Patents
Literature
178results about How to "Minimizing transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
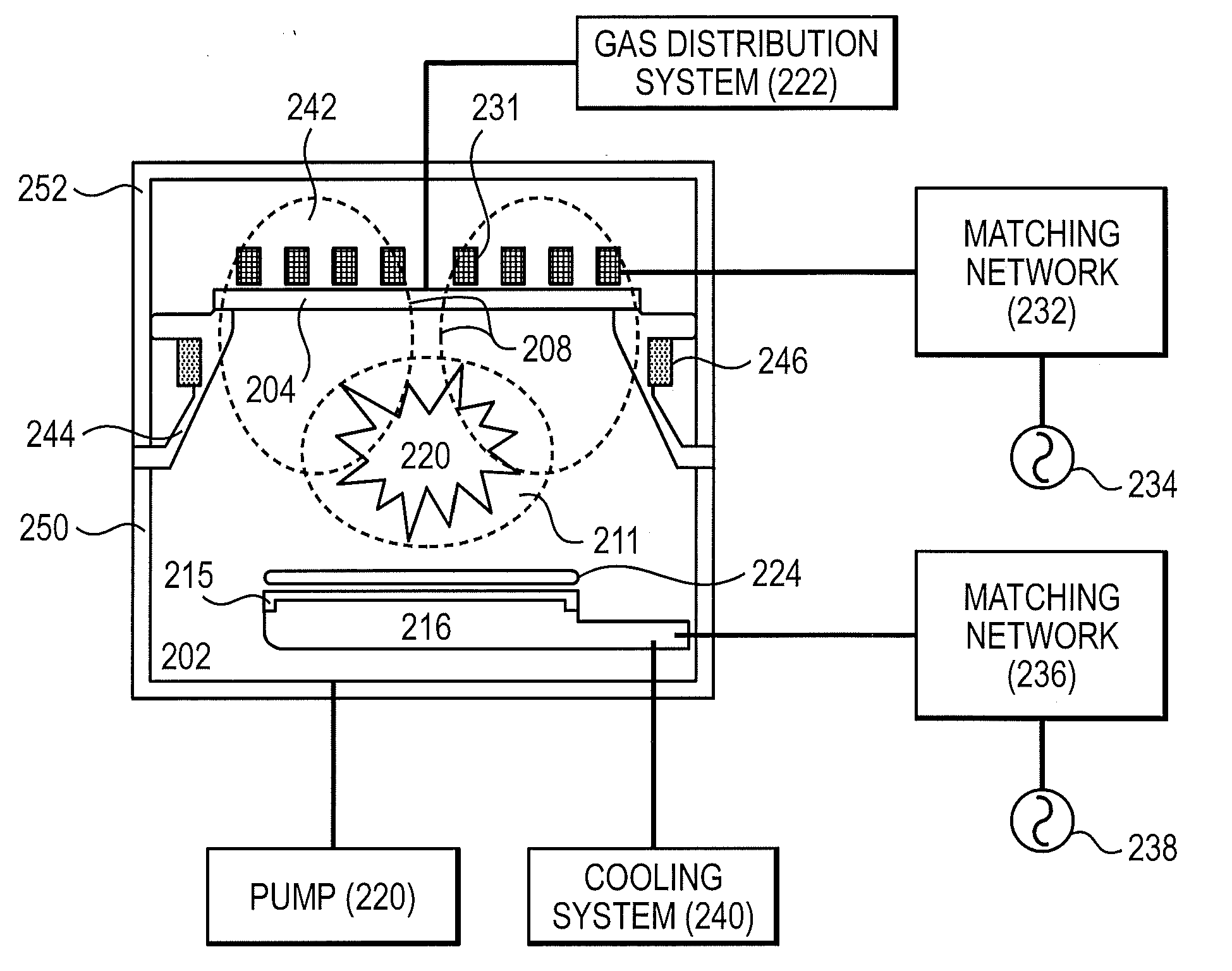
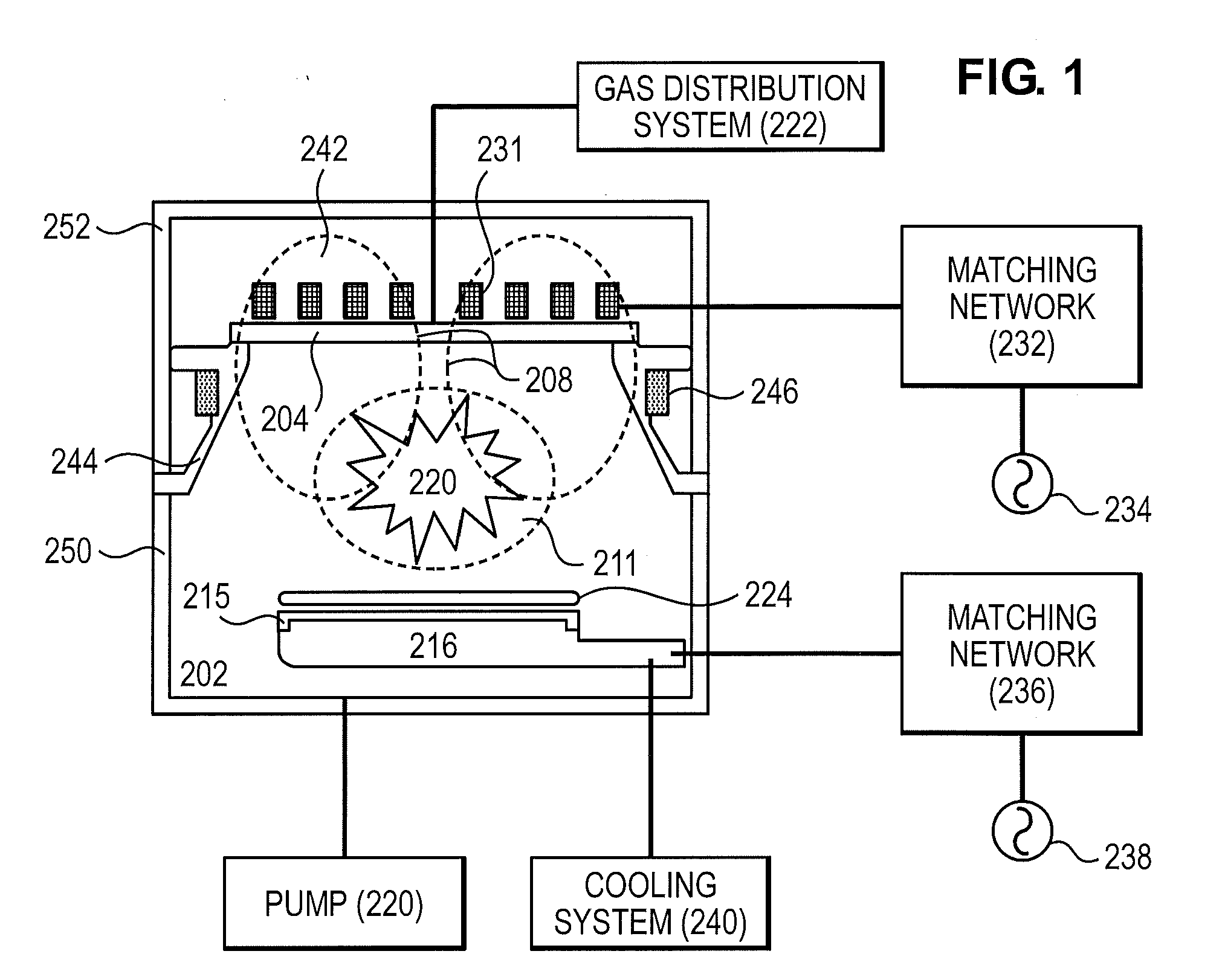
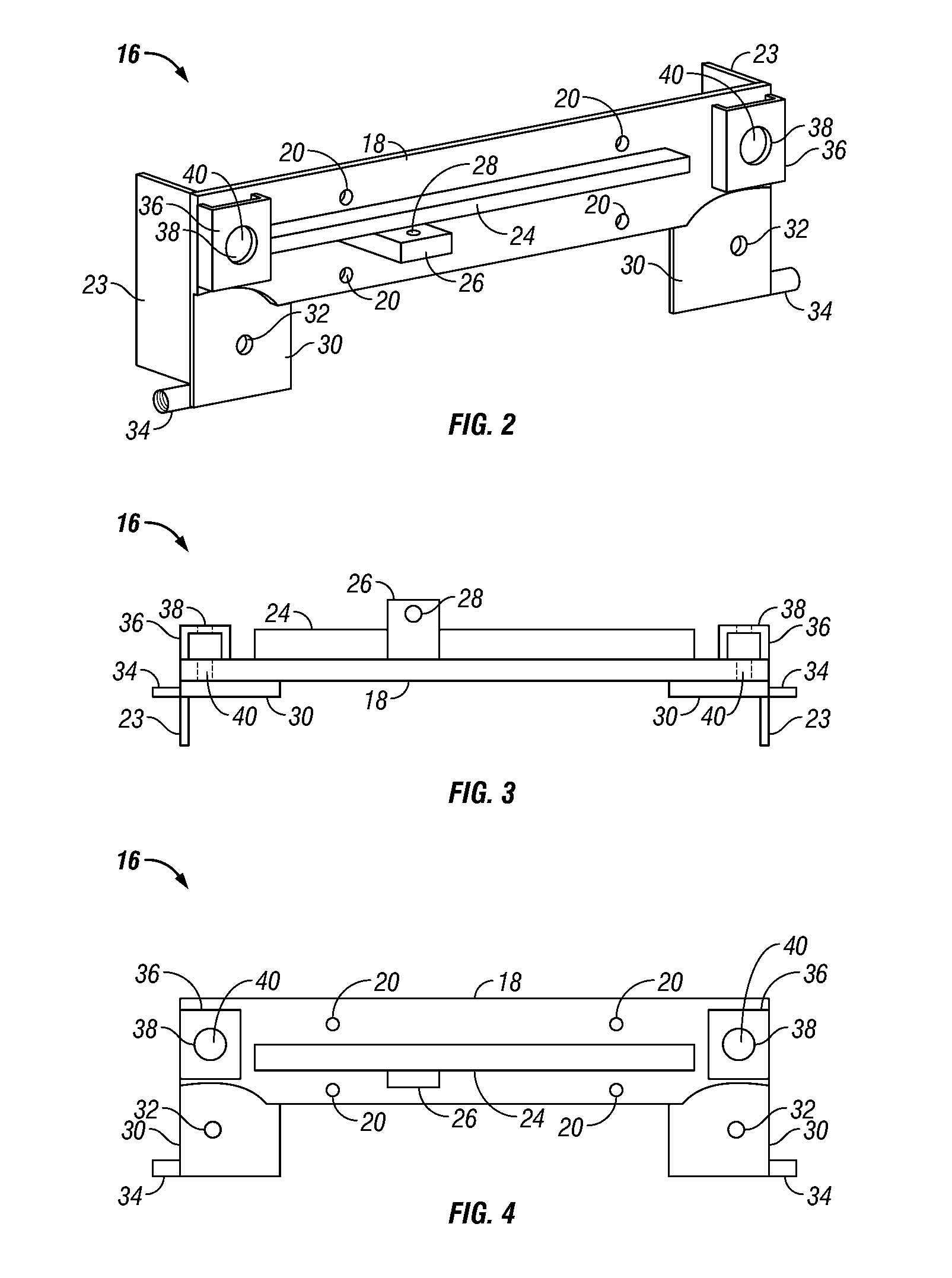
Replaceable upper chamber parts of plasma processing apparatus
ActiveUS20110056626A1Minimizing transferElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma reaction
An upper chamber section of a plasma reaction chamber includes a ceramic window with blind bores in an upper surface for receipt of a thermal couple and a resistance temperature detector, a top chamber interface which comprises an upper surface which vacuum seals against the bottom of the window and a gas injection system comprising 8 side injectors mounted in the sidewall of the top chamber interface and a gas delivery system comprising tubing which provides symmetric gas flow to the 8 injectors from a single gas feed connection.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
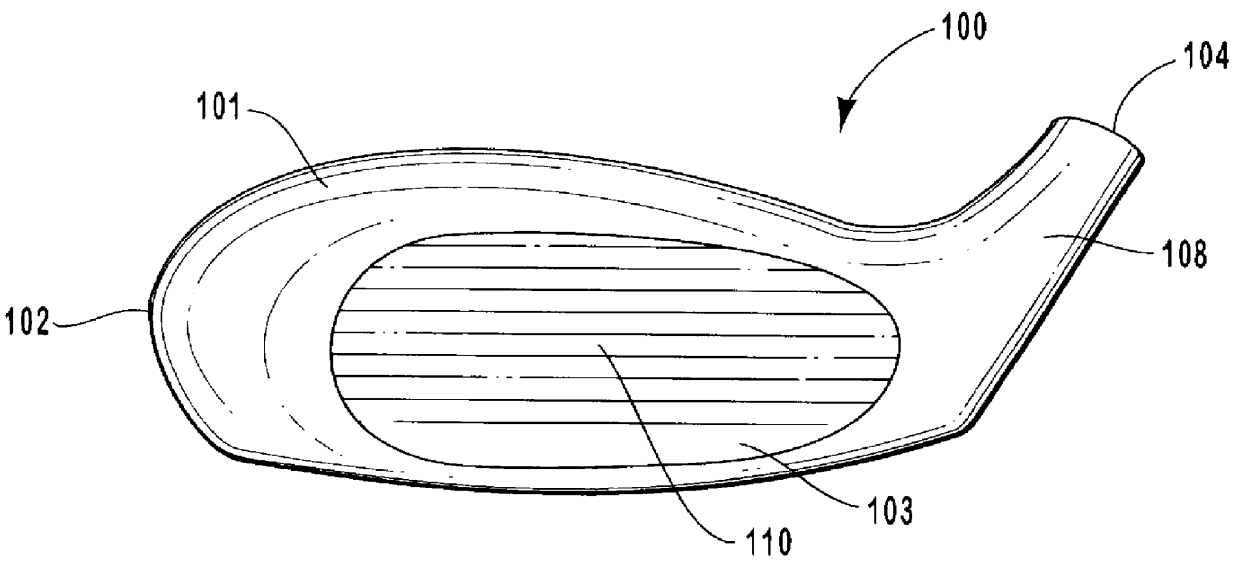
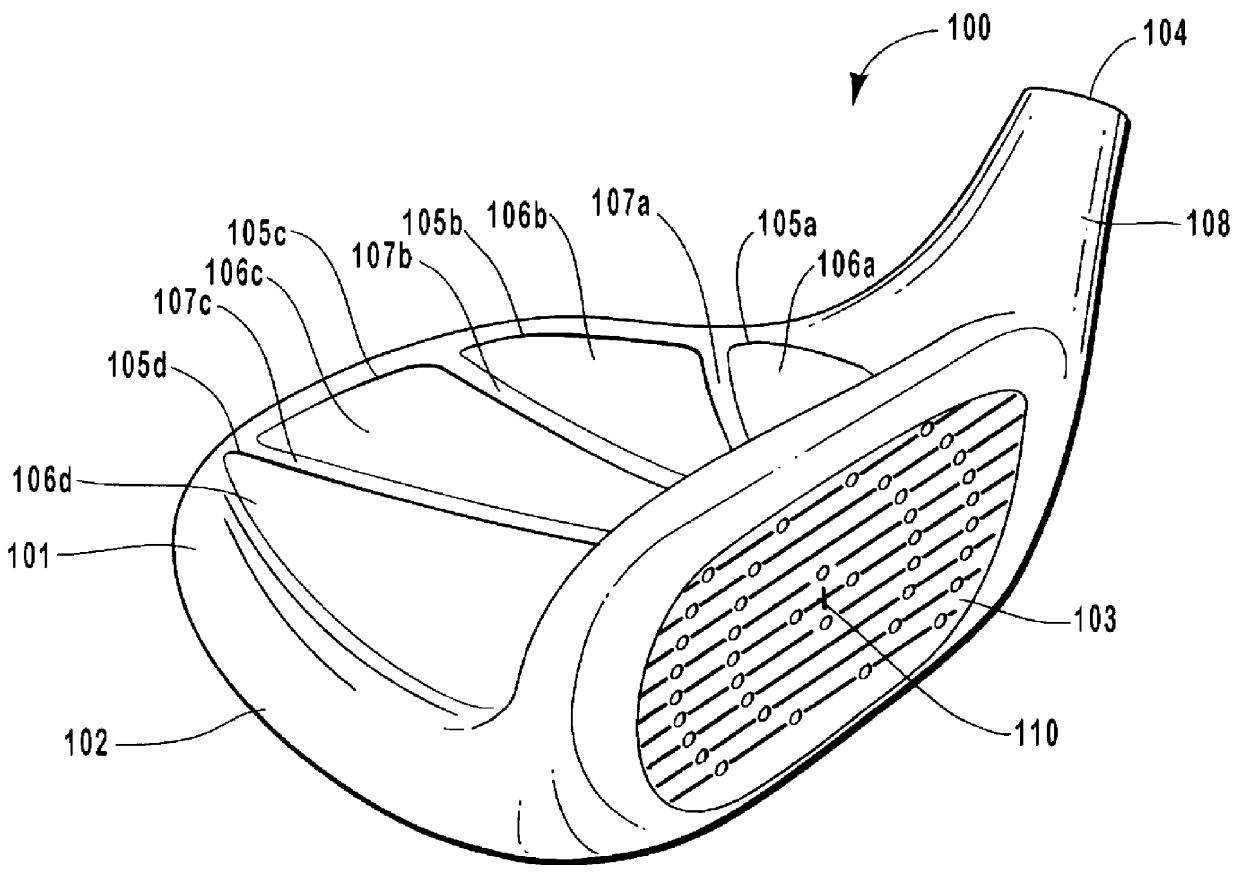
Golf club head having performance-enhancing structure
InactiveUS6059669AEconomical and labor-efficientGreat distance of ball flightGolf clubsRacket sportsFiberEngineering
A golf club that is preferably made from fiber-reinforced plastic composite by an injection molding process. The preferred golf club head includes a striking face for striking a golf ball, an outer periphery, a cavity formed between the outer periphery and the back of the striking face, a sole enclosing the bottom portion of said cavity, and at least one elongate power bar extending across the cavity from the striking face to the outer periphery. The sole is preferably integrally formed with the face plate and outer periphery. The cavity of the golf club head opens to the top of the club head. Each elongate power bar separates the cavity into receptacles. Inserts may be placed within the receptacles for aesthetic, aerodynamic, acoustic, and other purposes.
Owner:EDIZONE LC
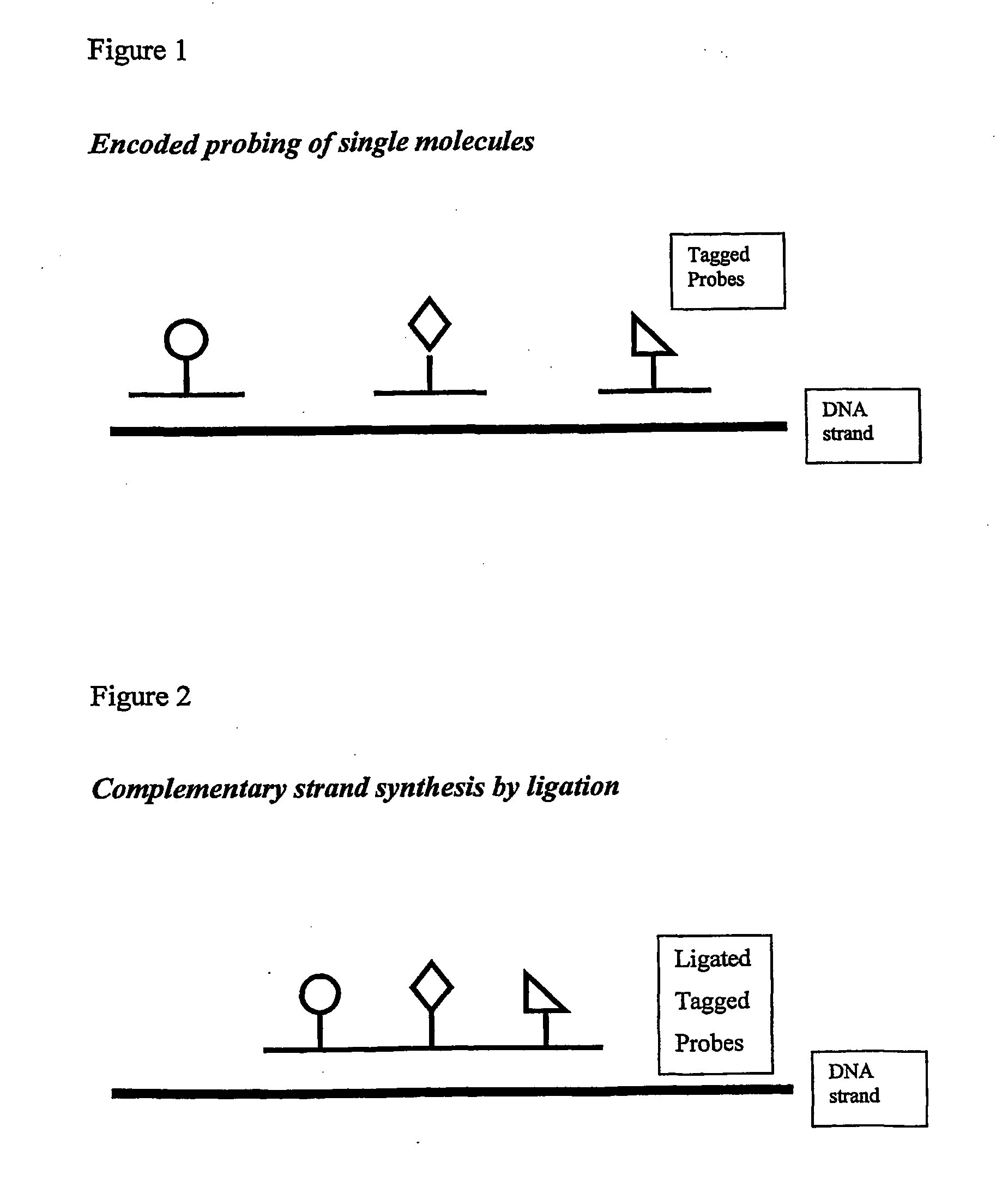
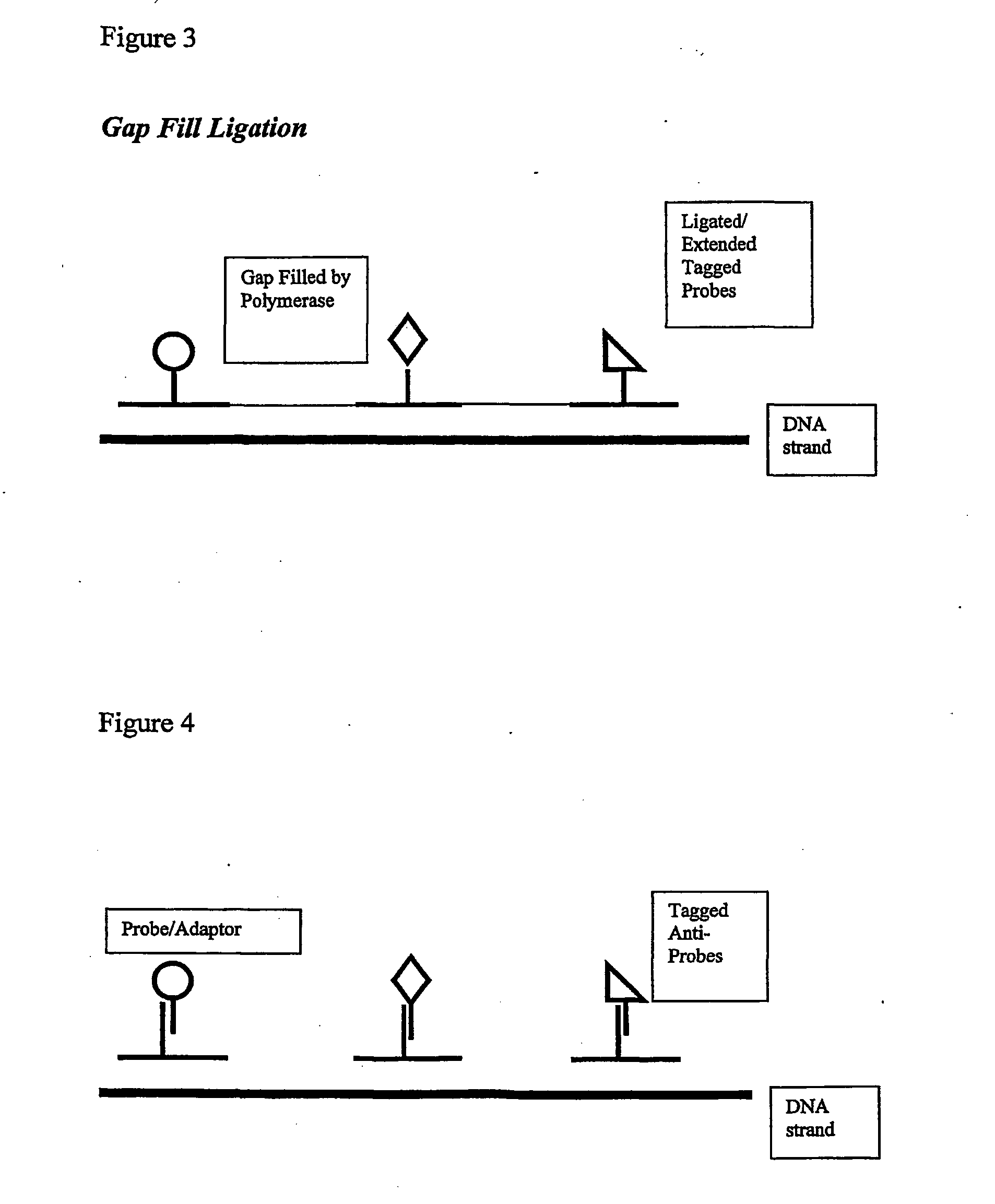
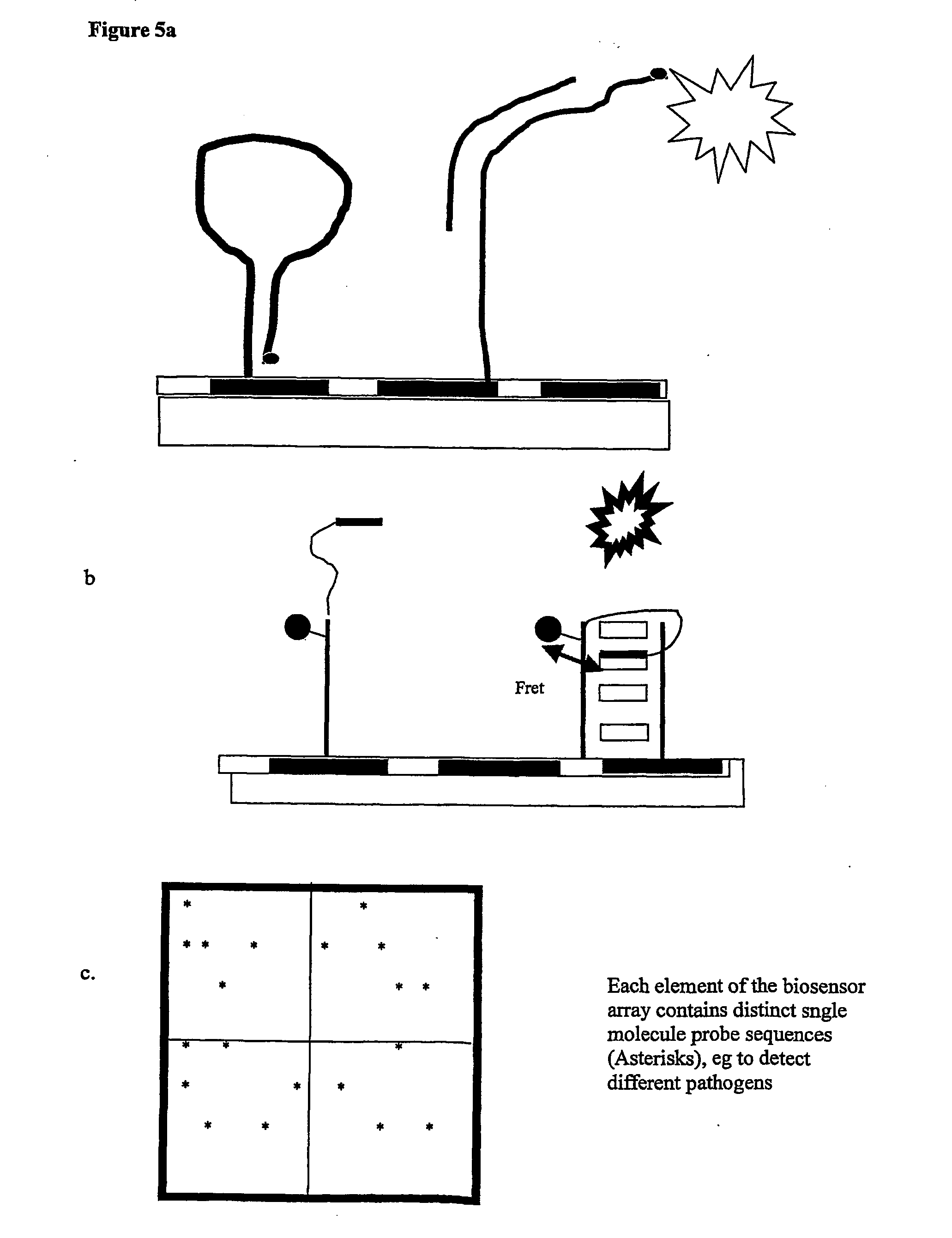
Arrays and methods of use
InactiveUS20040248144A1Minimise photobleachingMinimizing transferMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMolecular arrayAssay
Methods are provided for producing a molecular array comprising a plurality of molecules immobilised to a solid substrate at a density which allows individual immobilised molecules to be individually resolved, wherein each individual molecule in the array is spatially addressable and the identity of each molecule is known or determined prior to immobilisation. The use of spatially addressable lowdensity molecular arrays in single molecule detection and analysis techniques is also provided. Novel assays and methods are also provided.
