Method for improving competitive nodulation capacity of nodule bacteria USDA110
A rhizobia and nodulation technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of inoculated bacteria failing to achieve the expected effect, weak nitrogen fixation ability, and reducing the nodule occupancy rate of inoculated rhizobia, so as to improve the competitive nodulation ability and nitrogen fixation ability. , the effect of good symbiotic nitrogen fixation and competitive nodulation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1 Mutant bacterial strain construction
[0031] According to the genome of the wild-type strain Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110, the dgoK1 gene sequence was found in NCBI, the sequence of about 500 bp near the 5' end was selected, the upstream and downstream primers were designed, and appropriate restriction sites were added to obtain the target fragment by PCR. After recovery, the The target fragment was ligated with the T vector (pMD19-T) and sent to the company for sequencing.
[0032] Primer information:
[0033] F: CGGGATCC CCGCCTTGAAGCTTGCAA BamH1
[0034] R: GGAATTCCAGGTCCTGGCCGAACG EcoR1
[0035] Construction of pK19mob insertion inactivation plasmid. The correctly sequenced bacterial plasmid was digested and recovered, and connected to pK19mob. The insertion inactivation plasmid was transformed into E.coli DH5α, the plasmid was extracted, transformed into E.coli S17-1, and introduced into the wild-type bacteria USDA110 through conjugation of two...
Embodiment 2
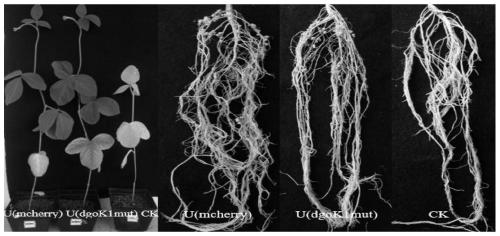
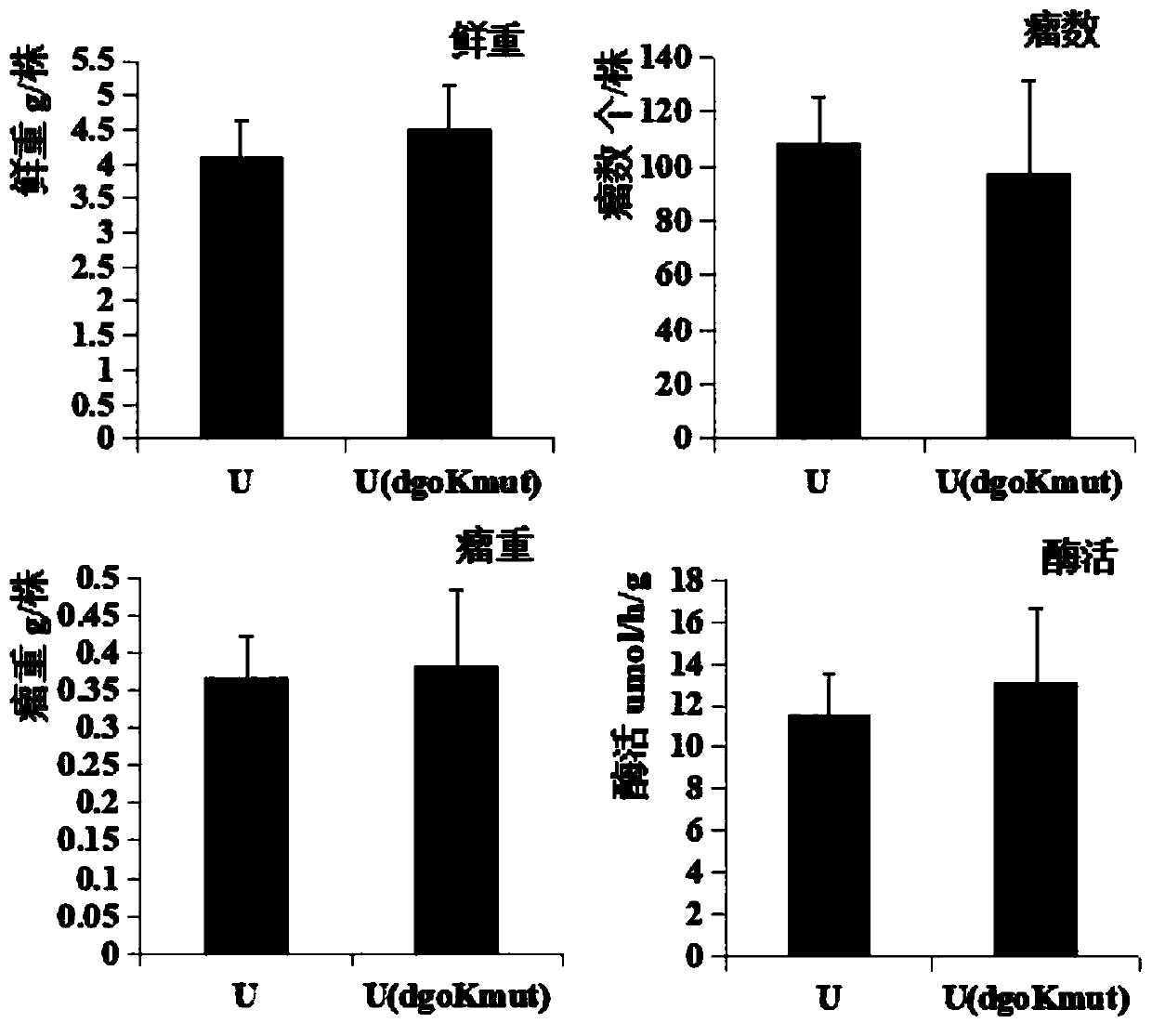
[0038] Embodiment 2 Pot experiment detects symbiotic nitrogen fixation traits
[0039] (1) Seed treatment: When soybeans are cultivated with sterilized vermiculite, the seeds are sterilized with 75% ethanol for 30 seconds, poured off the ethanol, then sterilized with 5% NaClO for 3 minutes, washed 10 times with sterile water, and spread on 1-2% water agar On a flat plate, cultivate in the dark at 28 degrees for 2 days; when planting with soil as the substrate, the seeds are not sterilized, soaked in water for 1 hour, and planted in the soil.
[0040] (2) Cultivation: Soybeans are planted with vermiculite, sterilized with clean vermiculite for 1 hour, large pots and plates are sterilized by ultraviolet light, filled with vermiculite, 6 pots are placed on each plate, and 3 soybeans are planted in each plate, and no The nitrogen nutrient solution was poured on the plate. If soil is used to plant soybeans, the soil samples are not sterilized and planted directly.
[0041] (3) Rh...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 Pot experiment detects competition nodulation ability
[0046] 1) Detection of competitive nodulation ability in sterile vermiculite
[0047] ①Williams 82 was planted in sterile vermiculite, and the seed treatment and cultivation methods were the same as those in 2.
[0048] ②Rhizobia inoculation: OD of all bacteria before inoculation 600 Adjusted to 0.5, USDA110 (dgoK mut) and USDA110 (mcherry) were mixed at a ratio of 1:1, 10:1, and 1:10 respectively. After mixing evenly, the plants were inoculated with 2 mL of bacteria.
[0049] ③ Competitive nodulation detection: Harvest plants, remove root nodules, observe with a fluorescence microscope, take pictures, and count non-luminescent nodules, which is the nodule rate of recombinant bacteria.
[0050] The result is as Image 6 As shown, when 1:1 mixed inoculation, USDA110 (dgoKmut) accounted for tumor rate of 84% greater than 50%, when 1:10 mixed inoculation, USDA110 (dgoKmut) accounted for tumor rate of 8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com