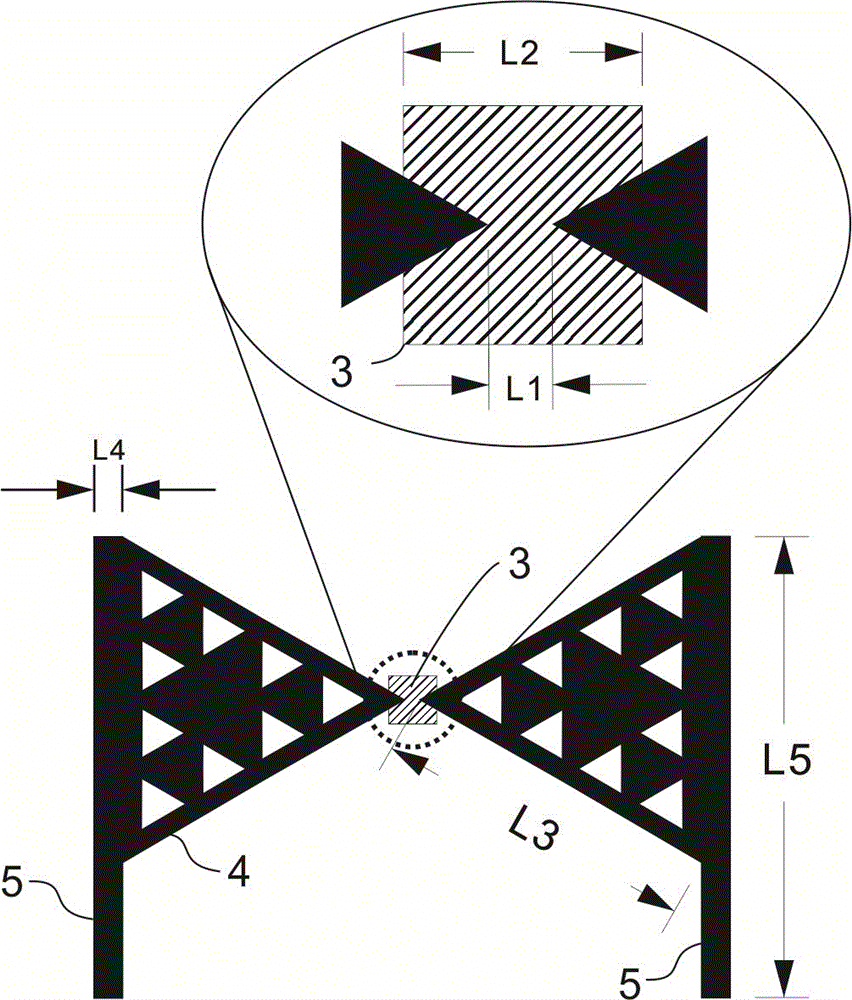
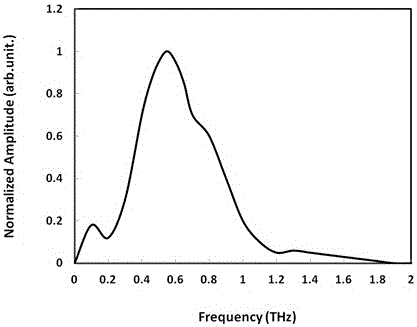
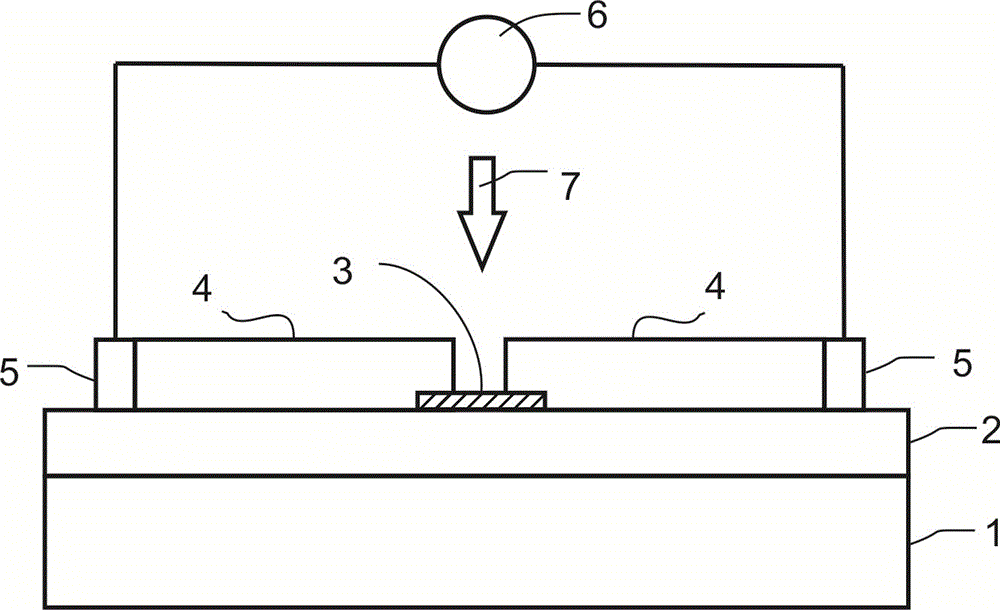
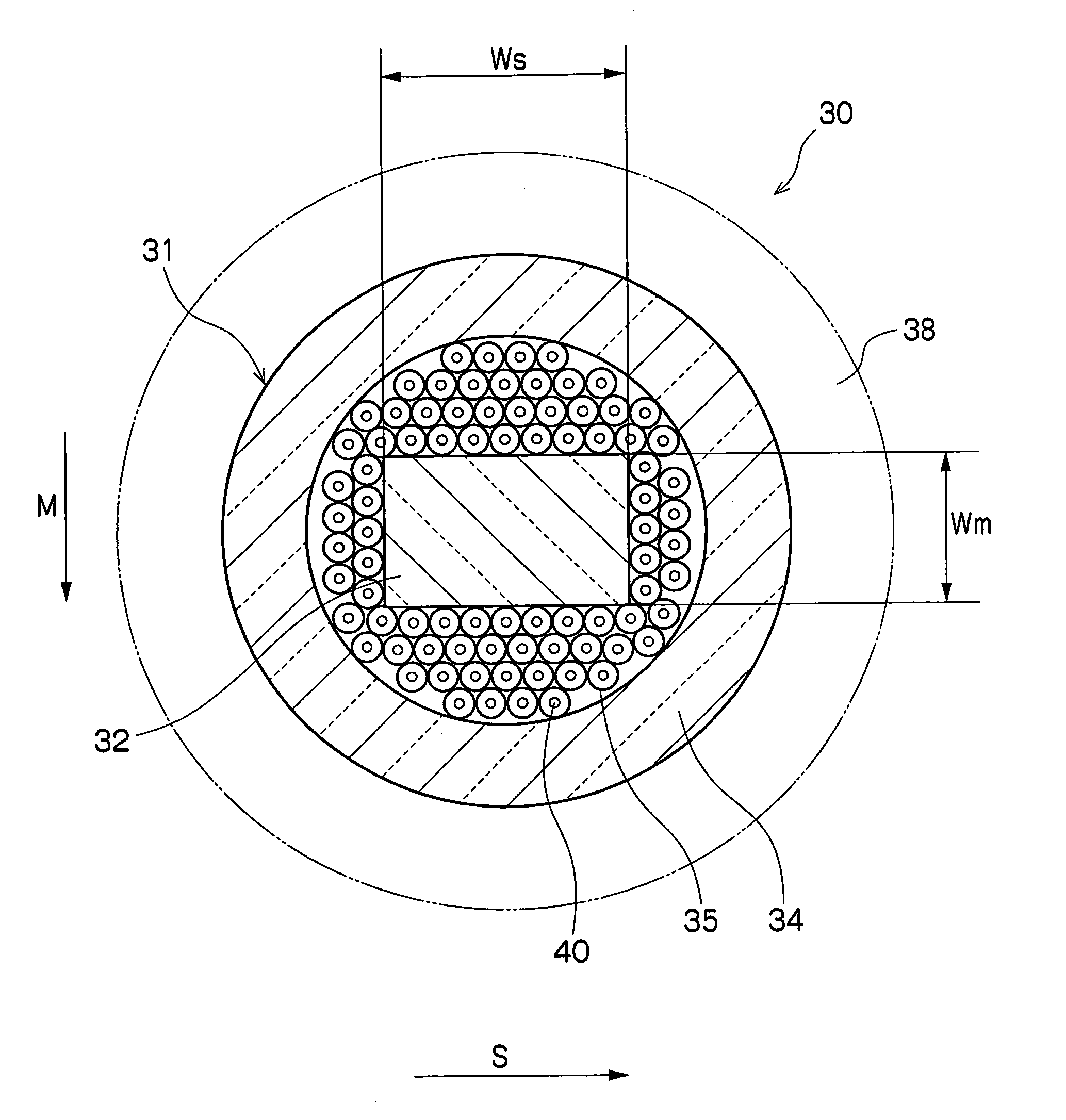
Patents
Literature
106results about How to "Small propagation loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
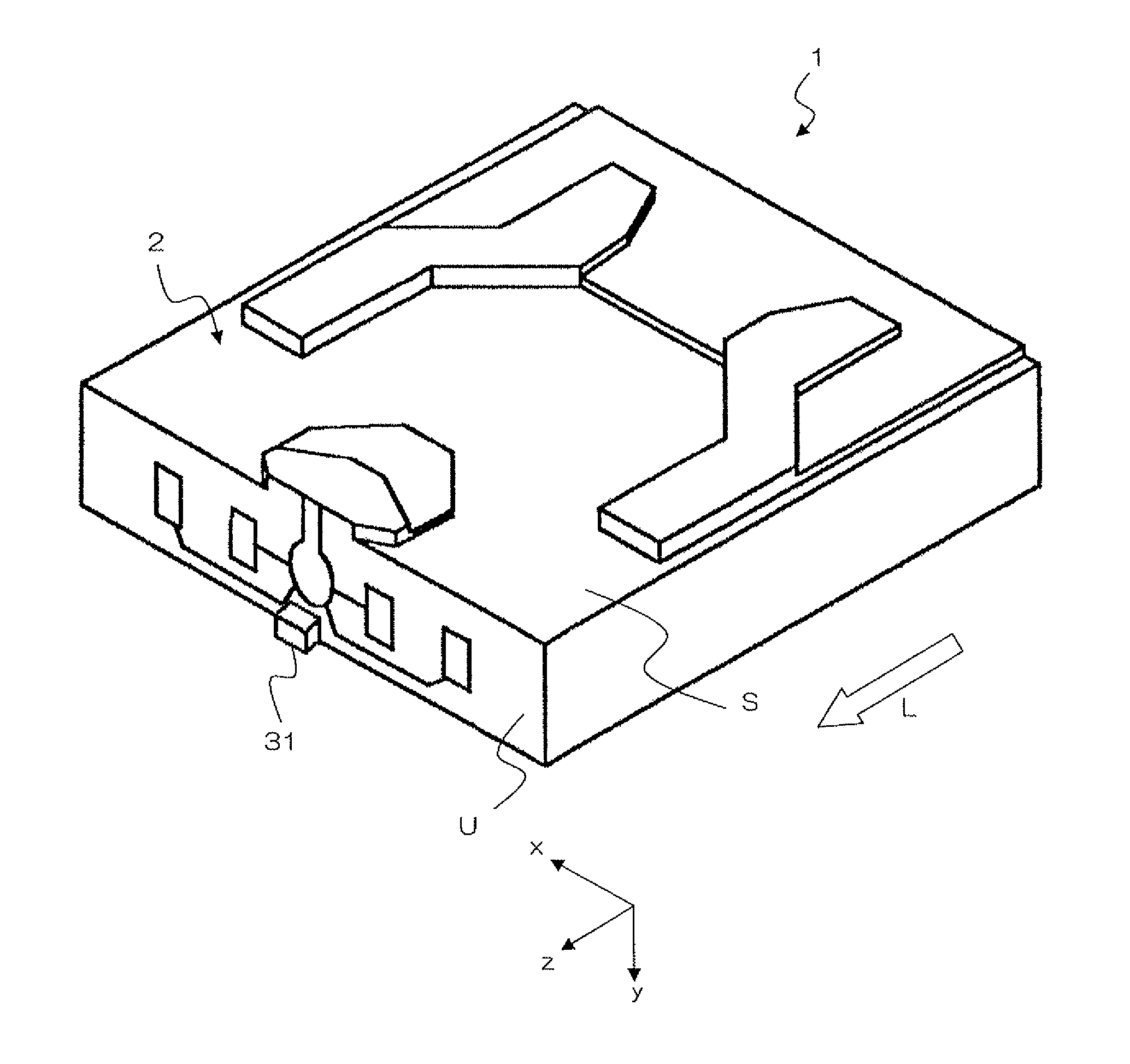
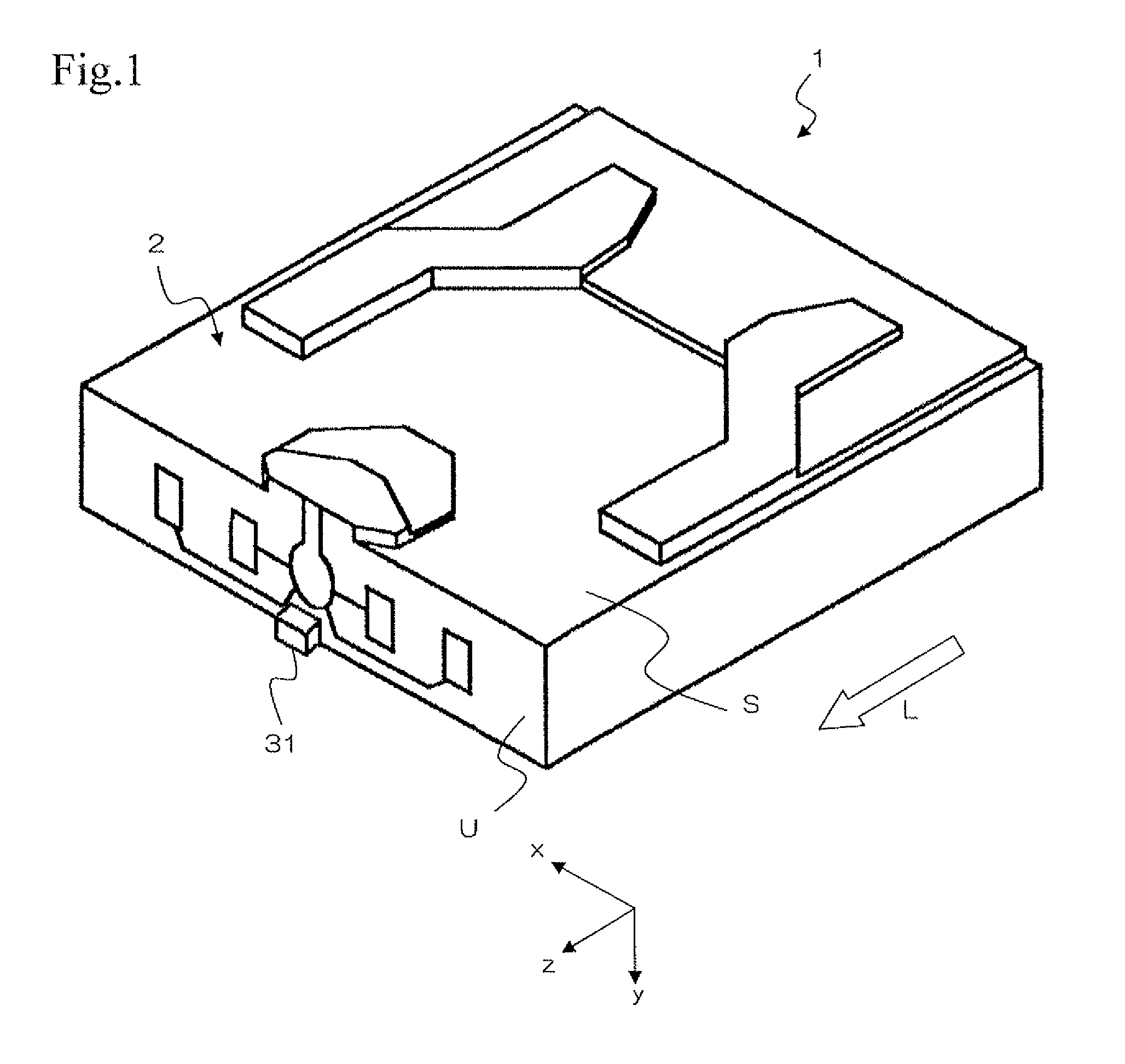
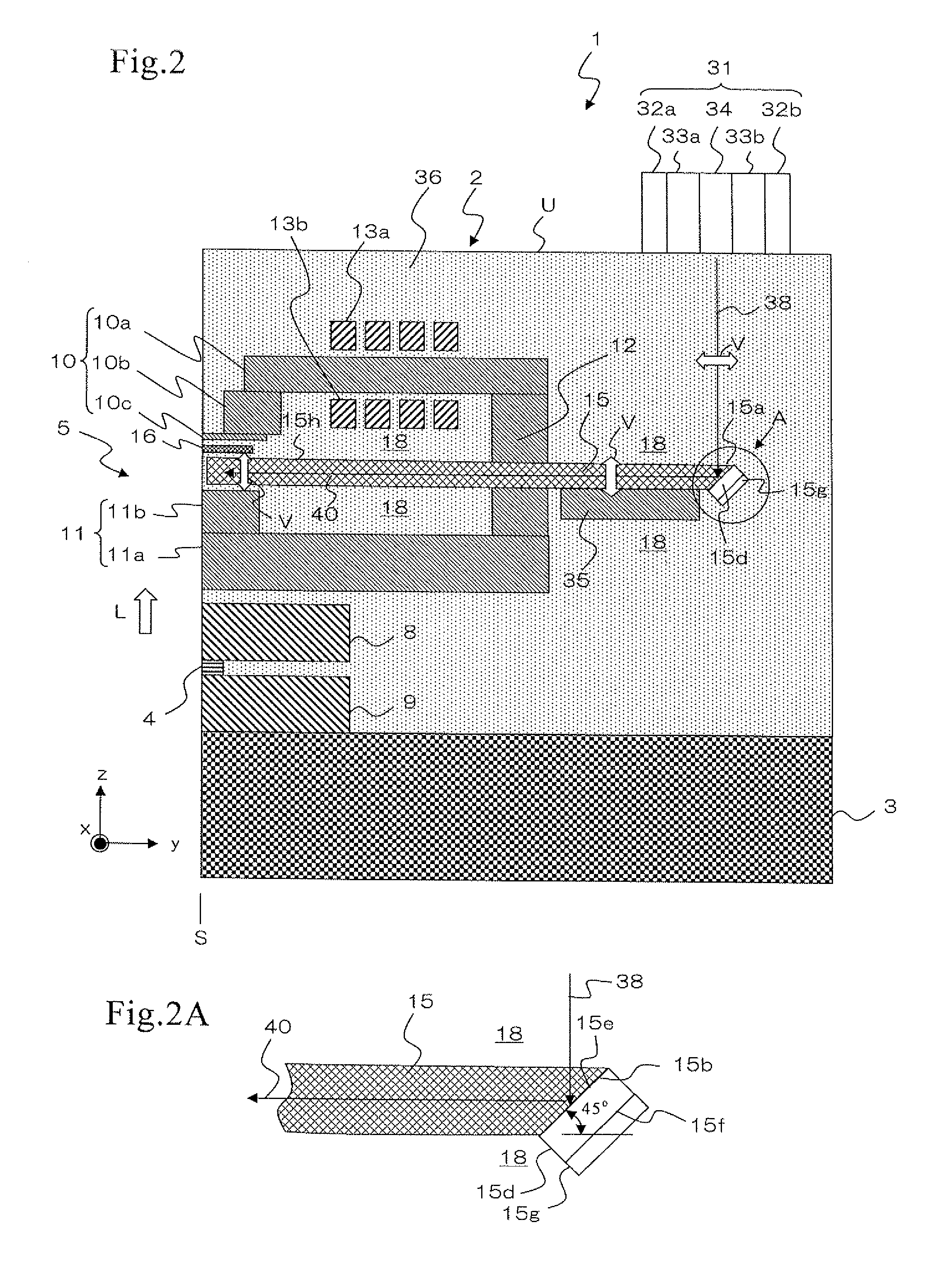
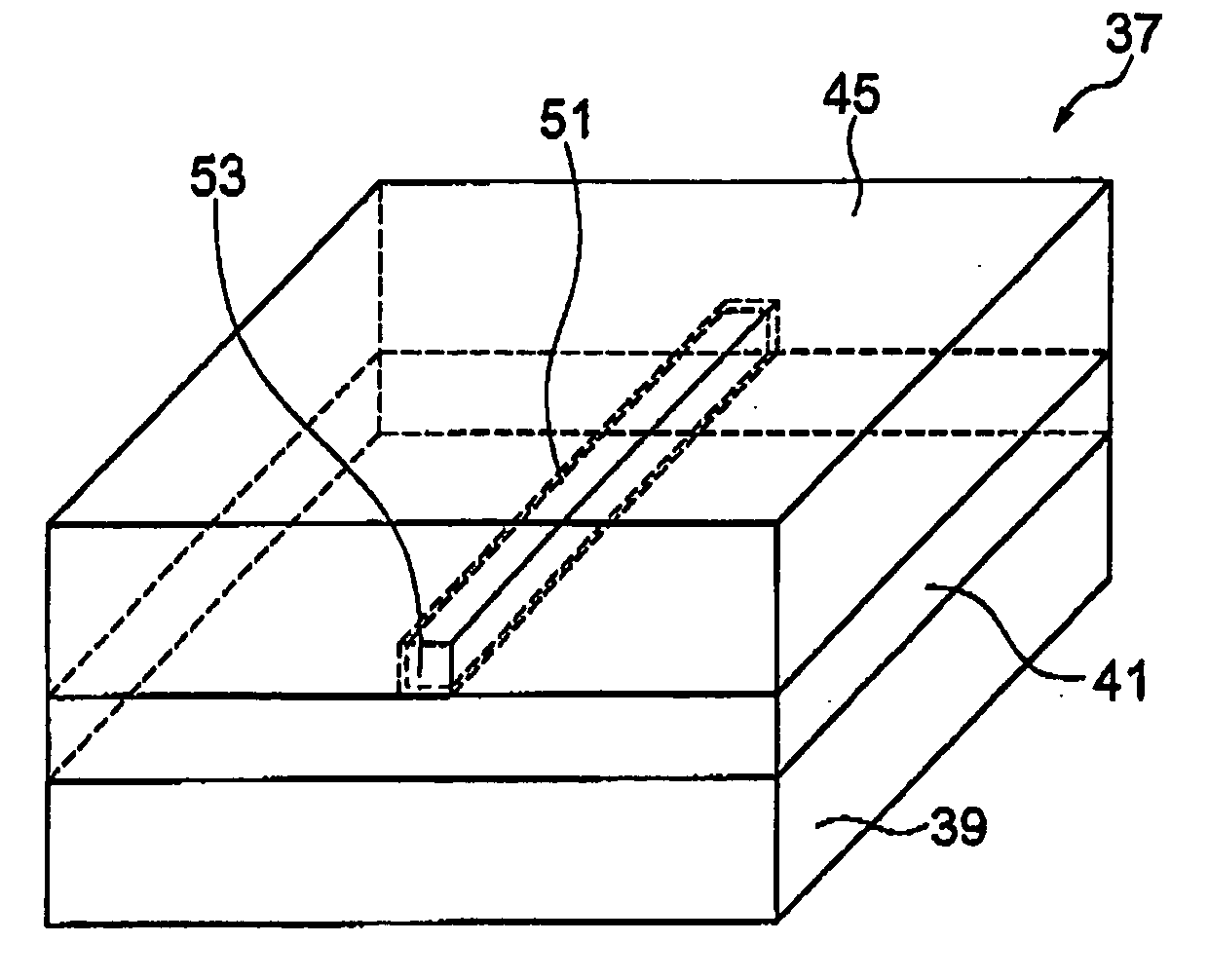
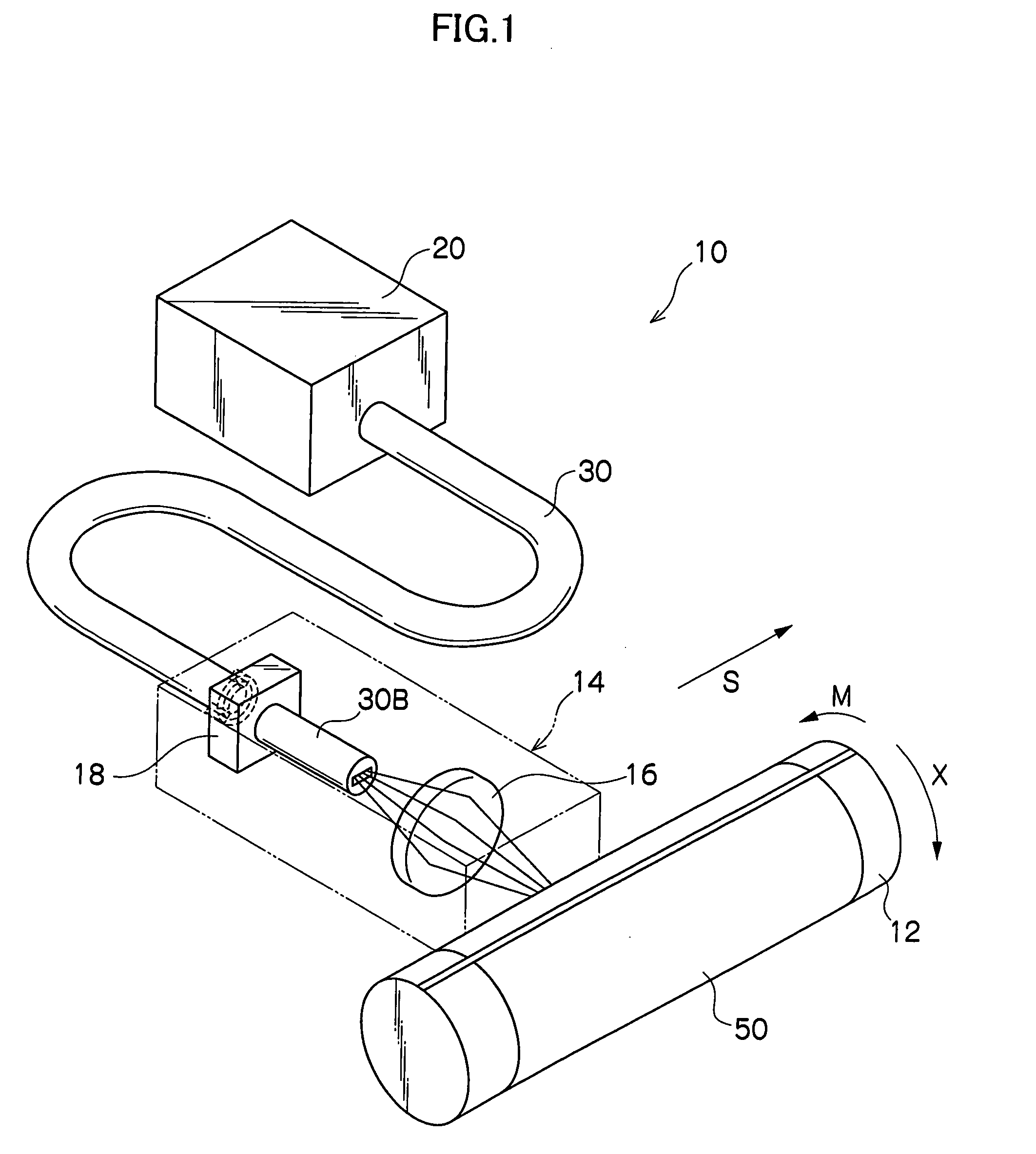
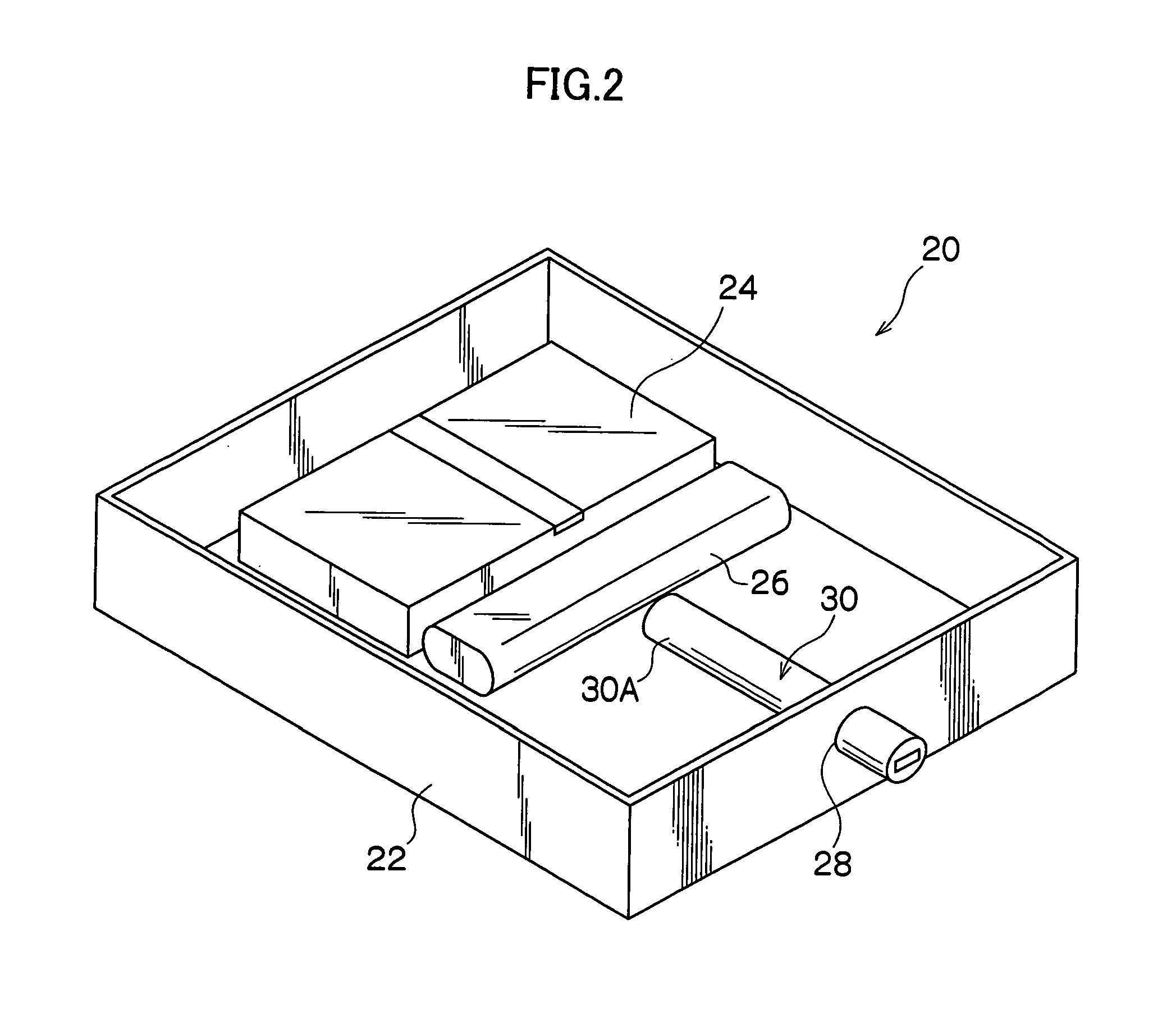
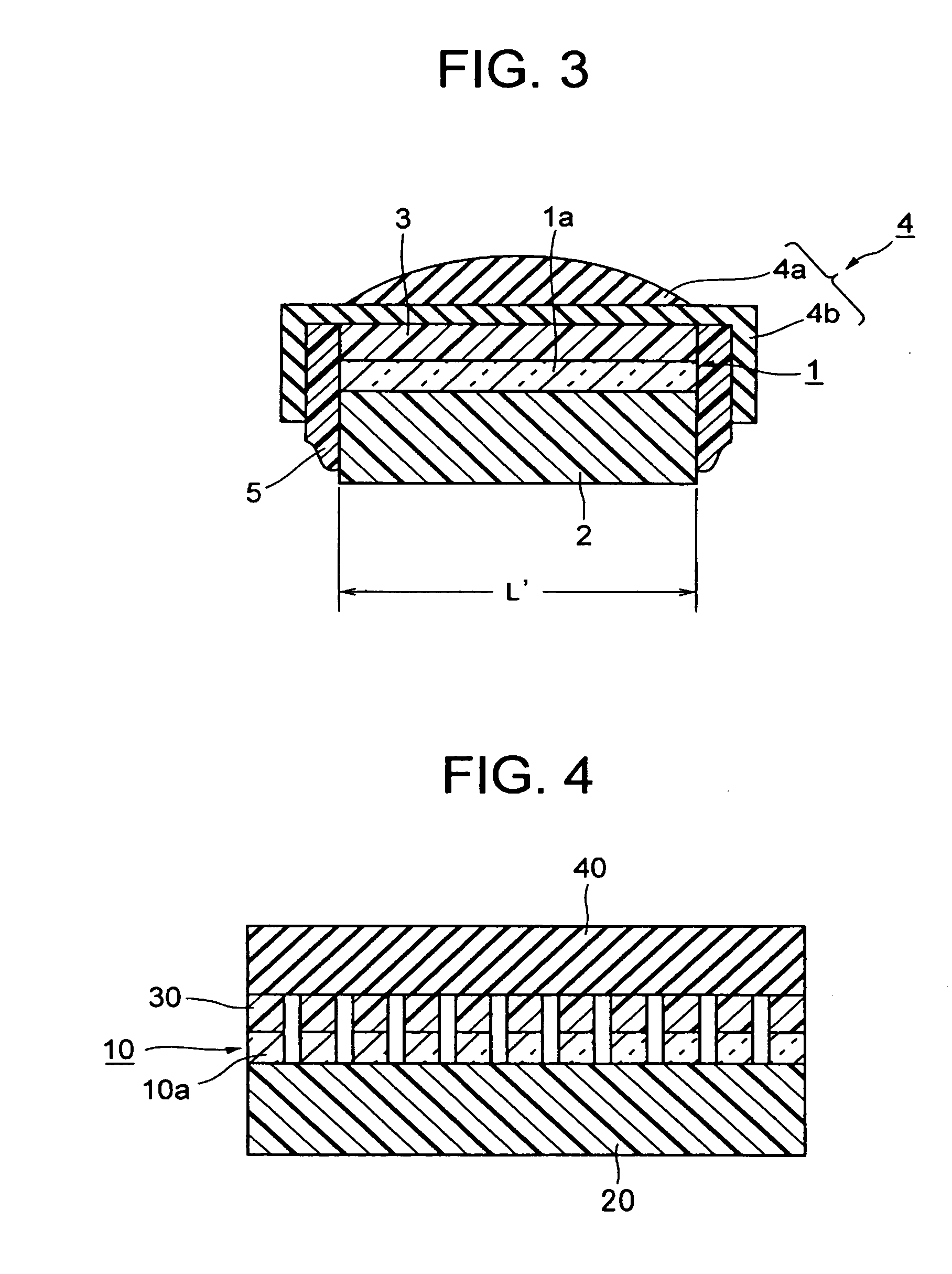
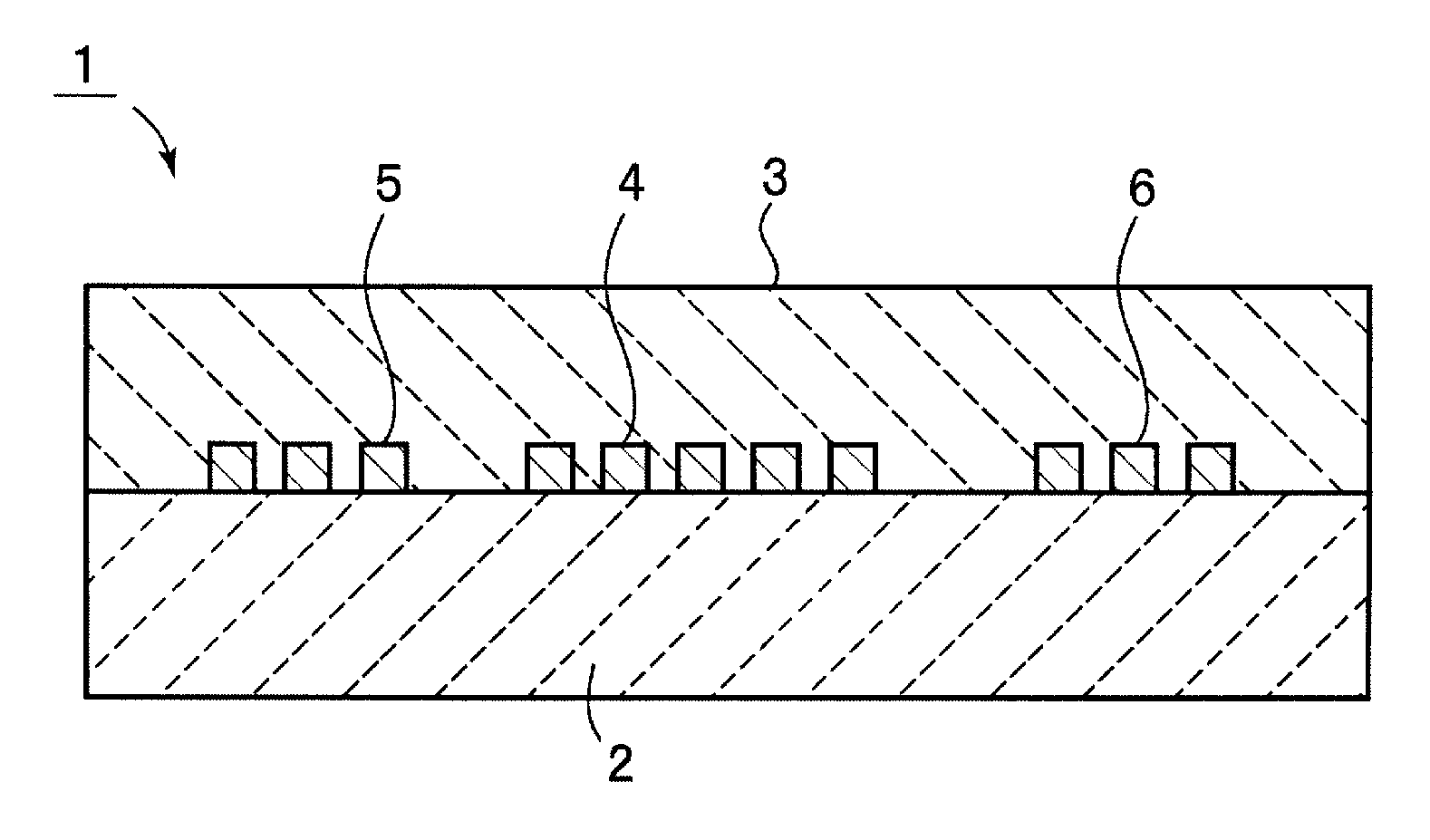
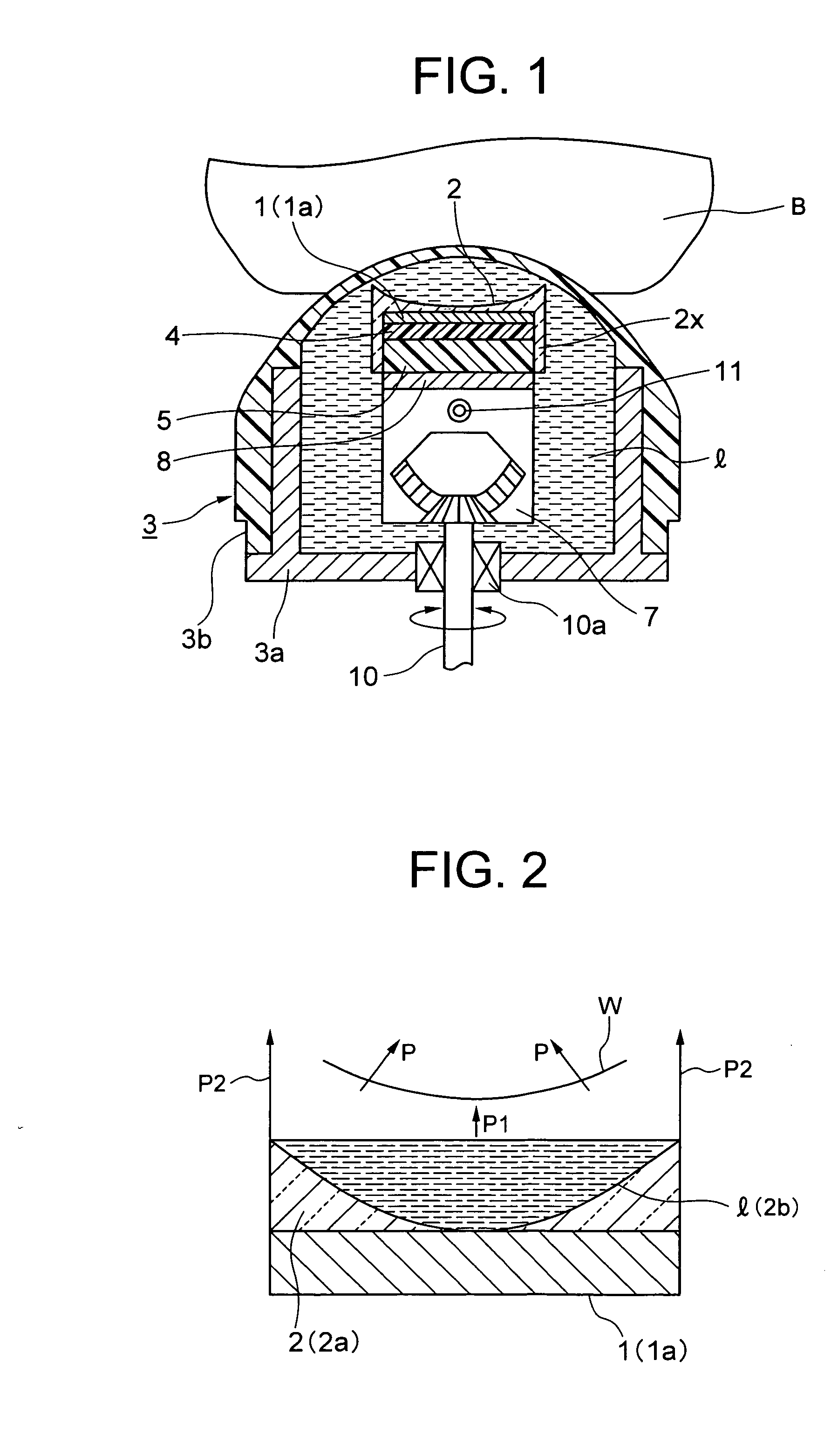
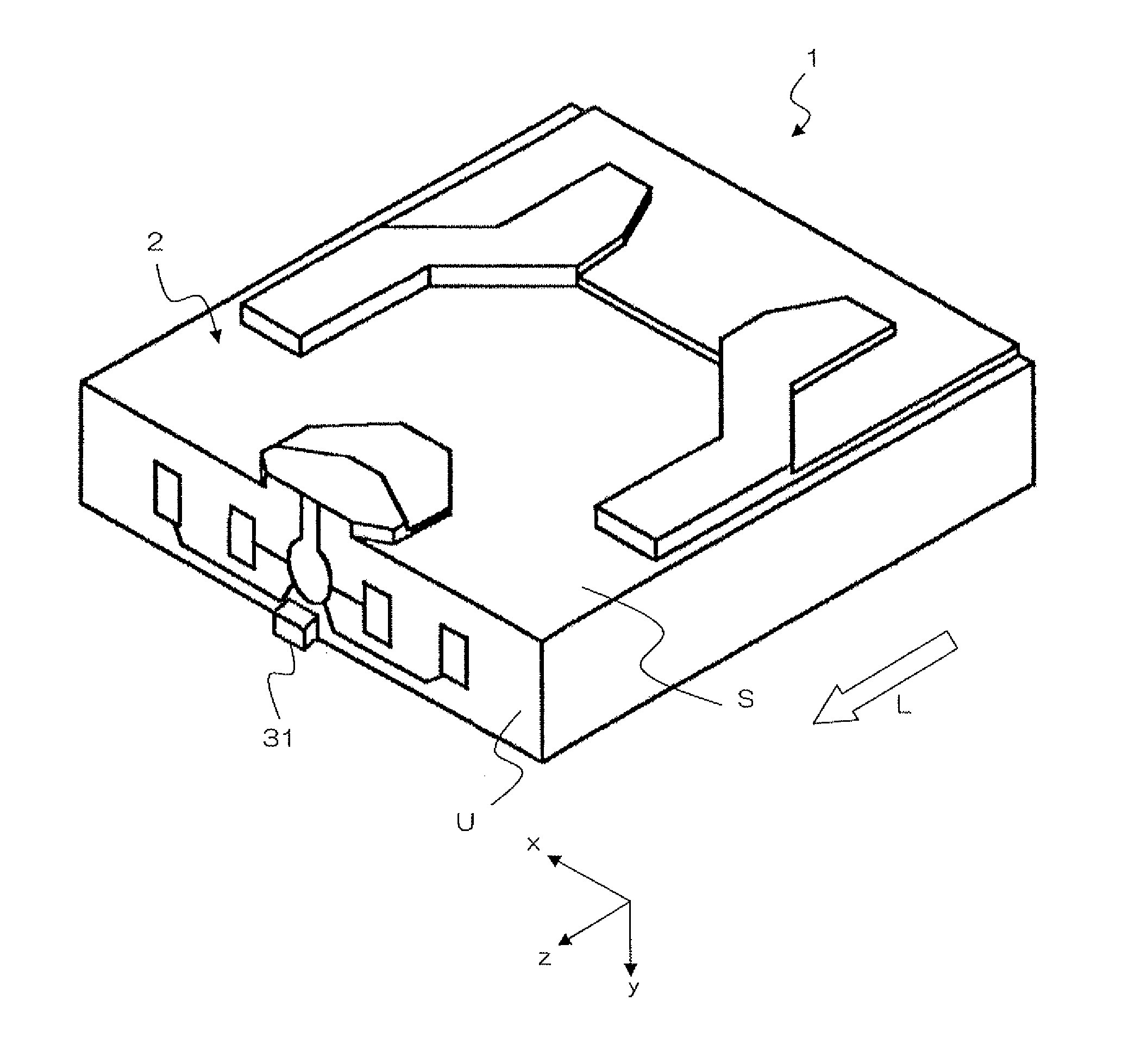
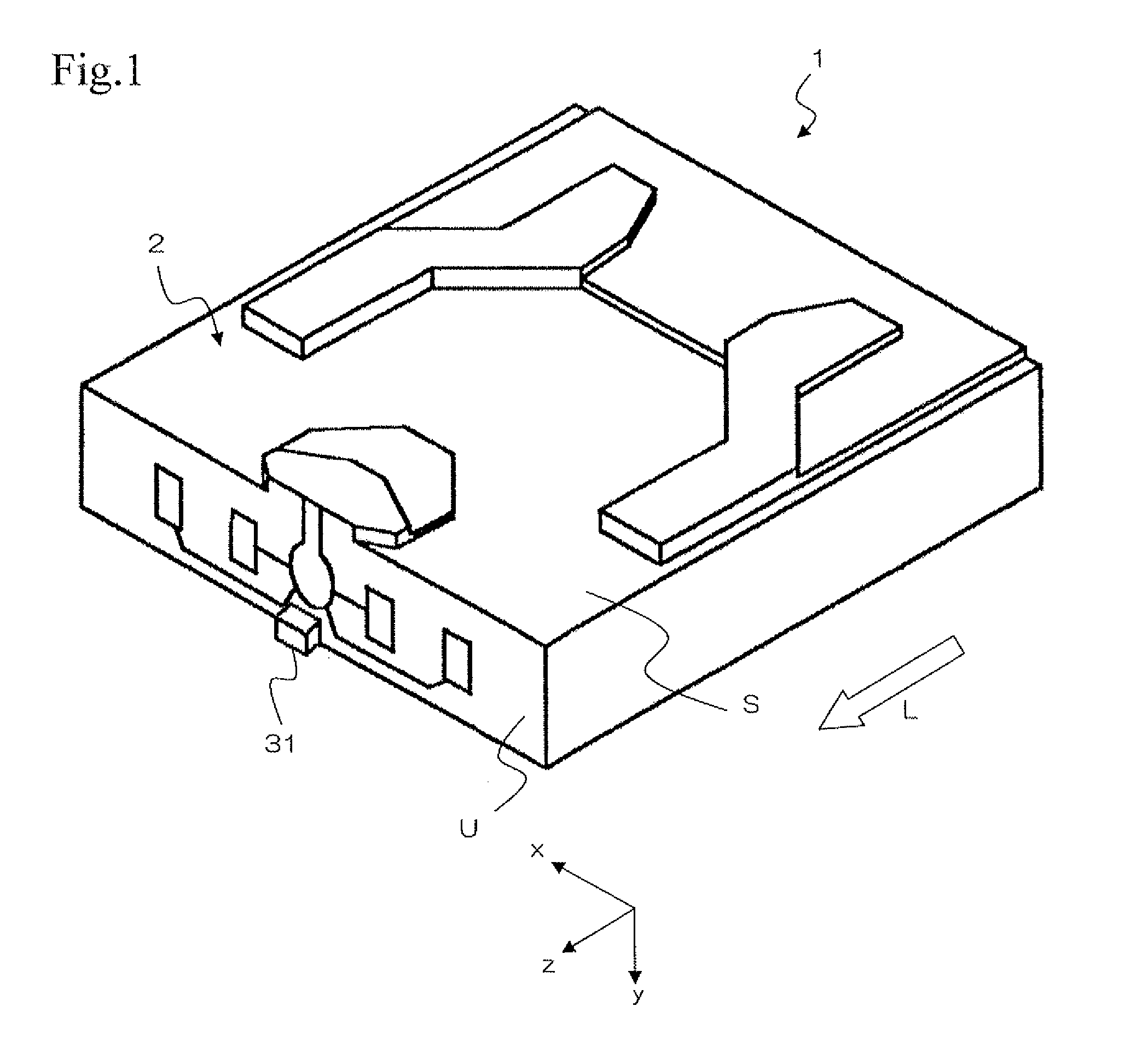
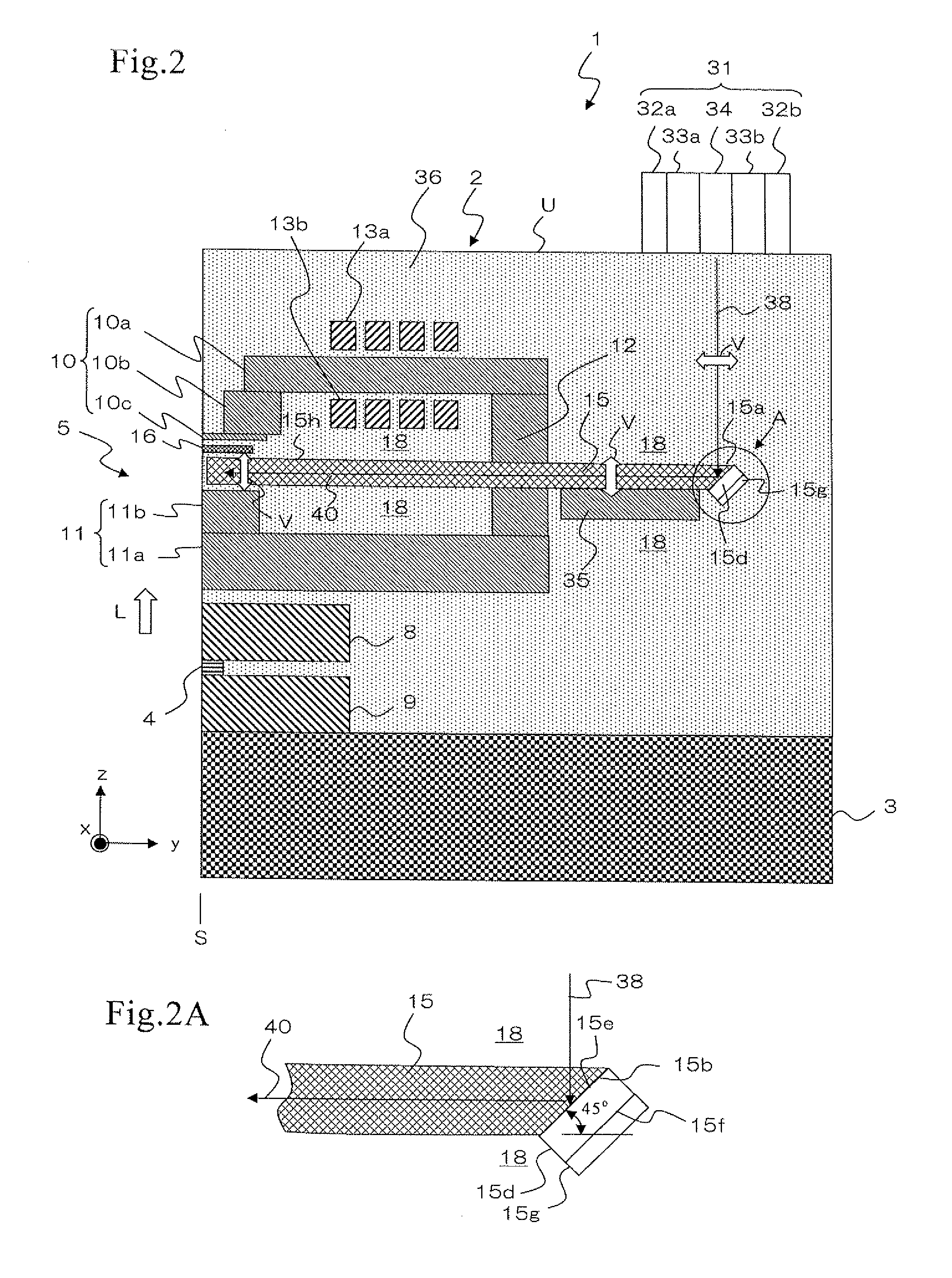
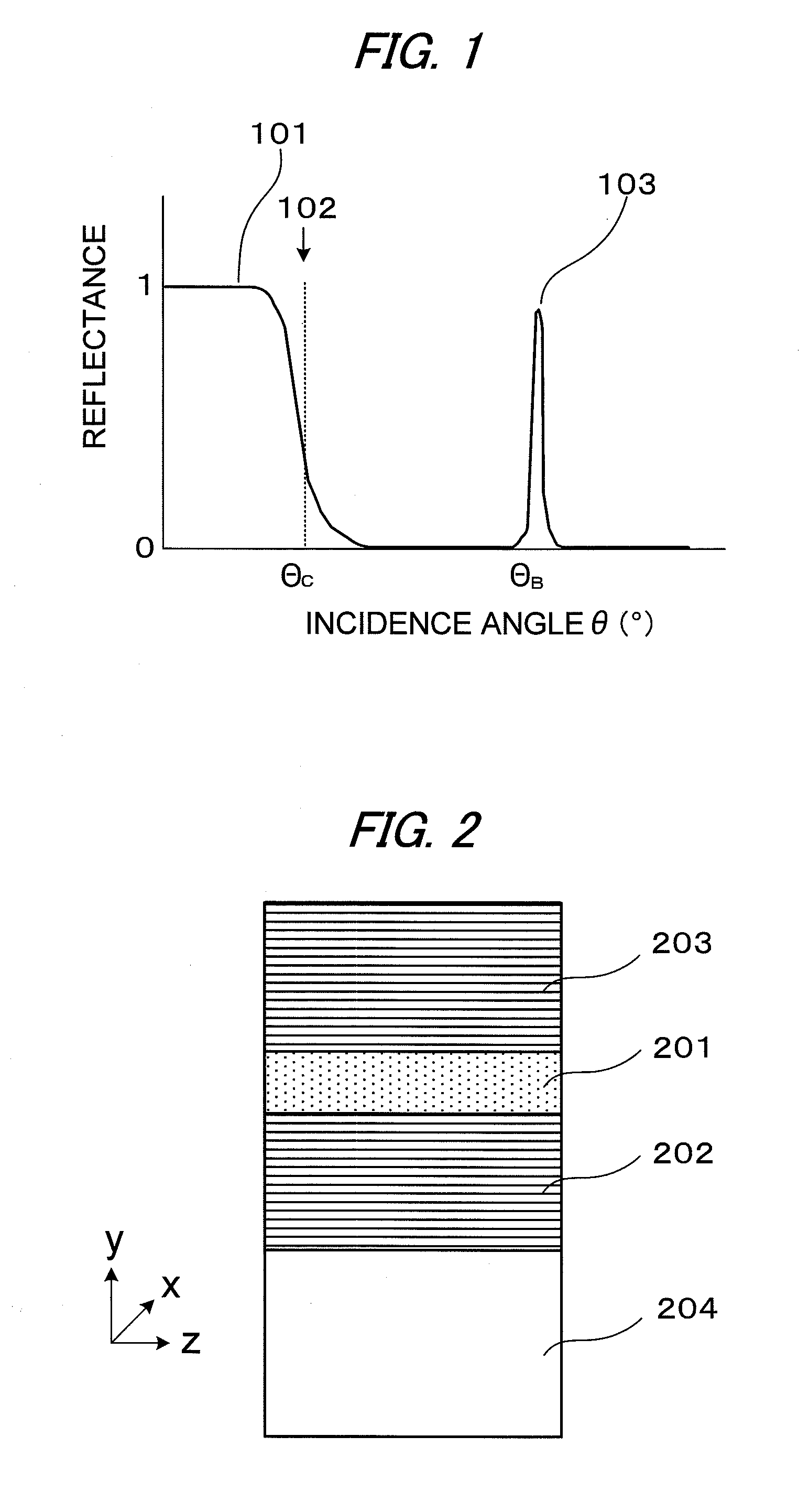
Thermally assisted head having reflection mirror for propagating light
ActiveUS8223597B2Suppresses plasmon generationPropagation loss of the light on the reflection layer is suppressedCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsRefractive indexLaser light
A magnetic head includes a magnetic head slider; and a laser diode that is positioned on a surface of a side opposite to a substrate of the magnetic head slider and that generates laser light; the magnetic head slider including: a core through which the laser light emitted from the laser diode propagates as propagating light; a cladding that covers the core and that has a refractive index that is smaller than that of the core; a near field light generating means that generates near field light from the propagating light on an air bearing surface; and a main pole for recording that is disposed adjacent to the near field light generating means and of which an edge part is positioned on the air bearing surface. The core includes a reflection layer and a seed layer, the reflection layer has a refractive index smaller than that of the core, and has a reflection surface on which laser light emitted from the laser diode reflects so as to enter the core as the propagating light, and the seed layer is positioned on a back surface of the reflection surface of the reflection layer and suppresses plasmon generation on the reflection surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
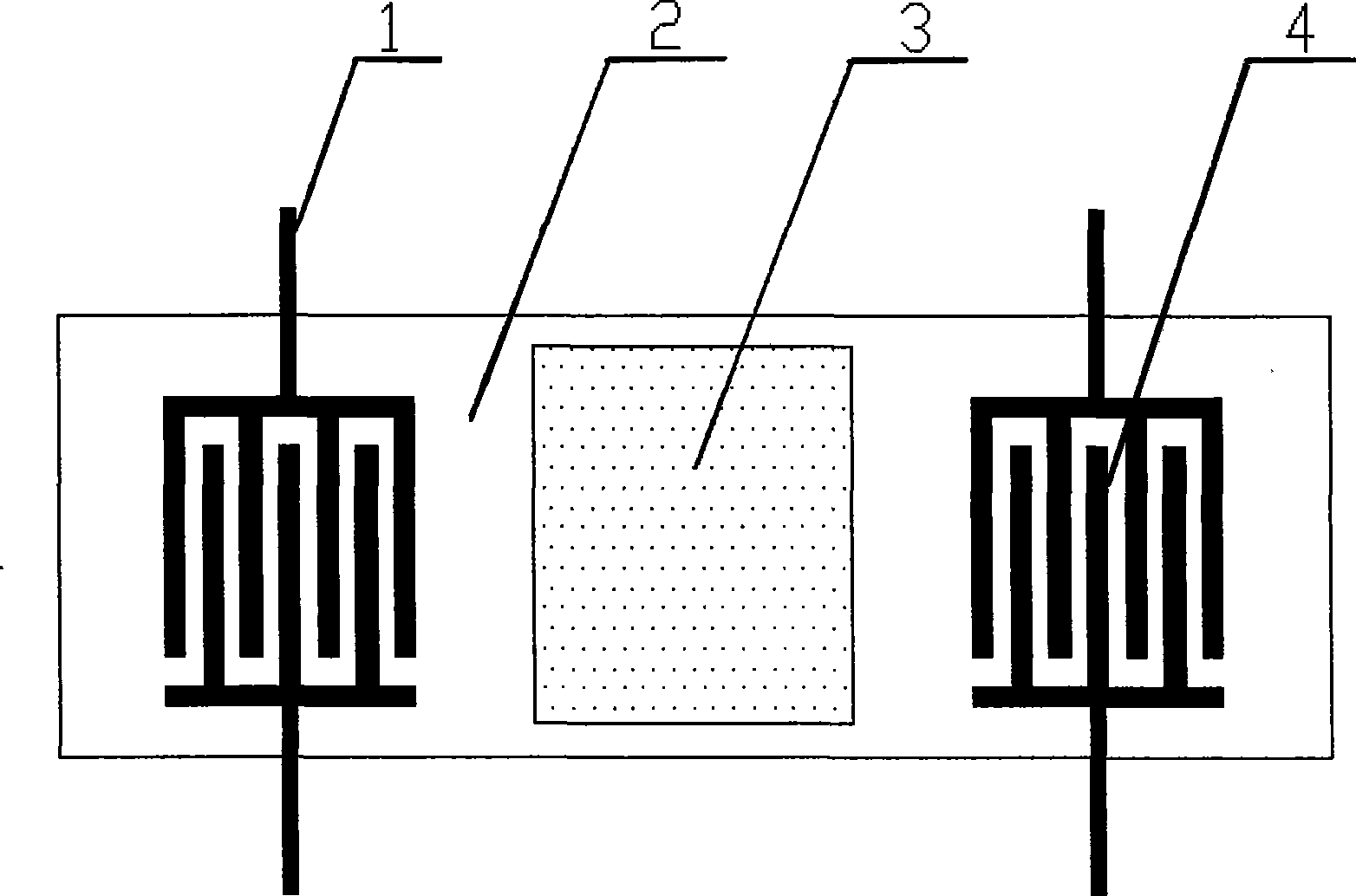
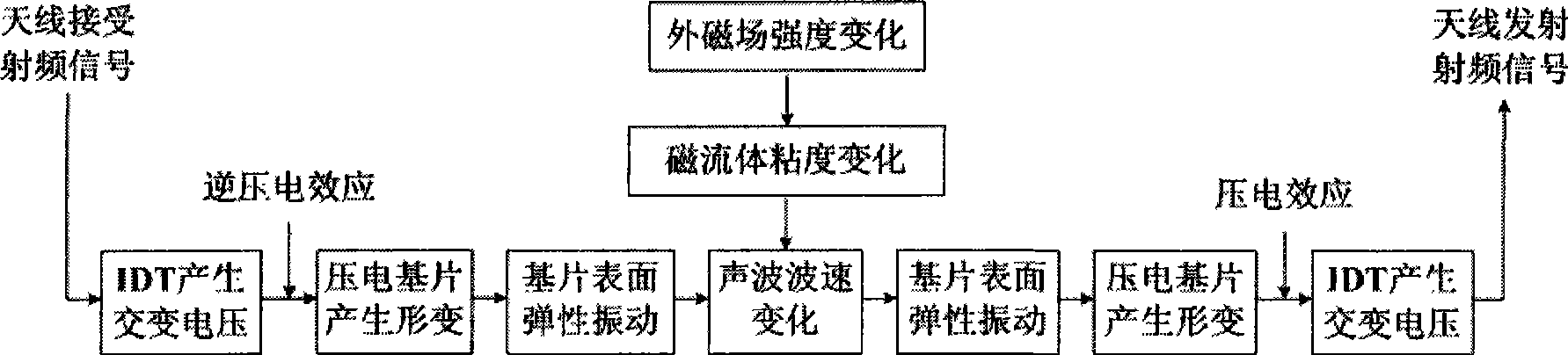
Thin film type structural magnetofluid-sonic surface wave integrated magnetic transducer
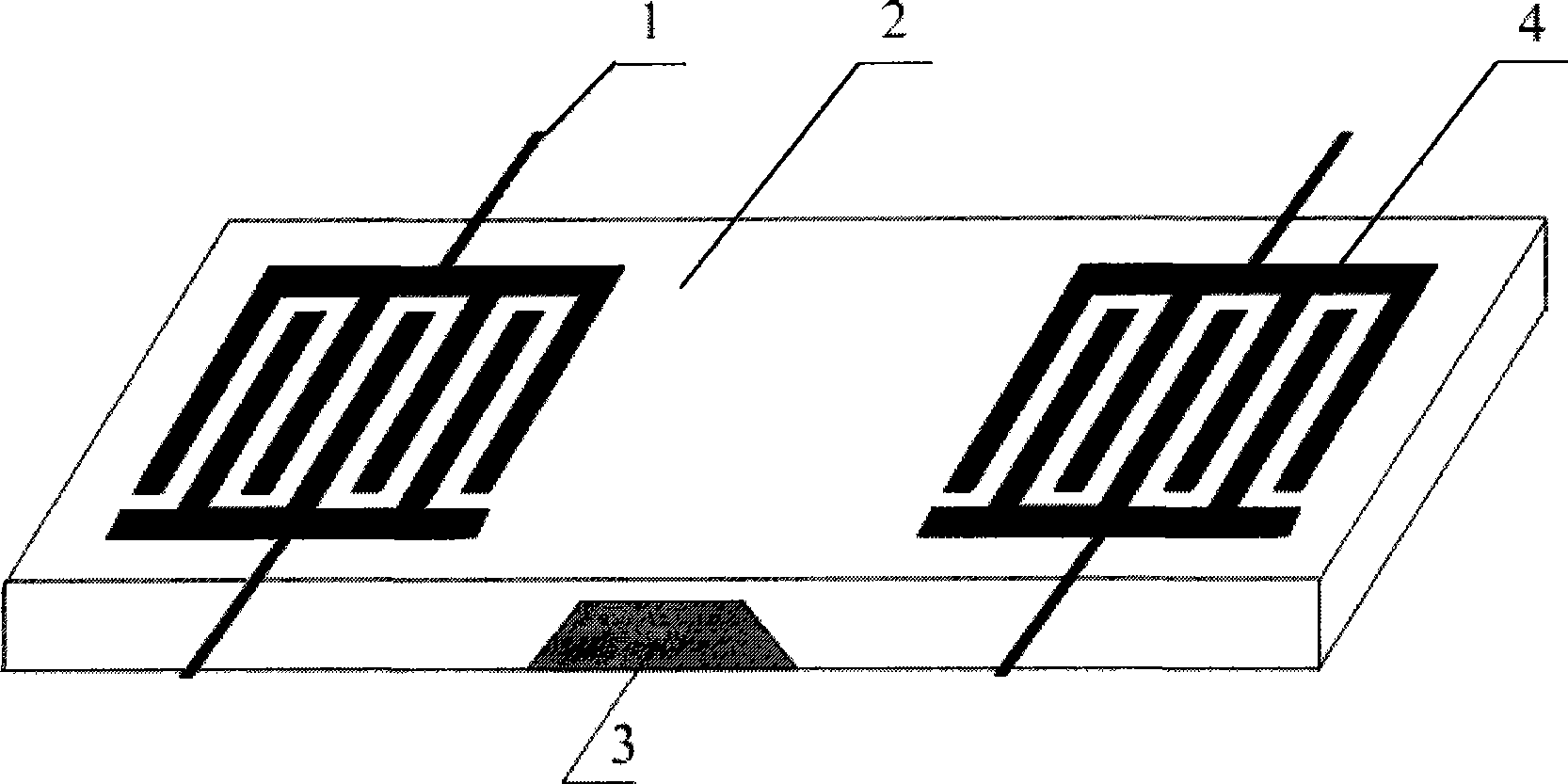
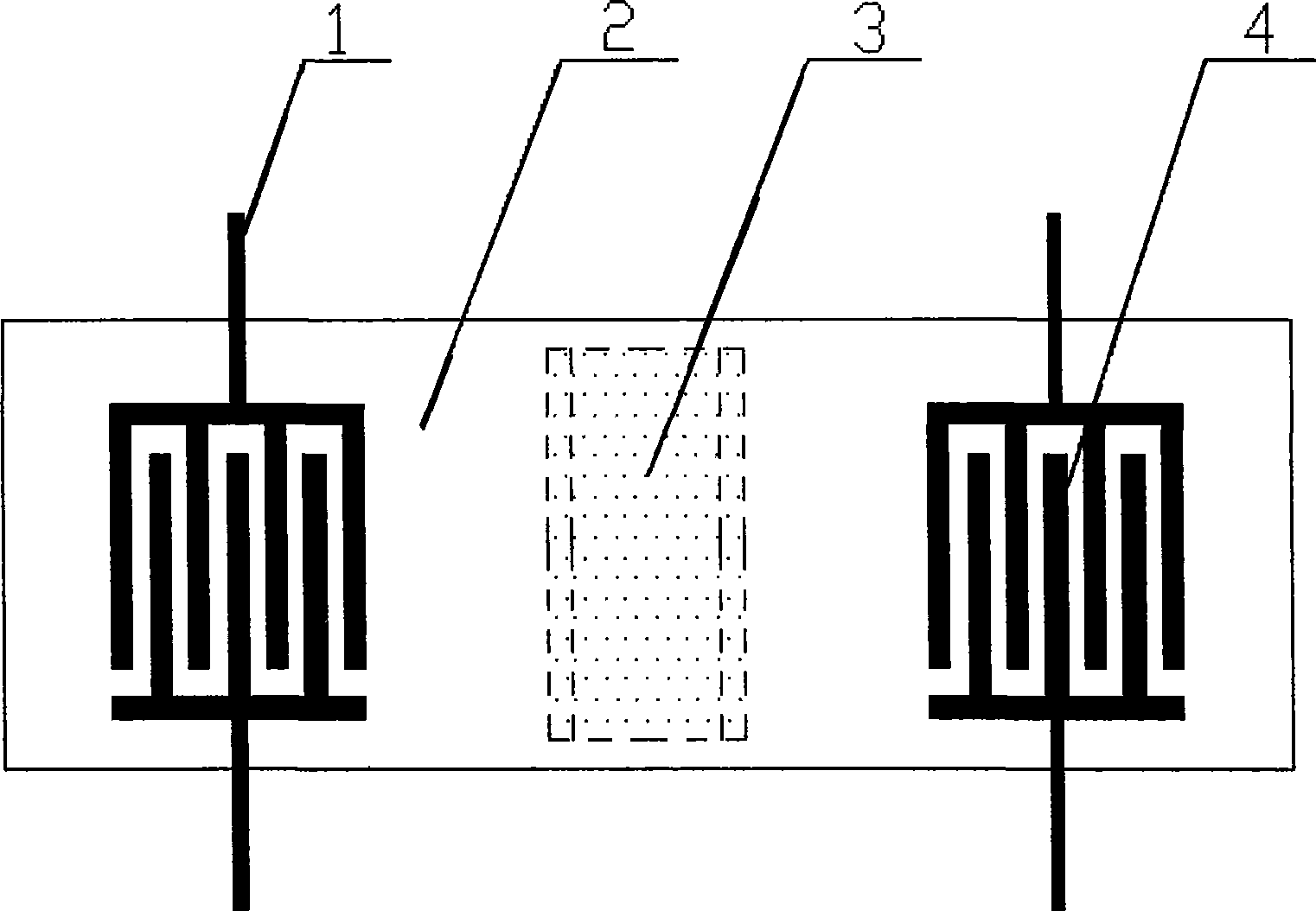
InactiveCN101504446AGood temperature characteristicsSmall propagation lossMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic transducersMagnetic field magnitude
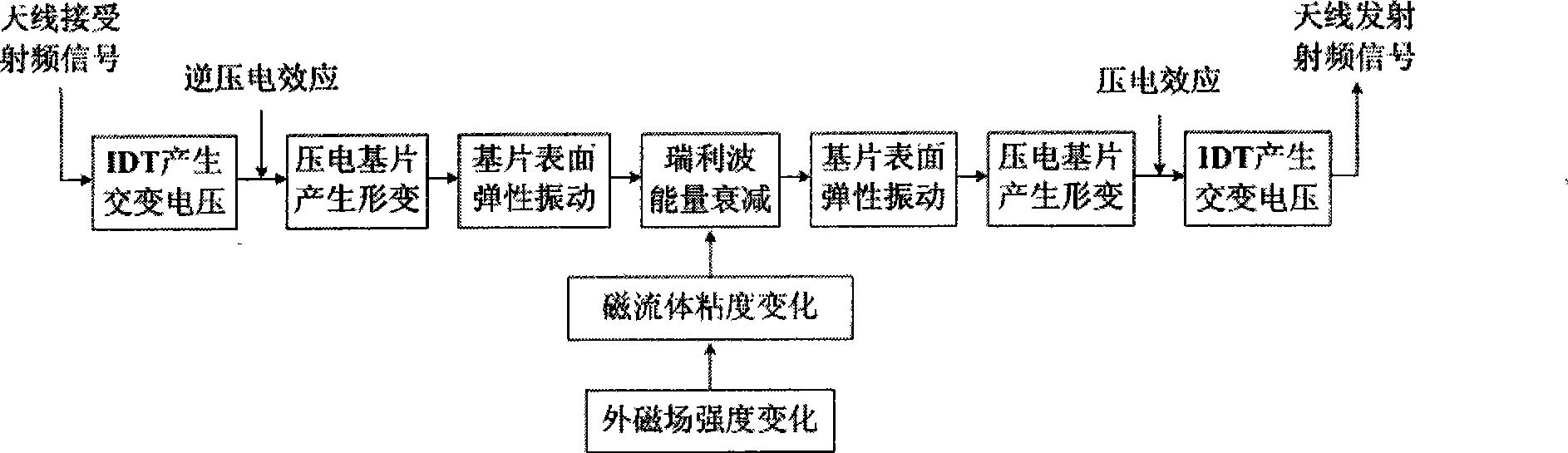
The invention discloses a sound surface wave integrated magnetic sensor for a magnetic fluid with a thin film structure, which comprises a piezoelectric substrate, two interdigital transducers (IDT), a magnetic fluid thin film and two sets of antennae for receiving and transmitting magnetic wave signals; the two interdigital transducers (IDT) are positioned at two ends of the substrate respectively; the magnetic fluid thin film is filled in a shallow groove between the two interdigital transducers on the surface of the sensor and encapsulates the groove; two sets of the antennae for receiving and transmitting the magnetic wave signals are connected to omnibus bars of the two IDTs respectively; the sensor can realize passive wireless high-precision real-time magnetic intensity measurement, and receive a radio frequency signal by the antennae, excite a horizontal shearing sound surface wave on the IDTs; the zero lagging response of the magnetic fluid on the change of an outer magnetic field instantaneously changes the delaying time of the sound surface wave delaying line, namely the viscosity change of the magnetic fluid changes the wave speed of the sound wave, converts the sound surface wave subjected to sound speed change into a magnetic wave by the IDTs and transmits the magnetic wave by the antennae. According to the corresponding relation of the delaying time and the magnetic filed intensity change, the magnetic filed change can be accurately measured.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Waveguide structure and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050089291A1Well couplingSmall propagation lossNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideOptoelectronicsPolymer
A waveguide structure having a cross-sectional structure wherein Si is in the center and it is surrounded by a peripheral material, which is either SiO2 or a polymer material. The above-mentioned peripheral material functions as a cladding.
Owner:NEC CORP
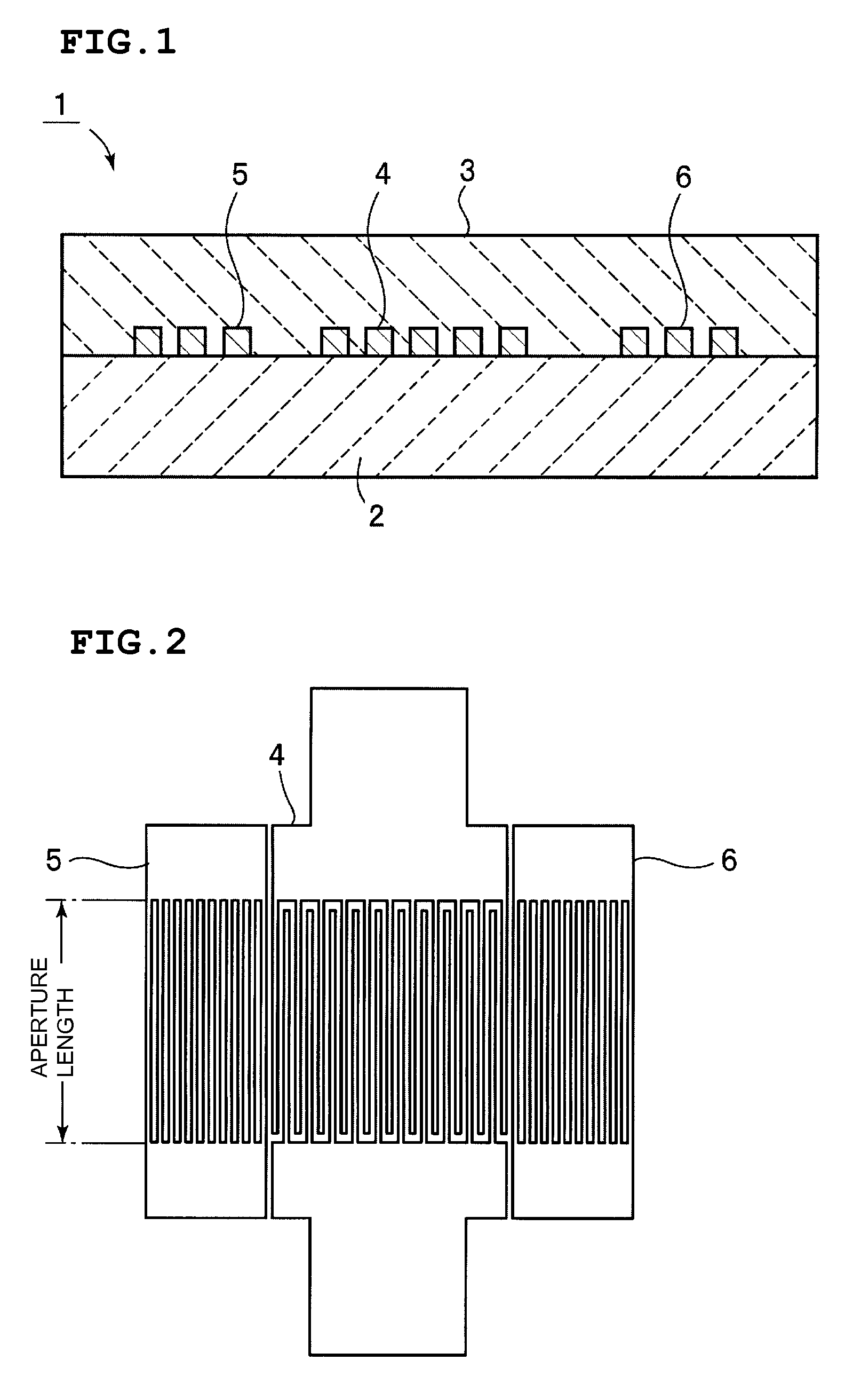
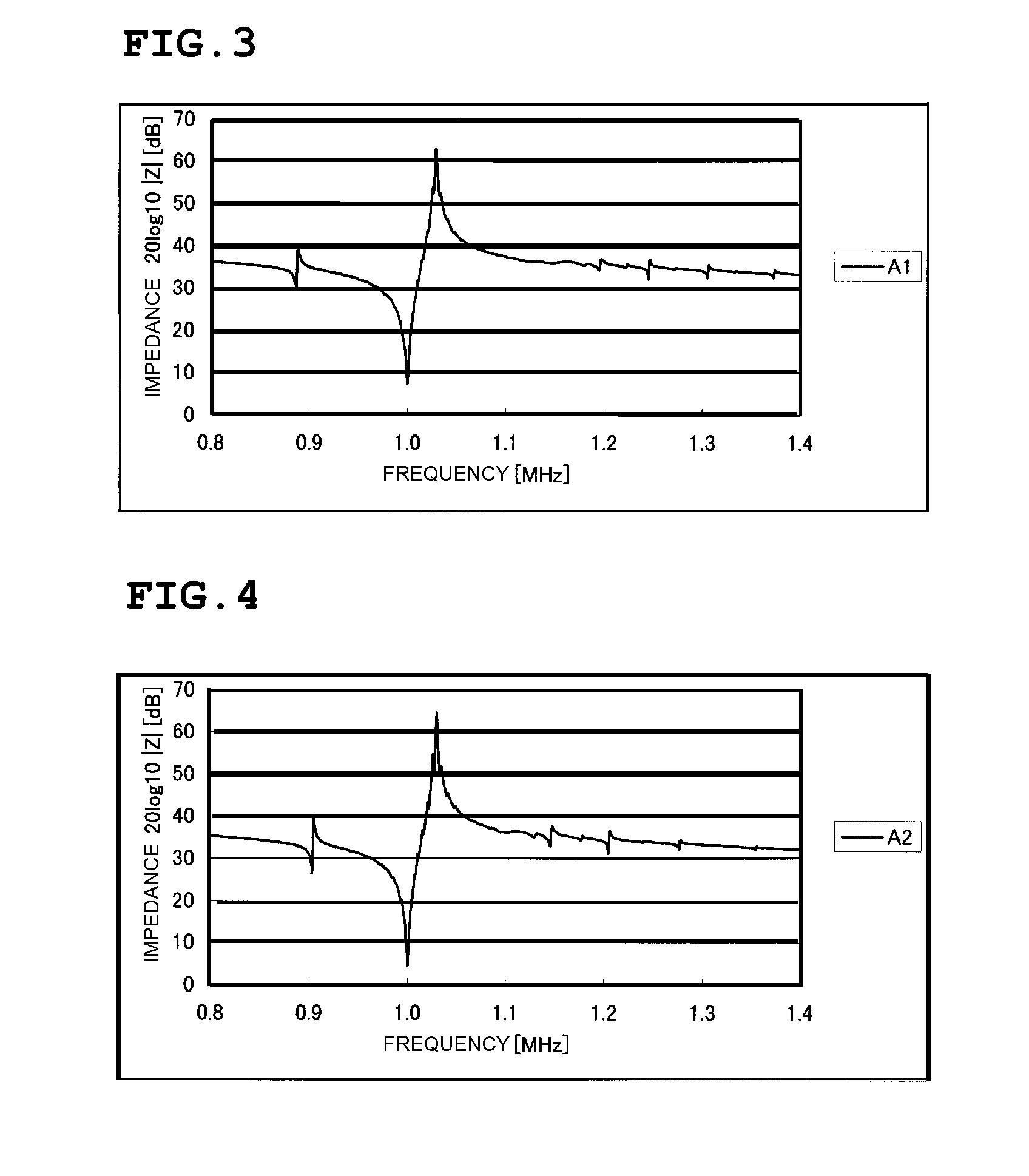
Boundary acoustic wave device
ActiveUS20070007852A1Large electromechanical coefficientSmall propagation lossPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcoustic waveStoneley wave
A dielectric substance is laminated on one surface of a piezoelectric substance, and an IDT and reflectors are disposed as electrodes at a boundary between the piezoelectric substance and the dielectric substance, and the thickness of the electrodes is determined so that the acoustic velocity of the Stoneley wave is decreased less than that of a slow transverse wave propagating through the dielectric substance and that of a slow transverse wave propagating through the piezoelectric substance, thereby forming a boundary acoustic wave device.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Back-trough type structural magnetofluid-sonic surface wave integrated magnetic transducer
InactiveCN101504445AGood temperature characteristicsSmall propagation lossMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectricityMagnetic transducers
The invention discloses a sound surface wave integrated magnetic sensor for a magnetic fluid with a back groove type structure, which comprises a piezoelectric substrate, two interdigital transducers (IDT), a magnetic fluid groove and two sets of antennae for receiving and transmitting magnetic wave signals; the two interdigital transducers (IDT) are positioned at two ends of the surface of the substrate respectively; the magnetic fluid groove is arranged in the middle of the bottom of the piezoelectric substrate between the two interdigital transducers; the antennae for receiving and transmitting the magnetic wave signals are connected to omnibus bars of the two IDTs respectively; the sensor can realize passive wireless high-precision real-time magnetic intensity measurement, and receive a radio frequency signal by the antennae, excite a Rayleigh wave (RSAW) on the IDTs; the zero lagging response of the magnetic fluid on the change of an outer magnetic field instantaneously makes the energy of the Rayleigh wave attenuated, converts the attenuated Rayleigh wave into a magnetic wave by the IDTs and transmits the magnetic wave by the antennae. According to the corresponding relation of the changes of the frequency and the amplitude of the transmitted magnetic wave and the magnetic filed intensity change, the magnetic filed change can be accurately measured.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Deposition method capable of enhancing preferred orientation growth of AlN film
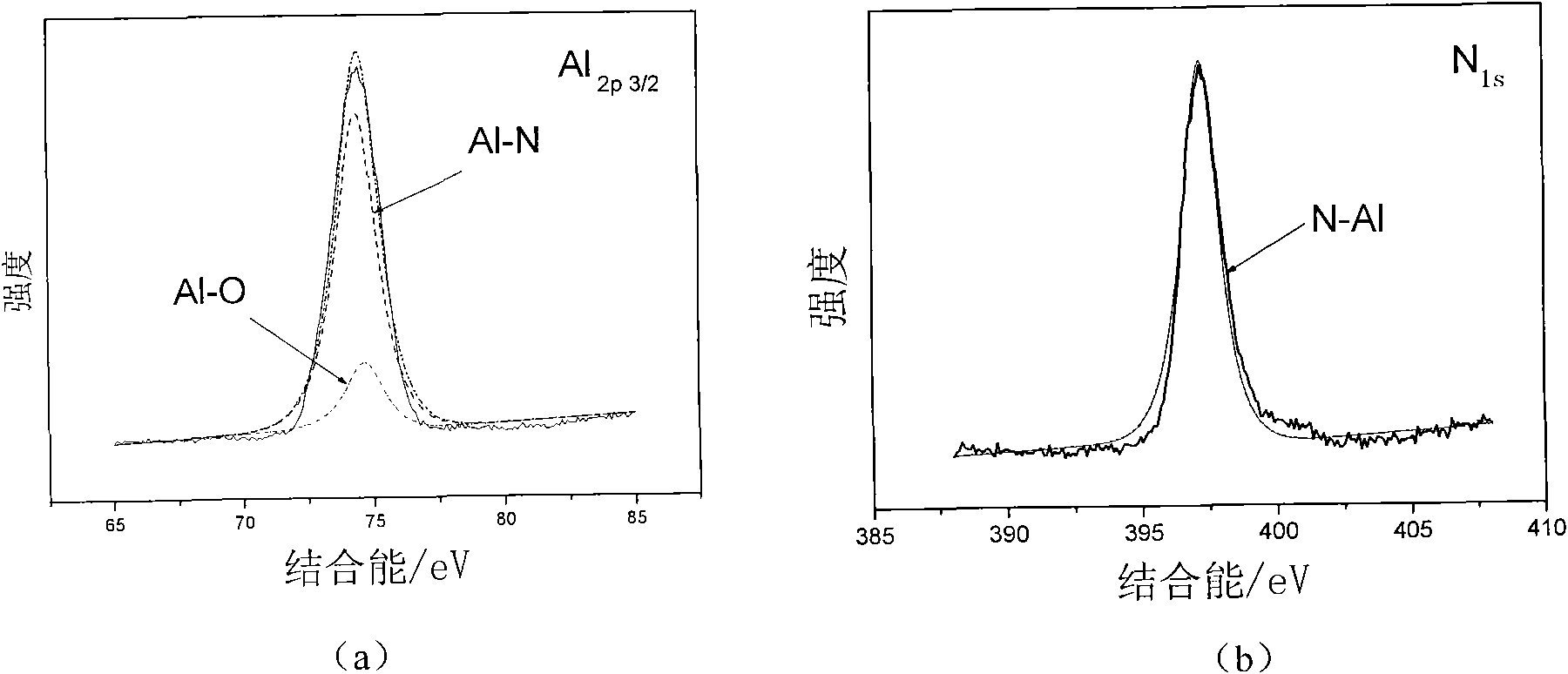
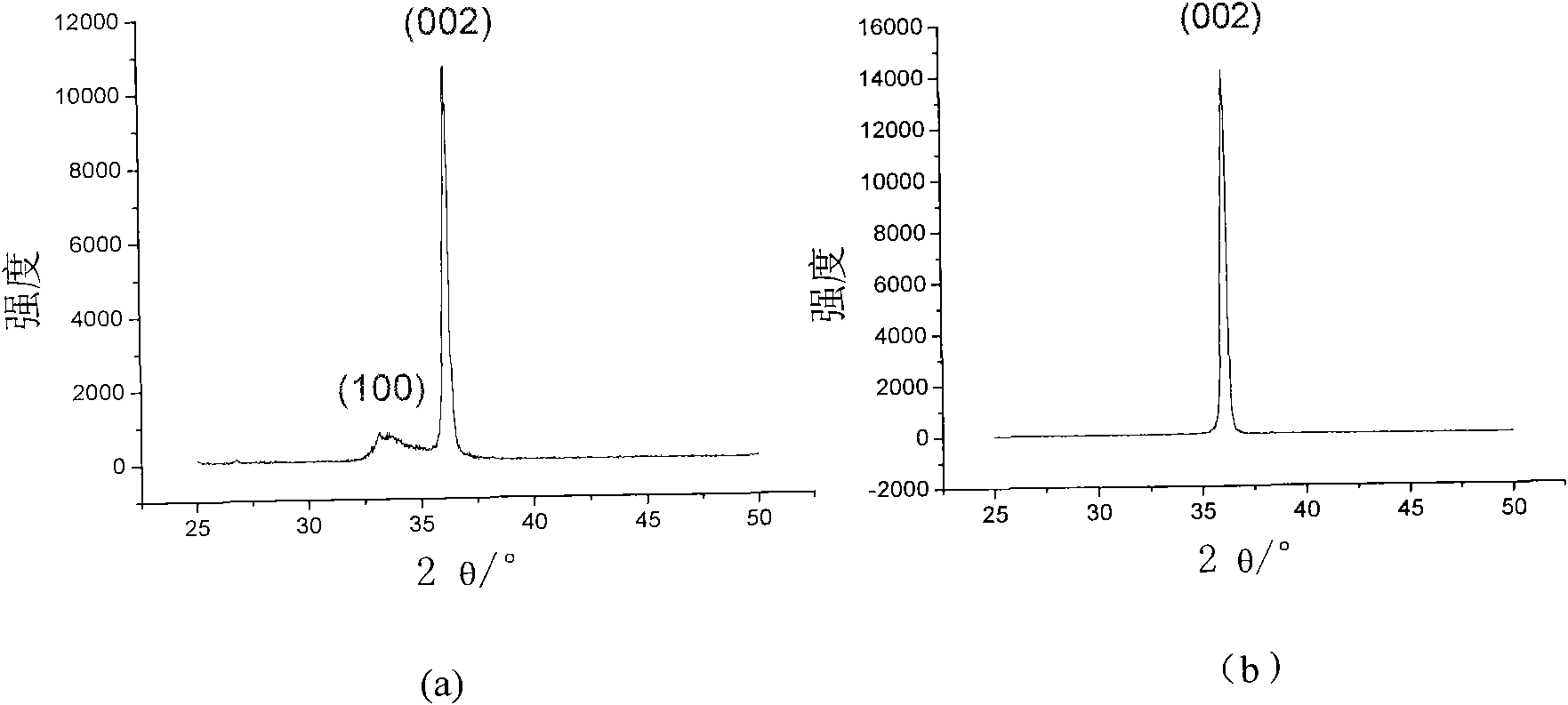
ActiveCN101824592AEasy to operateReduce manufacturing costVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSurface roughnessSurface acoustic wave
The invention relates to a deposition method capable of enhancing the preferred orientation growth of an AlN film. The deposition method comprises the following steps: adopting an ion beam-assisted deposition technique to prepare an AlN homogeneous transition layer: when using an Ar + ion beam of 2.0-2.5keV / 20-50mA for depositing an Al film in a sputtering way on a substrate, using a moderate-energy N+ ion beam of 20-35keV / 2-8mA for bombarding the Al film in an assisting way; and then depositing the AlN film by adopting magnetron sputtering, wherein base pressure is less than or equal to 5x10<-4>Pa, working air pressure is 0.5-10Pa and substrate temperature is 200 DEG C-500 DEG C. Through pre-depositing the homogeneous transition layer, the invention has the advantages that the internal stress between the film and the substrate can be effectively reduced, the full (002) orientation AlN film is formed, the surface roughness of the film is reduced, the bonding strength between the film and the substrate is increased and the film product can satisfy the requirements on the application in surface acoustic wave devices, acoustic bulk wave devices and other microelectronic devices and power devices.
