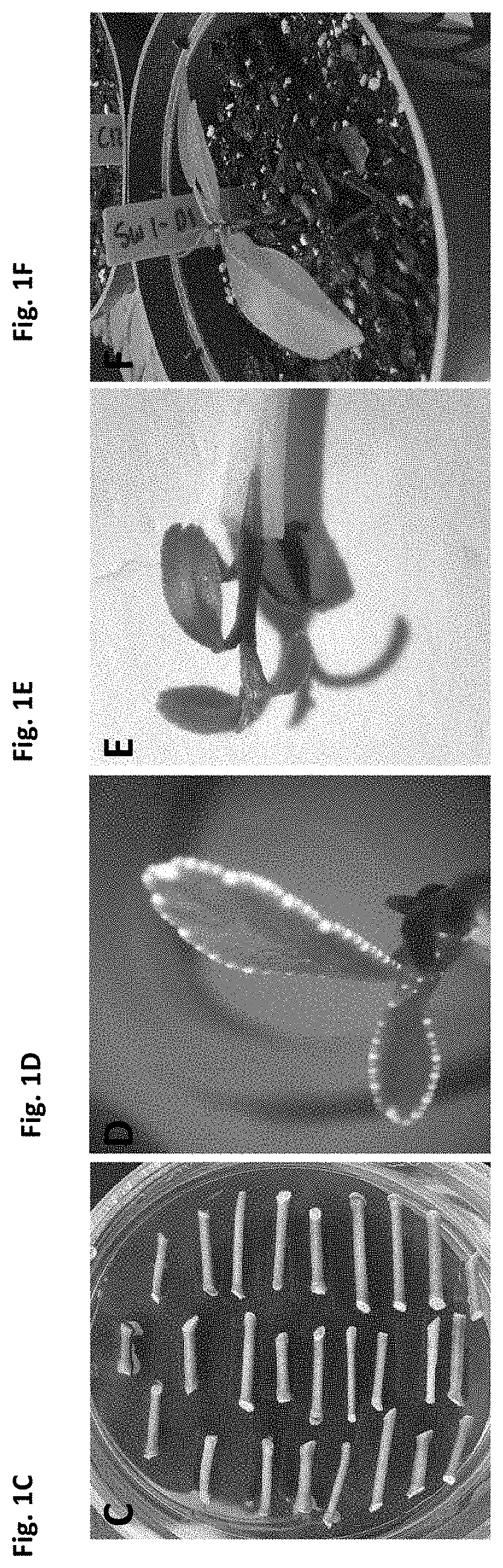
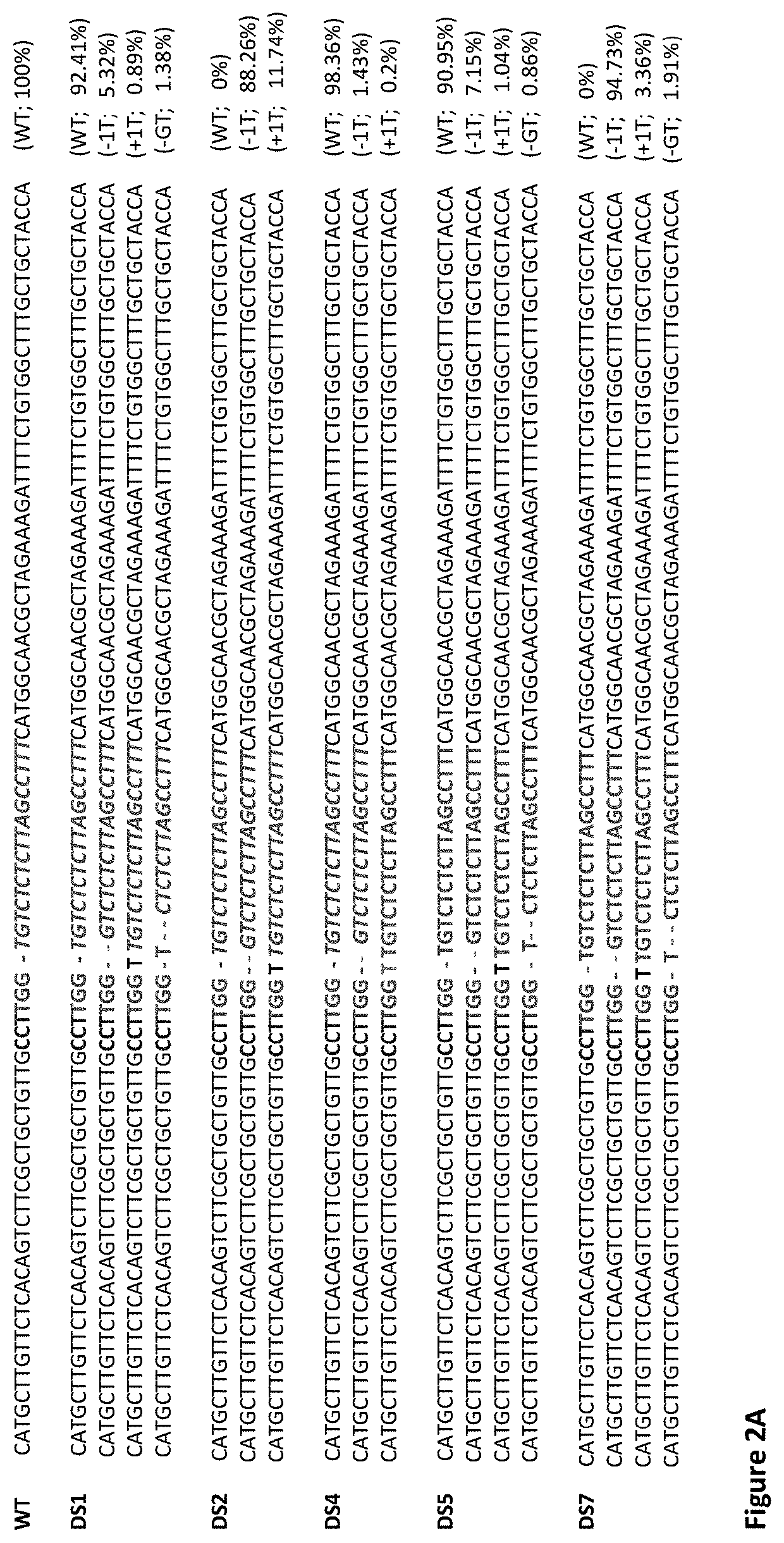
Patents
Literature
149 results about "Citrus greening disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
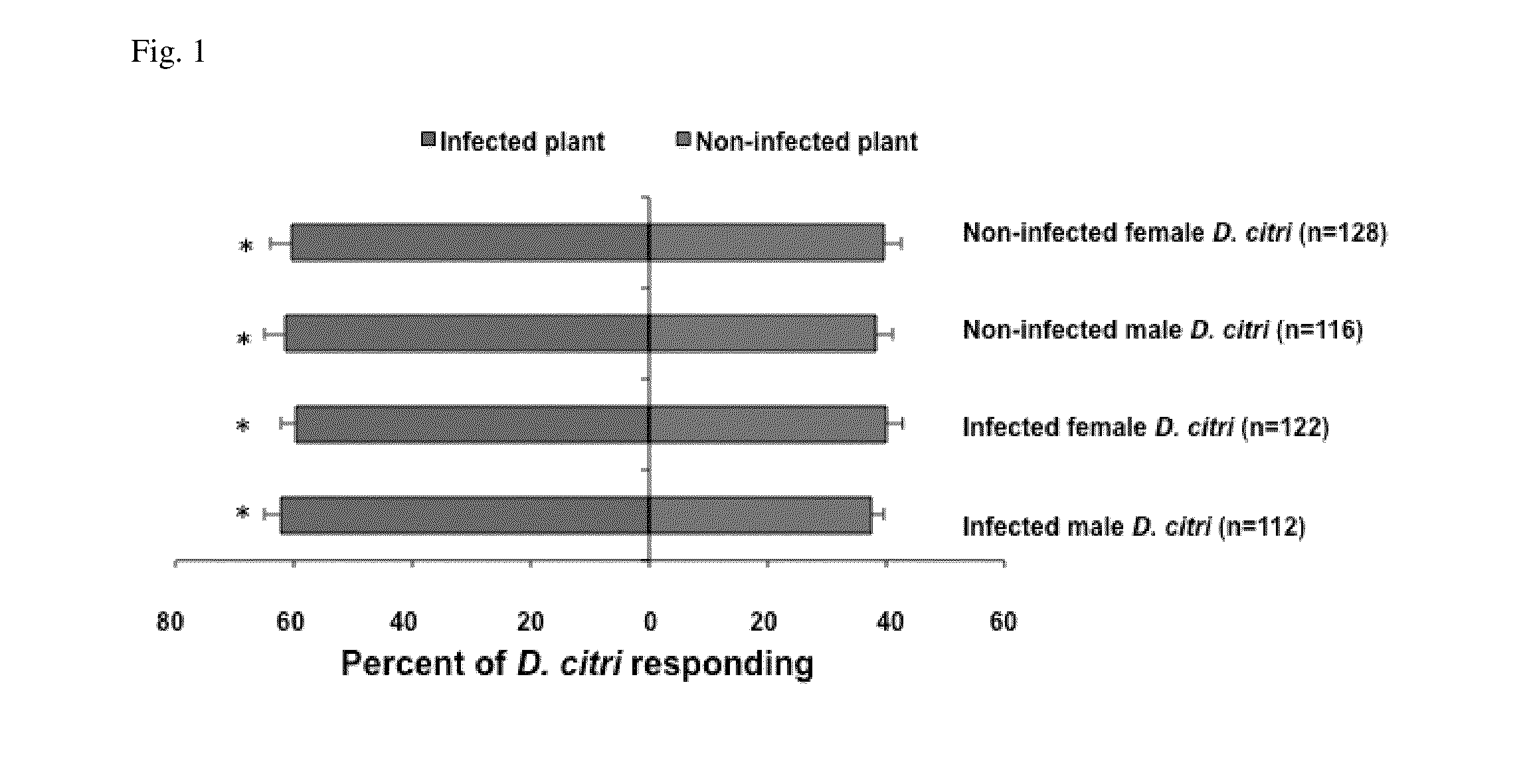
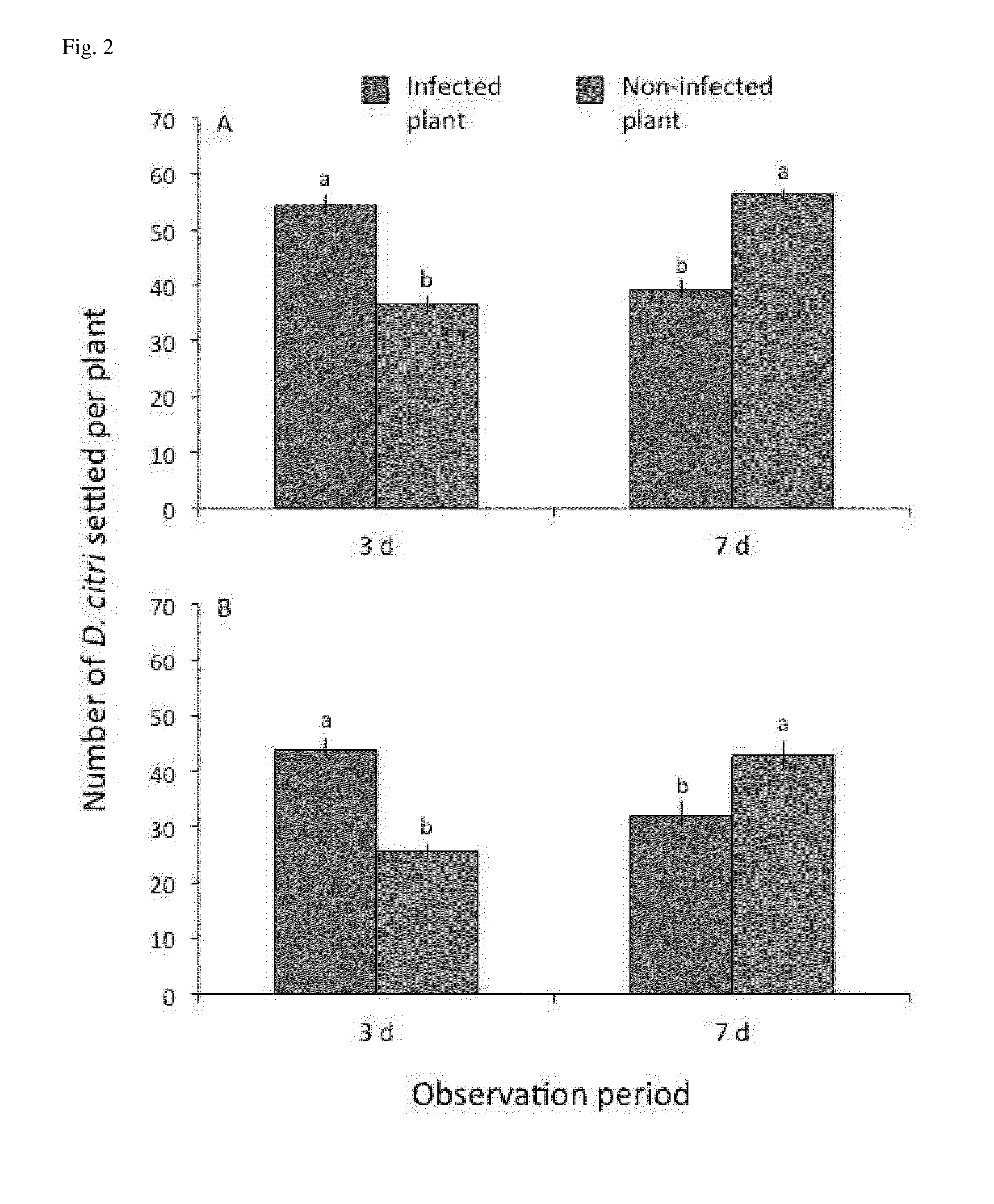
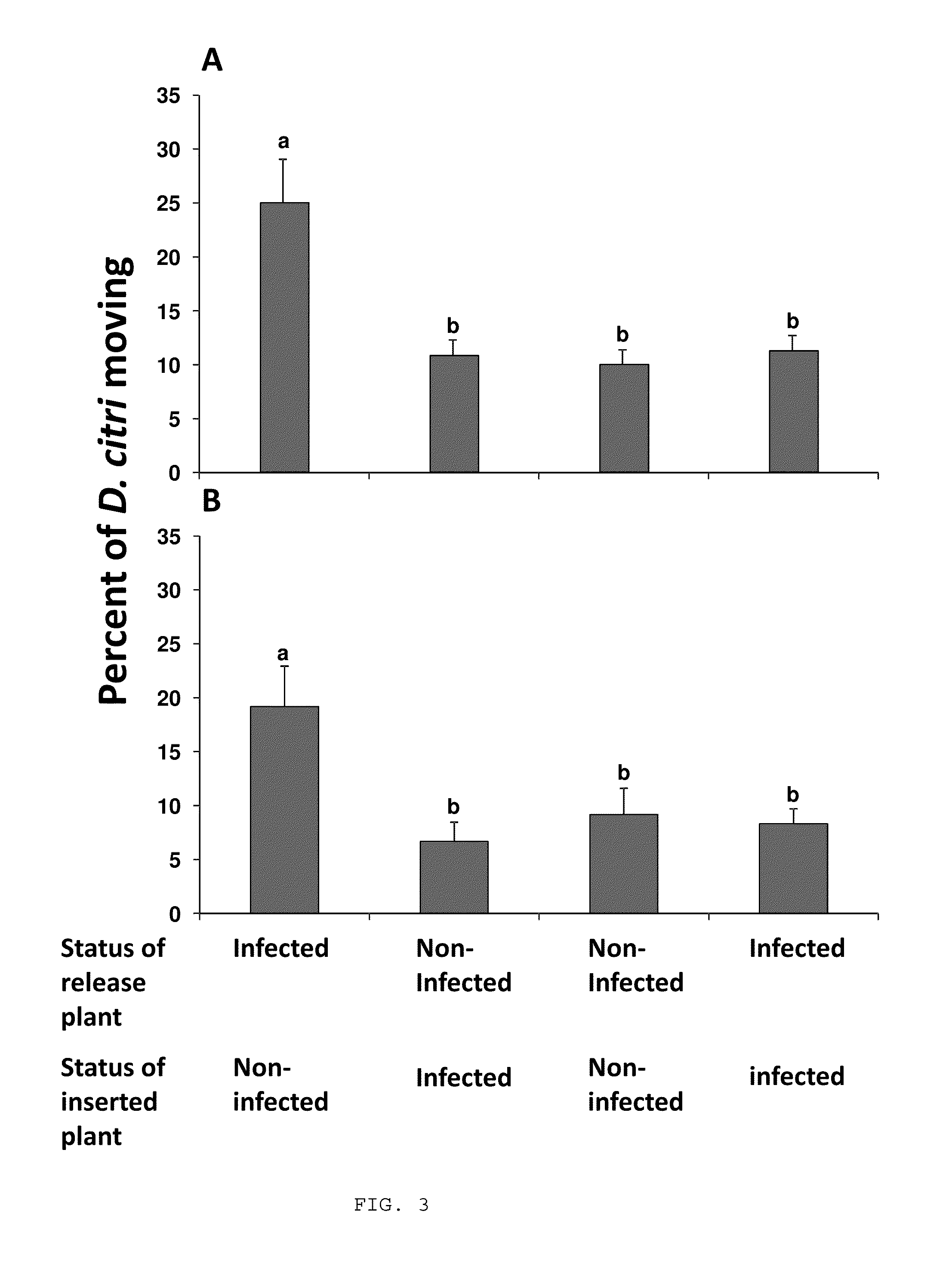
Citrus greening disease (Chinese: 黃龍病; pinyin: huánglóngbìng; literally: 'yellow dragon disease'; or HLB) is a disease of citrus caused by a vector-transmitted pathogen. The causative agents are motile bacteria, Candidatus Liberibacter spp. The disease is vectored and transmitted by the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri, and the African citrus psyllid, Trioza erytreae, also known as the two-spotted citrus psyllid. It has also been shown to be graft-transmissible. Three different types of HLB are currently known: The heat-tolerant Asian form, and the heat-sensitive African and American forms. The disease was first described in 1929 and first reported in China in 1943. The African variation was first reported in 1947 in South Africa, where it is still widespread. Eventually, it affected the United States, reaching Florida in 2005. Within three years, it had spread to the majority of citrus farms. The rapid increase in this disease has threatened the citrus industry not only in Florida, but the entire US. As of 2009, 33 countries have reported HLB infection in their citrus crop.
