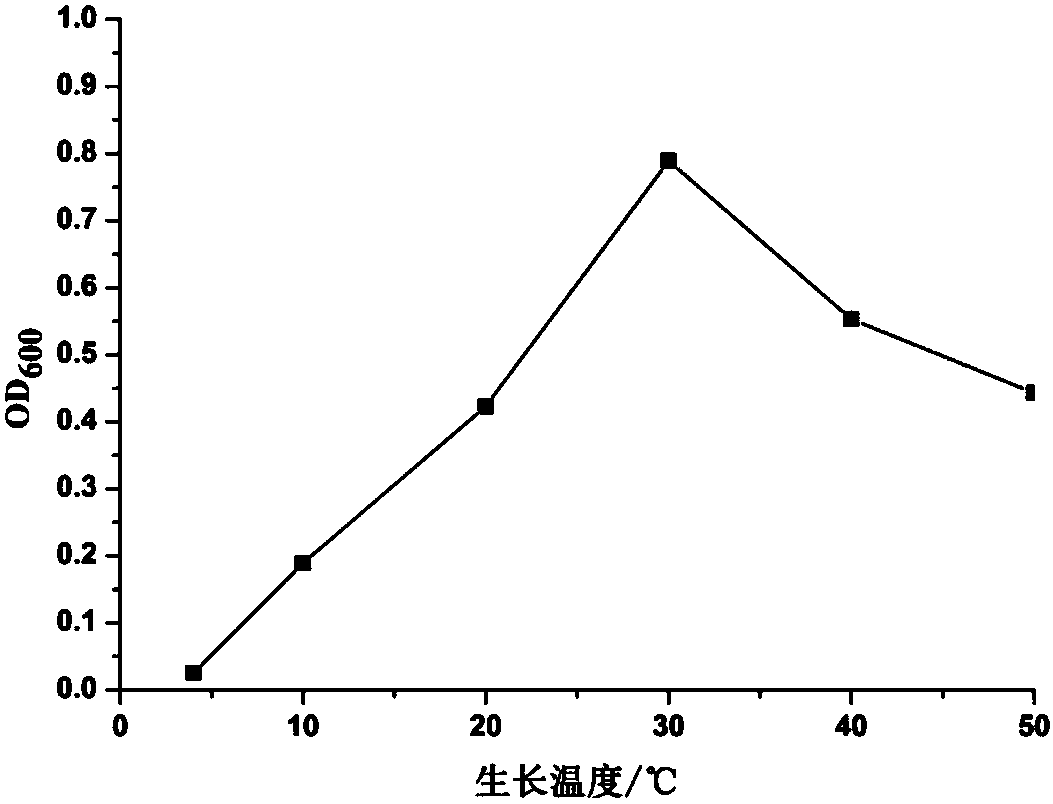
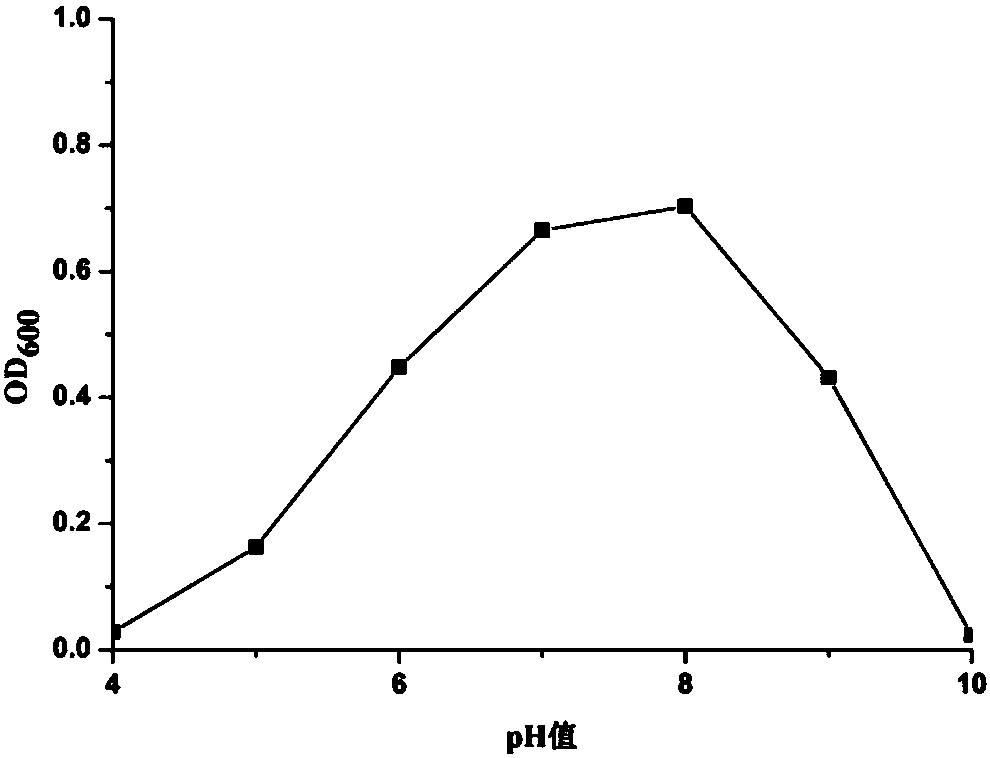
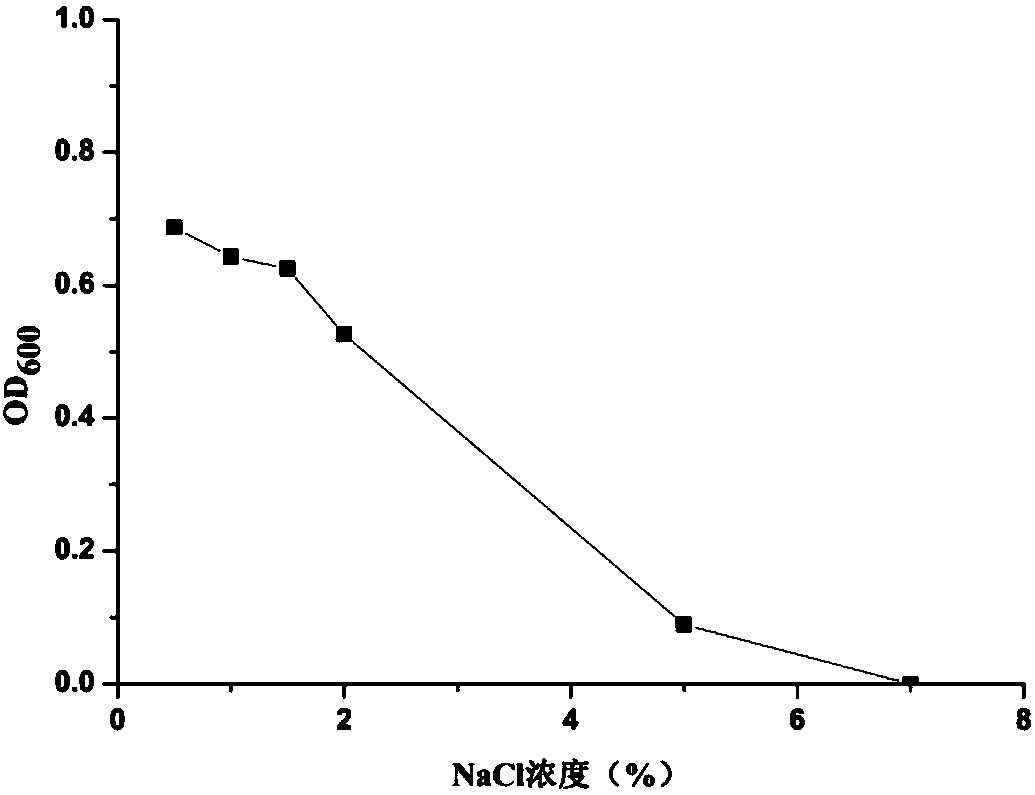
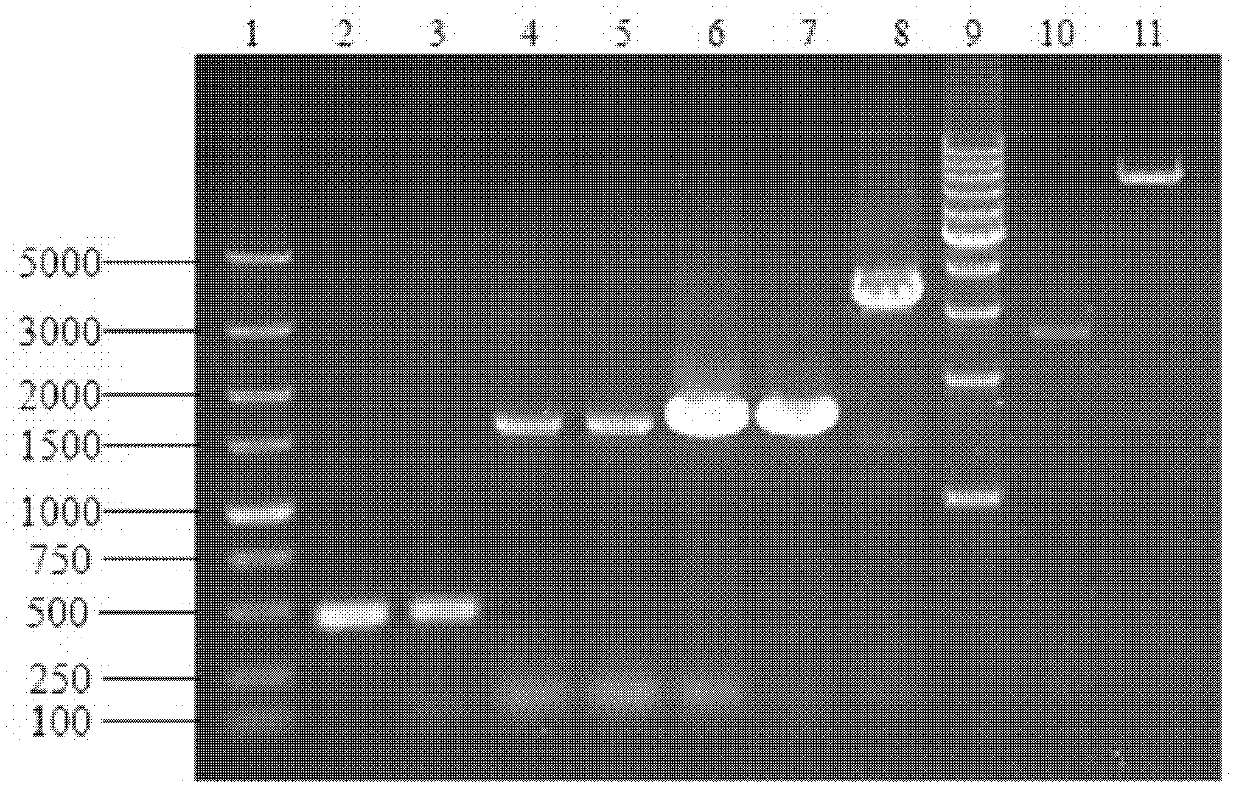
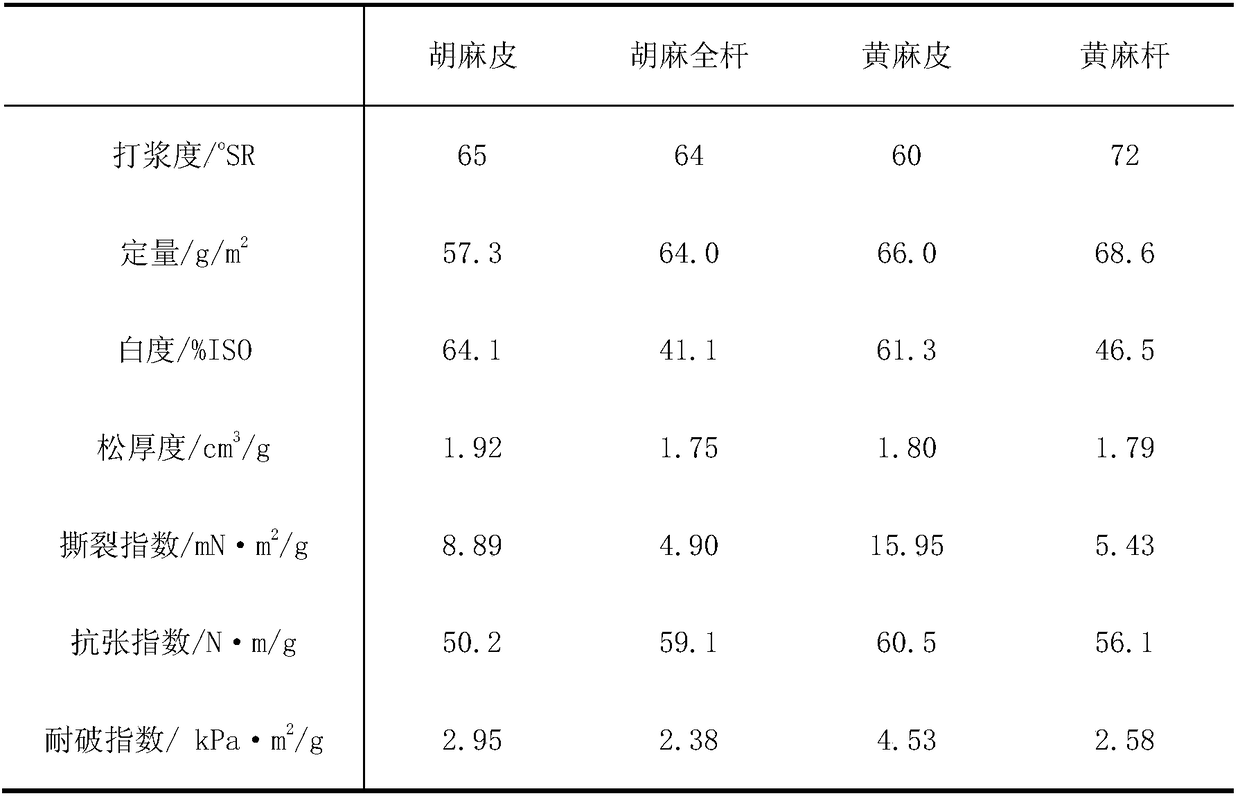
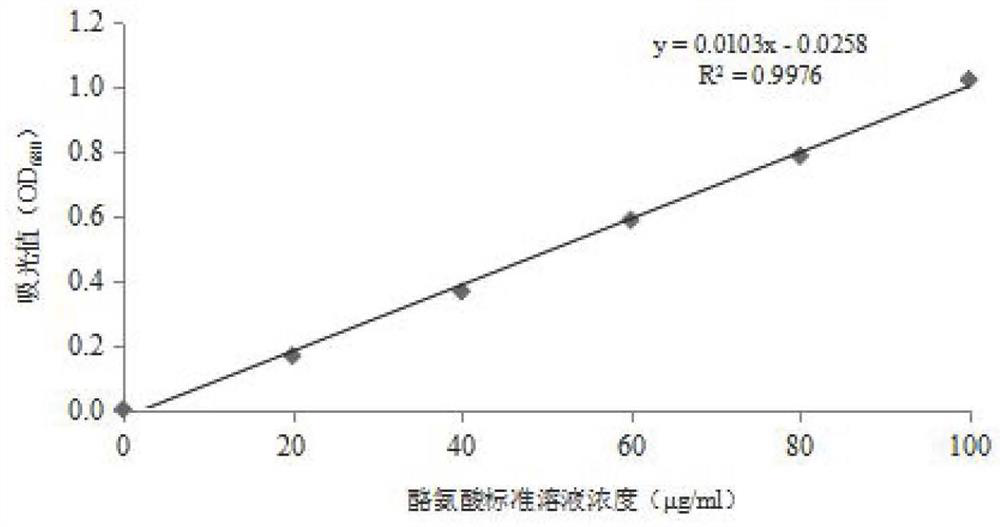
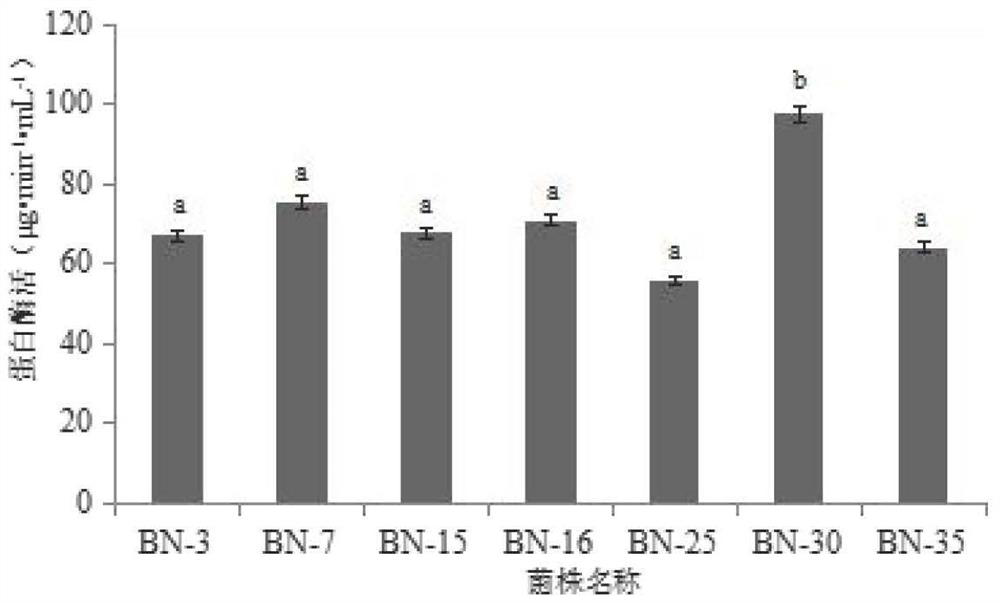
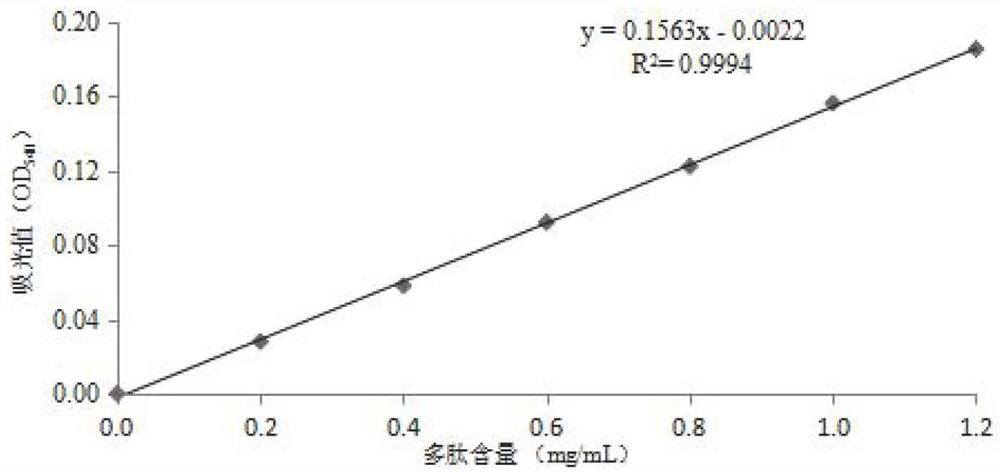
Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Excellent strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
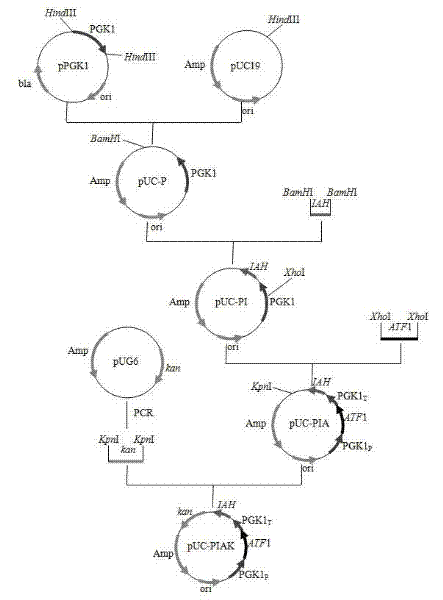
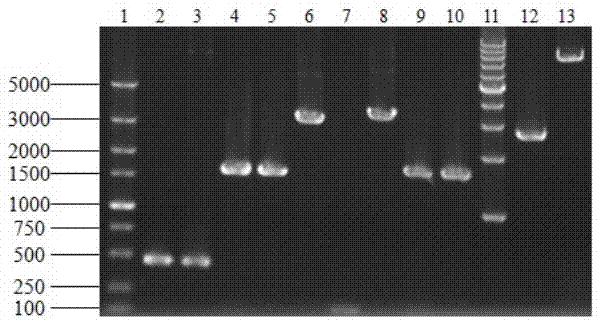
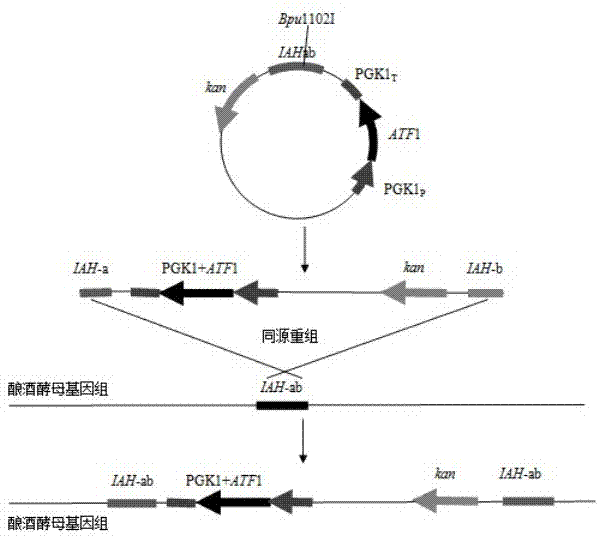
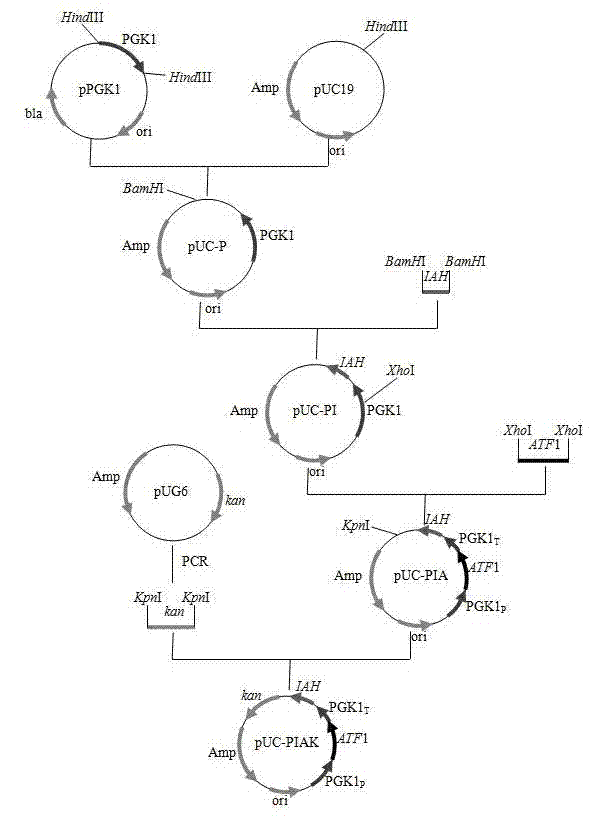
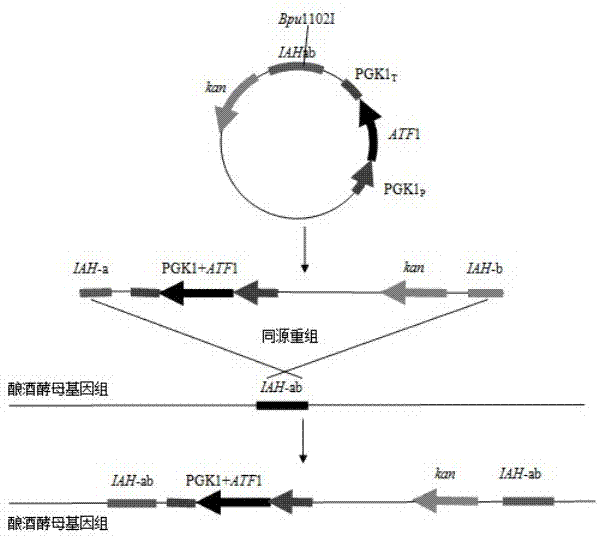
Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102199556AReduce contentIncrease contentFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationEster hydrolaseGenetic engineering
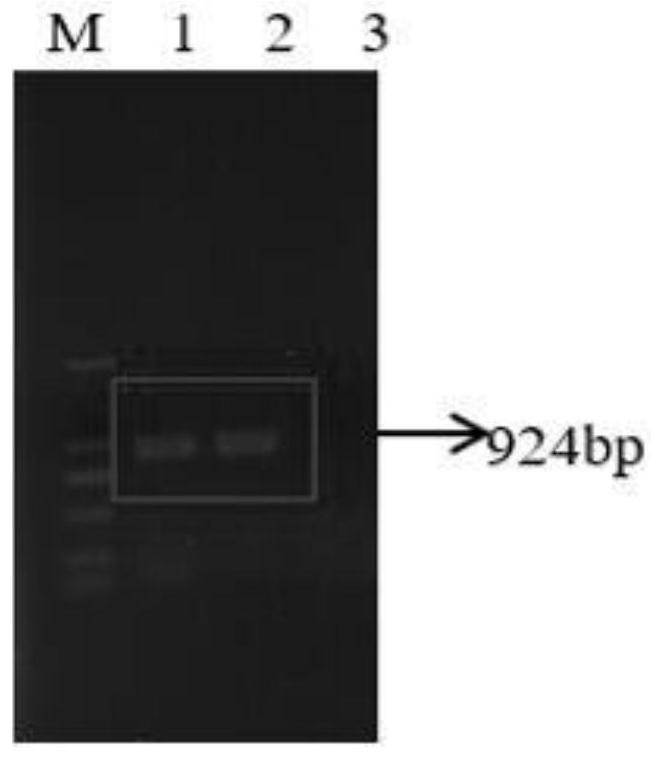
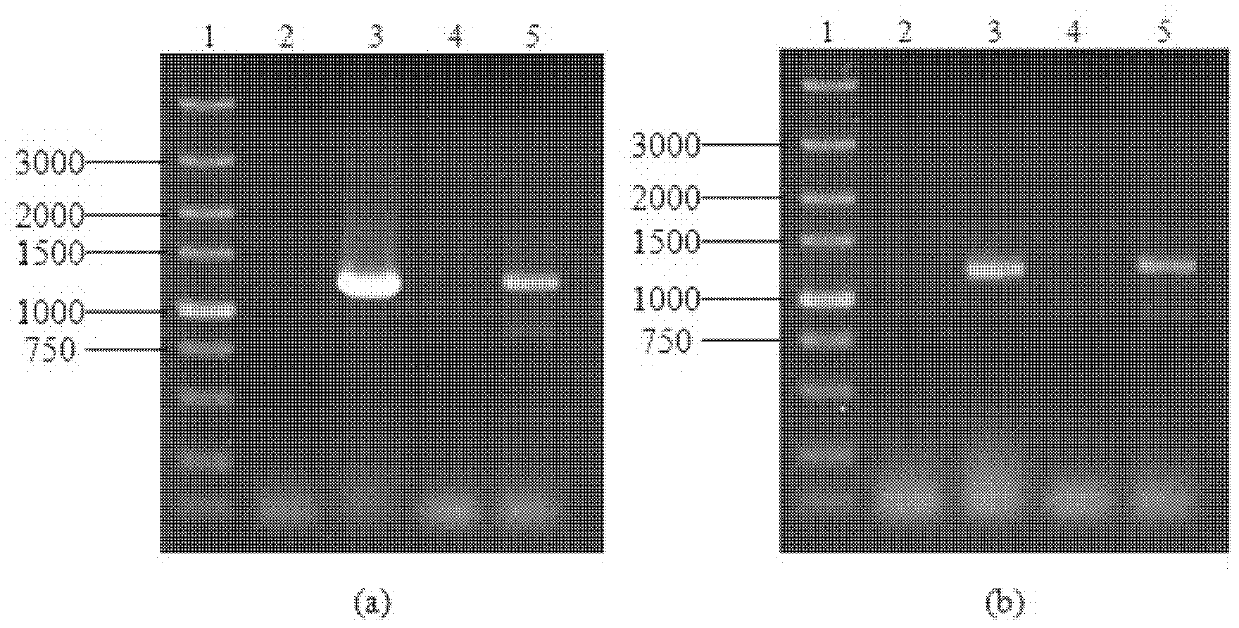
The invention discloses Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria EY-13 were collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 17, 2010, the collection number is CGMCC NO.4350, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria are recommended to be named Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PGK1 derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae is selected as a promoter; and the construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with the high esteryield comprises a step of knocking-out an IAH1 gene for encoding ester hydrolase in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome when an ATF1 gene which is derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is used for encoding alcohol acetyltransferase is overexpressed. Compared with initial recipient bacteria, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria have the advantages that: after rice wine fermentation is simulated, the content of isoamylol is about one half, the content of ethyl acetate is improved by 20 times, the content of isoamyl acetate is 100mg / L, and the content of isobutyl acetate is 5 to 7mg / L; and after liquor fermentation is simulated, the content of total esters is improved by 4 times and the content of the ethyl acetate is improved by 35 times, so an excellent strain is provided for the production of brewing industry.