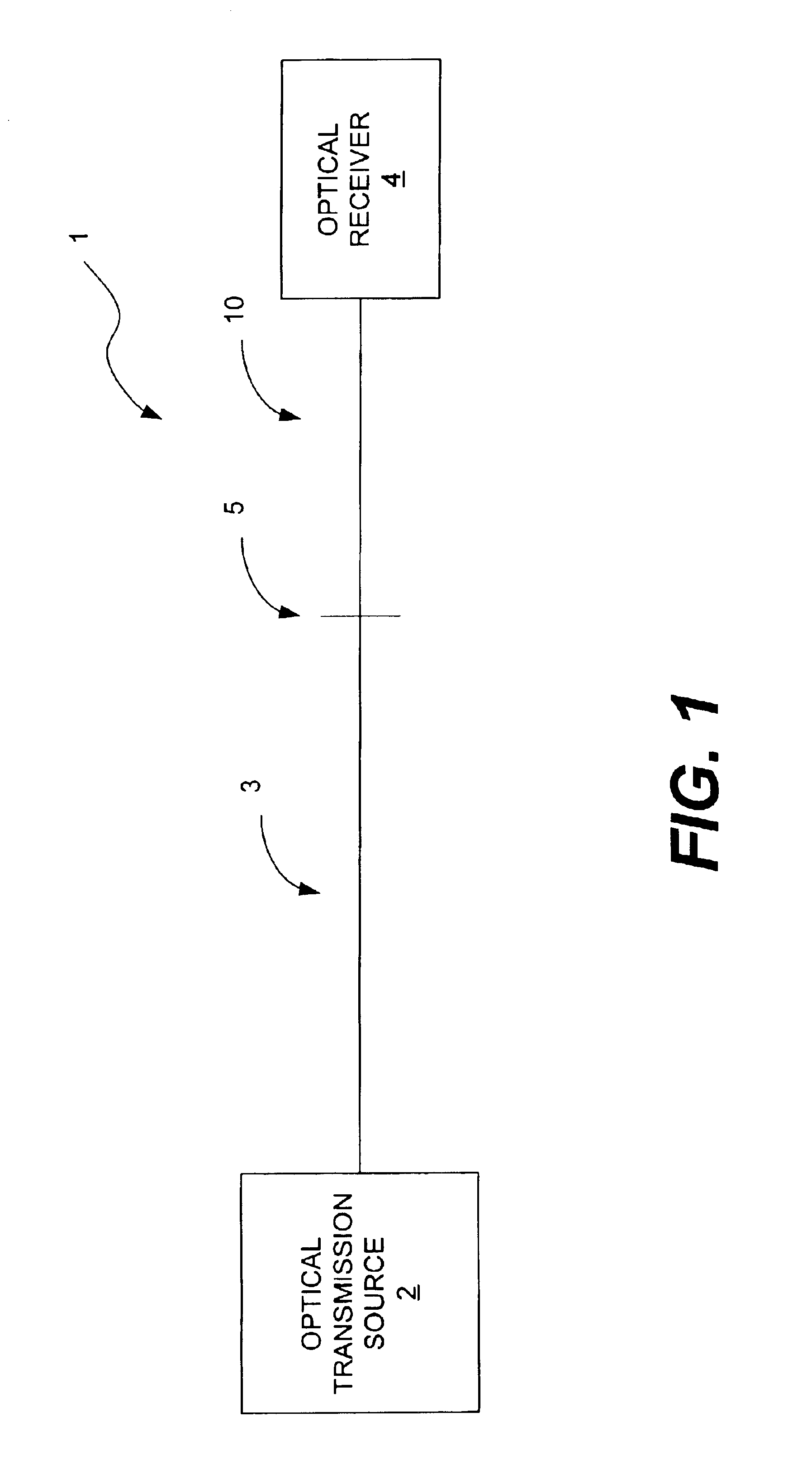
Large-effective-area inverse dispersion compensating fiber, and a transmission line incorporating the same
a technology of inverse dispersion compensation and optical fiber, which is applied in the direction of cladded optical fibre, instruments, optical elements, etc., can solve the problems of limiting signal degradation and increasing bandwidth capabilities, and achieve the effect of negative dispersion and negative dispersion slop
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
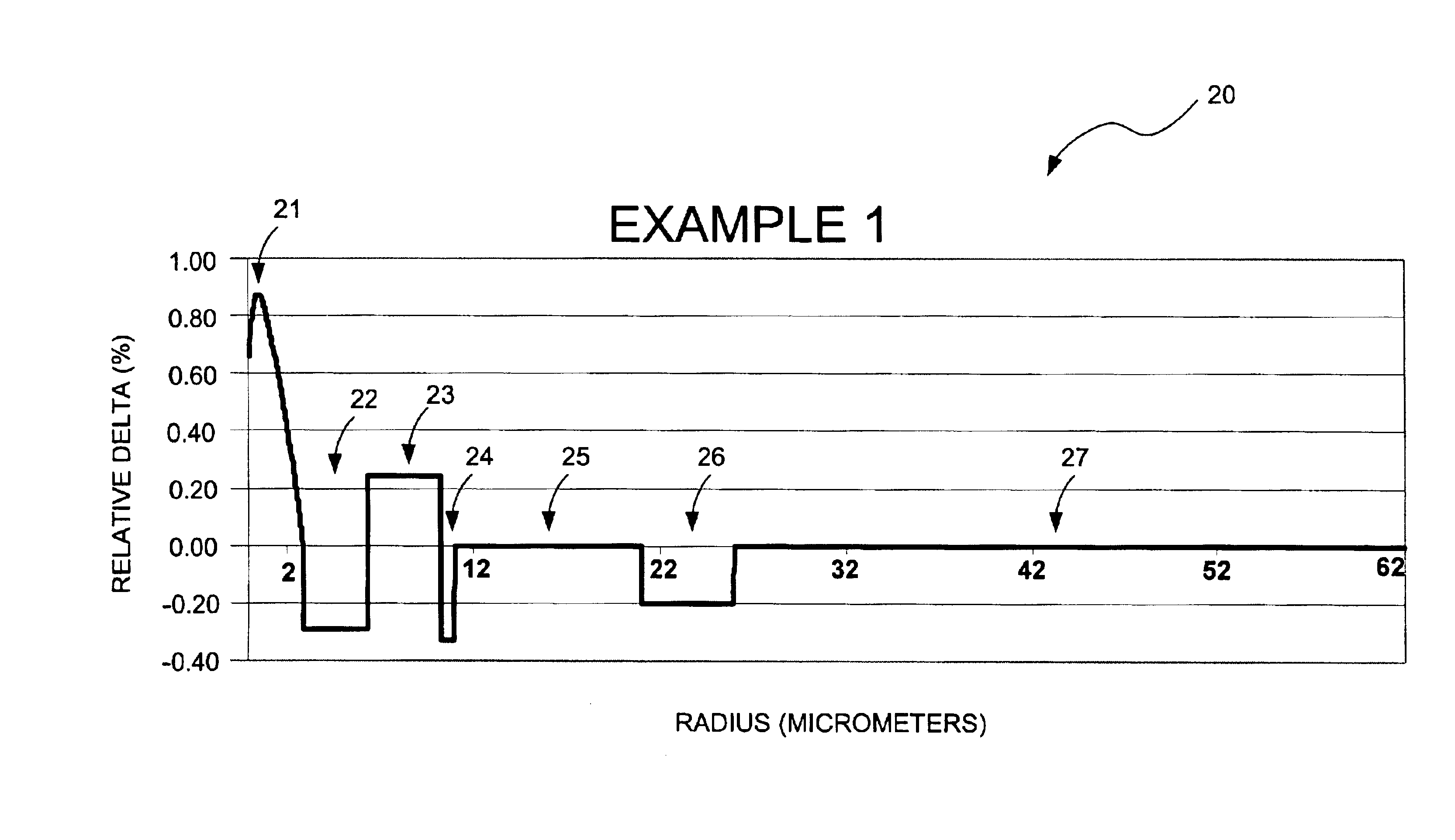