Owner:湖南特瑞精密医疗器械有限公司
Apparatus and Method for Transmission
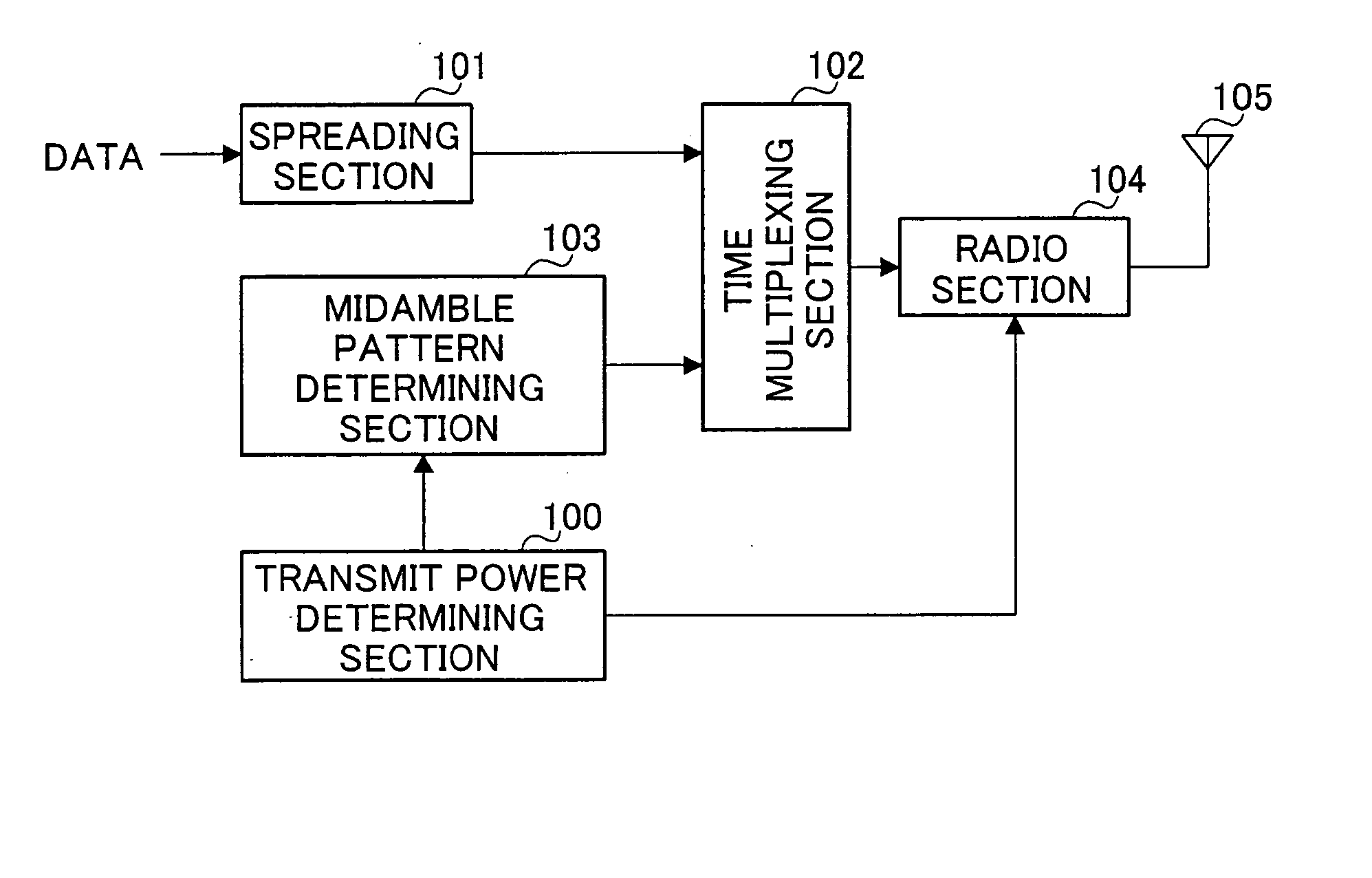
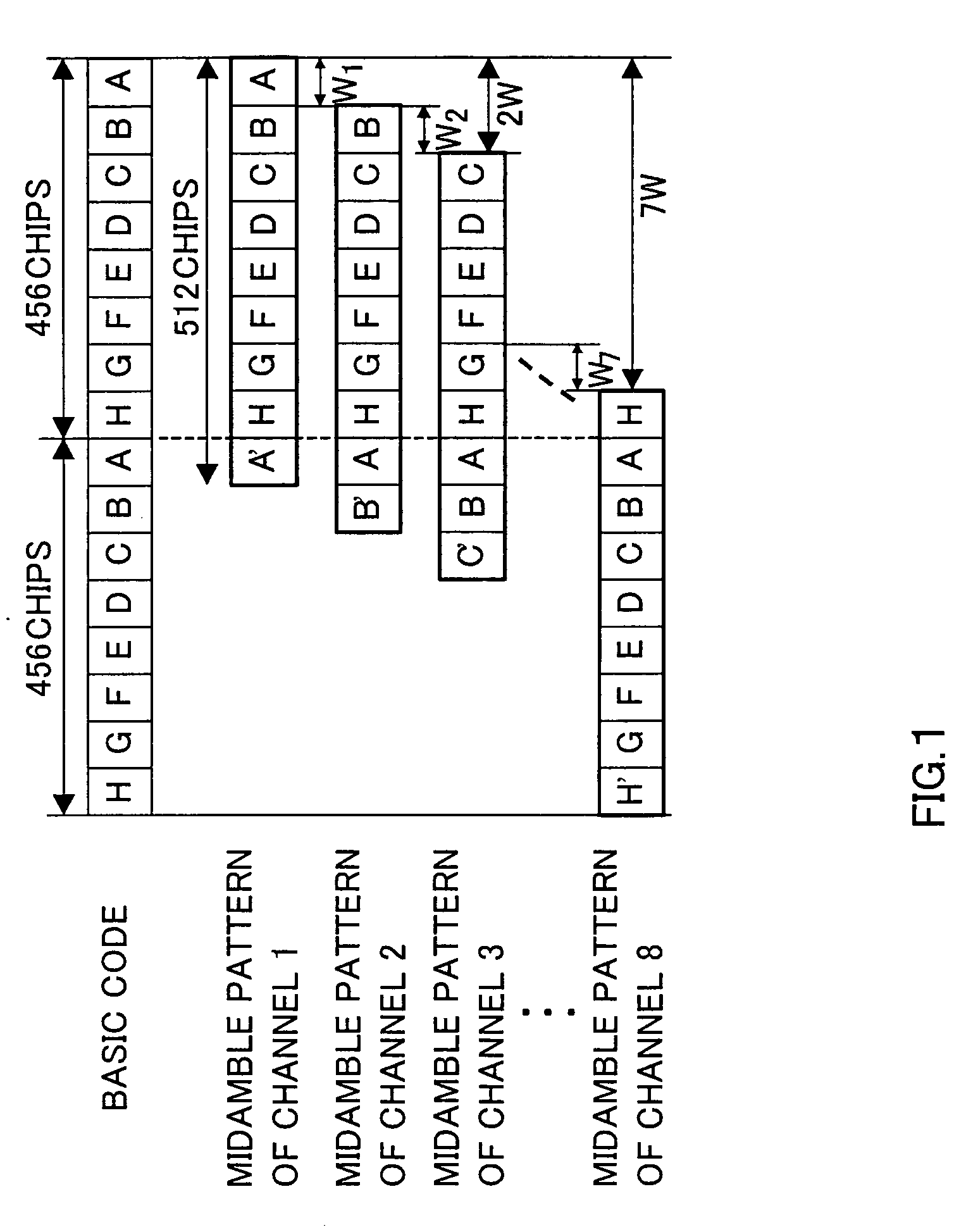
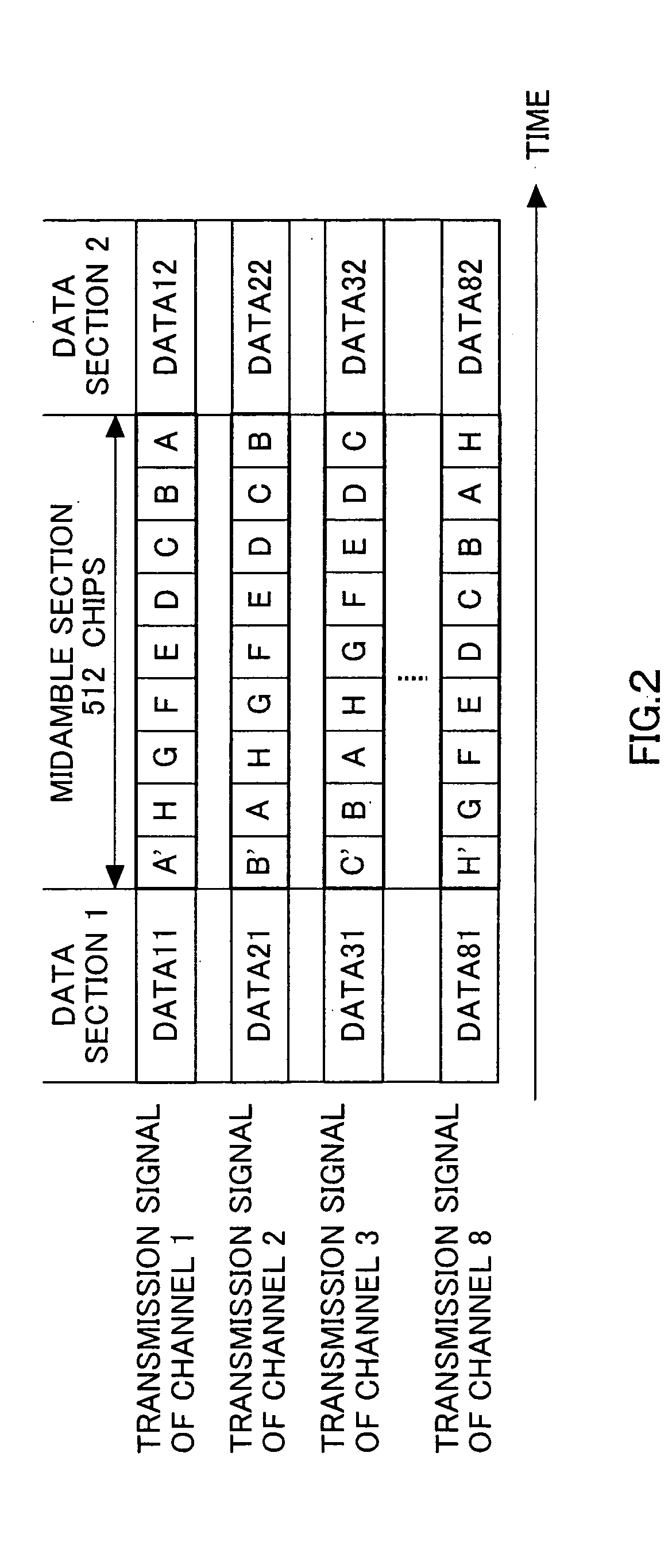
InactiveUS20050174968A1Increase probabilityShorten the lengthPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmitted powerRandom-access channel
Transmit power determining section 100 determines a transmit power value based on the condition of the propagation path estimated from a propagation loss and the number of times the random access channel signal is retransmitted. Midamble pattern determining section 103 determines a midamble pattern corresponding to the transmit power value from among a plurality of midamble patterns. Time multiplexing section 102 creates a transmission signal by multiplexing transmission data subjected to spreading processing and the midamble pattern. Radio section 104 applies predetermined transmission processing to the transmission signal generated and transmits the transmission signal subjected to the transmission processing above using the determined transmit power value as a random access channel signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High-frequency high-performance acoustic surface wave device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108493325AHigh speed of soundImprove thermal stabilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionSingle crystalCenter frequency
The invention discloses a high-frequency high-performance acoustic surface wave device and a preparation method thereof. The acoustic surface wave device comprises a silicon carbide monocrystal substrate, a piezoelectric thin film and an interdigital electrode which are stacked in sequence; the piezoelectric thin film is a lithium tantalate monocrystal thin film or a lithium niobate monocrystal thin film; and the silicon carbide monocrystal substrate is a 4H-SiC monocrystal substrate, a 6H-SiC monocrystal substrate, a 3C-SiC monocrystal substrate or a 3C-SiC epitaxial monocrystal substrate. The silicon carbide monocrystal substrate has relatively high sound velocity, excellent thermal stability and chemical stability and high heat conductivity; the lithium tantalate or lithium niobate piezoelectric monocrystal thin film is high in crystal quality, high in consistency and low in propagation loss; by adoption of the acoustic surface wave device with the interdigital electrode / lithium tantalate or lithium niobate monocrystal thin film / silicon carbide monocrystal substrate structural form, relatively high central frequency, high power tolerance and low temperature coefficient are achieved, so that the acoustic surface wave device has huge application prospect in the field of mobile communication.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Resin composition for optical wiring, and optoelectronic circuit board
InactiveUS20070147767A1Little dependencyDurable against temperature changeCircuit optical detailsPrinted circuit aspectsRefractive indexThermal expansion
This invention is a resin composition for optical wiring, comprising an inorganic filler with an average particle size of 1 nm to 100 nm and a resin, having a ratio nf / nr (where nf is the refractive index of the inorganic filler and nr is the refractive index of the resin) of 0.8 to 1.2, a thermal expansion coefficient of −1×10−5 / ° C. to 4×105 / ° C., and a true dependency value of its refractive index on the temperature of −1×10−4 / ° C. to 1×10−4 / ° C. in a temperature range from −20° C. to 90° C., and substantially incapable of absorbing light in a wavelength range from 0.6 to 0.9 μm or from 1.2 to 1.6 μm. This invention also provides an optoelectronic circuit board.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
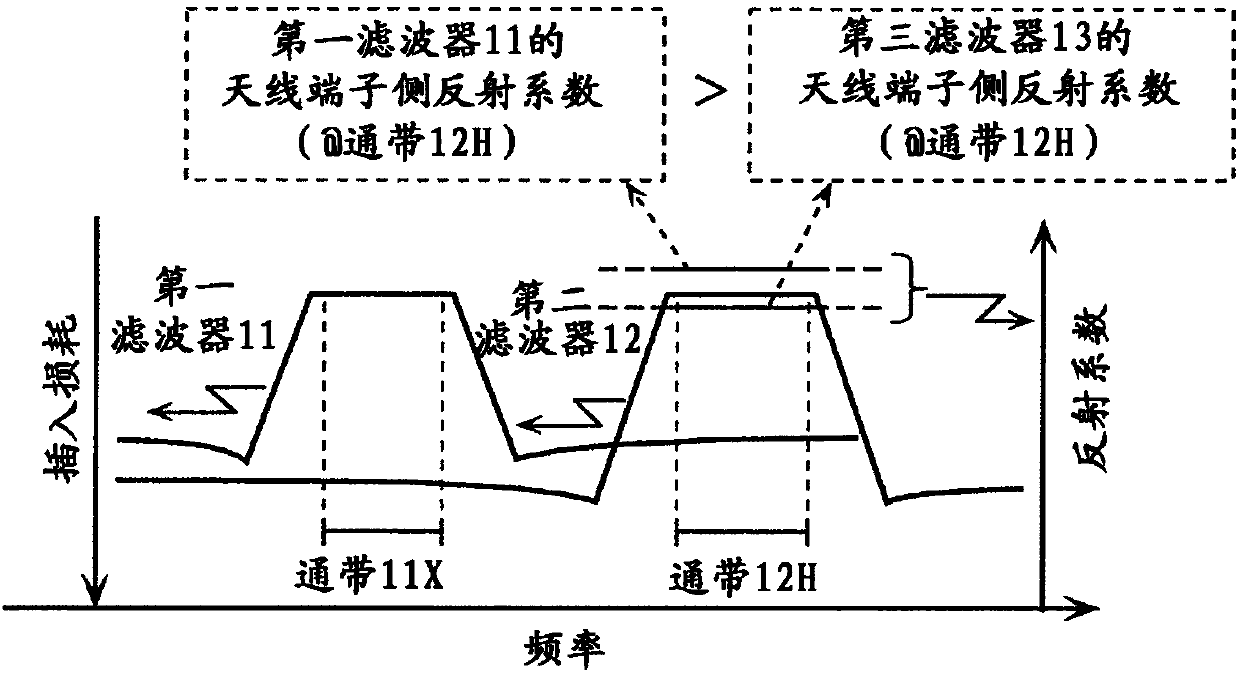
Radio-frequency front-end circuit and communication device
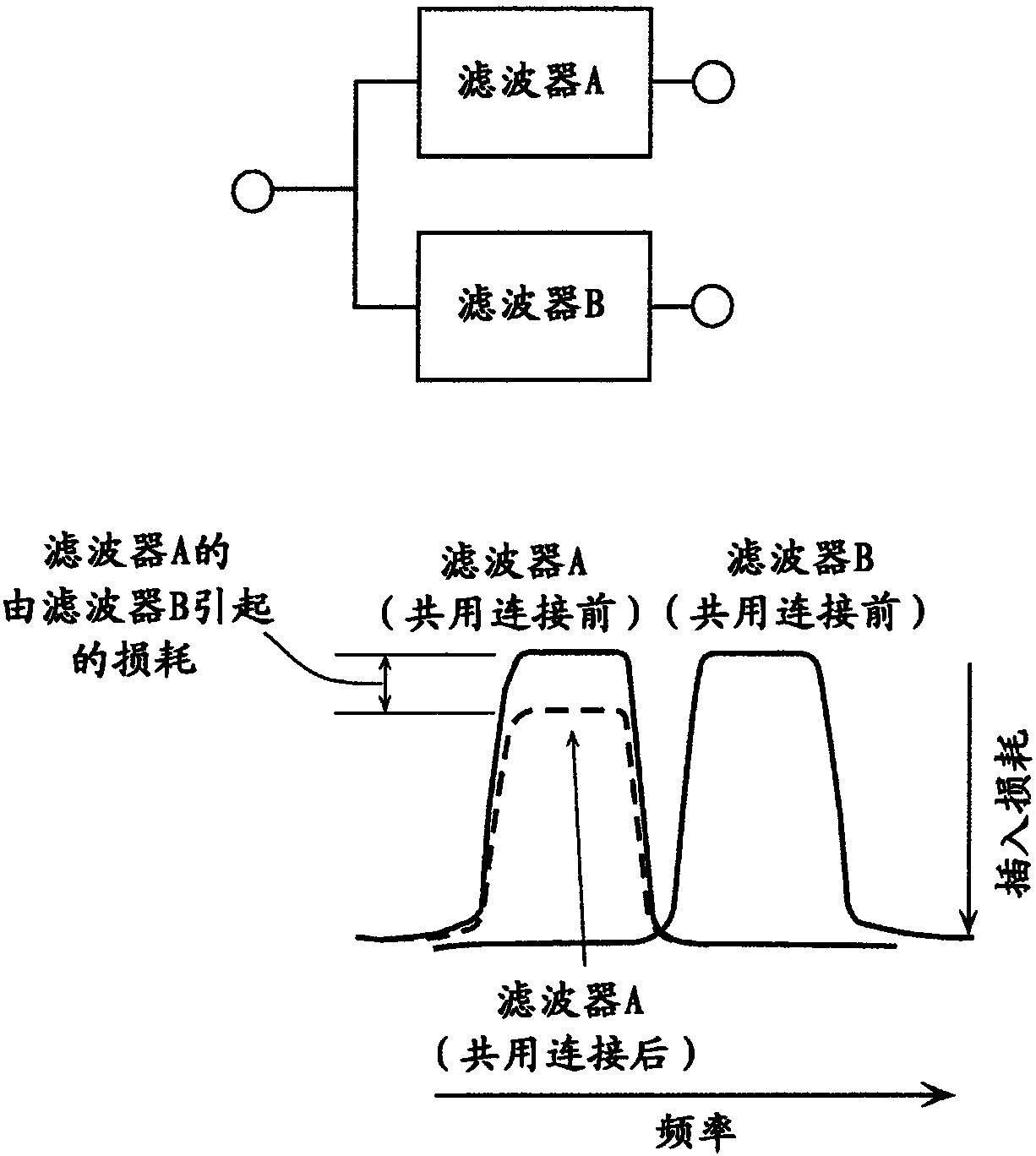