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Industrial production method of cordyceps mushroom
InactiveCN101195806AMore innovationHigh technology contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiCordycepsBiotechnology
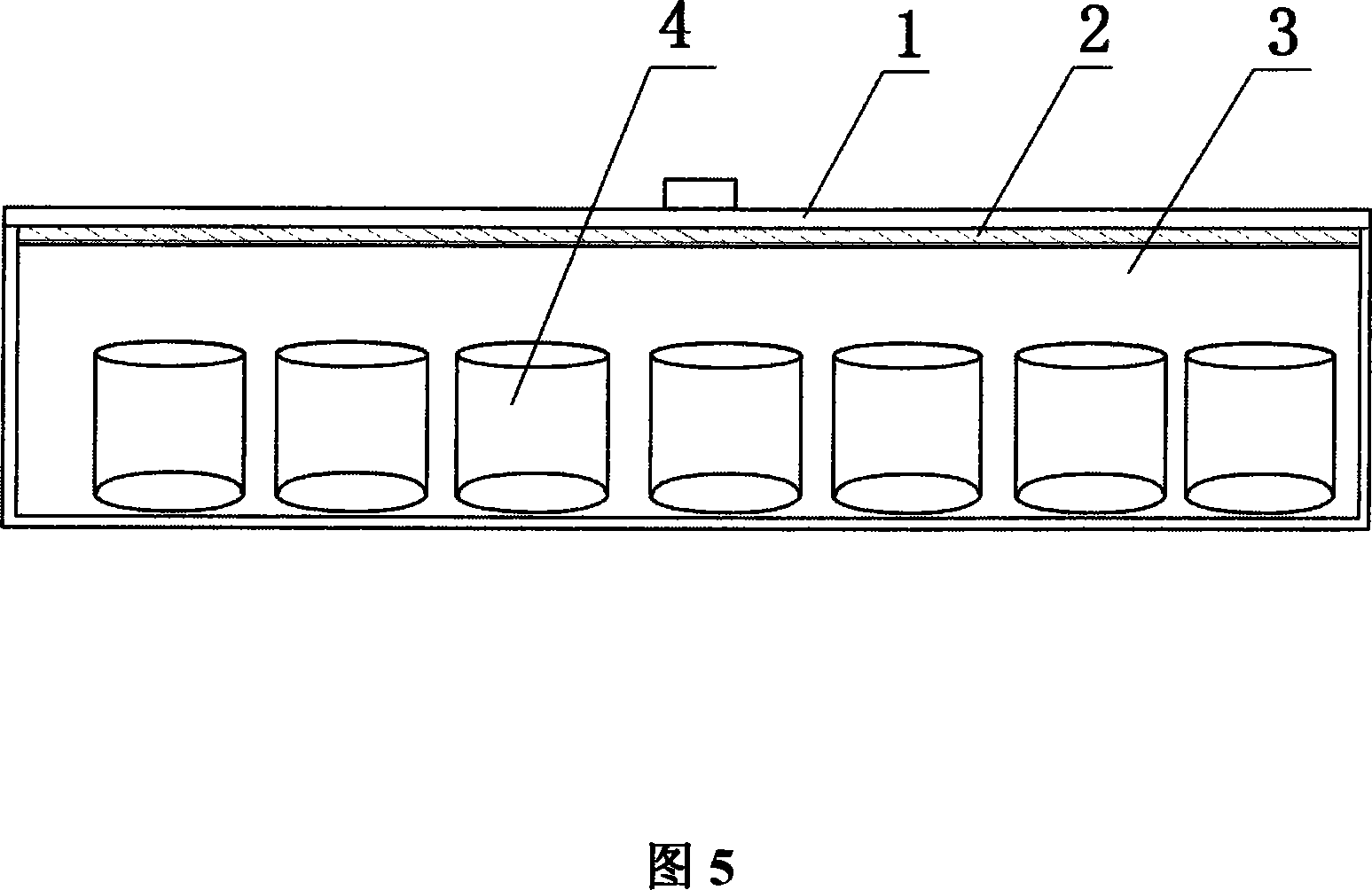
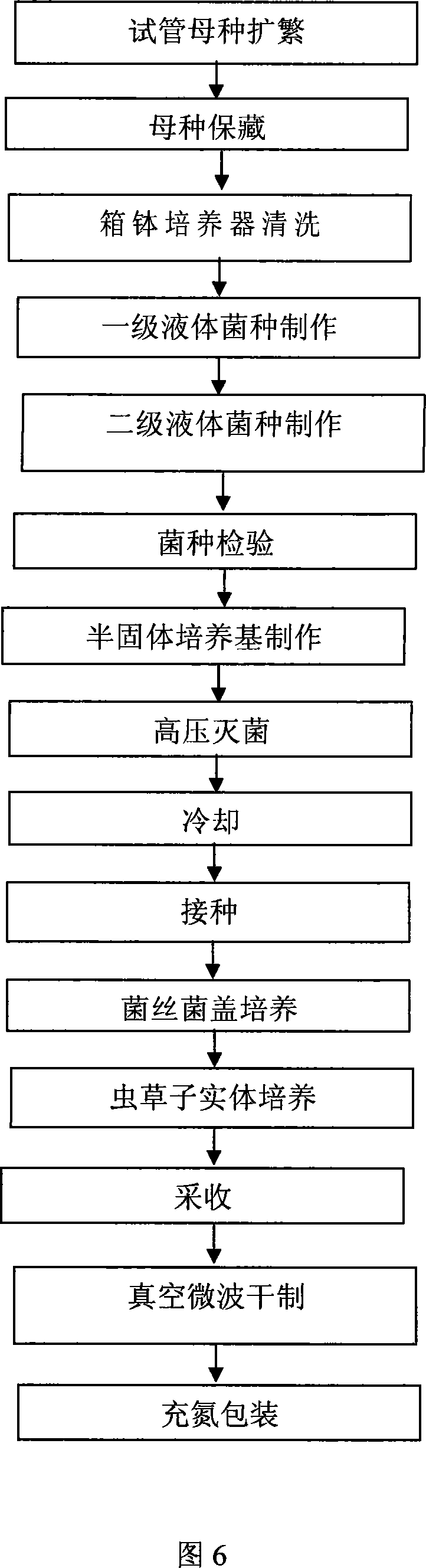
The invention provides an industrialized production method of cordyceps mushroom. The process of the invention comprises superior strain and liquid strain production, strain inspection, strain preservation, cordyceps mushroom culture equipment, culture medium formulary, culture medium preparation, culture medium subpackage, inoculation method, hairy fungus grass outgrowth management, collection and dry process, etc. The invention has the advantages that the technological innovation points are more, the invention is advanced and practical, the mechanization degree is high, and the invention is suitable for the scale and industrialized production. The selected superior strain has stronge prolificacy, the veraison is quick, and grass outgrowth is easy, the weed resistance and the stress resistance are outstanding, the invention is served with advanced liquid strain production equipment, semisolid culturemedium and case and bowl incubator, and other advanced production technologies, and can ensure the cordyceps mushroom which is a new member of the worm grass family to realize the high yield rate, the high quality and the high efficiency during the scale planting.
Owner:西宁市城西区食用菌研究所
Vinegar and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of old vinegar brewing and particularly relates to a vinegar and a preparation method thereof. The method includes raw material preprocessing, smashing, moisturizing, pasting, liquefying, liquid stationary alcoholic fermentation, stirring, vat feeding, solid acetic acid fermentation, smoking, vinegar