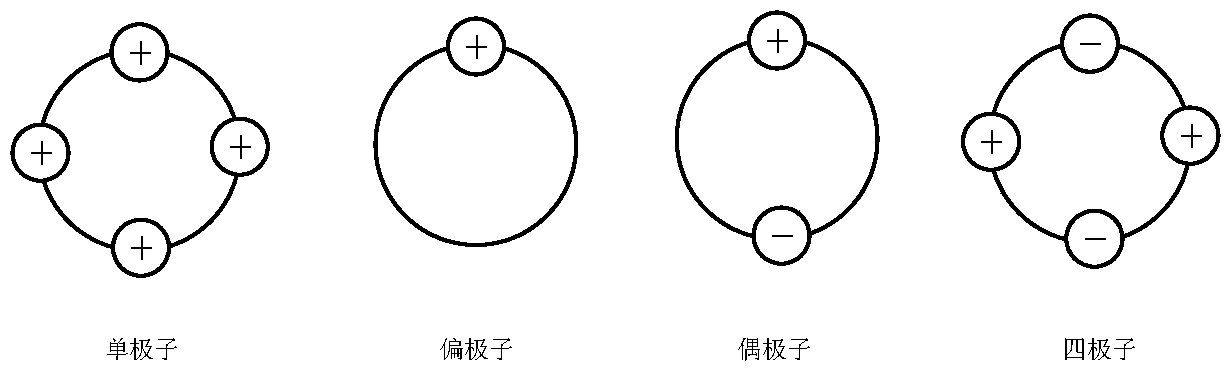
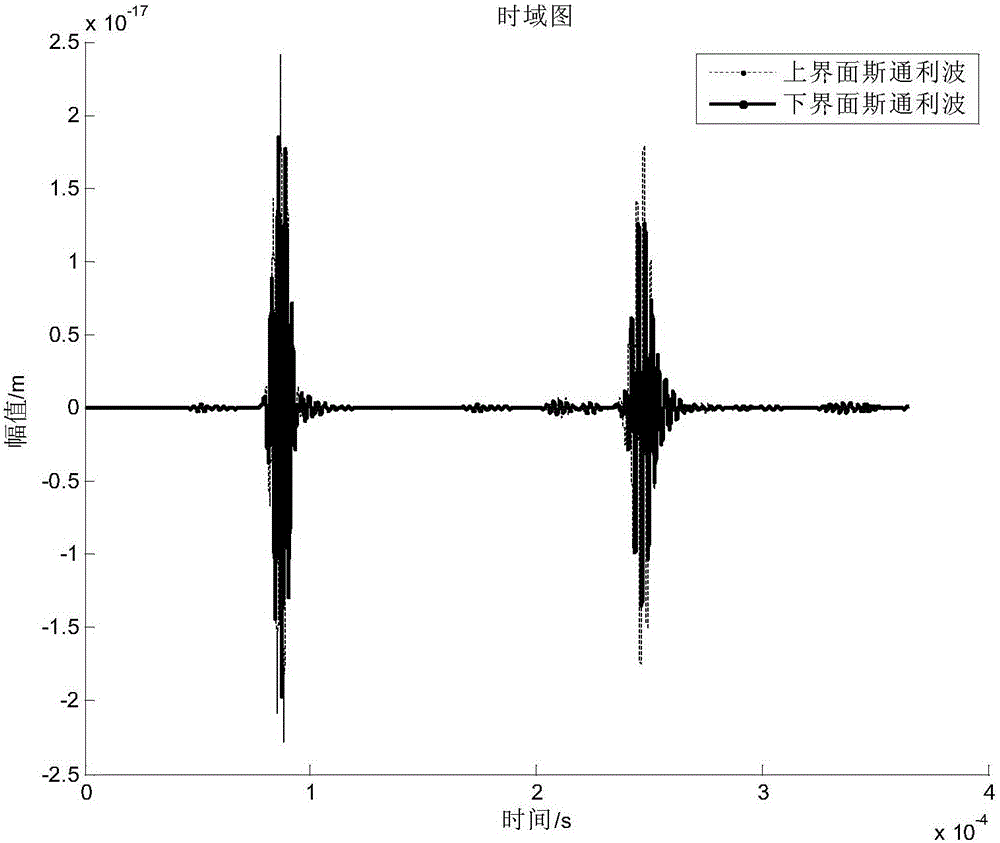
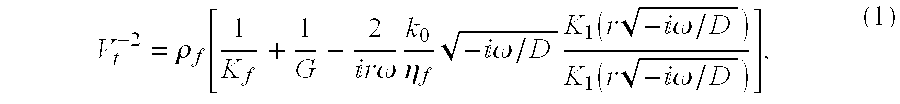Patents
Literature
61 results about "Stoneley wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
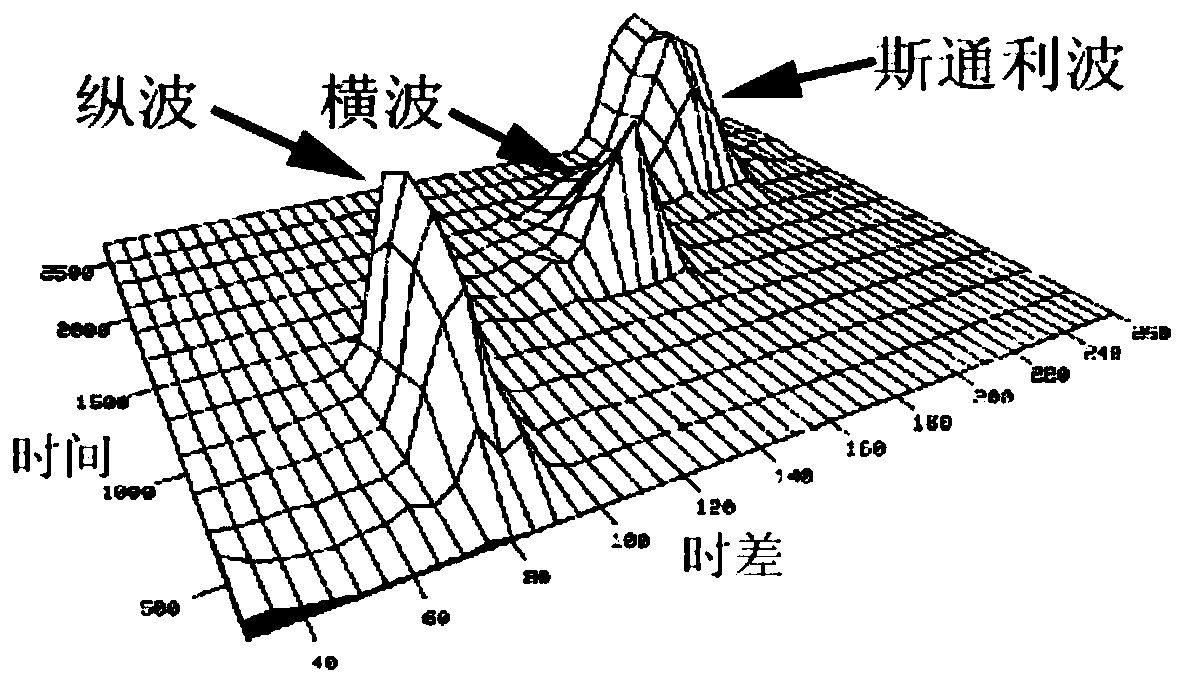
A Stoneley wave is a boundary wave (or interface wave) that typically propagates along a solid-solid interface. When found at a liquid-solid interface, this wave is also referred to as a Scholte wave. The wave is of maximum intensity at the interface and decreases exponentially away from it. It is named after the British seismologist Dr. Robert Stoneley (1894–1976), Emeritus Professor of Seismology at the University of Cambridge, who discovered it on October 1, 1924.
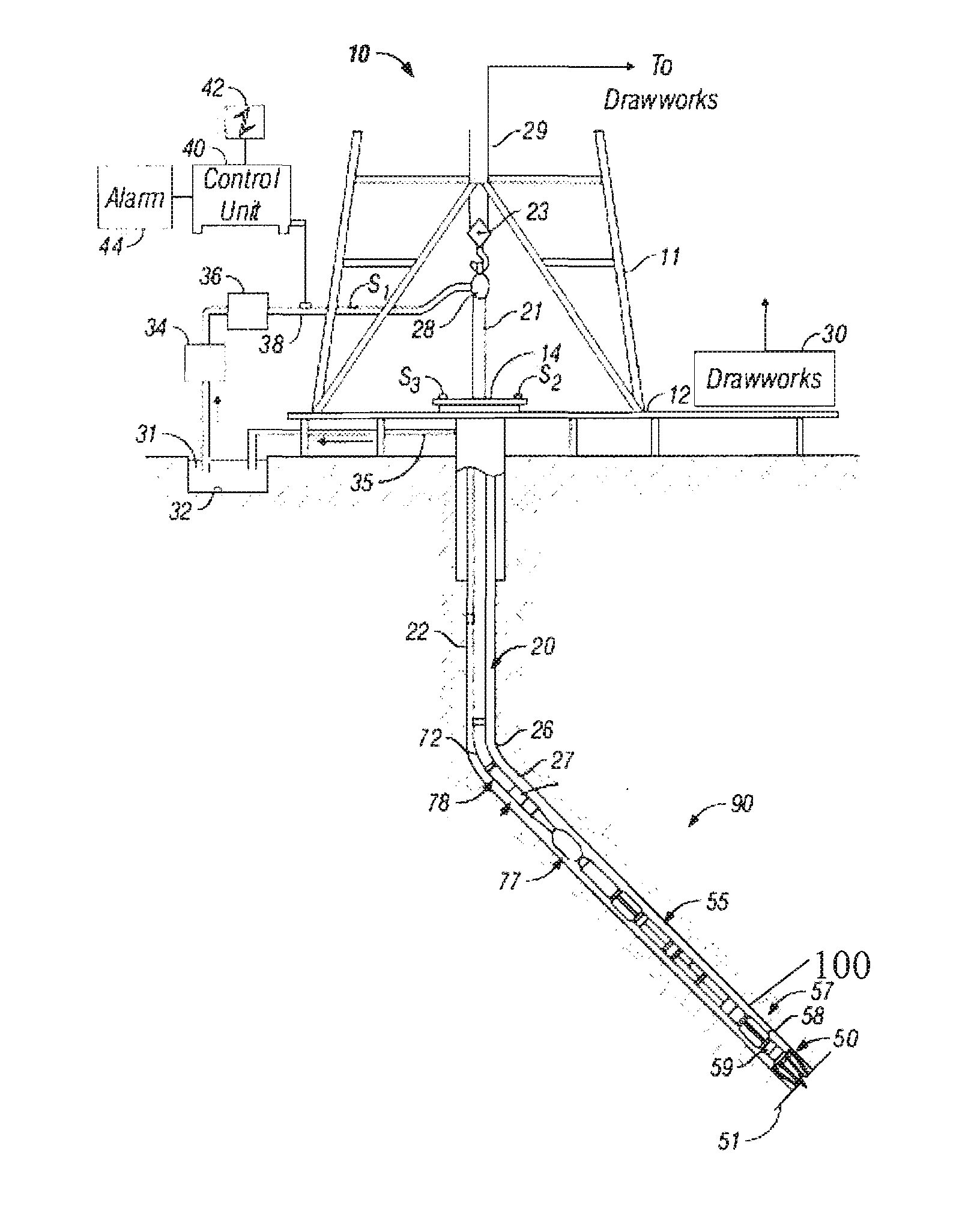
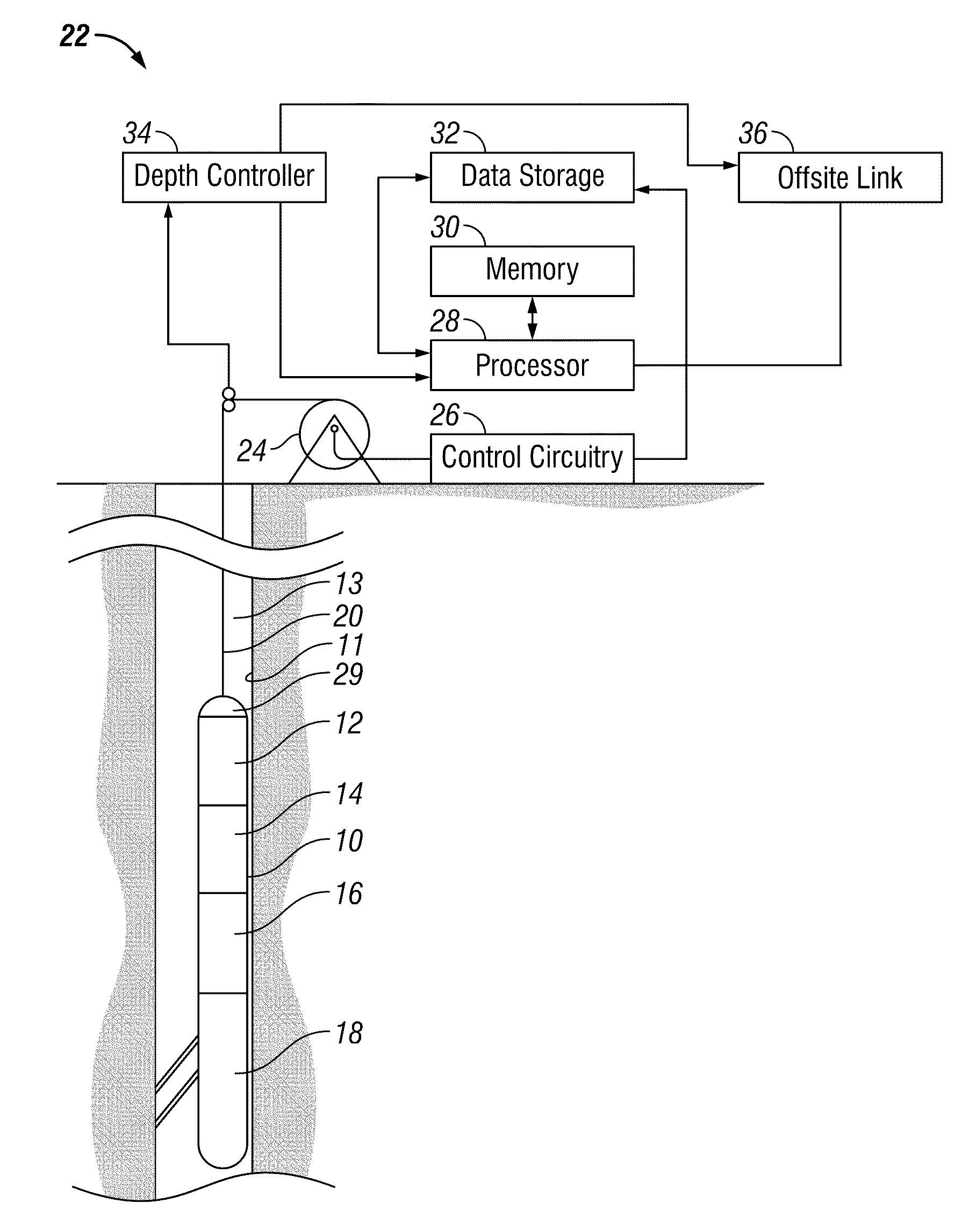
Method and Apparatus for Characterizing and Estimating Permeability Using LWD Stoneley-Wave Data
ActiveUS20090005995A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyUltrasound attenuationAmbiguity
Stoneley-wave data acquired in the LWD environment are used to characterize / estimate formation permeability. Real-time Stoneley-wave time-delay / slowness and center-frequency / attenuation data are used to indicate / characterize formation permeability even during drilling. The use of stabilizers mounted at the tool ends helps maintain the tool position from severe decentralization, reducing ambiguities in the permeability characterization / estimation. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:ENGIUS +1
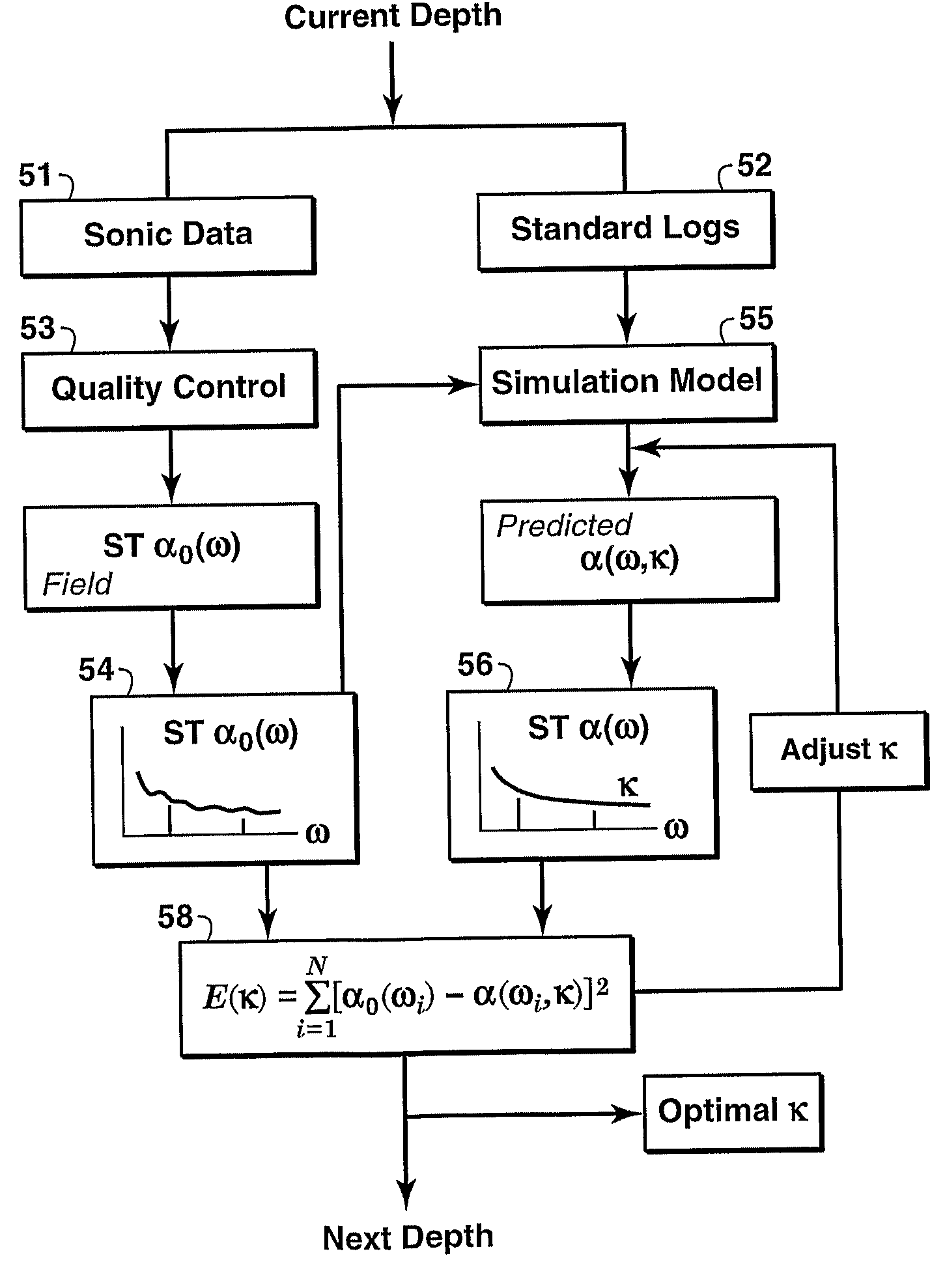
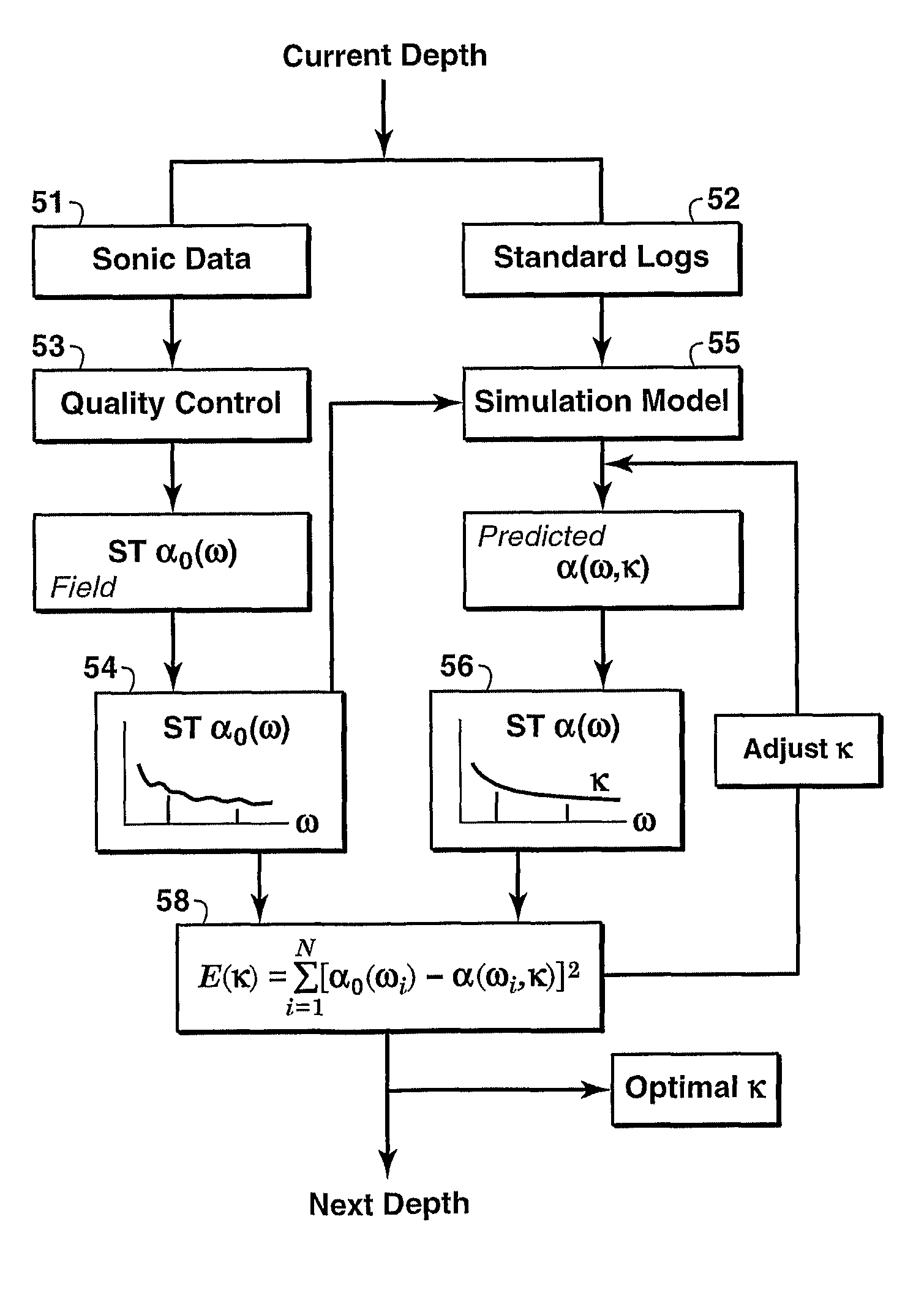
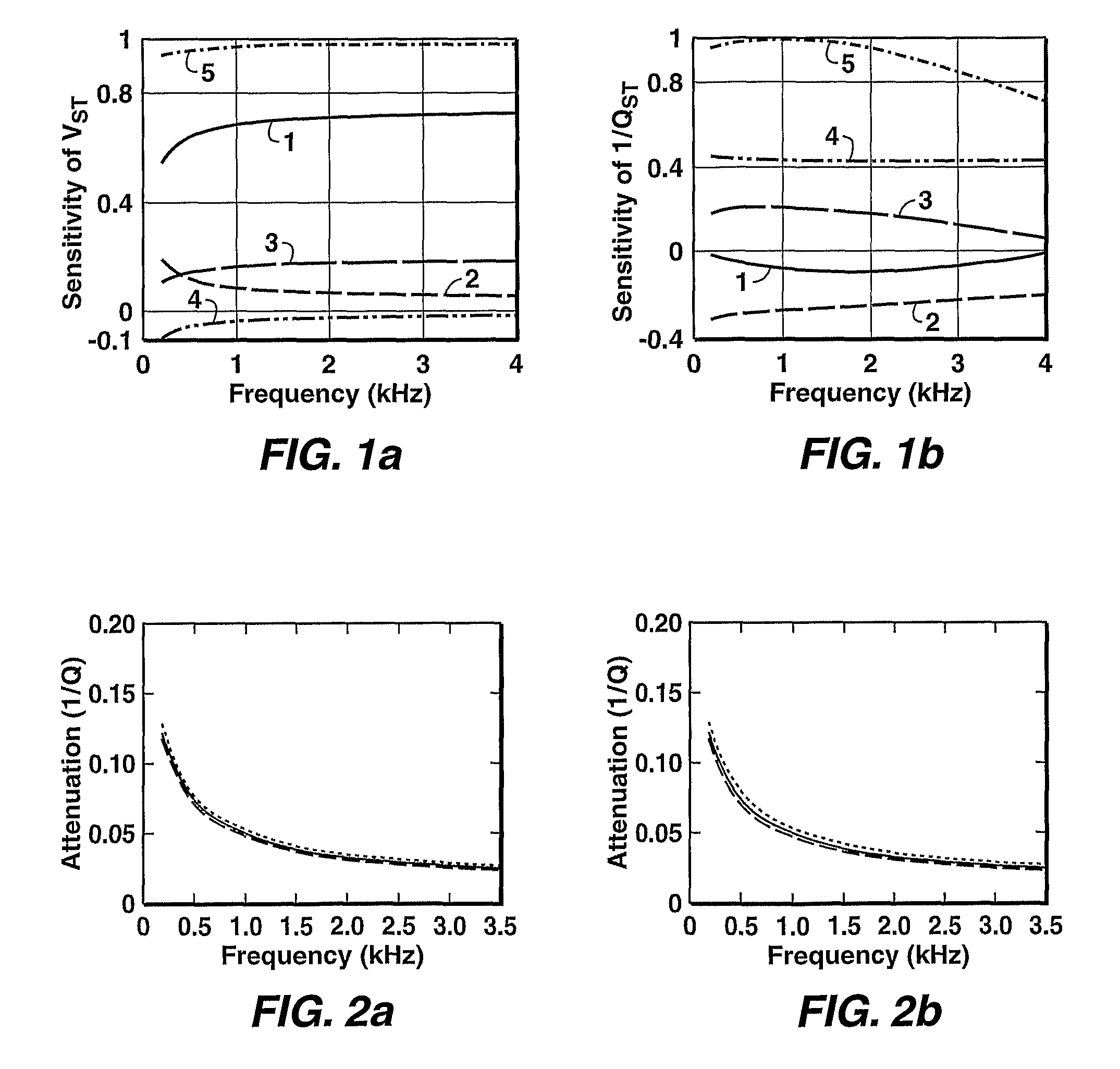
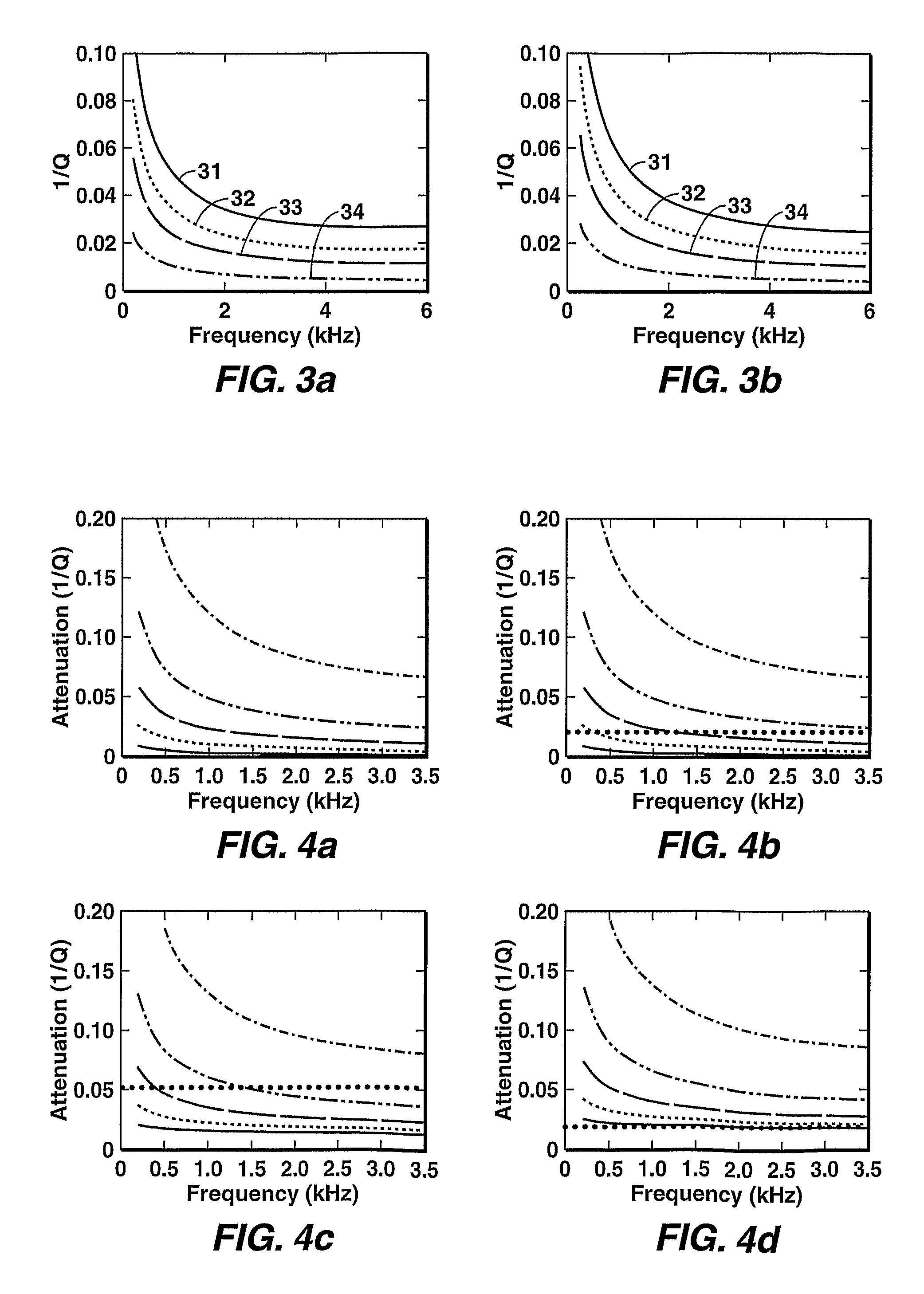
Method for determining reservoir permeability form borehole stoneley-wave attenuation using biot's poroelastic theory
ActiveUS20090145600A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyUltrasound attenuationPorous medium
Method for determining reservoir permeability from Stoneley wave attenuation extracted from conventional sonic logs by inversion of the full Biot wave equations for a porous medium. Frequency-dependent Stoneley-wave attenuation is extracted by analyzing array sonic measurements. Then, based on Biot's full theory applied to a borehole model and the standard logs (gamma ray, caliper, density, neutron, resistivity, sonic, etc.), a simulation model with the same parameters as the Stoneley-wave measurements is built. Next, a theoretical Stoneley-wave attenuation is computed for a given permeability. Finally, reservoir permeability is determined by comparing the modeled Stoneley-wave attenuation with the measured Stoneley-wave attenuation by an iterative inversion process.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Electro-magnetic acoustic measurements combined with acoustic wave analysis
ActiveUS20080125974A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentElectromagnetic pulseAcoustic wave
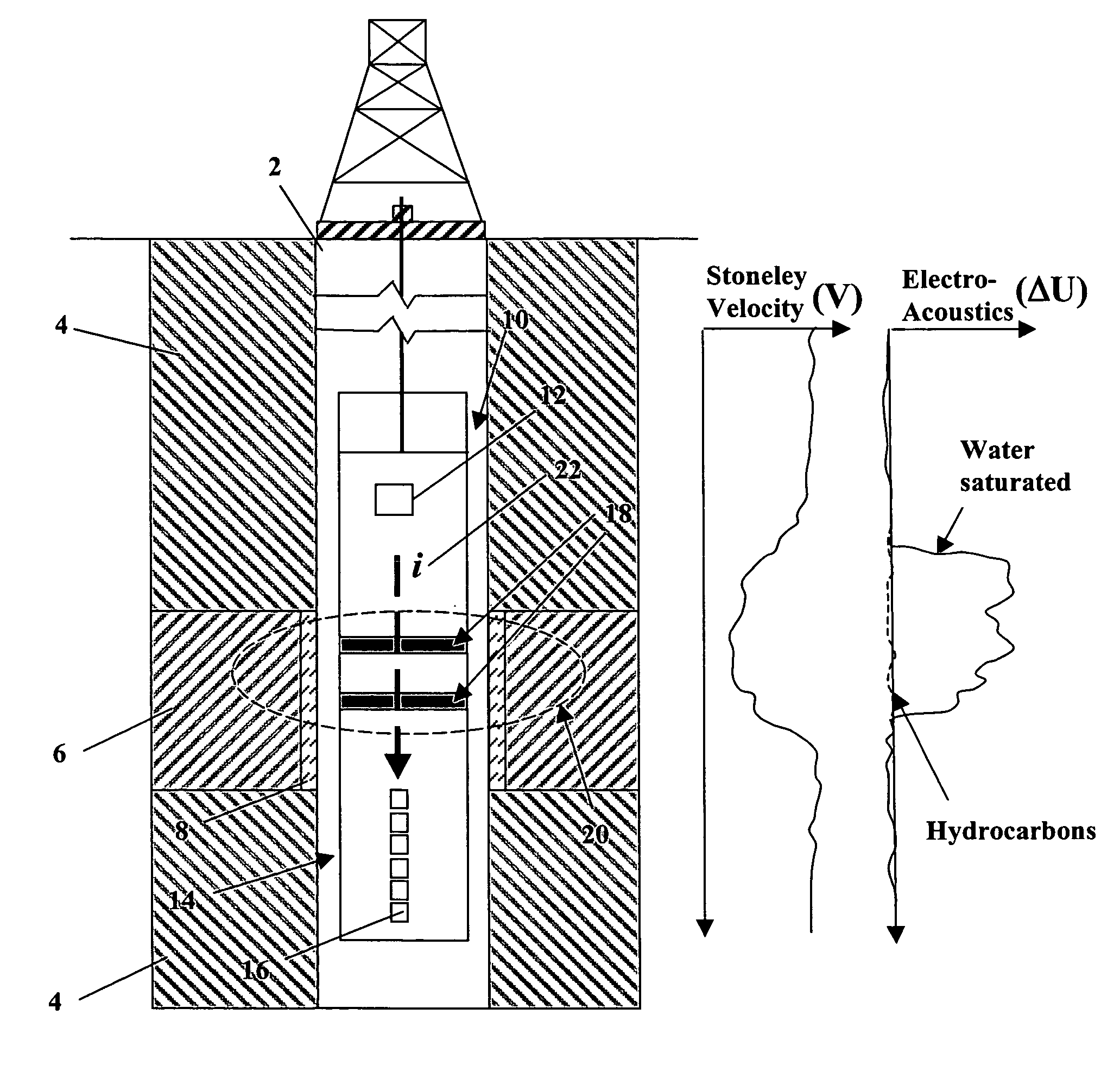
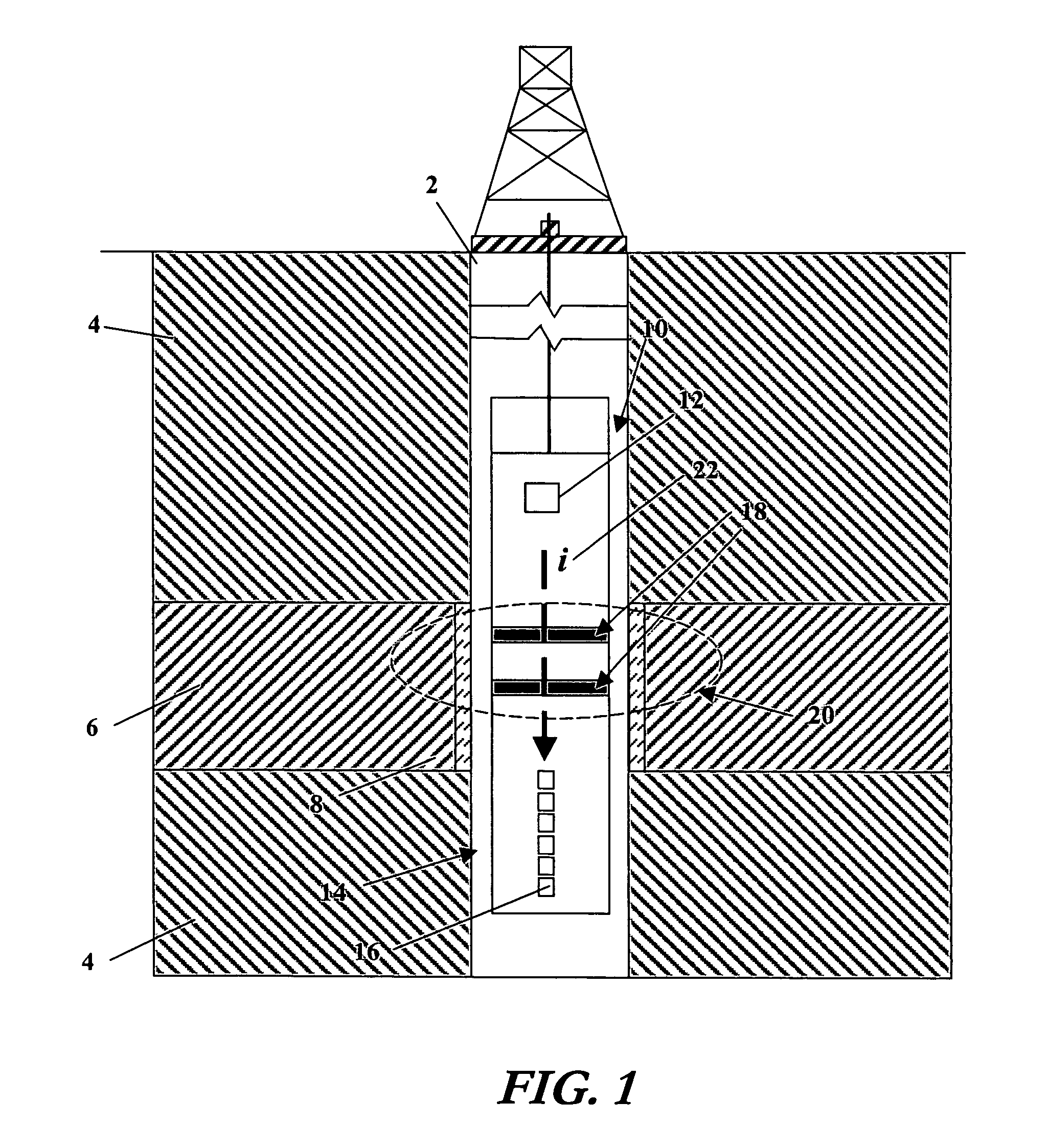
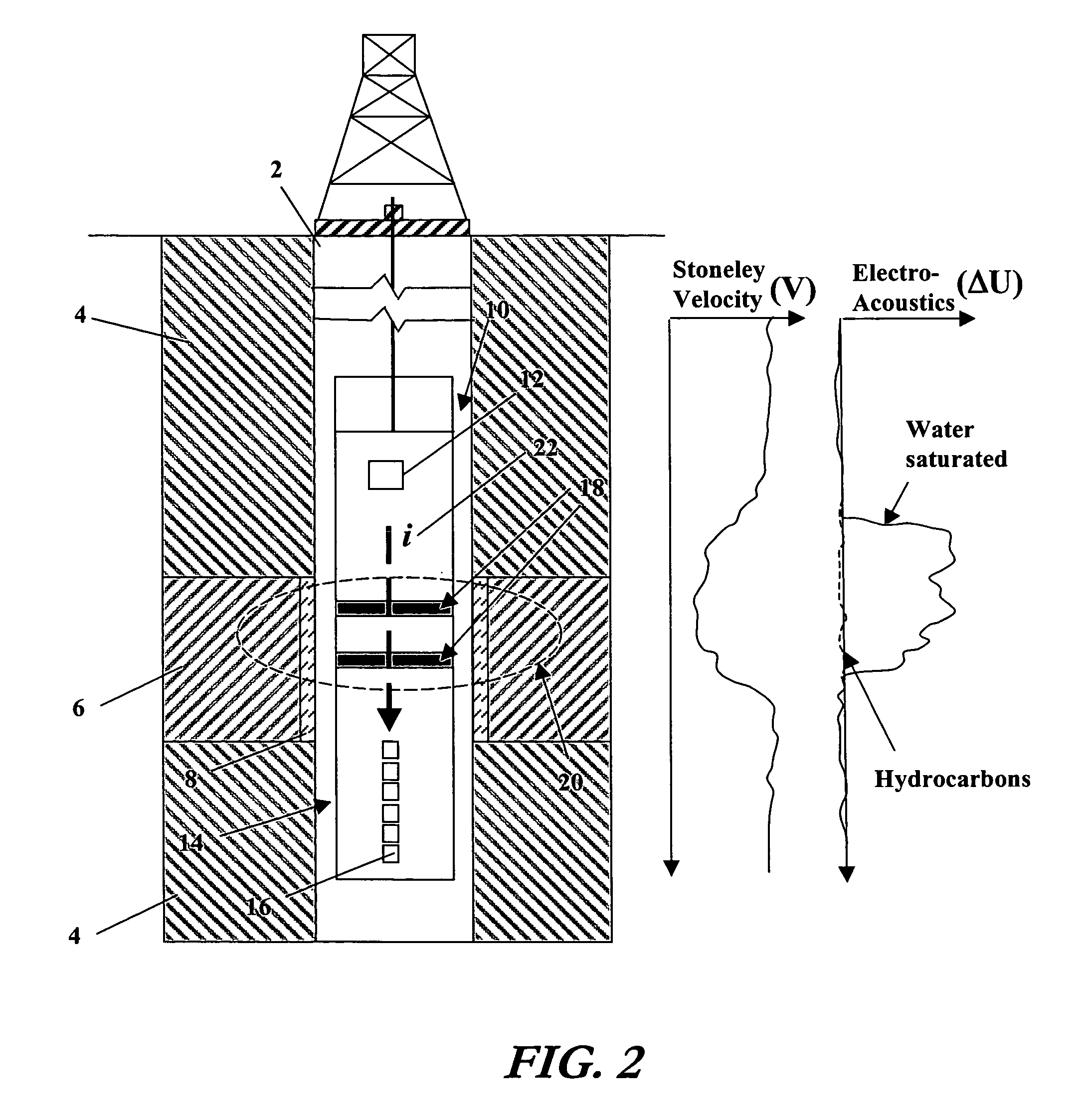
A method and apparatus for assessing the permeability of a subterranean formation and the hydrocarbon and / or water content of the formation. The method includes emitting an acoustic signal, such as a Stoneley wave into the formation and sending an electro-magnetic pulse into the formation. An analysis of the response of the Stoneley wave in conjunction with an analysis of a measurement of the electrical potential within the wellbore provides information pertinent to permeability and fluid composition.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Well logging prediction method of shale gas horizontal well single well production capacity