Owner:INVITAE CORP
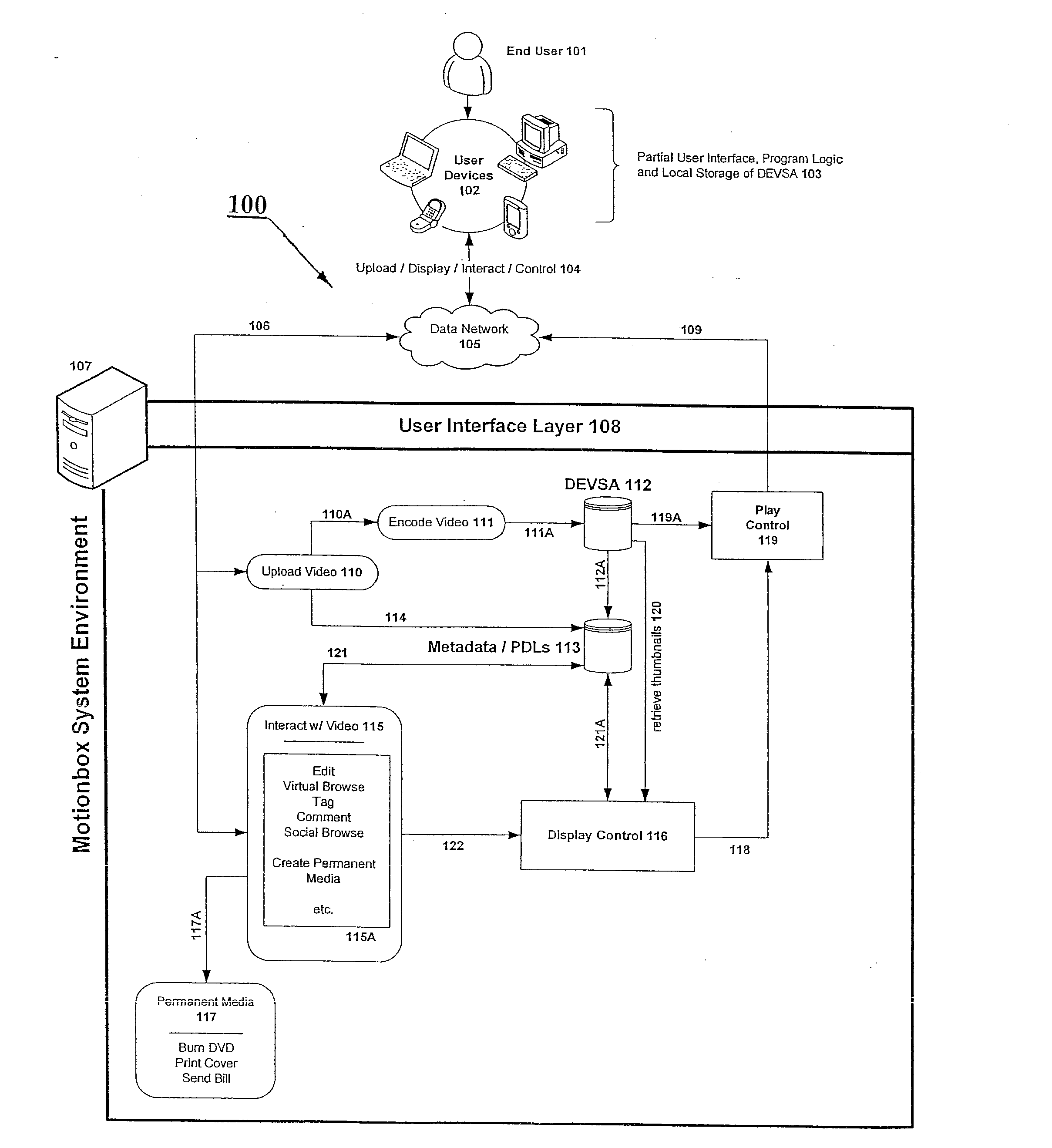
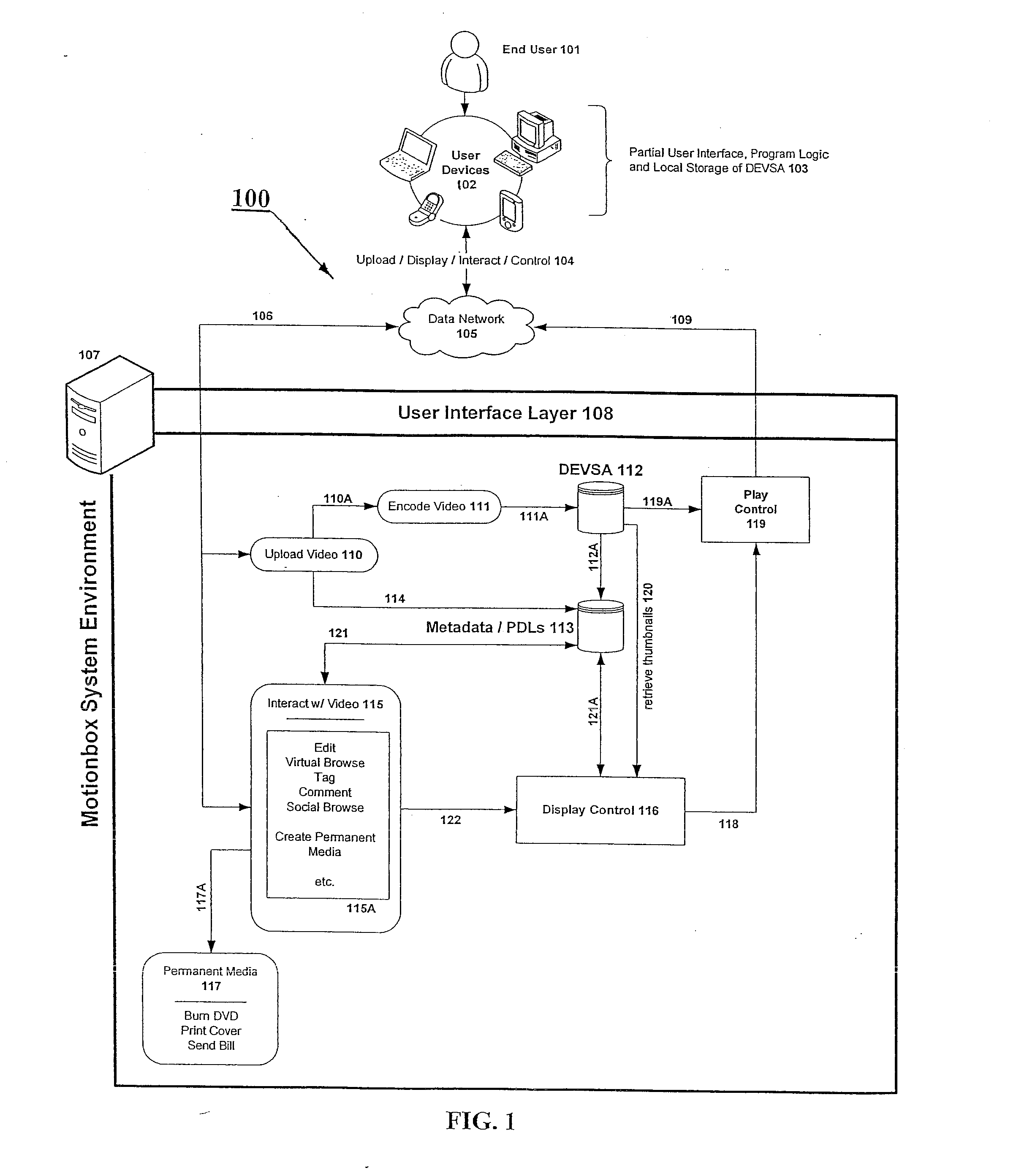
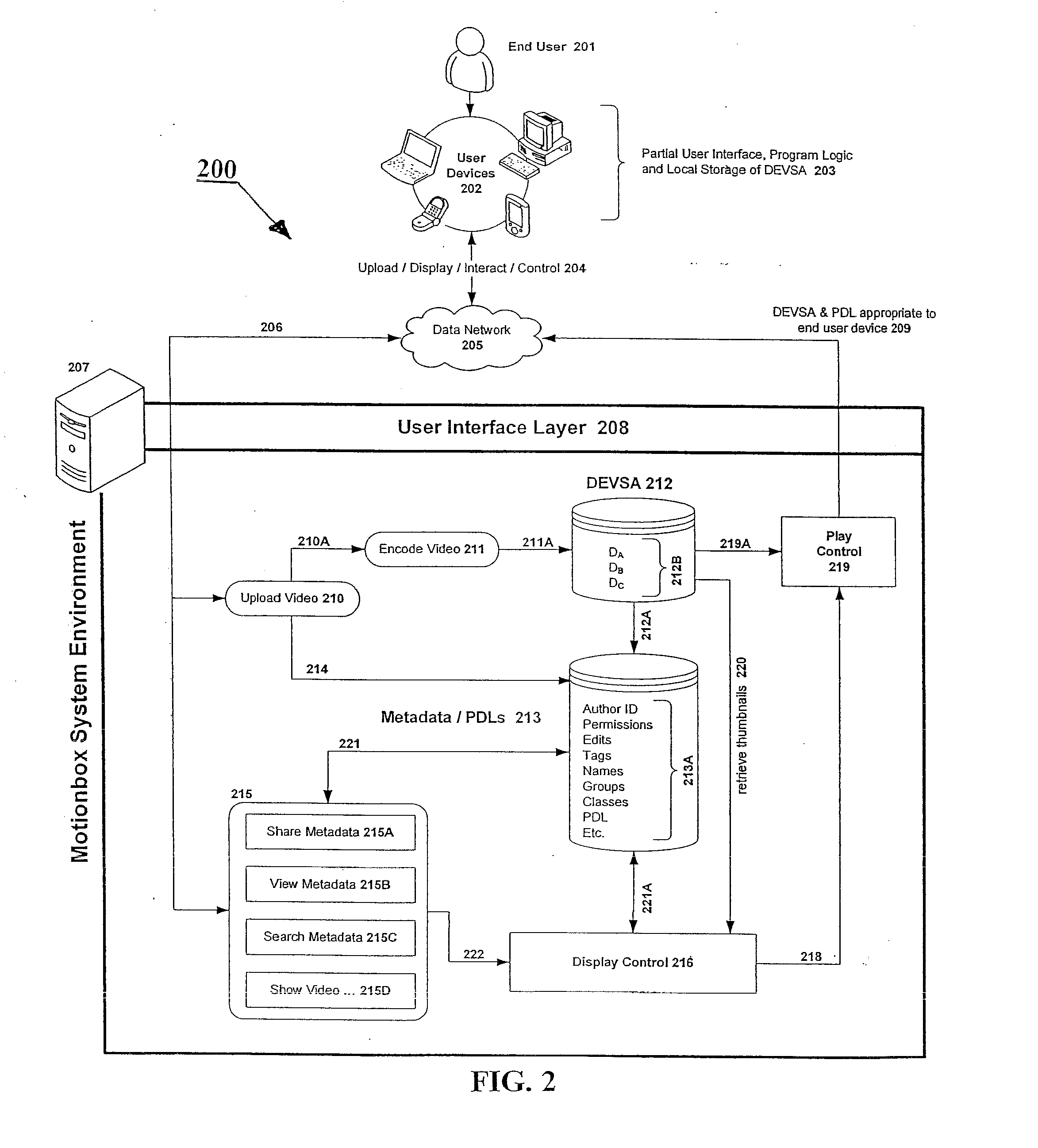
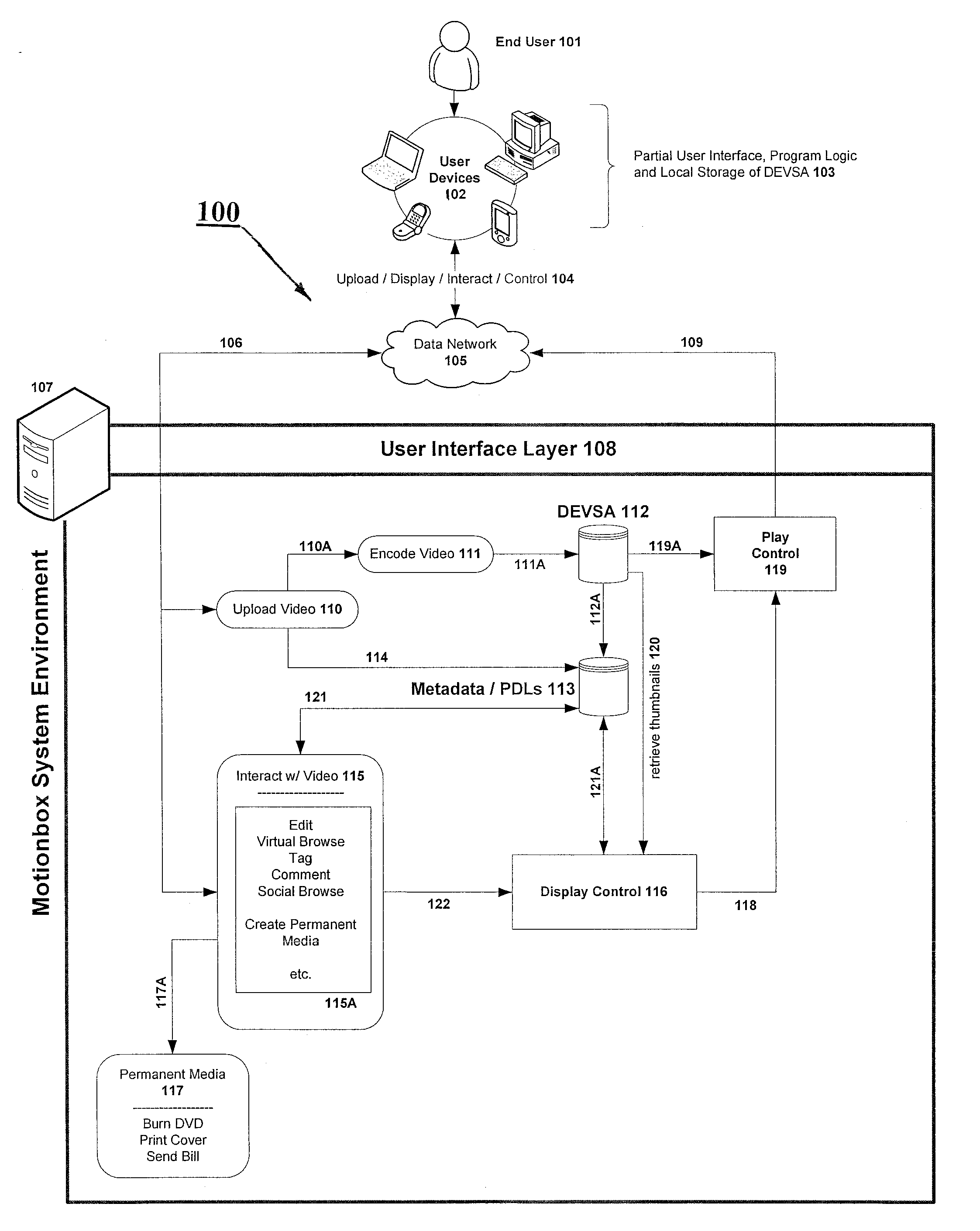
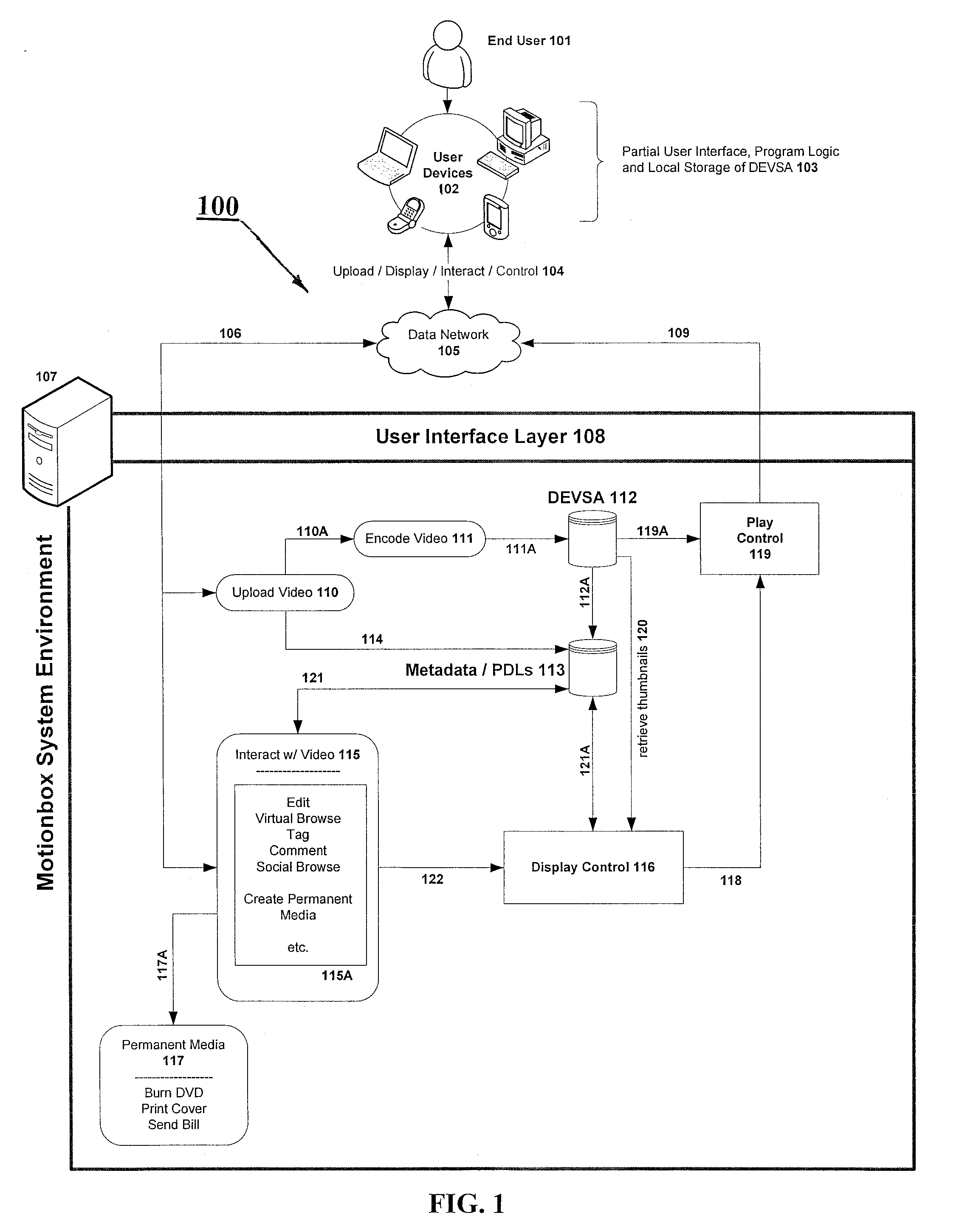
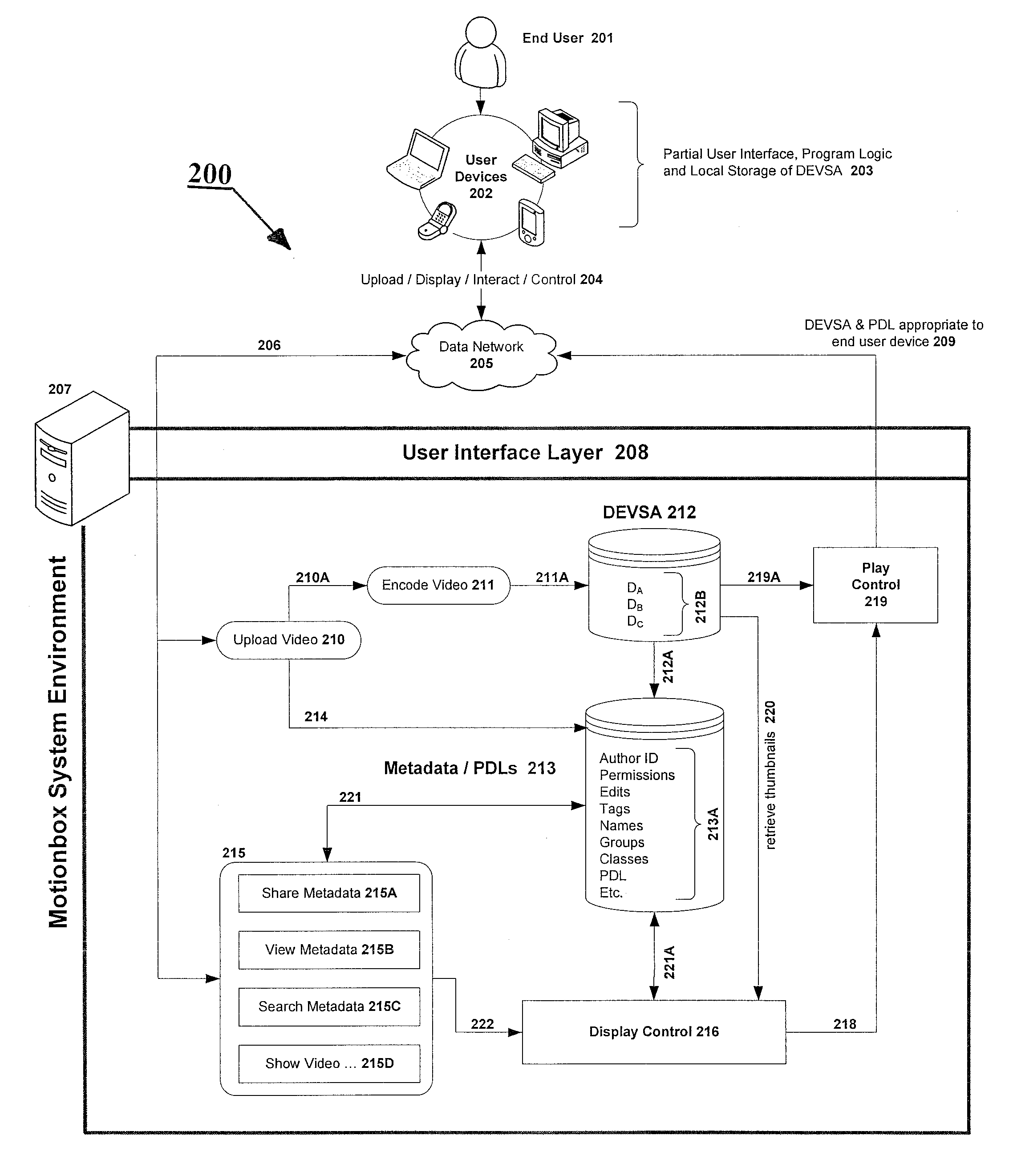
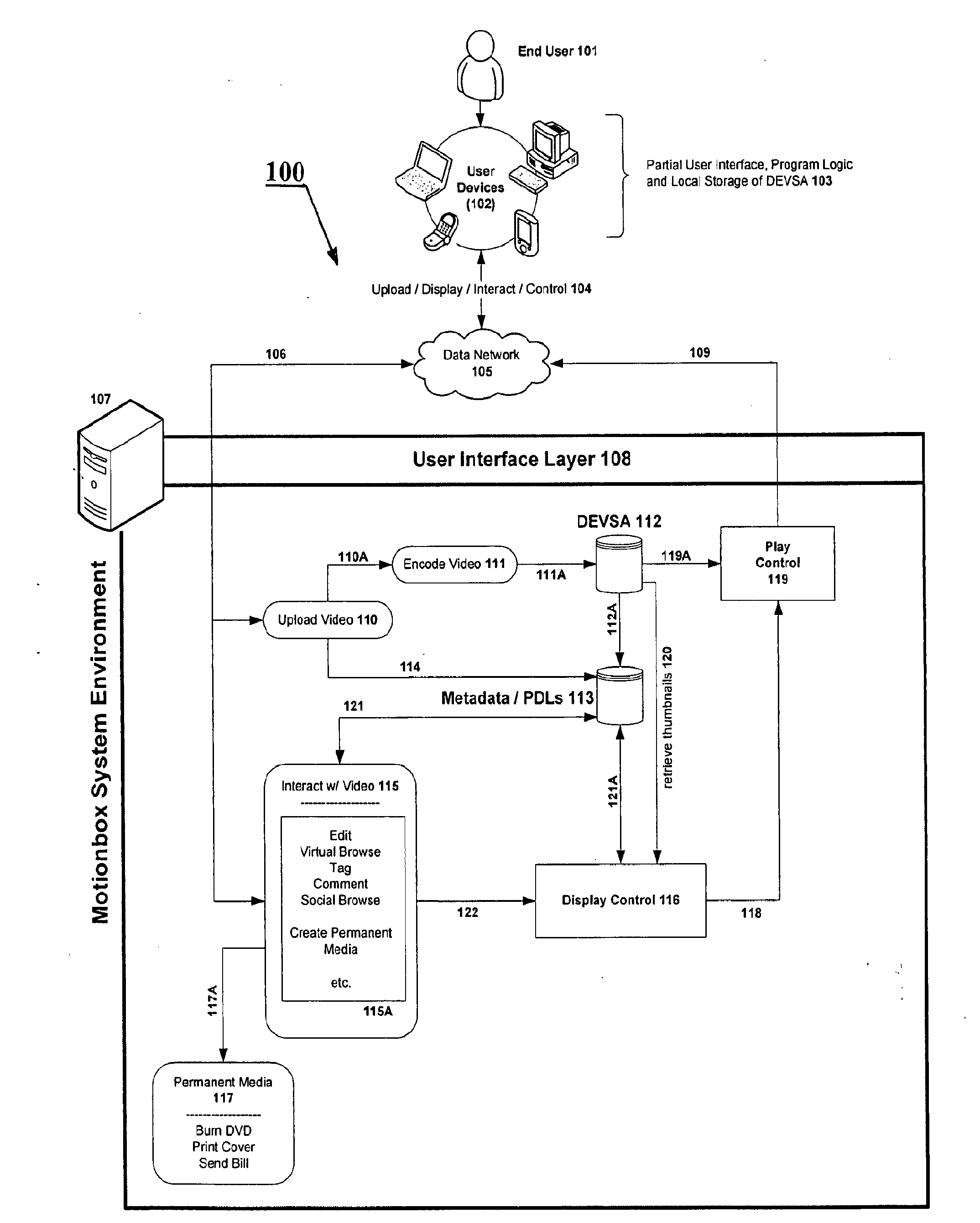
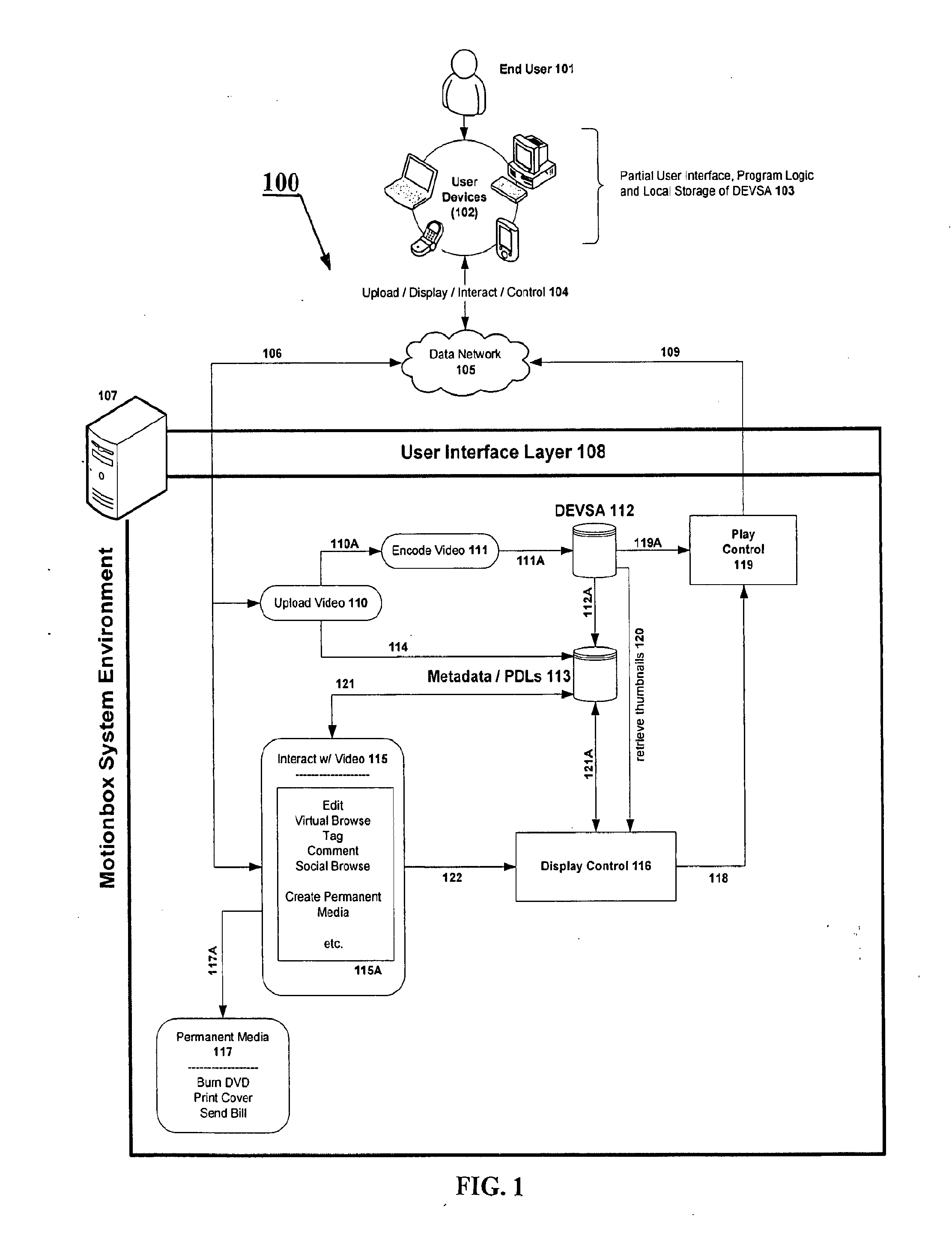
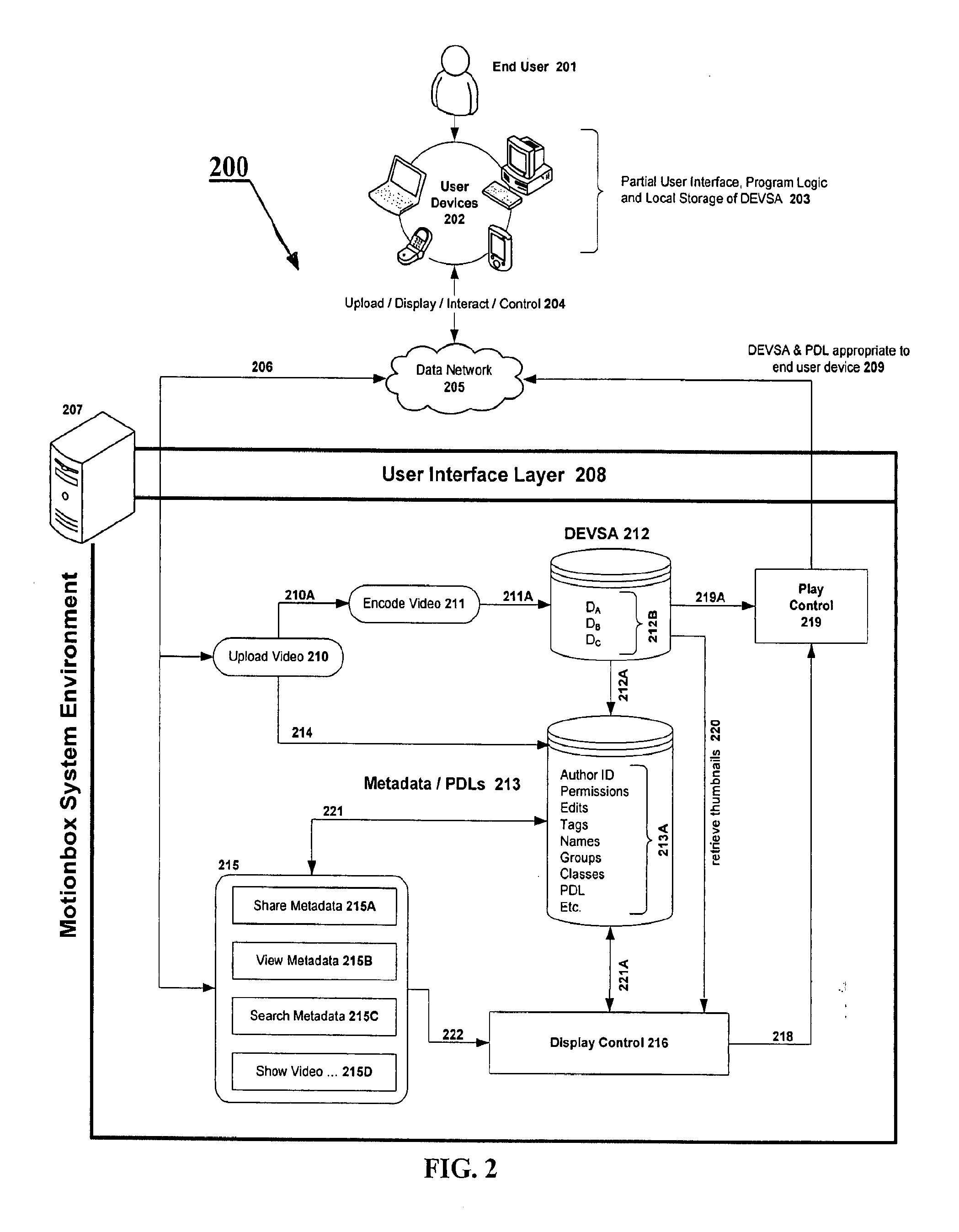
System and method for enabling social browsing of networked time-based media
InactiveUS20110107369A1Minimizing transferMinimizing dataInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsMapping systemUser interface
The present invention provides an easy to use web-based system for enabling multiple-user social browsing of underlying video / DEVSA media content. A plurality of user interfaces are employed linked with one or more underlying programming modules and controlling algorithms. A data model is similarly supported and used for managing complex social commenting and details regarding a particular video set of interest. An interest intensity measurement and mapping system and mode are provided for increased use.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
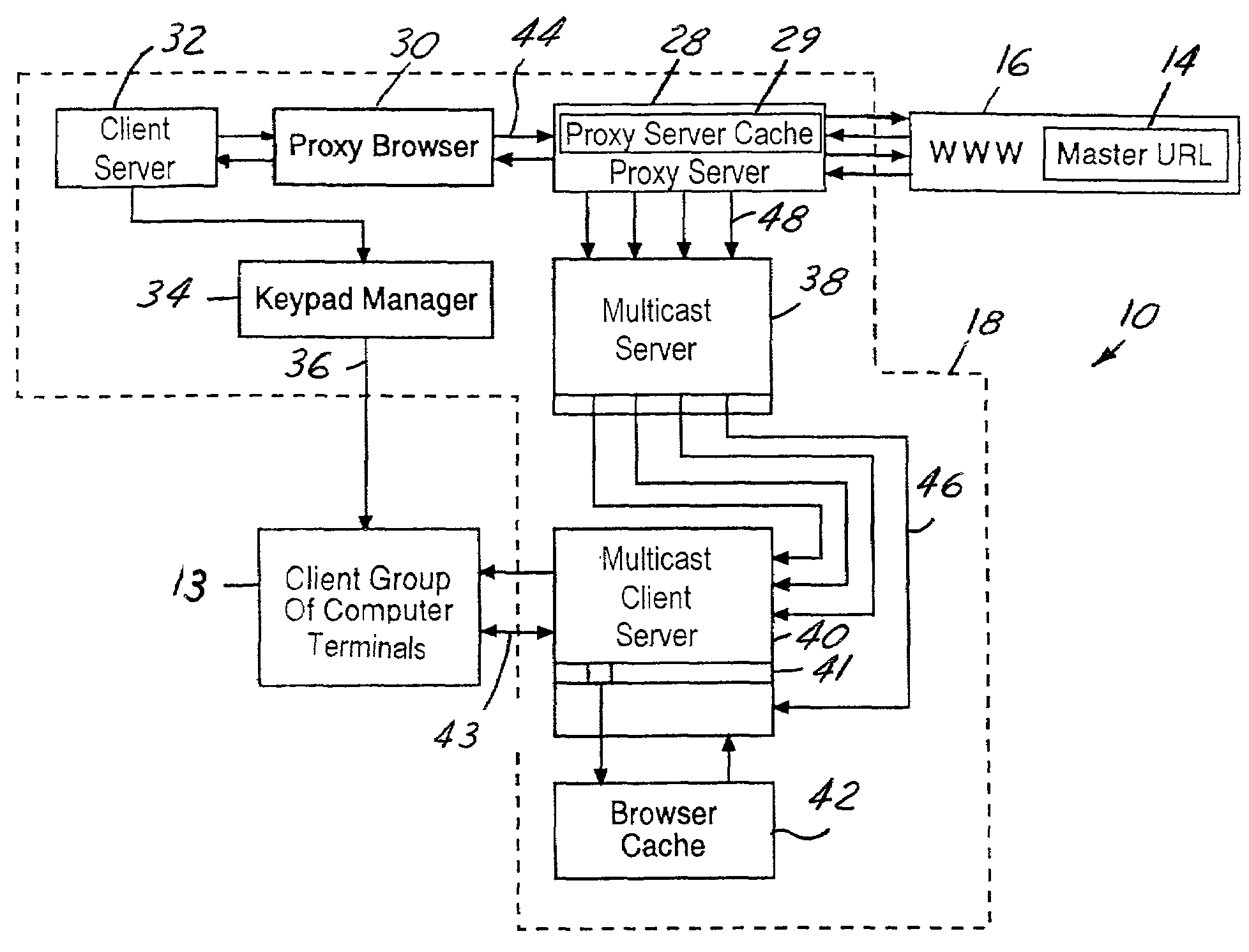
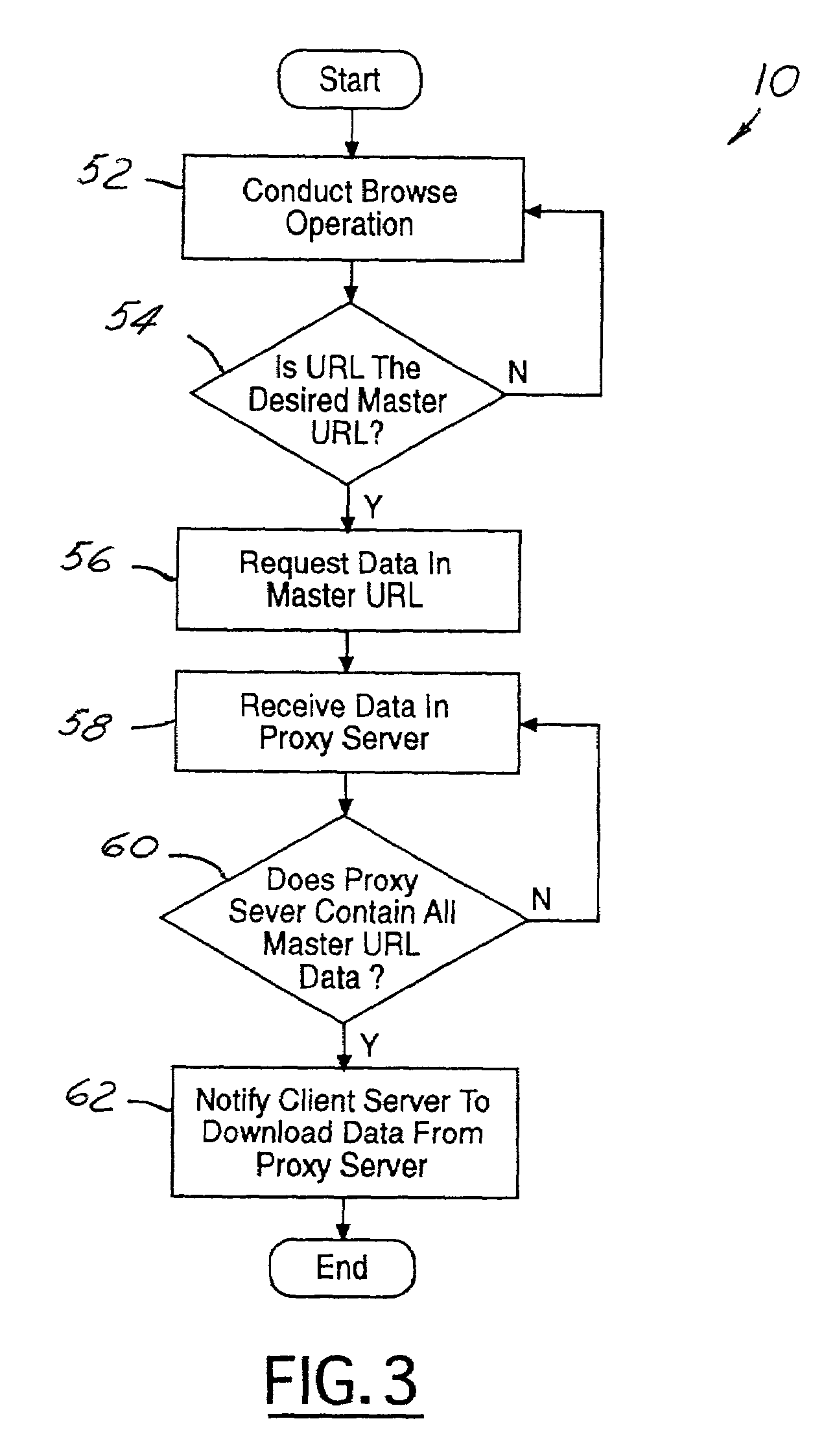
System for reducing server loading during content delivery
InactiveUS7149809B2Rapidly and efficiently downloadMinimize outdated information transferMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlUniform resource locatorClient-side