pouring and ageing. Meanwhile, a fulled-sealed device is adopted for automatic stirring, producing and fermenting during alcohol fermentation, a traditional vat is adopted during acetic acid fermentation, fermentation is implemented through manual turning, and the finished vinegar can be obtained. The method has the advantages of strain excellence and process reasonableness, the fermentation period is shortened, the raw material utilization rate and vinegar finishing rate are increased, season limitation is eliminated, and the advantages of sour, sweet, soft and sweet tastes of the traditional vinegar are maintained.
Owner:山西兰花酿造有限公司
Rhizobium capable of efficiently solubilizing phosphorus and application of rhizobium
ActiveCN105950520APhosphate dissolving ability enhancedHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFungicideRoot nodule
The invention discloses a rhizobium capable of efficiently solubilizing phosphorus and application of the rhizobium. The phosphorus solubilizing rhizobium is named as Rhizobium sp.P-1 and preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on June 16, 2016, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2016333. The rhizobium can convert difficultly-soluble inorganic phorphorus into a high-quality phosphorus compound which can be directly absorbed and utilized by plants. By using the screened rhizobium in a lettuce pot culture experiment, the content of effective phosphorus in soil can be obviously increased, it is guaranteed that the lettuce yield is not decreased on the condition that the application amount of phosphate fertilizer is decreased by 50%, and the nutritional quality of lettuce is improved. The rhizobium can be used for preparing a phosphorus solubilizing fungicide, be widely applied to agricultural production, improve the bio-availability of difficultly-soluble phosphorus in the soil, increase the phosphate fertilizer utilization efficiency, save fertilizer and increase the yield and has the important significance and application value on the aspect of keeping agricultural ecological balance.