InactiveCN106761677AIncrease profitAvoid post-correction problemsSurveyUltrasound attenuationAcoustic wave
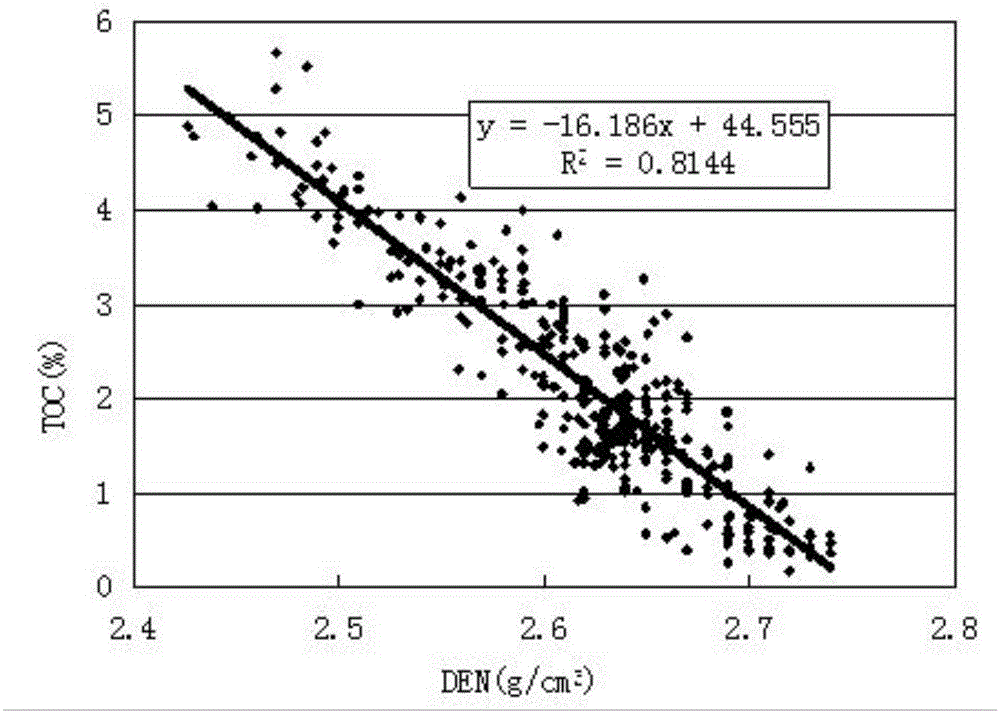
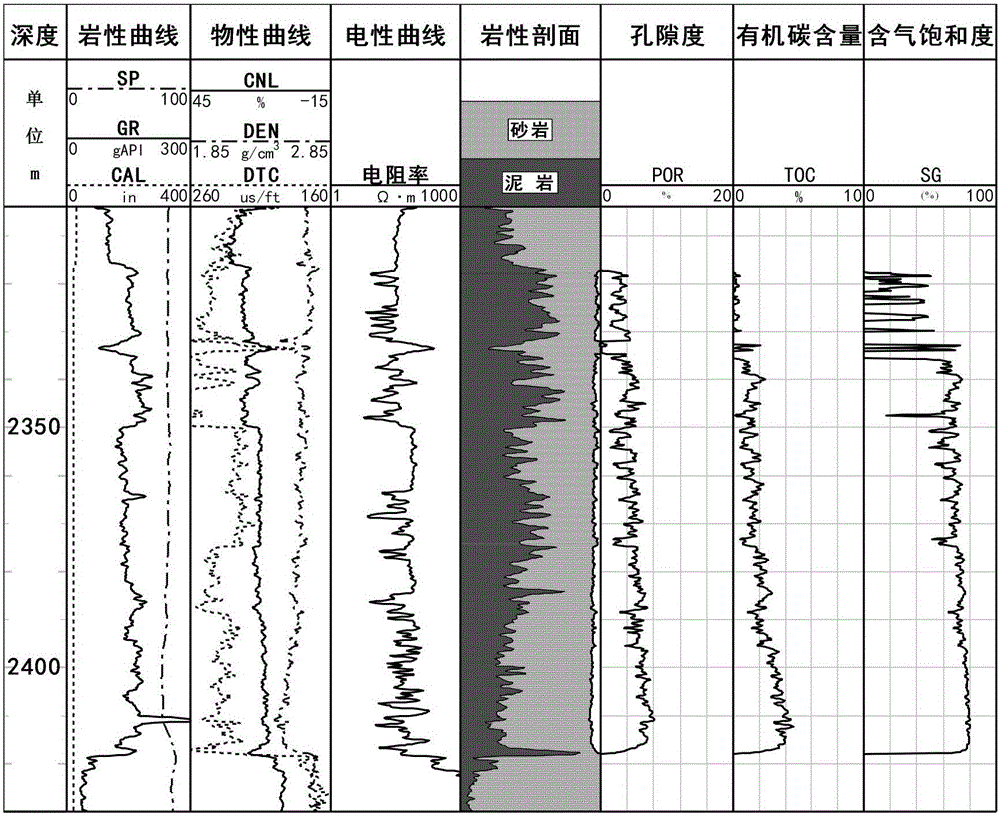
The invention provides a well logging prediction method of shale gas horizontal well single well production capacity. The method comprises the steps of firstly conducting well logging of interval transit time, density and neutron porosity in a drilled horizontal well, and recording the penetrating depth of a horizontal well section and the corresponding vertical depth; then using formation density well logging and compensated neutron well logging information to calculate formation brittle mineral content; utilizing the three well logging curves of the interval transit time, the density and the neutron porosity which reflect formation porosity in the well to calculate the formation porosity; utilizing a method of inverting reservoir permeability through stoneley wave attenuation to solve formation permeability; utilizing an organic carbon content experiment measurement value a stone sample taken in a formation and density well logging to establish a relation to obtain a calculation formula of organic carbon content; utilizing the formation organic carbon content to calculate to obtain formation gas saturation; finally according to the formation brittle mineral content, the formation porosity, the formation permeability and the formation gas saturation to calculate to obtain the daily production capacity of single well shale gas.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY +1
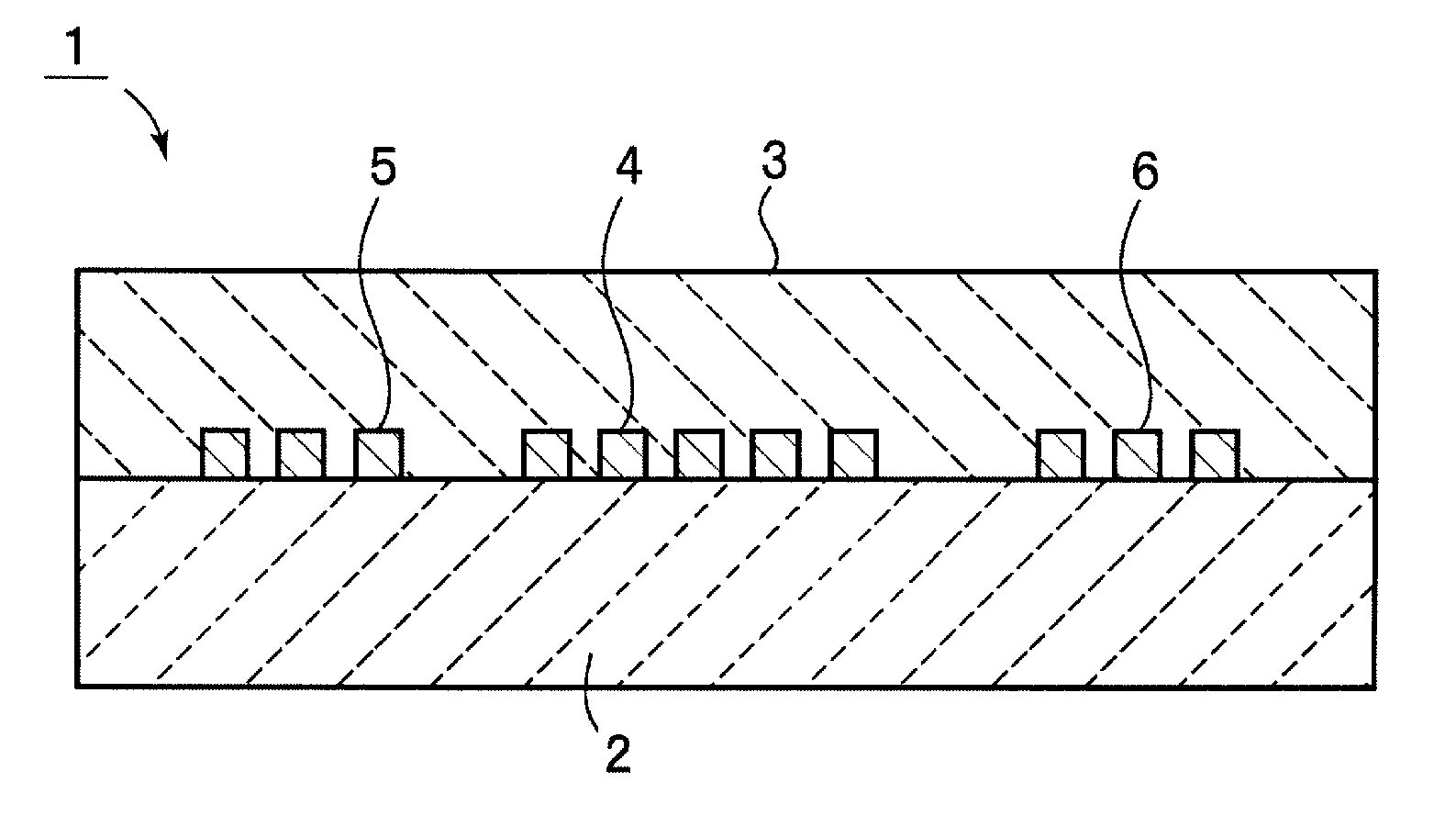
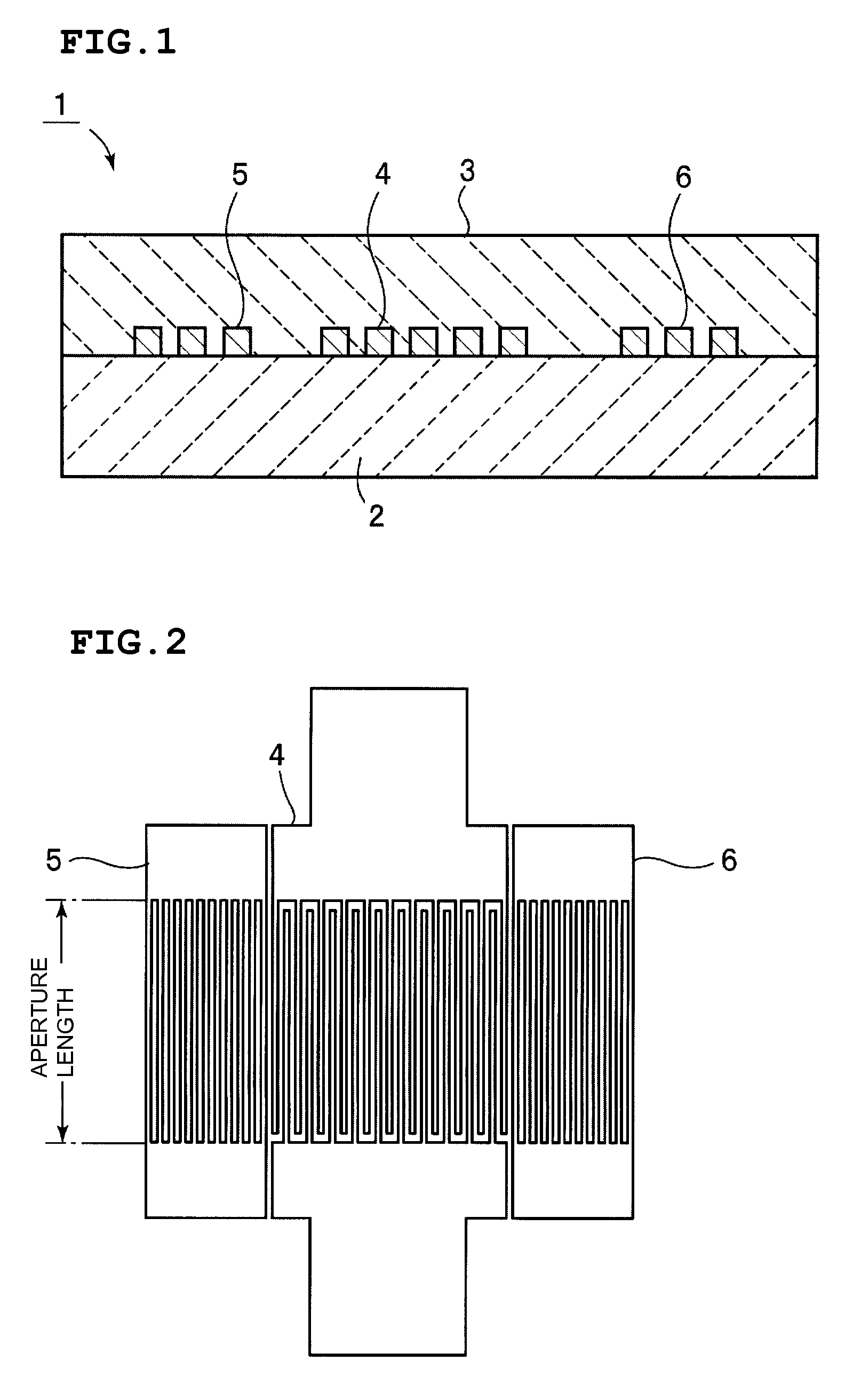
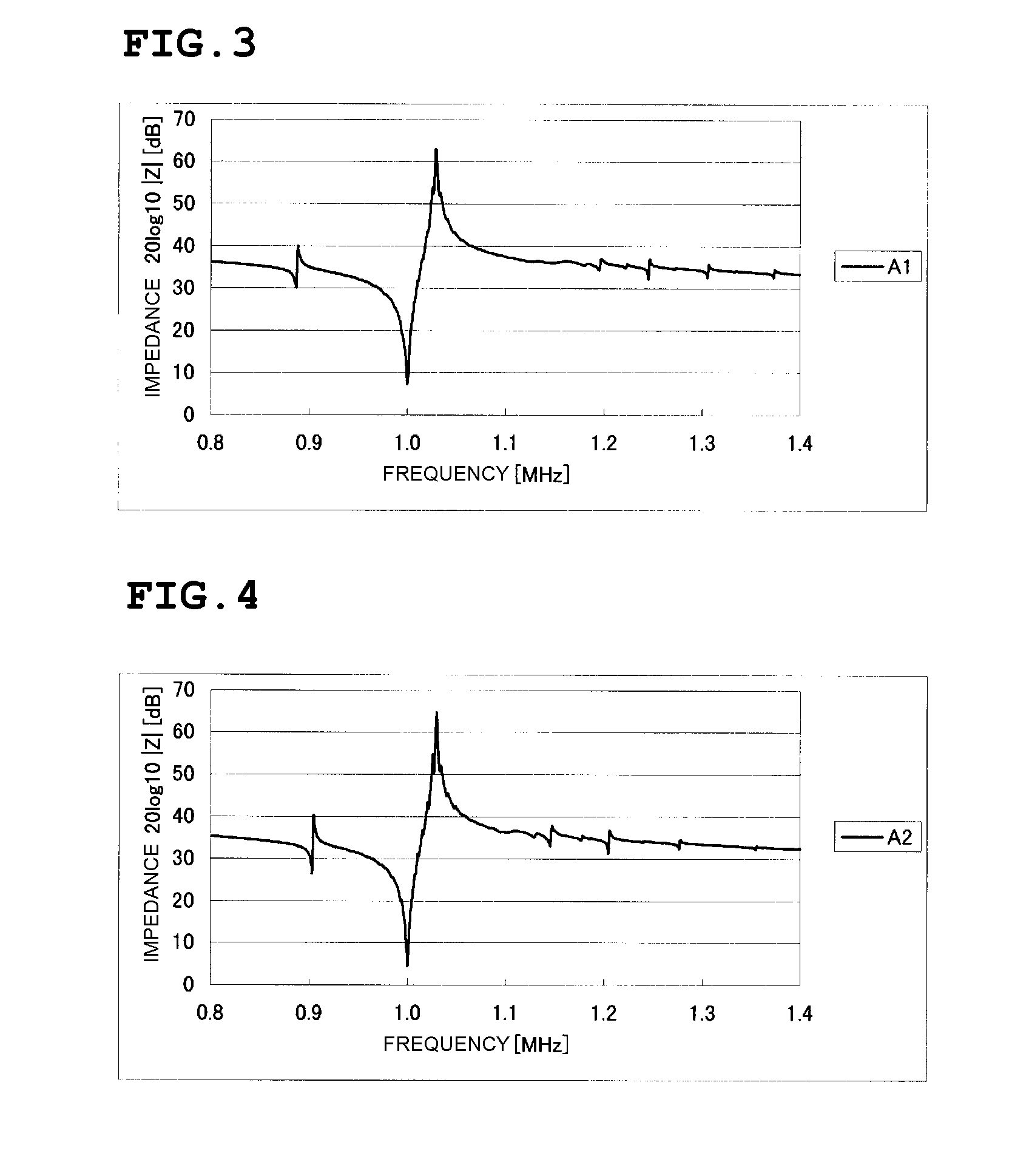
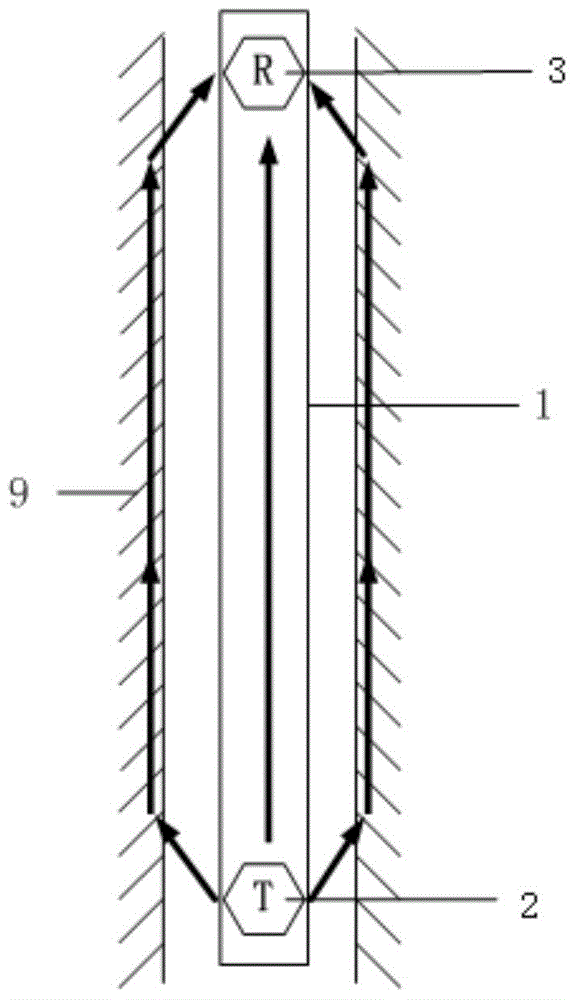
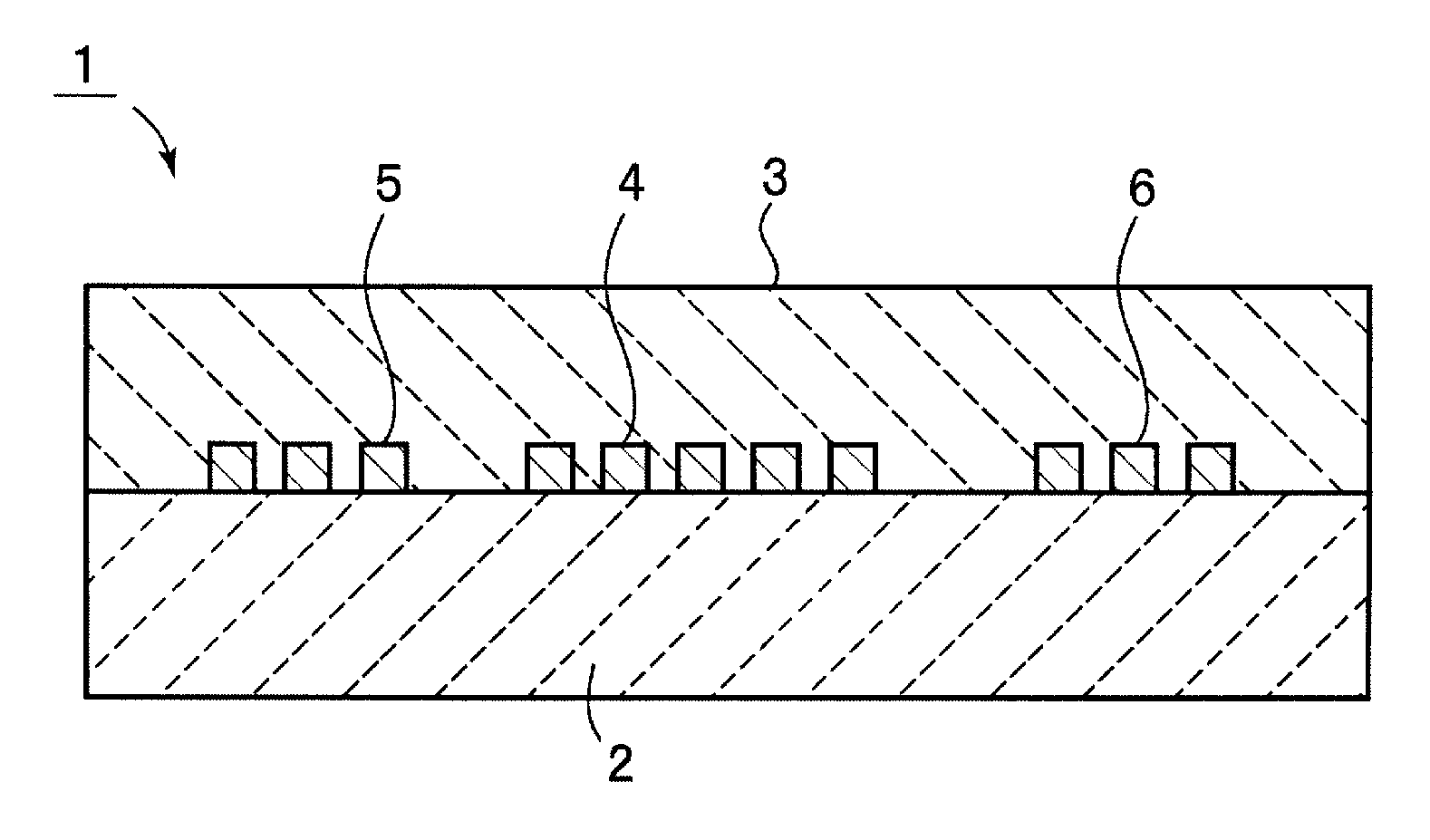
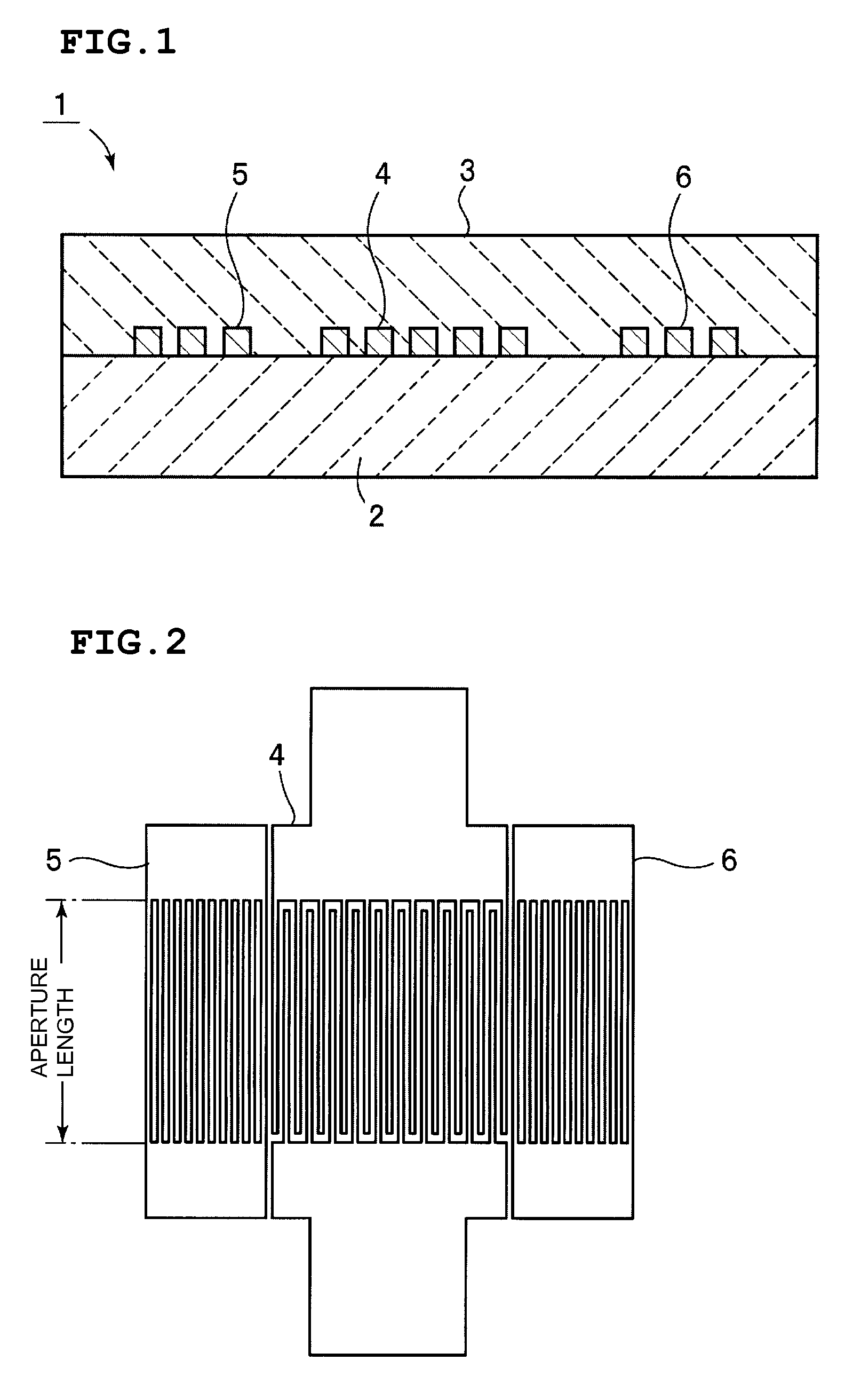
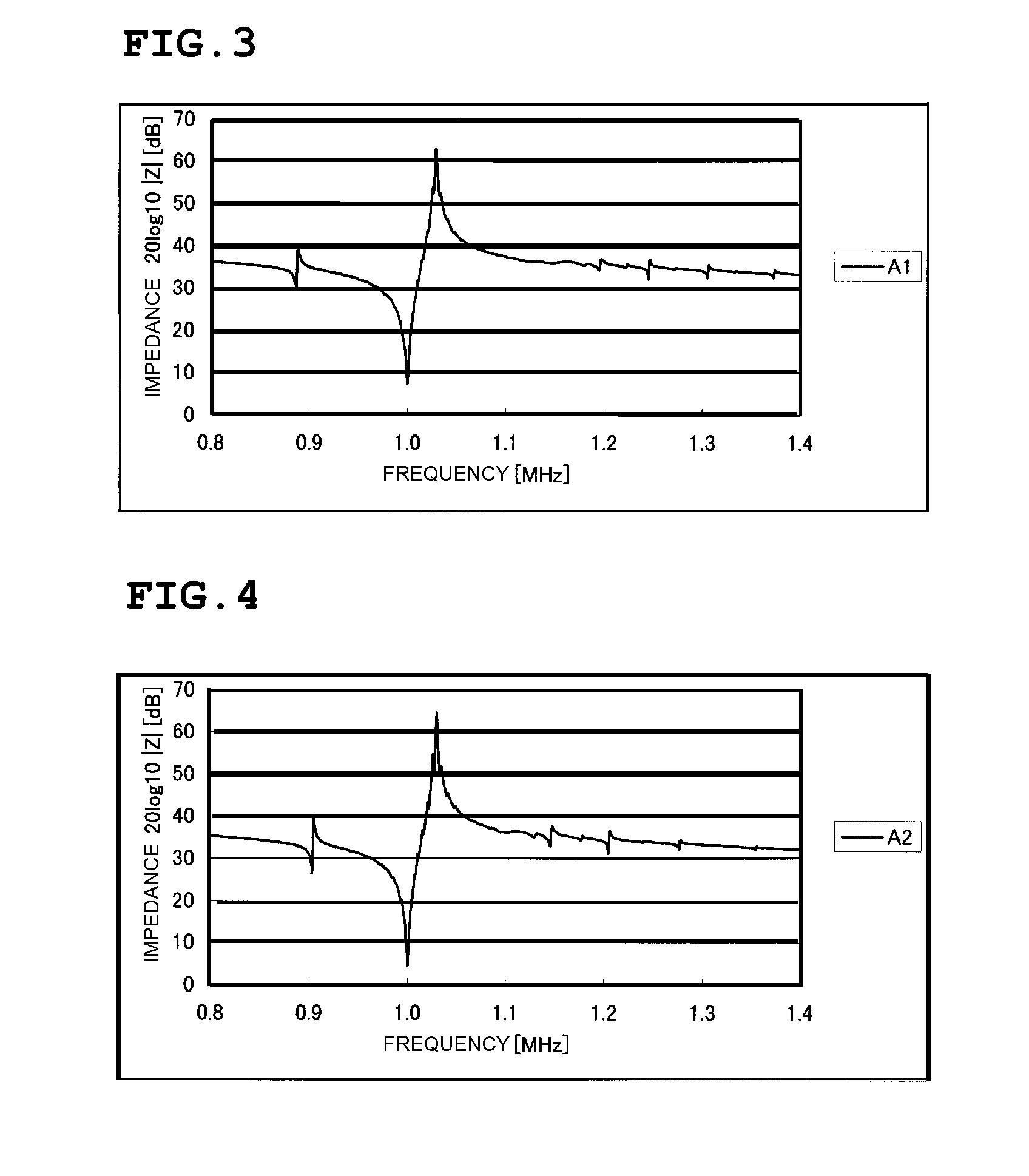
Boundary acoustic wave device
ActiveUS20070007852A1Large electromechanical coefficientSmall propagation lossPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcoustic waveStoneley wave
A dielectric substance is laminated on one surface of a piezoelectric substance, and an IDT and reflectors are disposed as electrodes at a boundary between the piezoelectric substance and the dielectric substance, and the thickness of the electrodes is determined so that the acoustic velocity of the Stoneley wave is decreased less than that of a slow transverse wave propagating through the dielectric substance and that of a slow transverse wave propagating through the piezoelectric substance, thereby forming a boundary acoustic wave device.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method for predicating productivity of nonhomogeneity ancient karst carbonate reservoir
InactiveCN104047598AImprove quantitative calculation accuracyAccurate calculationBorehole/well accessoriesUltrasound attenuationGeomorphology
The invention discloses a method for predicating productivity of nonhomogeneity ancient karst carbonate reservoir. The method includes the steps of firstly clarifying the reservoir through reservoir parameter processing and conducting the reservoir thickness statistics according to the clarified reservoir, secondly determining key parameters related to the productivity, such as matrix porosity, stoneley wave energy attenuation, the surface hole rate and the reservoir thickness, thirdly working out the comprehensive evaluation index RQ of reservoir quality according