The invention provides a small-size radio-frequency front-end circuit, by which a signal transmission character of low loss is maintained even CA motion is carried out. A radio-frequency front-end circuit (1) includes a first filter (11) that has a first pass band and is connected to an antenna common terminal (101), a second filter (12) that has a second pass band and is connected to the antennacommon terminal (101), a switch (21) that includes a common terminal (21c) and selection terminals (21a and 21b), the common terminal being connected to the first filter, and a third filter (13) thatis connected to one of the selection terminals and is disposed between the switch and an input / output terminal (102). A reflection coefficient of the first filter alone in the second pass band viewedfrom the antenna common terminal is larger than a reflection coefficient of the third filter alone in the second pass band viewed from the antenna common terminal.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method for producing a surface acoustic wave element
InactiveUS6996882B2Avoid it happening againEasy to handlePrinted circuit assemblingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblySurface acoustic wave sensorElectrode
A surface acoustic wave element includes a laminated substrate where a first substrate made of a piezoelectric material is laminated over a second substrate made of a material different from that of the first substrate, and at least one pair of comb-shaped electrodes formed on one main plane of the first substrate. A step or a notch is formed on the periphery of the laminated substrate on the side of the first substrate.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Terahertz wave generator based on graphene
PendingCN106299979AIncreased Radiation PowerIncrease antenna gainSolid masersAntenna gainEngineering
The invention discloses a terahertz wave generator based on graphene. The teraHertz wave generator comprises a substrate, a graphene film and a terahertz photoconductive antenna, wherein the graphene film is formed on the substrate and the terahertz photoconductive antenna is used for coupling Sierpinski fractal geometrical shape of the terahertz wave. According to the invention, bar-shaped electrodes are arranged at the two ends of inverse fractal antenna; a bias voltage is applied between the electrodes; the graphene film is pumped through femtosecond pulse laser; the electron motion in the graphene film is excited; the terahertz wave is irradiated under the effect of the bias voltage; the terahertz wave is coupled with the free space through the photoconductive antenna. Due to the high electronic mobility and the characteristic of easily generating terahertz wave of the graphene and the coupling function of the photoconductive antenna with similar characteristic, the emission efficiency of terahertz wave is increased, the antenna gain is increased, the power consumption and propagation loss of the antenna are reduced and the radiant power of the terahertz wave is increased.
Owner:郭玮
Optical fiber and manufacturing method thereof and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20050152655A1Enhance the imageLittle changeGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreOptical axisLight beam
The present invention provides an optical fiber having a rectangular core in which propagation loss of a light beam is small and manufacturing can be performed at low cost, a method of manufacturing the optical fiber, and an image forming apparatus including the optical fiber. The optical fiber having the core, whose sectional shape in a direction orthogonal to an optical axis direction of a light beam becomes rectangular, is formed by: filling a cylindrical tube with multiple hollow capillaries; extracting hollow capillaries located in a rectangular area having a predetermined size in a portion which is substantially central to the tube; inserting rods having the same diameter as the extracted hollow capillaries to replace the hollow capillaries to produce a preform; performing wire drawing while the preform is melt-fused; and covering the preform with a cover layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
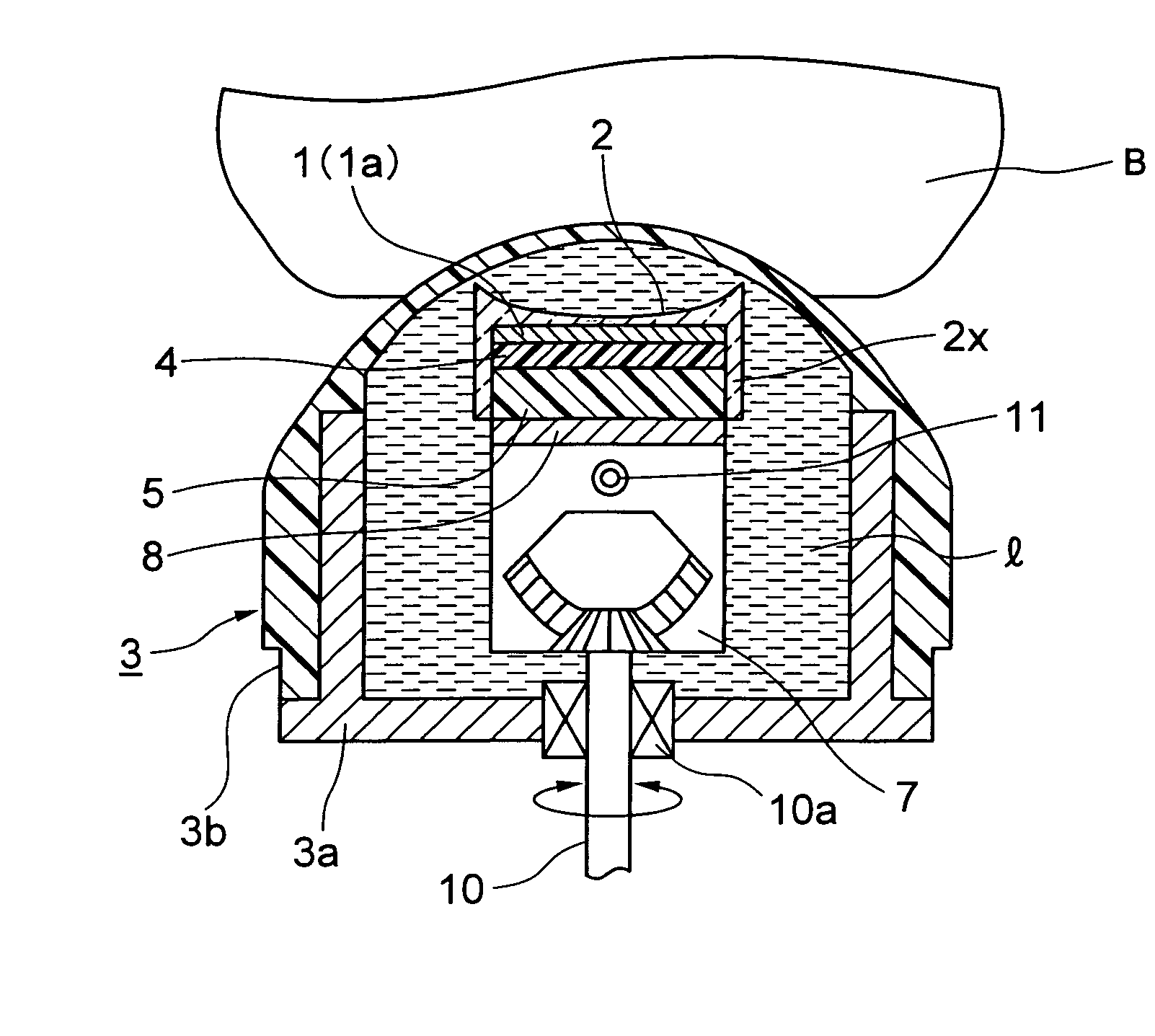
Acoustic lens and ultrasonic probe using the lens
InactiveUS20050245829A1High sensitivitySmall propagation lossUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasound attenuationCamera lens
