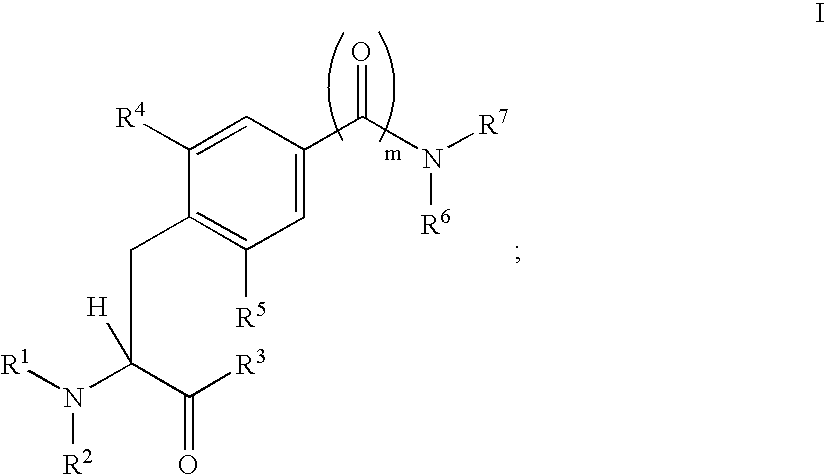
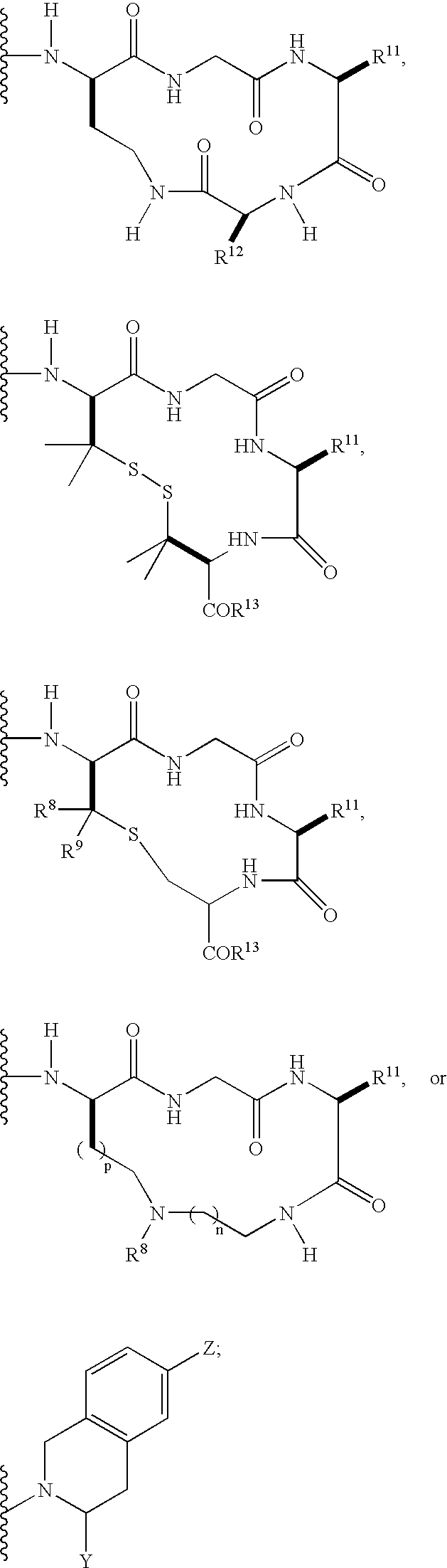
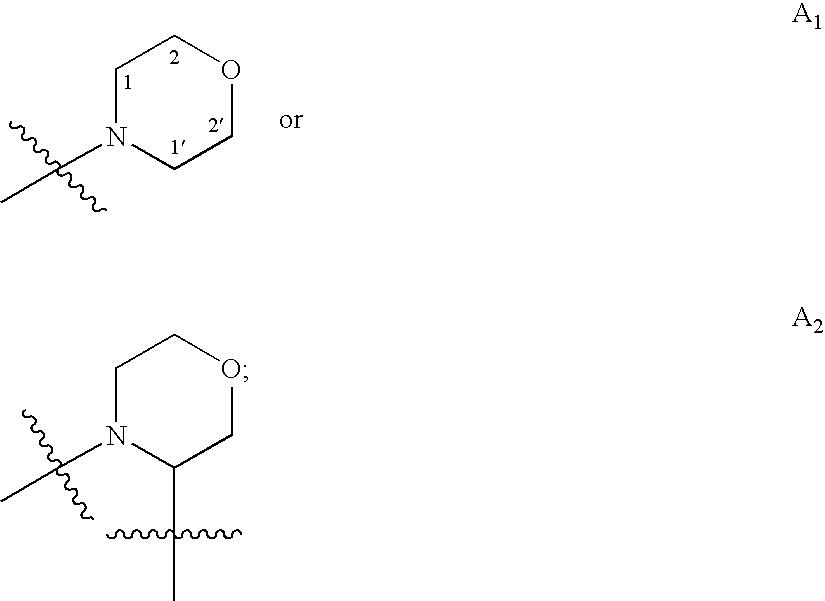
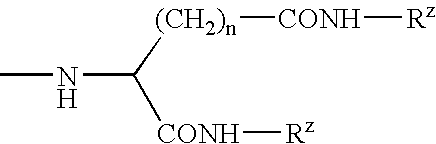
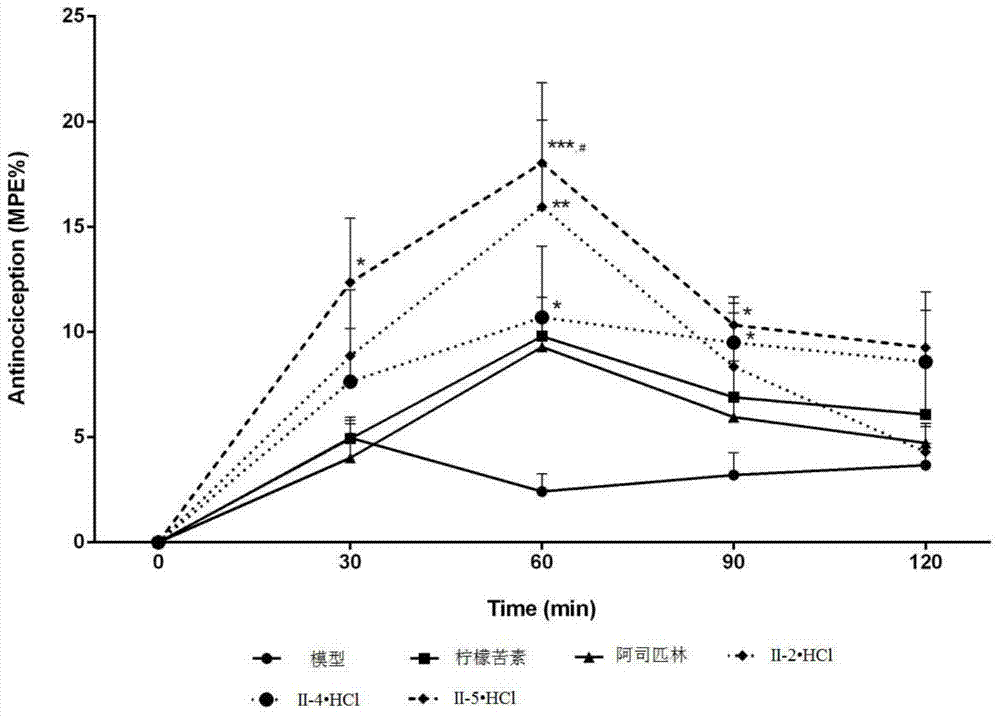
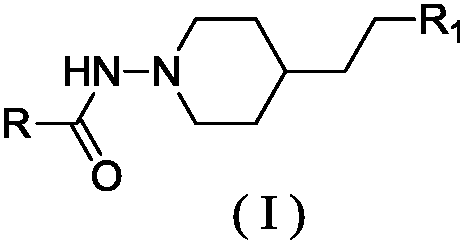
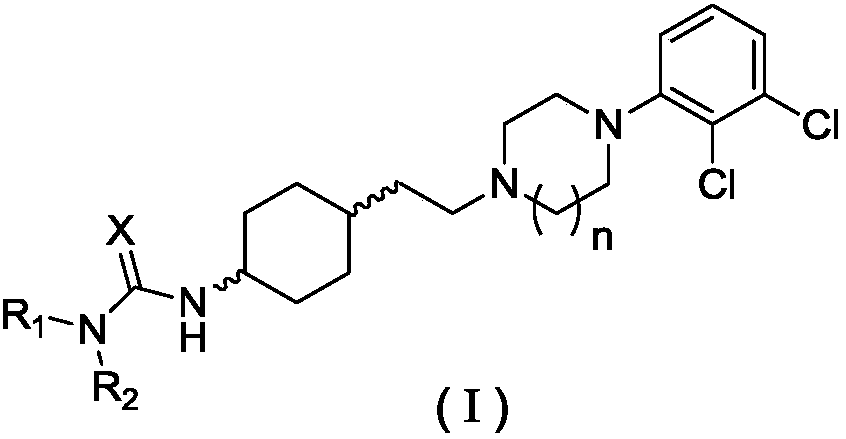
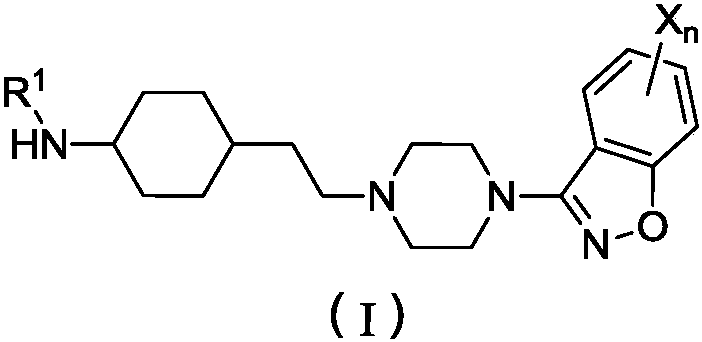
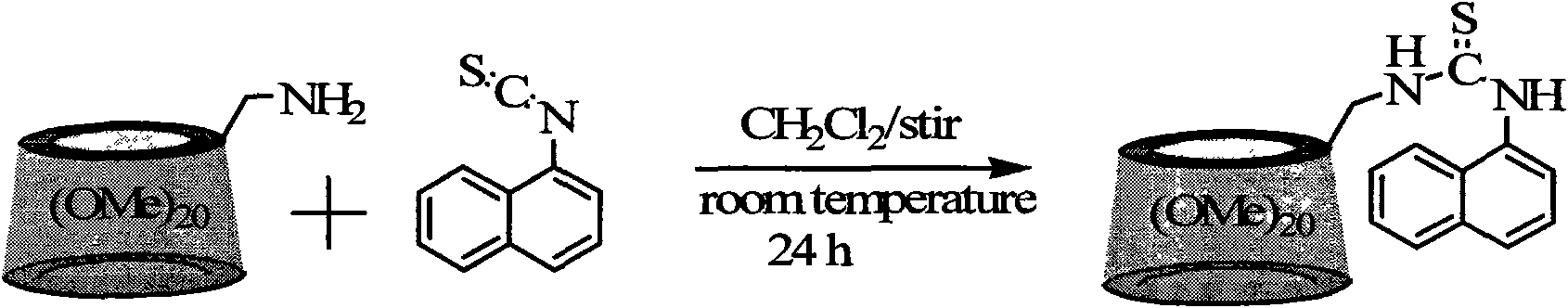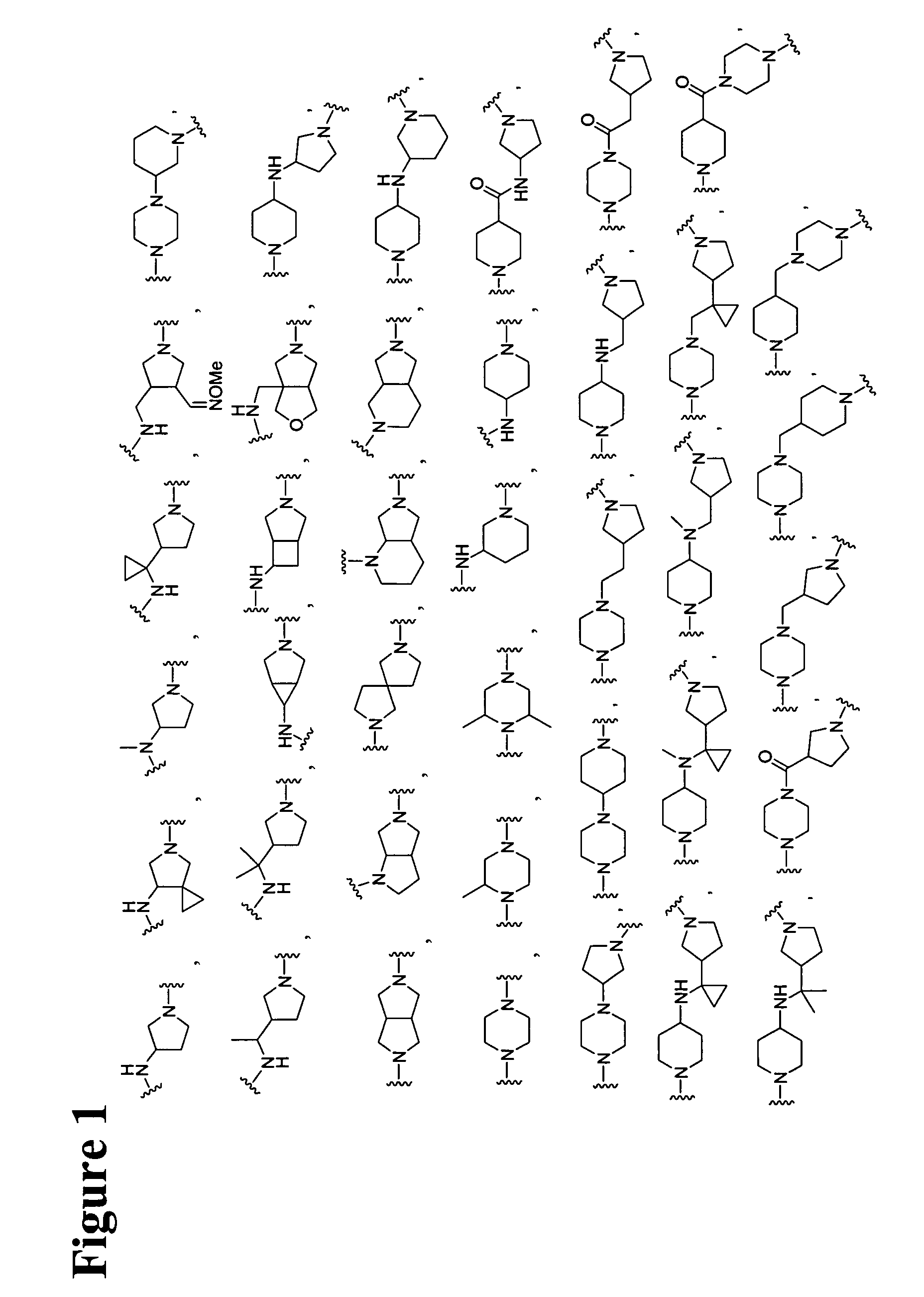Patents
Literature
148 results about "Amino derivatives" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amino acid derivatives are relatively small molecules that are structurally similar to amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. This group of hormones (sometimes known as the biogenic amines) includes epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, the thyroid hormones, and melatonin.
FSH mimetics for the treatment of infertility
InactiveUS6653338B2Easy to useMinimal supervisionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFollicle-stimulating hormoneTreatment infertility
"The present invention provides non-peptidic amino derivatives, their therapeutic use as well as pharmaceutical compositions that possess activity as Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) agonists and are useful in the treatment of infertility. In particular, the invention provides derivatives."
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Method for correcting immune system of live body
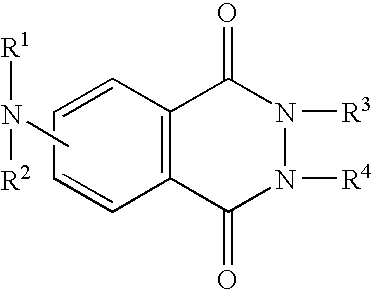
The present invention relates to medicine and veterinary, namely, to immunology, and to methods aimed at correcting the immune system of a living organism. The essence of the invention is in the immunocorrection of the organism using pharmacologically appropriate amino derivatives of 2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4~dione in their effective doses ranging from 0.2 mug to 1,000 mg.