to the determined key parameters, establishing a productivity predicating model according to the comprehensive evaluation index RQ of the reservoir quality, and finally conducting productivity predication of the nonhomogeneity ancient karst carbonate reservoir according to the established productivity predicating model. By means of the method, the fine depicting and representing of the nonhomogeneity ancient karst reservoir are achieved, the problem of permeability of the nonhomogeneity ancient karst reservoir is solved, the main control factor problem of the productivity of the nonhomogeneity ancient karst reservoir is solved, and quantitative calculation of the main control factor is achieved, so that accurate productivity prediction can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD
Cased-Hole Radial Profiling of Shear Parameters from Sonic Measurements
ActiveUS20140043938A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingShear modulusRadial position
Cased-hole radial profiling of shear parameters from sonic measurements is disclosed. Example methods disclosed herein include determining a variation of a first shear modulus at a first radial position from a cased borehole in a formation based on a first weighted average of fractional variations of Stoneley wave velocities for different wavenumbers, the first weighted average based on first weights determined using a perturbation model including parameters to model the borehole casing, and determining variations of second and third shear moduli at respective second and third radial positions from the borehole based on second and third weighted averages of fractional variations of respective first and second flexural wave velocities for different wavenumbers, the first and second flexural wave velocities associated with respective first and second orthogonal borehole axial planes of the formation, the second and third weighted averages based on respective second and third weights determined using the perturbation model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for characterizing and estimating permeability using LWD Stoneley-wave data
Owner:ENGIUS +1
Method for determining reservoir permeability form borehole Stoneley-wave attenuation using Biot's poroelastic theory
ActiveUS7830744B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingUltrasound attenuationWave equation
Method for determining reservoir permeability from Stoneley wave attenuation extracted from conventional sonic logs by inversion of the full Biot wave equations for a porous medium. Frequency-dependent Stoneley-wave attenuation is extracted by analyzing array sonic measurements. Then, based on Biot's full theory applied to a borehole model and the standard logs (gamma ray, caliper, density, neutron, resistivity, sonic, etc.), a simulation model with the same parameters as the Stoneley-wave measurements is built. Next, a theoretical Stoneley-wave attenuation is computed for a given permeability. Finally, reservoir permeability is determined by comparing the modeled Stoneley-wave attenuation with the measured Stoneley-wave attenuation by an iterative inversion process.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
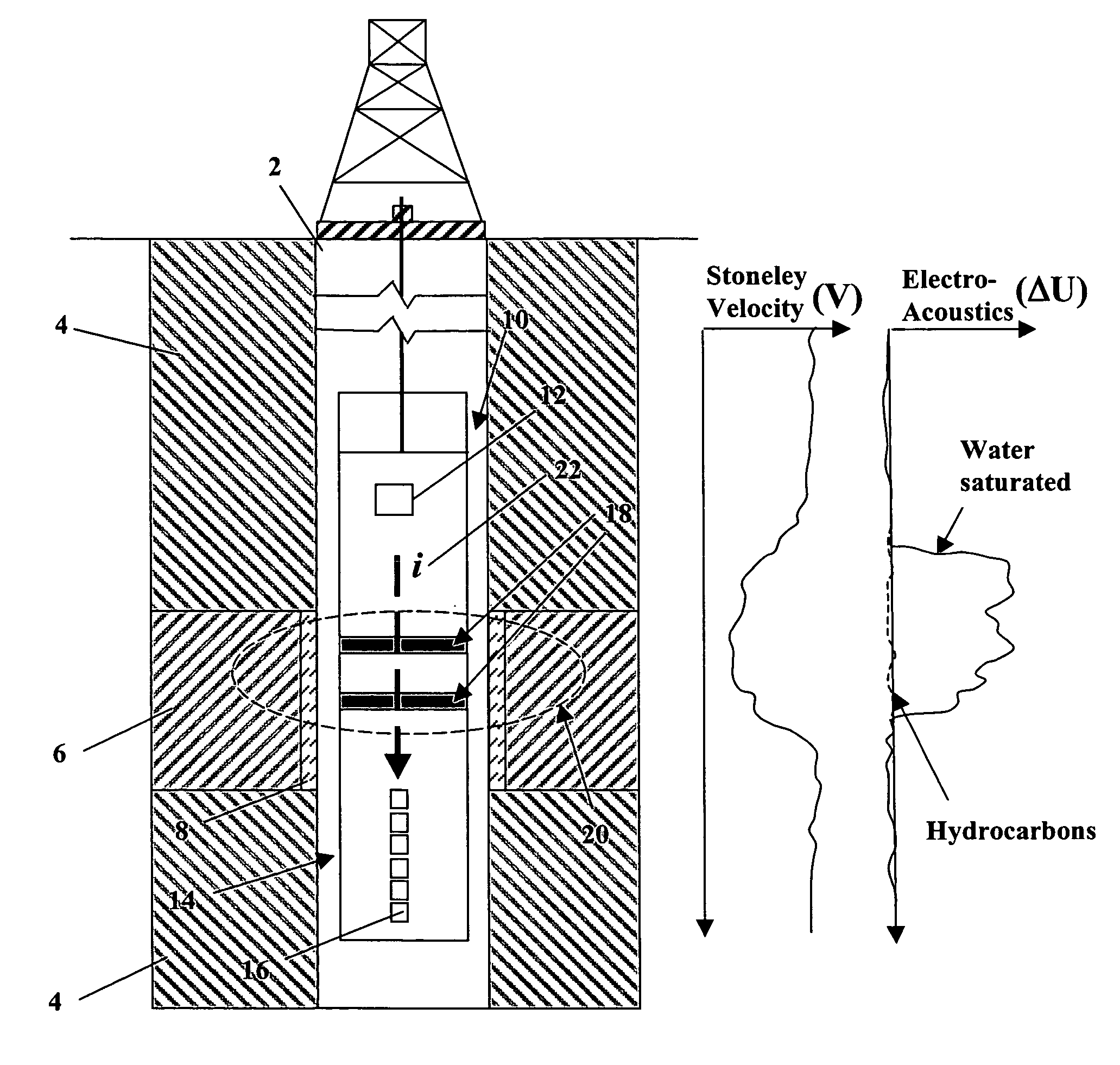
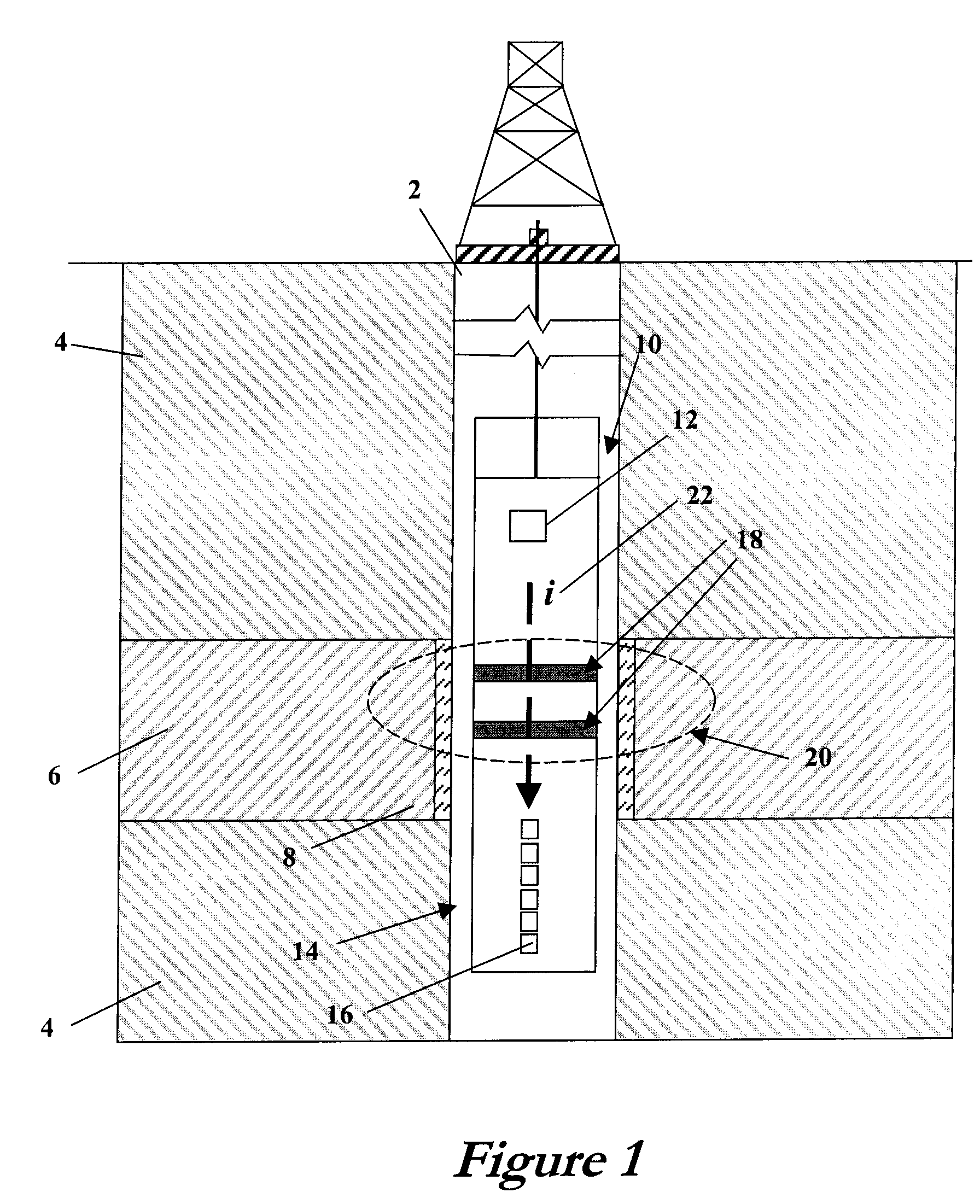
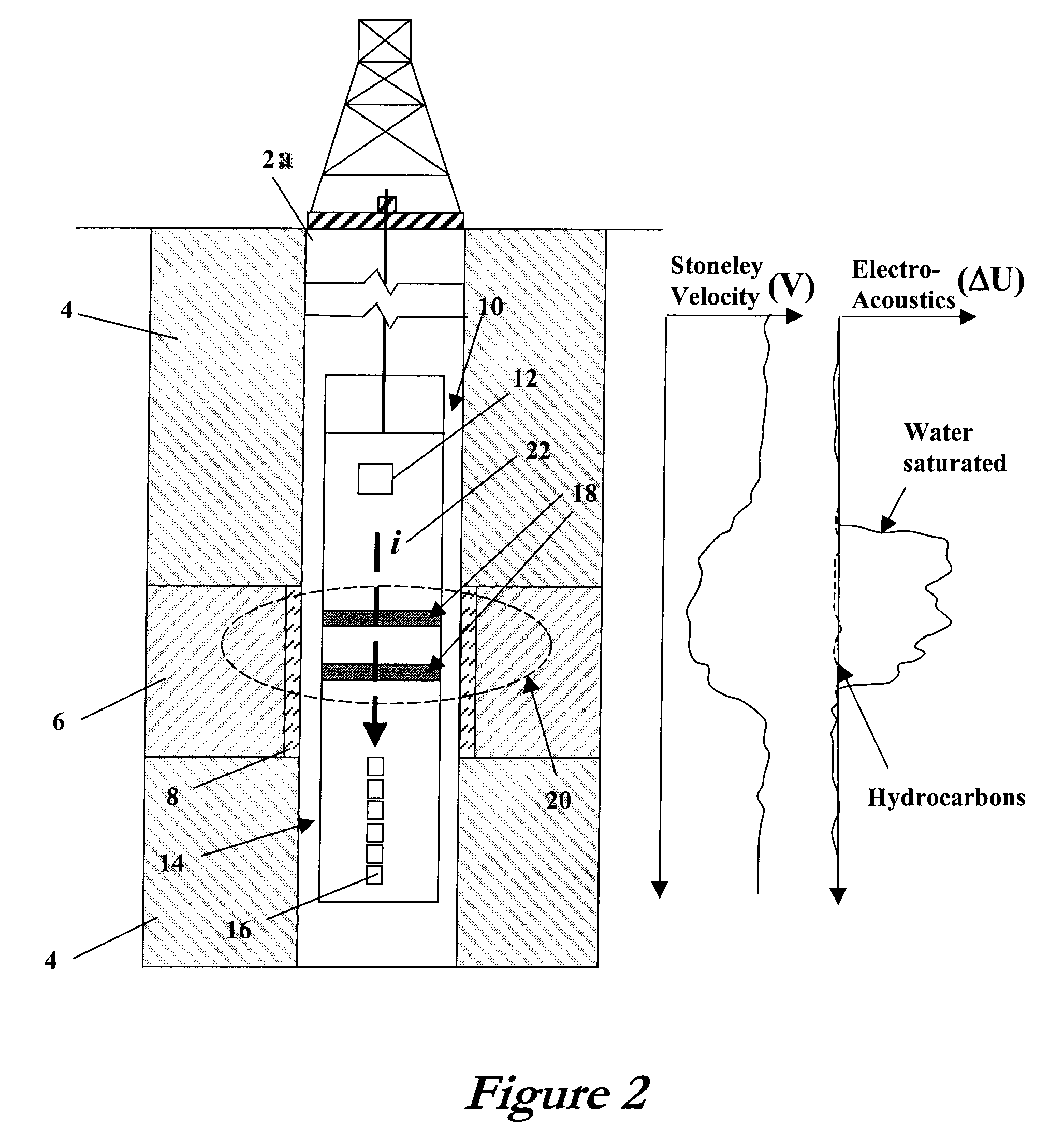
Method and Apparatus for Estimating Formation Permeability and Electroacoustic Constant of an Electrolyte-Saturated Multi-Layered Rock Taking Into Account Osmosis
ActiveUS20100254218A1Seismic energy generationMechanical vibrations separationHydrophoneAcoustic wave
