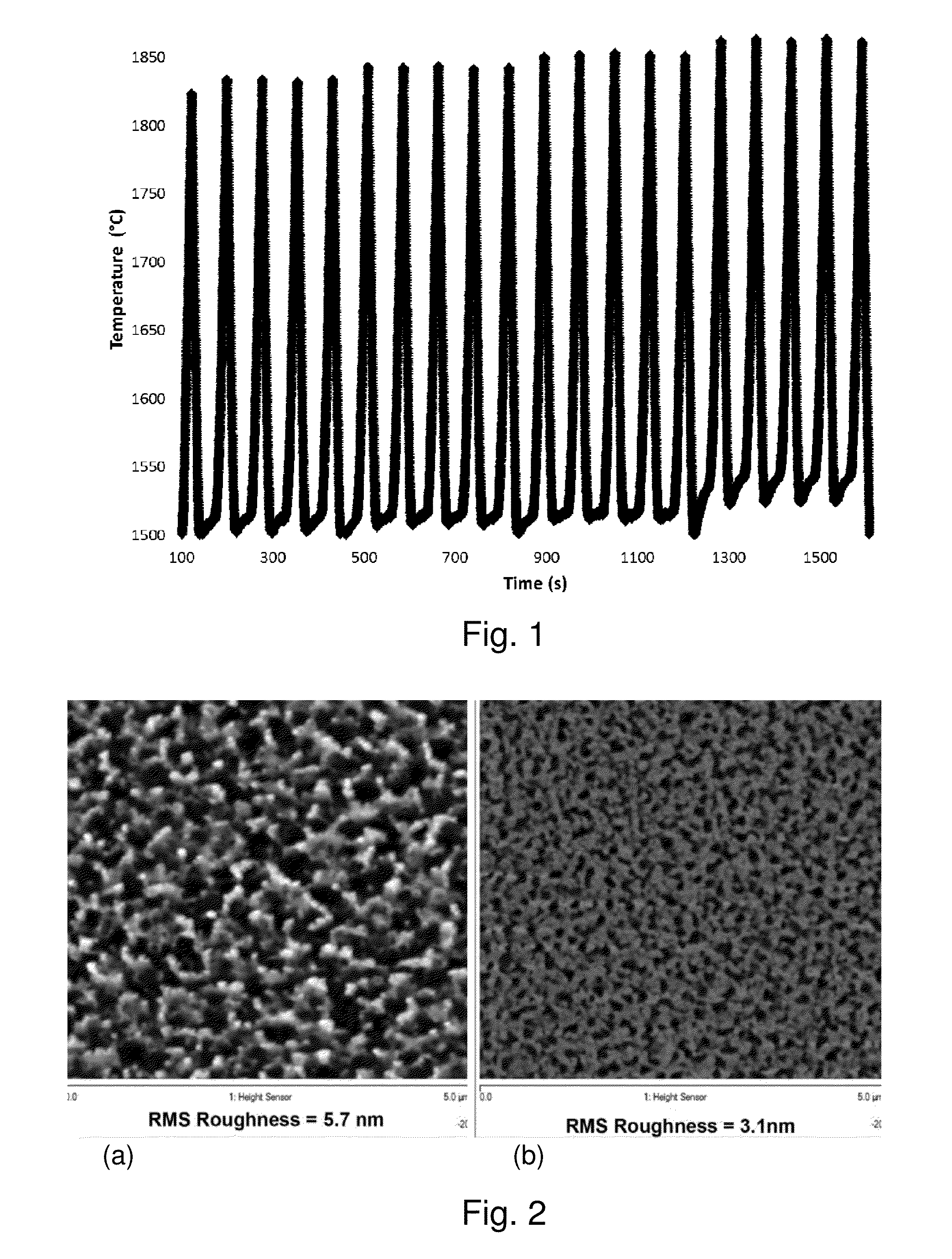
Basal plane dislocation elimination in 4h-sic by pulsed rapid thermal annealing
ActiveUS20150287613A1Reduce defectsEliminate misalignmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh pressureRapid thermal annealing
A method for removing existing basal plane dislocations (BPDs) from silicon carbide epilayers by using a pulsed rapid thermal annealing process where the BPDs in the epilayers were eliminated while preserving the epitaxial surface. This high temperature, high pressure method uses silicon carbide epitaxial layers with a carbon cap to protect the surface. These capped epilayers are subjected to a plurality of rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Method for prolonging service life of silicon carbide epitaxial wafer carrier
PendingCN114242566ASimple designInhibition formationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbide siliconGraphite
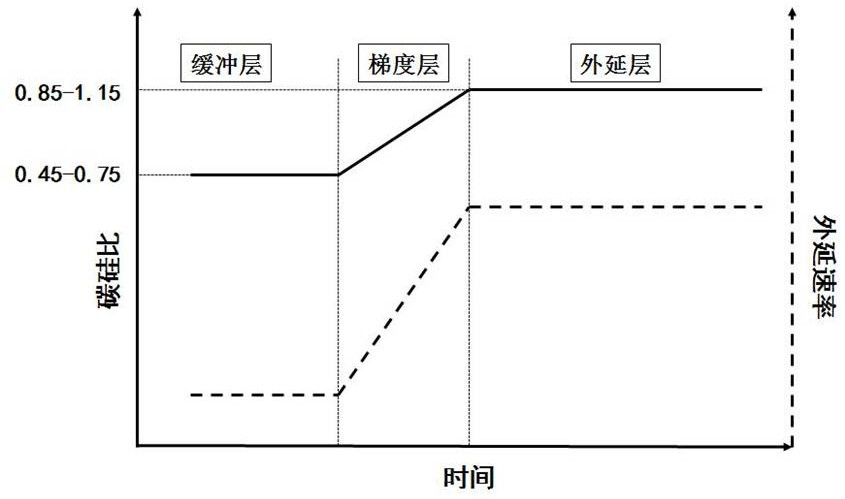
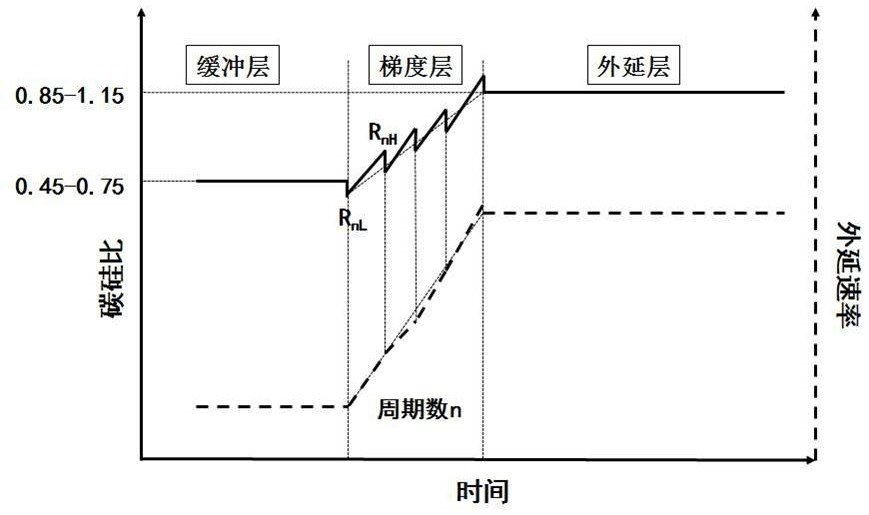
The invention provides a method for prolonging the service life of a silicon carbide epitaxial wafer carrier. The method comprises the following steps: S1, placing a silicon-surface silicon carbide substrate on a graphite base; s2, adjusting conditions in the reaction chamber and growing a buffer layer; s3, the growth temperature and pressure are kept unchanged, the C / Si ratio is reduced, and then the C / Si ratio is increased in a linear gradual change mode for first-time growth; s4, keeping the growth temperature and pressure unchanged, and continuing n times of rate switching gradient layer growth; s5, conditions in the reaction chamber are adjusted, and growth of an epitaxial layer is completed; s6, after epitaxial layer growth is completed, the growth source and the doping source are closed, finally, argon is used for inflating the pressure of the reaction chamber to atmospheric pressure, and then the chamber is opened to take the wafer. According to the invention, the gradient layer design is optimized by adopting the method of growing the plating layer in a stepped manner, the purposes of compensating the carbon vacancy generated by the buffer layer and inhibiting the formation of the carbon vacancy of the gradient layer are achieved, and the carrier lifetime of the silicon carbide epitaxial wafer is greatly prolonged.