Owner:ZHILOV VALERII KHAZHUMURATOVICH
Amino-functional polysiloxanes and their use in coatings
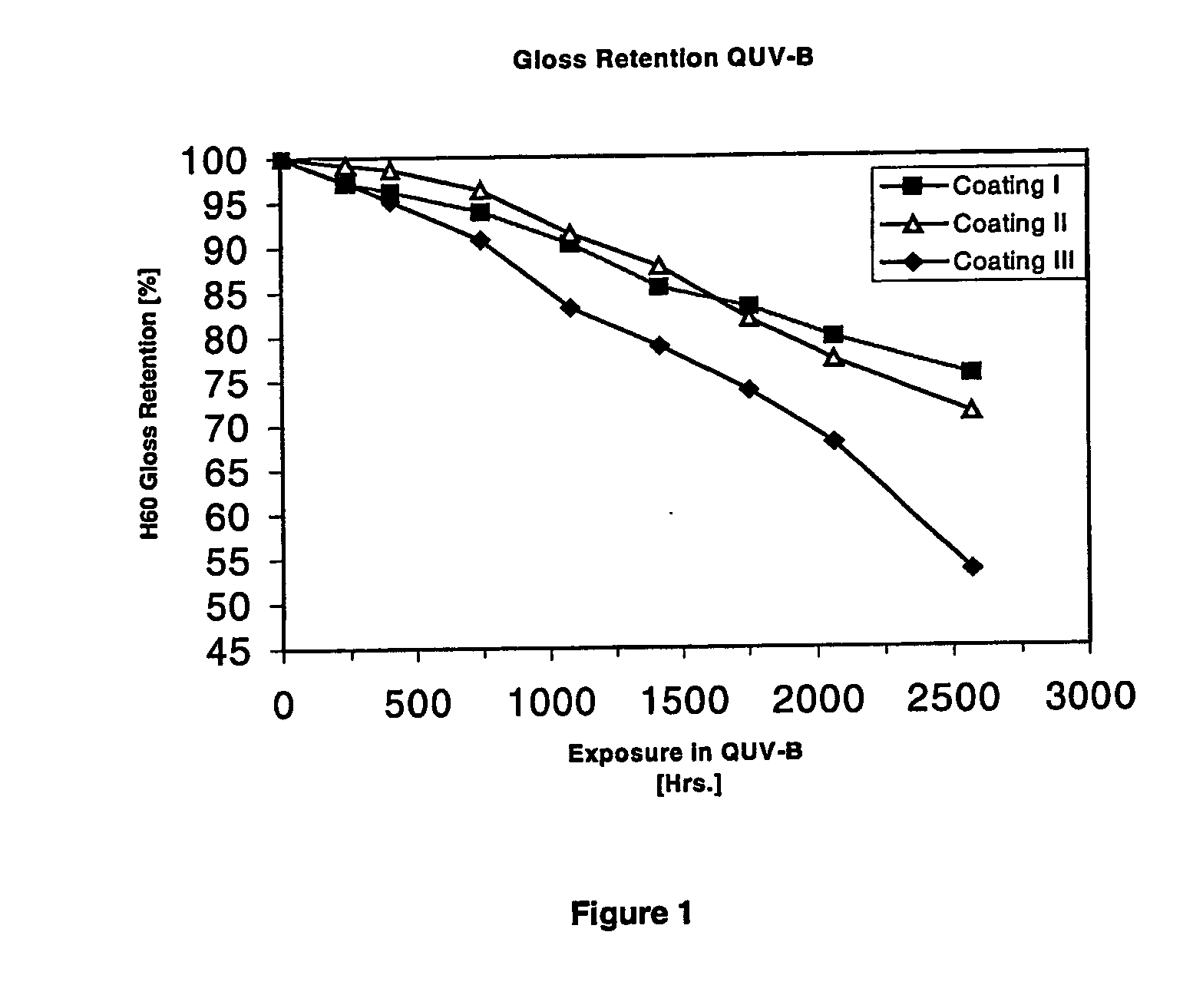
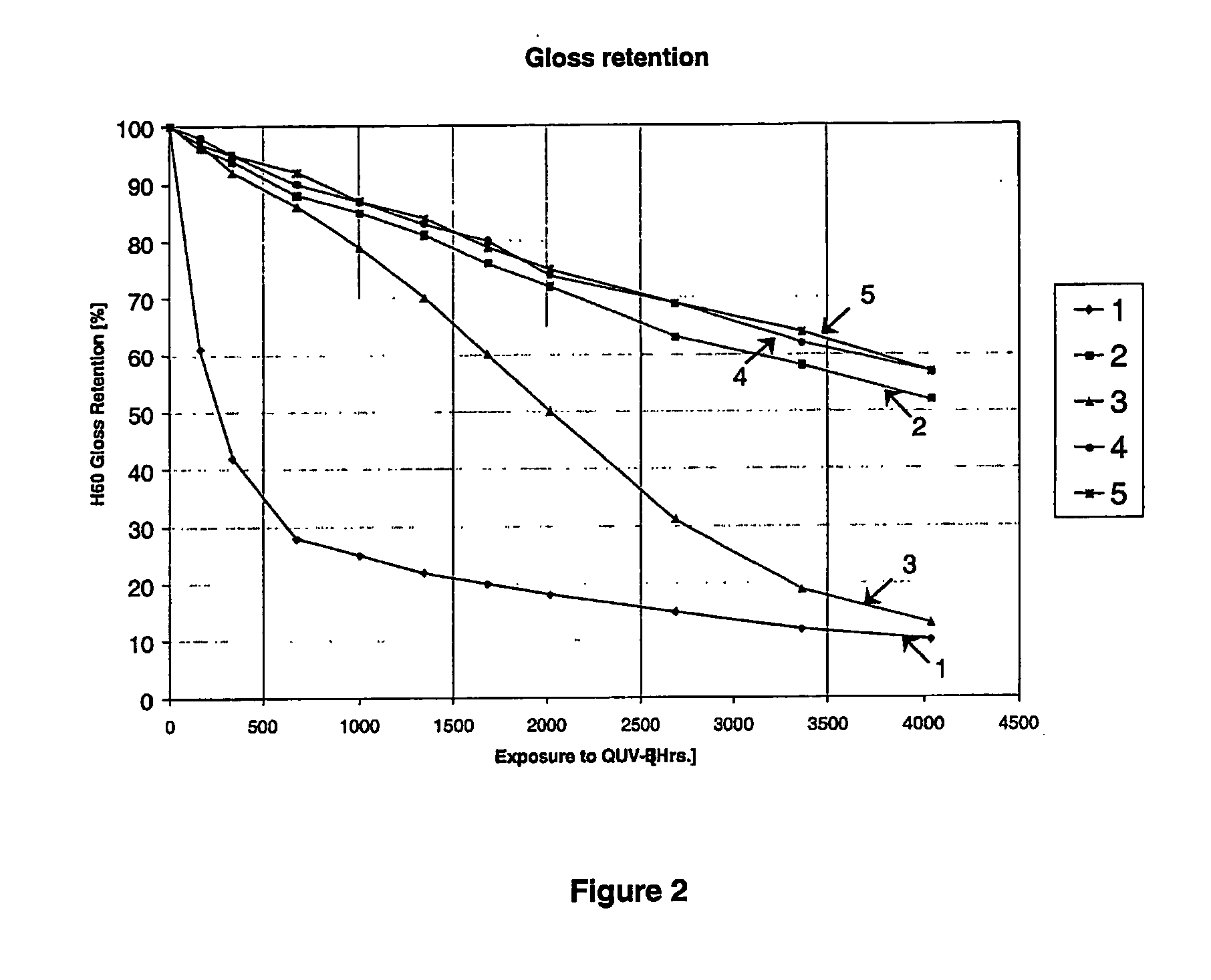
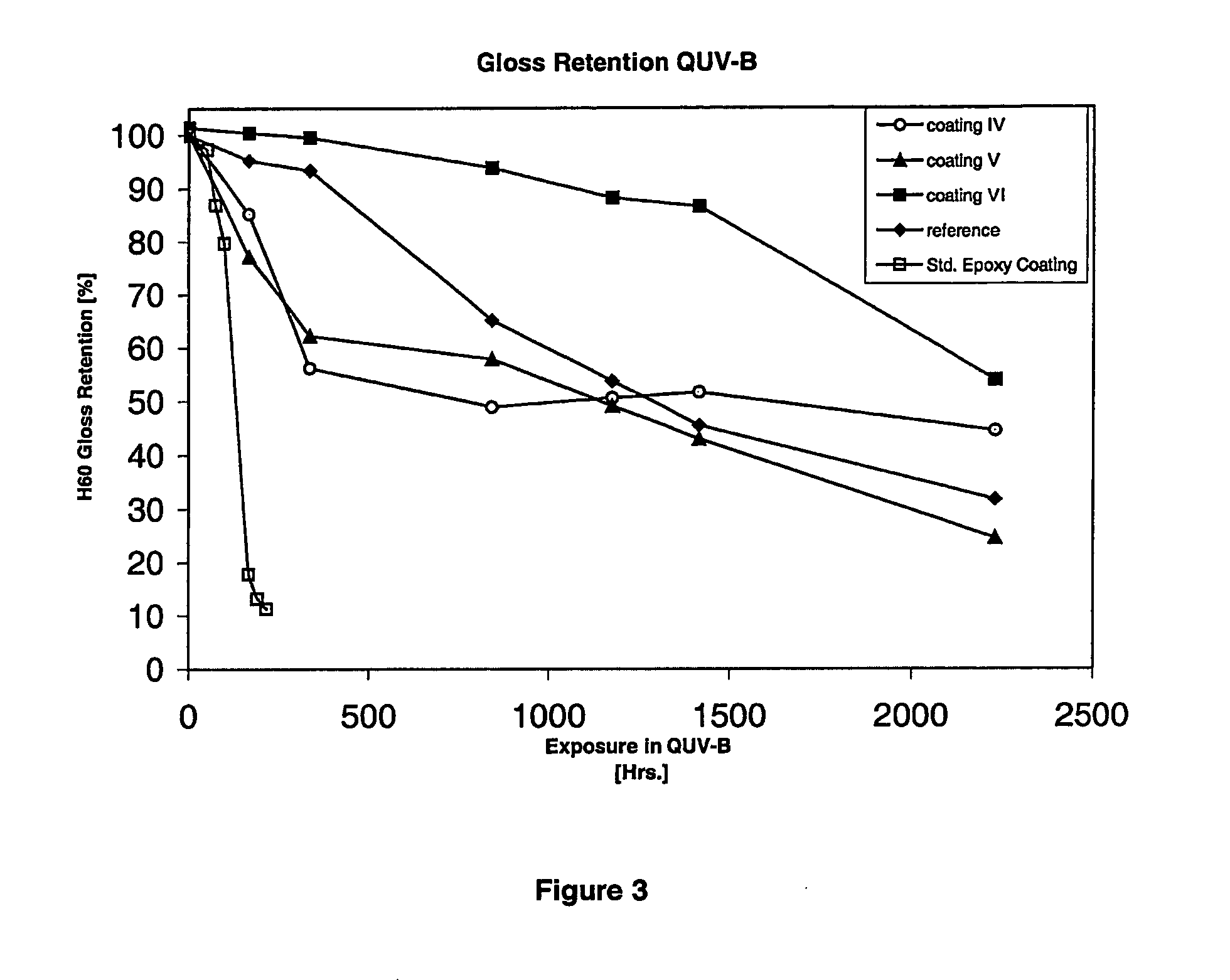
InactiveUS20050148752A1Good gloss retentionImproved mechanical cohesive strengthEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyPolymer science
The present invention relates to an amino-functional polysiloxane of formula (1) where each R1 is independently selected from alkyl or aryl radicals, each R2 is independently selected from hydrogen, alkyl or aryl radicals, n is selected so that the molecular weight for the functional polysiloxane is in the range of from 400 to 10,000 and R3 is a bivalent radical or —O—R3—NH—R5 is hydroxy or alkoxy, and R5 is selected from hydrogen, aminoalkyl, aminoalkenyl, aminoaryl, aminocycloalkyl radical, optionally substituted by alkyl, aryl, cycloalkyl, halogen, hydroxy, alkoxy, thioalkyl, amino, amino derivatives, amido, amidoxy, nitro, cyano, keto, acyl derivatives, acyloxy derivatives, carboxy, ester, ether, esteroxy, heterocycle, alkenyl or alkynyl and where 0 to 90% of —O—R3—NH—R5 is hydroxy or alkoxy. The present invention further relates to an epoxy-polysiloxane composition which includes an aminopolysiloxane hardener component or an amino-functional polysiloxane hardener component of formula (1), having active hydrogens able to react with epoxy groups in an epoxy resin to form epoxy polymers, and able to react with a polysiloxane to form polysiloxane polymers, wherein the epoxy chain polymers and polysiloxane polymers polymerize to form a cured epoxy-polysiloxane polymer composition.
Owner:SIGMAKALON SERVICES BV
Flux and process for hot dip galvanization
ActiveUS20070137731A1Convenient coatingHigh concentrationHot-dipping/immersion processesWelding/cutting media/materialsAlcoholHydrophile
A flux for use in a hot dip galvanization process has an acidic component so that the flux has a pH of about 1.5 or less. The flux also includes an alkali metal chloride and a nonionic surfactant containing polyoxyethylenated straight-chain alcohols with a hydrophile-lipophile balance (HLB) of less than 11. Depending on the particular application, the flux also includes other components, such as ferric chloride, an inhibitor containing an amino derivative and bismuth oxide.
Owner:TECK METALS +1
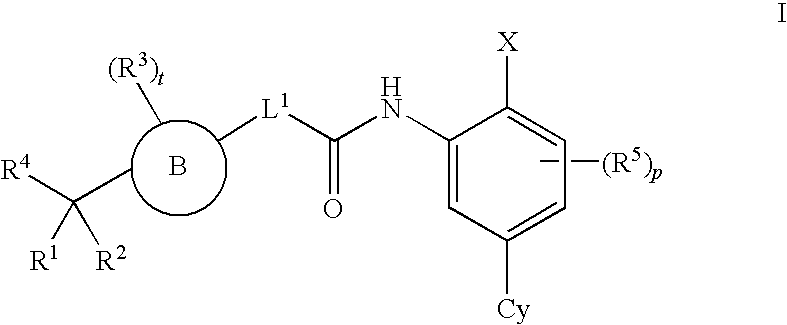
Carboxamide and amino derivatives and methods of their use
Carboxamide and amino derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, and methods for their pharmaceutical use are disclosed. In certain embodiments, the carboxamide derivatives are ligands of the δ opioid receptor and are useful, inter alia, for treating and / or preventing pain, anxiety, gastrointestinal disorders, and other δ opioid receptor-mediated conditions.
