Wheat stripe rust resistance genes and methods of use
A gene and resistance technology, applied in the field of disease resistance genes to enhance plant resistance to plant diseases, can solve the problems of destroying the linkage of harmful alleles, long breeding timeline, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0233] Example 1: Isolation and Fine Mapping of Rps6
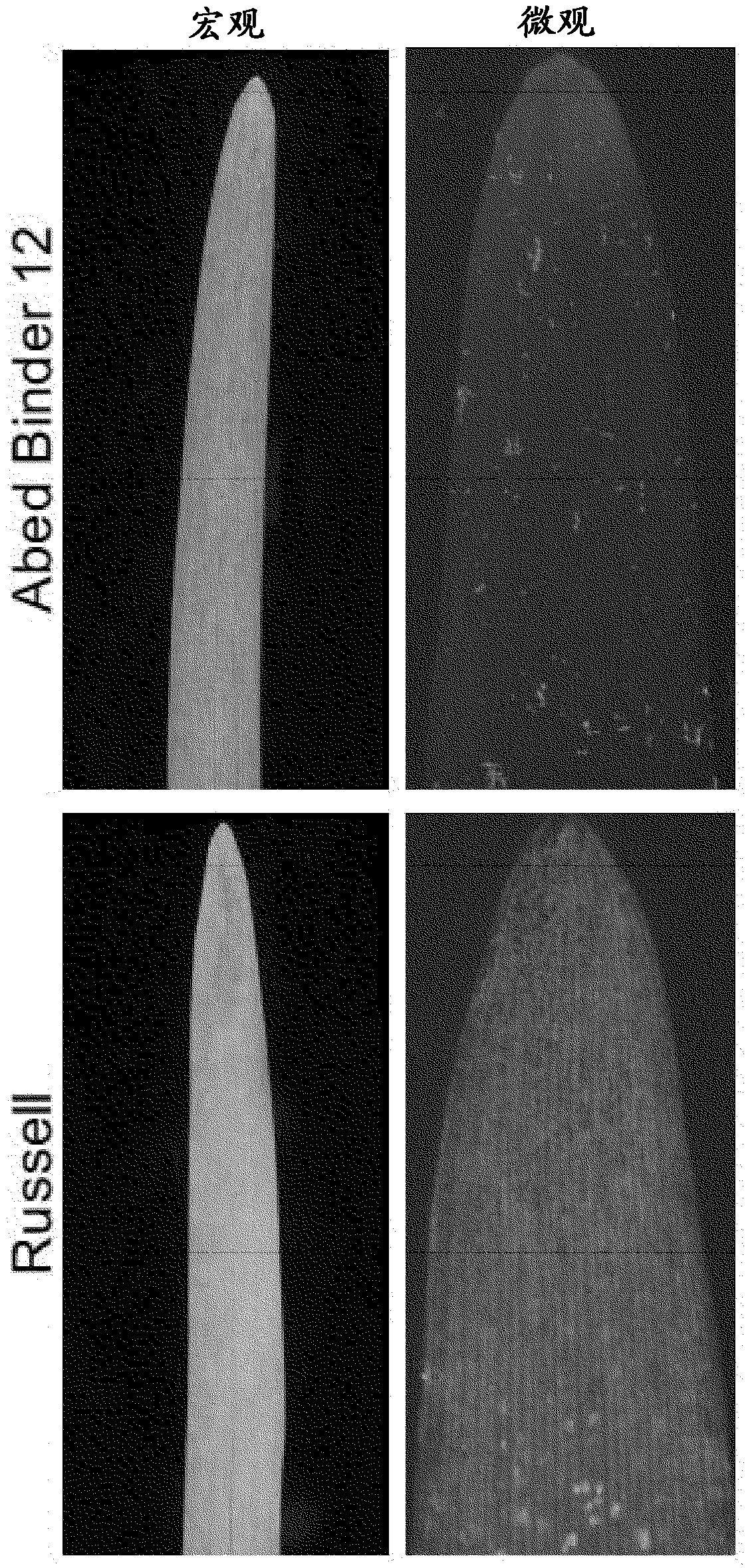
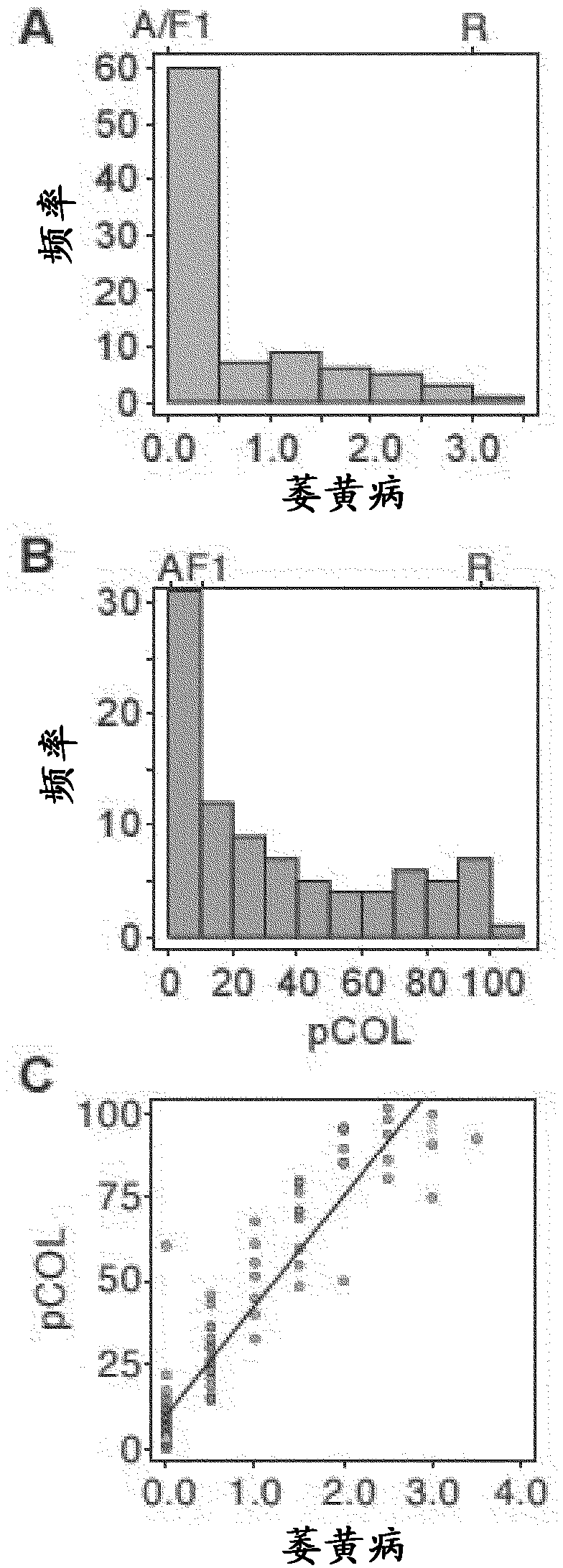
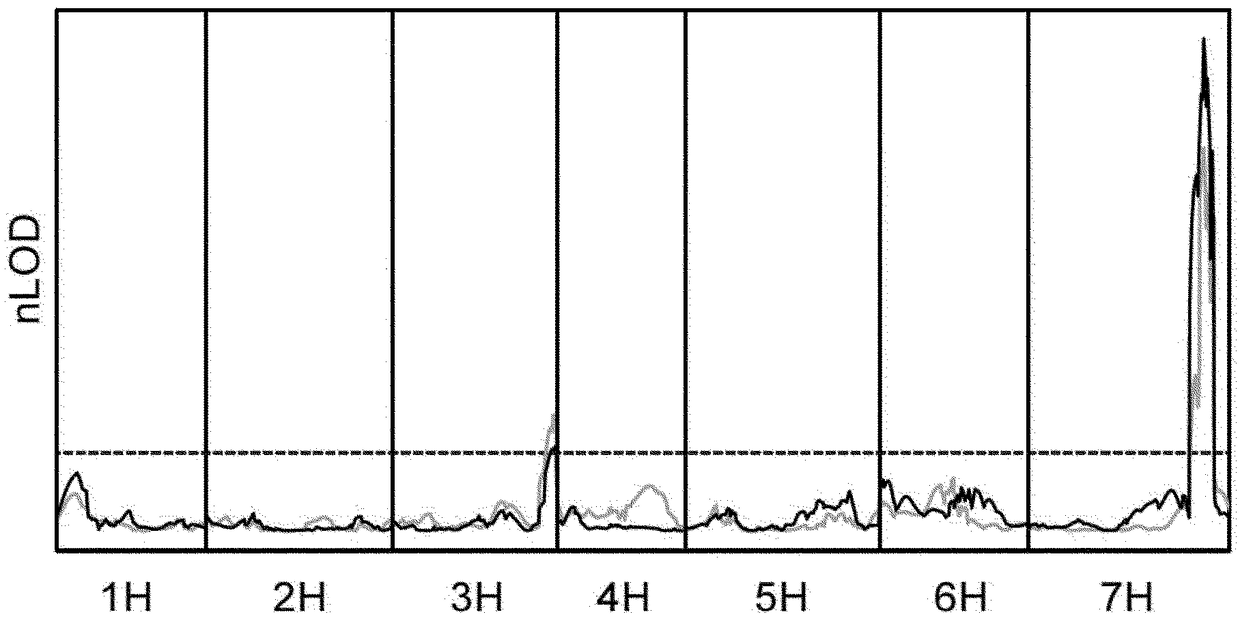
[0234]Mapping of Rps6: Different phenotypes were observed between Abed Binder 12 and Russell inoculated with Pst isolates 08 / 501 and 08 / 21. Russell showed less pustules but had a clear microscopic phenotype of colonization ( figure 1 ). We used Pst isolate 08 / 501 (AxR-Pst) to inoculate Abed Binder 12 x Russell F 2 group. Parental, F 1 and 92 F 2 Plants were phenotyped. For AxR-Pst F 2 Pustule formation was not observed for the population, but segregation was observed for chlorosis and pCOL ( figure 2 A-2B). A strong correlation between chlorosis and pCOL was observed (r 2 =0.88)( figure 2 C). f 1 Shows a resistance phenotype similar to Abed Binder 12. To map resistance to Pst, we used the barley oligonucleotide assay for AxR-Pst F 2 The population was phenotyped (BOPA1; 1,536 SNP-based markers; Close et al. 2009). Between Abed Binder 12 and Russell, a total of 535 polymorphic OPA markers were identified an...
Embodiment 2
[0308] Example 2: Transformation of barley using Rps6 and testing for wheat stripe rust resistance
[0309] Yeo et al. ((2014) Theor.Appl.Genet.127:325–337) previously established the double haploid population SusPtrit x Golden Promise (SxGP DH) to identify transformable barley numbers that have a significant contribution to barley A variety of heterologous rust pathogens are also susceptible. We found that accession SxGP DH-47 is susceptible to wheat stripe rust and was previously shown to be competent for Agrobacterium-based transformation (Yeo et al. (2014) Theor. Appl. Genet. 127:325-337). Transformation of SxGP DH-47 barley was performed as described by Bartlett et al. ((2008) Plant Methods 4:22) with the modification that immature embryogenic calli were infected with Agrobacterium tumefaciens instead of immature Embryo. Briefly, immature embryos, approximately 1.5 to 2 mm in diameter, were harvested from barley plants grown in the greenhouse. In contrast to what was des...
Embodiment 3
[0311] Example 3: Transformation of wheat by Rps6 and test for resistance to wheat stripe rust
[0312] Transformation of wheat (Tyticum vulgaris "Fielder") was performed as described by Periyannan et al. ((2013) Science 341 :786-788). The T-DNA insert comprises the original promoter and coding sequence for NLR-A (SEQ ID NO: 17) from barley contained in a T-DNA plasmid (SEQ ID NO: 15, 34 or 35), As described in Example 2, and a genomic fragment of the open reading frame of NLR-A (SEQ ID NO: 2) fused to the promoter and terminator of a highly expressed NLR gene from wheat. Phenotypic screening of transformed wheat plants for resistance or susceptibility to wheat stripe rust was performed against barley as described above in Example 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com