Patents
Literature
139 results about "Wavelength reuse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
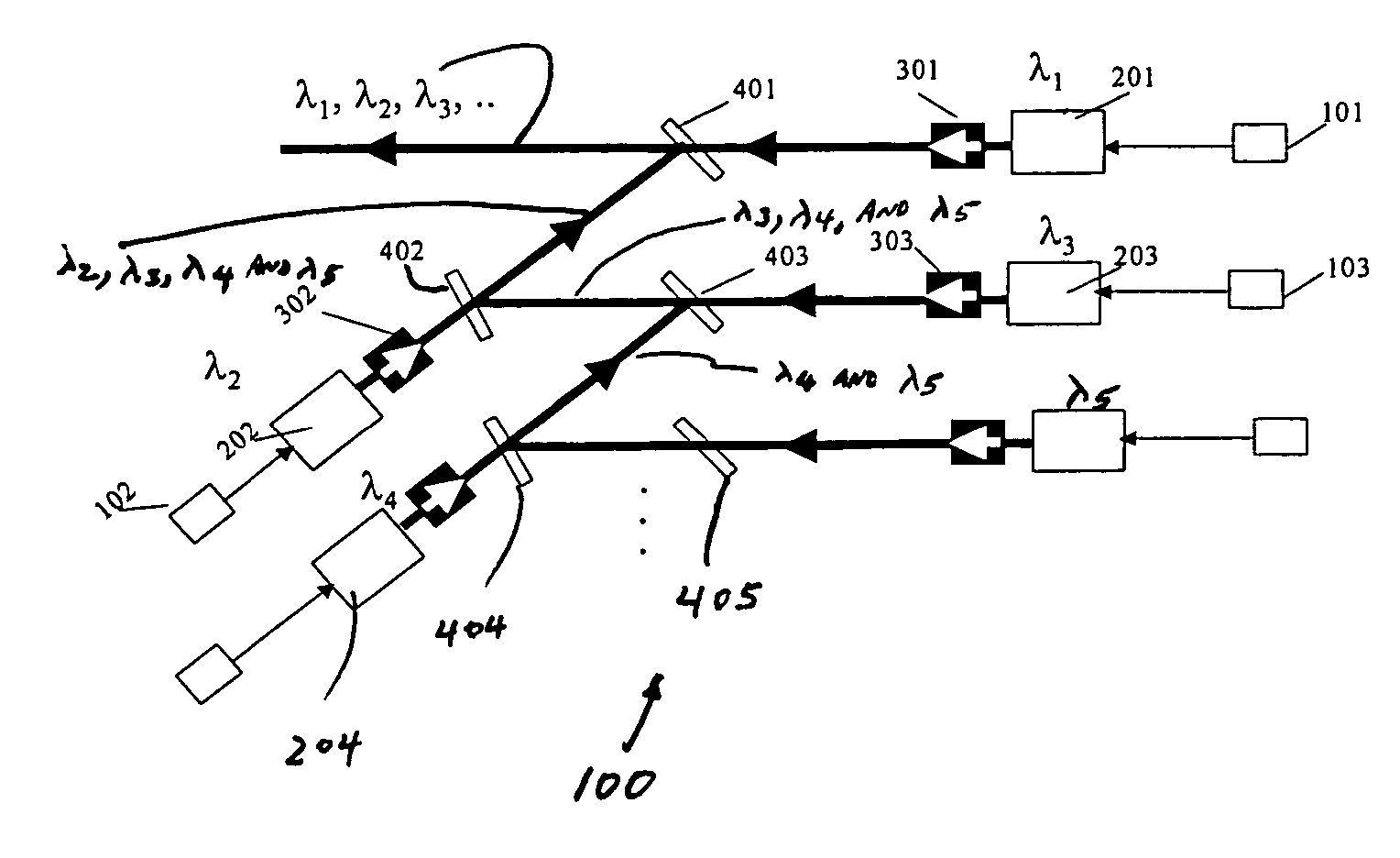
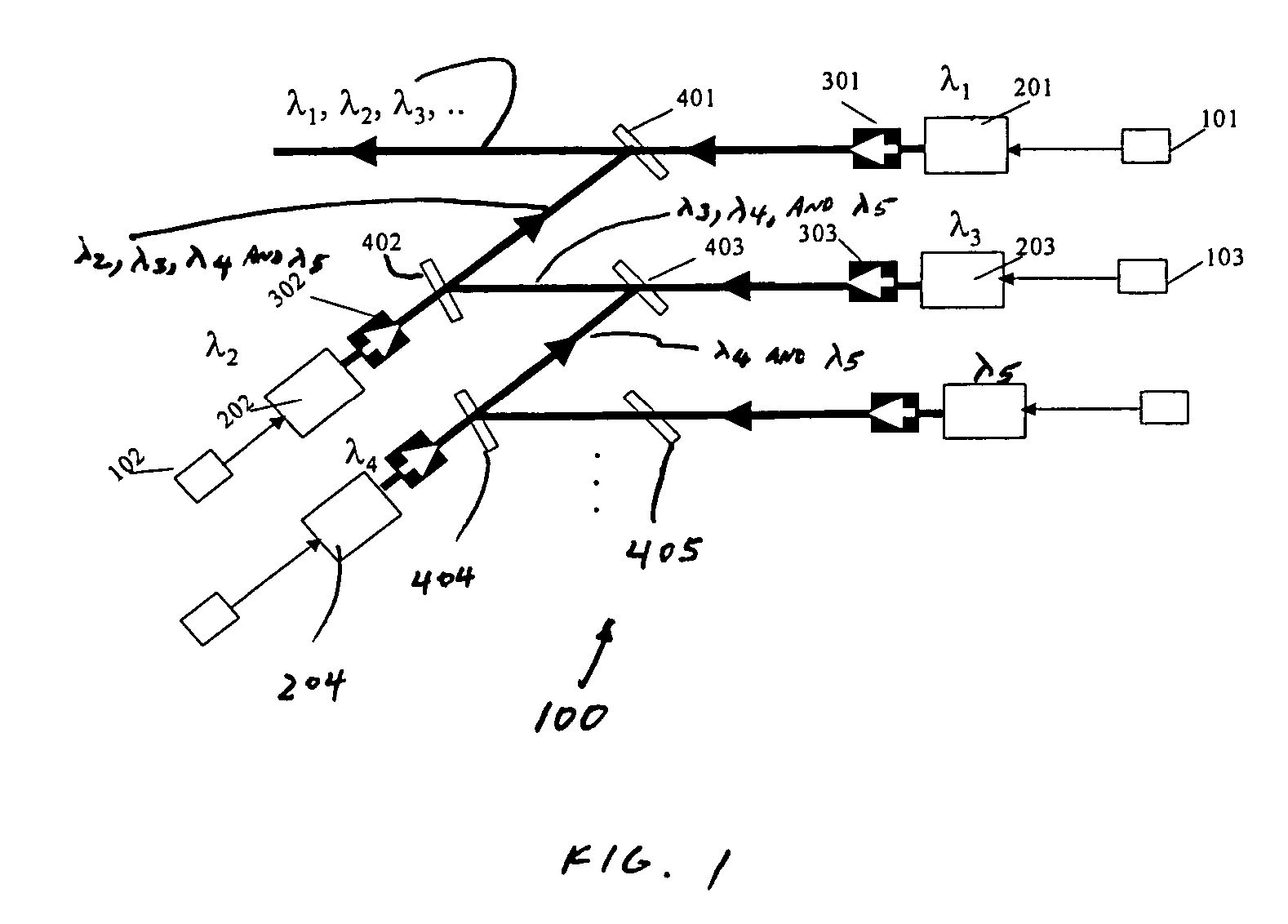
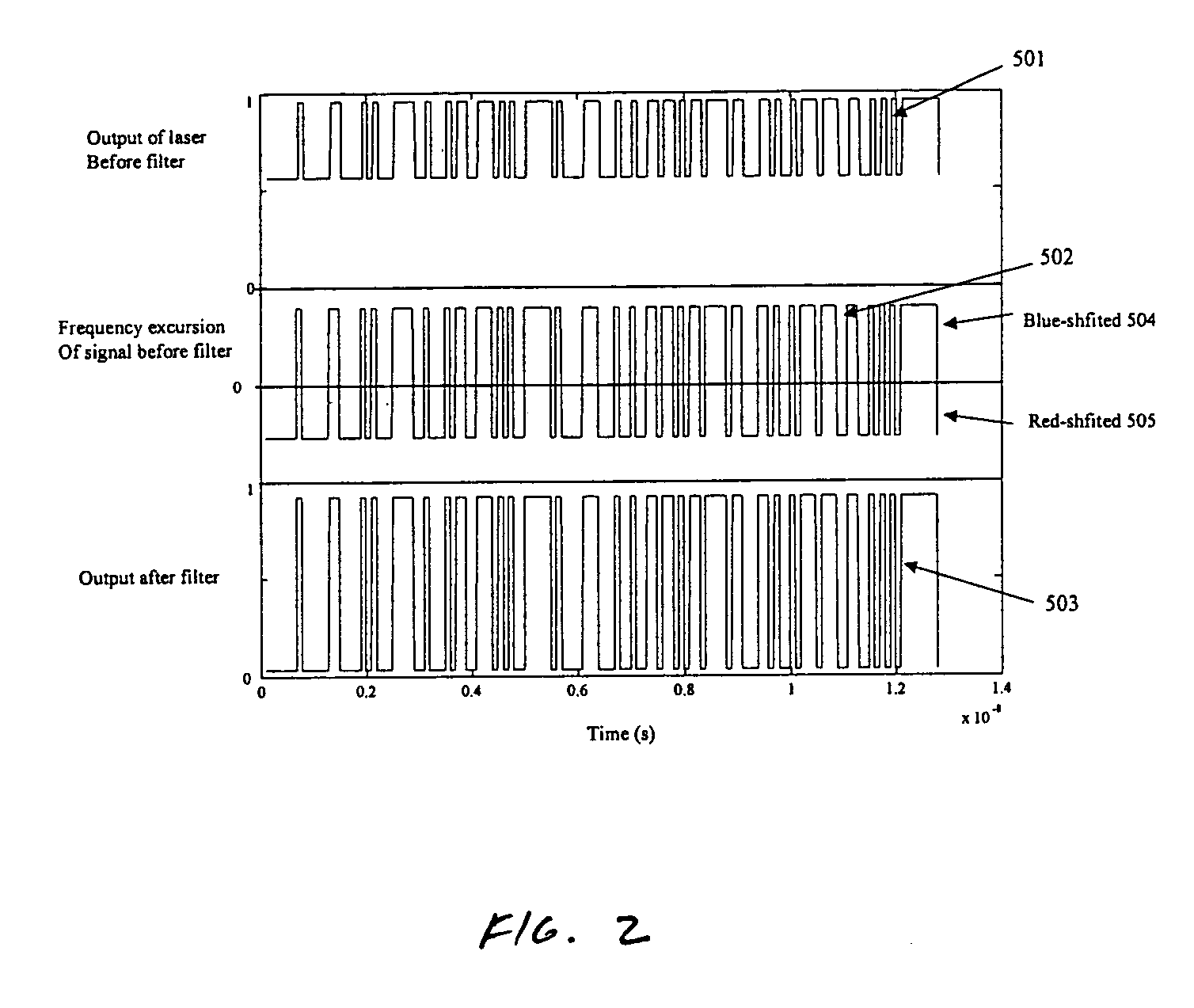
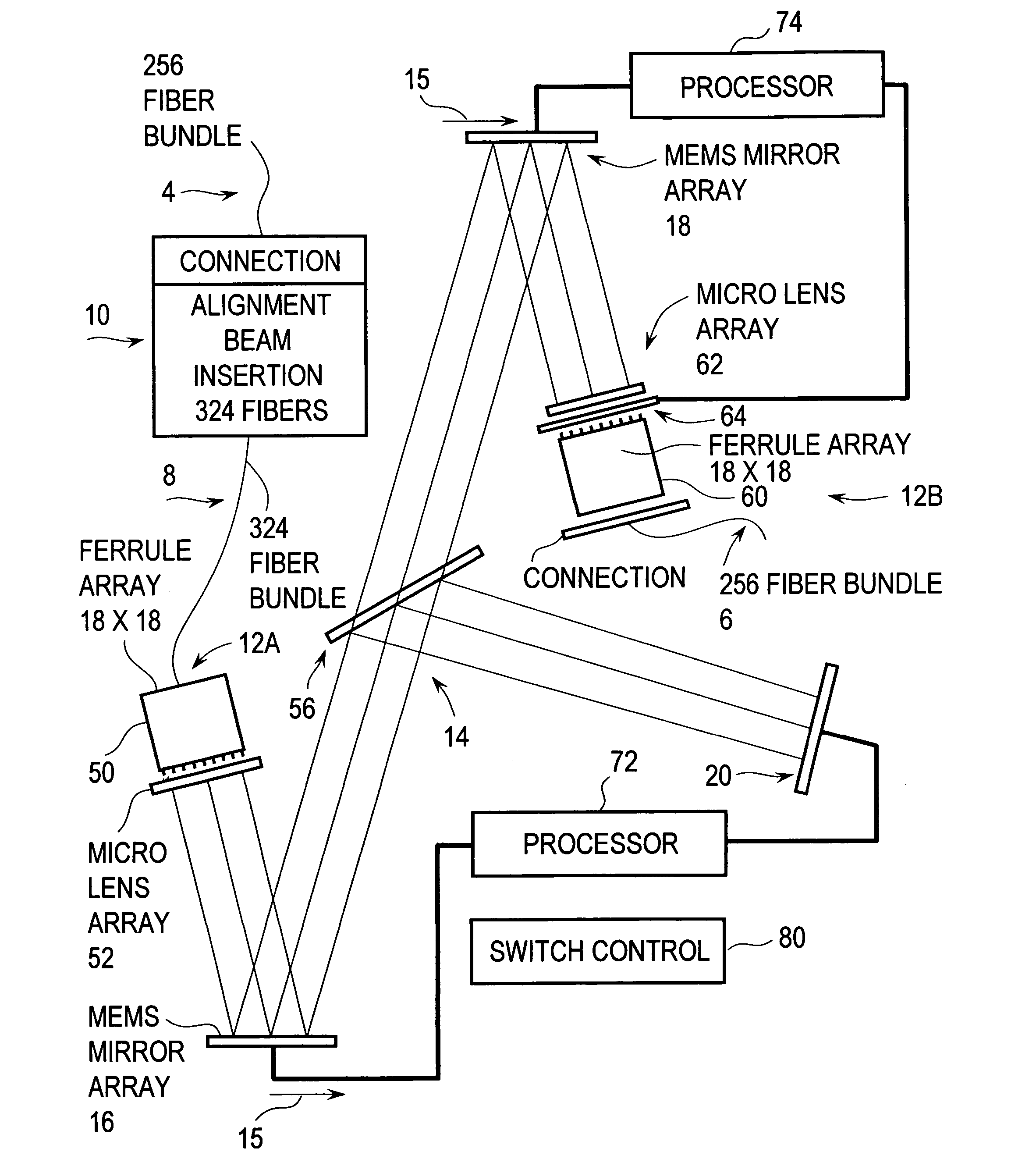
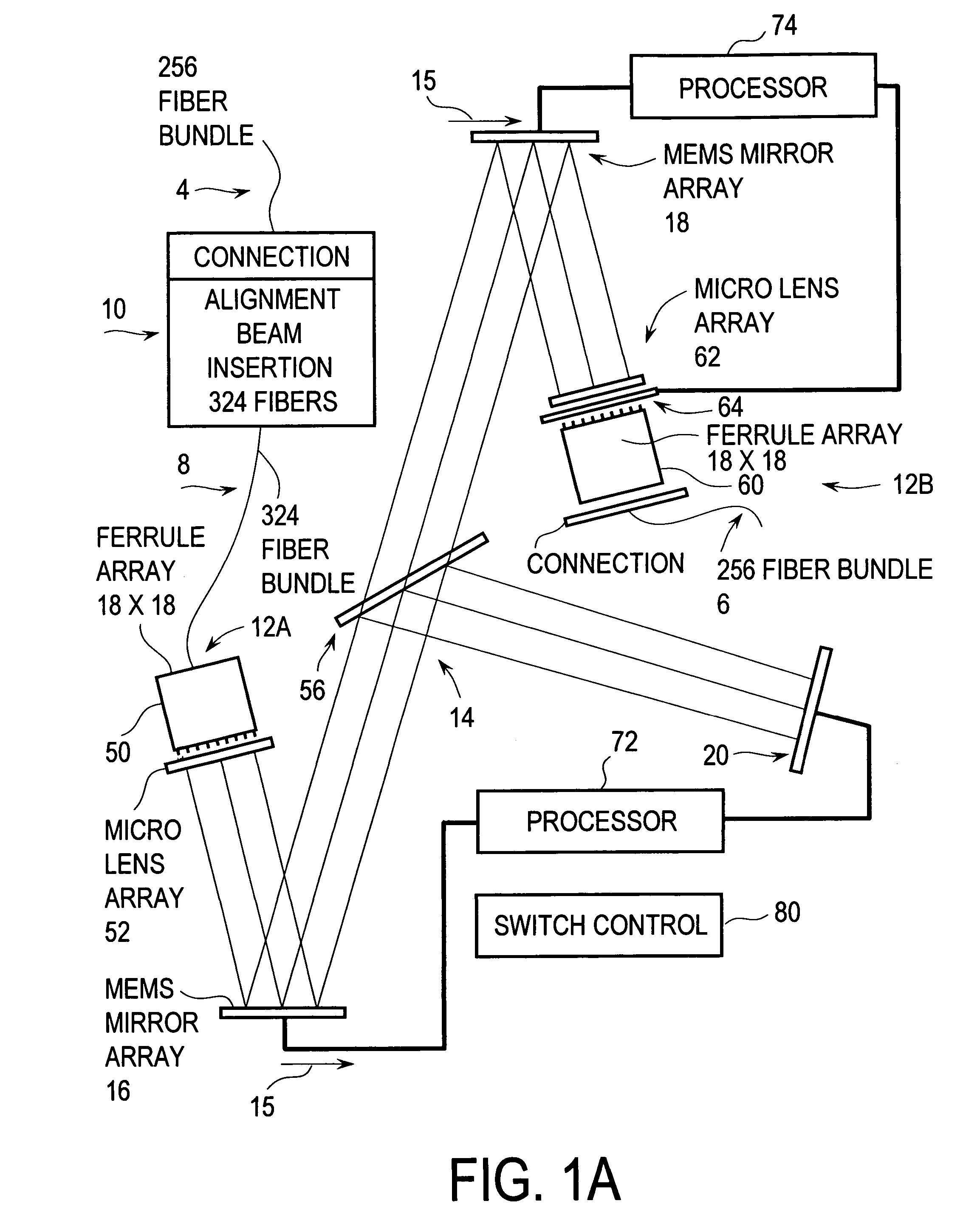
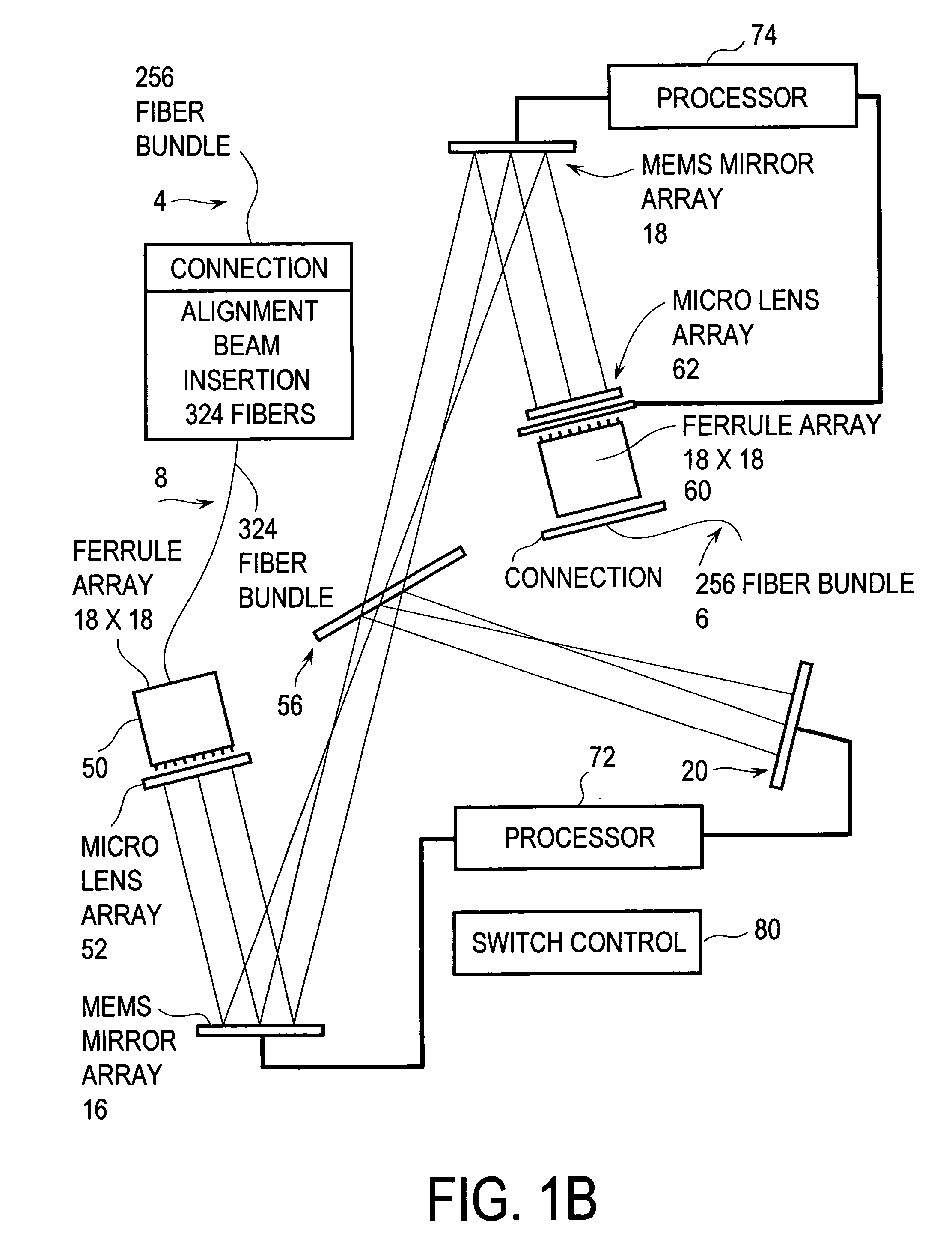
Wavelength division multiplexing source using multifunctional filters
ActiveUS7263291B2High extinction ratioReduced chirpWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesFiberDiscriminator
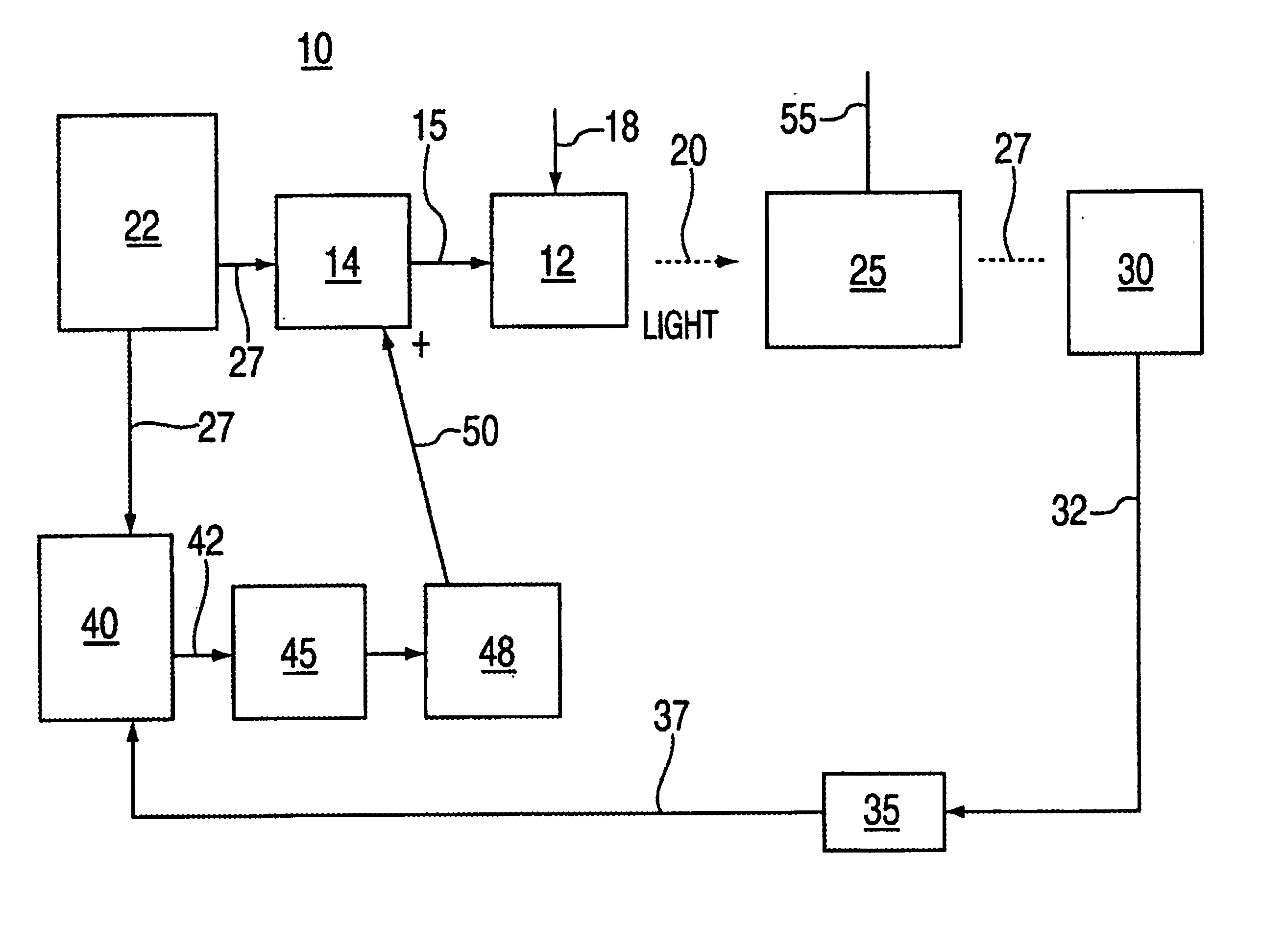
This invention provides a system that combines a wavelength multiplexer with an FM discriminator for chirp reduction and wavelength locker in a filter to produce a wavelength division multiplexed signal with reduced chirp. A partially frequency modulation laser signal is converted into a substantially amplitude modulation laser signal. This conversion increases the extinction ratio of the input signal and further reduces the chirp. A wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) method is used for transmitting high capacity information through fiber optics systems where digital information is carried on separate wavelengths through the same fiber. Separate transmitters normally generate their respective signals that are transmitted at different wavelengths. These signals are then combined using a wavelength multiplexer to transmit the high capacity information through the fiber optic system. Various technologies can be used to multiplex the signals such as, for example, thin film filters, or arrayed waveguide gratings. In a WDM system, a wavelength locker may also be used that fixes the center wavelength of a transmitter to a reference. Wavelength lockers may include etalons or fiber gratings, either of which provides a reference wavelength. A control circuit typically compares the wavelength of the transmitter to the reference. An error signal adjusts the transmitter format wavelength by varying temperature or by other means to keep it locked to the reference wavelength.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Integrated etched multilayer grating based wavelength demultiplexer