Multifunctional silica-based compositions and gels, methods of making them, and methods of using them
Briefly described, embodiments of this disclosure, among others, include compositions, gels, methods for synthesizing multifunctional silica based nanoparticle gel, method of treating, preventing, or both treating and preventing, a disease in a plant species, method for simultaneously treating citrus plants for citrus canker and preventing the invasion of an Asian Citrus Psyllid (ACP) vector that carries the pathogen and spreads the citrus greening disease in citrus plants, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Methods and Compositions for the Treatment and Prevention of Citrus Greening Disease
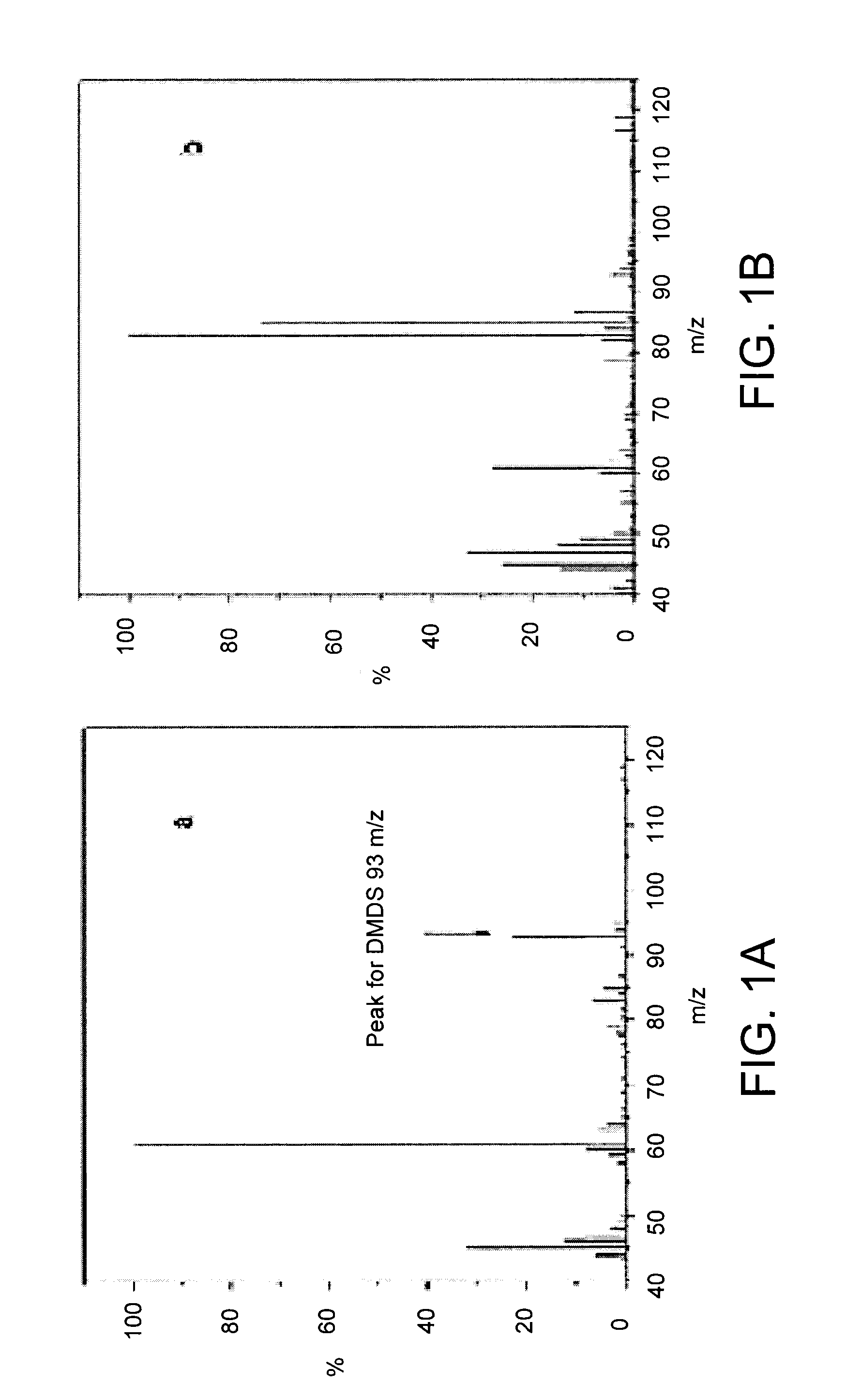
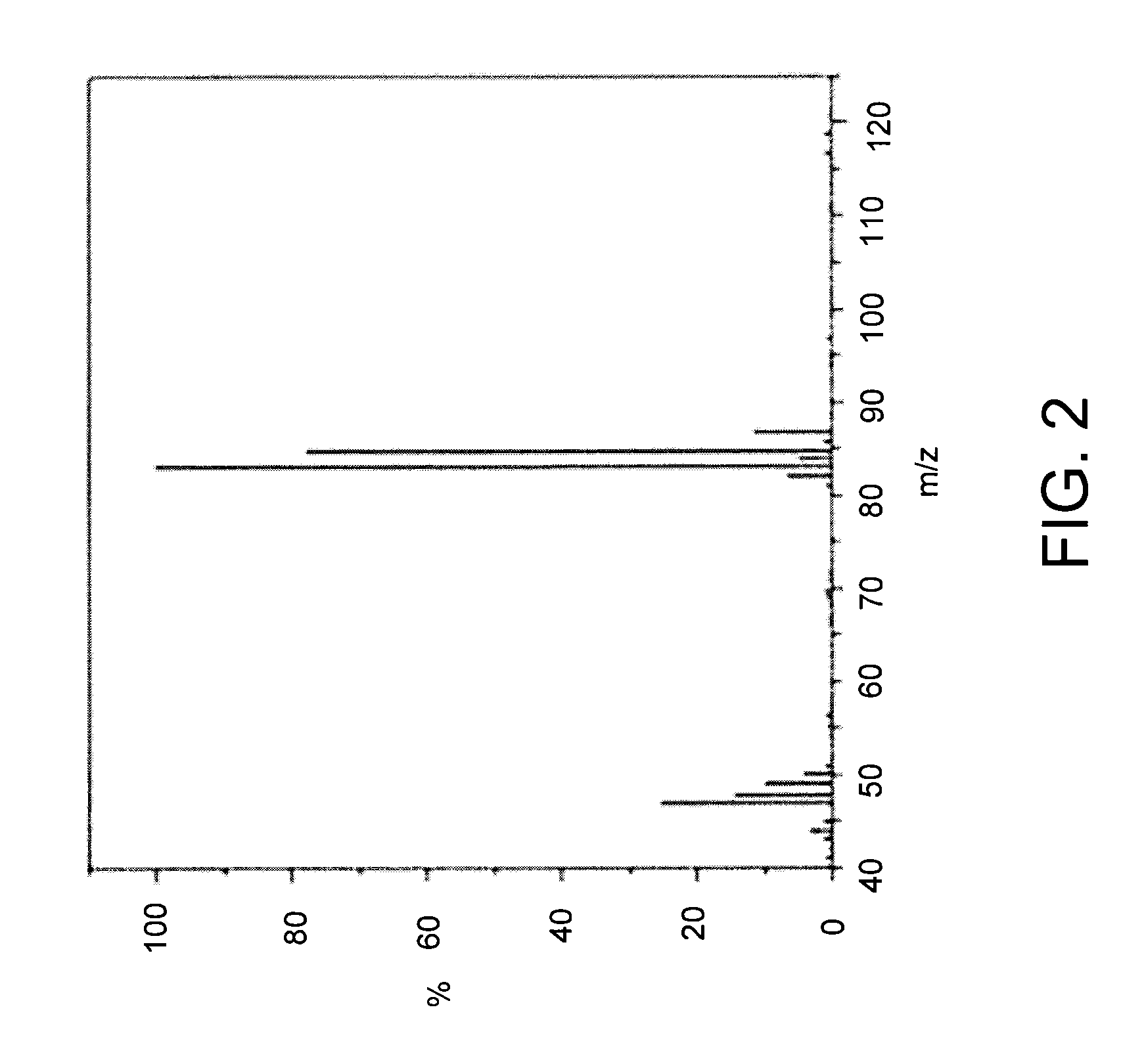
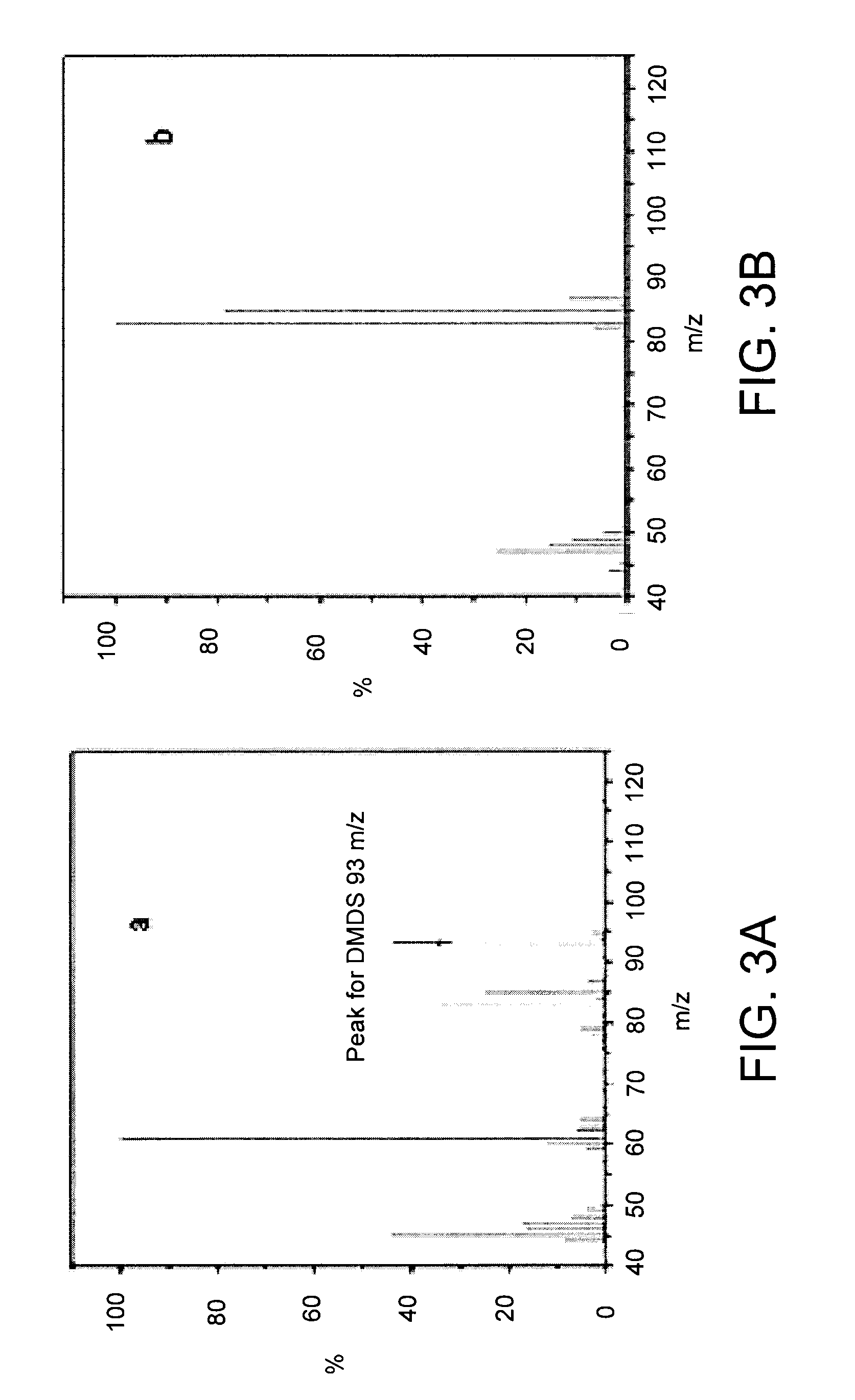
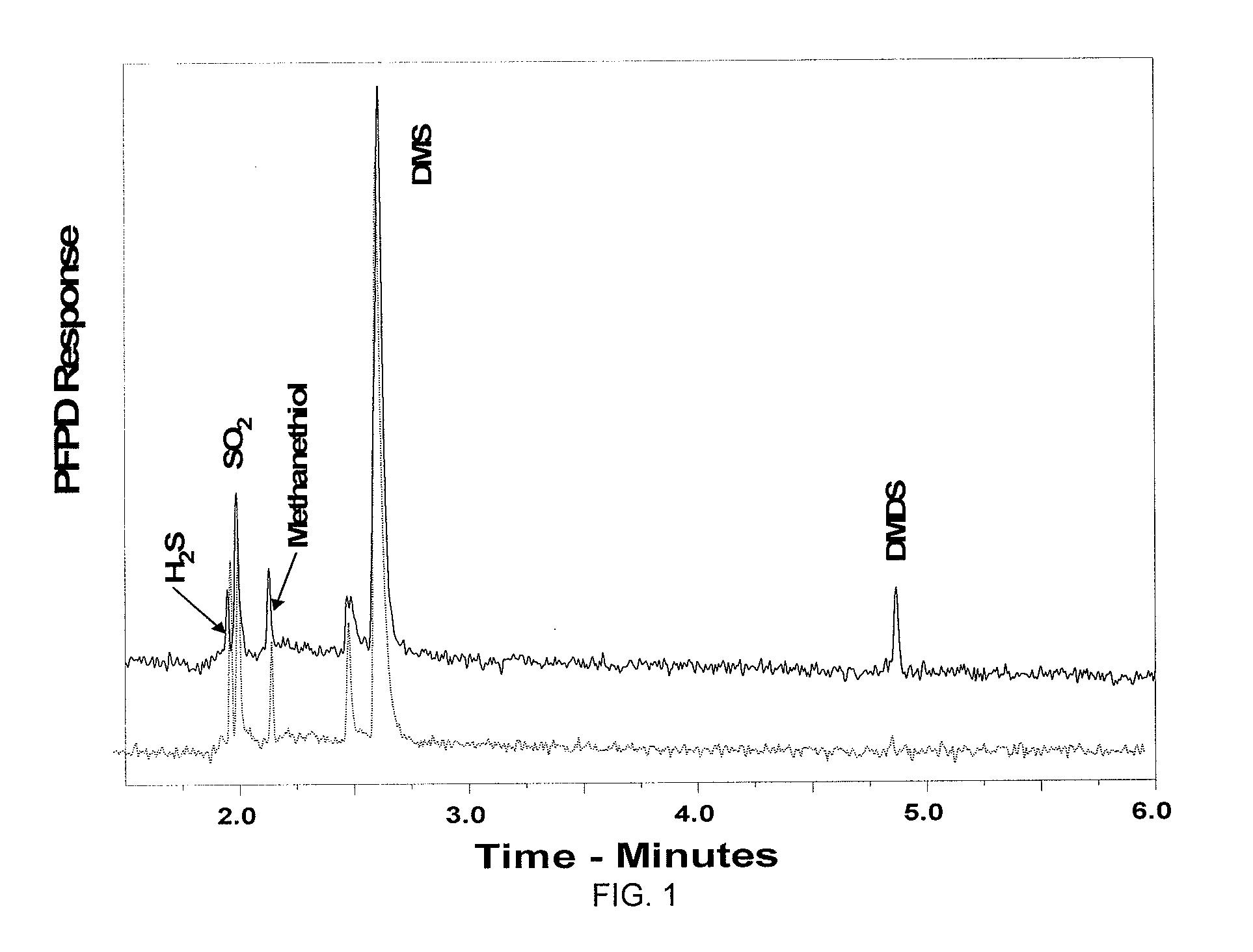
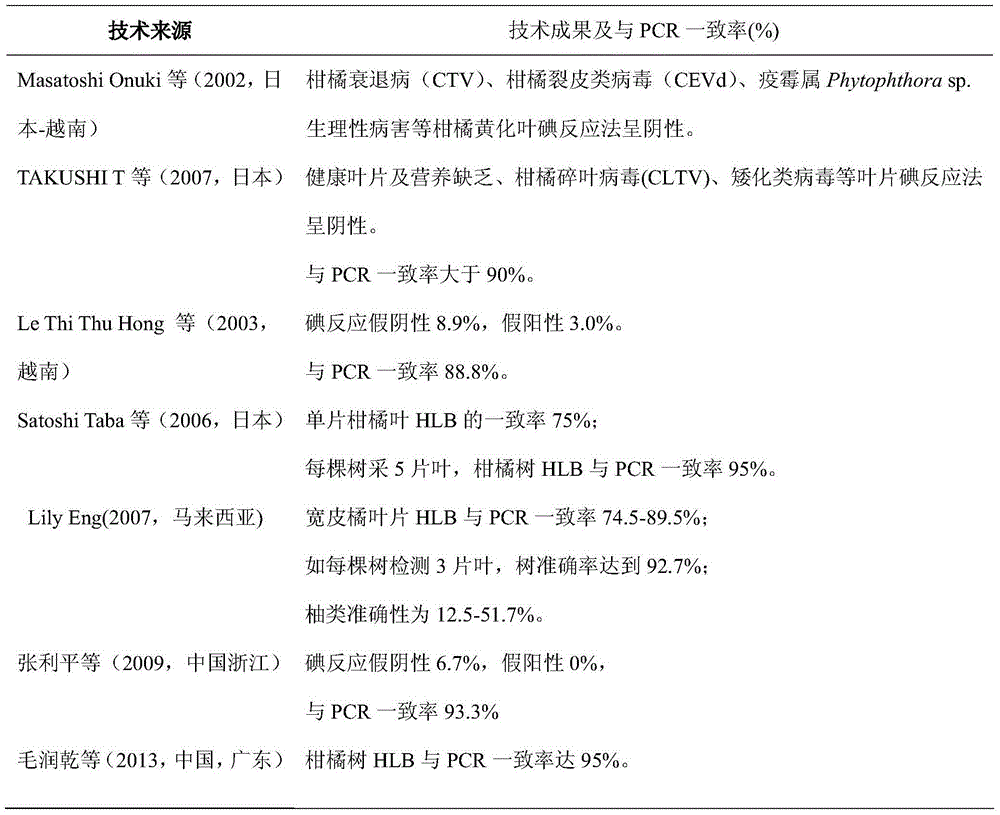
InactiveUS20100074972A1BiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsDiseaseCitrus greening disease
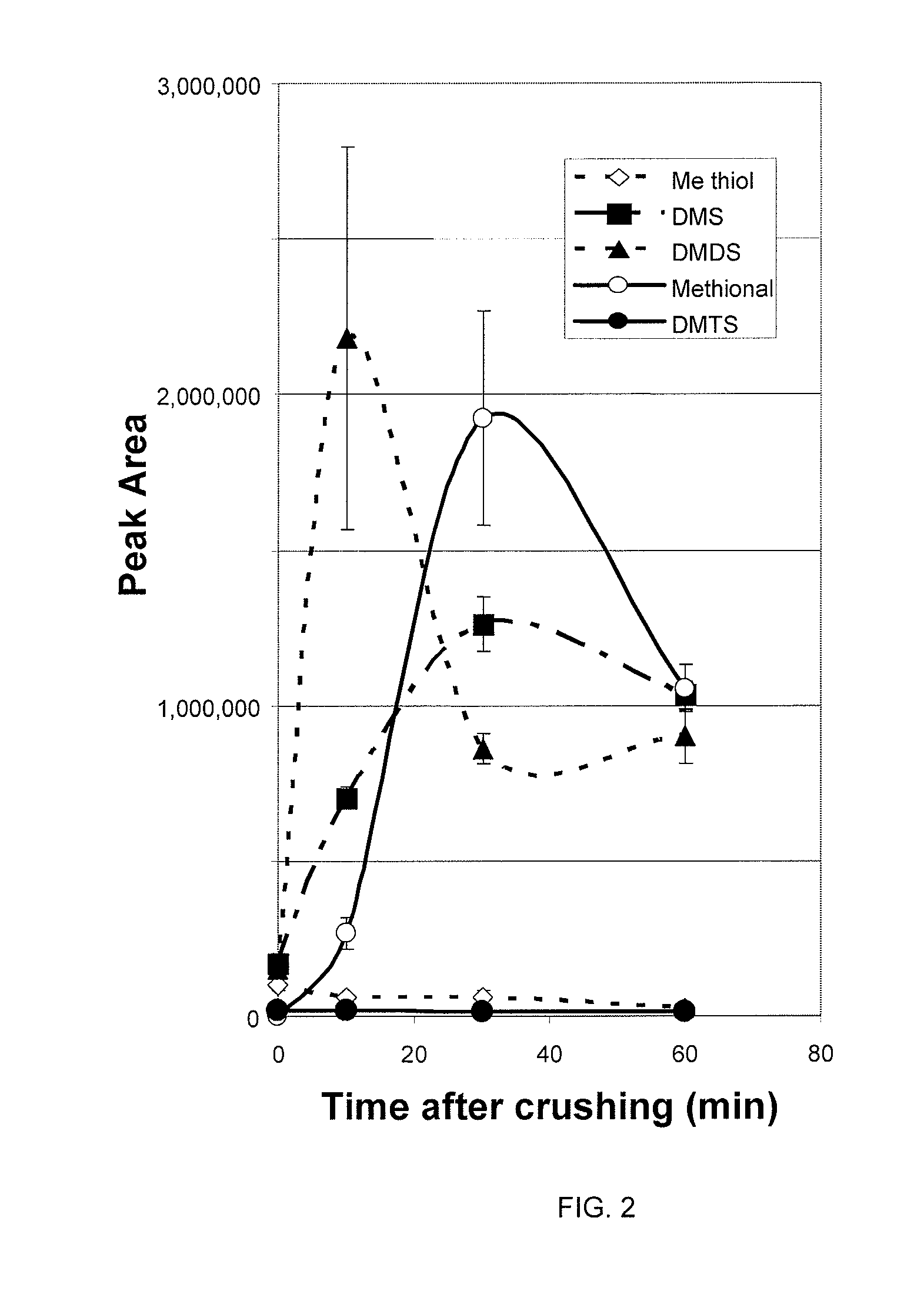
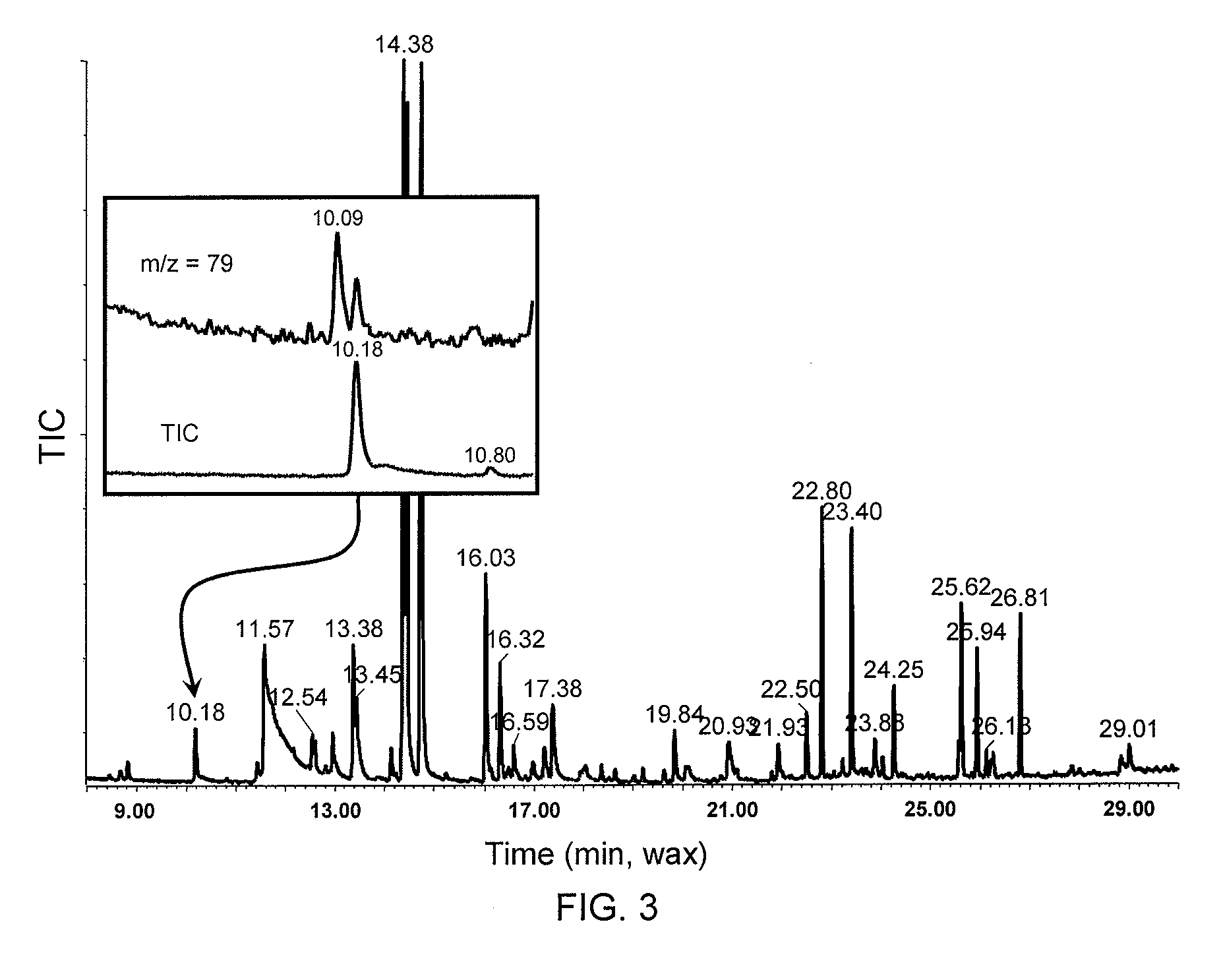
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the prevention of citrus greening disease. In one embodiment, there is provided a method for repelling or killing insect vectors of citrus greening disease comprising exposing the vectors to an effective amount of at least one volatile compound set forth in Tables 1 and 2 herein. In one embodiment, the volatile compound is dimethyl disulfide.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for preventing and treating candidatus liberibacter asiaticus by heat treatment
ActiveCN103404397APromote growthQuality returned to normalPlant protectionBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention specifically discloses a method for preventing and treating candidatus liberibacter asiaticus by heat treatment. The method comprises the specific steps as follows: a citrus tree body infected with candidatus liberibacter asiaticus is subjected to continuous heat treatment for 2-5 hours in the environment at the temperature of 45 DEG C-52 DEG C; then the tree body is cultivated at the environment temperature; and the operation is repeated in the next week, and continuous treatment is performed for 3-4 weeks. The method is economical and environment-friendly, the content of pathogenic bacteria in the infected tree can be greatly reduced or eliminated, the tree vigor of the experimental tree is recovered, the tree grows normally, and production and yield of citrus are obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Citrus yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus detection test paper
The invention belongs to the plant protection subject of the agricultural category, and particularly relates to citrus yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus detection test paper. The detection test paper is prepared through the following steps that pathogenic bacteria antigen is extracted and purifed from catharanthus roseus host with citrus yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus antigen and used for injecting immunized rabbits to obtain yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus specific antiserum, the yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus specific antiserum is purified to obtain the citrus yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus antigen, immune colloidal gold is prepared, a combined pad which is soaked with the immune colloidal gold and a chromatography membrane which is coated with a detection line T-citrus yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus antigen and a quality control line C-goat anti-rabbit antibody are further prepared, and finally a detection test paper product is assembled. Against for the requirement of the detection of a great amount of citrus yellow shoot samples, the citrus yellow shoot candidatus liberibacter asiaticus detection test paper which is convenient, rapid and high in specificity is provided. The test paper has following advantages that 1, convenience in use and simpleness in operation are realized; 2, a detection result can be obtained within a short period of time; 3, the stability is good; and 4, the cost is low, and the test paper is particularly suitable for the discrimination of citrus yellow shoot plants of a fruit garden.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Method for preventing citrus tristeza virus of fruit bearing production type citrus trees
ActiveCN105052659AReduce usageGrowth impactCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsCitrus volkamerianaShoot
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant disease and insect pest control, and particularly discloses a method for preventing the citrus tristeza virus. The method is especially suitable for preventing the citrus tristeza virus of fruit bearing production type citrus trees. According to the method, through special management of spring shoots, summer shoots, early and late autumn shoots and winter shoots of the citrus trees every year, the food sources and breeding sites of citrus psylla spreading the citrus tristeza virus can be effectively eliminated so that eggs and nymphs can not grow and develop normally, the number of subcultured pest sources is reduced greatly, and then an ideal preventing effect is realized; meanwhile, the usage amount of insecticides can be reduced, natural enemy protection is achieved, and prevention cost is reduced; furthermore, compared with the shoot control scheme, the method has the advantages that the growth of the citrus trees is not affected, and the effect of eliminating the food sources and breeding sites of citrus psylla spreading the citrus tristeza virus is remarkable.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG
Method for propagating citrus and pomelo seedlings resistant to citrus greening disease by chemical mutagenesis
InactiveCN103202187ACurb spreadTo achieve the purpose of immunity against diseaseHorticulture methodsPlant protectionDiseaseCitrus amblycarpa
The invention relates to a method for propagating citrus and pomelo seedlings resistant to citrus greening disease by chemical mutagenesis and belongs to the technical field of seedling propagation. The method is achieved by chemical mutagenesis and includes: selecting a citrus / pomelobudstick suffering from citrus greening disease as a scion, treating with sodium nitrite drug for the first time, treating with disodium hydrogen phosphate drug for the second time, flushing with fresh water, grafting for the first time to form a mutant, grafting for the second time to form a disease resistant, grafting for the third time to form a disease-resisting seedling, testing exterior syndromes, and propagating and popularizing. The disease-resisting seedling propagated by the method is resistant. After planted in a field and even infected with disease-carrying Diaphorinacitri, the seedling which is resistant and immune is capable of killing citrus greening disease invaded inside, and immunizing and disease resisting are achieved. The method is effective in restraining the citrus greening disease from spreading and conducive to promoting great development of citrus and pomelo industries in Guangdong province.
