Double T-DNA carrier and its application in cultivating of non selecting sign transgene rice
A technology of transgenic rice without selection marker, applied in recombinant DNA technology, application, genetic engineering and other directions, can solve the problems of double T-DNA vector, such as large molecular weight, limited effect, and lack of versatility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
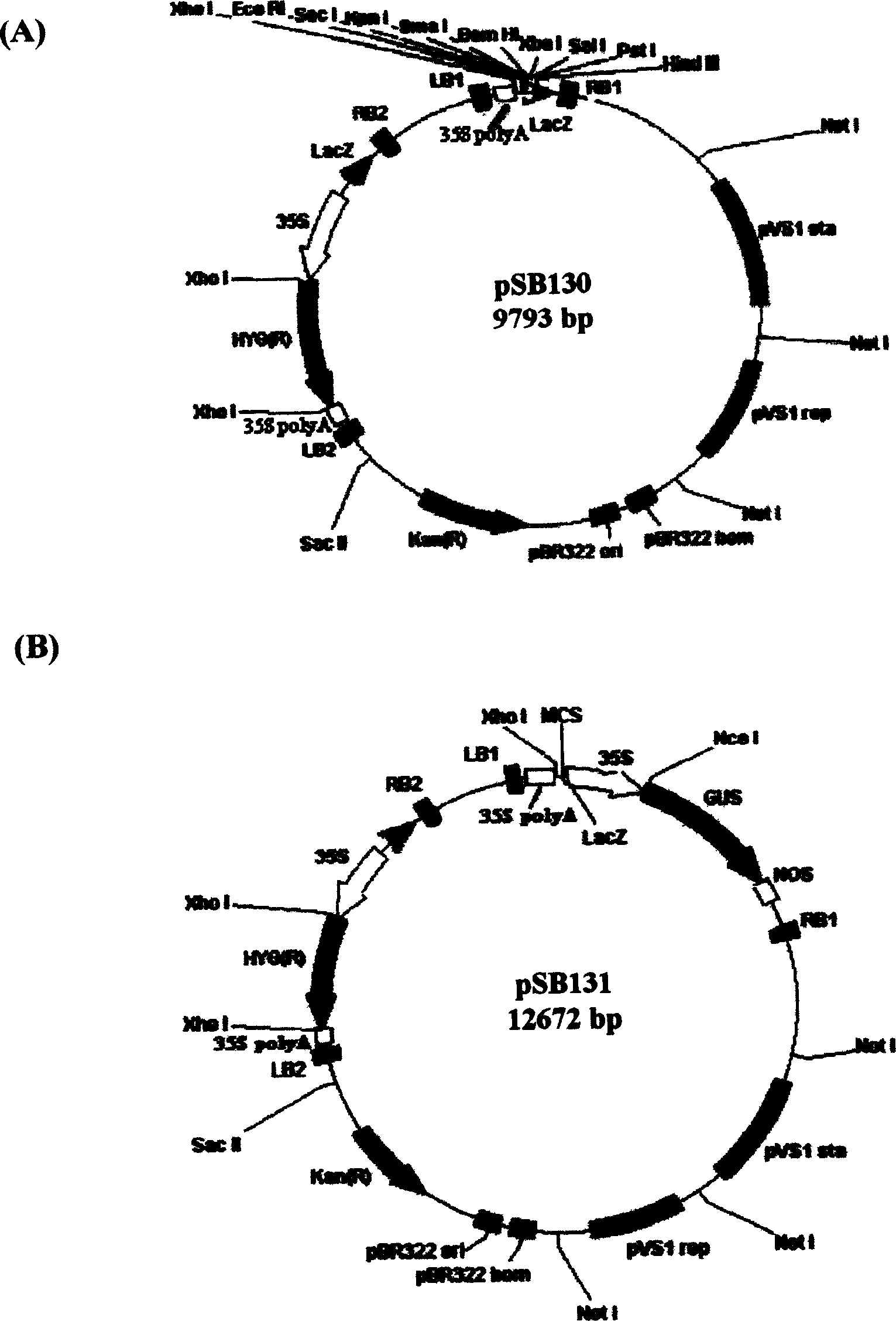
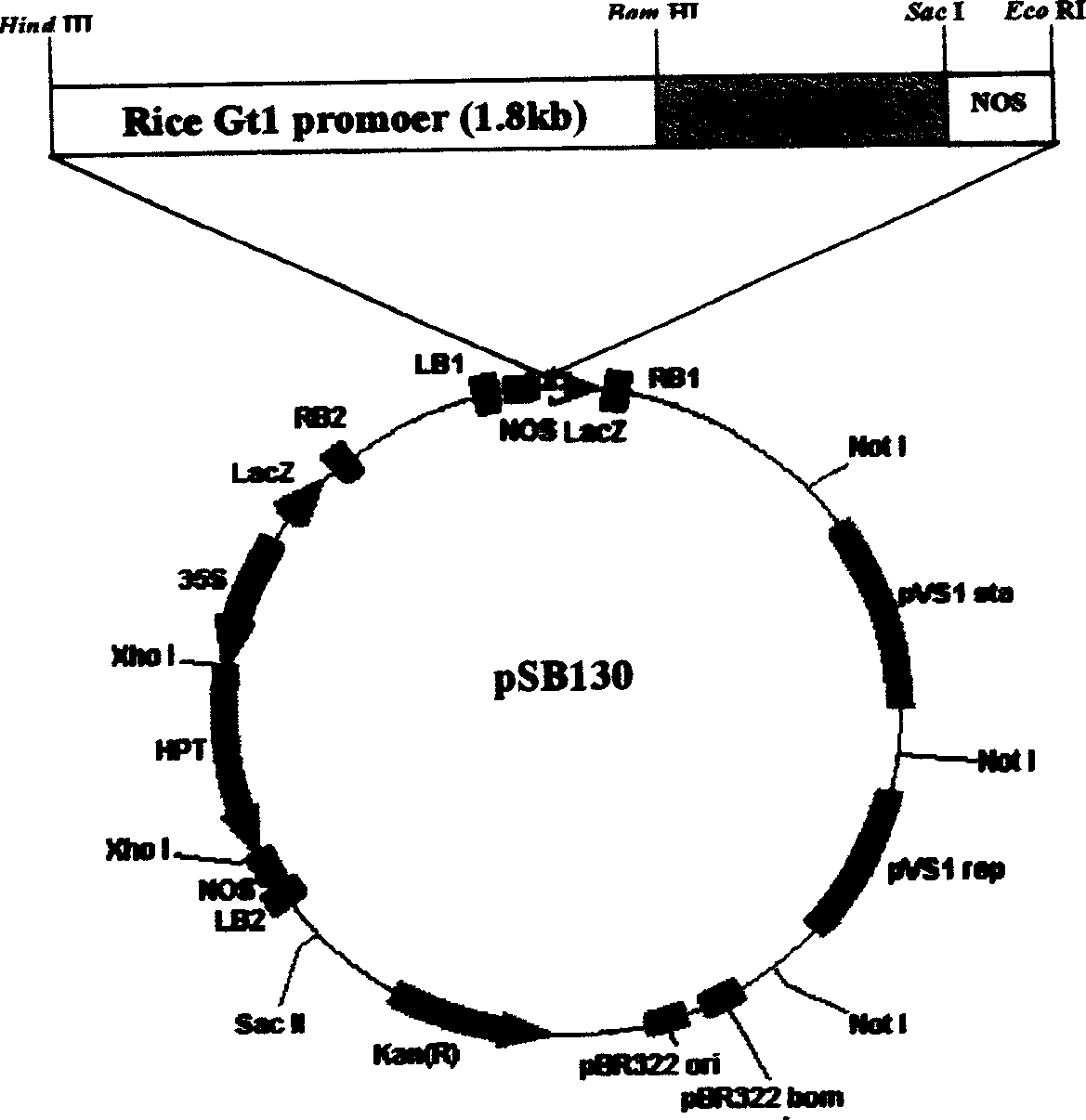
[0032] Example 1: Construction of Plant Double T-DNA Universal Binary Vectors pSB130 and pSB131
[0033] 1.1 According to the nucleotide sequence of the binary vector pCAMBIA1300 (CAMBIA, Australia), two primers LBP were designed 1 (5'-CAA GCGGCCGC GAGATCATCCGTGTTT-3') and LBP 2 (5'-GTA GAATTC GACCGGATCTGTCGATCGA-3') to amplify the left border sequence of its T-DNA region from the binary vector. Not I and Eco RI (underlined) enzyme cutting sites were added to the 5' ends of these two primers, wherein LBP 2 It is located on the side of the left border sequence close to the T-DNA. The conditions of the PCR reaction were 95°C, 5min; 95°C, 50sec, 55°C, 50sec, 72°C, 30sec, 30 cycles; 72°C, 7min. The 495bp PCR product was digested with Not I and Eco RI and cloned into the intermediate vector pBluescript SK - In , the identified positive clone is called pBSK / LB.
[0034] 1.2 Digest the binary vector pCAMBIA1300 with Hind III and Eco RI, fill it up with a large Klenow fragmen...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Utilizing double T-DNA vectors to cultivate high-quality transgenic rice with high lysine content without selection markers
[0040] 2.1 Construction of double T-DNA binary vector carrying high lysine content protein LRP gene