The invention has a structure, in an acoustic lens for an ultrasonic probe comprising leg portions which are connected by a planar shape, and a lens portion which is provided on the leg portions and has curvature in the lengthwise direction, wherein the leg portions are made from an attenuation prevention material having the less ultrasonic propagation loss than for the lens portion. Moreover, the leg portions of the acoustic lens are formed with opposite end sides thereof in a bent L-shape. Furthermore, an ultrasonic probe is constructed by adhering onto a piezoelectric element group where a plurality of piezoelectric elements are arranged side by side, an acoustic lens provided with curvature in the lengthwise direction.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
Flexible speed measuring device for Doppler ultrasonic detection and application of flexible speed measuring device
PendingCN111820946ASmall propagation lossImprove the coupling effectBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsEngineeringDoppler ultrasonics
The invention discloses a flexible speed measuring device for Doppler ultrasonic detection and application of the flexible speed measuring device, and belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic speed measurement. The flexible speed measuring device for Doppler ultrasonic detection comprises an ultrasonic phased array probe, a flexible packaging layer and a probe driving circuit; the flexible packaging layer wraps the ultrasonic phased array probe; the ultrasonic phased array probe consists of a plurality of ultrasonic transduction units in an array mode; the probe driving circuit changes theemission frequency of the ultrasonic transduction units in the ultrasonic phased array probe through sequential control, so that ultrasonic waves excited by the ultrasonic transduction units are superposed to form a new ultrasonic beam, and the ultrasonic beam is focused at the position of a fluid to be measured; and the ultrasonic phased array probe collects the reflected ultrasonic waves to obtain frequency data for speed measurement. According to the flexible speed measuring device, the ultrasonic focusing position can be regulated and controlled, frequency change information is obtained through array mapping transformation, the biological blood flow speed is measured based on a flexible ultrasonic array, and good comfort degree and large attachment angle freedom degree are achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Boundary acoustic wave device
ActiveUS7355319B2Large electromechanical coefficientSmall propagation lossPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAcoustic waveStoneley wave
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Minor axis motion type ultrasonic probe
ActiveUS20090299194A1Radius of curvature of the lens becomes greaterSuppress propagation lossUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityLiving body
The invention relates to a minor axis motion type ultrasonic probe with high sensitivity that suppresses propagation loss. The minor axis motion type ultrasonic probe of the invention comprises: a piezoelectric element group in which a plurality of piezoelectric elements are arranged in a line in a major axis direction of the piezoelectric element group; an acoustic lens that is provided on an ultrasonic wave transmitting / receiving surface side of the piezoelectric element group and that has a predetermined curvature in a minor axis direction of the piezoelectric element group; and a sealed container that houses the piezoelectric element group with the acoustic lens provided thereon and that is filled with a liquid serving as an ultrasonic wave medium, and the piezoelectric element group is moved in the minor axis direction and ultrasonic waves are transmitted and received to and from a living body, wherein the configuration is such that the acoustic lens is a concave lens formed from a material that has less propagation loss than a silicone resin and that has a greater acoustic velocity than a living body, and a relationship between acoustic velocity c1 of the concave lens, acoustic velocity c2 of the liquid, and acoustic velocity c3 of the living body is expressed as c1>c3>c2.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
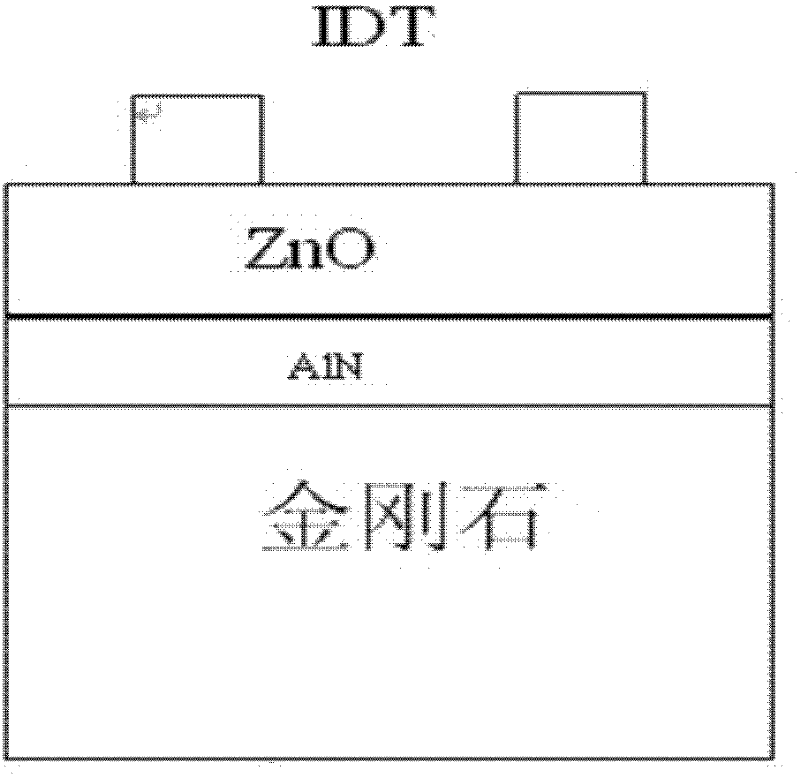
IDT/h-BN/c-BN/diamond multi-layer film structure surface acoustic wave device and its manufacture method
