Optical transmission network, optical transmission apparatus, dispersion compensator arrangement calculation apparatus and dispersion compensator arrangement calculation method
a technology of optical transmission network and compensation arrangement, applied in multiplex communication, electromagnetic repeaters, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the loss at the dispersion compensation, affecting the dispersion of waveforms, and causing wavelength deterioration, so as to reduce the dispersion compensation amount and the number of dispersion compensators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
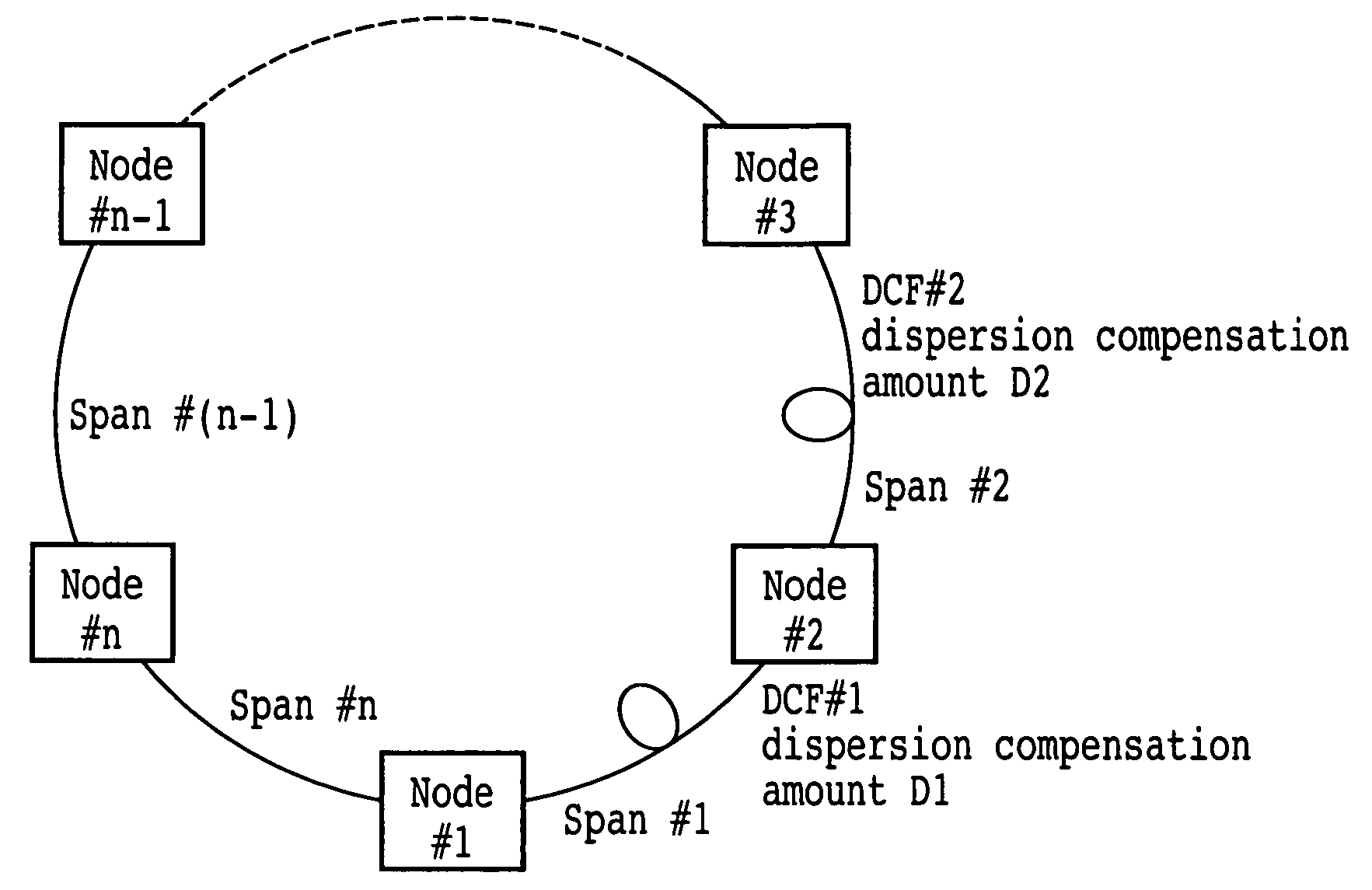
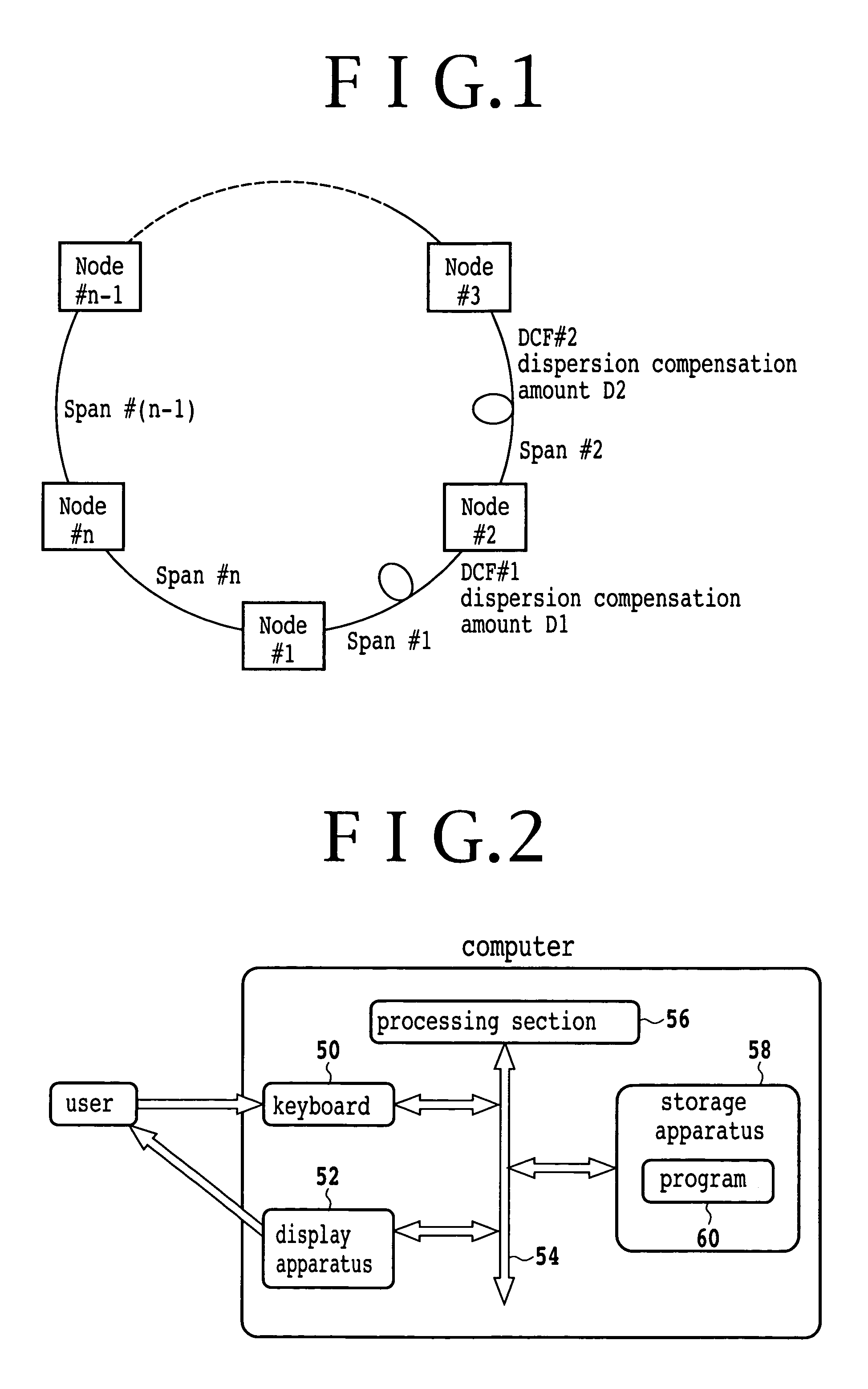
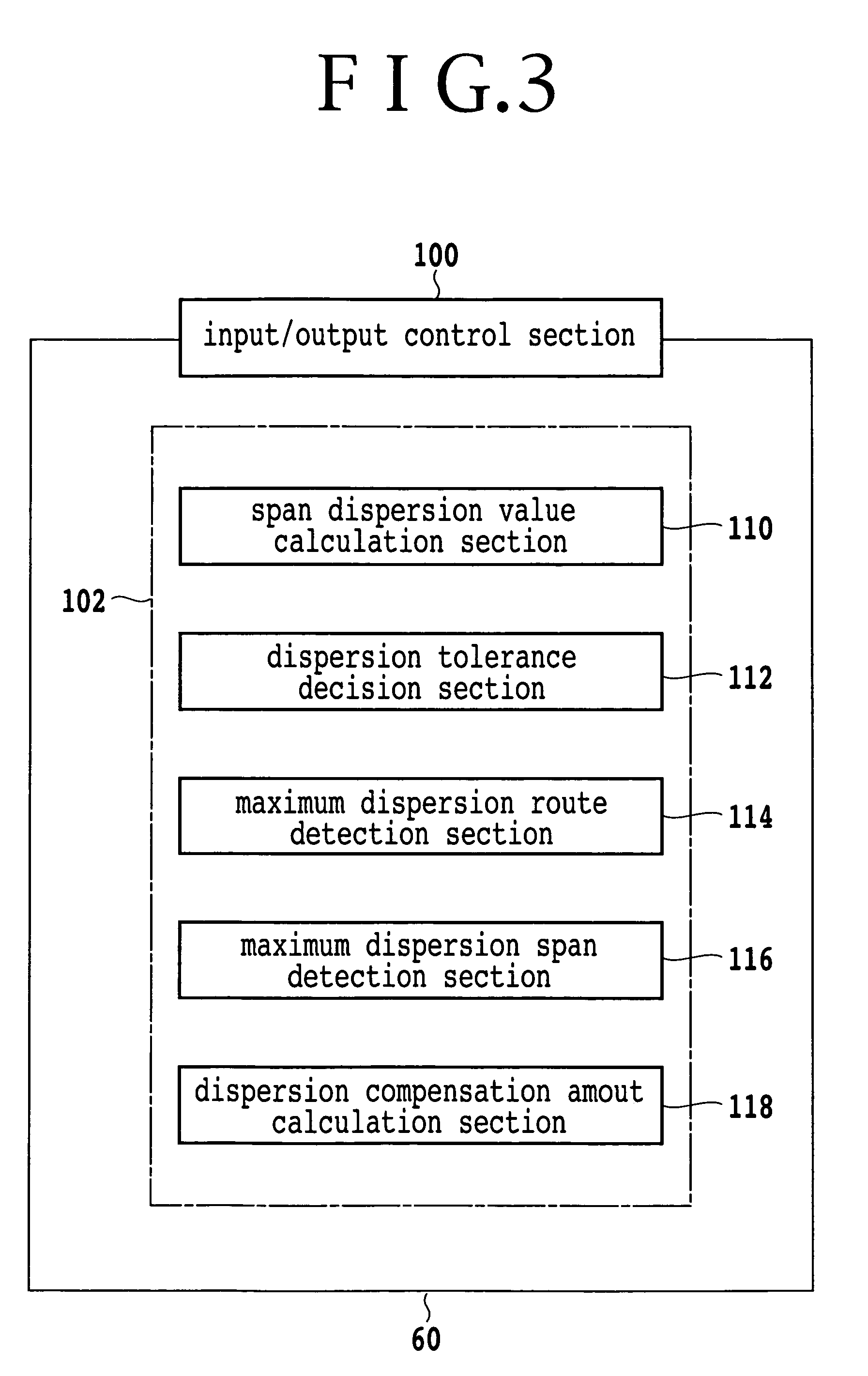
[0124]FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a dispersion compensator arrangement calculation apparatus of an optical transmission network according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 2, the dispersion compensator arrangement calculation apparatus includes a keyboard 50, a display apparatus 52, a bus 54, a processing section 56 and a storage apparatus 58. The keyboard 50 is an inputting apparatus for inputting design parameters for an optical transmission network and so forth. The design parameters include