Owner:武汉一禾生态环境检测中心 +1
Brewing yeast engineering bacteria containing Lg-ATF1 genes
ActiveCN102604847AIncrease contentExcellent strainFungiHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyBacterial strain
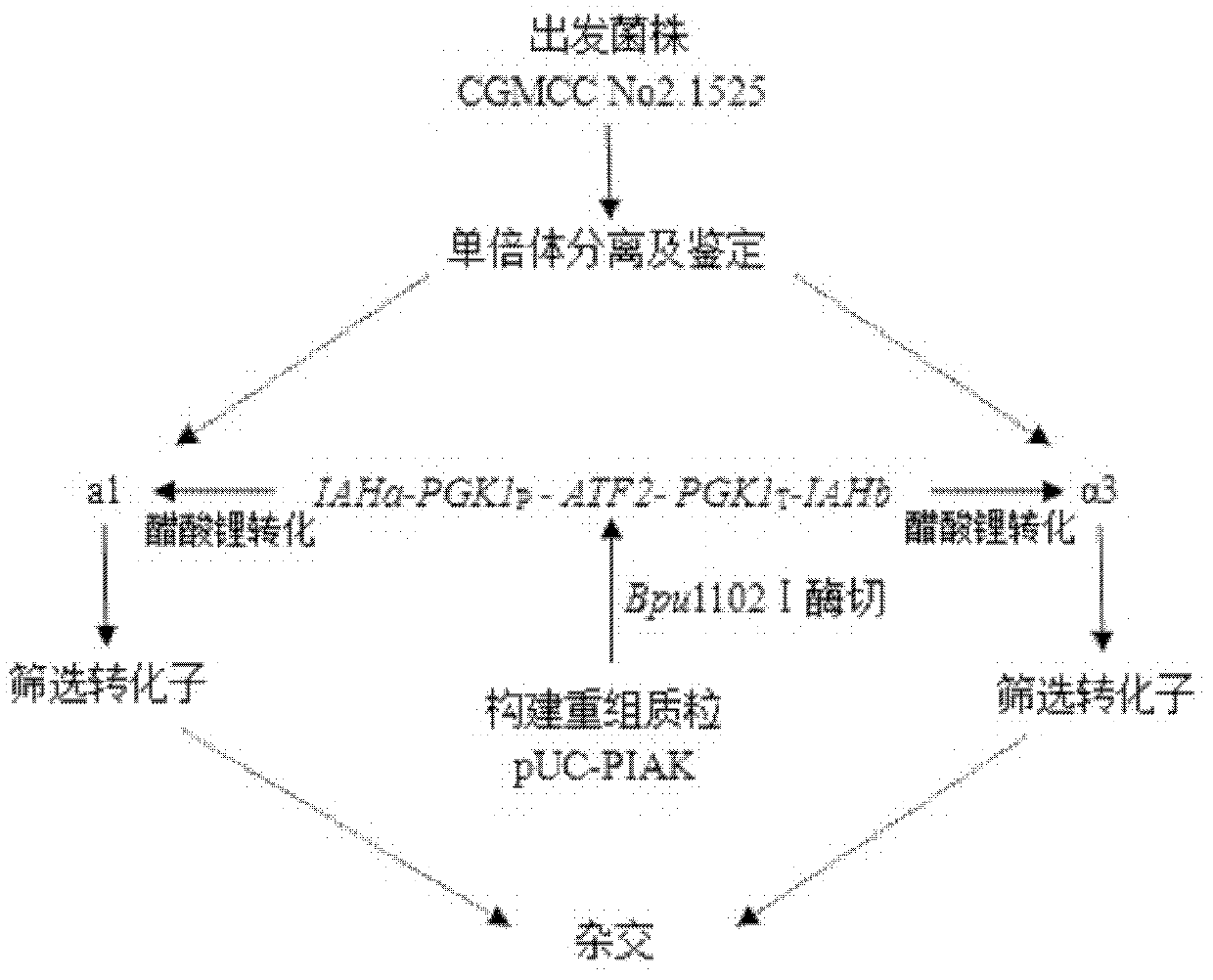
The invention relates to brewing yeast engineering bacteria containing Lg-ATF1 genes; a method for preparing the yeast engineering bacteria provided by The invention comprises the following steps: selecting strong promoters PGK1 so as to over express specific Lg-ATF1 genes coding alcohol acetyl transferase of beer yeast in brewing yeast, thereby obtaining the yeast engineering bacteria SaccharomycescerevisiaeEY-15 containing Lg-ATF1 genes, wherein a preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.5635. According to The invention, on a condition that other fermenting performance is not influenced, transformant bacterial strains are compared with parent strains (SaccharomycescerevisiaeCGMCC No.1525); after simulation of semi-solid fermentation, the content of ethyl acetate is increased by 1.6 times; the content of isoamyl acetate is increased to 26.6mg / L; the sifted engineering bacteria has no specific demand for fermentation equipment and conditions; the equipment and conditions of normal white sprits factories can be used; therefore, the engineering bacteria has wide application propose and brings marked economic benefit to industrial production of the white sprits factories.
Owner:河北琢酒集团有限公司
Construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of isobutanol
ActiveCN103789341AIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionIsobutanolBiotechnology
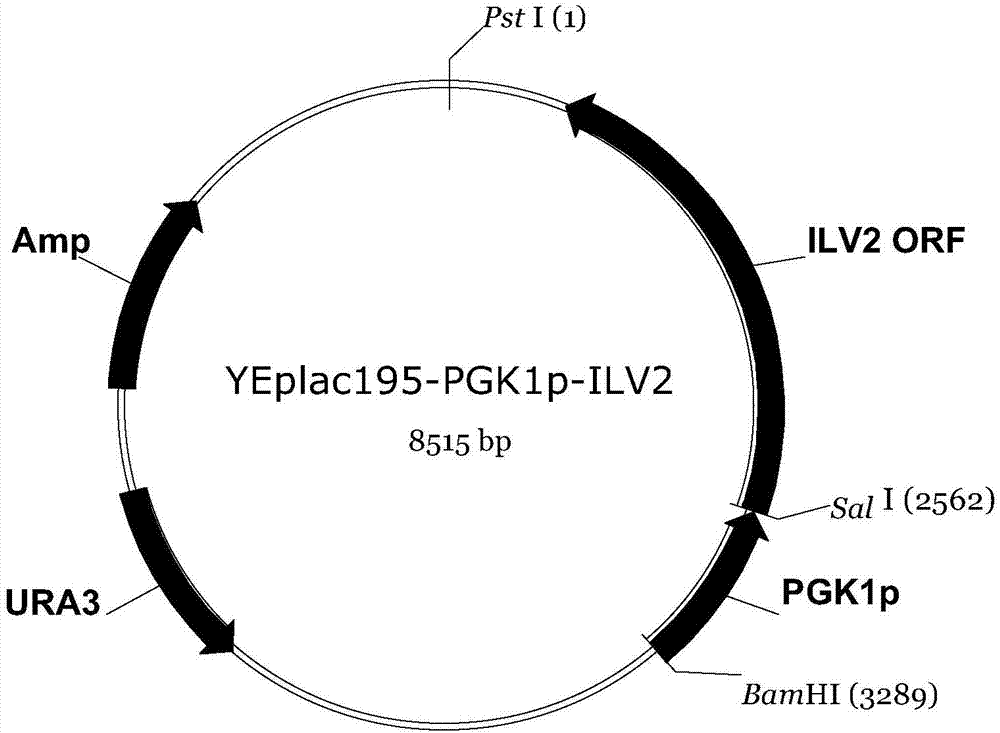
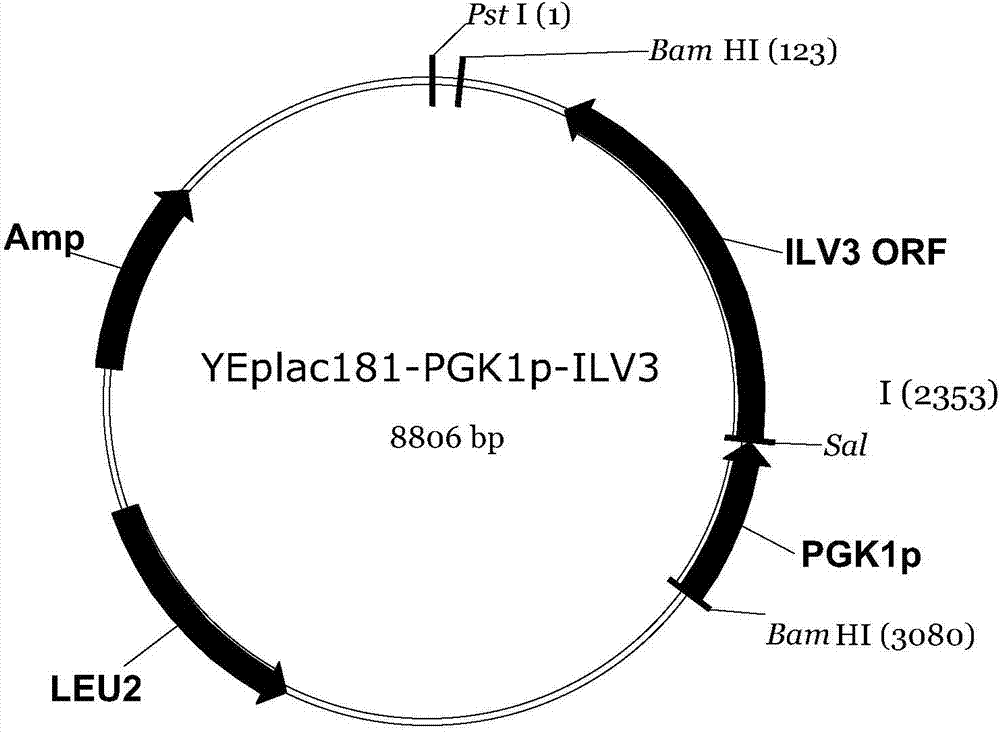
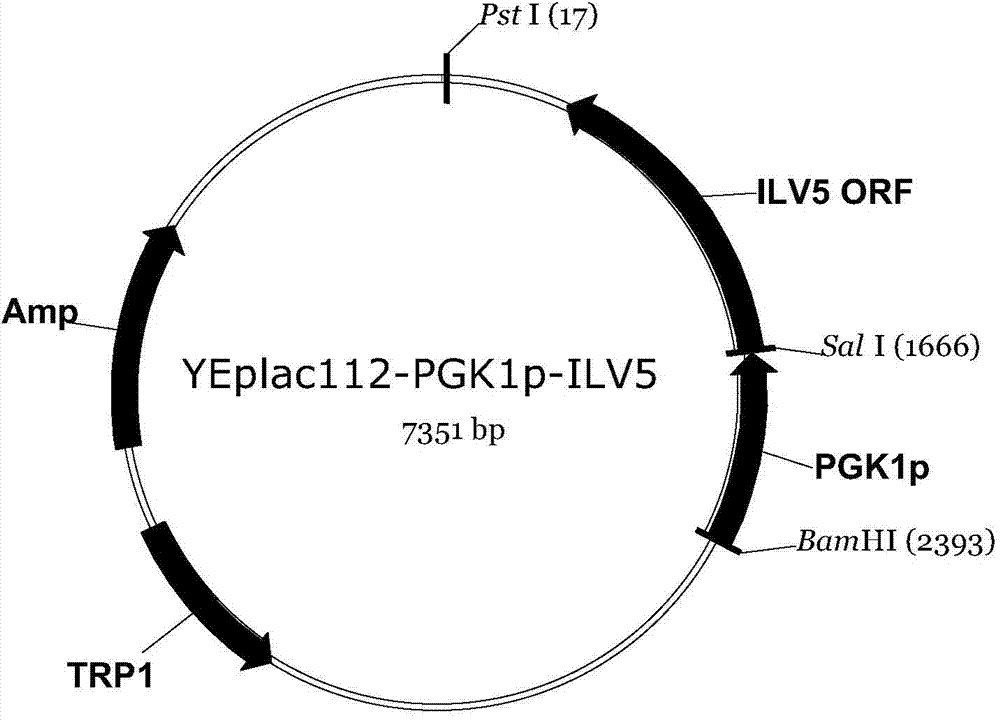
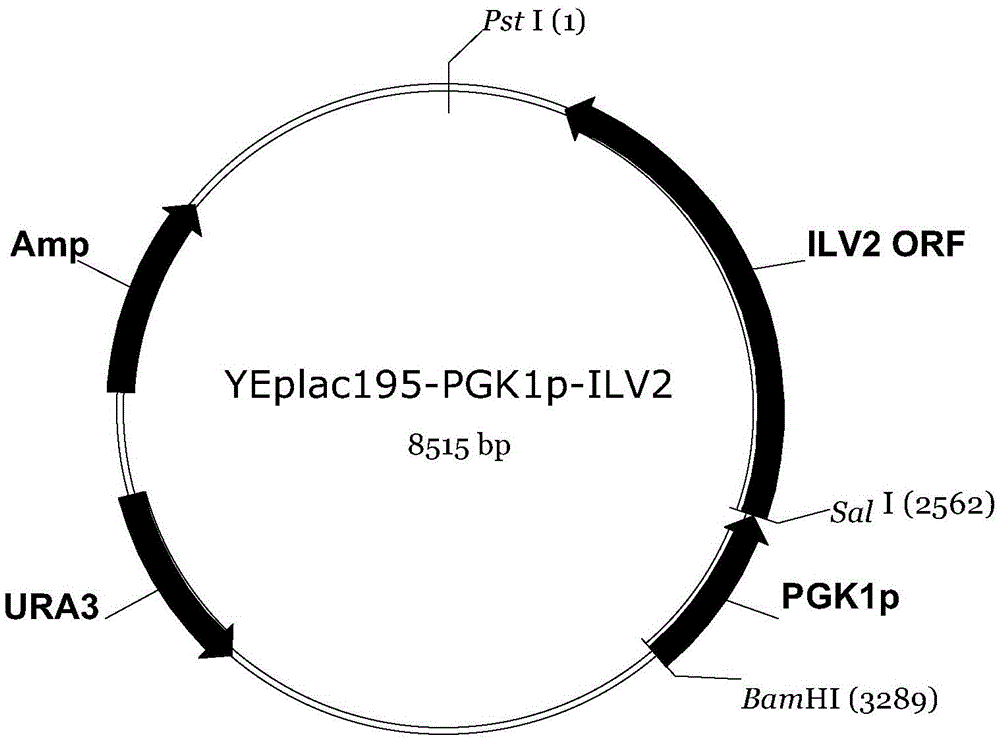
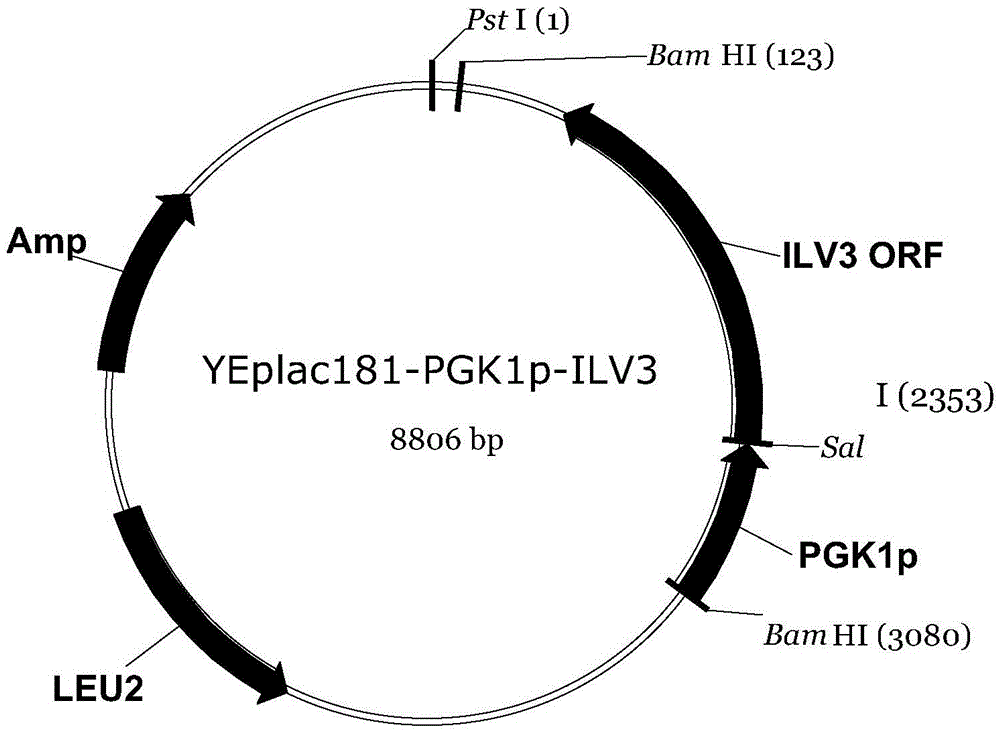
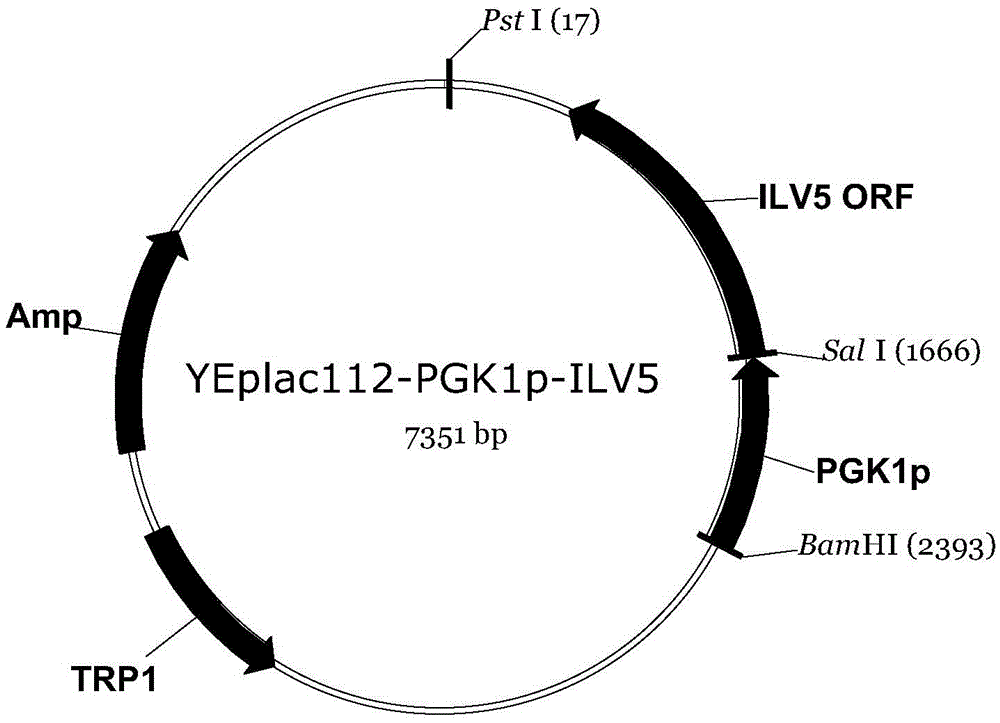
The invention discloses a construction method of a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with a high yield of isobutanol and relates to preparation of microorganism by a recombinant DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) technology. According to the method, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with the high yield of isobutanol is constructed by reforming saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by using molecular biology and the gene recombination technology. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing plasmids of over-expressing ILV2 (Induced Leukemia Virus), ILV3, ILV5 and ZWF1 genes of saccharomyces cerevisiae; and S2, constructing a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain HBGDAL-103 with the high yield of isobutanol. The method disclosed by the invention overcomes the deficiency that further improvement of the yield of isobutanol is restricted by factors such as imbalance of a coenzyme NADPH / NADP<+> (Reduced Form of Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) / (Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate<+>) from pyruvic acid to 2-one isovaleric acid due to over-expressed ILV2, ILV3 and ILV5 in the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells of yielding isobutanol in the prior art.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Androstenedione substrate-tolerant mutant strain and mutation breeding method thereof
InactiveCN104531548AImprove the ability to degrade phytosterolsStrong conversion potentialBacteriaMutant preparationMycobacterium neoaurumPhytosterol
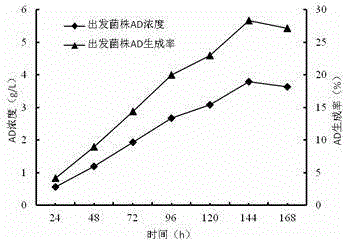
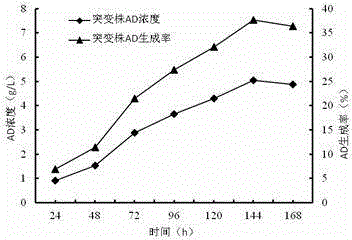
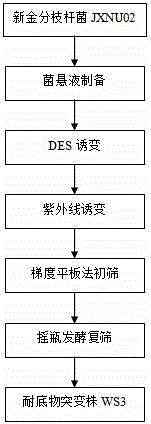
The invention discloses an androstenedione substrate-tolerant mutant strain and a mutation breeding method thereof. A mutant strain of mycobacterium neoaurum WS3 is preserved in China center for type culture collection with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M 2014322, and the preservation date is July 4, 2014. According to the invention, mycobacterium neoaurumJXNU02 is used as a starting strain; compound mutation is carried out by diethyl sulfate and an ultraviolet mutation method; primary screening is performed by a gradient plate method; secondary screening and verification are carried out by a shake flask fermentation method; and thus the mutant strain of mycobacterium neoaurum WS3 with high substrate tolerance and genetic stability is bred. The method of the invention effectively improves the capability of mycobacteria for degrading phytosterol to generate androstenedione, provides an excellent strain for producing androstenedione by a microbiological method, and has important significance on the pharmaceutical industry of our country.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Screening method for heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterial strain
InactiveCN109762747AImprove denitrification effectImprove purification efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesScreening culturesScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method for a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterial strain. The method comprises the following steps that sludge is put in a screening culturing medium, screened and purified to obtain a primary sample; the primary sample is firstly subjected to enrichment culturing and then is primarily screened to obtain a pure bacterium, the bacterial strain is pichia jadinii Pichia jadinii MA1, and the preservation number is CCTCCM 2018289; the method of first enrichment culturing and screening afterwards is adopted, the denitrification capacity ofthe bacterial strain can be greatly improved, and the efficiency and effect of purifying waste water are improved; under the circumstance of taking ammonium chloride as the unique nitrogen source, the total nitrogen removal rate of 100 mg / L of initial nitrate reaches 66.9% or above within 24 hours; the primary screening method is adopted, after the pure bacterium is selected, a secondary screening method is adopted to select a pure bacterial strain, the denitrification effect is the best, and therefore the best bacterial strain is obtained.
Owner:杭州民安环境工程有限公司
Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102199556BReduce contentIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesEster hydrolaseGenetic engineering