[0041] The lack of lysine in rice is considered to be the first limiting essential amino acid in rice. Using transgenic technology to express heterologous lysine-rich proteins in rice can provide the total lysine content in rice. The high lysine content protein (Lysine-rich protein, LRP) gene cloned from the square bean contains 10.7% lysine (Sun et al., USA patent, 1998) in its coded protein, is an ideal for Genes for improving the nutritional quality of rice. In order to express it specifically and highly in the endosperm of transgenic rice seeds, the cDNA encoding LRP was connected to the glutelin gene Gt1 promoter of rice itself, and then cloned into the double T-DNA binary vector pSB130( figure 1 -A) In the multiple cloning site...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3: Utilizing double T-DNA vectors to cultivate insect-resistant transgenic Bt rice without resistance selectable markers
[0063] 3.1 Construction of the double T-DNA binary vector carrying the Bt toxin gene
[0064] The Bt toxin gene derived from Bacillus thuringiensis is currently the most widely used insect resistance gene, and the Bt toxin gene has been successfully used in cotton, corn, etc.; the gene introduced into rice has good resistance to rice borer. In this example, the Bt poisonous protein gene is resynthesized according to plant preferred codons, which can make the gene more efficiently and stably expressed in transgenic plants; in addition, a transit peptide signal sequence from plants is added to the N-terminal of the Bt poisonous protein , the expression product can be localized in the endoplasmic reticulum, making the expression of the target protein more efficient (Peng Rihe et al., Acta Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2001, 33: 219-224). The te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com