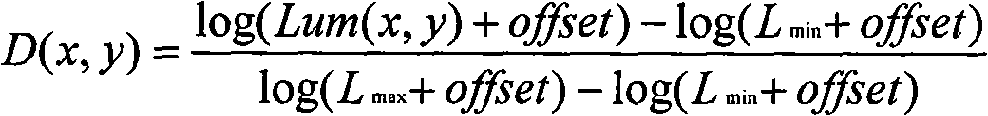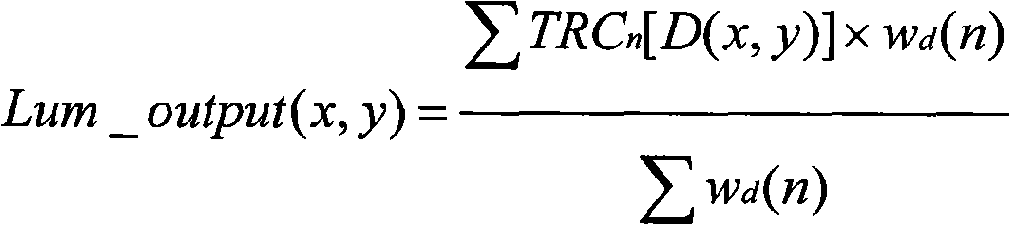Patents
Literature
108results about How to "Optimization of details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
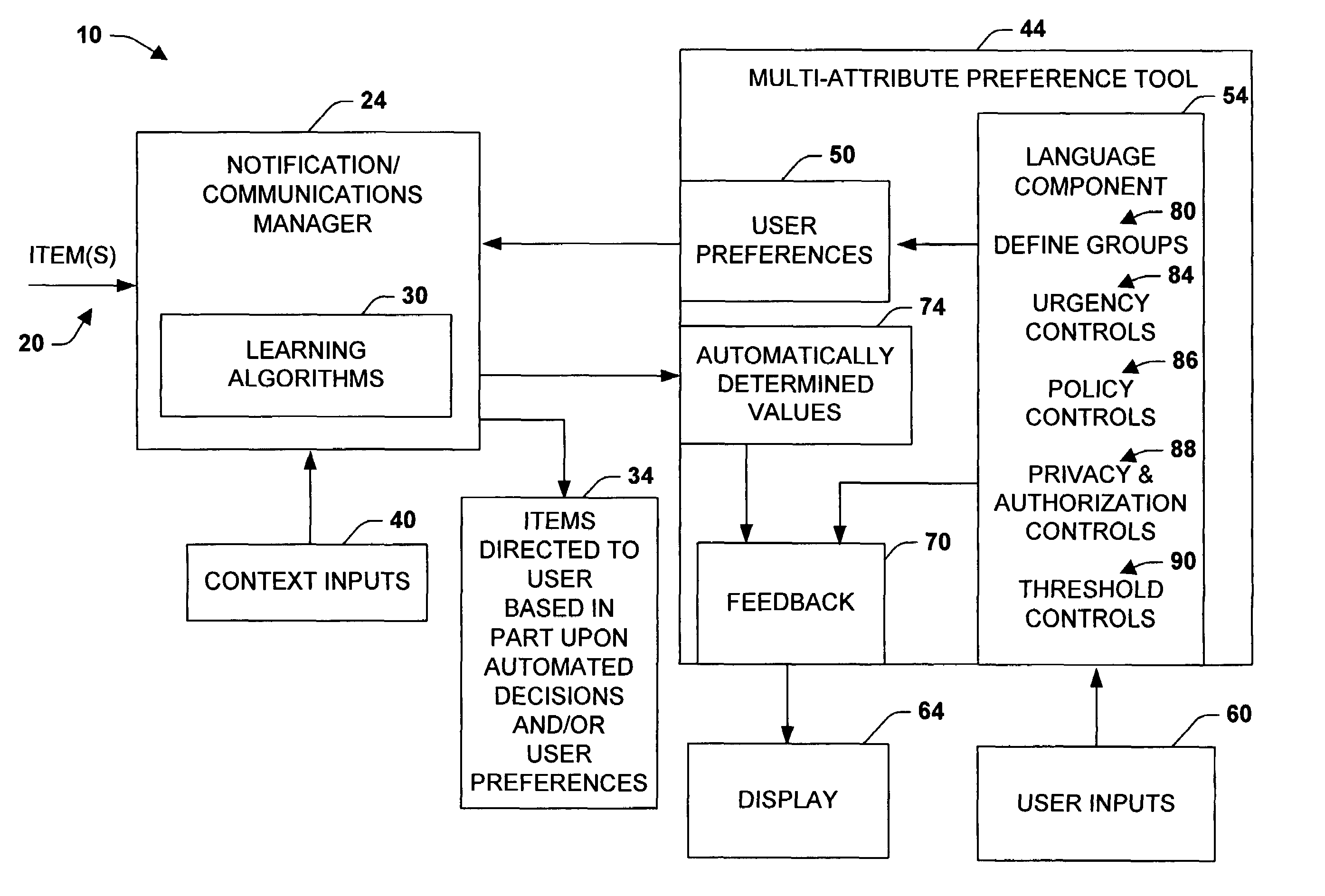
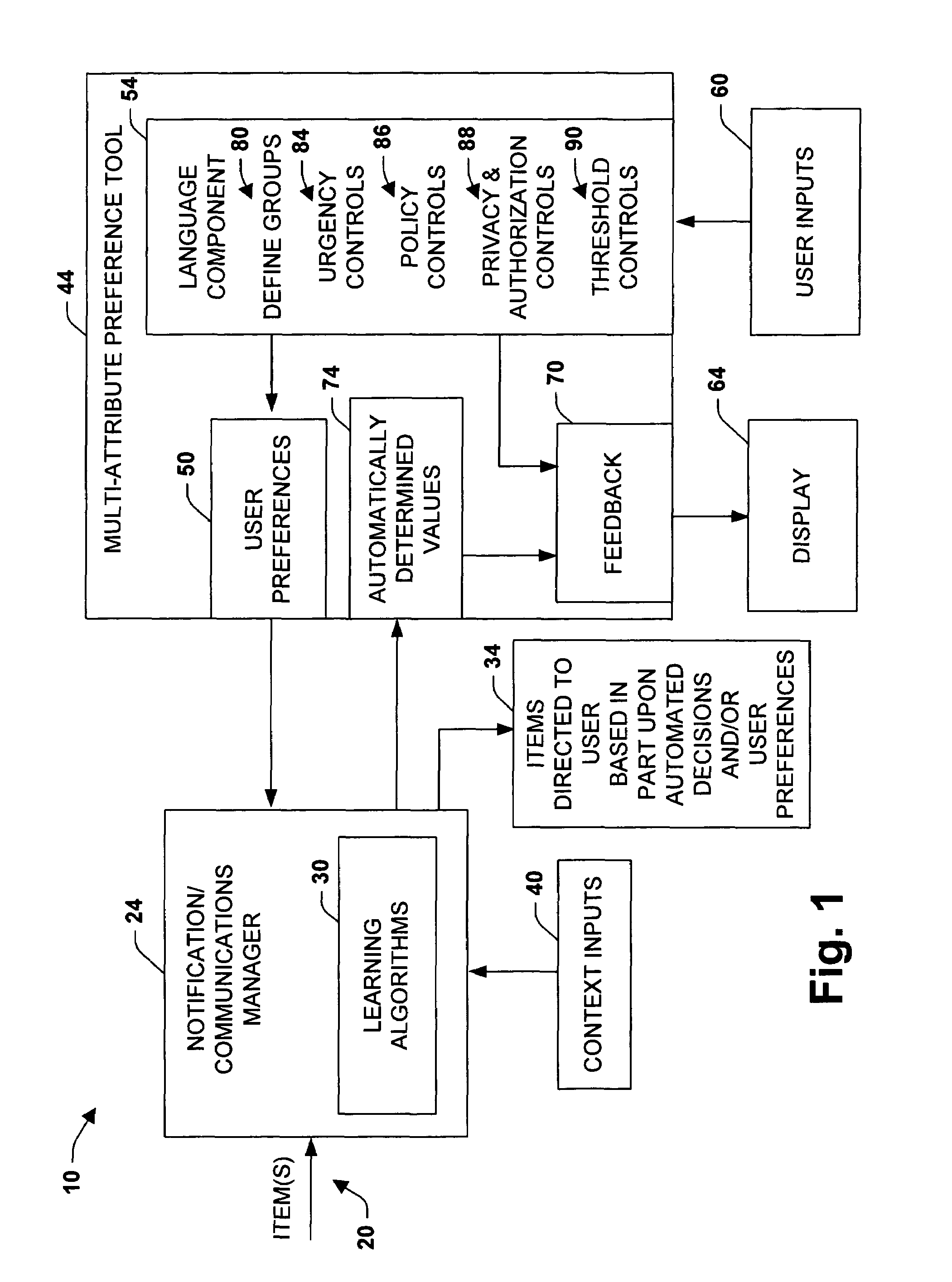
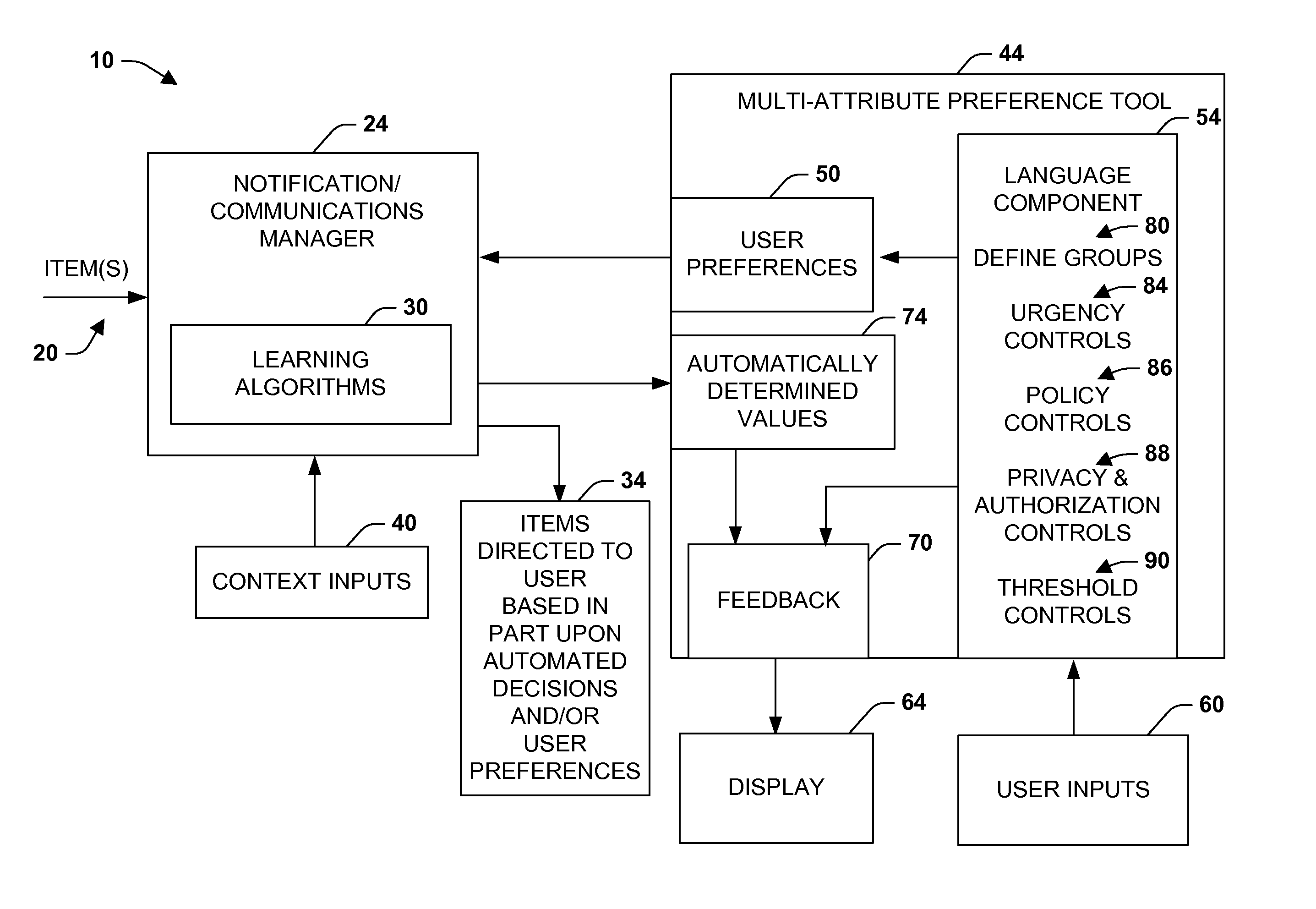
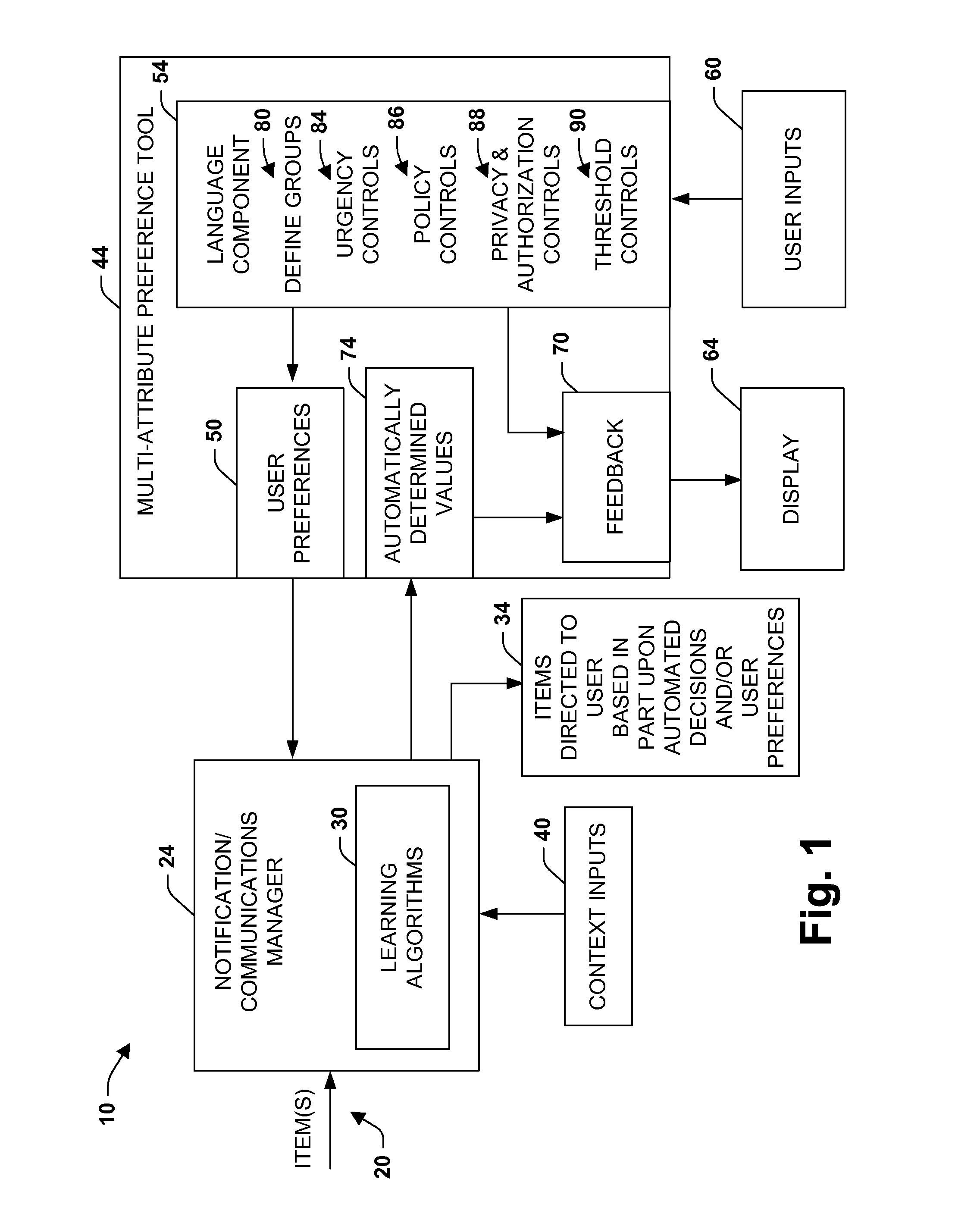
Multi-attribute specification of preferences about people, priorities and privacy for guiding messaging and communications
ActiveUS7069259B2Easy to findOptimization of detailsKernel methodsDigital computer detailsSpecification languageStudy methods
The present invention relates to a system and methodology to facilitate multiattribute adjustments and control associated with messages and other communications and informational items that are directed to a user via automated systems. An interface, specification language, and controls are provided for defining a plurality of variously configured groups that may attempt to communicate respective items. Controls include the specification of priorities and preferences as well as the modification of priorities and preferences that have been learned from training sets via machine learning methods. The system provides both a means for assessing parameters used in the control of messaging and communications and for the inspection and modification of parameters that have been learned autonomously.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
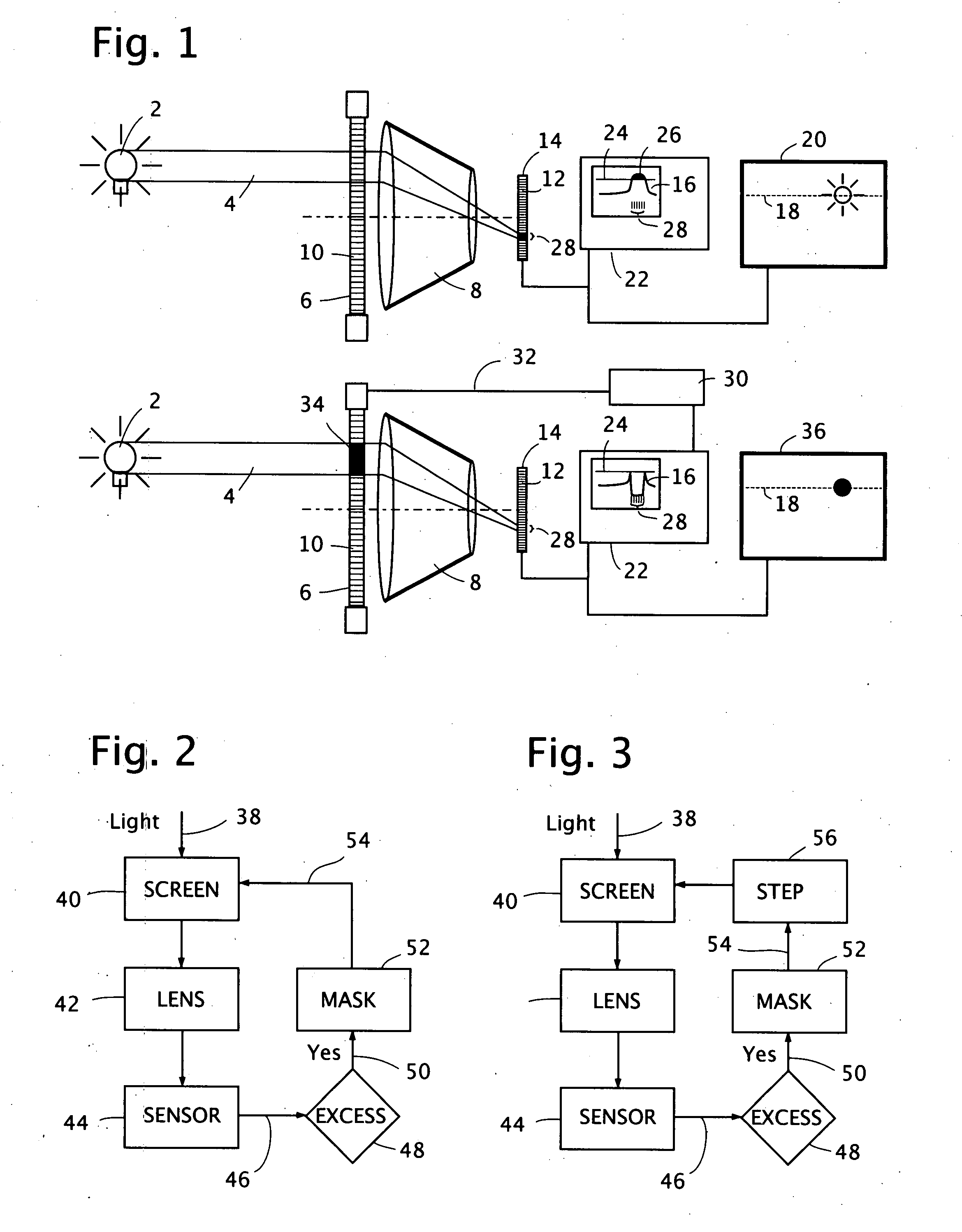
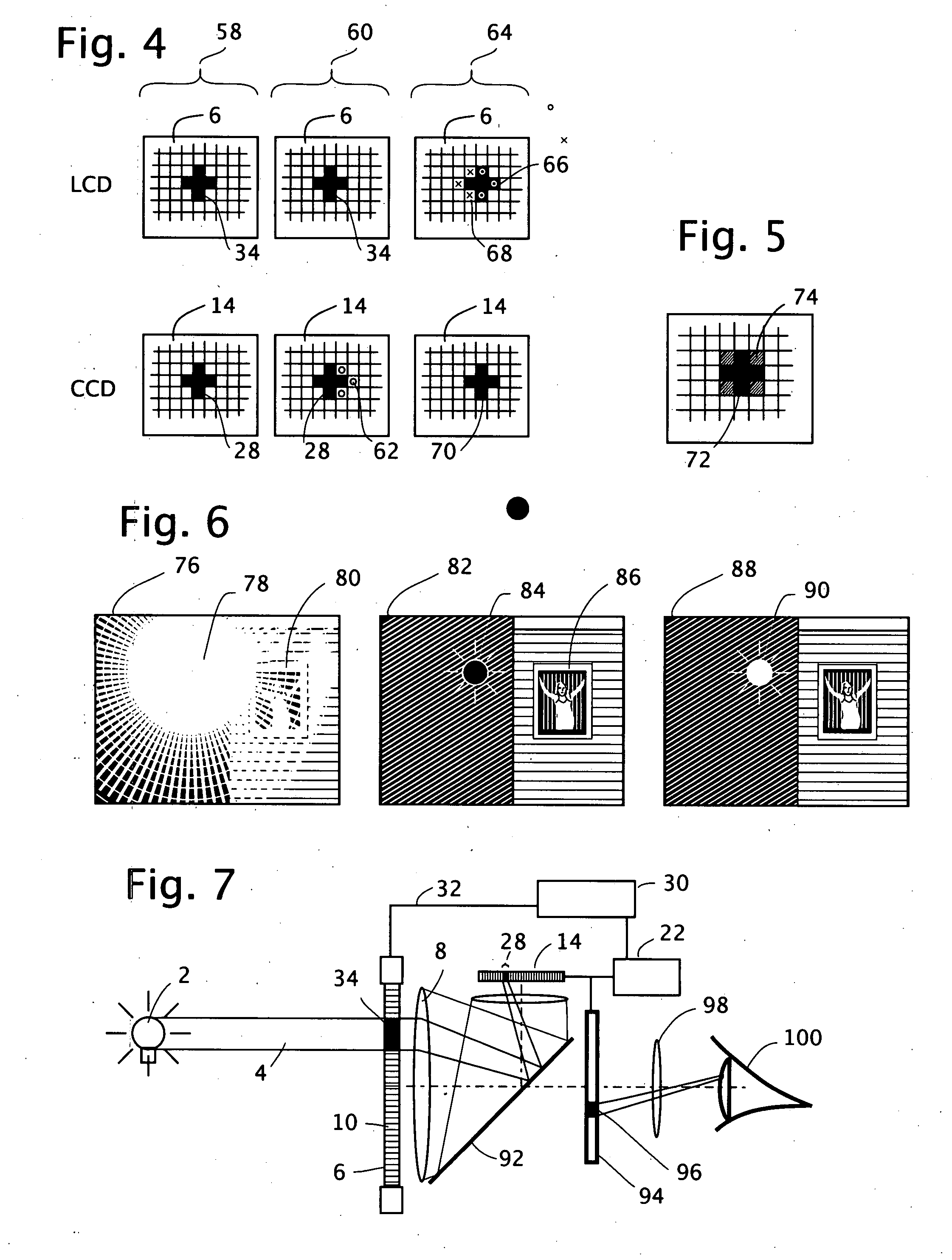
Active mask for electronic imaging system
InactiveUS20080007645A1Reduce and eliminate effect of glareOptimization of detailsTelevision system detailsPhotometry using reference valueElectronElectronic imaging
An active pixel masking system for automatic glare suppression uses a variably transmissive screen such as an LCD in front of a lens. A measurement by an image sensor of oversaturated pixels from one or more extremely bright lights is used to generate corresponding opaque pixels in the variably transmissive screen, thereby preventing the excess light from entering the lens, and thereby clarifying the appearance of any objects near to the bright light. A continuous reading of a motion picture image is used to move the location and area of the opaque pixels in response to the motion and area of the light.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
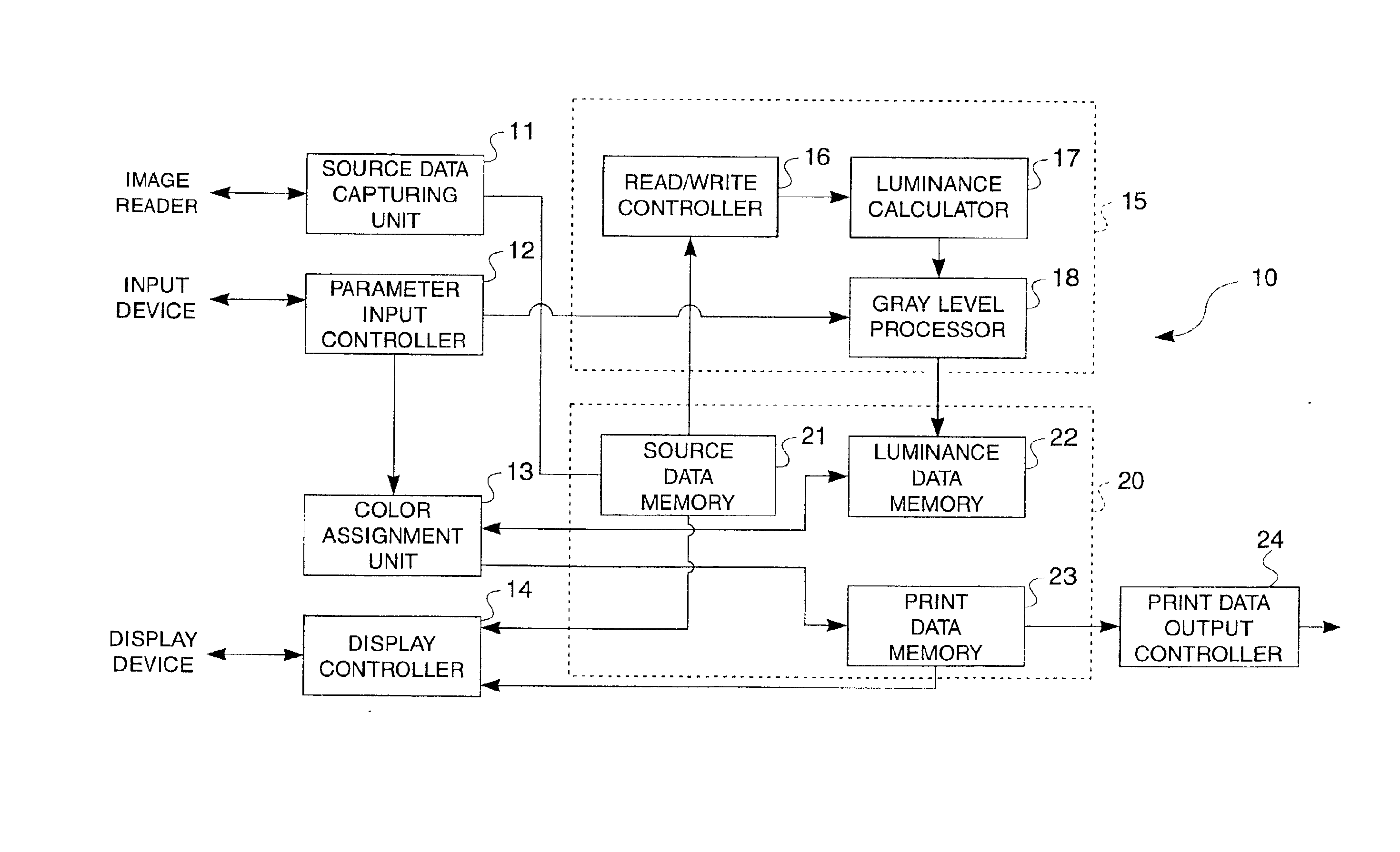
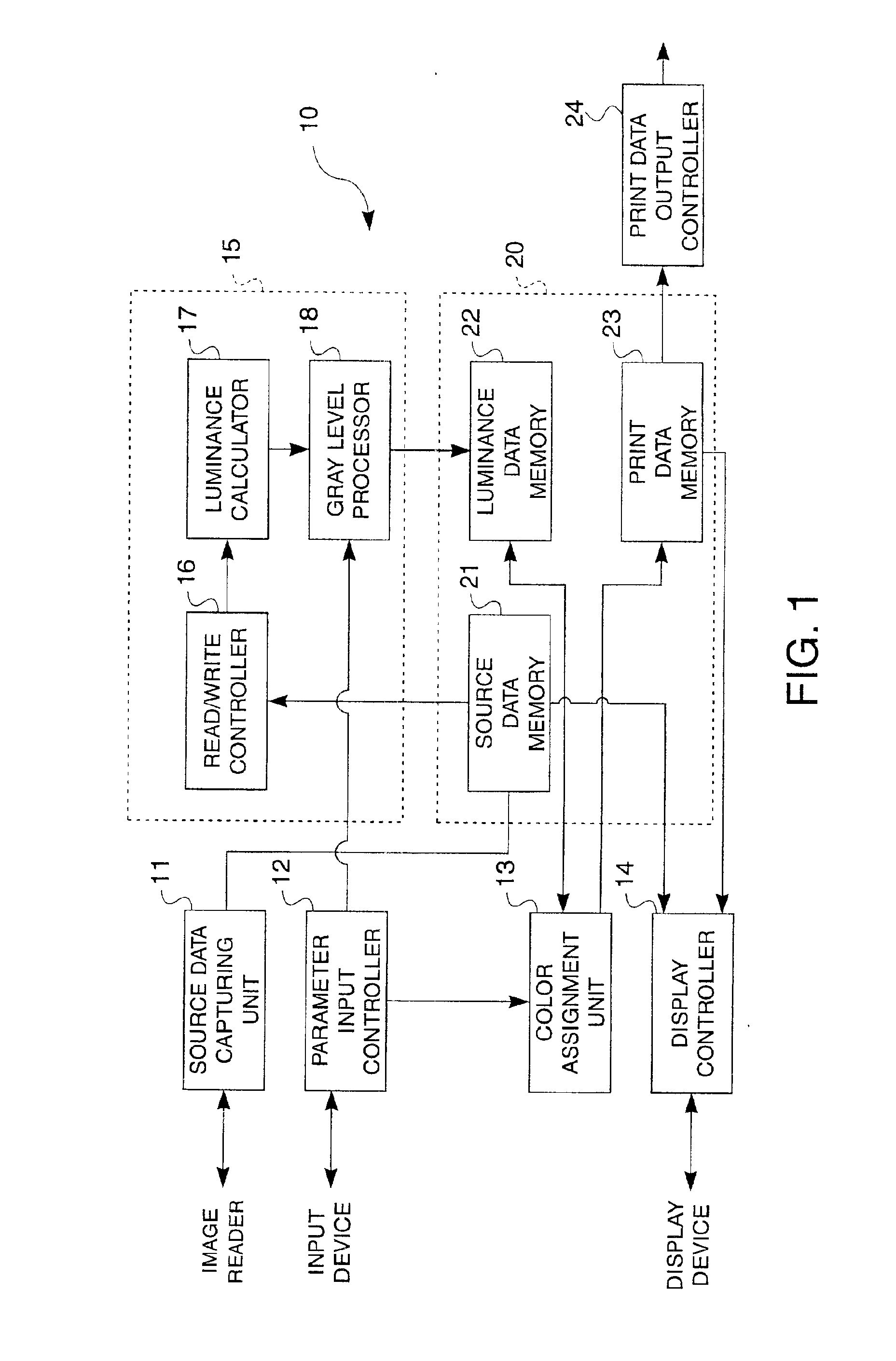
System, method and computer program converting pixels to luminance levels and assigning colors associated with luminance levels in printer or display output devices
InactiveUS6847377B2Less coloringIncrease the number ofVisual presentation using printersCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceOutput device