Owner:APOLOR CORP
Stick compositions
ActiveUS7347990B2Good storage stabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFiberCosmetic ingredient
Many cosmetic stick compositions containing a continuous phase of a water-immiscible cosmetic oil structured by a fibre-forming amido structurant and an active cosmetic ingredient either exhibit poor physical stability when formed, or cannot be made readily using conventional processes for making stick compositions. The problem can be ameliorated or overcome by the use of a combination of amido structurants comprising in class (i) an N-acylaminoacid amide in which the N-acyl substituent has the formula —CO—RX in which RX represents a branched C6 to C11 alkyl group in combination with a further amido structurant, (class (ii), including a polyamido-substituted cyclohexane, an amido derivative of di or tricarboxylic acids or an hydroxystearamide and particularly employing an N-acylaminoacid amide in which the N-acyl substituent contains a linear alkyl group, or a cyclodipeptide.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
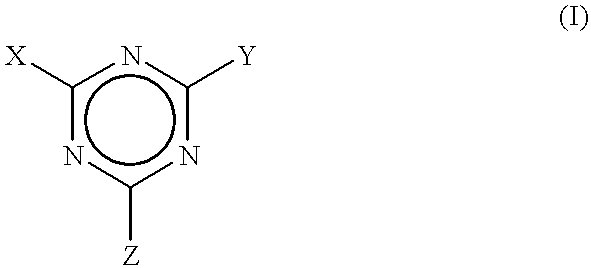
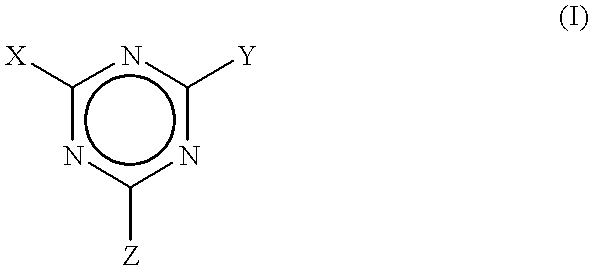
Process to scavenge amines in polymeric compounds by treatment with triazine derivatives and compositions therefrom
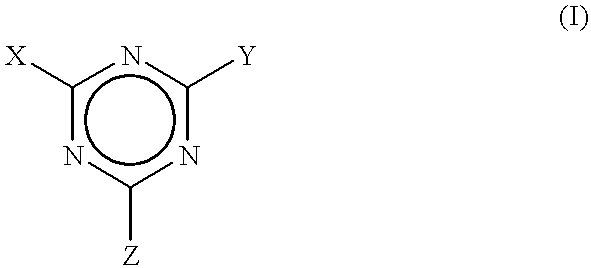
A method for scavenging amines within polymeric compositions of matter comprising the step of adding to a polymeric composition of matter at least one triazine compound, wherein said triazine compound is defined according to the formula:where X is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halides, amines, and organic groups having from 1 to about 20 carbon atoms, Y is selected from the group consisting of halides, alkoxy derivatives, amine derivatives, aryloxy derivatives, and urea derivatives, with the proviso that the substituent Y is displacable by a reaction with a secondary amine, and Z is selected from the group consisting of alkoxy derivatives, amino derivatives, aryloxy derivatives, and urea derivatives, with the proviso that the substituent Z is displacable by a reaction with a secondary amine.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
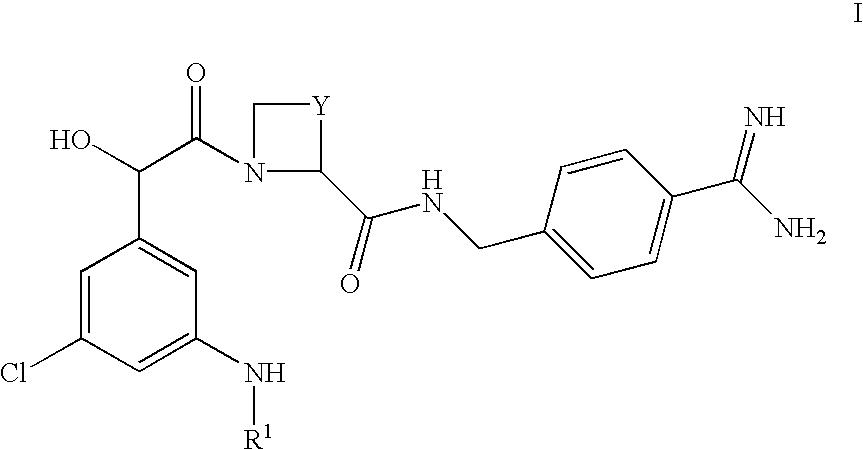
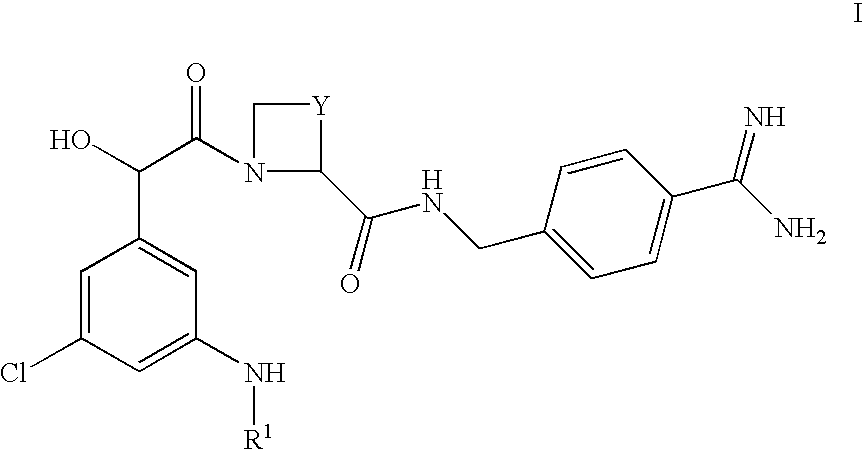
Amidino derivatives and their use as thormbin inhibitors
There is provided compounds of formula I,wherein Y and R1 have meanings given in the description, and pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives (including prodrugs) thereof, which compounds and derivatives are useful as, or are useful as prodrugs of, competitive inhibitors of trypsin-like proteases, such as thrombin, and thus, in particular, in the treatment of conditions where inhibition of thrombin is required (e.g. thrombosis) or as anticoagulants.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Fullerene multi-nitrogen heterocyclic water-soluble derivatives as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102001985AAchieving Water Solubility TransformationRich varietyOrganic chemistryNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSimple Organic CompoundsSide chain