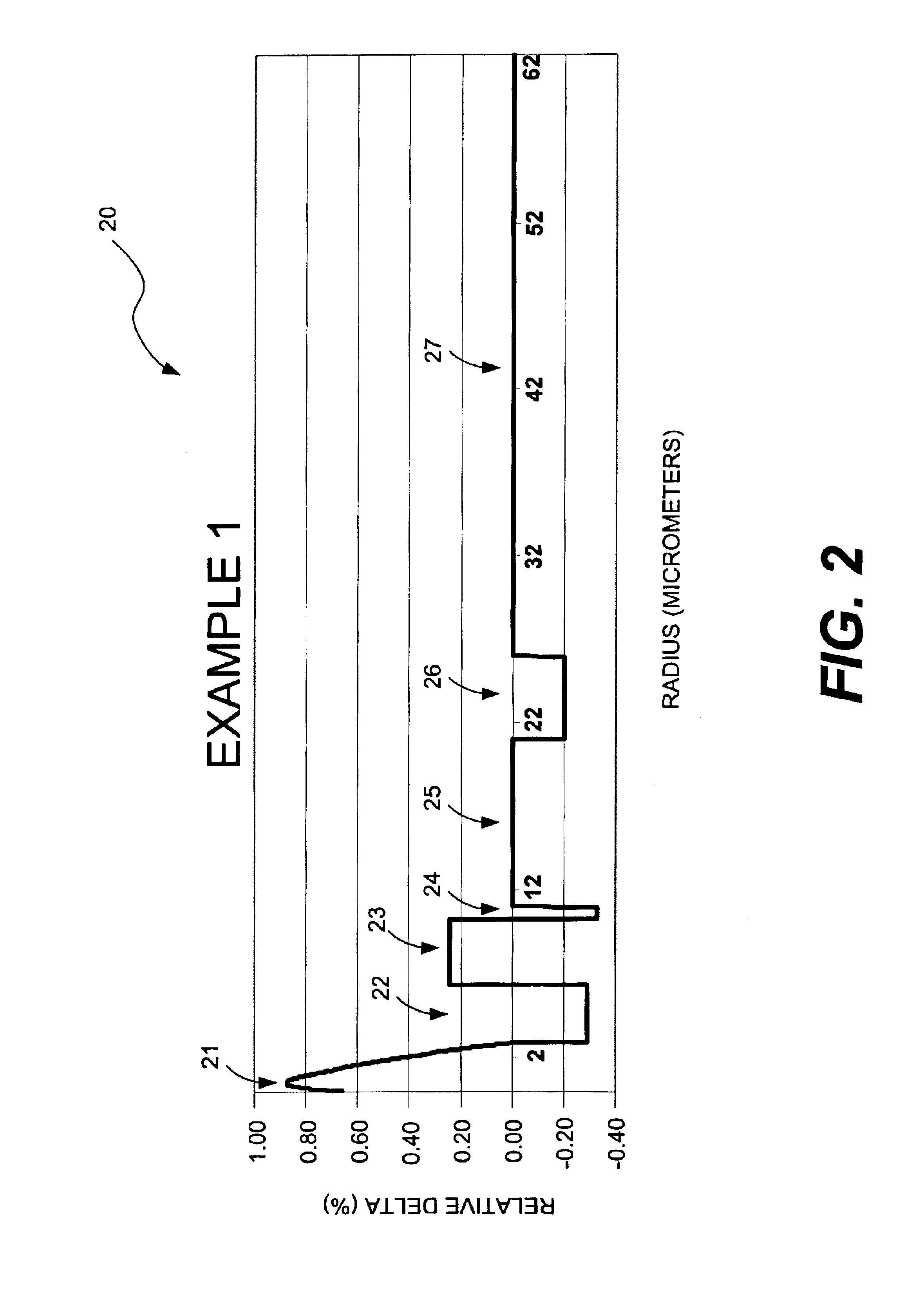
[0028]In accordance with the present invention, an IDF having a large effective area is provided. Furthermore, the IDF having the large effective area has desirable transmission characteristics. In particular, the large-effective-area IDF preferably has a cable cutoff wavelength below 1500 nm and bending loss sensitivities that allow low cabling loss to be achieved. In addition, to providing these desirable features, the IDF simultaneously compensates dispersion to a sufficiently precise degree to enable desired ((distance)×(bit-rate)) transmission capabilities to be achieved.
[0029]The large-effective-area IDF of the present invention is suitable for compensating dispersion in many types of optical fibers such as, for example, positive dispersion, pure silica core fiber from Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd., as described in “Ultra Low Nonlinearity Low Loss Pure Silica Core Fiber,” Electronics Letters Online No: 19991094, 3 Aug. 1999; Vascade 100 fiber from Corning; large effective...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com