Print data suitable for printing or displaying an image are generated by assigning print colors after color reduction using a process that removes color reduction noise and produces clear contours in the print image. A source data capturing unit obtains source data containing image data and / or text data in plural colors. A data conversion unit converts color data for each pixel in the source data to luminance data for each pixel. A color assignment unit assigns a printable color to each pixel according to the luminance level of the converted luminance data. Source data is thus converted to luminance data, and usable colors are then assigned according to the brightness values of the image represented by the converted luminance levels.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Video copy prevention systems with interaction and compression
ActiveUS20100061553A1Optimization of detailsAttenuation bandwidthTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionInteractive contentImage resolution
Disclosed are systems and methods for providing video content while inhibiting the copying of that content for later viewing. Video images may be made difficult to copy for presentation at later times by the omission or addition of content developed in relation to the particular initial viewing. For instance, video information may be customized by omitting information that is not likely to be substantially perceived by the initial viewer but that is substantially likely to be perceived as missing by at least some other viewers. As another example, video information may be customized for a particular viewing instance so that it contains modified, selected or injected information that is likely to be perceived as non-disruptive or unnoticeable by the original viewer but that would be perceived as substantially noticeable and / or disruptive by some other viewers, including when parts of more than one such video information are combined in an effort to remove customization related to their respective original viewings. Various means and methods for accomplishing the forgoing in a variety of settings are disclosed including also for providing privacy related to what is viewed. In some examples higher-resolution images are provided for the region near the viewer's point-of-regard and lower resolution images are provided elsewhere, which also has the effect of reducing the bandwidth required. For interactive content rendered from digital models, a model for a central foveal region may be provide greater detail and have greater computational requirements than a model for a peripheral view, providing both economy / performance in rendering and protection against copying.