An integrated etched multilayer grating-based wavelength multiplexer / demultiplexer is disclosed wherein an etched multilayer grating structure is monolithically integrated within the optical waveguide stack of the multiplexer / demultiplexer to reflectively diffract an input optical beam. The multilayer grating structure is generally comprised of a series of etched diffractive elements and an etched multilayer reflector, the combined optical response of which providing the desired multiplexing / demultiplexing effect. The etched structures are generally comprised of shallow etch structures in a top surface of the multiplexer / demultiplexer waveguide stack. Monolithically integrated input and output ridge waveguides may also be provided, optionally fabricated in a same etching step as the etched multilayer grating.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
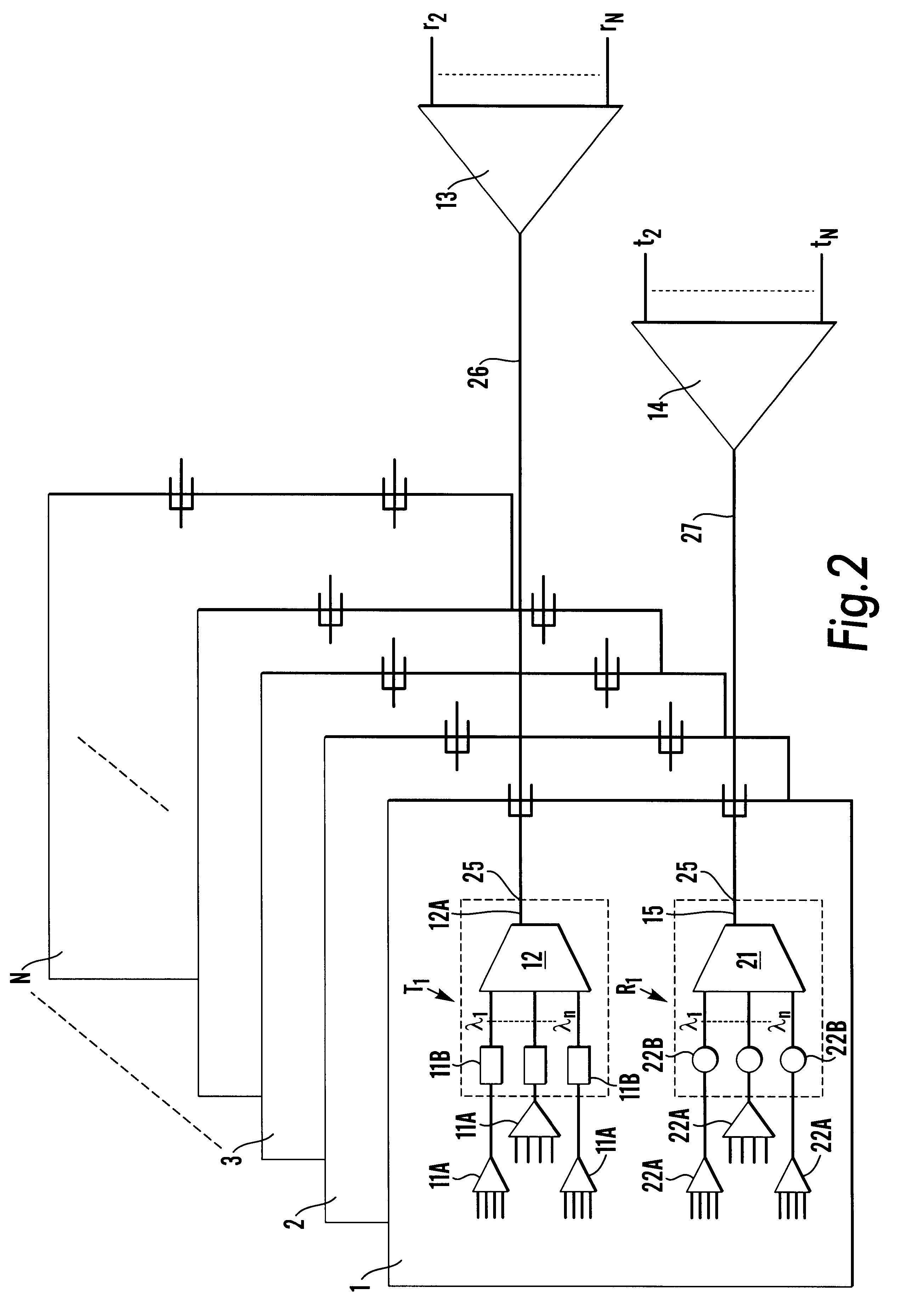
Connecting a plurality of circuit boards
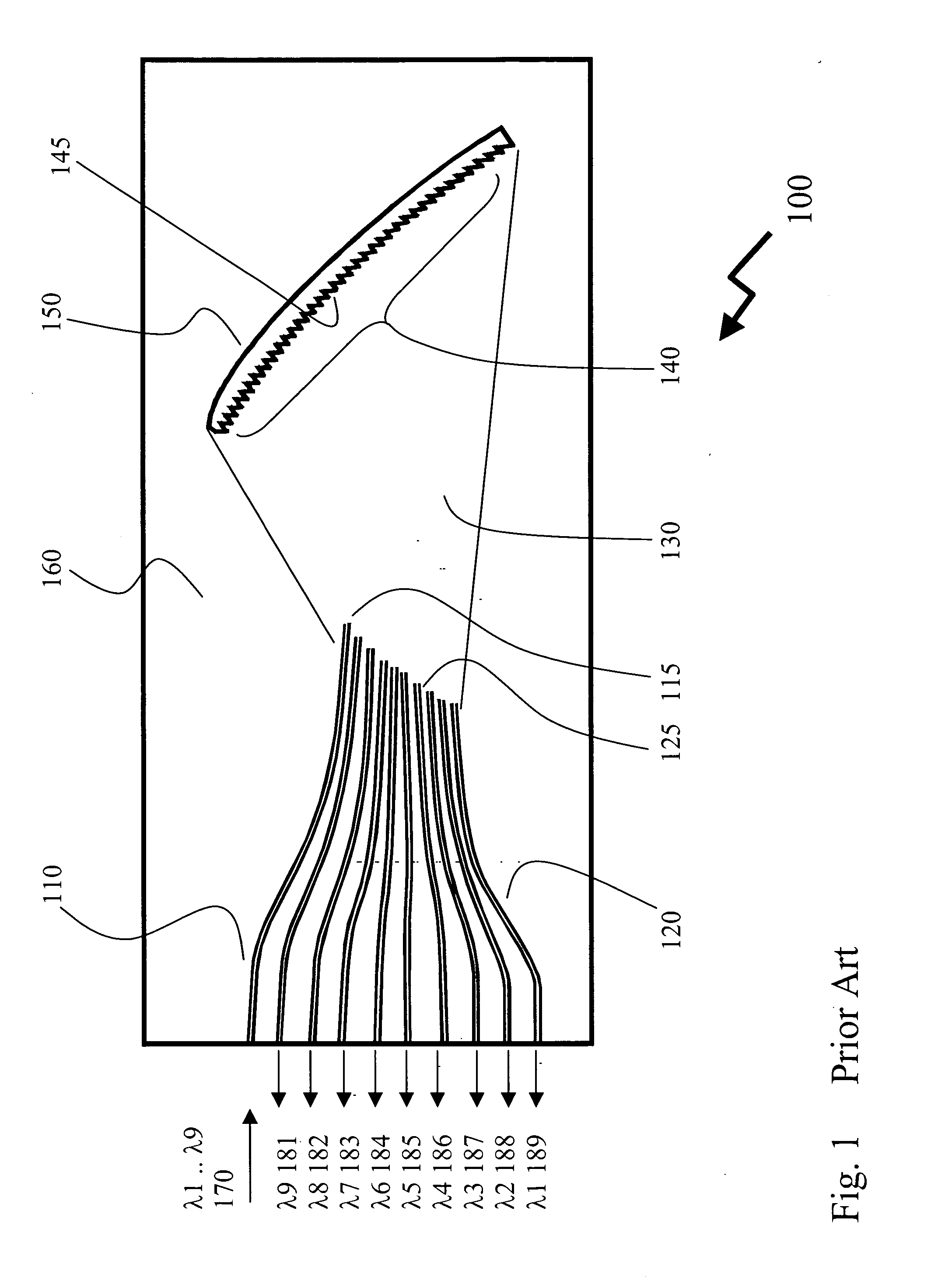
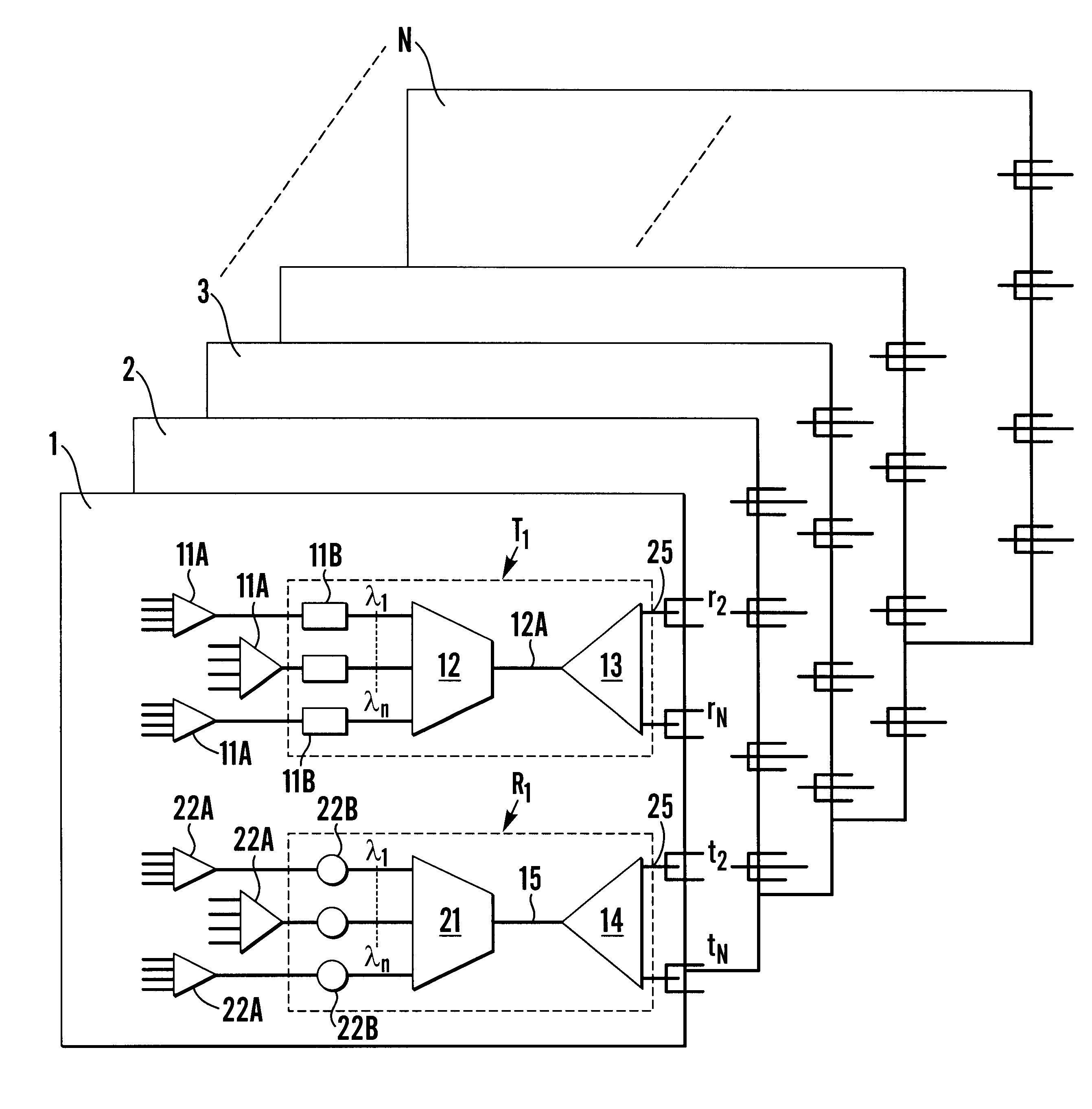
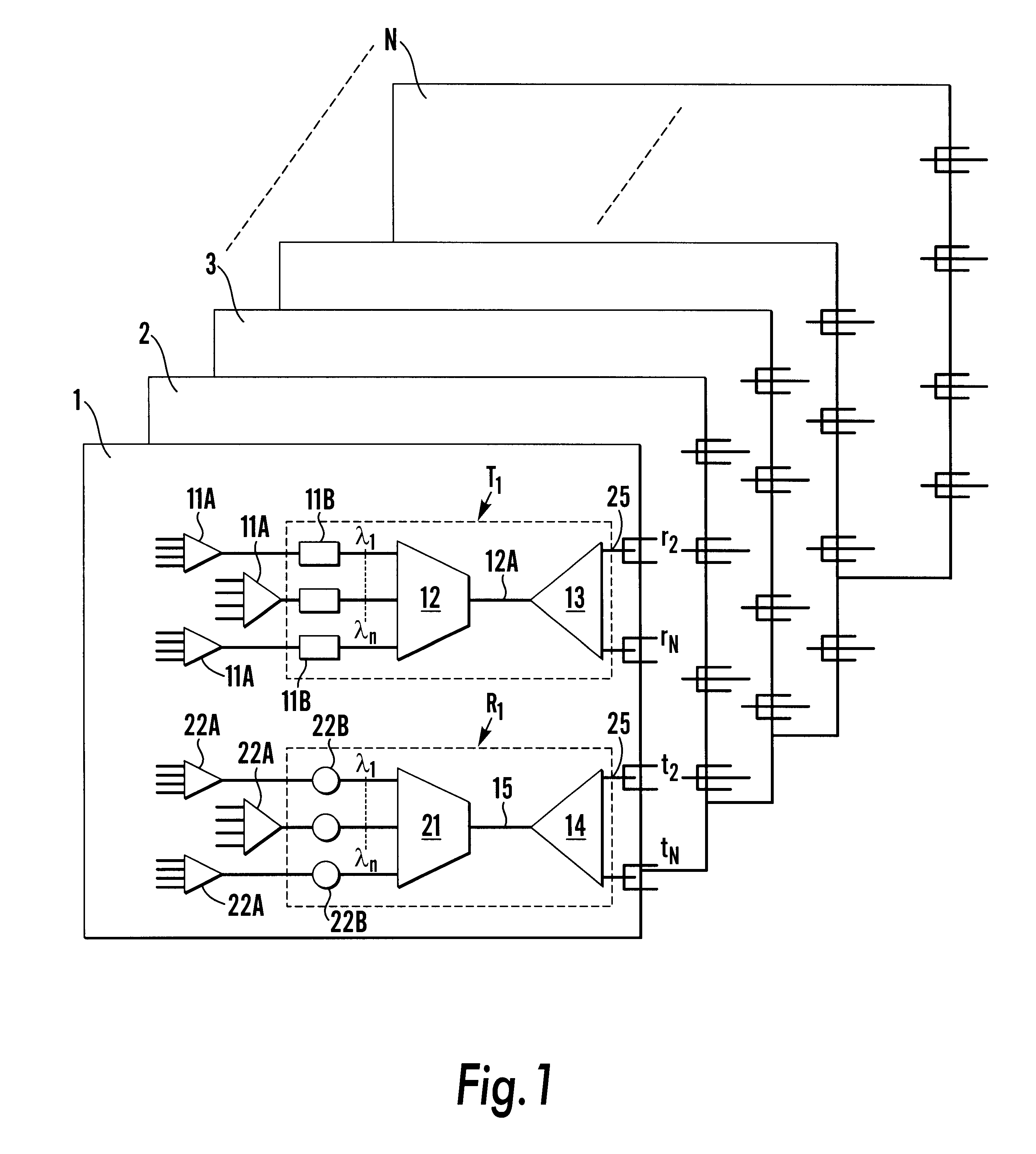
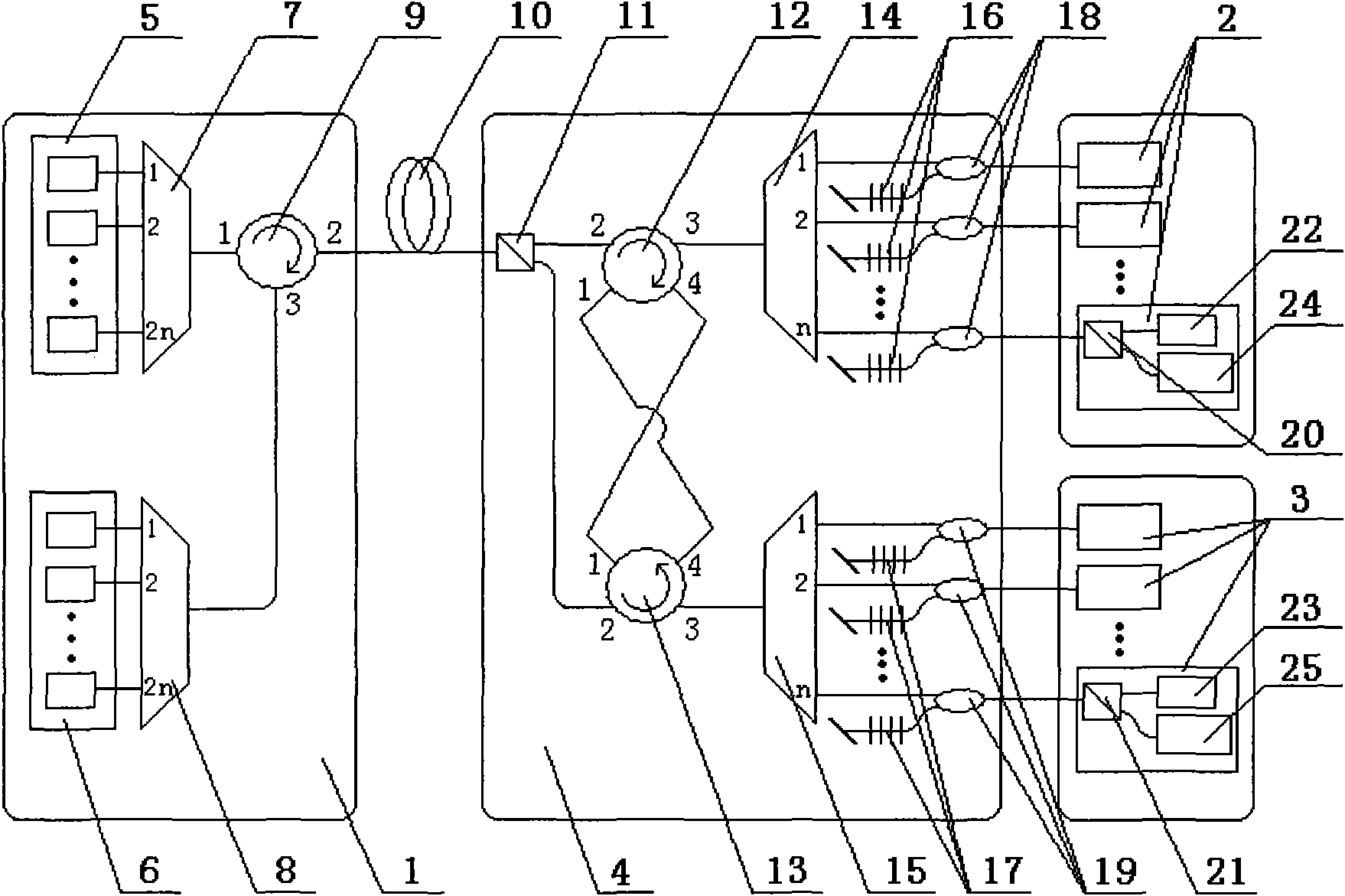
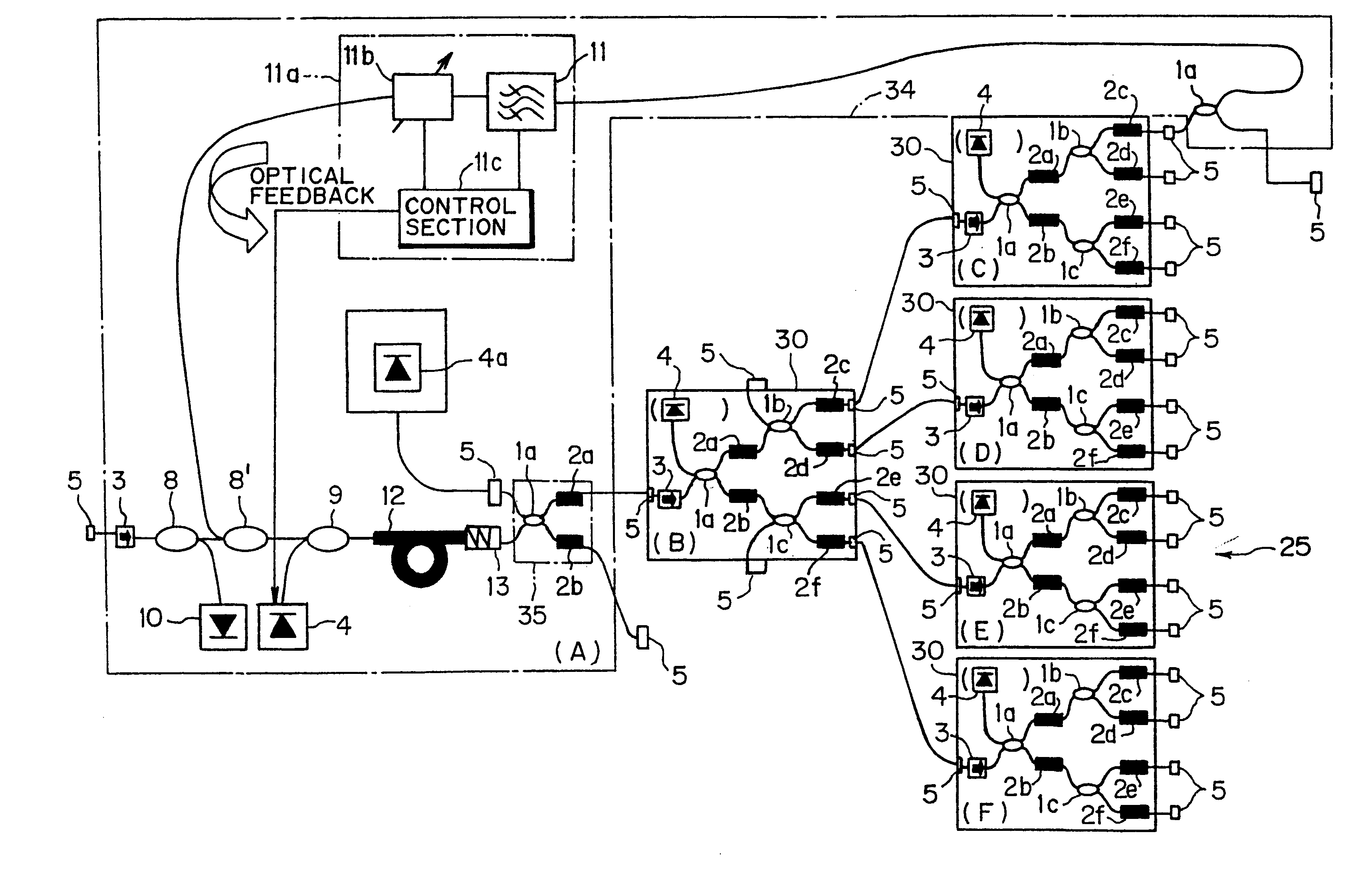
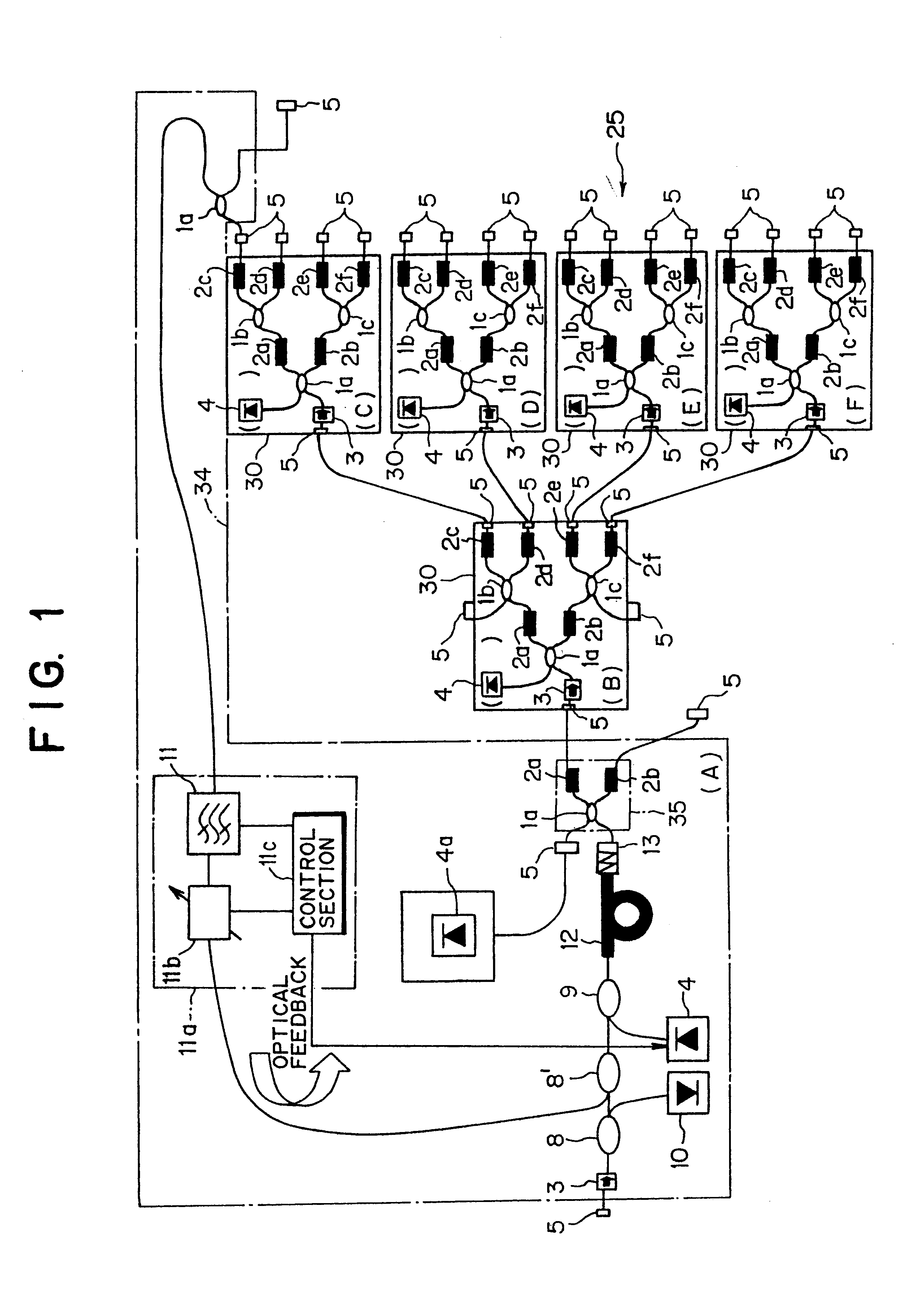
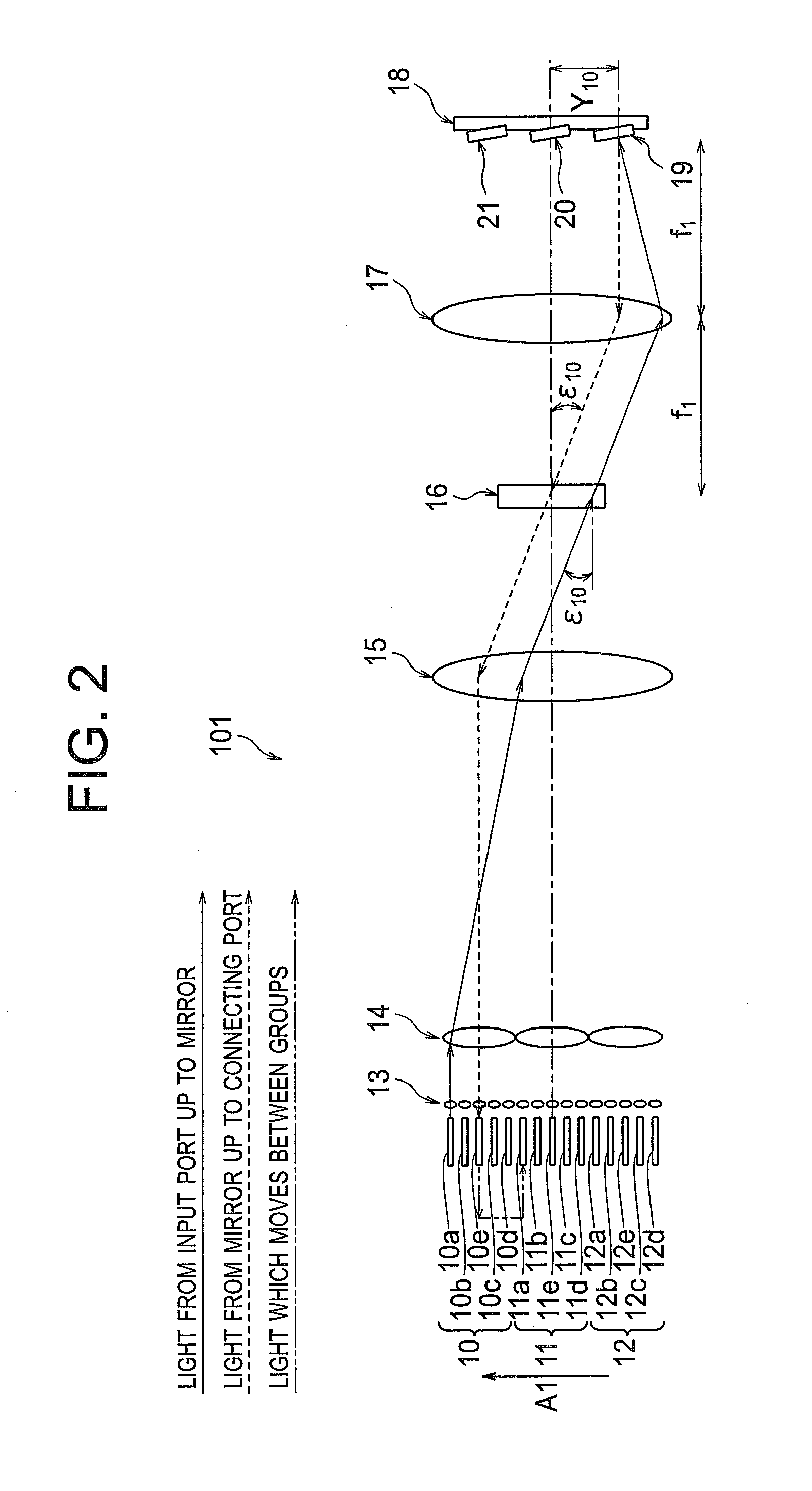
Apparatus connecting electrical circuit boards (1, 2, 3, . . . N) so each board can communicate with each other. Each board has an optical circuit, which in turn has a transmitter module (T) and a receiver module (R). The transmitter module (T) has electrical to optical converters (11B) for converting electrical signals into optical signals, a wavelength multiplexer (12) for multiplexing the optical signals into a single optical waveguide (12A), and an optical splitter (13) for dividing the multiplexed signal into a plurality of identical signals for transmission to each of the receiver modules (R). The receiver module (R) has an optical selector (14) for selecting signals from the transmission modules (T), a wavelength demultiplexer (21) for demultiplexing the selected signal into signals each of a different wavelength (lambd1 . . . lambdn), and optical to electrical converters (22B) for converting each of the signals of different wavelengths into an electrical signal.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
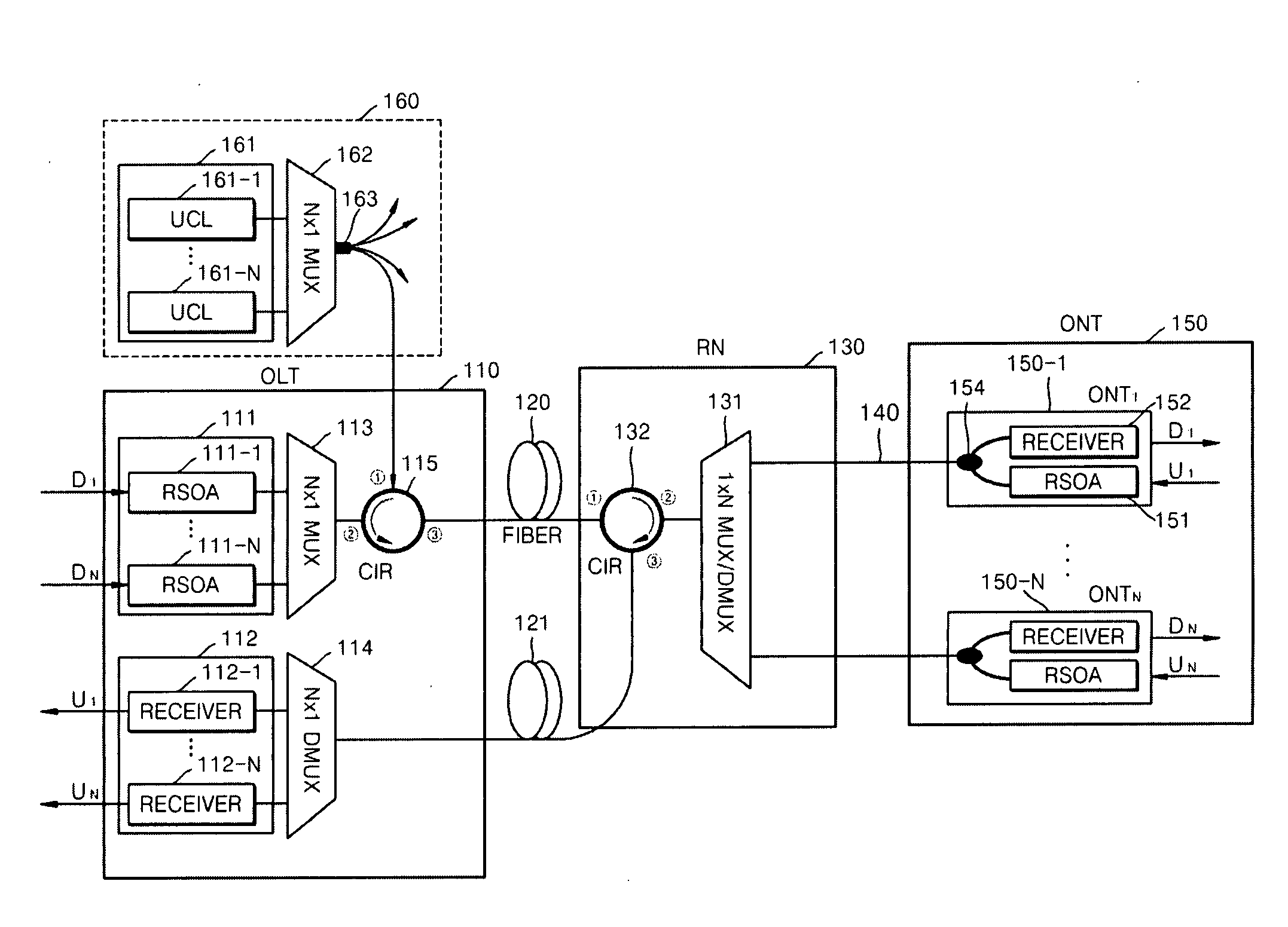
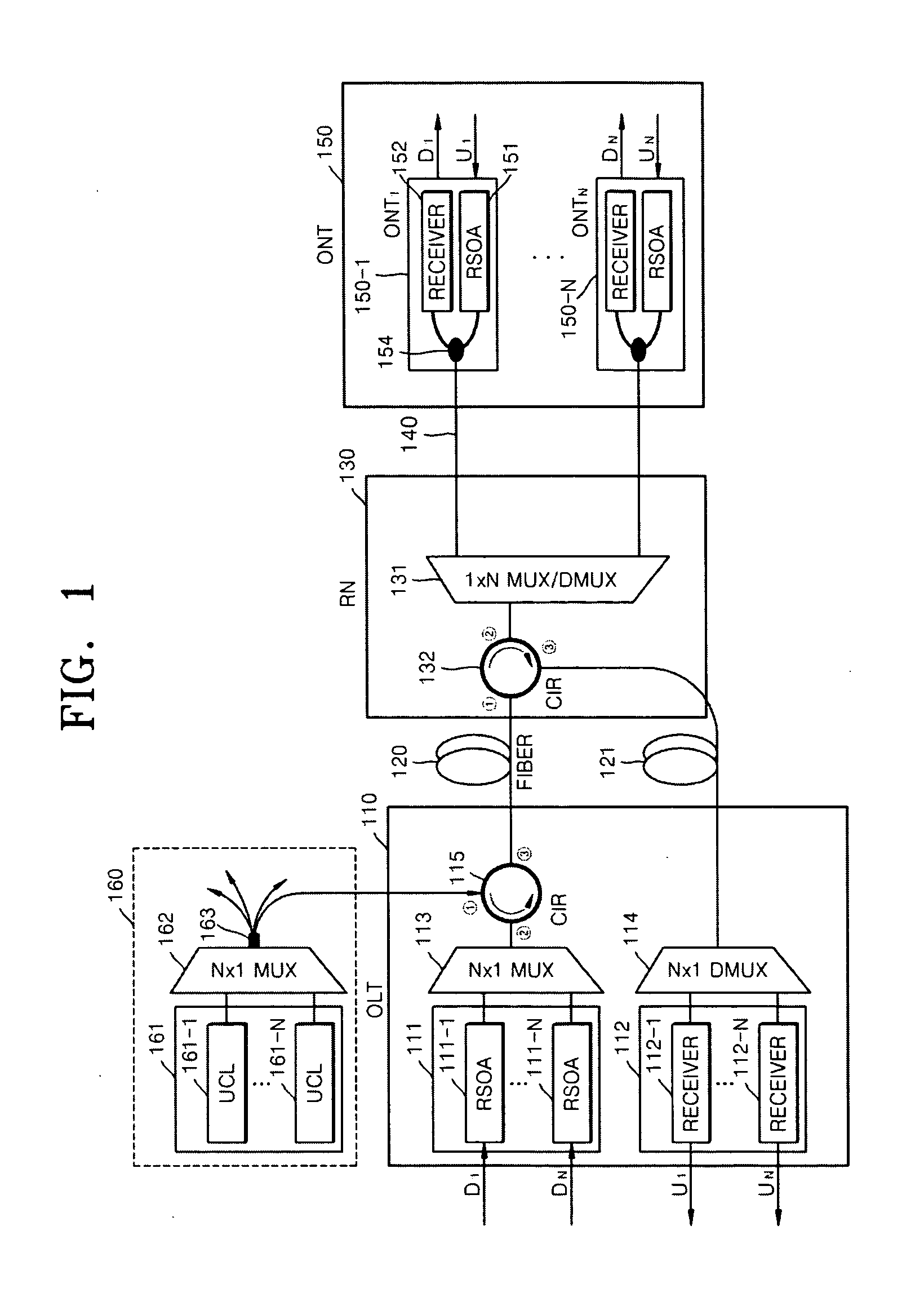
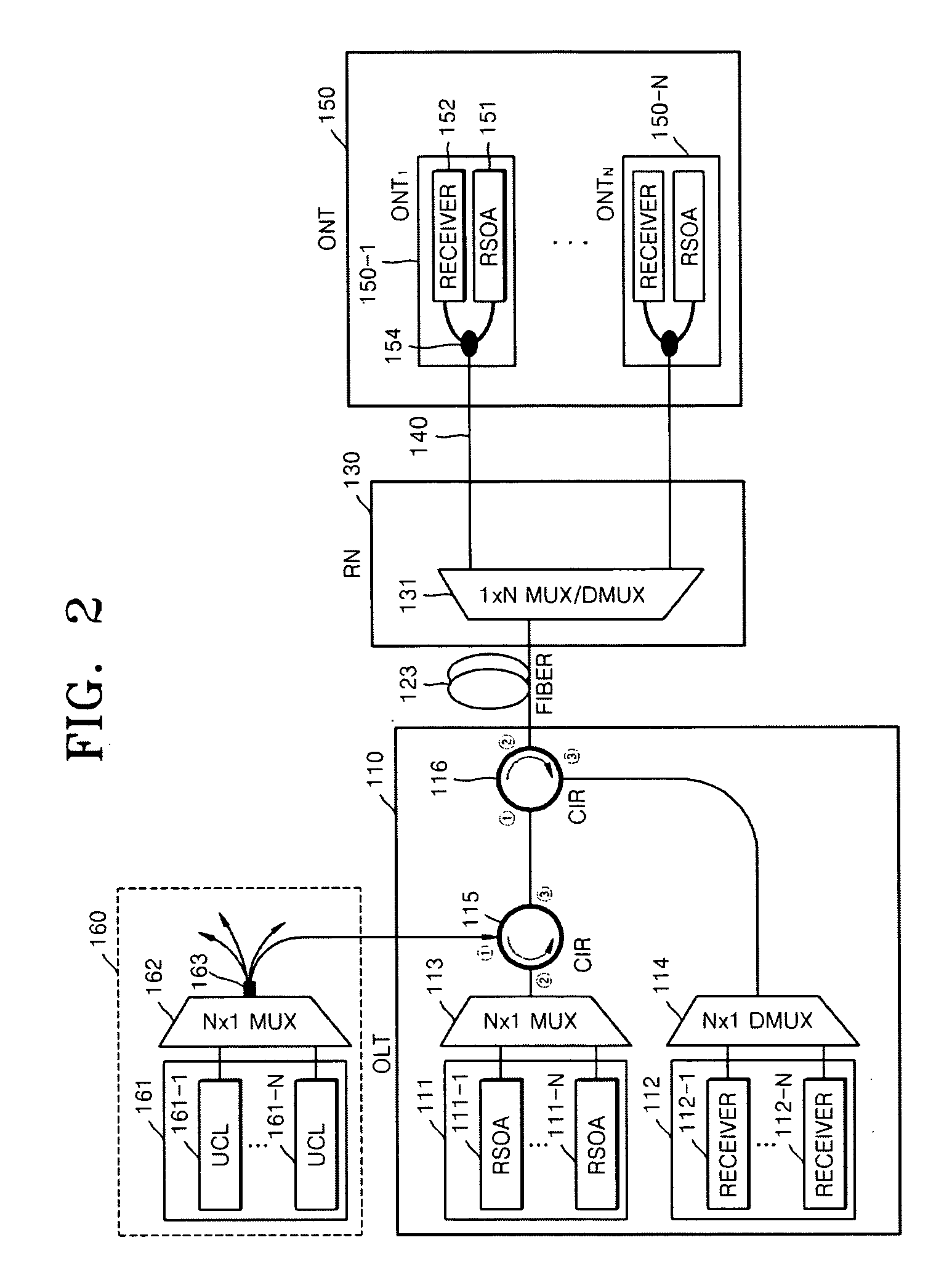
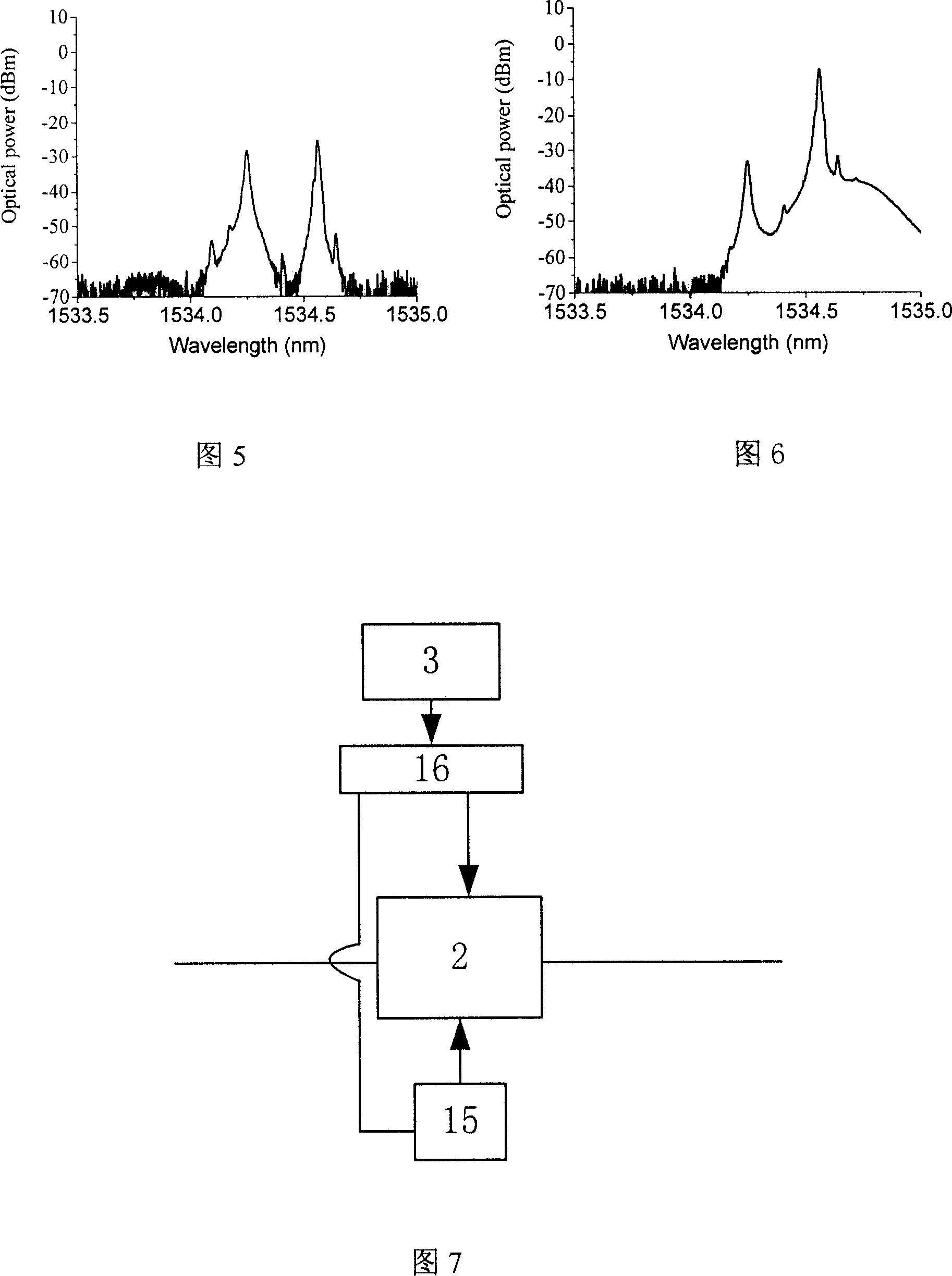
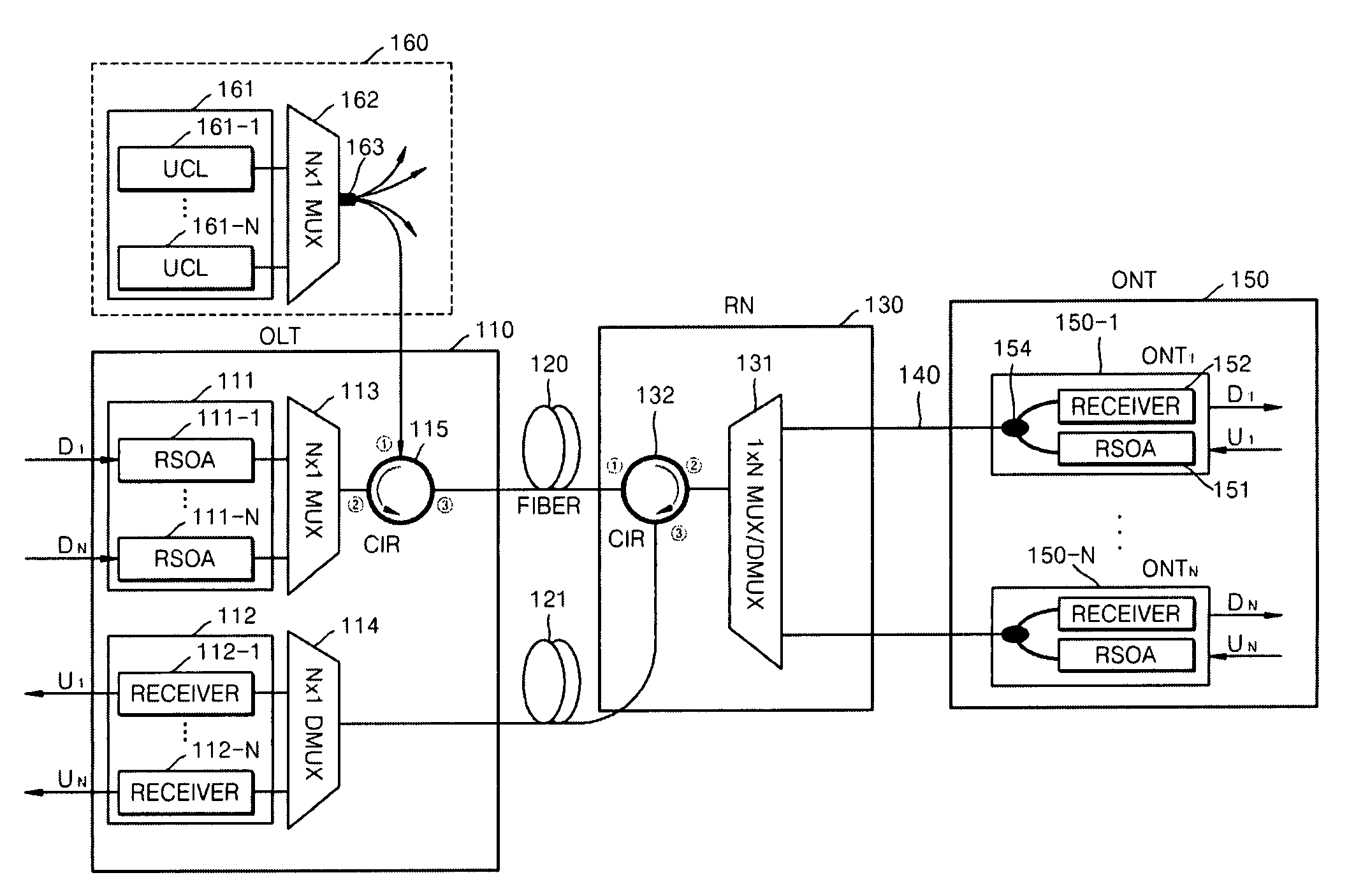
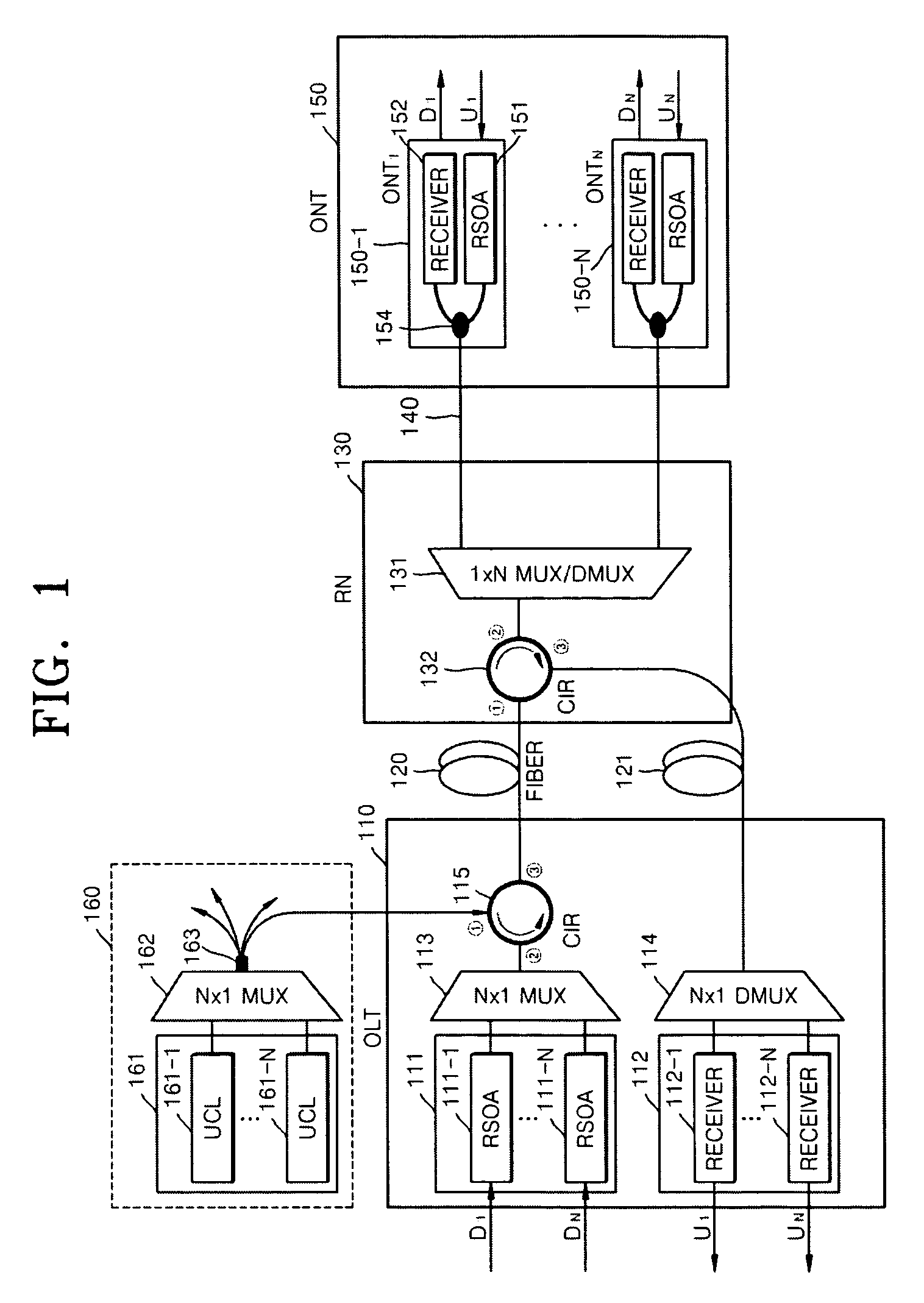
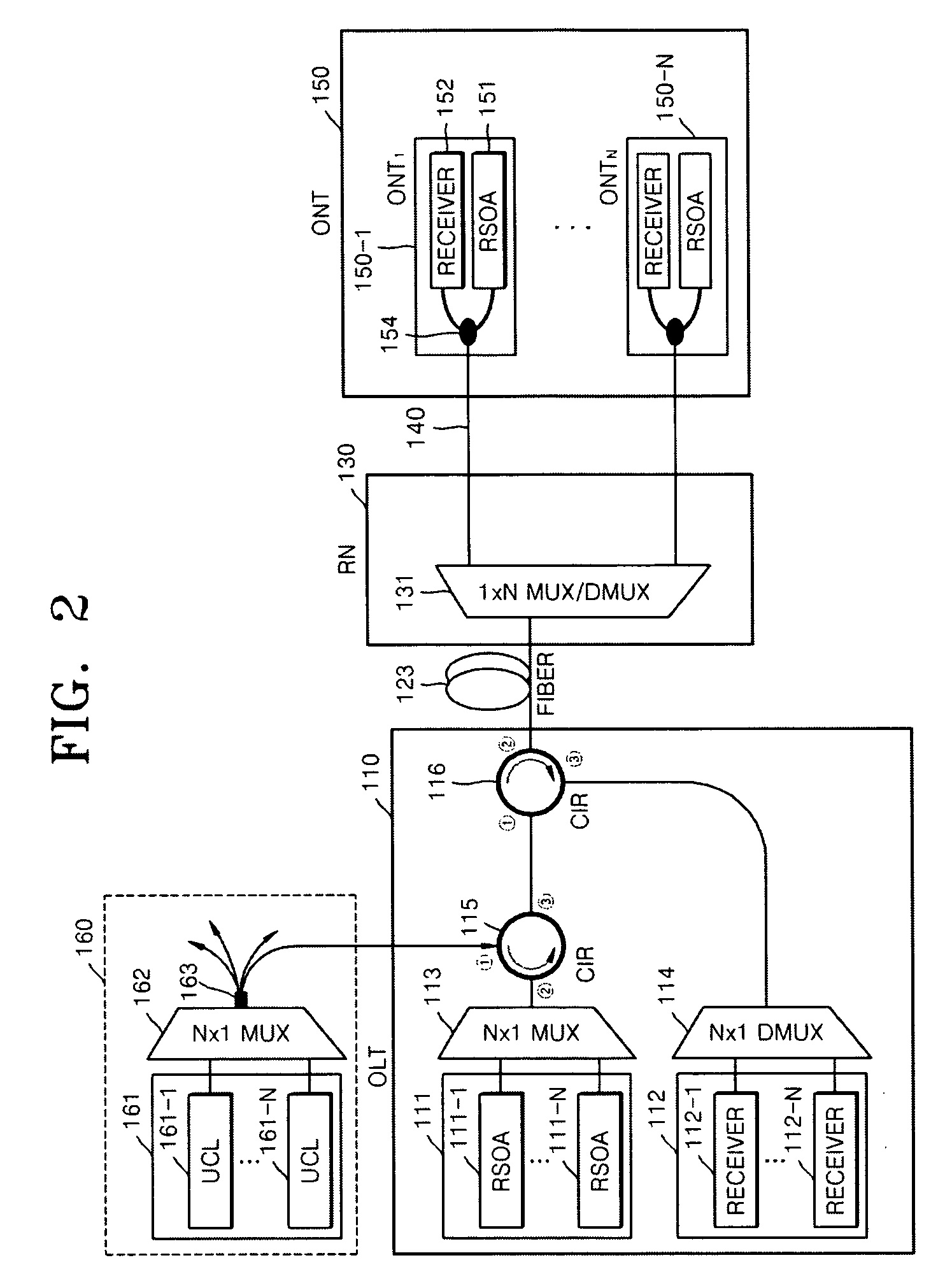