The invention discloses fullerene multi-nitrogen heterocyclic water-soluble derivatives as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The fullerene multi-nitrogen heterocyclic water-soluble derivatives are fullerene imino derivatives which prepared from fullerene C2n and nitrine organic compound by a cycloaddition reaction. The structural formula of the derivatives is C2n[N(CH2)mCH2NH2]x or C2n[N(CH2)m-1CH2COOM]x, wherein n=30-50, m=1-5, x= 8-24, and M is H, NH4, Na or K. The derivatives of the invention have good aqueous phase dissolubility, have perssad-NH2 or -COOH with reactivity at side chain end which are suitable for coupling and bonding various markers or large biological molecules, thereby being applied to nano-biomarkers and detecting techniques.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
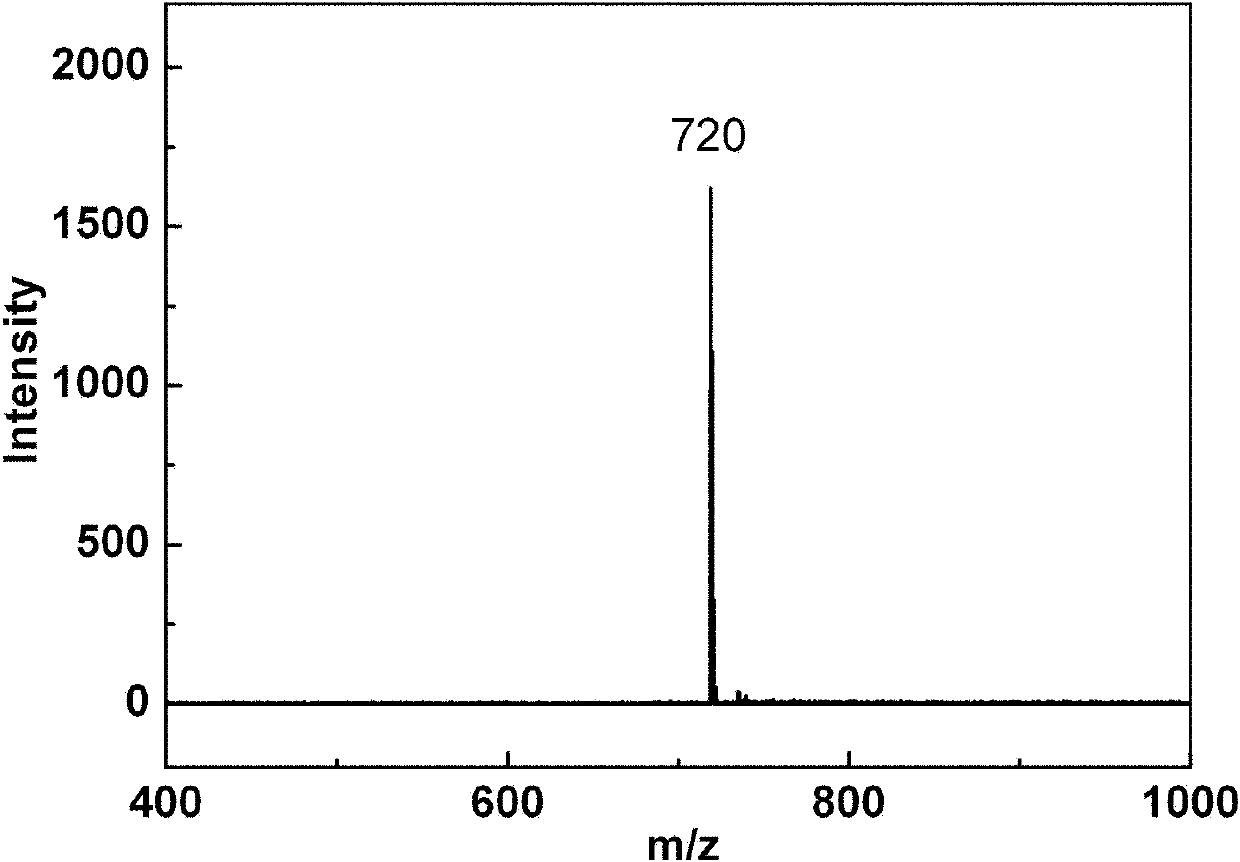
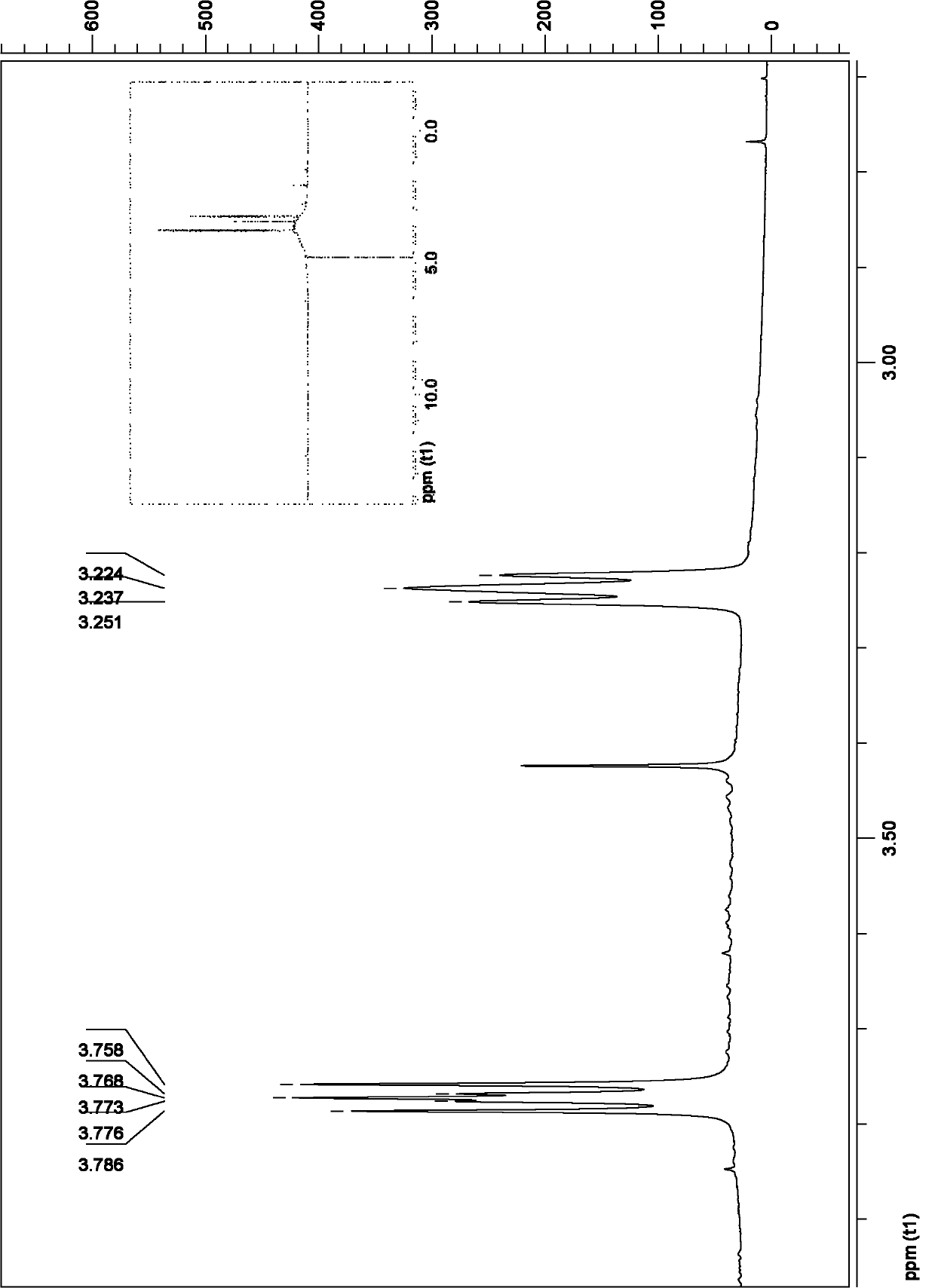
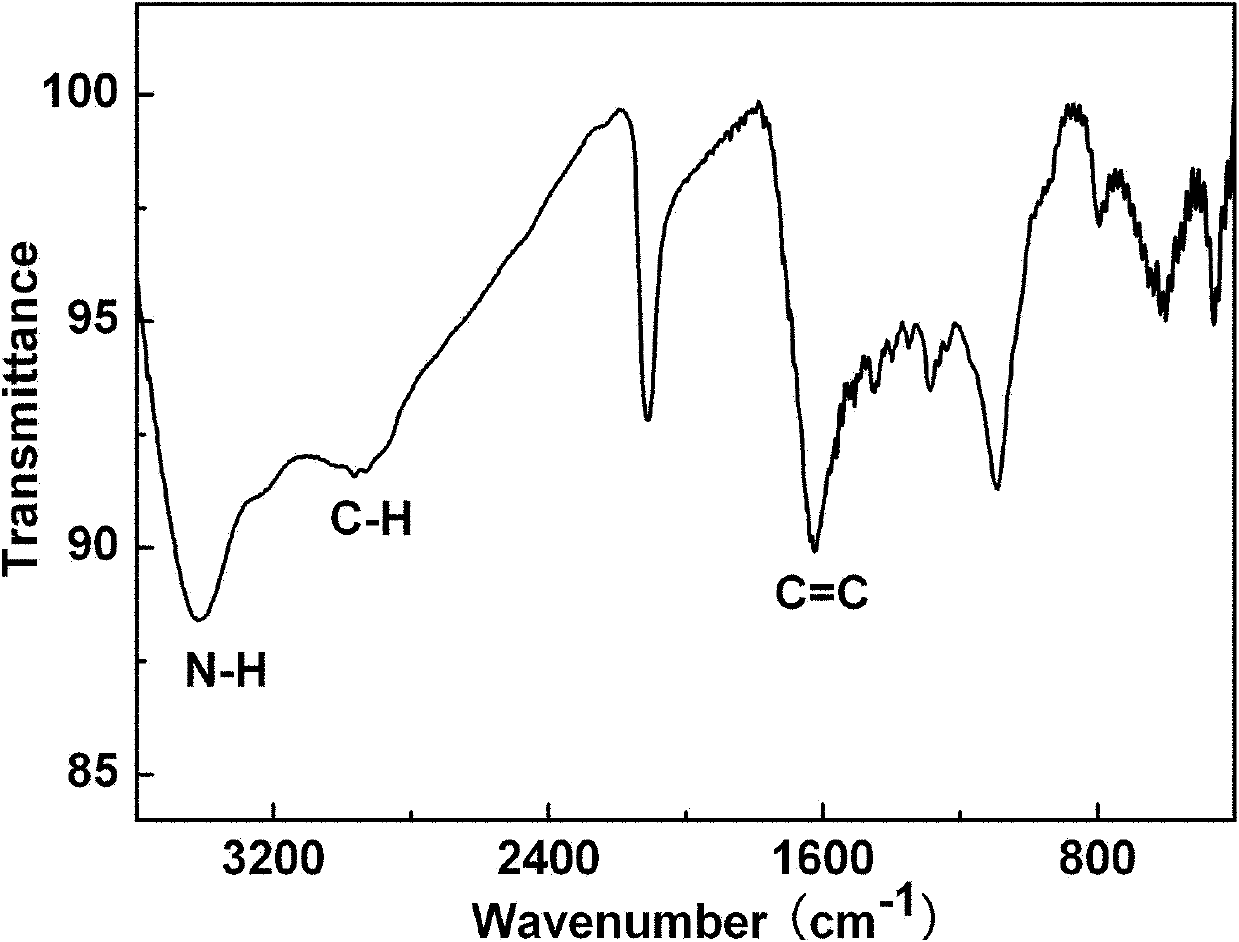
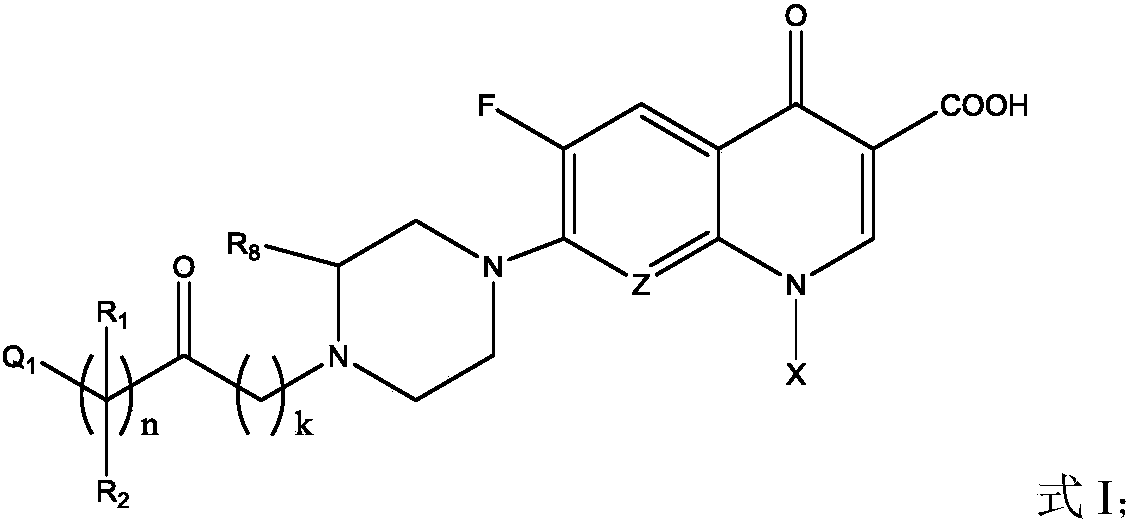
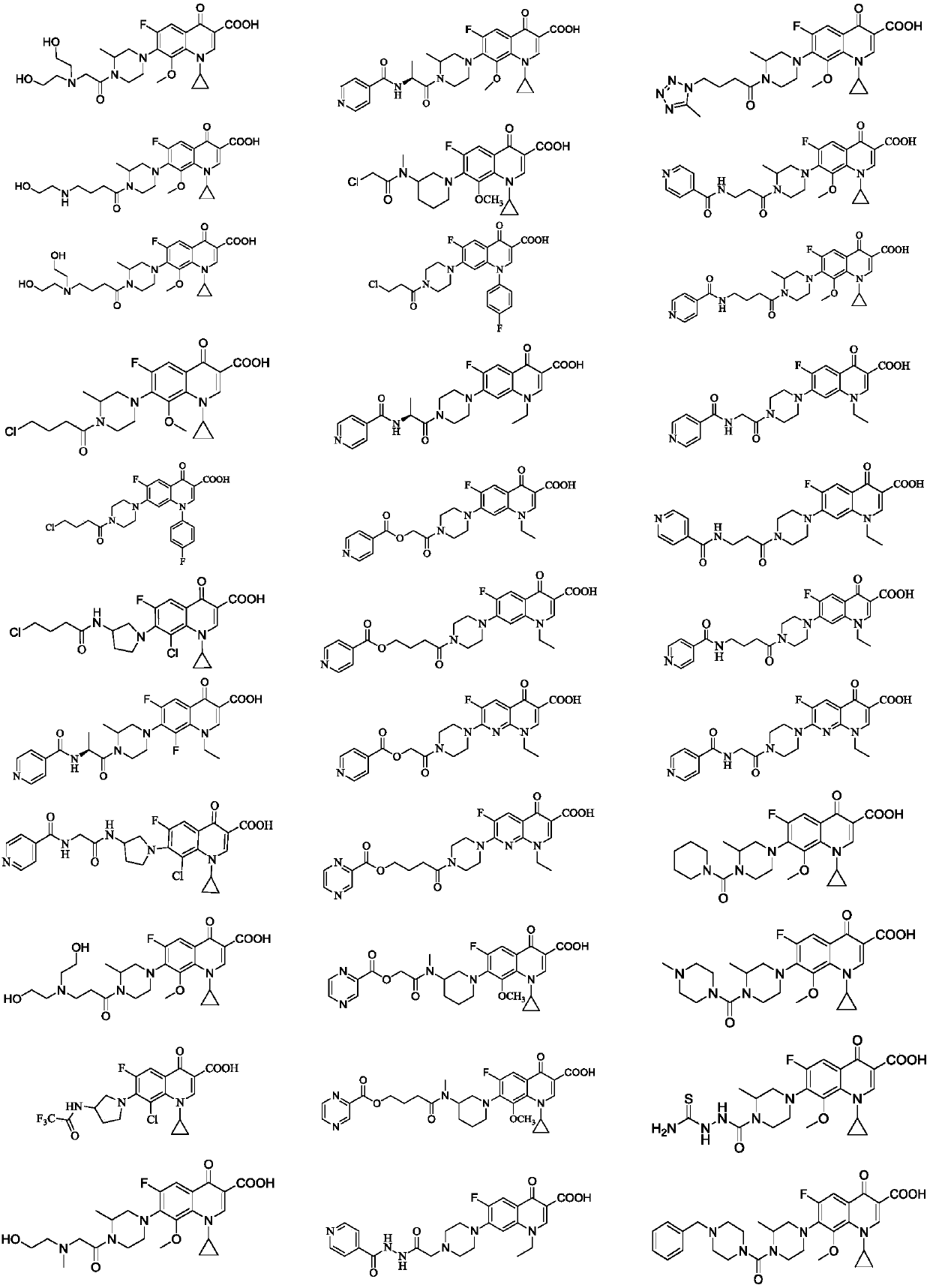
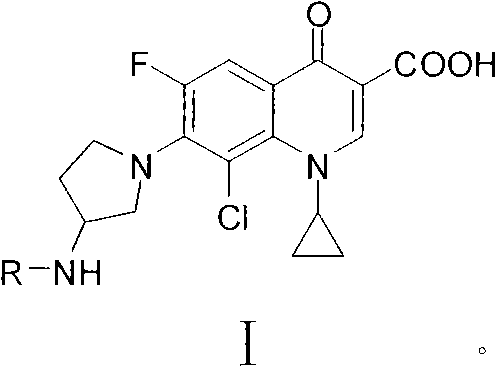
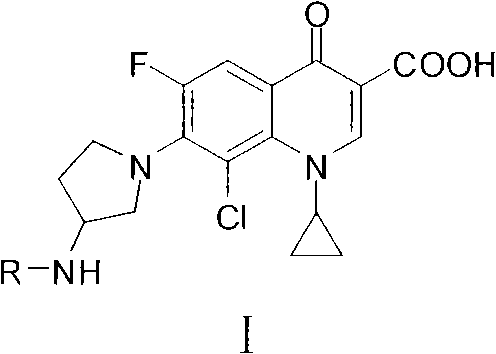
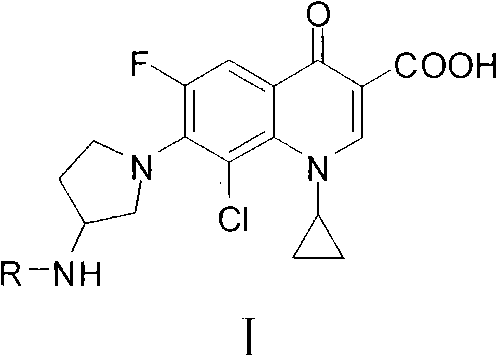
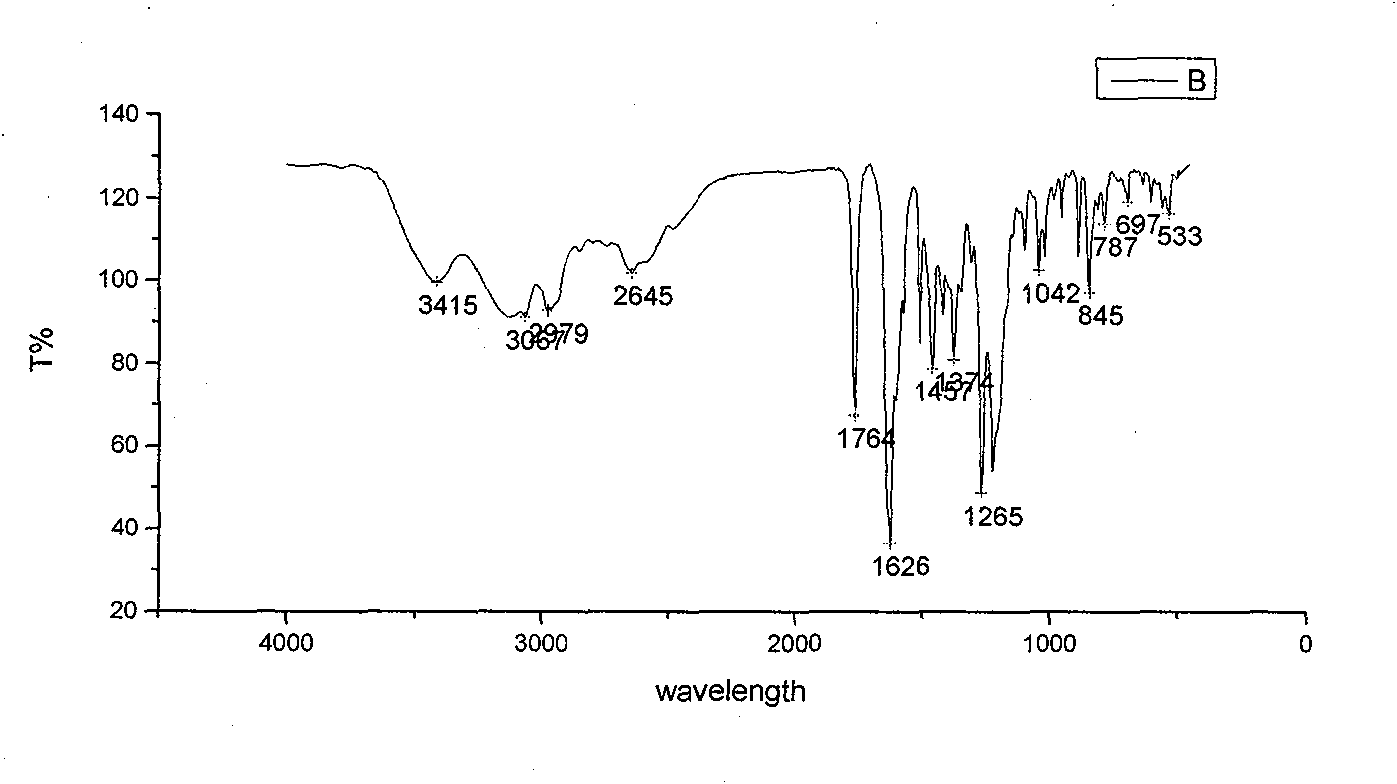
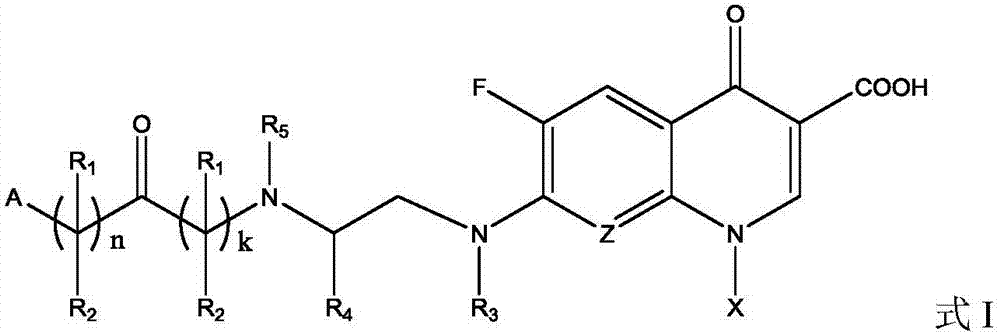
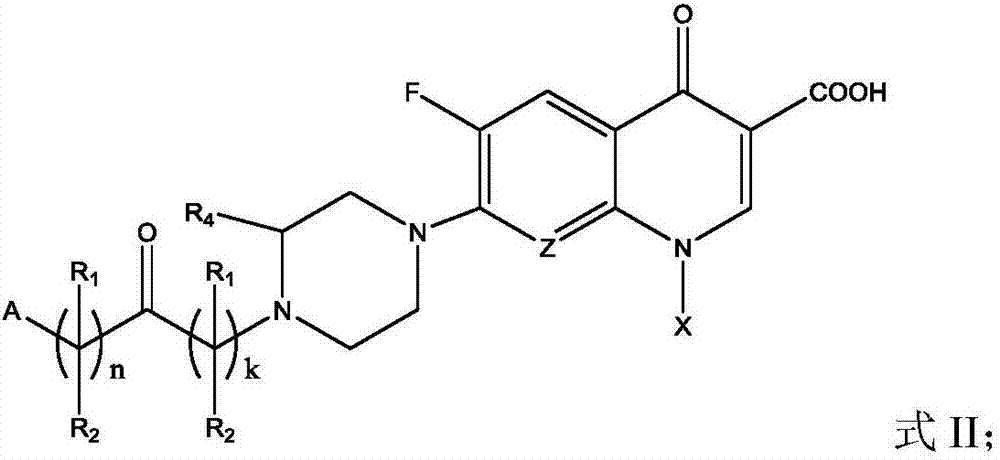
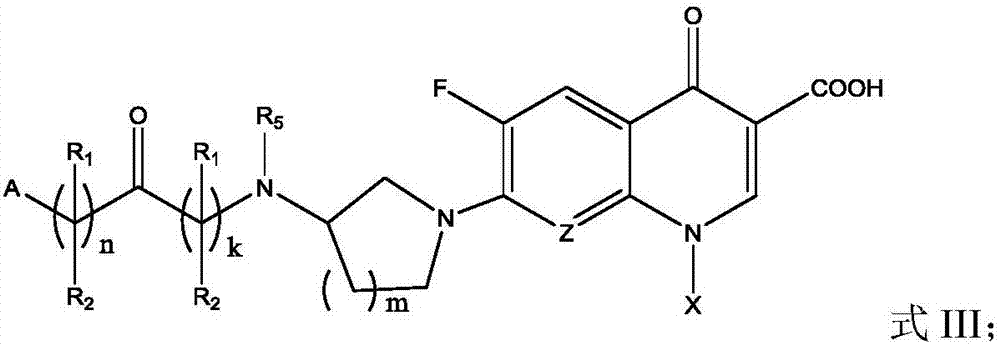
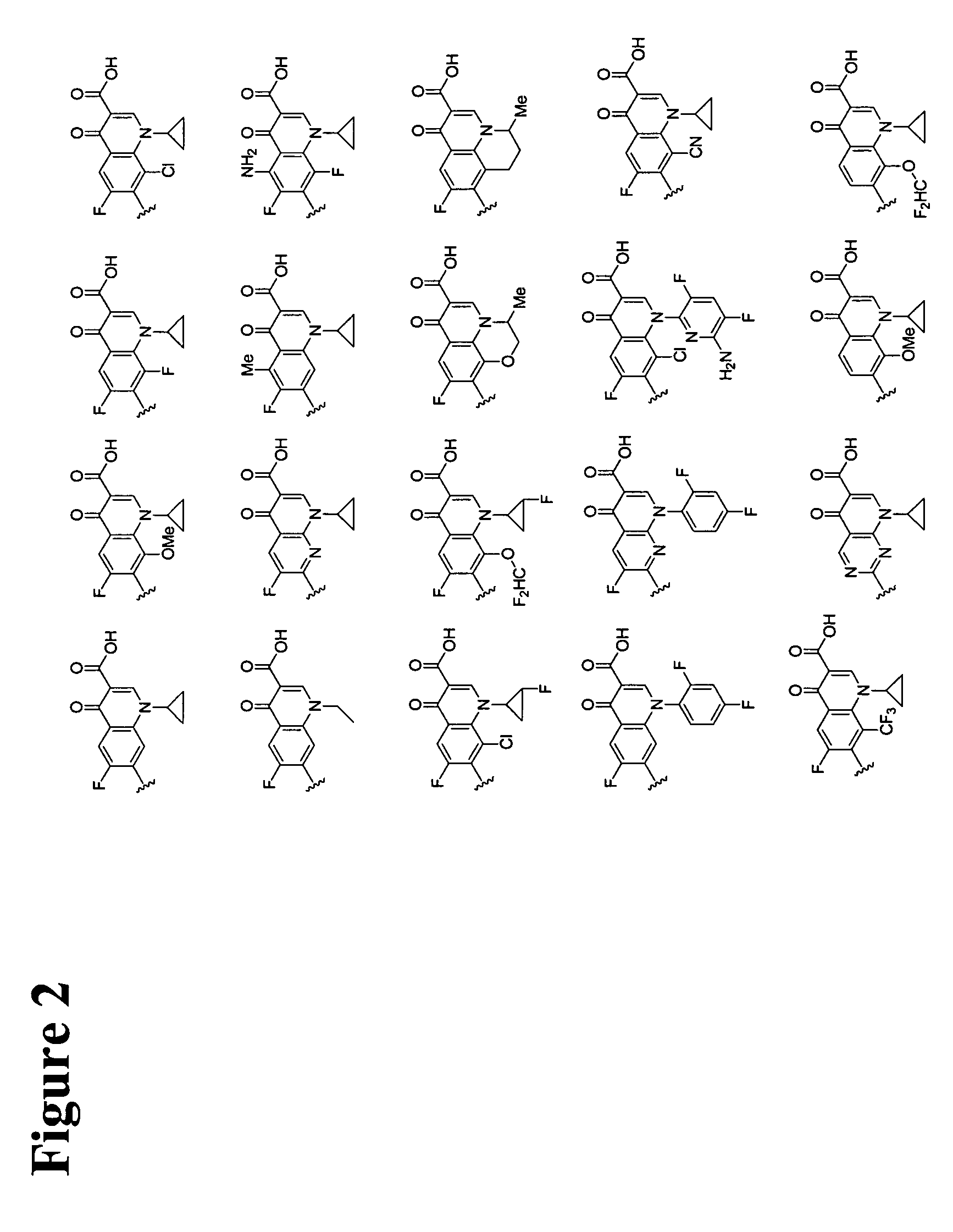
Fluoroquinolone amino derivatives and use thereof in prevention and control of citrus diseases
Citrus canker and brown spot are common diseases of citrus. At present, few drugs are available to prevent and control the two diseases and have certain defects. Amino groups at the 7th positions of fluoroquinolone drugs are linked with an active fragment by means of a connecting structure so as to obtain compounds shown in a formula I or a formula II. Experiments prove that the compounds providedby the invention have effects of preventing and controlling the citrus canker and the brown spot and have very good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
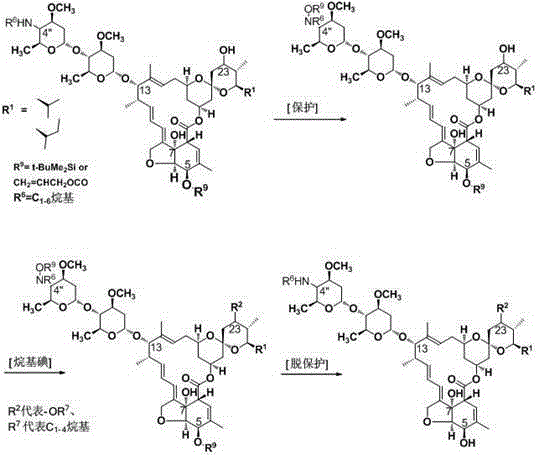
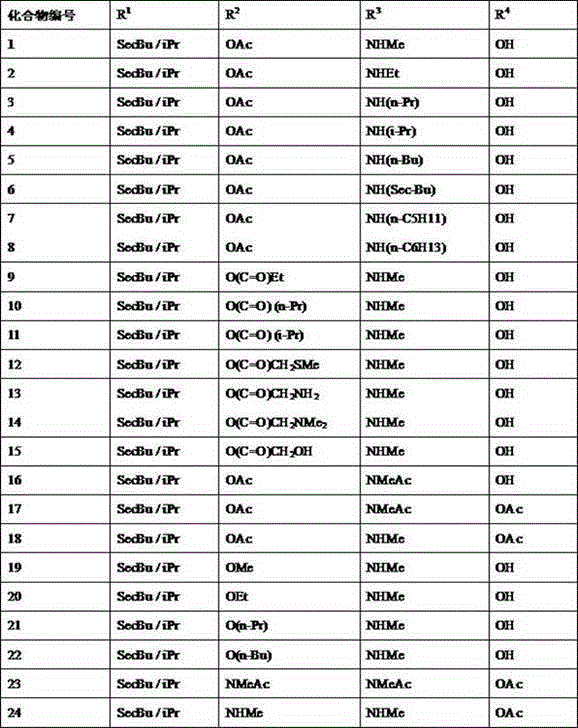
4'-desoxy-4'-alkylated or acylated amino avermectin B2a/2b derivative, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105037467AImprove insecticidal effectLong durationSugar derivativesInsecticidesAvermectinAmino derivatives
The invention provides a 4'-desoxy-4'-alkylated or acylated amino substituted avermectin B2a / 2b derivative which is an alkylated or acylated avermectin B2a / 2b amino derivative synthesized by using methylamino avermectin B2a / 2b as a matrix. The 4'-desoxy-4'-alkylated or acylated amino substituted avermectin B2a / 2b derivative widens the utilization range of avermectin B2a / 2b, enhances the disinsection effect of the avermectin B2a / 2b and effectively prolongs the duration time of the product. The invention also provides a preparation method of the 4'-desoxy-4'-alkylated or acylated amino substituted avermectin B2a / 2b derivative and application of the 4'-desoxy-4'-alkylated or acylated amino substituted avermectin B2a / 2b derivative in preparing preparations for controlling pests of plants and animals.