A server load reduction system includes a master URL containing data. The system further includes a proxy browser, which conducts a browse operation to request the data contained in the master URL. This browse operation is conducted through a proxy server. The proxy server is capable of receiving the data from the master URL. The proxy server includes logic operative to record and distribute the data to a client server. Logic contained in the proxy browser is operative to notify a client server to load the data when the proxy server contains all of the data.
Owner:ONE TOUCH SYST
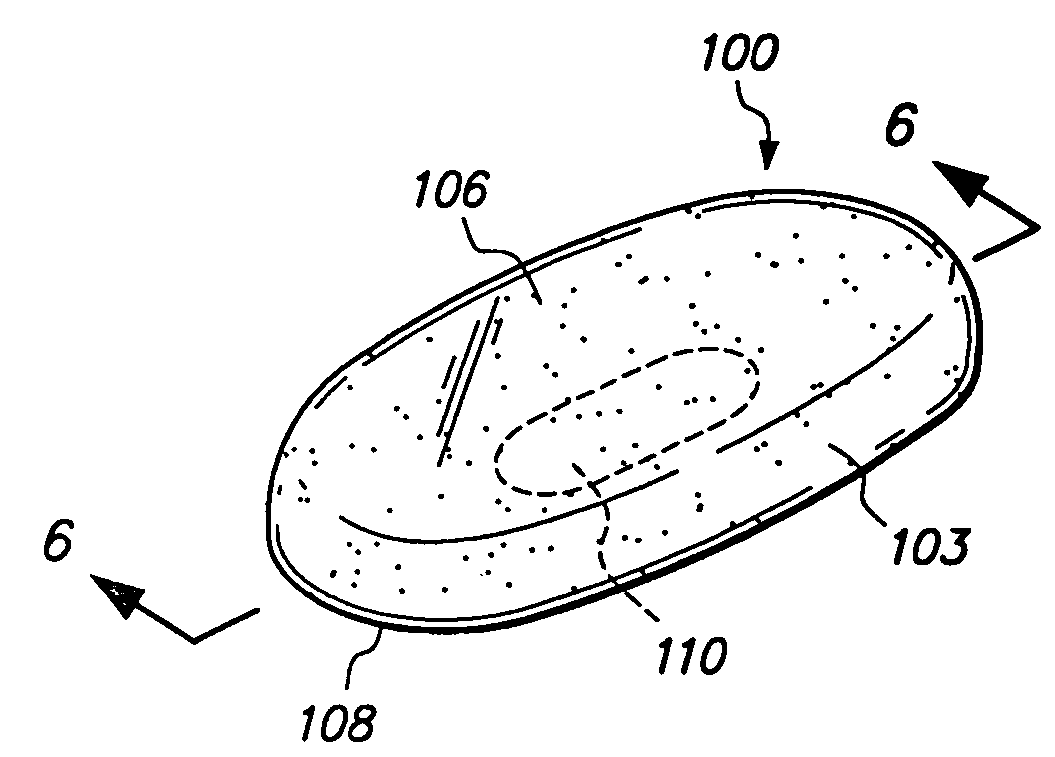
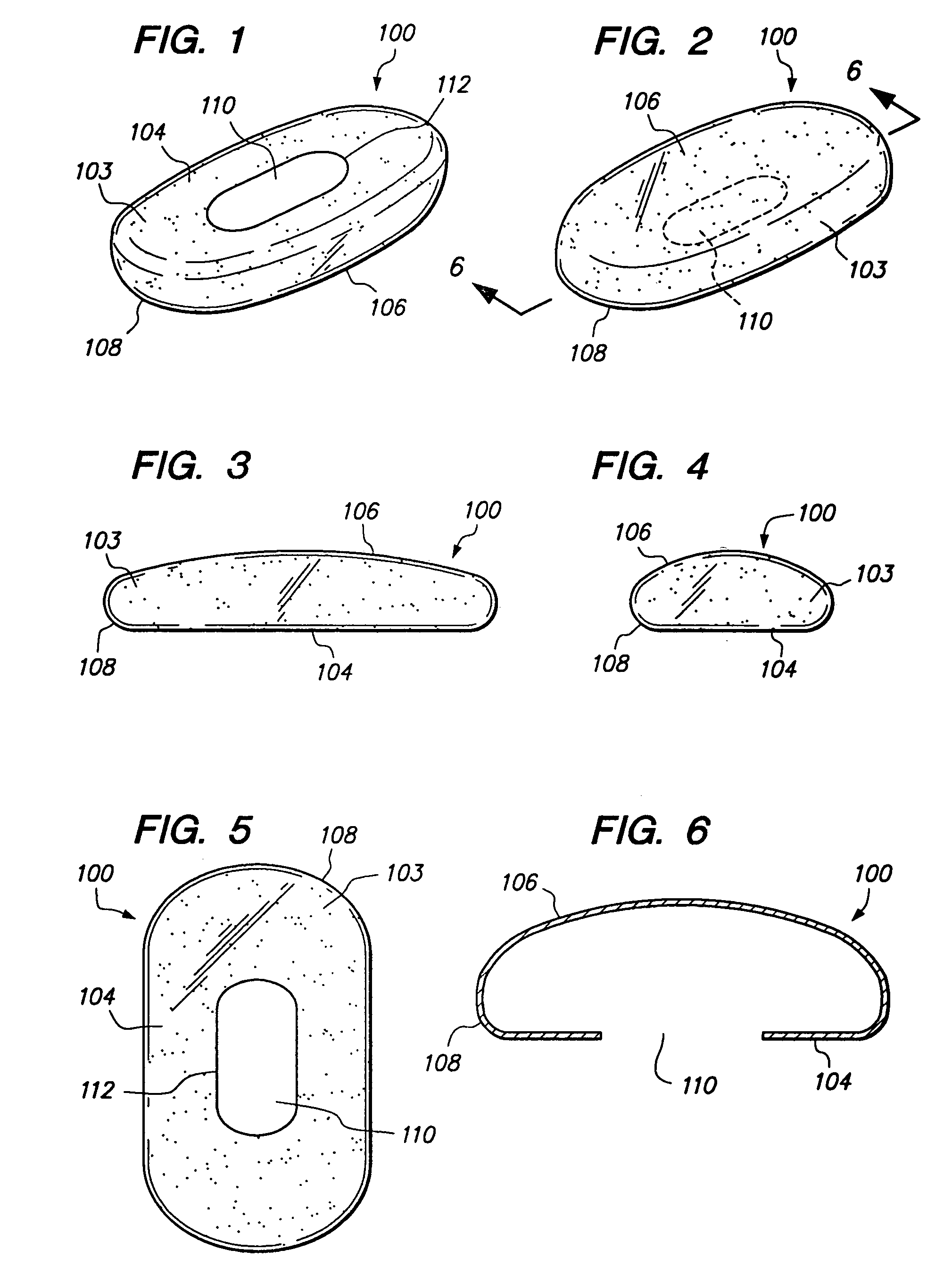
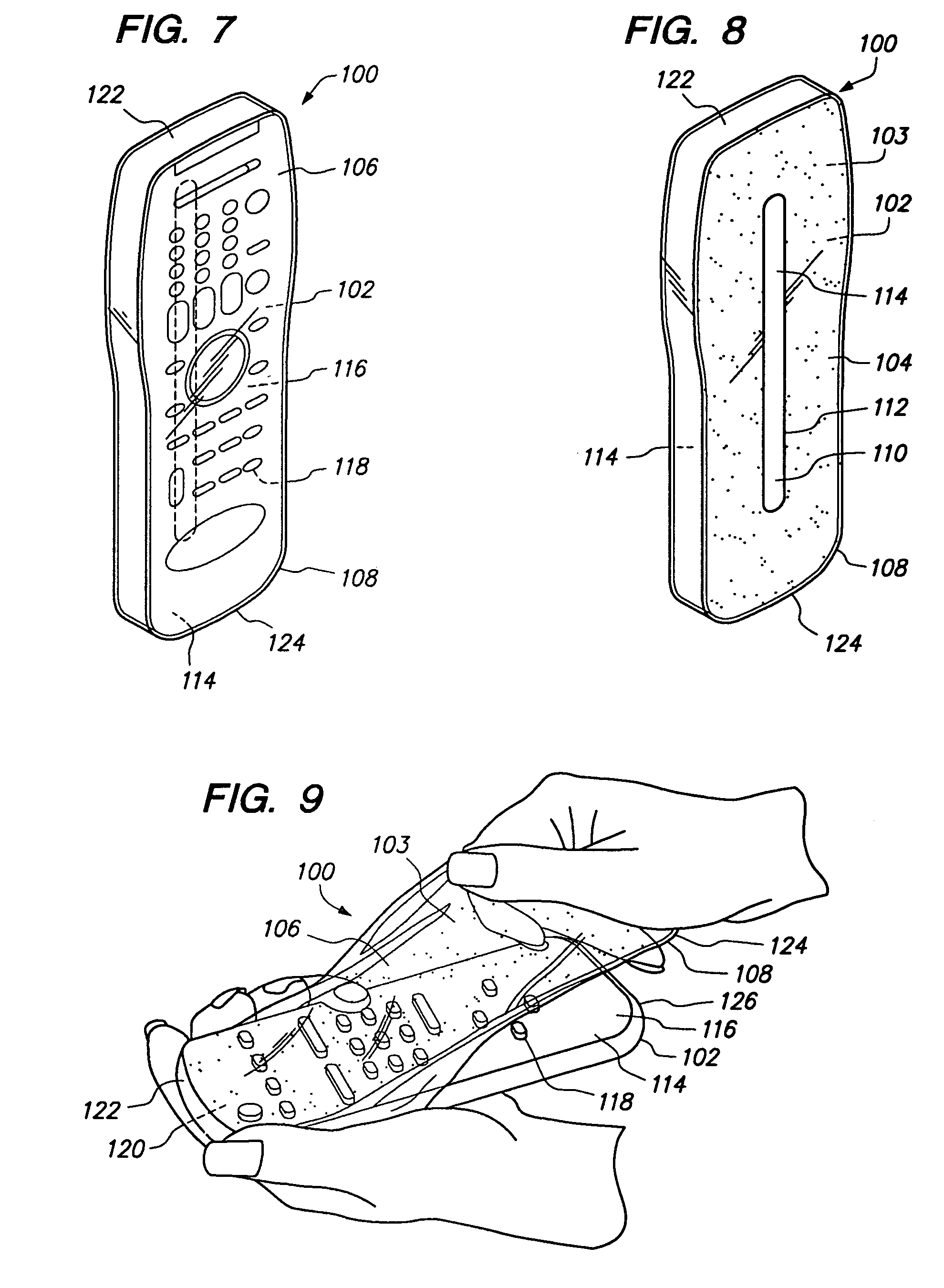
Cover for remote control device
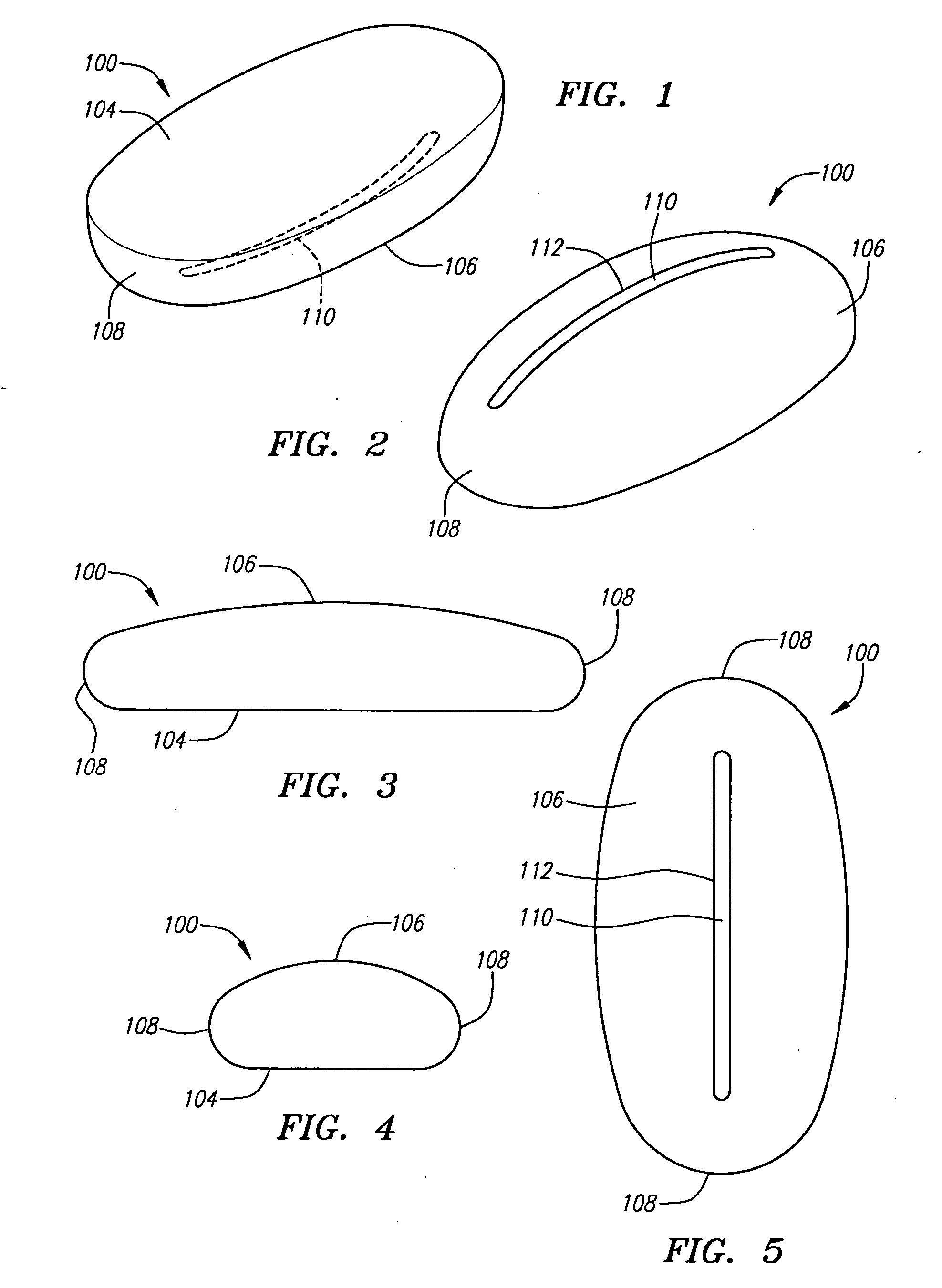
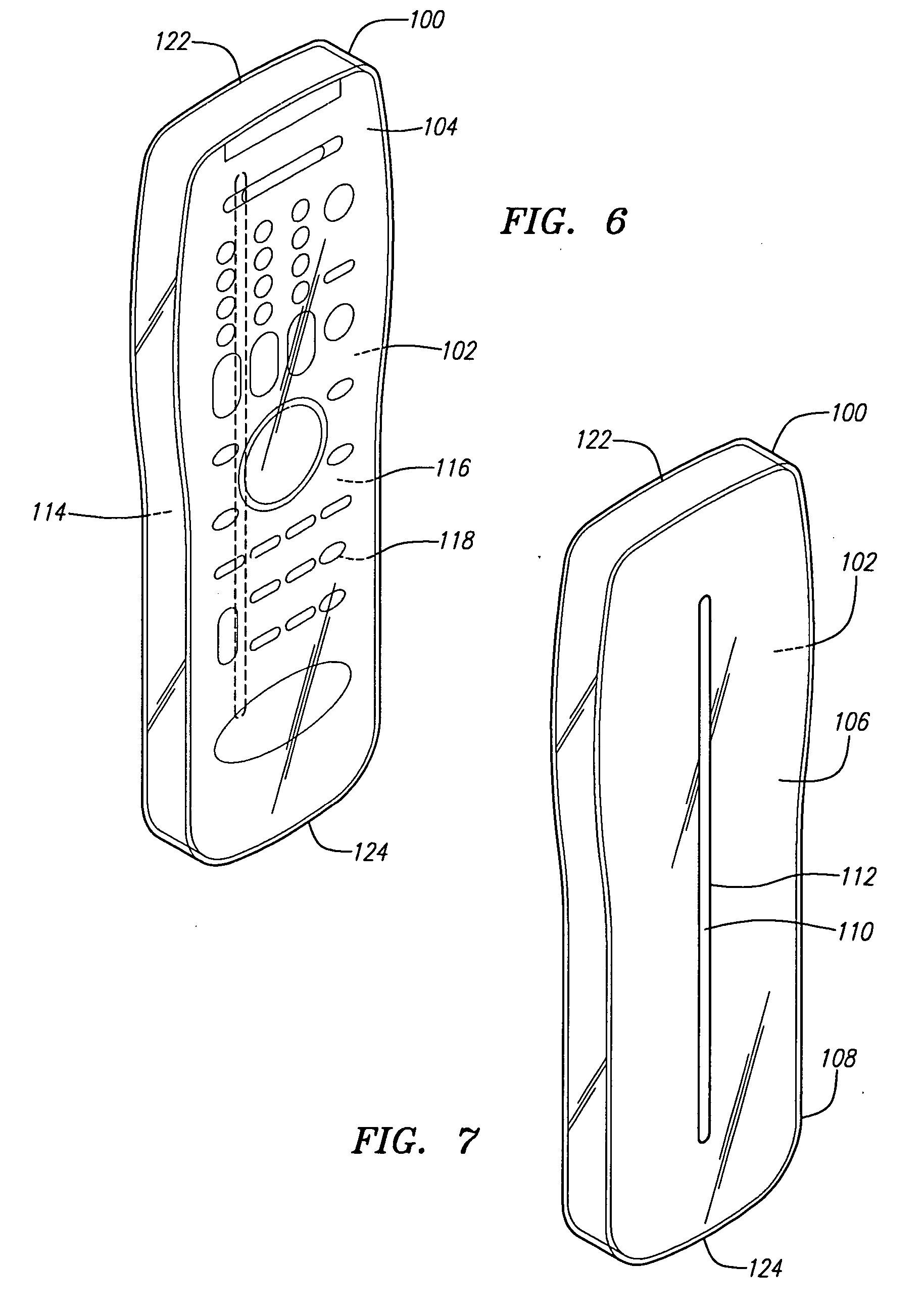
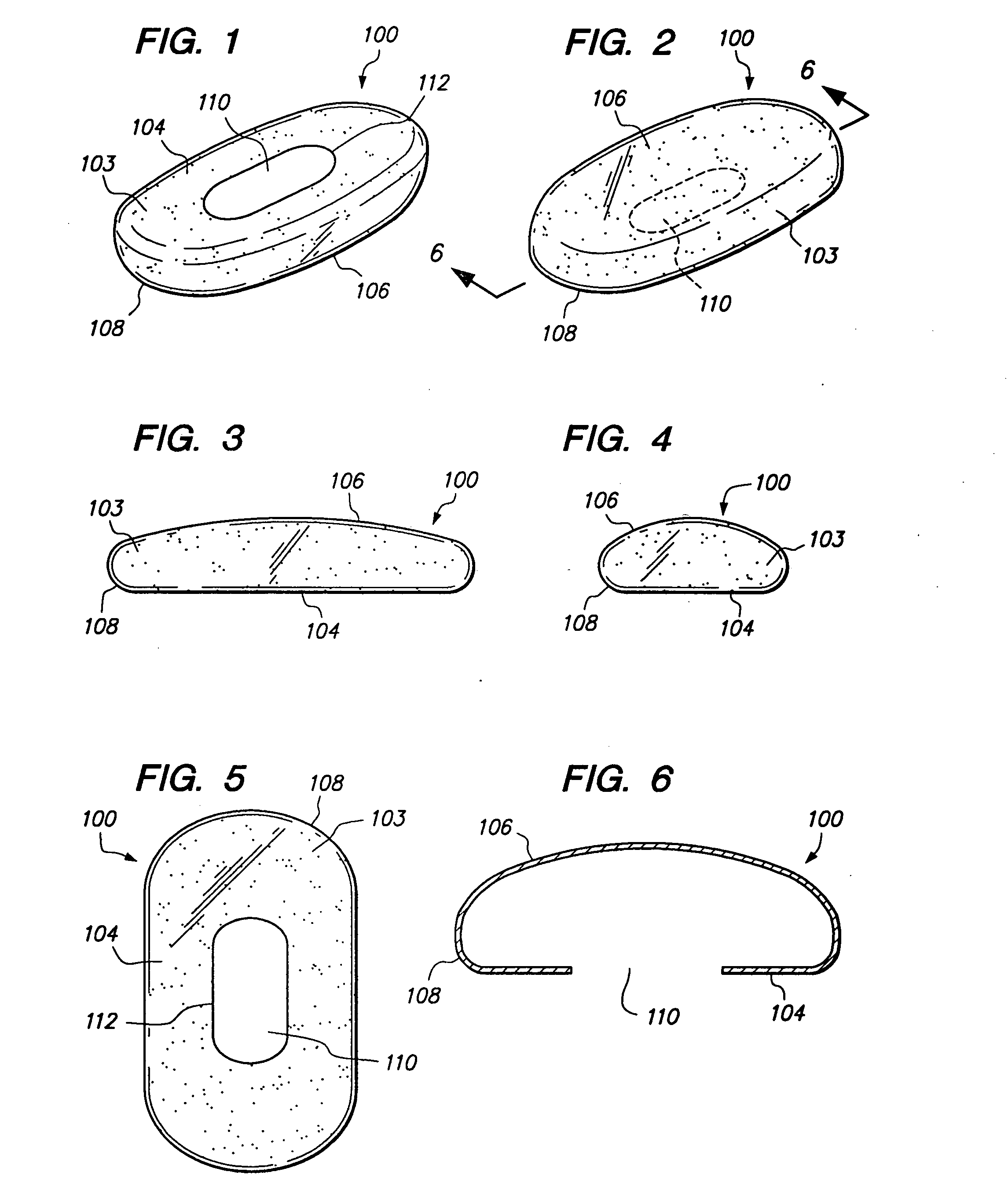
InactiveUS20050279661A1Minimizing transferEasy to captureFlexible coversWrappersRemote controlEngineering
A disposable cover for use with a remote control device for providing a protective barrier to human infection comprising a front member having a continuously flat surface and a rear member integrally molded in a seamless unitary, one-piece construction with the front member at a plurality of rounded surfaces for forming a single-use, disposable protective enclosure. An orifice is formed in and parallel to an oblong dimension of the rear member for enabling most any size remote control device to be inserted into and removed from the enclosure. The rounded surfaces designed into the disposable cover facilitate the closing of the orifice for enclosing the remote control device. The front member, rear member and rounded surfaces are each comprised of a flexible, stretchable and transparent material for conforming to the shape of the remote control device and for providing a disposable, protective sanitation barrier to human infection.
