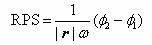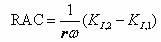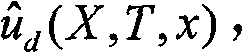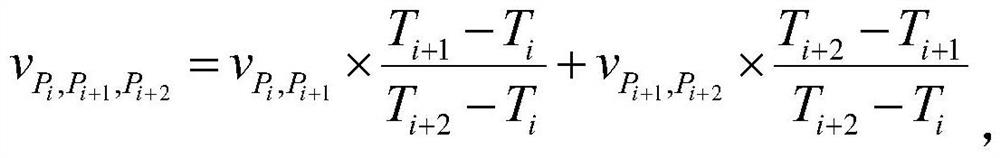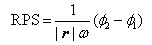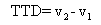Patents
Literature
31 results about "Relative attenuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Relative attenuation. The ratio of the peak output voltage of an electric filter to the voltage at the frequency being considered.
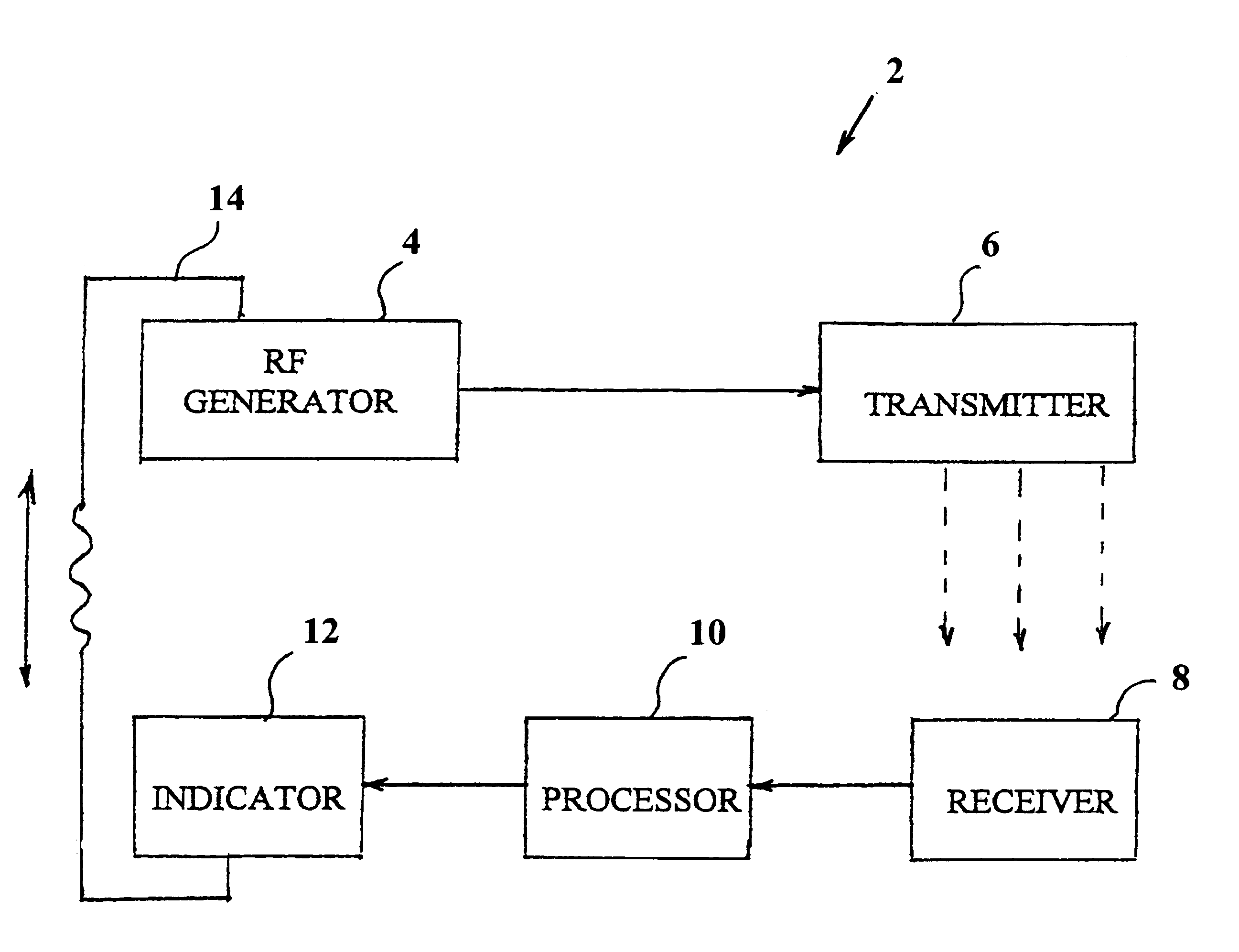
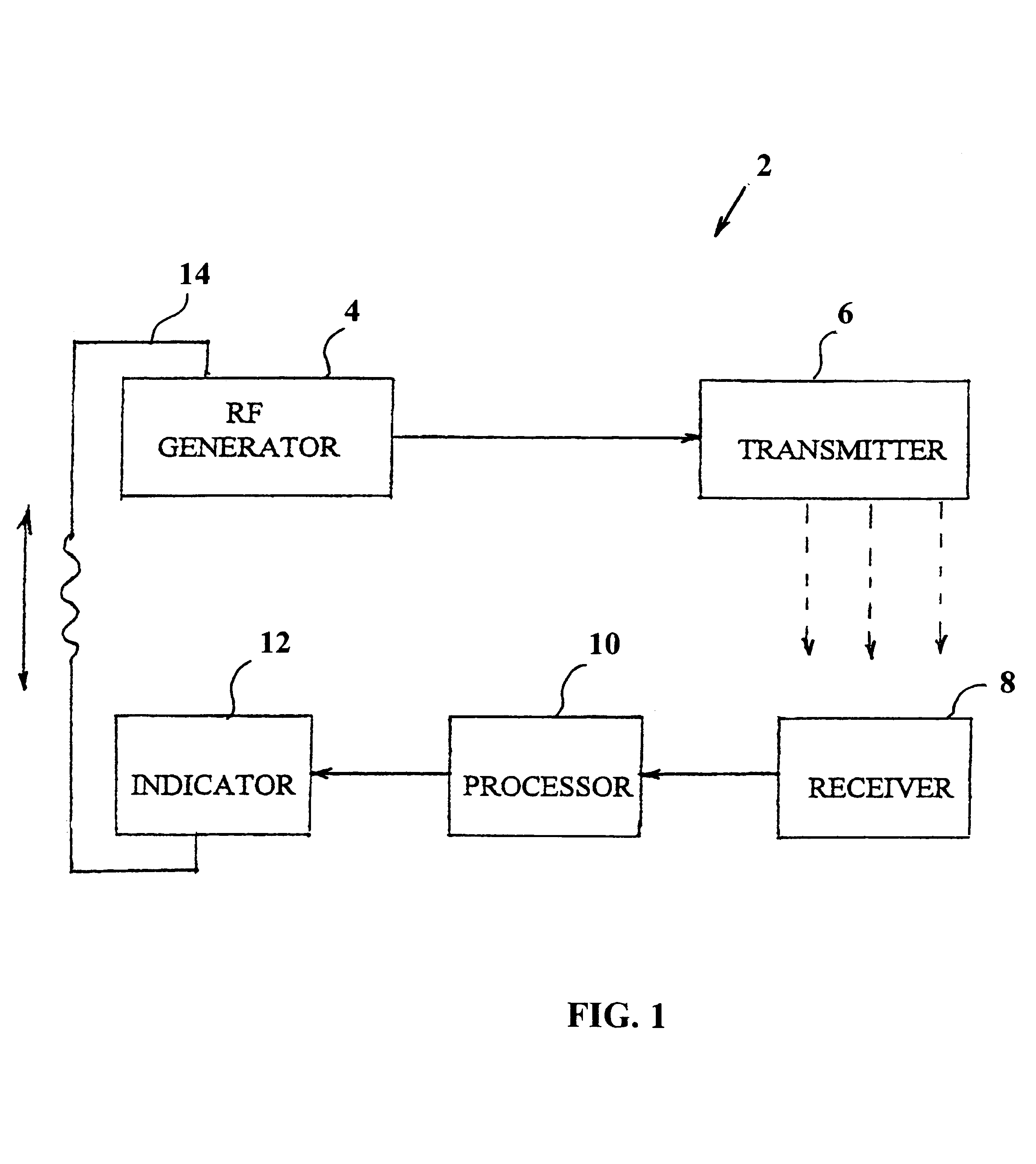
System and method for detecting the state of hydration of a living specimen
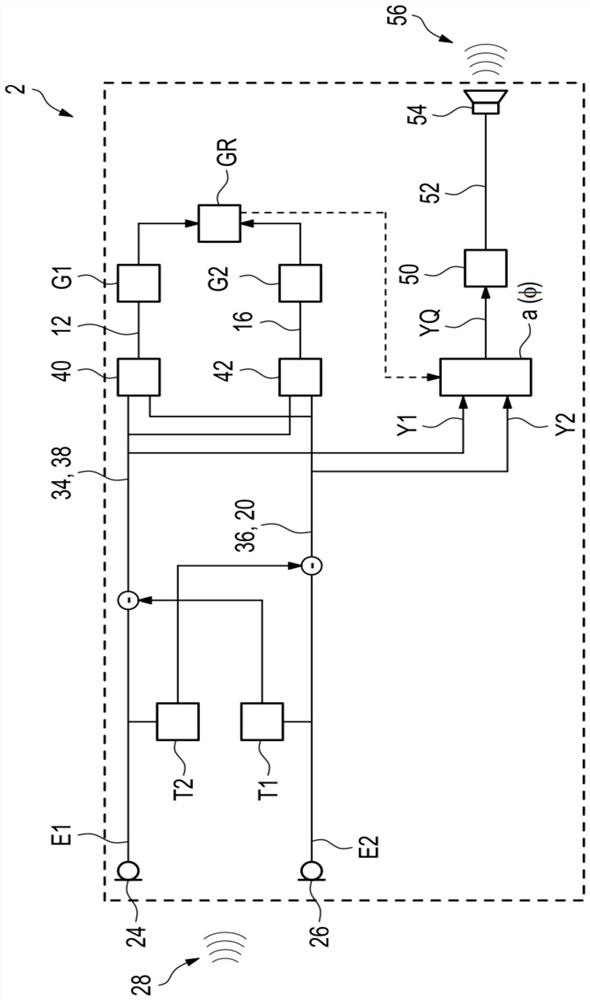
The invention provides a system (2) for non-invasive detection of the state of hydration in a living specimen, the system including an RF generator / transmitter (416) for emitting RF radiation signals and for transmitting the radiation signals through a tissue of a living specimen; an RF receiver (8) for receiving RF signals transmitted through the tissue, and for feeding the signals to a processor (10) for comparison of relative attenuation of RF frequencies passing through the tissue with a reference attenuation ratio signal, and an indicator unit (12) for providing an output signal representative of the water content level of the tissue. A method for non-invasive detection of the state of hydration in a living specimen is also described and claimed.
Owner:EYAL BICKELS ELAZAR +1
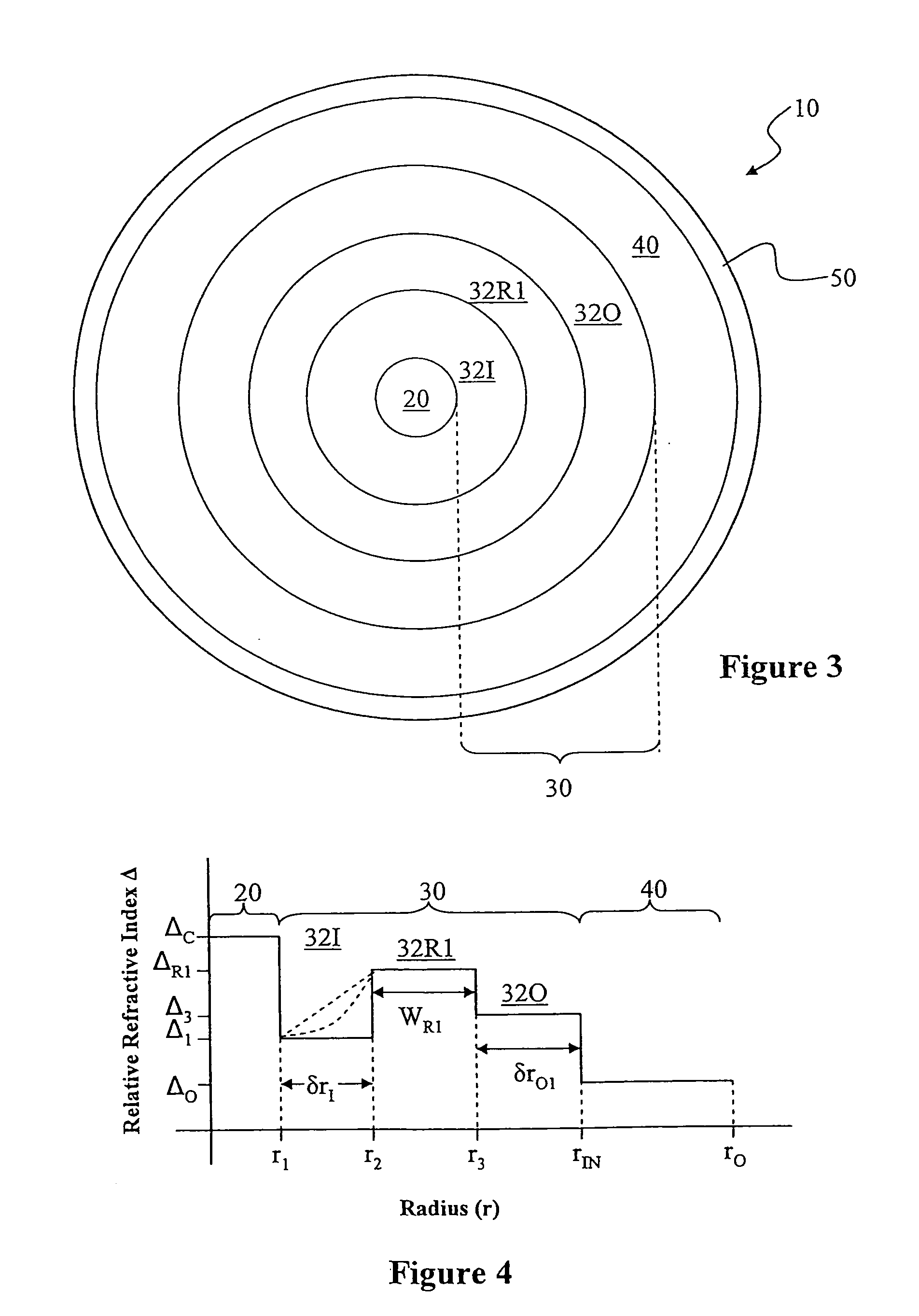
Large Mode Area Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20100195194A1Reduce nonlinear effectsIncrease optical powerLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationRelative attenuationUltrasound attenuation
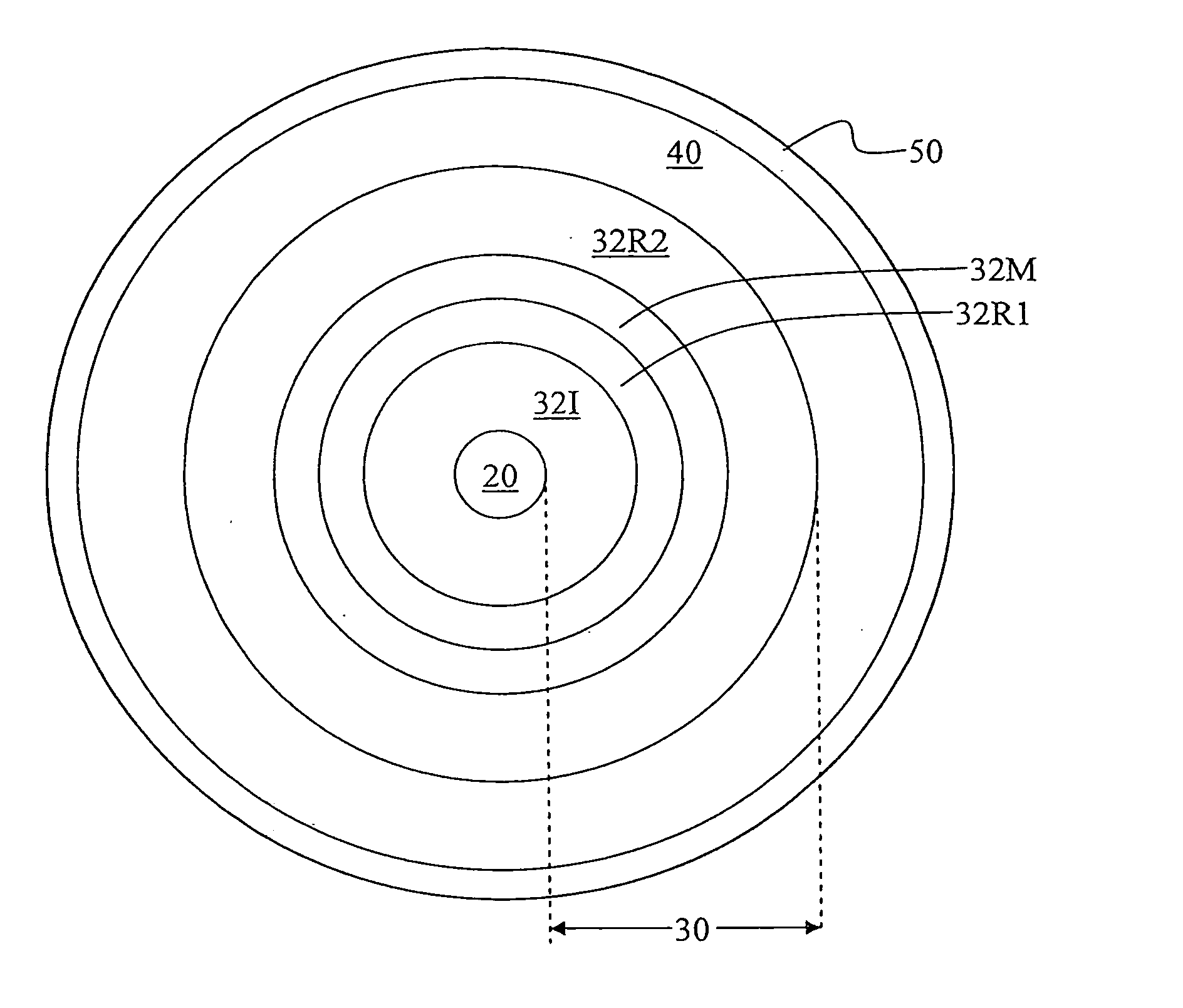
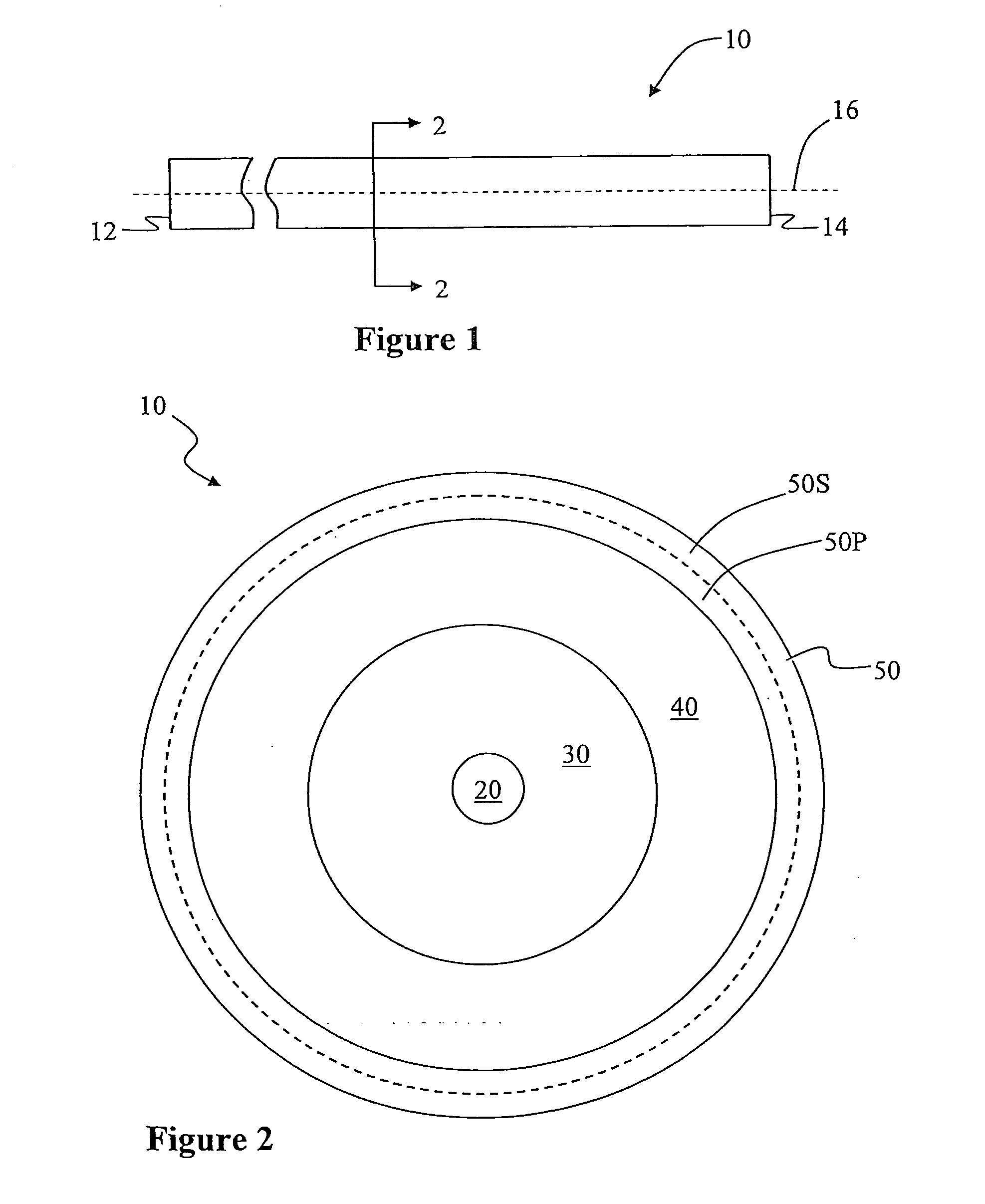
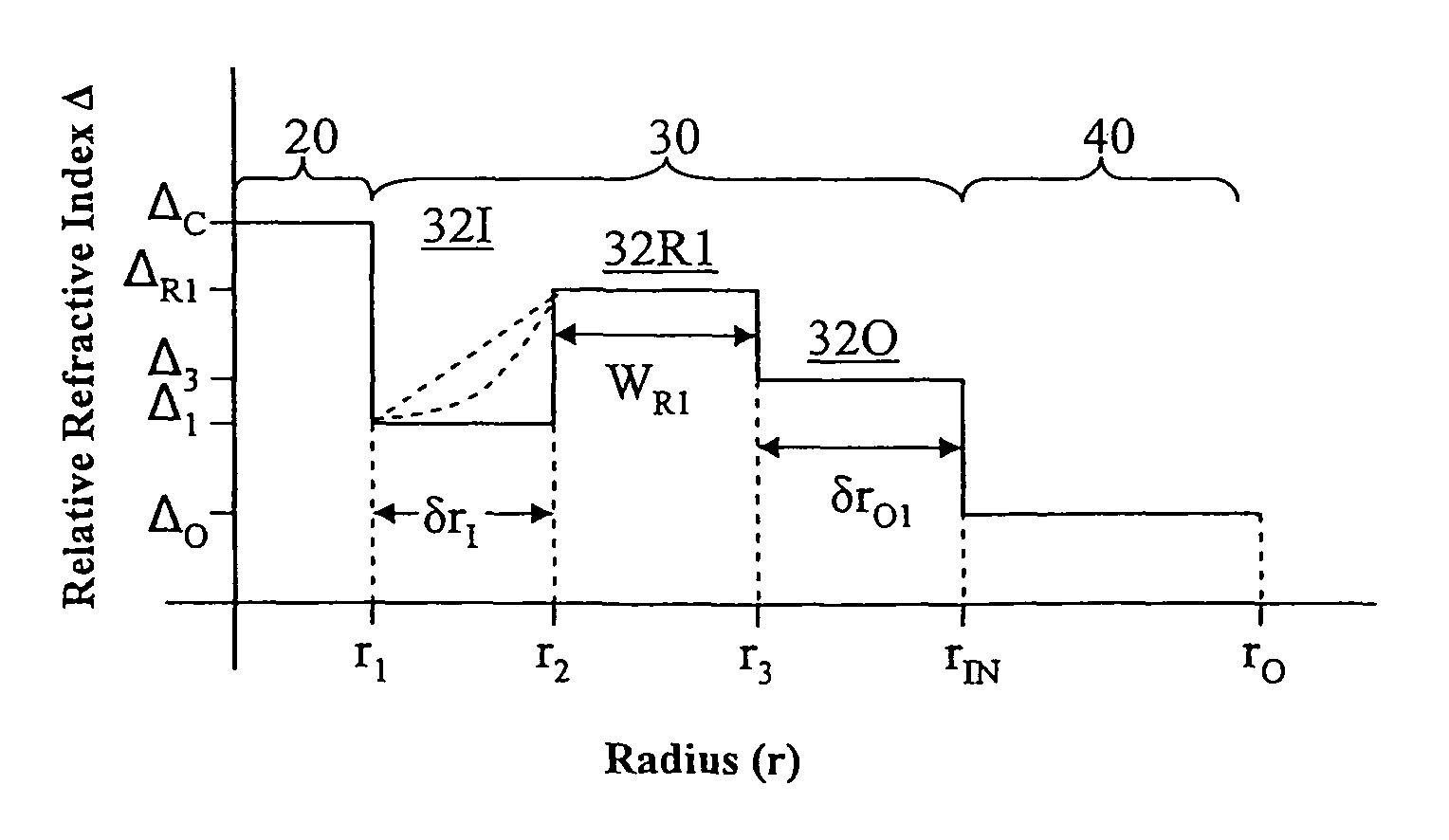
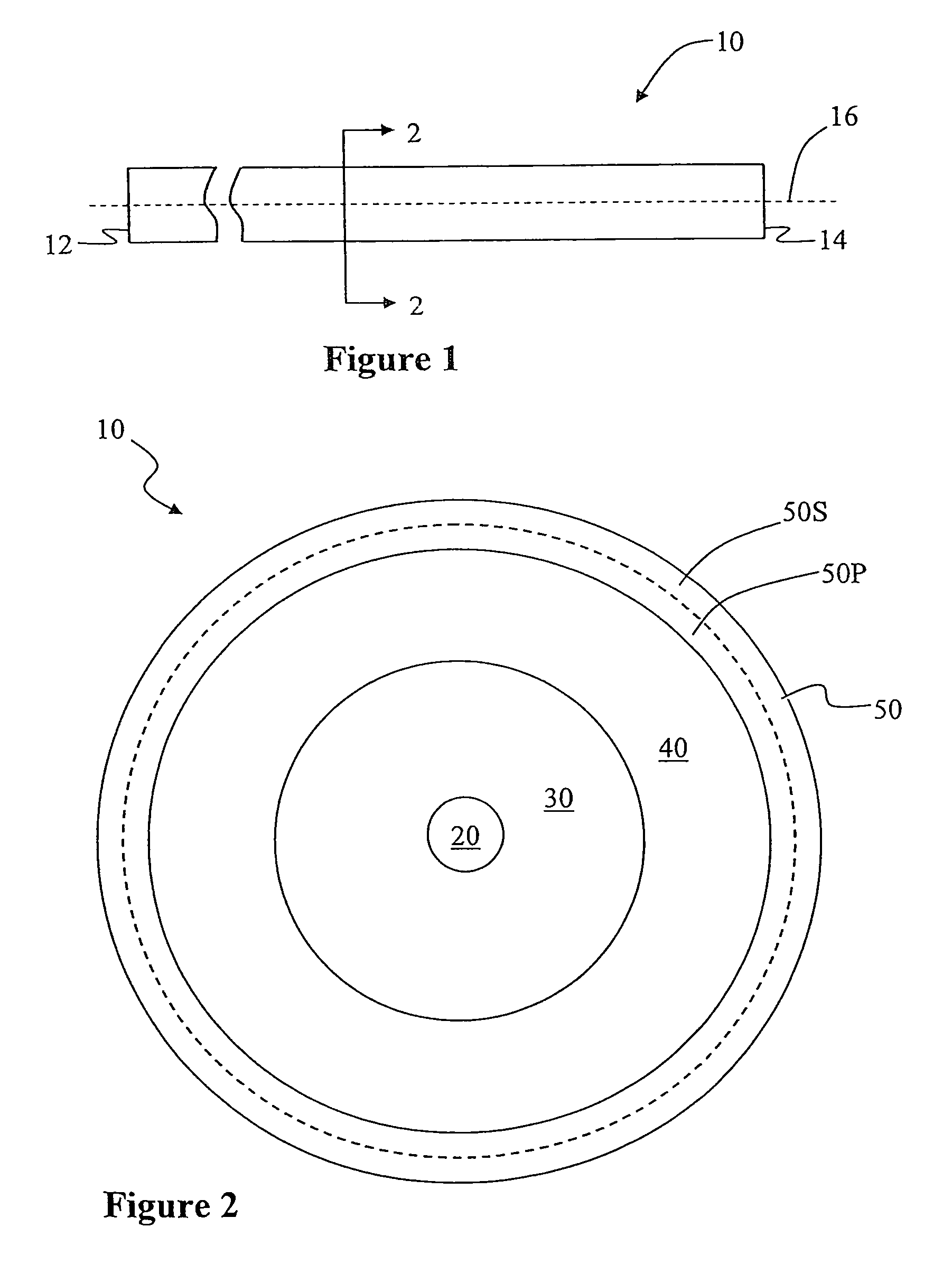
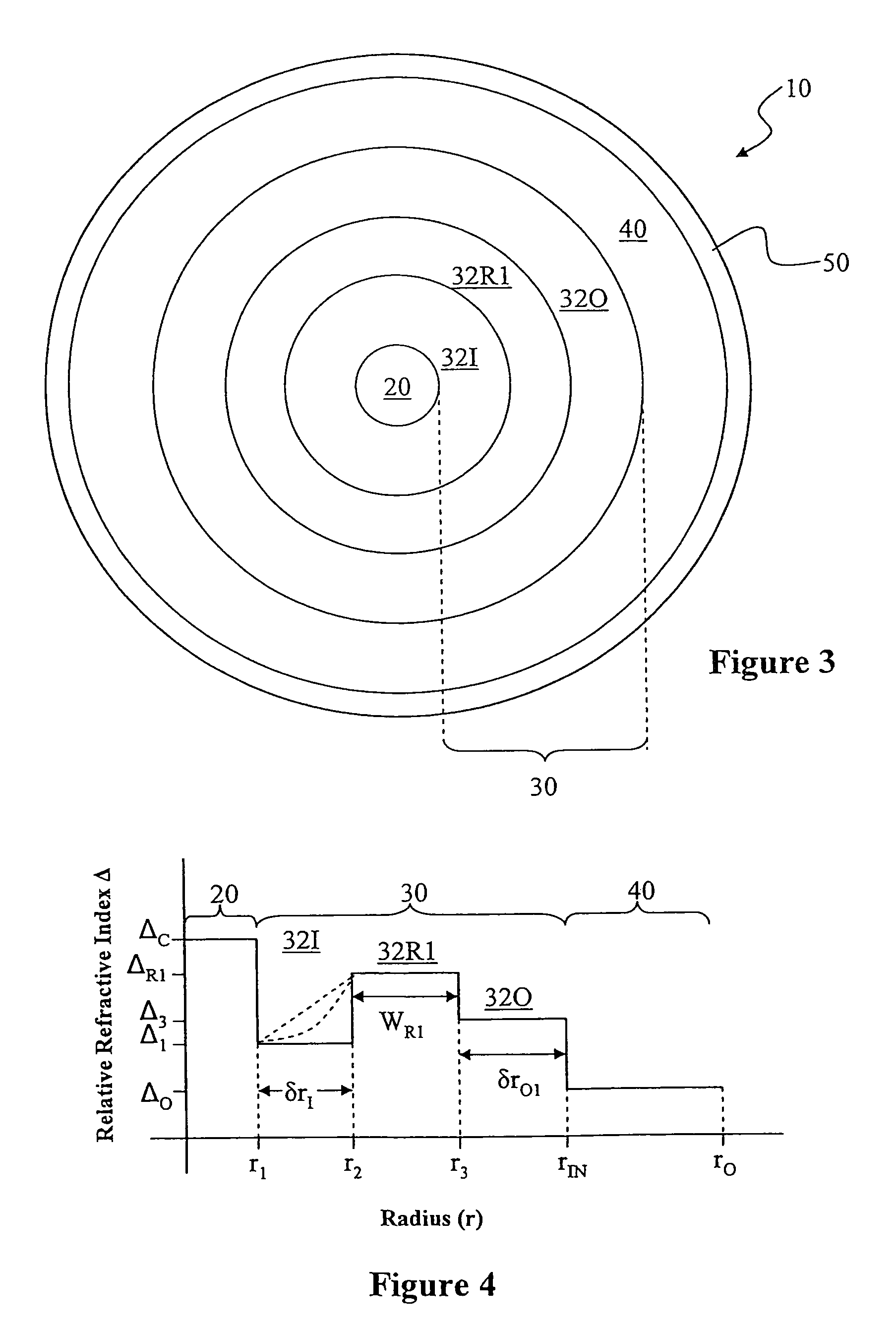
A large-mode-area (LMA) optical fiber (10) that operates as a single-mode optical fiber. The optical fiber includes a core region (20) surrounded by an inner cladding (32), which in turn is surrounded by an outer cladding (40). The inner cladding includes at least one up-doped ring region (32R1). The ring region is configured to form a large attenuation differential between the higher-order modes and the fundamental mode so only that the fundamental mode remains traveling in the optical fiber. If necessary, the optical fiber can include a bend (10B) having a select “resonant” bend diameter (DB) that increases the relative attenuation of the fundamental and higher-order modes. The optical fiber supports an effective mode field diameter (MFD) of up to 40 μm to 50 μm. As a result, detrimental non-linear effects are suppressed, which allows the optical fiber to carry substantially more optical power than conventional LMA optical fibers. The LMA optical fiber is thus eminently suited for a number of optical-fiber-based applications calling for high optical power, such as fiber lasers and pump sources for wavelength conversion.