The invention discloses Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria EY-13 were collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 17, 2010, the collection number is CGMCC NO.4350, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria are recommended to be named Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PGK1 derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae is selected as a promoter; and the construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with the high ester yield comprises a step of knocking-out an IAH1 gene for encoding ester hydrolase in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome when an ATF1 gene which is derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is used for encoding alcohol acetyltransferase is overexpressed. Compared with initial recipient bacteria, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria have the advantages that: after rice wine fermentation is simulated, the content of isoamylol is about one half, the content of ethyl acetate is improved by 20 times, the content of isoamyl acetate is 100mg / L, and the content of isobutyl acetate is 5 to 7mg / L; and after liquor fermentation is simulated, the content of total esters is improved by 4 times and the content of the ethyl acetate is improved by 35 times, so an excellent strain is provided for the production of brewing industry.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
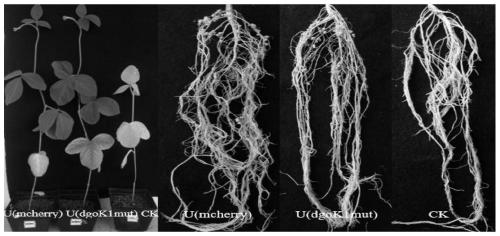
Method for improving competitive nodulation capacity of nodule bacteria USDA110
ActiveCN110452864AExcellent strainImprove nitrogen fixation capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesField experimentNodulations
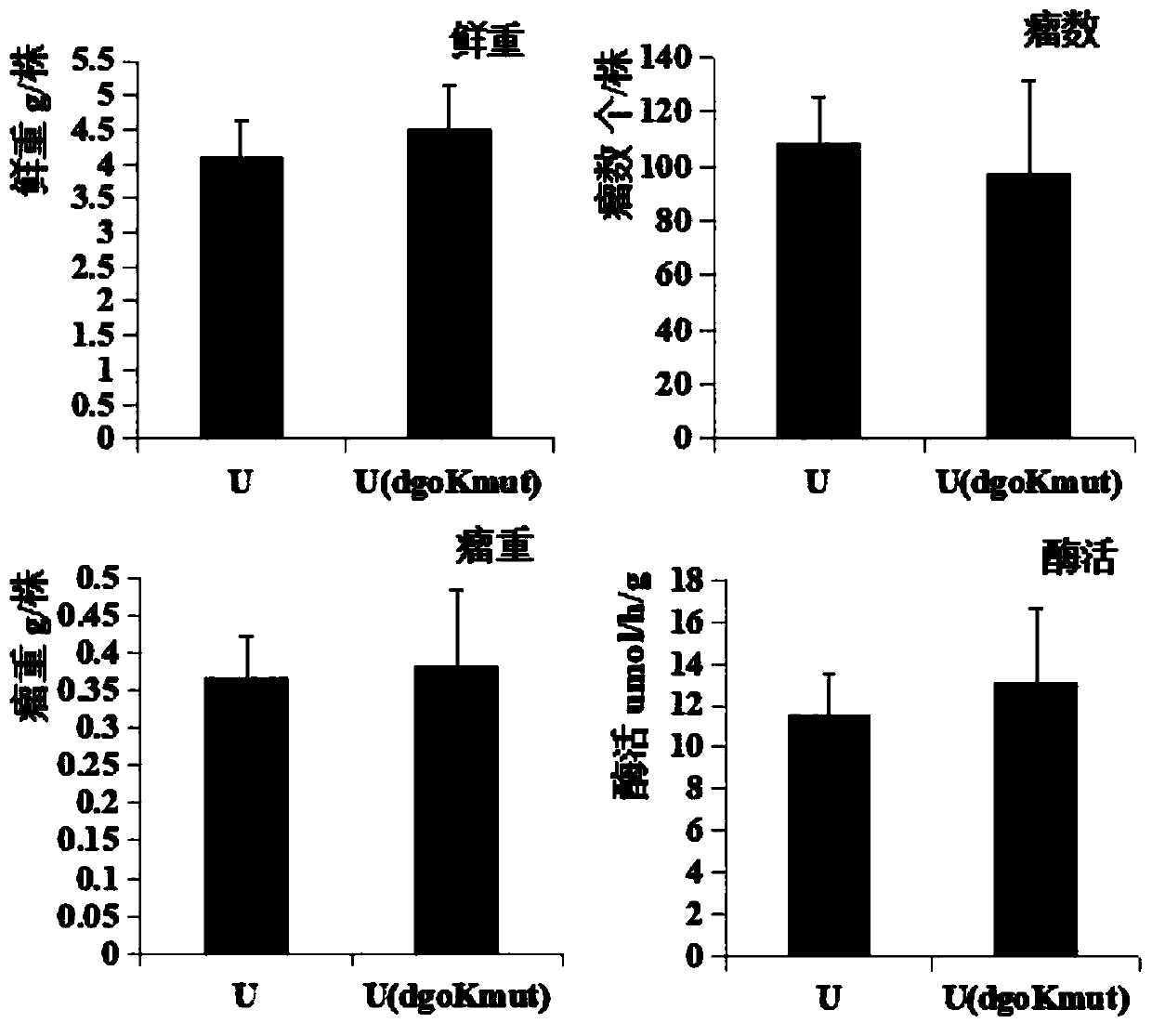
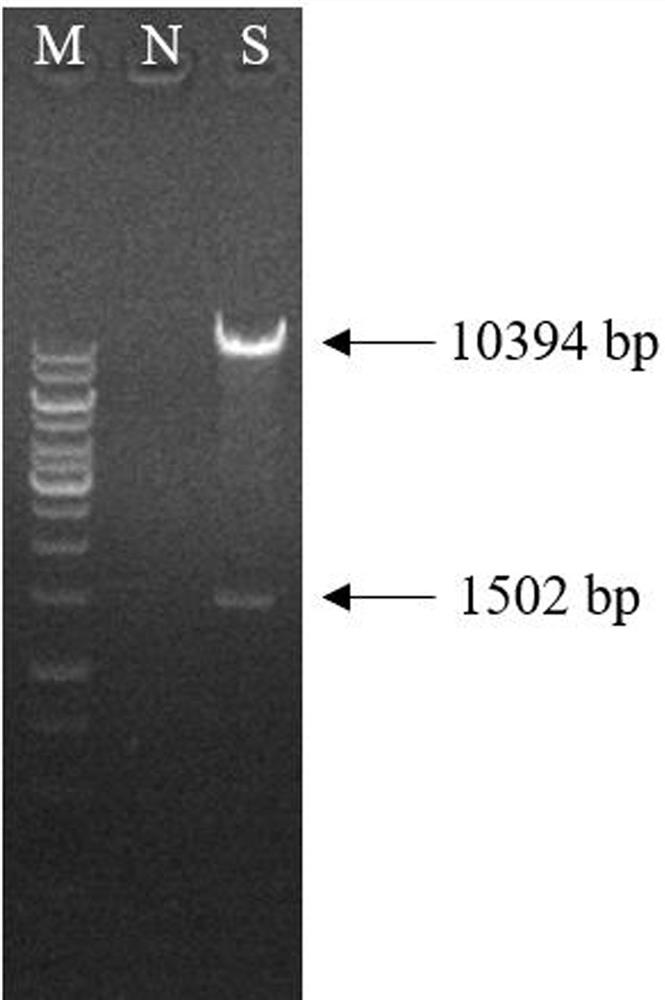
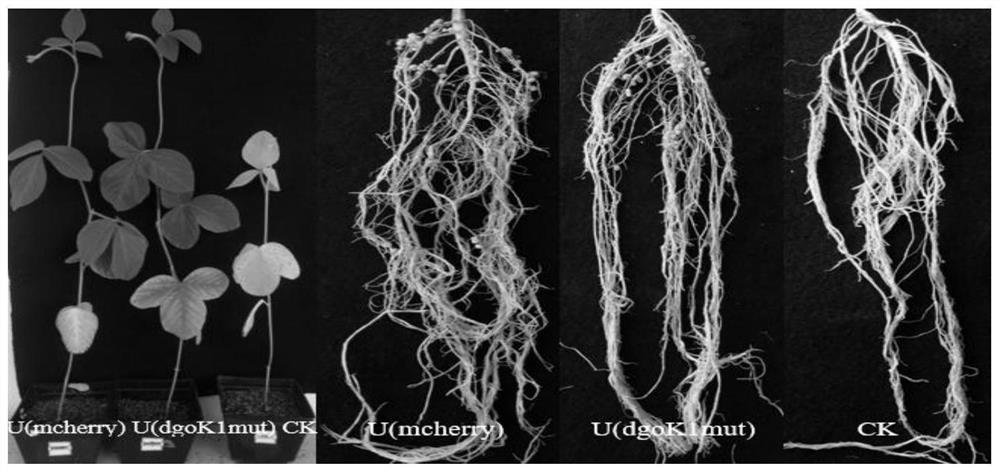
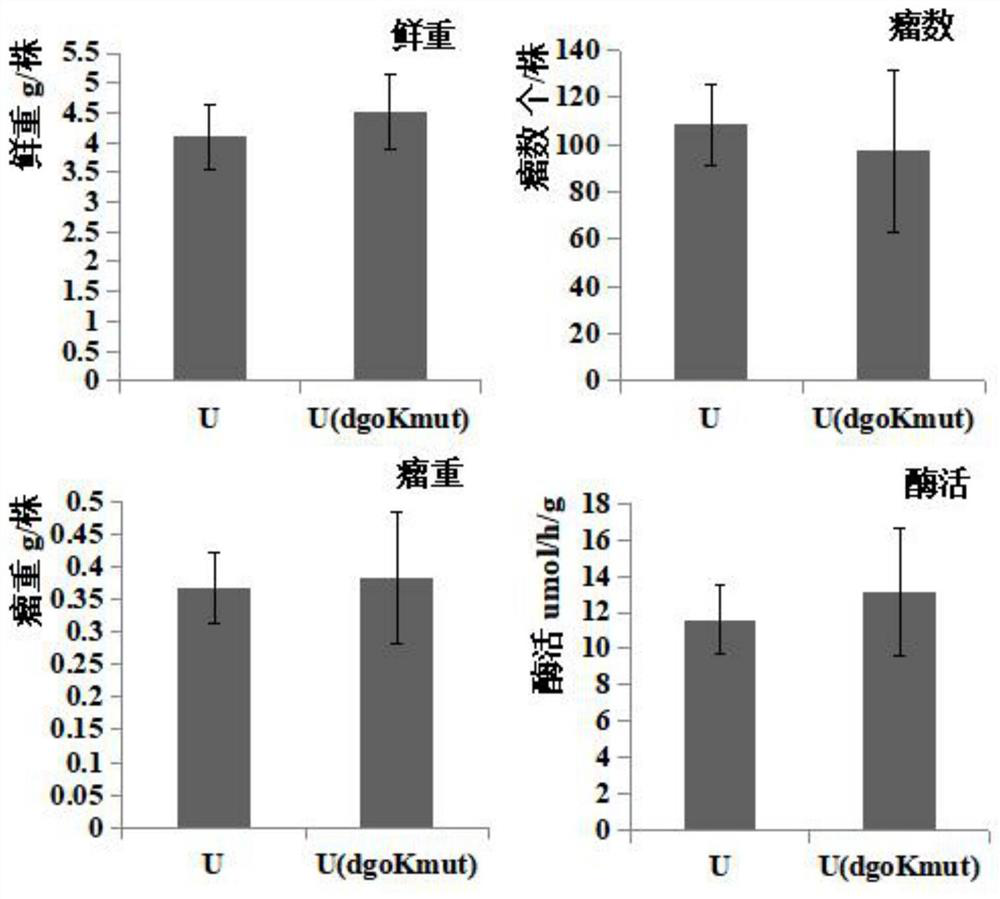
The invention discloses a method for improving a competitive nodulation capacity of nodule bacteria USDA110. A dgoK1 singly inserted mutant strain USDA110 (dgoKmut) is constructed through pK19mob, under the soil potting condition, compared with a plant inoculated with USDA110, the fresh weight, nodule number, nodule weight and enzyme activity of a plant inoculated with USDA110 (dgoKmut) are all significantly increased; compared with indigenous nodule bacteria, the competitive nodulation capacity of the USDA110 (dgoKmut) is improved by 24.5%, and can reach 31.8%. Therefore, the USDA110 (dgoKmut) has good symbiotic nitrogen fixation and competitive nodulation capacities, and can be used as a promising strain in field experiments.
Owner:华创佳农生物科技(武汉)有限公司
High-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102604848AIncrease contentExcellent strainFungiMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to high-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria; a method for preparing the brewing yeast bacteria provided by The invention comprises the following steps: selecting strong promoters PGK1 so as to overexpress ATF2 gene coding alcohol acetyl transferase, thereby obtaining high-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria SaccharomycescerevisiaeEY-14, wherein a preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.5635. According to The invention, on a condition that other fermenting performance is not influenced, transformant bacterial strains are compared with parent strains (SaccharomycescerevisiaeCGMCC No 2.1525); after simulation of semi-solid fermentation, the content of ethyl acetate is increased by 3.6 times; thecontent of isoamyl acetate is increased to 55.2mg / L; the content of isobutyl acetate is increased to 33.8mg / L; the sifted engineering bacteria has no specific demand for fermentation equipment and conditions; the equipment and conditions of normal white sprits factories can be used; therefore, the engineering bacteria has wide application propose and brings marked economic benefit to industrial production of the white sprits factories.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of composite zymoprotein
InactiveCN101507469AExcellent strainStrong generation stabilityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsNutritive valuesZymogen
The invention relates to a method for preparing a complex enzyme protein, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: preparing an aerobic fermentation medium, preparing an anaerobic fermentation medium, sterilizing the mediums, activating bacterial strains, performing amplification cultivation and inoculation, preparing an aerobic fermentation condition, preparing an anaerobic fermentation condition, drying at a low temperature, mixing the mixture, and packaging. The method has the advantages that: 1, the strains are excellent and the passage stability is strong; 2, each strain plays a synergetic role in the process of fermentation, the growth and the metabolism of each strain is thriving, and the enzyme productivity is strong; 3, aerobic zymogens and anaerobic zymogens perform fermentations separately so that each strain gives play to the best enzyme producing performance; and 4, proteins which are difficult to absorb by animals in raw materials are converted into thalli single cell proteins which are easy to absorb so that the nutritive value of products is improved.
Owner:江西普润药业有限公司
Method and strain for reducing by-product fumaric acid in L-malic acid fermentation process and application
ActiveCN113846024AReduce by-product fumaric acidLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesSide productMalate fermentation
The invention discloses an Aspergillus niger engineering strain for reducing a by-product fumaric acid in an L-malic acid fermentation process. A fumaric acid hydratase gene fum is knocked out of theAspergillus niger engineering strain. In order to overcome the defects in the prior art that in the existing process of producing malic acid through Aspergillus niger fermentation, the by-product fumaric acid is accumulated along with the generation of malic acid, and the cost of a subsequent malic acid purification process is increased, the invention provides the Apergillus niger engineering strain with the fum gene knocked out, and a method for greatly reducing the by-product fumaric acid in the Aspergillus niger fermentation process. The by-product fumaric acid accumulated in the process of producing the malic acid by fermenting the aspergillus niger is obviously reduced, the cost in the downstream separation and purification process of the malic acid is reduced, and an excellent strain is provided for industrial fermentation production of the malic acid.