Owner:HODGES RICHARD P
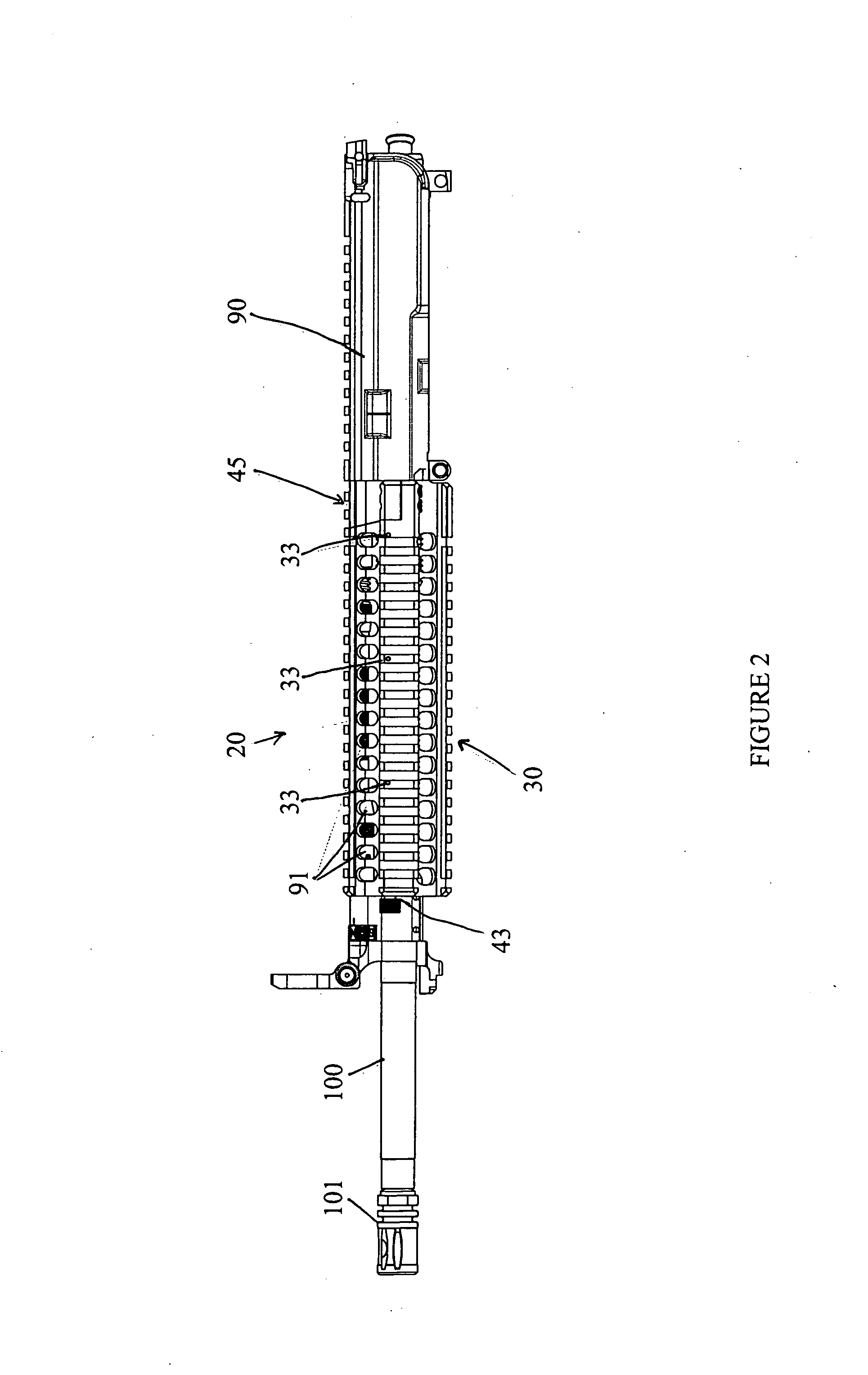
Top opening, modular top rail, multi-rifle adaptable free float rail adaptor system (arm-r)
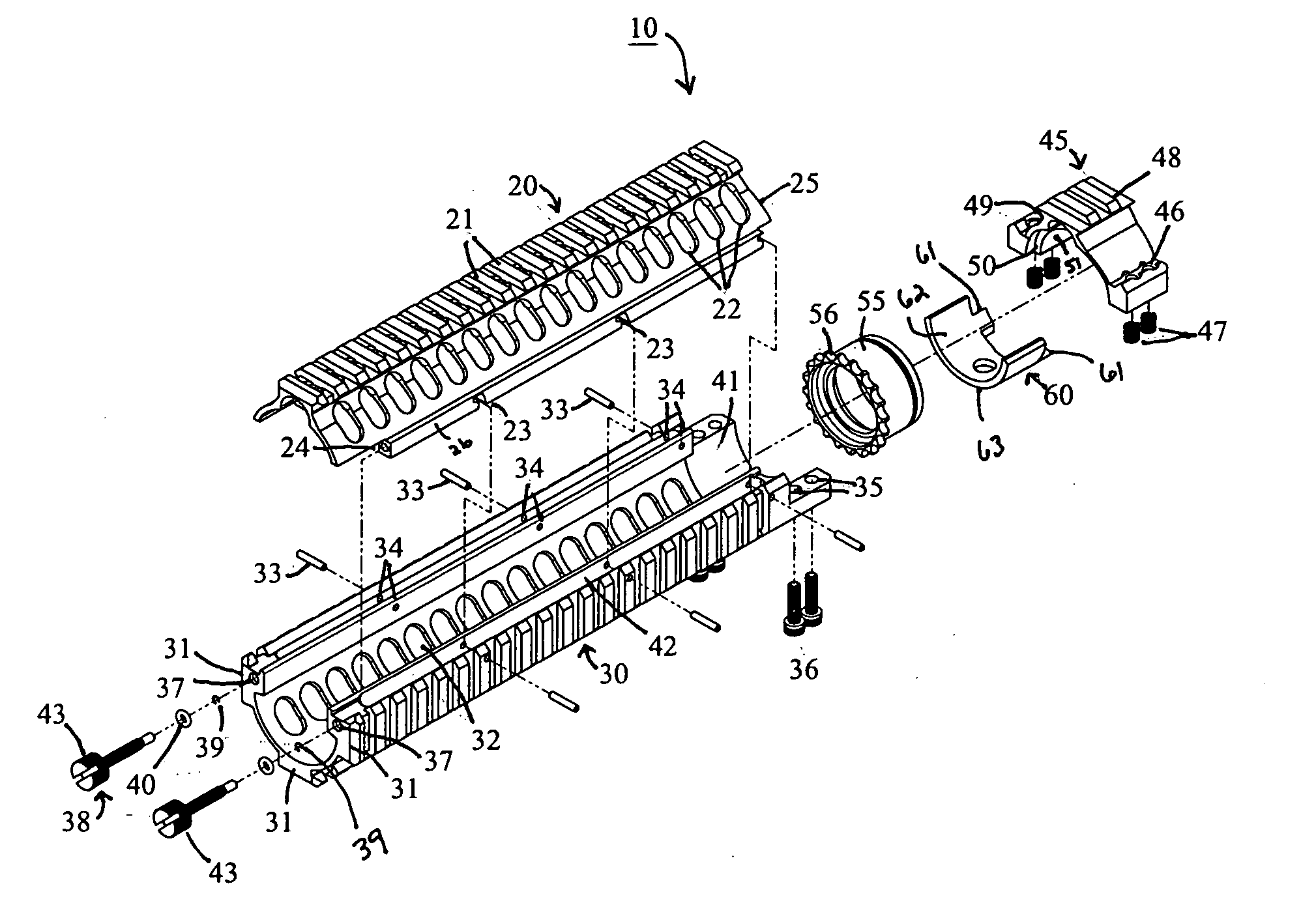
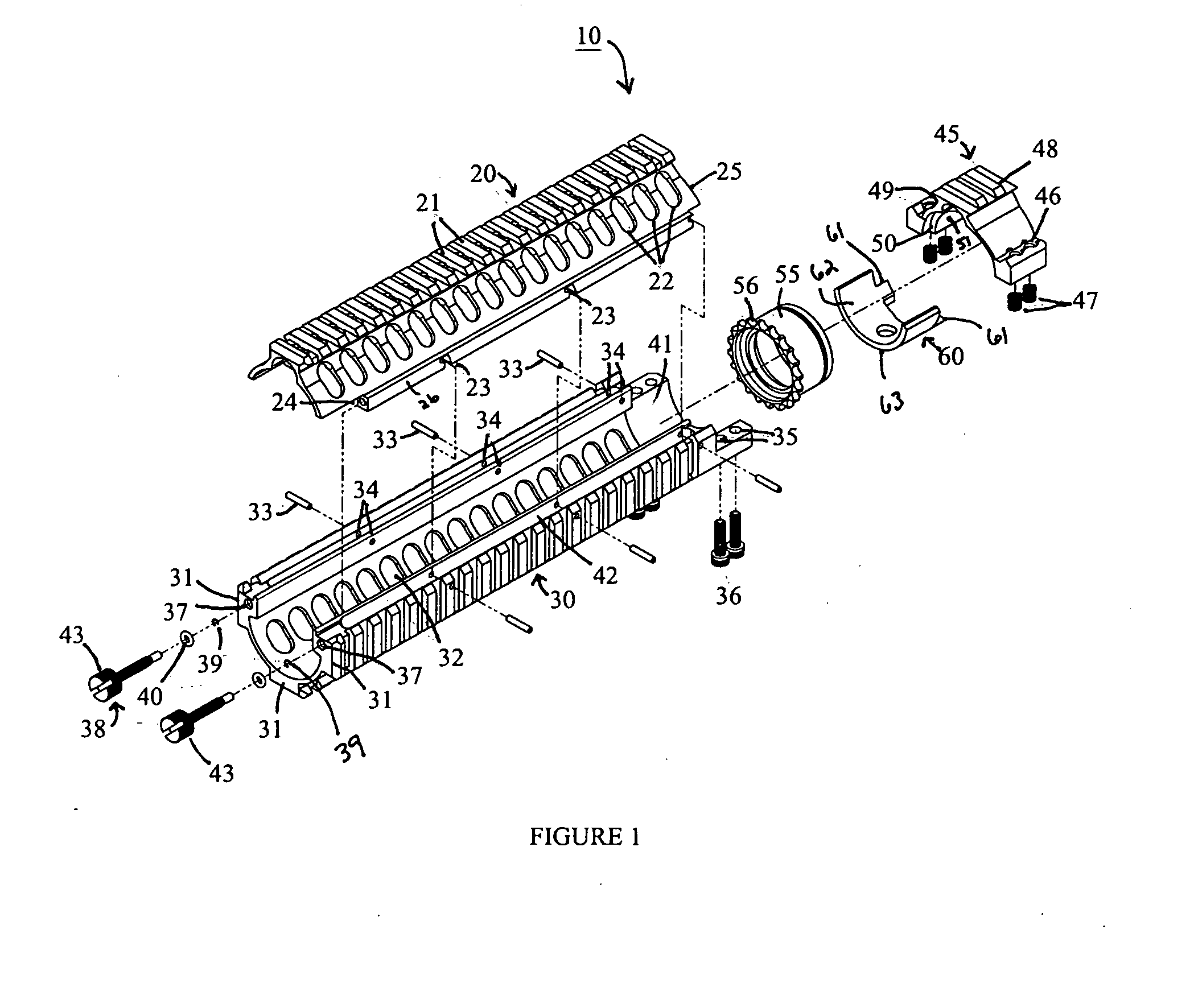
ActiveUS20120042557A1Minimizing transferImprove ventilationCartridge extractorsWeapon cleaningReturn-to-zeroHeat transmission
An improved Rail Adaptor System / Rail Accessory System (RAS) which attaches to a firearm. The rail is top opening, modular, and free floats the barrel. Provided is a rigid, lightweight, strong platform for mounting firearm accessories. Heat transmission from the barrel assembly to the user is limited. The user is also protected from ventilated gases originating from the operating system. A quick detachable top rail section is provided so that that gas system may be easily accessed. This removable top section of the rail is what makes this device unique because the RAS may be installed without removing the barrel, gas system, front sight base, flash hider or the barrel nut. The herein described RAS is adaptable to a wide variety of firearms with the use of conversion parts. The top rail “returns to zero” on reinstallation allowing the remounting of various optics and electronic gun sites without the need to realign them.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
Cover for remote control device
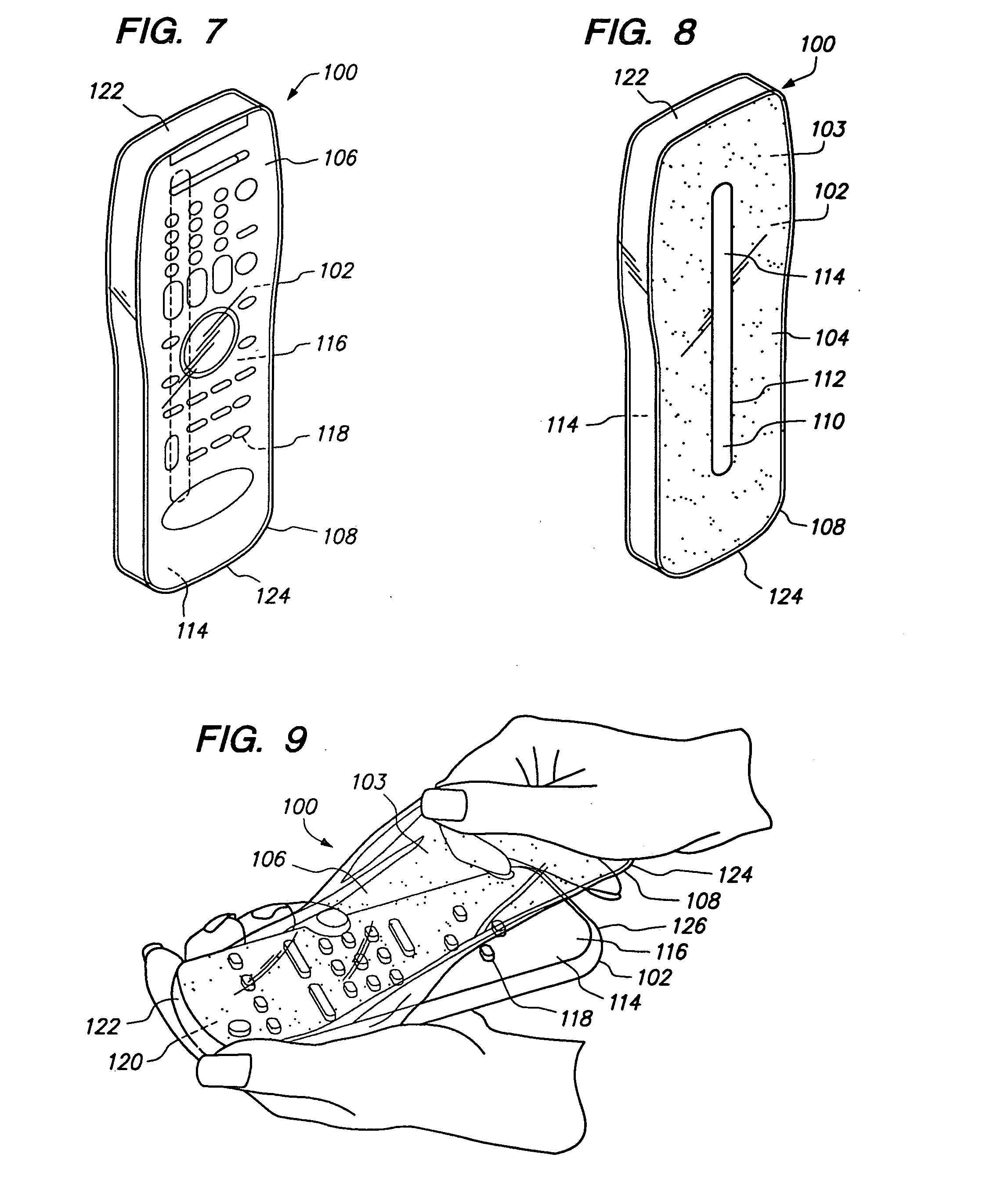
InactiveUS7290654B2Minimizing transferEasy to captureOther accessoriesElectric switchesRemote controlEngineering
A disposable cover for use with a remote control device for providing a protective sanitation barrier to human infection includes a rear member having a flat surface. A front curved member is integrally molded in a seamless unitary, one-piece construction with the rear member at a plurality of rounded surfaces to form a single-use, disposable protective enclosure. An anti-bacterial compound impregnates the rear member, the front curved member and the rounded surfaces for destroying bacteria on the remote control device. An orifice is formed in the rear member for enabling the remote control device to be inserted into and removed from the enclosure. Finally, the front member, rear member and the rounded surfaces are comprised of a flexible, stretchable and transparent material for conforming to the shape of the remote control device for providing a disposable, protective sanitation barrier to human infection.
Owner:HODGES RICHARD P
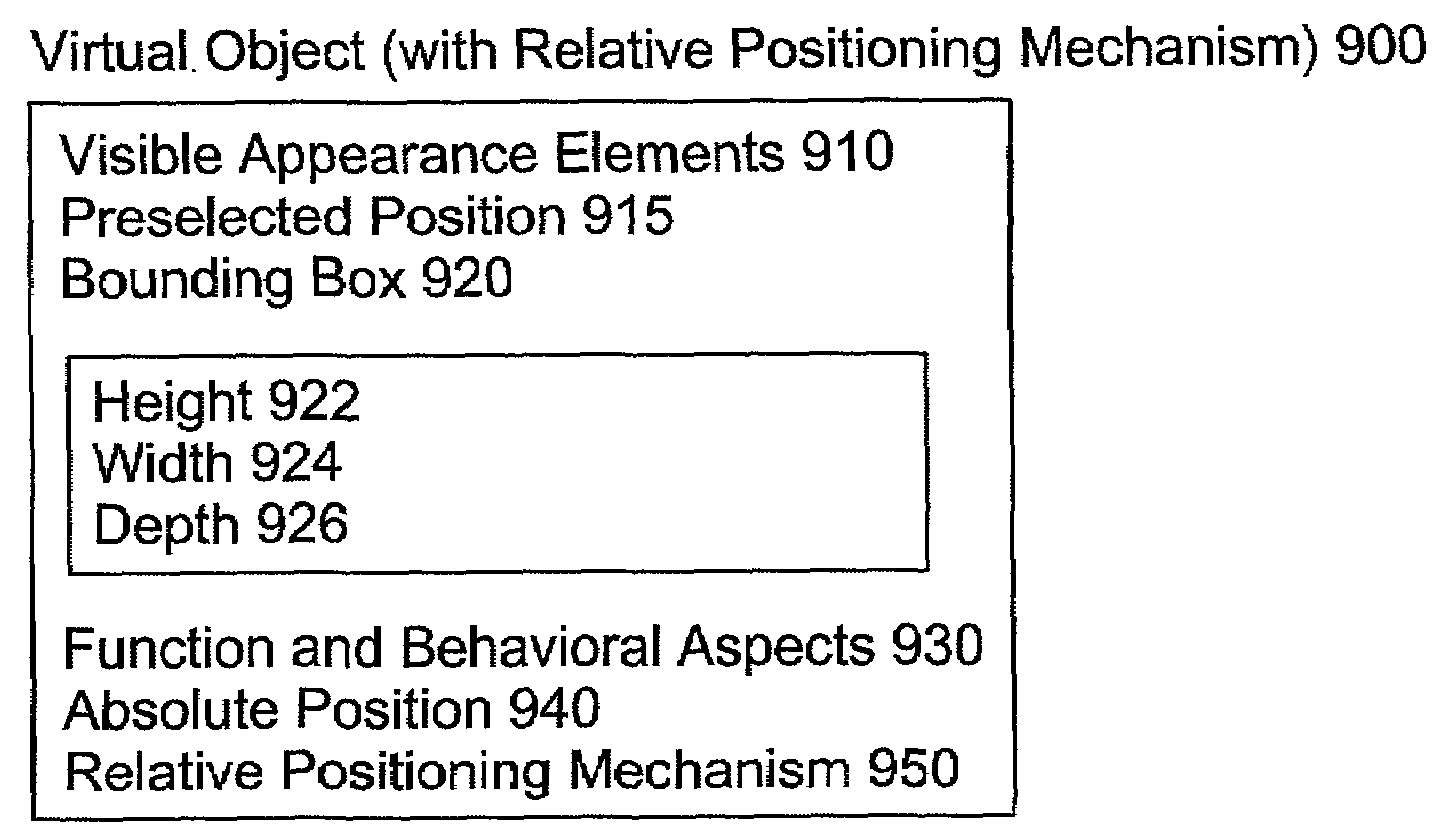
Object positioning and display in virtual environments
InactiveUS7043695B2Easy to placeMinimizing transferCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsCo ordinateNatural language
A virtual environment for user interaction, and virtual objects for use therein, the virtual objects having an internal co-ordinate system with natural language definition to allow simplified inter-object relationships. The internal co-ordinate system is used to define docking positions for connecting to other objects to allow logical or natural positional relationships. A dynamically defined menu system allows pop-up menus for simple user entry of required relationships.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
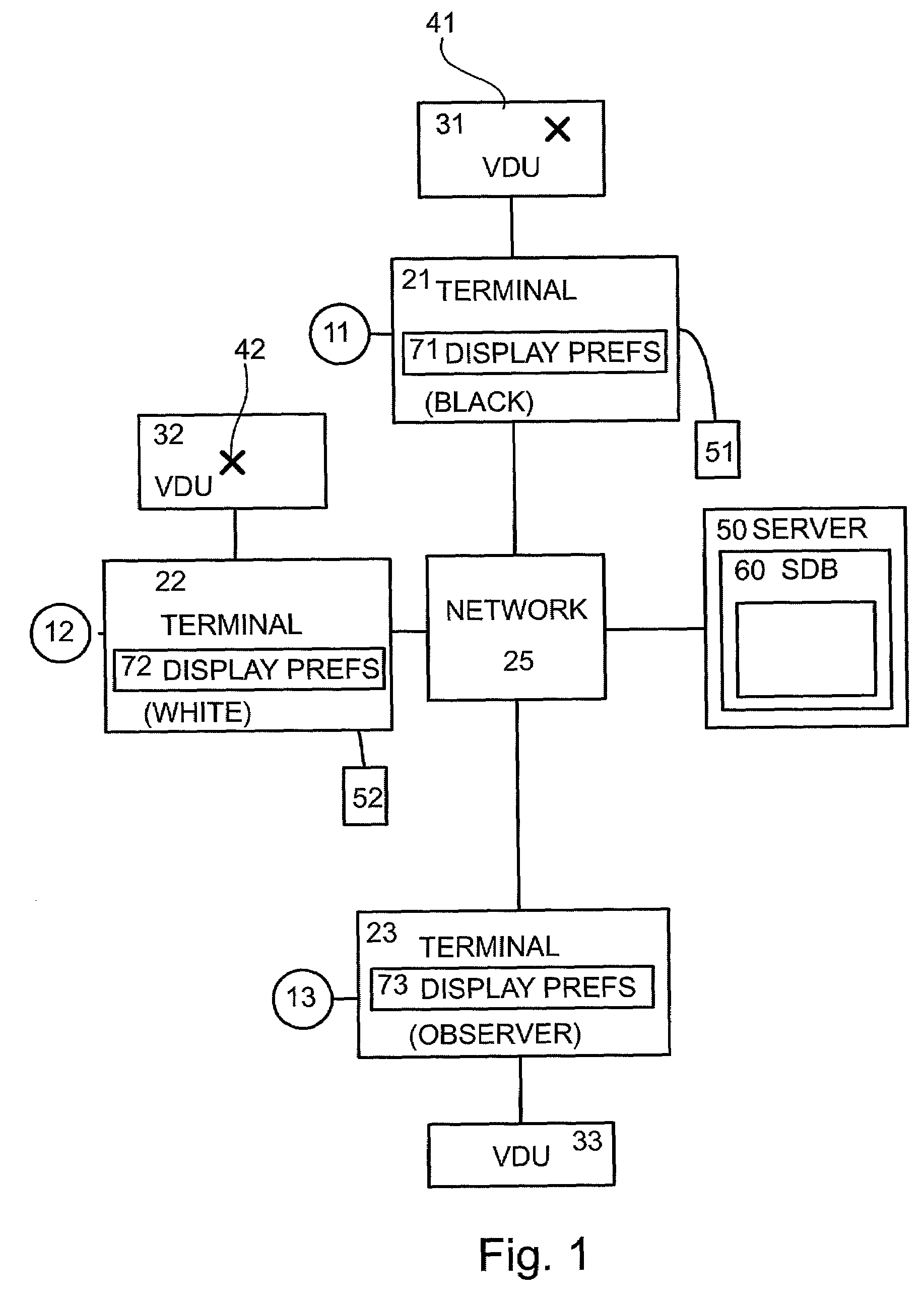
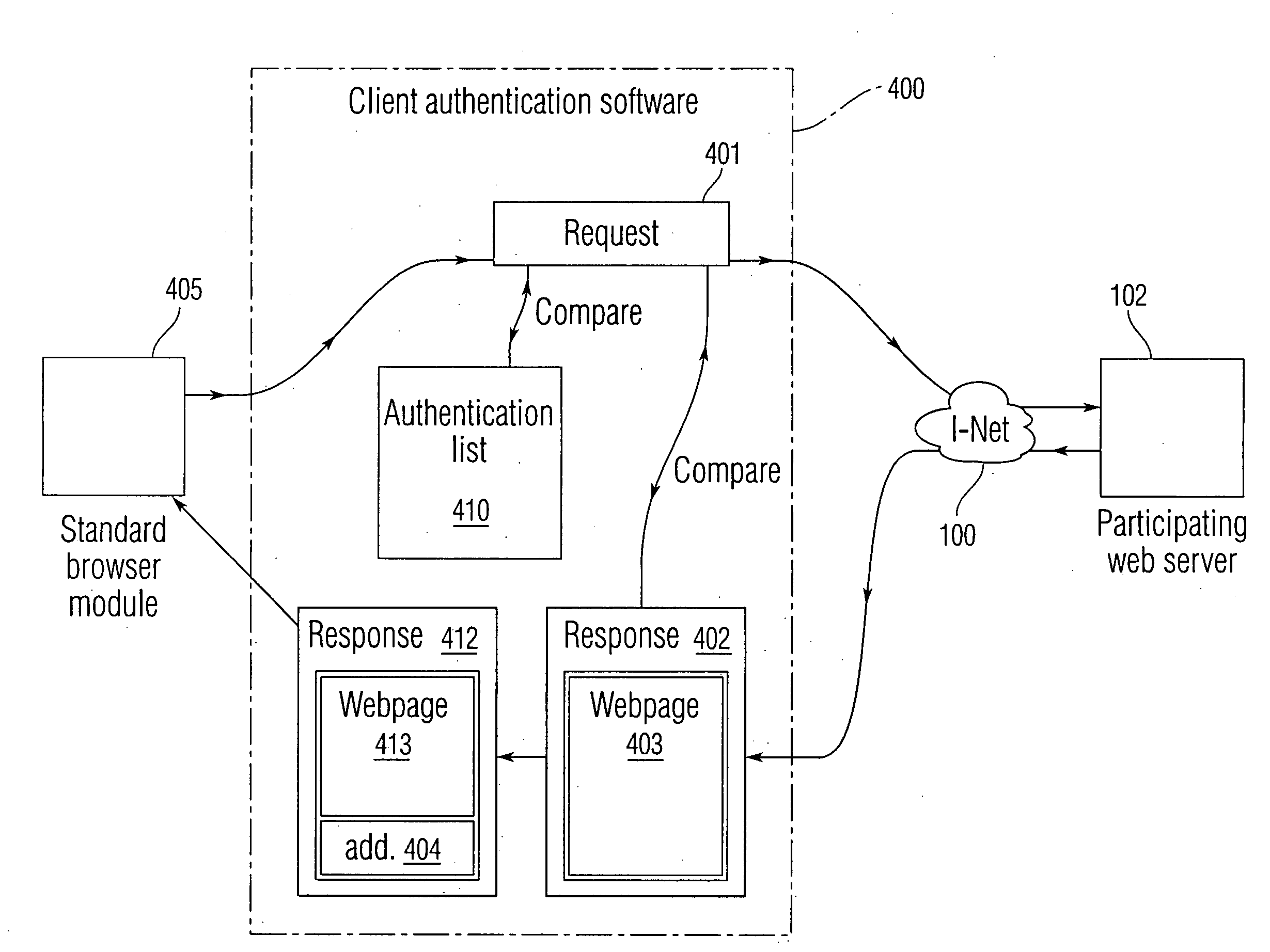
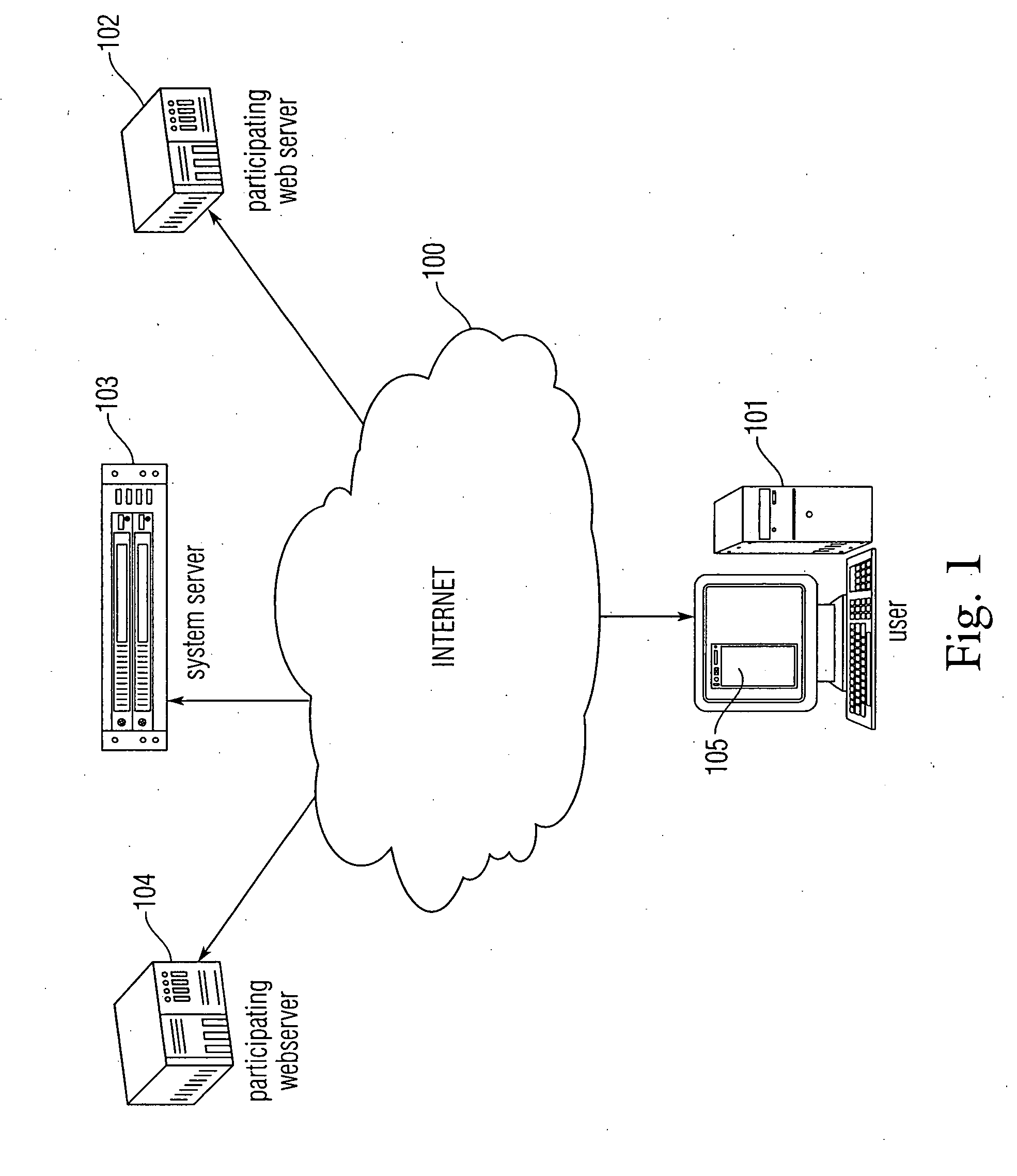
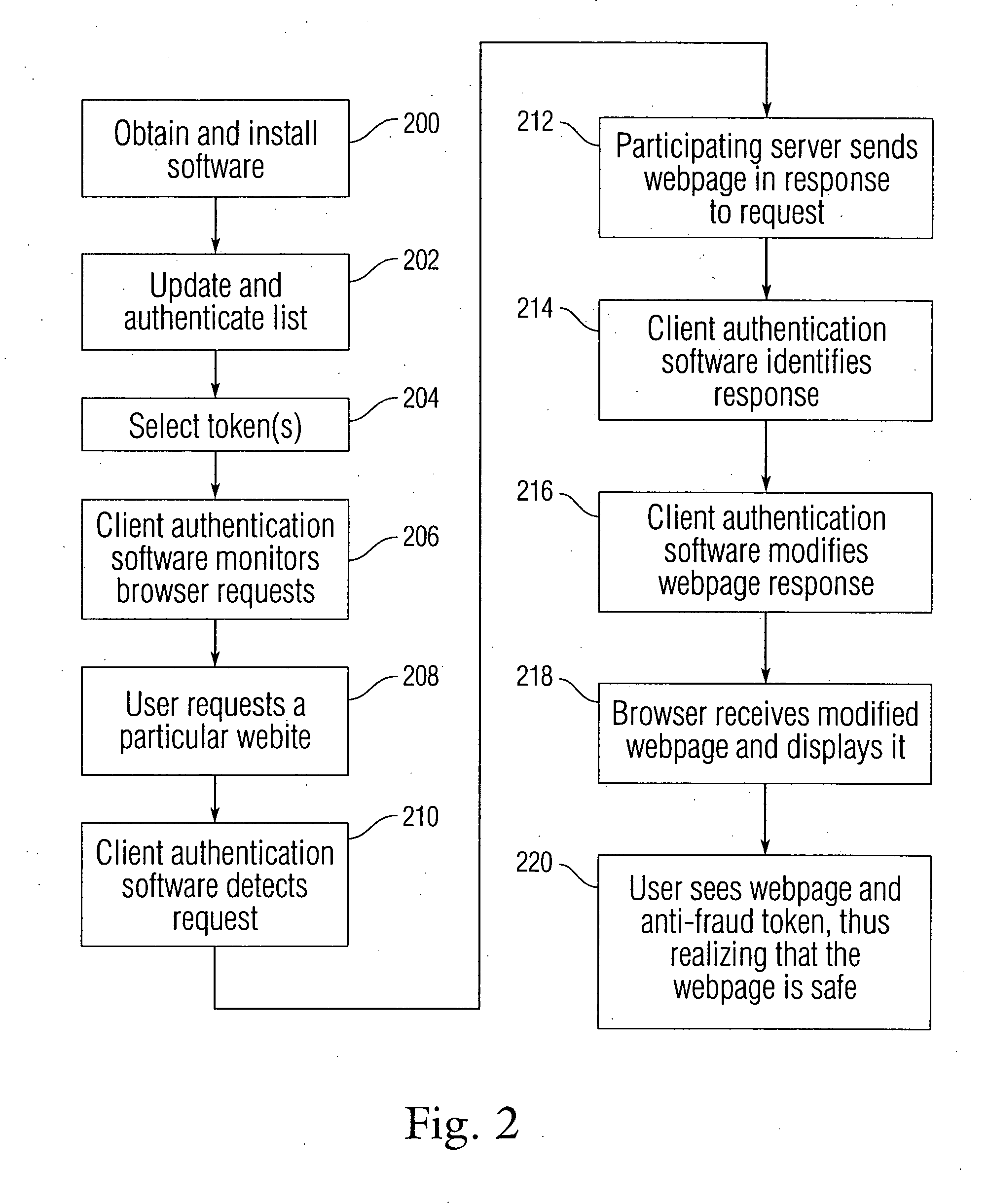
Client based online fraud prevention
InactiveUS20080127319A1Minimizing transferAvoid confusionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationClient-sideInternet privacy
An anti-fraud token system is disclosed in which the authentication process is performed primarily on the client side. A client according is provided with an authentication list of websites for which authentication is required, and their respective authentic addresses. The client also asks a user to select a token, which may include graphics, text, and / or sound. When the user accesses an information source from the authentication list, the client notes that the address which the user is accessing is on the list. The client then displays the token as previously selected by the user to the user along with the accessed information, so that the user knows that the information he / she is accessing is authentic.
