Late Blight Resistance Gene From Solanum Americanum And Methods Of Use
A transgenic plant, resistance technology, applied in the direction of genetic engineering, biochemical equipment and methods, introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to perform map-based cloning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0187] Example 1: Solanum nigrum is a rich source of late blight resistance genes
[0188] We set out to study the immune response to Phytophthora infestans in a panel of Solanum nigrum (2n) and Solanum nigrum (6n) lines obtained from three European seed collections (Table 1). Flow cytometry analysis identified lines 944750095, A54750014 and A14750006 originally listed as Solanum nigrum as diploid rather than hexaploid (data not shown). This is consistent with a previous report of frequent misidentifications between Solanum nigrum and Solanum nigrum (Manoko et al. (2007) Plant Syst. Evol. 267:1-11). For the purposes of the present invention, unless otherwise stated or apparent from the text of the examples, all plant lines will be assigned to the broadly defined Solanum nigrum group. It is furthermore recognized that the present invention is also not dependent on the R gene of the present invention being isolated from a particular plant species or even being said species of t...
Embodiment 2
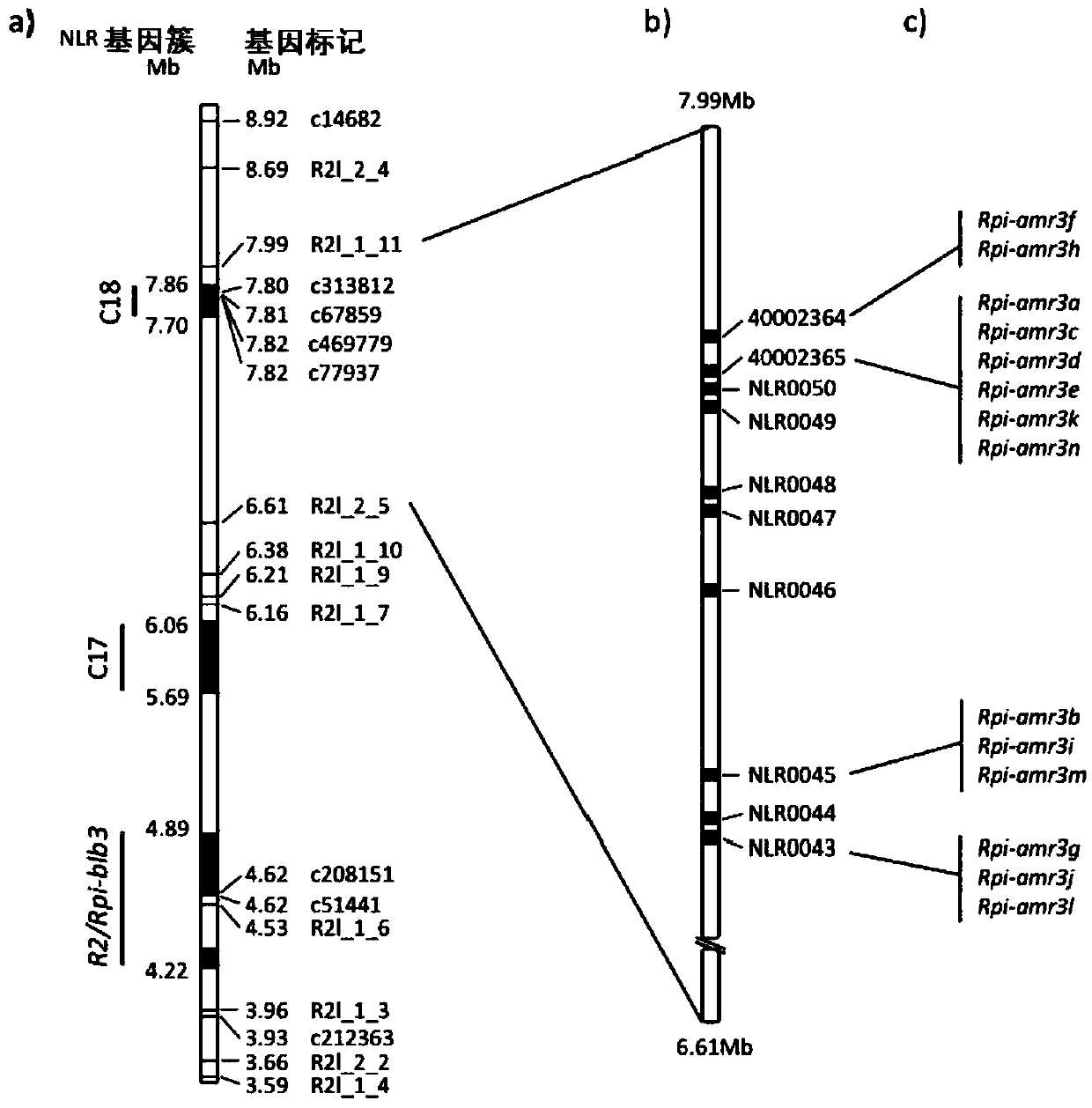
[0195] Example 2: RenSeq gene mapping shows that Rpi-amr3 is located near R2 on potato chromosome 4
[0196] Inoculation of the pathogen on the leaves of young F2 plants (F1 954750186x 944750095) revealed 99 resistant and 6 susceptible plants (15:1 segregation), indicating the presence of two unlinked dominant Rpi genes. To segregate the gene, we self-pollinated 15 disease-resistant F2 plants and determined resistance segregation patterns in 30-200 F3 progeny. In the DLA test on leaves from young plants (8-10 weeks old), the four populations segregated 3:1. Interestingly, this result was inconsistent with that in older plants, suggesting the presence of additional resistance genes in adult plants (greater than 12 weeks old), which were assessed as susceptible when young.
[0197] We hypothesized that the underlying late blight resistance genes encode NB-LRR / NLR proteins. We applied RenSeq to the resistant (R) and susceptible (S) parents, and to pooled DNA from the 50 most su...
Embodiment 3
[0200] Example 3: Combination of RenSeq and PacBio sequencing enables assembly of full-length sequences of 14 co-segregated full-length NLR genes
[0201] One of the main motivations of this project is to establish an R gene cloning method that does not require the construction of a BAC library. We previously found that the high copy number and sequence similarity of NLR genes complicates de novo assembly of short Illumina RenSeq reads (Jupe et al (2013) Plant J. 76:530-544; Andolfo et al (2014) BMC Plant Biol. 14:120). We therefore developed NLR enrichment combined with the longer read technology provided by PacBio RSII (Eid et al. (2008) Science 323:133-138). We used our Solanum NLR bait library (Jupe et al. (2013) Plant J. 76:530-544) from two independent libraries (1.5 kb and 2.5 kb gDNA fragments) derived from the Rpi-amr3-carrying parental line 944750095 The complete NLR complement was captured (see Methods for details). The 1.5kb and 2.5kb fractions were sequenced on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com