An acoustic source on a logging tool is used to generate acoustic waves in a borehole. Acoustic detectors on the logging tool measure the generated acoustic waves. Electrodes on the logging tool are used to measure the potential resulting from the generated acoustic wave. The output of the hydrophones and the electrodes corresponding to Stoneley wave components of the acoustic wave are processed to provide an estimate of formation permeability, acoustoelectric constant, and a velocity of a propagating second compressional wave in the formation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Drilling following type acoustic logging device
InactiveCN104806234AIncrease credibilityIncrease the scope of applicationSurveyUltrasound attenuationLongitudinal wave
The embodiment of the invention relates to a drilling following type acoustic logging device. The device comprises a drill collar, a transmission energy converter and a receiving energy converter, wherein the transmission energy converter and the receiving energy converter are arranged on the drill collar; the transmission energy converter comprises a first radiation metal block, a first mass metal block and a plurality of transmission type piezoelectric ceramic sheets; the receiving energy converter comprises a second radiation metal block, a second mass metal block and a plurality of receiving type piezoelectric ceramic sheets. According to the device, a multi-pole-source working mode combining a single pole, a dipole and quadrupole is utilized to directly measure stratum longitudinal wave, transverse wav, stoneley wave sound velocity, attenuation and other parameters which can provide reference and verification for each other or individually processed, so that the reliability and applicable scope of the device can be greatly improved and expanded.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Boundary acoustic wave device
ActiveUS7355319B2Large electromechanical coefficientSmall propagation lossPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcoustic waveStoneley wave
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Electro-magnetic acoustic measurements combined with acoustic wave analysis
ActiveUS7813219B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentAcoustic waveElectromagnetic pulse
A method and apparatus for assessing the permeability of a subterranean formation and the hydrocarbon and / or water content of the formation. The method includes emitting an acoustic signal, such as a Stoneley wave into the formation and sending an electro-magnetic pulse into the formation. An analysis of the response of the Stoneley wave in conjunction with an analysis of a measurement of the electrical potential within the wellbore provides information pertinent to permeability and fluid composition.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Method and device for determining horizontal crack widths
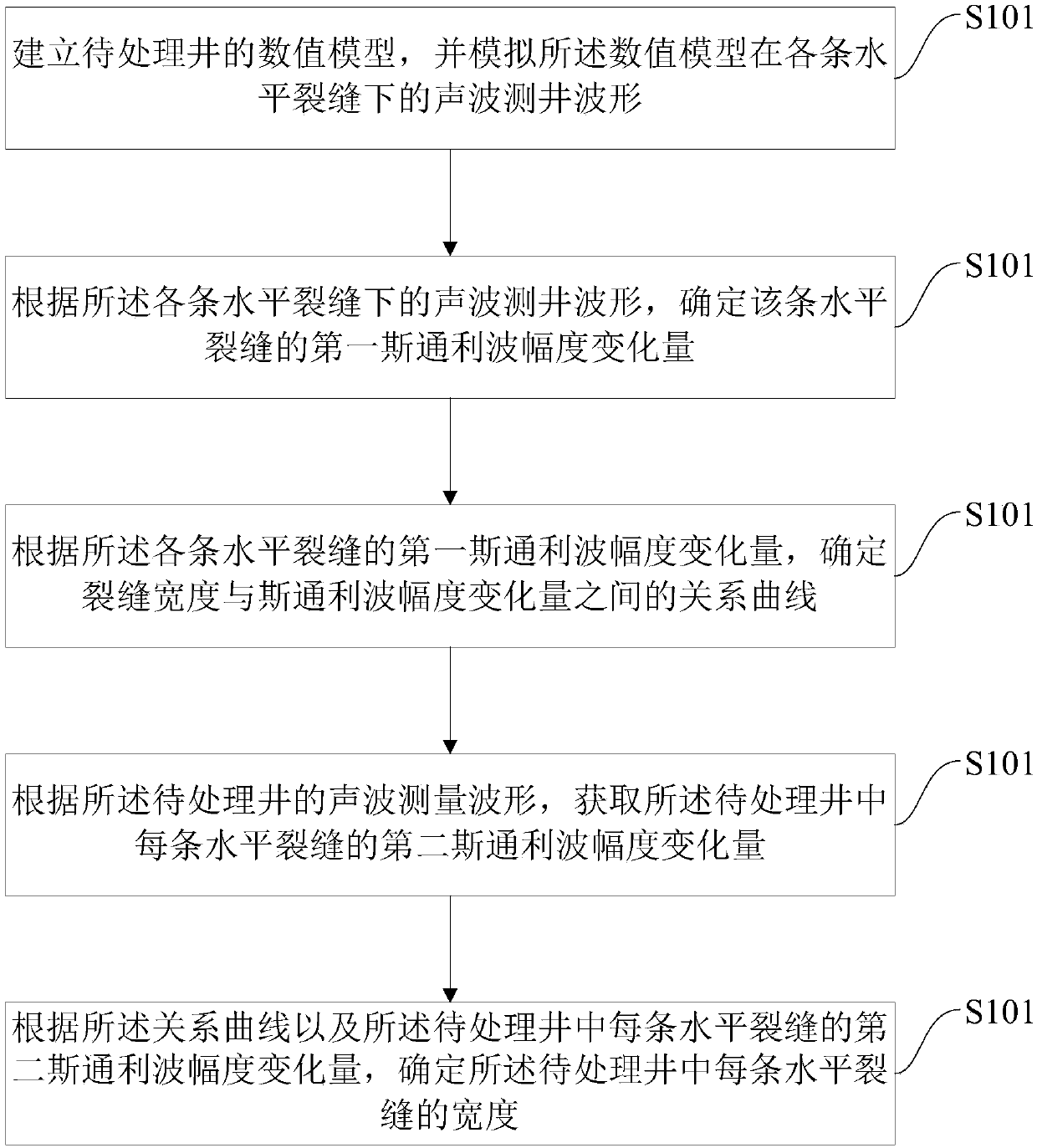
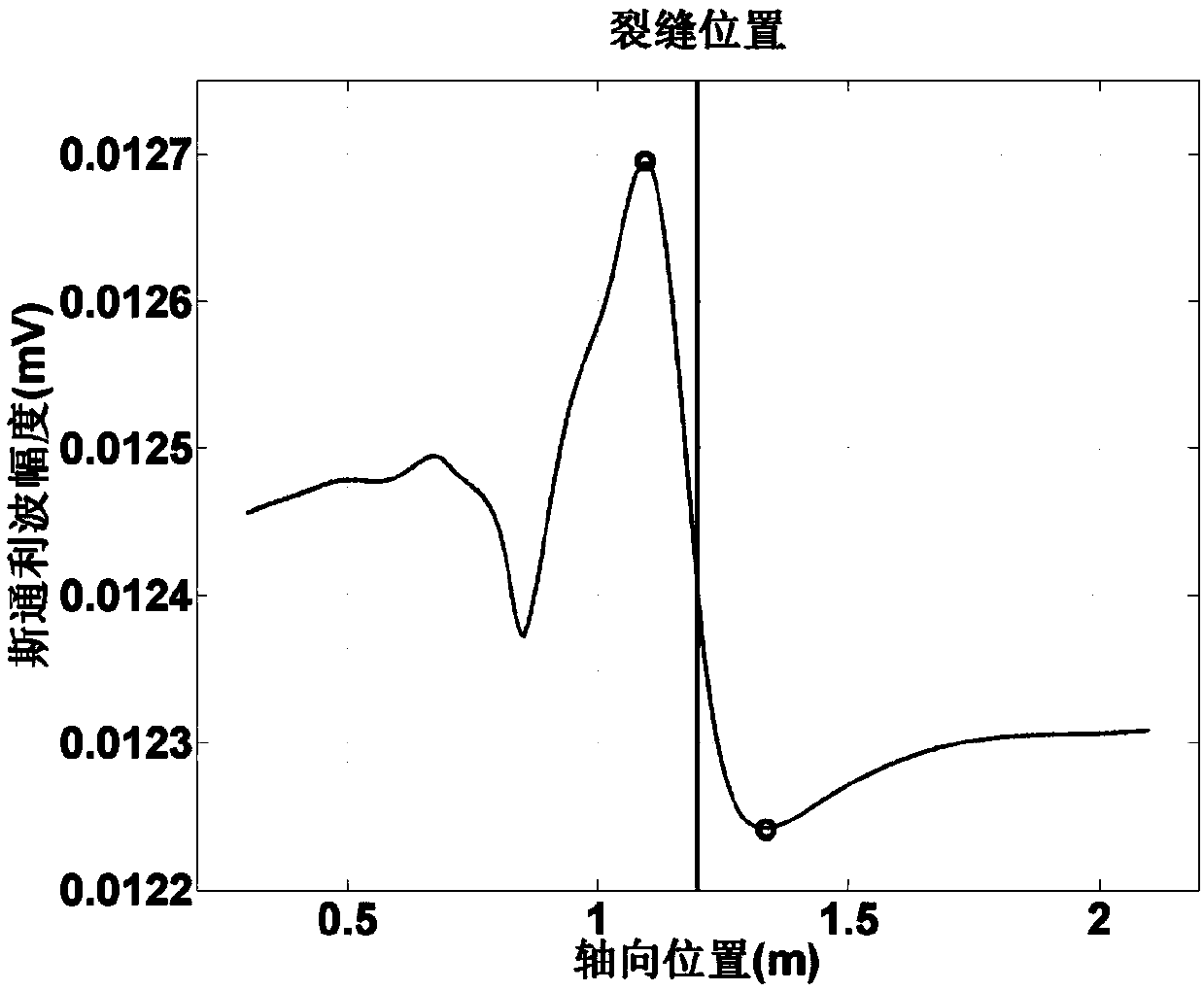
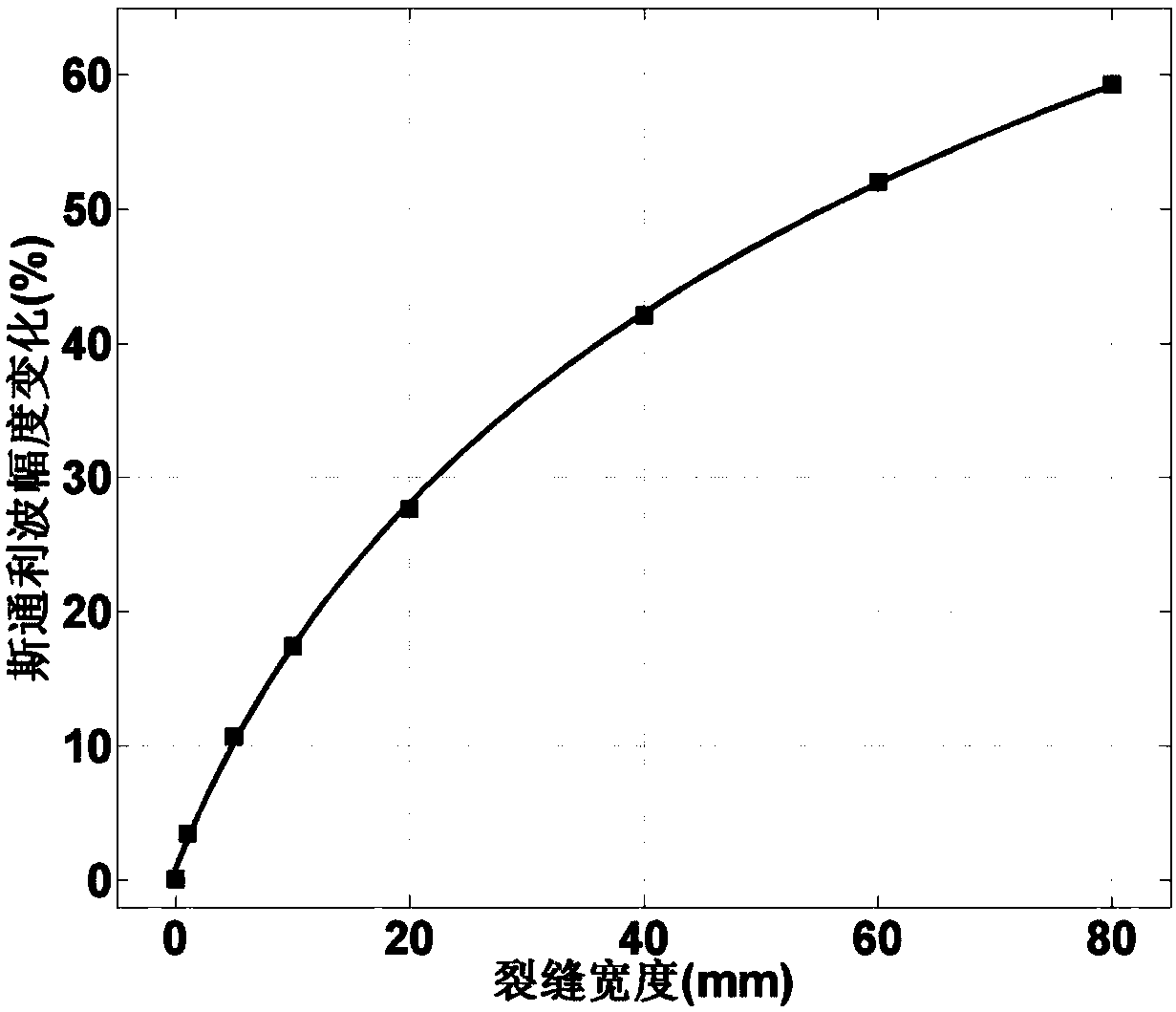
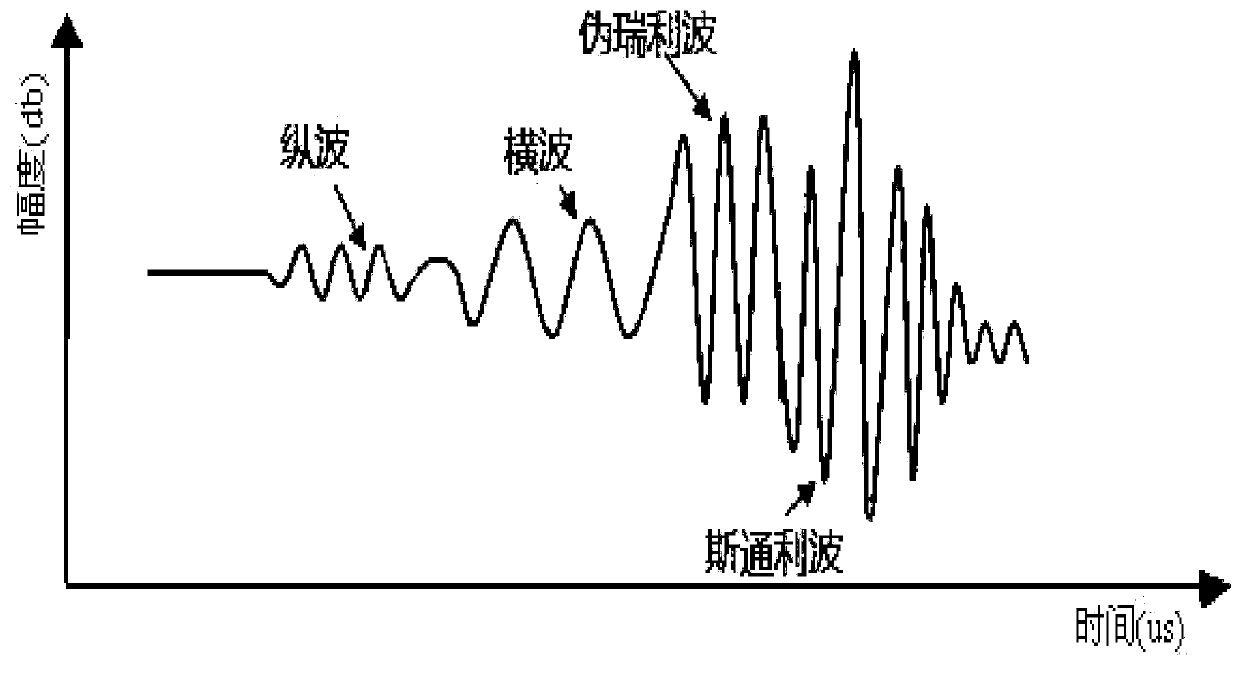
ActiveCN107587871AImprove accuracyReduce ambiguityBorehole/well accessoriesAcoustic waveNumerical models