Owner:OATH INC
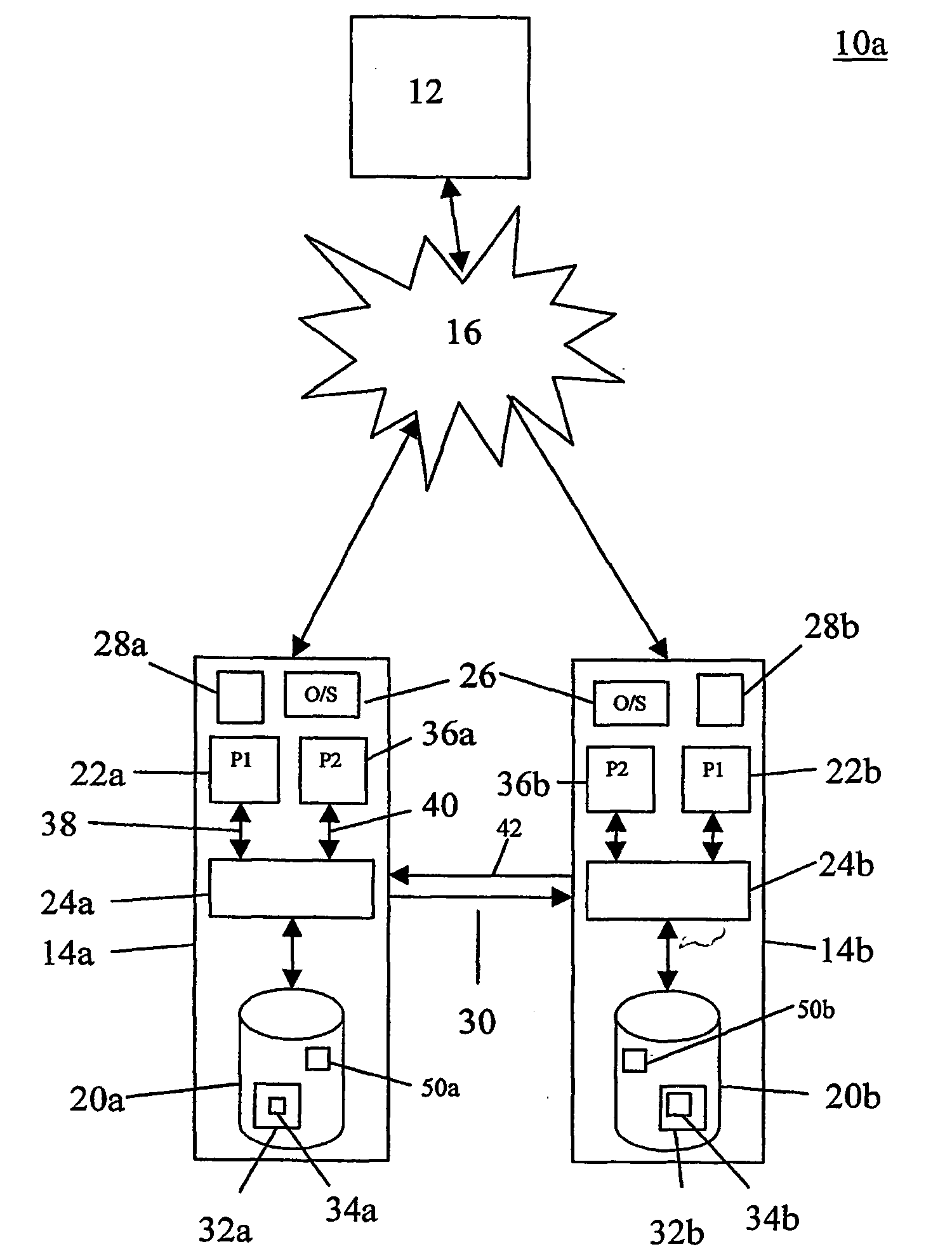
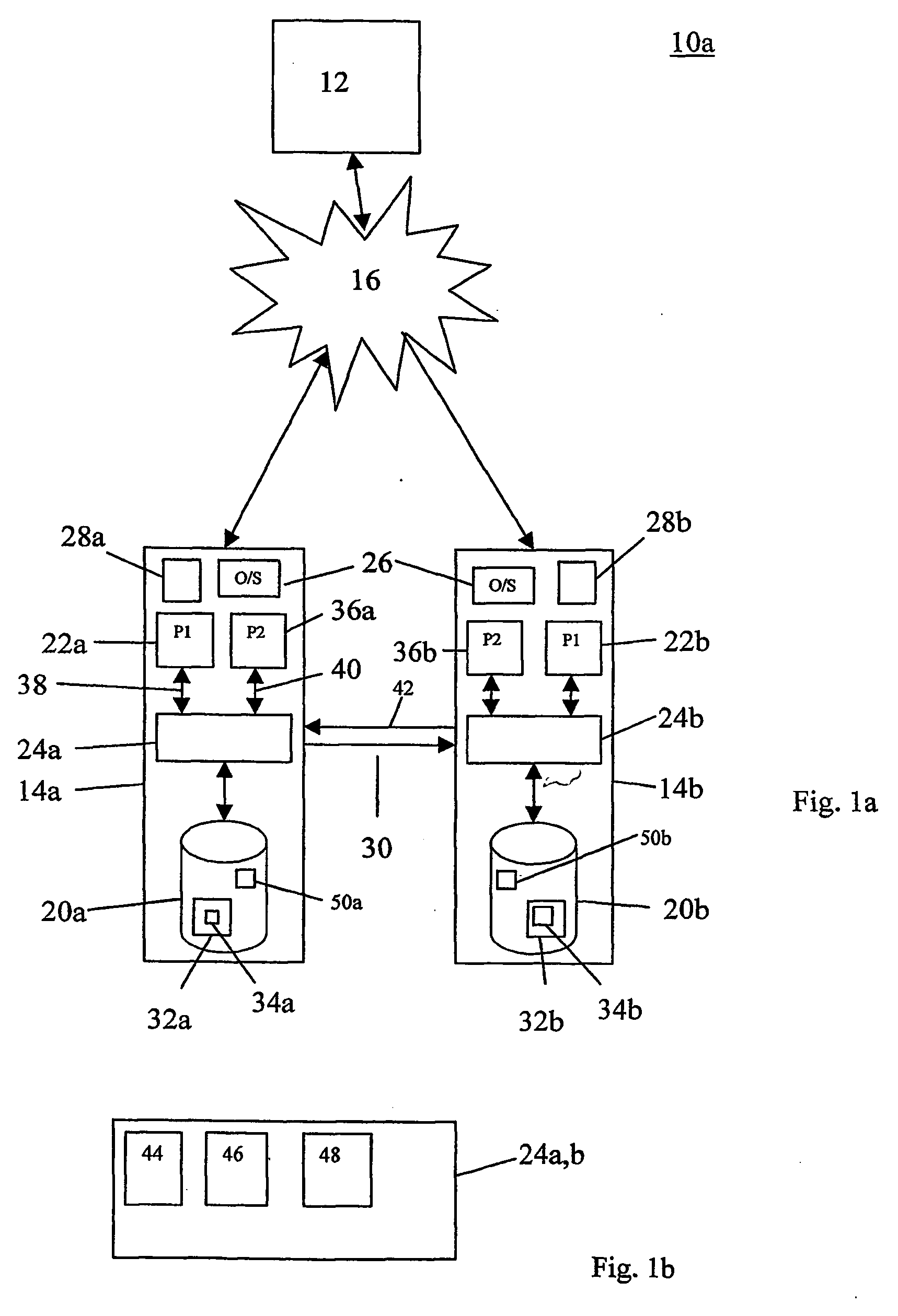
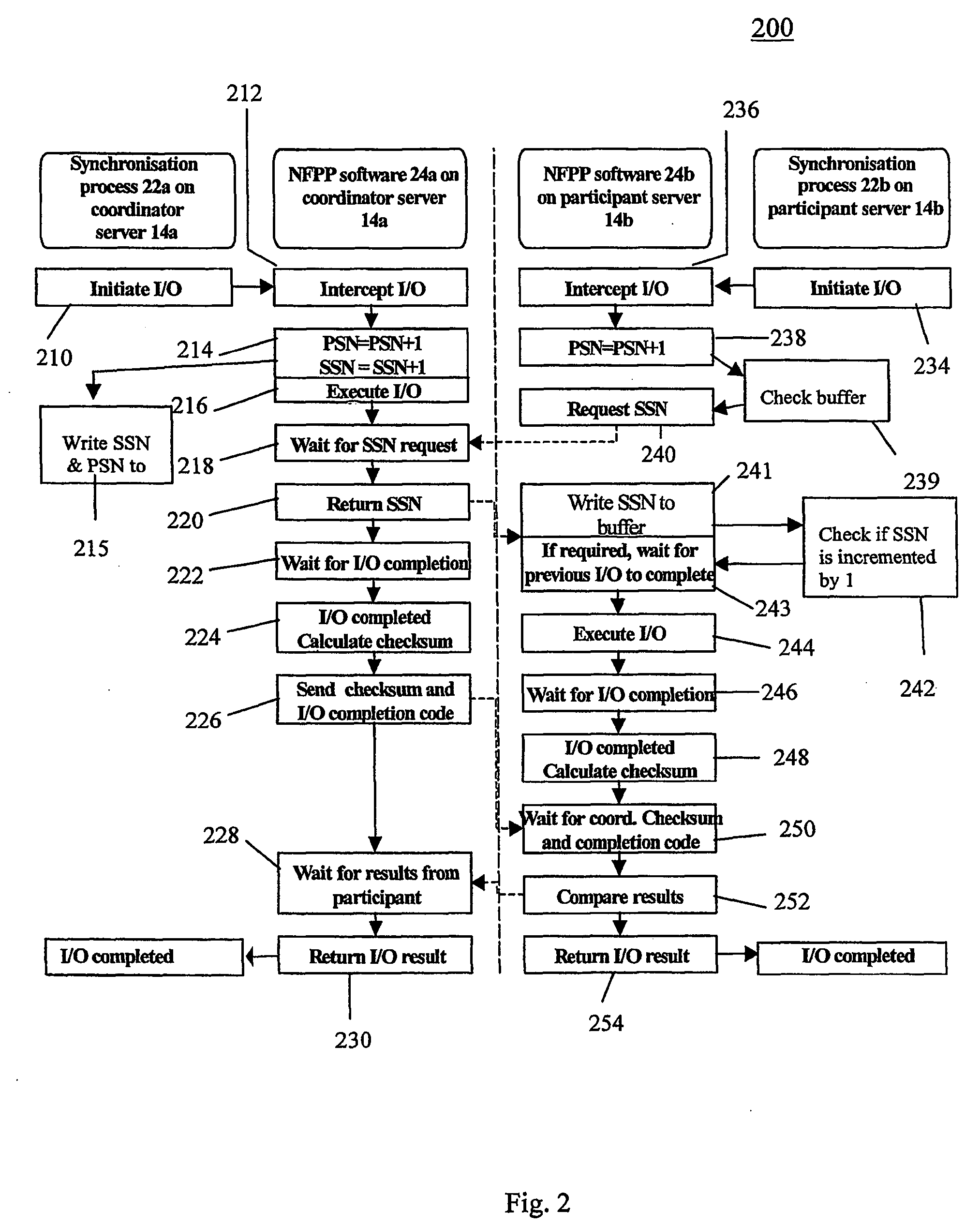
Fault-tolerant computers
InactiveUS20050160312A1Raise security concernsReduce the amount of informationRedundant hardware error correctionDistributed computing
A method of matching the operations of a primary computer and a backup computer for providing a substitute in the event of a failure of the primary computer is described. The method comprises assigning a unique sequence number to each of a plurality of requests in the order in which the requests are received and are to be executed on the primary computer, transferring the unique sequence numbers to the backup computer, and using the unique sequence numbers to order corresponding ones of the same plurality of requests also received at the backup computer such that the requests can be executed on the second computer in the same order as that on the first computer. In this manner, the status of the primary and backup computers can be matched in real-time so that, if the primary computer fails, the backup computer can immediately take the place of the primary computer.
Owner:NEVERFAIL GROUP
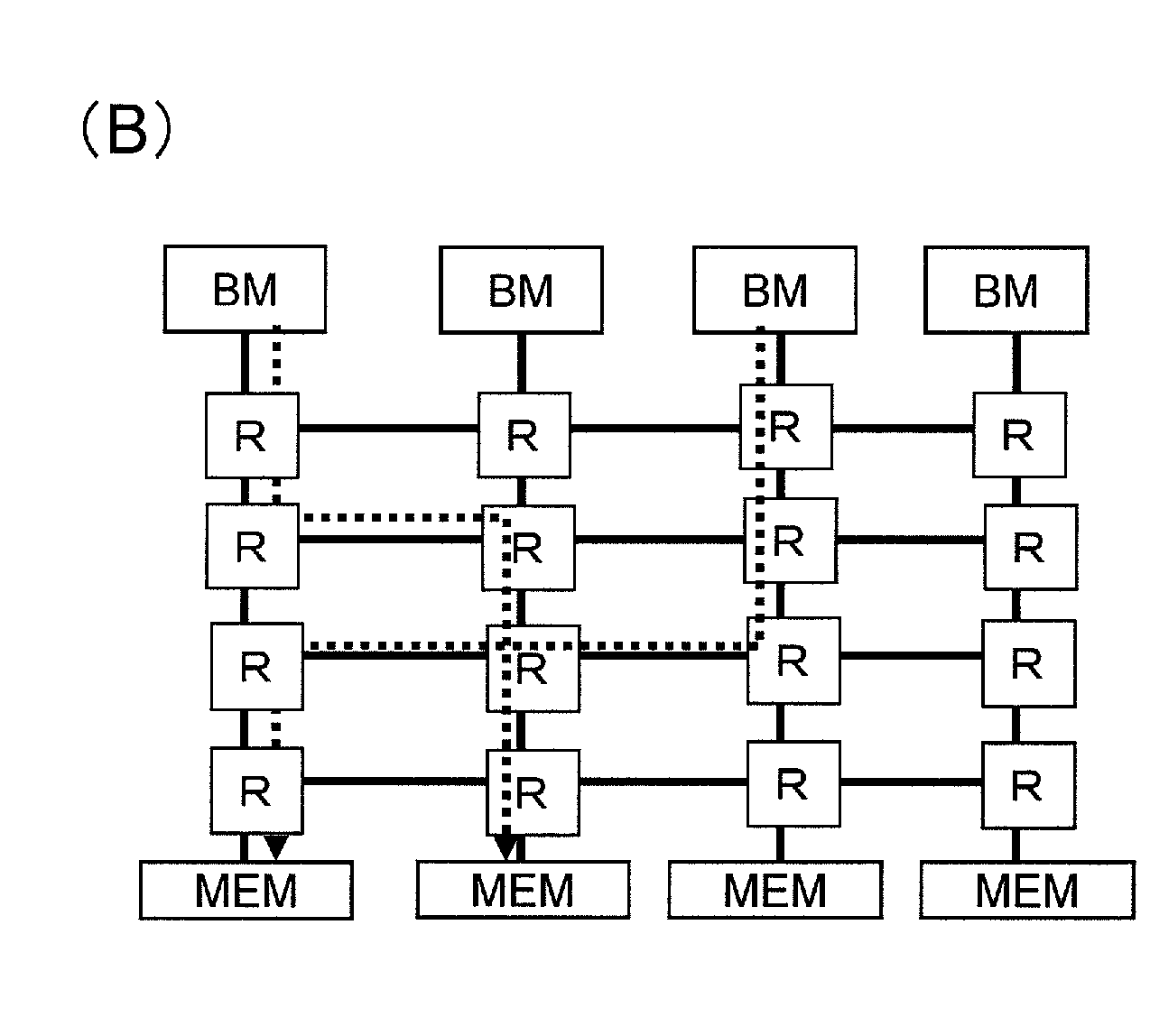
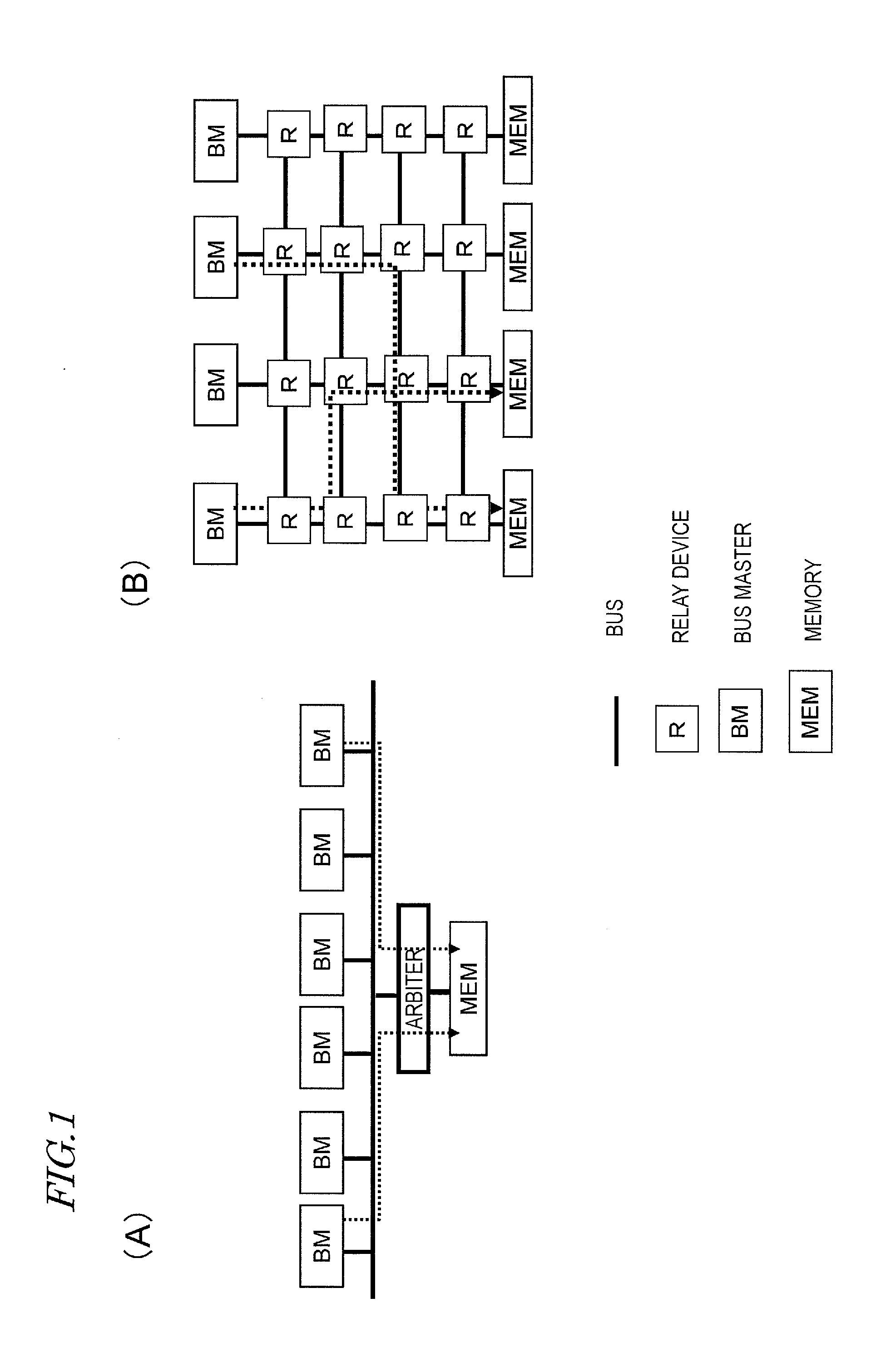
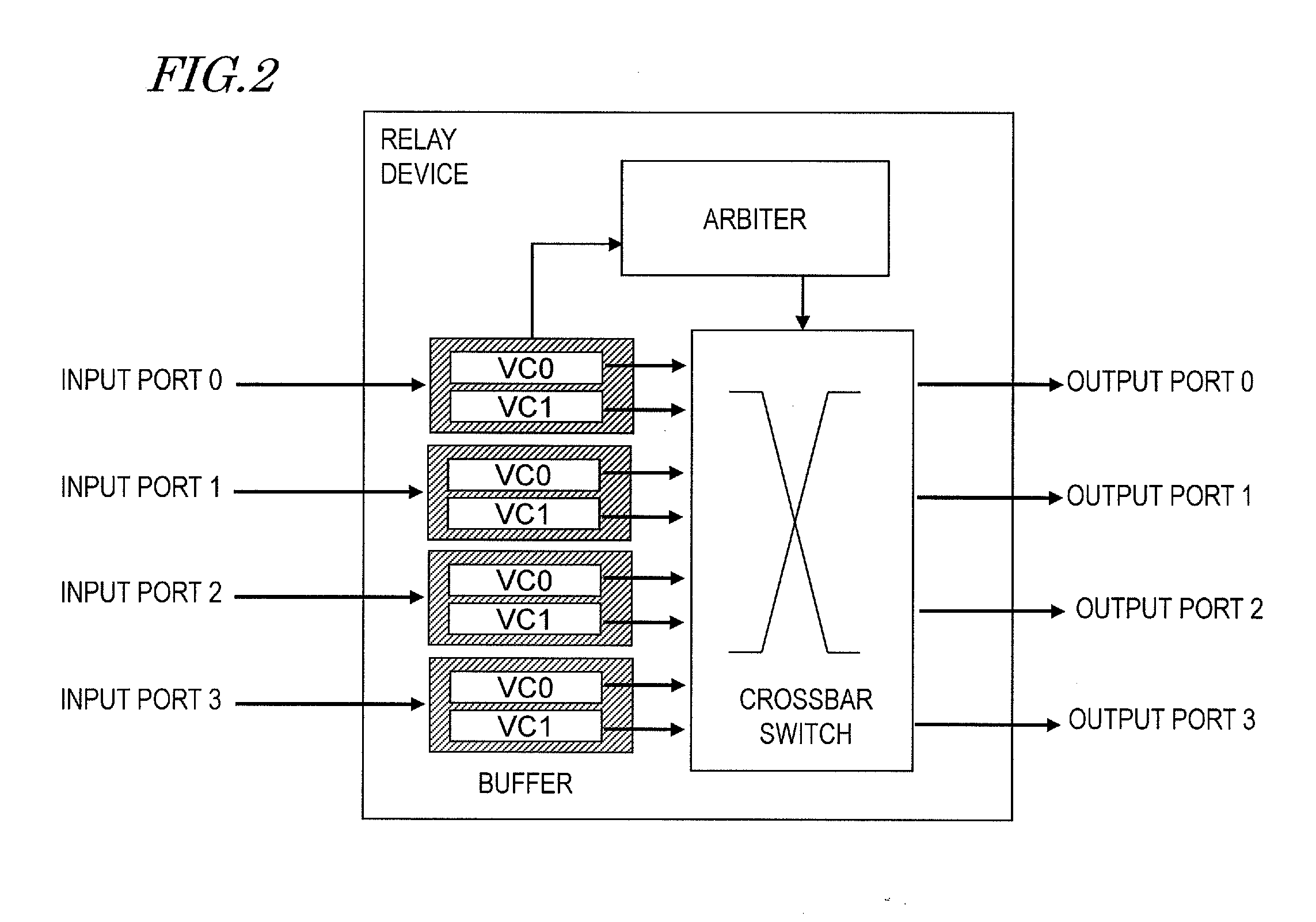
Relay device
ActiveUS20120072635A1Improve transmission performanceTransfer performance is reducedData switching by path configurationElectric digital data processingComputer hardwareVirtual channel
A relay device includes: an input buffer for receiving data units, each of which includes a header, to which multiple pieces of destination information have been added, and data associated with the header; multiple virtual channels for storing data units, each of the multiple virtual channels storing a data unit in accordance with the destination information; a destination comparing section for determining the order of allocation of virtual channels at a relay device on the receiving end with respect to the data units that are stored on the multiple virtual channels by seeing if their destinations are the same; and an output section for outputting the stored data units preferentially through one of the virtual channels that has already allocated at the relay device on the receiving end.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
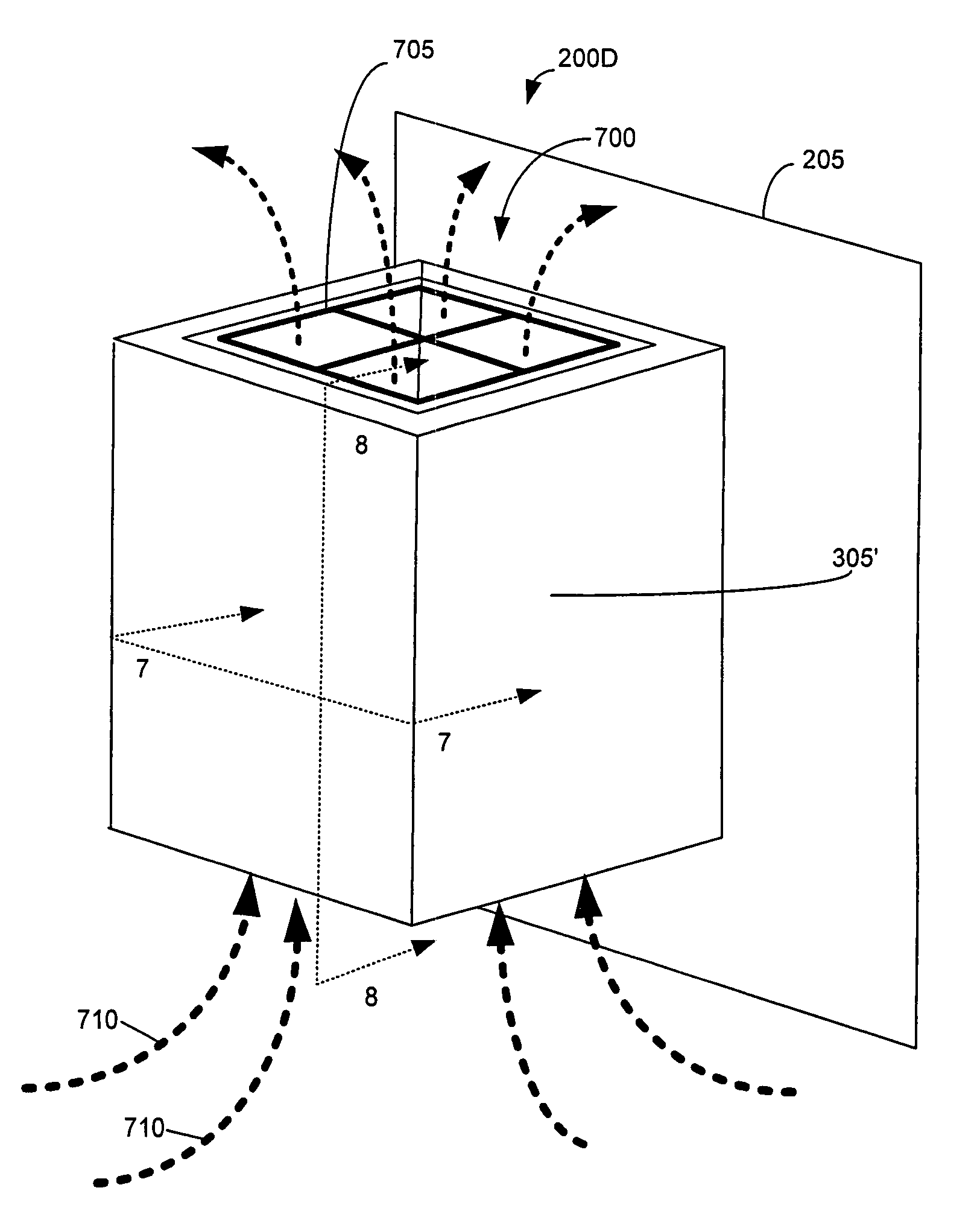
System and method for removing heat from a subscriber optical interface
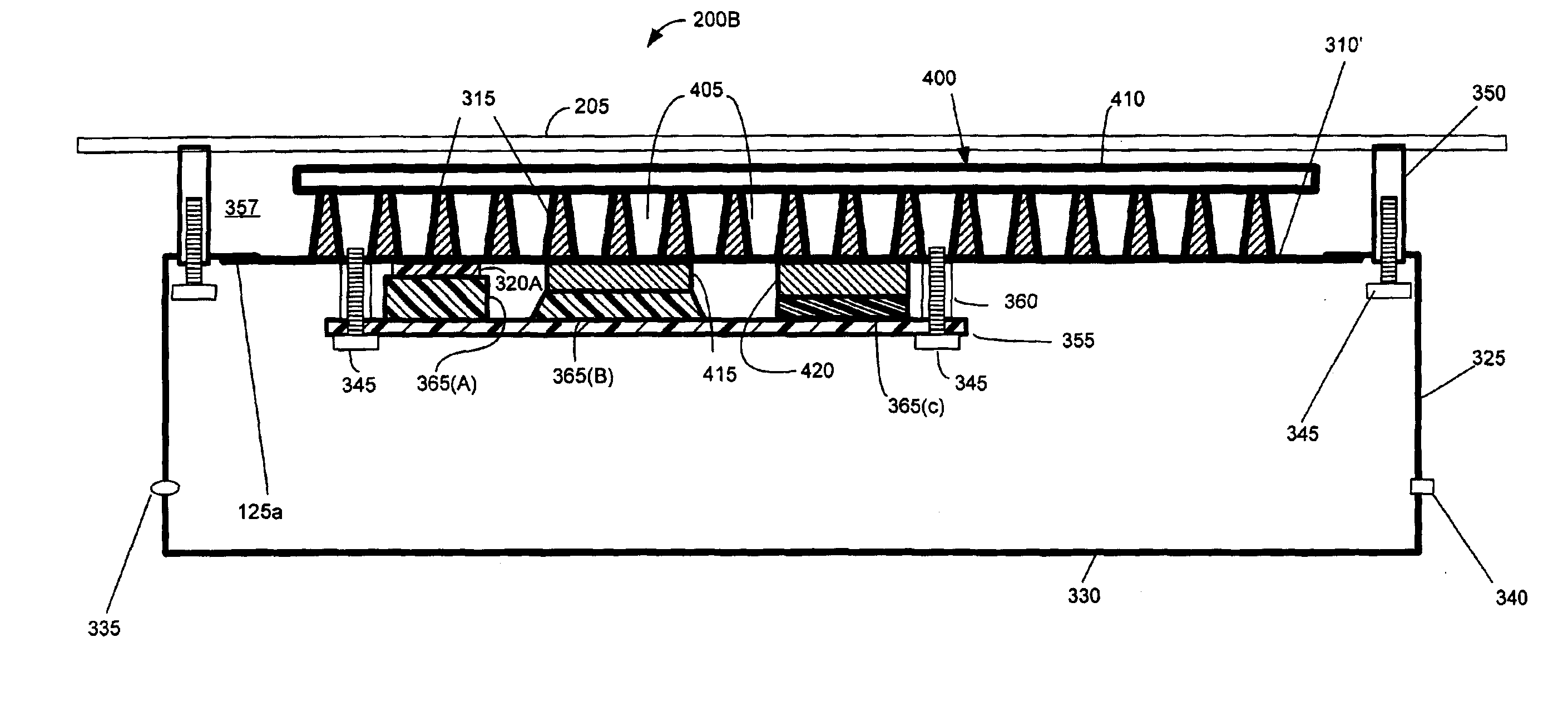
InactiveUS7038910B1Minimizing transferMaximize heat transferCouplings bases/casesHeat exchange apparatusEngineeringPartial closure
A system and method removes heat from an enclosure or housing of a subscriber optical interface. When a subscriber optical interface housing is attached to a structure such that a partially enclosed volume of space remains between the structure and the subscriber optical interface housing, this partially enclosed volume of space can produce a chimney effect when heat from the subscriber optical interface housing is intended to flow from fins towards the structure. This chimney effect can refer to a fluid such as air within the partially enclosed space that is heated by the fins and that rises upward when the ambient or surrounding fluid is cooler relative to the heated fluid. According to another exemplary embodiment, the subscriber optical interface can be shaped to form an internal chimney structure that is entirely surrounded by a housing of the subscriber optical interface.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
Cover for remote control device
InactiveUS20060124482A1Minimizing transferEasy to captureOther accessoriesElectric switchesRemote controlEngineering