Owner:吴世盘 +4
Composite microbial agent for citrus tristeza virus, preparation method thereof and special biological agent for citrus tristeza virus prepared by using same
InactiveCN108617696AControl infringementStructural regulationBiocideDisinfectantsEcological environmentAureobasidium sp.
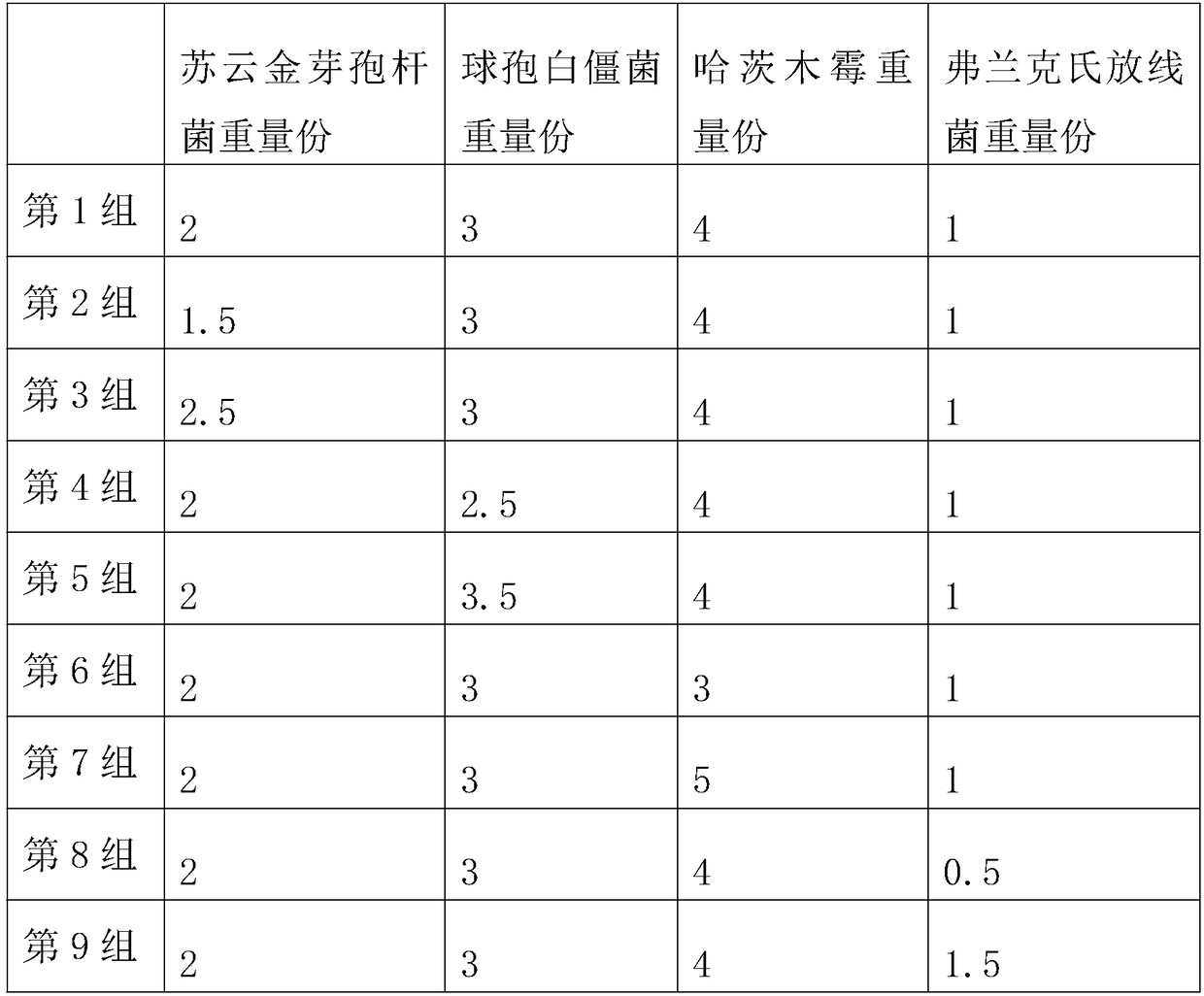
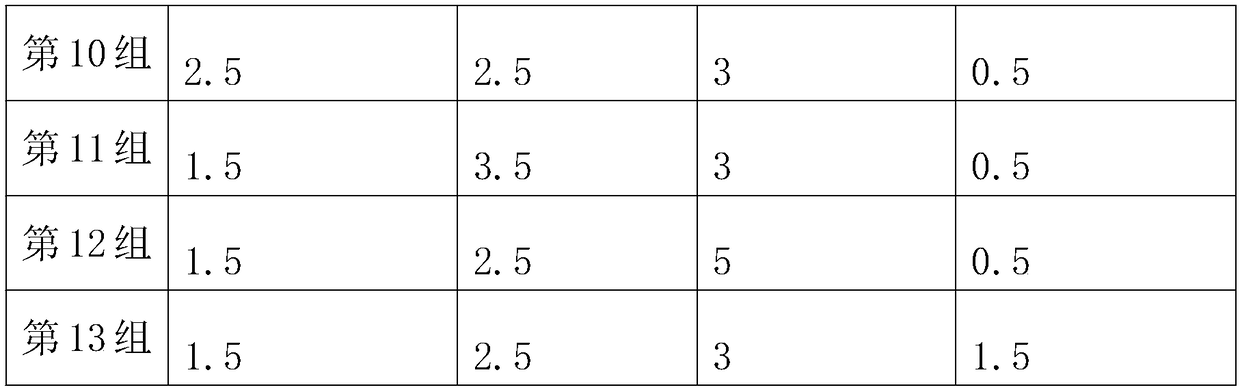
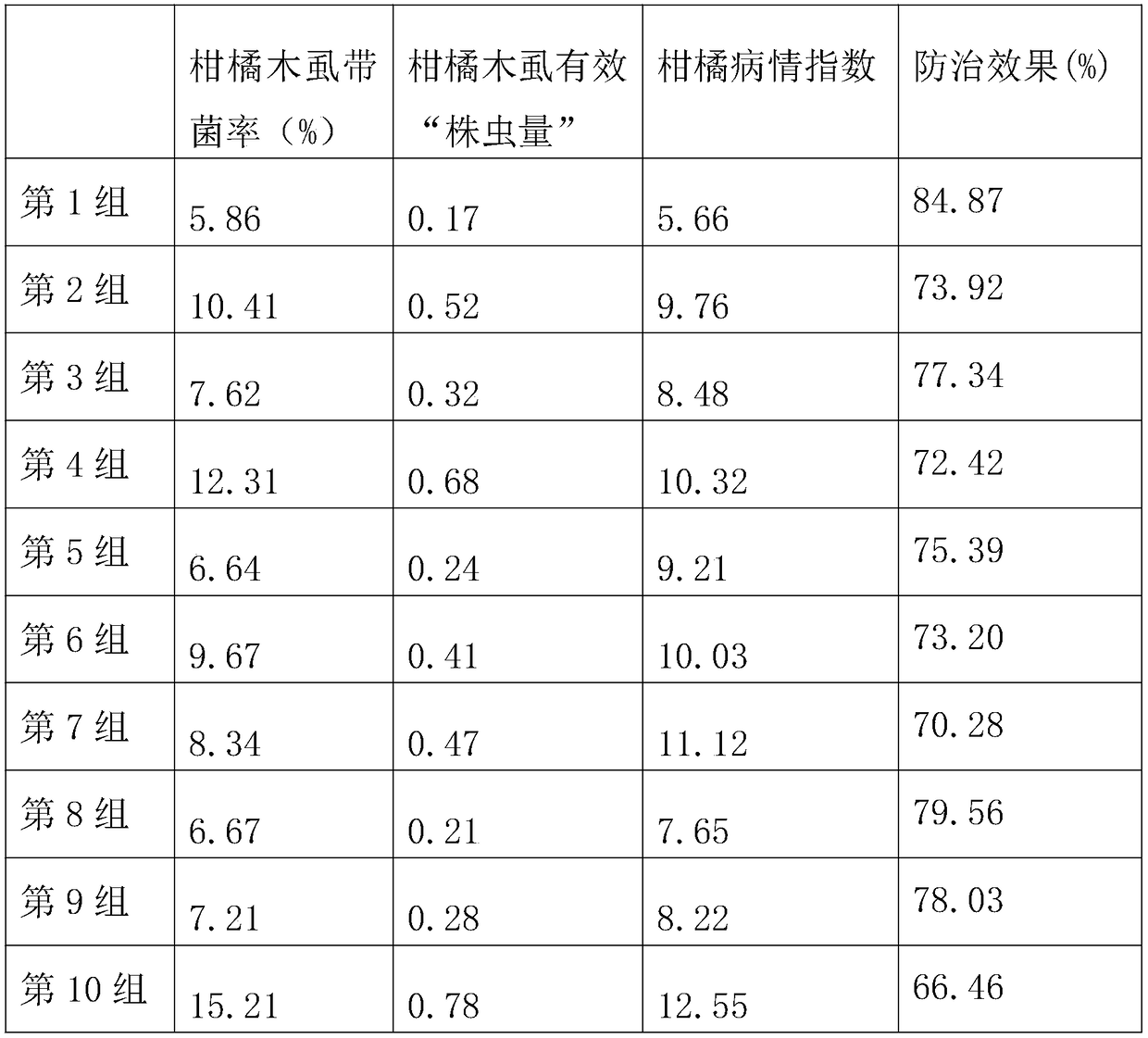
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural planting, in particular to a composite microbial agent for citrus tristeza virus, a preparation method thereof and a special biological agent for the citrus tristeza virus prepared by using the same. According to the invention, bacillus thuringiensis, beauveria bassiana and trichoderma harzianum are used to control the pathogen of citrustristeza virus pathogens on the ground and kill a spreading source wood louses and eggs thereof so as to effectively control the occurrence of the citrus tristeza virus, and four kinds of microorganism bacteria underground can effectively control the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms, effectively control the spread of pathogenic bacteria by nematodes, and simultaneously regulate the soil structure, decompose organic matters and improve the soil fertility. By promoting the growth of citrus roots with citrus specific AM fungi, citrus can grow new roots in clusters, the number of the new roots is enlarged, the tree vigor is enhanced, the immunity and disease resistance of trees are improved, a nitrogen fixation system is formed, and the pathogen control is combined with the improvement of the ecological environment for the growth of the citrus to achieve the effect of preventing and treating the citrus tristeza virus.
Owner:广西青又青生物肥业有限公司
Methyl salicylate-based attractants for vectors of citrus greening disease
The present invention is directed to an insect attractant having an amount of methyl salicylate effective to attract a plurality of vectors of citrus greening disease and an agriculturally acceptable carrier.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Microbial agent for preventing and treating cumquat huanglongbing and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a microbial agent for preventing and treating cumquat huanglongbing and a preparation method thereof, and particularly provides a microbial agent for preventing huanglongbing of cumquat, citrus shantianju and citrus and a preparation method thereof. The microbial agent is formed by fermenting and then mixing bacteria like Gulake streptomyces, Kawuer streptomyces, bacillus psychrosaccharolyticus, nissl bacillus and tufted trichoderma proportionally. Procreation and propagation of gram negative bacteria are inhibited by means of root irrigation and foliage spray, bacteria are used to treat bacteria, and harmful pathogenic bacteria in soil are killed, so that tree root systems are more developed, tree cell tubes are smooth, yellow leaves of fruit trees are turned green, and healthy new treetops are enabled to grow; the microbial agent generates insecticidal antibiotics like flavensomycin and inhibits or damages development process of eubactericera and eggs of other disease-transmitting insect (like citrus aphid), so that adult rate is reduced, orchard pest occurrence quantity is reduced, transmission media of huanglongbing are cut off, and effects on preventing and controlling citrus huanglongbing are realized.
Owner:FOSHAN YANHUI BIOTECH CO LTD
Liquid for Treatment of Citrus Greening Disease and Treatment Method Using Same
Provided are: a liquid for treatment of Citrus greening disease, which is capable of curing citrus trees with Citrus greening disease; and a treatment method using the liquid. The liquid for treatment of Citrus greening disease contains Fe ions and at least some of the Fe ions are present in the form of Fe2+ ions. This treatment liquid contains a predetermined amount of Fe ions and an acid. Citrus greening disease is able to be cured by spraying the treatment liquid onto leaves of citrus trees infected with Citrus greening disease or by pouring the treatment liquid on the roots of citrus trees infected with Citrus greening disease.
