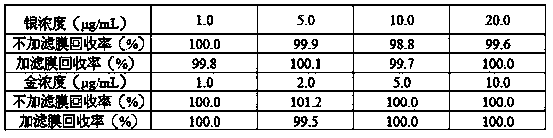
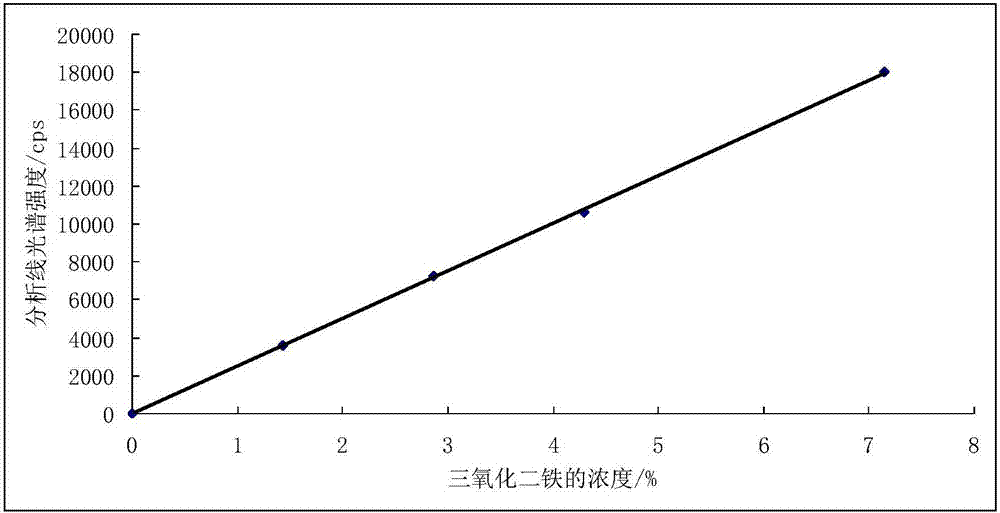
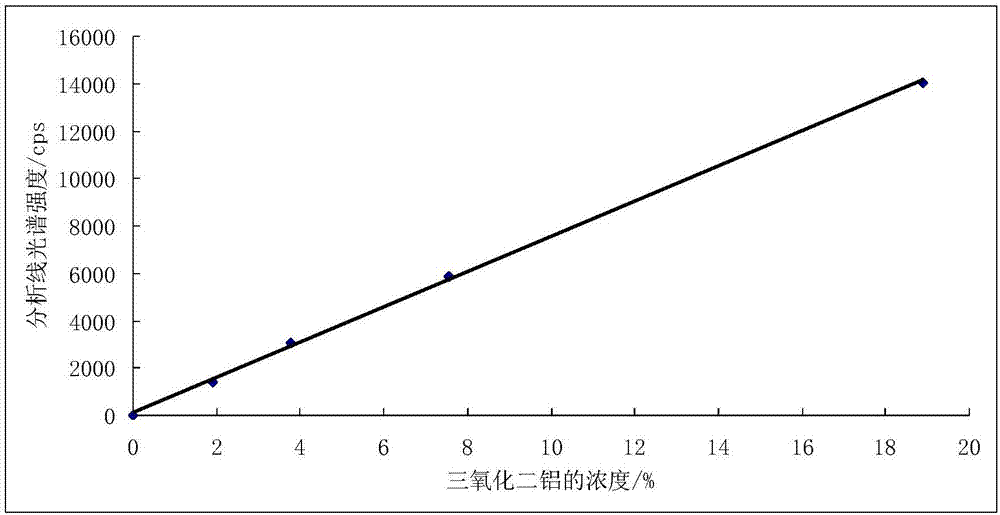
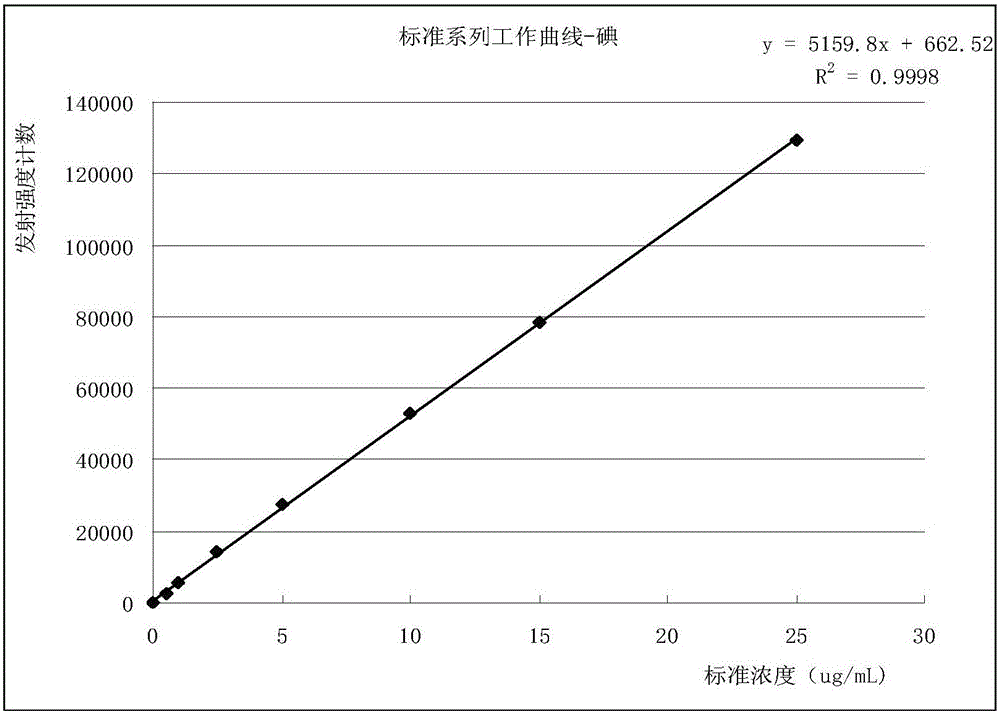
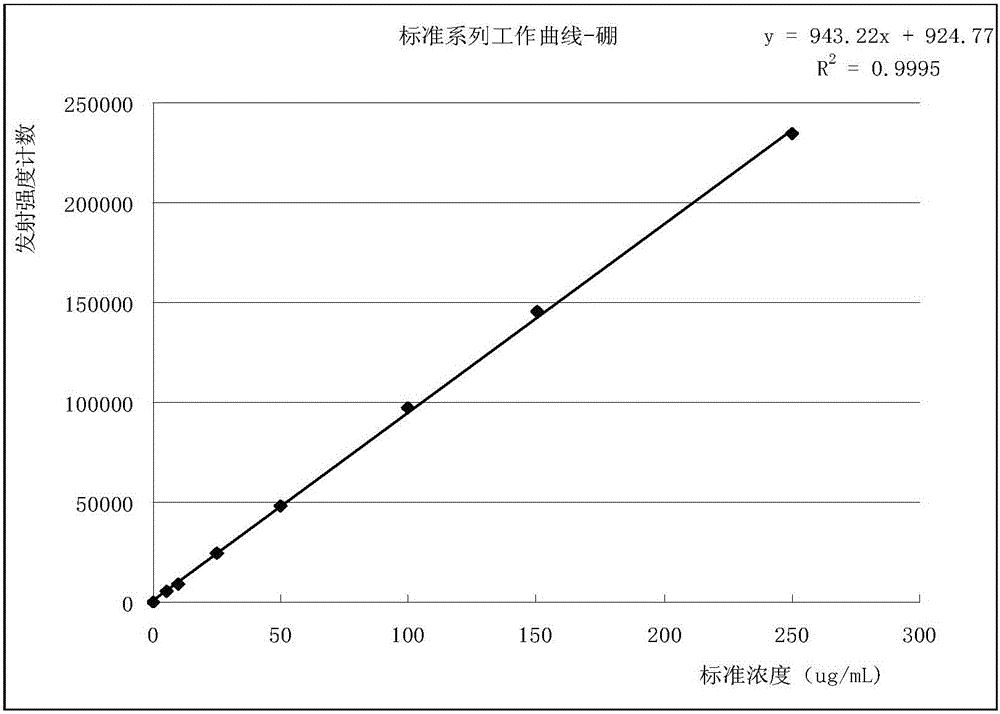
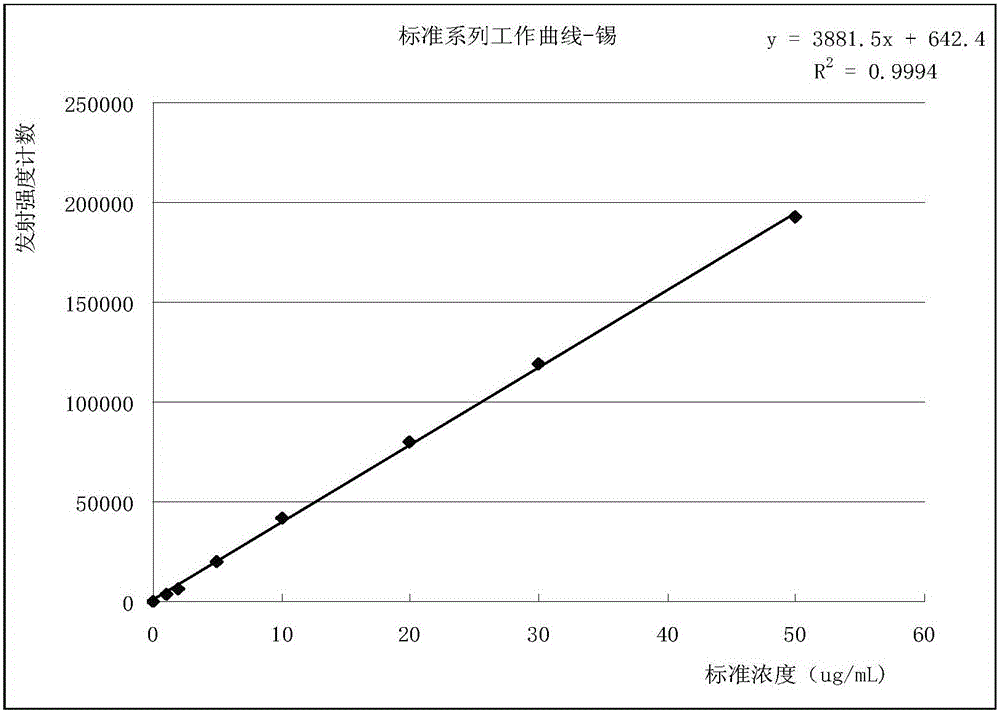
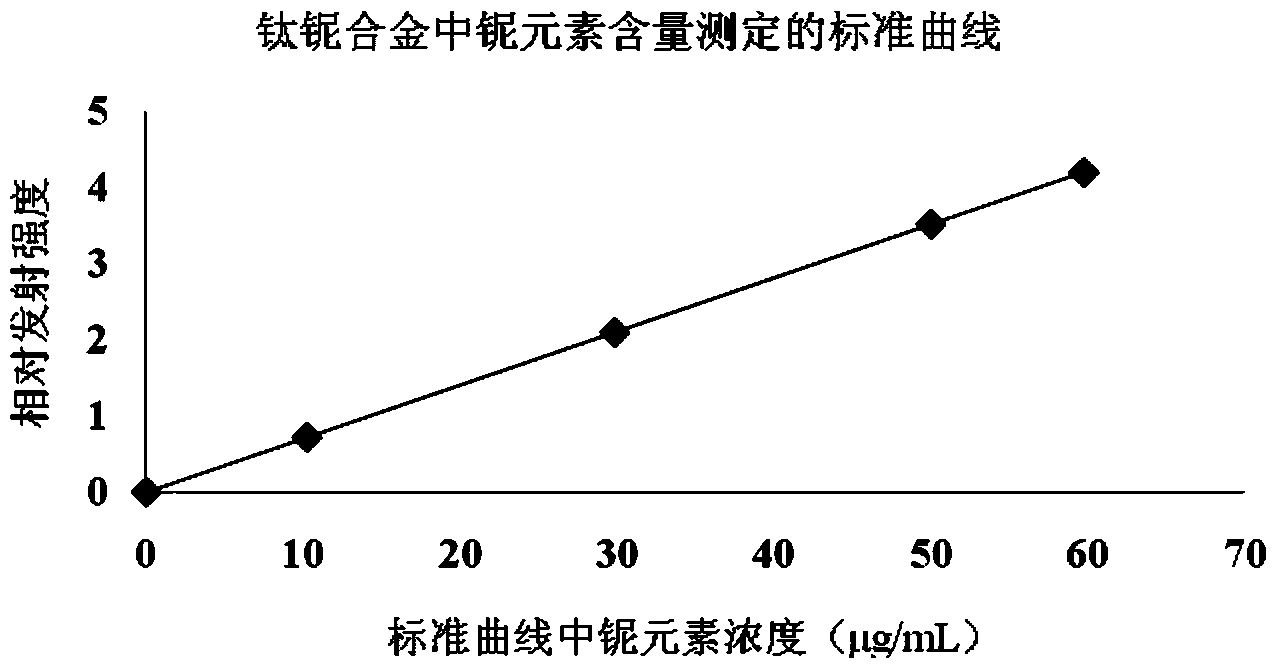
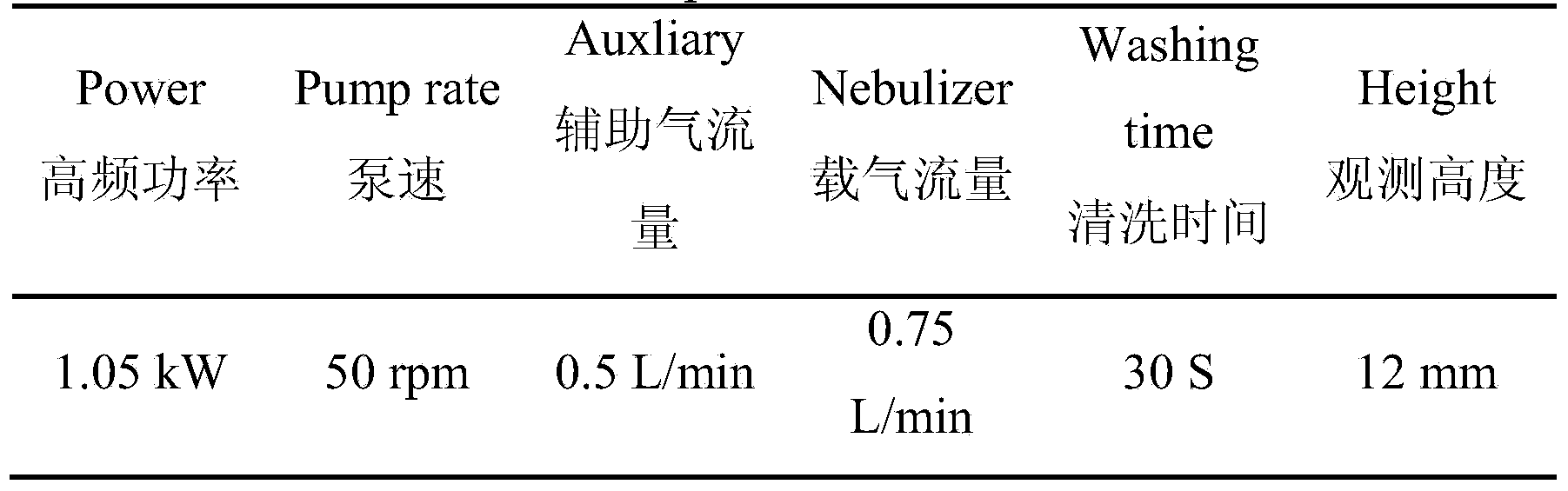
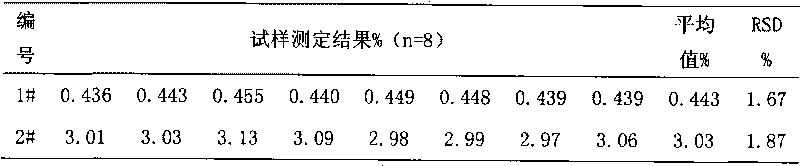
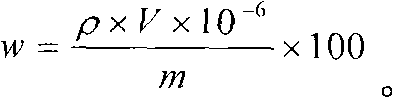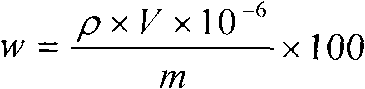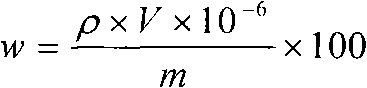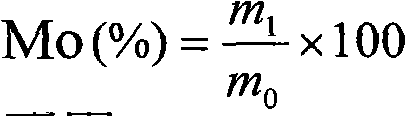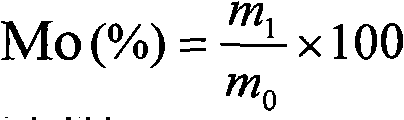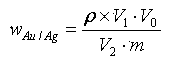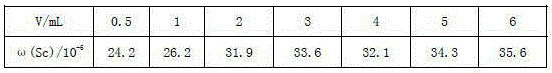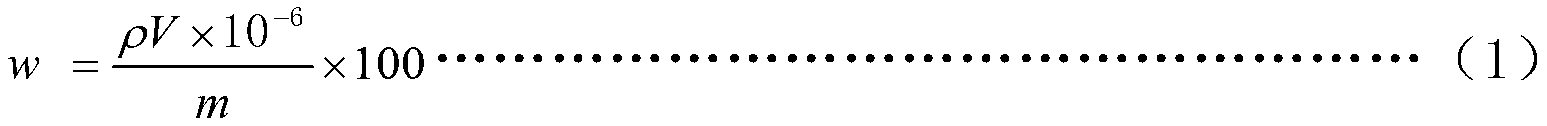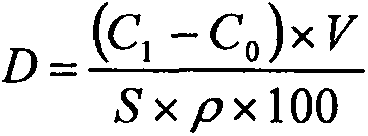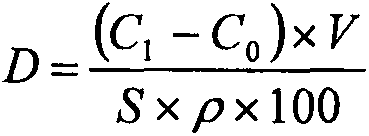Patents
Literature
332 results about "Inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
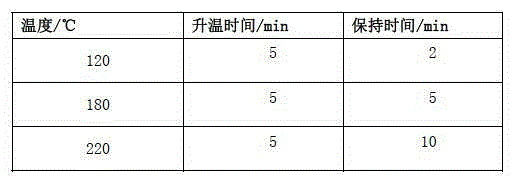
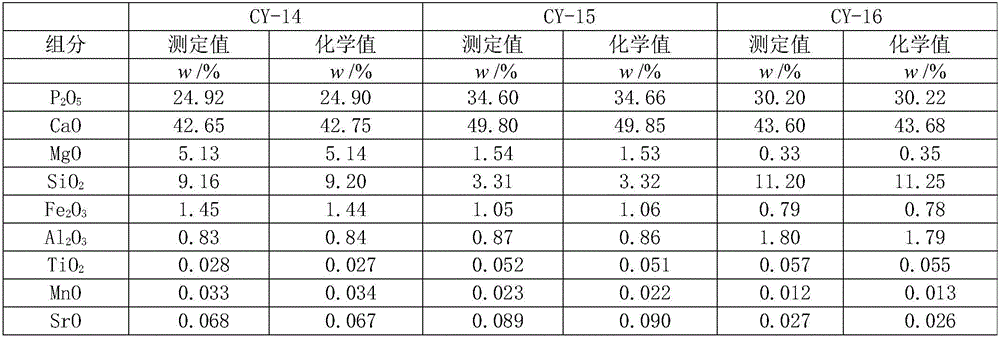
Method for determining impurity content in high-titanium slag
InactiveCN102253030AEasy to measureAccurate measurementPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationFritImpurity
The invention discloses a method for determining the impurity content in high-titanium slag, and belongs to the metallurgical chemical field. According to the method, a high-titanium slag sample is molten by a mixed flux; a frit is leached by a sulfuric acid solution to prepare a test solution; and the impurity component in the diluted high-titanium slag test solution is determined by an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer. With the invention, the content of the impurity component in high-titanium slag can be determined accurately, simply, and rapidly.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Method for measuring content of boron in cobalt-base alloy
ActiveCN101718688AAvoid interferenceImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsElement analysisMaterial resources
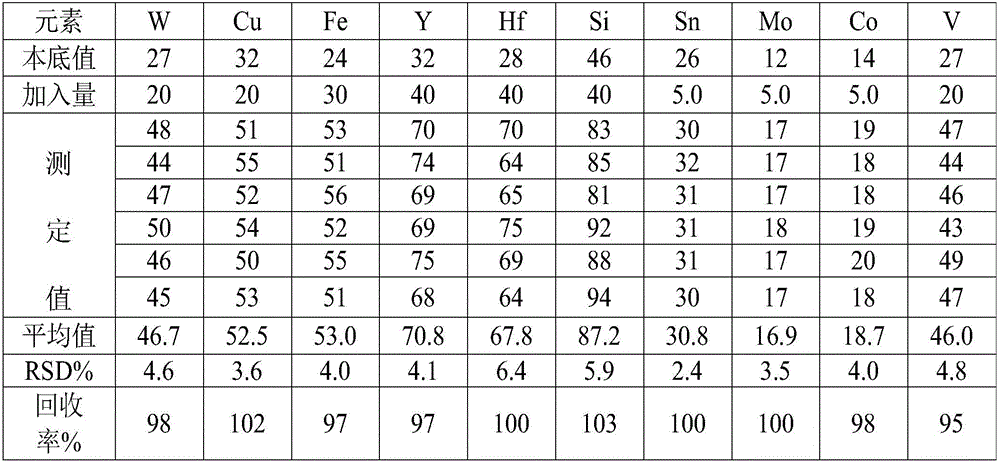
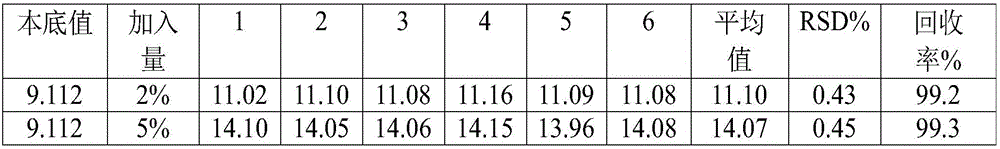
The invention belongs to a technique for analyzing trace elements of an alloy, and relates to a method for measuring the content of boron in a cobalt-base alloy. By adopting an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and treating a sample of the cobalt-base alloy in particular a high-tungsten sample by using 20mL of hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, the method solves the puzzling problems that the past dissolved sample has large reagent dosage and high reagent blank and cannot be measured normally by an instrument; by performing interference experiments and spectrogram analyses, the method finds the optimal analytical line, overcomes the interferences caused by a plurality of elements such as major elements of cobalt, chromium, tungsten and the like in the cobalt-base alloy, and improves the measuring accuracy; the method has wide measuring ranges, the measuring lower limit is 0.002 percent, and the measuring upper limit is 0.20 percent and is 101 times of the measuring lower limit; and the method can perform measurement quickly, is simple and convenient to operate, and saves a large quantity of manpower and material resources.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Stibium, barium, arsenic, zinc, strontium, zirconium rapid measuring method for TFT substrate glass
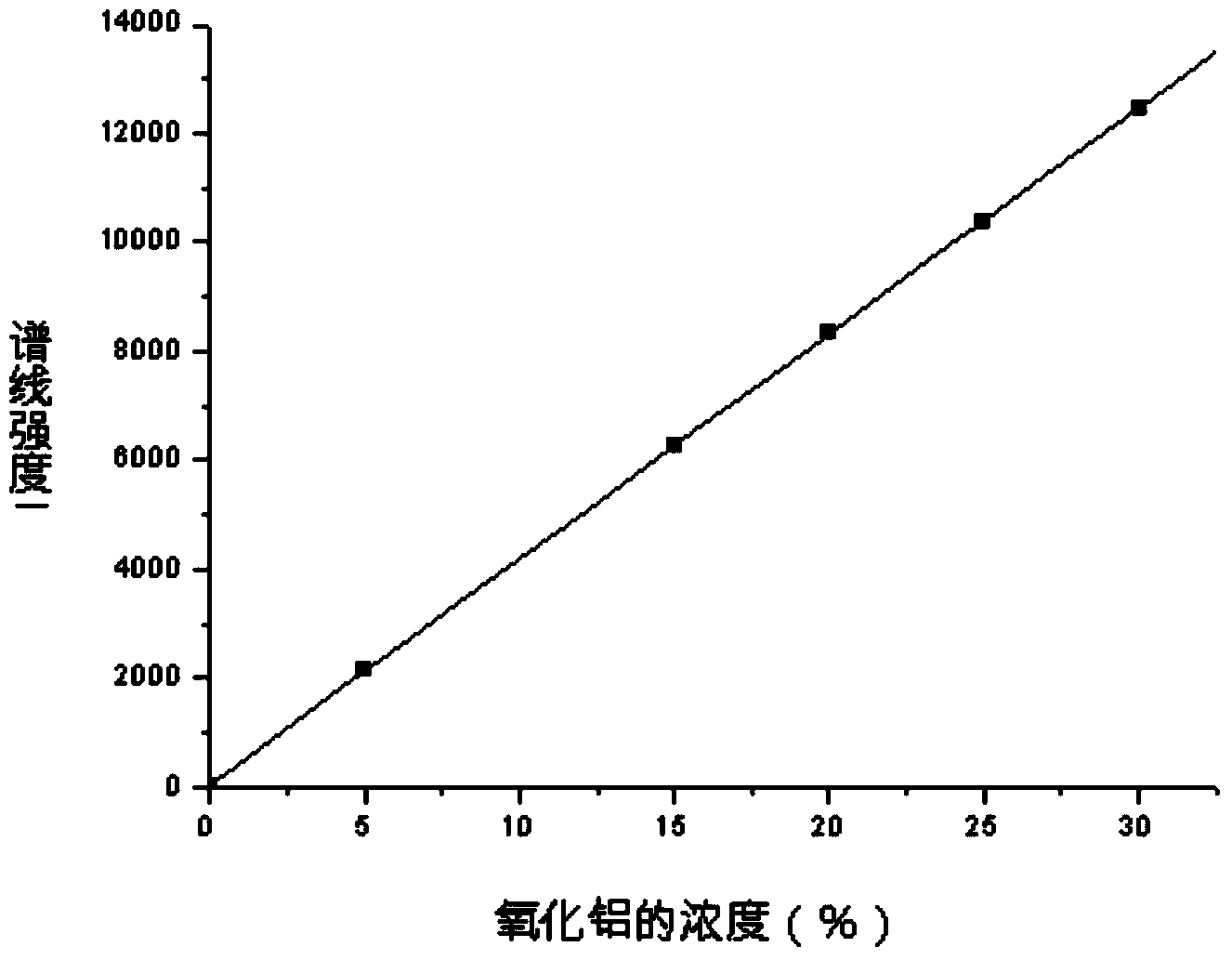
InactiveCN101344485AFit closelyImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by electrical excitationLinearityInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy
The invention discloses a method that is used for quickly measuring the content of stibium, barium, arsenic, zinc, strontium and zirconium in a TFT substrate glass, realizes measurement on the basis of the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, comprises the steps of experimental condition preparation, sample processing, working curve plotting, interfering and eliminating, and building of the linear relation condition, the detection limit condition and the accuracy condition of the method, wherein, the experimental condition preparation comprises instrument selection, acidity selection and analyzing spectral line selection; the sample processing comprises test sample processing, blank test fluid processing and the measurement, the working curve plotting comprises configuration of a solution in the standard series and the plotting of the working curve; the interfering and eliminating comprises chemical, physical and spectral interfering, background removing and building of the related coefficient between each measured element and the linear relation between the working curves; the blank sample is continuously measured for 10 times, the detection limit of the method is obtained according to a formula, the sample of the same TFT substrate glass is repeatedly measured for 10 times, the precision experiment is implemented, and finally the labeled recovery experiment of the sample is implemented.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
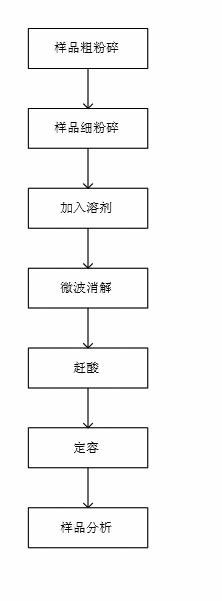
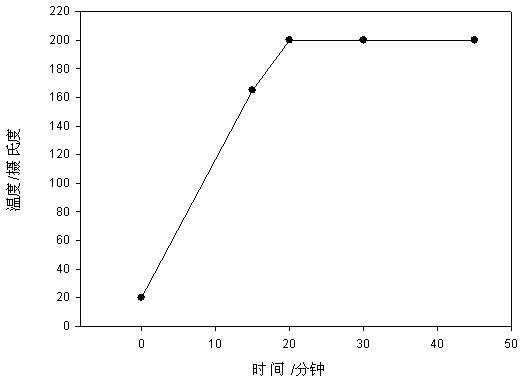
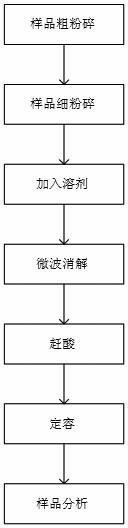
Rapid determination method for multiple component contents in mold flux
InactiveCN103529016AReduce dosageMeet the comprehensive utilizationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationInductively coupled plasmaOperational requirements
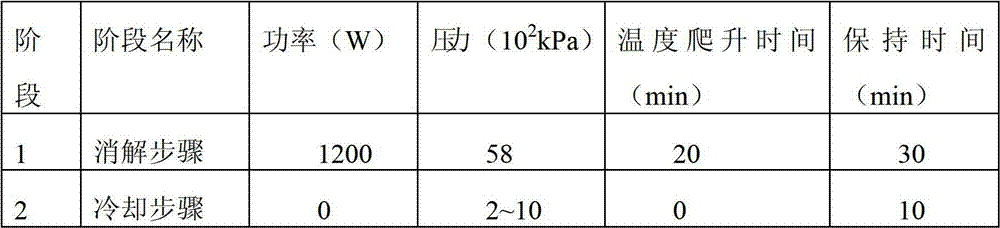
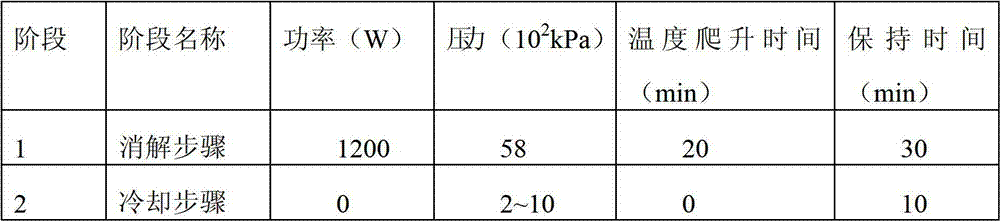
A disclosed rapid determination method for multiple component contents in mold flux comprises the following steps: 1) carbon-removing pretreatment on mold flux; 2) sample dissolving by microwave digestion; 3) preparation of standard solutions of to-be detected components; 4) drafting of standard curves; and 5) determination on contents of the various components in mole flux. By combining microwave digestion sample dissolving technology and inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry, the multiple component contents in mold flux are determined by one time; the rapid determination method has the advantages of being complete and rapid in reaction and low in blank value; the use amount of an agent is reduced by 50% or more; because microwave digestion is performed under the enclosed condition, the loss of to-be determined elements is reduced and laboratory pollution is reduced; the temperature is strictly controlled in the process of digestion, so that the accuracy of determination results is guaranteed; and the determination result is accurate and reliable, the operation is simple, the analysis speed is improved by 50% or more, the determination period is substantially shortened, and the rapid determination method satisfies comprehensive utilization of mold flux and practical operational requirements in production field.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Method for analyzing and measuring typical metal in circuit board of discarded electrical equipment
InactiveCN102169091ADosage ratio optimizationWith strong acidPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationDigestionRefrigerated temperature