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Photovoltaic nanocomposite comprising solution processed inorganic bulk nano-heterojunctions, solar cell and photodiode devices comprising the nanocomposite
ActiveUS9349888B2Improve carrier lifetimeEfficient separationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
Photovoltaic nanocomposite and solar cell device including the photovoltaic nanocomposite, where the photovoltaic nanocomposite includes a film of solution processed semiconductor materials having an n-type material selected from n-type quantum dots and n-type nanocrystals, and a p-type material selected from p-type quantum dots and p-type nanocrystals, and where the n-type material has a conduction band level at least equal, compared to vacuum level, to that of the p-type material, the p-type material has a valence band at the most equal, compared to vacuum level, to that of the n-type material. at least a portion of the n-type material and at least a portion of the p-type material are present in a bulk nano-heterojunction binary nanocomposite layer having a blend of the n-type material and the p-type material.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE CIENCIES FOT NIQUES
Method for prolonging carrier lifetime of silicon carbide epitaxial wafer
PendingCN111146075AImprove carrier lifetimeEliminate carbon vacancy defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbide siliconSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor material manufacturing, and particularly discloses a method for prolonging the carrier lifetime of a silicon carbide epitaxial wafer. According to the method for prolonging the carrier lifetime of the silicon carbide epitaxial wafer, a carbon atom layer with the thickness of 100-2000 nm is deposited on the surface of the silicon carbideepitaxial wafer, and then annealing treatment is carried out. According to the method, the carrier lifetime of the silicon carbide epitaxial wafer is effectively prolonged, the operation is simple, the efficiency is high, the cost is low, and the popularization value is extremely high.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Low phonon energy gain medium and related active devices
