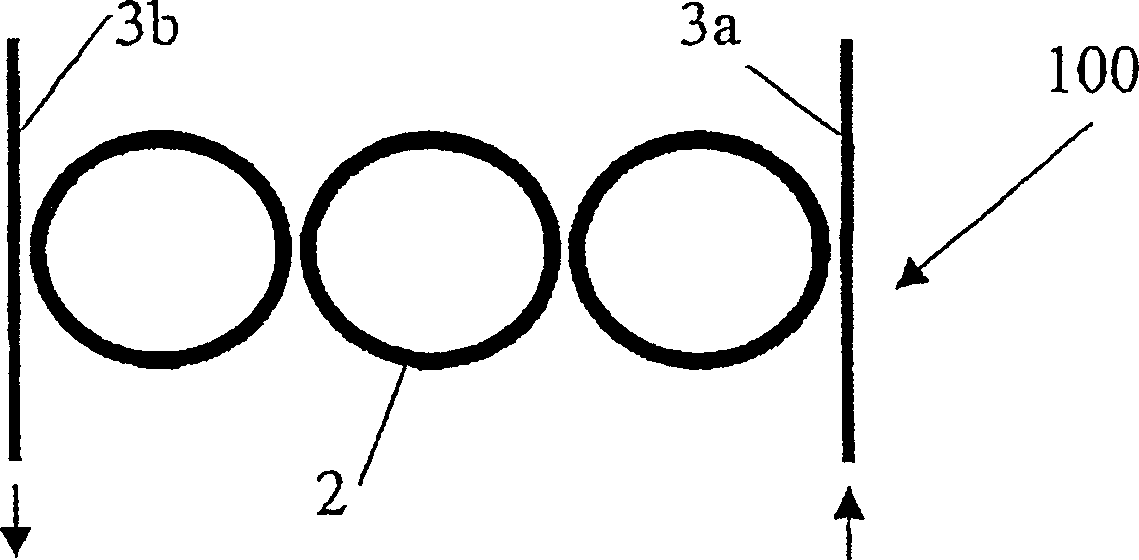Low loss microring resonator device
A ring resonator and resonator technology, applied in the direction of instruments, light guides, optics, etc., can solve the problem of increased loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
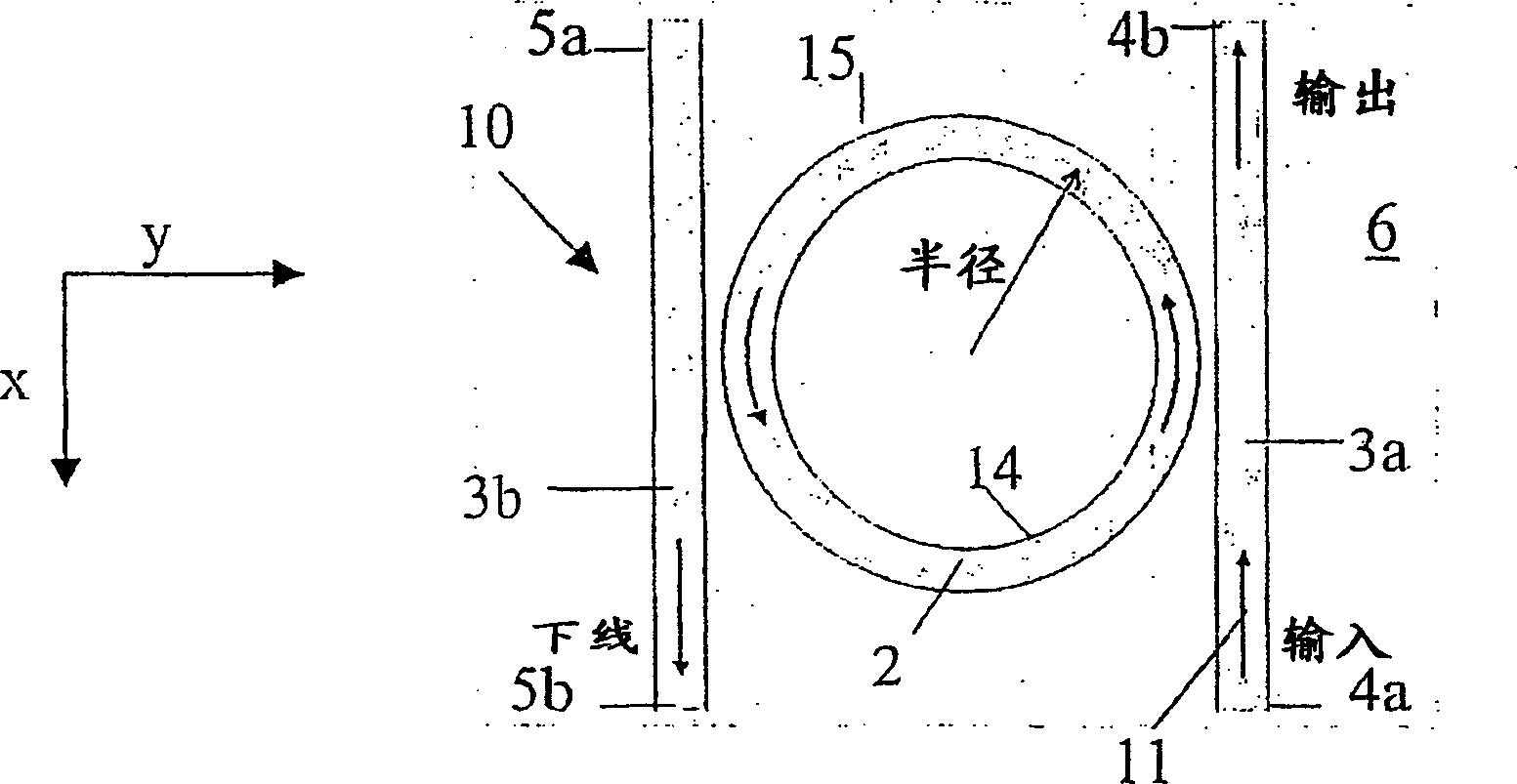
[0099] Consider the resonator device 10 of FIG. 6 . The resonator 2 and the bus waveguides 3a and 3b are on the same (X, Y) plane, and the gap between the first waveguide 3a or the second waveguide 3b and the resonator 2 is 100 to 15nm. The substrate 6 has a refractive index n r SiO = 1.45 2 , while the resonant waveguide 2 and the bus waveguide 3a, 3b have n b Silicon-rich Si = 2.2 3 N 4 accomplish. Side covering layer 21 is air (n lc =1), and the upper cover layer 20 is a Sylgard with a thickness h of 3 μm TM 184 (at room temperature n uc =1.4005) film. The refractive index is the refractive index when the wavelength is 1550nm. The cross section of bus waveguide and resonant waveguide is 1000×300nm 2 rectangle with 100nm overetch. The resonant waveguide 2 is a ring with a radius of 7 μm.
[0100] Applicants have found that the total round trip loss a of the device 10 is equal to 0.07 dB / round trip. If Sylgard covers the entire device, that is, both the upper and...
example 2
[0102] Device 10 is the same as that of Example 1, but with a cross-section of 1200×250nm 2 rectangles with 200nm overetch. The loss is equal to α = 0.1 dB / round trip, or equivalently α = 22.7 dB / cm. exist Figure 13 and 14 in, reproduced image 3 and 4 The graphs of , with a circle added within each graph, respectively show the bending loss and scattering loss of the device 10 studied in this example. From these figures it is clear that the device 10 of the present invention has much lower bending losses than device 50 in which the upper and side cladding layers are air and all other structural properties are the same, while scattering losses are hardly affected.
example 3
[0104] The device 10, whose busbar waveguide and resonant waveguide are all on the same plane, has the following characteristics:
[0105] Substrate 6: SiO 2 ; n r =1.45,
[0106] Resonant waveguide 2, busbar waveguide 3a, 3b: silicon-rich Si 3 N 4 ; n b = 2.2,
[0107] Side cover layer 21: air; n lc = 1,
[0108] Cross section of all waveguides: 1000×300nm 2 rectangle with 100nm overetch.
