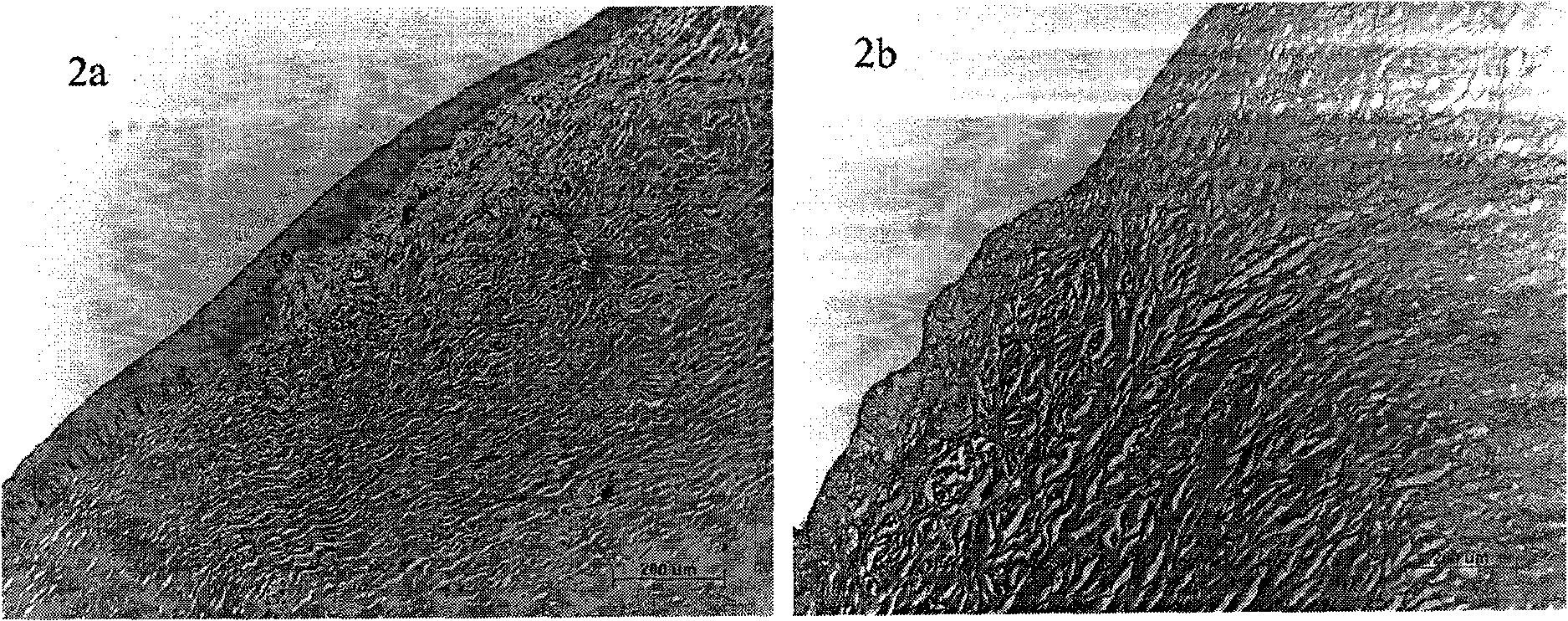
Method for preparing acellular matrix
A technology for decellularized matrix and tissue organs, which is applied in the field of preparing acellular matrix, can solve the problems of destroying the ultrastructure of extracellular matrix and excessive molecular weight, and achieve the effect of promoting hydrolysis reaction, strong specificity, and promoting decellularization effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The purpose of this example is to prepare porcine corneal decellularized matrix with porcine cornea. (note: the phospholipase solution used in this embodiment can contain phospholipase A 1 , A 2 , B 1 , B 2 , any one or more of C, D. The surfactants used can be ingredients with surface activity that can be produced in vivo or in the human body, such as: cholate, deoxycholate, chenodeoxycholate, glycocholate, glycochenodeoxychole Any one or more of salt, taurocholate, taurochenodeoxycholate, lipopolysaccharide, lipoprotein, lysolecithin, or polyethylene glycol, TritonX-100, its effect Same as below).
[0049] 1. Under normal aseptic operation at room temperature, use a 10.0mm trephine to remove fresh pig eye corneal slices. Soak the obtained porcine corneal slices in carbonate buffer solution containing antibiotics (100 U / ml penicillin G, 100 μg / ml streptomycin sulfate) for 2-5 times, each time for 2-10 minutes.
[0050] 2. Put the porcine corneal piece into 10ml ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The purpose of this example is to prepare porcine limbal acellular matrix with porcine limbal tissue. (note: the phospholipase solution used in this embodiment can contain phospholipase A 1 , A 2 , B 1 , B 2 , any one or more of C, D, the effect is the same as the following).
[0058] 1. At room temperature, under routine aseptic operation, remove fresh porcine corneal limbal tissue of 2 mm each area inside and outside, and use antibiotics (100 U / ml penicillin G, 100 μg / ml streptomycin sulfate) on the pig corneal limbal tissue. Soak in carbonate buffer solution 2-5 times, 2-10 minutes each time.
[0059] 2. Put the porcine limbal tissue into 10ml of sterile pure water and soak in a water bath at 4°C for 10-60 minutes.
[0060] 3. Put the porcine limbal tissue into 10 ml of sterile phospholipase solution, and shake it in a water bath at 4°C for 6-24 hours. (Sterile phospholipase solution: prepared using carbonate buffer, pH range 8-12, phospholipase A 1 +A 2 =50~...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The purpose of this example is to use porcine conjunctiva to prepare porcine conjunctival acellular matrix. (note: the phospholipase solution used in this embodiment can contain phospholipase A 1 , A 2 , B 1 , B 2 , any one or more of C, D. The surfactants used can be ingredients with surface activity that can be produced in vivo or in the human body, such as: cholate, deoxycholate, chenodeoxycholate, glycocholate, glycochenodeoxychole Any one or more of salt, taurocholate, taurochenodeoxycholate, lipopolysaccharide, lipoprotein, lysolecithin, or polyethylene glycol, TritonX-100, its effect Same as below).
[0065] 1. At room temperature, under routine aseptic operation, remove the fresh porcine conjunctiva tissue within a range of 1 × 1 cm, and use carbon dioxide containing antibiotics (100 U / ml penicillin G, 100 μg / ml streptomycin sulfate) on the obtained porcine conjunctiva tissue. Soak in salt buffer solution 2-5 times, 2-10 minutes each time.
[0066] 2. Put...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com