InactiveUS20050213624A1Easy to controlImprove carrier lifetimeGlass shaping apparatusActive medium materialCrystalline oxideSilicon dioxide
Using sol-gel techniques, an optical gain medium has been fabricated comprising a glass ceramic host material that includes clusters of crystalline oxide material, especially tin oxide, and that is doped with active ions concentrated at the clusters. The active ions are preferentially located at the nanoclusters so that they experience the relatively low phonon energy of the oxide and are insensitive to the phonon energy of the host. A host with a high phonon energy, such as silica, can therefore be used without the usual drawback of reduced carrier lifetimes through enhanced nonradiative decay rates.
Owner:UNIV OF HIGHFIELD
Method for annealing photovoltaic cells
ActiveUS7935562B2Improve photovoltaic conversion efficiencyImprove carrier lifetimeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenAmbient pressure
Method for annealing at least one photovoltaic cell comprising a substrate based on silicon with a first type of conductivity, a layer doped with a second type of conductivity produced in the substrate and forming a front face of the substrate, an antireflection layer produced on the front face of the substrate and forming a front face of the photovoltaic cell, at least one metallization on the front face of the cell and at least on metallization on a rear face of the substrate. This method comprises at least the steps of:a) a first annealing of the photovoltaic cell at a temperature between around 700° C. and 900° C.,b) a second annealing of the photovoltaic cell at a temperature between around 200° C. and 500° C., at ambient pressure and in ambient air,with hydrogen being diffused in the substrate during the process.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
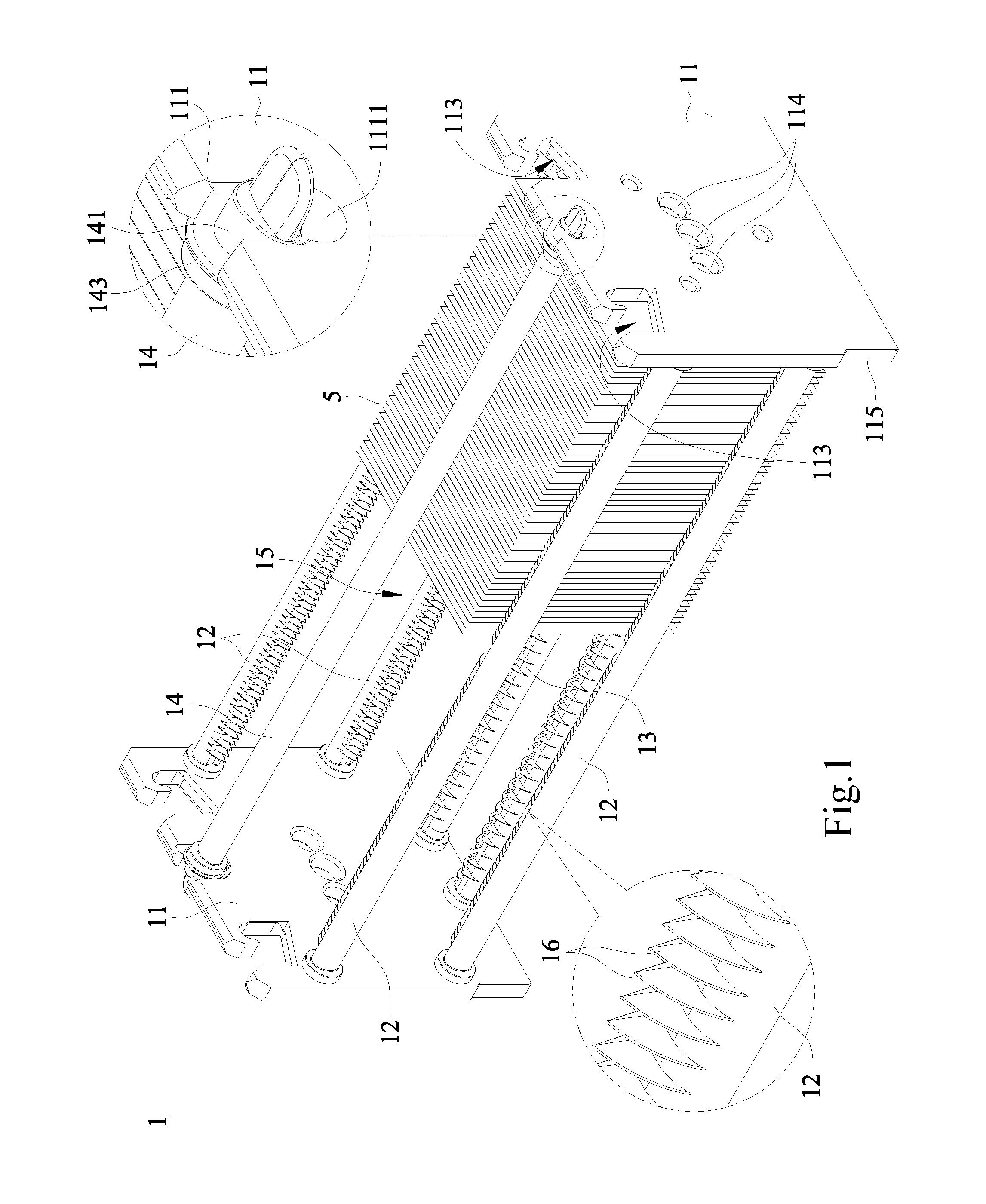
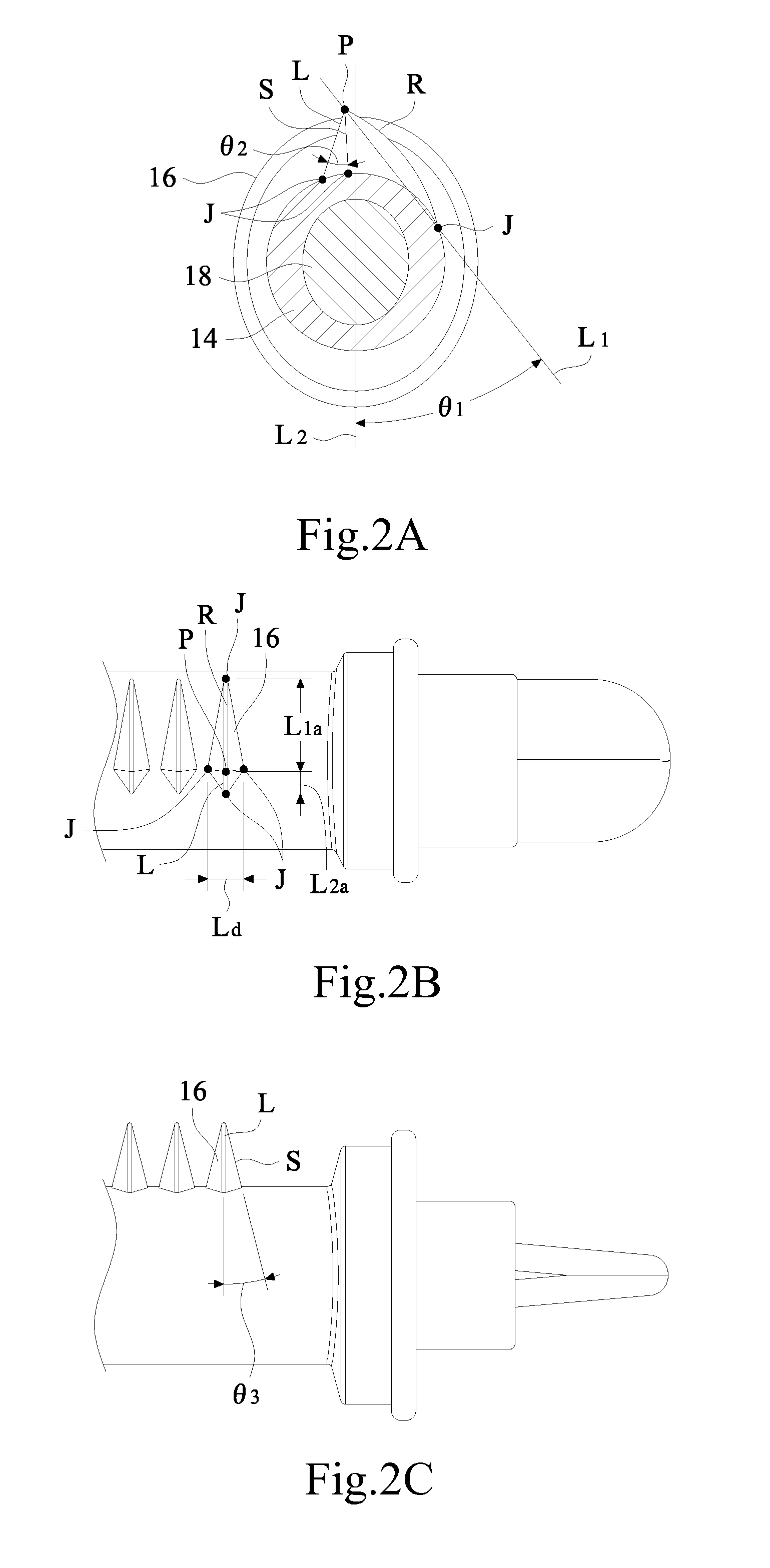