Owner:AICHI STEEL +1
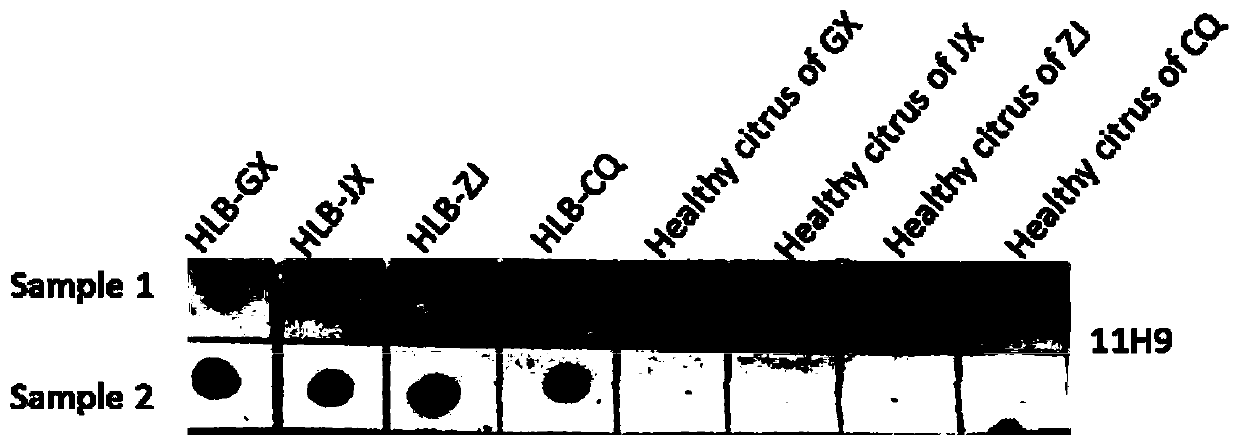
Hybridoma cell strain secreting monoclonal antibody resistant to Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus pathogens and application of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN109897829AAccurate detectionSensitive detectionImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibody typesBALB/c
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain secreting a monoclonal antibody resistant to Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus pathogens and an application of the monoclonal antibody. A Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus vein crude extract is taken as an antigen to immunize a BALB / c mouse, one hybridoma cell strain 11H9 capable of secreting the monoclonal antibody resistant to Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus pathogens is obtained by cell fusion, screening and cloning, and the preservation number of the hybridoma cell strain is CGMCC No.17285. Indirect ELISA valence of monoclonal antibody ascites secreted by the cell strain reaches 10<-7>, the type and the subclass of the antibody are IgG1 and kappa light chains, and the monoclonal antibody has a specific reaction with Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus pathogen protein of 56 kDa in sick leaves and avoids immunoreaction with healthy leaves. ACP-ELISA, dot-ELISA and Tissue blot-ELISA detection methods for detecting the Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus pathogens are established on the basis of the monoclonal antibody11H9, wherein sensitivity of the ACP-ELISA and dot-ELISA methods for detecting the Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus vein crude extract reaches 20480-fold dilution and 10240-fold dilution (w / v,g / mL). The material and technical support is provided for diagnosis and detection of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus, epidemiological analysis, sterile seedling production and scientific prevention and control through establishment of the preparation and detection methods of the monoclonal antibody resistant to the Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus pathogens.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
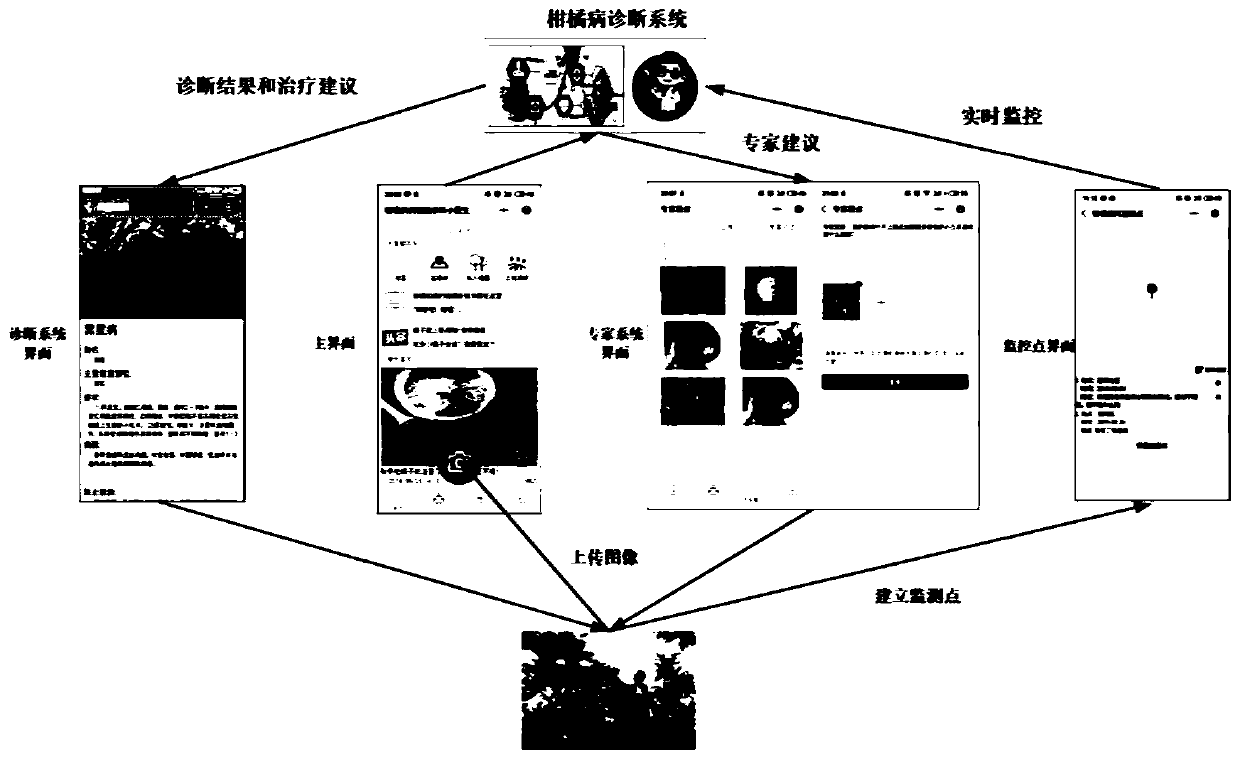
Intelligent citrus disease and pest diagnosis method and system based on deep learning
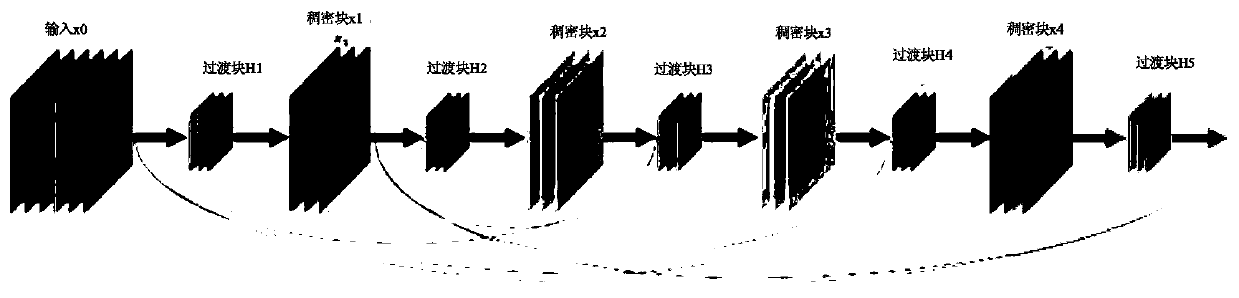
ActiveCN110245720AImprove learning abilityEfficient feature expression abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setNetwork model
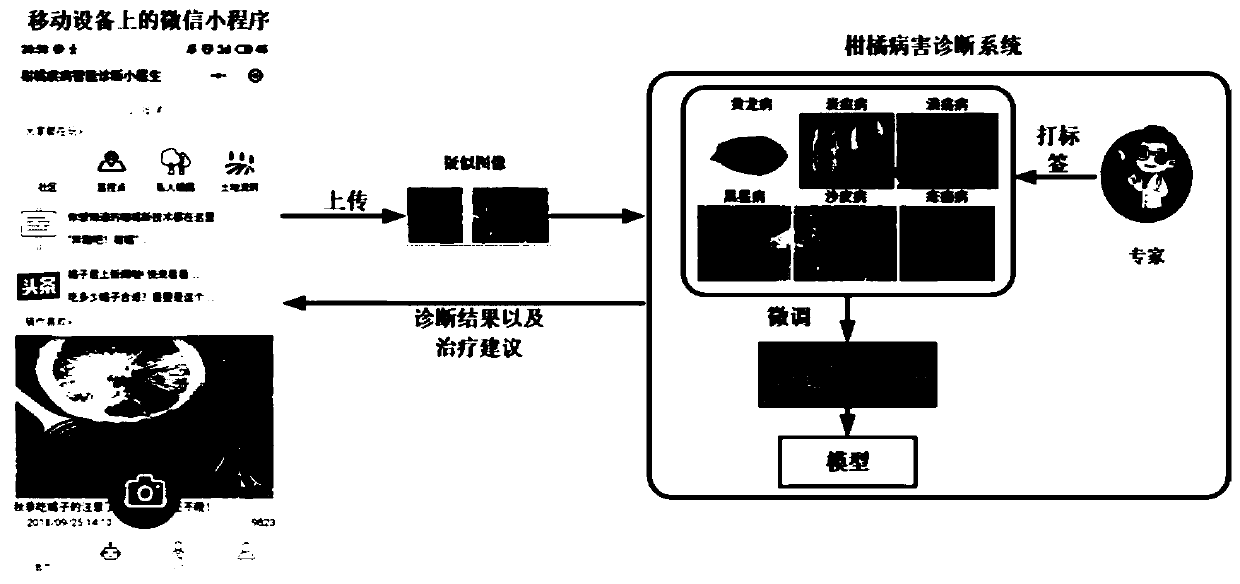
The invention discloses an intelligent citrus disease and pest diagnosis method and system based on deep learning. The intelligent citrus disease and pest diagnosis method comprises the steps: 1, establishing an image data set of six citrus diseases including Huanglongbing, anthracnose, canker, black spot, sand paper rust and scabis based on expert experience; 2, expanding the training set and the test set by using five data enhancement methods; using the enhanced training set and verification set to train the simplified DenseNet network, and storing the model in the system; evaluating the performance of the model by using the test set; and 3, establishing a citrus disease diagnosis system on the basis of the WeChat applet, photographing / uploading images by a user through a mobile phone by using the applet, performing diagnosis through the uploaded trained convolutional network model, and returning an intelligent diagnosis result and pest control suggestions to the user to realize intelligent diagnosis of citrus diseases and pests.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Compound pesticide for preventing and controlling liberobacter asiaticum and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105851029AImprove effectivenessReduce dosageBiocideDead animal preservationDiseaseInfusion method
The invention discloses a compound pesticide for preventing and controlling liberobacter asiaticum and a preparation method thereof. According to objective requirements of prevention and control of liberobacter asiaticum, ZhongShengmycin and oxytetracycline hydrochloride are used as sterilization pesticides, salicylic acid is used as an anti-disease regulation agent and alpha-naphthalene acetic acid is used as a rooting accelerant; the materials are reasonably blended, and pesticide application is carried out by adopting a trunk infusion method, so that the advantages of the agents are complementary to each other; and the compound pesticide has the properties of high efficiency, low toxin, safety, economy and multiple functions, and can be used for preventing and controlling liberobacter asiaticum very well.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
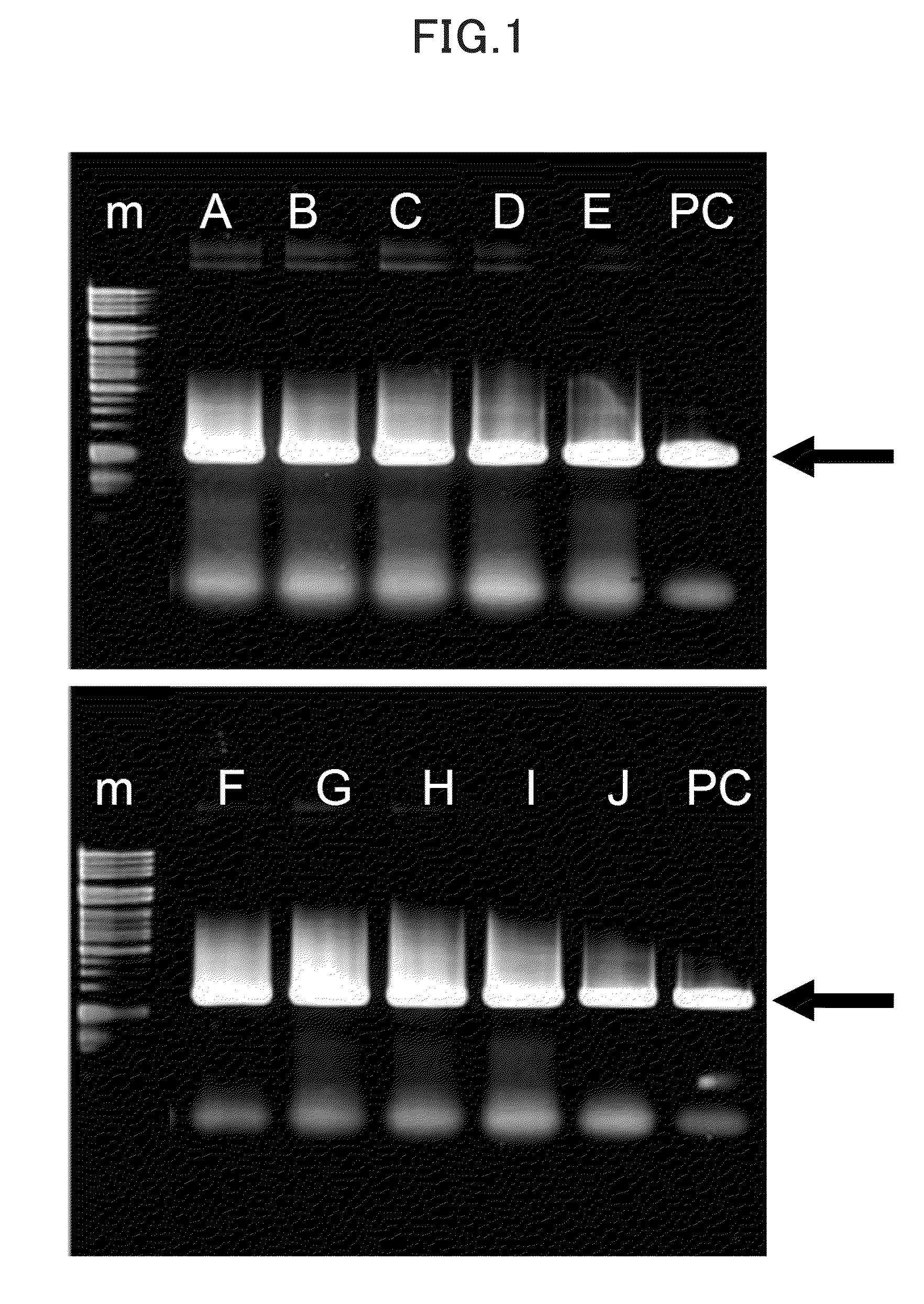
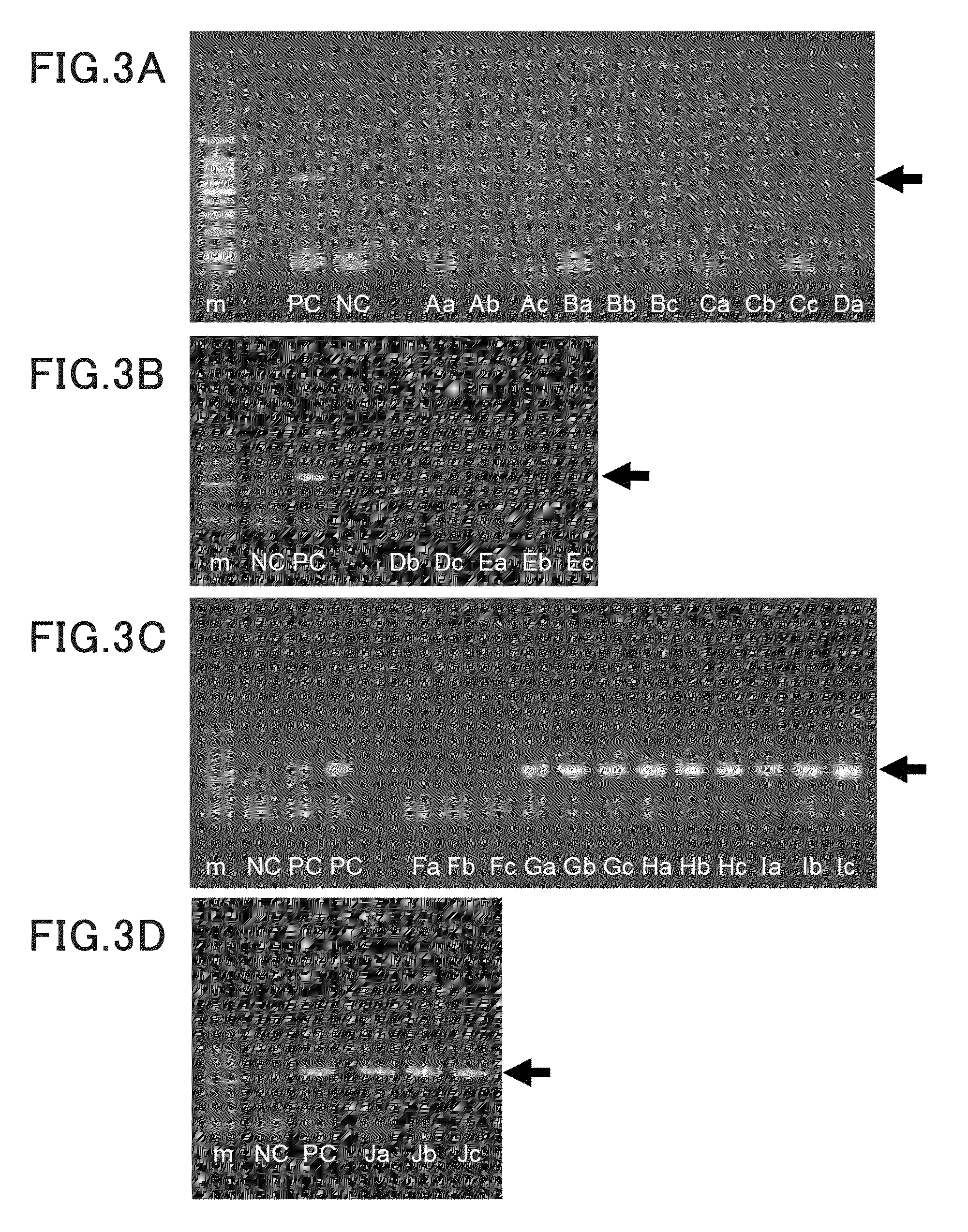
Method for PCR detection of pathogen of citrus greening disease
InactiveCN103525943AReduce the economic cost of testingReduce pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDistilled waterA-DNA
The invention relates to a bioinstrumentation detection and identification method, in particular to a method for PCR detection of a pathogen of the citrus greening disease. The method for PCR detection of the pathogen of the citrus greening disease comprises the steps that DNA of a sample to be detected is extracted; a PCR amplification system is prepared, wherein the PCR amplification system comprises a primary PCR amplification system and a secondary PCR amplification system; a PCR amplification reaction is conducted; PCR amplification products are detected, wherein the final volume of the primary PCR amplification system and the final volume of the secondary PCR amplification system respectively ranges from 7microliters 10 microliters, wherein the final volume of a DNA template is 2.5 microliters, the final volume of 2*Taq PCR Master Mix is 2.5 microliters, the final volume of a primer is 0.25 microliter, and the rest is sterilization double distilled water. According to the method for PCR detection of the pathogen of the citrus greening disease, the final volume of the primary PCR amplification system and the final volume of the secondary PCR amplification system respectively ranges from 7microliters 10 microliters, the detection effect of a 20-microliter reaction system or a 25-microliter reaction system can be achieved, the economic cost of detection is greatly reduced, the amount of needed reagents is small, and the pollution to the environment is reduced.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院园艺研究所
Citrus greening disease resistant liquid fertilizer and its preparation method and application method
InactiveCN106748468AImprove stress resistancePromote healthy growthAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersAmmonium nitrateAmino acid
The invention discloses citrus greening disease resistant liquid fertilizer, made from, by weight, 5-8 parts of Chinese herbal extract, 3-4 parts of urea, 4-5 parts of ammonium nitrate, 6-7 parts of ammonium polyphosphate, 6-8 parts of ammonia water, 26-32 parts of potassium fulvate, 2-3 parts of potassium nitrate, 5-6 parts of potassium chloride, 2-4 parts of calcium amino acid, 1-2 parts of magnesium amino acid, 0.2-0.3 part of zinc amino acid, 1-2 parts of water-soluble borax, 0.5-1 part of methyl jasmonate, 0.2-0.5 part of diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate, 32-34 parts of water, and 4-5 parts of auxiliaries. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application method of the Citrus greening disease resistant liquid fertilizer. The growth characteristics of citrus are fully considered to apply the fertilizer in suitable time, citrus greening disease is prevented and treated during supply of sufficient nutrients to citrus, hoppers can be well prevented and treated, germ propagation is significantly reduced, and stress tolerance of citrus is enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI SIERTE FERTILIZER IND
Nested-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification detection system and application of citrus yellow shoot Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticus
InactiveCN103820561ASmall reaction systemLess amount of reagentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCitrus volkamerianaCitrus greening disease
The invention relates to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection of citrus yellow shoot Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticus, particularly relates to a nested-PCR detection system and application of citrus yellow shoot Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticus, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The provided nested-PCR amplification detection system of citrus yellow shoot Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticus comprises a first-round PCR amplification system and a second-round PCR amplification system, final volumes of the first-round PCR amplification system and the second-round PCR amplification system range from 10 mu L to 20 mu L, and each of the first-round PCR amplification system and the second-round PCR amplification system comprises 1.0 mu L of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) templates, 5 mu L of 2*Taq PCR Master Mix, 0.5 mu L of primers and the balance of sterilizing double-distilled water; and the DNA template of the second-round PCR amplification system is prepared by diluting a first-round PCR amplification product for 10-20 times by volume. According to the invention, a first-round PCR amplification reaction system and a second-round PCR amplification reaction system are small, a dilution ratio of the first-round PCR product is small, a reagent required by the detection is also few, and the corresponding expense is low.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院园艺研究所 +1
Cocktail therapy method for preventing and treating plant diseases
The invention provides a method for preventing and treating plant diseases by cocktail therapy, which uses strong alkali minerals and microbial bacteria for cross use. The method of the present invention has a good curative effect on various plant diseases that are difficult to be treated by existing pesticides, such as lettuce root rot, lettuce stem rot, artichoke root rot, solanaceous melon blight, fusarium wilt , Citrus Huanglongbing, Luo Hanguo bacterial wilt, nematode, tomato bacterial wilt, root-knot nematode, melon bacterial wilt, root rot, Huizhou peach tree gummosis, etc. have immediate effects.