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for determining horizontal crack widths. The method includes the steps that a numerical model of a to-be-treated well is built, and acoustic logging waveforms of the numerical model under all horizontal cracks are simulated; according to the acoustic logging waveforms under all horizontal cracks, the first stoneley wave amplitude variation amounts of the horizontal cracks are determined; according to the first stoneley wave amplitude variation amounts of all horizontal cracks, a relationship curve between the crack widths and the stoneley wave amplitude variation amounts is determined; according to the acoustic logging waveforms of the to-be-treated well, second stoneley wave amplitude variation amounts of all horizontal cracks in the to-be-treated well are determined; according to the relationship curve and the second stoneley wave amplitude variation amounts of all horizontal cracks in the to-be-treated well, the width of each horizontal crack in the to-be-treated well is determined. By means of the embodiment, the calculation accuracy of the horizontal crack widths can be improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Processing and interpreting method of array acoustic imaging logging data
InactiveCN110456418AShear wave time difference is accurateReasonable shear time differenceSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingTime domainLongitudinal wave
The invention discloses a processing and interpreting method for array acoustic imaging logging data. The method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting and sorting multipole array acoustic logging data of a target well in a working area; S2, extracting the time difference of longitudinal waves, transverse waves and stoneley waves from the logging data with a time domain or a frequency domain method to obtain a time difference curve, and performing quality monitoring on the time difference curve; S3, constructing a transverse wave time difference curve of a dipole-free acoustic data well; S4, analyzing the fast and slow transverse wave anisotropy of acoustic imaging logging and applying analysis results. The method is simple, has low calculation workload and high calculation efficiency, can be applied to various geological target wells, and has high result precision.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Multipole combined logging-while-drilling mode and signal transceiving synchronization method
ActiveCN108979628ARealize full wave train measurementRealize azimuth imagingSurveySynchronous controlWell drilling
The invention relates to a combined logging mode of a multipole logging-while-drilling device. The combined logging mode which comprises a drilling logging mode and a lifting logging mode is providedaccording to the actual needs of well drilling operation, full wave train measuring and orientation imaging of stratum longitudinal waves, transverse waves, Stoneley waves and the like can be achievedat the same time, and rich stratum evaluation information can be provided. Aiming at the fact that the working diameters of the different modes of the combined logging mode are different and transmitting and receiving need to be controlled synchronously, the invention further provides a signal transceiving synchronization method combining transceiving communication and synchronous control, the fact that the multipole logging-while-drilling device works according to set flow under each working mode and during the switching of different modes is guaranteed, and measuring efficiency is increased.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
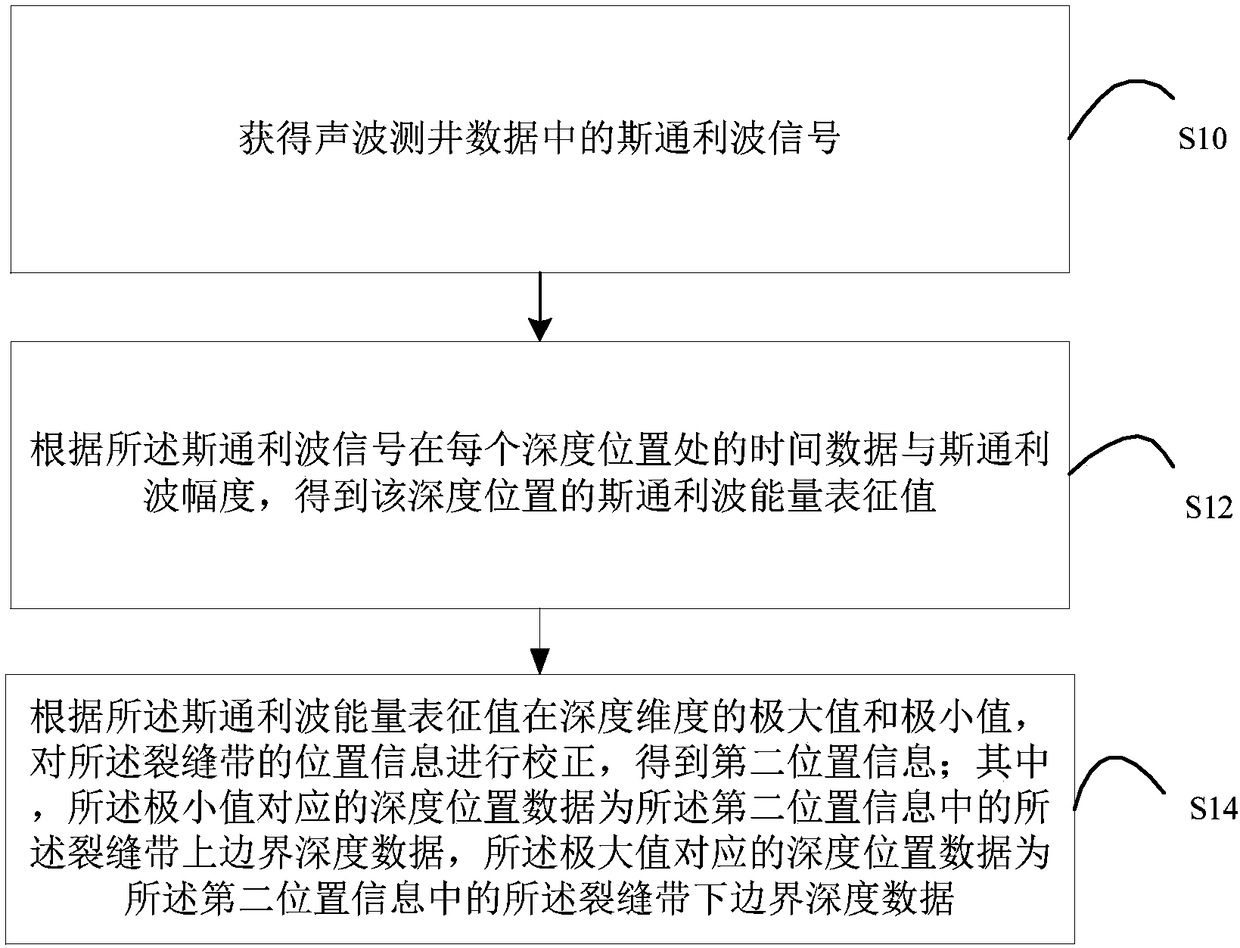
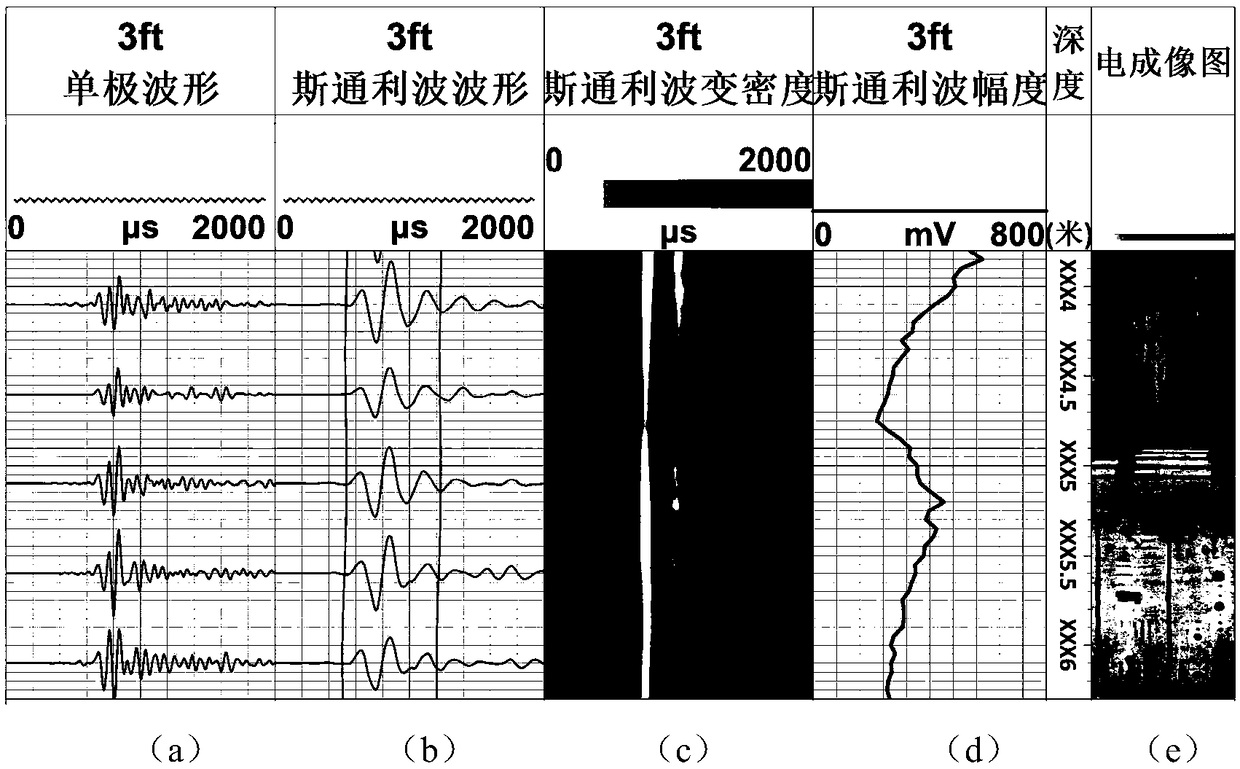
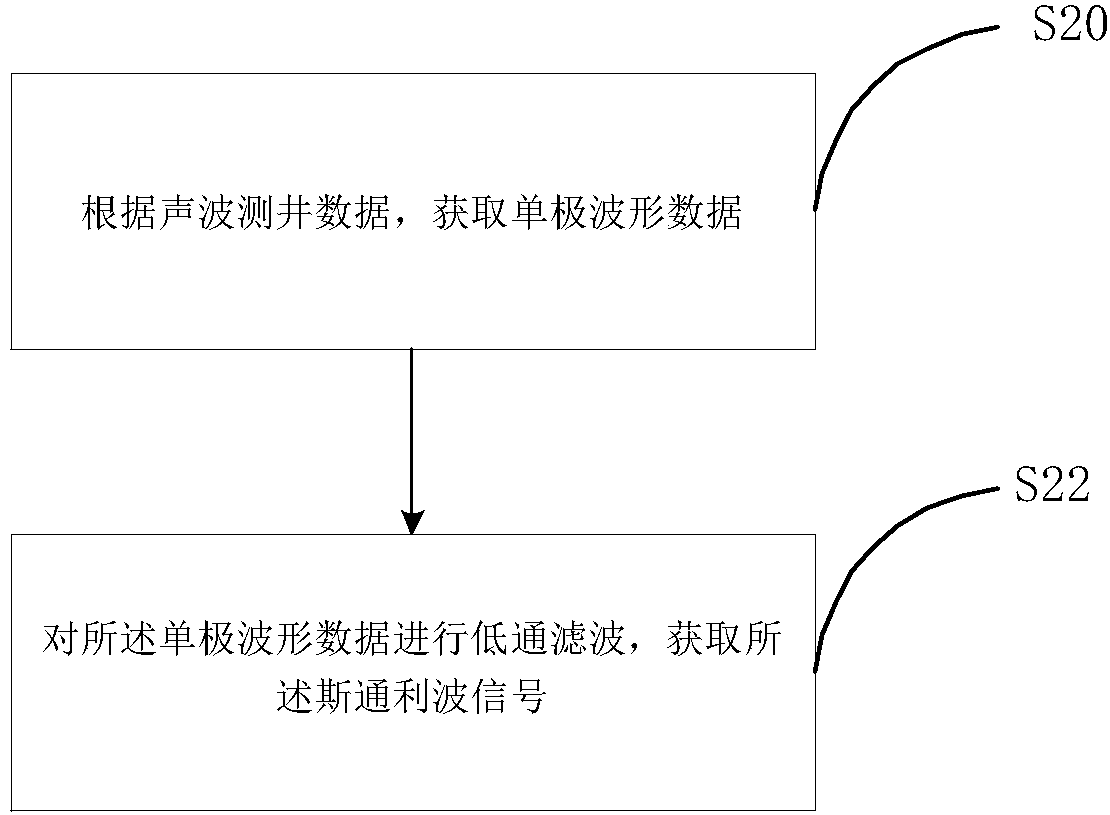
Method and device for correcting position of crack zone