Owner:DIGITAL COMMUNITY LLC
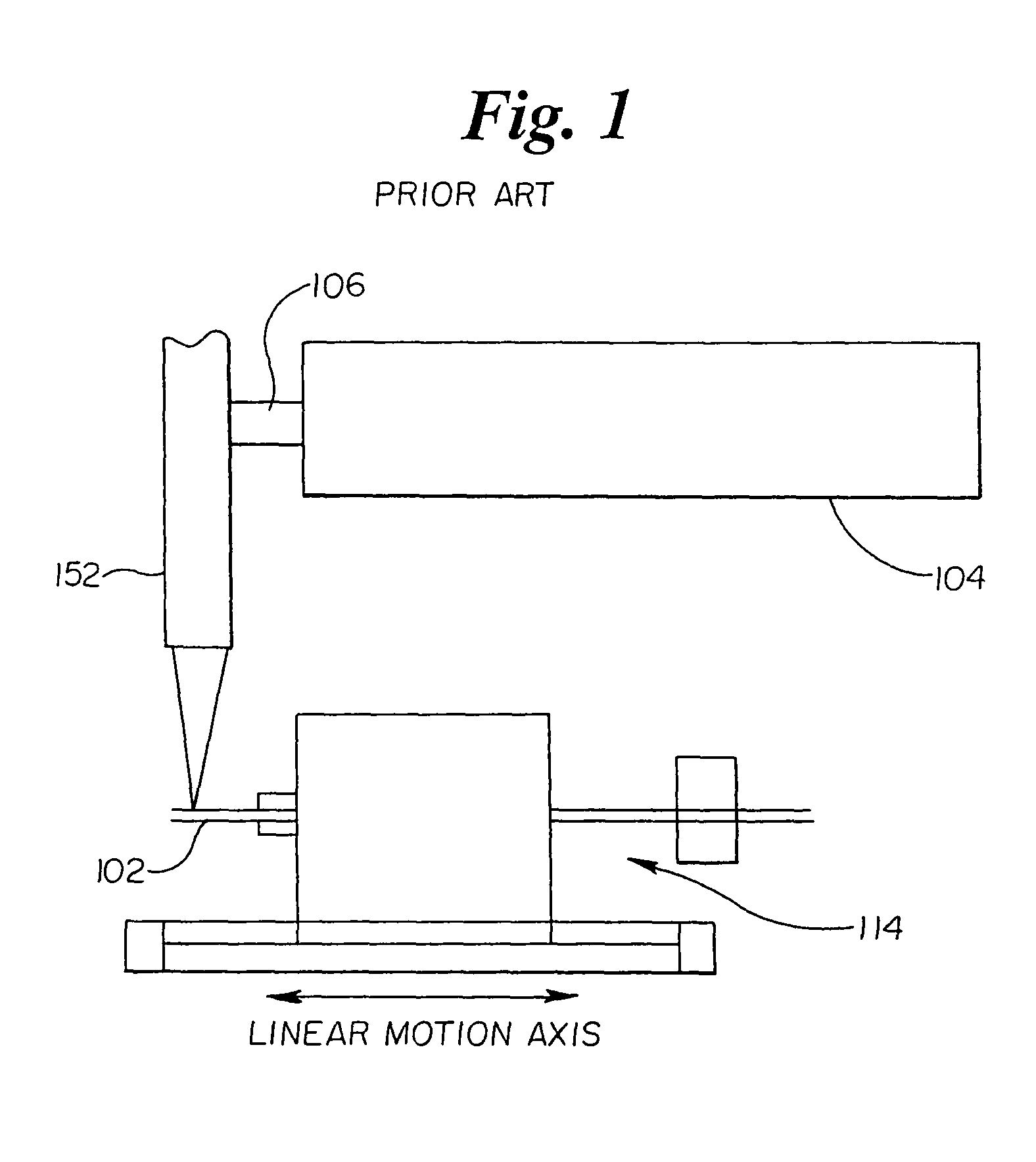
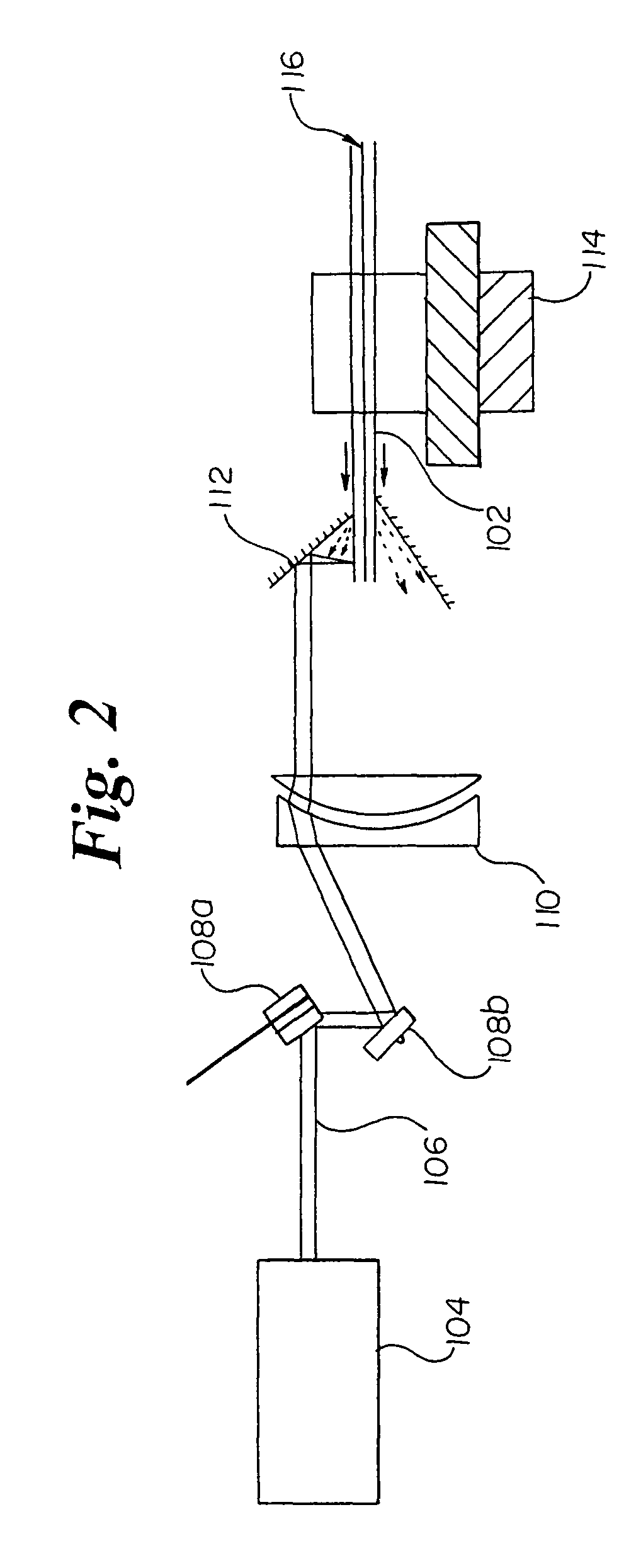
Laser stent cutting
A stent may be manufactured by providing a tube having a longitudinal axis therethrough, providing a stationary source of laser radiation, generating a beam of laser radiation using the source of laser radiation, and cutting a desired pattern into the tube by scanning the beam over a desired region of the tube.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
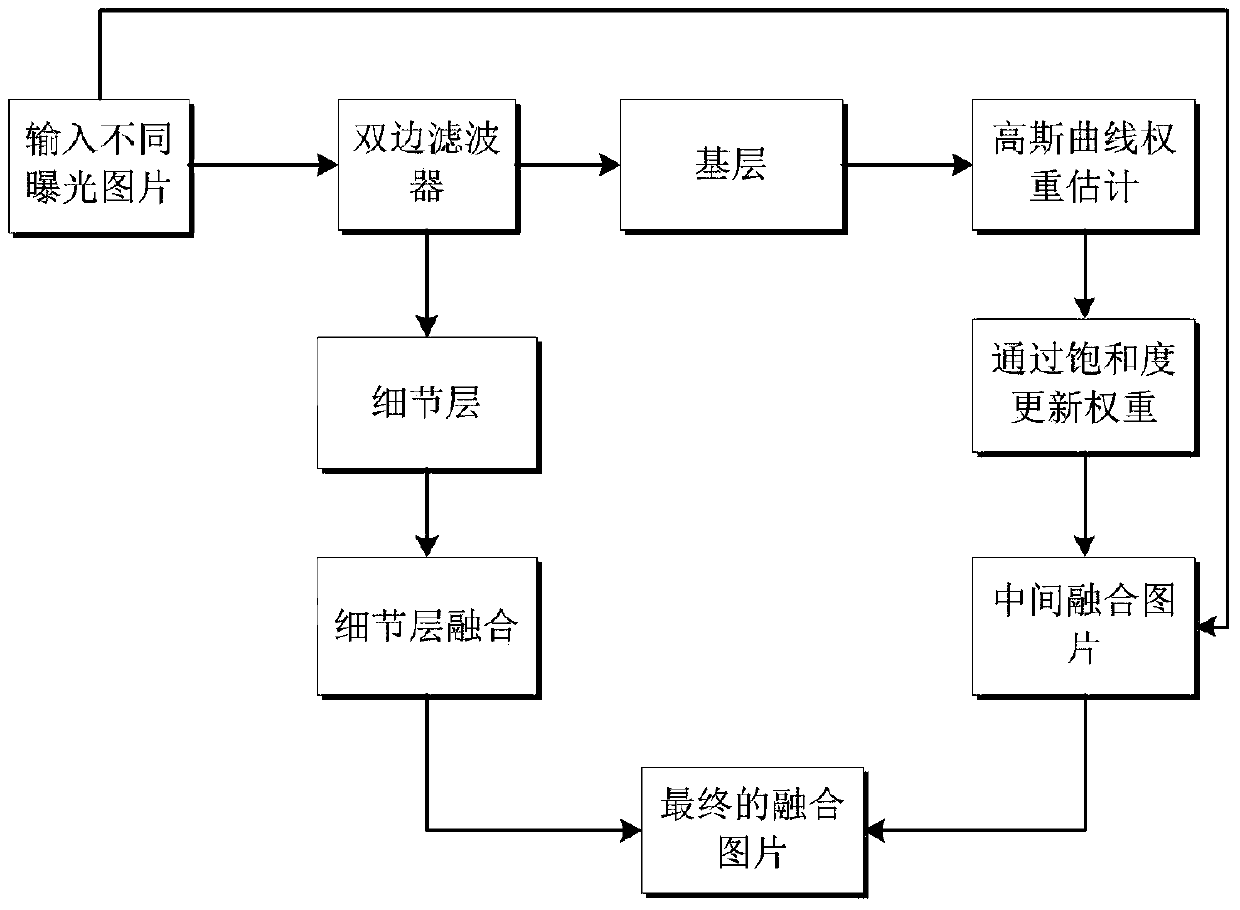
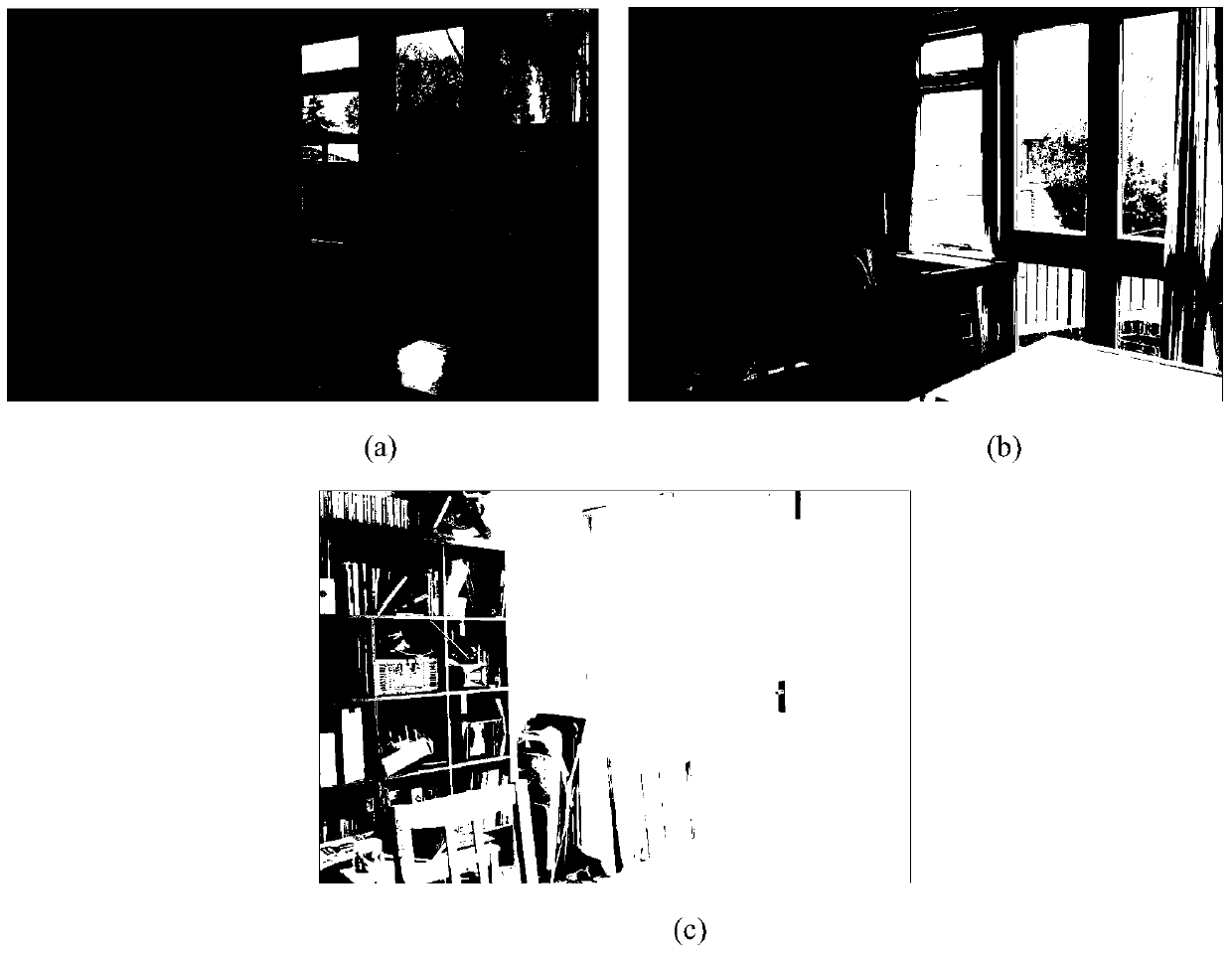
Multi-exposure image integration method based on bilateral filtering
InactiveCN105279746AImprove protectionClear edge textureImage enhancementComputation complexityImaging processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and particularly discloses a multi-exposure image integration method based on bilateral filtering. The method comprises the steps that (1) three static pictures of the same scene of different exposures are inputted; (2) the originally inputted pictures are divided into two parts of a detail layer and a basic layer based on a bilateral filter and then the detail layer and the basic layer are processed respectively; (3) weight of the basic layer is estimated by applying a Gaussian curve and weight is updated by applying picture saturation information; (4) an intermediate integration picture is preliminarily integrated by the updated weight; (5) the maximum value of each detail layer is obtained to act as a detail picture as for the detail layer; and (6) a final integration picture is obtained by synthesizing the obtained intermediate integration picture and the detail picture. Calculation complexity is low, and the details of the picture can be fully protected in the integration picture and the picture is enabled to be more natural in the aspect of color. The multi-exposure image integration method based on bilateral filtering can be widely applied to the field of image enhancement or cameras.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multiattribute specification of preferences about people, priorities, and privacy for guiding messaging and communications
InactiveUS20060206573A1Easy to findOptimization of detailsKernel methodsMultiple digital computer combinationsSpecification languageKnowledge management
The present invention relates to a system and methodology to facilitate multiattribute adjustments and control associated with messages and other communications and informational items that are directed to a user via automated systems. An interface, specification language, and controls are provided for defining a plurality of variously configured groups that may attempt to communicate respective items. Controls include the specification of priorities and preferences as well as the modification of priorities and preferences that have been learned from training sets via machine learning methods. The system provides both a means for assessing parameters used in the control of messaging and communications and for the inspection and modification of parameters that have been learned autonomously.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for calculating and using the profile of a surface
InactiveUS7044680B2Optimization of detailsIn situ pavingsRoads maintainenceRoad surfaceContact sensor
Knowledge of the profile of a road surface—most importantly its defects—is a must to construct an acceptable road surface in this day of high speed traffic. Measurement and calculation of the surface during the process of forming the road—when the road material is still plastic—provides the opportunity to repair unacceptable defects while the road surface material can still be worked. The benefits include a smoother, more durable surface at a lesser cost than methods used on hardened road surfaces. Shown herein is for a method and apparatus for calculating a surface's elevation profile using measurements taken by non-contact devices at a number of locations. Since non-contact sensors are used, elevation profiles of wet concrete can be measured and calculated. Such an apparatus can be mounted on a road paving machine to provide a real time feedback of the surface so corrections to the surface and to the paving machine's operation can be made as required. Alternatively, the method and apparatus can be used just after the pavement is formed but while the pavement is still in a plastic condition so that defects can be corrected before the pavement has hardened.