those of information relating to routes to be used, information relating to spans, information relating to transmission lines, information relating to dispersion compensators and information relating to dispersion tolerances. The information relating to routes to be used is path information of paths of the optical transmission network to be used. The information relating to spans is transmission distances of the spans. The information relating to transmission lines...
second embodiment
[0158]FIG. 6 is a view showing an optical transmission network according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 6, for the simplified description, a linear network including totaling four nodes is shown. Here, such prerequisites for the optical network as given below are used:[0159]SMF (single mode fiber);[0160]C-band[0161]maximum wavelength number: 40 waves;[0162]transmission line dispersion coefficient of ch1: 16 ps / nm / km, dispersion compensating fiber dispersion coefficient: −77 ps / nm / km (a dispersion compensator other than a dispersion compensating fiber may be used. In this instance, a dispersion compensation value (ps / nm) is used);[0163]transmission line dispersion coefficient of ch20: 17 ps / nm / km, dispersion compensating fiber dispersion coefficient: −80 ps / nm / km;[0164]transmission line dispersion coefficient of ch40: 18 ps / nm / km, dispersion compensating fiber dispersion coefficient: −83 ps / nm / km;[0165]dispersion tolerance at each node: −100 to +800 [ps / nm] ...
third embodiment
[0184]FIG. 7 is a view showing an optical transmission network according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Where a plurality of spans having a short propagation distance connect successively, or where the dispersion coefficient of the transmission line is low as in the case of a dispersion shift fiber or the like, or else where a part having a negative dispersion such as an optical coupler is used or in a like case, there is the possibility that the accumulated dispersion value may be lower than the lower limit of the dispersion tolerance. The present embodiment is ready also for such a case as just described. In FIG. 7, for the simplified description, a ring network including totaling four nodes is shown. Such prerequisites for parameters of the optical transmission network as given below are used:[0185]DSF (dispersion shift fiber) (while here a DSF is taken as an example of a transmission line having a low transmission light dispersion coefficient, a different fiber ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com