The invention aims to provide a method and a device for correcting the position of a crack zone. The method comprises the steps of acquiring Stoneley wave signals in sound wave logging data; obtainingthe Stoneley wave energy representation values of the depth positions according to the time data of the Stoneley wave signals at each depth position and Stoneley wave amplitude, correcting the position information of the crack zone according to the maximum value and the minimum value of the Stoneley wave energy representation values in the depth dimension to obtain second position information, wherein the depth position data corresponding to the minimum value is the upper boundary depth data of the crack zone in the second position information, and the depth position data corresponding to themaximum value is the lower boundary depth data of the crack zone in the second position information. According to the embodiment of the invention, the position information, including depth data and width data, of the crack zone is corrected.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for a formation properties determination
InactiveUS8607628B2Enhanced technological and functional featureEasy data collectionVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidUltrasound attenuationContinuous measurement
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
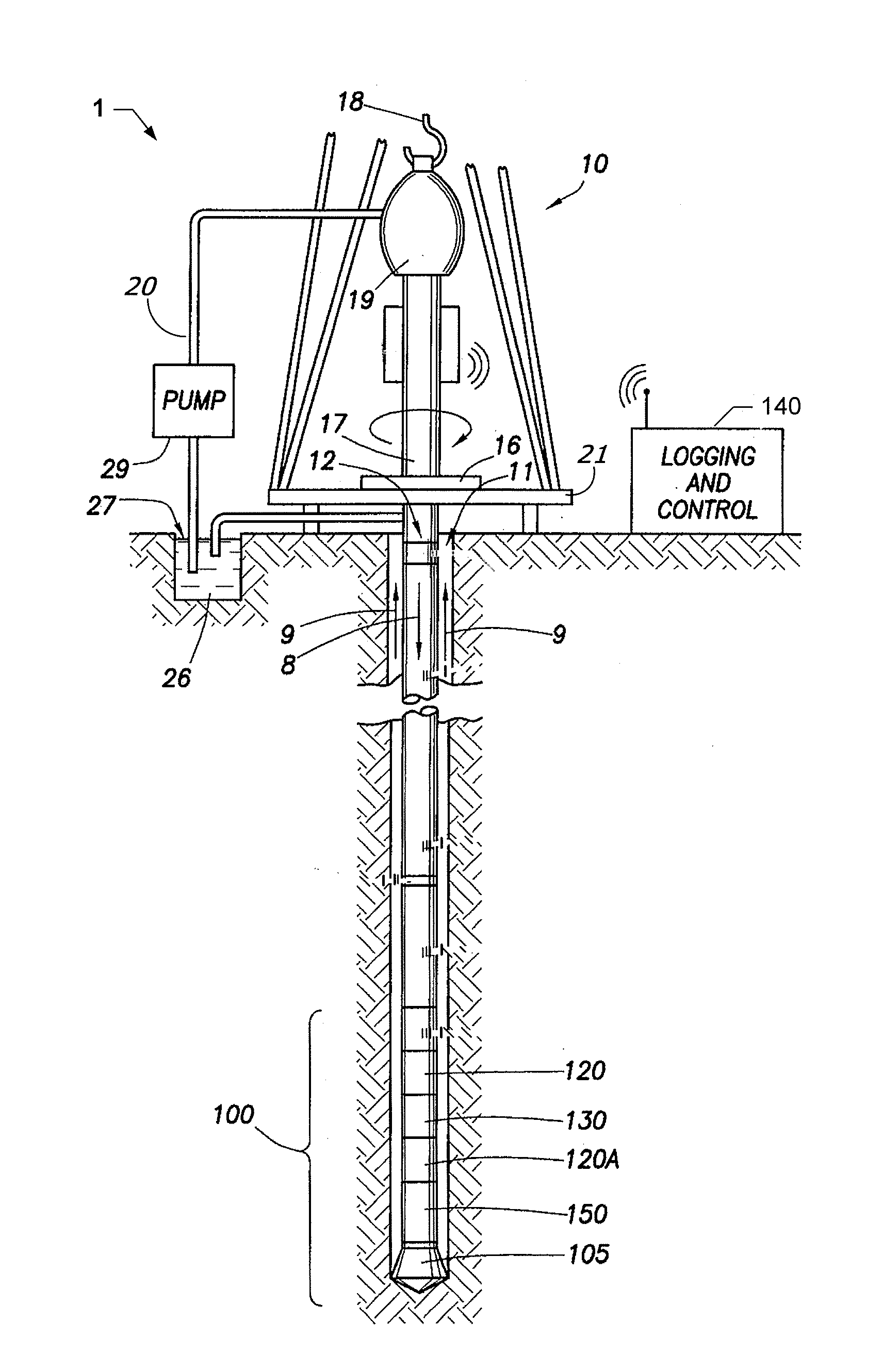
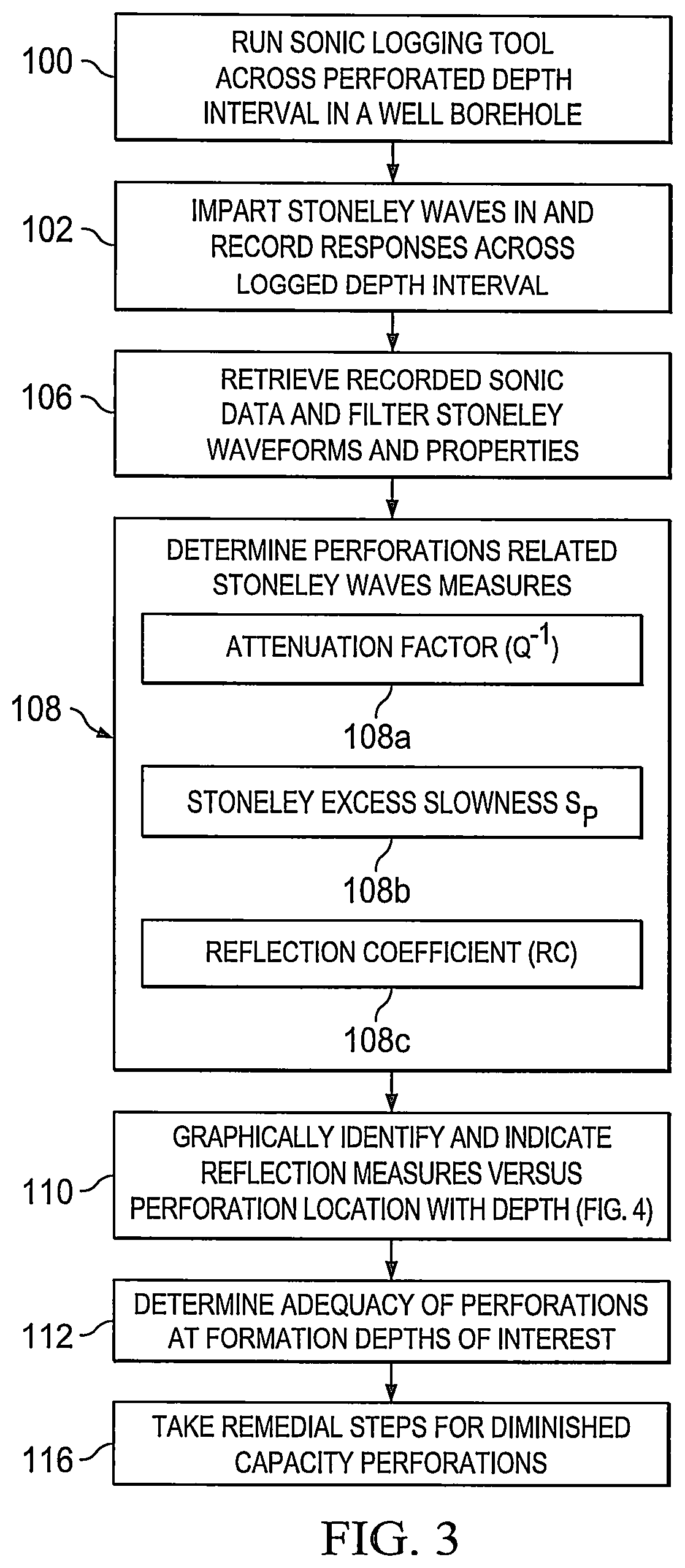
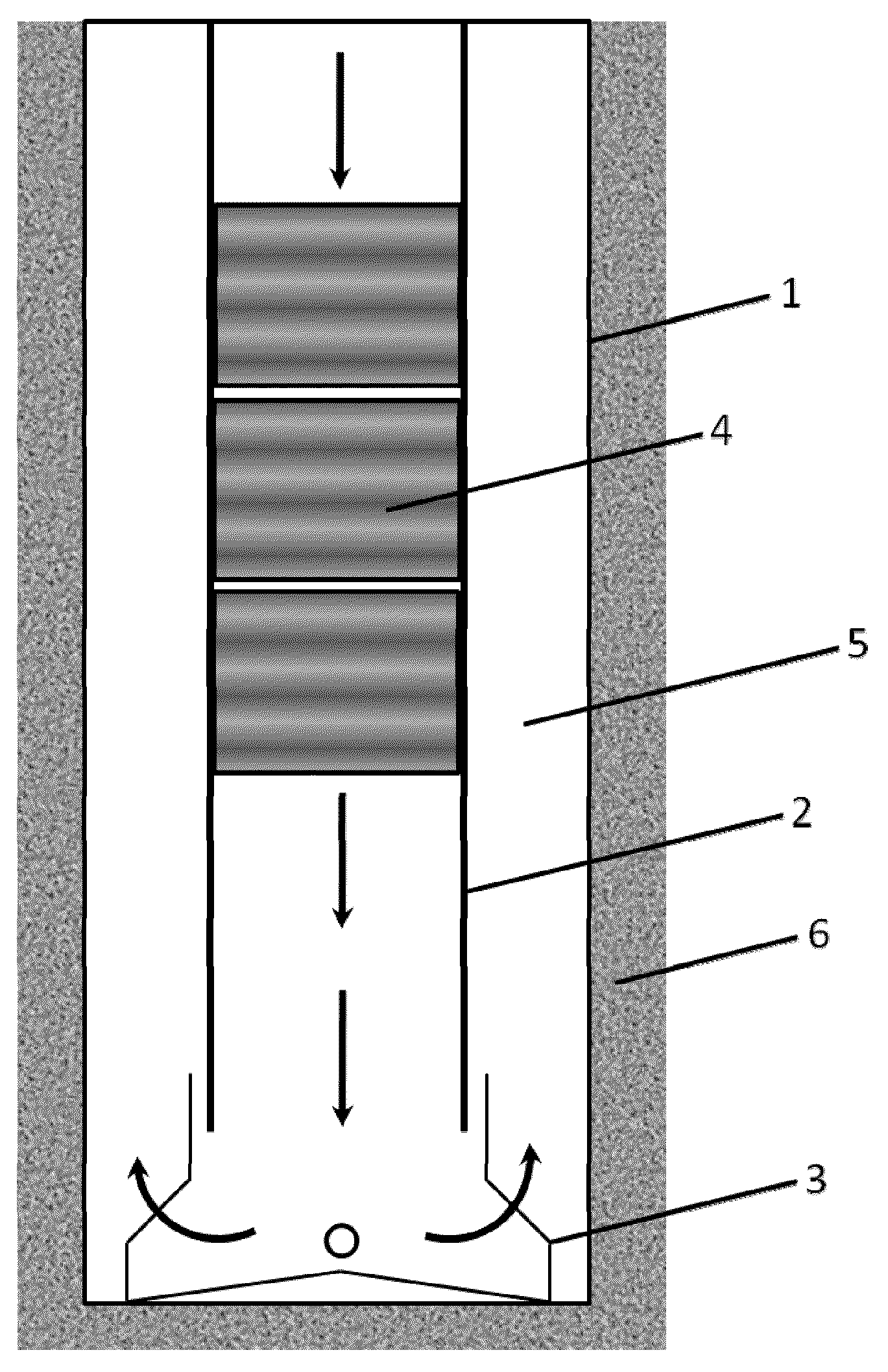
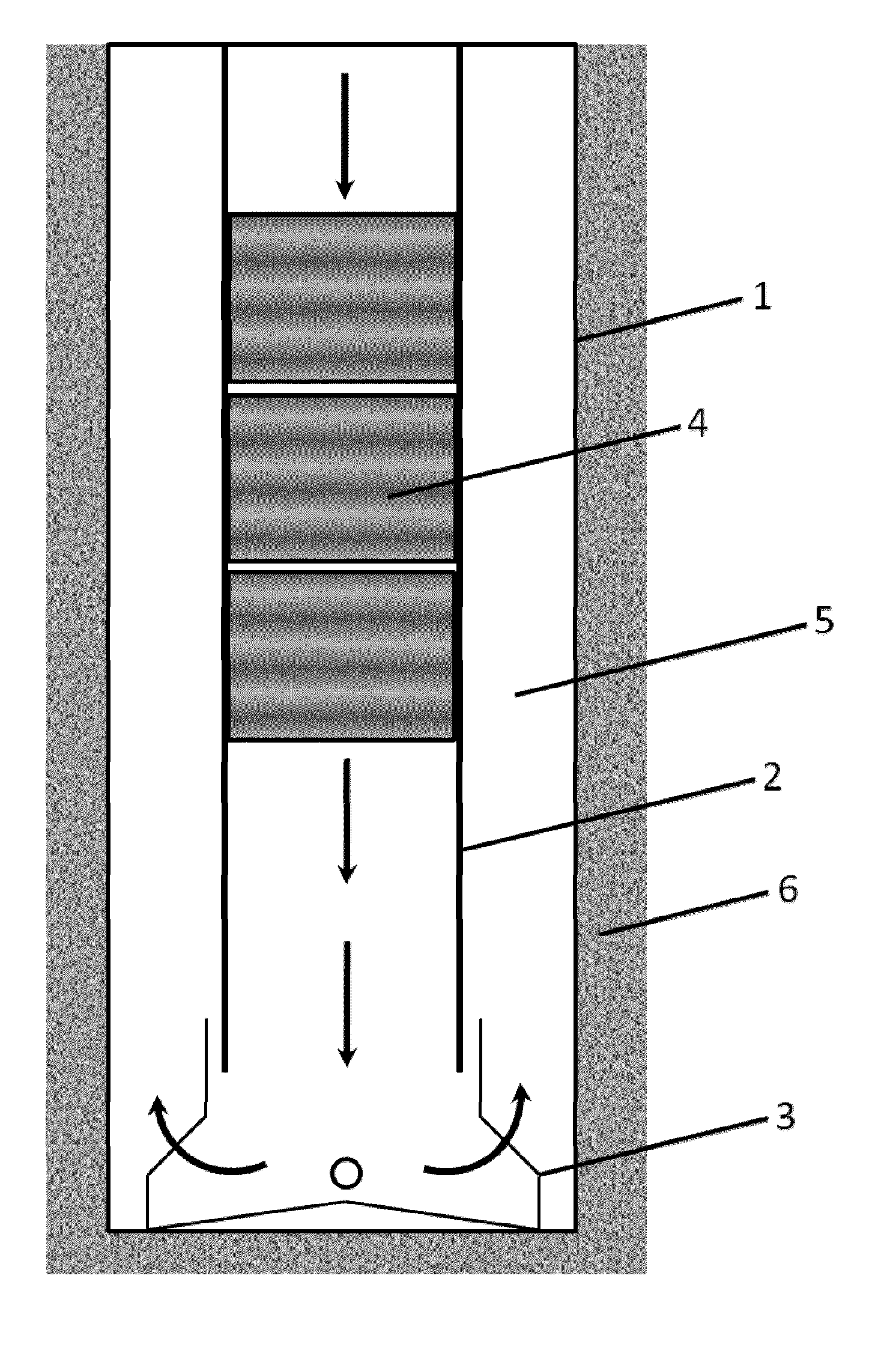
Evaluation of cased hole perforations in under-pressured gas sand reservoirs with stoneley wave logging
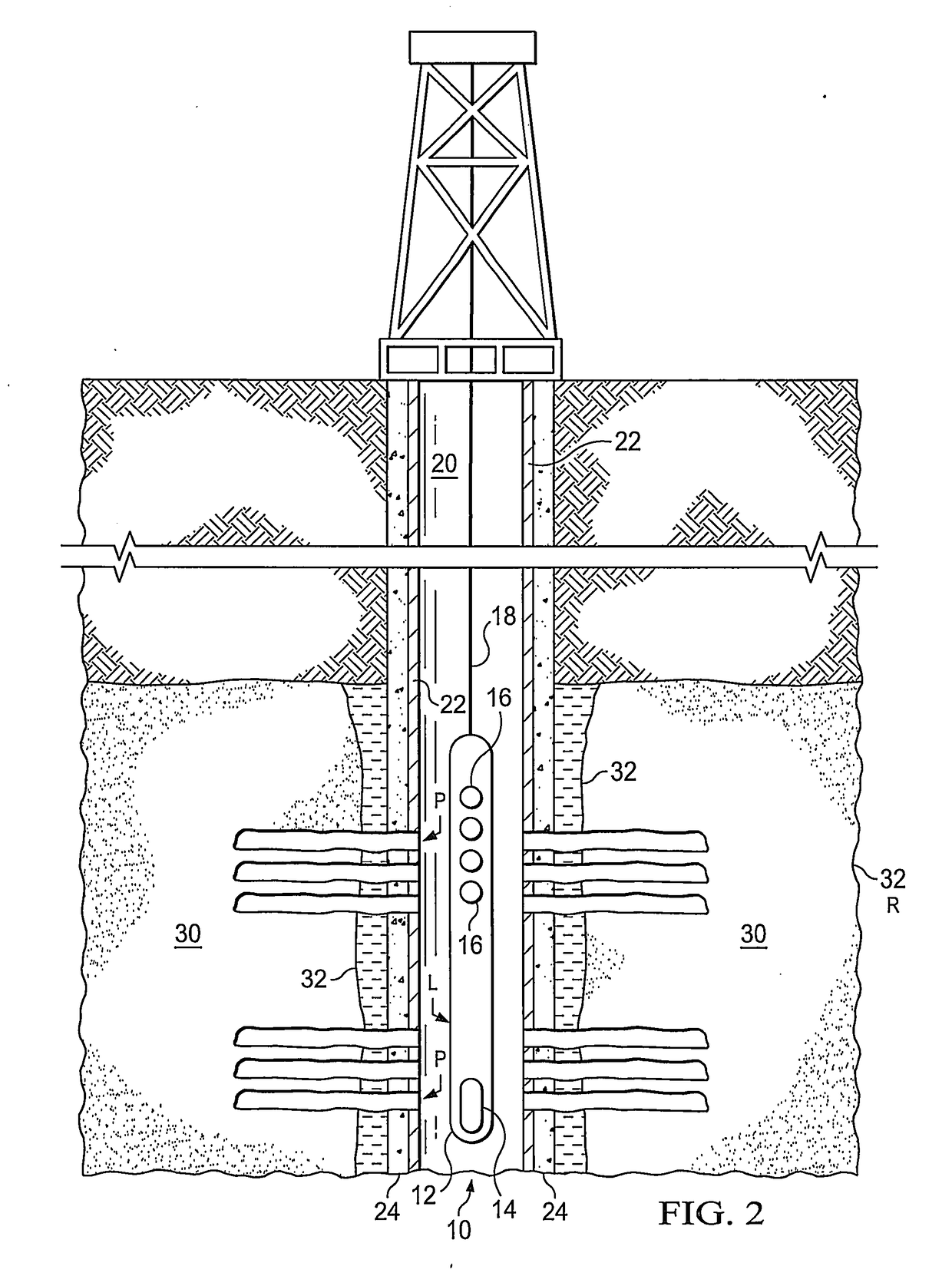
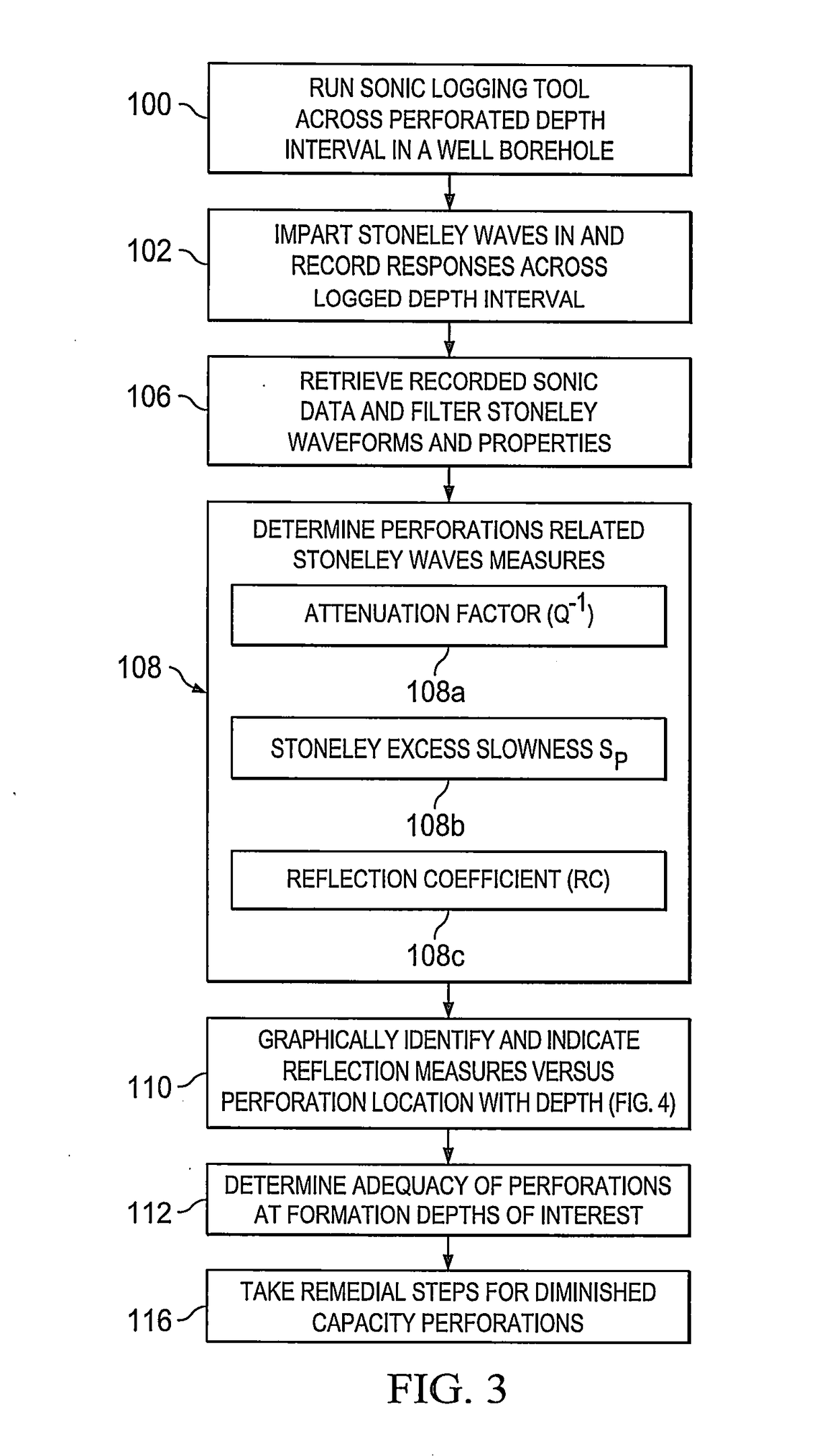
Production capability of cased hole perforations in a cased completed well lined with a casing in an under-pressured gas producing reservoir is tested. A sonde of a dipole shear or array sonic (full waveform) acoustic well logging tool is moved in a well bore of the cased completed well in the reservoir across a depth interval of interest, which covers cased hole perforations zones in the reservoir. The well logging sonde has in it an acoustic energy source and acoustic energy receivers. Responses are logged at depth intervals of interest to the transit of Stoneley waves along the casing walls from the acoustic energy source to the acoustic energy receivers. Measures of characteristics (e.g., travel time and attenuation) of the Stoneley wave are obtained. The responses are then processed to indicate production capability of the cased hole perforations.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Multi-layer board damage detection method based on Stoneley wave energy transfer characteristic
InactiveCN105116052AImproving Damage Detection EfficiencyEasy to operateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEnergy transferEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-layer board damage detection method based on a Stoneley wave energy transfer characteristic. According to the method, on the basis that in a multi-layer composite board, energy transfer exists on joints of two interfaces of Stoneley waves, under the condition of different excitation frequencies, distributions of energy magnitudes of the joints of interfaces between plates are different, and when a suitable excitation frequency is selected, independent detection of damage on a specific interface of the multi-layer composite board or simultaneous detection of damage on two interfaces of the multi-layer composite board can be achieved. The detection method is suitable for multi-layer composite board interface damage detection such as damage detection of a three-layer board, it can be guaranteed that fault information of all interfaces is detailed and accurate, the detection capacity is greatly improved, and implementation is convenient, easy and reliable.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Radial Waves In A Borehole And Stoneley Waves For Measuring Formation Permeability And Electroacoustic Constant