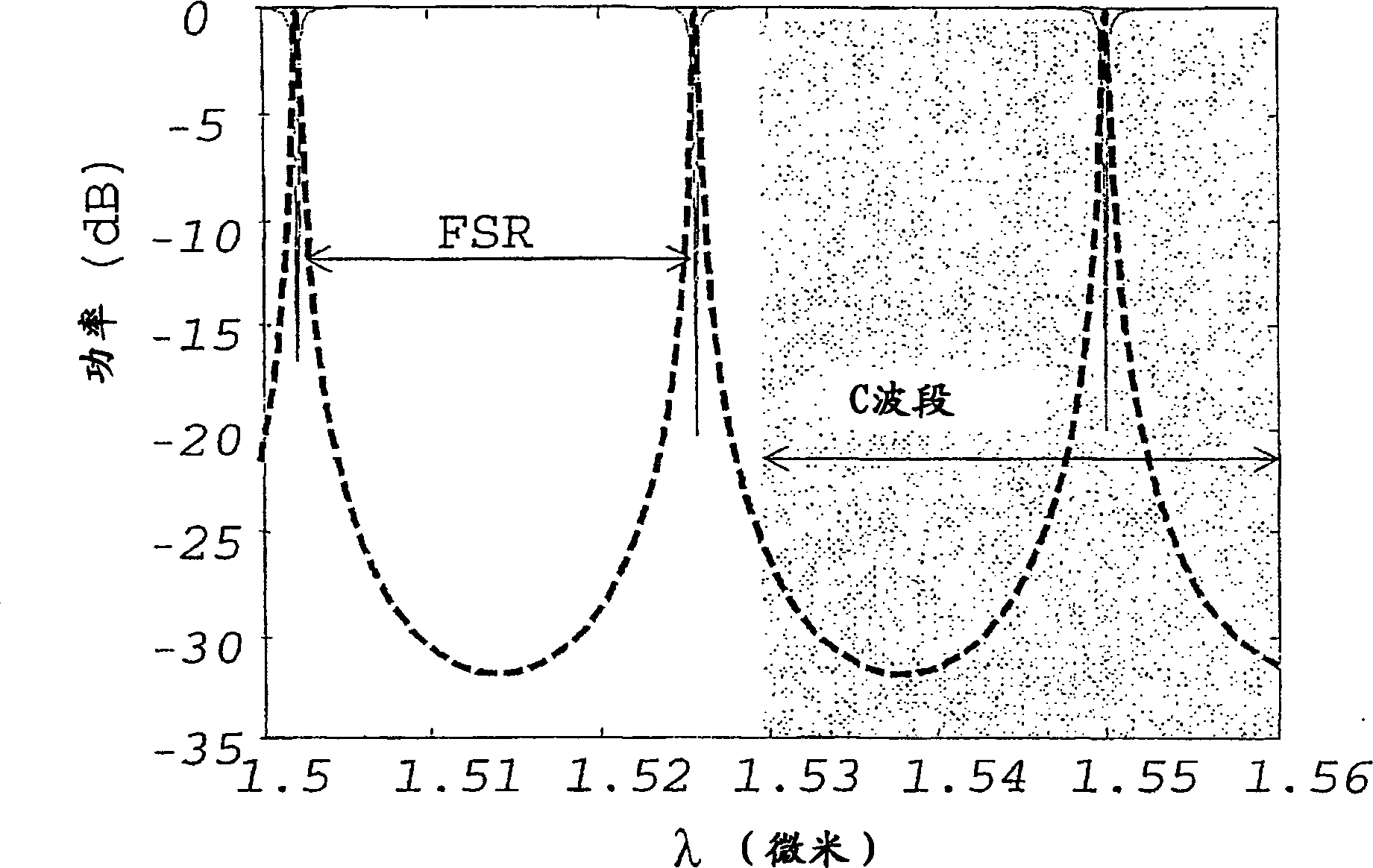
[0109] The propagation loss of this device was calculated for different resonant waveguide radii and different refractive indices of the upper cladding layer 20 . The result is as Figure 5 Shown: Round-trip loss vs. n uc functional relationship.
[0110] For some desired applications, the maximum allowable total loss is equal to 0.1 dB / round trip (equal to 22.7 dB / cm). Therefore, from Figure 8 A useful range of refractive index for an appropriate upper cladding layer 20 can be derived. For example, for a ring with R2 = 7 µm, the useful n uc The range is 1.3uc uc ≥1.8, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com