The invention relates to a method for analyzing and measuring typical metal in a circuit board of discarded electrical equipment and relates to the technology for pre-treating the circuit board of discarded electrical equipment and detecting and analyzing the content of the typical metal element. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a sample of the circuit board part of discarded electrical equipment and then performing the operations of surface dressing, cleaning, and rough and fine grinding on the sample; adding a proper amount of digestion reagent into the prepared sample, digesting the prepared sample by using a microwave digestion device and then extracting metal matter from the discarded circuit board; and using an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer to analyze the nature and quantity of the digested sample. According to the method, the operations of sample grinding and digesting are simple, the reagent consumption is less, the analysis result is accurate and reliable, the detection concentration range is wide, the technical problem of difficultly pre-treating the circuit board sample is solved, and the method is suitable for quickly identifying and accurately measuring the typical metal elements in the circuit boards of various discarded electrical products (such as televisions, refrigerators, washing machines, computers, printers, and the like) and the typical metal elements in the corner wastes generated in the circuit board production process.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for detecting content of main element in carbon coated lithium iron phosphate or lithium manganese ferric phosphate
InactiveCN105372229AUse less consumablesLess acid consumptionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationLithium iron phosphatePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for detecting the content of a main element in carbon coated lithium iron phosphate or lithium manganese ferric phosphate. The method comprises the steps of 1 sample pretreatment, wherein a sample to be detected is cleared up through acid and transferred, volume metering and still standing are carried out, and after a solution is layered, a middle clear part is sucked as liquid to be detected; 2 standard curve drawing, wherein a series of mixed standard solutions are prepared according to the variety of the main element to be detected, an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer is utilized for carrying out testing, and a standard curve is drawn; 3 main element content measuring, wherein the inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer is used for measuring the content of the main element in the solution to be detected. The pretreatment process is simple, the analysis result is accurate, the content of the main element in carbon coated lithium iron phosphate or lithium manganese ferric phosphate can be measured fast, accurately and quantitatively, and reliable guarantees are provided for improving the product quality of lithium iron phosphate and lithium manganese ferric phosphate and controlling the intermediate technological process.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
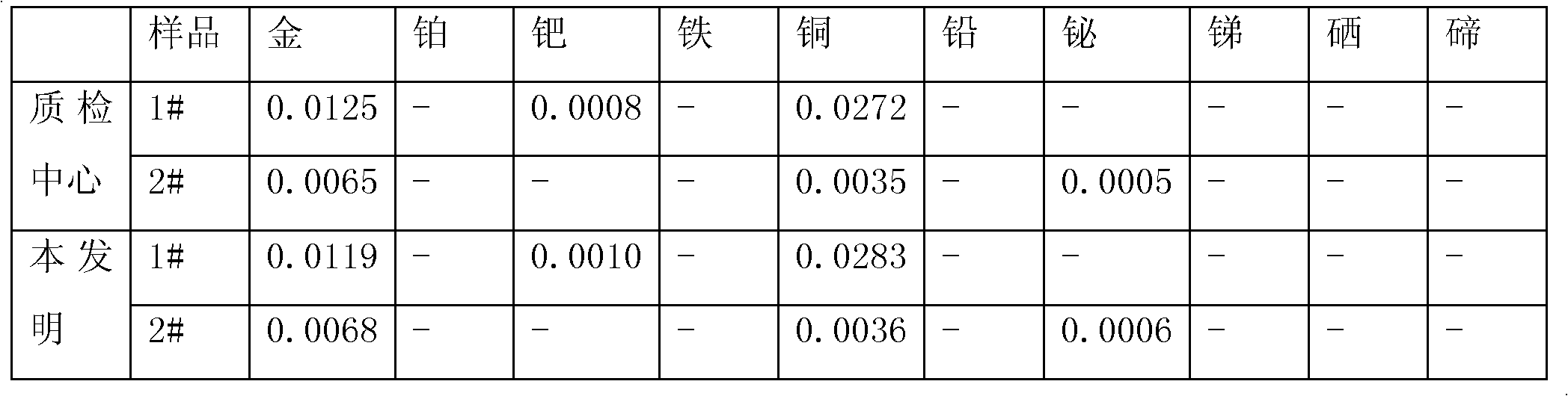
Method for measuring contents of gold, silver and palladium in crude copper
InactiveCN102778451AImprove accuracyGood reproducibilityAnalysis by thermal excitationInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopyPrecious metal
The invention provides a method for detecting metals such as gold, silver and palladium in crude copper, aiming at the situation that no method for measuring metal palladium in crude copper is available at present. According to the method, the fire assaying enrichment is adopted to obtain precious metal combined grains; and after the grains are dissolved by aqua regia, the contents of gold, silver and palladium in crude copper are measured by using an inductance coupling plasma emission spectrograph in a thiourea hydrochloride medium. The method has the advantages of high accuracy, good reproducibility and wide linear range.
