Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield and construction method thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the breeding of industrial microorganisms, high-yielding Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetically engineered bacteria and its construction, can solve the problems of poor quality of finished wine, low yield of raw materials, low content of ester aroma substances, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: Construction of genetically engineered strains of high ester-producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae
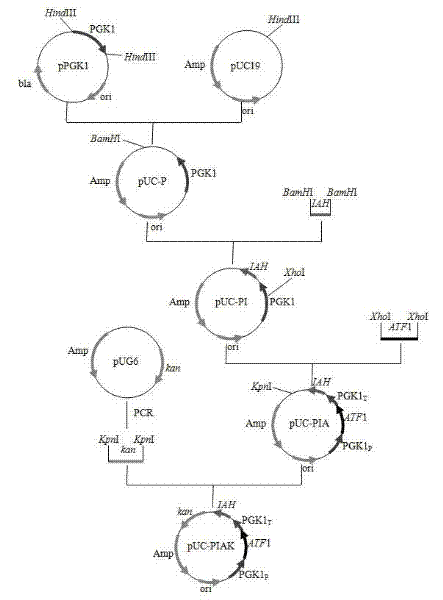
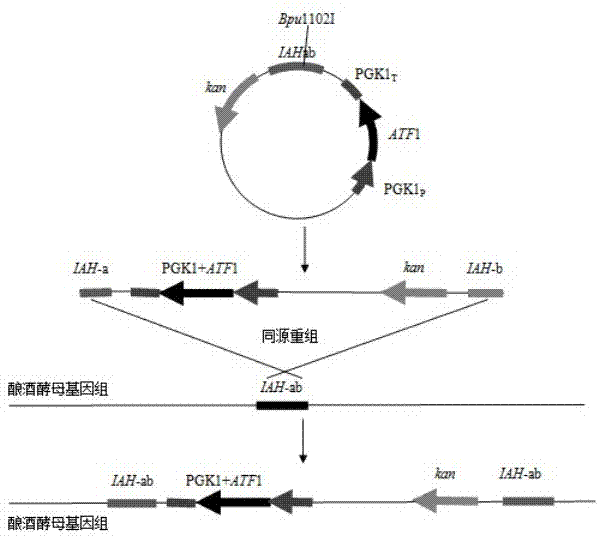
[0046] 1) Construction of pUC19-PIAK plasmid:
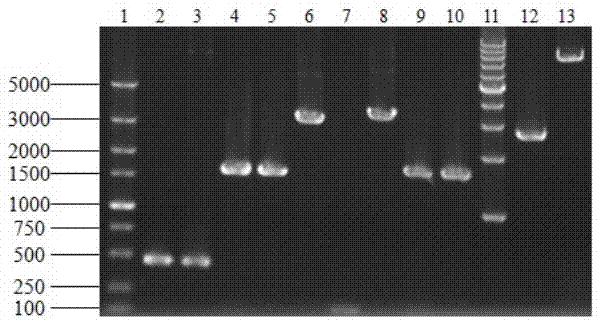
[0047] Hind III digested pPGK1 plasmid, releasing a PGK1 fragment of about 1.8 kb; digested vector pUC19 with Hind III; used T 4 DNA ligase connects PGK1 / Hind III and pUC19 / Hind III to form plasmid pUC-P; BamH I digests the homologous fragment of IAH1 and plasmid pUC-P respectively; 4 DNA ligase is ligated to form the pUC-PI; Xho I digests the ATF1 gene and the plasmid pUC-PI respectively; use T 4 DNA ligase ligation constitutes plasmid pUC-PIA. Using pUC-PIA as a template, corresponding primers were designed according to the sequence of PGK1 and ATF1 to verify the direction of ATF1; KpnI digested Kan gene and plasmid pUC-PIA respectively; using T 4 DNA ligase ligation to form plasmid pUC-PIAK, the construction process is as follows figure 1 Shown. figure 2 It is the verification electropherogram of pUC-PIAK plasmid: Lan...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2: Simulated rice wine fermentation experiment
[0064] 1) See the fermentation process route Figure 7 .
[0065] 2) Process conditions: rice soaking conditions: 25-30℃, 72h immersion; cooking conditions: steaming at atmospheric pressure for about 30 minutes, uniform particles and no white inside; pre-fermentation conditions: 28℃, 5 days.
[0066] 3) Ingredients: japonica rice: 100g; cooked wheat koji: 10g; water: 105ml, the water includes 60ml of clear water and 45ml of slurry water, excluding water absorption for soaking rice and water absorption for steaming rice; inoculation amount: 10% (20mL).
[0067] According to the above simulation process, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain EY-13 and its haploid (type a and α) and the starting strain (Saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No 2.1525) and its haploid (type a and α) were semi-solid respectively. Fermentation experiment; shake and weigh every 12h during the fermentation, record the weight loss; after the f...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3: Simulated liquor fermentation experiment
[0073] The slag fermentation method compares the ester production performance of three kinds of yeasts: alcohol ADY, Saccharomyces cerevisiae acceptor strain and Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain. Test method: raw material: distillers grains = 1:2.5, rice husk is 20% of the raw material, and the total weight of each jar is about 300g. The addition amount of saccharification enzyme is 250U / ml, and the addition amount of alcohol ADY and rice wine yeast is 1.2%. Ferment for 7 days in the altar. After the fermentation, the residual starch, alcohol volume fraction and main aroma component content of each jar were measured, and its comprehensive performance was characterized by fermentation capacity, residual sugar concentration and product production. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0074] Table 2 Liquor fermentation performance of alcohol ADY, Saccharomyces cerevisiae receptor strain and Saccharomyces cerevisi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com