Owner:CORNING INC
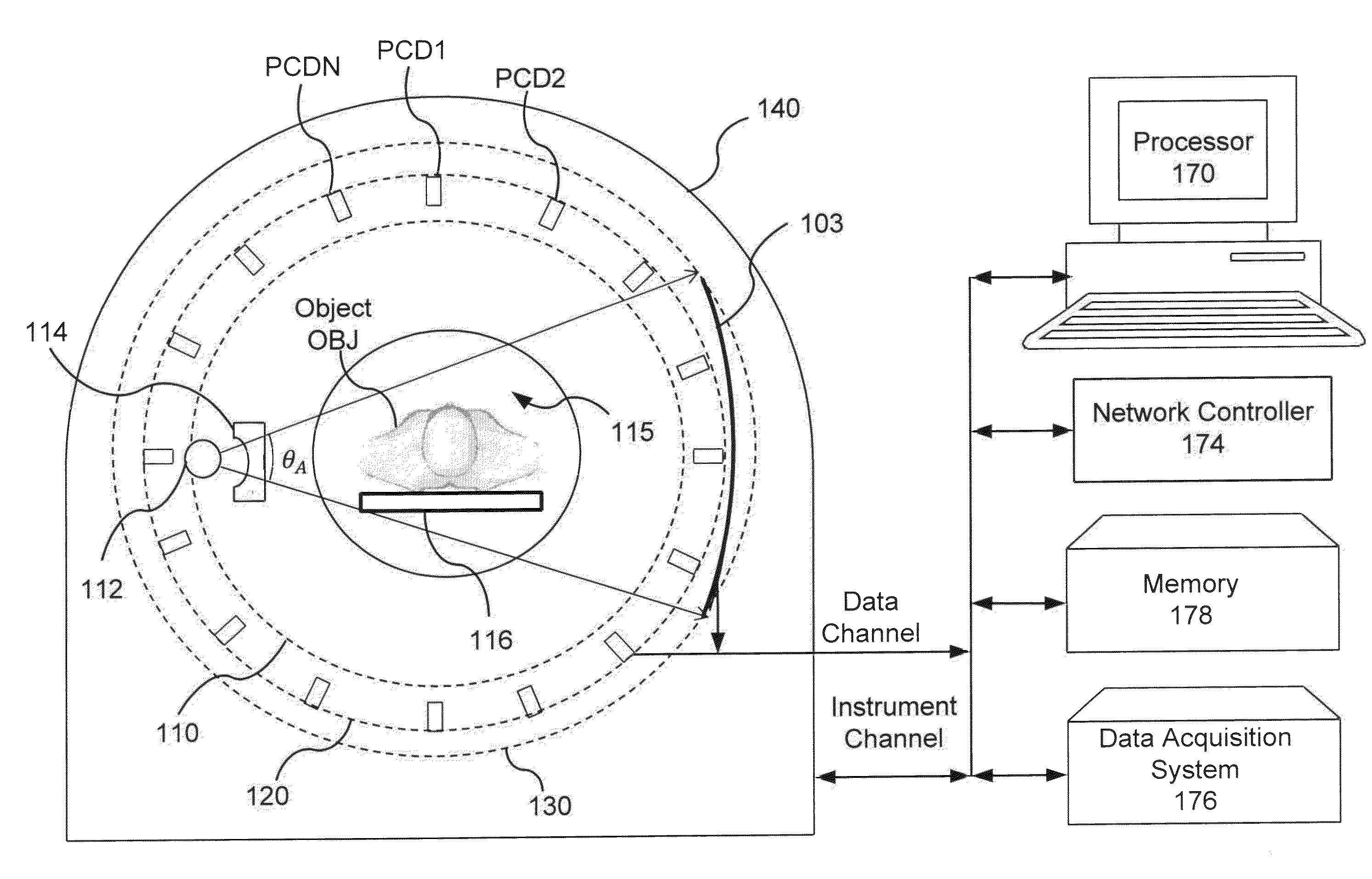
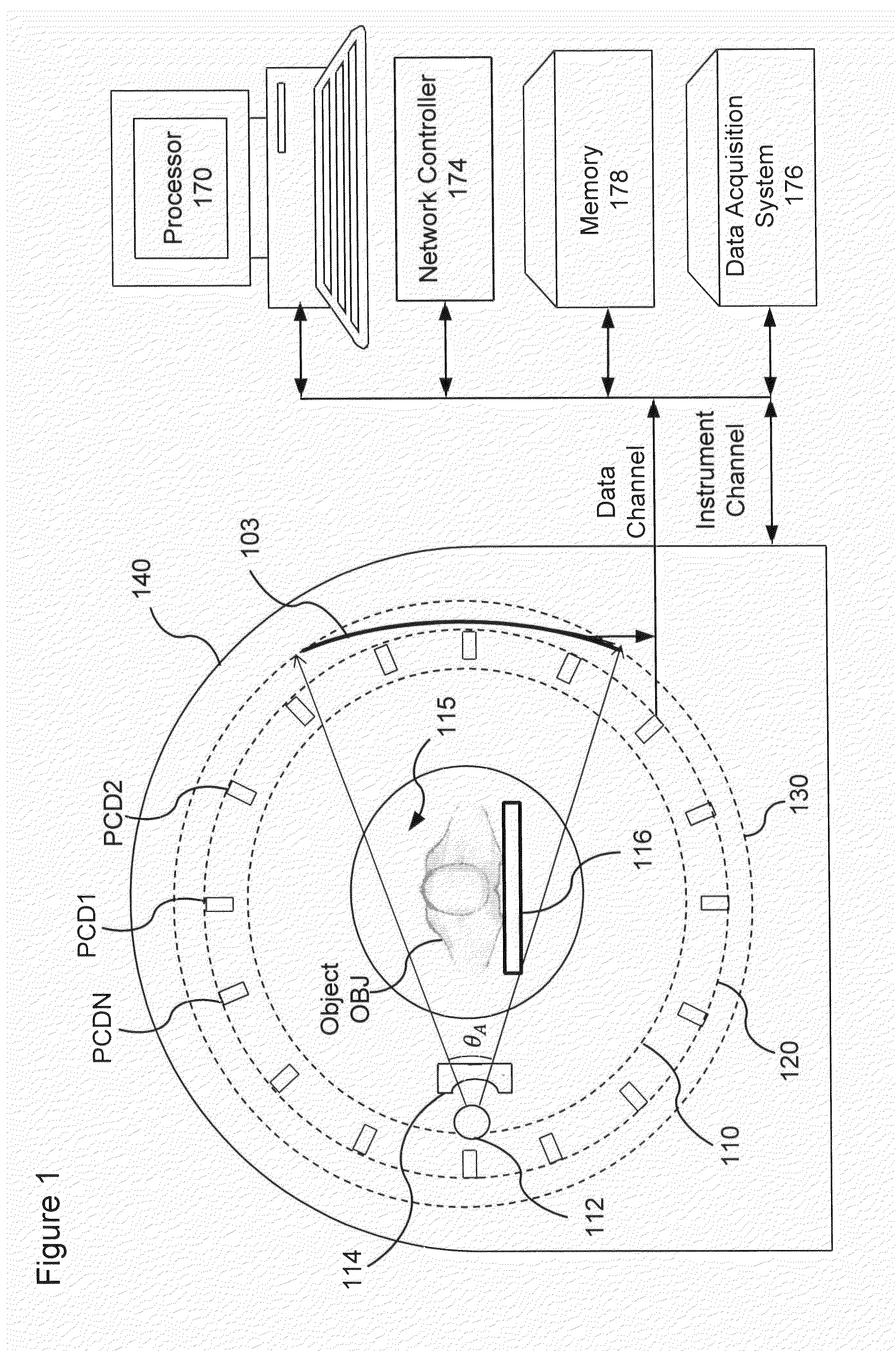
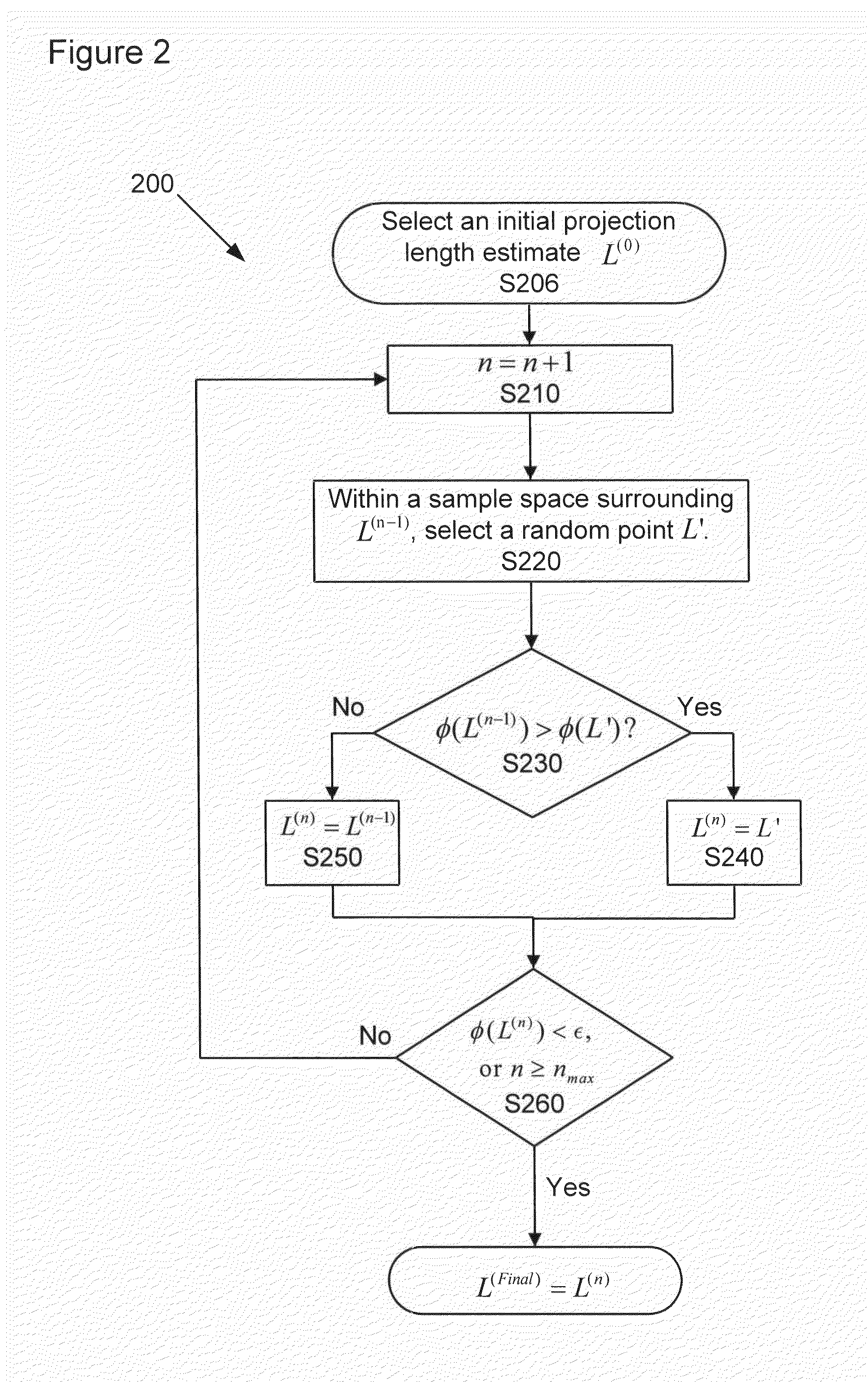
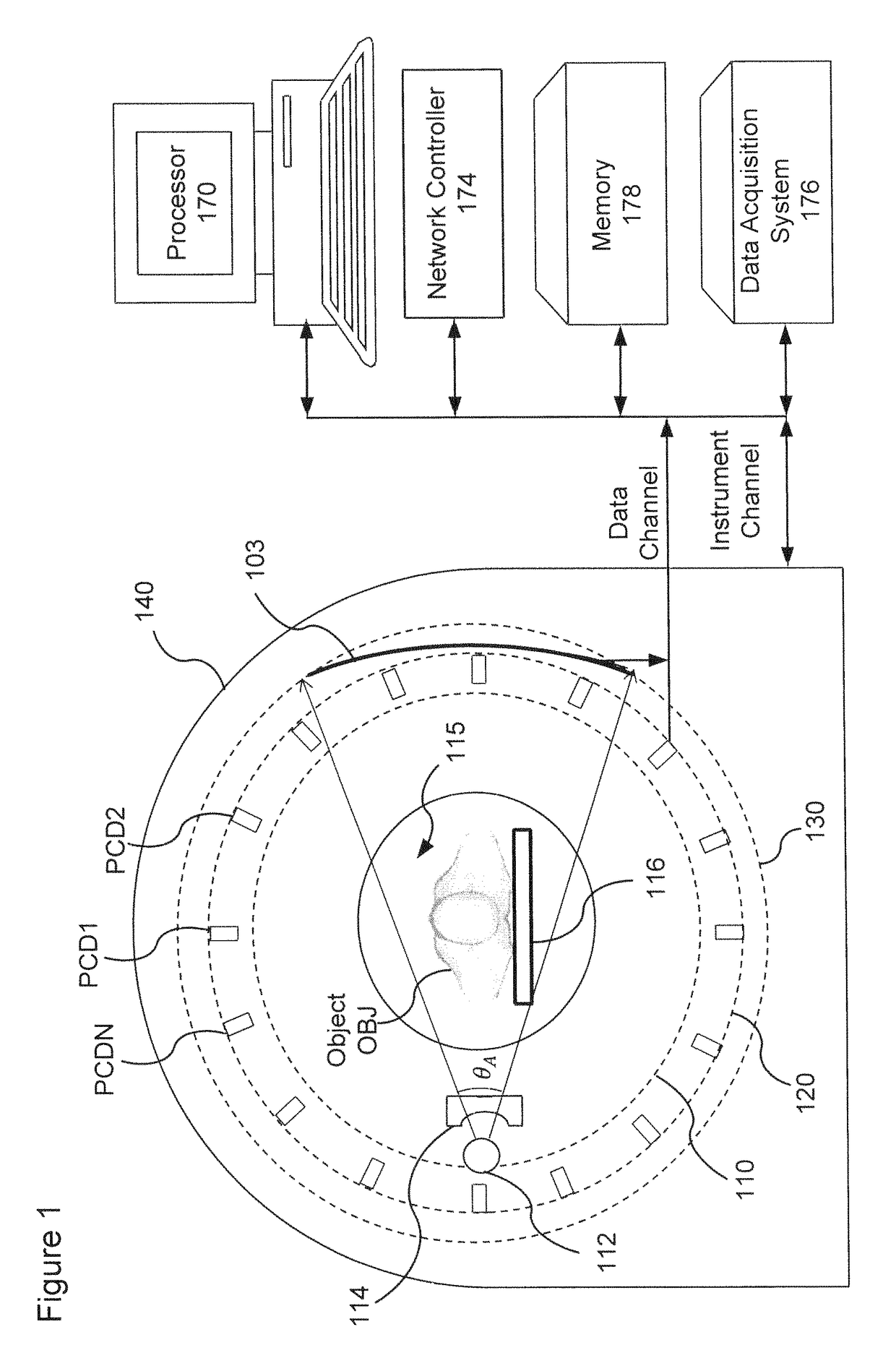
More efficient method and apparatus for detector response correction and material decomposition of projection data obtained using photon-counting detectors
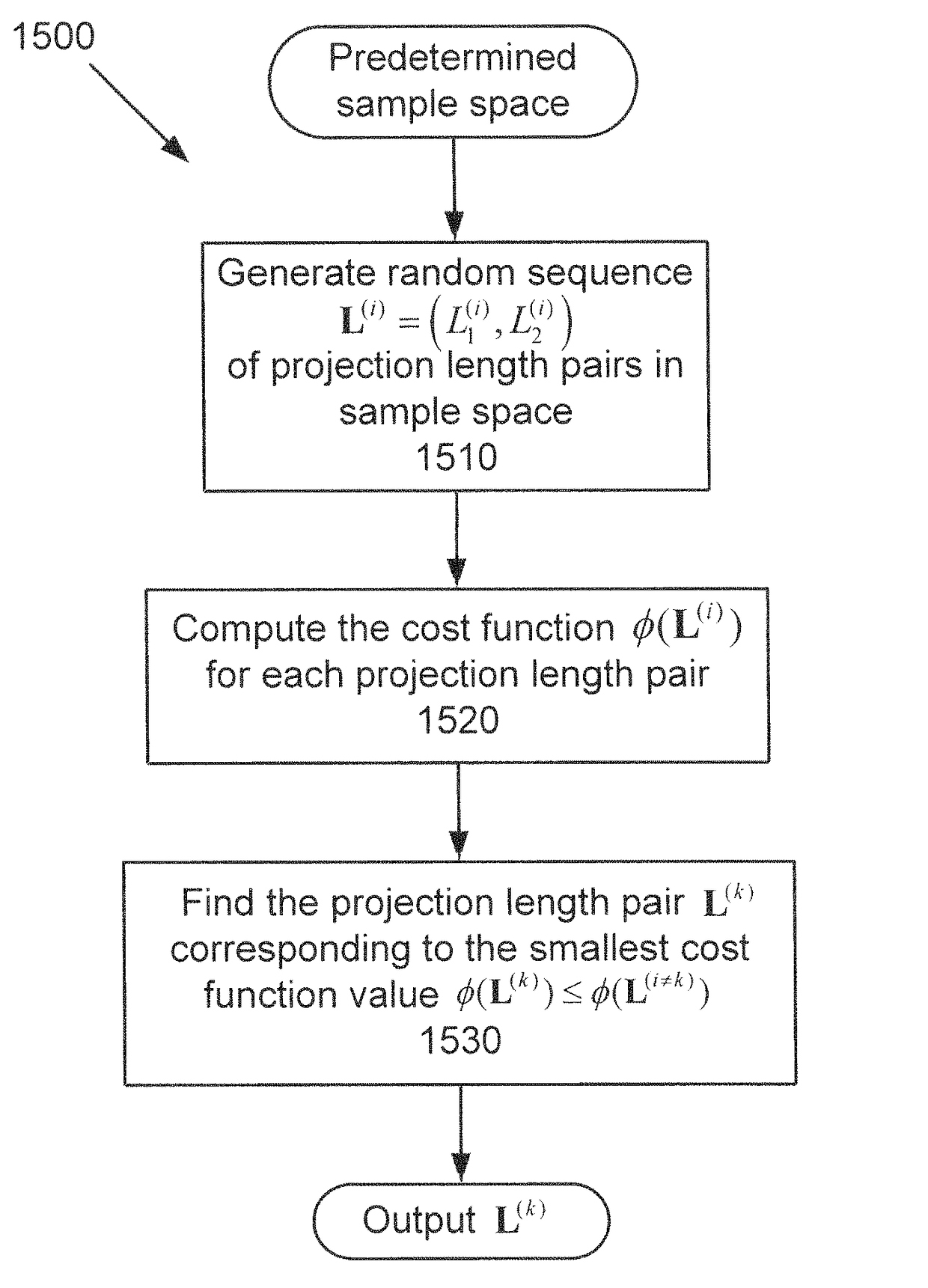
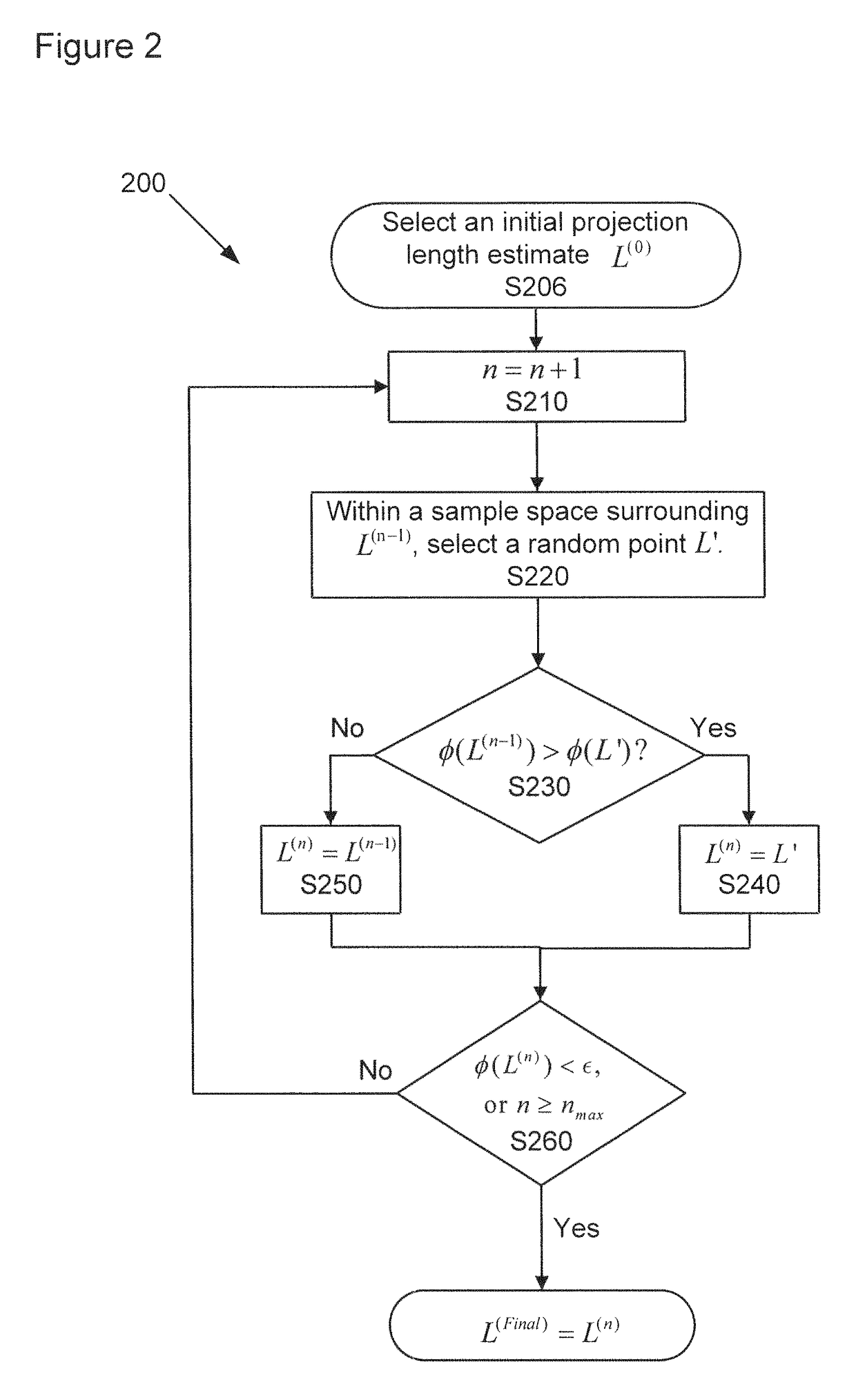
An apparatus and method of processing X-ray projection data including spectral computed tomography (CT) projection data. The spectral CT data is decomposed into material projection lengths using a material-decomposition method that includes an initial-estimate method to provide an initial projection-lengths estimate. The initial-estimate method can include first reconstructing an image using non-spectral CT data, and then subdividing the reconstructed image into materials according to the relative attenuation density of areas within the reconstructed image (e.g., high attenuation areas correspond to a high attenuation material such as bone). The projection length estimates of each material are then obtained by forward projecting the corresponding subdivision of the reconstructed image. Also, the initial estimate can be obtained / refined by selecting the projection lengths with smallest cost-function value from randomly chosen projection lengths within a sample space. The initial estimate can also be conditioned on the X-ray flux at the X-ray source.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Device and method for monitoring hydrocephalus and encephaledema
ActiveCN102579008AImprove medical safetyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRelative attenuationConverters
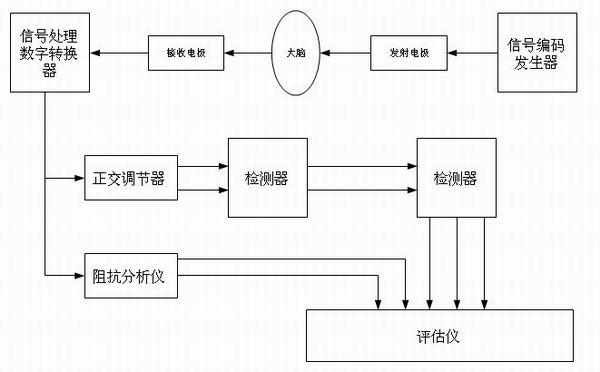
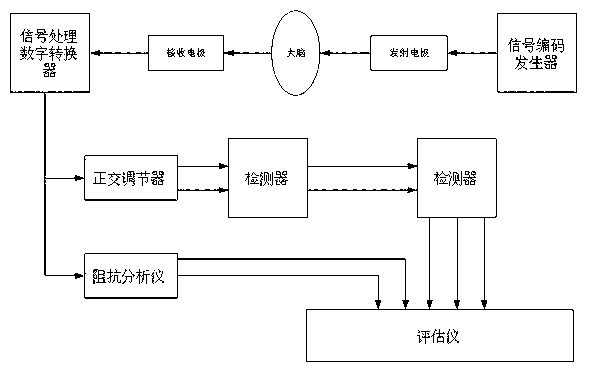
The invention relates to a device used for monitoring hydrocephalus and encephaledema. The device comprises a signal encoding generator, an emission electrode, a receiving electrode, a signal processing digital converter, an orthogonal regulator, a detector, a parameter assessment device, a resistance analyzer and an assessment instrument. The invention also relates to a method used for monitoring hydrocephalus and encephaledema, which comprises the following steps of: intruding into the lower part of the skull skin; emitting electromagnetic waves; carrying out amplification and filter processing on the received electromagnetic waves, and converting the electromagnetic waves into digital signals; carrying out orthogonalization processing on the digital signals; detecting synthetic signals and orthogonal signals of the