Owner:GOMACO
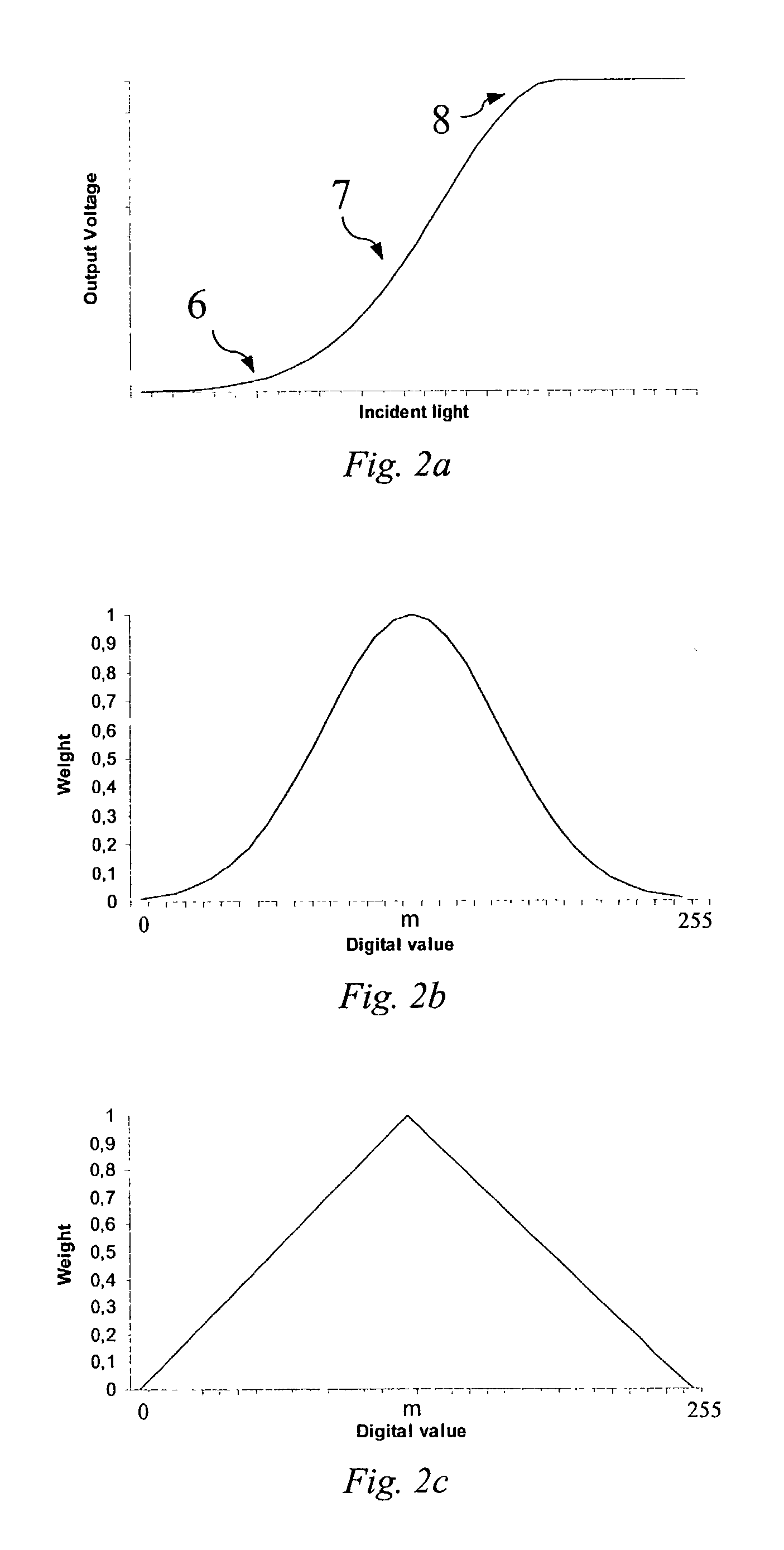
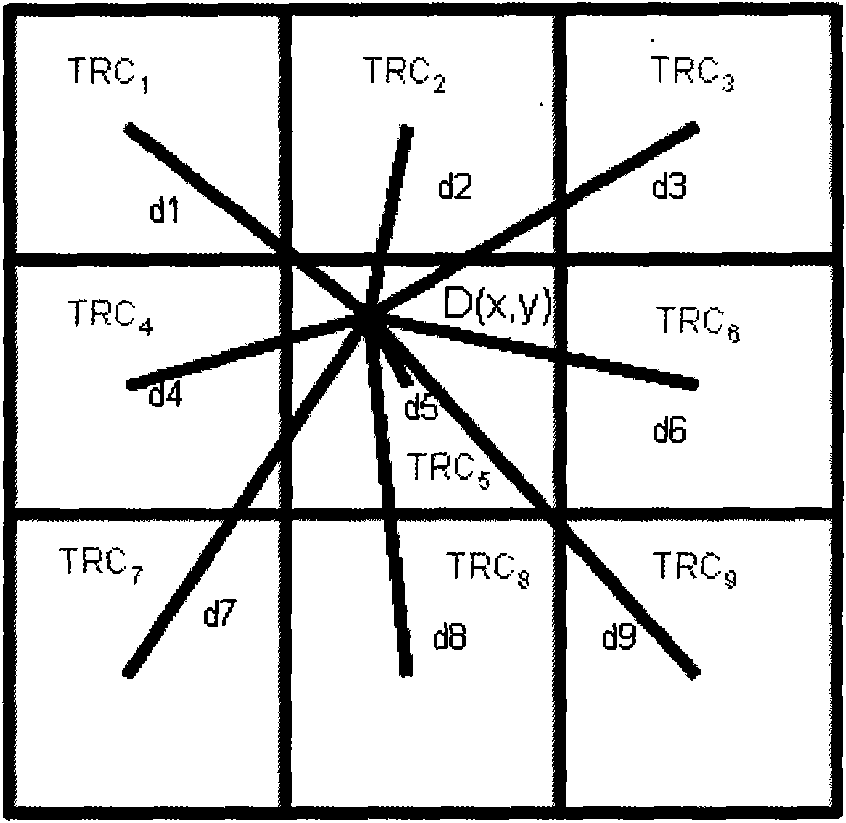
Method for merging digital images to obtain a high dynamic range digital image
ActiveUS7106913B2Quality improvementOptimization of detailsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsWeight coefficientExposure latitude
A method of processing digital source images, each represented by pixel matrices, to obtain from two or more source images, representing one and the same real scene and acquired by utilizing different exposure levels, a final digital image capable of reproducing the real scene with an exposure latitude greater than that of each of the source images. The method, which can be advantageously used in digital still cameras, produces the final image by combining the source images with the help of a weighted average constructed pixel by pixel. Thanks to a special filtering to which the weighting coefficients are subjected before the weighted mean operation, the method obtains a final image in which the source images are harmoniously combined with each other.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Methods for matching dynamic range of image signals
ActiveCN101540832AIncrease brightnessIncrease contrastTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging qualityOutput device
The invention provides methods for matching the dynamic range of image signals, in particular relates to methods for processing the image signals, aims at solving the problem of influenced image quality of the prior art, which is caused by the reason that the dynamic range of a digital image in a computer can not be well matched with the dynamic range of digital output equipment. The invention mainly adopts two methods: in the first method, the brightness signal of the image signal is extracted and then is processed by the steps of blurring, adjustment, stretching transformation, and the like, and detail signals in the brightness signal are correspondingly processed, so that the dynamic range of the digital image can be matched with the dynamic range of digital equipment; or in the second method, the brightness signal of the image signal is extracted and is divided into regional blocks; after being initially adjusted, the brightness signal of pixel in each regional block is processed by the operation of weighted average, so that the dynamic range of the digital image can be matched with the dynamic range of digital equipment. The methods can be used for processing the digital image so as to output high quality images.