Passive Optical Network Based On Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier
ActiveUS20090220230A1Increase powerIncrease input powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength reuseReflective semiconductor optical amplifier
Provided is a passive optical network (PON) based on a reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA). In the PON, seed-light-injection RSOAs are used in an optical line terminal (OLT) to achieve the color-less management of the wavelengths of OLT optic sources, and wavelength reuse RSOAs are used to achieve the color-less management of the wavelengths of ONTs. Therefore, problems related to ONT wavelength management can be eliminated by the wavelength reuse RSOAs, and problems related to OLT wavelength management can be eliminated by the seed-light-injection RSOAs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
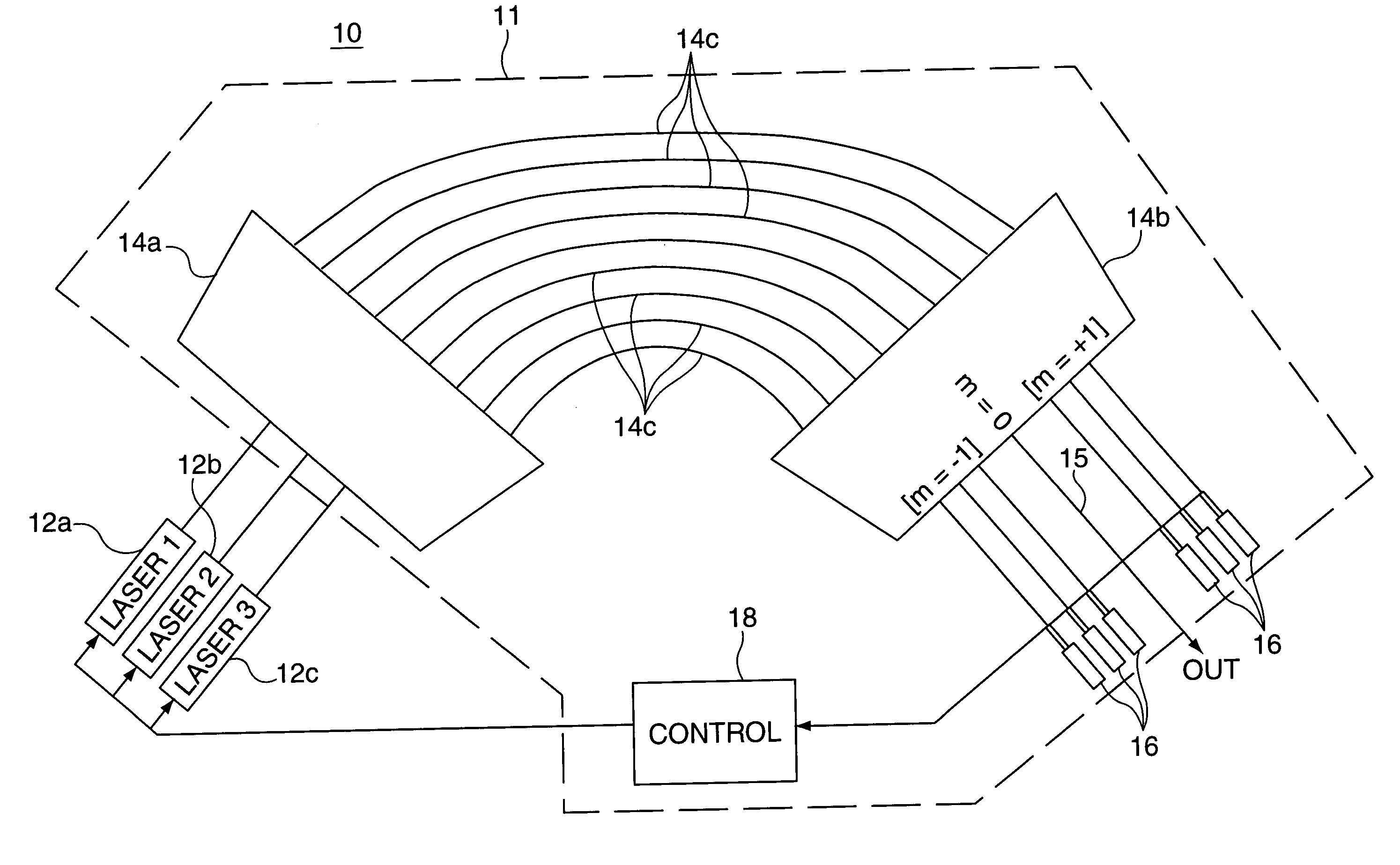
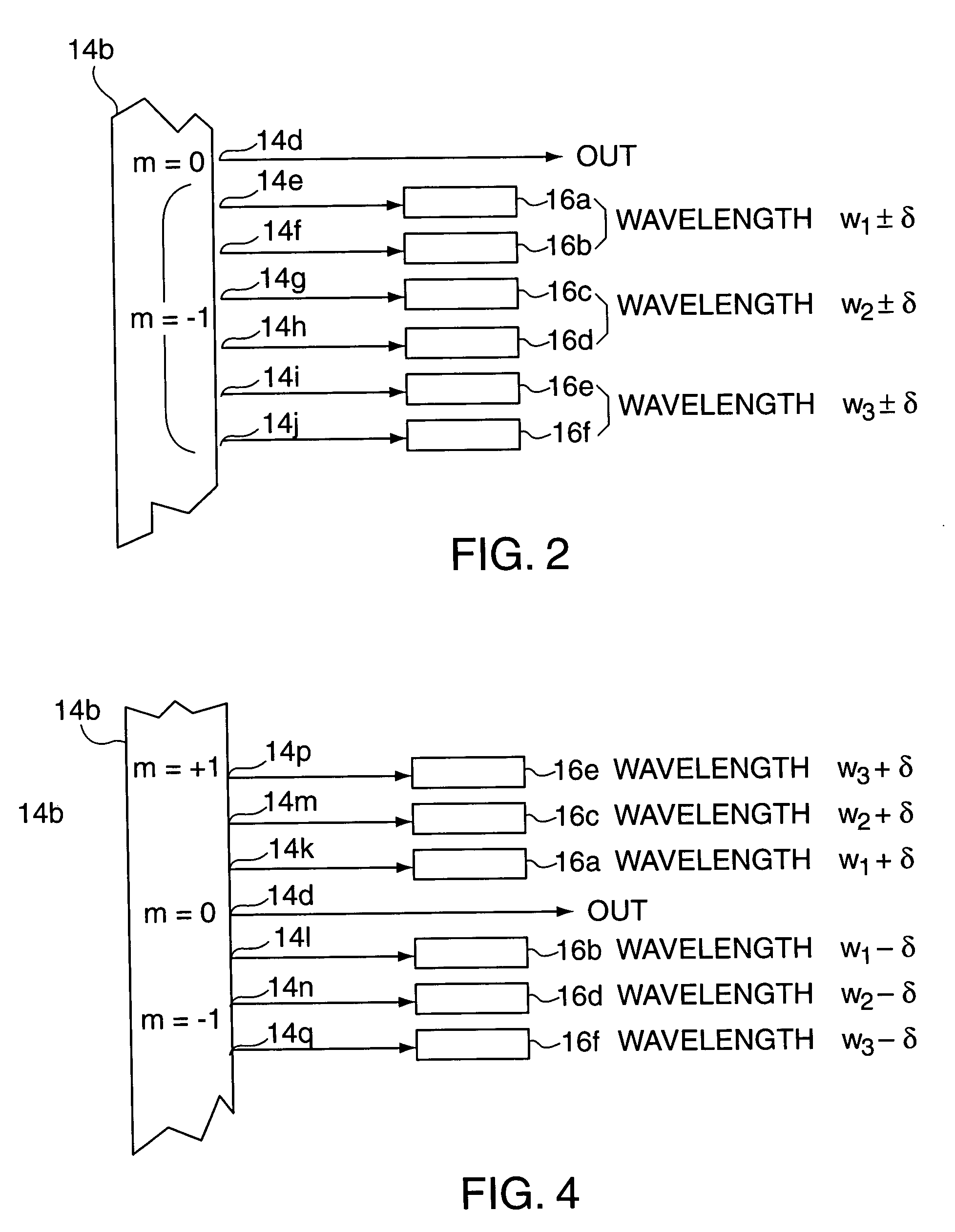
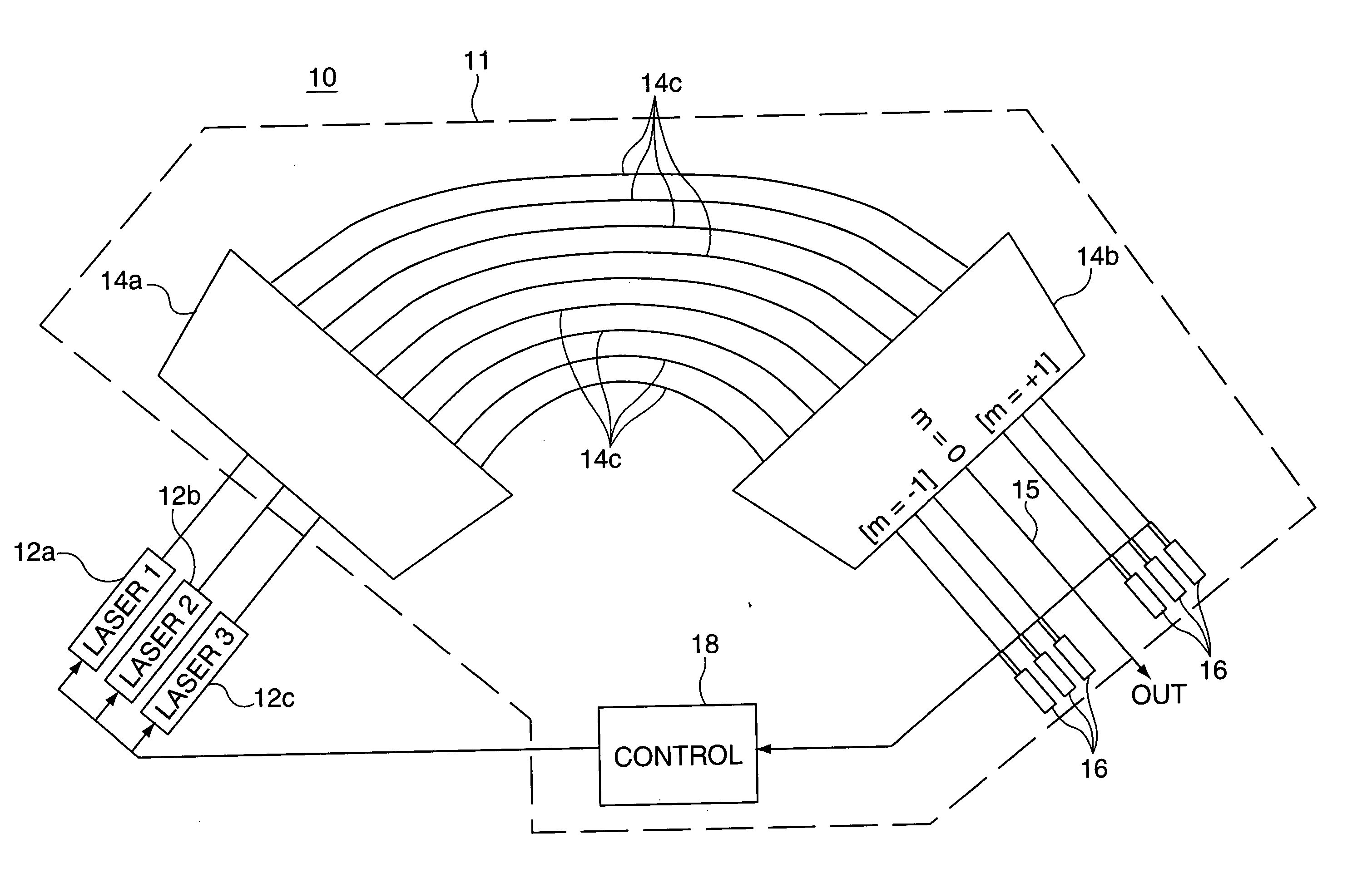
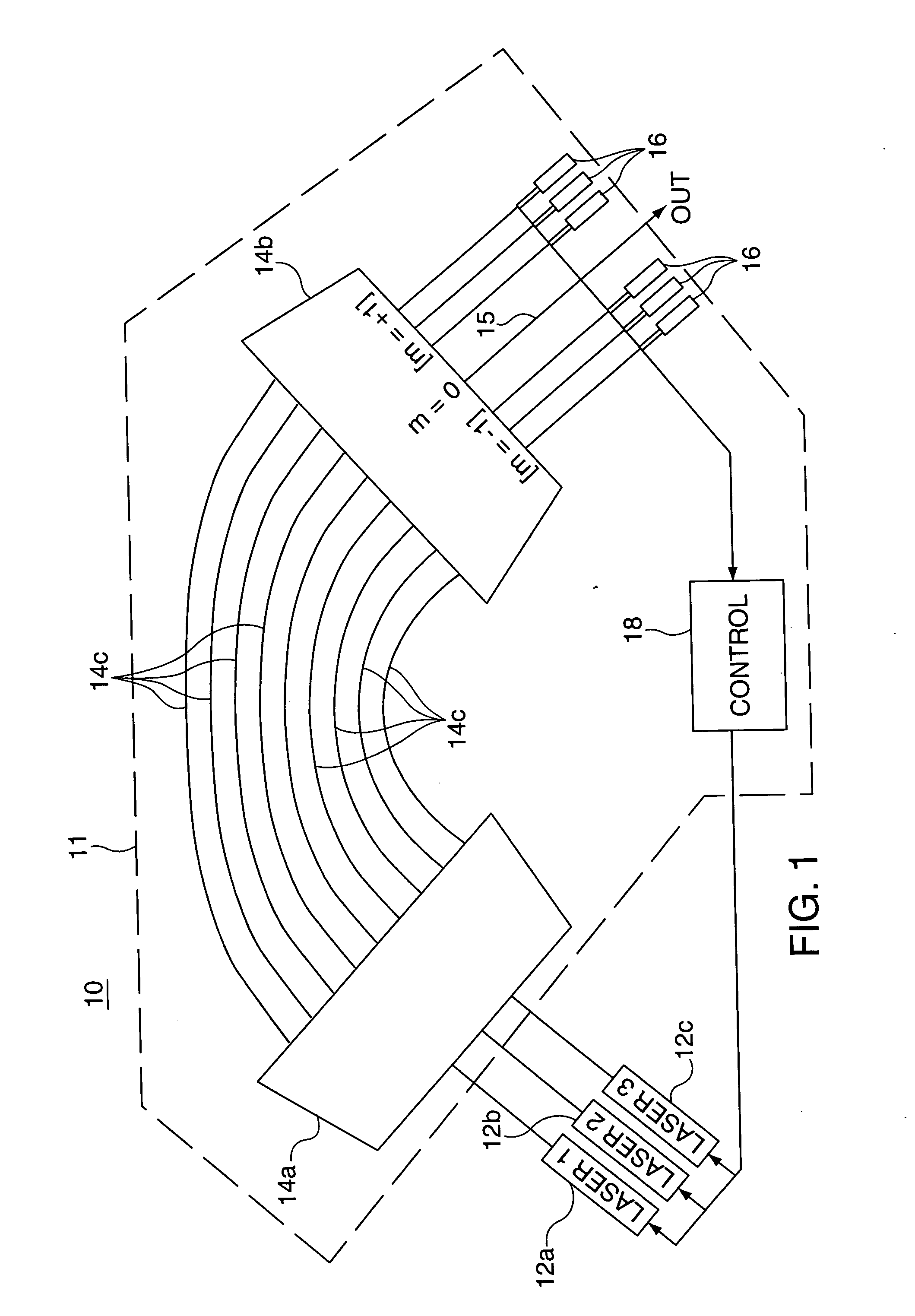
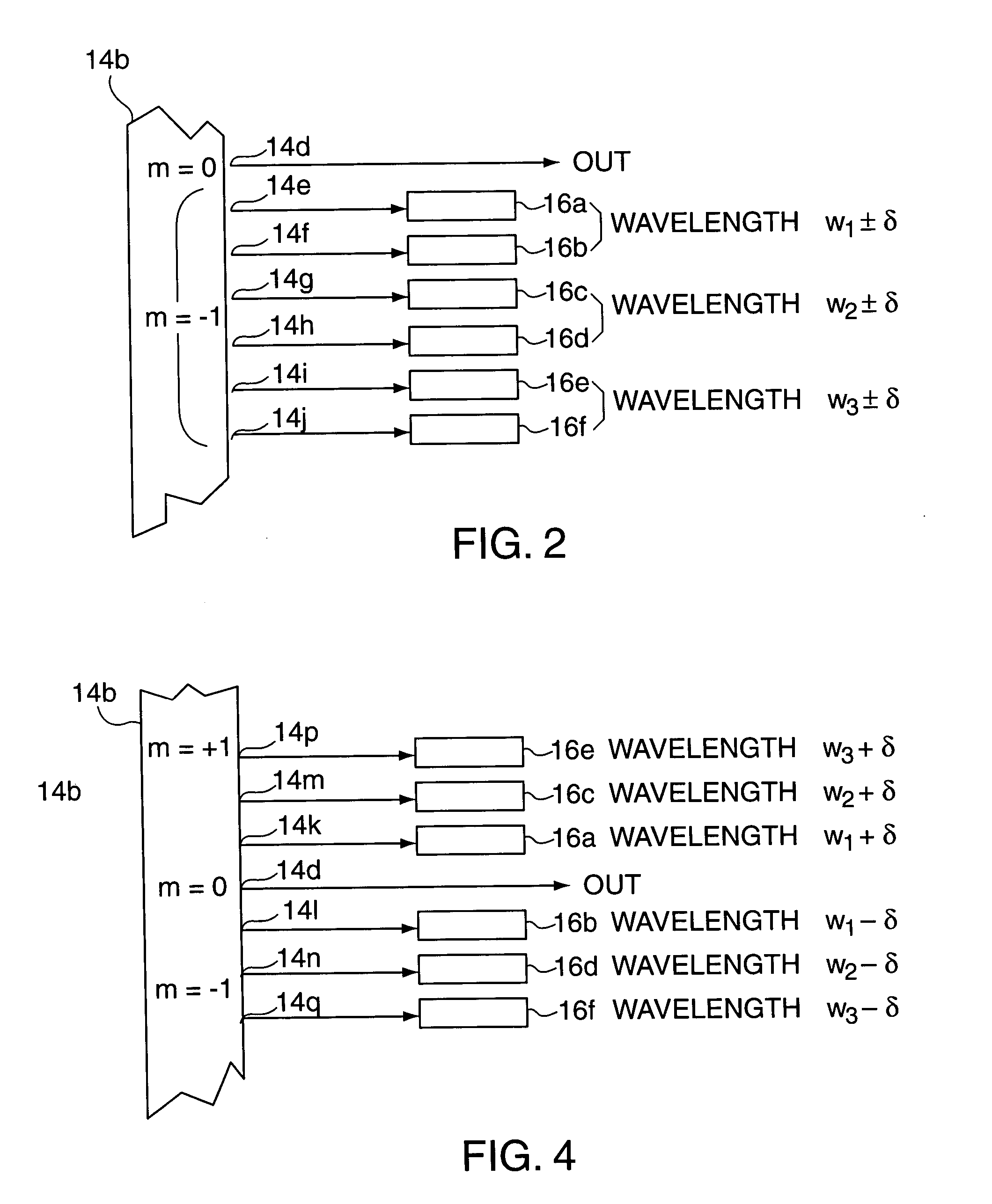
Combination wavelength multiplexer and wavelength stabilizer
InactiveUS6937795B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesDiffraction orderGrating
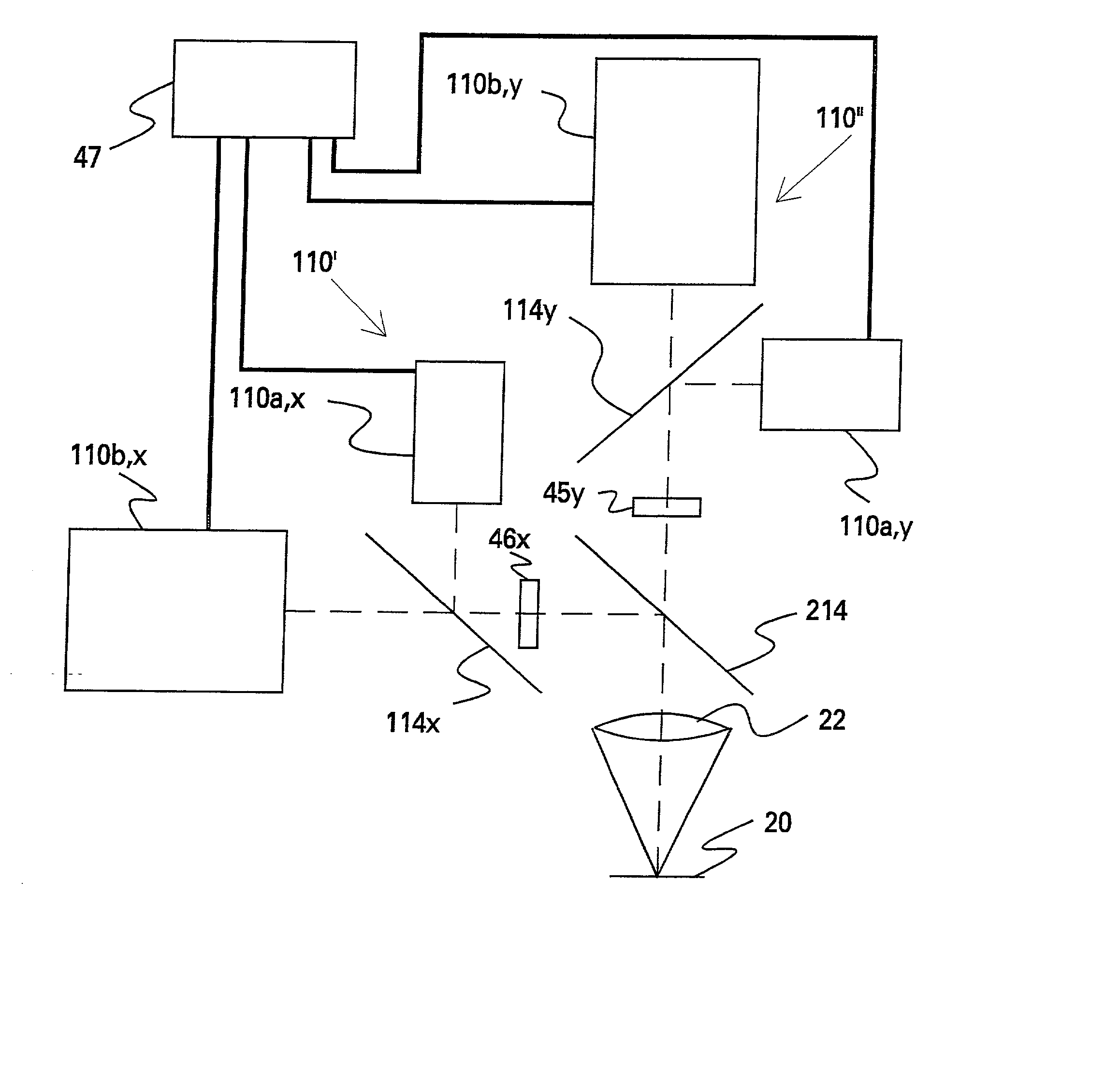
In an optical device, each of a plurality of radiation sources generates a separate different wavelength output signal to a wavelength locking device wherein a grating device receives the separate wavelength output signals from the plurality of radiation sources. The grating device generates a multiplexed wavelength output signal at a zero diffraction order output port thereof, and resolves separate symmetric wavelength−δ and wavelength−δ output signals at separate predetermined locations within at least one non-zero diffraction order thereof for each of the radiation sources. Each of a plurality of radiation detectors is coupled to receive a separate one of the symmetric wavelength−δ and wavelength−δ output signals and generate an output signal representing the magnitude of the received wavelength output signal. A control device is responsive to output signals from each pair of radiation detectors coupled to receive the separate symmetric wavelength+δ and wavelength−δ output signals from a specified predetermined radiation source for generating an output control signal appropriate to that radiation source for locking the wavelength thereof.