electromagnetic waves; calculating the relative attenuation coefficients, the relative phase displacement, the transmission speed difference and the complex wave value K; calculating the complex impedance Z and capacitance; and assessing hydrocephalus and encephaledema. According to the invention, hydrocephalus and encephaledema situations can be monitored and assessed all day in a non-intrusive mode so as to reduce the treatment risks.
Owner:CHONG QING BORN FUKE MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
More efficient method and apparatus for detector response correction and material decomposition of projection data obtained using photon-counting detectors
An apparatus and method of processing X-ray projection data including spectral computed tomography (CT) projection data. The spectral CT data is decomposed into material projection lengths using a material-decomposition method that includes an initial-estimate method to provide an initial projection-lengths estimate. The initial-estimate method can include first reconstructing an image using non-spectral CT data, and then subdividing the reconstructed image into materials according to the relative attenuation density of areas within the reconstructed image (e.g., high attenuation areas correspond to a high attenuation material such as bone). The projection length estimates of each material are then obtained by forward projecting the corresponding subdivision of the reconstructed image. Also, the initial estimate can be obtained / refined by selecting the projection lengths with smallest cost-function value from randomly chosen projection lengths within a sample space. The initial estimate can also be conditioned on the X-ray flux at the X-ray source.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
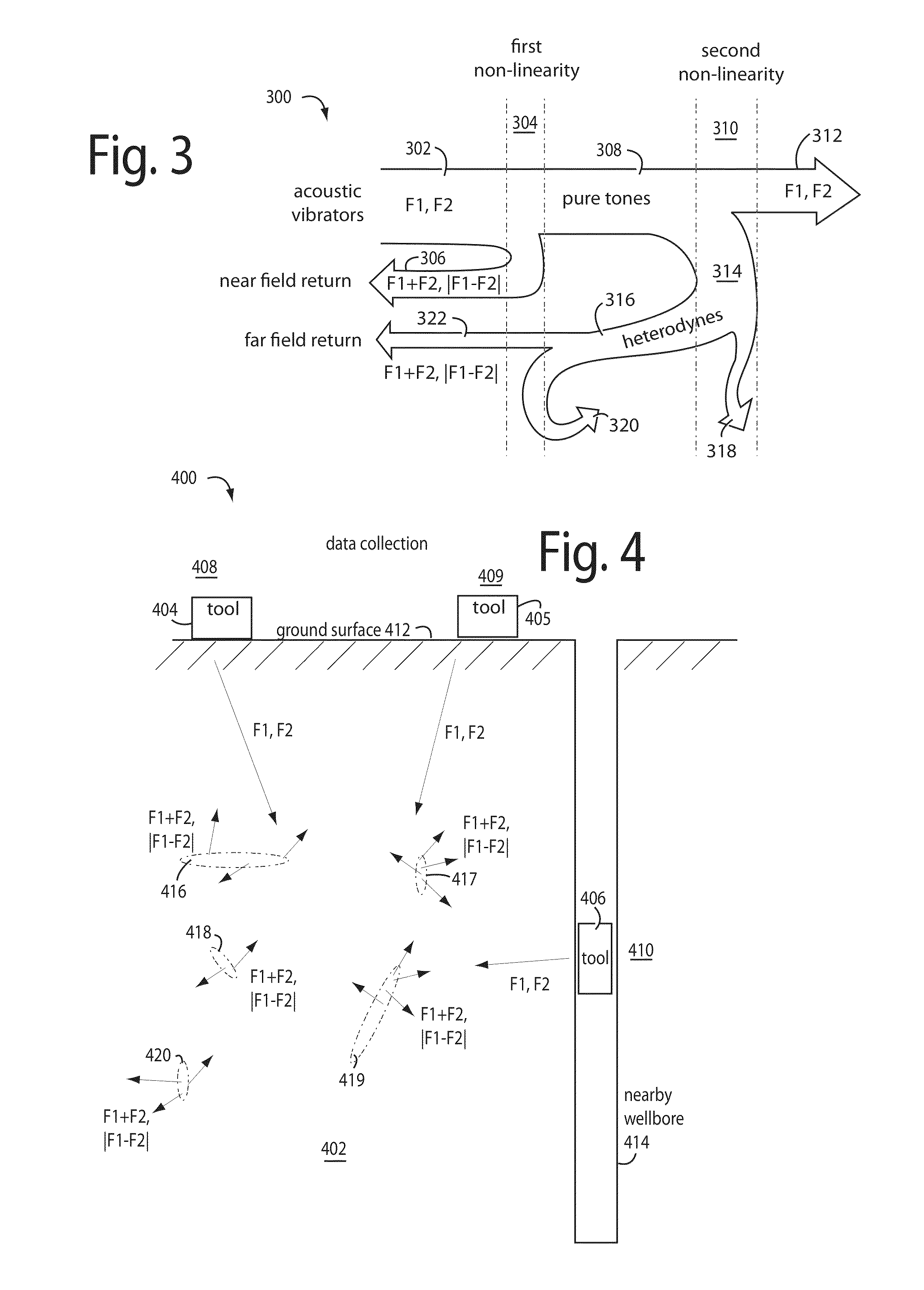
Acoustic heterodyne radar
InactiveUS20140043183A1Earthquake measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGraphicsRelative attenuation
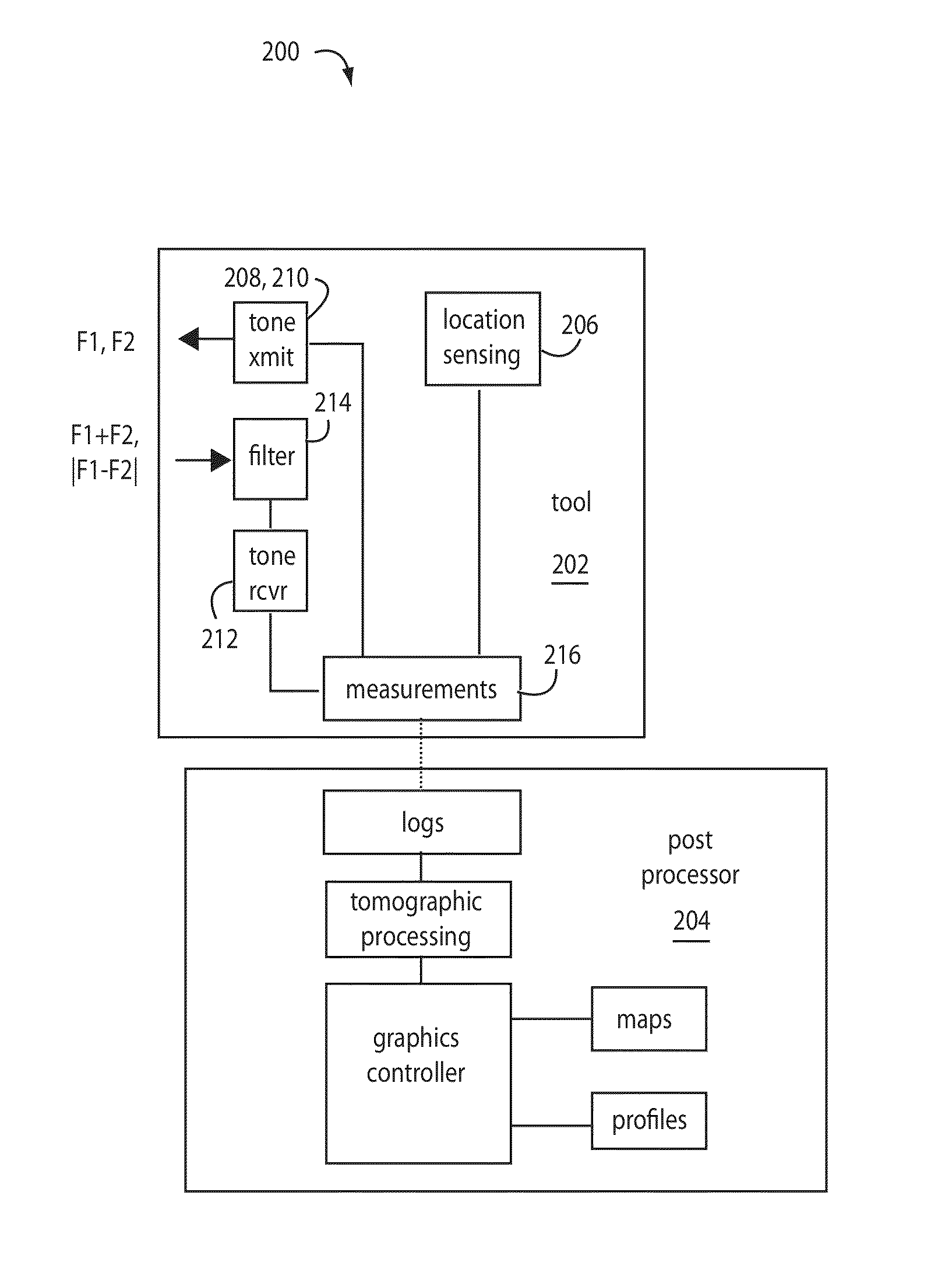
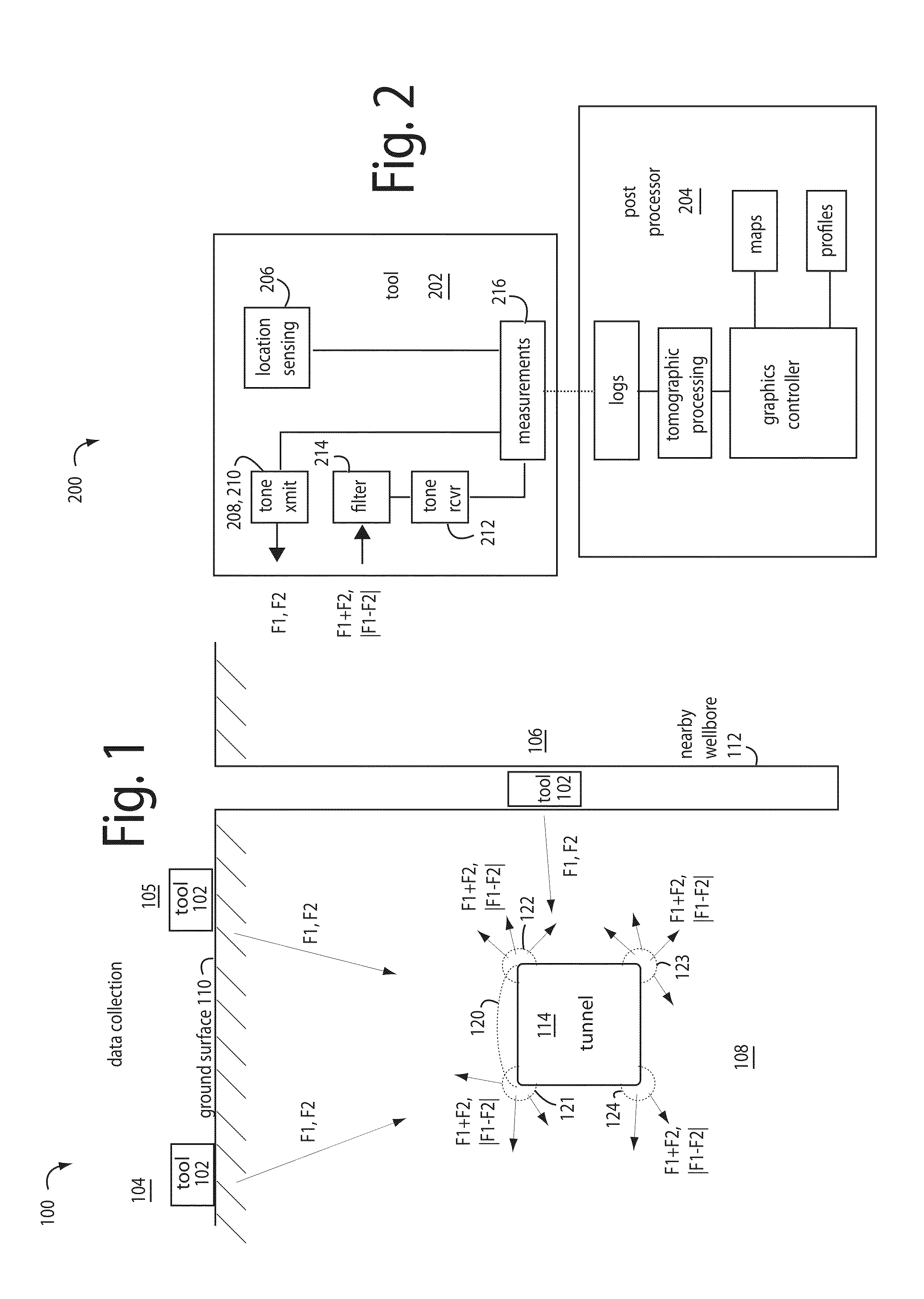
Acoustic heterodyne radars use accurately surveyed or otherwise known locations to repetitively launch at least two, intense acoustic tone soundwaves (F1, F2) into an underground area of search. An acoustic receiver is tuned to receive either the sum (F1+F2) or difference (|F1−F2|) heterodynes and is configured to measure and log the overall relative attenuation and roundtrip travel times of the soundwaves, like a typical radar. Any acoustic heterodynes received are assumed to be the work of non-linearities and stresses in the search area. A full-waveform three dimensional tomography algorithm is applied by a graphics processor to the collected and logged data to generate maps and profiles of objects beneath the ground which are interpreted to have produced the acoustic heterodynes.