Owner:南京昊禾生物科技有限公司
Compound bacteria, compound bacterial agent containing same, preparation method of compound bacterial agent containing same, and application of compound bacteria and compound bacterial agent containing same
InactiveCN108220181ANo pollutionRemarkable effect on degrading ligninFungiBacteriaMicrobiologyChrysosporium species
The invention provides compound bacteria, a compound bacterial agent containing the same, a preparation method of the compound bacterial agent containing the same, and application of the compound bacteria and the compound bacterial agent containing the same. The compound bacteria comprise acinetobacter lwoffii with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5973, wickerhamomyces anomalus with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5975, phanerochaete chrysosporium and pleurotus ostreatus; through synergistic interaction of various bacteria in the compound bacteria, the compound bacteria have a remarkable effect in the aspect of degrading lignin, particularly the lignin in a hemp rod; the problems of overlong time in bio-pulping, low fibre degree and low yield in the prior art are solved; remarkabletechnical effects of high fibre degree, high yield, short working hours, low cost and no environmental pollution are achieved.
Owner:康盛时代(北京)生物技术有限公司
A kind of construction method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae isobutanol high-yielding strain
ActiveCN103789341BIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismMother cells
The invention discloses a construction method of a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with a high yield of isobutanol and relates to preparation of microorganism by a recombinant DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) technology. According to the method, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with the high yield of isobutanol is constructed by reforming saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by using molecular biology and the gene recombination technology. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing plasmids of over-expressing ILV2 (Induced Leukemia Virus), ILV3, ILV5 and ZWF1 genes of saccharomyces cerevisiae; and S2, constructing a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain HBGDAL-103 with the high yield of isobutanol. The method disclosed by the invention overcomes the deficiency that further improvement of the yield of isobutanol is restricted by factors such as imbalance of a coenzyme NADPH / NADP<+> (Reduced Form of Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) / (Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate<+>) from pyruvic acid to 2-one isovaleric acid due to over-expressed ILV2, ILV3 and ILV5 in the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells of yielding isobutanol in the prior art.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Rhodopseudomonas palustris P-3 as well as screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN112481165AEnhanced inhibitory effectEfficient degradationBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyVibrio anguillarum
The invention discloses Rhodopseudomonas palustris P-3. The preservation number of the Rhodopseudomonas palustris P-3 is CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2020808. According to the strain, photosynthetic bacteria are separated and purified by adopting a double-layer plate coating method and a streaking method, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio vulnificus and vibrio anguillarum are used as indicator bacteria, and the bacteriostatic action of the marine photosynthetic bacteria strain is determined by adopting an oxford cup method. Naphthalene ethylenediamine hydrochloride spectrophotometry and indophenol blue spectrophotometry are adopted to determine the nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen degradation effects of different strains, and screening is performed to obtain the product. The strain P-3 has the composite functions of resisting vibrio and efficiently degrading nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen, has a strong inhibition effect on vibrio anguillarum, has thestrongest effect on vibrio anguillarum, and also has a certain nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen degradation effect. The strain P-3 is cultured in a culture medium containing 50mg / L ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen for 4 days, the degradation rates are 89.68% and 94.98% respectively, and the strain P-3 has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV
A method, strain and application of reducing by-product fumaric acid in L-malic acid fermentation process
ActiveCN113846024BIncreased purification process costsLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesIndustrial fermentationMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain of Aspergillus niger ( Aspergillus niger ) engineering strain, the Aspergillus niger engineering strain is to knock out the fumarate hydratase gene fum of Aspergillus niger engineered strains. The invention overcomes the deficiencies in the prior art. In the existing process of using Aspergillus niger to ferment and produce malic acid, the by-product fumaric acid will accumulate along with the production of malic acid, resulting in an increase in the cost of the subsequent malic acid purification process. The present invention provides a fum Knockout engineered strains of Aspergillus niger, and a method for greatly reducing fumaric acid by-products during fermentation by Aspergillus niger. The invention significantly reduces the by-product fumaric acid accumulated in the process of producing malic acid by fermentation of Aspergillus niger, reduces the cost in the process of downstream separation and purification of malic acid, and provides excellent strains for industrial fermentation and production of malic acid.