Owner:OPTOVIA +1
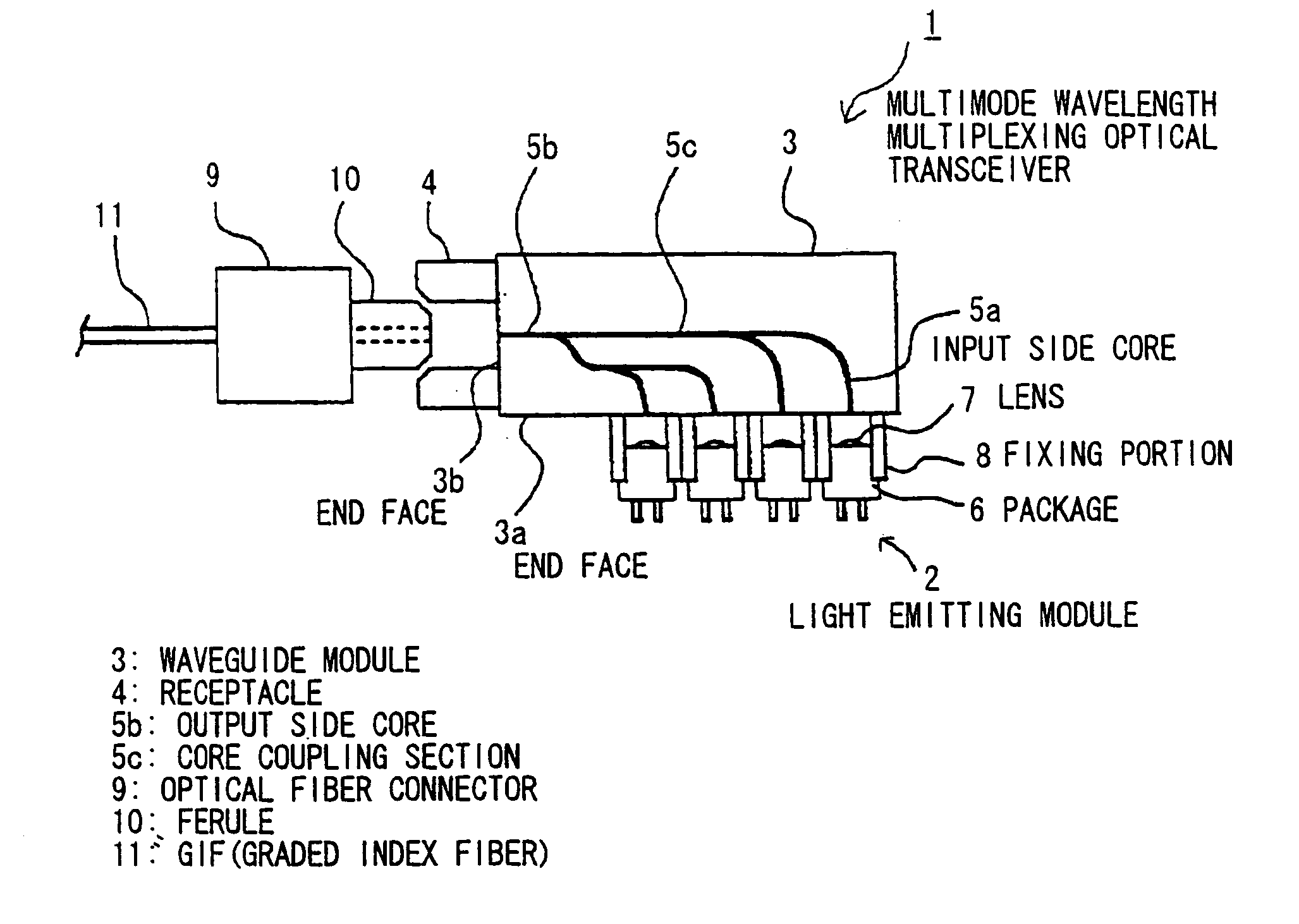
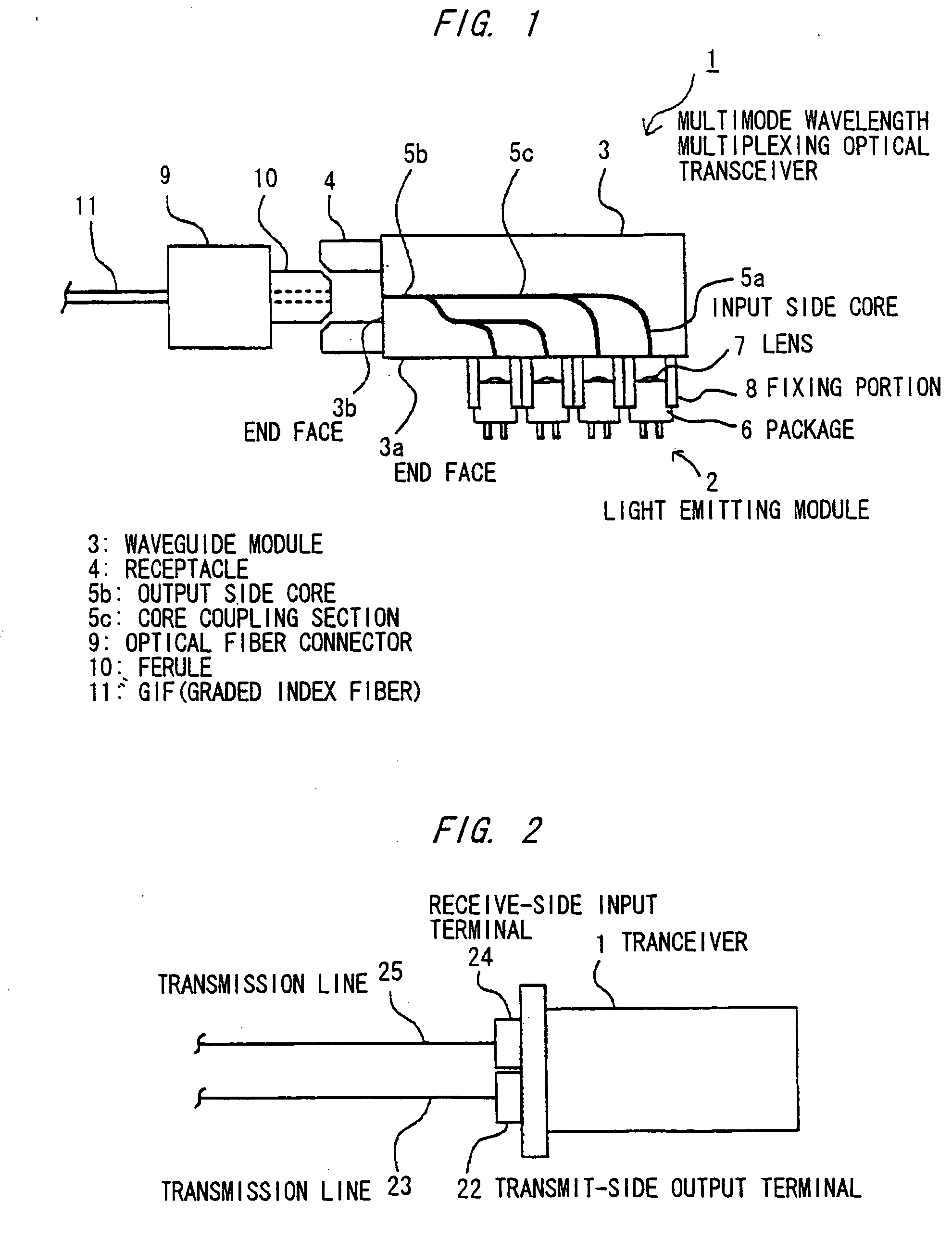
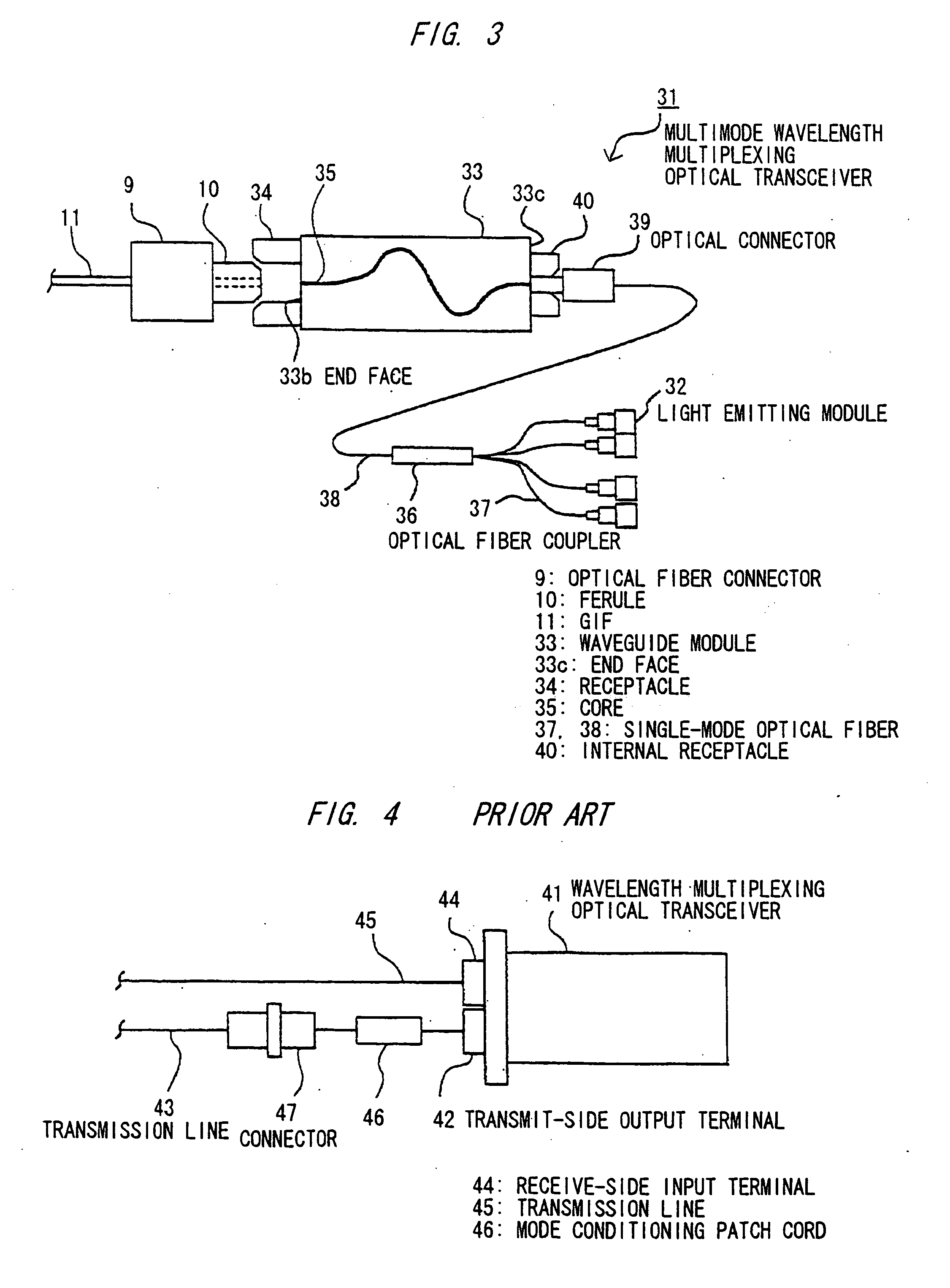
Multimode wavelength multiplexing optical transceiver
A multimode wavelength multiplexing optical transceiver has: a plurality of light emitting elements that emit single-mode lights with wavelengths different from each other; and a multimode waveguide module that is operable to multiplex the emitted single-mode lights into a multimode light. The multimode waveguide module is a step-index type multimode waveguide module that is operable to reduce a low-order mode component of the multimode light.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
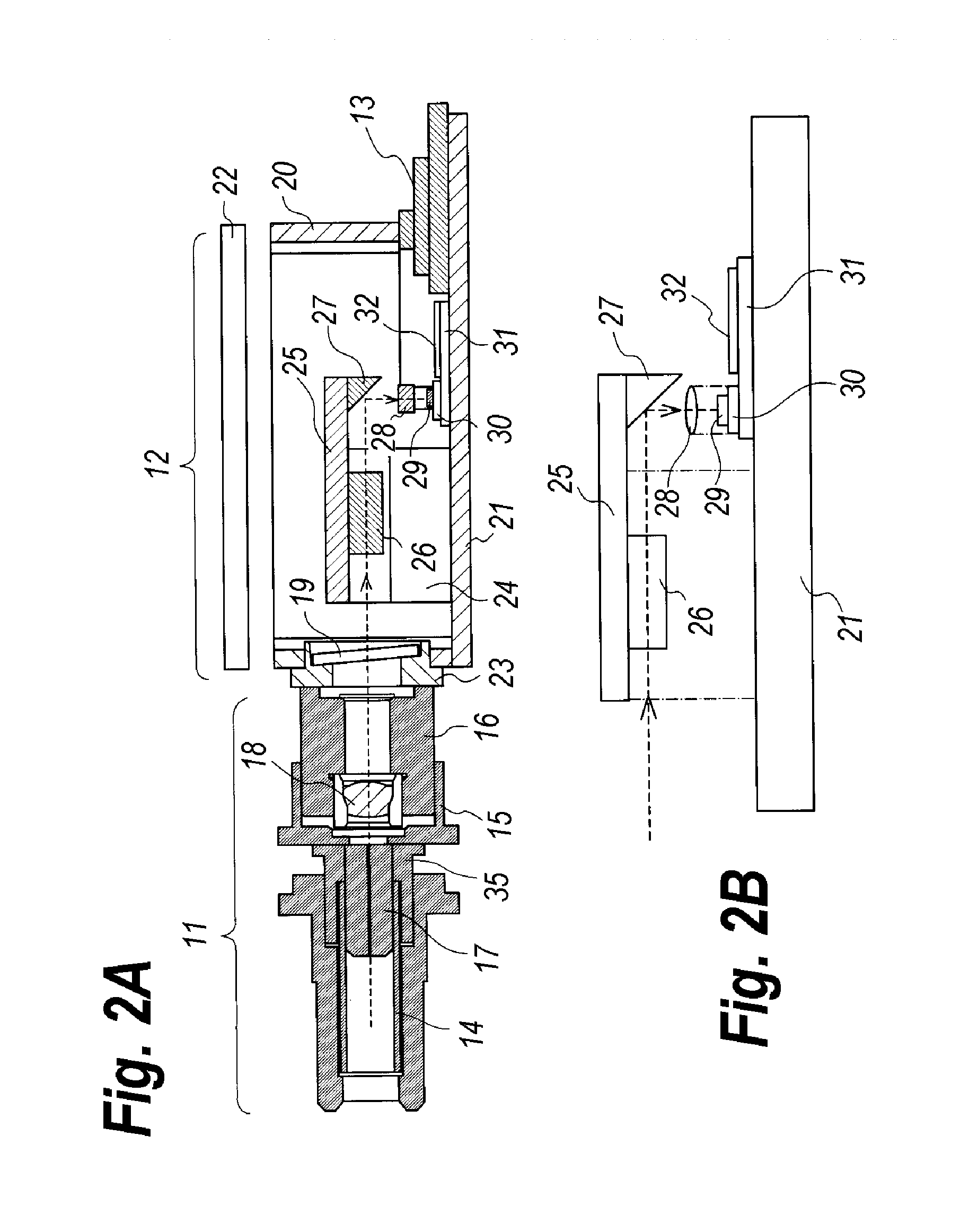
Receiver optical module for receiving wavelength multiplexed optical signals and method to assemble the same
ActiveUS20130148970A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesLight reflexOptical Module
A receiver optical module to facilitate the assembling is disclosed. The receiver optical module includes an intermediate assembly including the optical de-multiplexer and the optical reflector each mounted on the upper base, and the lens and the PD mounted on the sub-mount. The latter assembly is mounted on the bottom of the housing; while, the former assembly is also mounted on the bottom through the lower base. The upper base is apart from the bottom and extends in parallel to the bottom to form a surplus space where the amplifying circuit is mounted.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
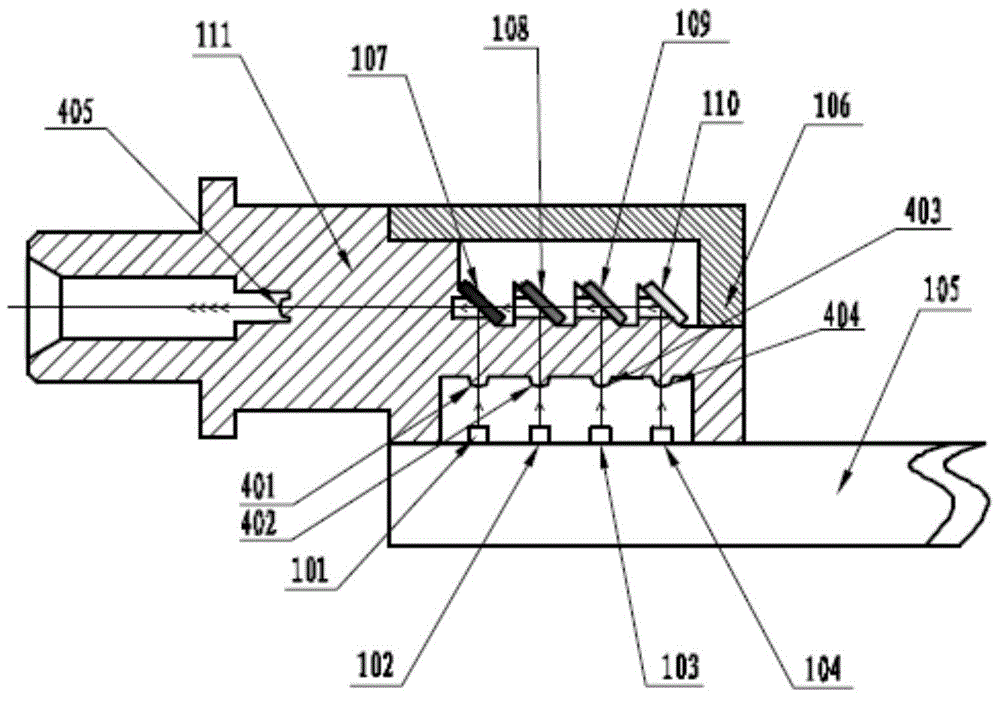
Multi-wavelength multiplexing/demultiplexing parallel light receiving/emitting component
InactiveCN104597575ALow costFirmly connectedCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transceiversLight spotOptical communication
The invention is suitable for the optical communication field and discloses a multi-wavelength multiplexing / demultiplexing parallel light receiving / emitting component. Four laser emitting chips or detector receiving chips arranged on a PCB circuit board are located on the same straight line; four collimating lenses are respectively located above the four laser emitting chips or detector receiving chips, and top light spots are aligned to the centers of photosensitive surfaces of the four detector receiving chips or the four laser emitting chips; four wavelength division multiplexing / demultiplexing optical filters are respectively arranged above the four collimating lenses and parallel to each other, the reflecting surfaces face to the downside, and the angle between each reflecting surface and the PCB circuit board is 45 degrees; a fifth collimating lens is located at one side of the reflecting surface of each wavelength division multiplexing / demultiplexing optical filter, and the optical paths between the fifth collimating lenses and the wavelength division multiplexing / demultiplexing optical filters are vertical to the optical paths between the wavelength division multiplexing / demultiplexing optical filters and laser emitting chips or detector receiving chips. Several channels only need one optical fiber to perform communication transmission, and the optical fiber cost is greatly saved.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Wavelength multiplexer/demultiplexer and method of manufacturing the same
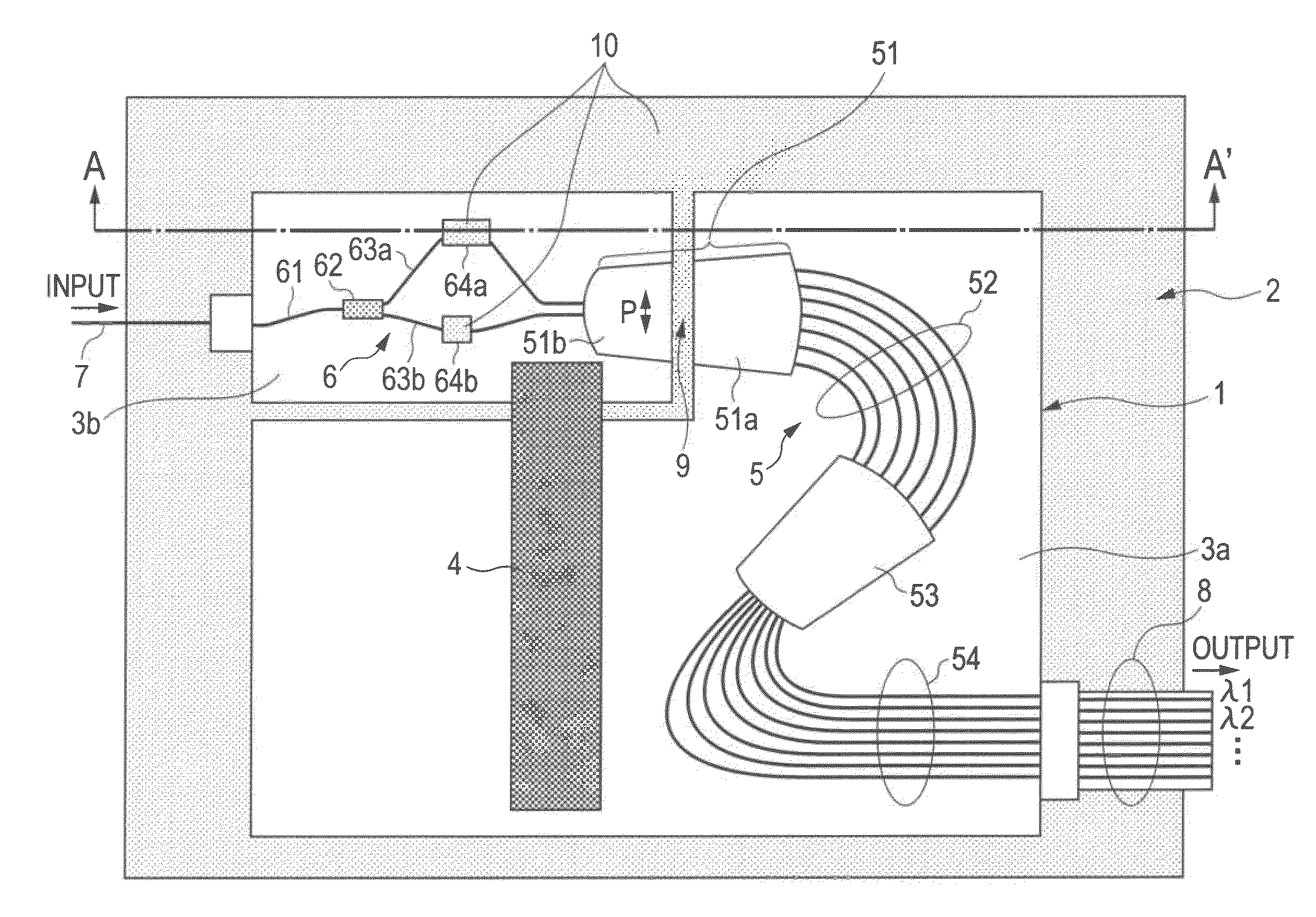
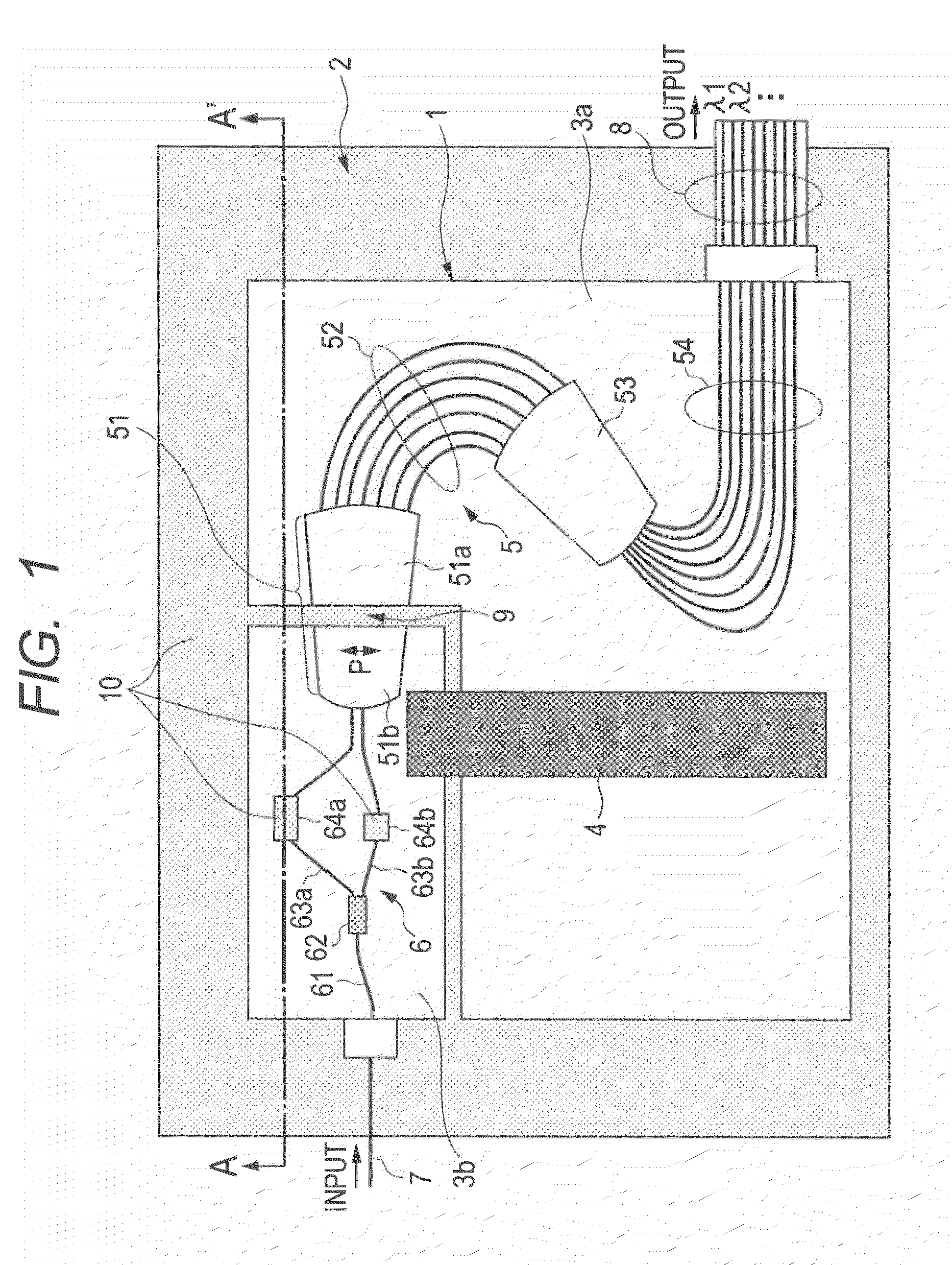
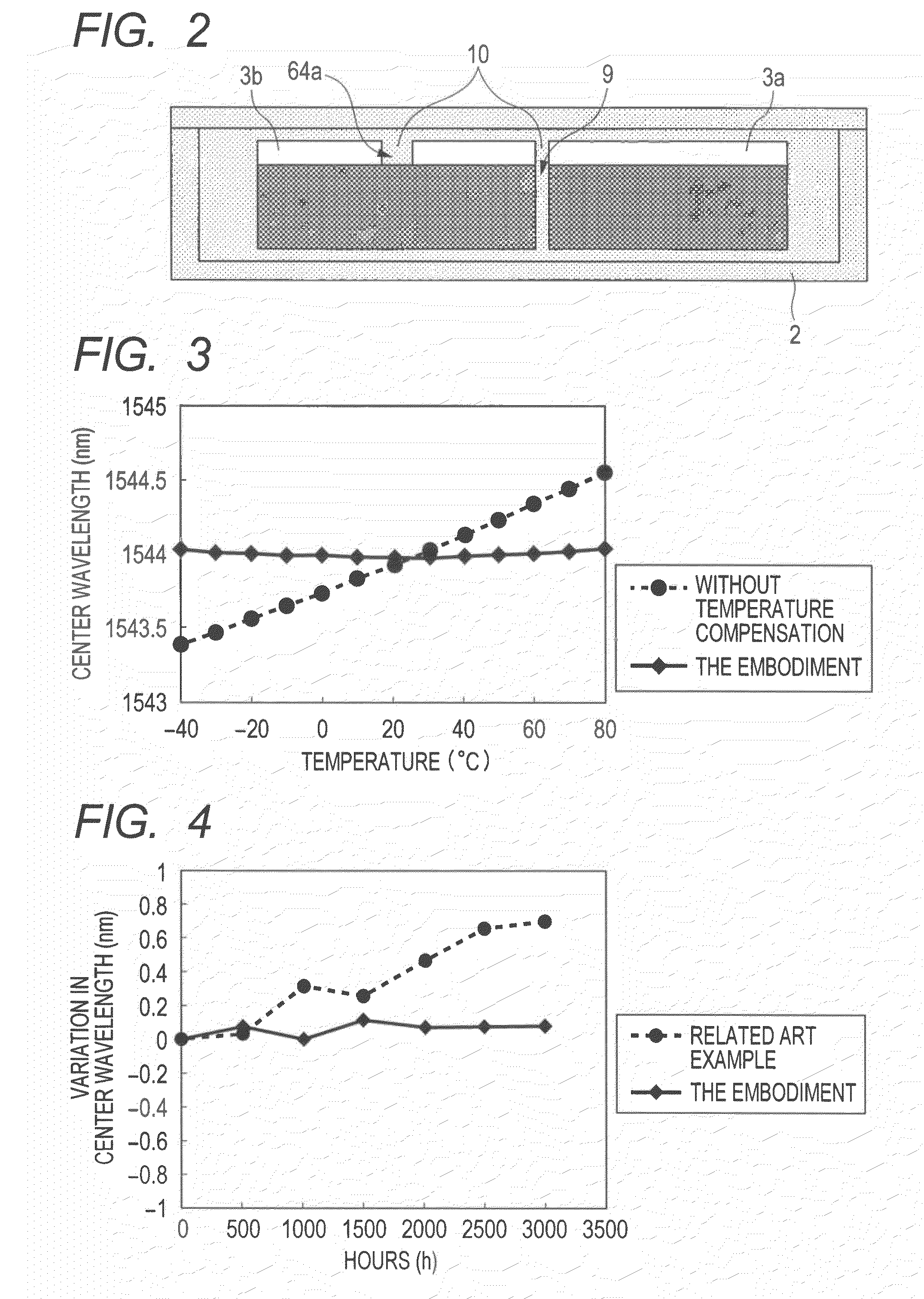
InactiveUS20120002918A1Degrade temperature compensationSimple configurationOptical articlesCoupling light guidesWavelength reuseMultiplexer
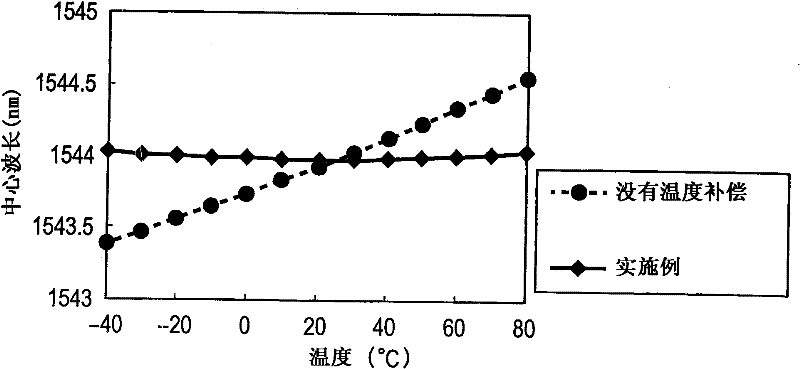
The present invention provides a wavelength multiplexer / demultiplexer comprising a Mach-Zehnder interferometer and an arrayed waveguide diffraction grating, the wavelength multiplexer / demultiplexer having a simple configuration and being capable of reducing the degradation in the temperature compensation characteristics of a temperature compensation material provided in the Mach-Zehnder interferometer or the peeling-off of the temperature compensation material, and a method of manufacturing the same. A wavelength multiplexer / demultiplexer comprises an AWG including two separated slab waveguides and an MZI including two arm waveguides. A temperature compensation groove is formed in the two arm waveguides, wherein in a space between the temperature compensation groove, and two separated slab waveguides, a compensation material, the refractive index matching that of the AWG or Mach-Zehnder interferometer, the compensation material having a temperature dependence coefficient with a sign different from that of the temperature dependence coefficient of the waveguide core and having plasticity or fluidity, is filled.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Arrayed waveguide grating based modular interconnection networks and methods for constructing and applying the same
ActiveUS20160056911A1Reduced Routing ComplexitySimplify networking maintenanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingTransceiver
An arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) based interconnection network and modular construction method, comprising N1 left nodes, with each left node having N2 ports, N2 right nodes, with each right node having N1 ports, where N1≧N2, N1 and N2 having a greatest common divisor r, and each port having an optical transceiver associated with a fixed wavelength; N1n2 r×1 wavelength multiplexers having their input ports respectively connected with the ports of N1 left nodes, where n2=N2 / r; N2n1 1×r wavelength demultiplexers having their output ports respectively connected with the ports of N2 right nodes, where n1=N1 / r; n1n2 r×r AWGs connecting the r×1 wavelength multiplexers and the 1×r wavelength demultiplexers r×rn1n2, and each of the r×r AWGs being associated with a wavelength subset {λk|k=0, 1, . . . , r−1}.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