InactiveCN101060318ASmall difference in phase velocity VSmall velocity dispersionImpedence networksTemperature coefficientFilm structure
The disclosed IDT / h-BN / c-BN / diamond multilayer membrane structure SAW device comprises: from bottom to top, a nano-diamond membrane base prepared on mirror silicon, a nano c-BN membrane intermediate layer, a high-C-axis preferred orientated nano h-BN membrane, and an IDT. This invention can be used on condition of 2. 5GHz, high electromechanical coupling factor, smaller loss at 8w propagation, and low frequency temperature coefficient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
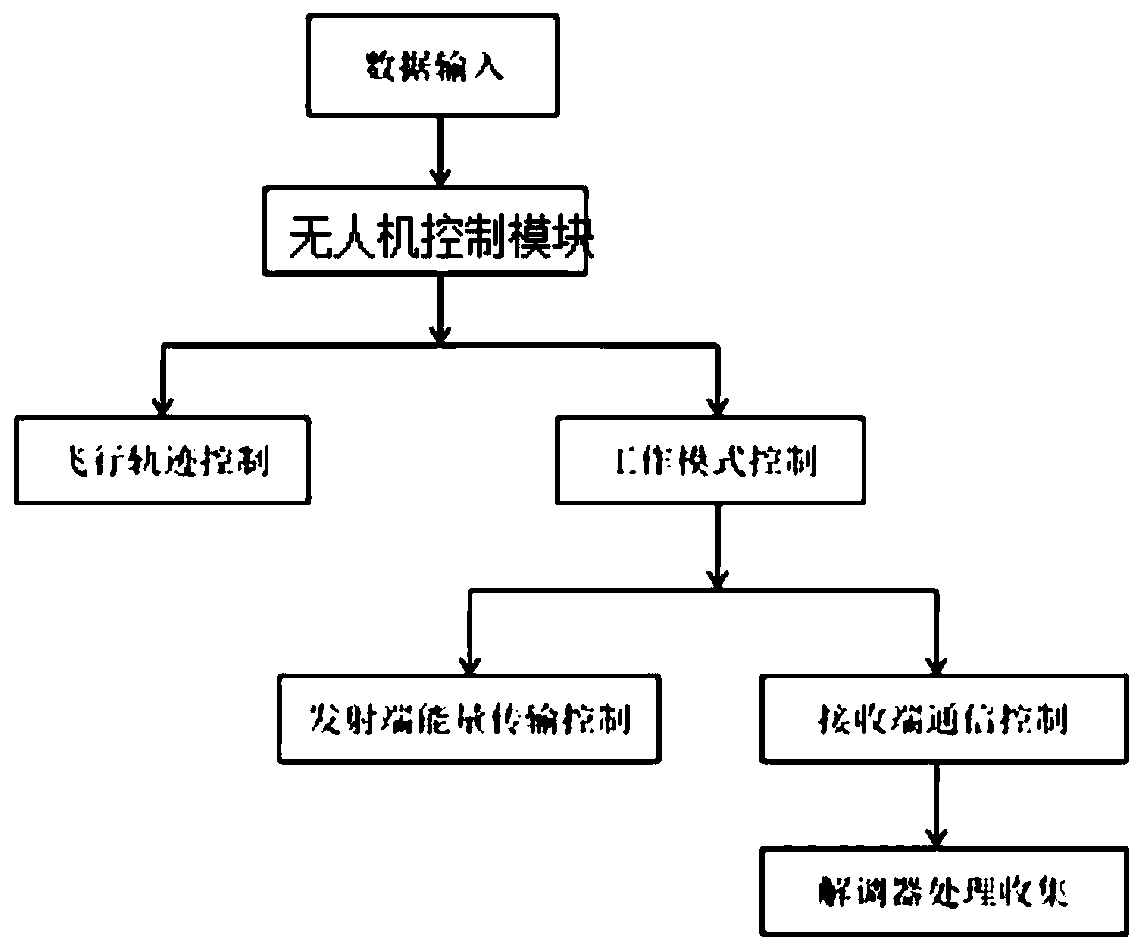
Unmanned aerial vehicle assisted backscatter communication device and resource allocation control method
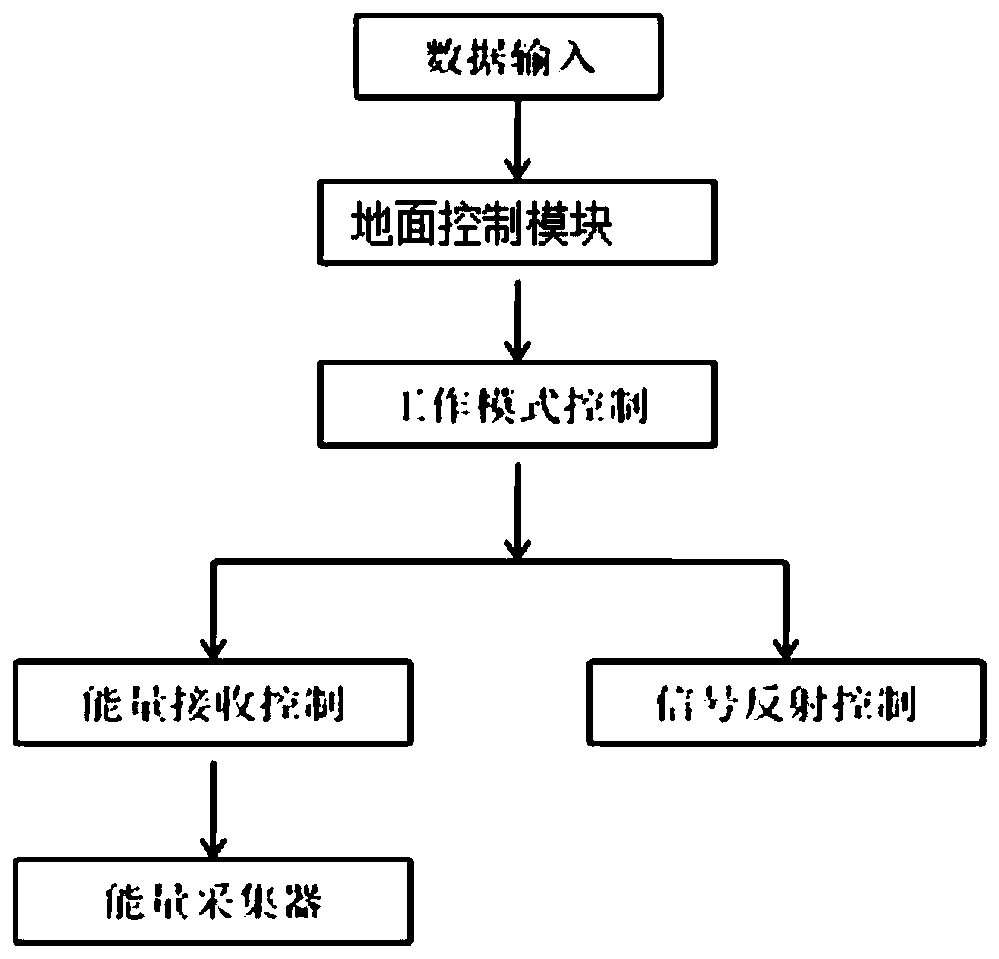
ActiveCN110730028AReduce distanceSmall propagation lossNear-field transmissionRadio transmissionResource assignmentSignal reflection
In existing backscatter communication research, the communication performance difference of backscattering equipment at different positions in the system is large, we face the serious fairness problemin order to overcome the defects of existing research,the invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle auxiliary backscatter communication device and a resource allocation control method. The control assembly comprises a data acquisition module, an unmanned aerial vehicle control module, a track control module, a communication control module and a working mode control module. The backscatteringequipment assembly comprises a ground control module, a working mode selection module, an energy receiving control module, a signal reflection control module and an energy collector. According to theinvention, the unmanned aerial vehicle is used as a control center to transmit and receive an information command to the equipment, and the backscattering equipment collects energy or reflects a signal to transmit information. The flight path is optimized by utilizing the flexible mobility and operability of the unmanned aerial vehicle, so that the distance between the unmanned aerial vehicle andthe sensor is effectively shortened, and the throughput of a communication system is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Tunable light wave beam splitter based on fluid light guide
ActiveCN103869477AControl concentrationControl spaceOptical waveguide light guideBeam splitterLight guide
A tunable light wave beam splitter based on a fluid light guide comprises the fluid light guide, an incident laser, a light beam receiving surface and a flowing-out fluid container, wherein the fluid light guide is provided with a passageway which comprises a core layer fluid inlet, two symmetric cover layer fluid inlets, a fluid microcavity and two symmetric fluid outlets, the core layer fluid inlet and the cover layer fluid inlets are all communicated with the inlet side of the fluid microcavity of which the outlet side is connected with the two fluid outlets, the fluid outlets are communicated with the flowing-out fluid container, the incident laser and the light beam receiving surface are arranged coaxially, the axes of the incident laser and the light beam receiving surface are vertical to the flowing direction of fluid, and flow rate adjusting equipment is arranged in the core layer fluid inlet and the cover layer fluid inlets and is connected with a beam splitting control module for controlling the flow rate of the fluid in a core layer and a cover layer to realize light wave beam splitting and splitting ratio control. The tunable light wave beam splitter can realize dynamic tuning and is high in integration level, simple in structure, convenient to manufacture and low in cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Thermally assisted head having reflection mirror for propagating light
ActiveUS20110310713A1Suppresses plasmon generationPropagation loss of the light on the reflection layer is suppressedCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsRefractive indexLaser light