Owner:成都恒图科技有限责任公司
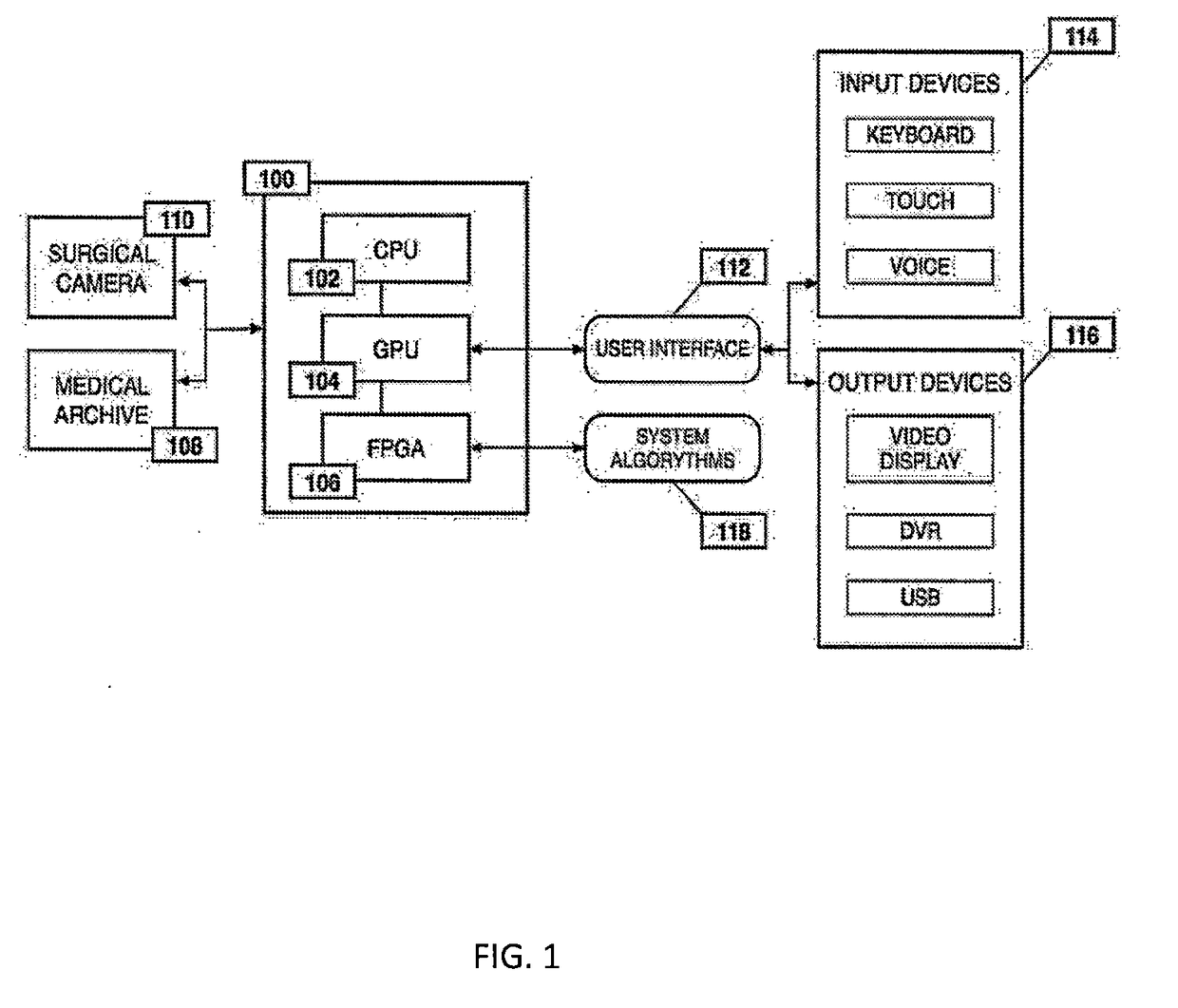
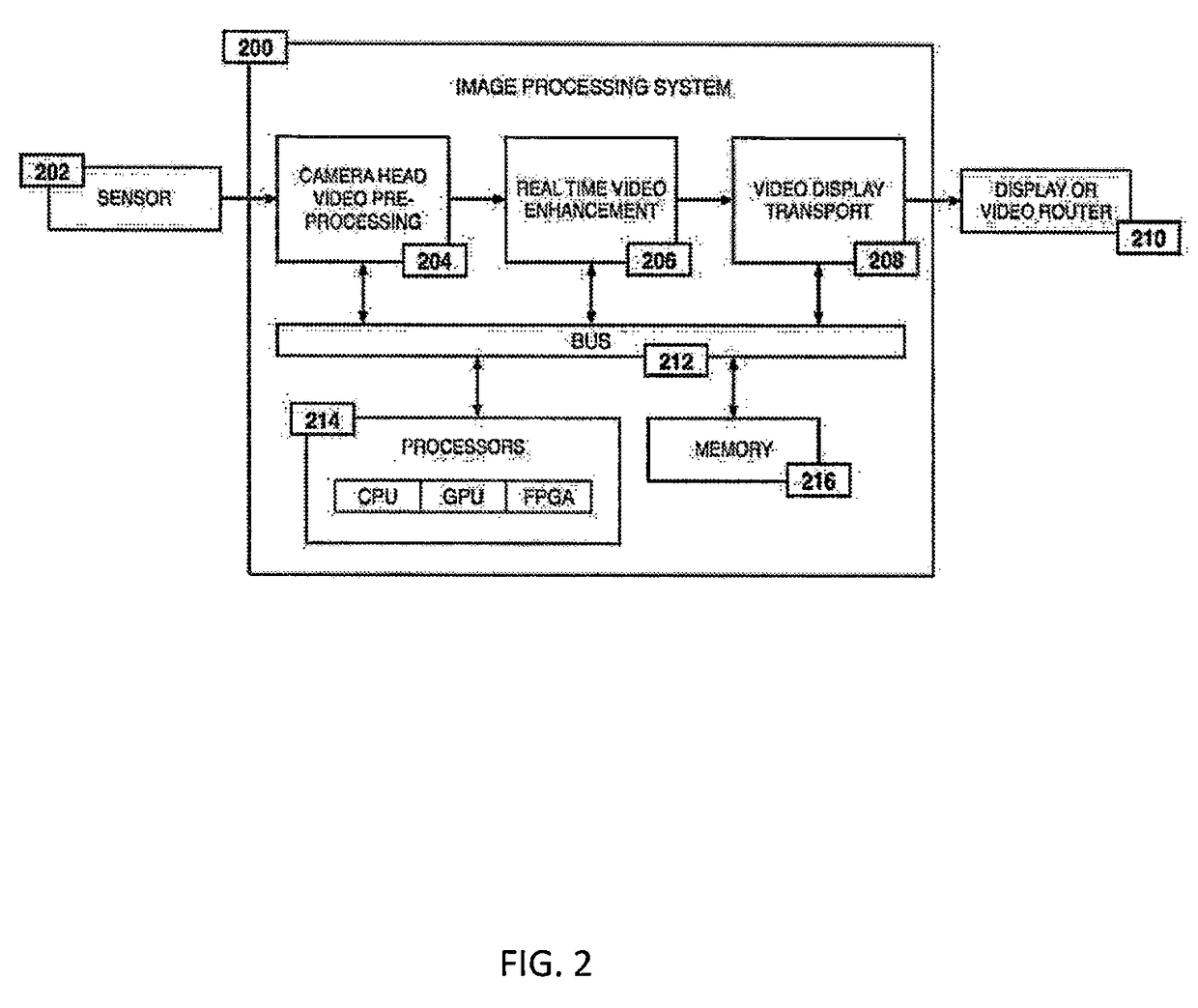
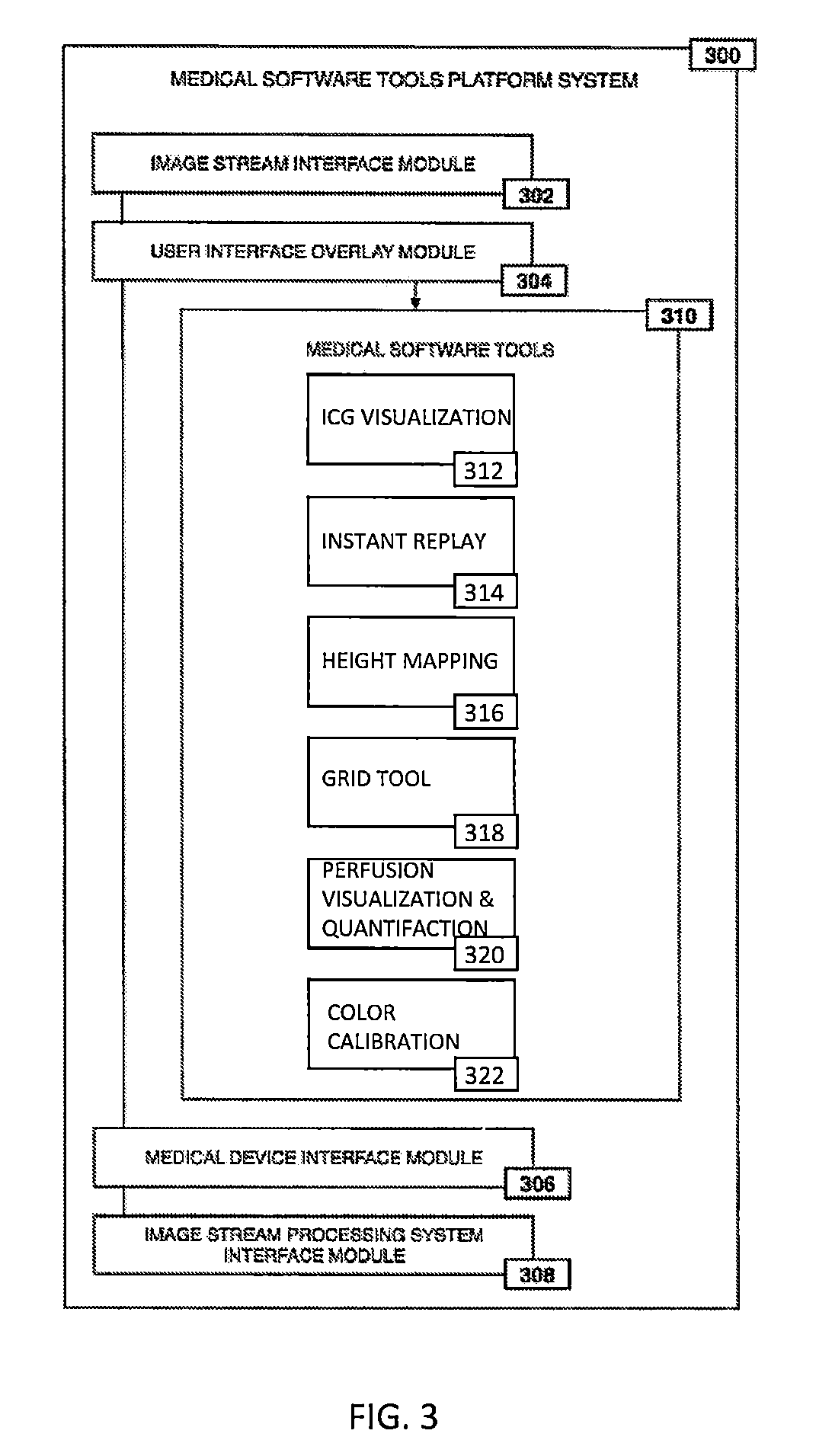
System and method for enhanced data analysis with video enabled software tools for medical environments
ActiveUS20180338802A1Easy to integrateIncrease awarenessImage enhancementMedical data miningMini invasive surgeryTissue fluid
Medical software tools platform utilizes a surgical display to provide access to specific medical software tools, such as medically-oriented applications or tools, that can assist those in the operating room, such as a surgeon or surgical team, with a surgery. In particular, an optical sensor located within an endoscopic camera may register subtle differences in color characteristics reflected from a tissue surface and in turn transmit the information to a medical image processing system. Moreover, the new tools are intended to help surgeons better determine the boundaries between healthy and diseased regions during surgical procedures. Various tools are intended to be used in procedures where indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescent dye is used. Intraoperative fluorescence imaging is commonly used during minimally invasive procedures to enable surgeons to visualize tissue perfusion and anatomical structures. The term perfusion refers to the passage of blood and tissue fluid through the capillary bed. Intraoperative fluorescence imaging can also be used to improve visualization of vessels and structures, which, in turn, may reduce the risk of complications during minimally invasive surgeries.
Owner:WADE JACK
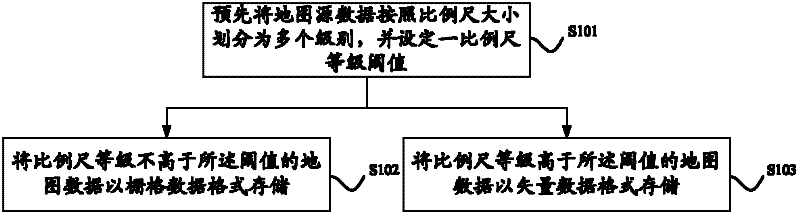
Electronic map data storage and query method, device and system
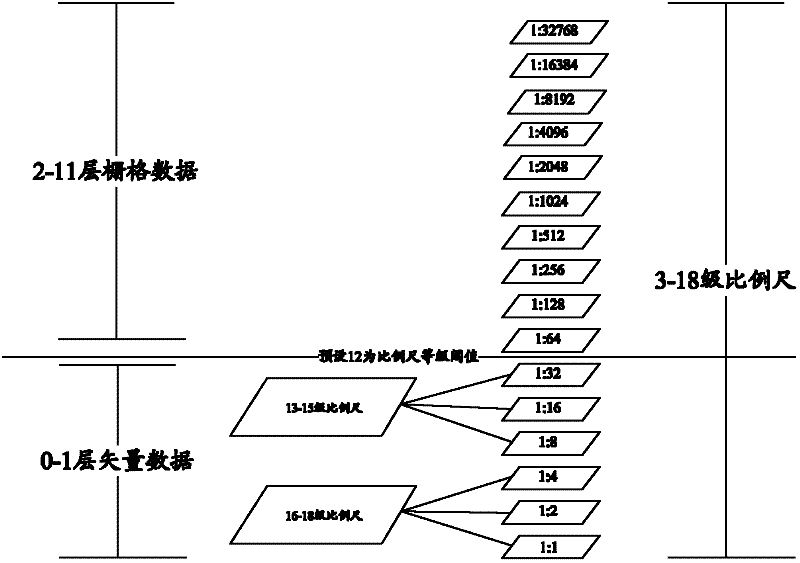
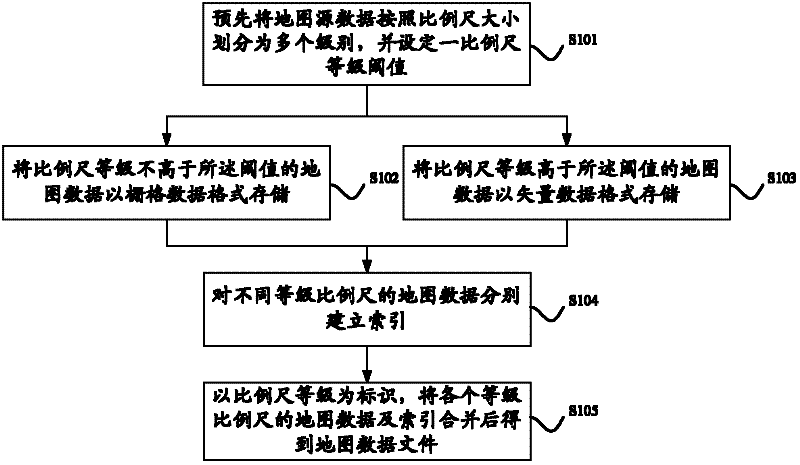
InactiveCN102368259AImprove image rendering speedReduce system processing resource requirementsSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic mapSource data
The invention discloses an electronic map data storage and query method, device and system. The electronic map data storage and query method comprises the following steps of: grading the map source data into a plurality of grades according to the sizes of proportional scales, and setting a proportional scale grade threshold; storing the map data, of which the proportional scale grade is not higher than the threshold, according to a raster data format; and storing the map data, of which the proportional scale grade is higher than the threshold, according to a vector data format. In the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the map data is stored according to two modes including a raster data mode and a vector data mode, so as to give consideration to the requirements on two aspects of exhibition effect and performance of the electronic map on a mobile terminal.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
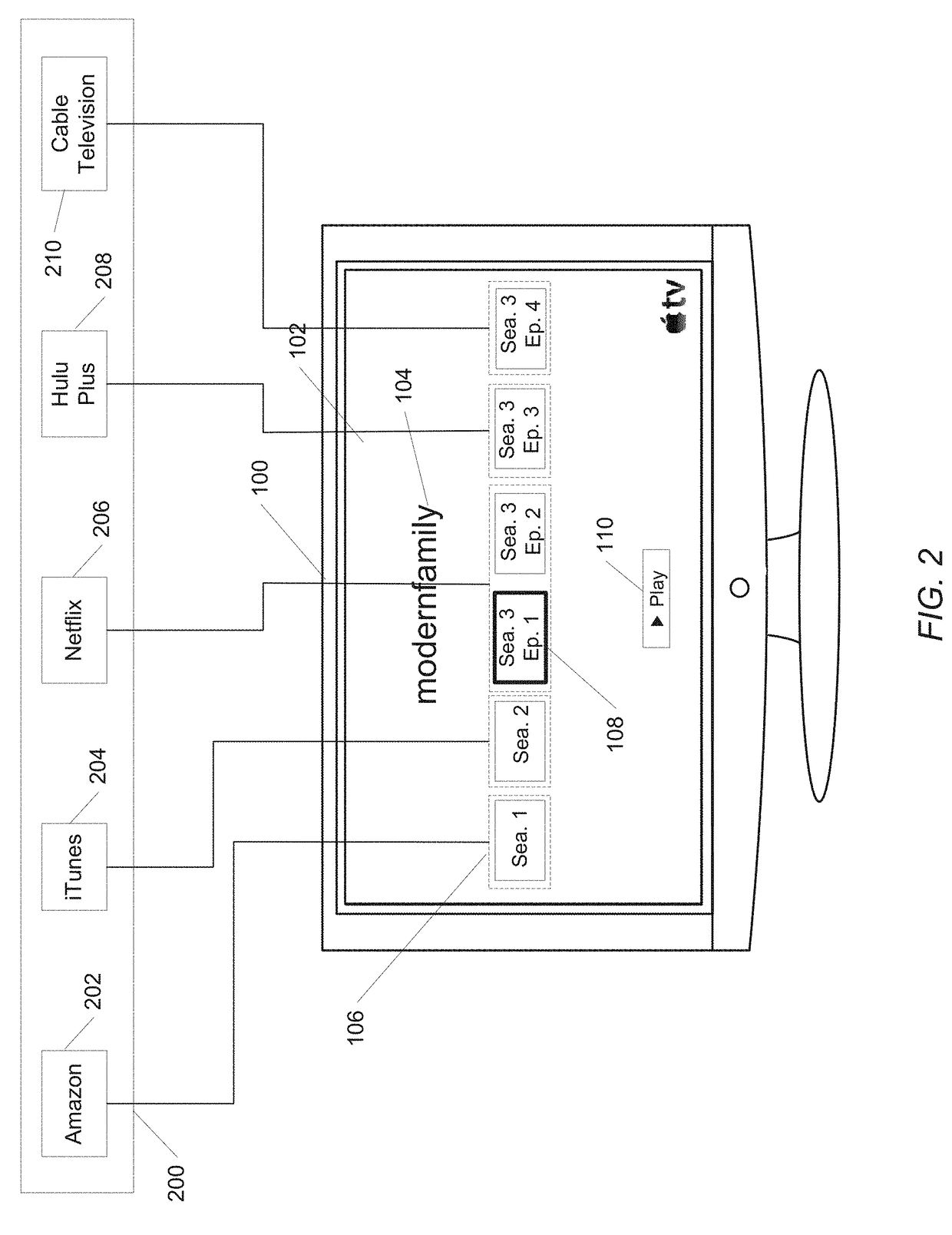
Channel bar user interface
ActiveUS20180041814A1Optimization of detailsDirect accessSelective content distributionMultiple modesLive video
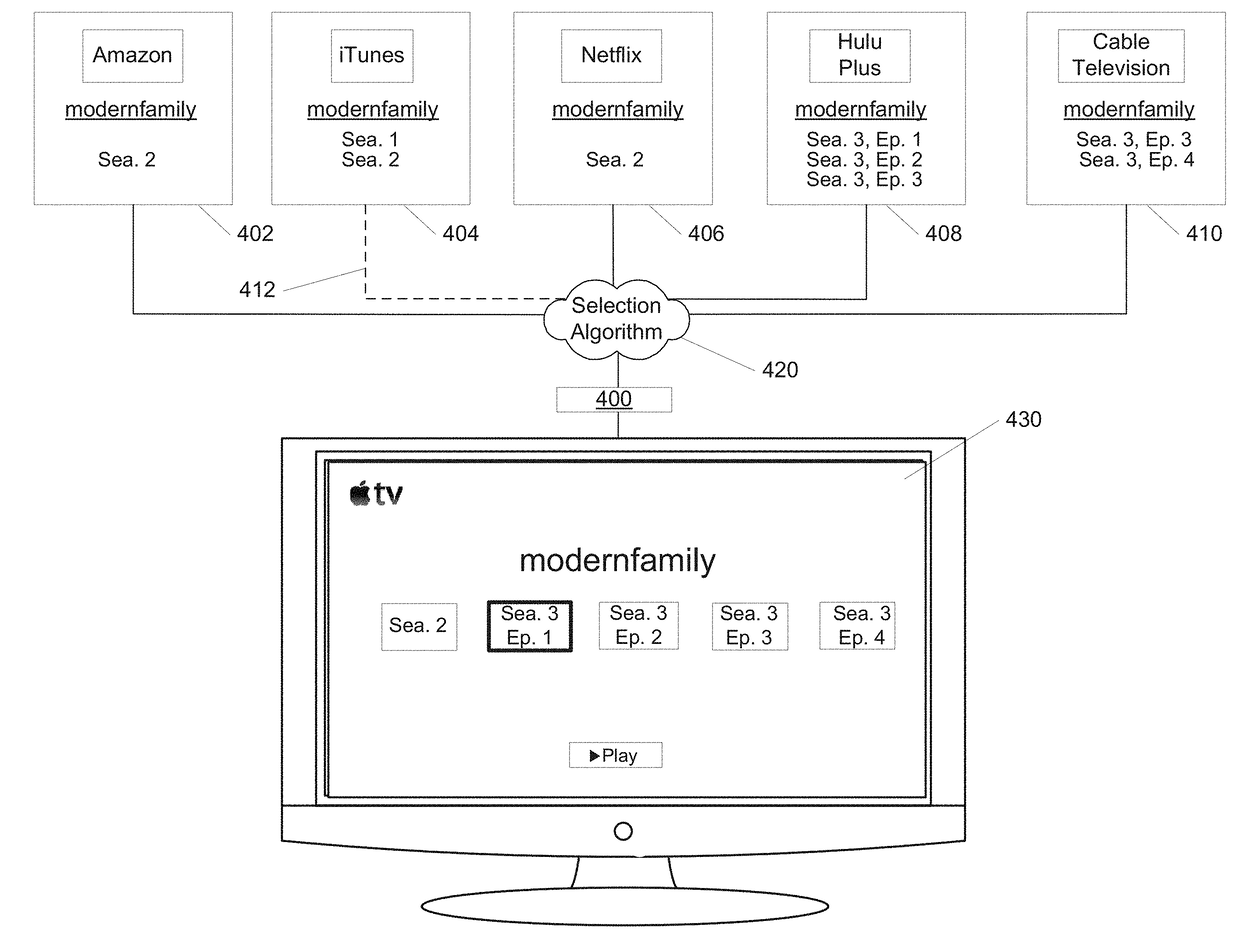
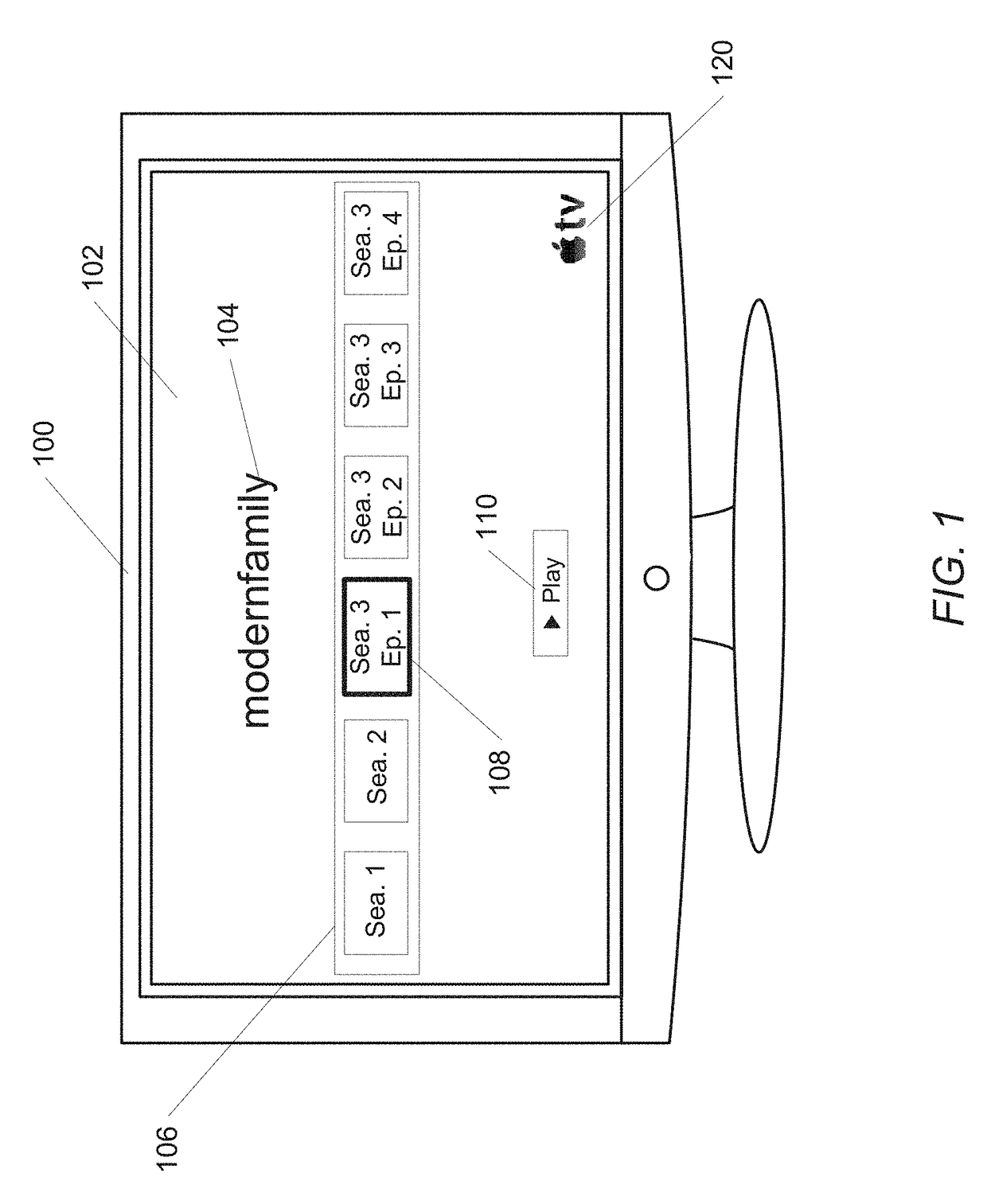
Systems and methods for a media content user interface. A media content provider includes storage for storing and serving video content to subscribers. The media content provider records and or otherwise stores video content from around the world. Subscribers are provided a user interface to the system that includes a channel bar. The channel bar is dynamically scoped responsive to interactions of a viewer with the system. Selectable elements within the channel bar provide direct access to related content regarding video content, such as television series information and cast information. In addition, the channel bar is operable in multiple modes. An EPG mode displays live video for multiple channels simultaneously. Themed modes permit channel bars that display content according to various themes which may be defined by a viewer, the provider, or both.