A disposable cover for use with a remote control device for providing a protective sanitation barrier to human infection includes a rear member having a flat surface. A front curved member is integrally molded in a seamless unitary, one-piece construction with the rear member at a plurality of rounded surfaces to form a single-use, disposable protective enclosure. An anti-bacterial compound impregnates the rear member, the front curved member and the rounded surfaces for destroying bacteria on the remote control device. An orifice is formed in the rear member for enabling the remote control device to be inserted into and removed from the enclosure. Finally, the front member, rear member and the rounded surfaces are comprised of a flexible, stretchable and transparent material for conforming to the shape of the remote control device for providing a disposable, protective sanitation barrier to human infection.
Owner:HODGES RICHARD P
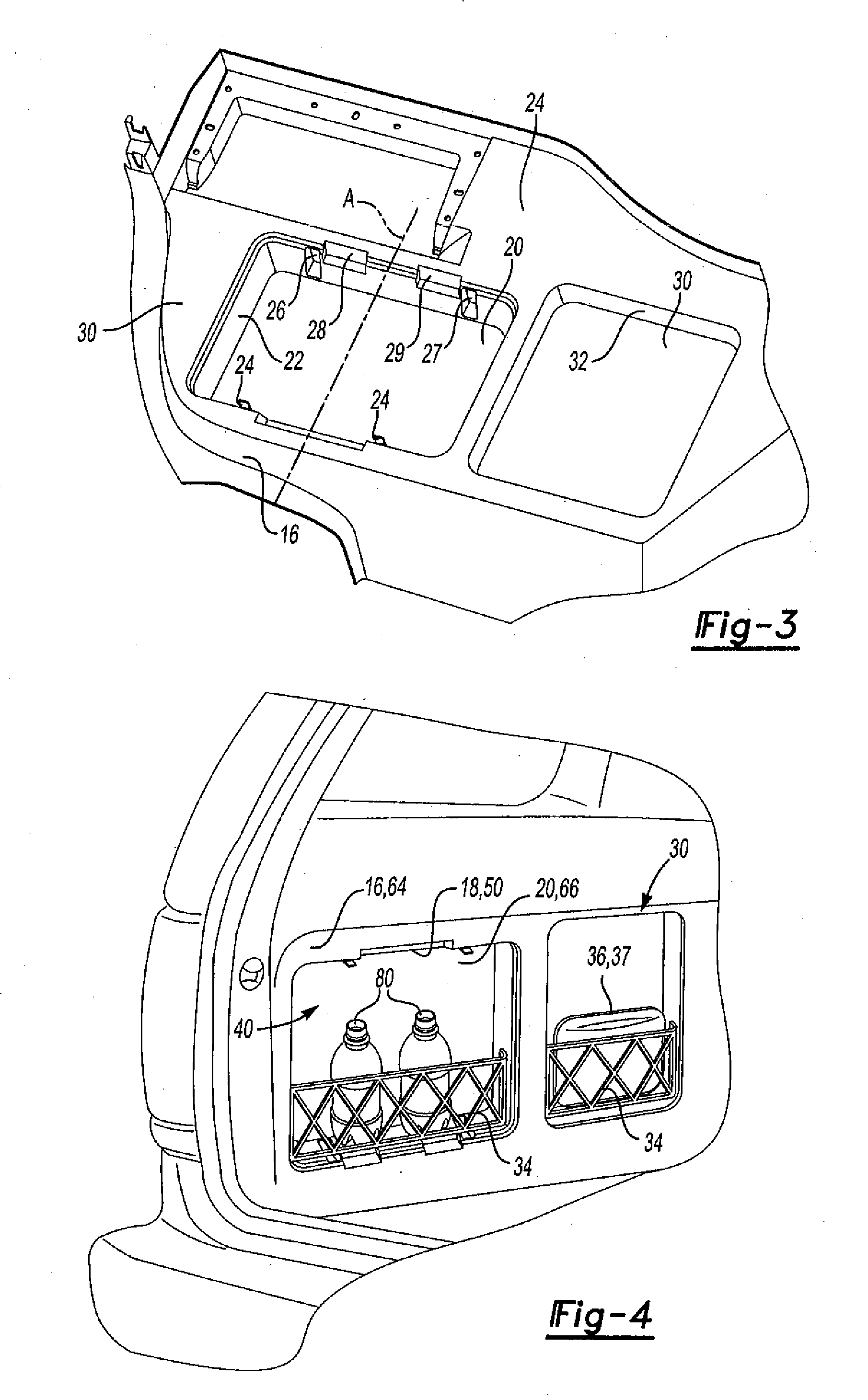
Trim Assembly For A Vehicle
InactiveUS20090001748A1Minimizing transferMinimizes ejectionMonocoque constructionsVehicle bodiesEngineeringConcave surface
A trim assembly for an interior of a passenger compartment of a vehicle comprises a first panel, a first shell, and a second shell. The first panel forms interior trim for the vehicle and defines a first receptacle. The first shell defines a convex surface and a concave surface and is removably coupled within the first receptacle so that one of the convex surface and the concave surface is exposed. The second shell defines a convex surface and a concave surface and is matable to the first shell to define a case. The case is removable from the first receptacle.
Owner:BBI ENTERPRISES GROUP
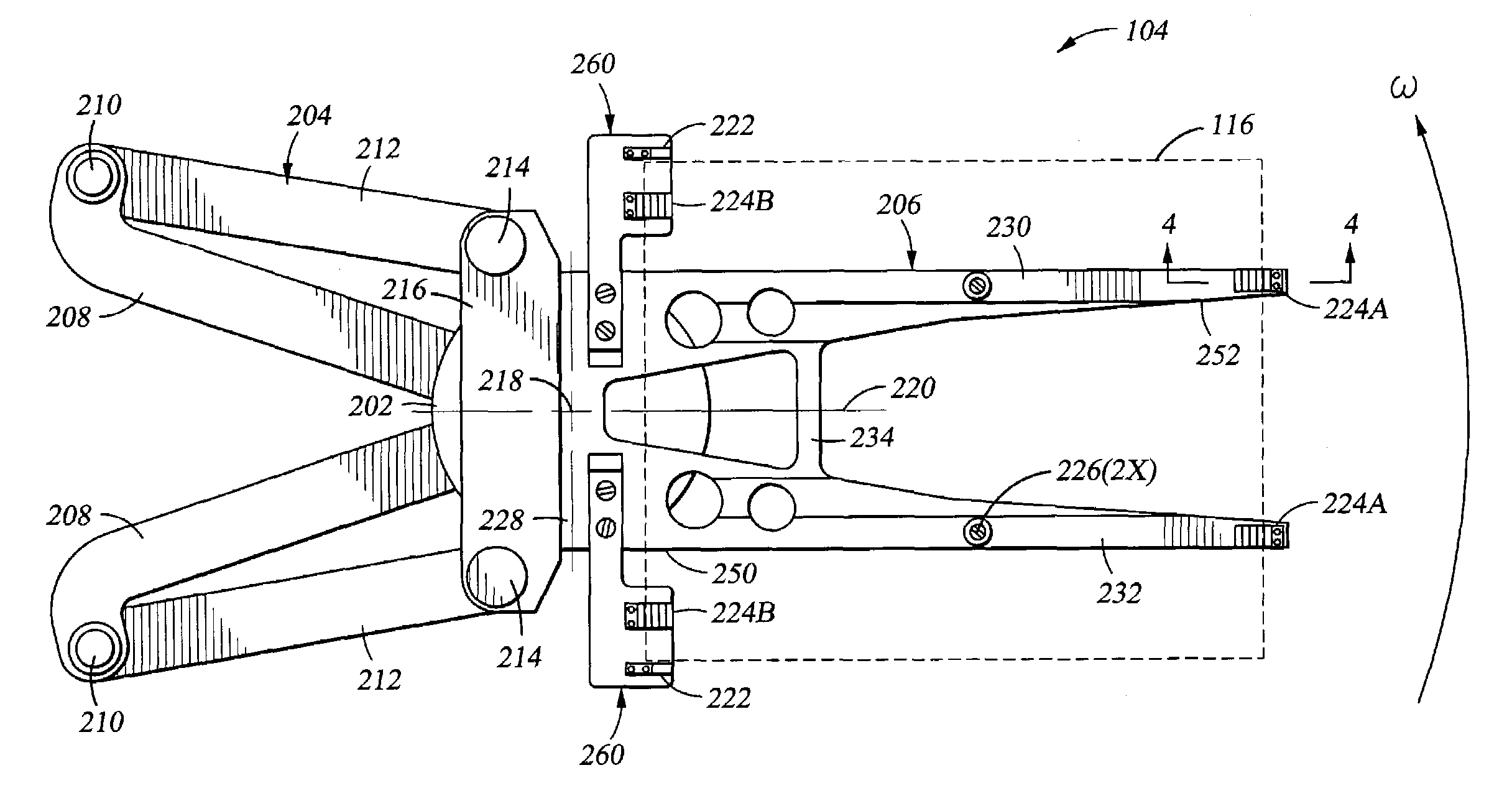
Clamp for clamping a blade for a wind turbine and method of installing wind turbine blades
InactiveUS20110185571A1Easy constructionLow costEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureTurbine bladeEngineering
A clamp for clamping a blade for a wind turbine is provided. The clamp includes a first contact surface adapted to contact a portion of a surface of the blade and a second contact surface adapted to contact another portion of the surface of the blade. The second contact surface is displaceable relative to the first contact surface. The clamp also includes a bar connected in an adjustable orientation relative to the first contact surface. Further, a method of installing wind turbine blades at a hub rotatable around a rotation axis along a horizontal direction is provided.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
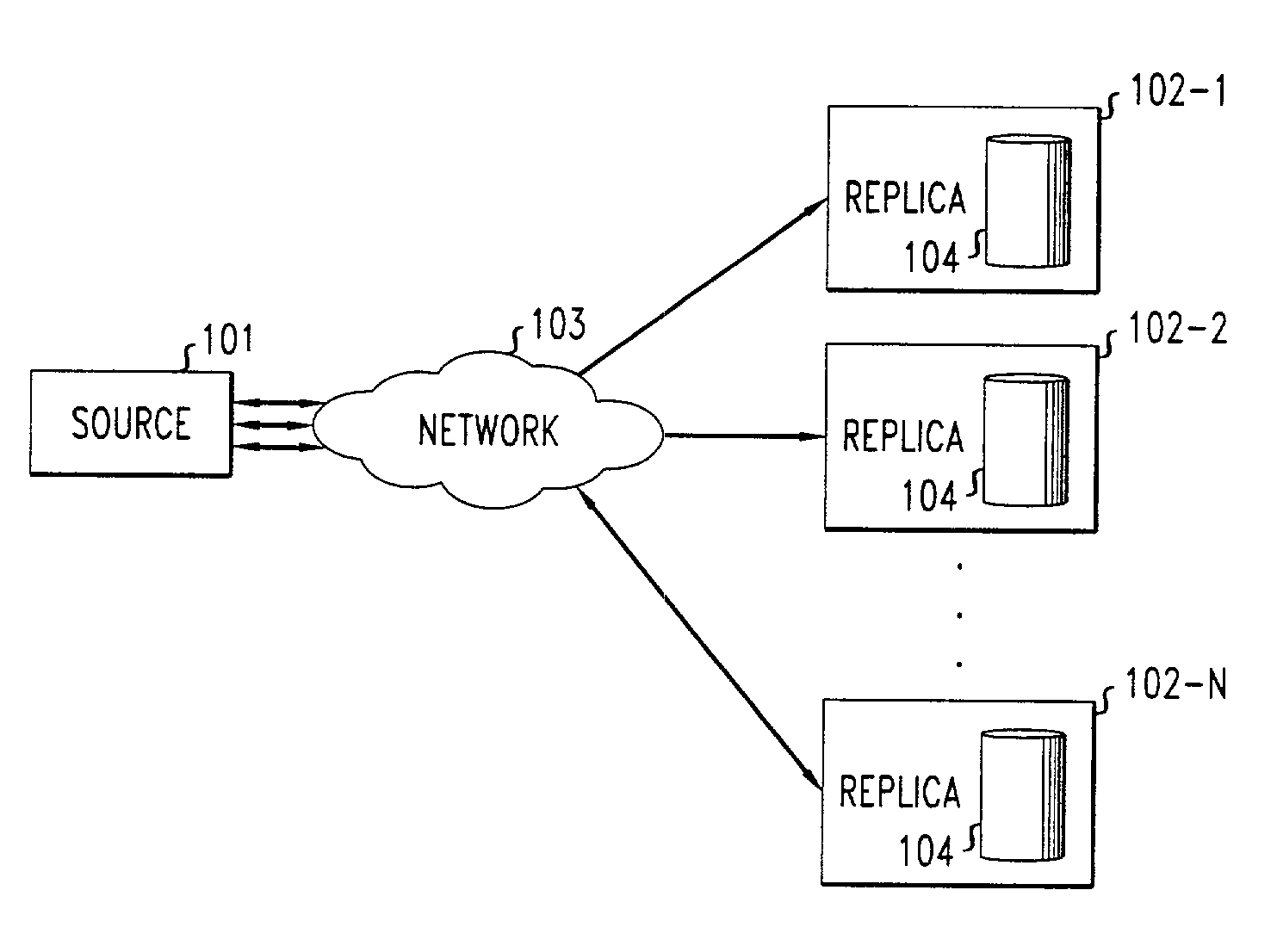
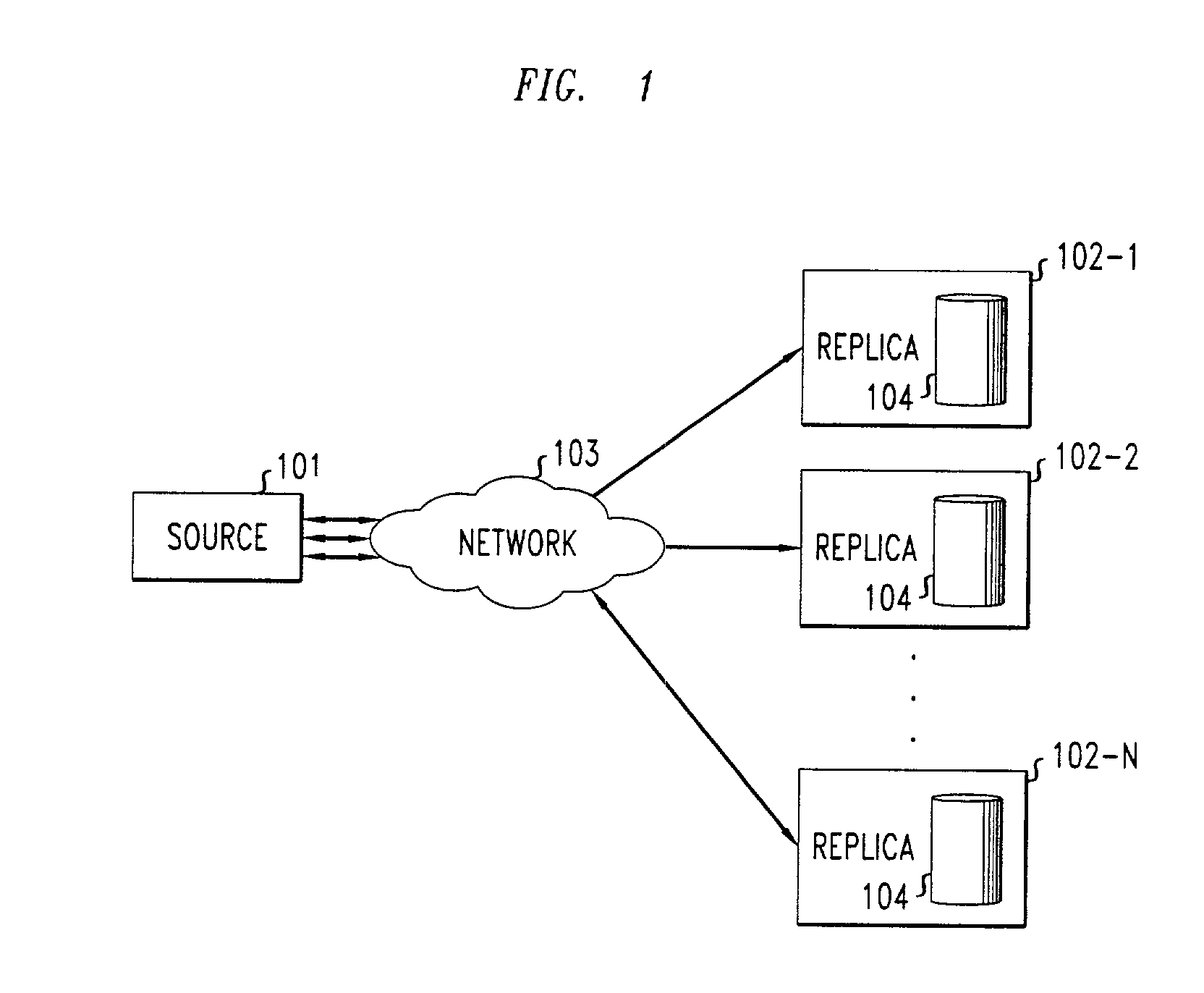
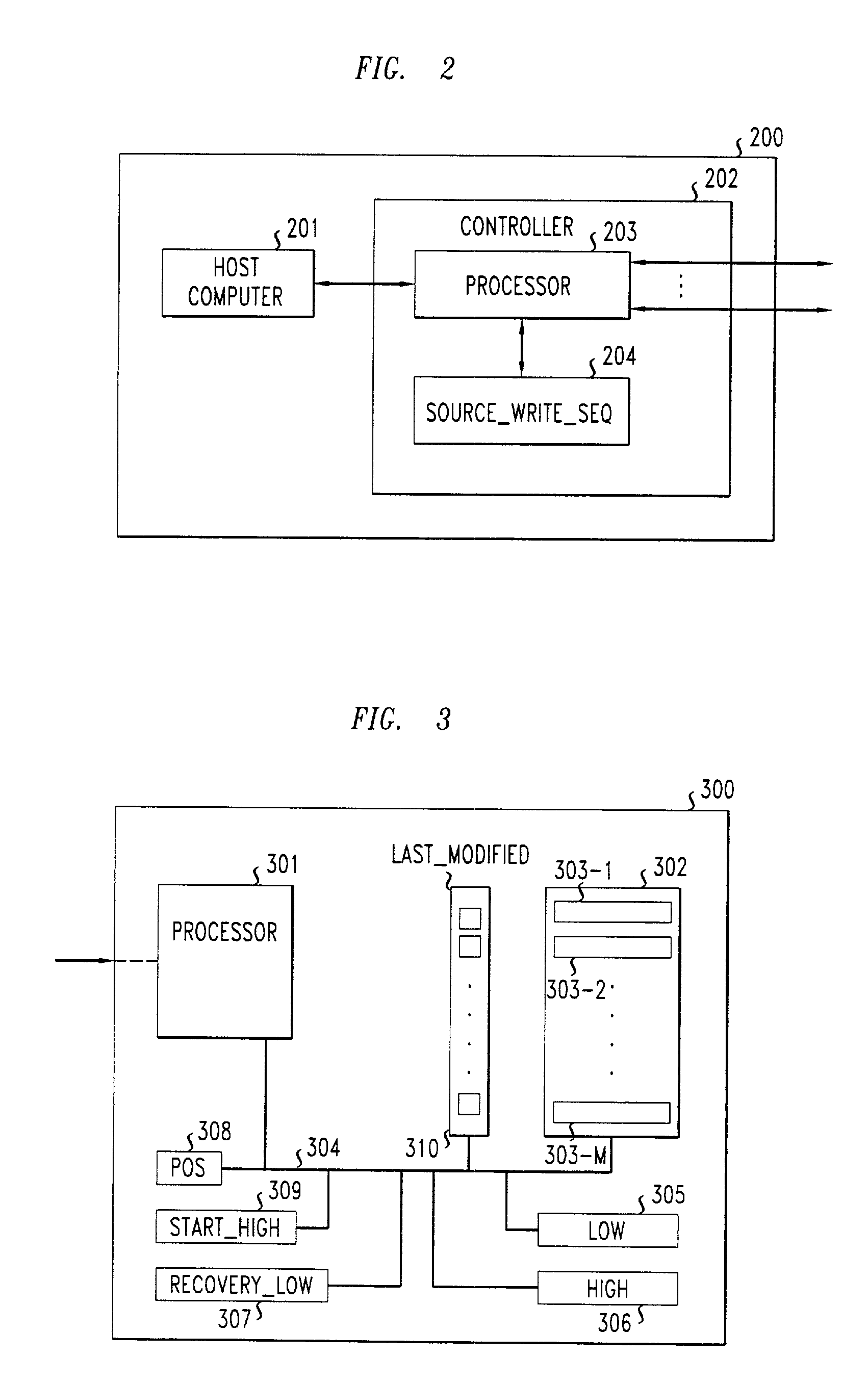
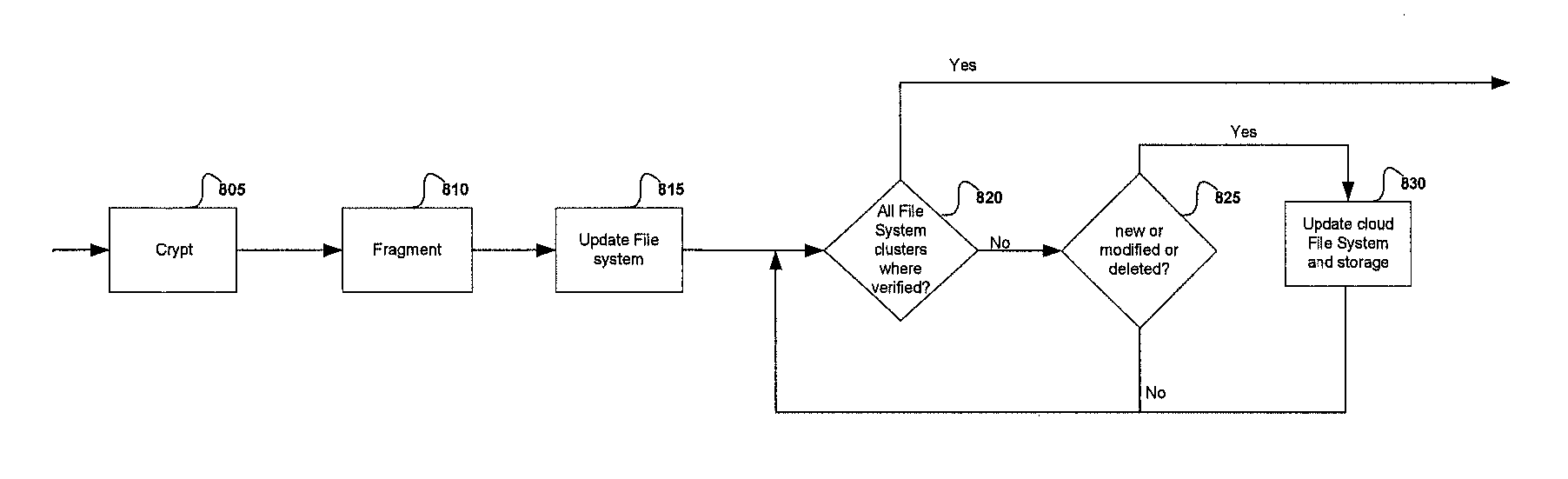
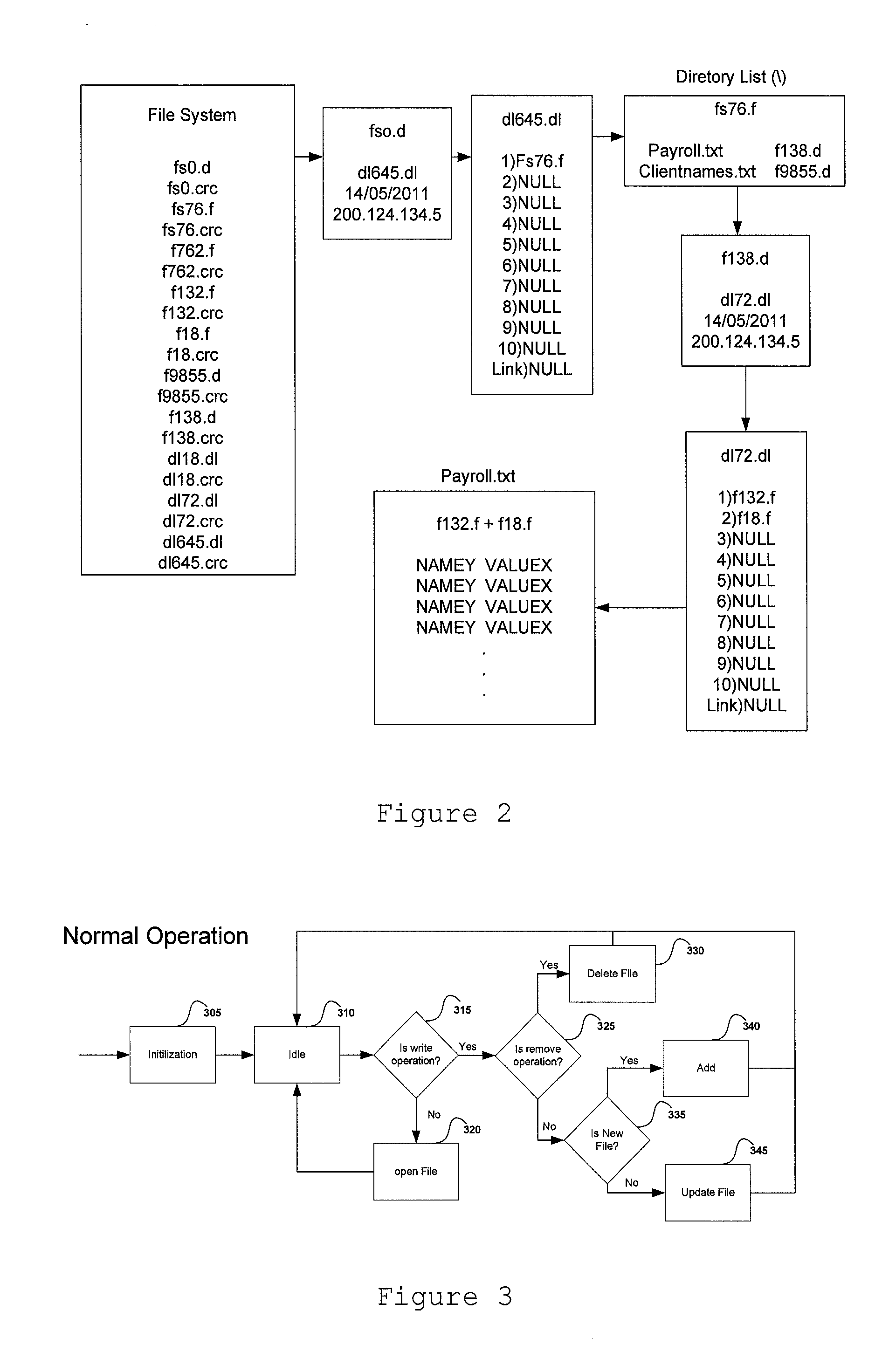
Method for maintaining consistency and performing recovery in a replicated data storage system
ActiveUS7103884B2Slow recoveryAchieve consistencyDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsData storage systemDistributed computing
A recovery process allows a recovering replica in a replicated data storage system to recover from a current replica the changes to the data that it has missed during a failure while, at the same time, the system is processing new requests issued by the source. Sequence numbers, assigned by the source to write requests and stored by each replica in association with the data item that the write request modifies, are used by the recovery process to determine when a replica has missed one or more write requests and requires recovery. During recovery, the recovering replica ignores all requests directly received from the source, and replaces the contents of a data item with the data received from the current replica only if the newly received data item has a higher sequence number than the corresponding sequence number of the data item already stored in the recovering replica. It also updates data items in response to new write requests that are forwarded to it by the current replica. At the same time, the current replica continues to receive requests from the source, performs those requests, and forwards those write requests to the recovering replica. It also scans its data items and sends to the recovering replica those data items and associated sequence numbers that have a sequence number higher than the sequence number of the last consecutive write request sent by the source that the recovering replica received before missing a write request.