A magnetic head includes a magnetic head slider; and a laser diode that is positioned on a surface of a side opposite to a substrate of the magnetic head slider and that generates laser light; the magnetic head slider including: a core through which the laser light emitted from the laser diode propagates as propagating light; a cladding that covers the core and that has a refractive index that is smaller than that of the core; a near field light generating means that generates near field light from the propagating light on an air bearing surface; and a main pole for recording that is disposed adjacent to the near field light generating means and of which an edge part is positioned on the air bearing surface. The core includes a reflection layer and a seed layer, the reflection layer has a refractive index smaller than that of the core, and has a reflection surface on which laser light emitted from the laser diode reflects so as to enter the core as the propagating light, and the seed layer is positioned on a back surface of the reflection surface of the reflection layer and suppresses plasmon generation on the reflection surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
X-ray waveguide
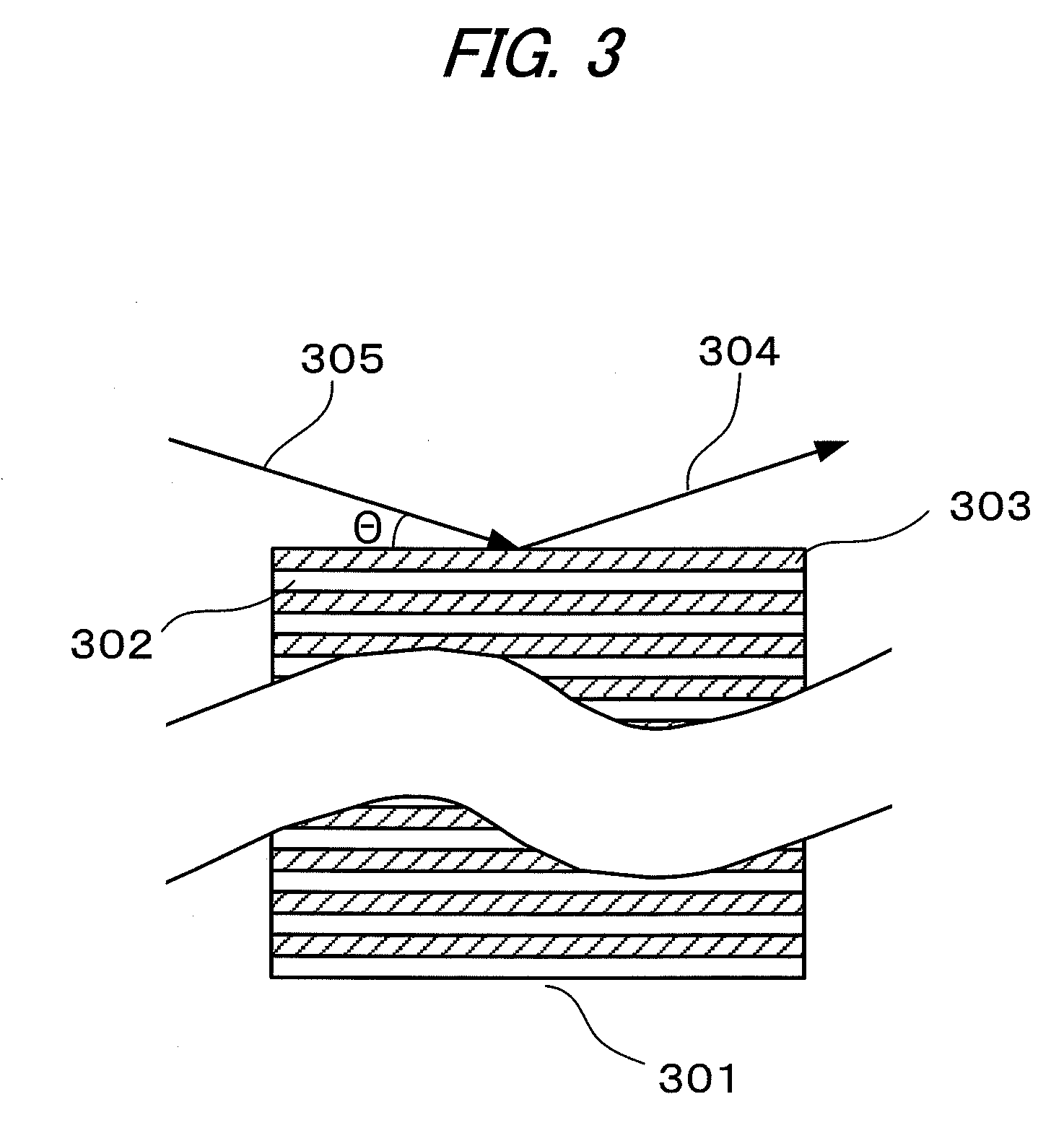
InactiveUS20110299662A1Small propagation lossEasy to produceRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsRefractive indexX-ray
An X-ray waveguide which: shows a small propagation loss of an X-ray; does not deteriorate owing to oxidation; and can be easily produced is realized with an X-ray waveguide, including: a core for guiding an X-ray in such a wavelength band that the real part of refractive index of materials is 1 or less; and a cladding for confining the X-ray in the core, in which: the cladding has a one-dimensional periodic structure consisting of at least two materials having different real parts of refractive index; one of the materials is inorganic one, and another one of materials is any of an organic material, a gas, or vacuum; and the core and the cladding are formed so that the critical angle for total reflection at the interface between the core and the cladding is smaller than a Bragg angle depending on the periodicity of the one-dimensional periodic structure.
Owner:CANON KK
Waveguide structure and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7376317B2Enhanced couplingRadius of curvature can be lessenedNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideOptoelectronicsPolymer
A waveguide structure having a cross-sectional structure wherein Si is in the center and it is surrounded by a peripheral material, which is either SiO2 or a polymer material. The above-mentioned peripheral material functions as a cladding.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and terminal for detecting and diagnosing atmospheric duct in real time
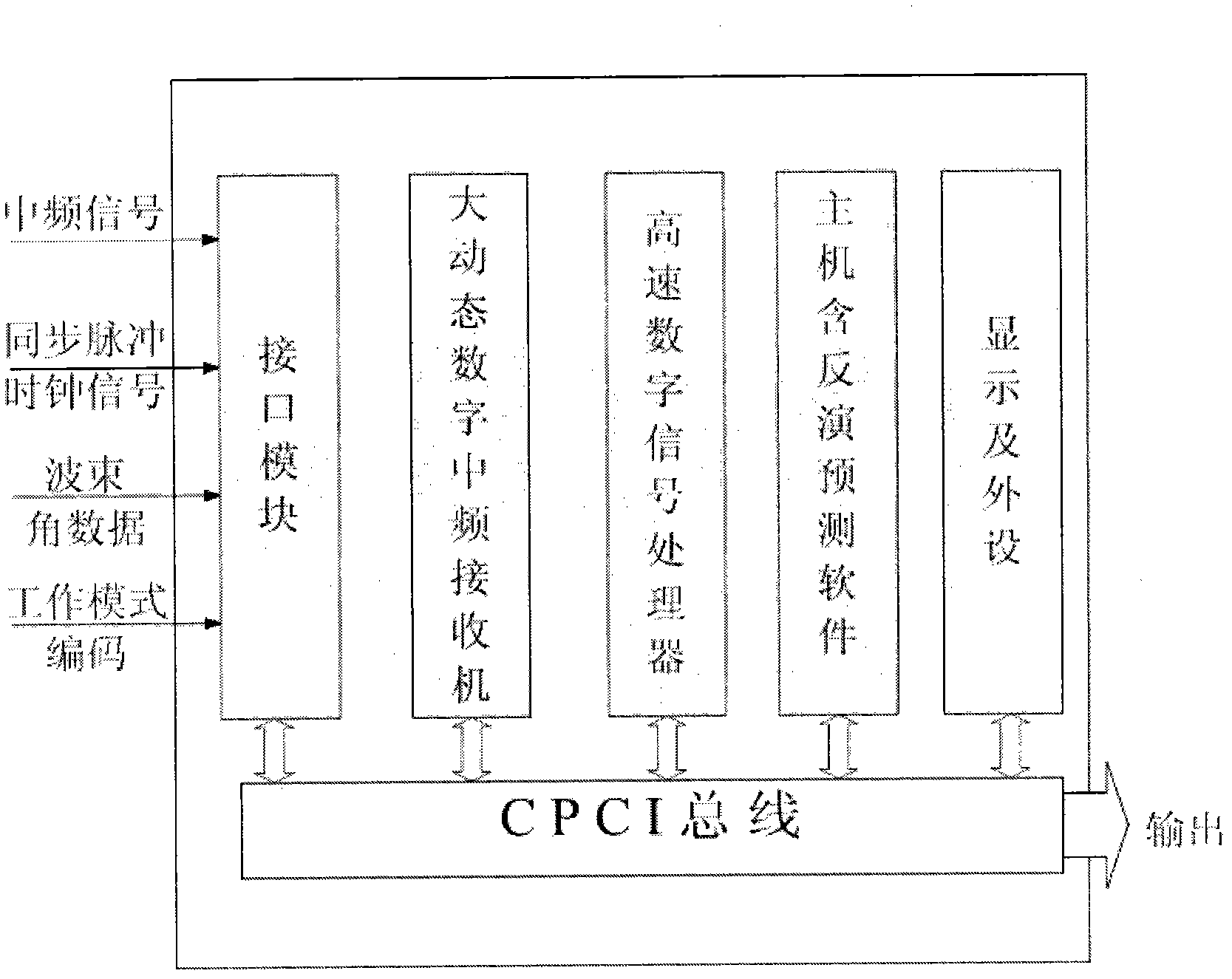
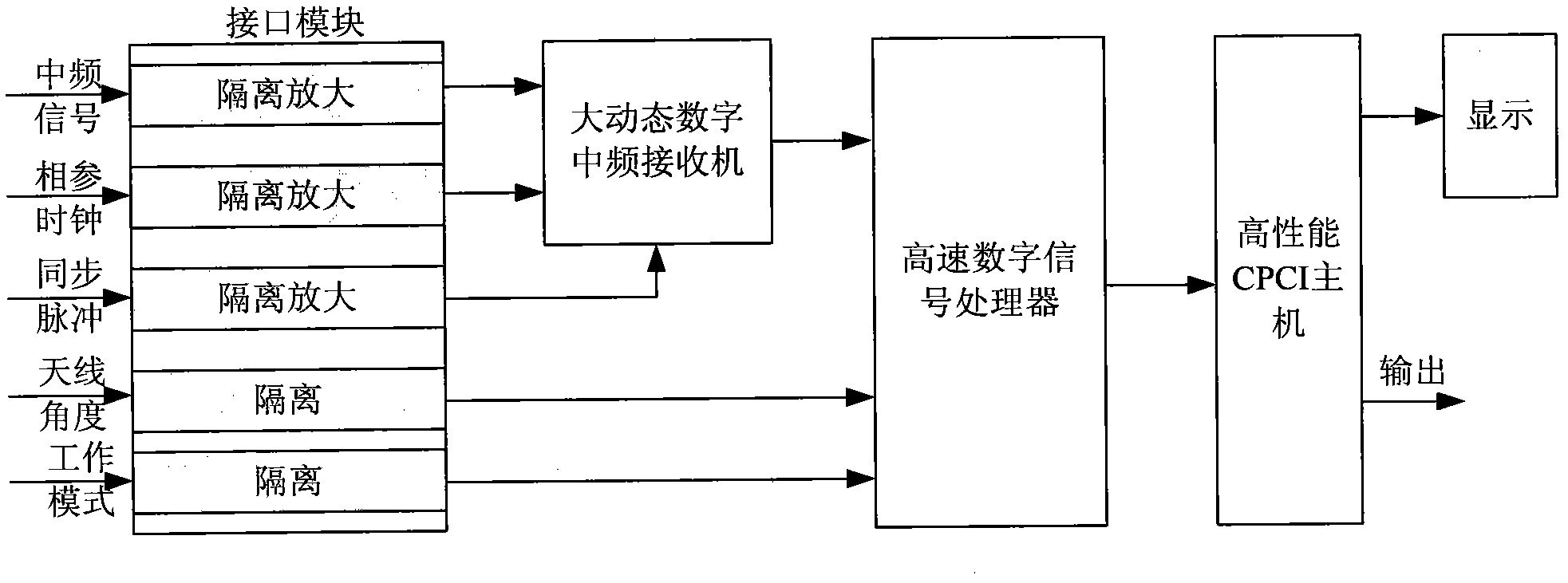
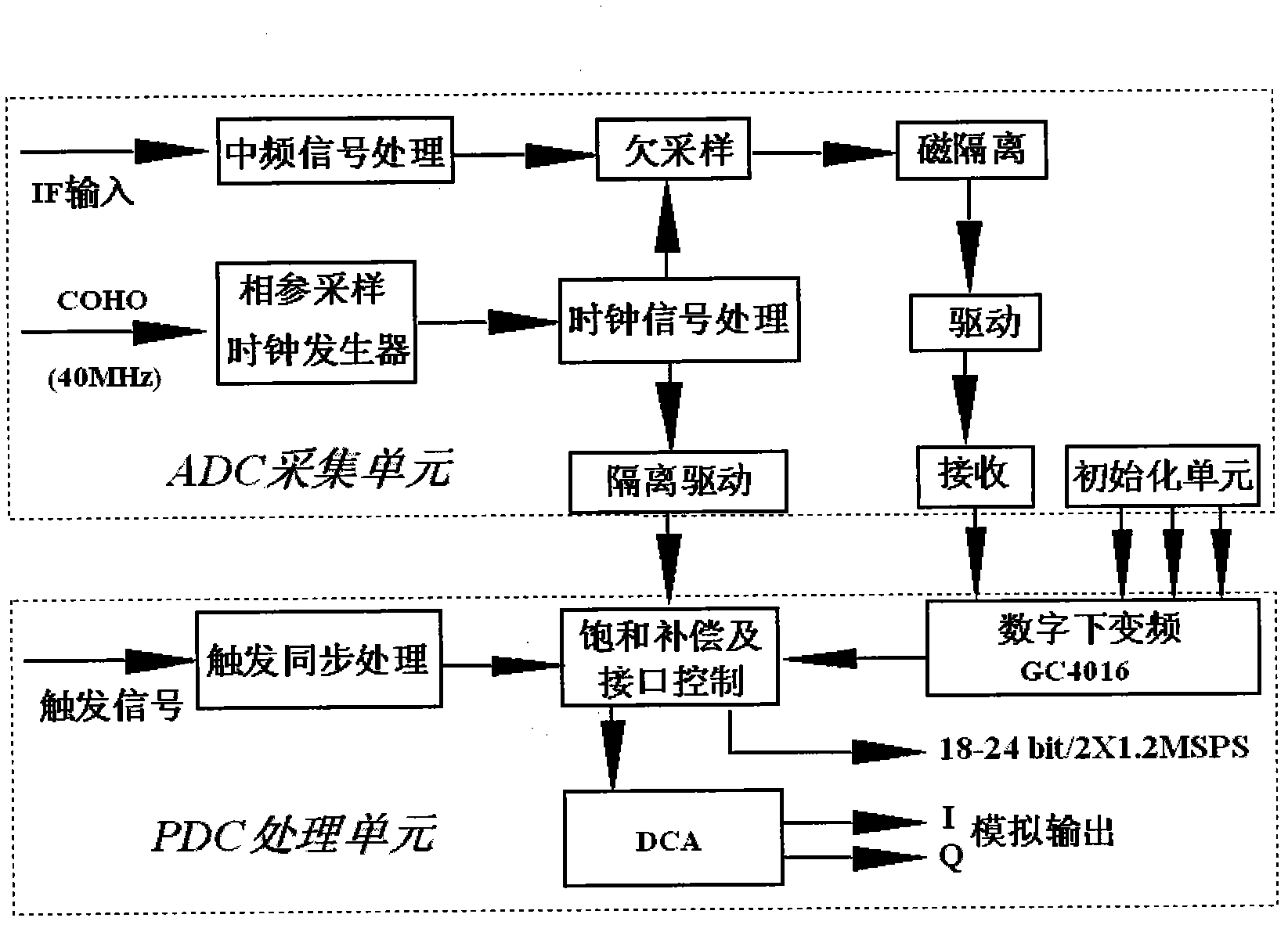
InactiveCN103135108ASuitable for useOvercoming conventional detectionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIntegratorX-wave
The invention provides a terminal for detecting and diagnosing atmospheric duct in real time. The independent terminal is connected onto a radar on active duty and has the capability for detecting and diagnosing the atmospheric duct on the premise that the work and the performance of a shore based radar or a ship-based connected radar are not influenced. The terminal comprises a work station (or a server) based on a compact peripheral component Interconnect (CPCI) bus, an interface module, a medium-frequency sampling digital receiver, a high-speed digital signal processor and an integrator formed by related software. The terminal acquires echoes and data by utilizing the connected radar, performs isolation and amplification through the interface module, then sends an original signal to the medium-frequency sampling digital receiver and the high-speed digital signal processor to be processed and converted so as to obtain sea clutter data, measures and calculates sea clutter power, performs atmospheric duct parameter inversion through atmospheric duct detecting and diagnosing software, and finally displays atmospheric duct parameters on a displayer of a control console. The terminal fully utilizes existing functions of the connected radar, does not influences normal usage, and is low in modification cost, convenient to install, high in reliability and suitable for radars with X wave bands, C wave bands and S wave bands.