Owner:STOLAR
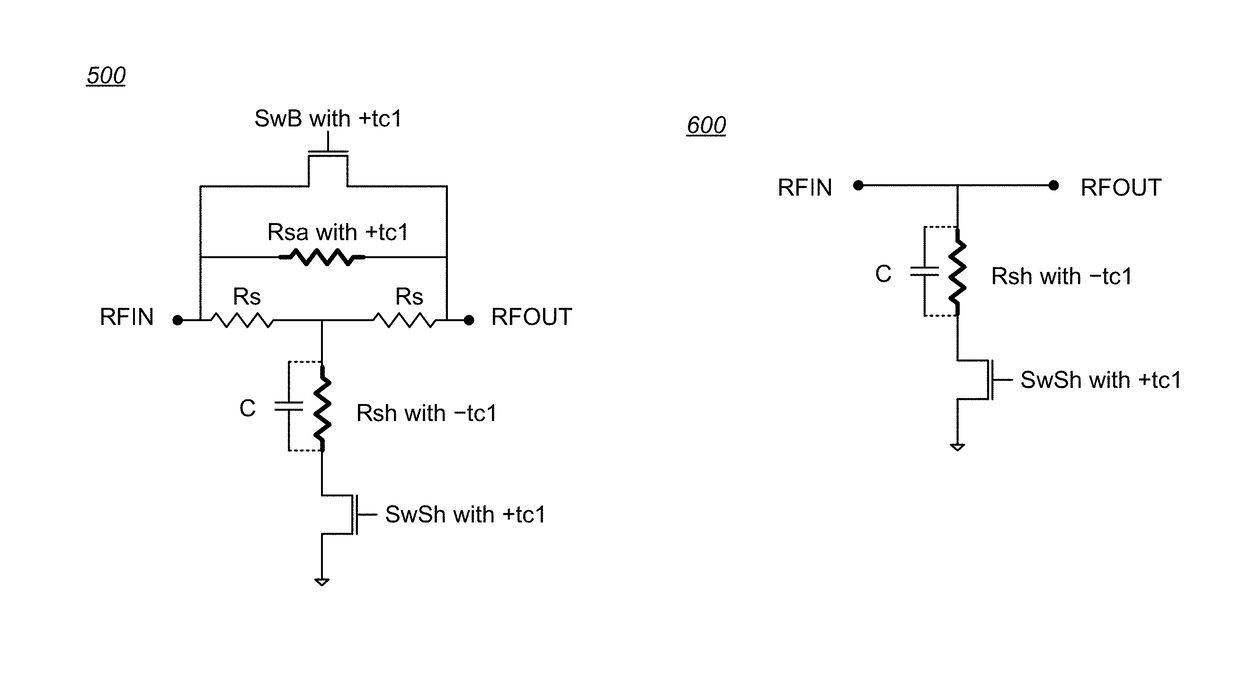
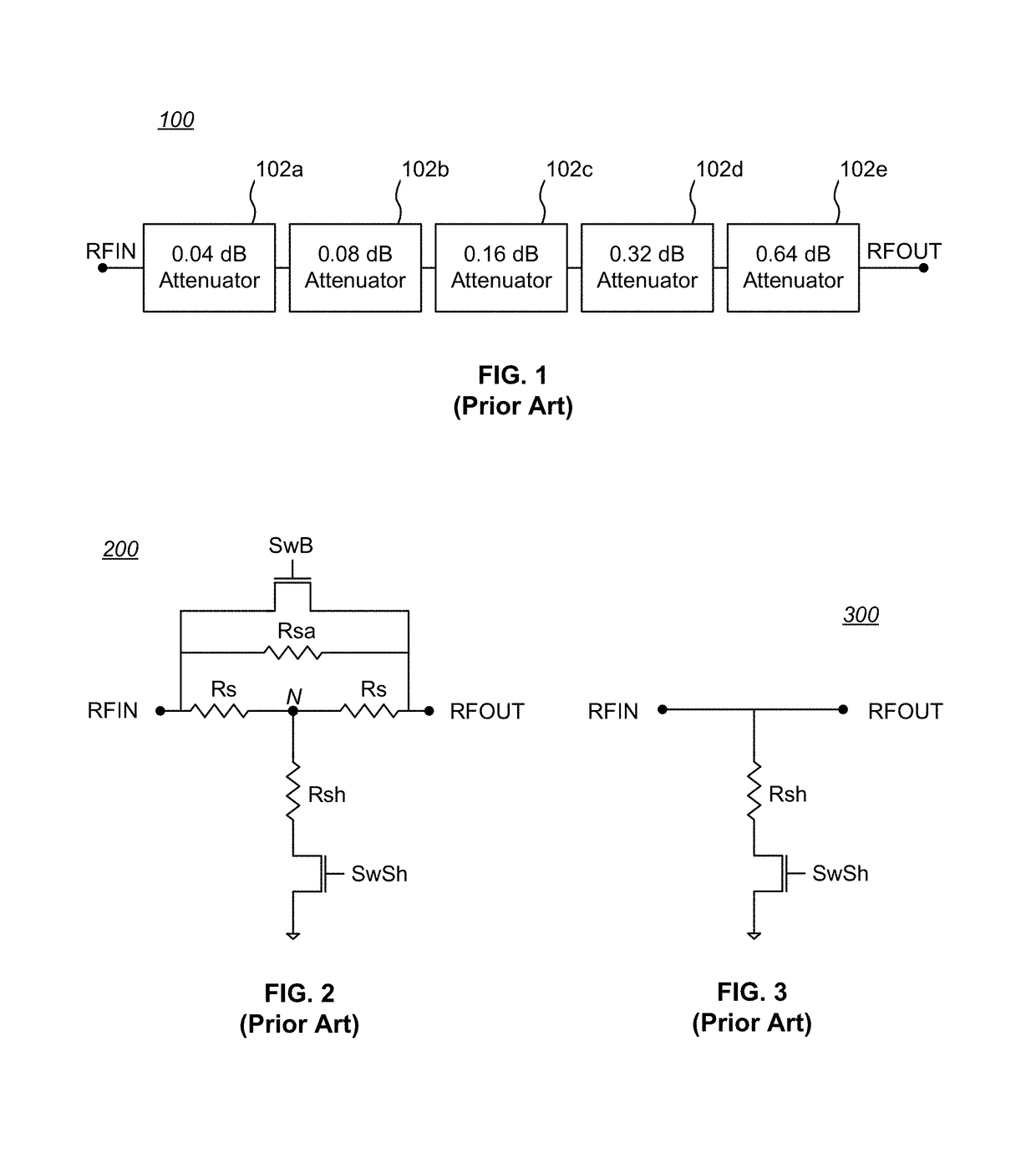
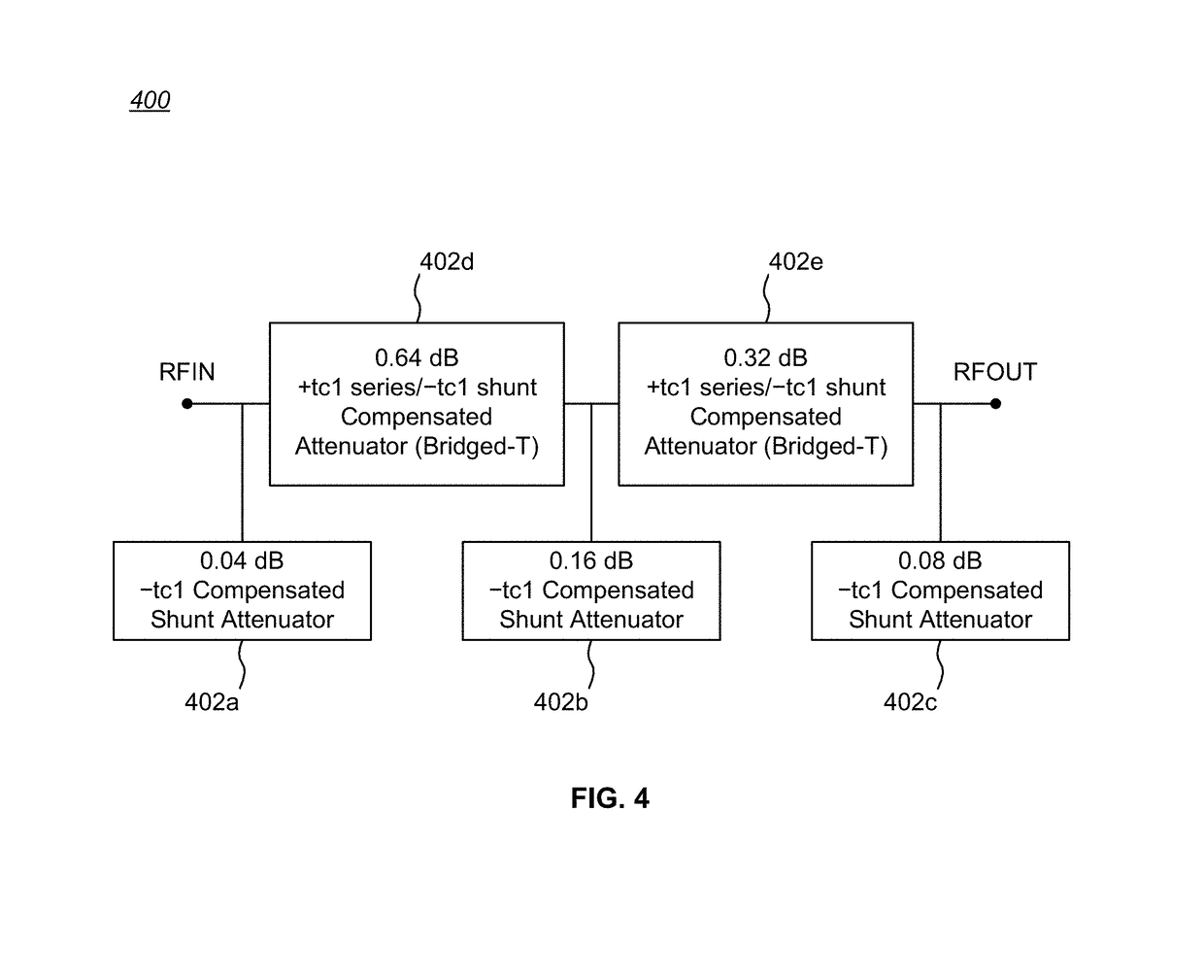
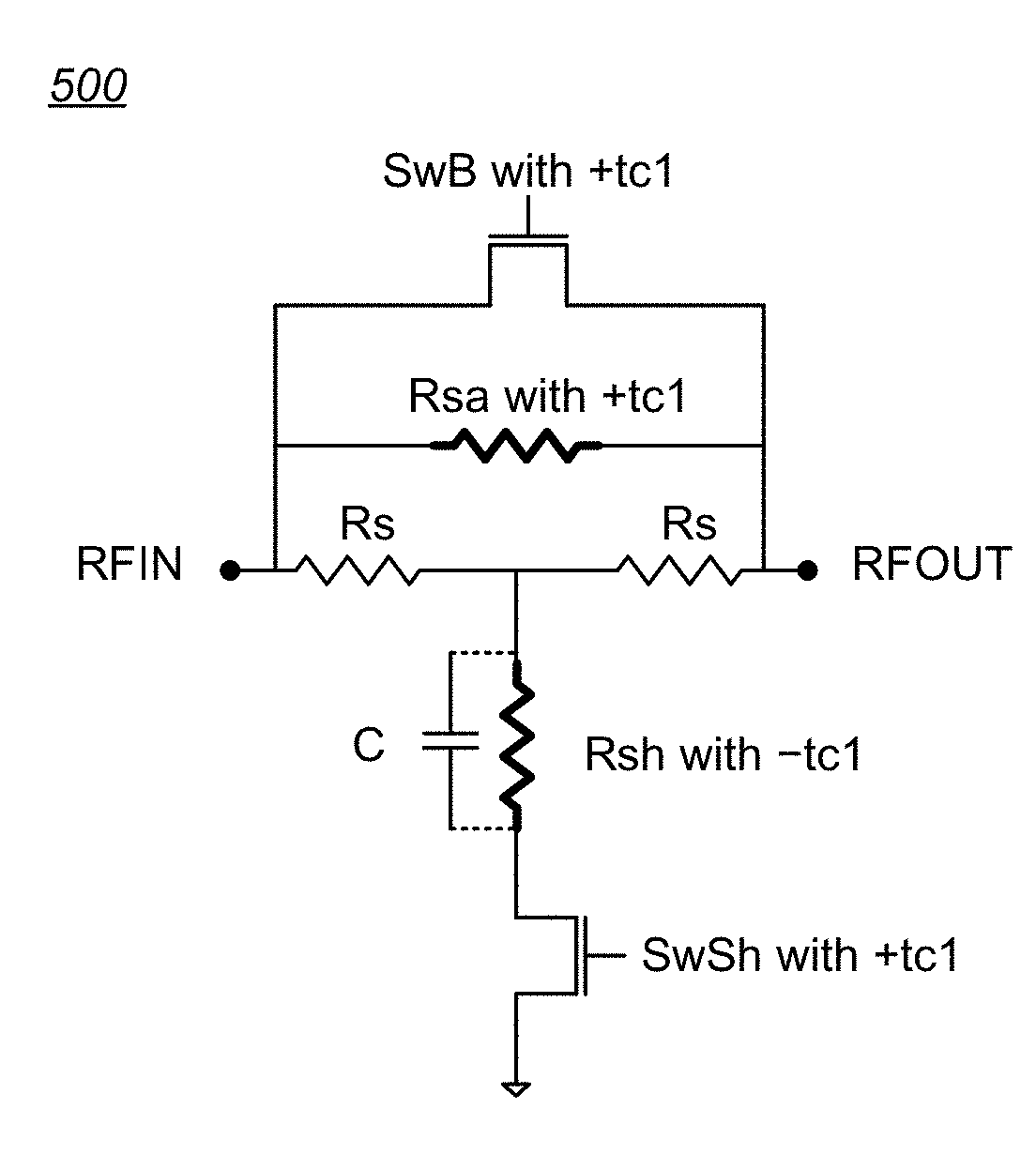
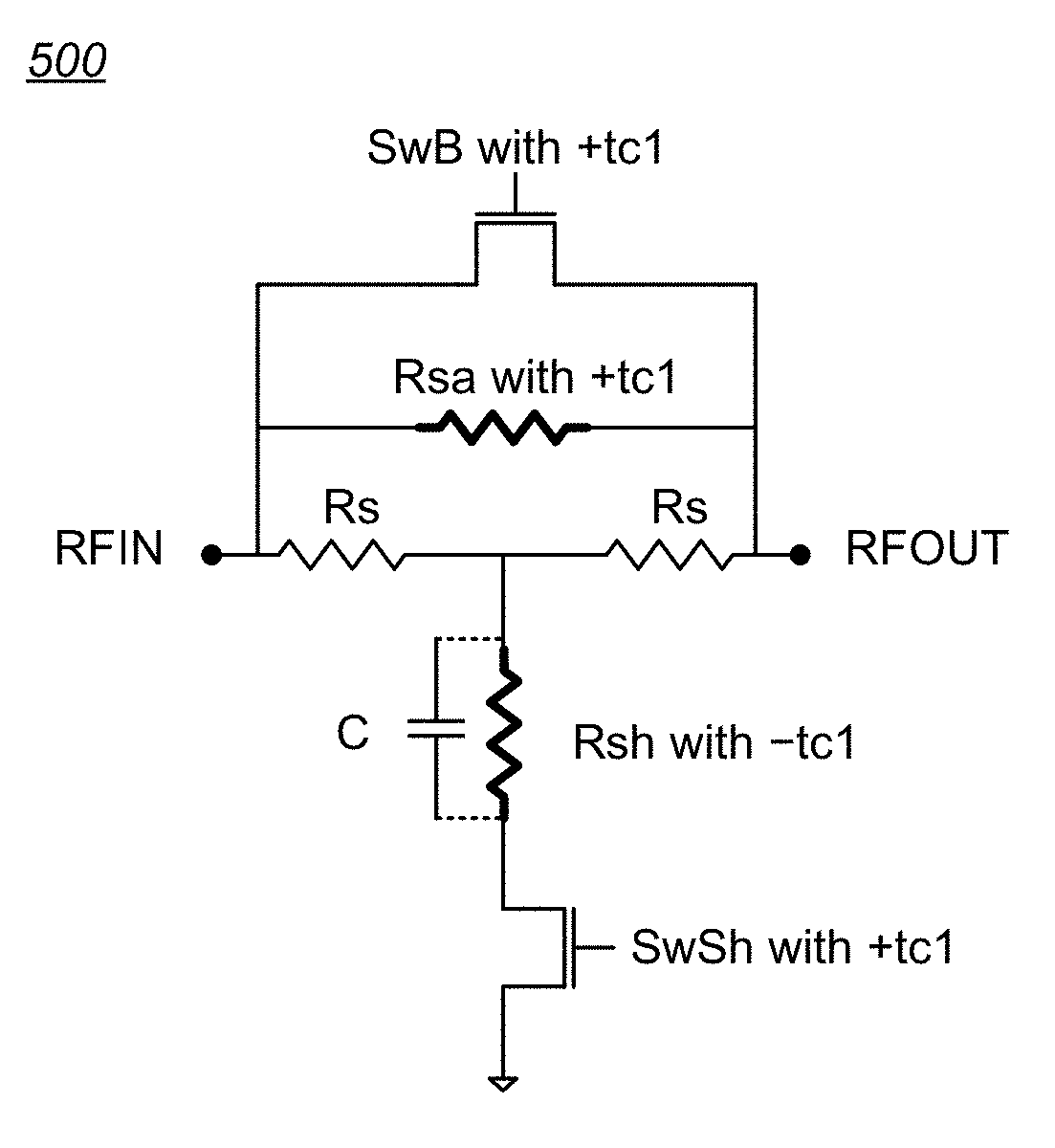
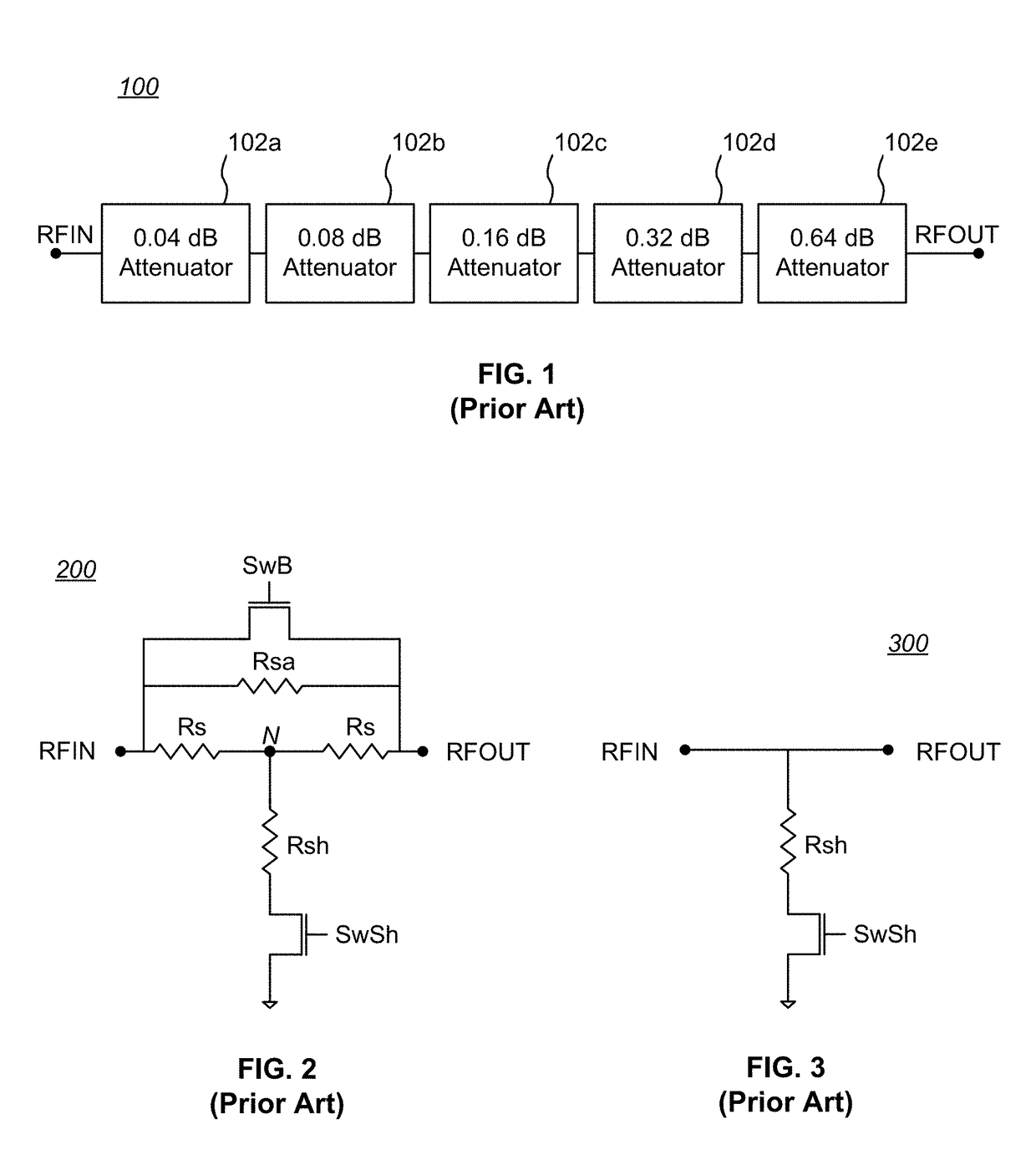
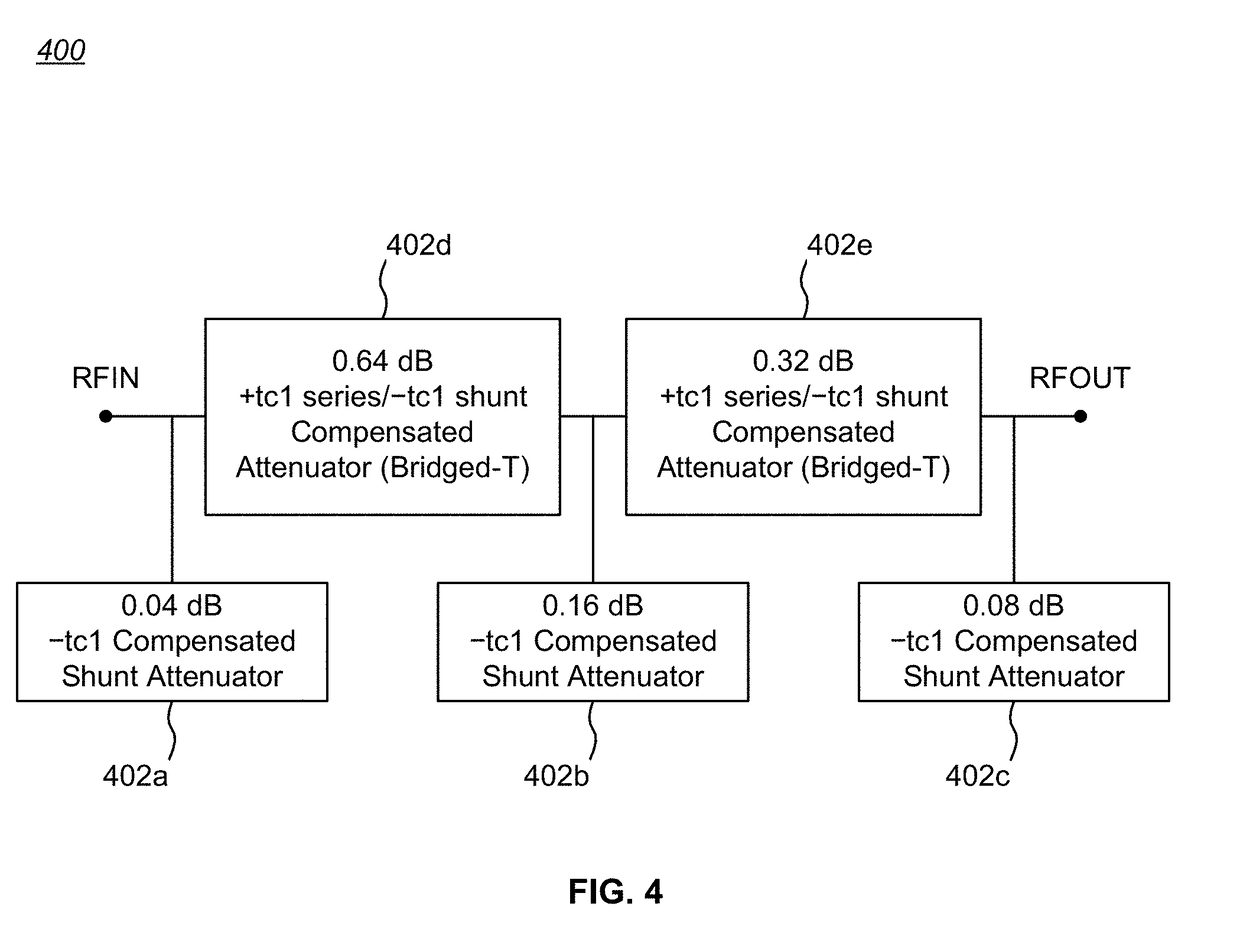
Temperature compensated digital step attenuator
ActiveUS10003322B2Multiple-port networksWaveguide type devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceRelative attenuation
Owner:PSEMI CORP
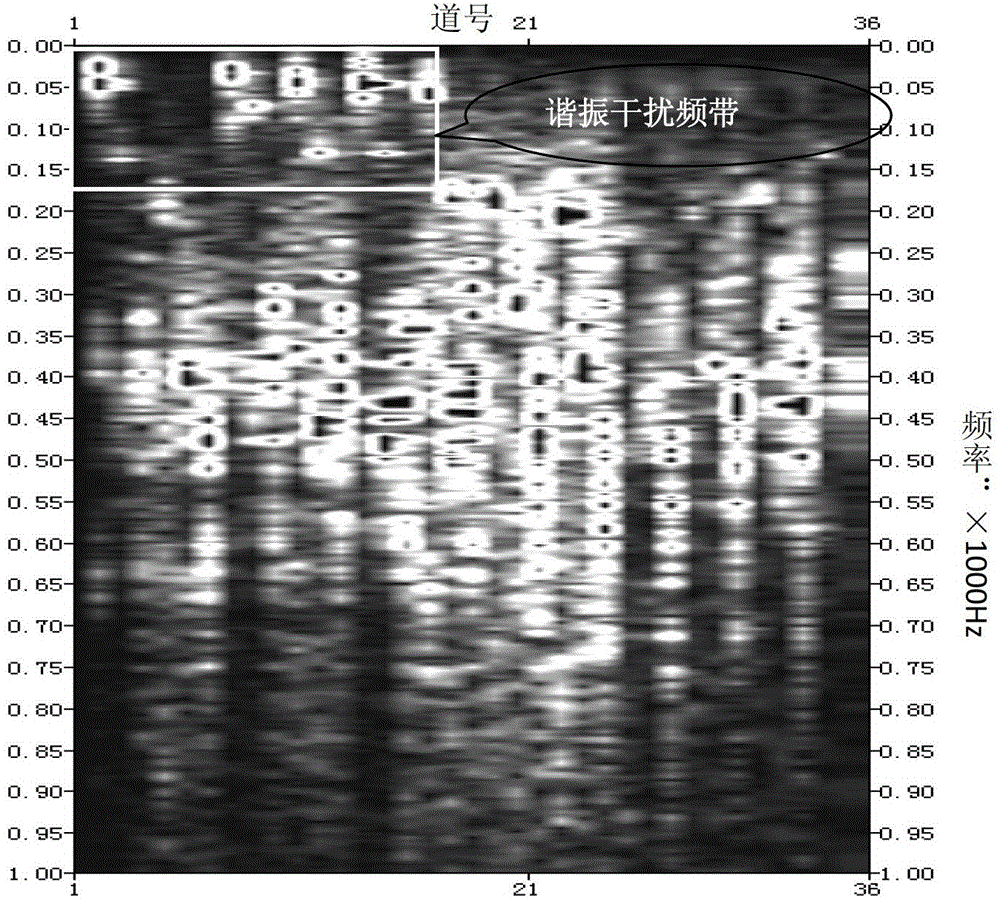
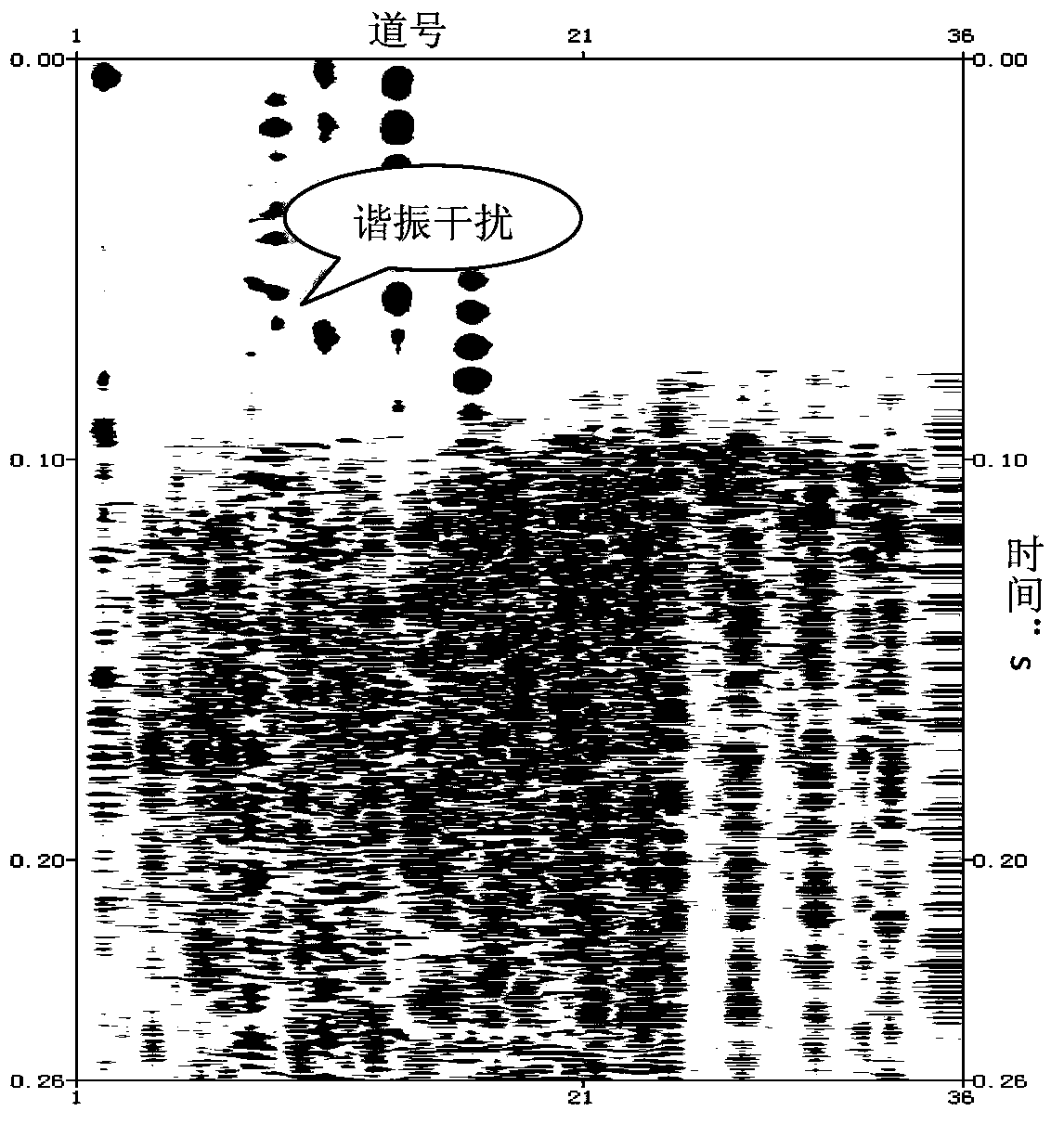
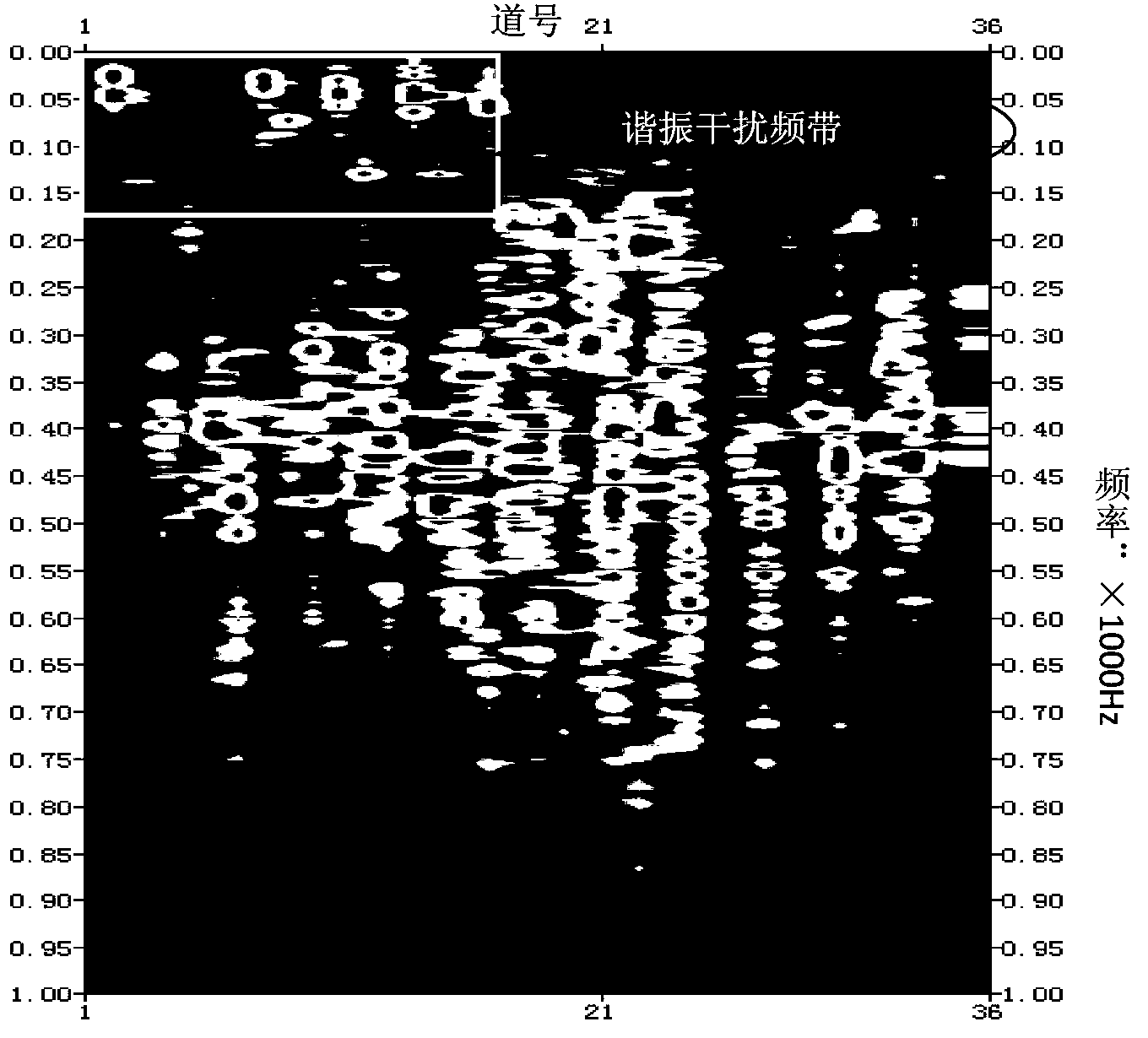
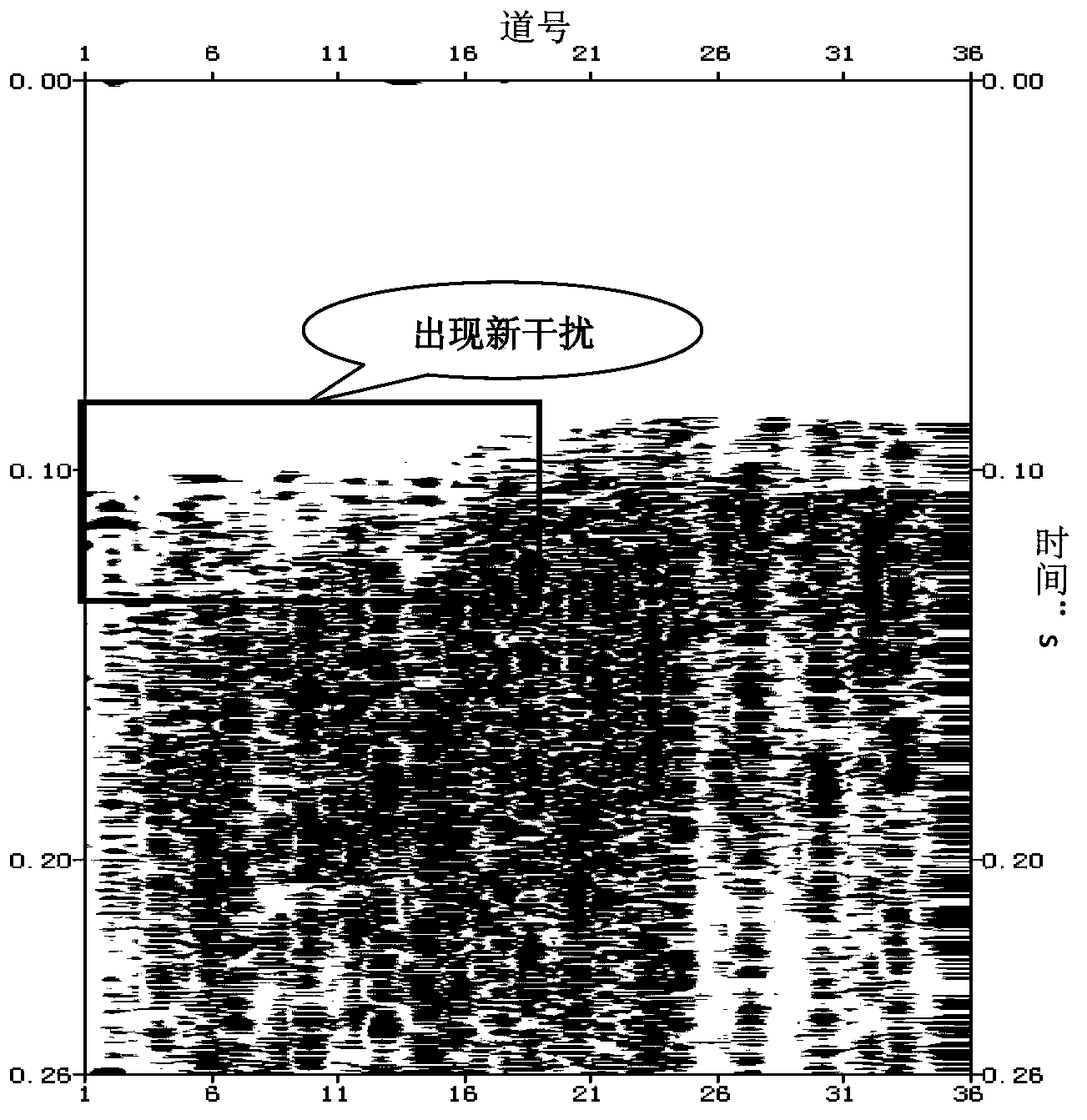
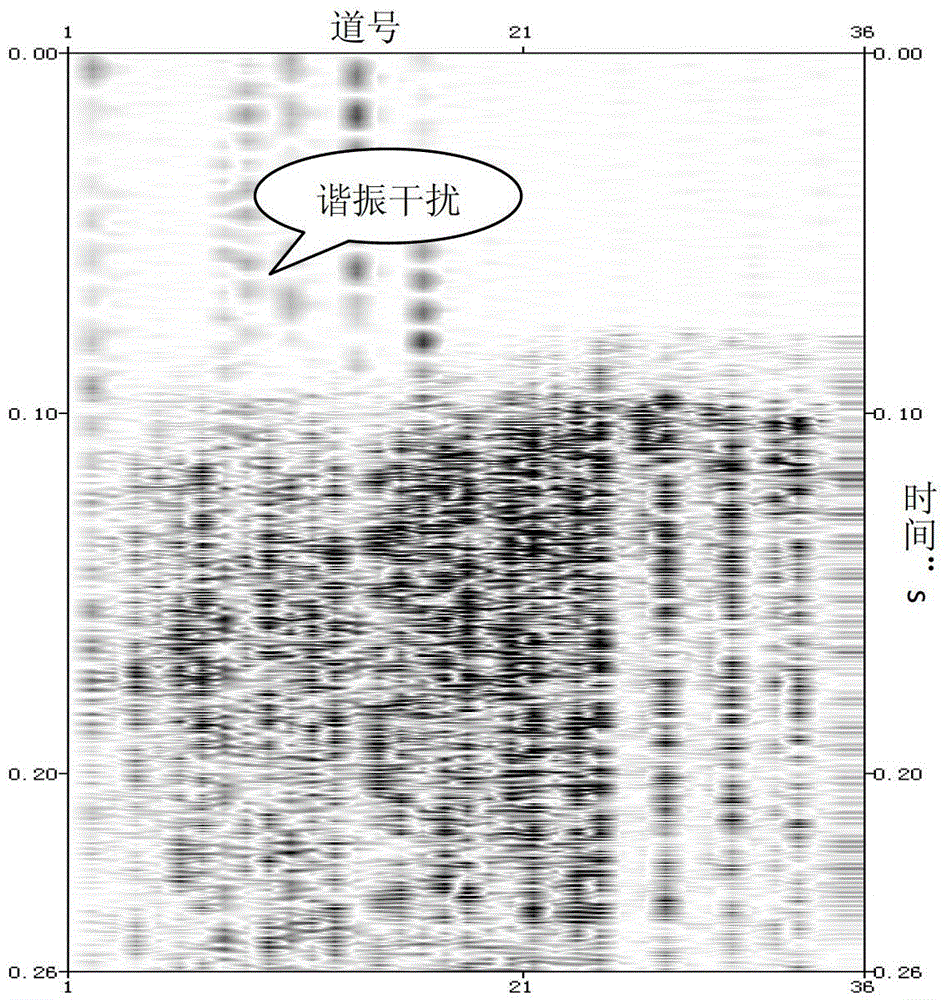
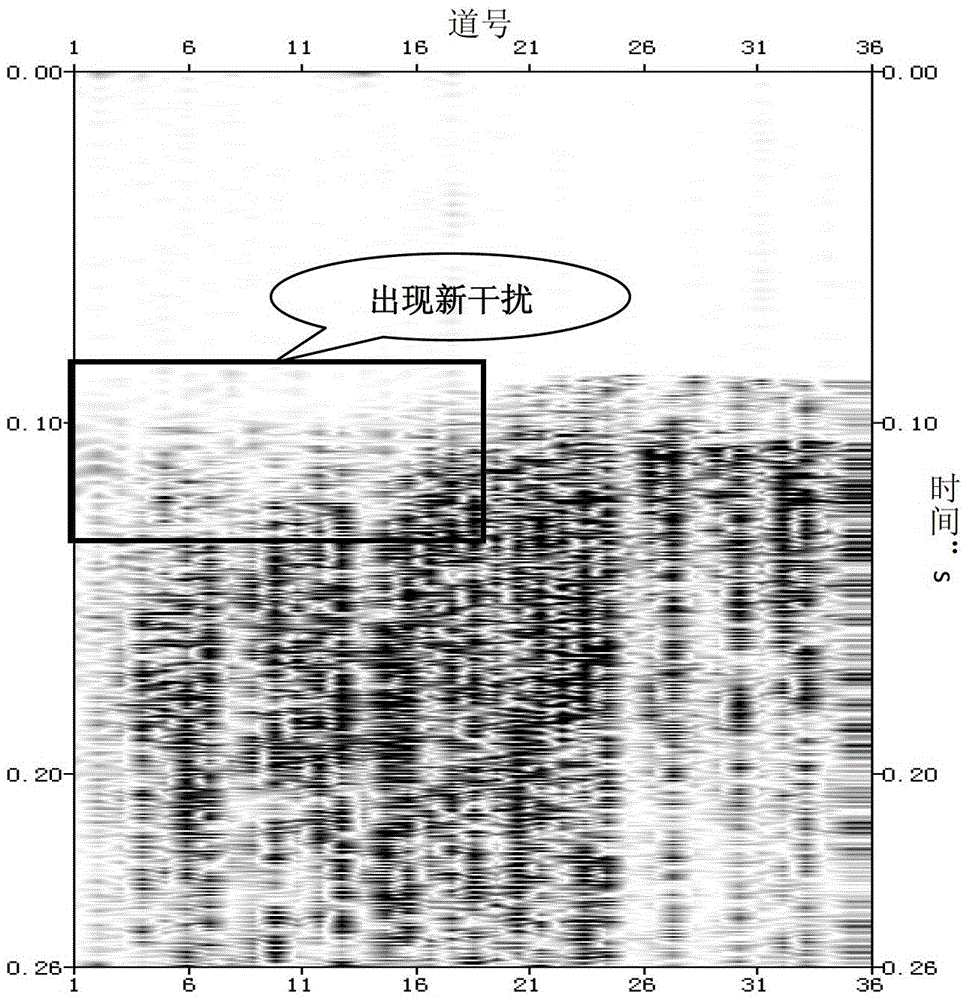
Method for identifying and effectively suppressing signal resonance interference during microseismic monitoring
ActiveCN103675917AImprove computing efficiencyReduce harmSeismic signal processingRelative attenuationAttenuation coefficient
The invention provides a method for identifying and suppressing signal resonance interference during microseismic fracture monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: transferring microseismic fracture event signals into a frequency domain; respectively arranging three-component spectrum in terms of horizontal and vertical component; determining the resonance signal band frequency range; selecting a non-resonance interference spectrum channel on the vertical component spectrum arrangement; calculating the energy of a frequency sampling point and that of whole-channel signal master frequency, wherein the ratio of the two energies is a relative attenuation coefficient of the microseismic signal at the sampling point; calculating the master frequency energies of all resonance interference spectrum of each arrangement of the three-component spectrum, allowing the result to multiply the attenuation coefficient of the corresponding sampling point to obtain a spectrum compensation value for resonance interference band frequency compensation; transforming the frequency domain signals to a time domain through an inverted Fourier transform so as to complete suppressing of resonance signals. Due to the adoption of the method, the resonance interference in microseismic signals can be effectively identified and suppressed, so as to minimize the damage for effective signals. Therefore, the method is simple to use and high in calculation efficiency.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
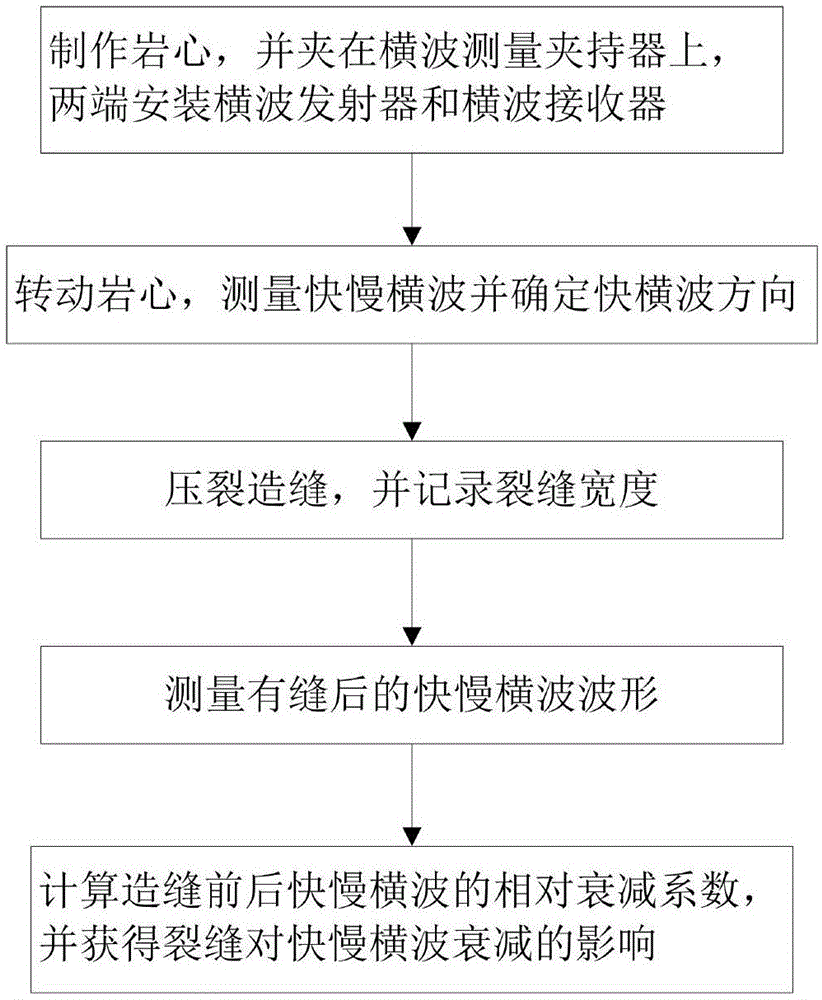
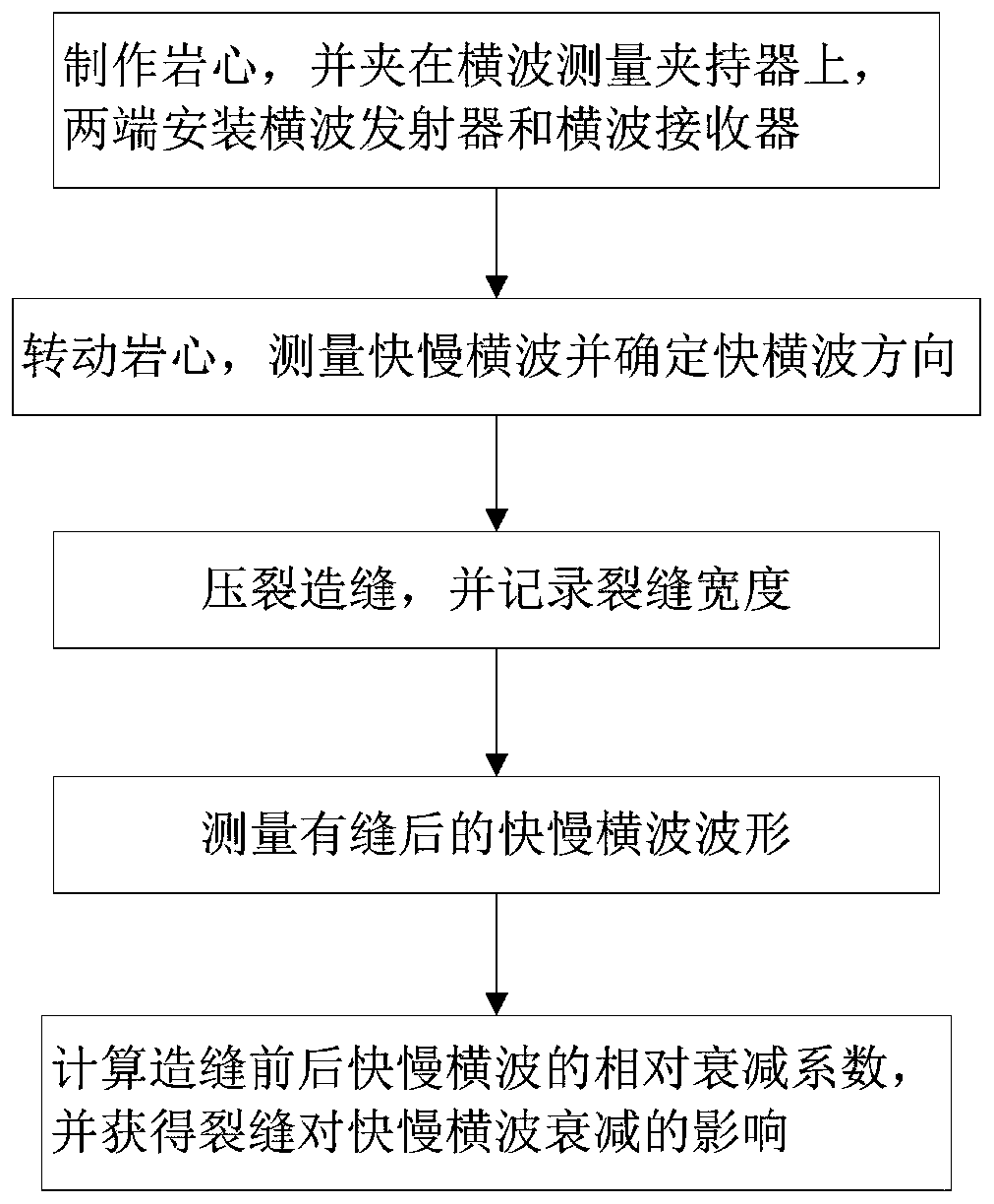
Method for measuring attenuation coefficient of fast and slow shear waves under crack width of rock core
ActiveCN106568846AFacilitate quantitative identificationContribute to researchAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