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
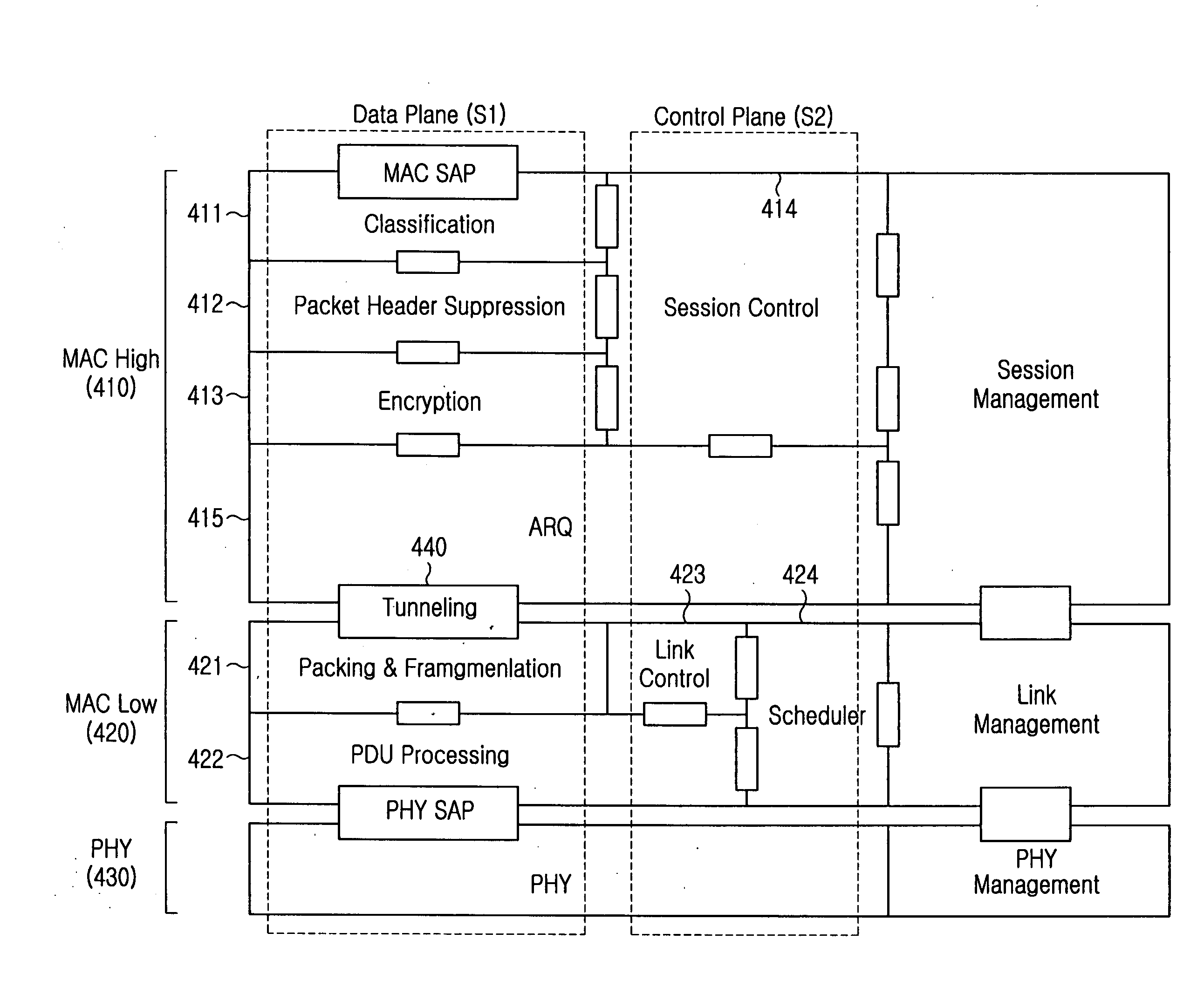
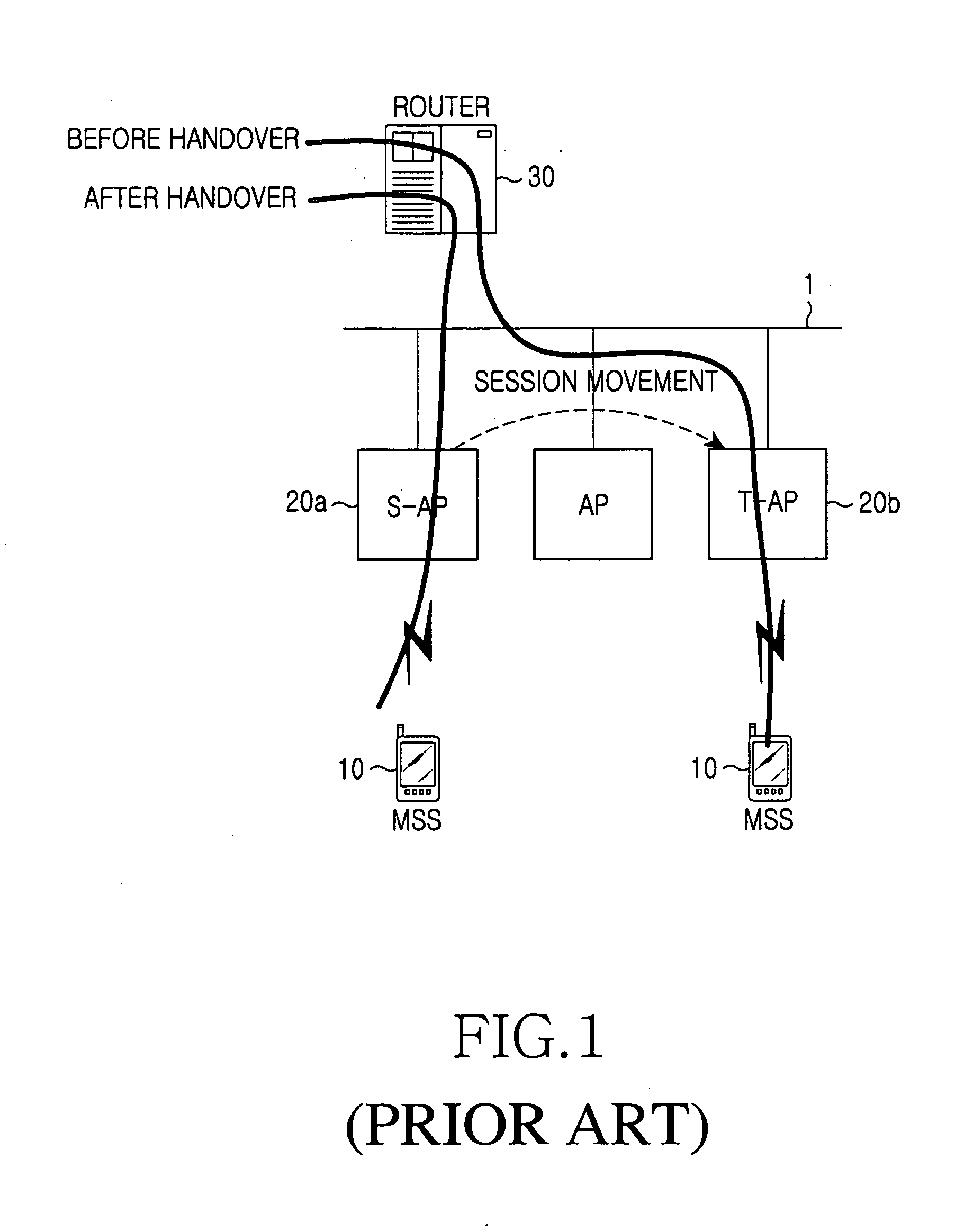
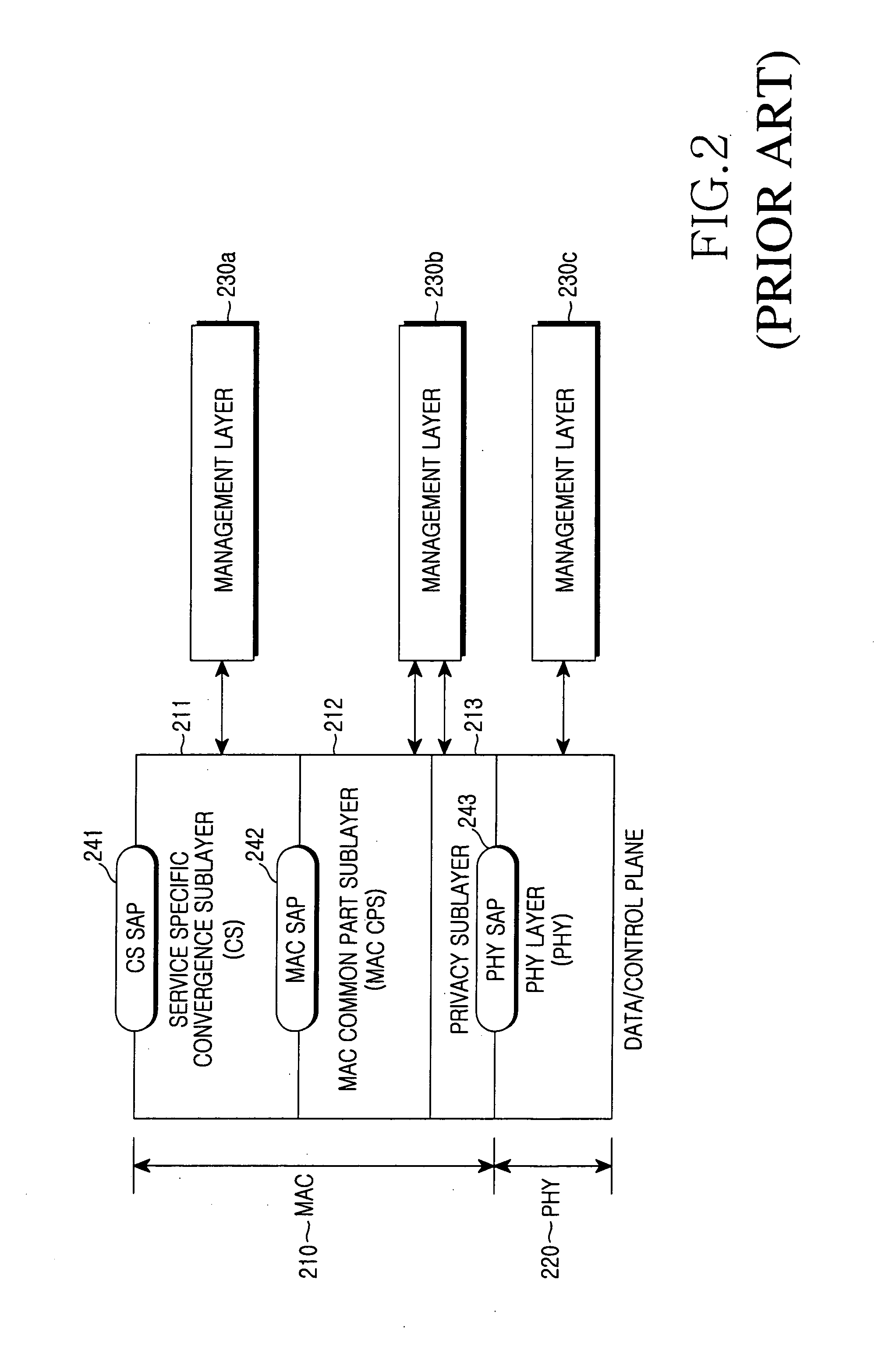
Divided MAC protocol structure, data transmission and reception method, and handover method and system using the structure in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20050195822A1Minimizing transferReduce loadError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemCommunication quality
A divided Media Access Control (MAC) protocol structure, a data transmission and reception method, and a handover method and system using the structure in a wireless communication system for efficiently managing session information in handover of an MSS (Mobile Subscriber Station). In the MAC protocol structure, a MAC is divided into a MAC-high layer and a MAC-low layer. The MAC-high layer performs session information-related functions and the MAC-low layer performs functions sensitive to a time delay in relation to handover of an MSS. In the handover method, when an MSS in the wireless communication system performs handover between Access Points (APs), session information is managed at a fixed position by an Access Point Controller (APC) including an MAC-high layer or a serving AP. Therefore, the system load can be reduced and communication quality can be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for removing heat from a subscriber optical interface
InactiveUS7355848B1Minimize heat transferMaximize heat transferCouplings bases/casesHeat exchange apparatusEngineeringStack effect
A system and method removes heat from an enclosure or housing of a subscriber optical interface. When a subscriber optical interface housing is attached to a structure such that a partially enclosed volume of space remains between the structure and the subscriber optical interface housing, this partially enclosed volume of space can produce a chimney effect when heat from the subscriber optical interface housing is intended to flow from fins towards the structure. This chimney effect can refer to a fluid such as air within the partially enclosed space that is heated by the fins and that rises upward when the ambient or surrounding fluid is cooler relative to the heated fluid. According to another exemplary embodiment, the subscriber optical interface can be shaped to form an internal chimney structure that is entirely surrounded by a housing of the subscriber optical interface.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
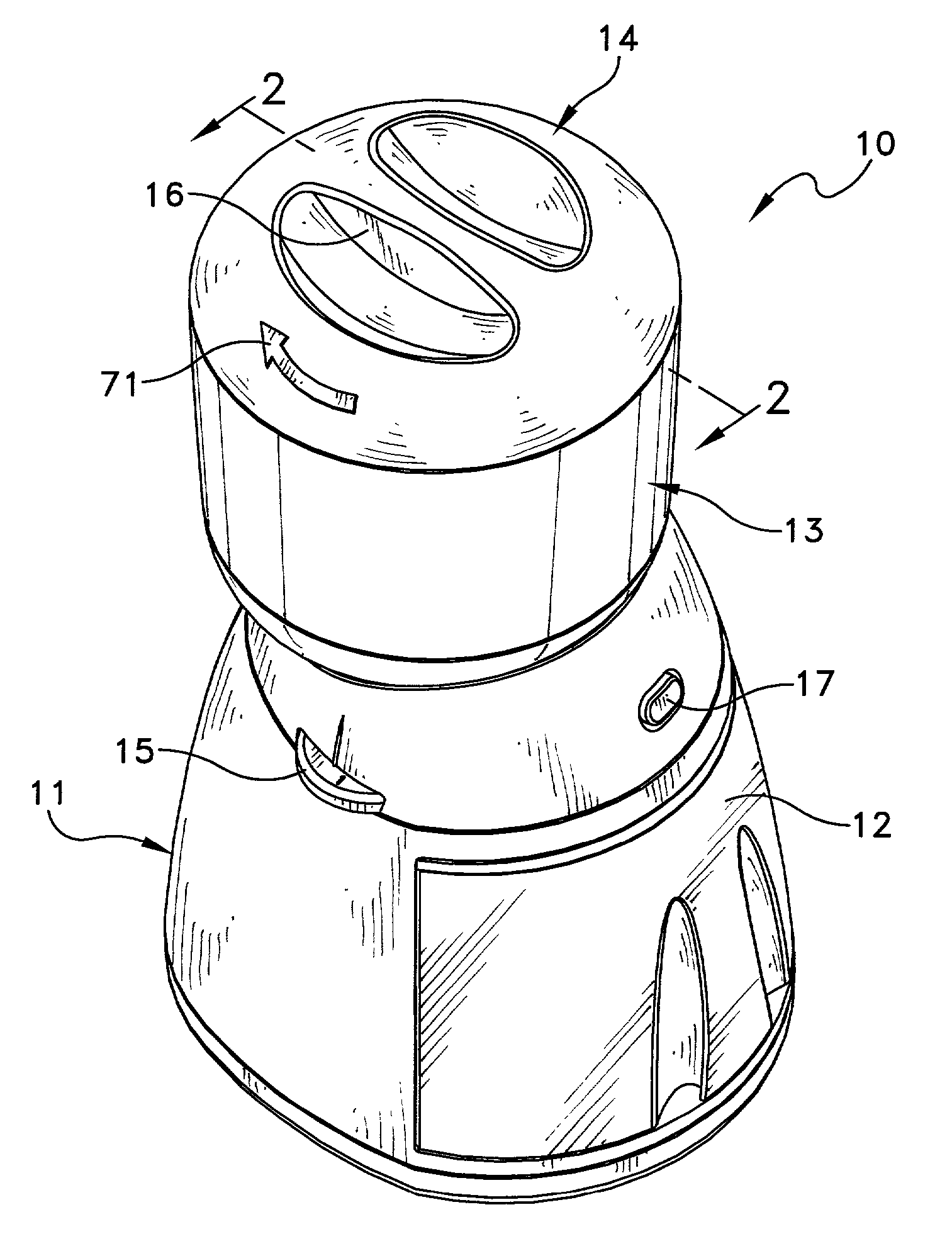
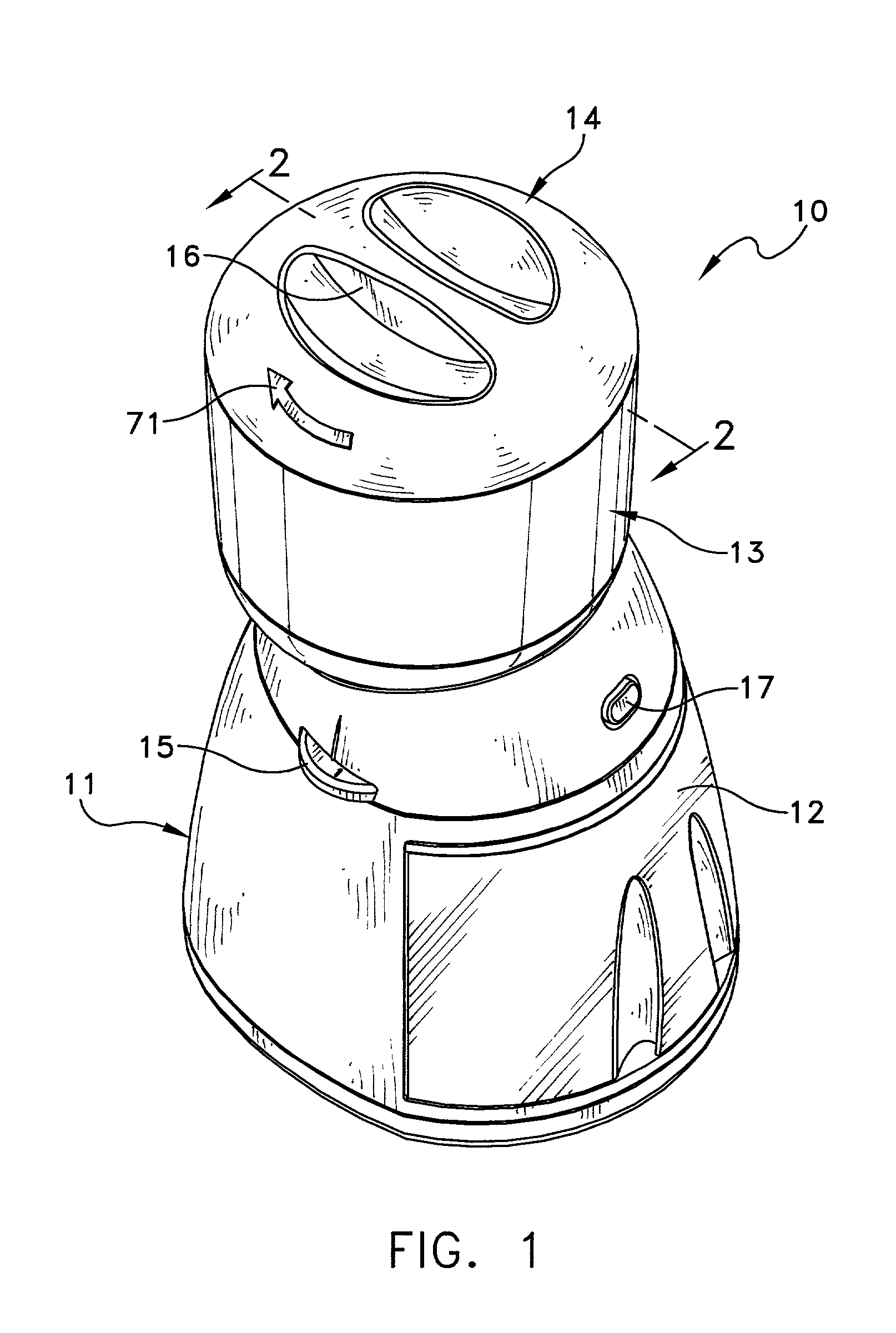
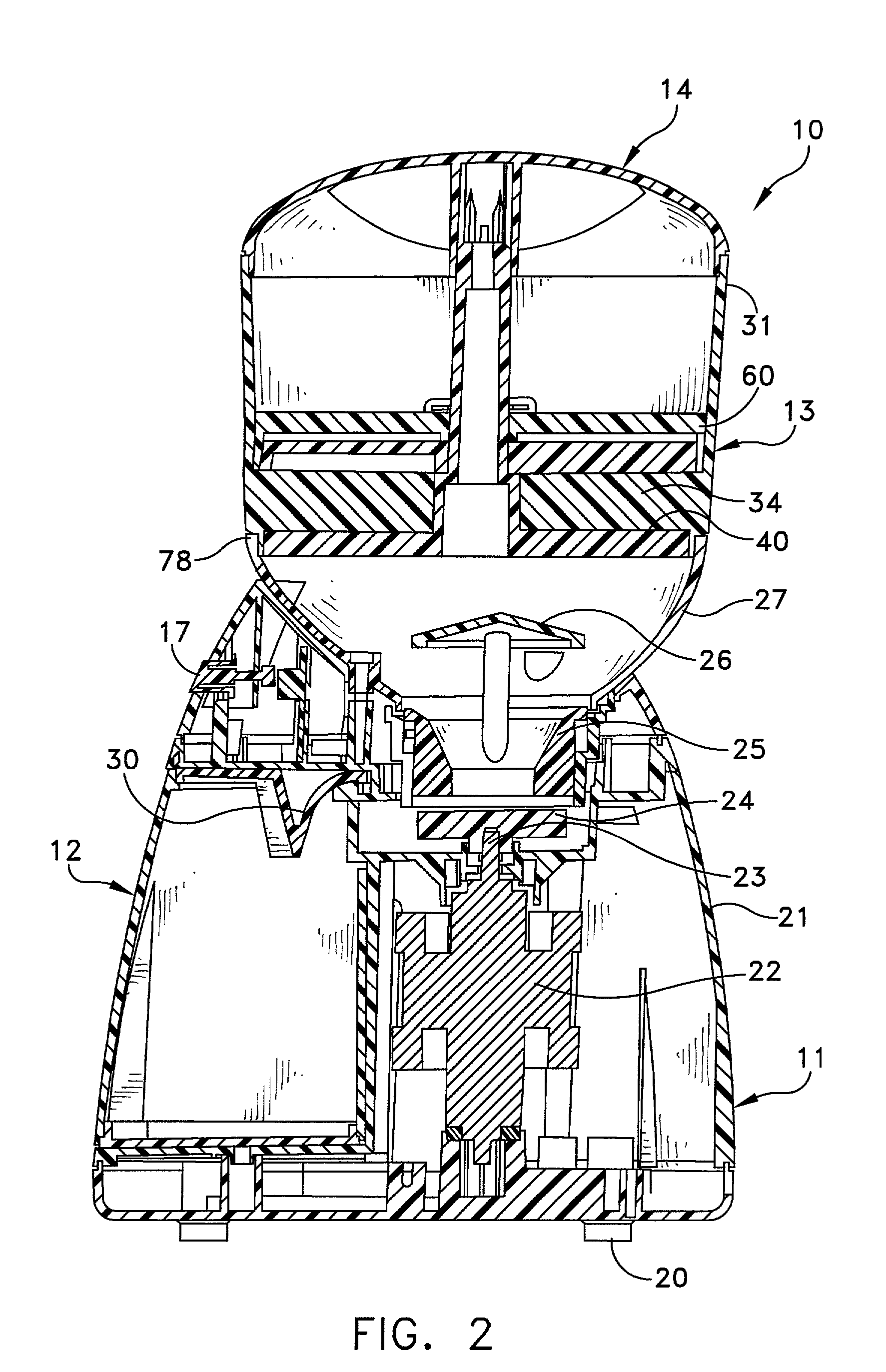
Coffee grinder with storage and dispensing means
InactiveUS20020153438A1Minimizing transferEasy to controlCoffee millsSpice millsEngineeringDistributor
A coffee grinder with a removable storage and dispensing element that has a housing and rotatable assembly in the housing. The rotatable assembly includes a distributor allows a single one of multiple open sectors to be filled in any given position. A dispensing component has an open sector angularly offset from the open sector of the distributor. When the dispensing component open sector aligns with a filled sector, the beans drop into a hopper for grinding. A grinder operates until all the beans in the hopper are ground.