Owner:APPLE INC
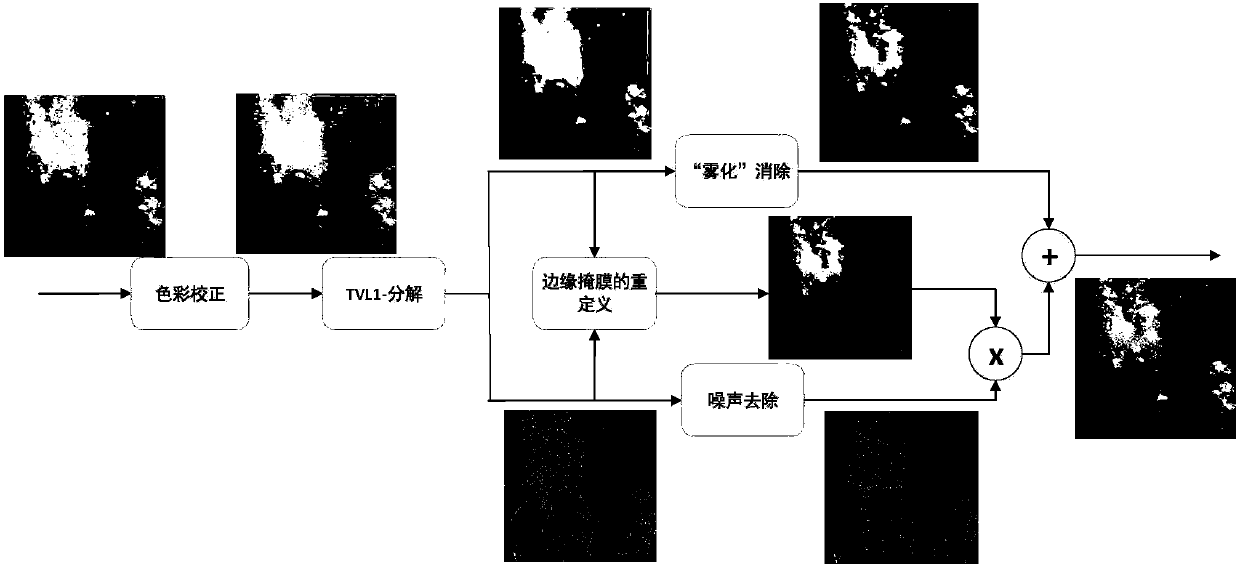
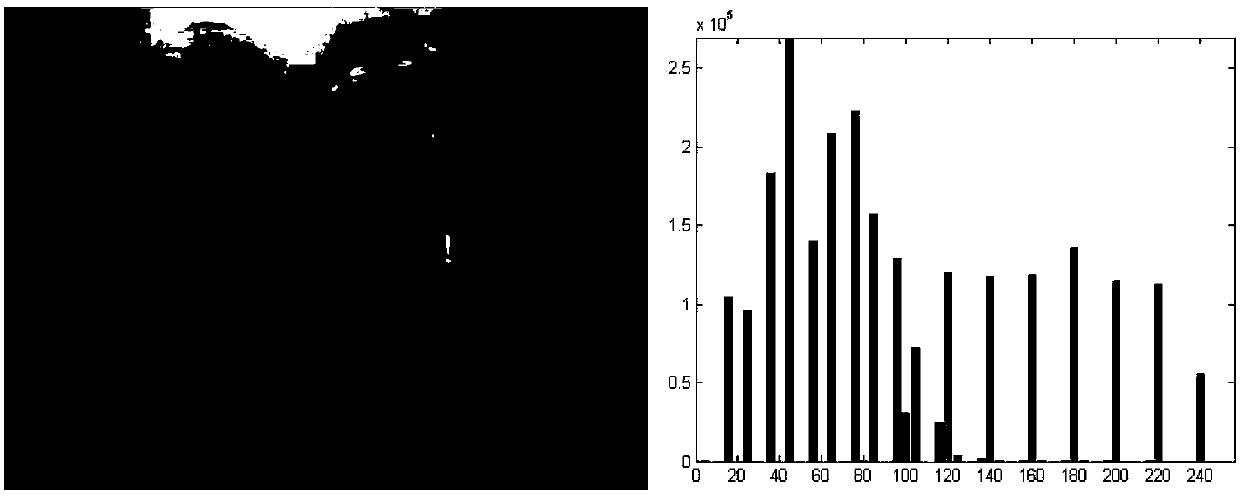
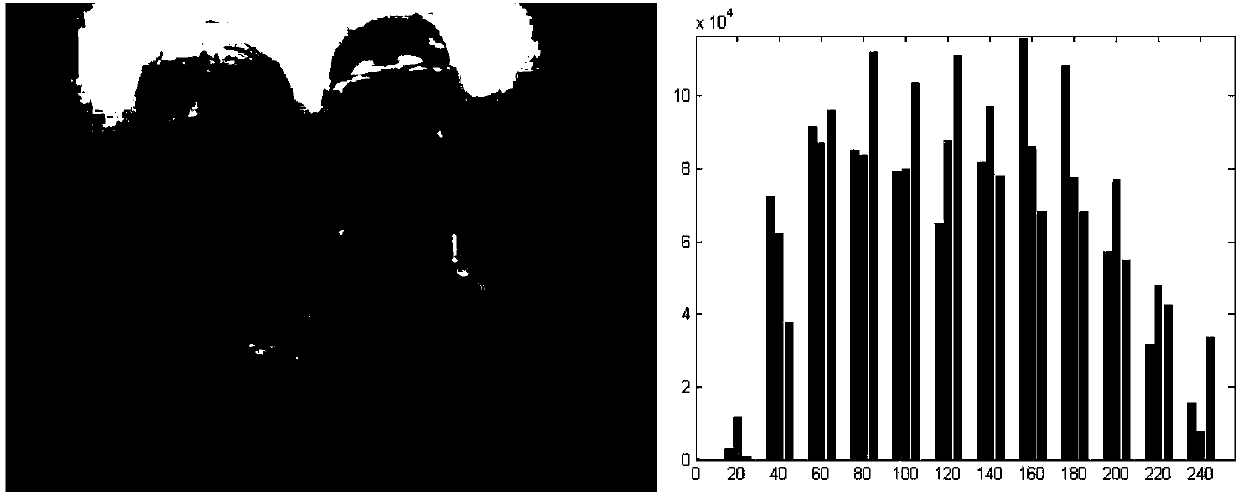
Underwater image enhancement method based on structure-texture layering
ActiveCN107798665AIncrease contrastGuaranteed naturalnessImage enhancementImage contrastTransmittance
The invention belongs to the field of computer vision, and provides good detail while improving image contrast, and the natural performance of the tone is kept while the noise is suppressed. An underwater image enhancement method based on structure-texture layering comprises the steps of firstly, carrying out color correction through histogram equalization, decomposing the image subjected to colorcorrection into a low-frequency structural layer and a high-frequency texture layer, leaving the noise on the texture layer, accurately estimating the transmission rate from the structural layer without noise based on a proposed fog line model to conduct enhancement processing, enhancing the texture layer by using a gradient residue minimization method, reconstructing the reinforced structural layer, the texture layer and the refined edge mask to form a final enhanced image through scaling, so that the problems that can not be solved through existing technology is solved. The method is mainlyapplied to underwater image enhancement and processing occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
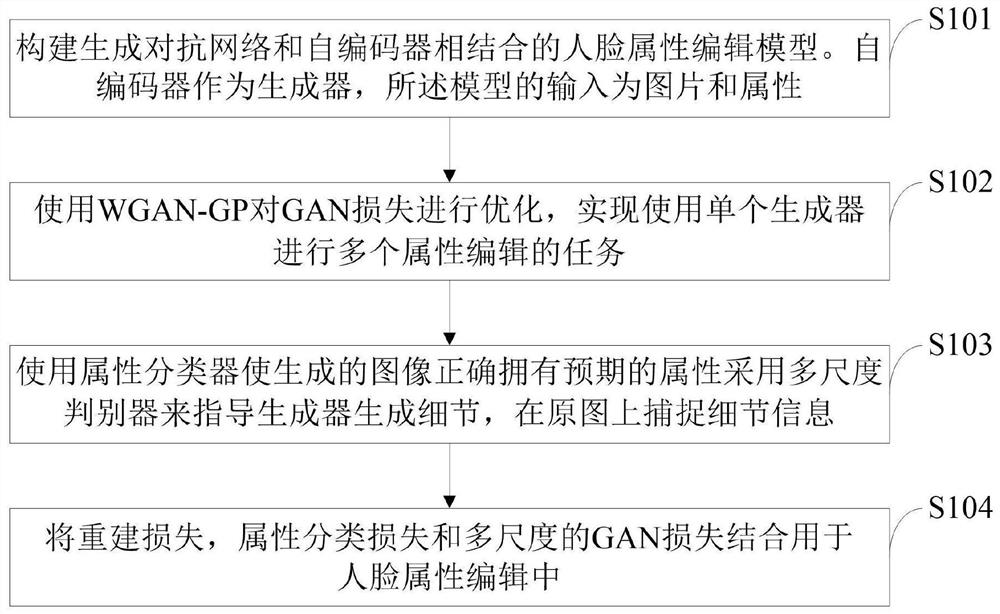
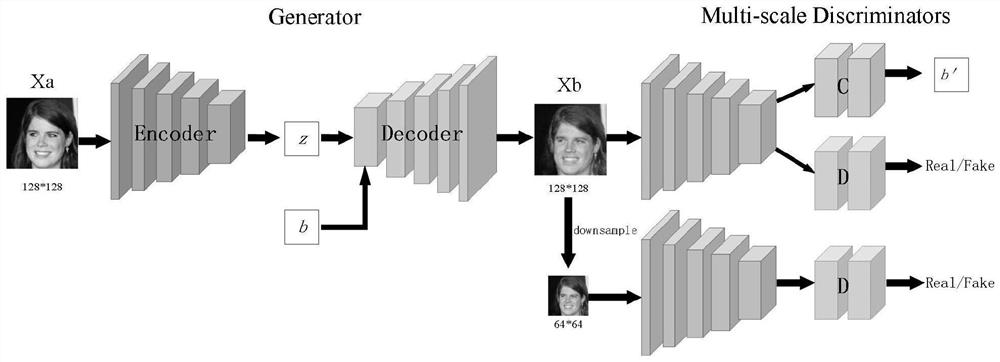
Face attribute editing method based on generative adversarial network and information processing terminal
ActiveCN111932444AImprove visual qualityOptimization of detailsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionInformation processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of human face attribute editing, discloses a human face attribute editing method based on a generative adversarial network and an information processing terminal, and constructs a human face attribute editing model combining the generative adversarial network and an auto-encoder. Wherein the auto-encoder is used as a generator, and the input of the model is pictures and attributes; optimizing the GAN loss by using the WGAN-GP to realize a task of editing a plurality of attributes by using a single generator; enabling the generated image to correctlyhave expected attributes by using an attribute classifier; a multi-scale discriminator is adopted to guide a generator to generate details, and detail information is captured on an original image; and combining the reconstruction loss, the attribute classification loss and the multi-scale GAN loss for face attribute editing. Experiments on a CelebA data set show that a high-quality face image isgenerated on the basis that expected attributes are correctly owned, and the method has good performance in the aspects of single-attribute face editing, multi-attribute face editing and attribute strength control.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
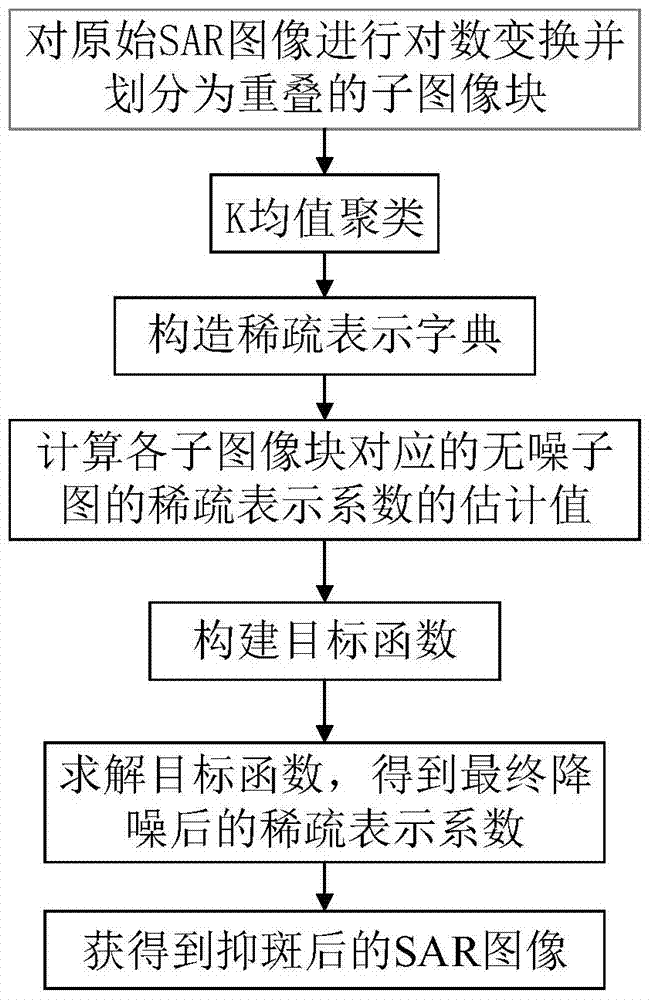
SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image spot-inhibiting method based on spare domain noise distribution constraint