The invention discloses a method for measuring attenuation coefficient of fast and slow shear waves under crack width of rock core. According to the method, by measuring amplitude of fast and slow shear waves before and after fracturing and introducing relative attenuation coefficient, corresponding relative attenuation coefficient of fast and slow shear waves before and after fracturing is calculated, and corresponding relative attenuation coefficient without cracks is subtracted from the relative attenuation coefficient after cracks so as to obtain the influence of cracks on attenuation of fast and slow shear waves. By the method, the influence of anisotropy of a rock sample on attenuation of fast and slow shear waves can be eliminated, and only by considering the influence of crack width on attenuation of fast and slow shear waves, quantitative evaluation of cracks can be realized.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Temperature Compensated Digital Step Attenuator
ActiveUS20180102763A1Variation in amountMultiple-port networksWaveguide type devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceRelative attenuation
Circuits and methods for eliminating or mitigating the amount of temperature-dependent variation in the relative attenuation of a multi-valued digital step attenuator (DSA) by using resistive components having temperature-dependent resistance values that compensate for or offset changes in the temperature-dependent ON resistance (RON) of the switches within the DSA. In some embodiments, DSA attenuator cell switches are fabricated to have positive first-order resistance temperature (FORT) coefficients, while temperature-compensating series attenuation resistances are fabricated as a positive FORT coefficient resistor and temperature-compensating shunt resistances are fabricated as either a negative FORT coefficient resistor or a combination of a negative FORT coefficient resistor in parallel with a positive FORT coefficient resistor.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Large mode area optical fiber
ActiveUS8797642B2Increase optical powerSpeed up the descentOptical fibre with polarisationLaser using scattering effectsRelative attenuationUltrasound attenuation
A large-mode-area (LMA) optical fiber (10) that operates as a single-mode optical fiber. The optical fiber includes a core region (20) surrounded by an inner cladding (32), which in turn is surrounded by an outer cladding (40). The inner cladding includes at least one up-doped ring region (32R1). The ring region is configured to form a large attenuation differential between the higher-order modes and the fundamental mode so only that the fundamental mode remains traveling in the optical fiber. If necessary, the optical fiber can include a bend (10B) having a select “resonant” bend diameter (DB) that increases the relative attenuation of the fundamental and higher-order modes. The optical fiber supports an effective mode field diameter (MFD) of up to 40 μm to 50 μm. As a result, detrimental non-linear effects are suppressed, which allows the optical fiber to carry substantially more optical power than conventional LMA optical fibers. The LMA optical fiber is thus eminently suited for a number of optical-fiber-based applications calling for high optical power, such as fiber lasers and pump sources for wavelength conversion.