Owner:HEBEI VEYONG BIO CHEM
Method of attaching a ligand to a solid support
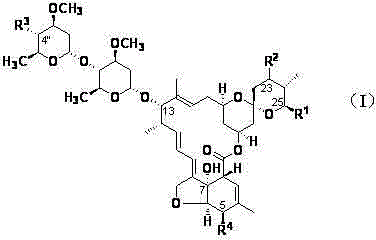
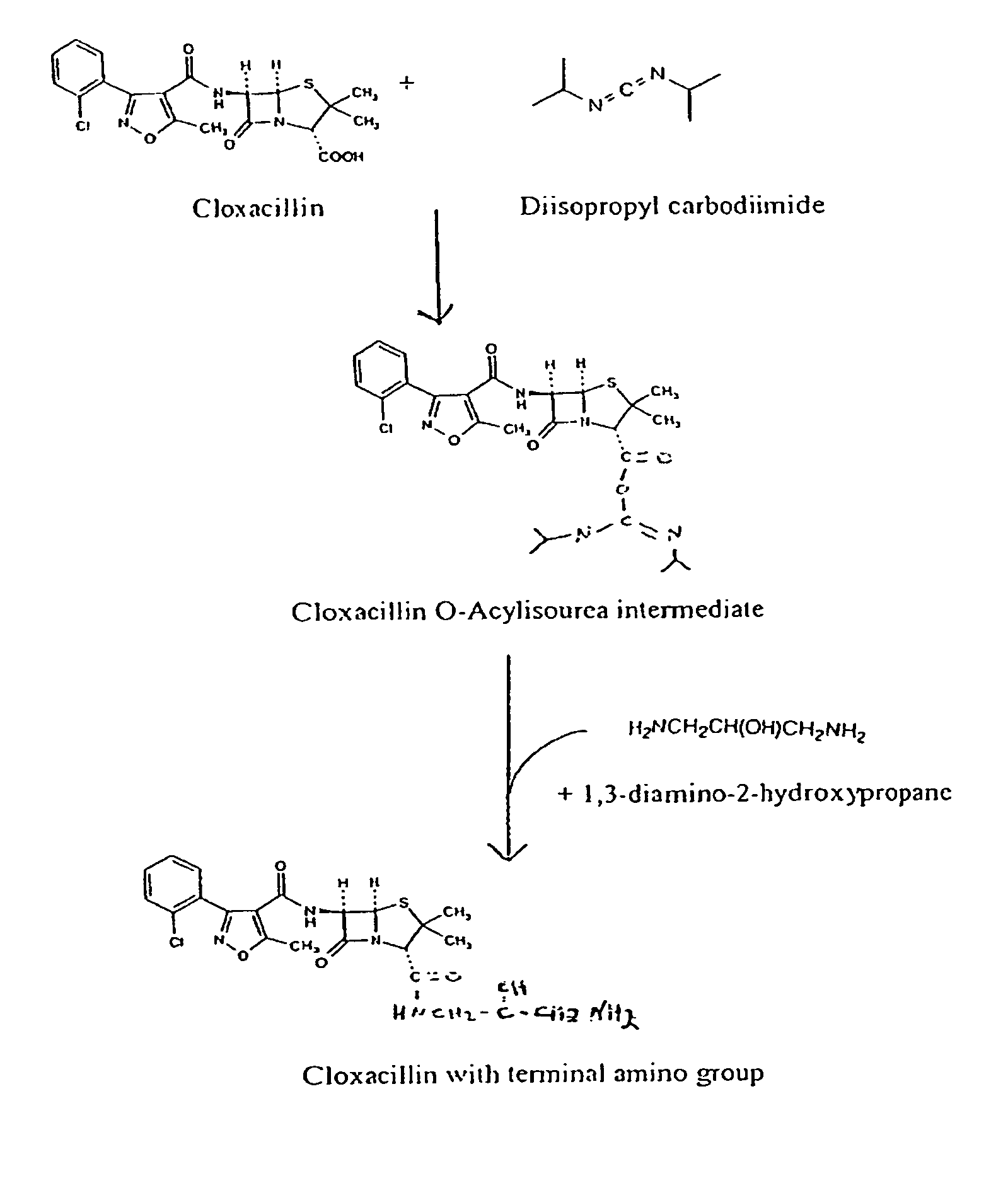
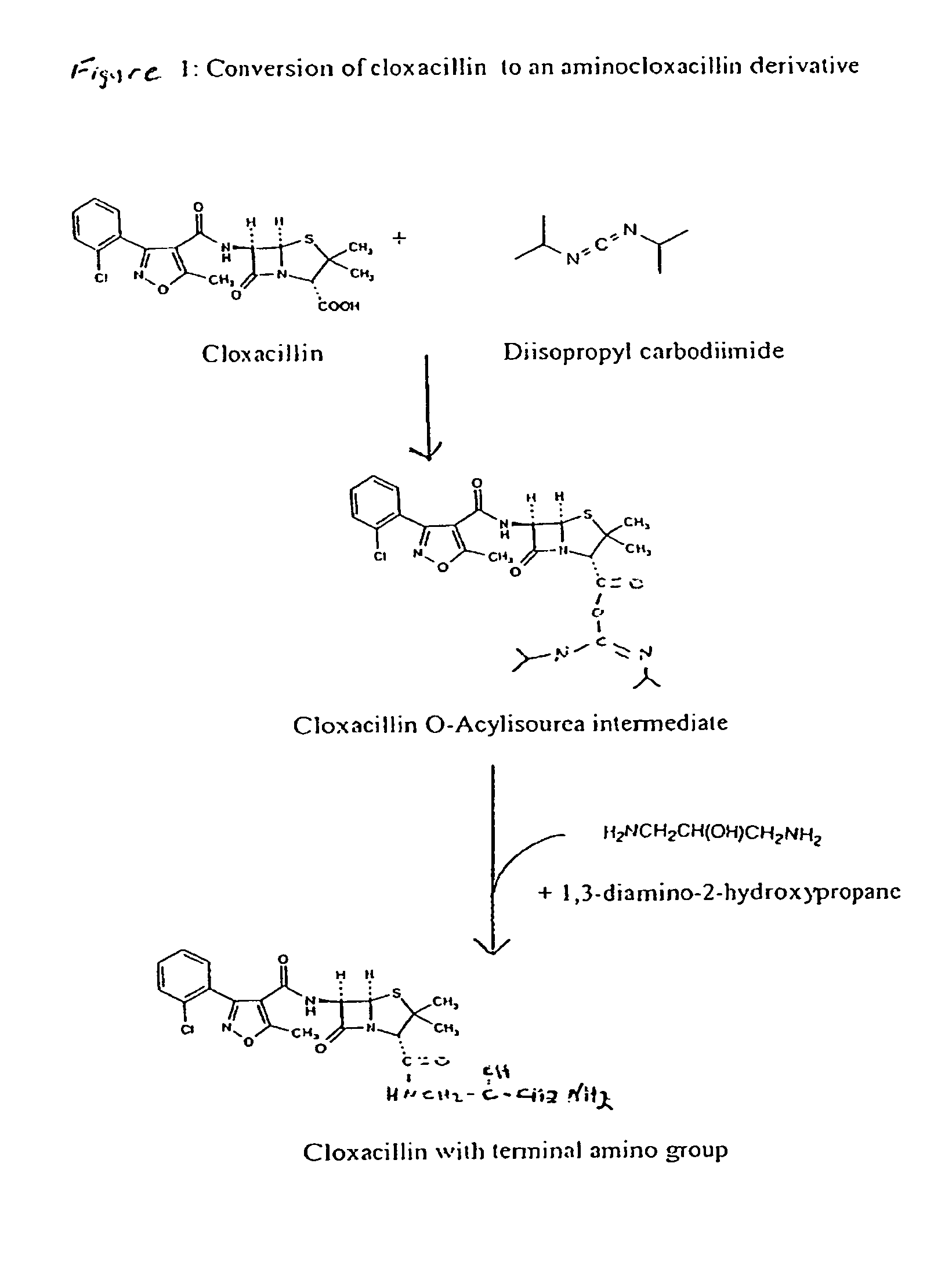
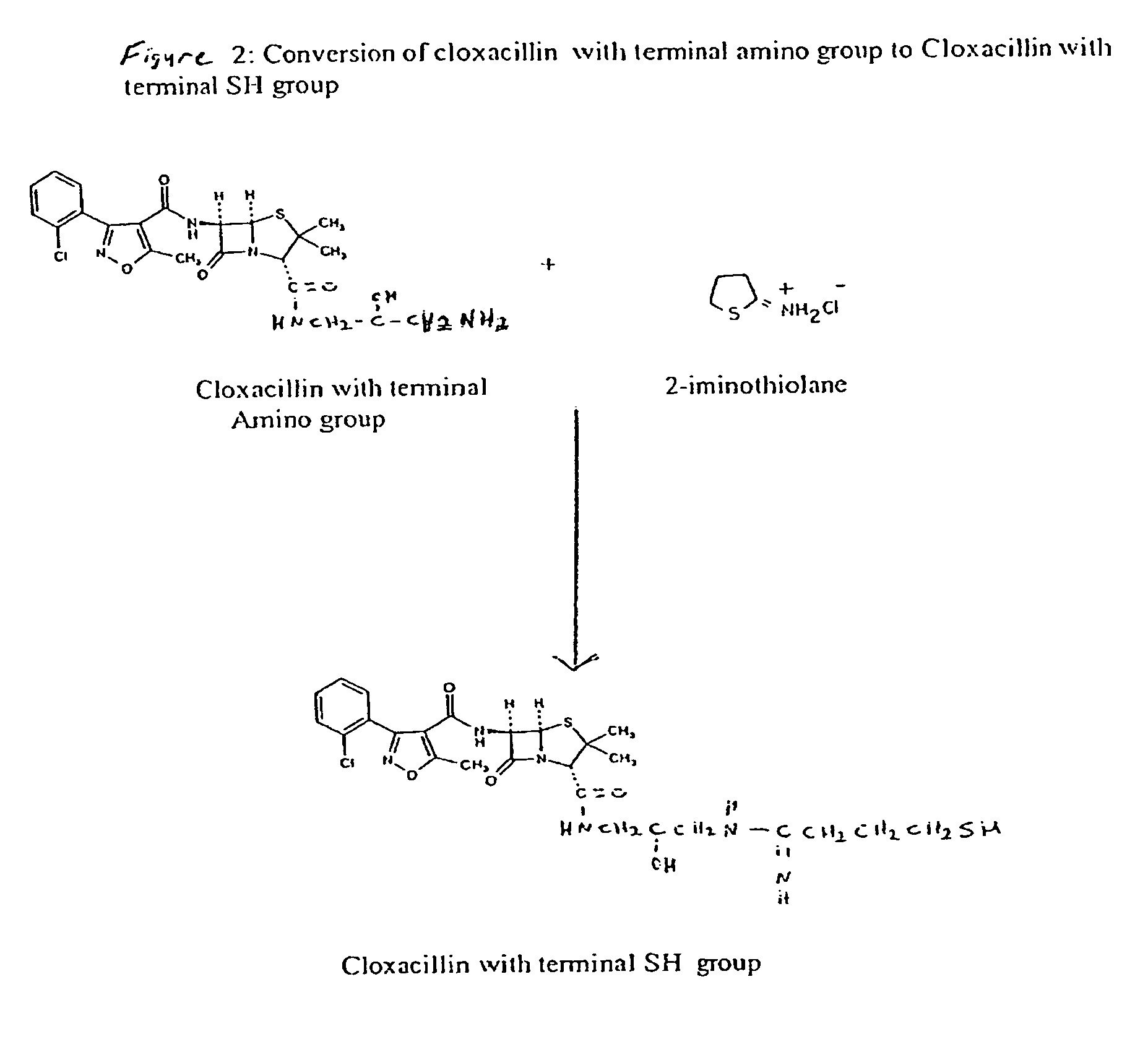
ActiveUS8481334B1Reduce the amount requiredReduces sensitivity of testAnalysis using chemical indicatorsDepsipeptidesAmino derivativesSmall molecule ligand
The invention features a method of attaching a ligand that has a free carboxyl group to a solid support by adding an amino group to the ligand to form a ligand-amino derivative, converting the ligand amino derivative to a ligand sulfhydryl derivative, attaching the ligand sulfhydryl derivative to a protein to form a ligand-linker-protein conjugate, and applying the ligand-linker-protein conjugate to the solid support. The method is particularly useful for immobilizing small molecule ligands having a free carboxyl group, such as cloxicillin, to a lateral-flow test strip, in order to make a detection zone on the test strip that exhibits a clear signal and enhanced sensitivity.
Owner:CHARM SCI
Isoalantolactone amino derivative and application of salt thereof in preparing anti-tumor medicament
The invention relates to an isoalantolactone amino derivative and application of a salt thereof in preparing an anti-tumor medicament. The isoalantolactone amino derivative has a structure shown as a general formula (I), wherein R1 is the same as or different from R2; R1 or R2 independently represents a hydrogen atom, straight-chain or branched-chain C1 to C6 alkyl, C2 to C6 alkyl or acyl, C1 to C6 alkoxy carbonyl, aryl or heteroaryl; or R1, R2 and a nitrogen atom which connects R1 with R2 jointly form a ternary, quaternary, quintuple, hexahydric or heptabasic ring which contains one or more of C, N, O and S atoms; the salt refers to hydrochloride, hydrobromide, sulfate, phosphate, mesylate, fumarate, succinate, benzoate, acetate, malonate, malate, citrate, tartrate or maleate.
