Application of chitosan in prevention and treatment of rice bacterial leaf streak
A chitosan and bacterial technology, applied in the application field of chitosan in the prevention and treatment of rice bacterial streak disease, can solve the problems of poor control effect and less pesticides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Embodiment 1 prepares chitosan solution
[0019] Dissolve chitosan powder with a deacetylation degree of 85% in 1% acetic acid by volume to prepare a chitosan solution with a concentration of 5 mg / mL, adjust the pH to 6.0 with NaOH, shake at room temperature for 24 hours, Sterilize in an autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes and set aside. Sterile deionized water with a pH of 6.0 was used as the control of chitosan treatment in the experiment.
Embodiment 2
[0020] The impact of chitosan on the growth of Xoc BLS-01 was detected under the conditions of embodiment 2 in vitro
[0021] The strain Xoc BLS-01 in this example is provided by the Institute of Biotechnology of Zhejiang University. This strain is the test material, and its characteristics have no influence on the test results. The present embodiment adopts counting method to detect the impact of chitosan on the growth of Xoc BLS-01, and the specific method is as follows:
[0022] Xoc BLS-01 was cultured in agar medium at 28°C for 48 hours, and the bacterial suspension was prepared with sterile water (10 9 CFU / mL). 10-fold serial dilution, pipette 10 μL of Xoc bacterial suspension of each concentration onto the plate, and place the treated plate in an incubator at 28°C for 48 hours. In the experiment, sterile deionized water with a pH of 6.0 was used as the control of chitosan treatment, and six replicates were set up for each treatment. Experiments were repeated twice.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Antibacterial activity when embodiment 3 detects different concentrations of chitosan
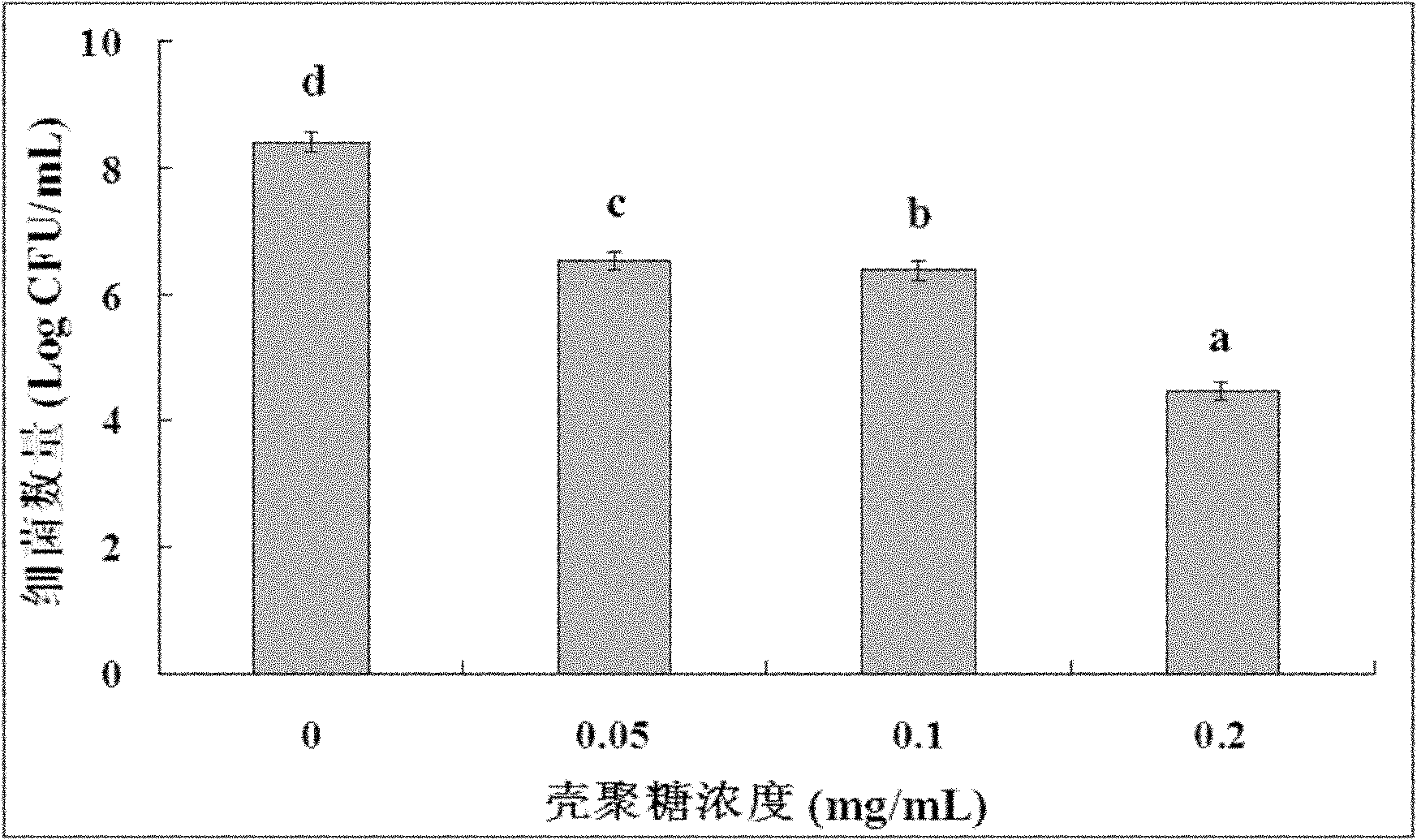
[0024] In the chitosan solution of 5 mg / mL prepared in Example 1, add sterile deionized water to prepare a concentration of 0.05, 0.10, and 0.20 mg / mL chitosan solution. Inoculate Xoc bacteria suspension (10 8 CFU / mL), shaking culture at 160r / min, 28°C for 4 hours, collect samples to detect the number of bacteria according to Example 2. Sterile deionized water with a pH of 6.0 was used as the control of chitosan treatment in the experiment.
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, chitosan solution showed significant antibacterial activity against Xoc BLS-01 at different concentrations, and the antibacterial activity gradually increased with the increase of concentration. Compared with the control, the number of cells in the chitosan solution decreased by 1.88Log CFU / mL at a concentration of 0.05mg / mL, and the number of bacteria decreased by 2.05Log CFU / mL at a concentration of 0.10mg / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com