Owner:GEM CO LTD
Method for detecting impurity element in tungsten carbide
ActiveCN105823772ASuitable for accurate determinationSuitable for determinationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationManganeseCobalt
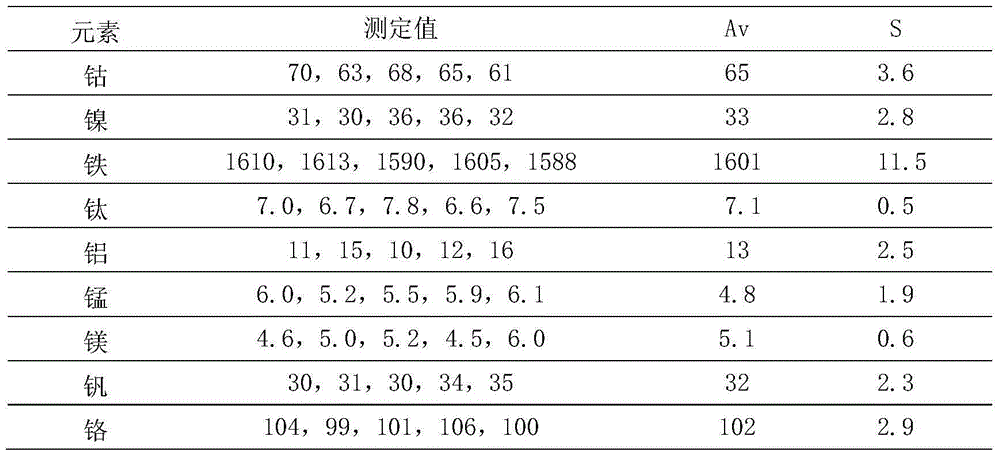
The invention provides a method for detecting impurity elements in tungsten carbide, and concretely relates to the method for rapidly detecting tungsten carbide as well as cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, and molybdenum in casting of tungsten carbide by using an inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. A sample is digested in an electrothermal digestion instrument by employing hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, under condition that a tungsten matrix is not separated, the high purity tungsten matrix is used for preparing a standard work curve, spectrum interference of the tungsten matrix to a to-be-measured element is solved, optimum wavelength of each element is selected, background correction is carried out, and tungsten carbide as well as cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, and molybdenum in casting of tungsten carbide are rapidly detected by using the inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. The detection method has the advantages of simple operation, short detection period, simple sample processing, and wide detection scope, and is suitable for batch production analysis.
Owner:ZIGONG CEMENTED CARBIDE CORP
Method for determining chromium content and aluminum content in nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite
ActiveCN102735678ALarge amount of solutionSolve solubilityPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationElement analysisMaterial resources
The invention belongs to a nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite element analysis technology, and relates to a method for determining chromium content and aluminum content in nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite, wherein microwave sample digestion and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy are adopted to determine the chromium content and the aluminum content in the nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite. According to the method, 5-10 mL of hydrochloric acid, 1-5 mL of nitric acid and 5-10 drops of hydrofluoric acid are adopted to treat (metal-inorganic non-metal powder) nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite, such that problems of large use amounts of reagents for dissolving the sample, difficult dissolving of the sample, incomplete dissolving of the sample, and the like in the prior art are solved. With the present invention, spectrum analysis is performed to find the best analysis line so as to overcome interference of the major element nickel in the nickel-chrome-aluminum coated diatomite and improve measurement accuracy; the study results show that the established method for determining the chromium content and the aluminum content in the nickel-chromium-aluminum coated diatomite is accurate and reliable, and can meet requirements of research and production; and the method of the present invention has characteristics of rapidness, easy operation, manpower saving and material resource saving.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
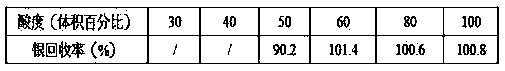
Joint measurement method of impurity elements in silver
ActiveCN102279176APlay a role in precipitationShorten the timePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopyChemistry
The invention provides a simultaneous measuring method for impurity elements in silver. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: dissolving nitric acid, precipitating sodium chloride, filtering, complexing, dissolving aqua regia, filtering, complexing, dissolving the aqua regia, refiltering, measuring by utilizing an ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry) and the like. By utilizing the method provided by the invention, a method for respectively measuring elements which are dissolved in the nitric acid and are not dissolved in the nitric acid by utilizing different methods is changed, more than a half of analysis time is shortened, the method provided by the invention is easy to learn and use, is easy to popularize and apply and also maintains higher accuracy.
Owner:山东黄金冶炼有限公司
Method for measuring aluminum content of high temperature alloy
ActiveCN102072897AEffective dissolutionDissolve completelyAnalysis by thermal excitationLower limitDissolution
The invention discloses a method for measuring the aluminum content of a high temperature alloy, which ensures high sample dissolution speed, high analysis accuracy and high efficiency and is simple and convenient to operate. In the method, acid-insoluble aluminum in the high temperature alloy can be effectively dissolved, so that aluminum is more completely dissolved. An analytical spectral line aluminum 394.40nm selected by the method is uninterrupted by a substrate element and coexisting elements in the high temperature alloy on each of a plurality of optical spectrum instruments. Therefore, the method is applicable to almost all inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometers, has a wide measurement range, from a lower measurement limit of 0.05 percent to an upper measurement limit of 7.5 percent, and can meet the analysis requirements of the aluminum in great majority of grades of high temperature alloys.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for rapidly measuring gold and silver in crude copper
InactiveCN103728289APreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWorking environmentAnalysis method
The invention discloses a method for rapidly measuring gold and silver in crude copper and relates to a precious metal testing analysis method, in particular to a method for rapidly measuring precious metals of gold and silver in the crude copper. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps in the measuring process: (1) dissolving a crude copper sample by acid to separate out copper to obtain filter residues; (2) then dissolving the filter residues by mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid; (3) carrying out analytic determination of gold and silver by adopting an ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry). The method for rapidly measuring gold and silver in the crude copper, disclosed by the invention, is an analysis method of dissolving and separating a copper matrix by sulfuric acid, then directly dissolving the obtained filter residues by the mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid and measuring gold and silver in the crude copper on the ICP-AES; the method does not adopt the fire assay enrichment and ash blowing operation, improves the working environment of workers and shortens the analysis process.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Determination method for iron, aluminum, manganese, calcium, titanium, silicon and magnesium in casting powder
InactiveCN107024468AMeet the comprehensive utilizationFulfil requirementsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerManganese
The invention discloses a determination method for iron, aluminum, manganese, calcium, titanium, silicon and magnesium in casting powder. The method comprises the following steps: melting a test sample, which is subjected to pre-carbon removal treatment, with a sodium carbonate-boric acid mixed flux; dissolving a leached and cooled melted block with hydrochloric acid and heating at low temperature to decompose the melted block; diluting to a specified volume; taking one part of the solution, atomizing the solution and introducing the atomized solution into an inductive coupling plasma optical emission spectrometer; measuring relative intensity of an element to be detected in the solution to a yttrium internal standard element at a selected wavelength; calculating the mass percent of each element to be detected according to a calibration curve manufactured by a standard solution. The determination method provided by the invention is an ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) light spectrum method and the content of various components in the casting powder is determined in one step; the determination method has an accurate and reliable measured result and is simple to operate; the dosage of reagents is greatly reduced and the analysis speed is improved by 70 percent or more, so that a determination period is greatly shortened, and comprehensive utilization of the casting powder and requirements of actual working in a production field are met.
Owner:TANGSHAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
A method of simultaneously measuring contents of Al, Cu, Mn, P and Si in ferrotitanium by utilizing an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer
ActiveCN105699361AWith energy savingAvoid pollutionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationSubstrate compositionStandard samples
A method of simultaneously measuring contents of Al, Cu, Mn, P and Si in ferrotitanium by utilizing an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer is provided. The method includes (1) a step of preparing a test sample solution, (2) a step of selecting element spectral lines, namely a step of selecting the optimum spectral line of each element according to substrate composition of a test sample, (3) a step of mapping standard curves, namely a step of preparing standard solutions of the Al, the Cu, the Mn, the P and the Si, measuring emission light intensity of each element under the optimum spectral line by utilizing the inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer, and mapping the standard curves, and (4) a step of detecting the test sample, namely a step of introducing the test sample solution to the inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer through a feeding system, measuring emission light intensity corresponding to each element, and determining the content of each element according to a corresponding standard curve. The linear relations of the standard curves obtained by the method are good, measurement of contents of the elements is high in accuracy and precision, and the method can be used for analyzing standard samples and production test samples.