Owner:刘华
4-carboxybenzylamino derivatives as histone deacetylase inhibitors
ActiveUS20100324046A1Prevent proliferationArrest cell growthBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationDiseaseDosing regimen
The present invention relates to a novel class of 4-carboxybenzylamino derivatives. The 4-carboxybenzylamino compounds can be used to treat cancer. The 4-carboxybenzylamino compounds can also inhibit histone deacetylase and are suitable for use in selectively inducing terminal differentiation, and arresting cell growth and / or apoptosis of neoplastic cells, thereby inhibiting proliferation of such cells. Thus, the compounds of the present invention are useful in treating a patient having a tumor characterized by proliferation of neoplastic cells. The compounds of the invention may also be useful in the prevention and treatment of TRX-mediated diseases, such as autoimmune, allergic and inflammatory diseases, and in the prevention and / or treatment of diseases of the central nervous system (CNS), such as neurodegenerative diseases. The present invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the 4-carboxybenzylamino derivatives and safe dosing regimens of these pharmaceutical compositions, which are easy to follow, and which result in a therapeutically effective amount of the 4-carboxybenzylamino derivatives in vivo.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
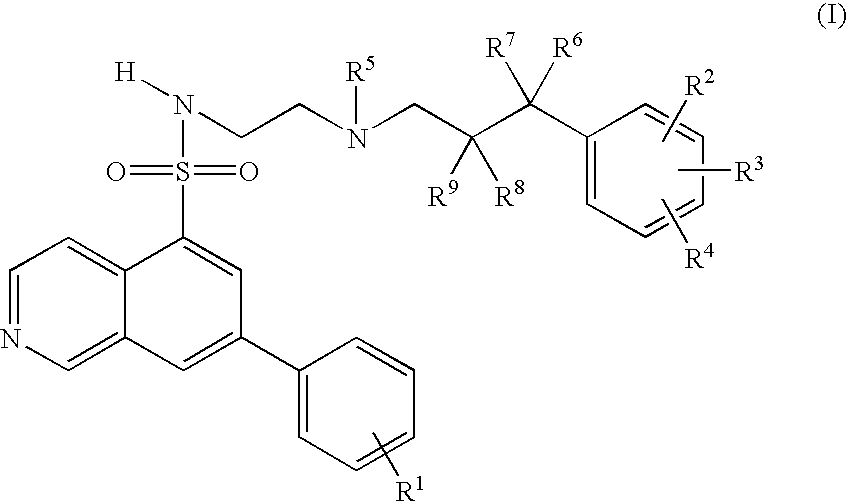
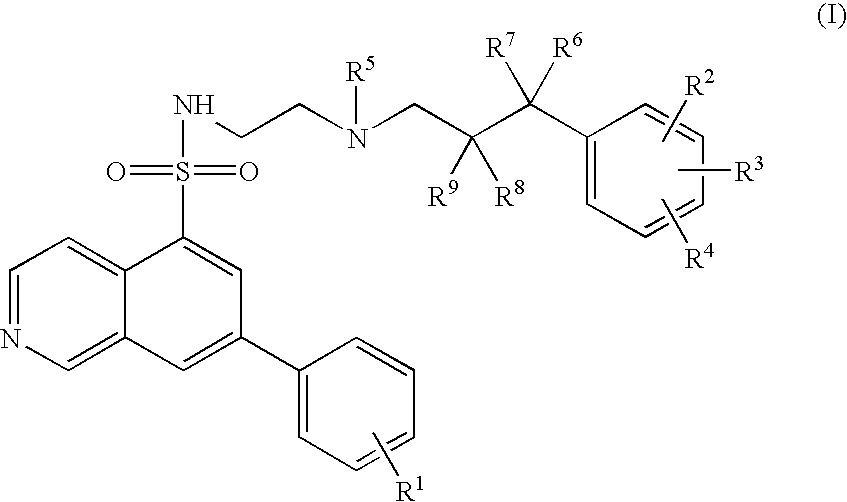
7-Phenyl-isoquinoline-5-sulfonylamino derivatives as inhibitors of akt (proteinkinase b)
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Clinafloxacin amino derivatives and application thereof
InactiveCN102030737AHigh antibacterial activityLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityAntibacterial activity
The invention belongs to the field of chemistry and pharmacy, and particularly relates to clinafloxacin amino derivatives and application thereof. The clinafloxacin amino derivatives are the compounds shown in the formula 1 (R is -SO2R1 or -COR2) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The antibacterial activity of the derivatives is close to or superior to that of clinafloxacin, the toxicity of the derivatives is lower than that of clinafloxacin, and the solubility and the stability of the solution of the derivatives are superior to those of clinafloxacin. The derivatives can be used for preparing antibacterial medicines, thereby providing more efficient and safe alternative medicines for clinical treatment of infectious diseases and satisfying the demands for clinical treatment in many aspects.
Owner:CHONGQING BASHIDI ANIMAL PHARMA
Calixarene acetamido derivatives, preparation and use thereof for extracting strontium
The invention concerns derivatives of calixarene having the formula:in which:R<1 >represents various hydrocarbon groups,R<2 >and R<3 >represent an alkyl, cycloalkyl or aryl group or a group having the formula: O(CH2)n[O(CH2)p]q OR<4>, or form a heterocyclic group with the nitrogen atom, and,n equals 6, 7 or 8.These derivatives can be used for extracting strontium from aqueous solutions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Amidino derivatives and anticoagulants and thrombosis therapeutic agents containing them
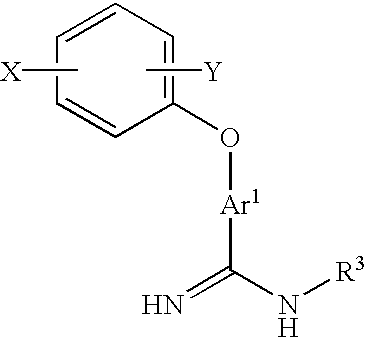
Amidino derivatives represented by the following general formula (I): {where X is a group represented by R1SO2NR2— (wherein R1 represents optionally substituted C6-14 aryl, etc. and R2 represents hydrogen atom, etc.), etc., Ar1 represents 2,6-naphthylene, etc., R3 represents hydrogen atom, etc. and Y represents carboxyphenyl, etc.}and their pharmacologically acceptable salts or solvates.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Redispersible silver nanowire mixture and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104999072ALower surface energyImprove the reunion situationMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compoundSurface modification
The invention discloses a redispersible silver nanowire mixture and a preparation method thereof. The redispersible silver nanowire mixture comprises a silver nanowire and a dispersing agent, wherein the dispersing agent comprises an organic silicon compound, a high molecular compound containing at least one group of ether or carboxyl or amido or carboxyl derivative or amido derivative, and a long chain macromolecule containing at least one group of ether or carboxyl or amido or carboxyl derivative or amido derivative, or a combination thereof. As the surface modification is performed for the silver nanowire, the surface energy of the silver nanowire is prominently reduced to realize the hydrophobic / hydrophilic property, and the agglomeration condition of the silver nanowire in a solution is improved; and the silver nanowire also can be prepared to a state of such solid fixtures as powder or paste, so that the long-time preservation of the silver nanowire is realized, and the silver nanowire can achieve excellent redispersibility in an organic solvent.
Owner:游京晶
Daidzein derivative and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101659648AChange polarityChange the spatial structureOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySolubilityDaidzein
The invention relates to a daidzein derivative which has the following chemical formula: in the chemical formula, at least one of R1 and R2 is carbonyl containing 1 to 3 carbon atoms, R3 and R4 are selected from alkyl, amino, amino derivative, ureido, guanidyl and amino acid containing 1 to 4 N atoms. The derivative adopts the daidzein as raw material, firstly carries out acylation with acylate reagent so as to obtain a midbody, and then obtains target product by reaction of midbody with R3 and / or R4. The derivative changes the polarity of the daidzein and space structure, improves water solubility, also improves permeability function of the cellular membrane and effectively improves the oral bioavailability thereof.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Fluoroquinolone amino derivatives and application thereof
ActiveCN107880023AHigh antibacterial activitySmall toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityDisease
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry, and in particular relates to fluoroquinolone derivatives and an application thereof. The compounds shown in a formula (I) are obtained by structural modification of fluoroquinolone medicines. The compounds provided by the invention can not only treat the infection caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis and common bacteria, but also can has activity inhibition effects on bacterial persister, citrus pathogenic bacteria, nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) and interleukin IL-17 PPI; and the compounds have a simple and easy preparation process and mild conditions, a plurality of the compounds with enhanced antibacterial activity, improved water solubility and reduced toxic and side effects are obtained, and the compounds are expectedto reduce the dosage, shorten the treatment cycle and improve patient compliance, thereby providing novel molecular types and research ideas for medicines of tuberculosis and other diseases.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