System for realizing wavelength reuse of self-injection wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network and method thereof
InactiveCN101557540AIncrease profitReduce light intensityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberWavelength reuse
The invention relates to a system for realizing wavelength reuse of a self-injection wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network and a method thereof. The system is formed by an optical line terminal OLT connected with remote nodes RN through a feed fiber, and the remote nodes RN connected with a plurality of optical network units ONU, wherein 2n optical network units ONU are divided into a group I of the optical network units ONU and a group II of optical network units ONU, and the number of the optical network units ONU in each group is the same, while uplink signals and downlink signals of two groups of the optical network units ONU are just opposite and do not have interaction with each other; the remote nodes are connected with the two groups of the optical network units ONU respectively and realize downlink signal separation, uplink signal combination and generation and return of seed light of the two groups of the optical network units ONU. The method realizes wavelength reuse by the system, divides the usable wave band into a wave band A and a wave band B, wherein the group I of the optical network units ONU carries the uplink signal and the seed light thereof by the wavelength of the wave band A, carries the downlink signal by the wavelength of the wave band B, while the group II of the optical network units ONU are just the opposite, thereby reusing the uplink signal and the downlink signal of the group I of the optical network units ONU by the group II of the optical network units ONU, not only avoiding that the seed light and the downlink signal cannot be separated by the optical network units ONU due to the fact that the seed light and the downlink signal are in the same wave band and are aliased with each other, but also realizing doubling of the number of the optical units ONU supported by the system and the wavelength utilization ratio.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Wavelength multiplexing in waveguides
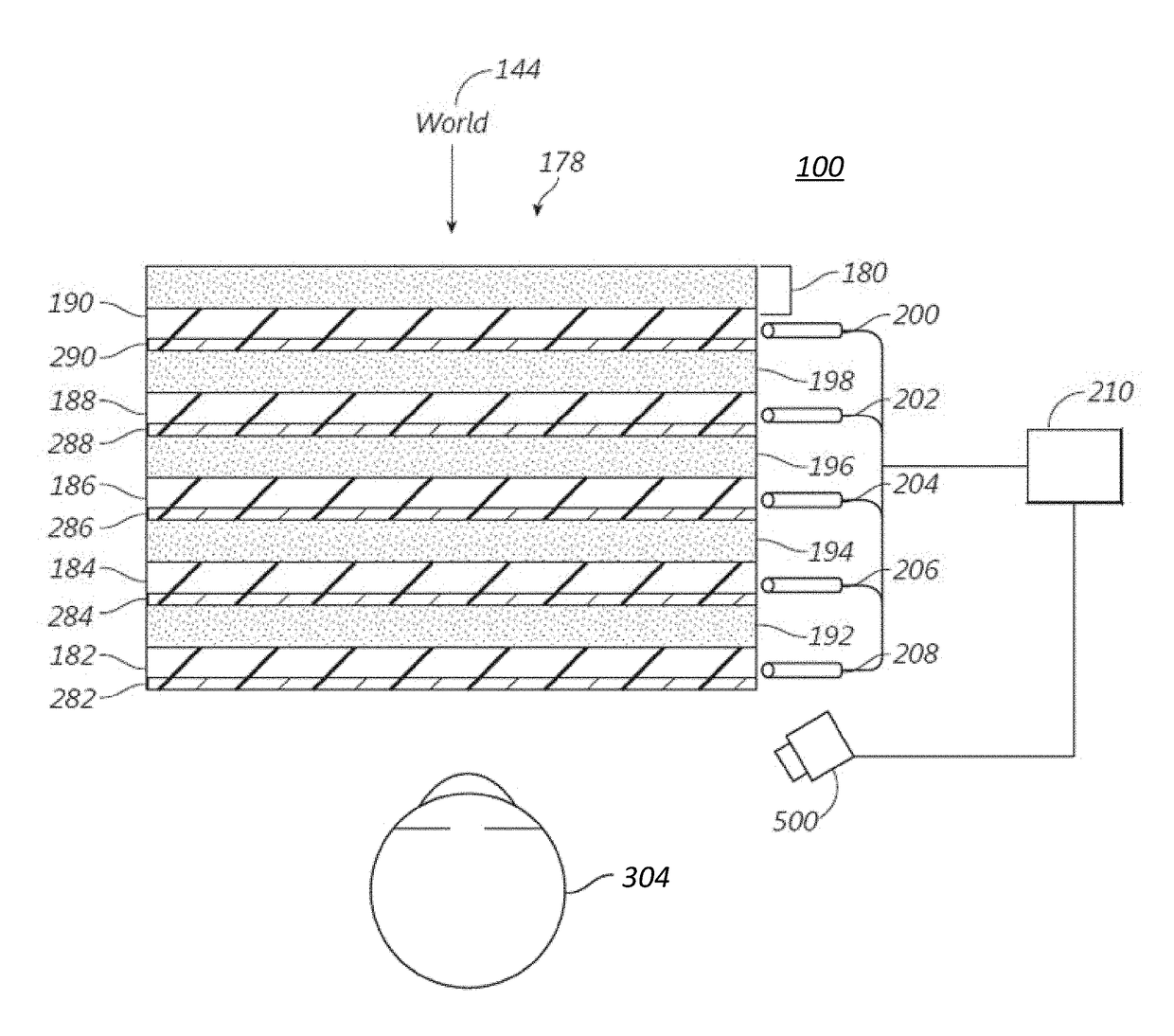
A stacked waveguide assembly can have multiple waveguide stacks. Each waveguide stack can include a plurality of waveguides, where a first waveguide stack may be associated with a first subcolor of each of three different colors, and a second waveguide stack may be associated with a second subcolor of each of the three different colors. For example, the first stack of waveguides can incouple blue, green, and red light at 440 nm, 520 nm, and 650 nm, respectively. The second stack of waveguides can incouple blue, green, and red light at 450 nm, 530 nm, and 660 nm, respectively.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Wavelength multiplexed quantitative differential interference contrast microscopy
InactiveUS20020089741A1Rapid and robust measurementMaximize useUsing optical meansMicroscopesBeam splitterPupil
A differential interference contrast (DIC) microscope system is provided comprising: (a) an illumination source for illuminating a sample ; (b) a lens system for viewing the illuminated sample, including an objective, defining an optical axis; (c) at least one detector system for receiving a sample image; (d) mechanisms for wavelength multiplexing the shear direction or shear magnitude or both on the sample and demultiplexing the resultant DIC images on the detector; and (e) a mechanism for modulating the phase of the interference image. Various approaches are disclosed to accomplish wavelength multiplexing of shear direction and demultiplexing the two DIC images that result. It is possible for the two, wavelength multiplexed DIC images to differ in either or both shear direction or magnitude. These approaches include (1) two DIC microscopes, each operating at a different wavelength, but which share a single objective through a beam splitter; (2) a segmented DIC prism that is made in four sections where opposite sections are paired and have the same shear direction and amount, and each pair of sections have filters transmitting different wavelengths; (3) a segmented DIC prism that is located in or near an aperture stop or pupil of said DIC microscope to obtain data in two shear directions that is multiplexed by wavelength; (4) a dual field-of-view optical system with two DIC prisms, one in each path to wavelength multiplex shear direction or shear magnitude through said objective; (5) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of a wavelength selective beam splitter and two detectors; (6) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of a wavelength controlled source and a single detector; and (7) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of dual field-of-view optics and a single detector. These various approaches permit rapid, robust measurement of slope in two directions. Further, phase shifting and DIC microscopy are limited to measurements within the depth of focus (DOF) of the objective while WLI microscopy is not.
Owner:KUHN WILLIAM P
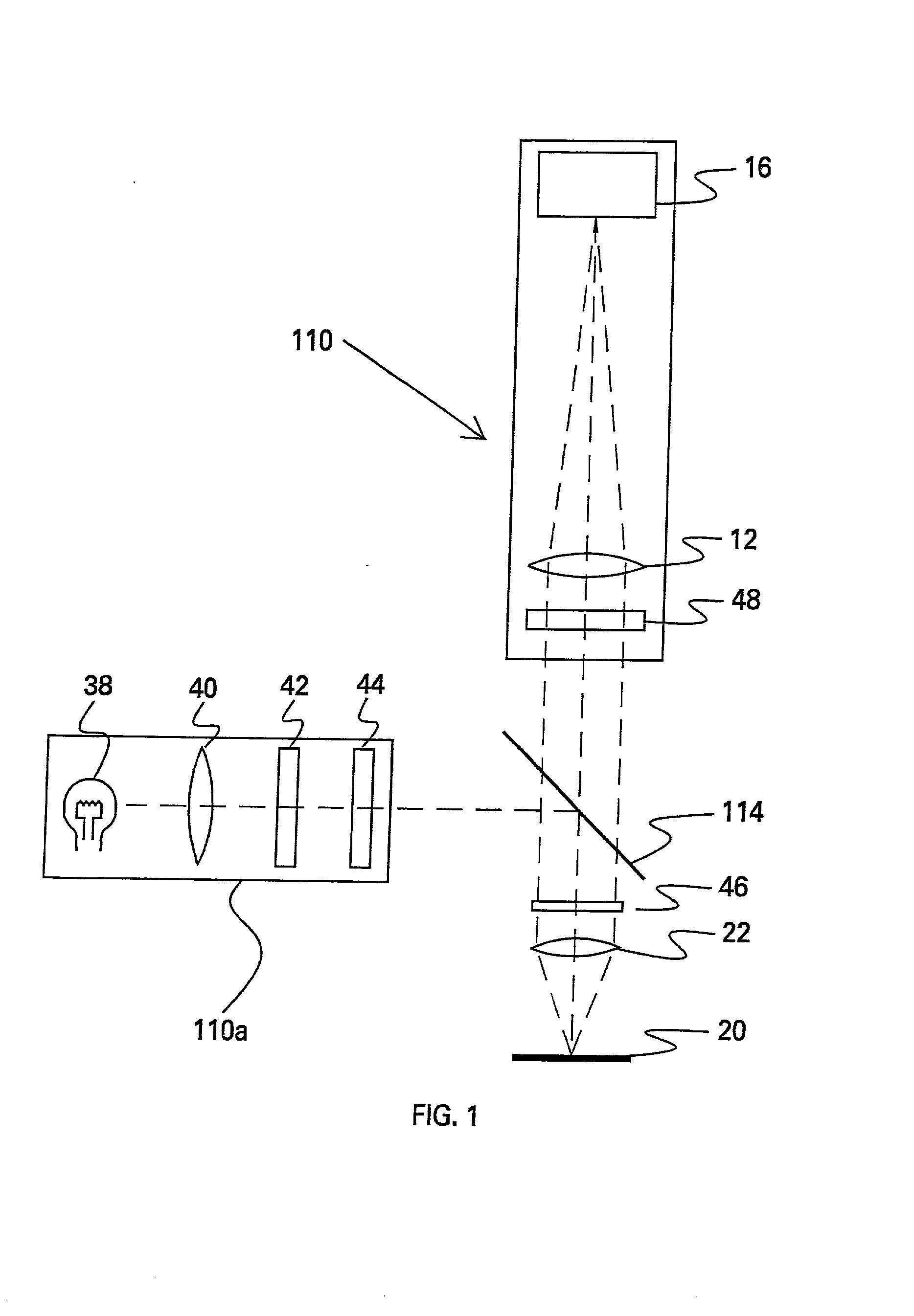