Light source heat-dissipation structure of backlight module
InactiveUS20120250288A1Improve efficiencyEnhancing lifetimeLighting heating/cooling arrangementsIlluminated signsEngineeringSupport surface
The present invention provides a light source heat-dissipation structure of a backlight module having: a light-source structure, the heat-dissipation base and a carrier. The light-source structure has leads, respectively. The heat-dissipation base has a supporting surface, an attachment surface and first through holes. The carrier has second through holes, and the carrier is attached to the attachment surface of the heat-dissipation base. The light-source structure is set on the supporting surface of the heat-dissipation base, and the leads of the light-source structure pass through the first through holes and the second through holes and then electrically connect with the carrier. Hence, the heat-dissipation base may directly support and thermally contact the light-source structure for relatively enhancing the heat-dissipation efficiency of the light-source structure.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Double-amino organic compound passivation material and application thereof
ActiveCN111892504APassivated charged defectsGood control effectOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsCrystallinity
The invention provides a double-amino organic compound passivation material. The double-amino organic compound passivation material comprises an alkyl chain segment, aromatic hydrocarbon or heterocyclic compound, wherein the alkyl chain segment, aromatic hydrocarbon or heterocyclic compound comprises at least two functional groups A, and the functional groups A are amino groups. According to the double-amino organic compound passivation material provided by the invention, two amino groups in the molecule of the material can form hydrogen bonds with halogen ions in perovskite, so the crystallinity of a perovskite thin film is enhanced, the service life of a carrier is prolonged, and perovskite defects are passivated. The material has good application potential in the field of photoelectricdevices.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for prolonging minority carrier lifetime of silicon carbide epitaxial material