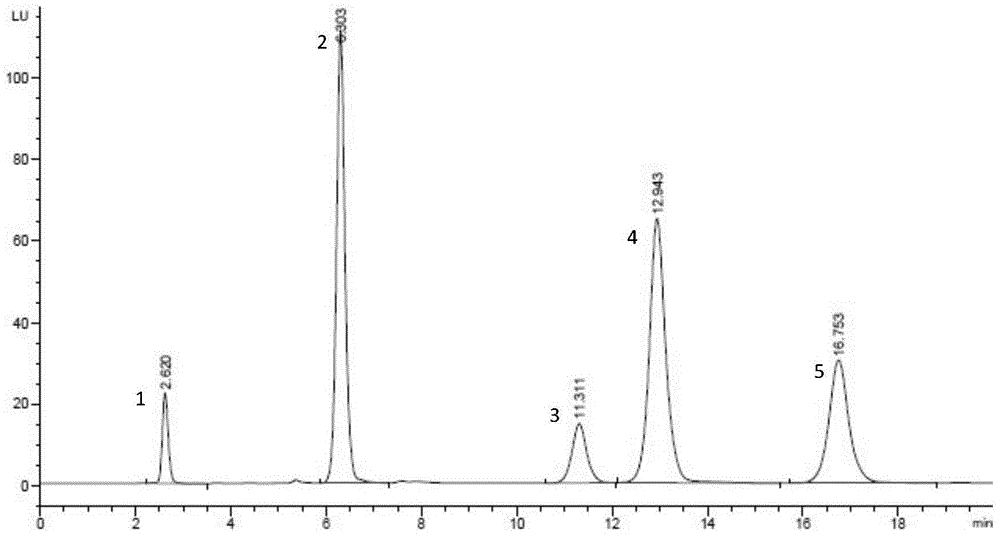
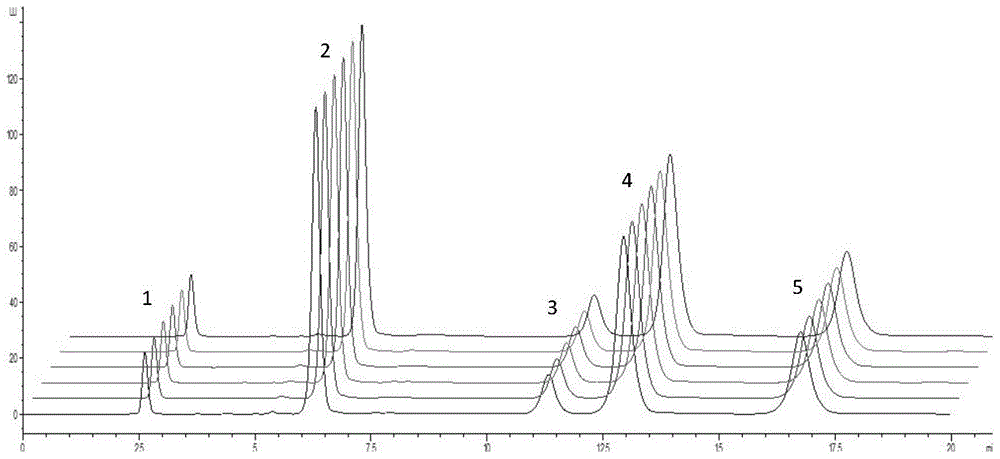
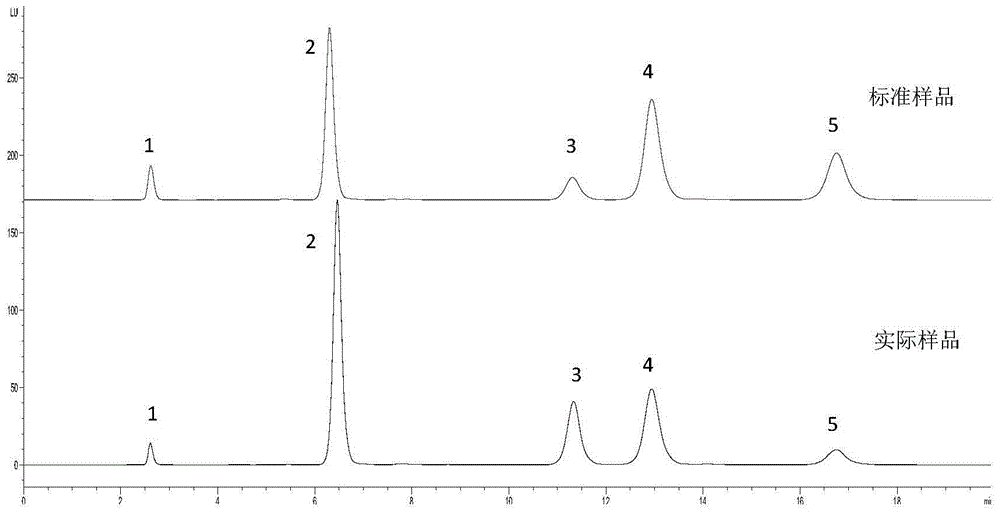
HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) detection method for simultaneously determining five substances in reaction system for producing L-Ala-L-Gln (L-alanyl-L-glutamine) with microbial enzyme method
InactiveCN105675756AEasy to separateShort runtimeComponent separationL-alanyl-l-glutaminePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses an HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) detection method for simultaneously determining five substances (L-Ala-L-Gln (L-alanyl-L-glutamine), L-Gln, L-AlaOMe, L-Glu and L-alanyl-L-alanine) in a reaction system for producing L-Ala-L-Gln with a microbial enzyme method. The five substances are subjected to pre-column automatic derivatization treatment by ortho-phthaladehyde, so that the five substances have fluorescence groups and are detected by a fluorescence detector. The chromatographic condition is as follows: a high performance liquid chromatograph Agilent 1260 Infinity is adopted; an Agilent ZORBAX SB-Aq, 5 mu m, 4.6*250 mm C18 column is adopted as a chromatographic column; an Agilent 1260 Infinity fluorescence detector is adopted; a mobile phase comprises acetonitrile and a phosphate buffer solution in the volume ratio being 12:88, and the pH of the mobile phase is adjusted to 7.4 by the aid of phosphoric acid; the flow velocity of the mobile phase is 1.0 ml / min; the column room temperature is 40 DEG C; detection wavelength comprises excitation wavelength Ex 338 nm and emission wavelength Em 450 nm. The method realizes simultaneous determination of oligopeptide, amino acid and amino derivatives, is simple to operate and high in sensitivity and has important application value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
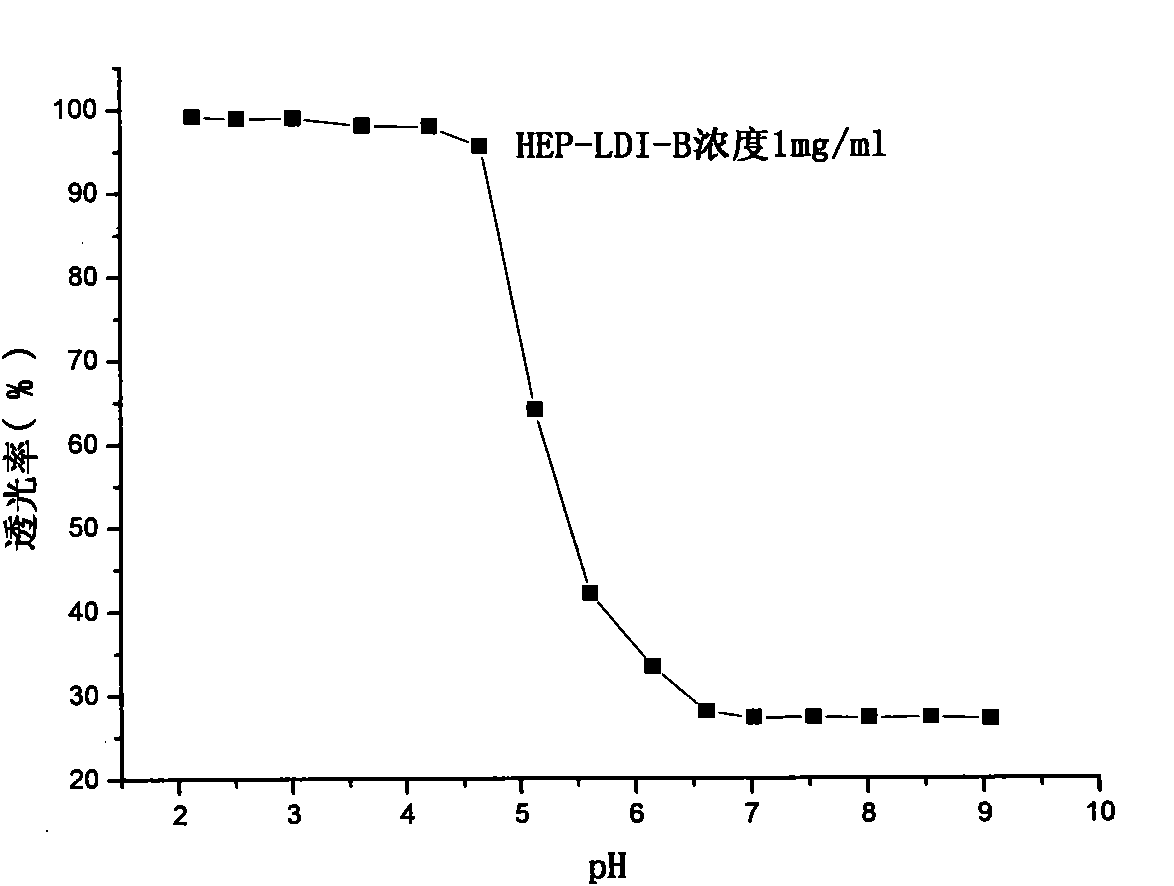
Method for preparing biodegradable polyurethane material with pH responsiveness
InactiveCN102030882APH sensitiveEasy Macromolecular ModificationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBlock structureRaw material
The invention discloses a method for preparing a biodegradable polyurethane material with pH responsiveness. Diisocyanate compounds and amino derivatives of polyhydroxyl compounds or amino derivatives of polyhydroxyl polymers serve as raw materials, and a conventional in-situ reaction method in solution polymerization is adopted to prepare the material in the presence of a catalyst. The invention has the advantages that: the preparation method is simple, is easy to operate and is suitable for industrial production, the raw materials are readily available, and the product efficiency is high; the prepared multi-block polyurethane material has a special characteristic of pH sensitivity, can be assembled into the needed structure and shape, has an alternating block structure and a plurality of reactivity points, is easily subjected to macromolecular modification, and is introduced with functional groups to realize structural and functional diversity. For instance, the material is combined with targeting molecules in the field of medicines to serve as a targeted release carrier material and the like; meanwhile, the material has biodegradability, meets the environmentally-friendly requirement of society, and can be widely applied to the fields of materials science, biology, medical science and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
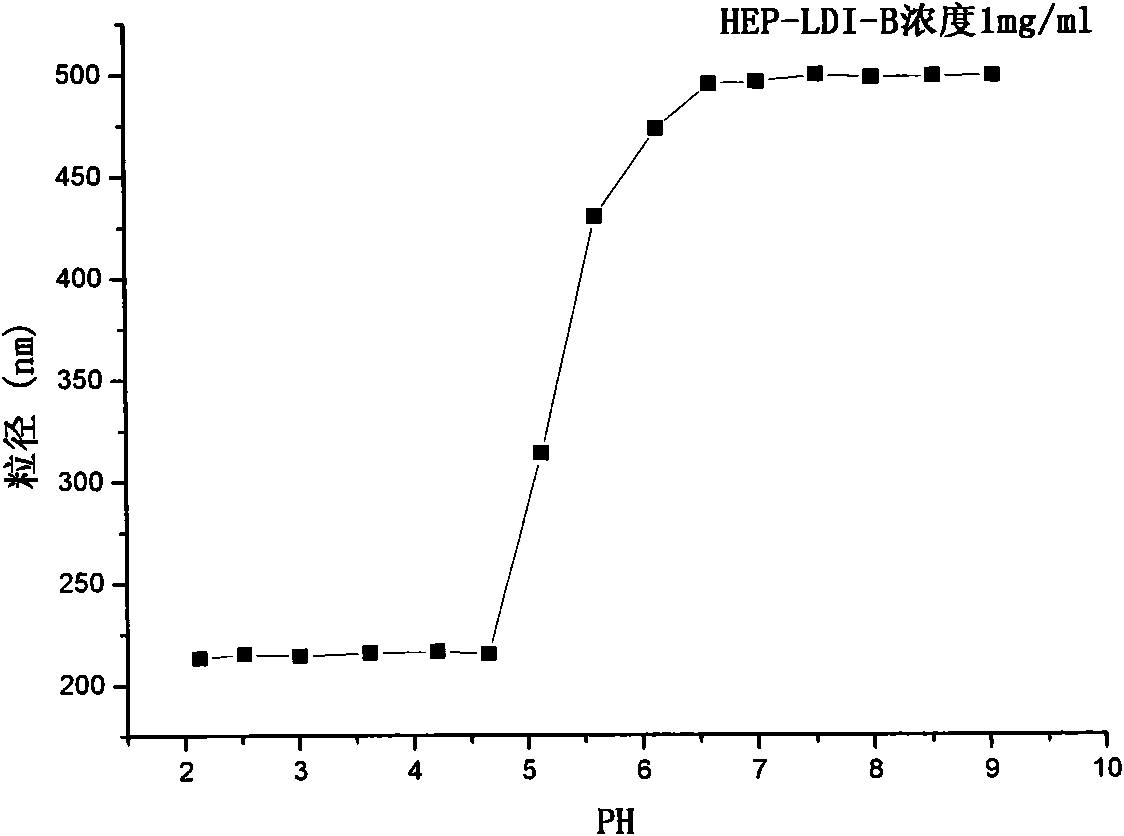
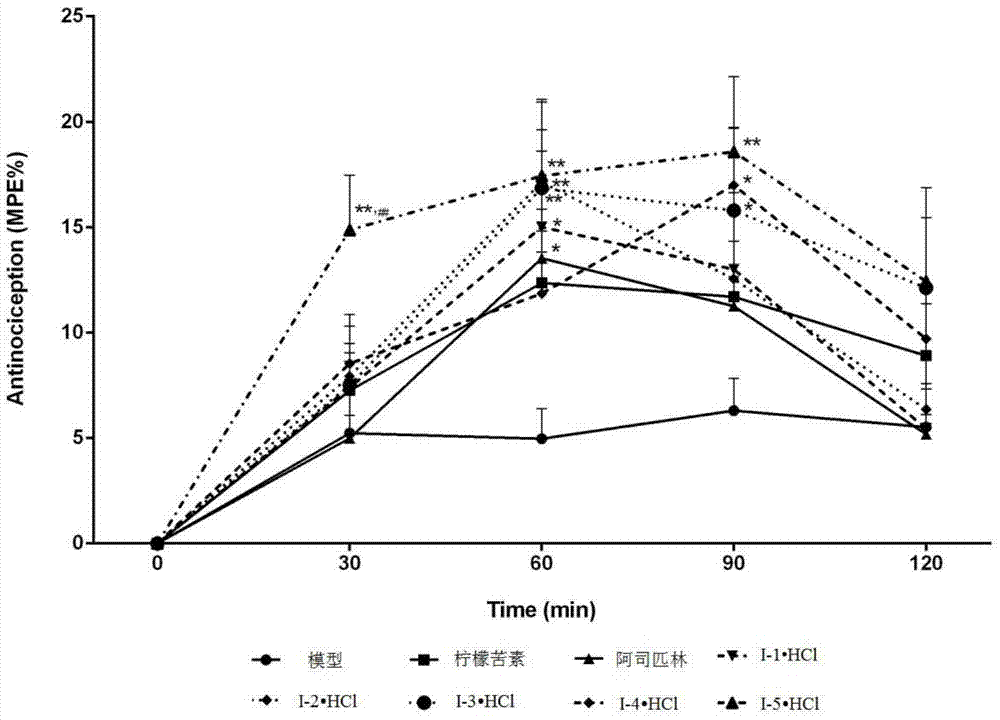
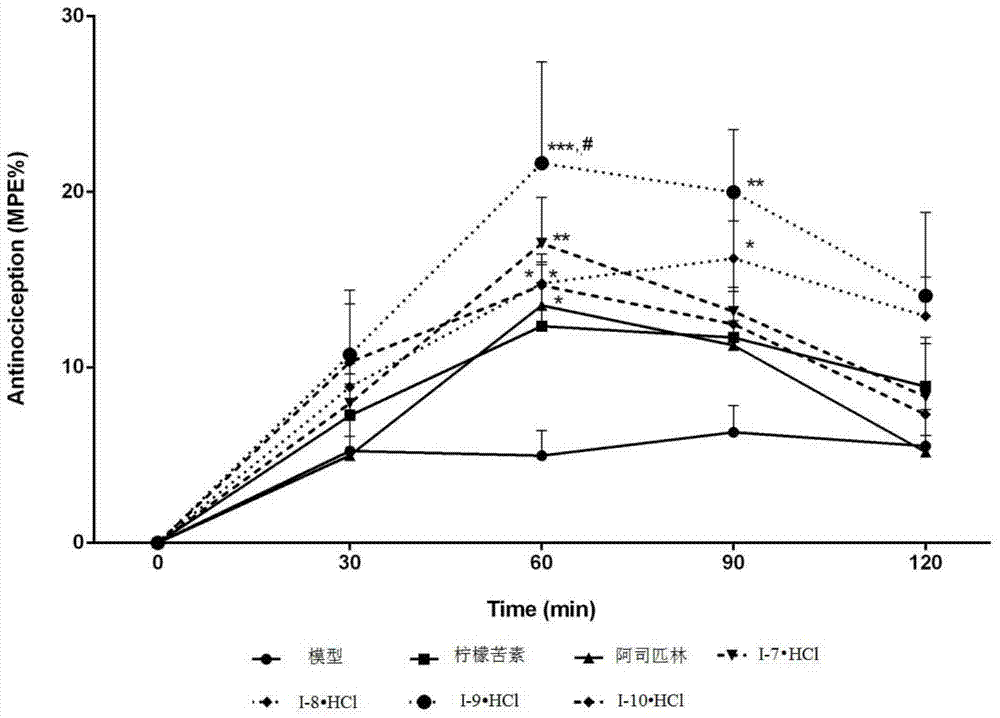
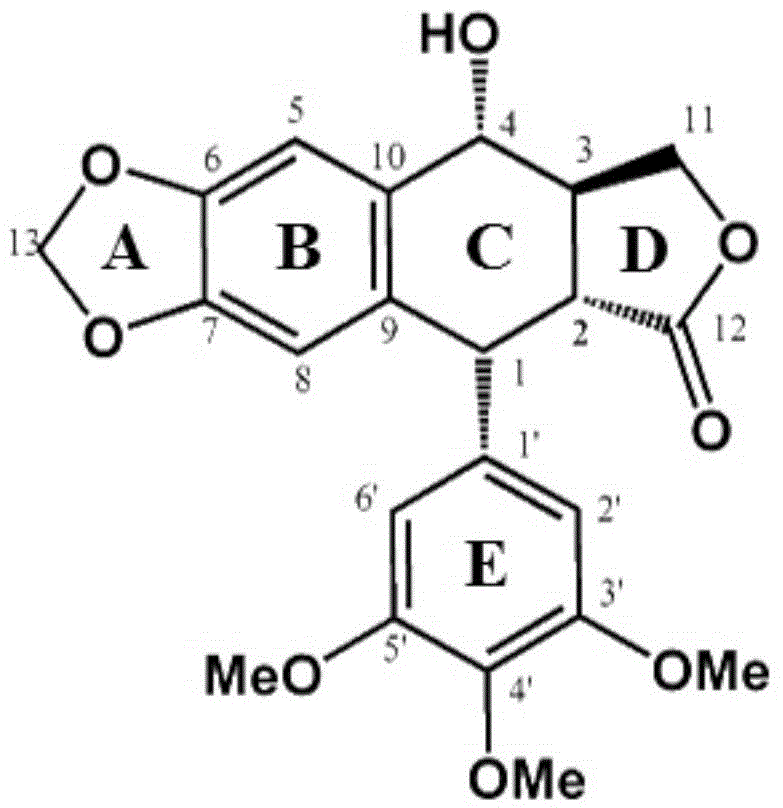
Limonin-7-amino derivatives and preparation method and medicine application thereof
The invention relates to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry and particularly relates to water-soluble limonin-7-amino derivatives (I) and (II) shown in the specification, and a preparation method and medicine application thereof. Pharmacological experiments prove that the compounds disclosed by the invention have the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects and can be clinically used for relieving pain and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Piperidine amino derivative and application thereof in fighting schizophrenia
The invention discloses a piperidine amino compound and an application thereof in fighting schizophrenia. Pharmacological experiment results show that the piperidine amino compound related to by the invention has good water solubility, has high affinity with dopamine D<2>, D<3>, 5-HT<1A>, and 5-HT<2A> receptors, and has good selectivity on D<3> / D<2> receptors. In-vivo test results show that a preferable compound has a good anti-schizophrenia effect, is relatively low in acute toxicity, high in safety and good in pharmacokinetic characteristic, and has a development value as a high-efficiency low-toxicity novel anti-schizophrenia new drug. The piperidine amino compounds are compounds represented as a structural general formula (I), or salts of the compounds, or hydrates of the salts.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
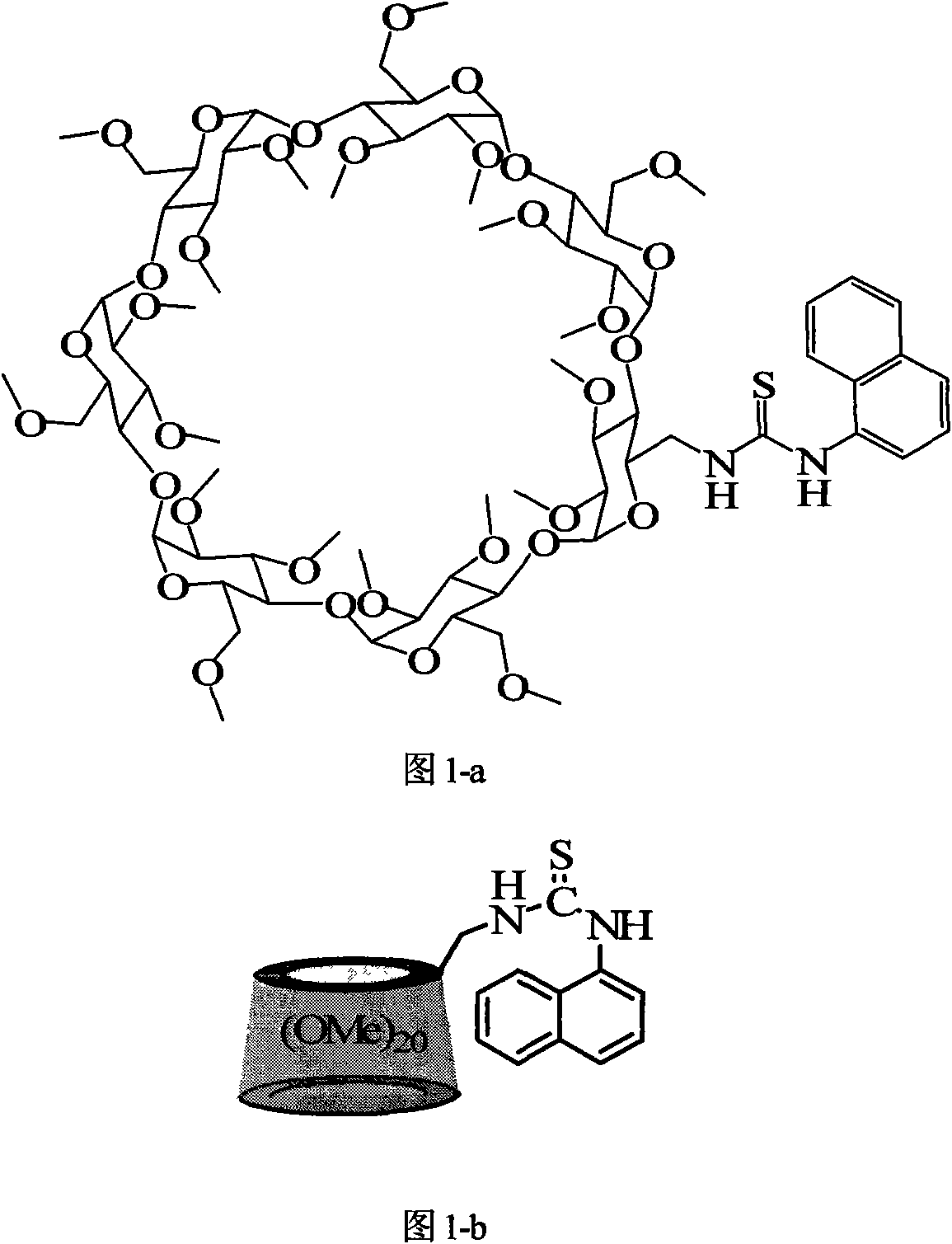
Naphthylthiourea-modified permethylated beta-cyclodextrin derivative, preparation method and application method thereof
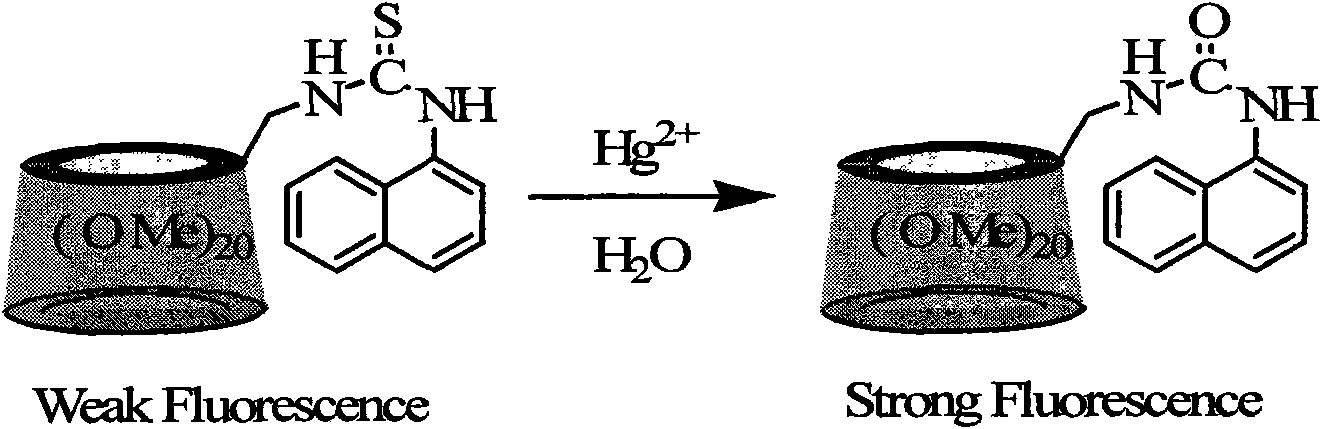
InactiveCN101643517AThe synthetic route is simpleMild reaction conditionsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityFluorescence
The invention discloses a naphthylthiourea-modified permethylated beta-cyclodextrin derivative, a preparation method and an application method thereof, the chemical formula of the compound is C73H118N2O34S, and the structure and the schematic diagram are shown as attached figures. The compound is simply prepared by the reaction of an amino derivative of cyclodextrin and naphthalene isothiocyanatewith high yield. The compound has high selectivity and high sensitivity on the recognition of mercury ions due to high sulphophile affinity of mercury. The divalent mercury ions are added in the compound in a water phase, fluorescence can be greatly ascended in a short period of time, the detection limit is 50ppb, the compound is resistant to the addition of other ions, such as, Li<+>, Na<+>, K<+>, Mg<2+>, Ca<2+>, Sr<2+>, Ba<2+>, Ag<+>, Cd<2+>, Ce<2+>, Co<2+>, Cu<2+>, Ni<2+>, Pb<2+>, Sr<2+>, Zn<2+> and the like, and the compound has no obvious change after the addition of other ions. The invention provides a reagent and a method which can rapidly test water solubility of the mercury ions in an environment and a biological body with high selectivity, high sensitivity and fluorescence enhancement and is applicable to the wider pH range of (3-12).