Owner:CHENGDE JIANLONG SPECIAL STEEL
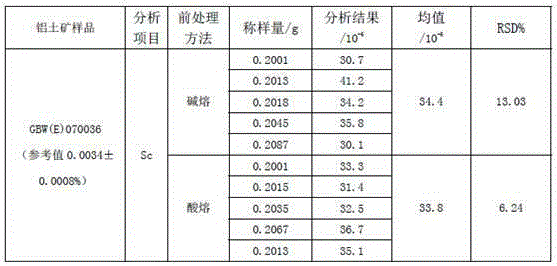
Method for determination of scandium in bauxite by microwave digestion inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry
InactiveCN105223050AReduce dosageReduce consumptionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by material excitationO-Phosphoric AcidScandium
The invention provides a method for determination of scandium in bauxite by microwave digestion inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Specifically, a sample is digested through hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide and phosphoric acid under the action of microwave, ultrapure water is added to a constant volume, an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer is employed to determine Sc so as to realize accurate determination of the trace element Sc in the bauxite sample. The method provided by the invention reduces tedious operation process, employs microwave to digest the sample and direct instrument determination, and has no need for acid removal. Compared with the traditional sample processing method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation steps, little reagent consumption, and rapid analysis speed. At the same time, the method employs microwave digestion to decompose the sample, and can greatly lower the reagent dosage, reduce the reagent blank and matrix interference, and improve the sensitivity and accuracy of analysis elements.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Method for determining zirconium and impurity contents in uranium-zirconium alloy
ActiveCN106596518AAccurate determination of contentThe detection data is accuratePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationHydrofluoric acidChemical test
The invention belongs to the establishment of a novel chemical test method, and particularly relates to a specific method for determining zirconium and impurity contents in uranium-zirconium alloy by inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry. The invention establishes the test method for determining impurity elements and zirconium in uranium-zirconium alloy by plasma emission spectrometry. A sample is dissolved by nitric acid-hydrochloric acid mixed acid and hydrofluoric acid, matrix interference is eliminated by a matrix matching method and a multispectral fitting correction method, and a plasma emission spectrometer is used for detecting the contents of elements to be detected. The method is accurate and reliable, and meets the index requirement of the analysis technique of the project.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR BAOTOU GUANGHUA CHEM IND
Determination method for calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide
InactiveCN103257136AAnalytical methods are accurate and reliableMeet the requirements of scientific research and productionAnalysis by thermal excitationMaterial resourcesDissolution
The invention provides a determination method for calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide. The method employs inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry for determination of the content of calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide, and analytical ranges are as follows: Ca 0.005 to 2%, Co 1 to 15%, Cr 1 to 15% and Fe 0.005 to 10%. According to the invention, a tungsten carbide sample can be effectively dissolved, so the problem of difficult dissolution of the sample is overcome and a sample dissolution speed is accelerated; an optimal analytical line is found through interference experiments and spectrum analysis, interference among spectral lines is eliminated, accurate and reliable determination of the content of calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide is realized, and requirements of scientific research and production are met; and the method has the advantages of rapid measurement, easy and convenient operation and conservation of considerable manpower and material resources.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Coating thickness test method
InactiveCN108692664AHigh precisionWide thickness rangeAnalysis by thermal excitationUsing optical meansOptical Emission SpectrometerPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a coating thickness test method. According to the method, a sample to be tested is made into a sample block of which the coating area can be accurately calculated; a coating onthe sample block is completely digested with strong acid, so that a test solution of a certain volume can be prepared; the content of a coating metal component in the solution is measured by an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer; the mass of the coating component is calculated; and the thickness of the coating is calculated on the basis of the measured area of the sample block. The test method of the invention has the advantages of high test accuracy, strong representativeness, less interference, small error, and wide test coating thicknesses range. With the coating thickness test method adopted, the thickness of the coating can be tested in general chemical laboratories, and professional thickness gauges are not required.
Owner:青岛谱尼测试有限公司
Method for detecting rare earth elements in steel
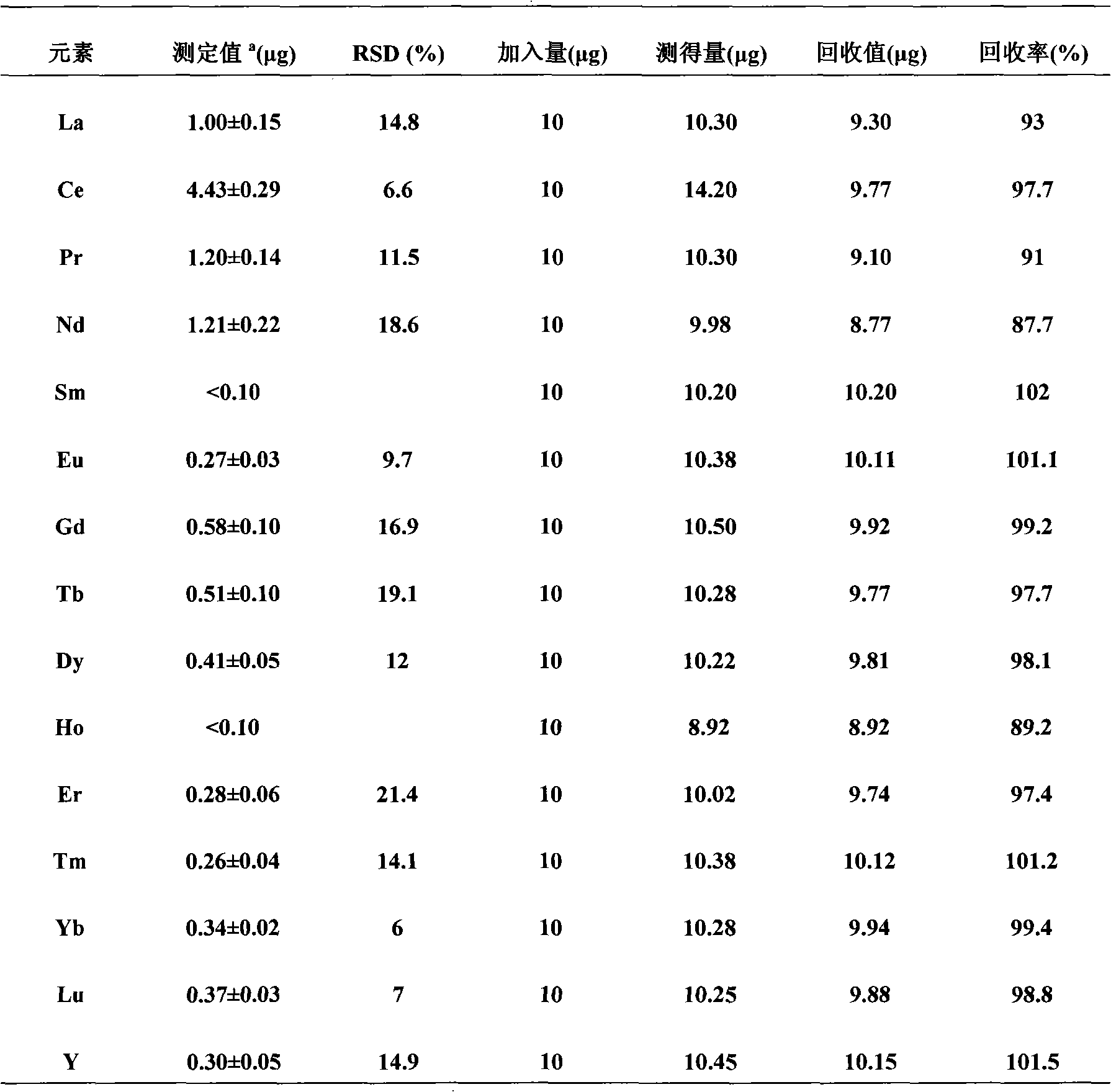
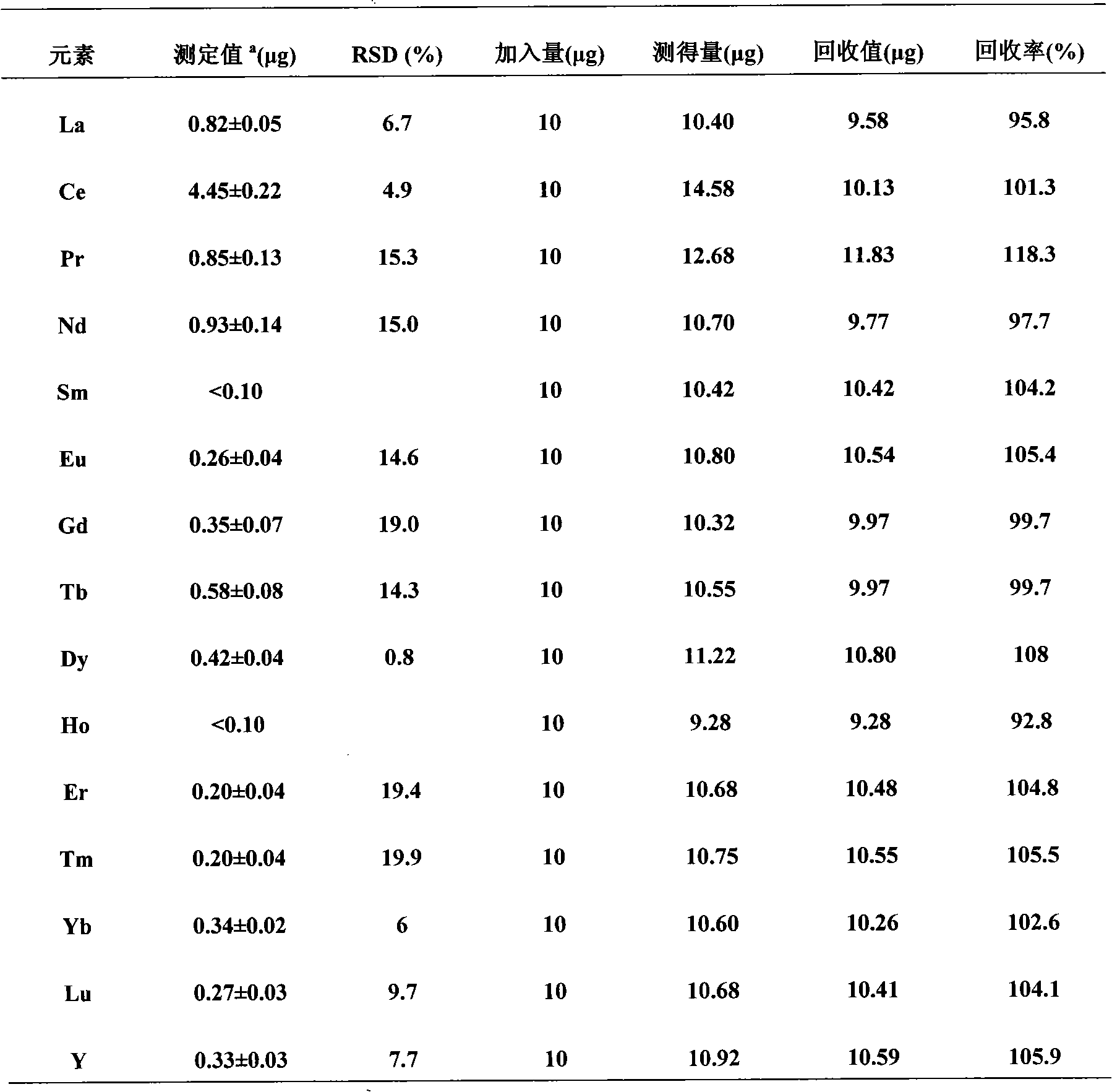
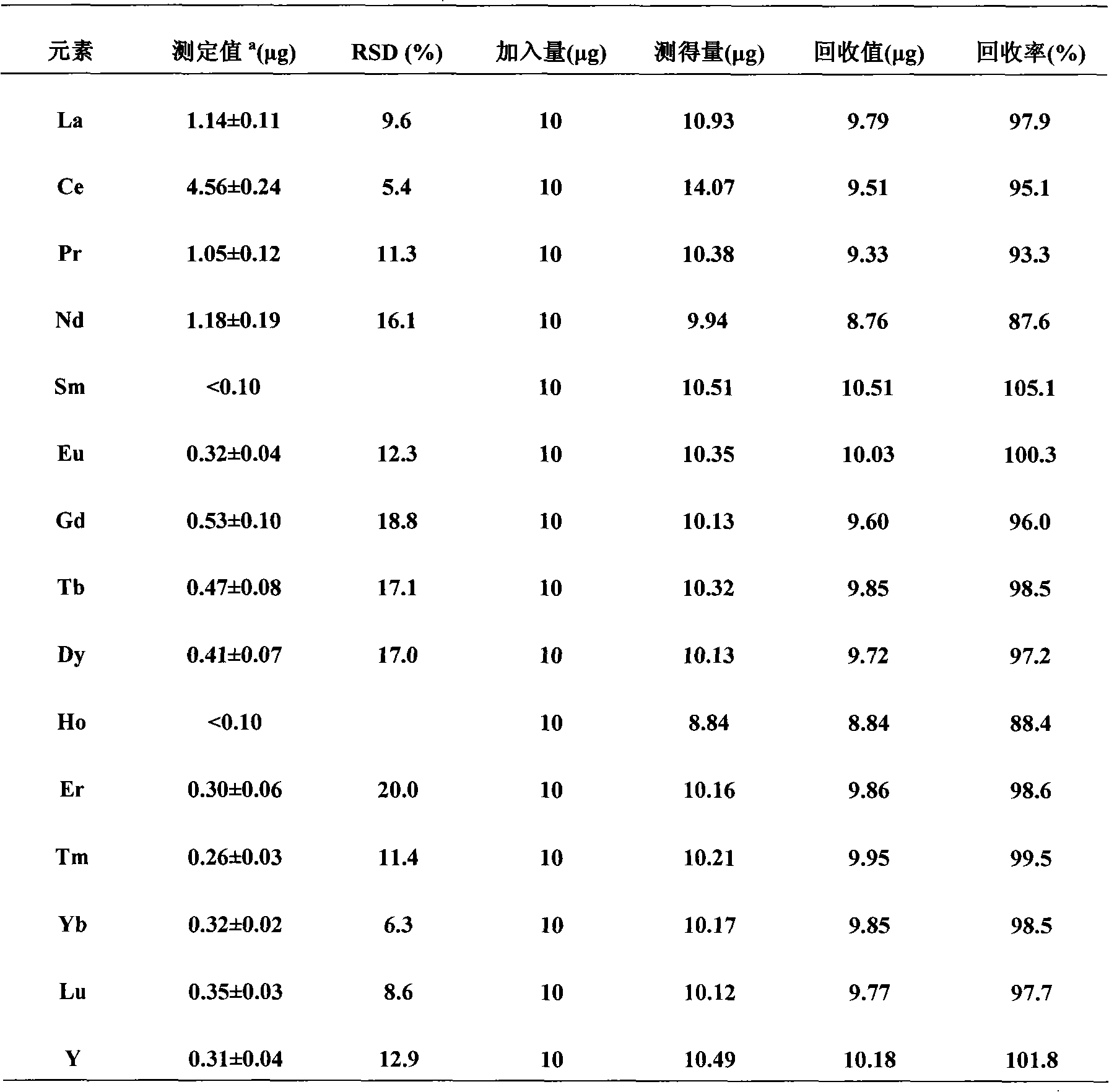
InactiveCN101975772AReduce method stepsOperational requirements are not harshPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationRare-earth elementIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for detecting rare earth elements in steel, comprising the steps of: sampling and sample dissolving: weighing a crushed steel sample, placing the crushed steel sample in a first container, adding nitric acid into the first container, heating till boiling, dropwise adding hydrochloric acid to completely dissolve the steel sample, and steaming to be almost dry to obtain a substance to be set with constant volume; setting volume: setting the volume of the substance to be set with the constant volume with the hydrochloric acid, and controlling the proportion of the steel sample to the hydrochloric acid to obtain a constant volume solution; ion exchanging: taking partial constant volume solution from the constant volume solution, to be used as a solution sample, leading the solution sample into an anion exchange resin column under a state with controlled flow velocity, collecting an outflow solution in a second container, washing unabsorbed rare earth elements with the hydrochloric acid, collecting the rare earth elements obtained through washing into the second container, controlling the volume of the collected solution, uniformly mixing to obtain a solution to be detected; and detecting: detecting the content of all rare earth elements in the solution to be detected by using an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer. The invention can be used for separating and detecting fourteen rare earth elements in a lanthanum series, has fewer steps and is convenient to operate.