InactiveCN103971346AStrong anti-spot abilityGood anti-spot abilityImage enhancementFeature extractionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image spot-inhibiting method based on spare domain noise distribution constraint, which mainly solves the problem that existing spot-inhibiting method cannot keep image texture details and radiation characteristic at the same time. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out logarithm transformation on an original SAR image, dividing the transformed image into overlapped sub image blocks which are same in size and clustering the image blocks by a K mean value clustering method; 2, solving a sparse representation sub dictionary of each cluster by a principal component analysis method and calculating an estimated value of a sparse representation coefficient of a noise-free sub image corresponding to each sub image block by non-local mean value algorithm; 3, solving the final noise-free sparse representation coefficient by soft threshold shrinking algorithm and obtaining the de-noised sub image blocks through reverse sparse transformation; and 4, splicing the sub image blocks and carrying out reverse logarithm transformation to obtain the spot-inhibited SAR image. The method disclosed by the invention is strong in coherent spot inhibiting ability, and the image texture details and radiation characteristic are kept well, so that the method can be used for target identification and characteristic extraction.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Molding composition and method of use
ActiveUS20050061471A1Reducing necessary finishing workFaster turn around timeButtonsRecord carriersColloidal silicaSlurry
A slurry composition for a mold and method of use thereof. The slurry composition includes about 45-80% by weight alumina, about 10-30% by weight silicon carbide, and about 10-50% by weight colloidal silica. In one aspect, the alumina component comprises a material selected from the group consisting of brown fused alumina, white fused alumina, tabular alumina, calcined alumina, and mixtures thereof. In another aspect, the composition includes fumed silica at 2-5% by weight. The composition may also include a setting agent at 0.05-2% by weight.
Owner:MAGNECOMETREL
Molding composition and method of use
A slurry composition for a mold and method of use thereof. The slurry composition includes about 45-80% by weight alumina, about 10-30% by weight silicon carbide, and about 10-50% by weight colloidal silica. In one aspect, the alumina component comprises a material selected from the group consisting of brown fused alumina, white fused alumina, tabular alumina, calcined alumina, and mixtures thereof. In another aspect, the composition includes fumed silica at 2-5% by weight. The composition may also include a setting agent at 0.05-2% by weight.
Owner:MAGNECOMETREL
Method of Processing Images and Apparatus
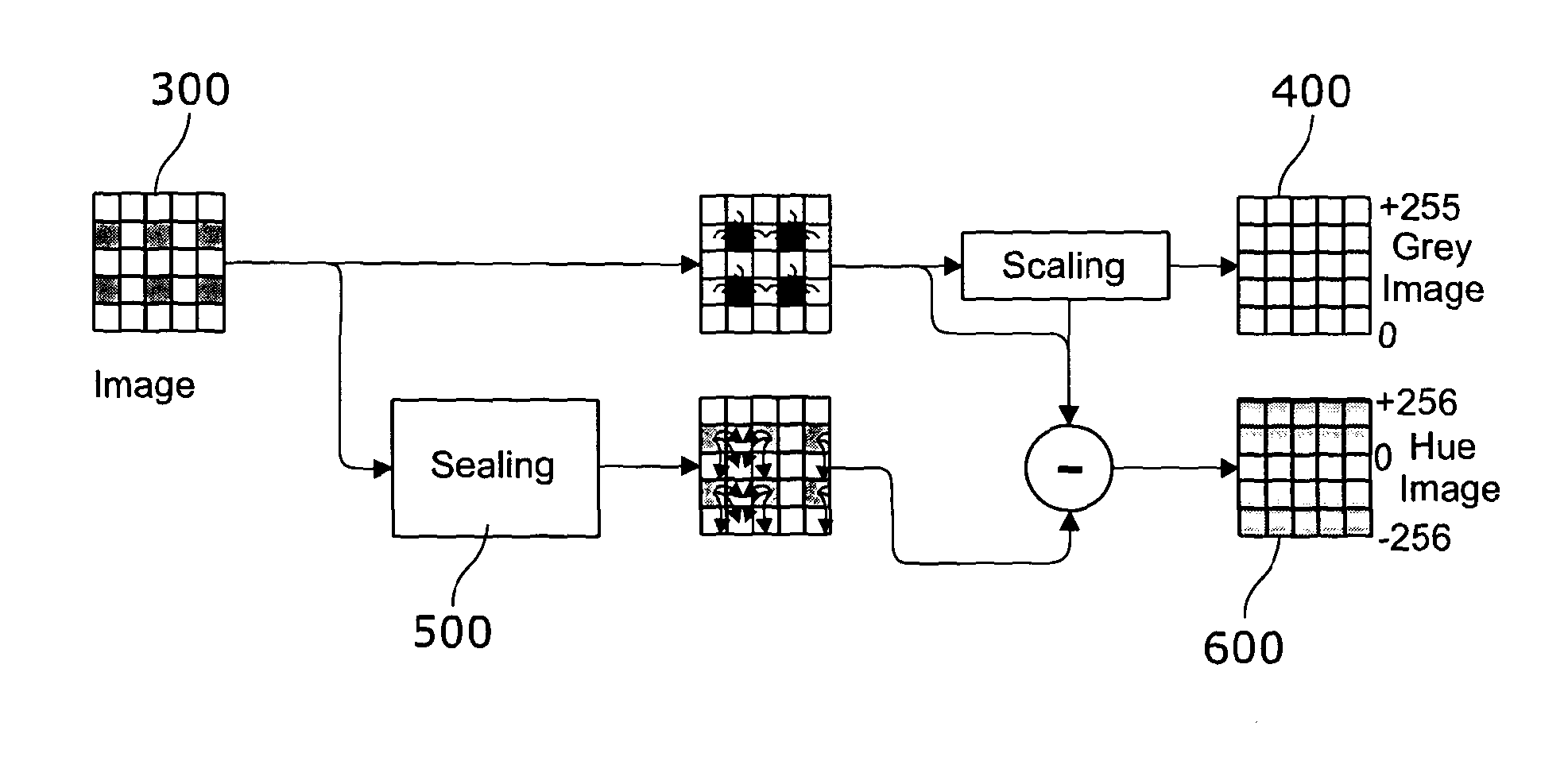
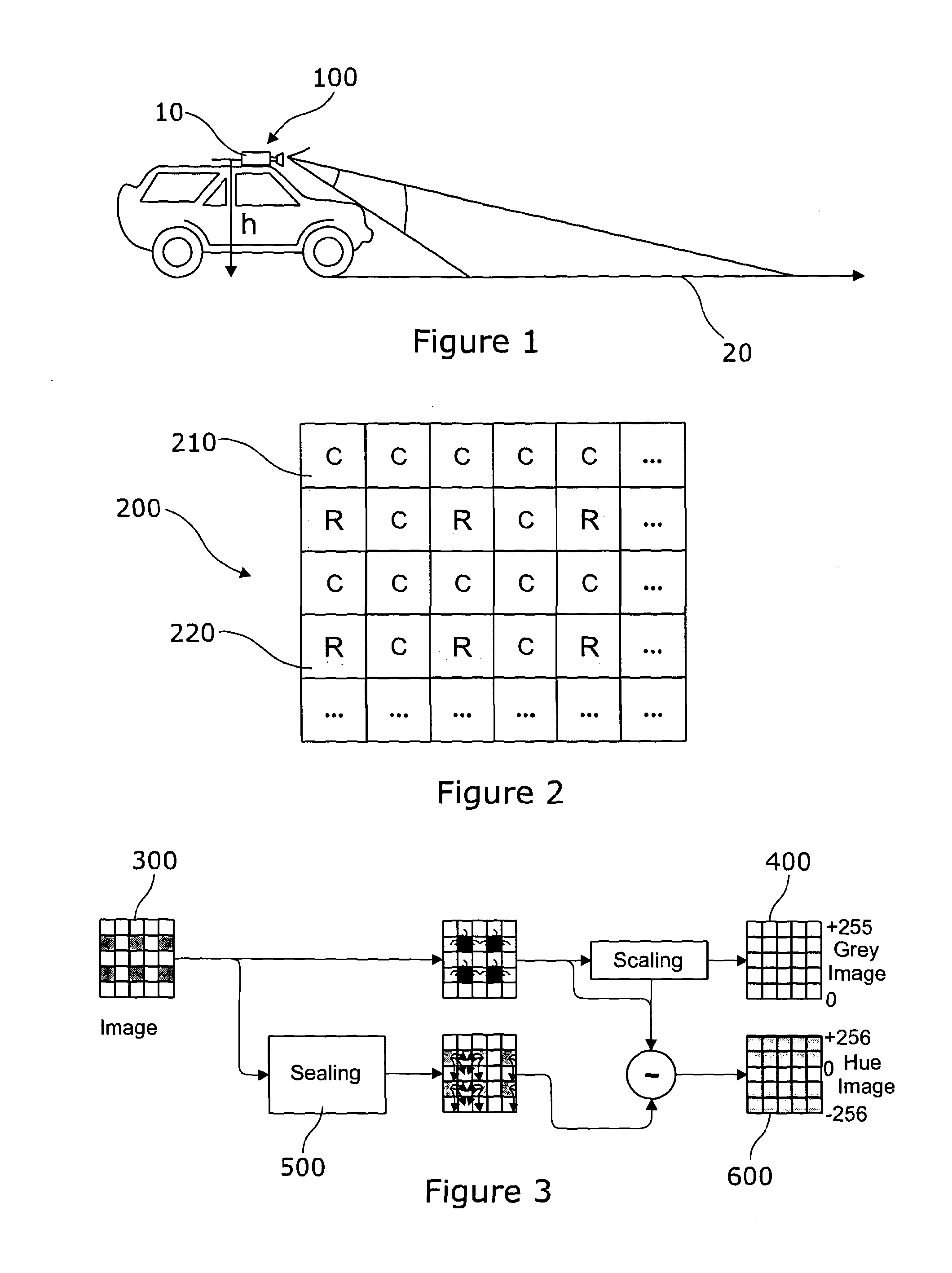
ActiveUS20130342698A1Easy to identifyRaise the possibilityCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsHueIntensity change
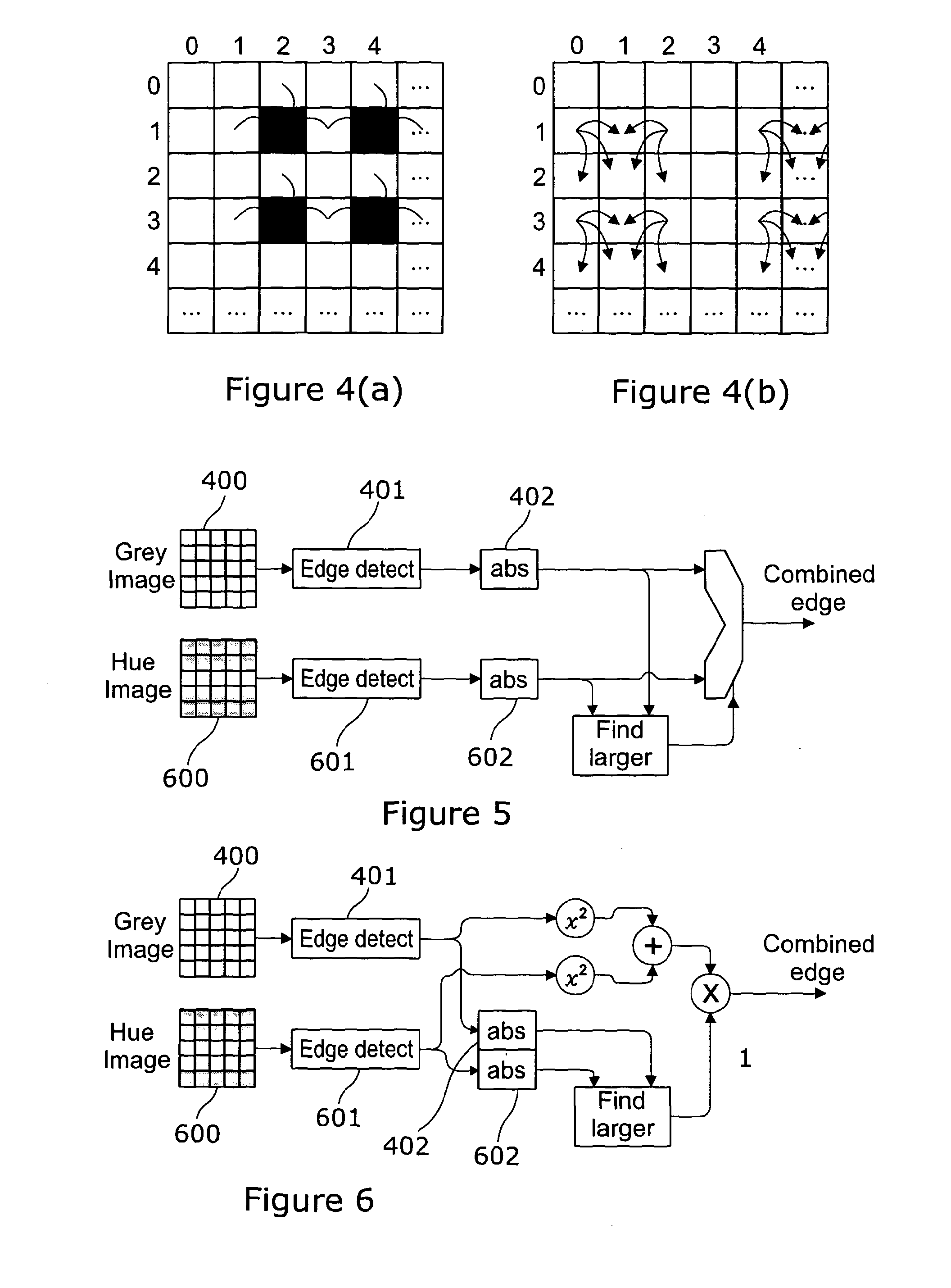
A method of processing an image includes a region of a highway in front of the vehicle captured using an imager having a two dimensional array of image capturing pixels. The array includes a first set of pixels substantially independent of hue and a second set of pixels dependent of a limited range of hues. The method further includes the steps of producing a first image where each pixel is assigned a value derived from the first set of pixels and producing a second image where each pixel is assigned a value derived from the first set of pixels and the second set of pixels. The method includes identifying-for at least one pixel in the first image a first intensity change value indicative of the difference between that pixel and at least one adjacent pixel identifying for a corresponding pixel in the second image a second intensity change value indicative of the difference between that pixel and at least one adjacent pixel. A combined image is formed using a defined set of combination rules to assign a value to the corresponding pixel in the combined image which depends on the first and second identified intensity change values for that corresponding pixel.