Owner:APPLIANCE DEVMENT
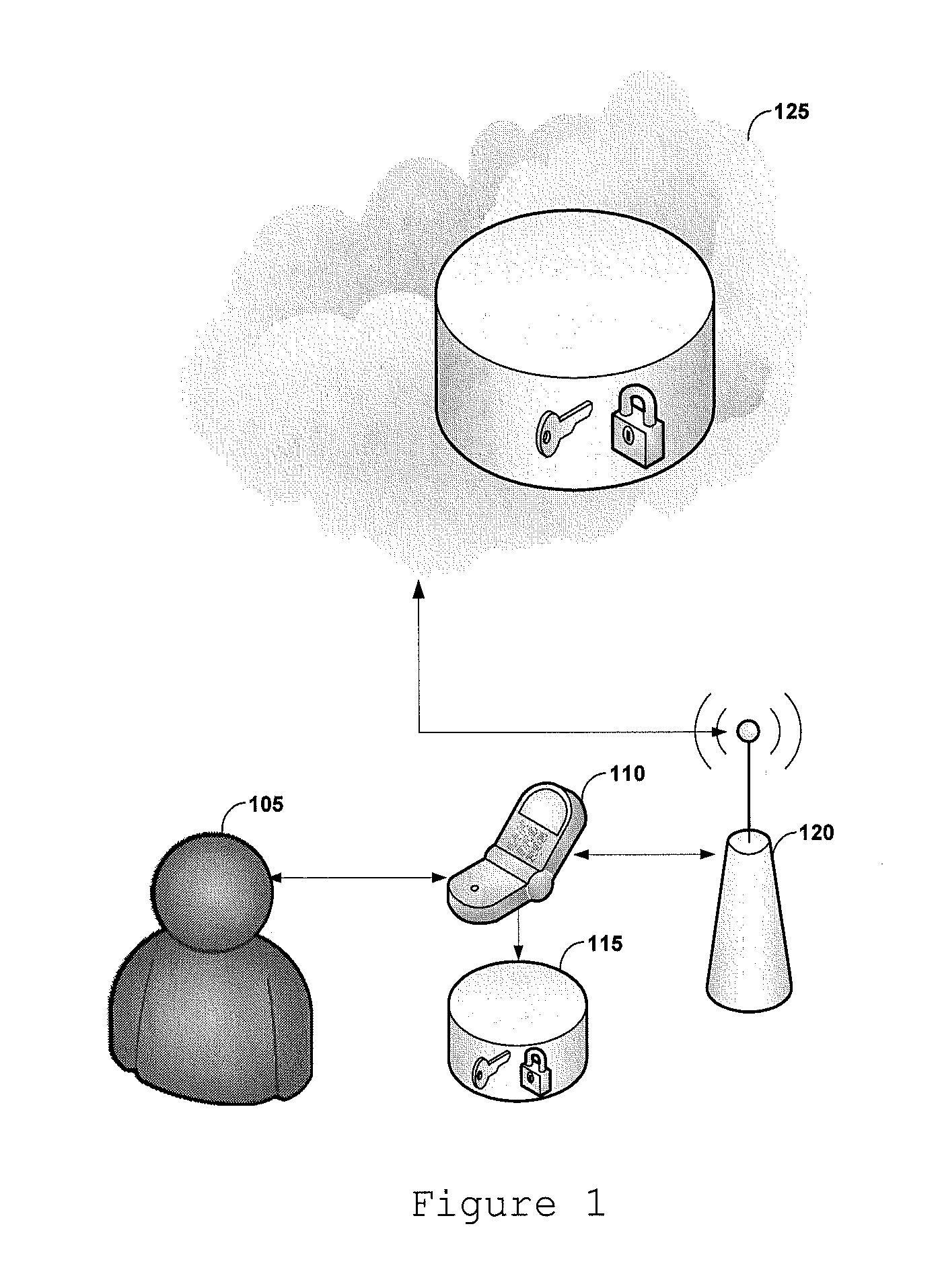
Secure storage system for distributed data
ActiveUS20130173916A1Minimizing transferImprove securityComputer security arrangementsSecuring communicationComputer securityCloud storage
The present invention relates to a system for distributed data storage that ensures the safety of the user data. In particular, the system of the present invention provides that the data stored in a cloud storage service are encrypted and their cryptographic keys are created from a remote device. In the context of the present invention, cloud is a set of servers that form an online service over the Internet, these servers are invisible to the user of the service pretending they form only a single server, thus forming a “cloud servers”. These keys will be divided and stored in cloud storage part and part on other devices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICSA AMAZONIA
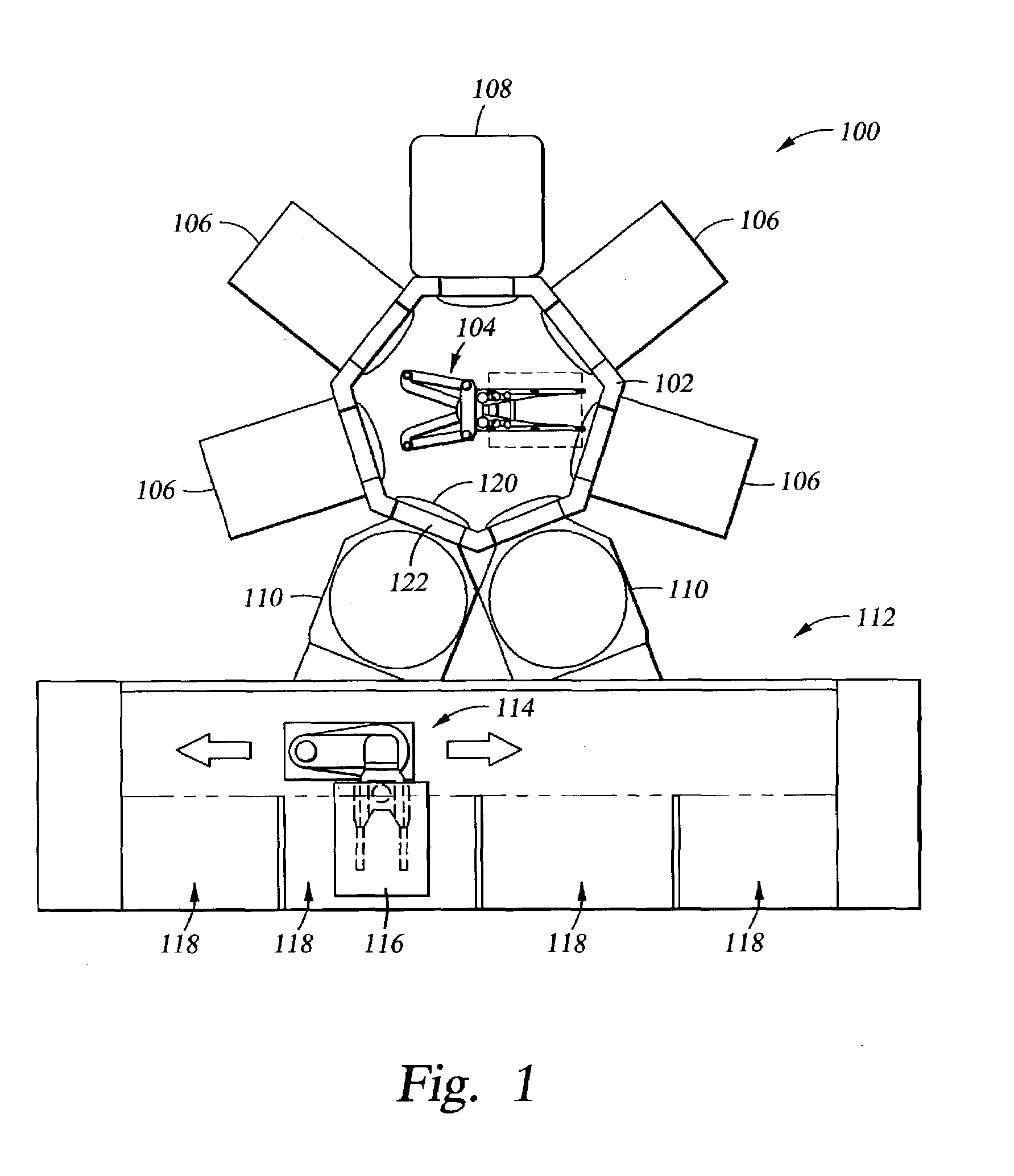
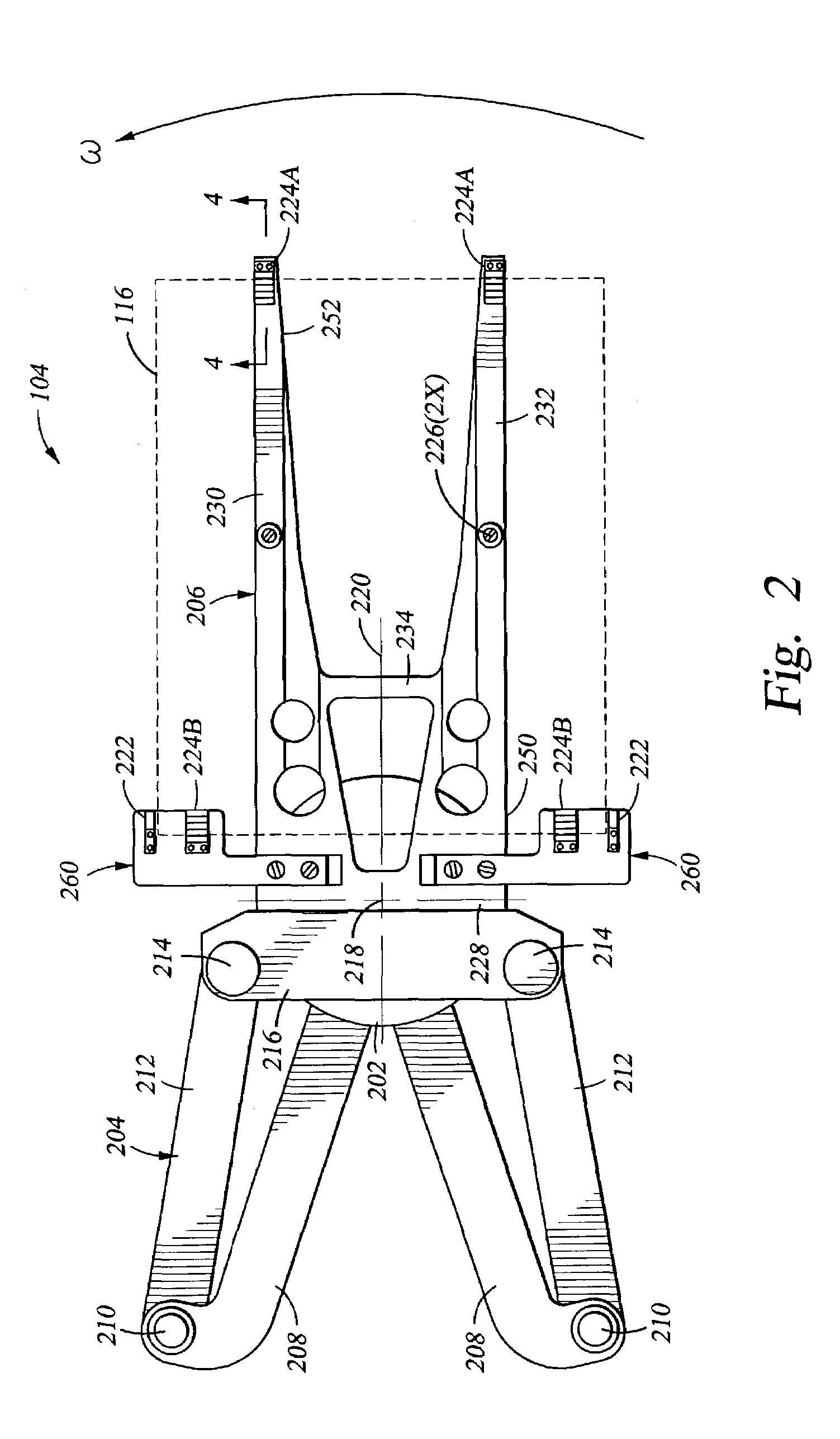
End effector assembly for supporting a substrate
InactiveUS7641247B2Minimizing transferEasy to captureGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringActuator
Generally, an end effector assembly for a substrate transfer robot is provided. In one embodiment, an end effector assembly for supporting a quadrilateral substrate during substrate transfer includes an end effector having an inner edge support disposed on a first end and a first outer edge support disposed on a distal end. The first end of the end effector is adapted for coupling to a robot linkage. The first inner edge support has a face that is oriented parallel to and facing the face of the first outer edge support. This configuration of edge supports captures the substrate to the end effector thereby minimizing substrate slippage during transfer. In another embodiment, lateral guides may be utilized to further enhance capturing the substrate along the edges of the substrate open between the inner and outer edge supports.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
System for individual and group editing of networked time-based media
InactiveUS20090129740A1Minimizing transferMinimizing dataTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer graphics (images)Video Media
The present invention provides an easy to use web-based editing tool for time-based video content and media. The proposed system operates with metadata drivers for controlling a playing device without changing underlying encoded video data by tracking and recording playback decision actions by an operator / editor / user. Multiple user edits and multiple edit levels are enabled by tracking each step of the playback decision action and linking each to the underlying time-based video media.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
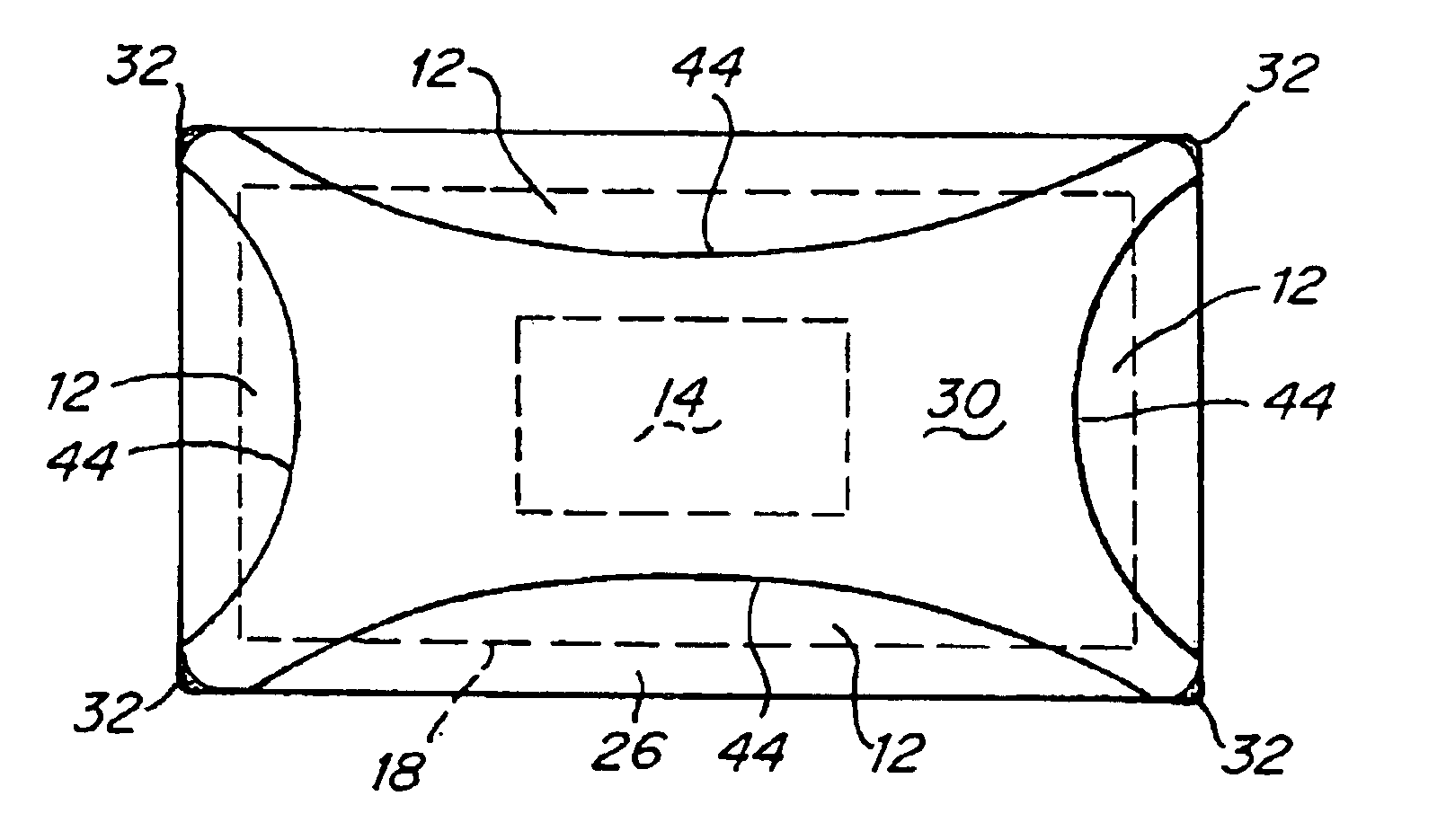
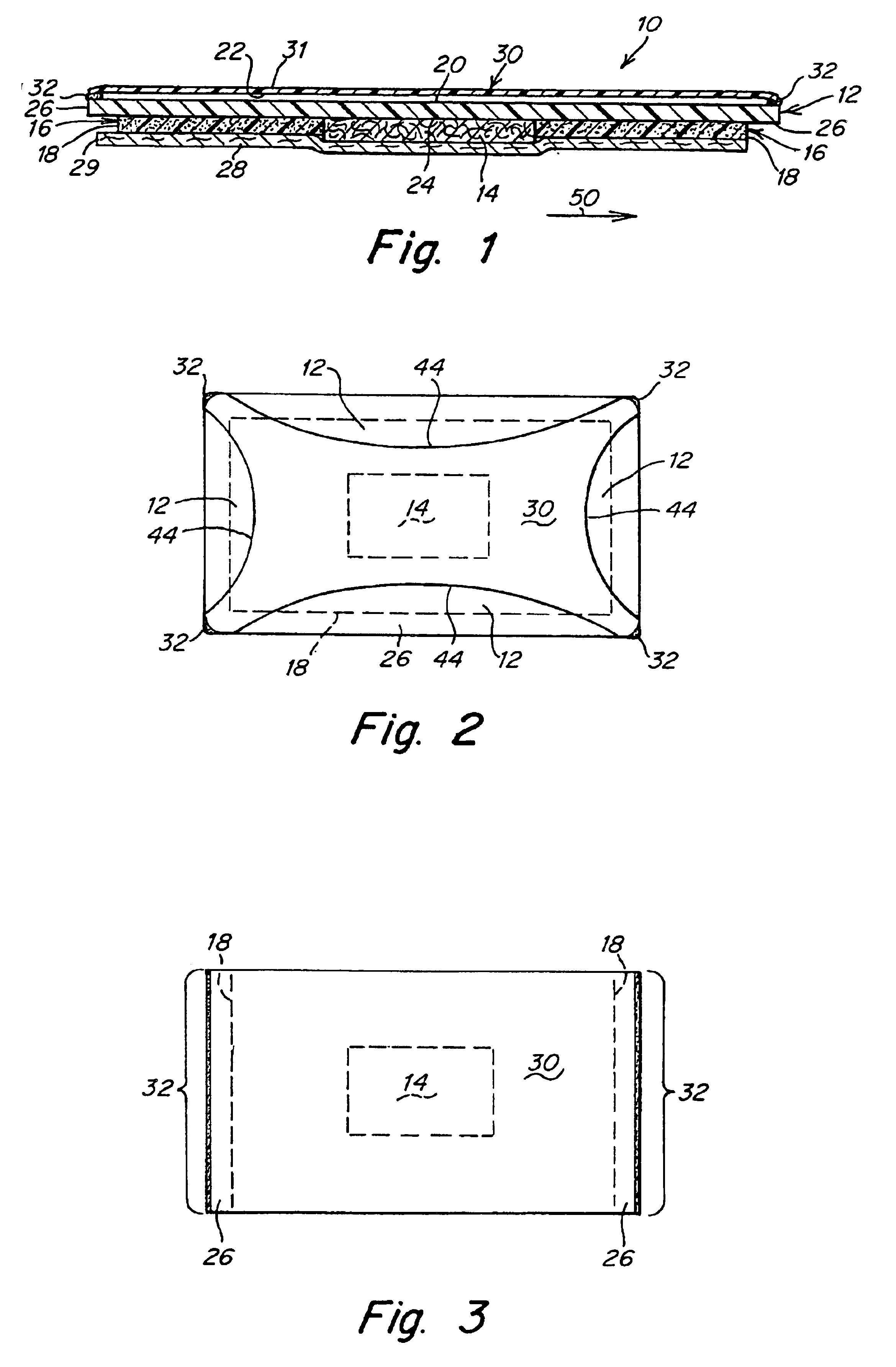
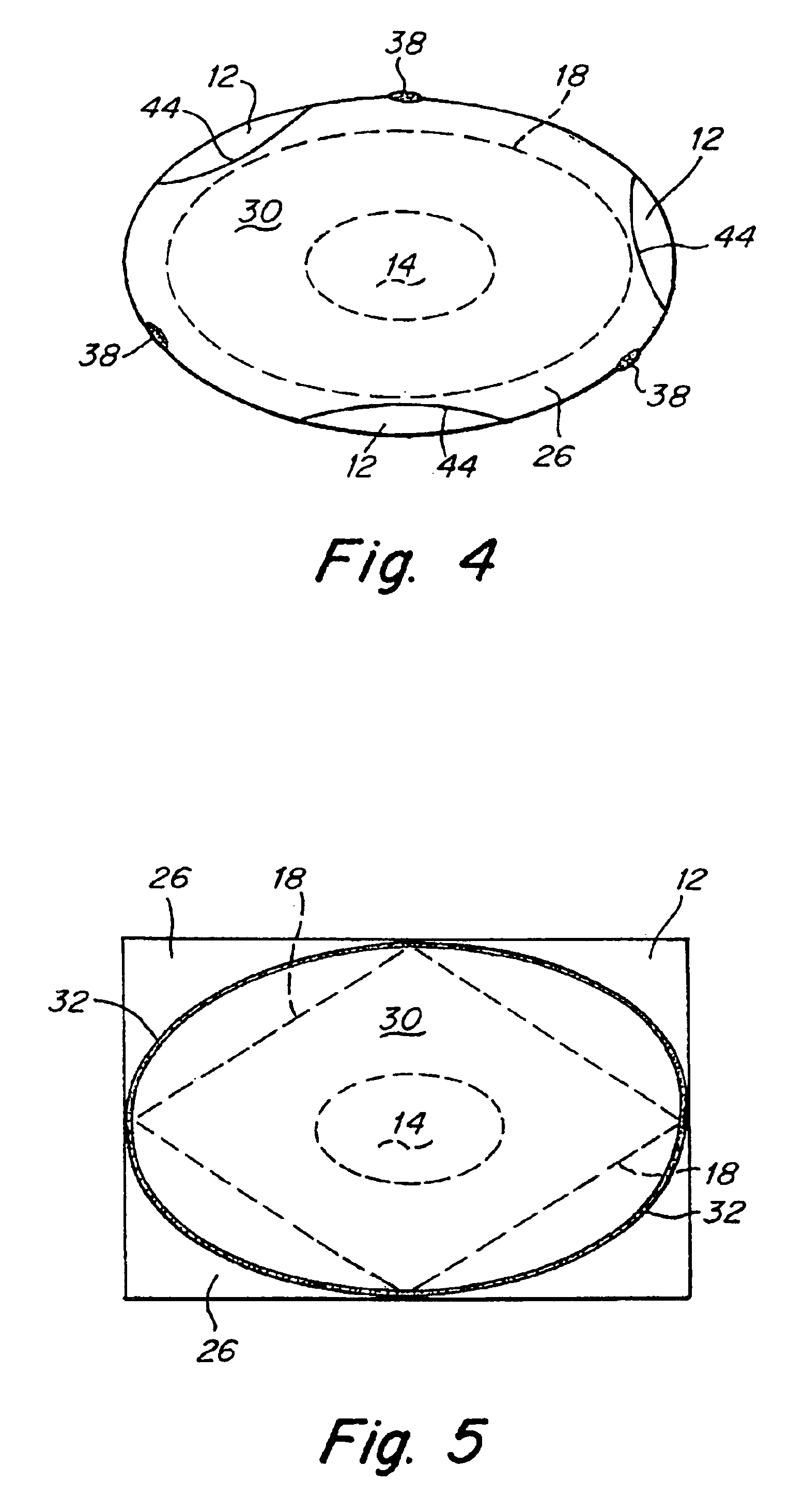
Adhesive bandage for protection of skin surfaces
An adhesive bandage is disclosed for protecting blisters or wounds, or for preventing chaffing or the formation of blisters. In one embodiment, the bandage includes a protective layer for covering the blister or area of skin to be protected, and an adhesive layer surrounding the protective layer. The opposite side of the bandage contains a low-friction layer or surface and a separate sheet of low-friction material adjacent to but movable with respect to the low-friction layer or surface. The sheet of low-friction material is attached to the bandage in such a way that it can move with respect to the bandage in response to frictional forces, thereby minimizing a transfer of frictional forces from clothing or the like to the bandage. A method of treating blisters, as well as a method of preventing chaffing and the formation of blisters are also disclosed.
Owner:DMWCO LLC
Motor driven sampling apparatus for material collection
InactiveUS20050044971A1Eliminates manual exertionReduce torqueWithdrawing sample devicesMotor driveSource material
An apparatus to excise a sample of material and temporarily store sample has a tubular clamshell casing at an angle to the horizontal, blended to a tubular boss under which is a tubular sample sleeve extending downwards from the boss. Within the casing an electric motor is housed which drives, via gears, the sample sleeve in a rotational manner. The end of the sleeve, distal from the boss, forms a cutting edge circumscribing a circular region. An ejection rod slides reciprocally within the sample sleeve between a stowed position and an expulsion position. When the ejection rod moves from the stowed position to the expulsion position, it will extend past the cutting edge and expel any sample of material contained within the cutting sleeve. A user cuts a sample from a source material using the cutting blade of the apparatus when the ejection rod is in the stowed position. The sample is cut when the cutting blade engages contact against the sample and gentle downward pressure is applied while a finger trigger activates the electric drive to rotate the cutting sleeve. Alternately a user may cut a sample from a source material by engaging contact between the cutting edge of the tubular sleeve and the source material, applying downward pressure against the source material thereby activating the electric drive to rotate the tubular cutting sleeve. Once the source material has been cut it is simultaneously extracted and lodged within the tubular sleeve. The extracted sample remains lodged in the tip of the tubular cutting sleeve until the user actuates the ejection rod through the sleeve to the expulsion position to eject the sample of source material. Return actuation of the eject rod is comprised of a coil spring that biases the rod in the retracted stowed position.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Recording apparatus equipped with heatsink
A recording apparatus having: (a) a head unit including an actuator which generates energy required for recording predetermined patterns of image on a recording medium; (b) a circuit board including a driver element which drives the actuator of the head unit; and (c) a heatsink disposed in thermally conductive communication with the driver element. The heatsink has a void portion which is opposed to the head unit.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Multilayer structure for the manufacture of packaging and packaging thereof
InactiveUS20100272936A1Minimizing transferFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsChlorideEngineering
A multilayer structure comprises at least one barrier layer comprising at least one vinylidene chloride polymer, at least one UV protecting layer, and at least one reflective layer wherein none of these layers also serve as a sealing layer. The multilayer structure is preferably a film, more preferably in the form of a pouch, preferably for packaging flowable product, especially milk. When used as a milk pouch, the structure is more effective at protecting milk from deterioration at ambient temperature and humidity than is a similar multilayer structure having an ethylene vinyl alcohol barrier layer. The multilayer structure preferably has more than one reflective layers and is preferably in the form of a pillow pouch. The invention also includes a process comprising steps of (a) supplying at least one first composition comprising at least one vinylidene chloride polymer, at least one second composition comprising UV absorbing pigment or agent, and at least one third composition comprising at least one light reflective material, to a coextrusion die and (b) coextruding the first, second and third compositions as layers referred to herein after as the barrier layer, UV protecting layer, and reflective layer respectively.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Air ride system for a tractor cab
InactiveUS7950726B2Smooth rideRestricts vertical movementVehicle seatsStands/trestlesJoystickAir line
An air ride system is provided for tractors and other agricultural vehicles to provide a smooth operator ride. The system includes a bracket mounted to the transmission housing beneath the cab. A pair of shock absorbers and a pair of air bags extend between the bracket and the cab so as to absorb forces generated during travel of the vehicle over the ground. A laterally extending control rod provides anti-sway for the cab. Stop members limit the upward and downward travel of the cab relative to the transmission housing. A compressor and air lines allow air to be supplied to or removed from the air bags to adjust the ride.
Owner:BROWN KEITH R
Method of making a laundry detergent article containing detergent formulations
InactiveUS6864196B2Reduce usageEasily solubilizedInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsEngineeringLaundry
A laundry sheet is disclosed which is a substrate having a laundry detergent applied thereto. The laundry detergent readily solubilizes off of the substrate sheet during the washing process to provide a total laundering process that cleans and softens. Also disclosed are several laundry detergent formulations which are preferably applied onto the substrate to make the laundry sheet of the present invention and a process for making the laundry sheet.
Owner:NEWLUND LAB +1
System and data model for shared viewing and editing of time-based media
InactiveUS20090116812A1Minimize total bit transferMinimizing data transferTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMetadataData model
The present invention provides a system and method for enabling shared viewing and editing of time-based media with improved speed by avoiding manipulation and re-manipulation of a stored underlying video data format through the use of metadata processes and cross-linked multi-level metadata processes and systems for operating with a decision list tracking device.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com