Owner:东莞市瑞丰生物科技有限公司
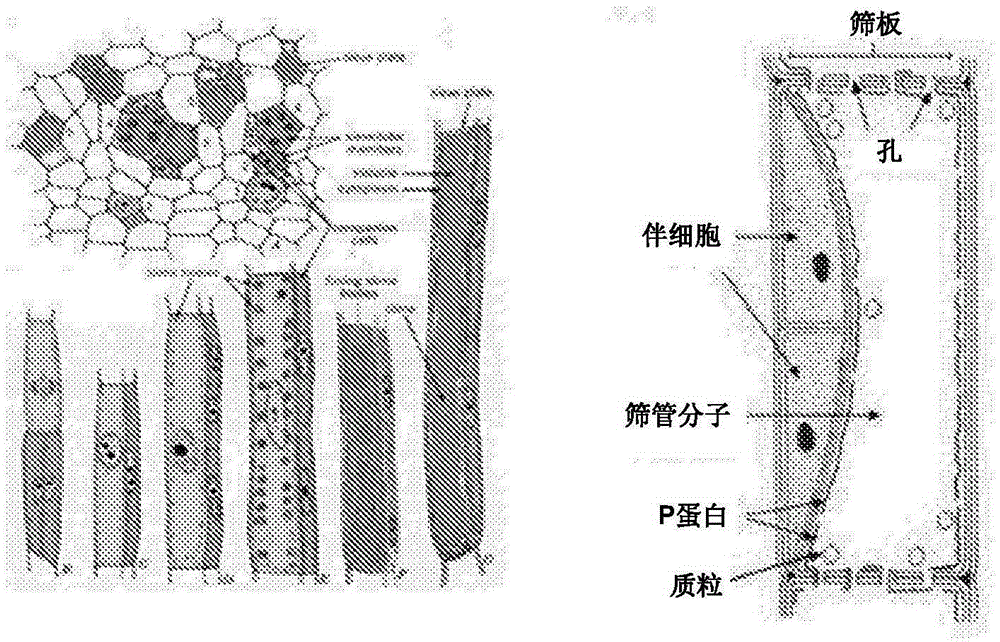
Plants resistant to pathogenic microorganisms growing in vascular tissues
The present invention relates to the generation of transgenic plants resistant to infections caused by microorganisms restricted to the phloem, and it comprises the induction of the expression of a chimeric or fusion protein, which comprises a phloem protein of Citrus aurantifolia (CsPP16), a linker protein and a protein with antimicrobial activity; for example, with antibacterial activity or antibacterial hydrolytic enzyme. The portion of the fusion protein corresponding to the CsPP16 protein can exert its function of simplasmic movement, which occurs via the plasmodesmata of the plant to reach the phloem sieve tubes, while the antimicrobial portion can act to eliminate the microorganism, which settles in the phloem. The invention allows controlling the disease that causes the citrus yellowing or Huanglongbing (HLB), also applying to the treatment of other diseases caused by bacteria and other microorganisms that settle in the vascular tissue of higher plants. The invention includes the designed molecular vectors carrying and expressing a fusion protein and the transgenic plants obtained with a stable expression of said fusion protein and the transformation method of adult plants, healthy or diseased, to express the chimeric proteins and controlling, e.g., HLB disease. The transformation of diseased plants with the fusion protein is a method to produce healthy shoots free from the microorganism causing the disease; e.g., free from HLB bacteria.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACION & DE ESTUDIOS AVANZADOS DEL INST POLITECNICO NACIONAL +1
Pathogenesis Quantification Systems and Treatment Methods for Citrus Greening Blight
ActiveUS20160319379A1Reduce deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiviralsCitrus greening diseaseTreatment strategy
The invention relates to a novel pathogenesis model, method, or kit for detecting pathogenesis in a subject. In particular, the invention provides a pathogen index derived from a ratio of the amount of dual pathogen targets relative to the amount of host quantitative measures. The pathogen index is used in diagnosis, prognosis, and / or treatment strategy of any disease, including citrus greening diseases (HLB). Research tools and methods for screening drugs for treating or preventing citrus greening diseases, as well as treatment or prevention methods for citrus greening diseases are also provided.
Owner:GREEN LIFE BIOTECH
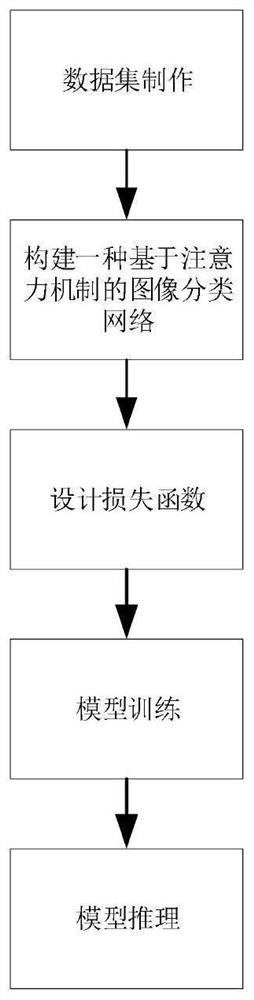
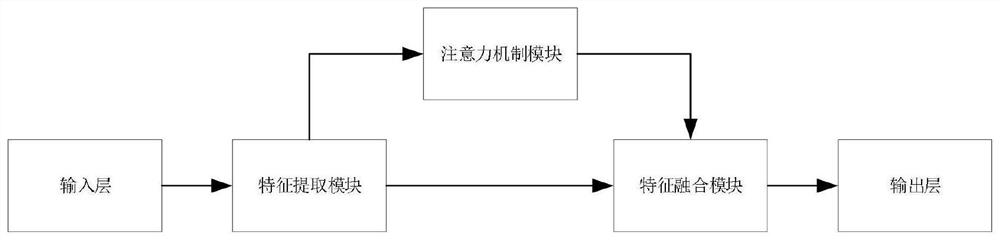
Citrus huanglongbing image recognition method based on attention mechanism
PendingCN112801942ALow costImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisCitrus greening diseaseBiology
The invention relates to the field of image recognition, and particularly discloses a citrus huanglongbing image recognition method based on an attention mechanism, and the method specifically comprises the steps: collecting the data of diseased leaves and diseased fruits of citrus huanglongbing as positive samples, collecting the data of other non-huanglongbing as negative samples, constructing an image classification network based on the attention mechanism, designing a loss function, inputting the training set into the image classification network based on the attention mechanism, carrying out supervised training by adopting the loss function, and inputting the verification set into the trained model for verification in the training process; and loading the trained model parameters to an image classification network based on an attention mechanism, and sequentially inputting thecitrus huanglongbing images of the test set into the network for reasoning to obtain a citrus huanglongbing image classification result. By introducing an attention mechanism module, key features of the citrus huanglongbing are autonomously selected, and the citrus huanglongbing detection method which is low in cost, high in efficiency and high in recognition rate is achieved based on image recognition.
Owner:GUANGXI TALENTCLOUD INFORMATION TECH
Artificial feeding method for diaphorina citri
The invention discloses an artificial feeding method for diaphorina citri. The method includes the following steps that feed plant cultivation and management are conducted, wherein feed plants include murraya paniculata and citrus; woodlice are fed; a woodlouse feeding cage is cleaned; and the feed plants are repaired. According to the method, a large number of woodlouse imagoes and nymphs not carrying Candidatus liberobacter asiaticus can be bred, and a large number of indoor woodlouse insect sources not carrying germs can be provided for areas where few woodlice or no woodlouse exists so as to meet needs of relevant tests.
Owner:赣州市柑桔科学研究所
Targeted editing of citrus genes for disease resistance
PendingUS20210189410A1Reduce commercial valueCrop yield lossHydrolasesPlant peptidesBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
Disclosed herein our novel methods of increasing resistance of Citrus plants to diseases, in particular, citrus canker disease caused by Xanthomonas citri ssp. citri and Huanglongbing disease. Some embodiments relate to novel methods of altering gene sequence, structure and expression of certain disease susceptibility genes in the Citrus plant. Other embodiments relate to gene constructs equipped to be introduced into Citrus cells and direct modifications to target gene sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Compositions and Methods for the Treatment of Huanglongbing (HLB) aka Citrus Greening in Citrus Plants