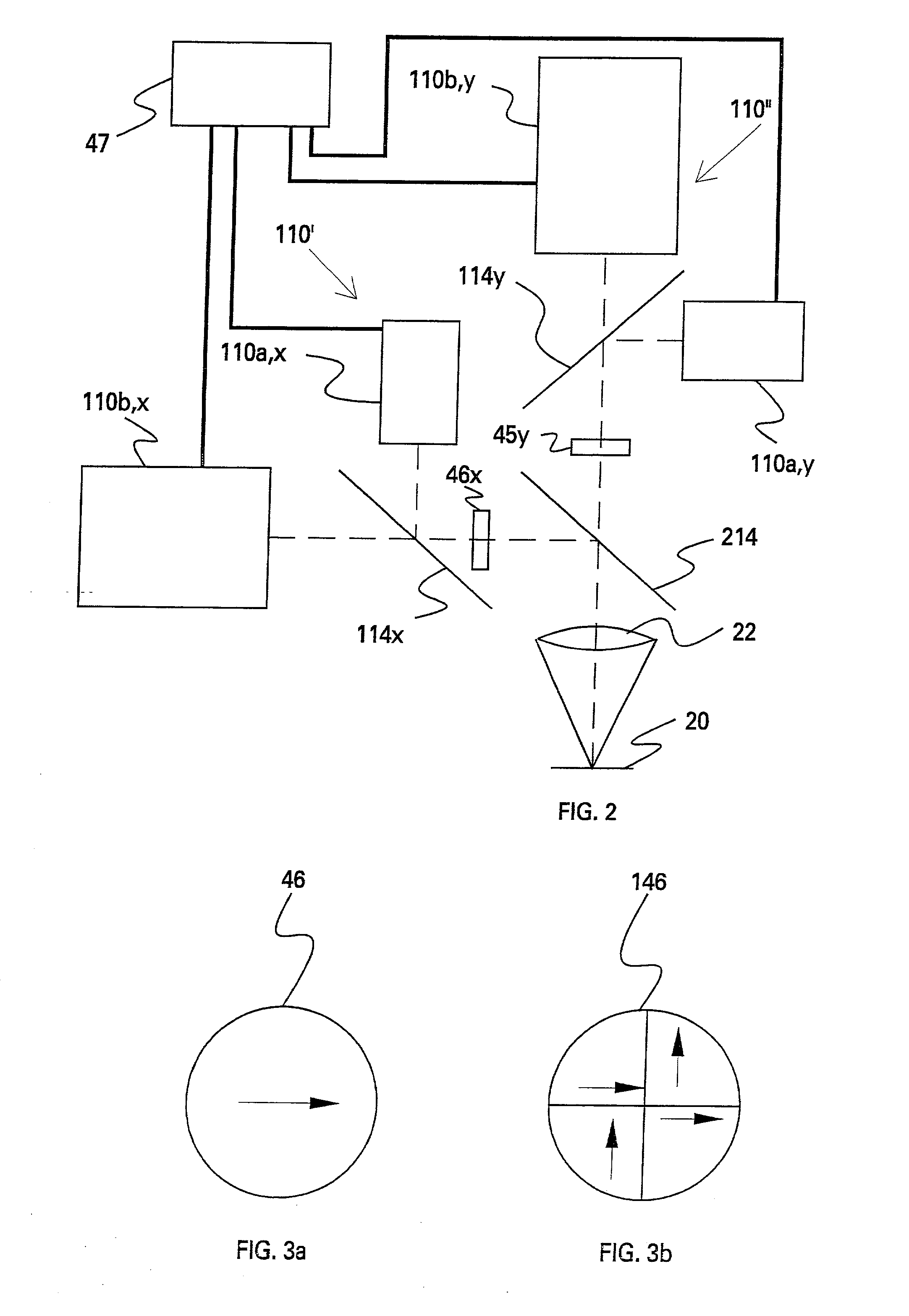
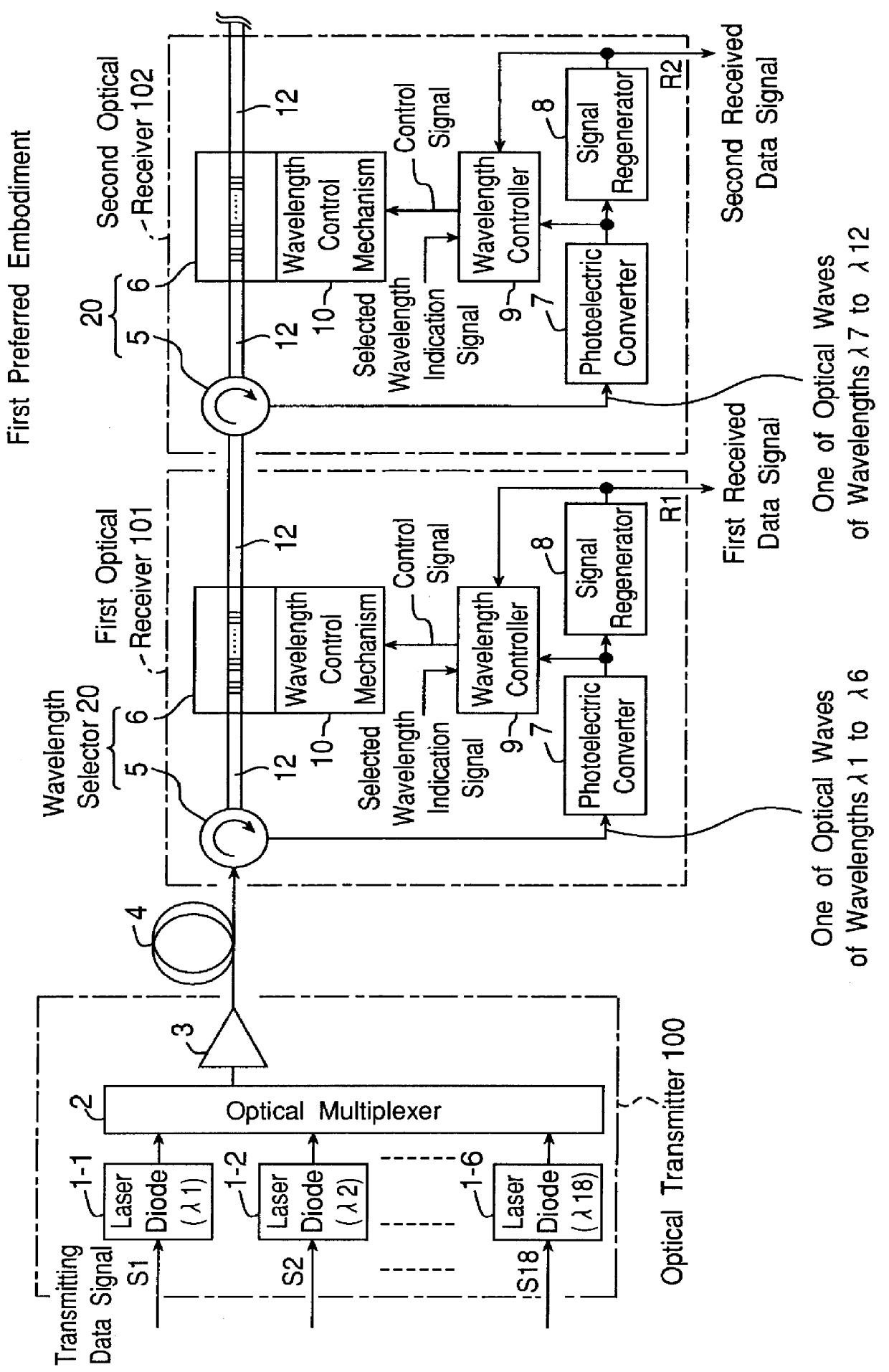
Wavelength-multiplexing optical transmission system provided with wavelength selectors
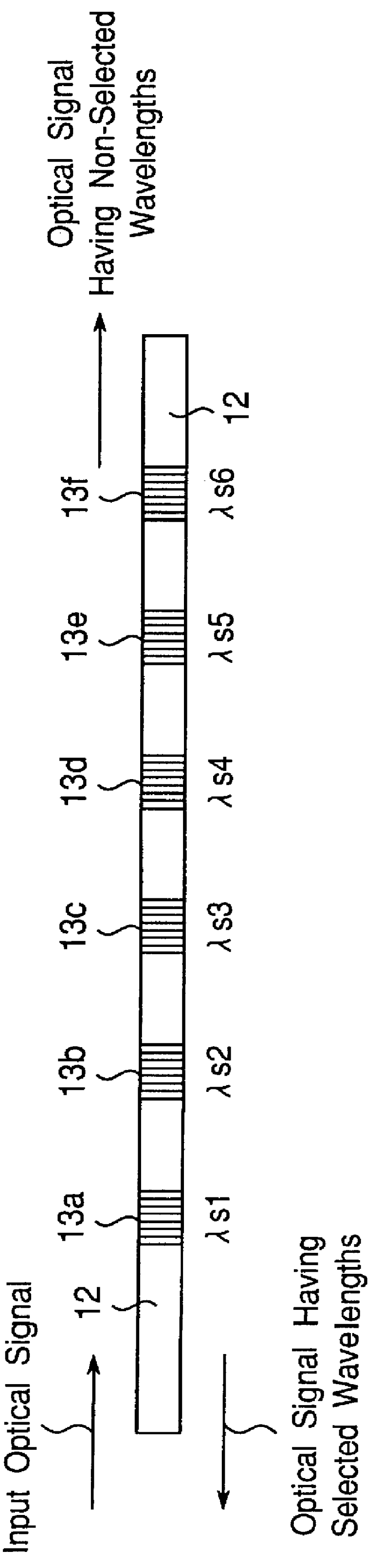
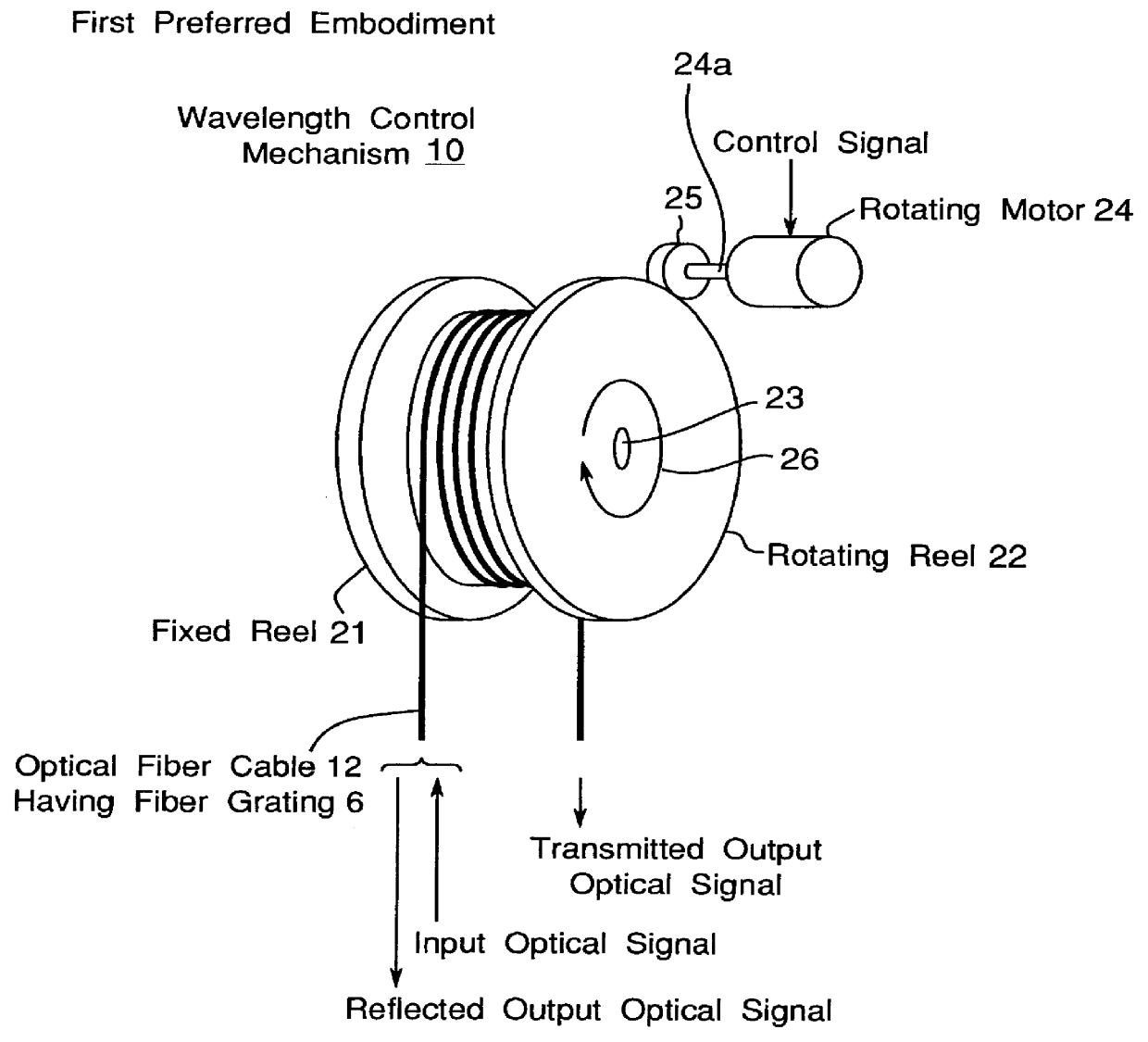
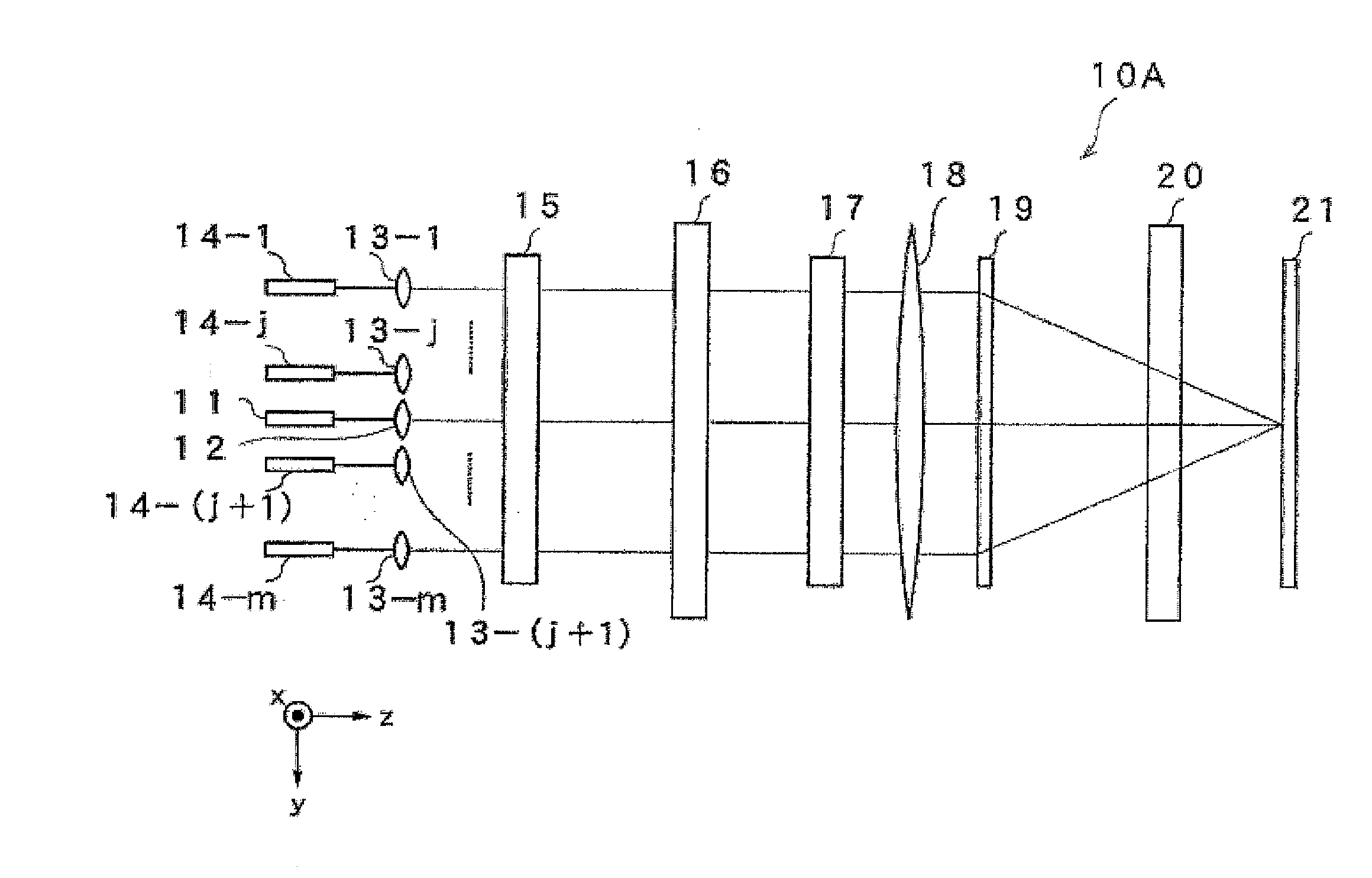
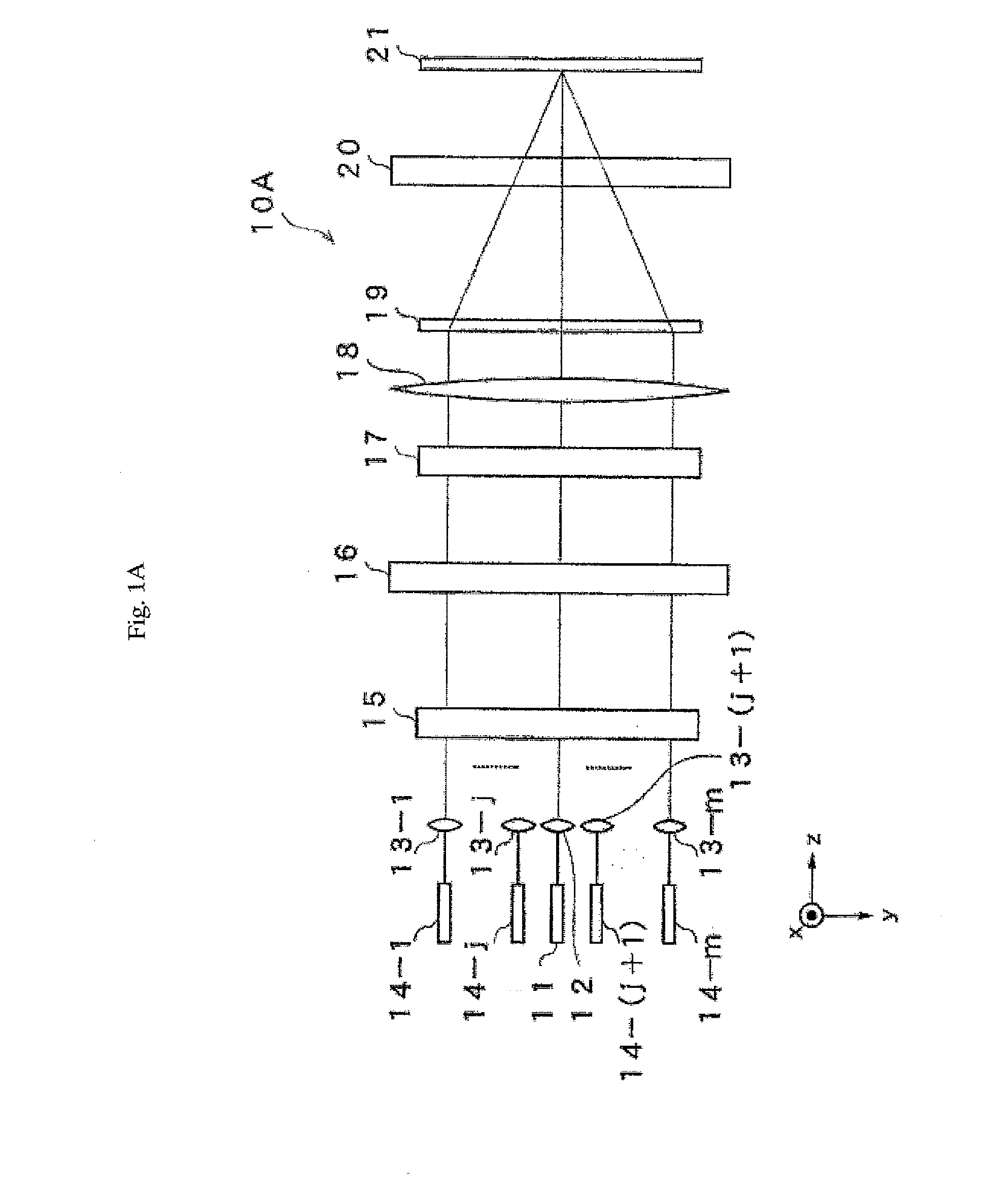
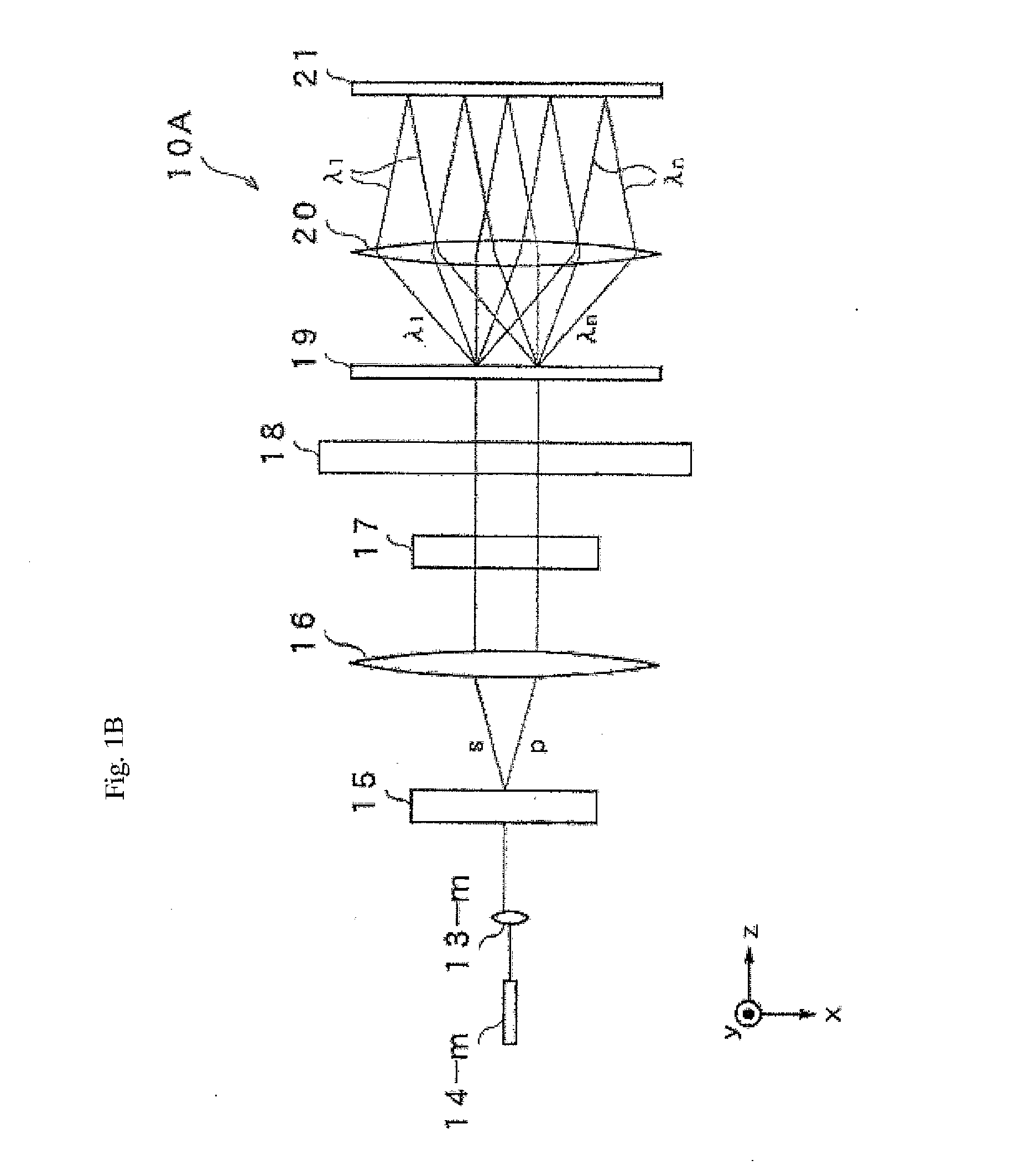
A wavelength-multiplexing optical transmission system includes (a) an optical transmitter 100 for wavelength-multiplexing a plurality of optical signals having different wavelengths and transmitting a wavelength-multiplexed optical signal, (b) an optical fiber cable 4 for transmitting a plurality of transmitted optical signals, and (c) an optical receiver 101 for receiving a plurality of transmitted optical signals. The optical receiver 101 includes a wavelength selector 20 for demultiplexing an optical signal having a predetermined wavelength of a plurality of received optical signals and outputting the demodulated signal. The wavelength selector 20 has comb-shaped wavelength selection characteristics for selectively filtering an optical signal having a plurality of selected wavelengths. A wavelength selection interval DELTA lambda between two adjacent selected wavelengths of the wavelength selection characteristics is different from a signal wavelength interval delta lambda between two adjacent signal wavelengths of a plurality of wavelength-multiplexed optical signals. The difference therebetween is set so that substantially a single optical signal is selectively filtered from a plurality of received optical signals. The wavelength selector 20 includes a wavelength control mechanism 10 for shifting the selected wavelengths of the wavelength selection characteristics, respectively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wavelength selective optical switching devices
ActiveUS20130128215A1Reduce polarizationPolarization lossCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsPolarization diversityWavelength reuse
A wavelength selective switch device includes an incidence part where wavelength multiplexed light made of light of a plurality of wavelengths enters, an exit part that includes a plurality of fiber that outputs light of a wavelength selected from a signal in which wavelength multiplexed light that entered from the incidence part enters, a polarization diversity part that separates incidence light that entered the incidence part according to polarization components of the incidence light to make first and second optical beams, a wavelength dispersion and synthesis element that spatially disperses incidence light according to a wavelength of the incidence light and multiplexes the spatially dispersed reflected light according to the wavelength, and a wavelength dispersion and synthesis element that spatially disperses incidence light according to a wavelength of the incidence light and multiplexes the spatially dispersed reflected light according to the wavelength.
Owner:SANTEC
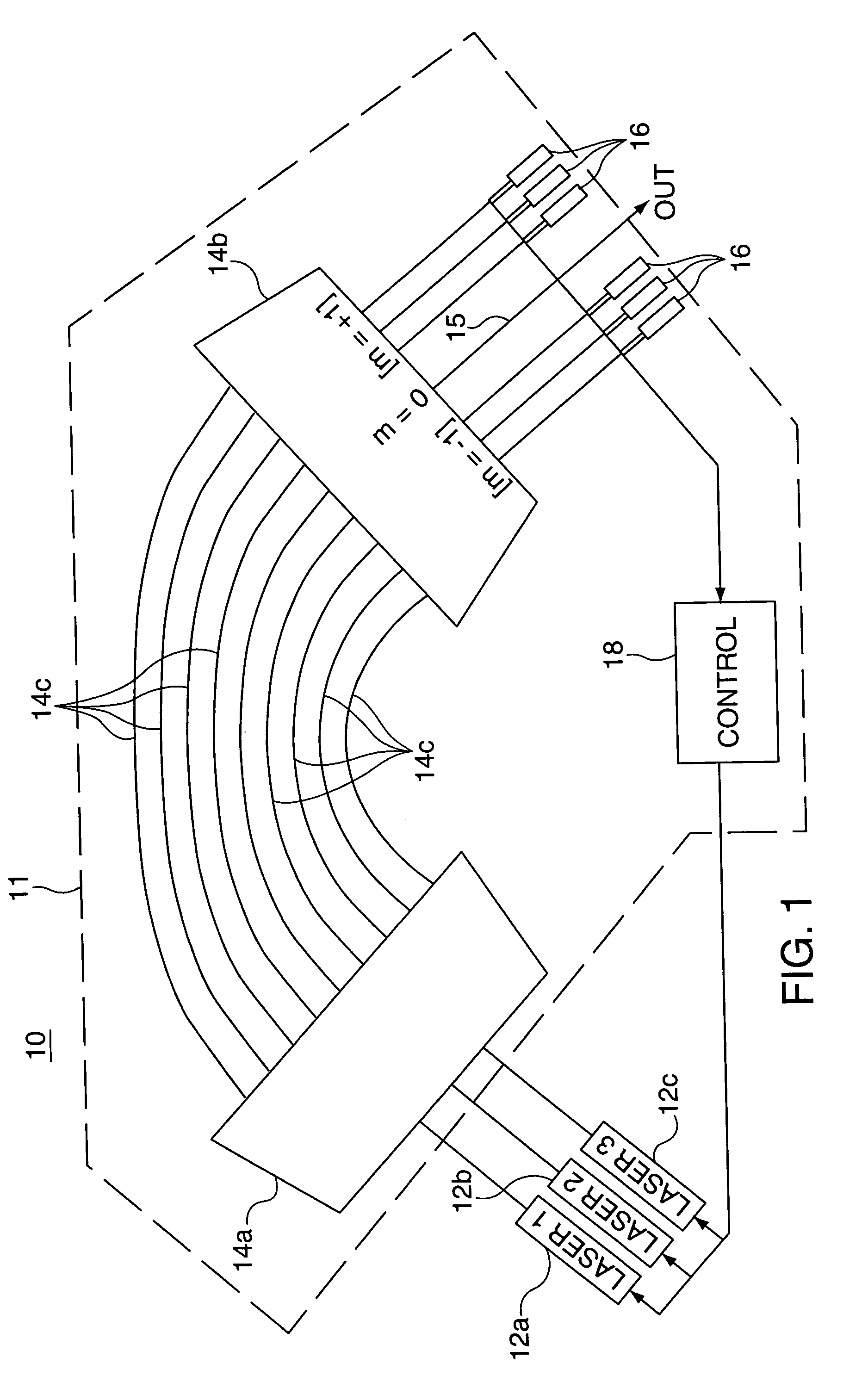
Combination wavelength multiplexer and wavelength stabilizer
InactiveUS20050089273A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingGrating
In an optical device, each of a plurality of radiation sources generates a separate different wavelength output signal to a wavelength locking device wherein a grating device receives the separate wavelength output signals from the plurality of radiation sources. The grating device generates a multiplexed wavelength output signal at a zero diffraction order output port thereof, and resolves separate symmetric wavelength+δ and wavelength−δ output signals at separate predetermined locations within at least one non-zero diffraction order thereof for each of the radiation sources. Each of a plurality of radiation detectors is coupled to receive a separate one of the symmetric wavelength+δ and wavelength−δ output signals and generate an output signal representing the magnitude of the received wavelength output signal. A control device is responsive to output signals from each pair of radiation detectors coupled to receive the separate symmetric wavelength+δ and wavelength−δ output signals from a specified predetermined radiation source for generating an output control signal appropriate to that radiation source for locking the wavelength thereof.
Owner:OPTOVIA +1
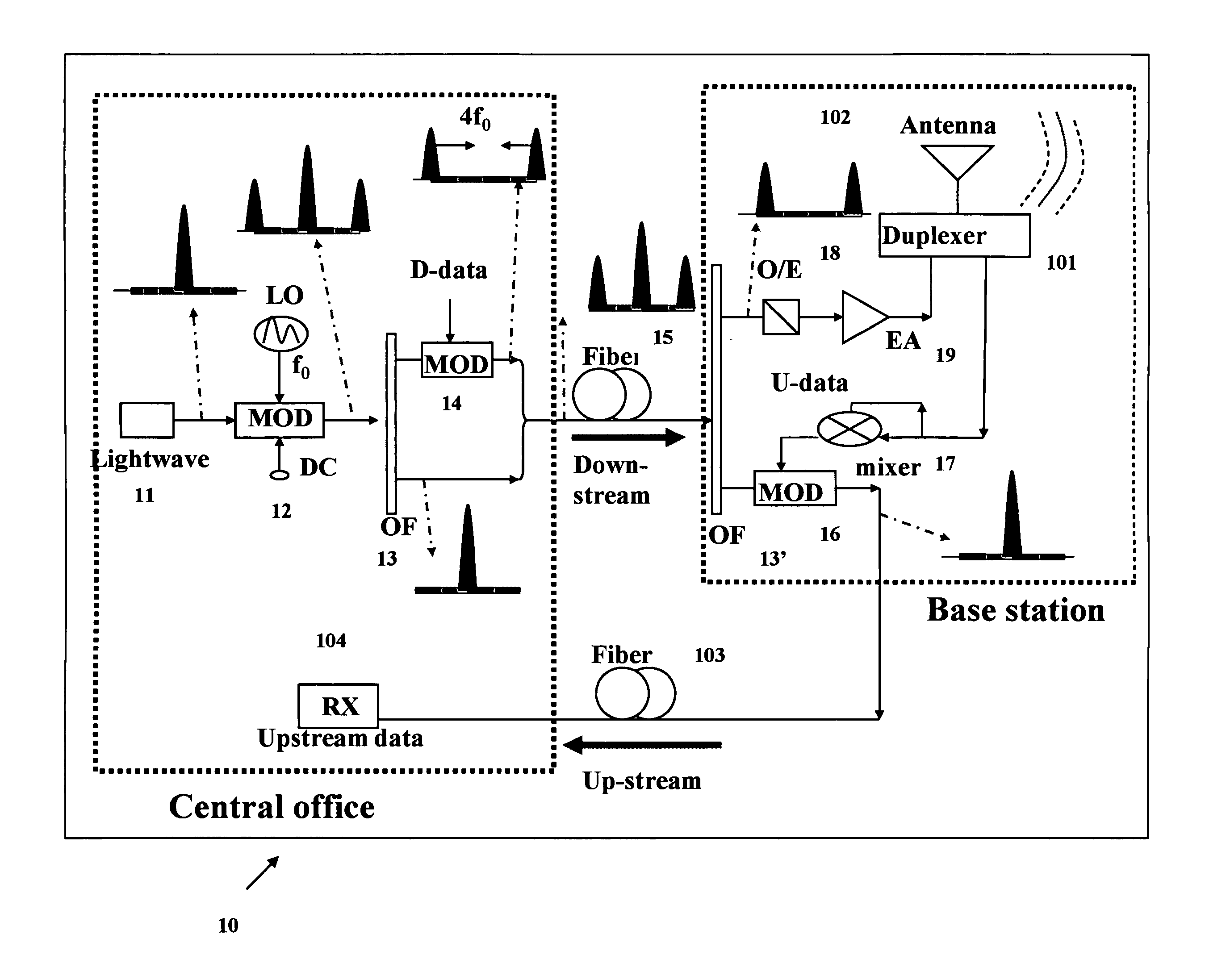
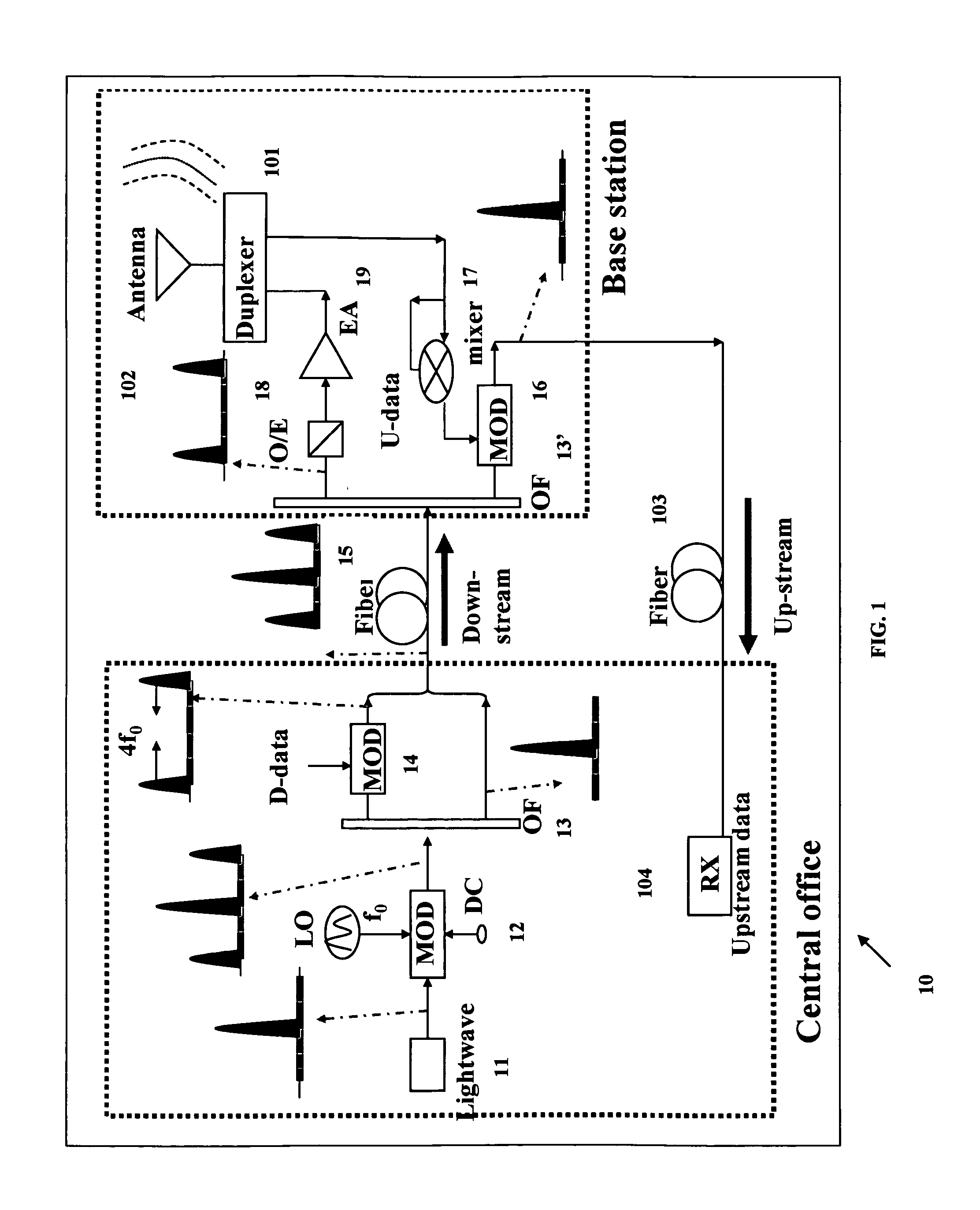
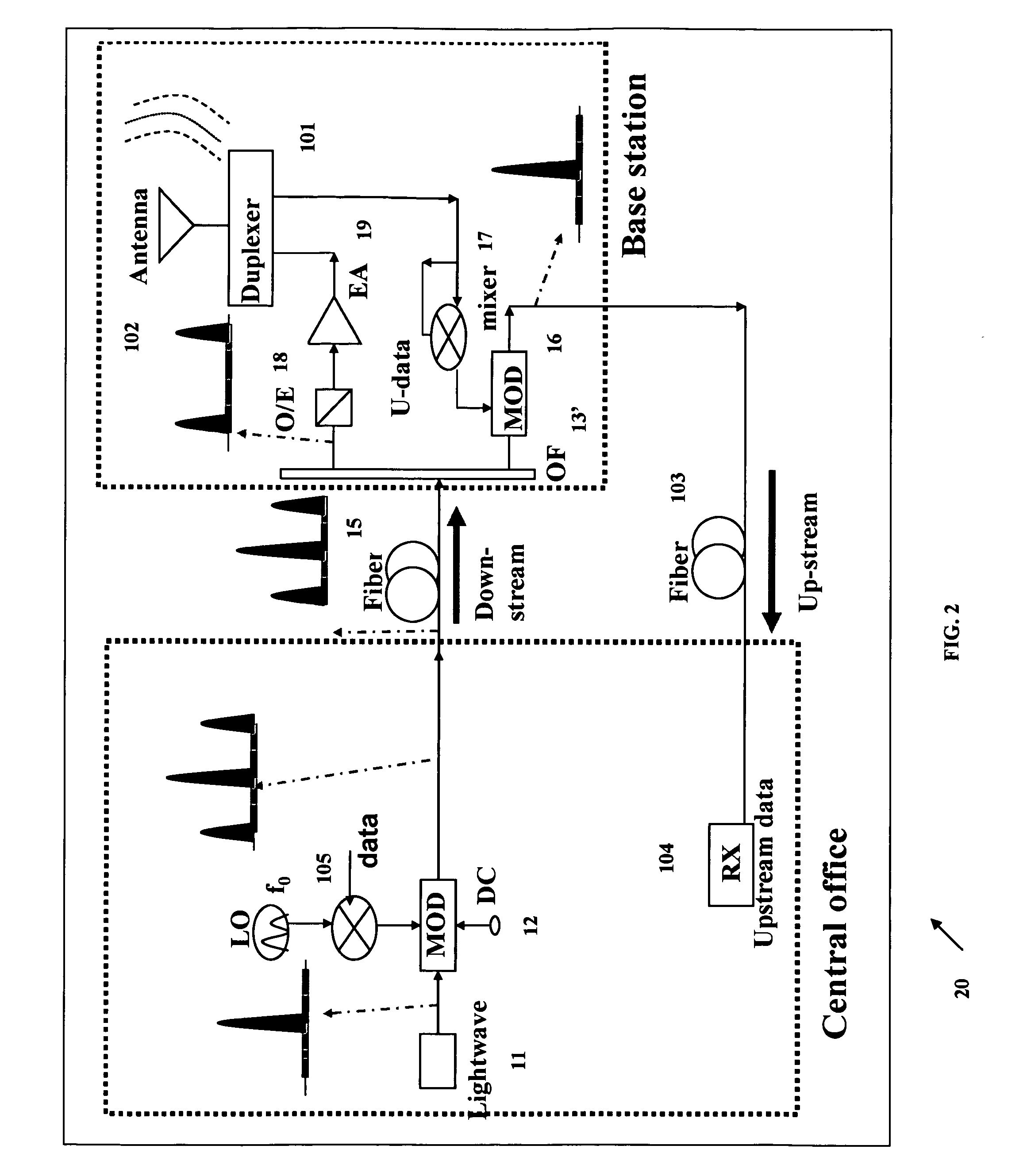
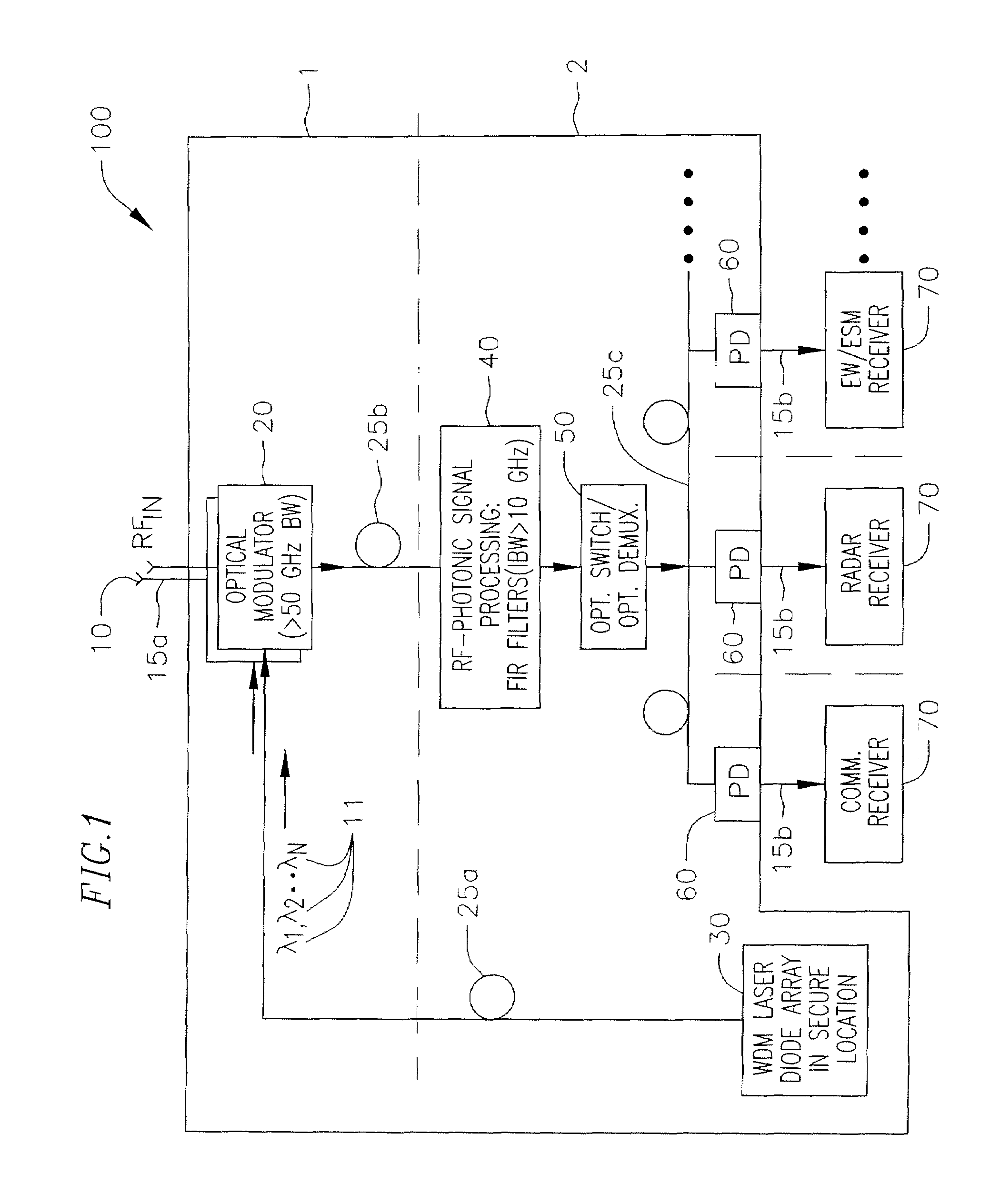
High Frequency Optical Millimeter-Wave Generation and Wavelength Reuse
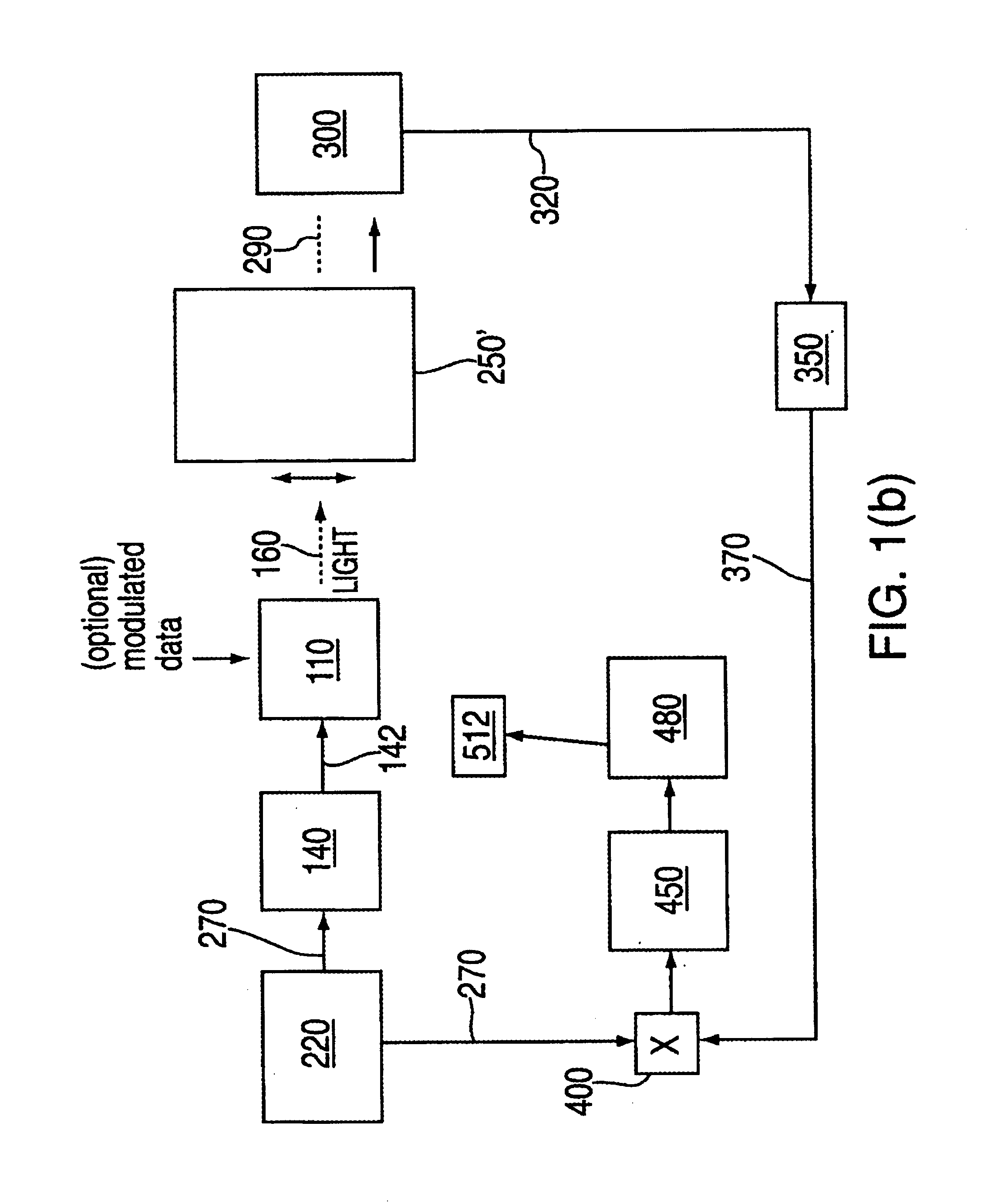
A method includes generating an optical millimeter wave signal for modulation of a first data signal, and deriving from the generated optical millimeter wave signal a subsequent light source for modulation of a second data signal. More specifically the generating includes modulating a light wave to a multiple of a frequency of an oscillating signal. Alternatively, the generating includes modulating a data signal mixed with an oscillating signal to a multiple of a frequency of the oscillating signal. The deriving includes modulating a frequency component filtered from a data modulation of the generated optical millimeter wave signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Wavelength multiplexer/demultiplexer and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveCN102313925AReduced deterioration of temperature compensation characteristicsReduce sheddingOptical waveguide light guideMultiplexerWavelength reuse
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