Owner:COMPREHENSIVE TECH SERVICE CENT OF CHANGSHU ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
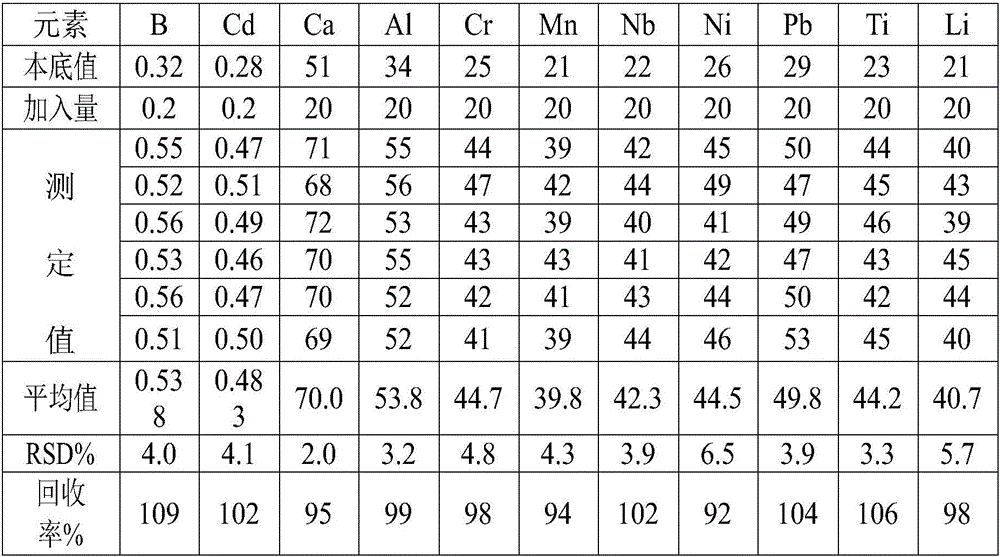
Method for determining impurity elements in high-purity aluminum through microwave digestion-inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer
InactiveCN108375568ALow detection limitAccurate measurementPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerMethod test
The invention provides a method for determining impurity elements in high-purity aluminum through a microwave digestion-inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and belongs to the technical field of analysis and test. The invention provides an analysis method for determining 20 impurity elements including Ag, Ba, Bi, Cd, Co, Cu, Ga, Fe, In, Li, Mg, Mn, Mo, Pb, Sb, Ti, V, Sr, Zn and Zr in the high-purity aluminum through a microwave digester and an inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) by adopting a standard curve method. A sample is dissolved into a sealed high-pressure microwave digestion tank by utilizing a proper amount acid, so as to avoid external factor pollution better. Optimal working parameters of an instrument are determined through a single-factor experiment. A standard curve-method test sample is selected so that matrix interference is reduced. The method is a simple, rapid and accurate modern detection technology capable of determining 20elements in one step.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A method for determining contents of potassium element, sodium element, calcium element, silicon element, and magnesium element in nickel oxide
ActiveCN102721582AImprove analysis efficiencyQuality improvementPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationPotassiumDissolution
The invention provides a method for determining contents of potassium element, sodium element, calcium element, silicon element and magnesium element in nickel oxide. The method capable of effectively dissolving a nickel oxide sample, is a method which can determine the contents of the potassium element, the sodium element, the calcium element, the silicon element and the magnesium element in the nickel oxide with high speed of sample dissolution, high analysis precision, simple and convenient operation as well as high efficiency. Analytical spectral lines selected by the method are as follows: K766.490 nm, Na588.995 nm, Ca393.366 nm, Si251.611 nm and Mg279.553 nm which are on multiple spectral instruments and are not affected by interference of matrix elements and coexisting elements in the nickel oxide; therefore, this method can be applied to almost all inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometers. The method has a wide measurement range with a measurement lower limit being 0.0001% and a measurement upper limit being 0.5% and can satisfy requirements for analyzing the potassium element, the sodium element, the calcium element, the silicon element and the magnesium element in the nickel oxide.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for simultaneously determining iodine, boron, tin and germanium elements in soil
ActiveCN105758927AImprove work efficiencyHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopyRaw material
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining iodine, boron, tin and germanium elements in soil. The method comprises the following steps of pre-treating raw materials, preparing a determination solution, drawing a working curve and determining the content of each element in the soil, wherein the step of pre-treating the raw materials comprises the step of pre-treating with sodium oxide; a citric acid solution and cation resin are added into the pre-treated sample to prepare the determination solution; the obtained determination solution is determined by adopting an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously determining the plurality of elements including iodine, boron, tin and germanium in the soil, and is high in working efficiency and simple to operate; the inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry is used for determining; compared with an inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy, the method has the advantages of relatively high sensitivity, relatively low detection limit, relatively strong anti-interference capability, relatively high precision and the like. The detection limits of the detected elements that the iodine is 0.10Mug / g, the boron is 0.92Mu g / g, the tin is 0.29Mu g / g and the germanium is 0.02Mug / g, and are lower than the detection limits of the inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy.
Owner:广西壮族自治区地质矿产测试研究中心
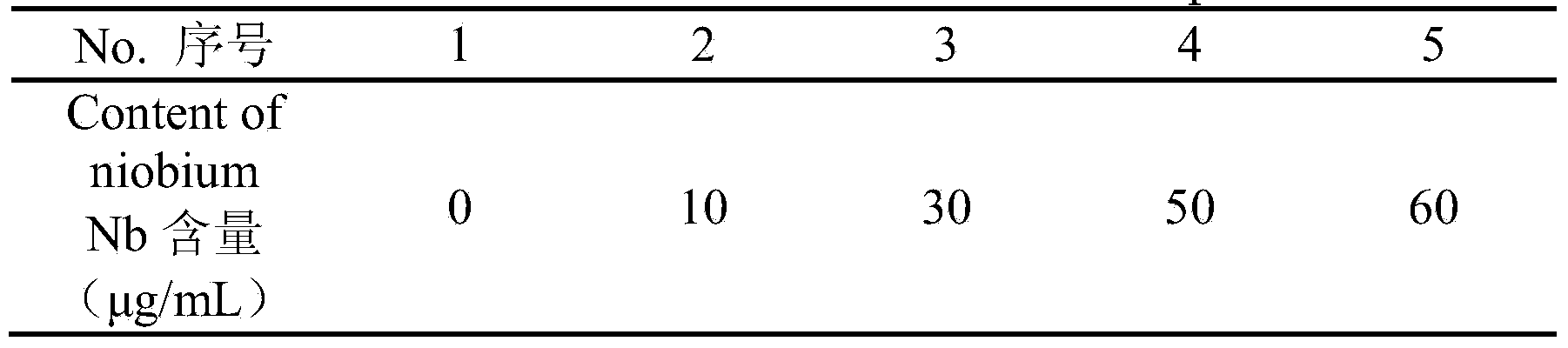
Method for measuring elemental niobium content of titanium-niobium alloy
ActiveCN104020157AAchieve complete dissolutionGuaranteed accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationObservational errorRelative standard deviation
The invention provides a method for measuring the elemental niobium content of a titanium-niobium alloy. The method comprises the following steps of dissolving a titanium-niobium alloy specimen by using sulfuric acid and a small amount of hydrofluoric acid, adding an internal standard solution, and after diluting to a certain volume, performing measurement by using an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. Before the measurement, five niobium standard solutions with different concentrations are prepared, titanium substrates of the five niobium standard solutions are matched, the same amount of internal standard solution is added, a standard working curve is drawn, and the elemental niobium content of the titanium-niobium alloy is calculated with reference to the standard working curve. According to the method, the titanium-niobium alloy is completely dissolved, the internal standard solution is added to cancel measurement errors caused by the fluctuation of spectral line intensity due to the fluctuation of working conditions of an instrument, and a substrate matching method is used for reducing the interference of a substrate effect; by the measures, the accuracy of the curve is ensured, and the relative standard deviation is 0.29 percent; the method is high in precision and easy to operate, the elemental niobium content of the titanium-niobium alloy can be accurately measured, and quality guarantee is provided for the use of materials.