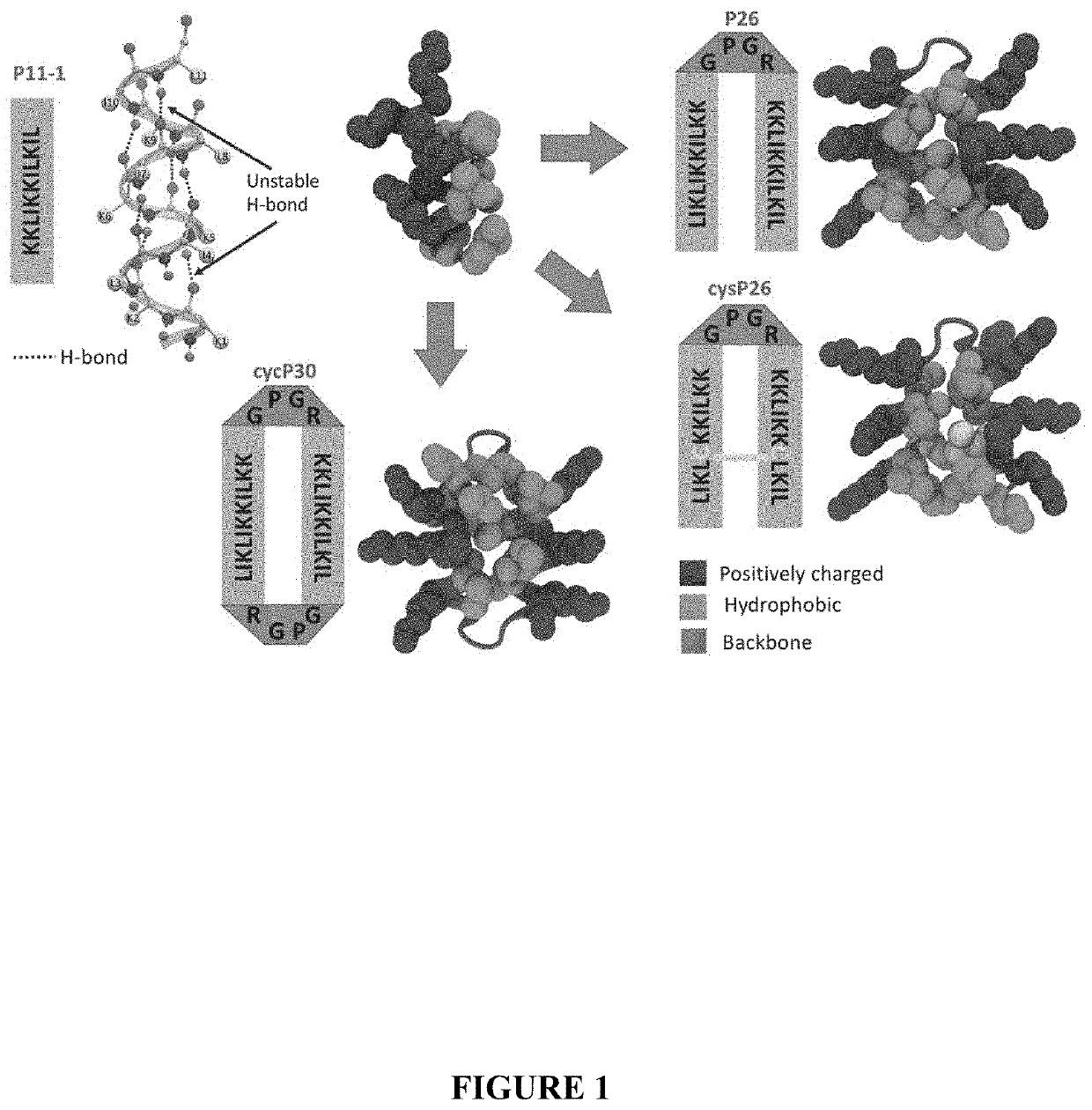
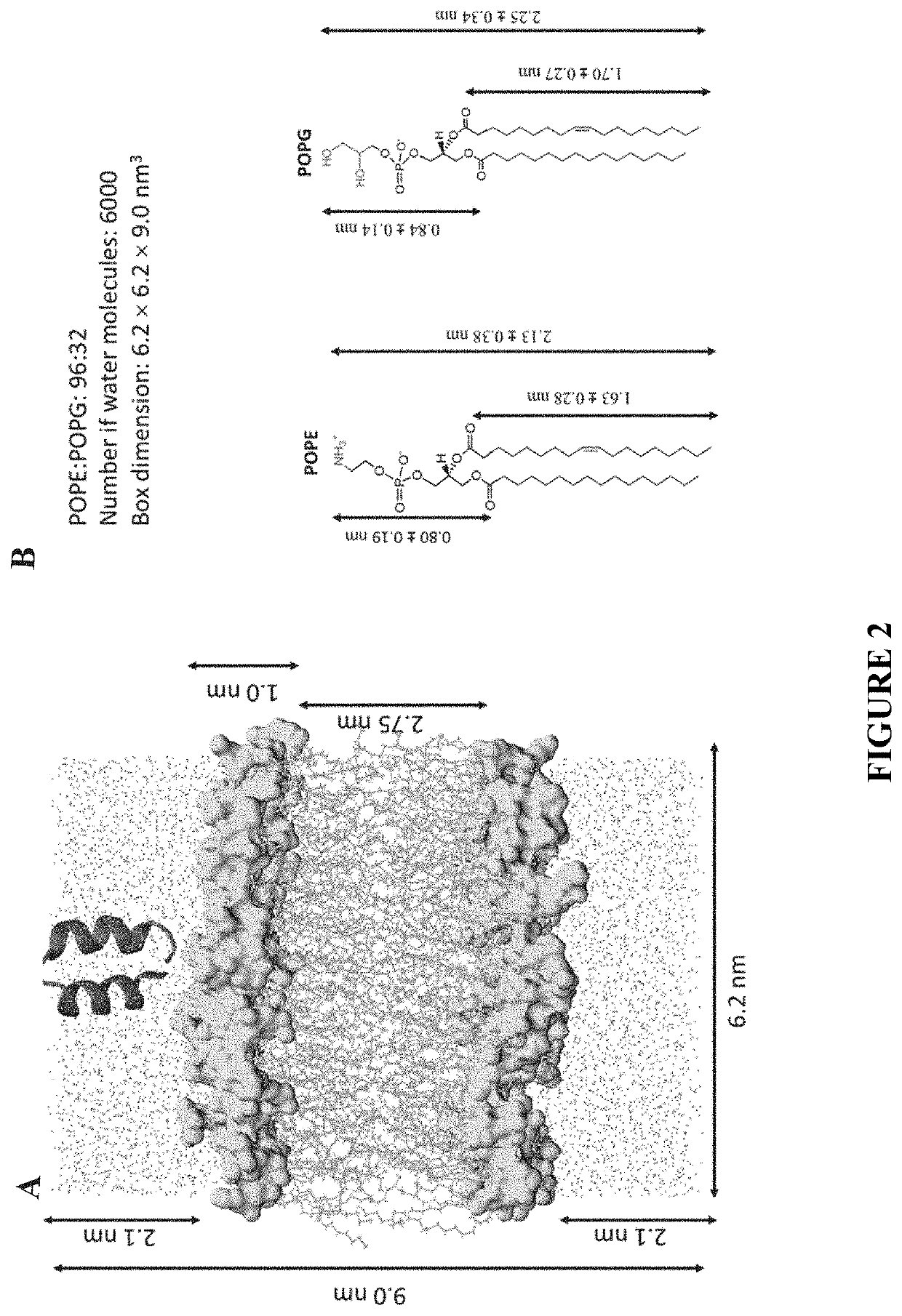
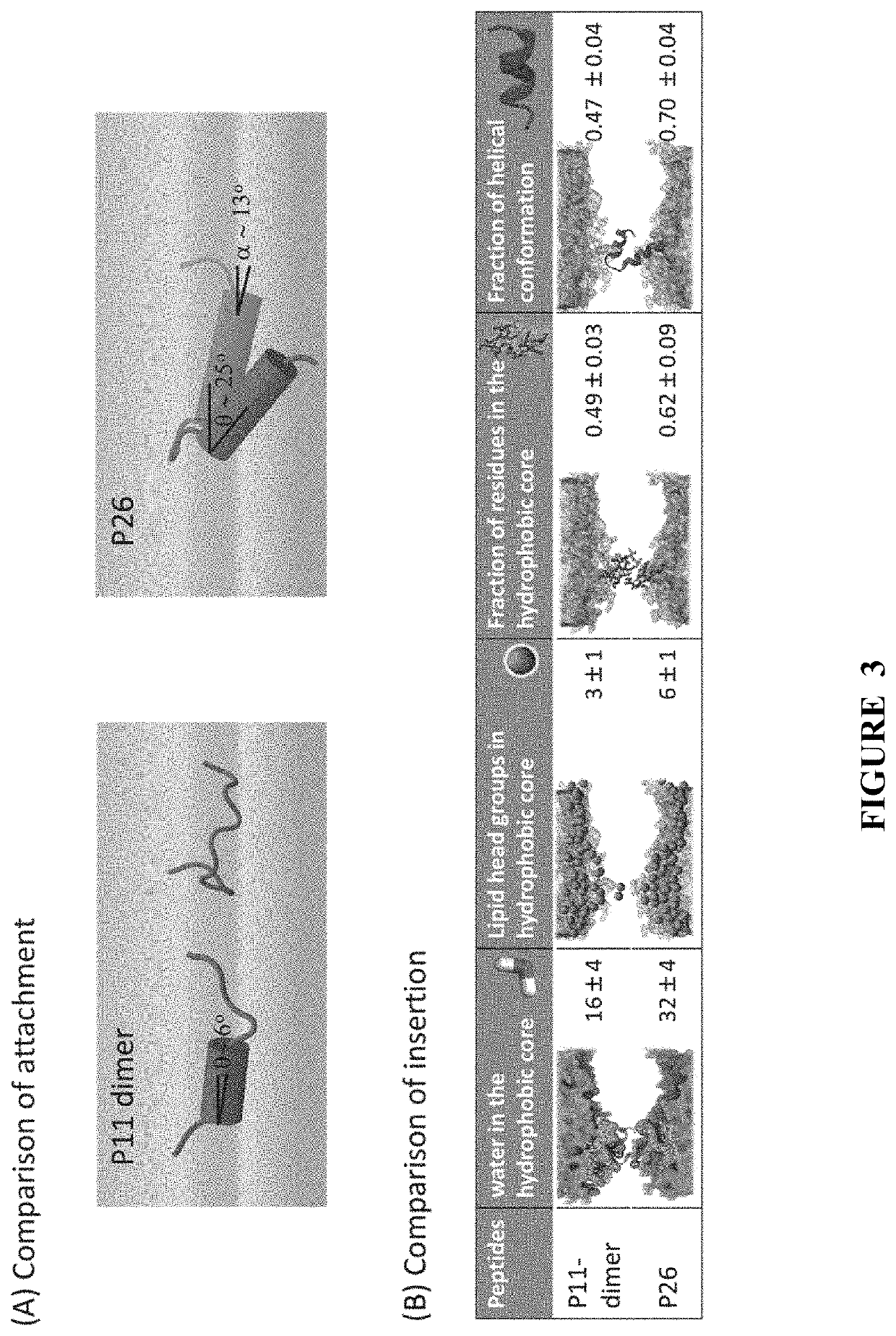
PendingUS20200102356A1Improve the bactericidal effectReduce sensitivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPlant peptidesAnti microbial peptideAmphipathic helix
The invention may include engineered antimicrobial peptides to treat HLB disease, preferably in citrus plants. Specifically, the invention may include novel antimicrobial peptide derived from amphipathic helical peptides that may further be used to treat HLB disease in citrus plants. In one embodiment, the invention may include an engineered antimicrobial peptide formed by coupling two amphipathic helical peptides. Specifically, a generalized antimicrobial peptide of the invitation may include a first amphipathic helical peptide coupled with a second amphipathic helical peptide by a linker domain forming a helix-turn-helix scaffold formation. Such amphipathic helical peptides may be endogenous to a target host, preferably a citrus plant.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Bactericide compound for preventing and treating candidatus liberibacter and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105801246AConvenient prevention and controlBiocideMagnesium fertilisersMonopotassium phosphateAntibiotic Y
The invention provides a bactericide compound for preventing and treating candidatus liberibacter and a preparation method thereof. The bactericide compound is a compound composition prepared from antibiotics, ammonium nitrate, monopotassium phosphate, magnesium sulfate, EDDHA-Fr, EDTA-Mn, EDTA-Zn, EDTA-Cu, EDTA-Co, EDTA-Ca, borax, sodium molybdate, trehalose, potassium fulvic acid, a stabilizing agent, an antifreezing agent, novel permeation promoter, a dispersing agent, an emulsifying agent and co-solvent, the pH value is regulated to 6.5, and 1000-2000ml of water is added. The composition is reasonably mixed by bactericide and multiple nutritional substances according to objective requirement of prevention and control of candidatus liberibacter, is applied by adopting a trunk transfusion method to complement advantages, has the characteristics of high efficiency, low toxicity, safety and multiple functions, and can be used for better preventing and controlling candidatus liberibacter.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Citrus greening disease rapid detection method
InactiveCN104132938AIntegrity guaranteedClear colorMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationChange colorCitrus tree
The invention discloses a citrus greening disease rapid detection method. The method comprises the following steps: step a, polishing citrus leaves which have been subjected to a dark treatment to get rid of the wax layer on the leaf surfaces, soaking the leaves in a chlorophyll decoloring liquid until the leaves turn white; step b, color development detection: dropwise adding a starch color developing solution on the discolored leaves, and observing the color change of the leaves, if the leaves turn blue, the citrus leaves must be from a citrus tree affected by citrus greening disease, and if the leaves do not change color, the leaves are healthy. The method has the advantages of more convenient operation, shorter time, and more precise result, and can be operated by farmers themselves.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF APPLIED BIOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Application of biological control agent for removing Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticum
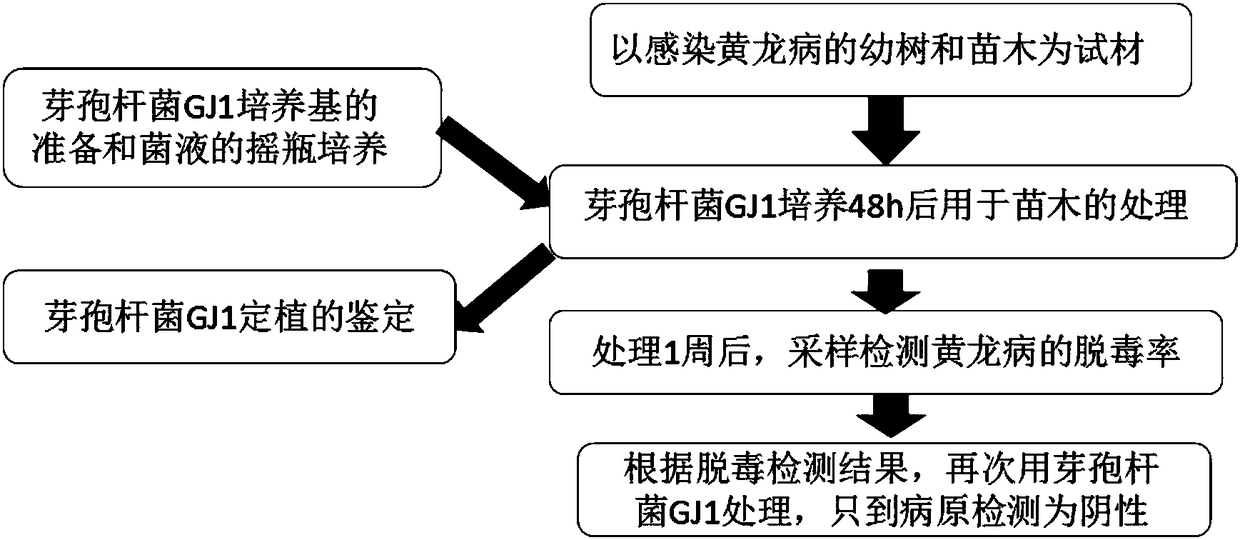
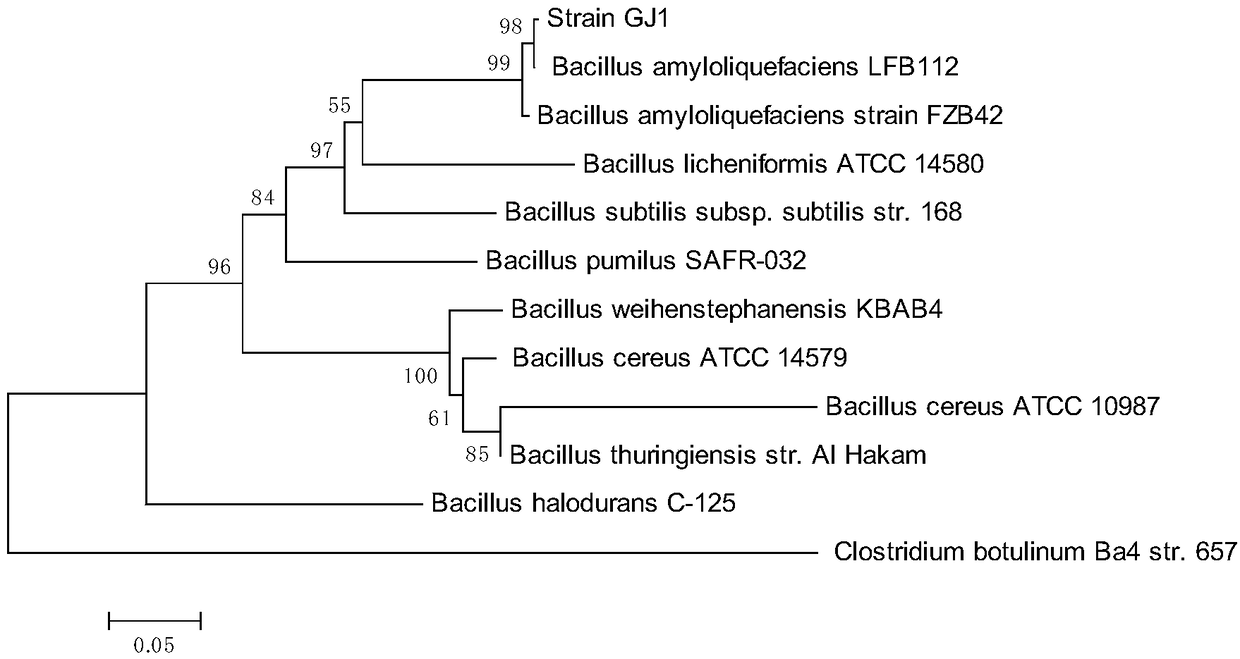
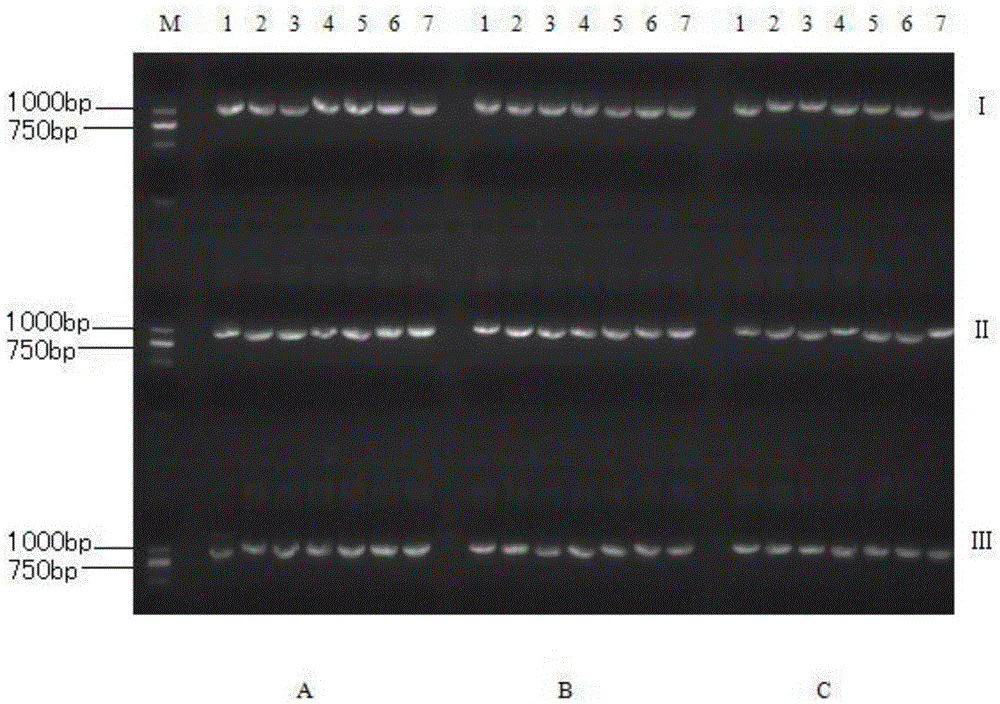
The invention discloses an application of biological control agent for removing Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticum. The biological control agent is prepared from bacillus GJ1, the bacillus GJ1 is conserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in 28th July, 2017, and the conservation number is CCTCC M 2017456. The application comprises the following steps: removing the nursery stock in Liberobacter asiaticum infection by using the above bacillus GJ1 bacteria solution. The bacillus GJ1 fungicide has a certain detoxification effect for the Liberobacter asiaticum, and the aim ofremoving the pathogen can be achieved by repeatedly inoculating to the seventh treatment.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A PCR amplification detection system and application of citrus huanglongbing asiatic species
InactiveCN103820561BSmall reaction systemLess amount of reagentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention relates to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection of citrus yellow shoot Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticus, particularly relates to a nested-PCR detection system and application of citrus yellow shoot Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticus, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The provided nested-PCR amplification detection system of citrus yellow shoot Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticus comprises a first-round PCR amplification system and a second-round PCR amplification system, final volumes of the first-round PCR amplification system and the second-round PCR amplification system range from 10 mu L to 20 mu L, and each of the first-round PCR amplification system and the second-round PCR amplification system comprises 1.0 mu L of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) templates, 5 mu L of 2*Taq PCR Master Mix, 0.5 mu L of primers and the balance of sterilizing double-distilled water; and the DNA template of the second-round PCR amplification system is prepared by diluting a first-round PCR amplification product for 10-20 times by volume. According to the invention, a first-round PCR amplification reaction system and a second-round PCR amplification reaction system are small, a dilution ratio of the first-round PCR product is small, a reagent required by the detection is also few, and the corresponding expense is low.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院园艺研究所 +1