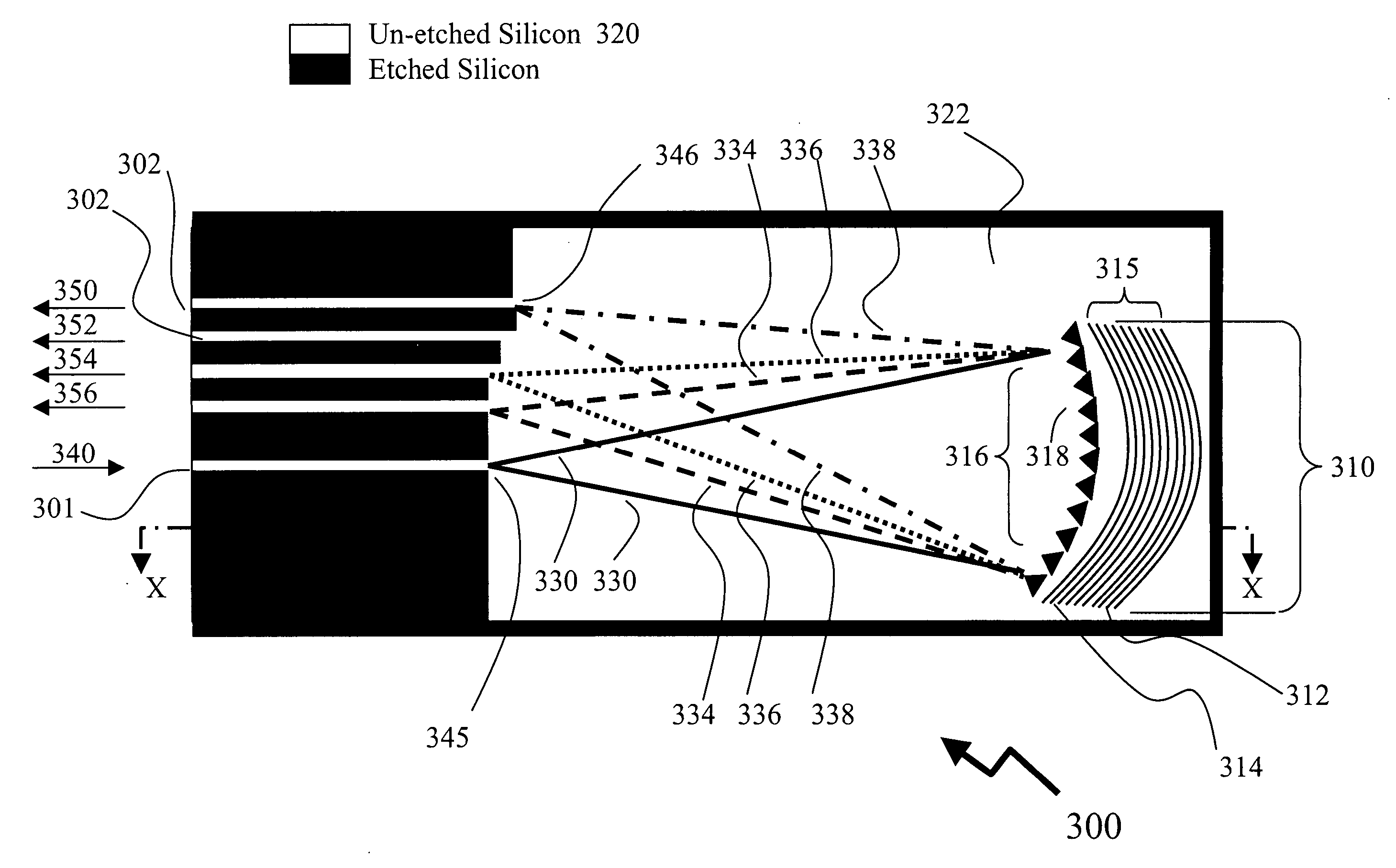
Porous silicon filter for wavelength multiplexing or de-multiplexing
A porous silicon filter for wavelength multiplexing and de-multiplexing. Preferred embodiments include rugate-type porous silicon filters with pores having continuously varying widths with pore depth an optical cross connect switch. In other preferred embodiments, the pores are filled with a material that changes index of refraction with changes in applied voltage, current or temperature. Important applications of these porous silicon filters are for multiplexing and de-multiplexing in fiber optic communication systems. For example, a preferred embodiment is an all optical fiber optic switch utilizing these filters.
Owner:CROSSFIBER +1
First and second derivative processing of wavelength multiplexed optical signals
ActiveUS7062166B2Minimize optical signal attenuationMinimize degreeWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringUltrasound attenuationTransmission channel
A system and method for optimizing performance characteristics of optical networks. The system and method exploits a wavelength-locked loop servo-control circuit and methodology that enables real time adjustment of optical signals in accordance with attenuation characteristics of an optical transmission channel. Particularly, the invention enables alignment of optical signal center wavelengths and optical wavelength selective devices exhibiting a peaked passband function in optical networks utilizing information included in first derivative and second derivatives of dither modulated optical signals extracted from a feedback signal provided in the wavelength-locked loop servo-control circuit.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wavelength-multiplexed light amplifying apparatus, optical amplifier and optical add-and-drop apparatus using wavelength-multiplexed light amplifying basic unit
The present invention relates to a wavelength-multiplexed light amplifying apparatus to be used in a state of being connected to a branching portion of a multiplexing / branching unit or to be used for a mxn matrix optical switch of an optical cross-connect. The wavelength-multiplexed light amplifying apparatus is composed of a plurality of wavelength-multiplexed light amplifying units and an optical feedback loop system. A signal input port of an optical branching section in one wavelength-multiplexed light amplifying unit is connected to an output side of an optical amplifying section in the preceding wavelength-multiplexed light amplifying unit. This configuration disperses the power loss of an optical signal to perform amplification with high efficiency and further enables the expansion of the branching port in the in-service. Additionally, it can eliminate the need for the installation of an optical isolator or reduce the required value of isolation to stabilize the system, or can accomplish the control to maintain the gains of all ports constant.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High-frequency-response distributed optical fiber vibration sensing device and implementation method
InactiveCN107894276ANo crosstalkSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansRayleigh scatteringFrequency shift
The invention relates to a high-frequency-response distributed optical fiber vibration sensing device and an implementation method. The high-frequency-response distributed optical fiber vibration sensing device is provided with a light source module, a 1* n +1 light splitting modules, n frequency shifting modules, a 1*n coupling modules, an amplifying module, a polarization control module, a 2*2 couplers, an annular device, a sensing optical fiber, a detection module, a frequency mixing demodulation module, a synchronous acquisition module and a detection analysis module. The frequency division multiplexing technology is applied to a distributed optical fiber vibration sensing device, and the wavelength multiplexing optical pulse signals generate a backward rayleigh scattering signal in asensing optical fiber according to a time sequence. The signals are independent from each other, and crosstalk is prevented. The number of the samples of each detection point of the distributed optical fiber vibration sensing device is increased along with the number of the multiplexed wavelengths, the frequency response of the vibration signals is also increased along with the number of the multiplexed wavelengths, and the detection frequency response of the long-distance distributed optical fiber vibration device is not limited due to the distance.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
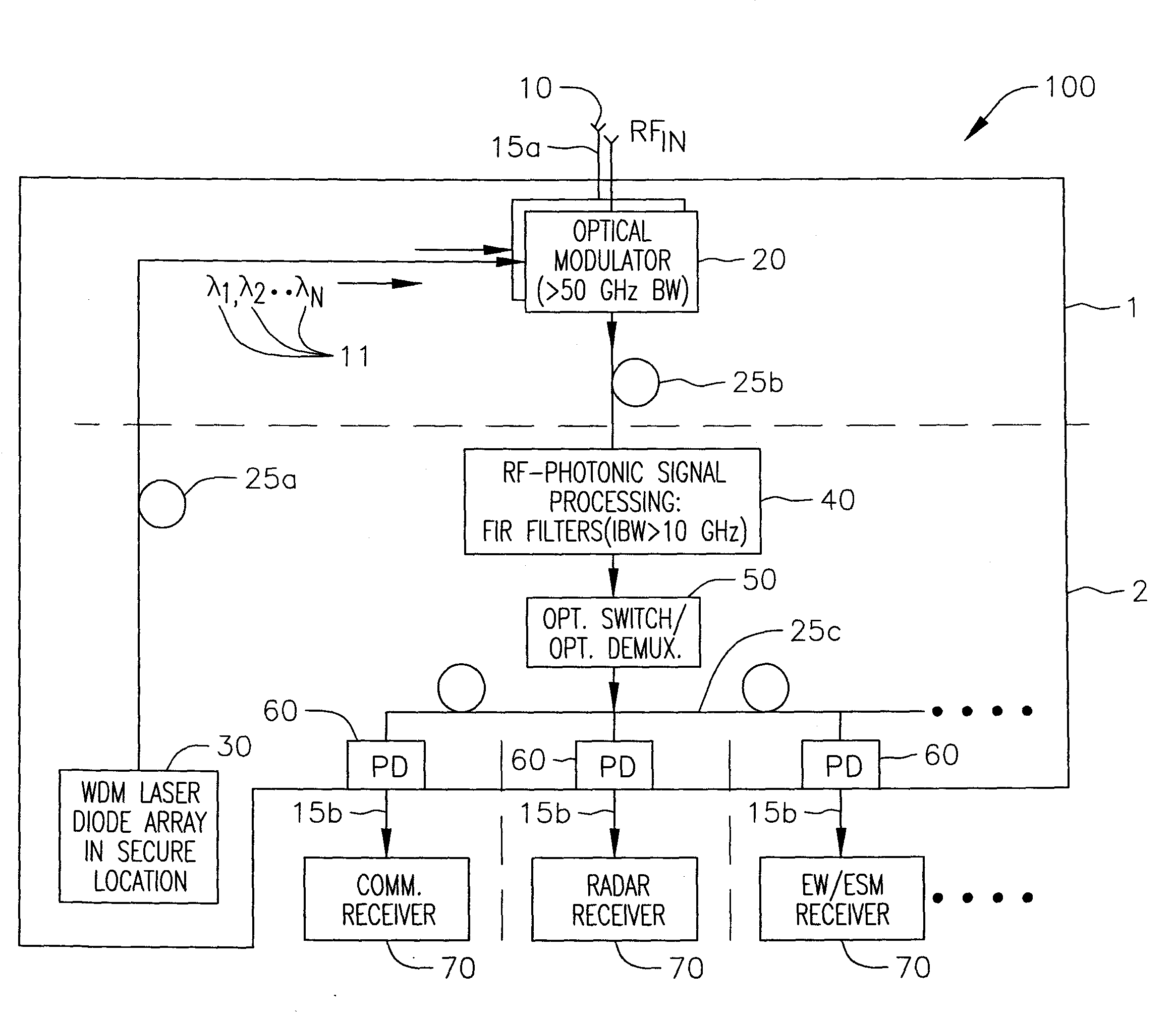
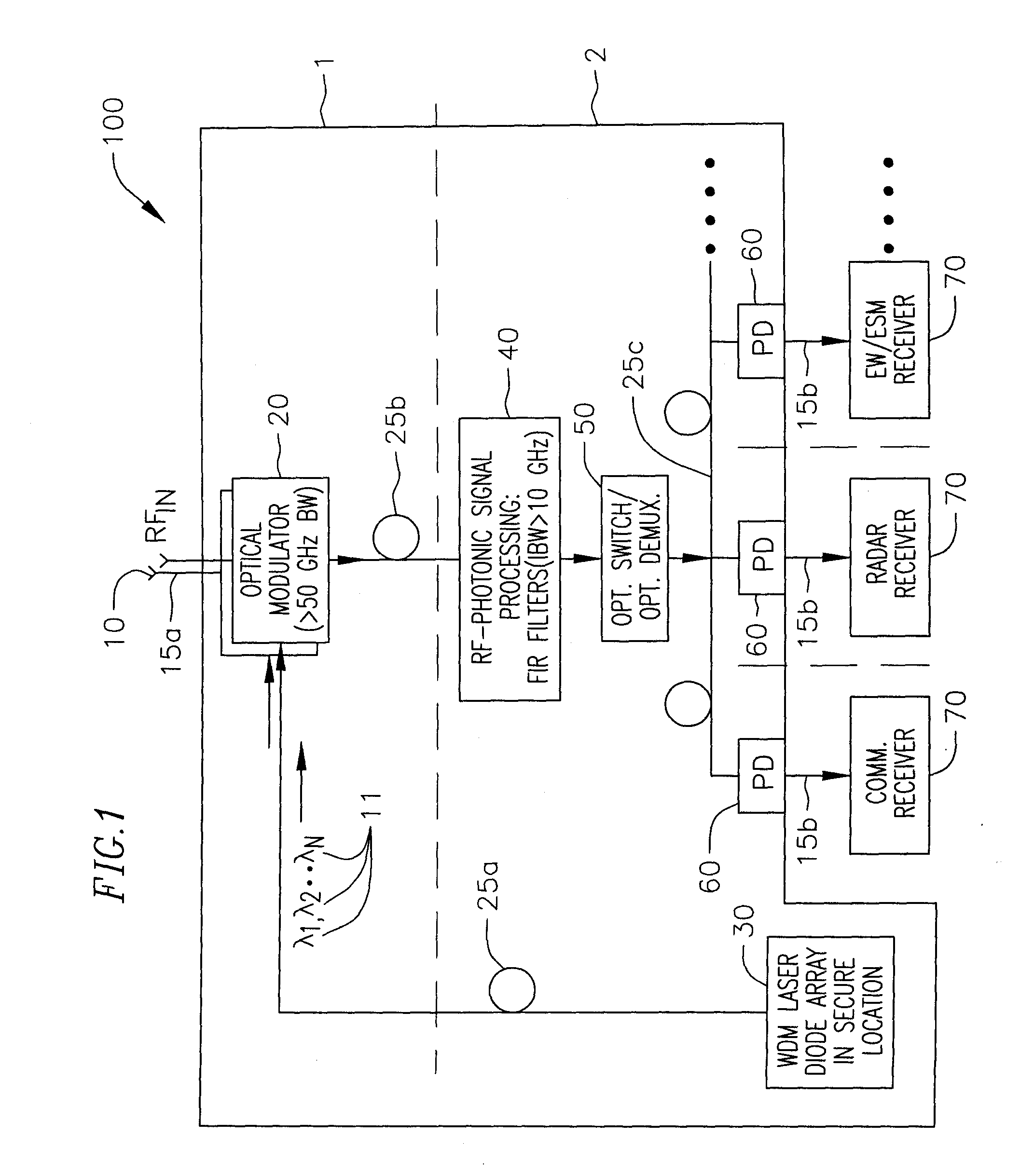
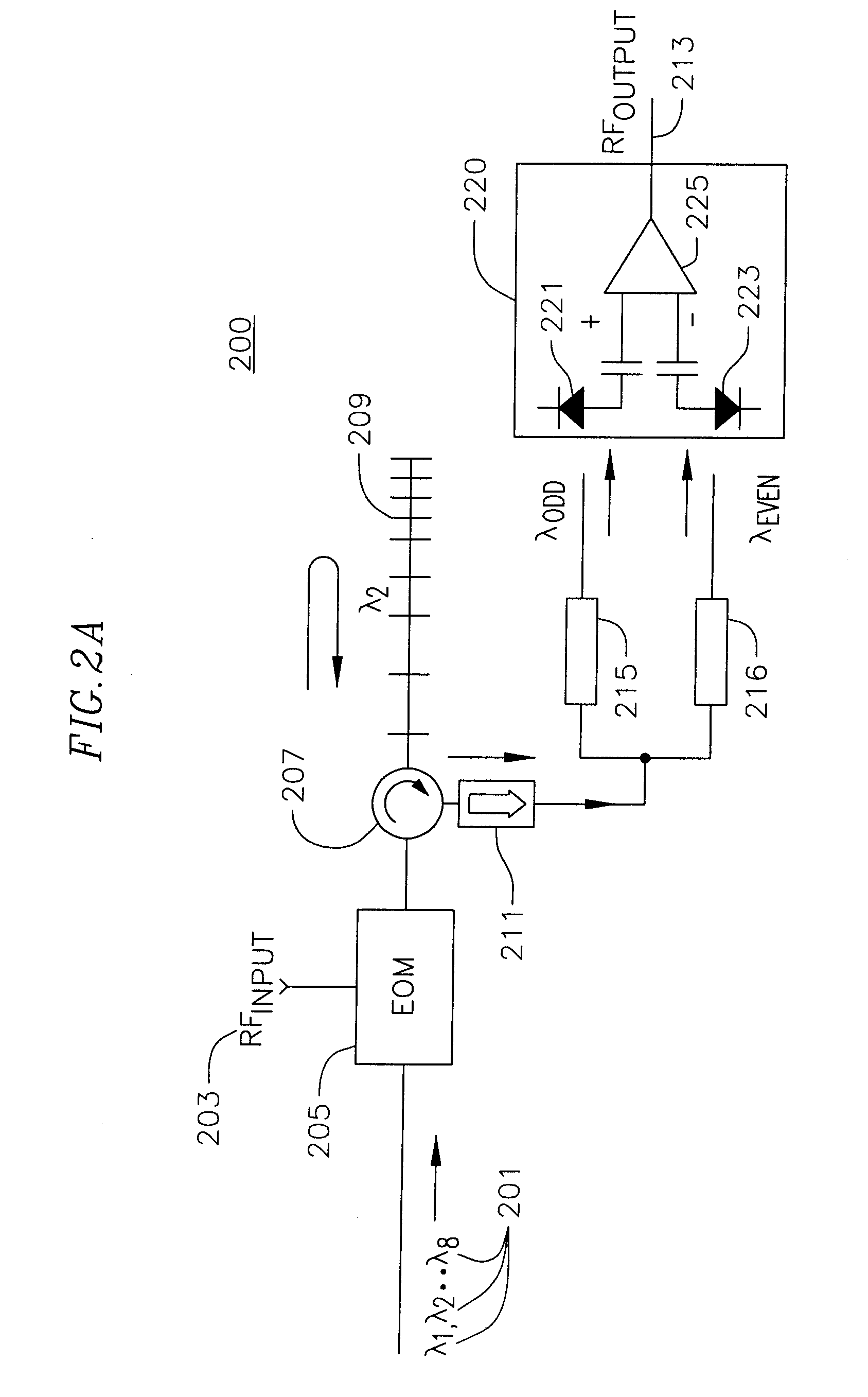
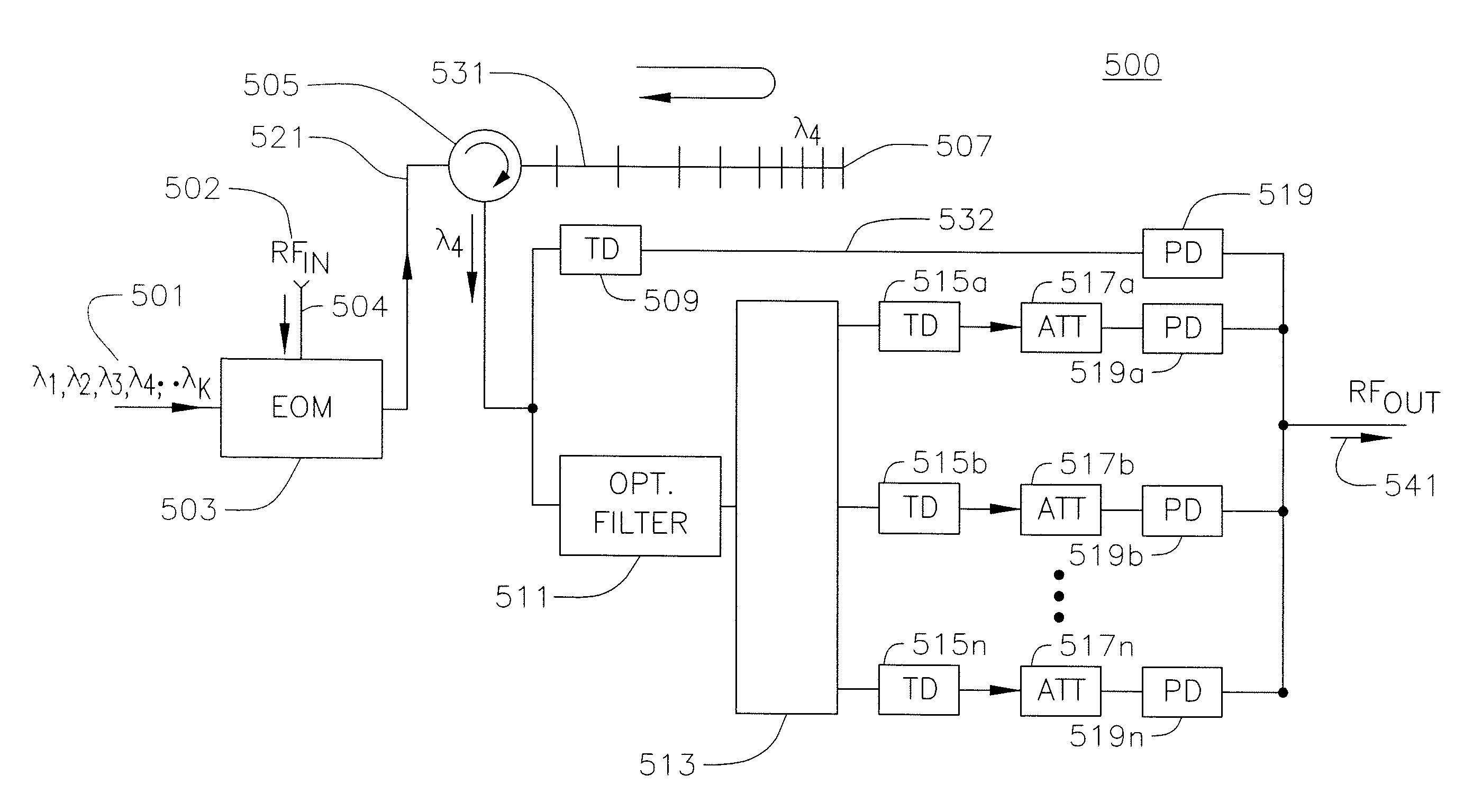
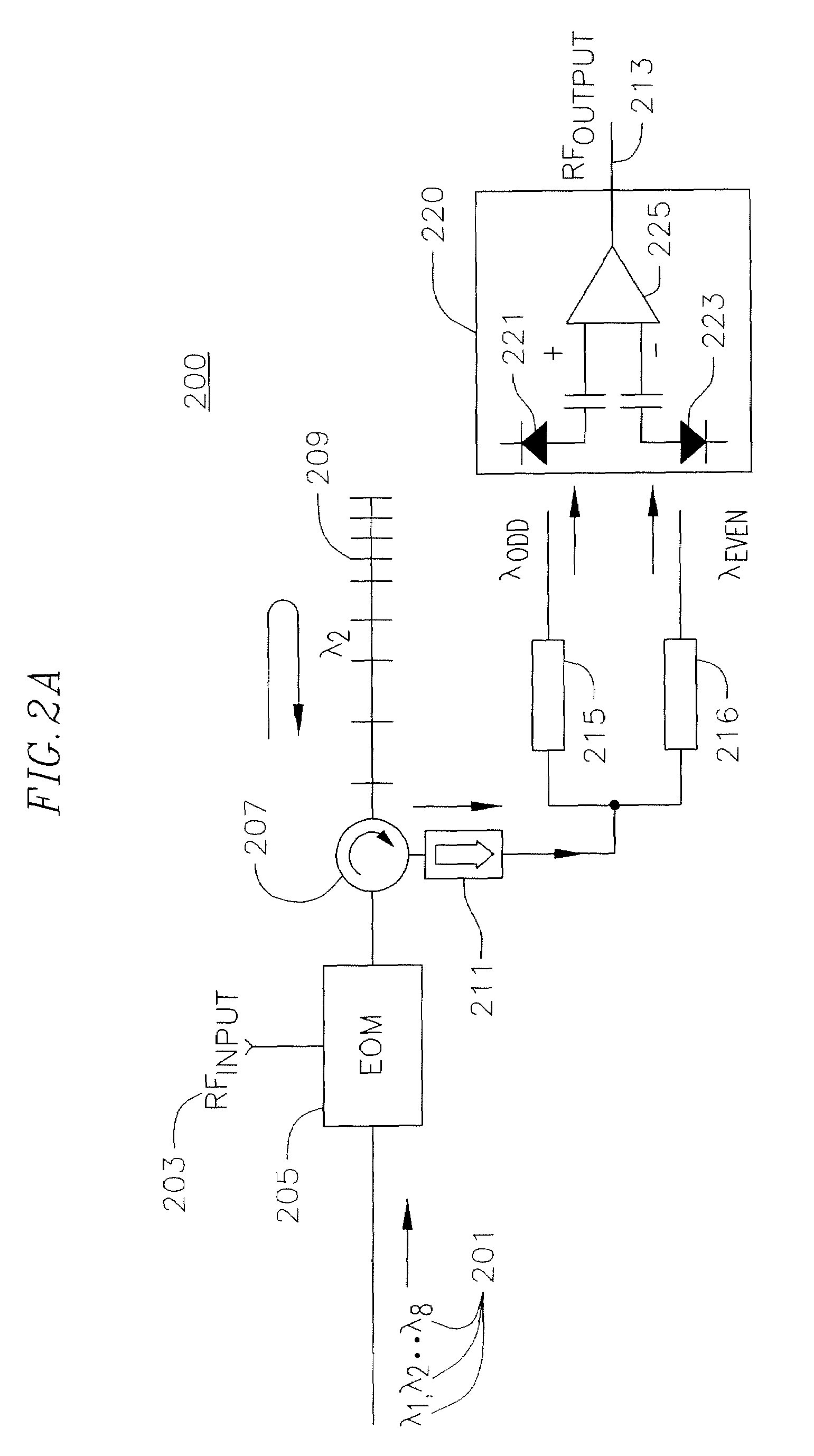
Rf-photonic transversal filter method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100028012A1Significant changeHigh SLSRTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingPhotonics
A method and apparatus for implementing an RF photonic transversal filter that utilizes tap apodization and wavelength reuse to obtain a high side lobe suppression together with narrow and configurable passbands. Several taps are obtained from one wavelength by using dispersive optical delay lines such as chirped fiber gratings that introduce a delay between successive wavelengths. A selected subset of the input wavelengths is utilized to generate multiple taps per wavelength. Some of the taps are apodized to generate various filter transfer functions that yield a high side lobe suppression ratio.