Owner:BEIJING LEIYIN ELECTRONICS TECH DEV
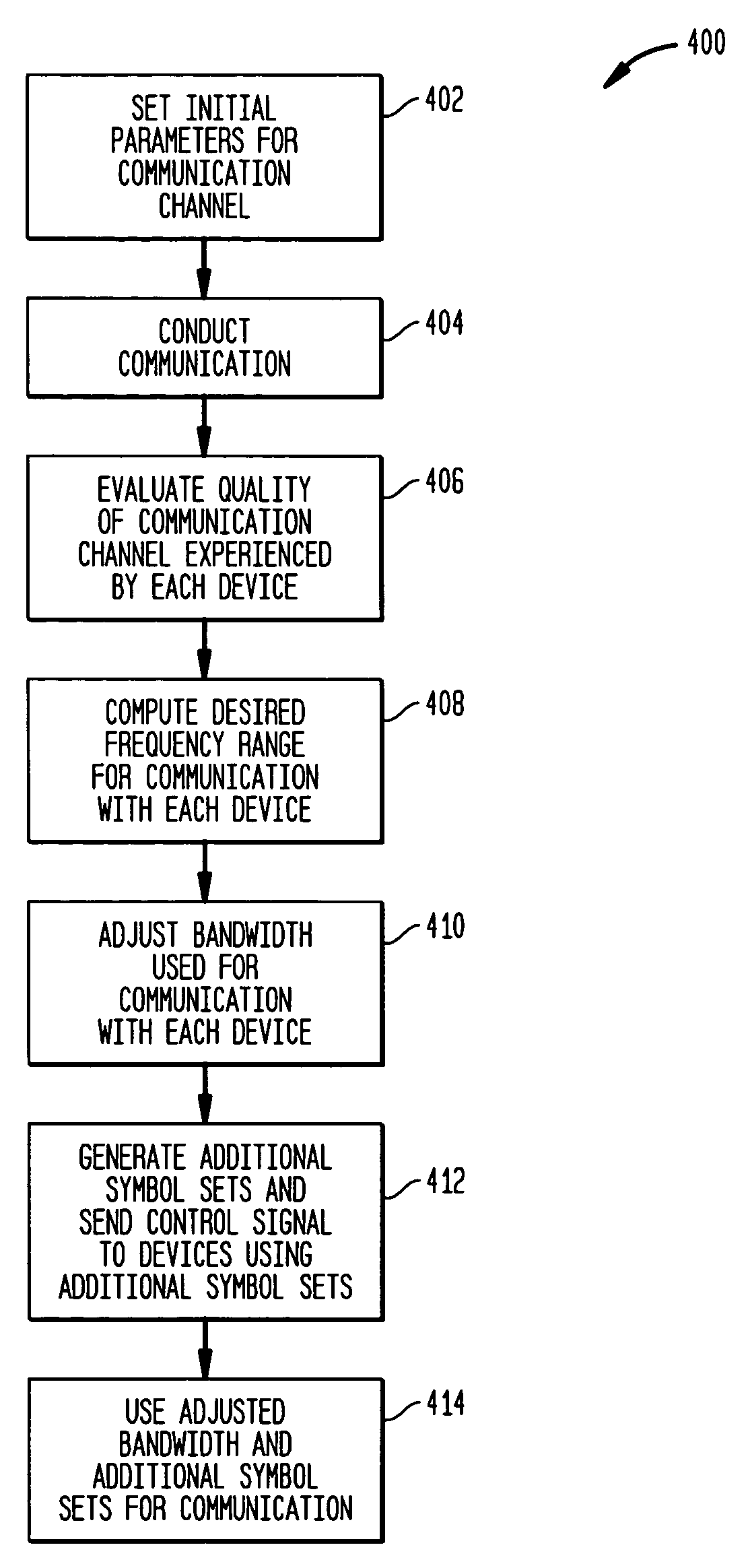
Methods and apparatus for allocating bandwidth to communication devices based on signal conditions experienced by the communication devices
ActiveUS7440760B2Bandwidth adjustableConstant signal to noise ratioRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringCommunications systemCommunication device
Techniques and systems for allocating bandwidth in a communication channel to devices using the communication channel are described. A communication system includes a central device and one or more remote devices. The central device may transmit information to and receive information from each of the remote devices and each of the remote devices may transmit information to and receive information from the base station. The central device receives information relating to the quality of the communication channel experienced by remote device and adjusts the bandwidth allocated to each remote device based on the communication channel quality experienced by that device. The total frequency range encompassed by the communication channel may also increase or decrease as the average quality of the communication channel for all remote devices increases or decreases. Increasing the frequency range available to a device while maintaining the channel quality allows a directly proportional increase in the communication rate with the device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
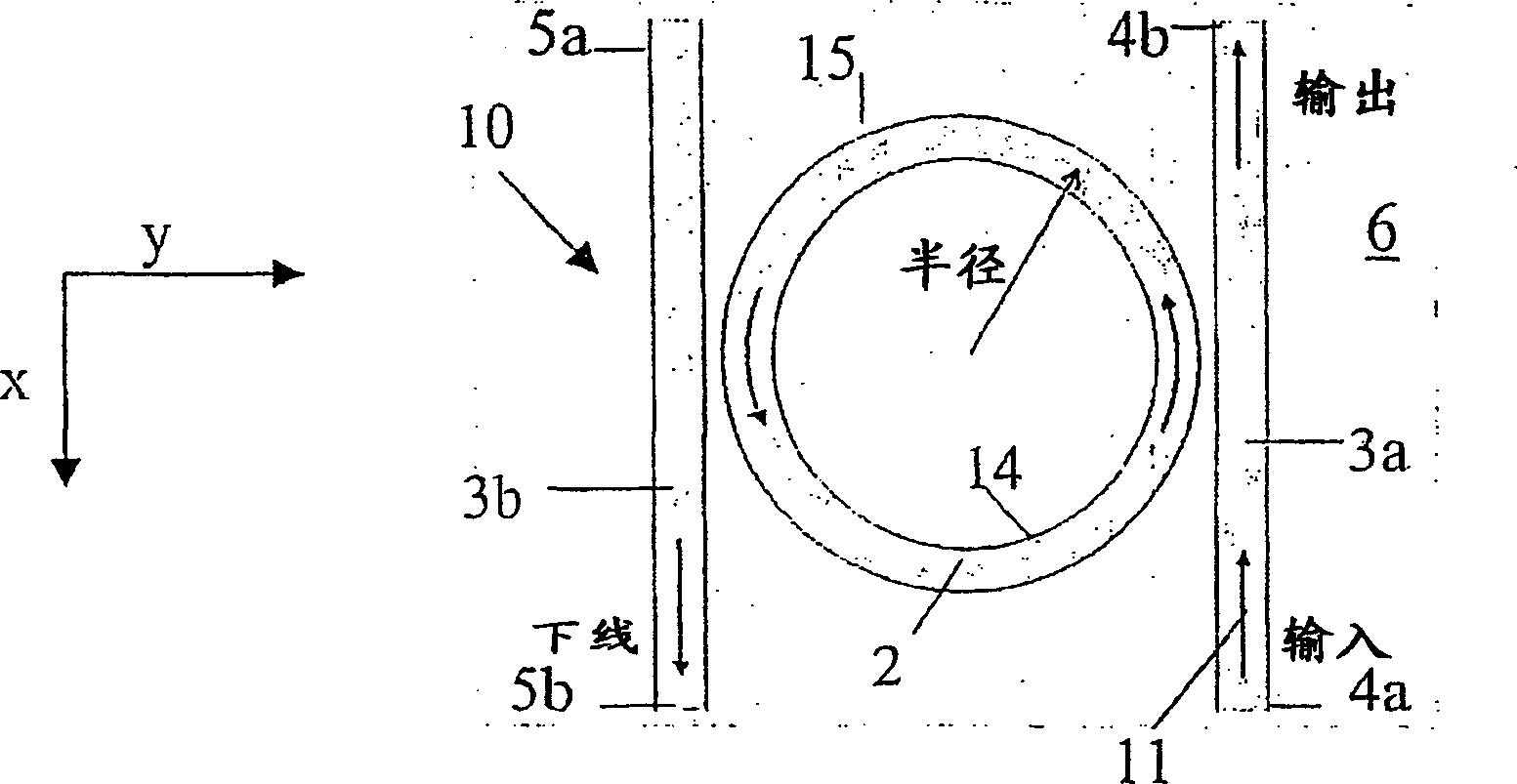
Low loss microring resonator device
InactiveCN1886686ASmall propagation lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideClosed loopRefractive index
It is disclosed a low loss micro-ring resonator device (10; 100; 10') which comprises a closed-loop resonator waveguide (2) having a first refractive index (nr), the resonator waveguide (2) defining an inner (16) and an outer region (17) by an outer curved edge (15) of the waveguide (2). The resonator waveguide is arranged on a substrate (6; 6') having a second refractive index (nb), the refractive index difference (Deltan1) between the first refractive index (nr) and the second refractive index (nb) is greater than 0.3. The device (10) also comprises an upper cladding (20) covering the inner region (16) of the resonator waveguide (2) having a third refractive index (nuc); and a lateral cladding (21) in contact with the outer curved edge (15) and extending in the outer region (17), said lateral cladding (21) having a fourth refractive index (nlc), the fourth refractive index (nlc) being lower than said third refractive index (nuc). A method for reducing propagation losses of a resonator device (10; 100;10') is also described.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
X-ray waveguide and x-ray waveguide system
InactiveUS20130142312A1Small propagation lossRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsRefractive indexEngineering
An X-ray waveguide includes a core configured to guide X-ray therethrough and a cladding. In a section perpendicular to an X-ray guiding direction, the core has threefold or more rotational symmetry and has a periodic structure made of plural substances each having a different value of a real part of refractive-index, and a critical angle for total reflection of an X-ray at an interface between the core and the cladding is larger than a Bragg angle of the X-ray for the periodic structure of the core. A waveguide mode having a two-dimensionally spatial coherence over a wide cross-section of the core and exhibiting a small propagation loss is realized.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray circularly polarized ranging method
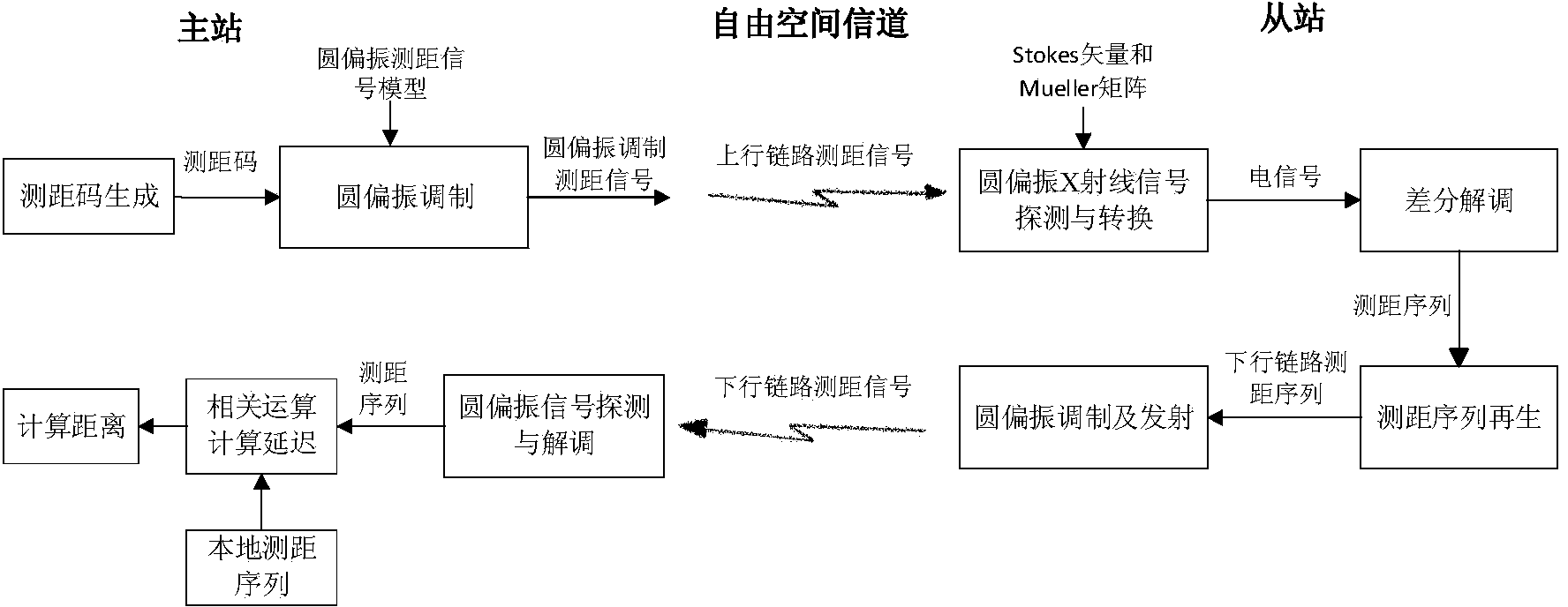
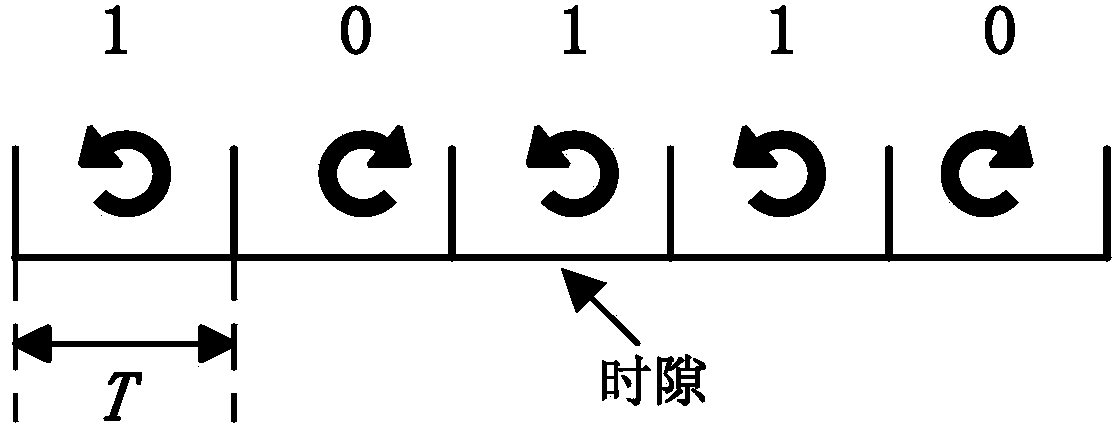
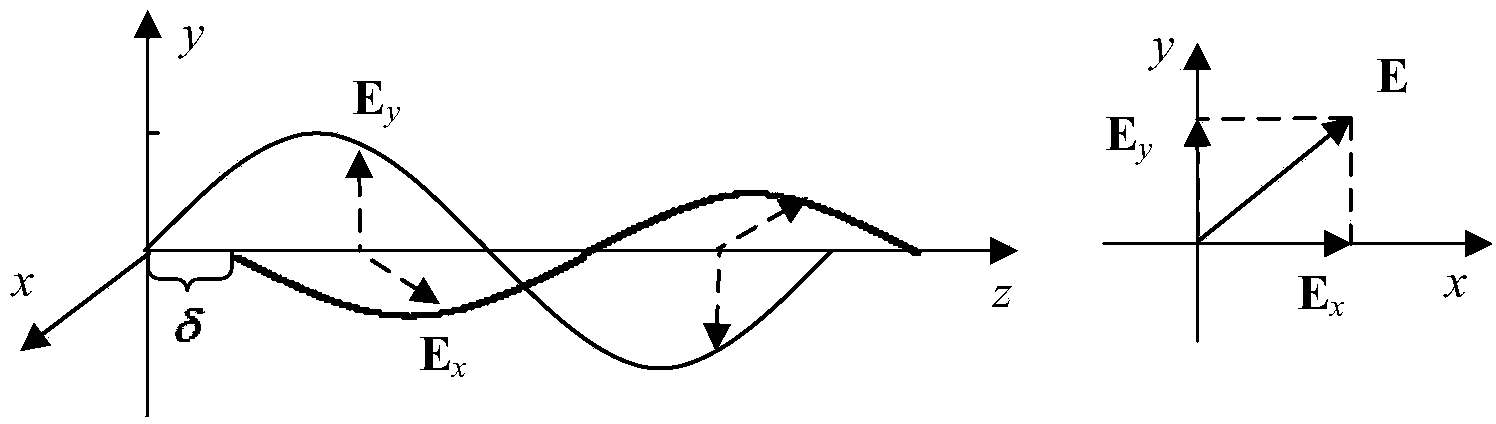
ActiveCN104237873AHigh energyGood orientationUsing reradiationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Left handed
The invention discloses an X-ray circularly polarized ranging method. The method includes: modulating ranging signals by utilizing the circularly polarized modulation technology, and adopting Stokes vectors and a Mueller matrix to perform mathematical modeling on polarized signals in each stage in the ranging process; describing changing of the polarization state in the processes of modulation and demodulation on the basis of a signal model, and further explaining detection of left-handed circularly polarized light and right-handed circularly polarized light and the principle of differential demodulation for noise suppression; restoring ranging codes at a receiving station, and reducing background noise and increasing the signal to noise ratio by taking the measure of regenerating ranging codes. X-rays have characteristics of high energy, low propagation loss and high directivity, thereby being suitable for ranging in free space; the circularly polarized modulation technology has higher anti-interference performance, thereby being suitable for information transmission in the free space under harsh conditions.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Light beam shaping method based on microfluidic optical technology
ActiveCN103792664ASmall propagation lossFlexible and variable refractive index distributionOptical elementsDiffusionLight beam
The invention discloses a light beam shaping method based on a microfluidic optical technology. The light beam shaping method based on the microfluidic optical technology comprises the steps that (1) diffusion and convection movement only exist between core layer fluid and wrapping layer fluid, the wrapping layer fluid surrounds the core layer fluid uniformly, the core layer fluid and the wrapping layer fluid are two kinds of fluid with different refractive indexes, and the core layer fluid and the wrapping layer fluid flow in a fluid micro cavity and jointly form a fluid optical waveguide; (2) an incidence laser emits a laser beam with a set wave length into the fluid optical waveguide, the included angle between the light beam spreading direction and the fluid flowing direction is 90+ / - 10 degrees, and a light beam receiving surface receives a light beam which is output after flowing through the fluid optical waveguide; (3) light beam shaping is achieved by adjusting the flowing speed, temperature and concentration of the fluid and the types of micro fluid and controlling the diffusion process of the fluid and the space distribution of the refractive indexes. The light beam shaping method based on the microfluidic optical technology is small in loss in the light spreading process, simple in structure, convenient to manufacture and good in adjustment flexibility.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
High frequency surface acoustic wave device with AlN (aluminum nitride) film as interlayer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102412803ASmall velocity dispersionHigh electromechanical coupling coefficientImpedence networksVacuum evaporation coatingFrequency dispersionChemical vapor deposition
The invention provides a high frequency surface acoustic wave device with an AlN (aluminum nitride) film as an interlayer. The device is characterized in that an a-axis preferred orientation AlN film is taken as a CVD (chemical vapor deposition) diamond substrate and a c-axis preferred orientation ZnO film is taken as an interlayer, the substrate and the interlayer are formed into an IDT(interdigital transducer) / ZnO / a-axis preferred orientation AlN / diamond multi-layered membrane structure and the structure is stacked with the IDT in sequence to form the high frequency surface acoustic wave device; the preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing an a-axis preferred oritention AlN film interlayer, and preparing a c-axis preferred oritentation ZnO film on the a-axis preferred orientation AlN film interlayer. The device and the preparation method provided by the invention have the following advantages that the sound velocity frequency dispersion caused by a large sound velocity gap between nanodiamond and ZnO can be solved, the application demand of the surface acoustic wave with high frequency above 4.8 GHz can be met, and moreover, the process is simple and easy to implement, and is beneficial for large-scale population and application.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com