Owner:AEROSPACE PRECISION PROD INC LTD
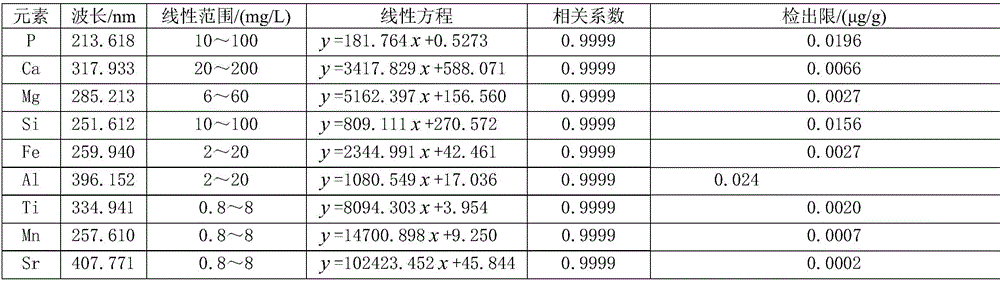
Method for simultaneously determining content of phosphorus, magnesium, iron, aluminum, silicon, calcium, titanium, manganese and strontium in phosphorite by adopting ICP-AES
InactiveCN106290318ANo distractionNo apparent interferencePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationLithium metaborateLithium bromide
The invention relates to the technical field of analysis test, and in particular relates to a method for simultaneously determining content of phosphorus, magnesium, iron, aluminum, silicon, calcium, titanium, manganese and strontium in phosphorite by adopting inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). Specifically, lithium metaborate is a non-oxidant solvent with a high melt point, has high decomposition capacity for a majority of test samples, and can effectively decompose rocks and minerals difficult to dissolve. The method comprises the following steps: placing a phosphorite test sample into a platinum crucible, adding the lithium metaborate solvent and a lithium bromide releasing agent, melting and decomposing the phosphorite sample by using a high-frequency sample melting machine, pouring in a polytetrafluoroethylene beaker with 10 percent nitric acid at a high temperature by virtue of a magnetic stirrer, after the primary sample melting acidification sizing, performing matrix matching by adopting a national grade-I phosphorite, establishing a standard curve by adopting a Yttrium internal standard method, and determining the content of phosphorus pentoxide, magnesium oxide, iron oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, calcium oxide, titanium oxide, manganese oxide and strontium oxide in the phosphorite by adopting the ICP-AES. The method has the advantages of rapidness, convenience and accuracy, and is particularly suitable for batch determining the phosphorite samples.
Owner:YUNNAN PHOSPHATE CHEM GROUP CORP
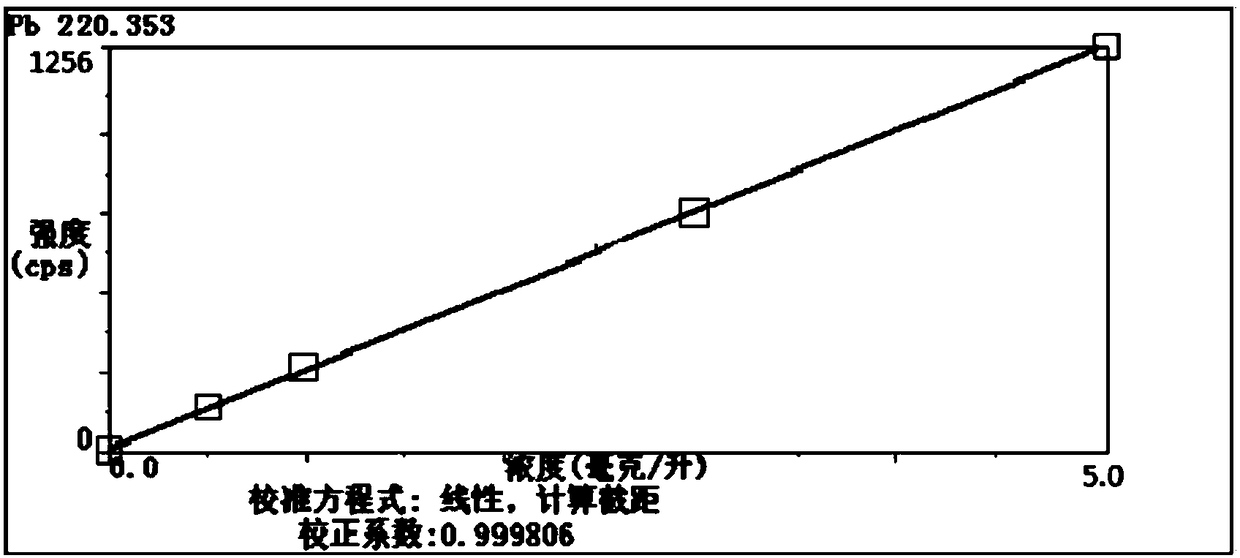
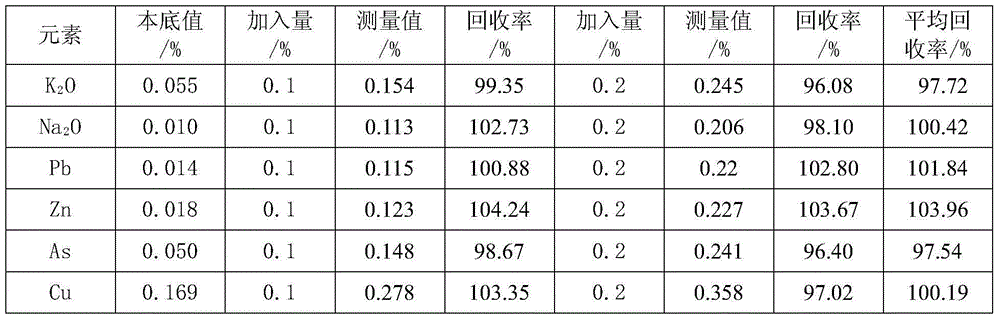
Method for measuring contents of potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, arsenic and copper in ferrous metallurgy materials
InactiveCN104897647AWide measurement rangeHigh precisionAnalysis by electrical excitationPotassiumSpectrometer
The invention discloses a method for measuring contents of potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, arsenic and copper in ferrous metallurgy materials. The method includes drawing working curves of standard liquor of the potassium, the sodium, the lead, the zinc, the arsenic and the copper; measuring the light intensity of sample dissolving liquor by the aid of an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer; acquiring the contents of the potassium, the sodium, the lead, the zinc, the arsenic and the copper according to the working curves of the standard liquor of the potassium, the sodium, the lead, the zinc, the arsenic and the copper and the light intensity of the sample dissolving liquor. The method has the advantages that a technology for processing samples, a technology for matching matrixes and parameters of the spectrometer are optimized, accordingly, the diversified materials can be measured in ferrous metallurgy procedures, the contents of diversified elements such as the potassium, the sodium, the lead, the zinc, the arsenic and the copper in the materials can be simultaneously measured, the method is wide in measuring range, high in precision and accuracy, simple in operation and easy to master, and obvious economic and social benefits can be created.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
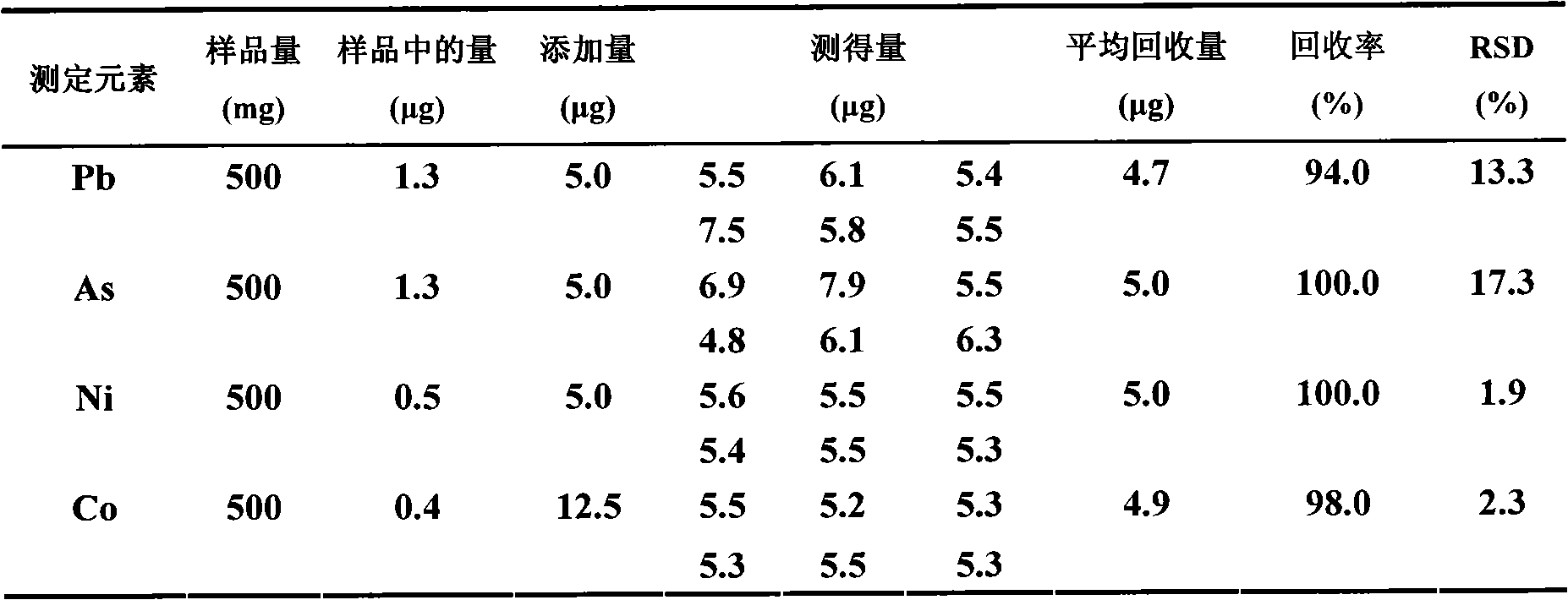
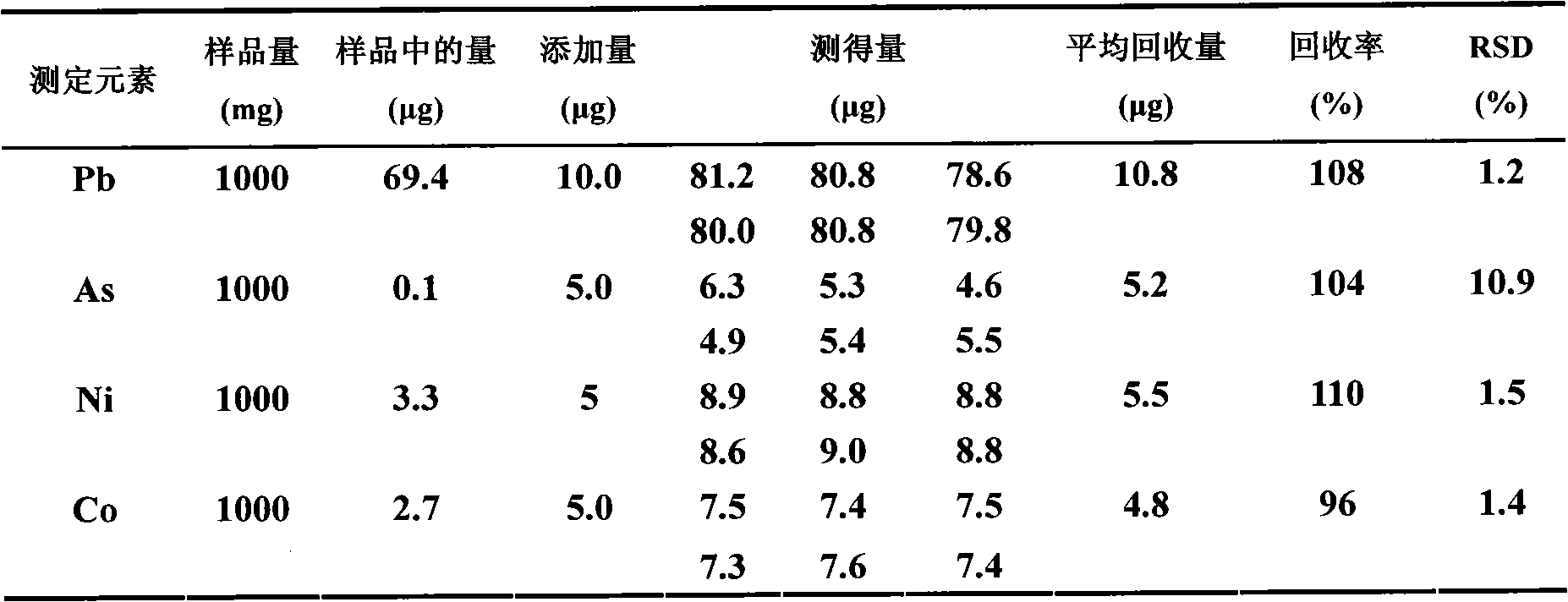
Method for measuring lead, arsenic, nickel and cobalt in ferric oxide powder
InactiveCN101975771AEasy to separateFast determination and analysisPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationPhysical chemistryCobalt
The invention relates to a method for measuring lead, arsenic, nickel and cobalt in ferric oxide powder, comprising the following steps of: sampling and dissolving the sample: weighing the ferric oxide powder sample, placing the sample in a first container, adding hydrochloric acid to the first container, heating until boiling, dropping a strong oxidizer until the ferric oxide powder is completely dissolved, cooling to obtain a dissolving sample; column chromatography: introducing the dissolving sample in a gathers drench resin column under the state of controlling the flow speed, removing the front part of effluent liquid flowing from the gathers drench resin column, controlling the amount of the front part of effluent liquid, collecting the remained effluent liquid in a second container, washing the lead, the arsenic, the nickel and the cobalt failing to be adsorbed by the gathers drench resin with hydrochloric acid, collecting in the second container, and evaporating and drying to obtain a constant-volume substance to be measured; volume fixing: fixing the volume of the substance with nitric acid, controlling the proportion of the nitric acid to the ferric oxide powder sample to obtain a constant-volume solution; and measuring: measuring the content of the lead, the arsenic, the nickel and the cobalt in the constant-volume solution with an inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer. The invention has the advantages of good separation effect, rapid and accurate measurement and analysis, and simple operation.