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
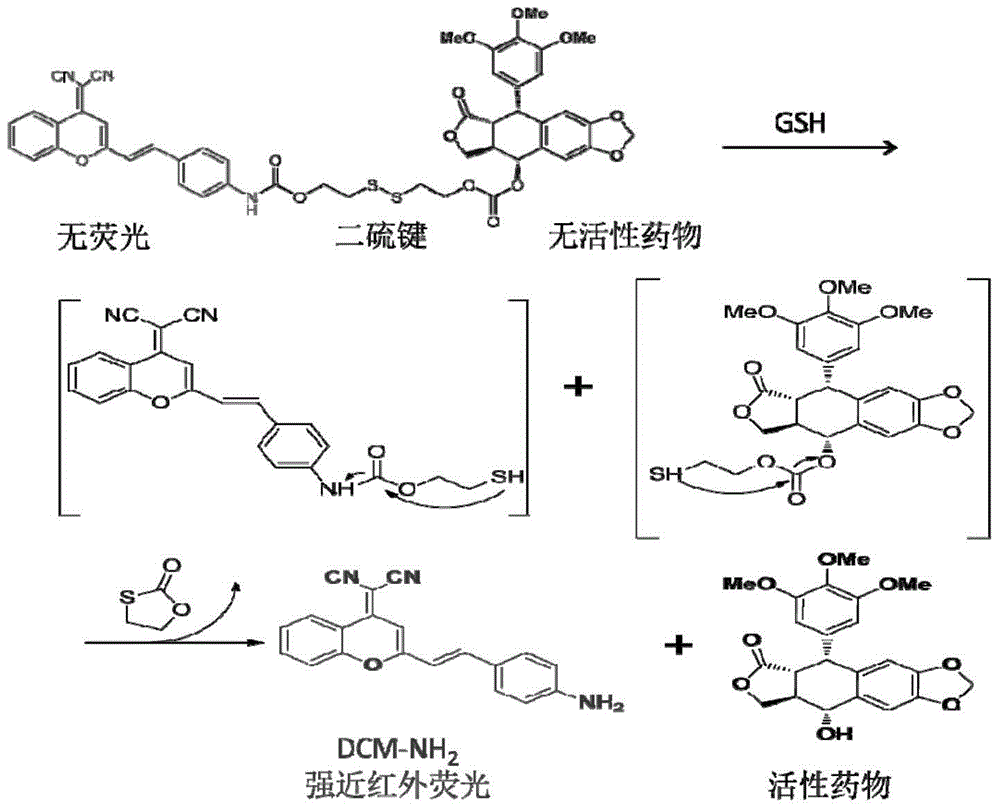
Prodrug of compound podophyllotoxin PPT with anti-tumour activity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104945409ASmall side effectsHigh activityOrganic chemistryLuminescence/biological staining preparationFluorescencePodophyllotoxin
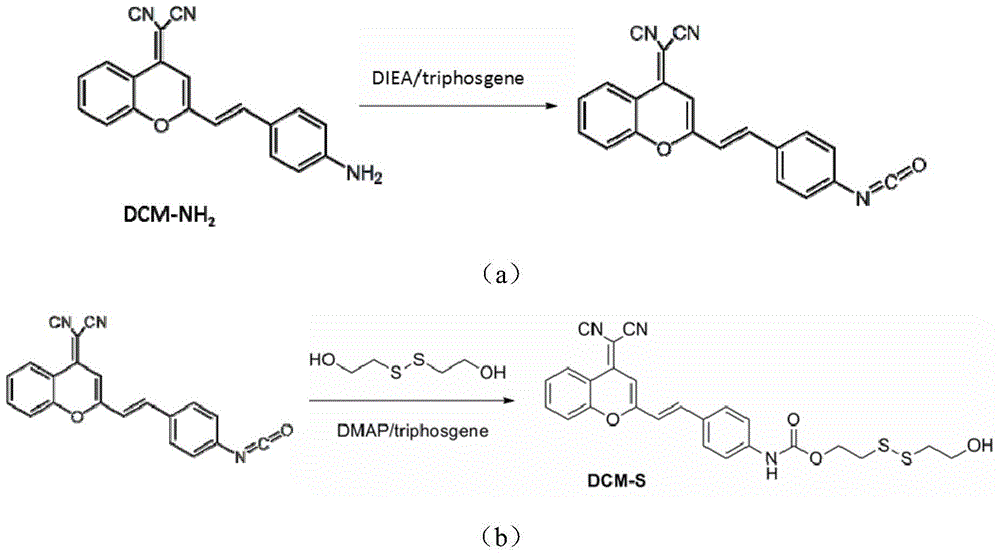
The invention relates to a prodrug of a compound podophyllotoxin PPT with an anti-tumour activity and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: converting the hydroxyl group of C4 of the C-ring of the PPT to chloro-carbonic ester, and reacting the group with the addition product DCM-S of 2-hydroxyethyl disulphide and a benzopyranyl nitrile amino derivative DCM-NH2 to generate a GSH-sensitive PPT-S-DCM prodrug compound. The compound obtained by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the characteristic of selectively releasing the PPT in vitro and in vivo through tumour cell targeting (GSH sensitivity), and a clinical application prospect; meanwhile, the release behaviour of the PPT prodrug compound can be detected and researched by virtue of the near-infrared fluorophore of benzopyranyl nitrile.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
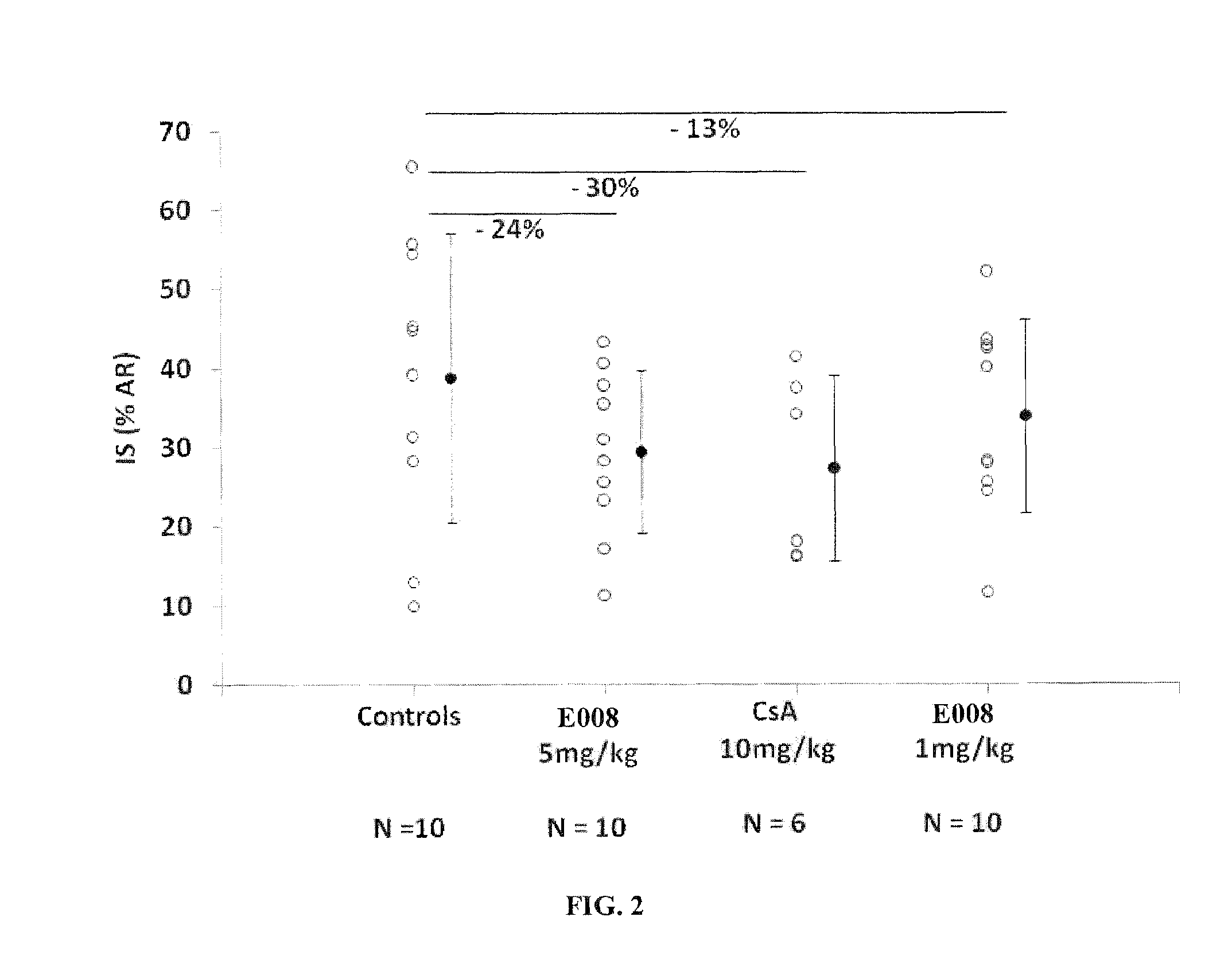
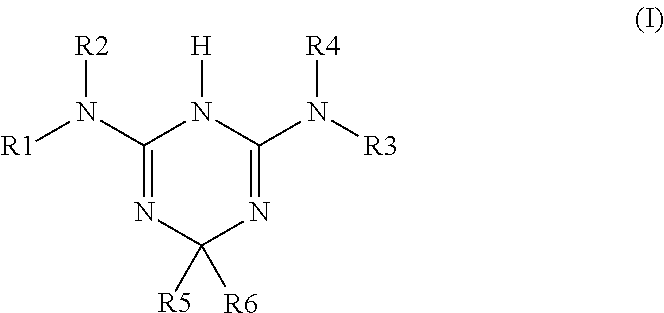
Amino derivatives of dihydro-1,3,5-triazine used in the treatment of ischemia and/or reperfusion related diseases
The invention relates to amino derivatives of dihydro-1,3,5-triazine, used for the treatment and / or prevention of diseases induced by ischemia and / or reperfusion, notably cardiac and renal complications.
Owner:POXEL +1
Application of clinafloxacin amino derivatives and medicinal salts thereof in preparing antitubercular medicaments
ActiveCN103405435AHas inhibitory effectStrong anti-tuberculosis activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsThioureaMoxifloxacin
The invention discloses an application of clinafloxacin amino derivatives and medicinal salts thereof in preparing antitubercular medicaments. In the structural general formula of the clinafloxacin amino derivatives, R is -(CH2)nNR<1>R<2>, -CH(CH2CH2XCH3)NH2, 2-pyrrolidyl or -OR3; n is 0 or 1; R1 and R2 are separately hydrogen, methyl, 2-hydroxyethyl, (R)-1-ethyl-2-hydroxyethyl, 2-aminoethyl, 3-(dimethylamino)propyl, hydroxyl, amino, methylamino, methoxyl or thiourea group; X is S or SO2; R3 is methyl or isobutyl; the compounds have certain inhibitory effect on standard sensitive strains, clinically isolated sensitive strains and clinically isolated drug-resistant strains of mycobacterium tuberculosis, the antitubercular activity of a part of compounds is stronger than that of ofloxacin and clinafloxacin and weaker than that of moxifloxacin, thus providing a new research direction for the antitubercular medicaments, and being beneficial to clinical treatment of tuberculosis.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
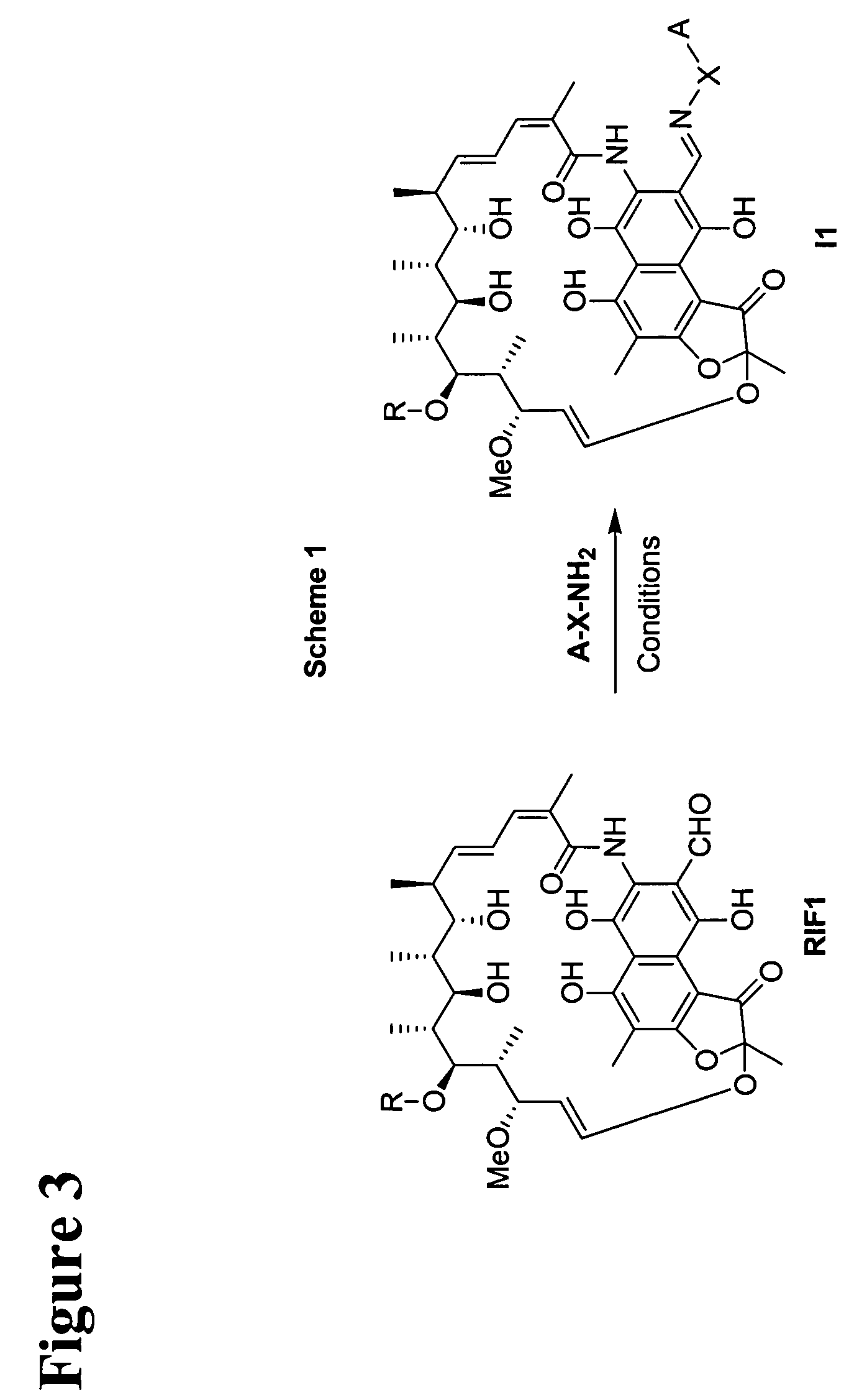
Rifamycin imino derivatives effective against drug-resistant microbes
The present invention relates to rifamycin 3-iminomethylenyl (—CH═N—) derivatives having antimicrobial activities, including activities against drug-resistant microorganisms. The claimed rifamycin derivative has a rifamycin moiety covalently linked to a linker through an iminomethylenyl (—CH═N—) group at the C-3 carbon of the rifamycin moiety and the linker is, in turn, covalently linked to a quinolone structure or its pharmacophore within the DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV inhibitor family. The inventive rifamycins are novel and exhibit activity against both rifampin and ciprofloxacin-resistant microorganisms.
Owner:TENNOR THERAPEUTICS (SUZHOU) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com