ActiveUS20120095688A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisStoneley waveElectric field
A Stoneley wave is generated in a borehole in a saturated porous earth formation. Measurements are made of the velocity of motion of the formation and the fluid in the formation. The difference in the velocities is indicative of formation permeability. An additional measurement of the electric field at the borehole wall enables determination of the electroacoustic constant.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method of evaluating anisotropism of stratum by acoustic logging while drilling
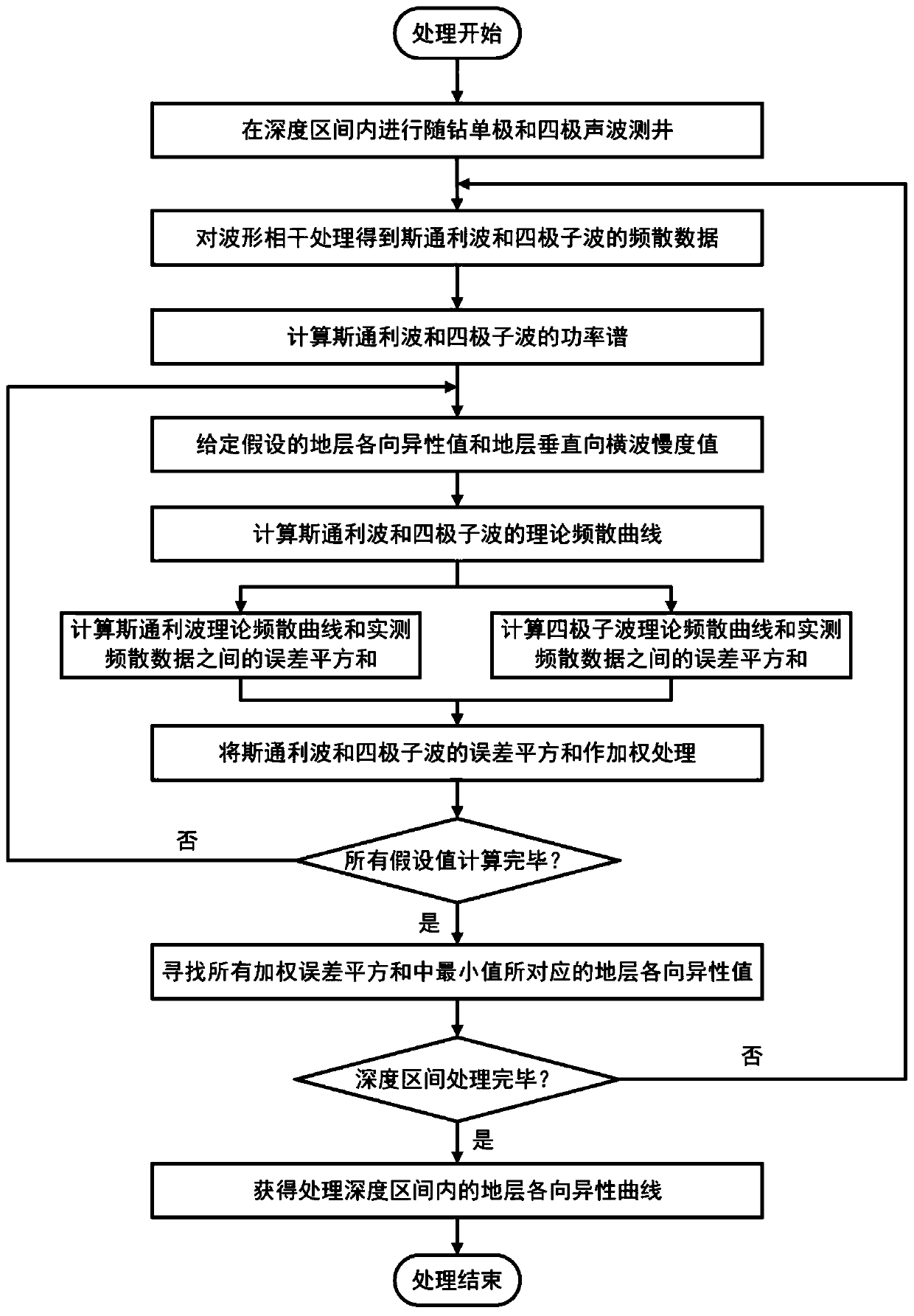
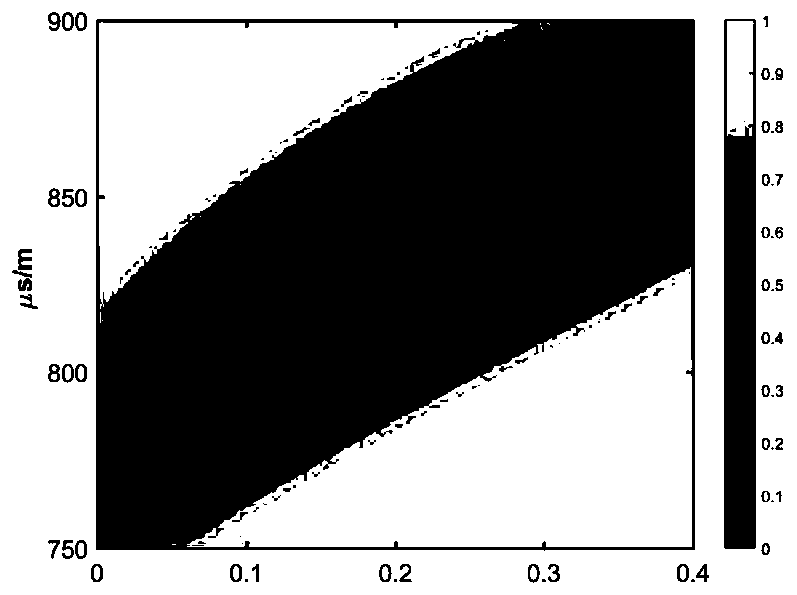
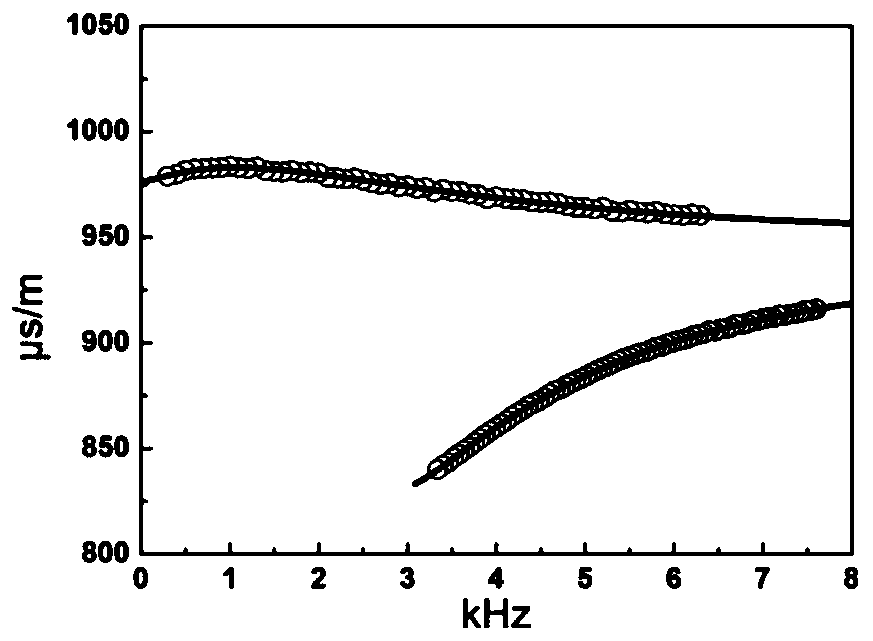
ActiveCN110318740AFully excavatedNo increase in on-site operating costsSurveyData processing applicationsFull waveAcoustic wave
The invention discloses a method of evaluating anisotropism of a stratum by acoustic logging while drilling. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring full acoustic wave array data in a depth interval and processing the data to obtain frequency dispersion data of stoneley waves while drilling and quadrupole waves and respective power spectra; separately calculating theoretical frequencydispersion curves of stoneley waves and quadrupole waves by means of an assumed anisotropic value of the stratum and a slowness value of transverse waves; in respective processing frequency bands, calculating the error sum of squares of the theoretical frequency dispersion curves relative to the actually measured frequency dispersion data by weighting the power spectra and weighting the result; repeating the steps till all assumed values are calculated, and searching for the anisotropic value corresponding to the minimum value in a target function; and repeating the steps till the whole depthinterval is processed to obtain the anisotropic curve of the stratum in the processed depth interval. As a result of instantaneity of measurement while drilling, the processing result is truer and more accurate. The method suppresses the nonuniqueness problem in an inversion process effectively, and the inversion precision is relatively high.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
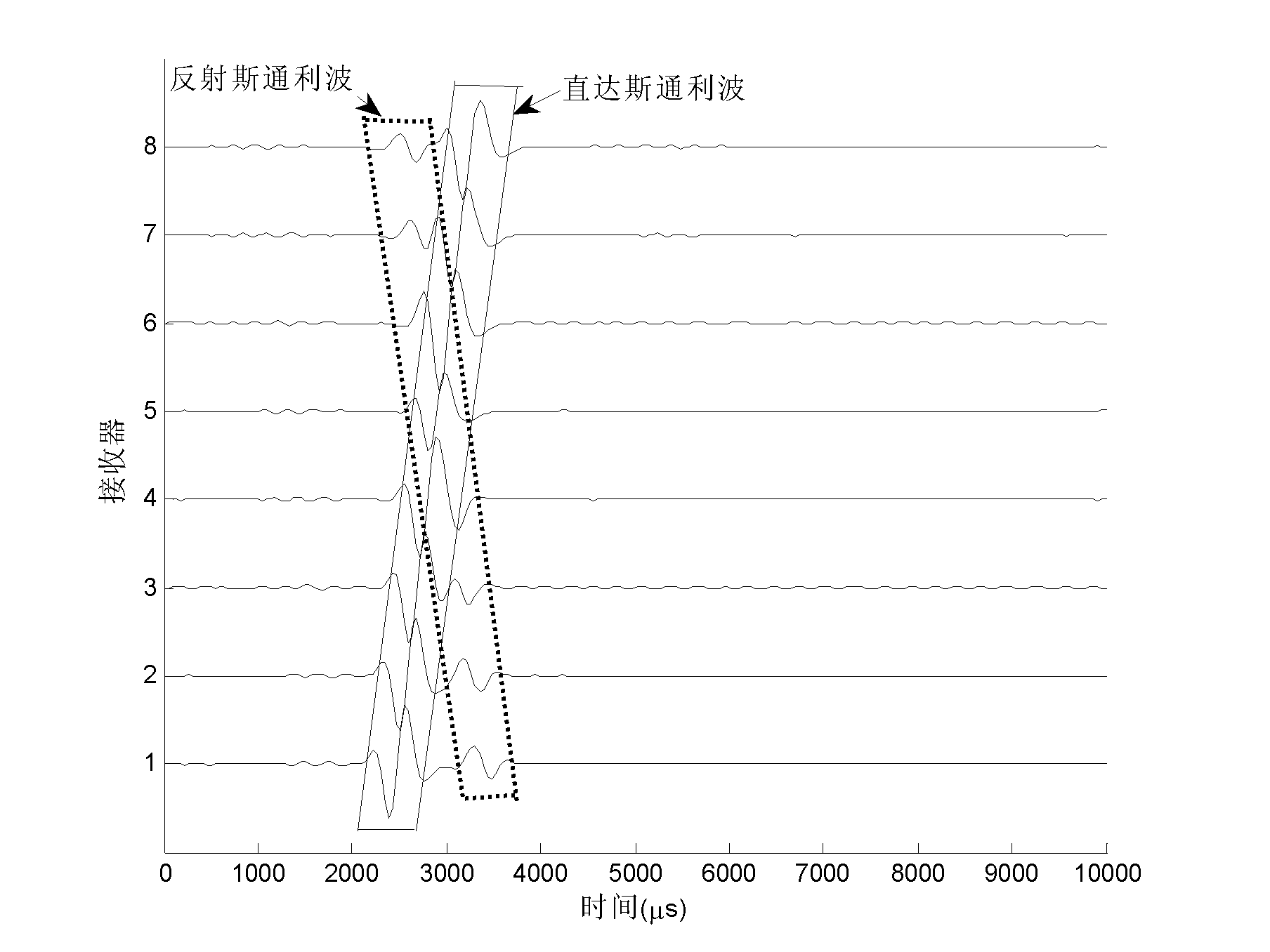
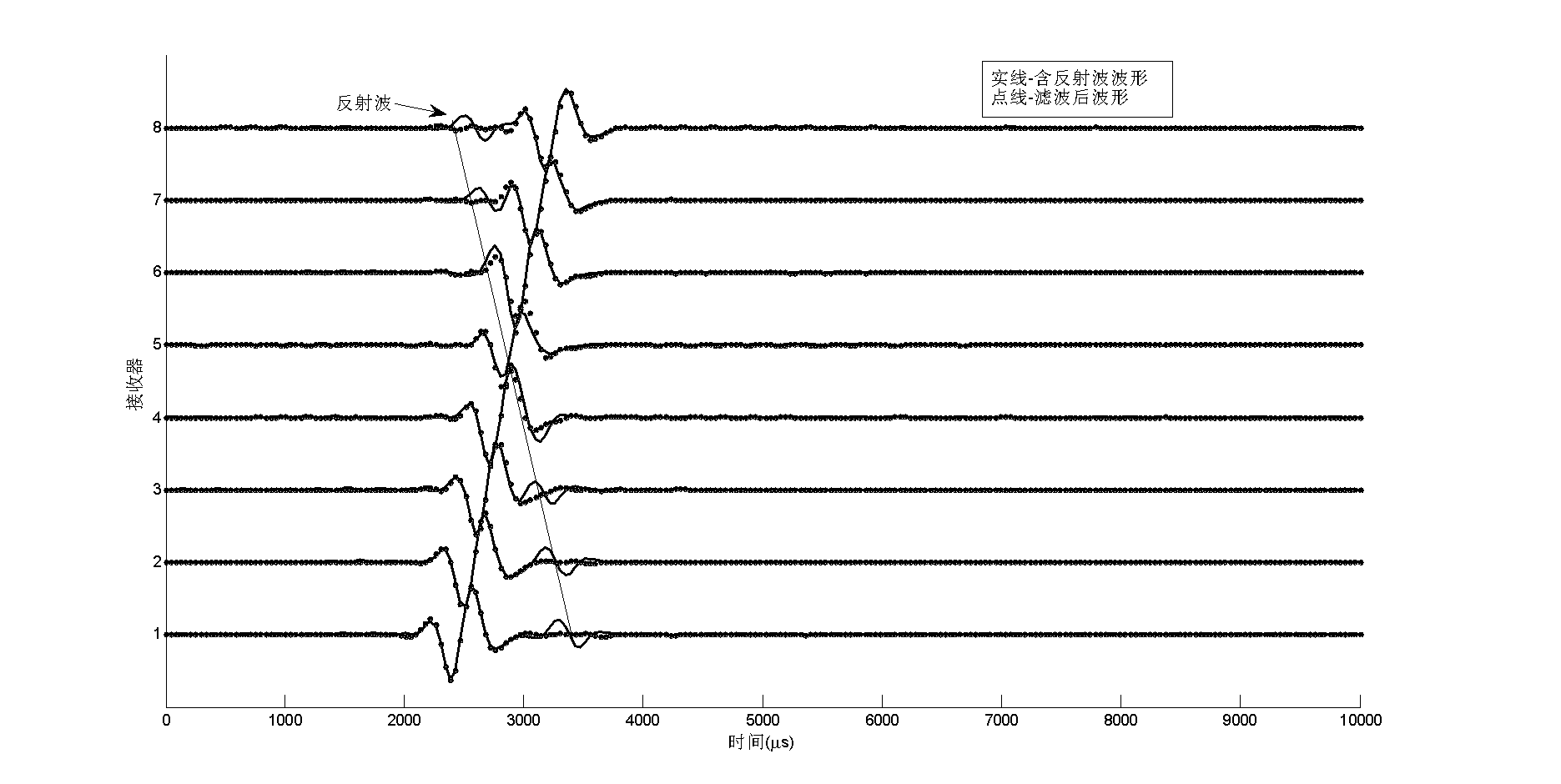
Slowness measurement method for stoneley wave of well hole
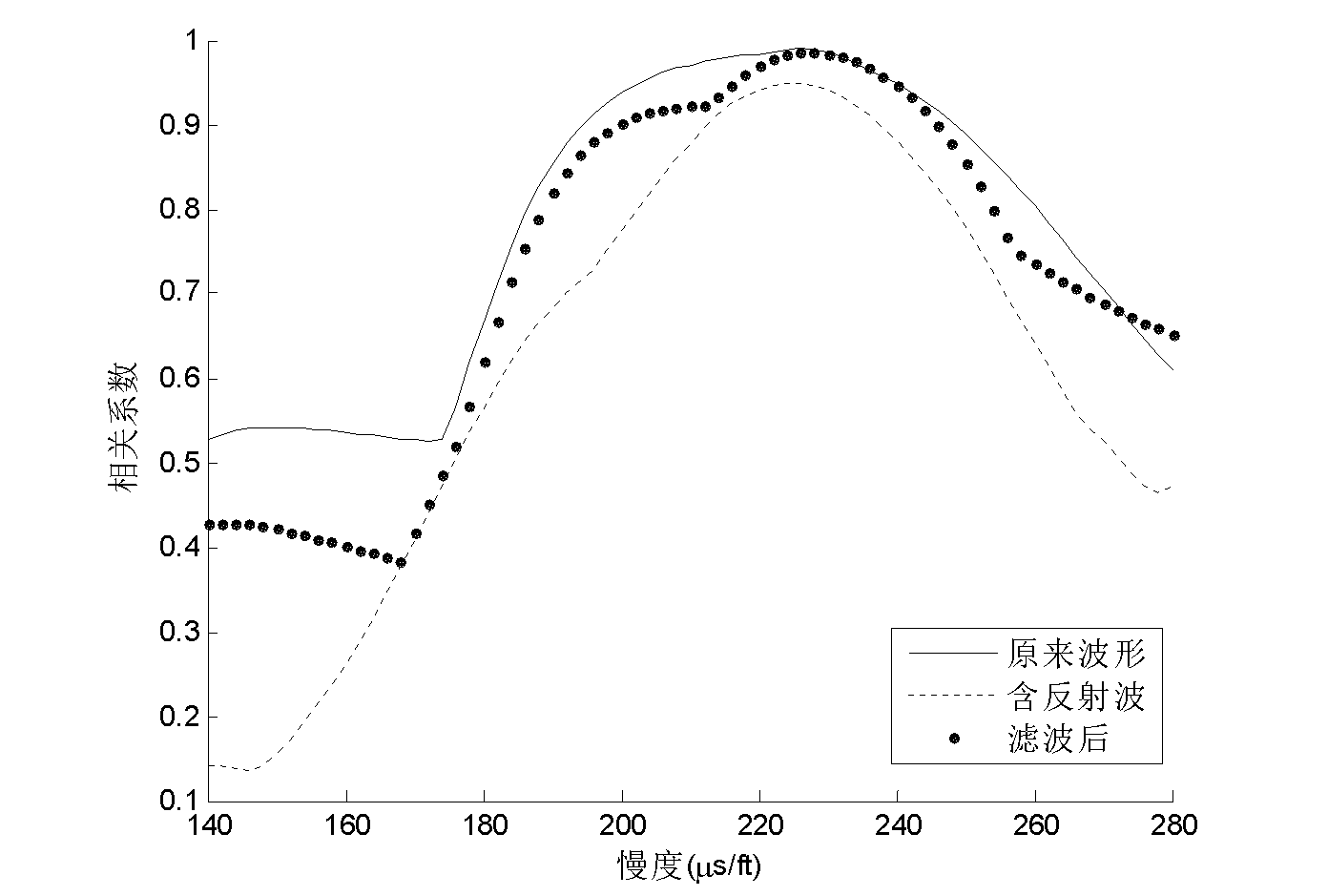
InactiveCN103852798AEliminate reflectionsHigh precisionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementGravitational wave measurementObservational errorWave shape
This invention discloses a slowness measurement method for stoneley waves of well holes. In a monopole acoustic logging instrument, the reflection phenomenon of the stoneley wave is very obvious because of the size change of the well hole and the parameter change of the crack and the stratum. Theses reflection waves are influences for the extraction of the slowness of the stoneley waves, and thus relative big errors could be caused. This slowness measurement method for stoneley waves of well holes performs wave filtration on array wave shape so as to eliminate reflection stoneley wave, reduce slowness measurement errors and improve measurement precision.