Owner:南京昊禾生物科技有限公司
A method for improving the nodulation competition ability of rhizobia usda110
ActiveCN110452864BExcellent strainImprove nitrogen fixation capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for improving a competitive nodulation capacity of nodule bacteria USDA110. A dgoK1 singly inserted mutant strain USDA110 (dgoKmut) is constructed through pK19mob, under the soil potting condition, compared with a plant inoculated with USDA110, the fresh weight, nodule number, nodule weight and enzyme activity of a plant inoculated with USDA110 (dgoKmut) are all significantly increased; compared with indigenous nodule bacteria, the competitive nodulation capacity of the USDA110 (dgoKmut) is improved by 24.5%, and can reach 31.8%. Therefore, the USDA110 (dgoKmut) has good symbiotic nitrogen fixation and competitive nodulation capacities, and can be used as a promising strain in field experiments.
Owner:华创佳农生物科技(武汉)有限公司
Production technology and special equipment of the mushroom block and block
ActiveCN103704012BImprove efficiencyLow costHorticultureFertilizer mixturesAgricultural scienceEdible mushroom
The invention belongs to the field of edible mushrooms and discloses a novel pholiota nameko mushroom block, a mushroom block production process and a special device of production of the mushroom block. The pholiota nameko mushroom block comprises a strain, a cultivation material and a mushroom bag with a breathable film; the production process of the mushroom block comprises the steps of bagging, pressing blocks, sterilizing, inoculating, culturing; the production of the mushroom block is realized by a special device which is block pressing machine; the mushroom block and the production process of the mushroom block are low in pollution rate; through an automatic production device, the production efficiency is improved and the production cost is reduced; meanwhile, the yearly culture times are increased; a factory is positioned in an artificial climate chamber, mycelia are cultured; the mushroom blocks capable of directly producing mushrooms are delivered to mushroom growers; after the mushroom growers cultivate the mushrooms, the mushrooms are changed from being harvested for one time in a year to being harvested for 2-4 times in a year.
Owner:DALIAN GAISHI FOOD
Applications of bacillus subtilis in biological control for shoot blight of phellodendron amurense
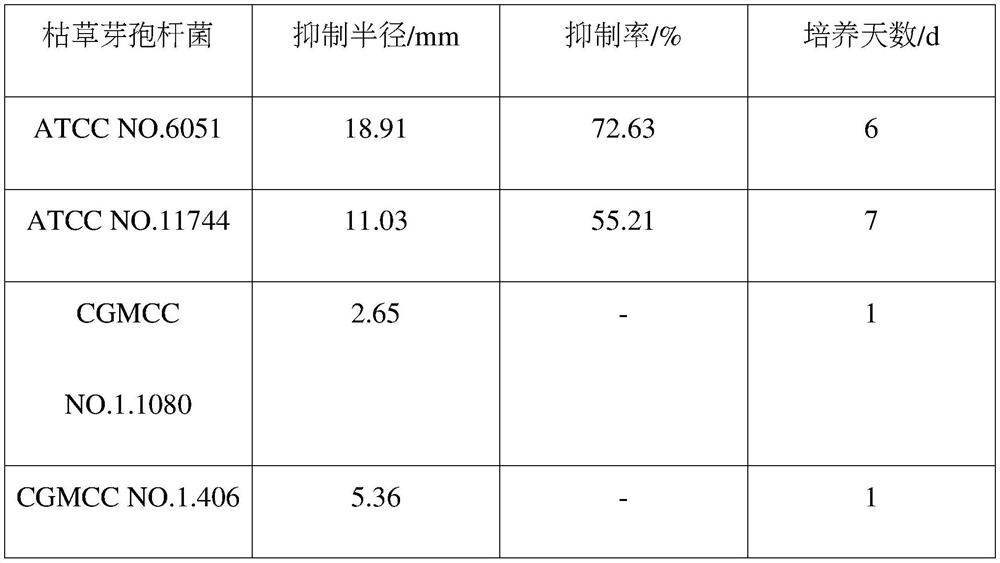
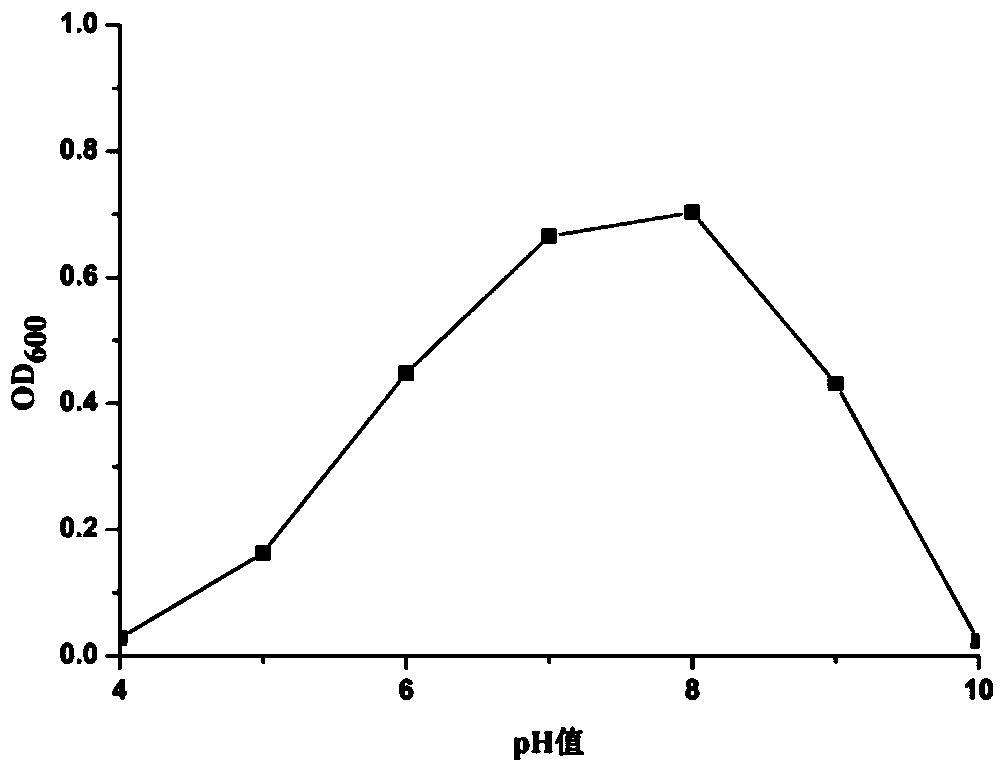
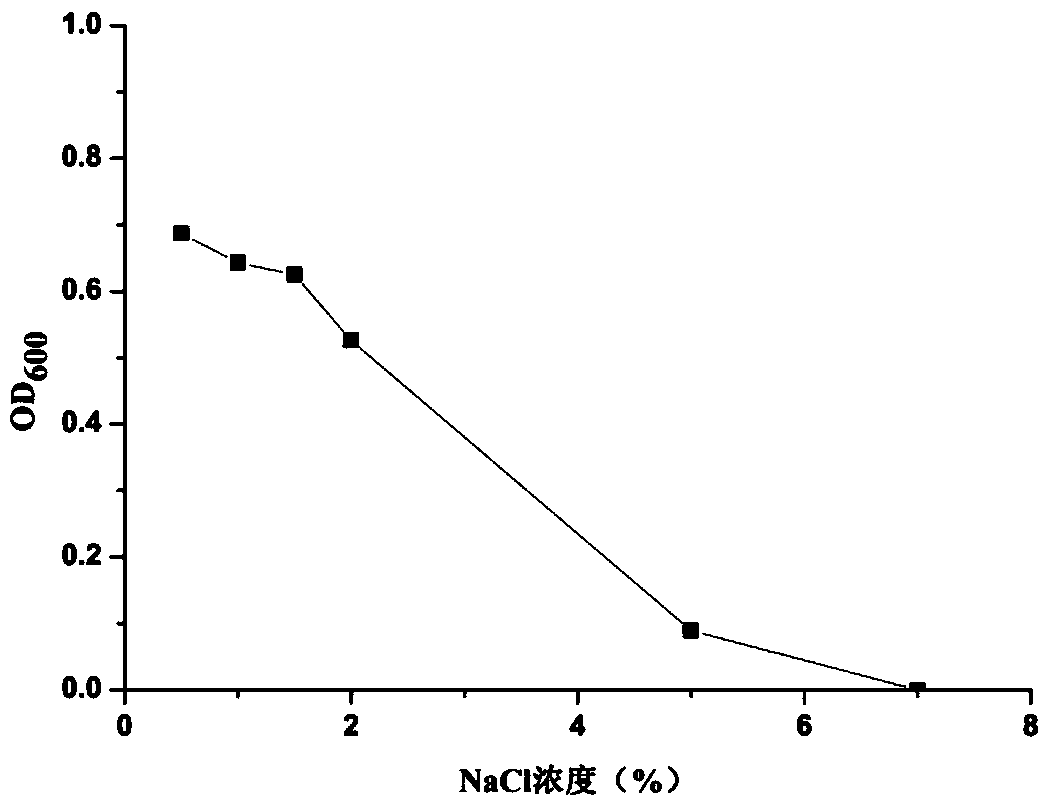
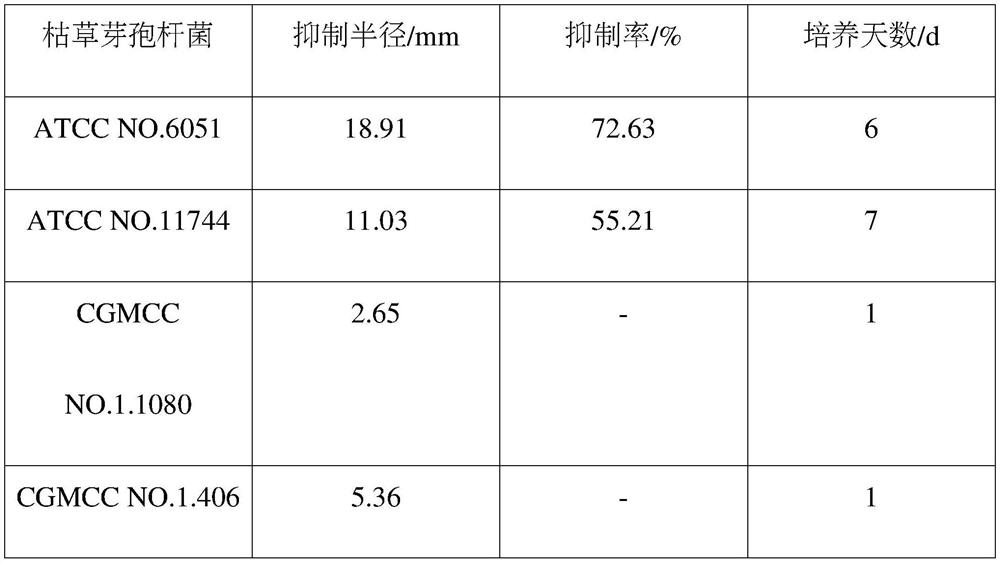
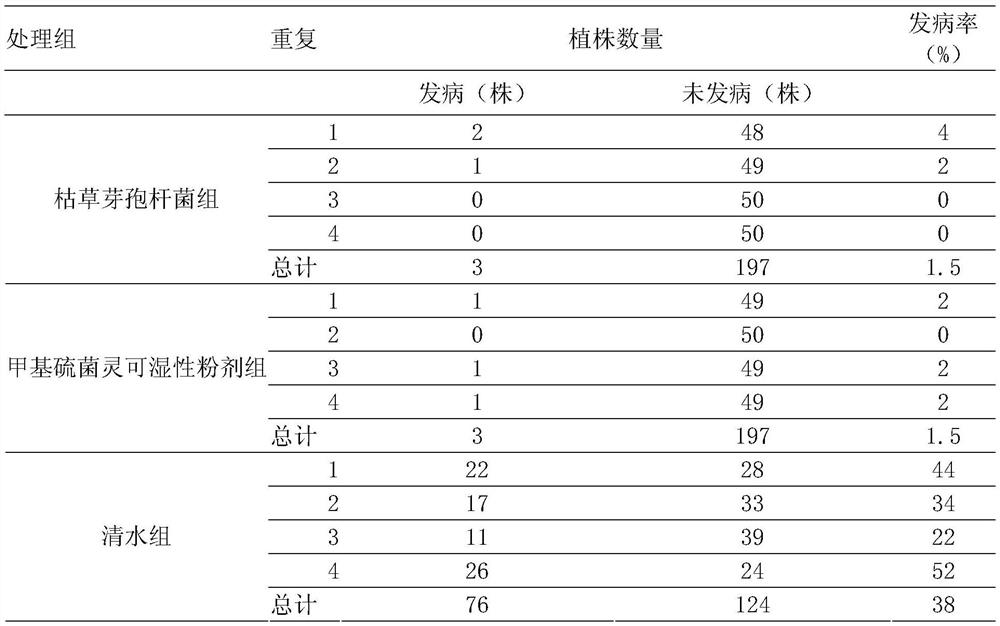
ActiveCN112522154AGood application prospectInhibit growthBiocideBacteriaPhellodendron amurenseBacillus <bacterium>
The invention provides bacillus subtilis used for inhibiting shoot blight of phellodendron amurense. The accession number of the strain is ATCC NO. 6051. The strain has good control efficiency on theshoot blight of the phellodendron amurense.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
A strain of Lactobacillus plantarum that degrades nitrite and has the ability to inhibit ace
ActiveCN111154692BEfficient degradation abilityHas inhibitory effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention provides a Lactobacillus plantarum strain with nitrite degrading activity and ACE inhibitory activity and application thereof, which has degrading effect on nitrite and can be widely used in fermented food and fermented feed. The preservation number of Lactobacillus sp. FJS 002 provided by the present invention is CGMCC No 18378. The plant lactobacillus provided by the invention is applied in the field of food processing or feed processing. The present invention obtains excellent bacterial strains with efficient degradative effect on nitrite and inhibitory effect on ACE by screening, and can provide theoretical basis and scientific knowledge for solving the problem of nitrite residue in food, especially fermented food, and the high blood pressure that plagues human health. means.
