Rhizobium capable of efficiently solubilizing phosphorus and application of rhizobium
A rhizobia and phosphorus-resolving technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem that the phosphorus-resolving mechanism of bacteria is not completely clear.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Obtaining Phosphobacteria P1:
[0033] The culture medium formula involved in this embodiment is as follows:
[0034] Plate screening medium is: glucose 10g, tricalcium phosphate 5g, ammonium sulfate 0.5g, sodium chloride 0.3g, potassium chloride 0.3g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.3g, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.03g, manganese sulfate monohydrate 0.03g, 18g agar powder, 1L distilled water, pH7.0-7.2, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, set aside.
[0035]Shake flask re-screening medium is: glucose 10g, tricalcium phosphate 5g, magnesium chloride 5g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.25g, potassium chloride 0.2g, ammonium sulfate 0.1g, distilled water 1L, pH7.0-7.2, sterilized at 121°C Bacteria for 20 minutes, cool at 30-40°C for later use.
[0036] LB liquid medium: tryptone 10g, yeast extract powder 5g, NaCl 10g, distilled water 1L, pH7.0-7.2, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, cooled at 30-40°C for later use.
[0037] Primary screening of phosphate-solubiliz...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Identification of Phosphobacteria P1
[0045] 1) Colony morphological characteristics of Phosphobacteria P1:
[0046] After cultured on LB medium at 28-32°C for 2-3 days, the colonies of the P1 strain were round, dot-shaped, with neat edges, moist and smooth surface, opaque, white, and raised in the center.
[0047] 2) Physiological and biochemical characteristics of Phosphobacteria P1:
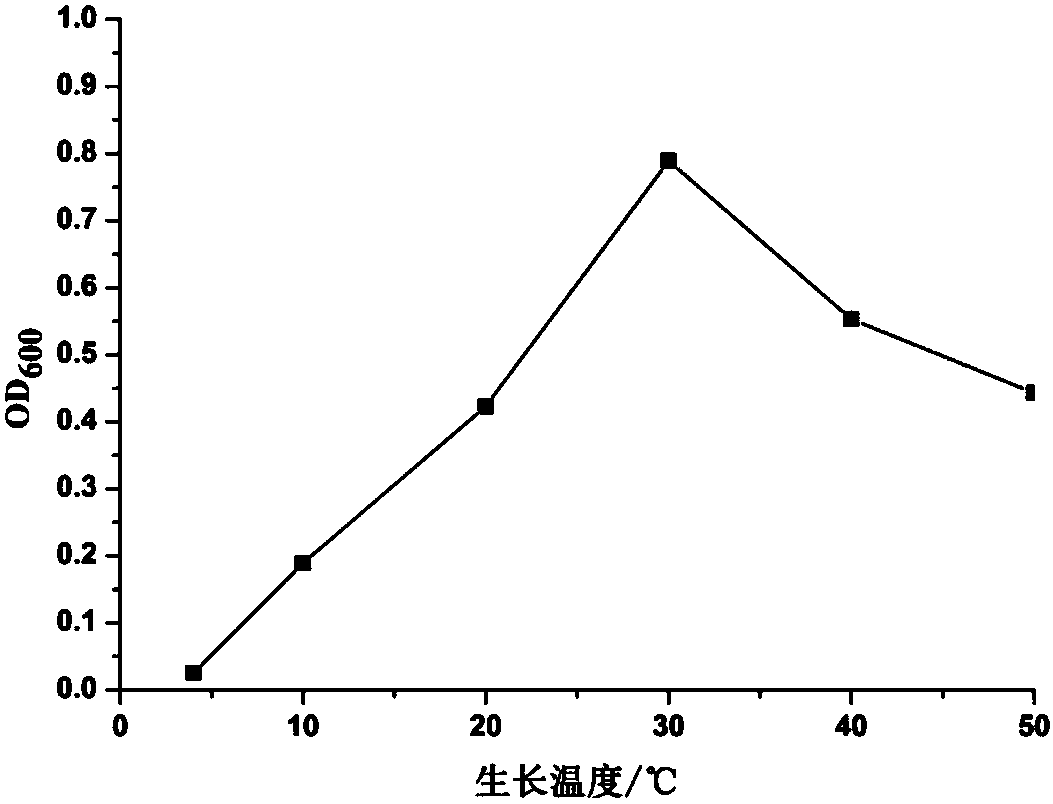
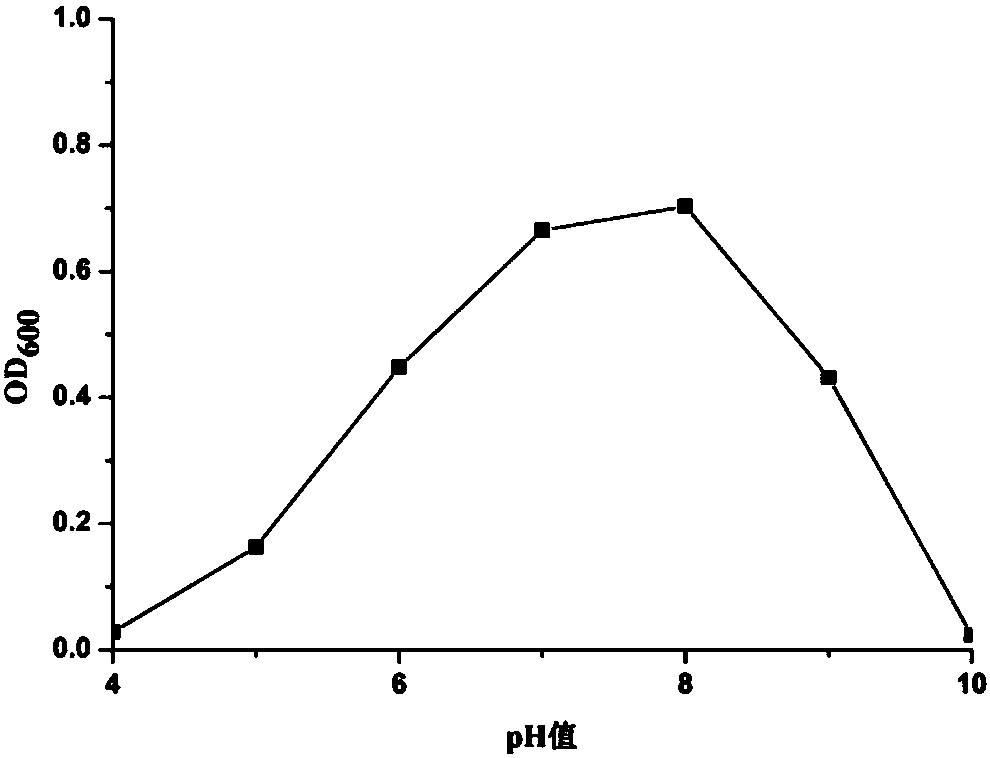
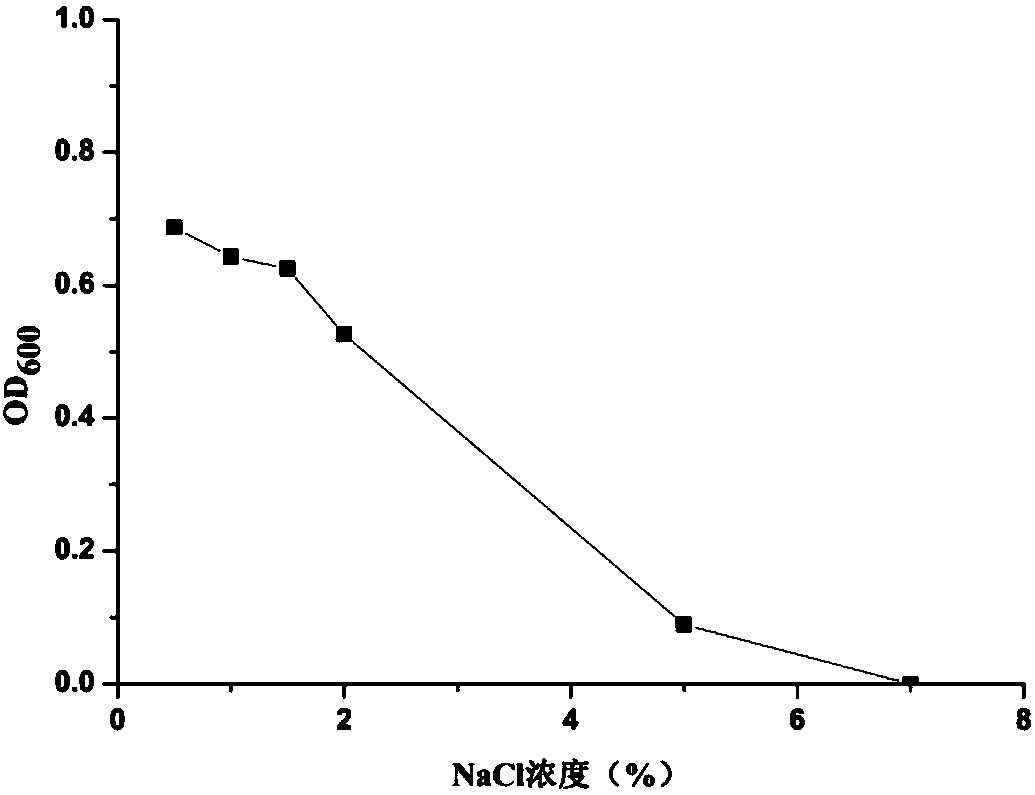
[0048] Phosphorus solubilizer P1 is a trophic, Gram-negative bacterium; it cannot utilize citrate and propionate, it can grow normally on a medium lower than 2% NaCl, and cannot grow on a medium higher than 5% NaCl; contact with enzymes Reaction, V-P reaction, oxidase reaction, glucose fermentation acid production, H2S production, nitrate reduction, motility test were positive; methyl red test, gelatin liquefaction and starch hydrolysis test were negative; glucose, arabinose and xylose could be utilized Sugar thrives and cannot utilize mannose.
[0049] 3) Molecular biological ident...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The fermentation method of Rhizobium sp.P-1, comprising:
[0054] 1) Preparation of seed medium
[0055] Tryptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, NaCl 10g, water 1L, pH 7.2-7.5, sterilize at 121°C for 20-40 minutes, cool at 30-40°C for later use;
[0056] 2) Preparation of fermentation medium
[0057] The components of the fermentation medium are: glucose 1.5%, soybean flour 1%, corn flour 0.5%, peptone 0.5%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.05%, magnesium sulfate 0.03%, manganese sulfate 0.002%, ferrous sulfate 0.002%, all of the above is the mass ratio, pH 8.0, sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes, cooled at 30-40°C for later use;
[0058] 3) Seed expansion and cultivation
[0059] Take the lawn of 1-2 rings of Rhizobium P1 from the slope, inoculate it into 50ml of sterilized seed culture medium, place it on a shaker at 30°C with a rotation speed of 200r / min for 22h, and use it as a fermented seed solution for later use;
[0060] 4) Preparation of Rhizobium P1
[0061] Put ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com