Owner:HRL LAB
RF-photonic transversal filter method and apparatus
InactiveUS7627253B1Significant changeHigh SLSRTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingPhotonics
Owner:HRL LAB
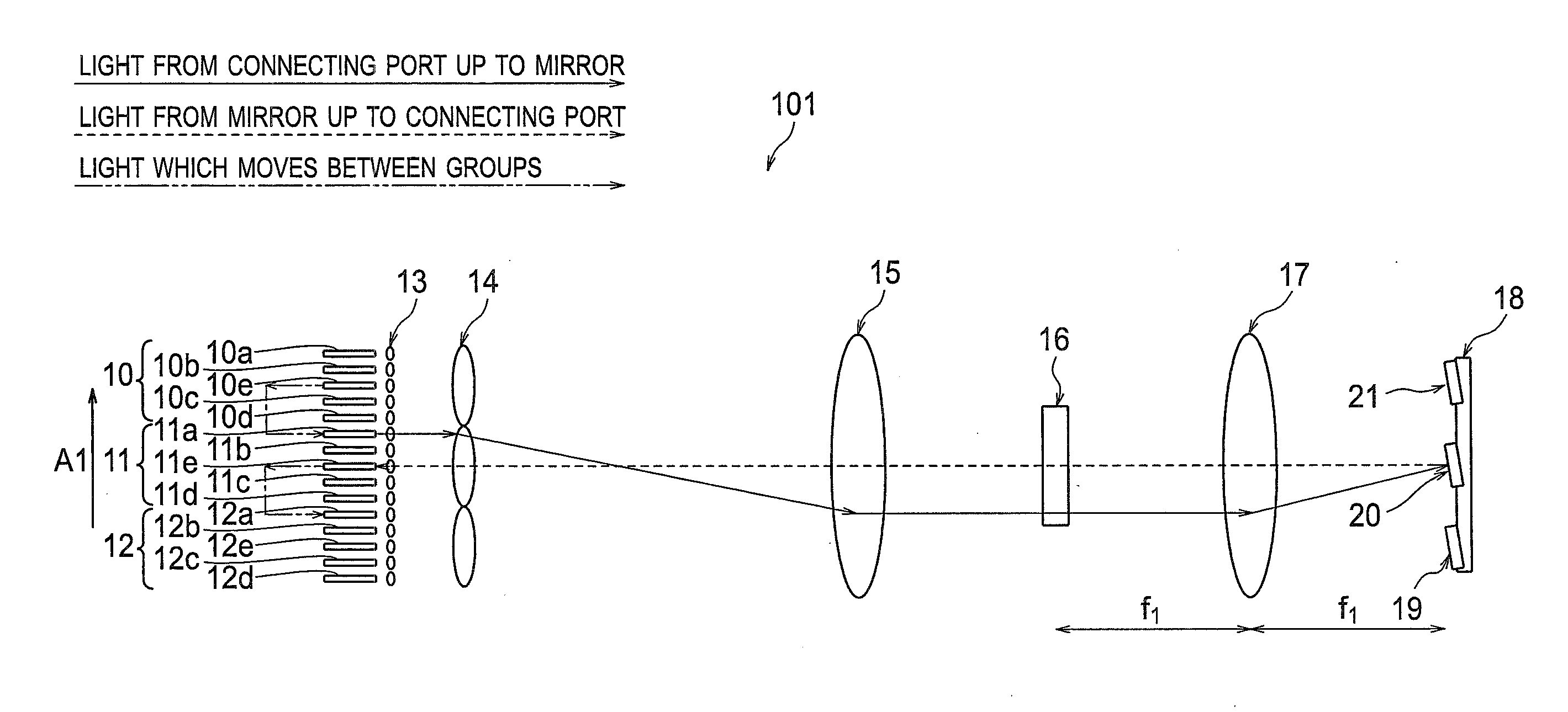
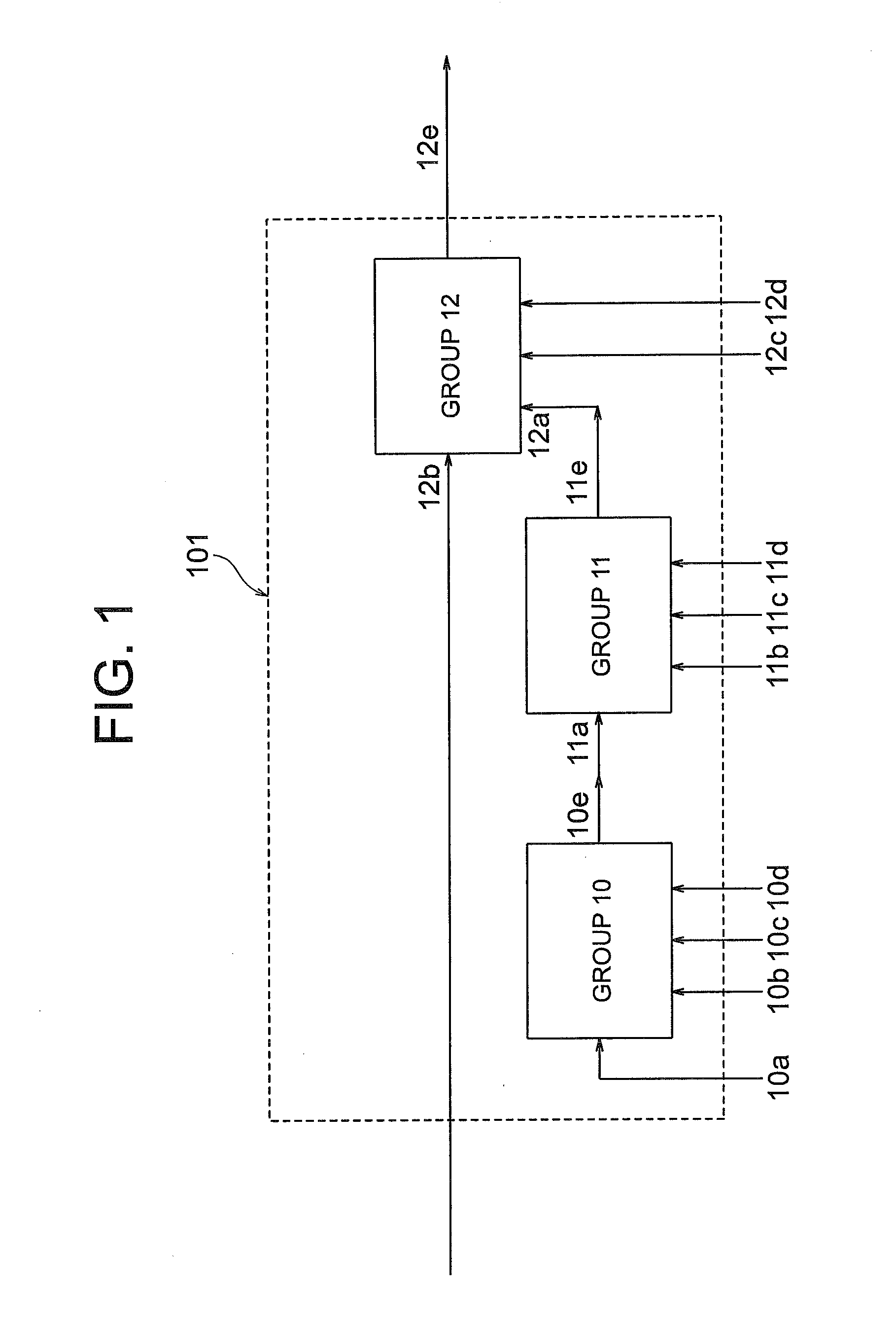
Wavelength selective switch
A wavelength selective switch includes a light input output portion having an input port and an output port for a wavelength-multiplexed light, which are arranged in an array form in a first direction, a light dispersive unit which separates the wavelength-multiplexed light which has been input from the input port, into respective signal wavelengths, a condenser element which condenses light which has been separated into the signal wavelengths, and a light deflective element array which deflects the signal light in the first direction such that, respective signal wavelength light which has been condensed by the condenser element is switched to a desired output port. In such wavelength selective switch, when m is let to be an integer, the light input output portion is divided into m number of groups, and the light deflective element array is arranged in m number of rows in the first direction to correspond with the m number of groups of the light input output portion, and the light dispersive unit is in common for the m number of groups of the light input output portion.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
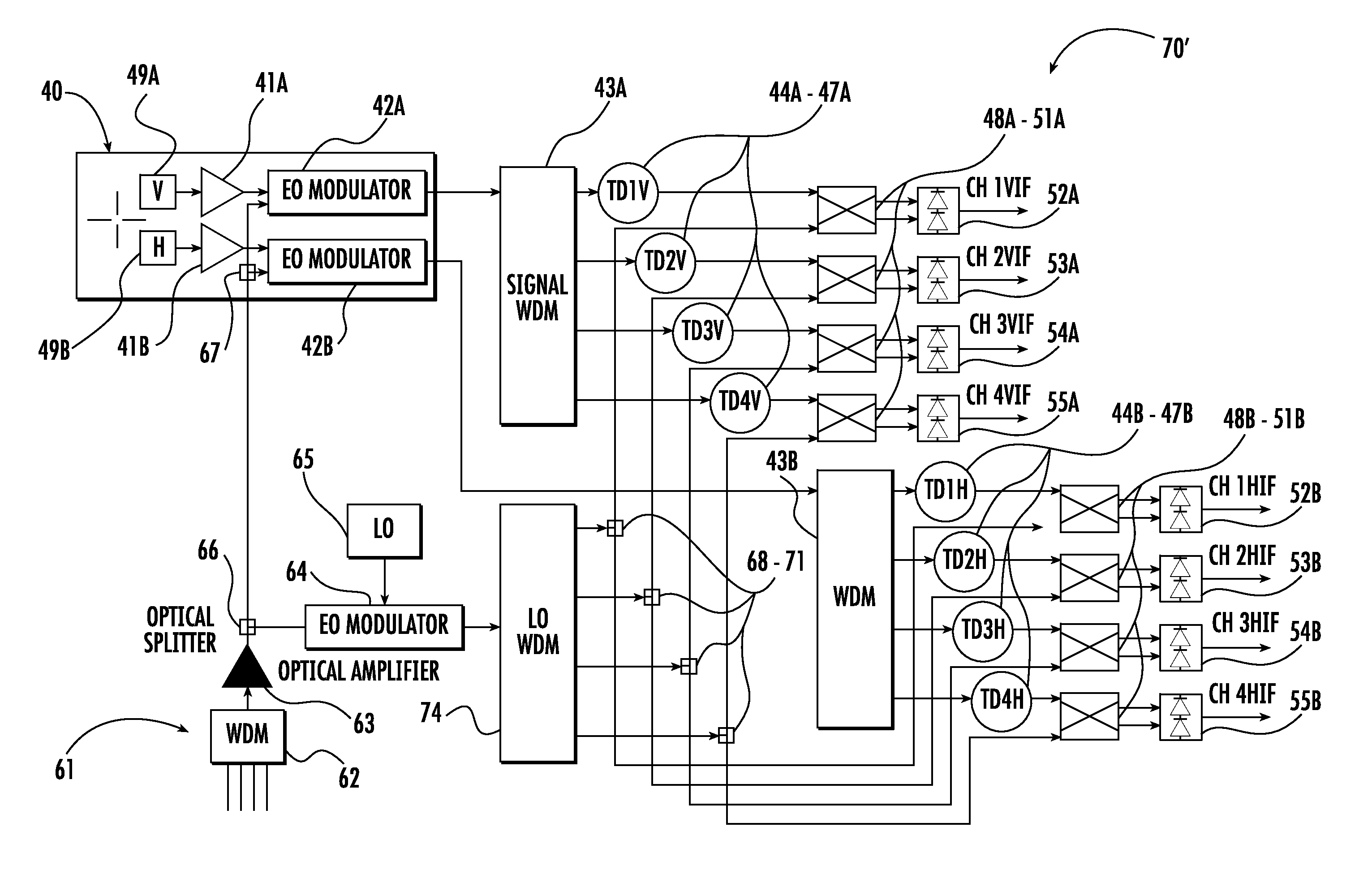
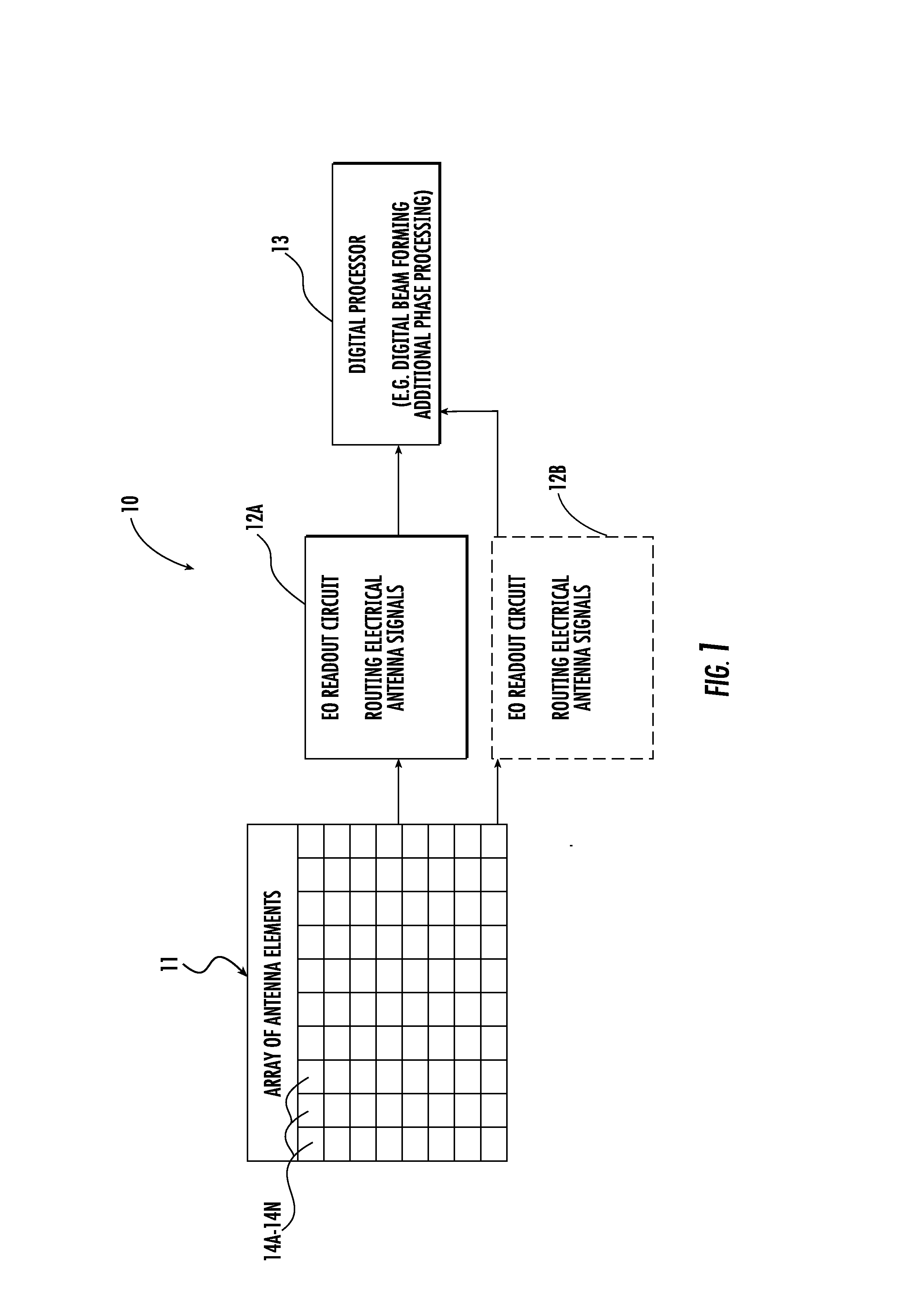
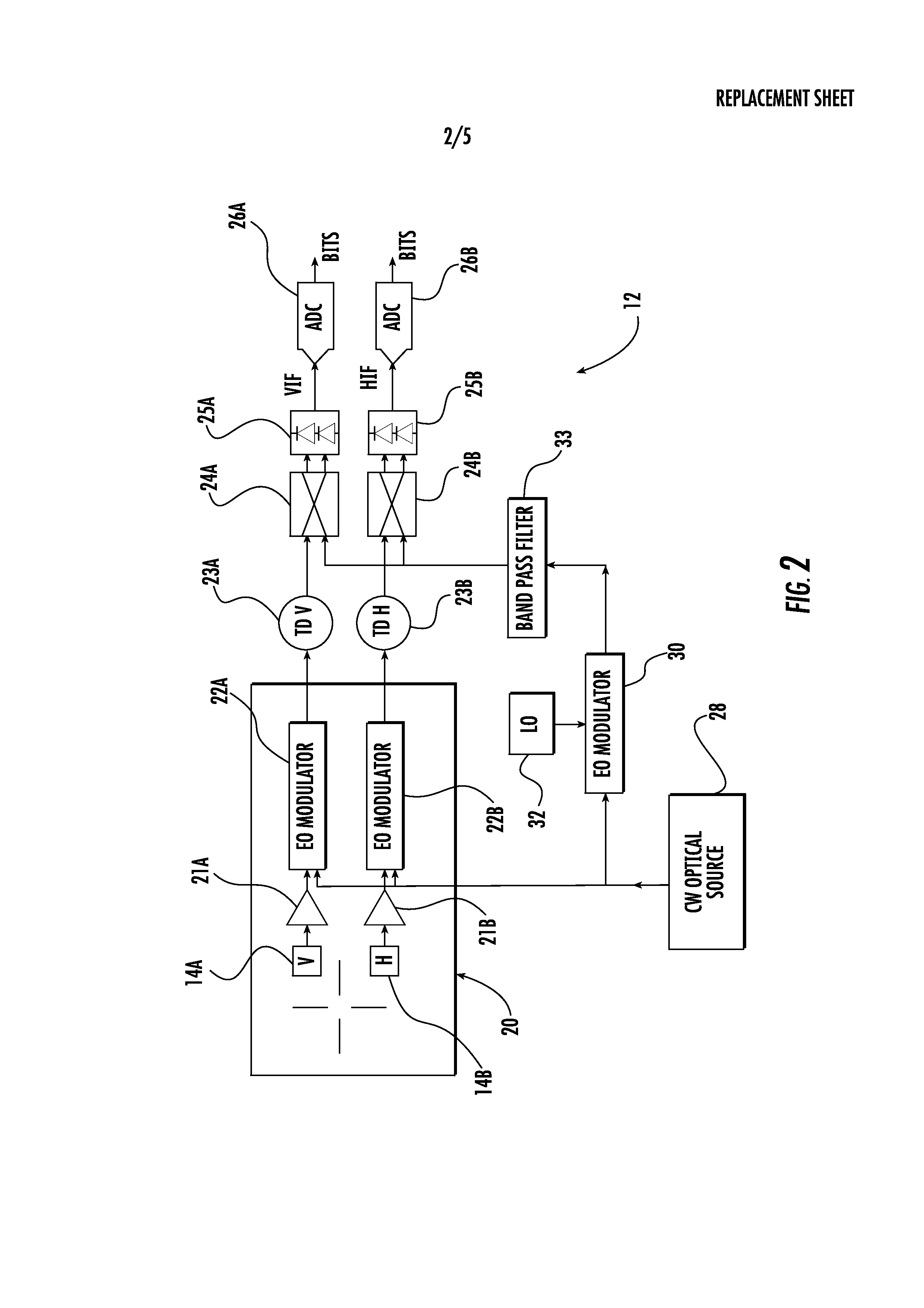
Phased antenna array with electro-optic readout circuit with multiplexing and MLL and related methods
InactiveUS20130177315A1Easy to operateEfficient processingWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmission non-optical aspectsMultiplexingLight beam
A phased antenna array includes an array of antenna elements, and an electro-optic (EO) readout circuit coupled to the array of antenna elements. The EU readout circuit includes an optical source including a mode locked laser (MLL) configured to generate an optical carrier signal having beam carrier wavelengths, an EO modulator configured to modulate a signal from an antenna element based upon the optical carrier signal, a first WDM coupled downstream from the EO modulator, and optical-to-electrical converters coupled downstream from the first WDM. The first WDM is configured to multiplex each modulated beam carrier wavelength to a respective optical-to-electrical converter.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Porous silicon filter for wavelength multiplexing or de-multiplexing
A porous silicon filter for wavelength multiplexing and de-multiplexing. Preferred embodiments include rugate-type porous silicon filters with pores having continuously varying widths with pore depth an optical cross connect switch. In other preferred embodiments, the pores are filled with a material that changes index of refraction with changes in applied voltage, current or temperature. Important applications of these porous silicon filters are for multiplexing and de-multiplexing in fiber optic communication systems. For example, a preferred embodiment is an all optical fiber optic switch utilizing these filters.
Owner:CROSSFIBER +1
Optical mm wave generating and wavelength reuse method and system in all-duplex communication radio Over-Fiber
InactiveCN101001126ASolve wavelength reuseSolving problems with mmWave generation in the downlinkWavelength-division multiplex systemsRadio-over-fibreRadio over fiberCommunications system
This invention discloses a method and a system for generating and re-using full light millimeter waves of full duplex communication and re-using wave lengths in the Radio-on-Fiber ROF communication system, which applies a carier suppression method by double pole modulator and filters by an optical filter to separate two vertical modes of a carrier suppression signal, one of which is modulated in its baseband signals and couples to the other one un-modulated to generate optical millimeter waves to simplify, stabilize the structure of the central station at low cost, and an optical filter is used in the base station to filter out the vertical mode with un-modulated signals as the optical carrier of up link and realizes repeatedly using the wavelength in down-link in the up link so that light source is not used any more in the base station and the structure is simple and cost, besides, a ROF system is provided for realizing generating light millimeter waves and re-using up link wavelength.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Passive optical network based on reflective semiconductor optical amplifier
ActiveUS8086102B2Improving budgetImprove reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength reuseReflective semiconductor optical amplifier
Provided is a passive optical network (PON) based on a reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA). In the PON, seed-light-injection RSOAs are used in an optical line terminal (OLT) to achieve the color-less management of the wavelengths of OLT optic sources, and wavelength reuse RSOAs are used to achieve the color-less management of the wavelengths of ONTs. Therefore, problems related to ONT wavelength management can be eliminated by the wavelength reuse RSOAs, and problems related to OLT wavelength management can be eliminated by the seed-light-injection RSOAs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Wavelength multiplexer/demultiplexer
ActiveUS20060023989A1Reflection lossEasy to separateCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDielectricMultiplexer
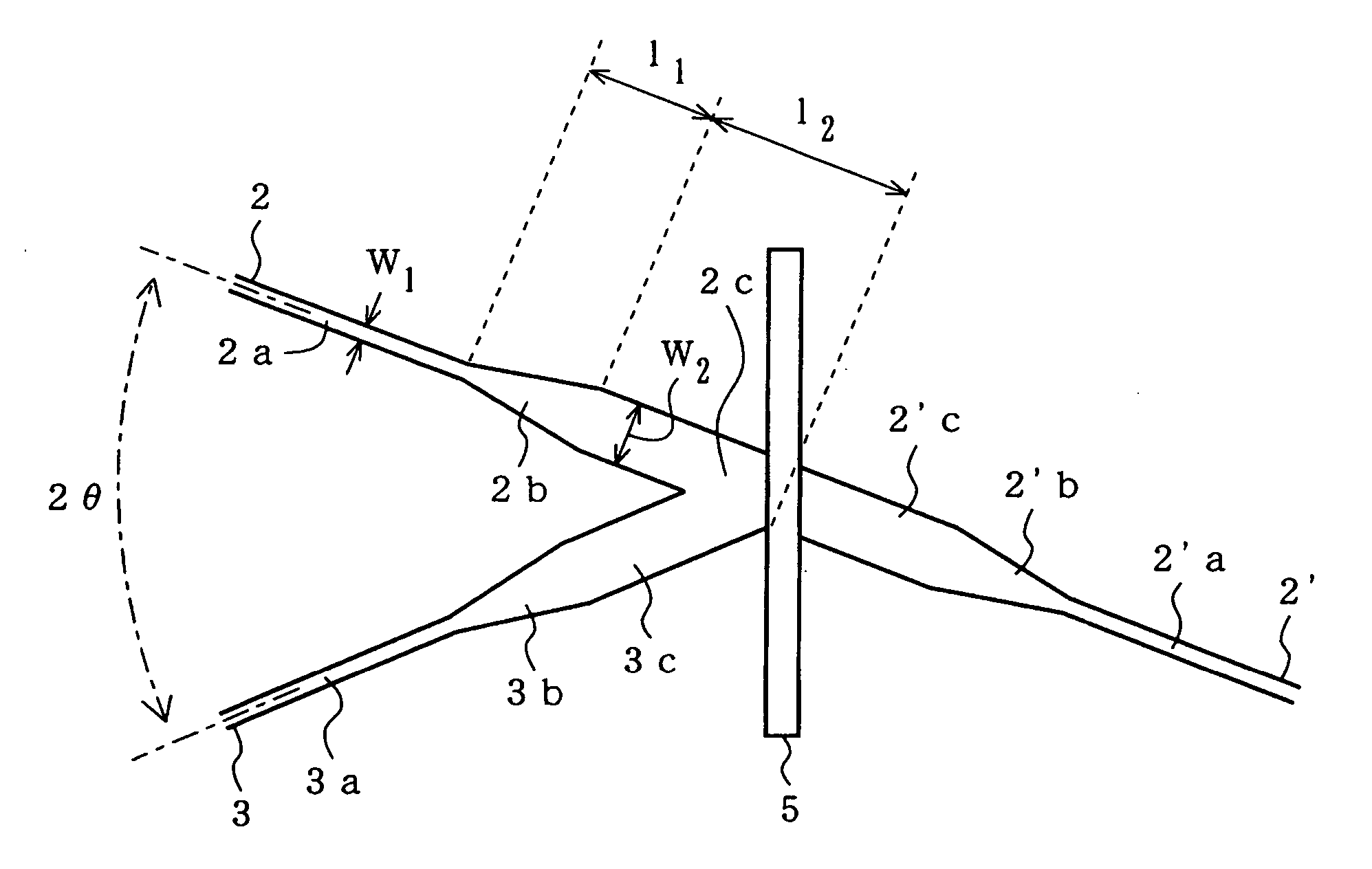
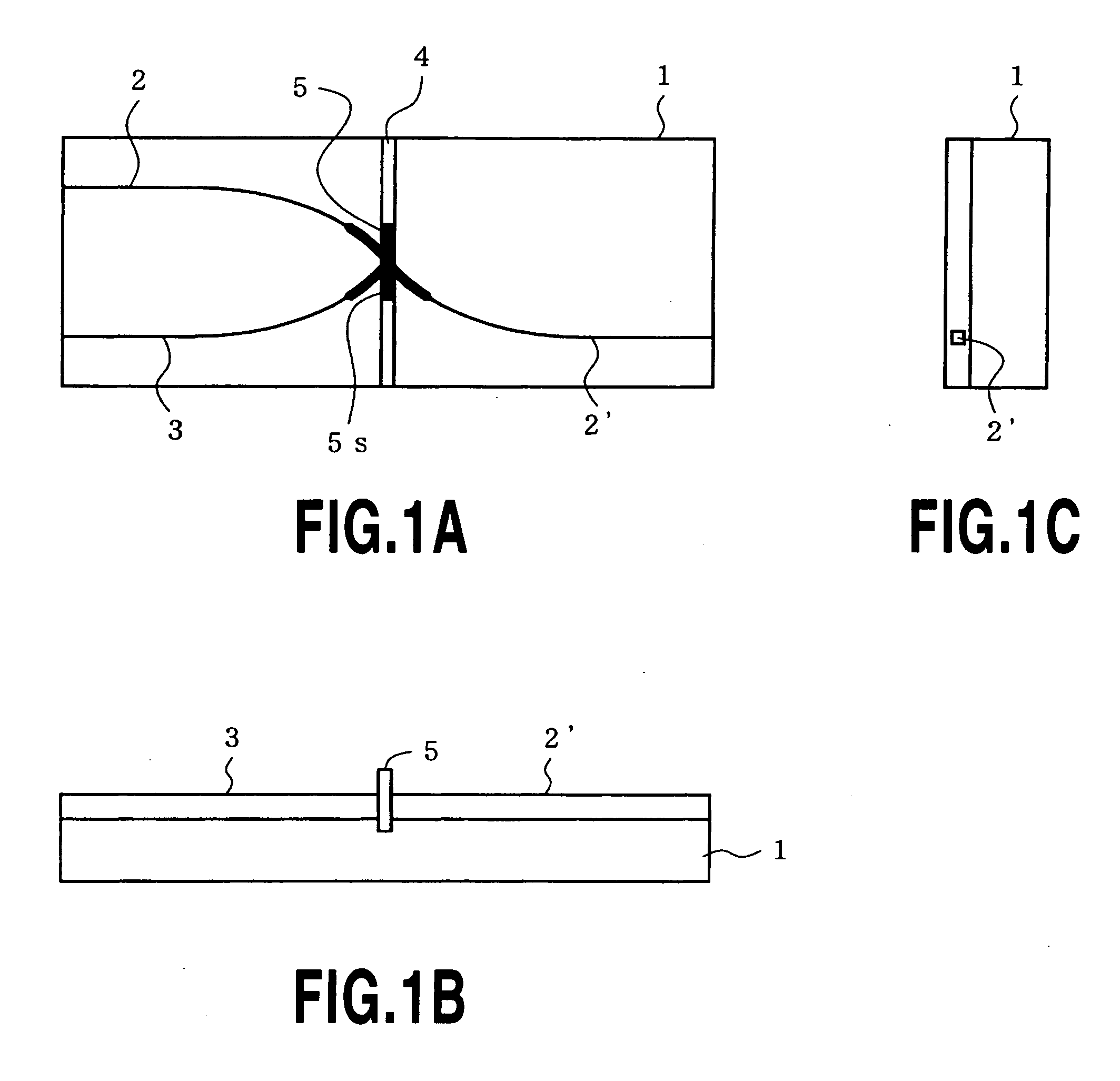
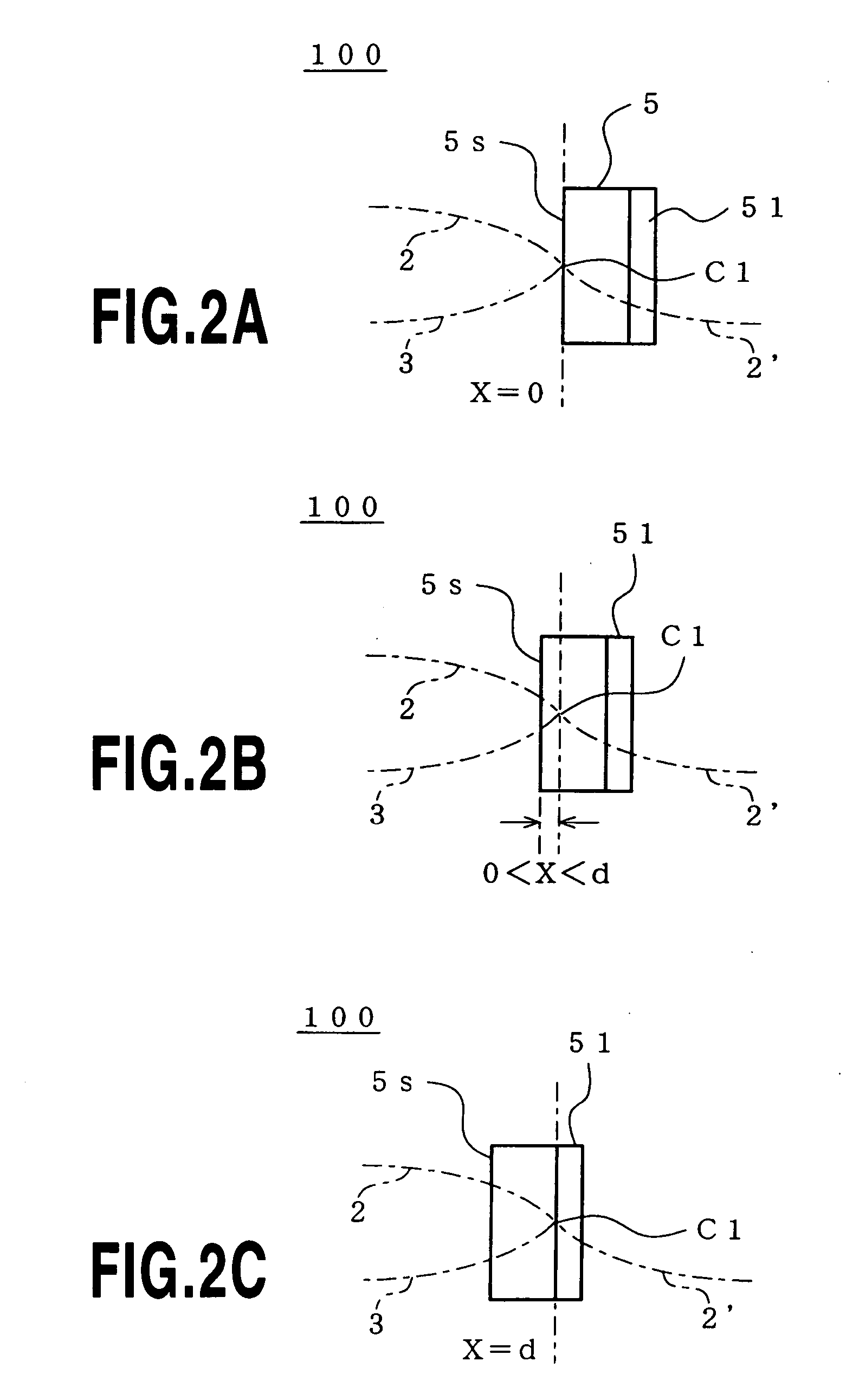
Disclosed is a wavelength multi / demultiplexer for separating two wavelength bands with a narrow wavelength spacing. A dielectric multilayer filter is provided in an intersection portion where two optical waveguides intersect each other and separates incident light to the dielectric multilayer filter to transmitted light and reflected light. Here, the distance X from the multilayer surface on the light-incident side of the dielectric multilayer to the central intersection point of the two intersecting optical waveguides is arranged to satisfy 0≦X≦d / 2 (where “d” represents the thickness of the dielectric multilayer). With this configuration, a multi / demultiplexer can be realized that shows good wavelength response without spectral degradation even for two wavelengths having narrow wavelength spacing.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com