Owner:潍坊益昊生物技术有限公司
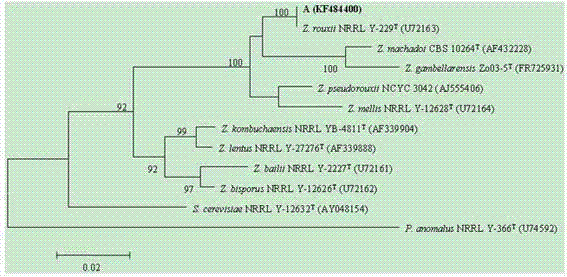
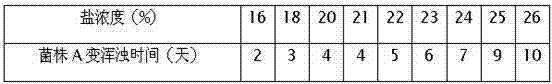
A highly salt-tolerant Zygomyces rouckeri
ActiveCN103589651BSalt toleranceImprove growthFungiMicroorganism based processesFlavorZygosaccharomyces
The invention discloses a high-salt-tolerance Zygosaccharomyces rouxii A strain of which the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2013310. The strain has high salt tolerance and favorable growth stability, has the characteristic of being capable of producing full-bodied mellow and ester-like aromatic flavors, and can be used for brewing high-salt diluted soy sauce, shortening the fermentation period and improving the flavor and quality of the soy sauce.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
A strain and application of black mold gene engineering projects and applications with high -yield organic acid under low -soluble oxygen conditions
ActiveCN110029068BImproved ability to produce organic acidsExcellent strainFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousEngineered genetic
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Bird probiotic premix taking orange seeds as auxiliary material, and preparation method of premix
InactiveCN103461671AExcellent strainHigh content of live bacteriaAnimal feeding stuffMicroecologyProbiotic
The invention relates to a bird probiotic premix taking orange seeds as an auxiliary material, and a preparation method of the premix. The premix comprises probiotic and a fermenting auxiliary material, and is characterized in that the probiotic is bacillus subtilis, and the fermentating auxiliary material comprises the orange seeds. The preparation method comprises the steps that (1) the orange seeds, a carbon source and a nitrogen source are crushed to 60-80 meshes, weighed according to the formula quantity, and mixed; and (2) the probiotic is put into a mixture, and cultivated for 24-48h at a constant temperature of 36-37 DEG C; cultivation is stopped when a detection concentration of a culture of the probiotic reaches 10<7>-10<9> pieces / ml; and the probiotic premix is obtained. The premix contains a high-quality effective bacterium; the culture is selected and bred in strict accordance with a microecology rule; the excellence of the culture is ensured; the content of viable bacteria is high; the quality guarantee period is 24 months; and the premix has good microecology regulation, sputum reduction and cough relieving effects, and is stable in quality, safe, reliable, green, environment-friendly and pollution-free.
Owner:GREAT BIOLOGY PHARMA TIANJIN
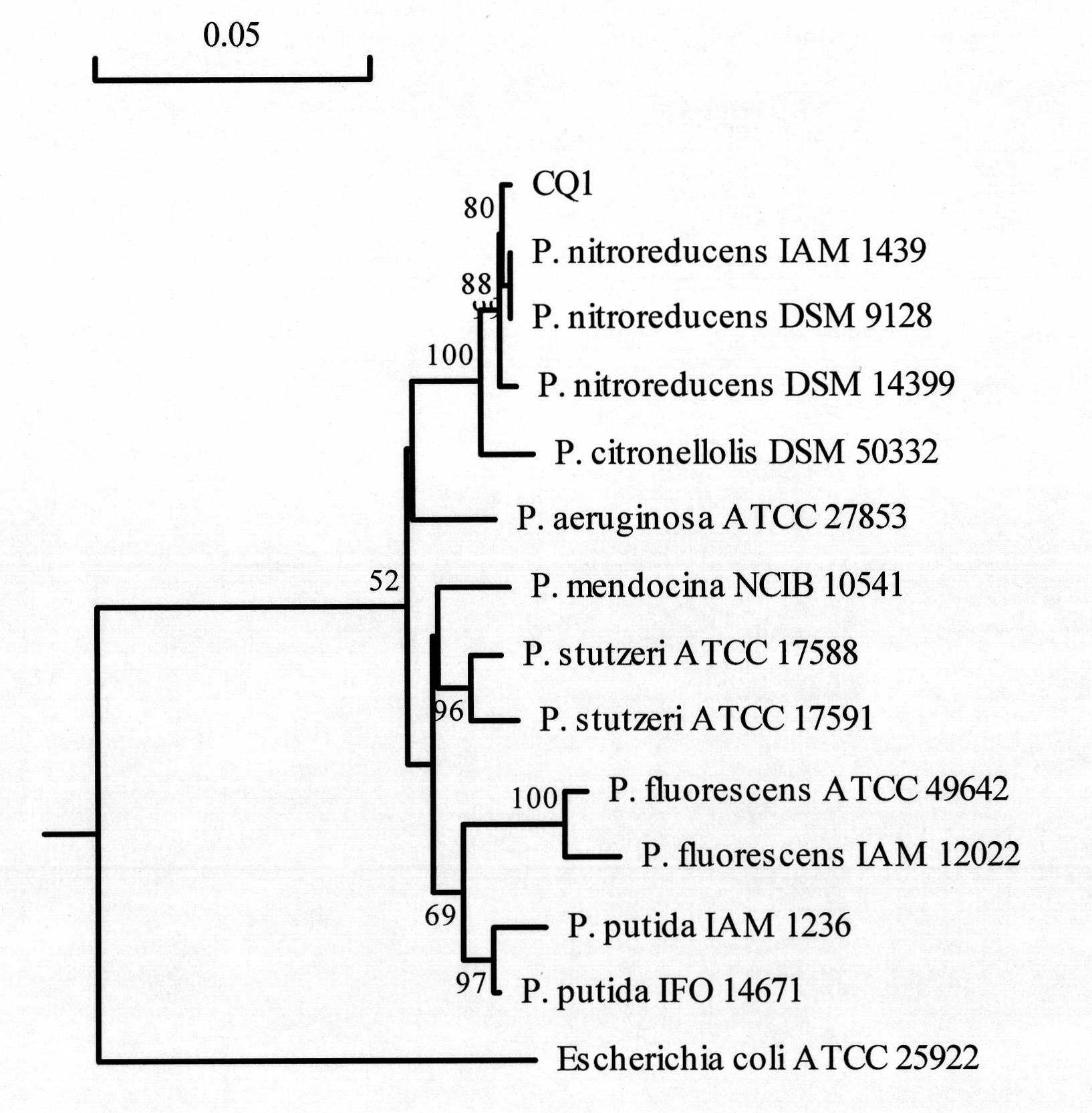
Pseudomonas nitroreducens and application thereof
The invention discloses Pseudomonas nitroreducens and application thereof, belonging to the field of environmental microorganism. The Pseudomonas nitroreducens CQ1 of the invention is derived from the sewage of oxidation ponds in the sewage treatment system of Beijing Yanshan Petrochemical Co., Ltd., and obtained by enriching, separating and purifying. The Pseudomonas nitroreducens CQ1 is cultured and collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (hereinafter referred to as CGMCC) with the collection number being CGMCC No.3159. The invention further discloses the application of Pseudomonas nitroreducens in the biodegradation of quinoline or derivatives thereof. Quinoline or derivatives thereof with the concentration reaching 700mg / L can be degraded by Pseudomonas nitroreducens of the invention, and the degradability can reach 100% after treating for 72h. Moreover, the Pseudomonas nitroreducens CQ1 of the invention is sensitive to kanamycin sulfate, tetracycline and gentamicin and does not carry plasmids.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
High-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102604848BIncrease contentExcellent strainFungiMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to high-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria; a method for preparing the brewing yeast bacteria provided by The invention comprises the following steps: selecting strong promoters PGK1 so as to overexpress ATF2 gene coding alcohol acetyl transferase, thereby obtaining high-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria SaccharomycescerevisiaeEY-14, wherein a preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.5635. According to The invention, on a condition that other fermenting performance is not influenced, transformant bacterial strains are compared with parent strains (SaccharomycescerevisiaeCGMCC No 2.1525); after simulation of semi-solid fermentation, the content of ethyl acetate is increased by 3.6 times; the content of isoamyl acetate is increased to 55.2mg / L; the content of isobutyl acetate is increased to 33.8mg / L; the sifted engineering bacteria has no specific demand for fermentation equipment and conditions; the equipment and conditions of normal white sprits factories can be used; therefore, the engineering bacteria has wide application propose and brings marked economic benefit to industrial production of the white sprits factories.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of high-efficiency phosphorus-solubilizing rhizobia and its application
ActiveCN105950520BPhosphate dissolving ability enhancedHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNutritional qualityPhosphate fertilizer
The invention discloses a high-efficiency phosphorus-dissolving rhizobia and its application. The phosphorus-dissolving rhizobia is named Rhizobium Rhizobium sp.P‑1 has been deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on June 16, 2016, with the deposit number CCTCC M 2016333. The rhizobia can convert insoluble inorganic phosphorus into high-quality phosphorus compounds that can be directly absorbed and utilized by plants. In the lettuce pot test, the rhizobia screened by the present invention can significantly increase the content of available phosphorus in the soil, and in the case of reducing the amount of phosphorus fertilizer applied by 50%, the lettuce output is not reduced, and the nutritional quality of the lettuce is also improved. . The rhizobia can be used to prepare phosphate-dissolving bacteria, which is widely used in agricultural production to improve the bioavailability of insoluble phosphorus in soil and the utilization efficiency of phosphate fertilizers, reduce fertilizer and increase production, and has important significance and application value in maintaining agricultural ecological balance. .
Owner:武汉一禾生态环境检测中心 +1
Application of a kind of Bacillus subtilis in biological control of Phellodendron blight
The invention provides a Bacillus subtilis used for inhibiting Phellodendron twig blight, the preservation number is ATCC NO.6051, and the bacterial strain has good control effect on Phellodendron twig blight.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for producing gamma-linolenic acid protein by biofermentation
InactiveCN1580236AStable productivityRaise the level of fermentationFungiFermentationMushroomThallus
The invention is a kind of craft for produce gamma-linolenic acid albumen. It contains approaches, such as activation and cultivation of original mushroom, rock and shock culure, first level fermentation, second level fermentation, third level fermentation, dehydration and drying. The mushroom is better, output is great, dry thallus yield is 3.5-4.1%, aliphatic acid is 25-39%, linolenic acid is 20-24% and the cost is low. The cost of raw material can be reduced by 50-80%. The craft is scientific and maturity, so it is able to manufacture in large scale of industrialization and can reach the 3-4 level of 10-30T.
Owner:SHENGJIE BIOLOGICAL SCI TECH CHANGCHUN
Bacillus natto and its application in the preparation of ace-inhibiting peptides from fermented scallop skirts
InactiveCN108424863BEasy to handleHigh resource utilizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus subtilis var. natto
The invention discloses the application of Bacillus subtilis subsp.natto ACE-IP and Bacillus subtilis subsp.natto ACE-IP in the preparation of ACE-inhibiting peptides from fermented scallop skirts, and its preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2018081. The screening and identification method of Bacillus subtilis natto subspecies ACE‑IP includes: raw material processing and amino acid composition analysis; preparation of scallop skirt fermentation medium; primary screening of Bacillus natto; secondary screening of Bacillus natto; identification of strains . The Bacillus natto screened by the present invention is prepared by fermenting the scallop skirt to obtain the ACE inhibitory peptide, which fully exerts the effect of producing various proteases during the fermentation of the scallop skirt, and decomposes the scallop skirt macromolecular protein into small molecule ACE Inhibiting peptides with high inhibitory activity; not only provide excellent strains for industrial production of ACE inhibitory peptides that are safe, have no side effects and have high activity, but also provide a theoretical basis for the development, utilization and further processing of scallop skirts.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com