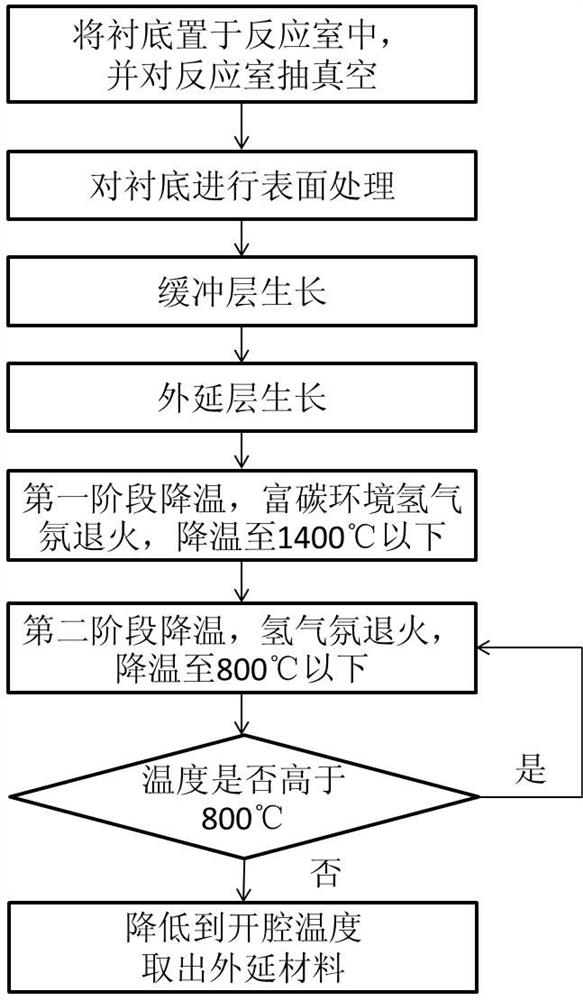
PendingCN114334609AThe process is simpleImprove carrier lifetimePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsCarbide silicon
The invention provides a method for prolonging the minority carrier lifetime of a silicon carbide epitaxial material, and the method comprises the steps: 1, placing a SiC substrate in a reaction chamber, and carrying out the vacuum pumping; 2, introducing hydrogen into the reaction chamber, and introducing a carbon source, a silicon source and a doping source for surface treatment; 3, a carbon source, a silicon source and a doping source are introduced into the reaction chamber for growth of a buffer layer; 4, epitaxial layer growth and epitaxial layer doping are carried out; step 5, first-stage cooling: closing the silicon source and the doping source, performing hydrogen atmosphere annealing treatment, and closing the carbon source after annealing is finished; 6, second-stage cooling is conducted, specifically, hydrogen atmosphere annealing treatment is conducted; seventhly, the sixth step is repeated for multiple times till the temperature requirement is met; and 8, reducing the cavity opening temperature, opening the reaction chamber, and taking out the silicon carbide epitaxial material. The method provided by the invention is simple in process and suitable for industrial production; the service life of a carrier is prolonged to the maximum extent, and damage to the surface of the material due to long-time high-temperature annealing can be avoided.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Passivation film, coating material, solar-cell element, and silicon substrate with passivation film attached thereto
InactiveCN104471716AImprove carrier lifetimeFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical batteryEngineering
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Method for passivating perovskite thin film layer and perovskite solar cell
PendingCN112467038AImprove stabilityReduce the density of defect statesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfonatePerovskite solar cell