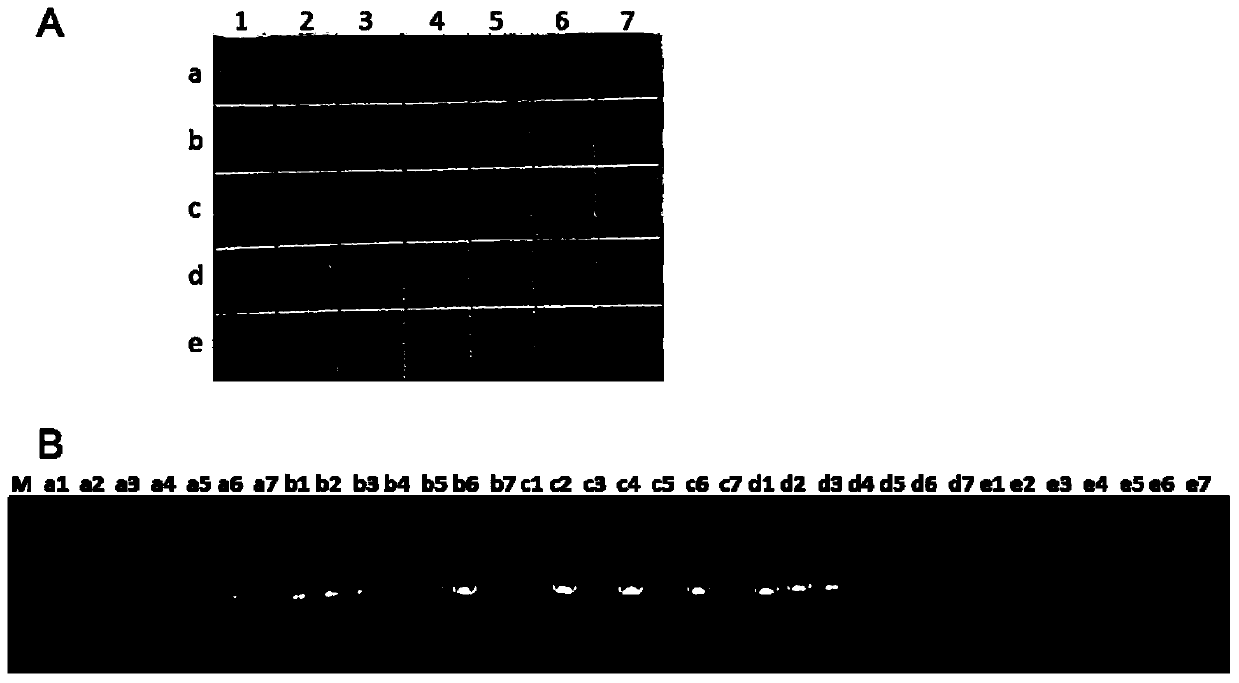
Citrus candidatus liberibacter and citrus canker pathogen dual detection kit and application thereof
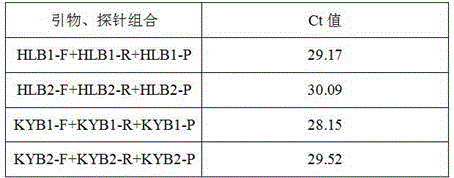
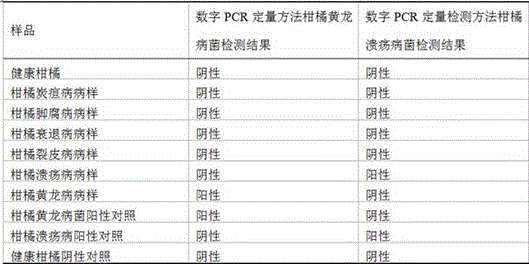
ActiveCN106399547ASimple and reliable absolute quantificationAbsolute quantitative realizationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseasePositive control
The invention discloses a citrus candidatus liberibacter and citrus canker pathogen dual detection kit and application thereof. A dual digital PCR quantitative detection agent composition for the citrus candidatus liberibacter and citrus canker pathogen is designed. The kit comprises a citrus disease sample DNA extraction agent, a digital PCR reaction agent, a citrus liberibacter asiaticus and citrus canker positive control sample template and a citrus liberibacter asiaticus and citrus canker negative control sample template. The kit has the advantages of being high in specificity, higher in impurity interference resistance, simple and fast when used for detecting the citrus candidatus liberibacter and citrus canker pathogen, the detection sensitivity is higher than that of an existing real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection method by about 10 times, and the kit can be used for early-stage qualitative and quantitative detection of the citrus candidatus liberibacter and citrus canker pathogen and epidemiologic investigation.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
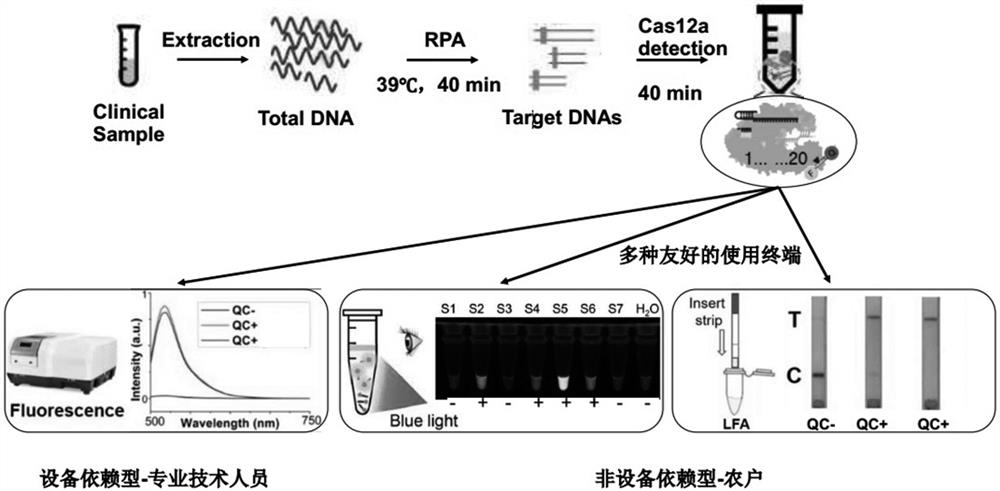
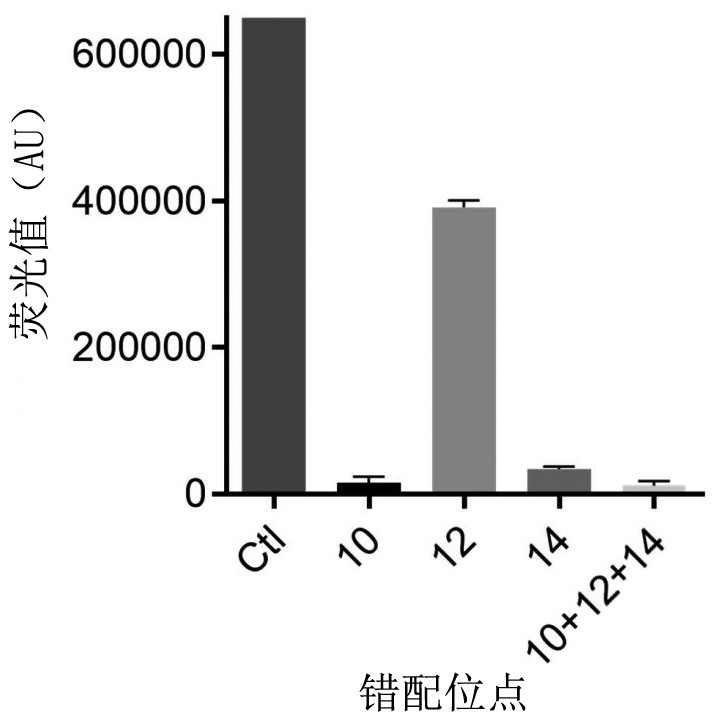
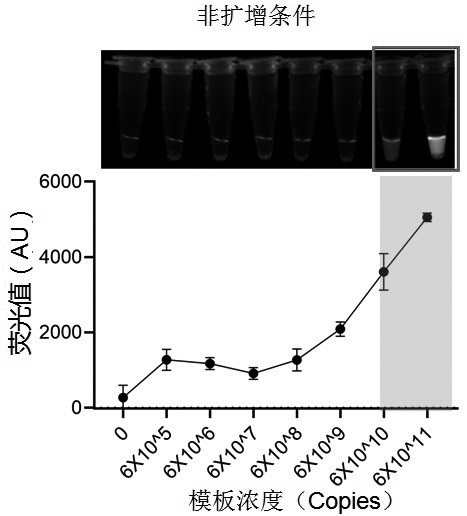
Kit and method for visual detection of citrus huanglongbing based on RPA-CRISPR-Cas12a system
ActiveCN114045356AOut of dependenceStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFluoProbes
The invention discloses a kit and a method for visual detection of citrus huanglongbing on the basis of an RPA-CRISPR-Cas12a system. The kit comprises an RPA primer and a crRNA guide sequence. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out RPA amplification on a to-be-detected sample, guiding a CRISPR-Cas12a system to carry out recognition combination on an RPA amplification product under the mediation of a crRNA sequence, cutting target double-stranded DNA to activate a non-specific nuclease function, randomly cutting an ssDNA fluorescent probe in the system to obtain a split product, and finally carrying out judgment through color development detection of the split product. The citrus huanglongbing can be duplexly and specifically detected through RPA amplification and crRNA recognition, high specificity is realized, sensitivity can be as low as 2 copies / [mu]L, plants infected with the citrus huanglongbing can be found earlier, and the citrus huanglongbing can be prevented and treated.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG
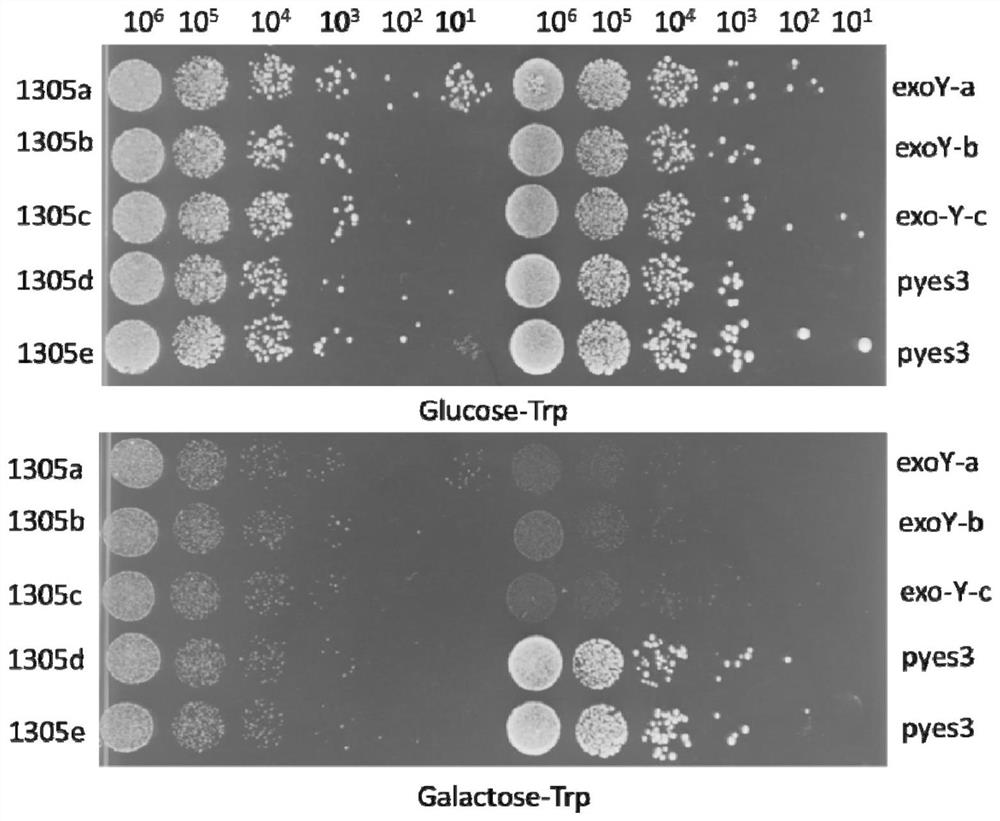
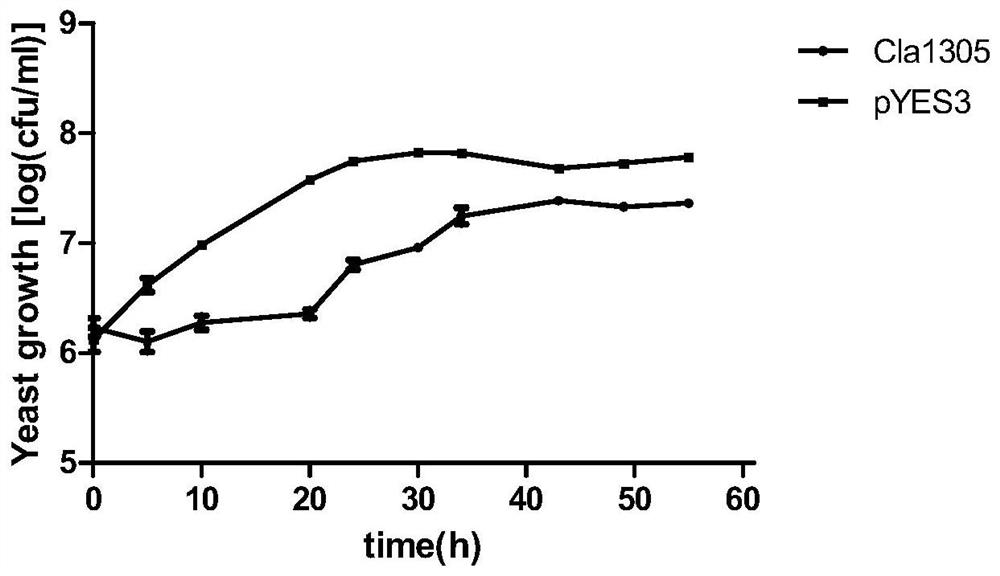
Application of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticum effector as target for screening anti-Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticum drugs
ActiveCN113862295APrevent proliferationEasy to trainBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCallose
The invention discloses an application of a Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticum effector as a target for screening anti-Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticum drugs, and finds that the Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticum flagellum matrix P-ring protein as the effector can cause significant callose deposition, and an inhibitor of the P-ring protein can be used for preventing and treating Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticum, and has a good application prospect in the field of prevention and treatment of Candidatus Liberobacter asiaticum. Meanwhile, the characteristics of small genome, simple culture, short life cycle and stable genetic manipulation of the saccharomyces cerevisiae are utilized, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae is used as a model organism for researching the effector of the bacterium CLas. Candidatus liberobacter asiaticum effector bacterium flagellum matrix P-ring protein is overexpressed in the saccharomyces cerevisiae, so that the inherent physiological function of the saccharomyces cerevisiae is disturbed, the phenotype of the saccharomyces cerevisiae is changed, and the proliferation of saccharomyces cerevisiae cells is inhibited. Meanwhile, transient expression in the Bensi tobacco leaves under agrobacterium tumefaciens mediation verifies and identifies that the gene can induce plant defense reactions such as local allergic necrosis of tobacco leaves and callose deposition.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com