Owner:CORNING INC
Numerical control attenuator based on capacitance compensation
PendingCN110011641AFlexible compensation for parasitic phase modulationReduce size requirementsFrequency-independant attenuatorsCapacitanceRelative attenuation
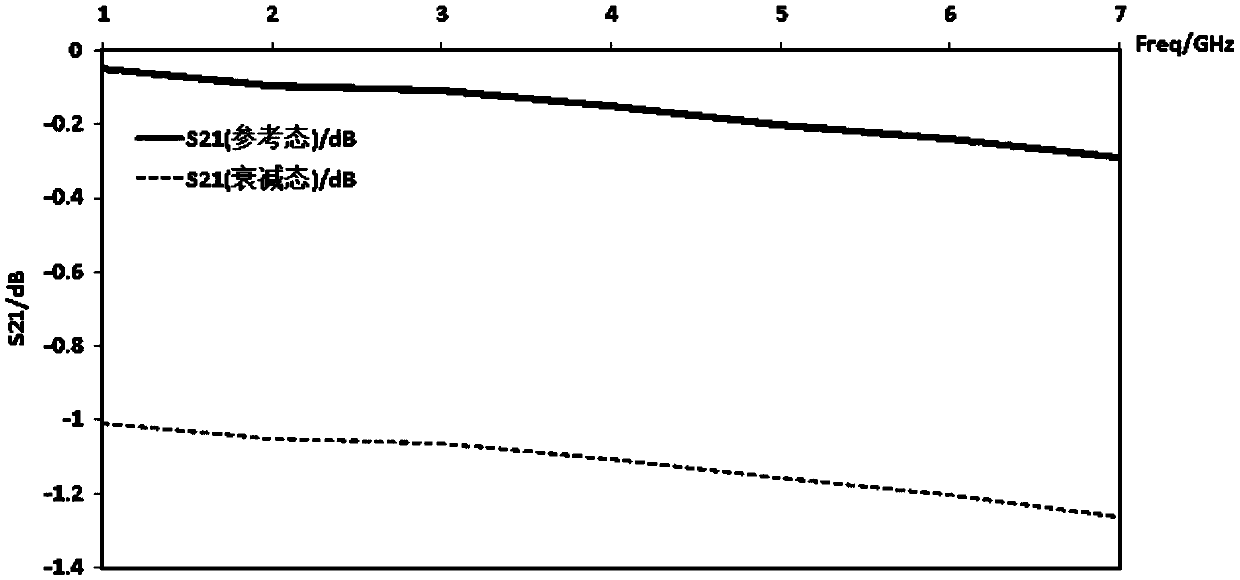
The invention discloses an attenuator based on capacitance compensation, the attenuator comprises a transistor switch, a parallel attenuation resistor, a parallel open-circuit line capacitor and a matching transmission line, and the attenuator utilizes the switch to switch an attenuation state and a direct connection state so as to realize the control of relative attenuation; the attenuator is simple in structure, small in occupied area and good in parasitic phase modulation and attenuation characteristic bandwidth, and has great advantages and application space in monolithic integrated circuit application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHENGCHANG TECH
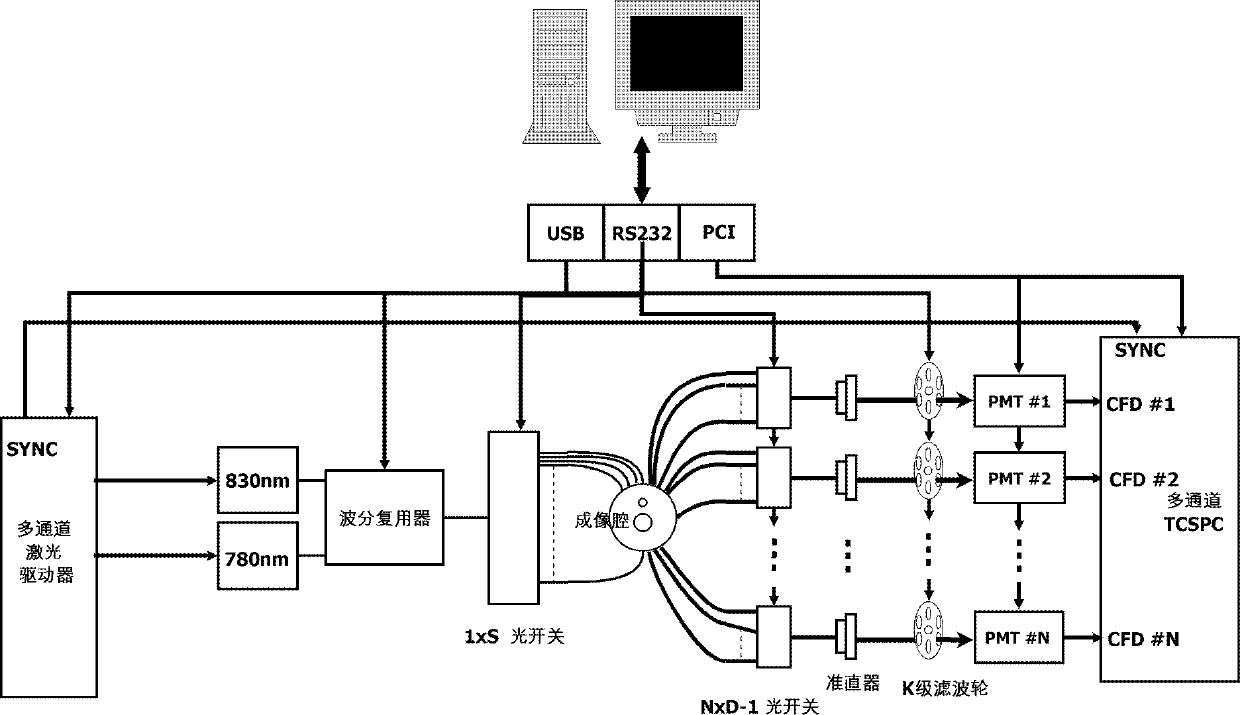
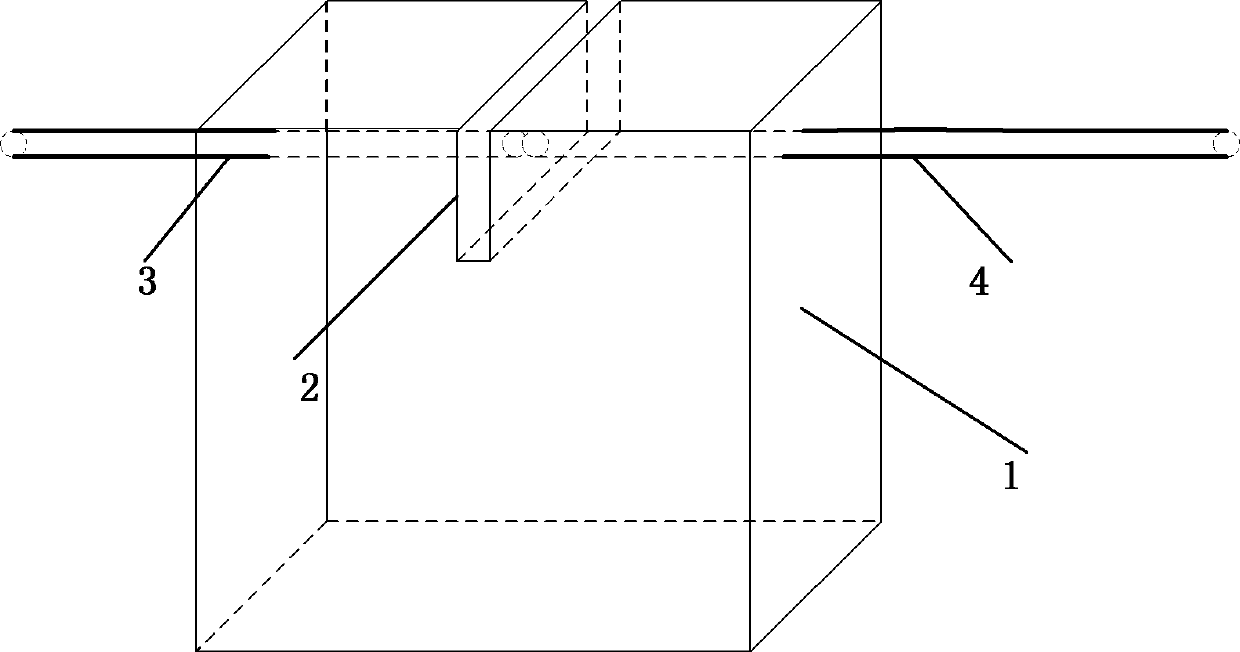
Calibration method for multi-passage time domain fluorescence chromatography imaging system
ActiveCN102525420ALarge dynamic rangeEliminate variance in transfer performanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRelative attenuationCamera lens
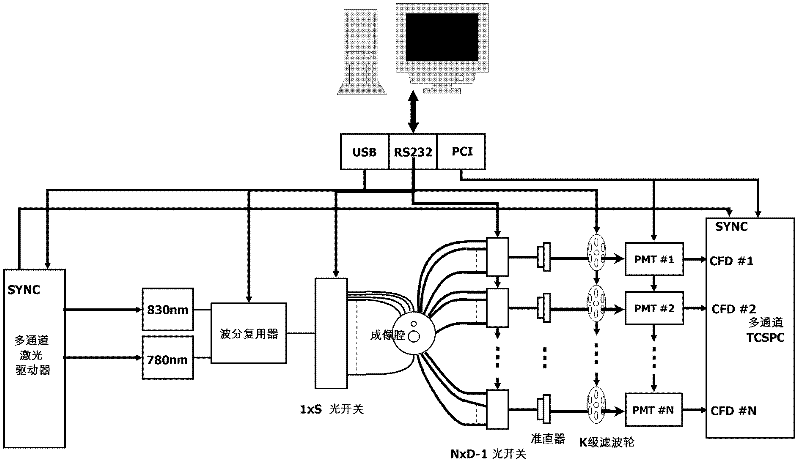
The invention belongs to the technical field of tissue optical measurement and relates to a calibration method for a time domain fluorescence chromatography imaging system. The method is used for calibrating transmission factors of each passage of a system and comprises the following steps that: a calibration device used for replacing an imaging cavity in an imaging system is built; a source optical fiber and a detection optical fiber are respectively inserted onto the imaging cavity; some pieces of lens paper are placed into an insertion groove, and the detection optical fiber is connected with the first passage; a 780nm laser is opened, and the attenuation rate of all neutral filters arranged on a filter wheel corresponding to the passage is calibrated; the 780nm laser is turned off, an830nm laser is turned on, and the transmission rate of 830nm long pass filters arranged on a filter wheel corresponding to the passage is calibrated; and the steps are repeated, and the calibration of the relative attenuation rate of all neutral filters arranged on the filter wheel on each passage and the transmission rate of the 830nm long pass filters is completed. The differences on the systempassage transmission performance can be eliminated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Device for improving error of digital controllable attenuation semiconductor chip
PendingCN114268292AImprove isolationReduce attenuation errorMultiple-port networksRelative attenuationSemiconductor chip
The invention discloses a device for improving errors of a digital controllable attenuation semiconductor chip, which comprises a bypass series switch group and a regulation and control device, and is characterized in that the bypass series switch group and a digital controllable attenuator are arranged in parallel at an electric node between a port P1 and a port P2; the bypass series switch group is connected with the regulation and control device and then is grounded. The regulation and control device is used for improving the isolation degree between the port P1 and the port P2 in the attenuation state. According to the device, the grounded bypass series switch group is connected in parallel on the attenuator, so that the isolation degree of the port P1 and the port P2 in the attenuation state can be effectively improved, the attenuation error is reduced, and the accuracy and the stability of relative attenuation in the straight-through state and the attenuation state are ensured.
Owner:南京元络芯科技有限公司
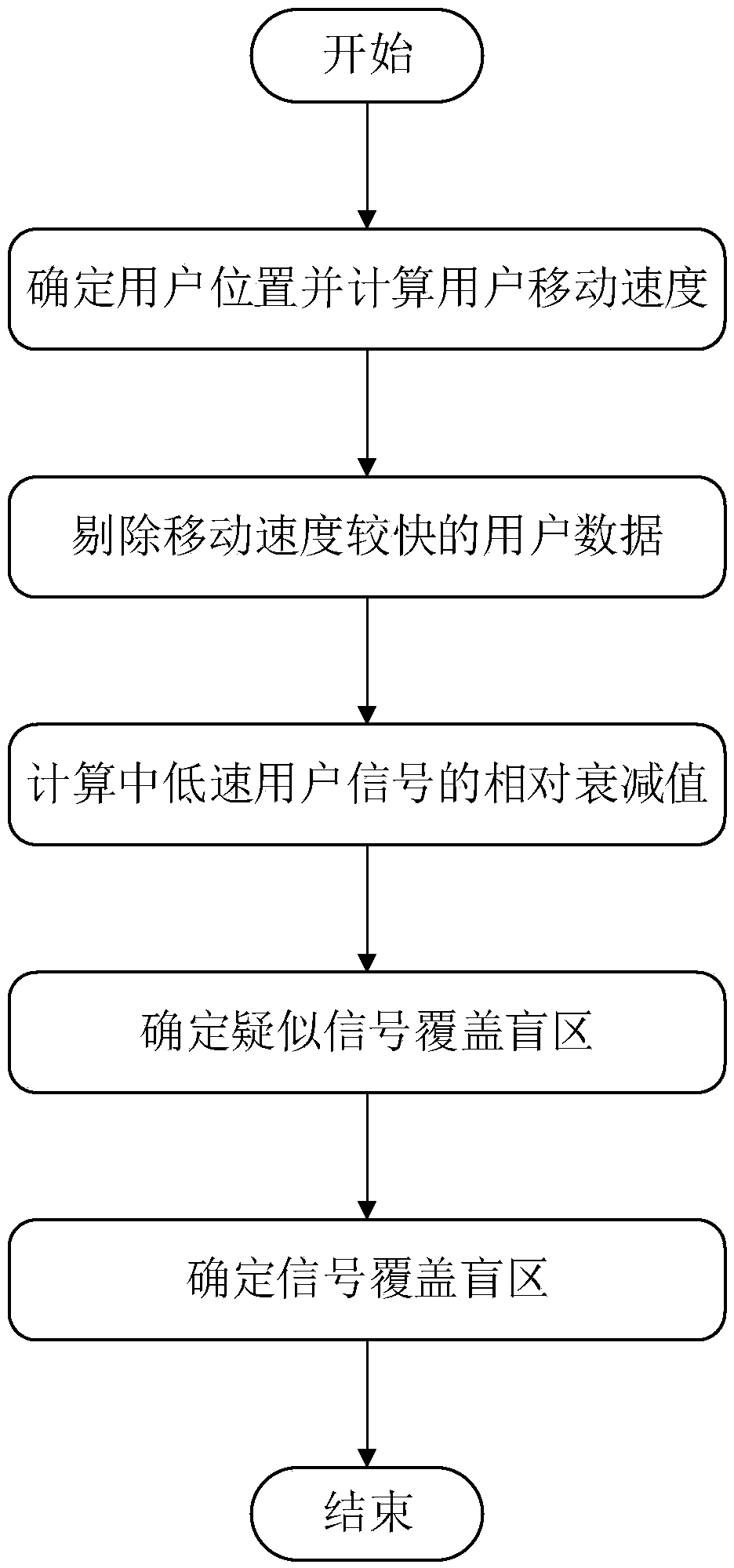
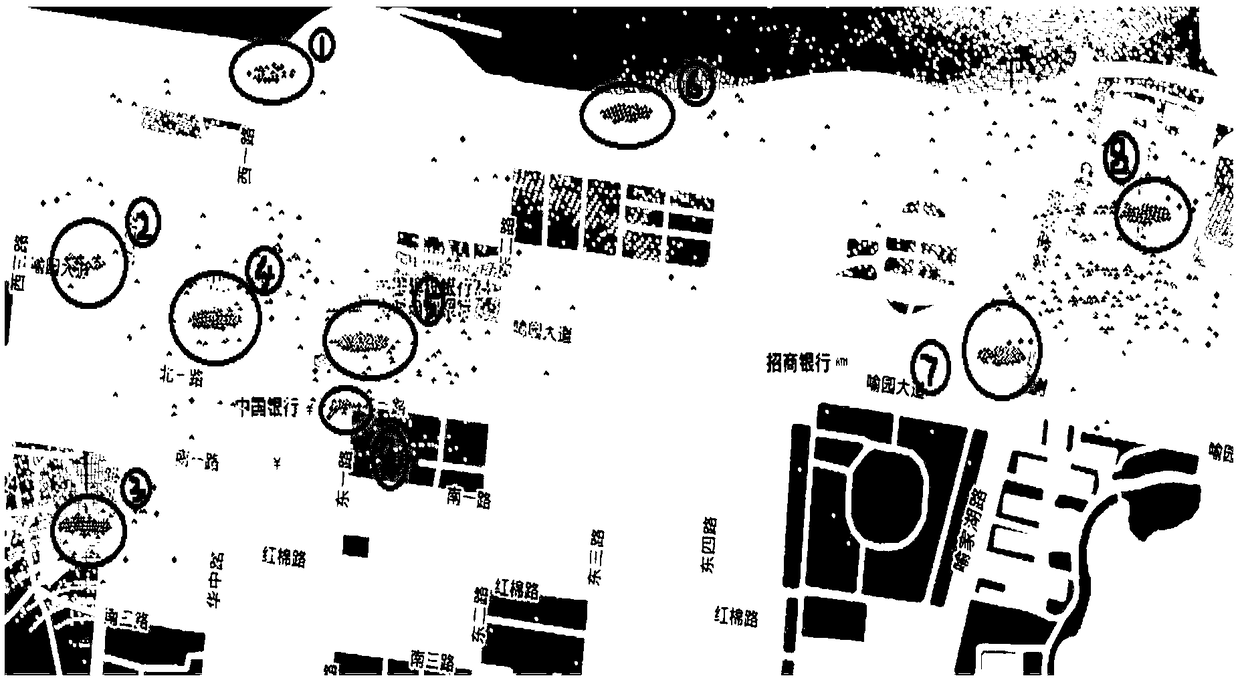
A wireless network coverage blind area detection method
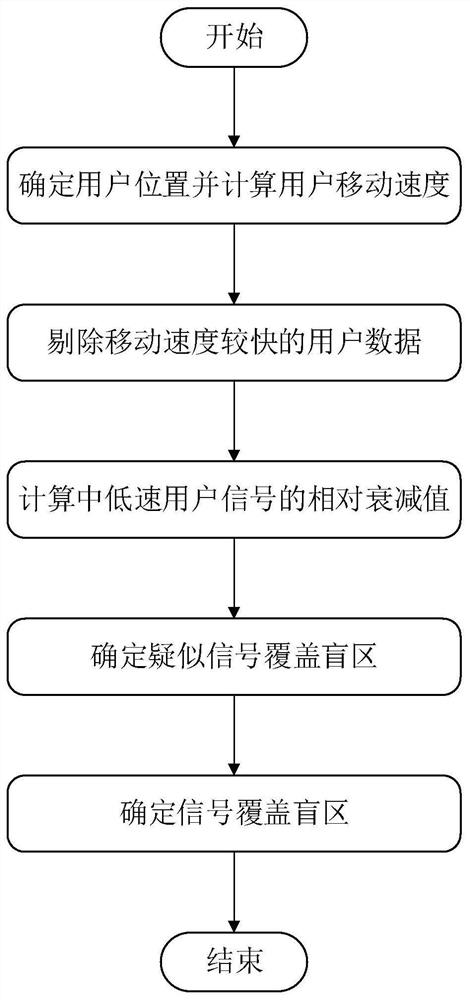
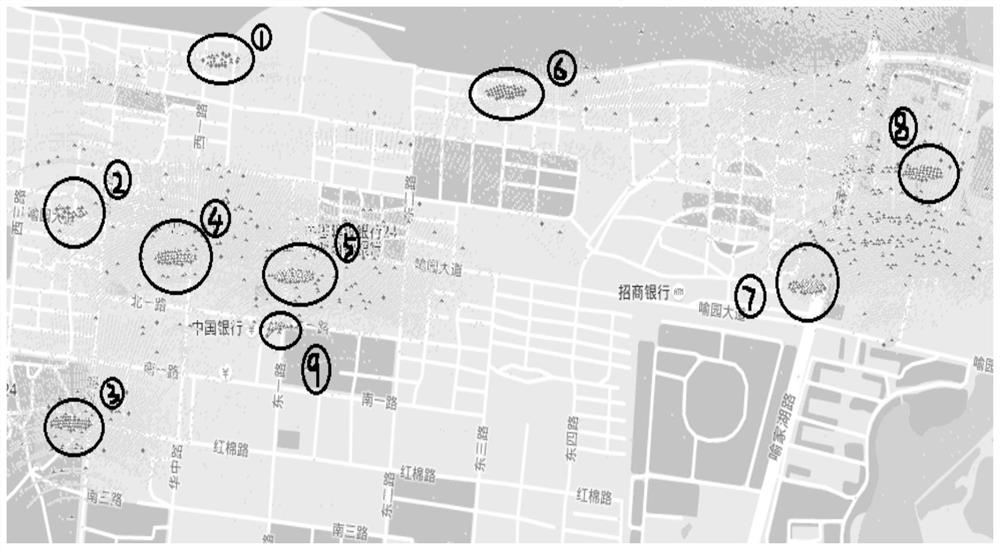
ActiveCN108990095ASave manpower and material resourcesStatistical movement speed is accurateWireless communicationRelative attenuationTelecommunications
The invention discloses a wireless network coverage blind area detection method, which comprises the following steps: determining a user position and a user moving speed according to signaling data fed back by a user terminal; removing user data of fast moving users; calculating a relative attenuation value of a medium-low speed user signal; determining the depth fading point according to the relative attenuation value of the user signal, and determining the suspected coverage blind area according to the distribution of the depth fading point. if the suspected coverage blind area is kept in the deep fading state, determining the suspected coverage blind area as the signal coverage blind area. Compared with the existing method, the method of the invention fully utilizes the existing data ofthe operator, can calculate and obtain more accurate user moving speed so as to effectively eliminate invalid user data, and utilizes the relative attenuation value of the user signal, thereby improving the detection precision of covering the blind area and saving manpower and material resources.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Fuel cell voltage attenuation quick determination method and device
InactiveCN101144850BLow costCurrent/voltage measurementFuel cell auxillariesRelative attenuationUltrasound attenuation
The present invention discloses a quick voltage attenuation measuring method and the device thereof for the fuel cell, and belongs to the clean energy technology field. The quick measuring device is used to respectively connect the test circuit of the fuel cell to be tested and the sub-circuit of a reference cell with the in-phase input terminal and the reversed phase input terminal of a differential amplifier, and to connect the output terminal of the differential amplifier with a microprocessor. The quick measuring method is used to first determine the voltage attenuation and the power attenuation as a physical quantity for representing the service life or the durability of the fuel cell, to transform the measuring object from the output voltage of a single-plate or a galvanic pile intothe attenuation or the relative attenuation of the output voltage of the single-plate or the galvanic pile at the front stage, and to measure the attenuation of the output voltage directly, and a normal precise amplifier and a simulated switch can be adopted at the back stage; the output of the differential amplifier can be send to the microprocessor for a further process after being transformed by the modulus, thus the voltage attenuation and the power attenuation of the fuel cell to be tested can be obtained for estimating the service life or the durability of the fuel cell.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A method for identifying resonance interference of microseismic monitoring signals and effectively suppressing it
ActiveCN103675917BImprove computing efficiencyReduce harmSeismic signal processingRelative attenuationTime domain