The invention provides a method for passivating a perovskite thin film layer. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a perovskite precursor solution; pre-treating a substrate formed by conductive glass / electron transport layer; coatingthe substrate with the perovskite precursor solution and heating to generate a perovskite thin film layer; and further passivating and modifying the perovskite thin film layer by using fluorine-containing sulfonate to form the fluorine-containing sulfonate modified perovskite thin film layer. According to the method for passivating the perovskite thin film layer provided by the invention, the passivated perovskite thin film layer has excellent stability, low defect state density and long carrier lifetime, and the conversion efficiency and stability of a solar cell assembled by the perovskite thin film layer prepared by the method provided by the invention are obviously improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Semiconductor radiation detector based on bi-based quaternary halide single crystal and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20190019905A1Suitable bandgapImprove mobilitySemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor radiation detectors
The present invention discloses a semiconductor radiation detector based on Bi-based quaternary halide single crystal and a manufacturing method, and relates to the technical field of ray imaging detector manufactured by a semiconductor material. The semiconductor radiation detector in this example includes: a light absorption layer made of Bi-based quaternary halide single crystal; an electron selective contact layer and a hole selective contact layer respectively provided on upper and lower sides of the light absorption layer; and two electrodes which are respectively in contact with the two charge selective contact layers and used as positive and negative electrodes of the device. The semiconductor radiation detector in the present invention has advantages such as high sensitivity, good stability and environmental friendliness.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com