Owner:CNPC GREATWALL DRILLING ENG
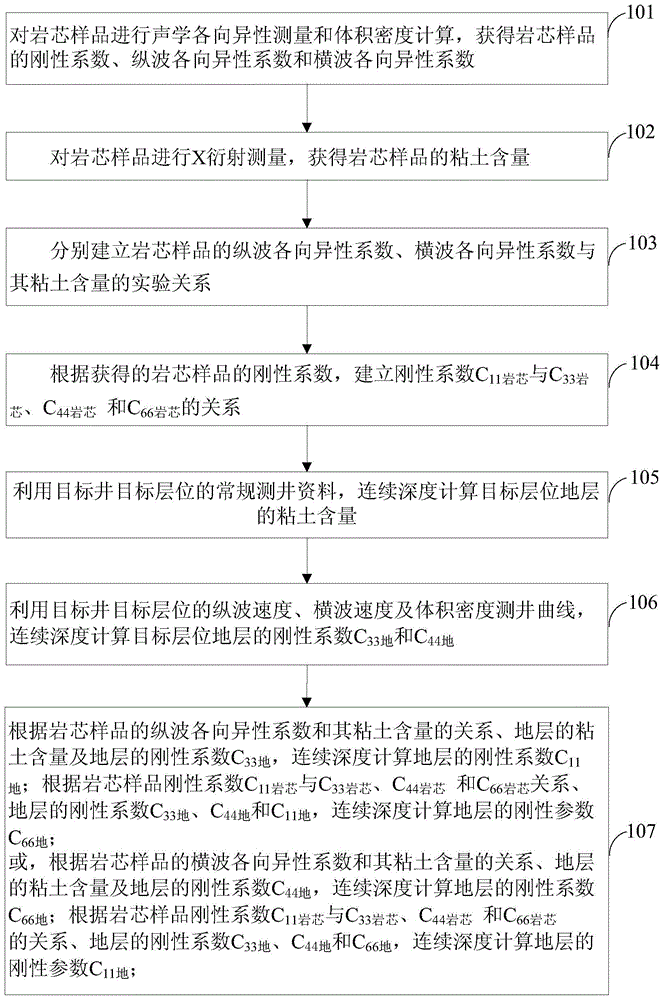
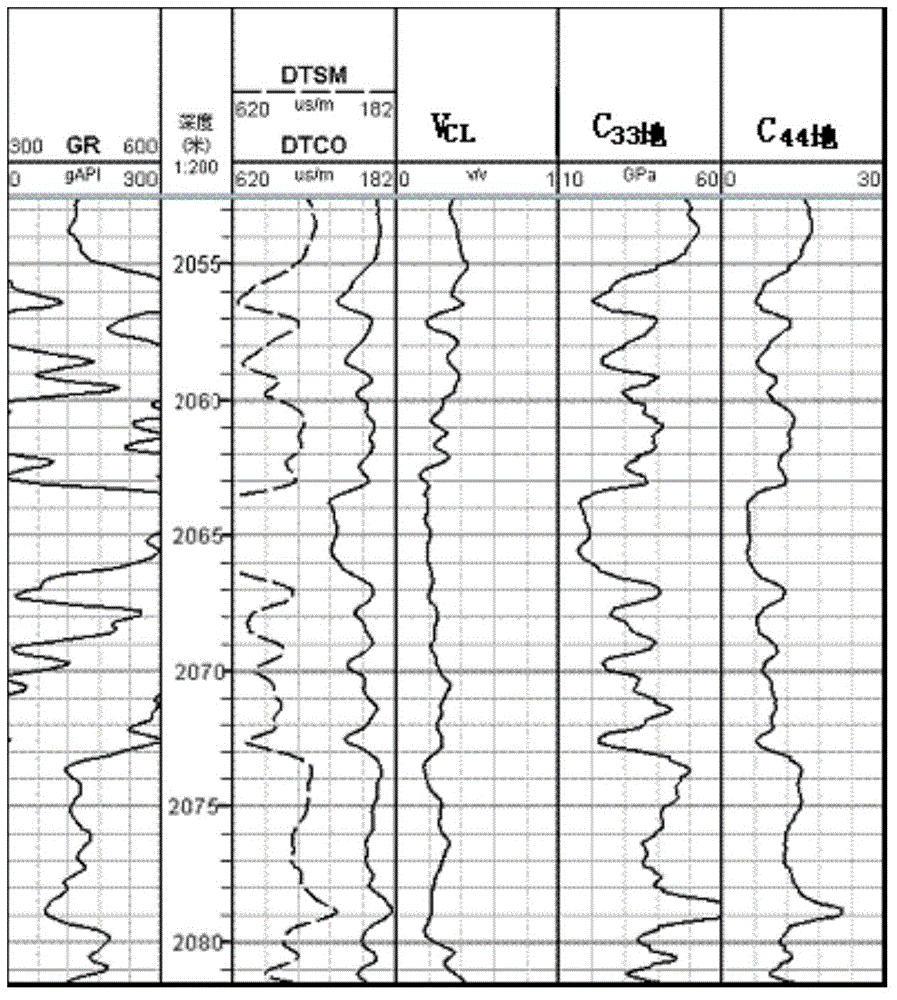
Novel calculating method for rigidity coefficient of stratum
ActiveCN104484573ACalculation is simple and efficientSeismology for water-loggingSpecial data processing applicationsWell loggingEngineering
The invention provides a novel calculating method for the rigidity coefficient of a stratum. The method comprises the following steps: performing acoustic anisotropy measurement and volume density calculation on rock core samples to obtain a stiffness coefficient and a longitudinal wave anisotropy coefficient; performing X-diffraction measurement on the rock core samples to obtain clay content; building a relation between the longitudinal wave anisotropy coefficient and the clay content; building relations between a C11 rock core and a C33 rock core as well as between a C44 rock core and a C66 rock core; calculating the clay content by using conventional logging data of a target level of a target well; calculating the rigidity coefficients of C33 ground and C44 ground of the stratum by using the longitudinal and shear wave velocities and a volume density logging curve of the target level of the target well; calculating the rigidity coefficient C11 ground of the stratum according to the relation between the longitudinal wave anisotropy coefficient and the clay content, the clay content of the stratum and the rigidity C33 ground of the stratum; calculating the rigidity coefficient C66 ground of the stratum according to the relations between the C11 rock core and the C33 rock core as well as between the C44 rock core and the C66 rock core, the C33 ground, the C44 ground and the C11 ground. By adopting the novel calculating method, the rigidity coefficient can be calculated without utilizing a horizontal shear wave velocity obtained by performing reverse calculation on extracted stoneley waves, the extracting process of horizontal shear waves is avoided, and the calculation is easy, convenient and efficient.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for determining properties of a formation
InactiveUS20120327743A1Detection/prospecting using thermal methodsSeismic signal processingUltrasound attenuationActivation energy
A method for determining properties of a formation comprises disposing at least one acoustic logging tool in a well and moving the logging tool along the well. An acoustic logging is performed during movement of the acoustic logging tool together with simultaneous thermal treatment of the formation. A temperature of a formation zone being thermally treated is measured as well as attenuation and velocity of the Stoneley waves excited by the acoustic logging tool. Based on the obtained dependencies of measured parameters as functions of the formation zone temperature formation relative phase permeabilities, formation fluid viscosity and viscous flow activation energy are determined.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for distinguishing effectiveness of reservoir bed through stoneley wave energy loss degree
InactiveCN104314558AImprove effectivenessAvoid cumbersome stepsBorehole/well accessoriesPorosityAcoustic wave
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing the effectiveness of a reservoir bed through stoneley wave energy loss degree. The method comprises the steps of regarding stoneley wave energy extracted from array acoustic logging information as comprehensive response of stoneley wave energy of stratum rock and stoneley wave energy loss degree in pores, establishing a relational expression between the stoneley wave energy and porosity, working out the stoneley wave energy loss degree in pores, and distinguishing the effectiveness of the reservoir bed according to the stoneley wave energy loss degree. The method not only takes the stoneley wave energy of the stratum rocks into account, but also establishes the relational expression between the stoneley wave energy and the porosity, can work out the loss degree of the stoneley wave energy in the pores of the reservoir bed according to the relational expression, and further distinguishes the effectiveness of the reservoir bed.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD
Evaluation of cased hole perforations in under-pressured gas sand reservoirs with stoneley wave logging
Production capability of cased hole perforations in a cased completed well lined with a casing in an under-pressured gas producing reservoir is tested. A sonde of a dipole shear or array sonic (full waveform) acoustic well logging tool is moved in a well bore of the cased completed well in the reservoir across a depth interval of interest, which covers cased hole perforations zones in the reservoir. The well logging sonde has in it an acoustic energy source and acoustic energy receivers. Responses are logged at depth intervals of interest to the transit of Stoneley waves along the casing walls from the acoustic energy source to the acoustic energy receivers. Measures of characteristics (e.g., travel time and attenuation) of the Stoneley wave are obtained. The responses are then processed to indicate production capability of the cased hole perforations.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Method for determining properties of a formation
InactiveUS9013954B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection/prospecting using thermal methodsUltrasound attenuationActivation energy
A method for determining properties of a formation comprises disposing at least one acoustic logging tool in a well and moving the logging tool along the well. An acoustic logging is performed during movement of the acoustic logging tool together with simultaneous thermal treatment of the formation. A temperature of a formation zone being thermally treated is measured as well as attenuation and velocity of the Stoneley waves excited by the acoustic logging tool. Based on the obtained dependencies of measured parameters as functions of the formation zone temperature formation relative phase permeabilities, formation fluid viscosity and viscous flow activation energy are determined.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
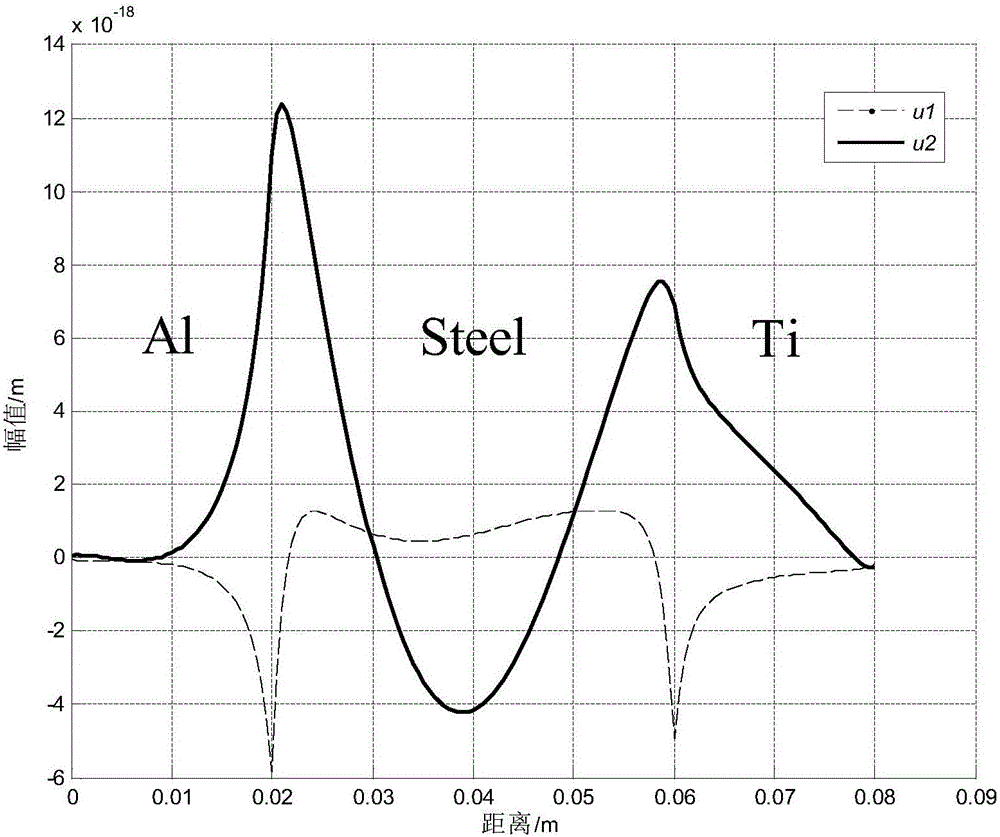
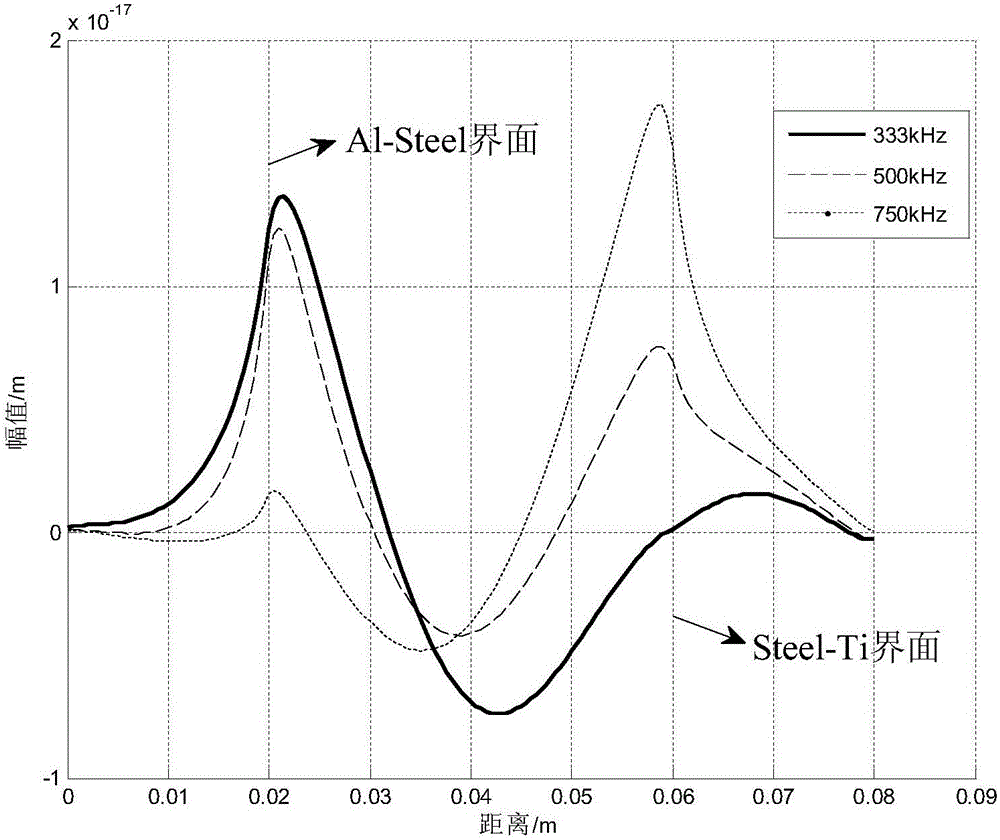
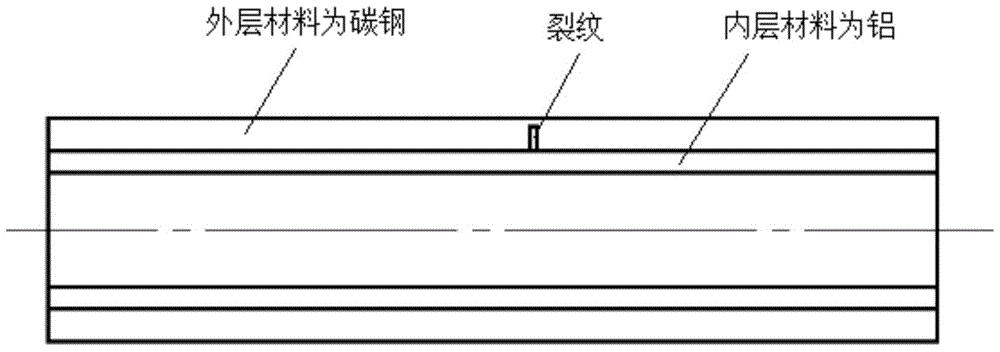
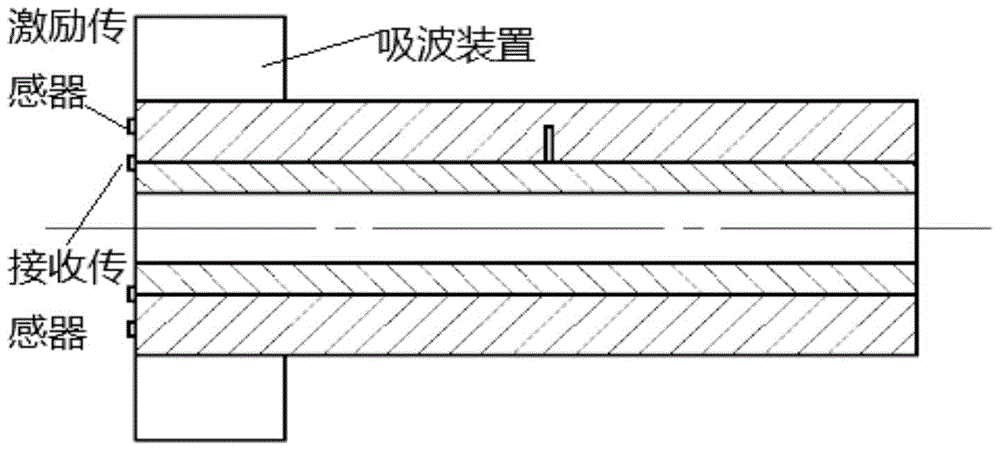
A method for detecting transverse cracks between layers of carbon steel/aluminum explosive composite pipe
InactiveCN104359979BThere is no dispersion phenomenonSuitable for solving interface problemsMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesSignal wavePropagation time
The invention discloses a method for detecting interlamination transverse cracks of a carbon steel / aluminum explosion composite pipe. The method comprises the following steps: exciting to generate and receive guided wave signals at an end surface of the carbon steel / aluminum explosion composite pipe by using Stoneley ultrasonic interface guided waves suitable for analyzing interface problems; then analyzing excitation signals and a plurality of received signal waves, and realizing positioning of interlamination cracks according to a propagation time difference method by using the characteristic that Stoneley waves do not have frequency dispersion; and obtaining an amplitude ratio by using excitation signal amplitude and reflected signal amplitude, changing the excitation frequency for a plurality of times to obtain a plurality of signal amplitude ratio numerical values corresponding to different frequencies, and drawing a relation curve of the signal amplitude ratio and wavelength, wherein the wavelength of the Stoneley waves corresponding to a turning point from a slowly decreasing zone to a quickly decreasing zone of the curve is a quantitative estimated value of the sizes of the interlamination transverse cracks. The detection method disclosed by the invention is reliable in result and simple and feasible to operate, and is suitable for parameter quantitative identification of the interlamination transverse cracks of the carbon steel / aluminum explosion composite pipe.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for detecting liquid level position based on surface wave mode conversion
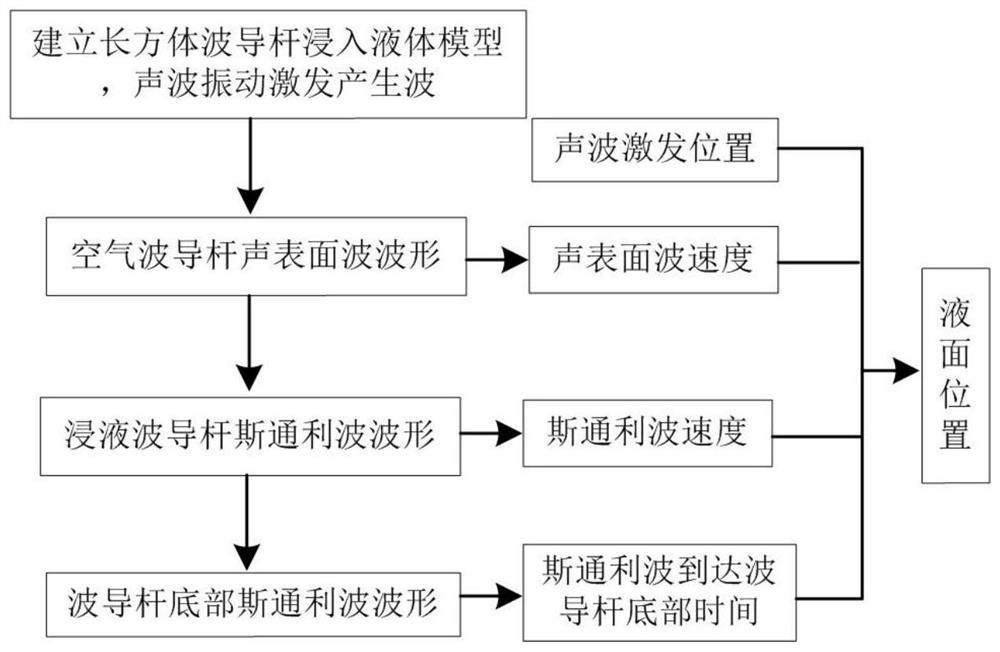
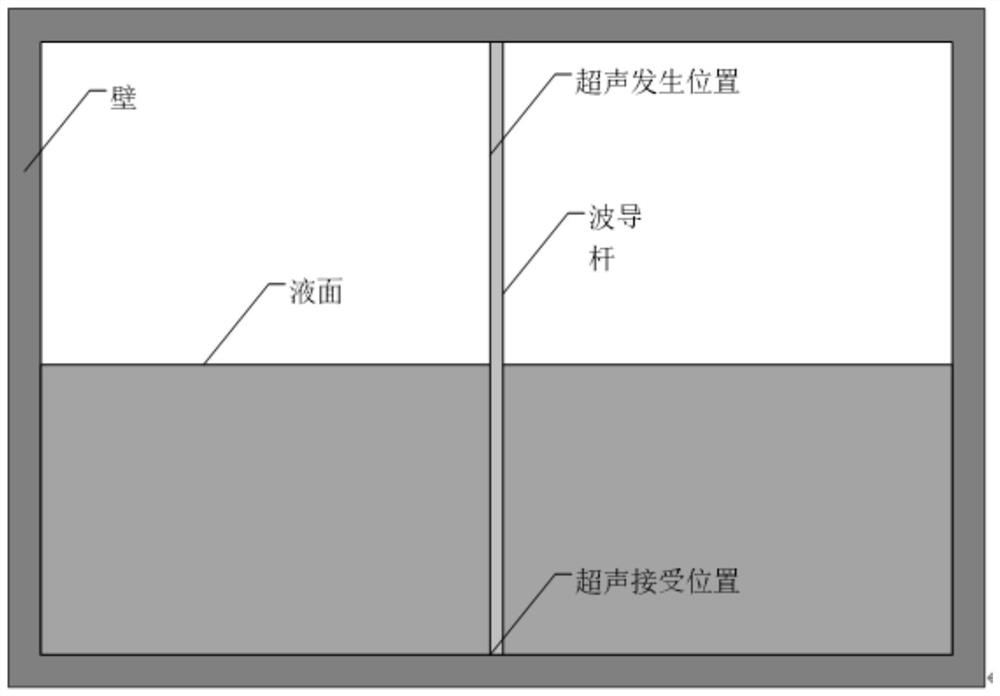
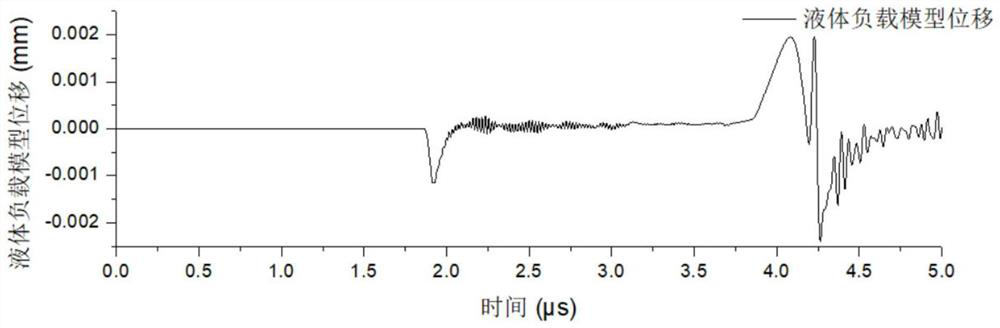
PendingCN113340380APrecise positioningFew measurement parametersMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsEngineeringUltrasonic vibration
The invention discloses a method for detecting a liquid level position based on surface wave mode conversion, and the method comprises the following steps: vertically inserting a cuboid waveguide rod into the bottom of liquid, and exciting a surface wave model on the surface of the waveguide rod by utilizing ultrasonic vibration; enabling the air waveguide rod and the immersion waveguide rod to receive the arrived sound waves; on the surface of the waveguide rod, acquiring the point displacement along the sound wave propagation path, and obtaining the surface acoustic wave speed in the air waveguide rod and the stoneley wave propagation speed in the immersion waveguide rod respectively; and determining the liquid level position according to the time when the stoneley wave reaches the bottom of the waveguide rod and the surface wave speed, the stoneley wave speed and the sound wave excitation position. The invention provides a reliable method for measuring the position of the liquid level, and provides a guidance basis for realizing online detection of the position of the liquid level.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com