The invention provides a method for identifying and suppressing signal resonance interference during microseismic fracture monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: transferring microseismic fracture event signals into a frequency domain; respectively arranging three-component spectrum in terms of horizontal and vertical component; determining the resonance signal band frequency range; selecting a non-resonance interference spectrum channel on the vertical component spectrum arrangement; calculating the energy of a frequency sampling point and that of whole-channel signal master frequency, wherein the ratio of the two energies is a relative attenuation coefficient of the microseismic signal at the sampling point; calculating the master frequency energies of all resonance interference spectrum of each arrangement of the three-component spectrum, allowing the result to multiply the attenuation coefficient of the corresponding sampling point to obtain a spectrum compensation value for resonance interference band frequency compensation; transforming the frequency domain signals to a time domain through an inverted Fourier transform so as to complete suppressing of resonance signals. Due to the adoption of the method, the resonance interference in microseismic signals can be effectively identified and suppressed, so as to minimize the damage for effective signals. Therefore, the method is simple to use and high in calculation efficiency.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
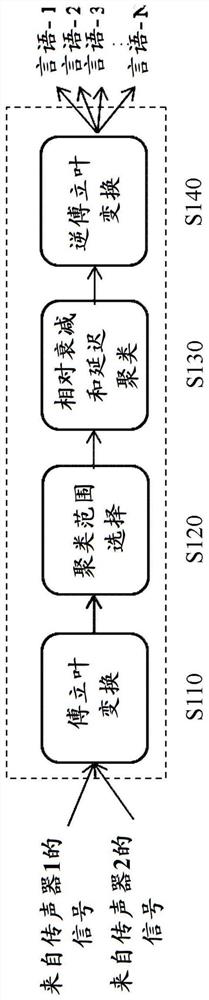
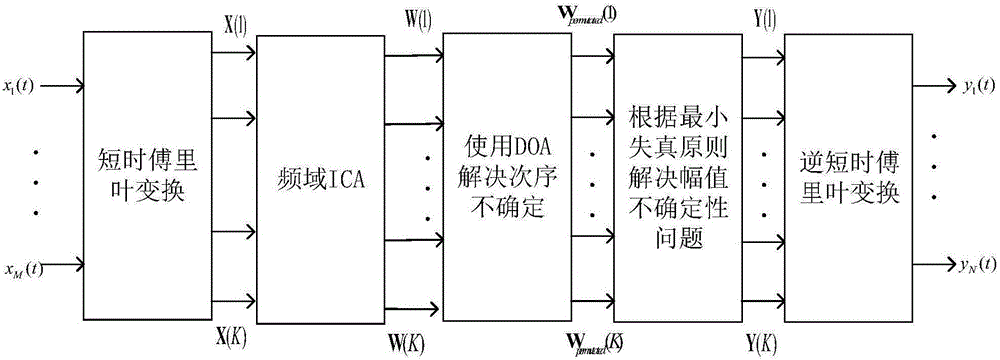
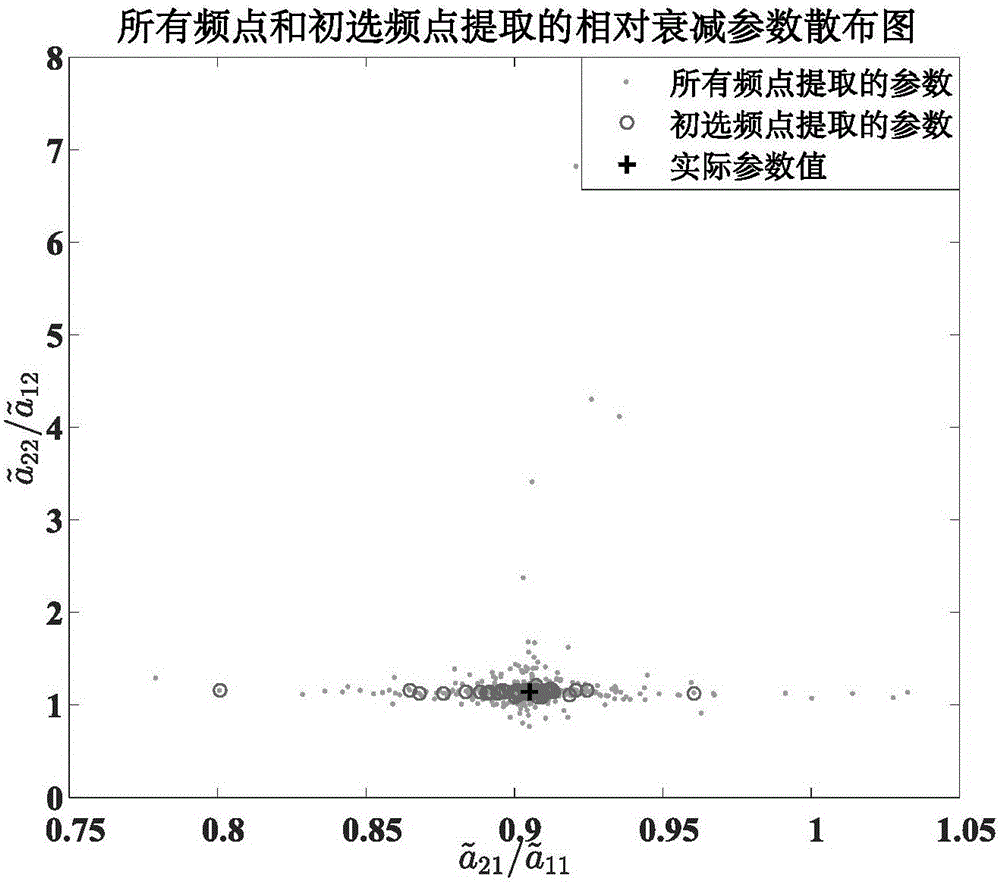
Method and system for voice separation based on degenerate unmixing estimation technique
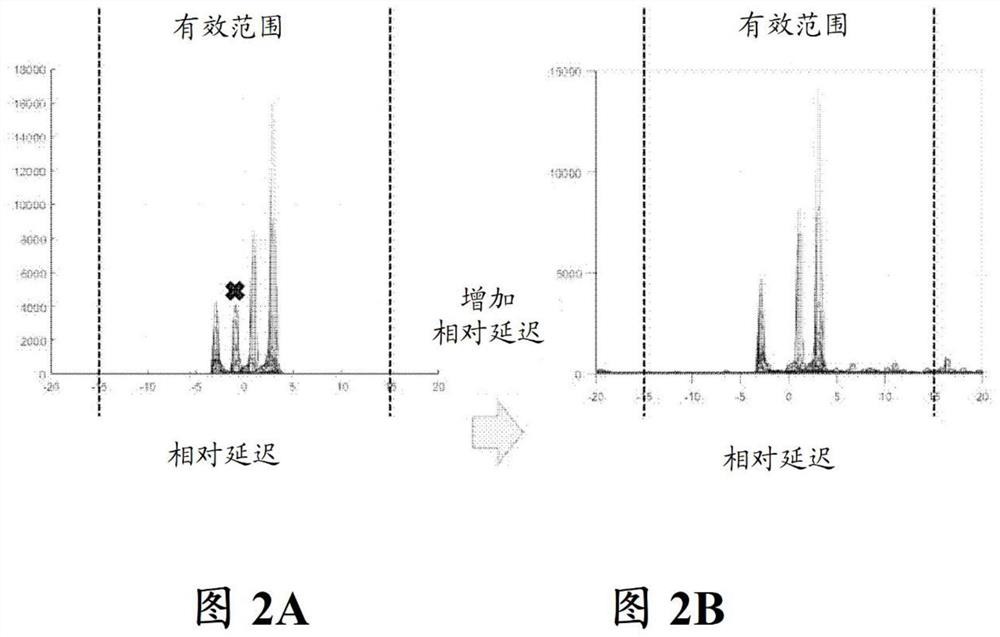
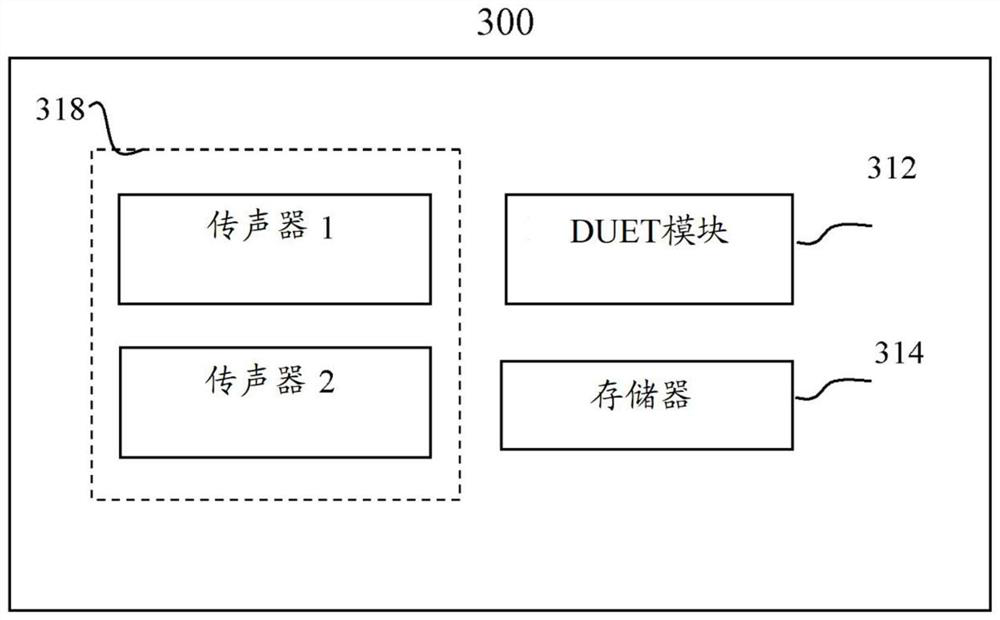
A method and system for voice separation based on DUET algorithm is disclosed. The method comprises: receiving signals from microphones; performing a Fourier transform on the received signals (S110); calculating a relative attenuation parameter and a relative delay parameter for each data point (S120); selecting a clustering range for the relative delay parameters based on a distance between the microphones and a sampling frequency of the microphones, clustering the data points within the clustering range for the relative delay parameters into subsets (S130), and performing an inverse Fourier transform on each subsets (S140). It provides an efficient and intelligent solution to deploy DUET on the software and / or hardware.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
A wireless network coverage blind spot detection method
ActiveCN108990095BSave manpower and material resourcesStatistical movement speed is accurateWireless communicationData feedRelative attenuation
The invention discloses a wireless network coverage blind area detection method, which comprises the following steps: determining a user position and a user moving speed according to signaling data fed back by a user terminal; removing user data of fast moving users; calculating a relative attenuation value of a medium-low speed user signal; determining the depth fading point according to the relative attenuation value of the user signal, and determining the suspected coverage blind area according to the distribution of the depth fading point. if the suspected coverage blind area is kept in the deep fading state, determining the suspected coverage blind area as the signal coverage blind area. Compared with the existing method, the method of the invention fully utilizes the existing data ofthe operator, can calculate and obtain more accurate user moving speed so as to effectively eliminate invalid user data, and utilizes the relative attenuation value of the user signal, thereby improving the detection precision of covering the blind area and saving manpower and material resources.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Calibration method for multi-passage time domain fluorescence chromatography imaging system
ActiveCN102525420BLarge dynamic rangeEliminate variance in transfer performanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRelative attenuationFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of tissue optical measurement and relates to a calibration method for a time domain fluorescence chromatography imaging system. The method is used for calibrating transmission factors of each passage of a system and comprises the following steps that: a calibration device used for replacing an imaging cavity in an imaging system is built; a source optical fiber and a detection optical fiber are respectively inserted onto the imaging cavity; some pieces of lens paper are placed into an insertion groove, and the detection optical fiber is connected with the first passage; a 780nm laser is opened, and the attenuation rate of all neutral filters arranged on a filter wheel corresponding to the passage is calibrated; the 780nm laser is turned off, an830nm laser is turned on, and the transmission rate of 830nm long pass filters arranged on a filter wheel corresponding to the passage is calibrated; and the steps are repeated, and the calibration of the relative attenuation rate of all neutral filters arranged on the filter wheel on each passage and the transmission rate of the 830nm long pass filters is completed. The differences on the systempassage transmission performance can be eliminated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Measuring method of fast and slow shear wave attenuation coefficient under core fracture width
ActiveCN106568846BFacilitate quantitative identificationContribute to researchAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasound attenuationRelative attenuation
The invention discloses a method for measuring attenuation coefficient of fast and slow shear waves under crack width of rock core. According to the method, by measuring amplitude of fast and slow shear waves before and after fracturing and introducing relative attenuation coefficient, corresponding relative attenuation coefficient of fast and slow shear waves before and after fracturing is calculated, and corresponding relative attenuation coefficient without cracks is subtracted from the relative attenuation coefficient after cracks so as to obtain the influence of cracks on attenuation of fast and slow shear waves. By the method, the influence of anisotropy of a rock sample on attenuation of fast and slow shear waves can be eliminated, and only by considering the influence of crack width on attenuation of fast and slow shear waves, quantitative evaluation of cracks can be realized.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
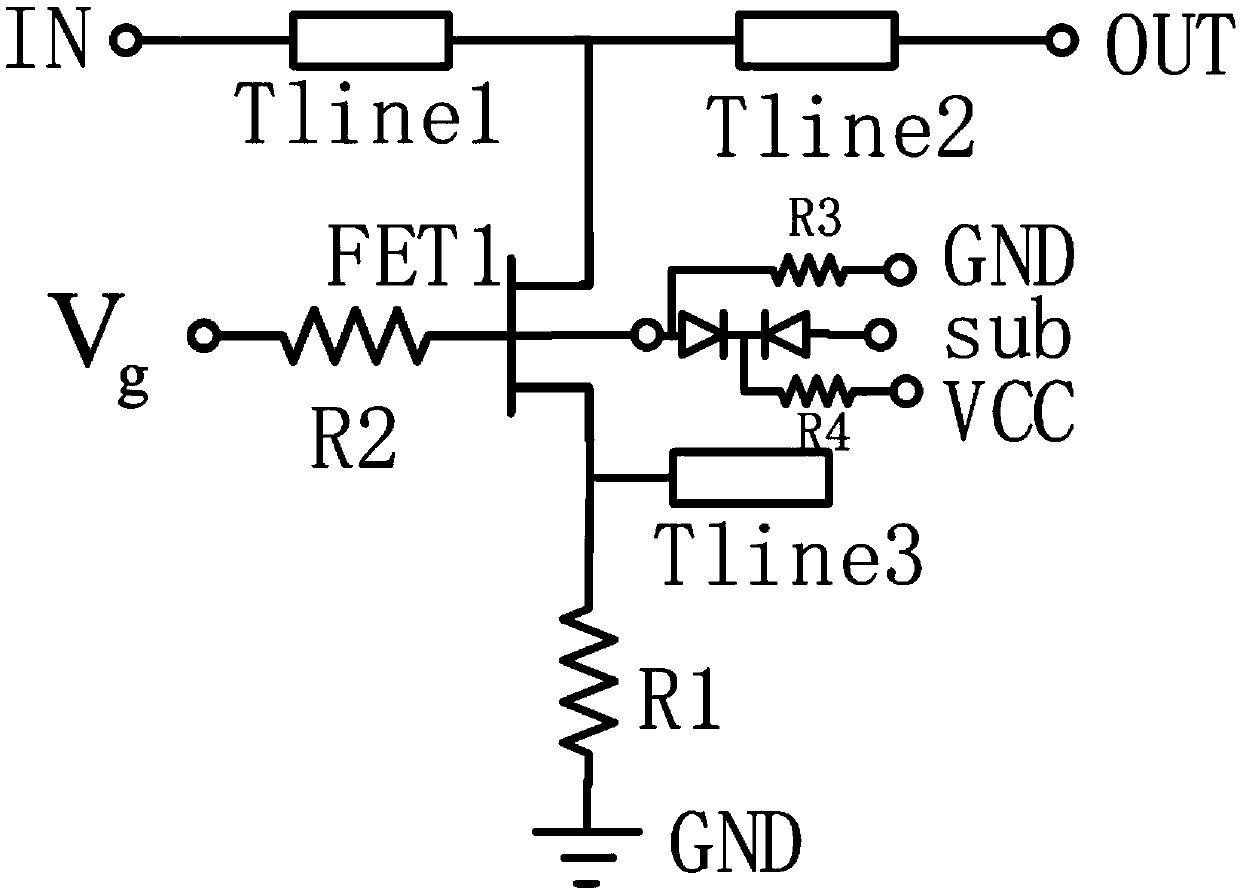
Catheter device
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
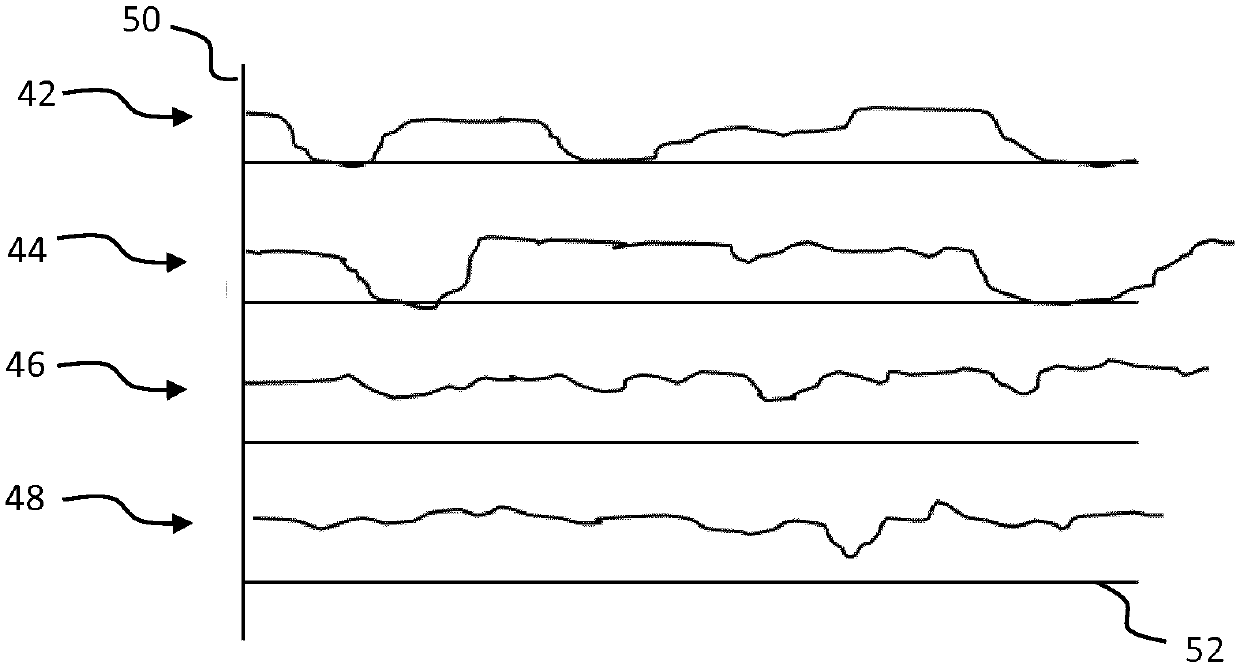
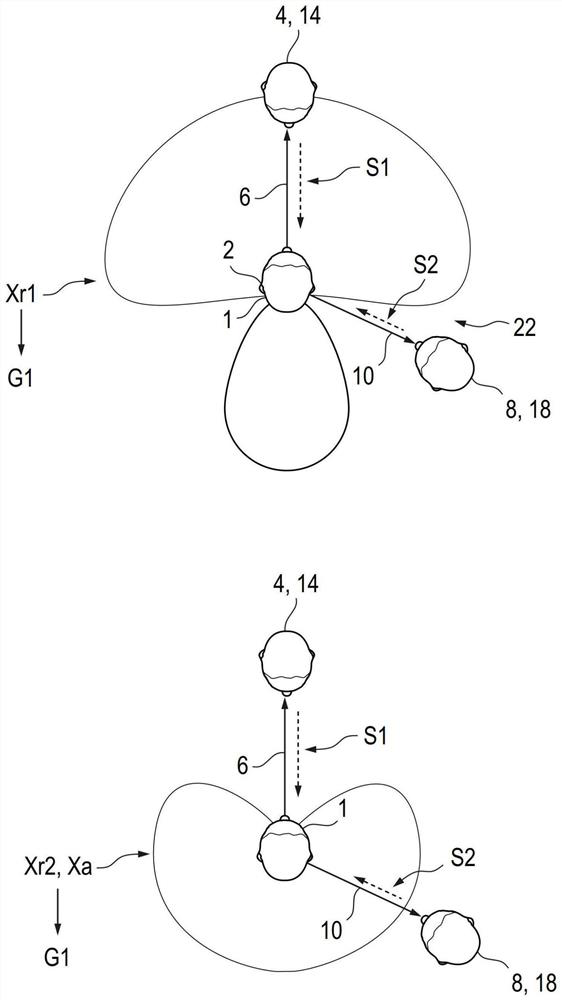
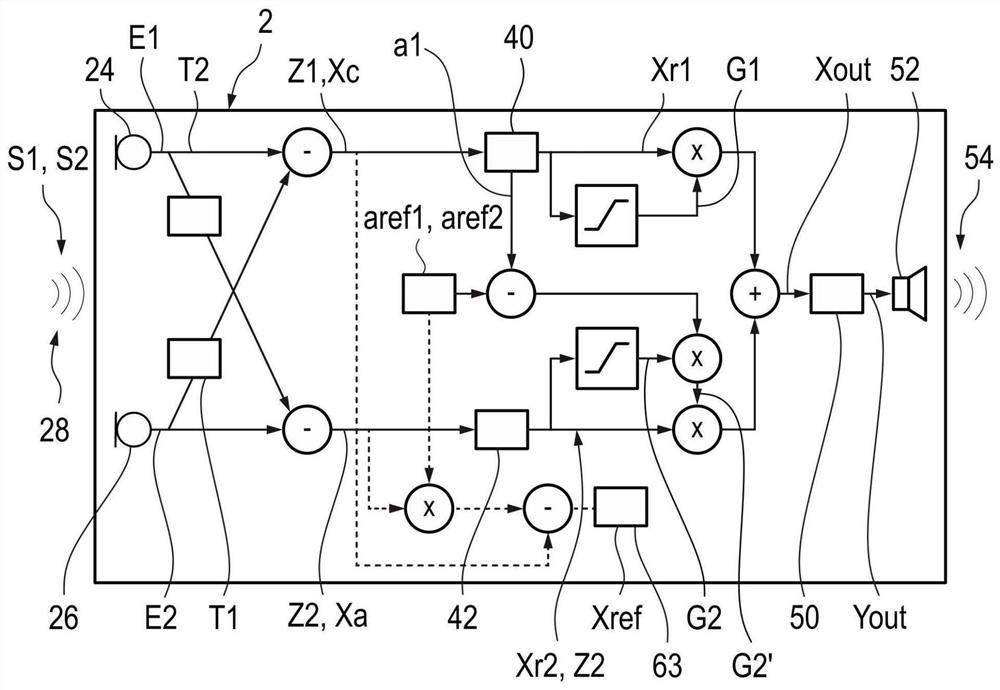
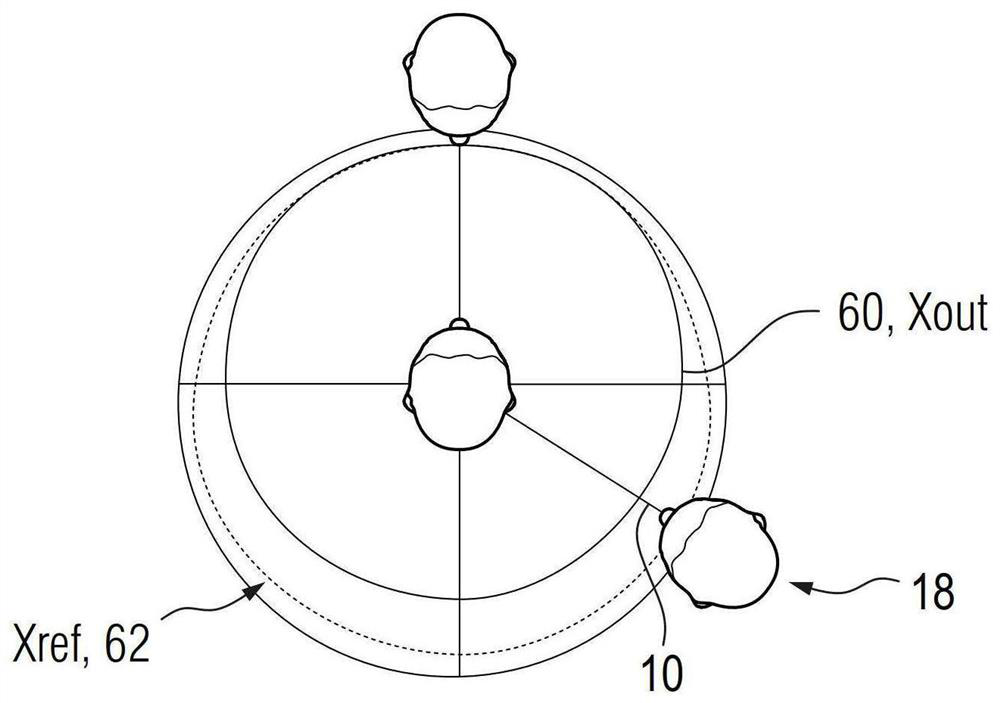
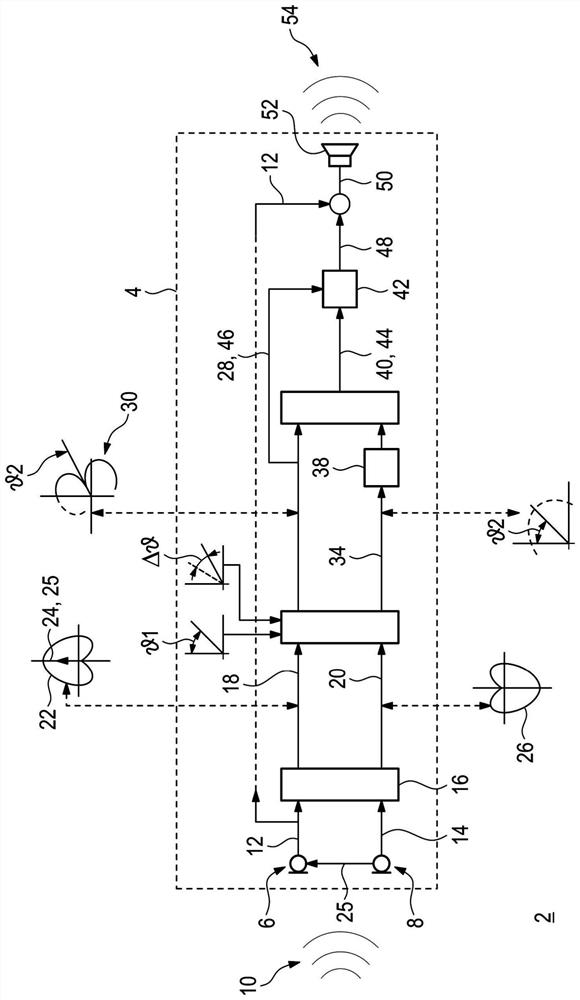
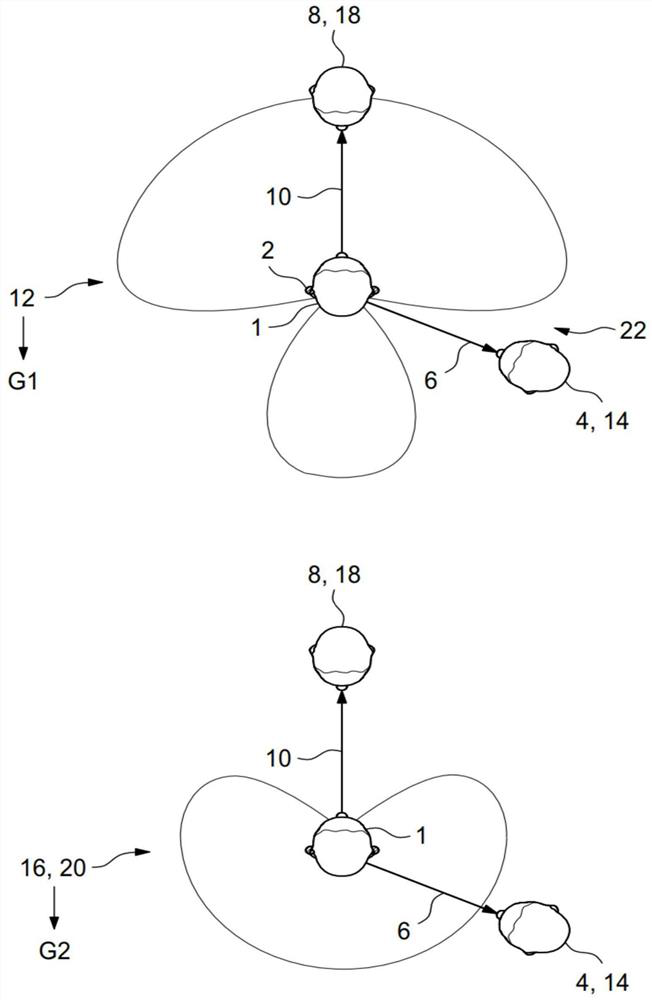
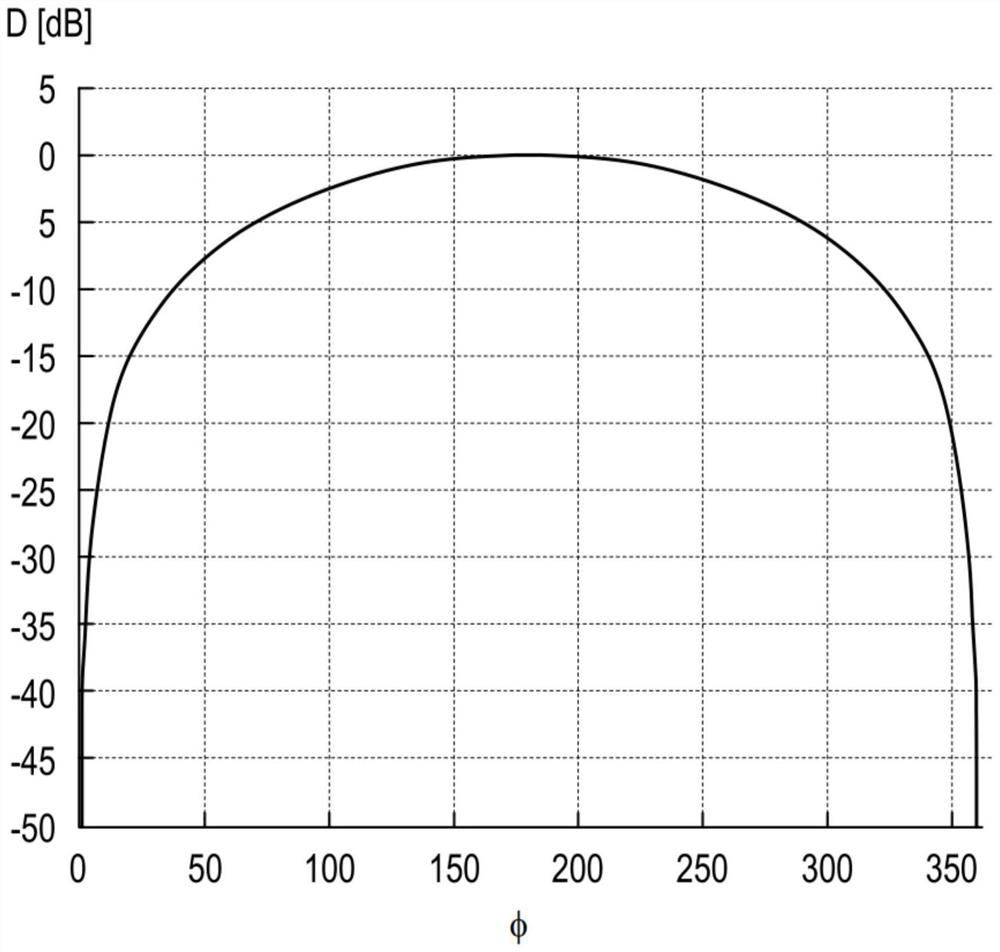
Method for directional signal processing for hearing aid
PendingCN114071314AHearing aids signal processingFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsRelative attenuationTransducer