Owner:COMPREHENSIVE TECH SERVICE CENT OF CHANGSHU ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for detecting heavy metals in plastics
InactiveCN104122253ASolve the influence of measuring timeOvercome the conditionsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWater bathsSolubility
The invention discloses a method for detecting heavy metals in plastics. The method comprises the following steps: S1. putting the plastics to be detected in an airtight container filled with an organic solvent, and carrying out ultrasonic oscillation in a water bath to dissolve the plastics, thus obtaining a plastic dissolution solution; S2. adding dilute nitric acid to the plastic dissolution solution, carrying out ultrasonic oscillation at room temperature, and carrying out filtration, washing and constant volume achievement to extract heavy metals in the plastic dissolution solution, thus obtaining a solution to be detected, containing the organic solvent; S3. qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing the heavy metals in the solution to be detected by adopting an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES). The method has the beneficial effects that by utilizing the characteristic that the plastics have better solubility in the organic solvent, the plastics are dissolved by using the proper organic solvent, and then the heavy metals in the plastics are extracted to form the solution to be detected, containing the organic solvent; then the heavy metals dissolved in the organic solvent are qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by adopting the ICP-OES. The method has the advantages of simple and fast operating process, mild reaction conditions, accuracy in detection, high recovery rate and good stability and is suitable for mass treatment.
Owner:深圳出入境检验检疫局玩具检测技术中心
Method for measuring Ti content in low-carbon ferrophosphorus
InactiveCN101750406AControl acidityAnalysis by thermal excitationPollutionInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy
The invention relates to a technical field of ferrous metallurgical analysis and discloses a method for measuring the Ti content in low-carbon ferrophosphorus. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a sample through a nitric acid and a hydrofluoric acid; fuming the sample by a perchloric acid; diluting to a certain volume with water; introducing atomization solution into an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer; and measuring the intensity of a spectral line to be tested; and calculating the content of the corresponding element of the substance to be tested according to the intensity of the spectral line which is measured by the standard substance at known concentration. The method has the advantages of capacity of quickly and accurately analyzing the Ti content in low-carbon ferrophosphorus and no pollution.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Method for simultaneously determining contents of phosphorus, magnesium, iron and aluminum in phosphate ores by using ICP (inductively coupled plasma) method
ActiveCN102128822AImprove accuracyReduce distractionsAnalysis by thermal excitationMaterials scienceInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously determining contents of phosphorus, magnesium, iron and aluminum in phosphate ores by using an ICP (inductively coupled plasma) method, which comprises the following steps: preparing a phosphorus, magnesium, iron and aluminum standard solution; preparing a sample solution; and using an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer for determination, wherein the phosphorus, magnesium, iron and aluminum standard solution is prepared by dissolving a phosphate ore sample in accordance with the standard GB / T 1871-1995 method and then determining the result. The standard solution and the sample solution to be determined are the same in basic element composition, total salinity, acid concentration, solution viscosity, surface tension and other aspects, and the physical interference and spectrum interference can be efficiently reduced, thereby increasing the accuracy of the determination result.
Owner:ANHUI LIUGUO CHEM CO LTD
Solid-state radio frequency generator
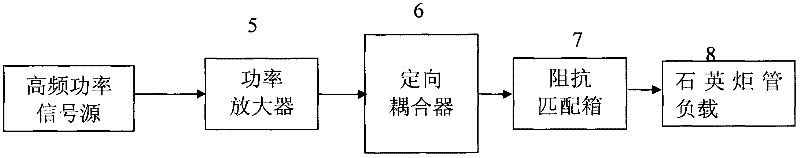
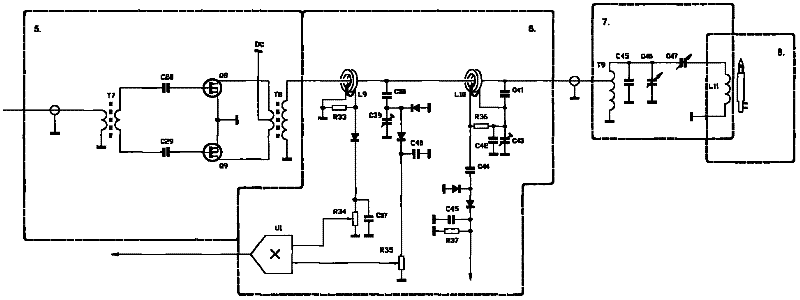
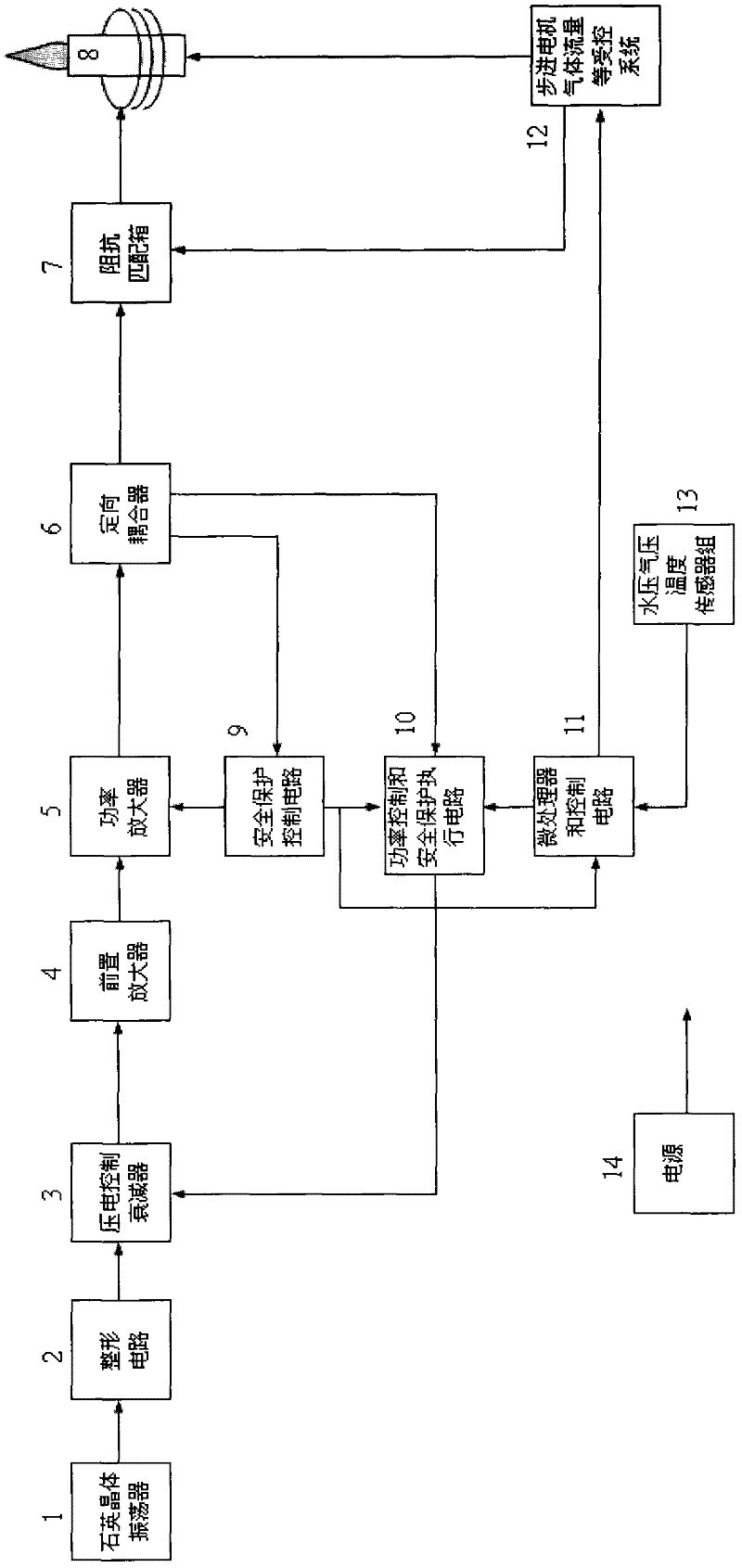
InactiveCN102355205AImprove performanceReduce volumePower amplifiersHigh frequency powerAutomatic control
The invention discloses a power amplifier and an output circuit thereof. The invention comprises the power amplifier, a directional coupler and an impedance matching box, wherein the power output stage of the power amplifier consists of two semiconductor field effect transistors, and performs power amplification on a received pre-high-frequency power signal; the directional coupler acquires an incident power signal of the power amplifier and a reflection power signal in impedance mismatching, performs automatic power control by using the incident power signal and performs circuit protection by using the reflection power signal; and the impedance matching box receives high-frequency power from the power amplifier, outputs stable high-frequency power and adds the stably output high-frequency power to a quartz torque tube load after impedance matching to realize a radio frequency generator manufactured by adopting solid devices in an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. The solid-state radio frequency generator has a simple circuit, is stable, reliable and convenient to debug, and adopts fewer devices.
Owner:夏义峰
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com