The invention relates to a method for directional signal processing for a hearing aid, which includes generating first and second input signals from an ambient sound signal using first and second input transducers of the hearing aid; forming first and second directional signals based on the first and second input signals, the second directional signal having relative attenuation in directions of a first useful signal source, the first directional signal having relative attenuation in directions of a second useful signal source; ascertaining first and second amplification parameters; defining a reference directional characteristic; as a function of the reference directional characteristic, ascertaining corrected first and second amplification parameters so that an output directional signal, formed as a sum of the first directional signal weighted by using the first corrected first amplification parameter and the second directional signal weighted by using the corrected second amplification parameter, merges into a linearly scaled reference directional signal upon the first amplification parameter being equal to the second amplification parameter.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Device for monitoring hydrocephalus and encephaledema
ActiveCN102579008BImprove medical safetyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRelative attenuationBrain edema
The invention relates to a device used for monitoring hydrocephalus and encephaledema. The device comprises a signal encoding generator, an emission electrode, a receiving electrode, a signal processing digital converter, an orthogonal regulator, a detector, a parameter assessment device, a resistance analyzer and an assessment instrument. The invention also relates to a method used for monitoring hydrocephalus and encephaledema, which comprises the following steps of: intruding into the lower part of the skull skin; emitting electromagnetic waves; carrying out amplification and filter processing on the received electromagnetic waves, and converting the electromagnetic waves into digital signals; carrying out orthogonalization processing on the digital signals; detecting synthetic signals and orthogonal signals of the electromagnetic waves; calculating the relative attenuation coefficients, the relative phase displacement, the transmission time difference and the complex wave value K; calculating the complex impedance Z and capacitance; and assessing hydrocephalus and encephaledema. According to the invention, hydrocephalus and encephaledema situations can be monitored and assessed all day in a non-intrusive mode so as to reduce the treatment risks.
Owner:CHONG QING BORN FUKE MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Temperature Compensated Digital Step Attenuator
ActiveUS20180262181A1Multiple-port networksWaveguide type devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceRelative attenuation
Circuits and methods for eliminating or mitigating the amount of temperature-dependent variation in the relative attenuation of a multi-valued digital step attenuator (DSA) by using resistive components having temperature-dependent resistance values that compensate for or offset changes in the temperature-dependent ON resistance (RON) of the switches within the DSA. In some embodiments, DSA attenuator cell switches are fabricated to have positive first-order resistance temperature (FORT) coefficients, while temperature-compensating series attenuation resistances are fabricated as a positive FORT coefficient resistor and temperature-compensating shunt resistances are fabricated as either a negative FORT coefficient resistor or a combination of a negative FORT coefficient resistor in parallel with a positive FORT coefficient resistor.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
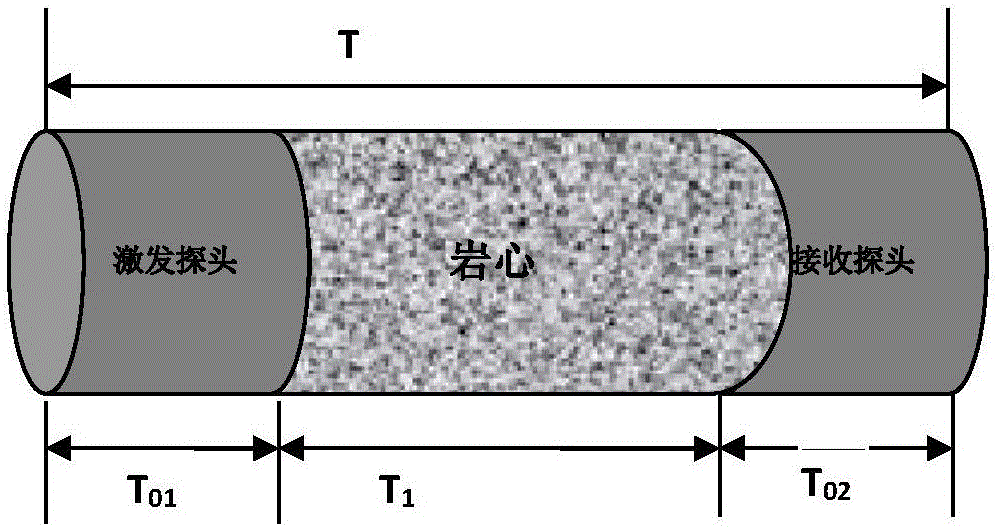
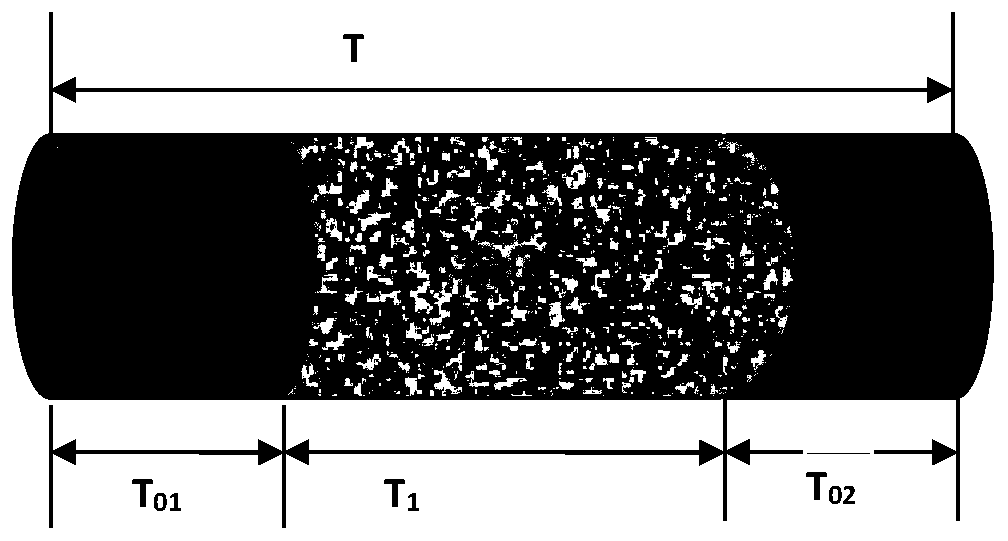
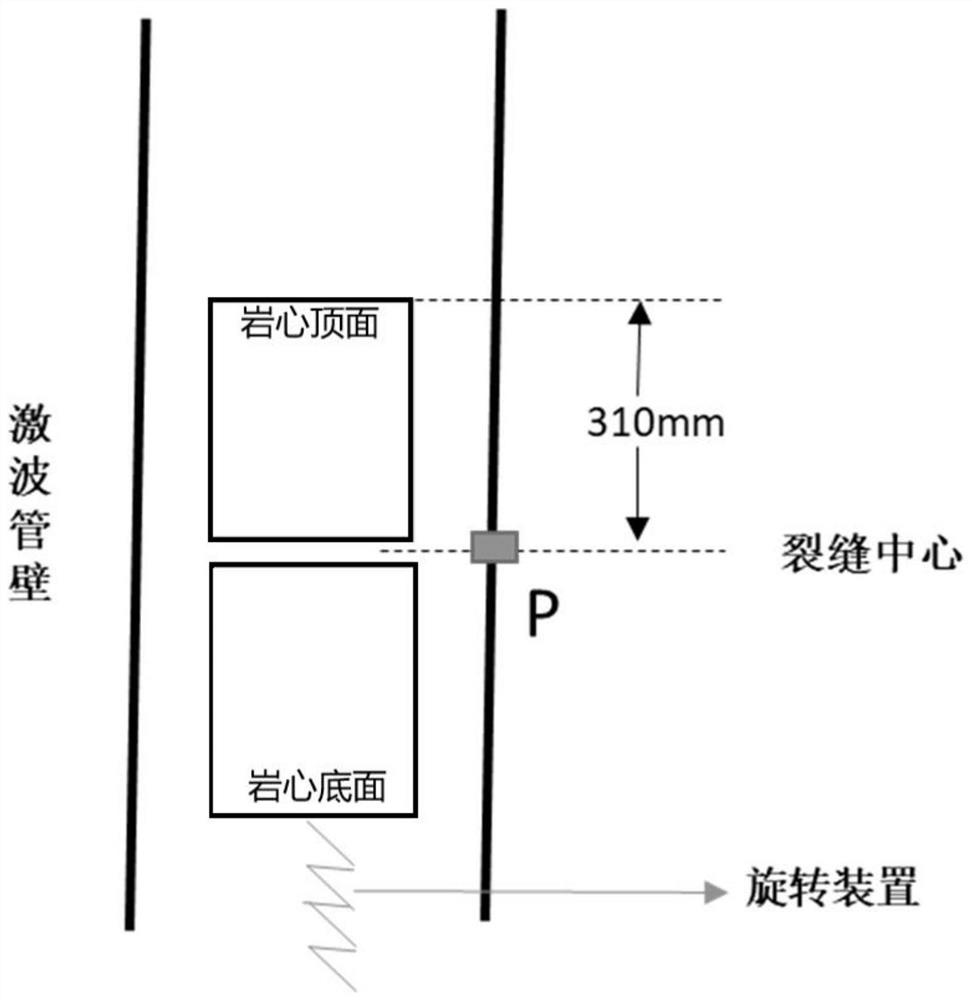
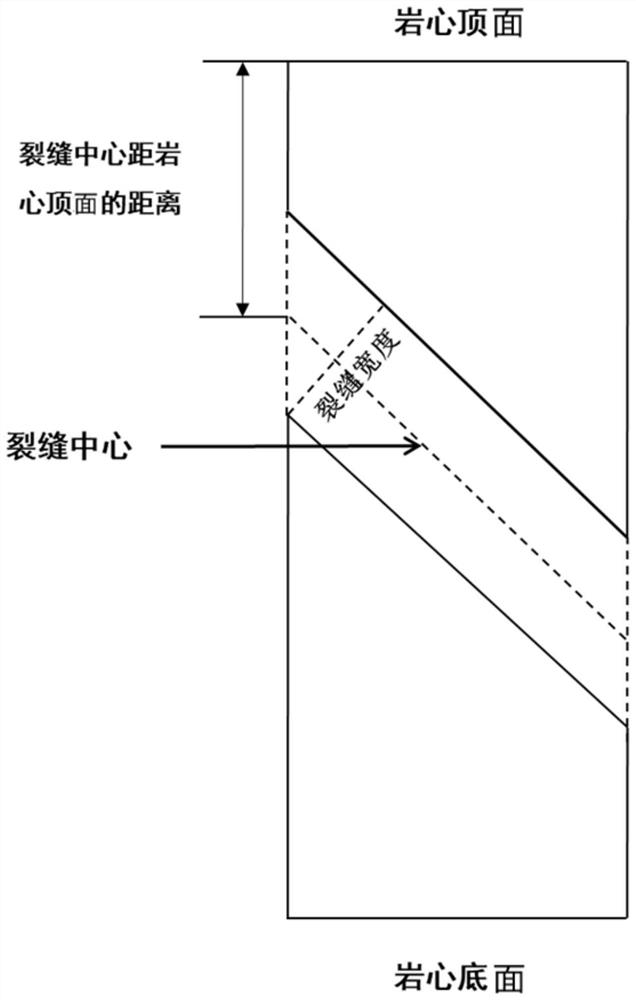
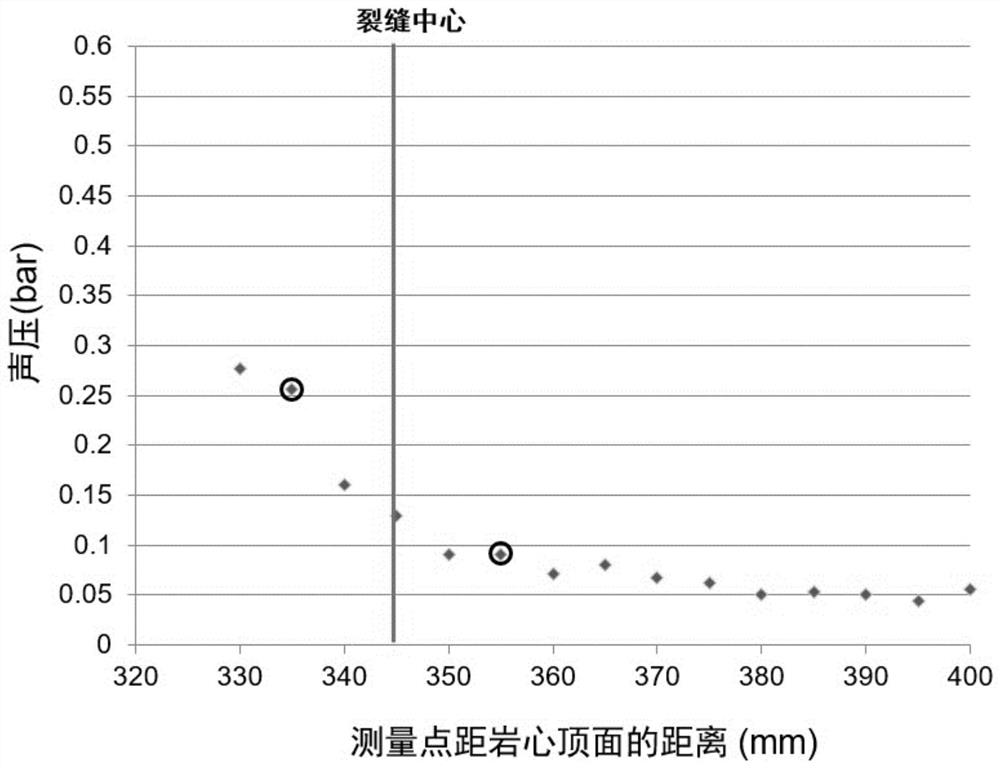
Crack-containing core model shock tube stoneley wave experiment method
PendingCN113533528ASymmetricalThe experimental method is simpleAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalRelative attenuationRock core
The invention discloses a crack-containing rock core model shock tube stoneley wave experiment method. The experiment method comprises the following steps: S100, preparing a crack-containing rock core model, and determining a crack inclination angle; S200, performing stoneley wave measurement on the crack-containing rock core model by using a shock tube, and changing the relative position of the crack and a sound pressure measurement point to obtain sound pressure values at different measurement point positions so as to establish a sound pressure change diagram of sound pressure along with the change of the measurement point positions; S300, determining the position of a crack center in the sound pressure change diagram; S400, determining the position of an attenuation starting point before the stoneley wave passes through the crack and the position of an attenuation ending point after the stoneley wave passes through the crack in the sound pressure change diagram; and S500, according to the sound pressure corresponding to the attenuation starting point position and the attenuation ending point position, calculating the relative attenuation amplitude before and after the stoneley wave passes through the crack.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for directional signal processing for hearing devices
ActiveCN111836162BSignal processingHearing aids signal processingRelative attenuationHearing apparatus
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Fast speech blind source separation method based on frequency point selection under binaural distance
ActiveCN106057210BReduce computational complexityShorten operation timeSpeech analysisRelative attenuationSeparation algorithm
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for running hearing aids
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Method for directional signal processing for hearing aid
A method performs directional signal processing for a hearing aid. First and second input transducers of the hearing aid generate first and second input signals, respectively, from a sound signal. A first calibration directional signal which has a relative attenuation in the direction of a first useful signal source is generated from the first and second input signals, and a second calibration directional signal which has a relative attenuation in the direction of a second useful signal source is generated from the first and second input signals. A relative gain parameter is determined from the first and second calibration directional signals. First and second processing directional signals are generated from both the first and second input signals. A source-sensitive directional signal isgenerated from the first and second processing directional signals and the relative gain parameter. An output signal of the hearing aid is generated from the source-sensitive directional signal.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com