Owner:TRW LIMITED
Reducing particle implantation
ActiveUS20110049364A1Less imaging artifactOptimization of detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesParticle beamParticle physics
Methods disclosed herein include: (a) forming a channel in a sample, the channel extending one micron or more along a direction oriented at an angle to a surface of the sample; (b) exposing a portion of the sample above the channel to a particle beam to cause particles to leave the surface of the sample; and (c) forming an image of the sample based on particles that leave the surface.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Imaging system
InactiveUS20160127657A1Optimization of detailsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionImage extraction
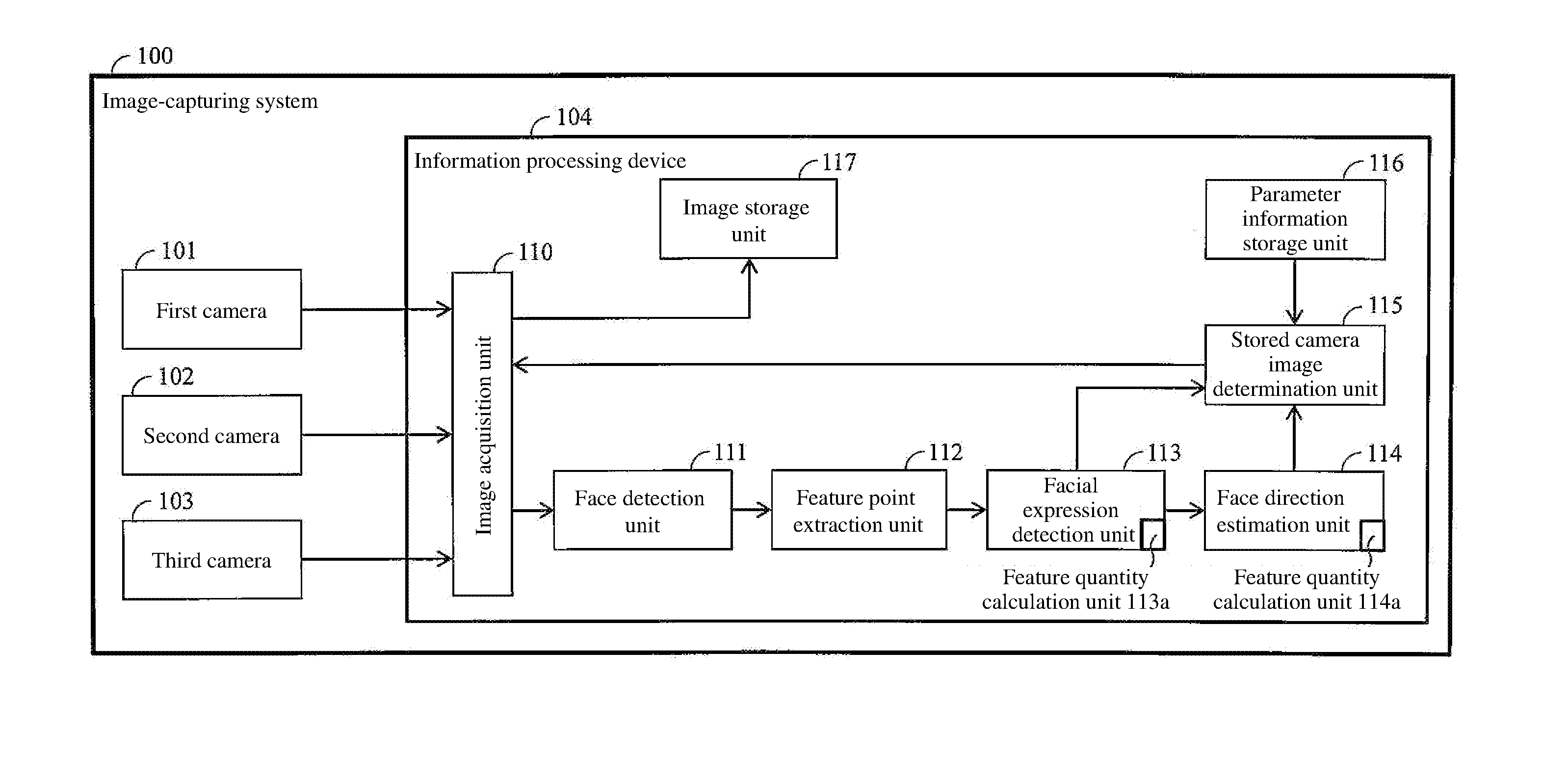
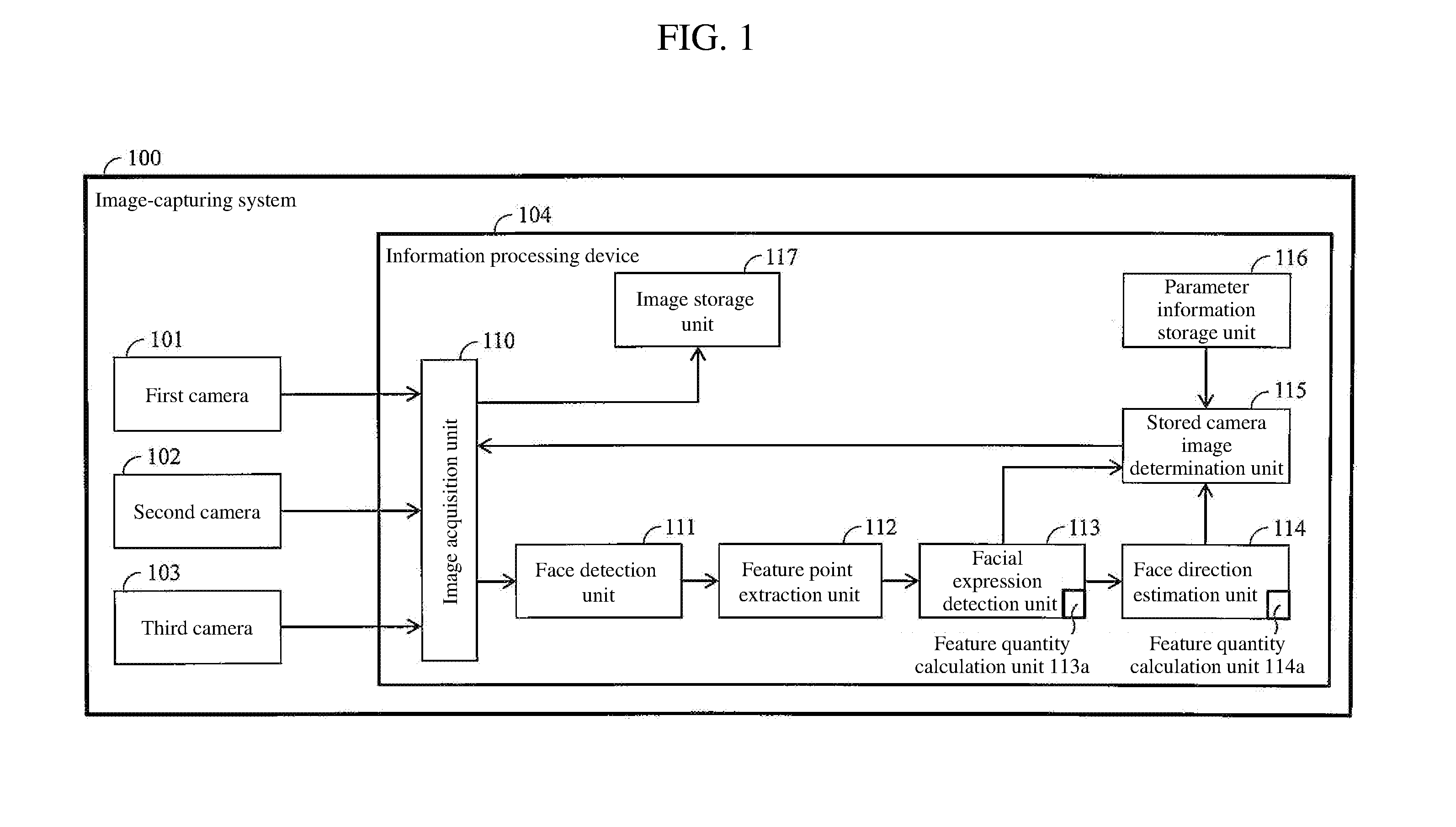
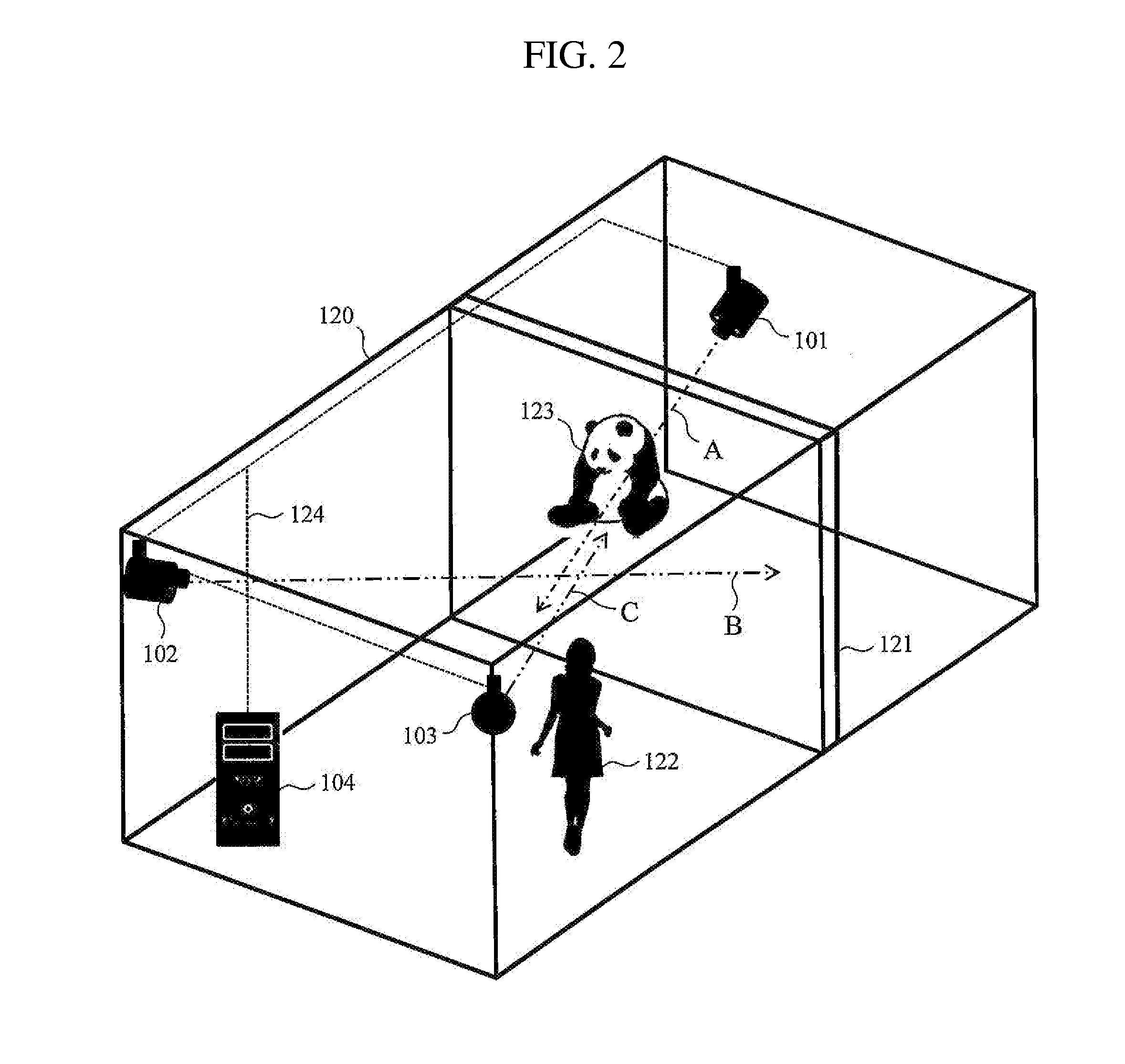
An image-capturing system including at least three cameras with different image-capturing directions, a feature point extraction unit that extracts a feature point of a subject from images captured by the camera, and an image storage unit that stores images captured by the cameras is characterized by: a feature quantity calculation / detection unit that calculates a feature quantity of the subject from the feature point extracted by the feature point extraction unit; a direction estimation unit that estimates a direction in which the subject is oriented from the feature point extracted by the feature point extraction unit; and a stored camera image determination unit that determines a camera image to be stored in the image storage unit, wherein, when a difference between the feature quantity calculated by the feature quantity calculation unit and a particular feature quantity set in advance is not more than a certain value, the stored camera image determination unit determines, as a first stored image, the image from which the feature point has been extracted by the plurality of the feature point extraction unit, and determines a second stored image by identifying a camera in accordance with the direction in which the subject is oriented as estimated by the direction estimation unit from the feature point extracted in the first stored image.
Owner:SHARP KK
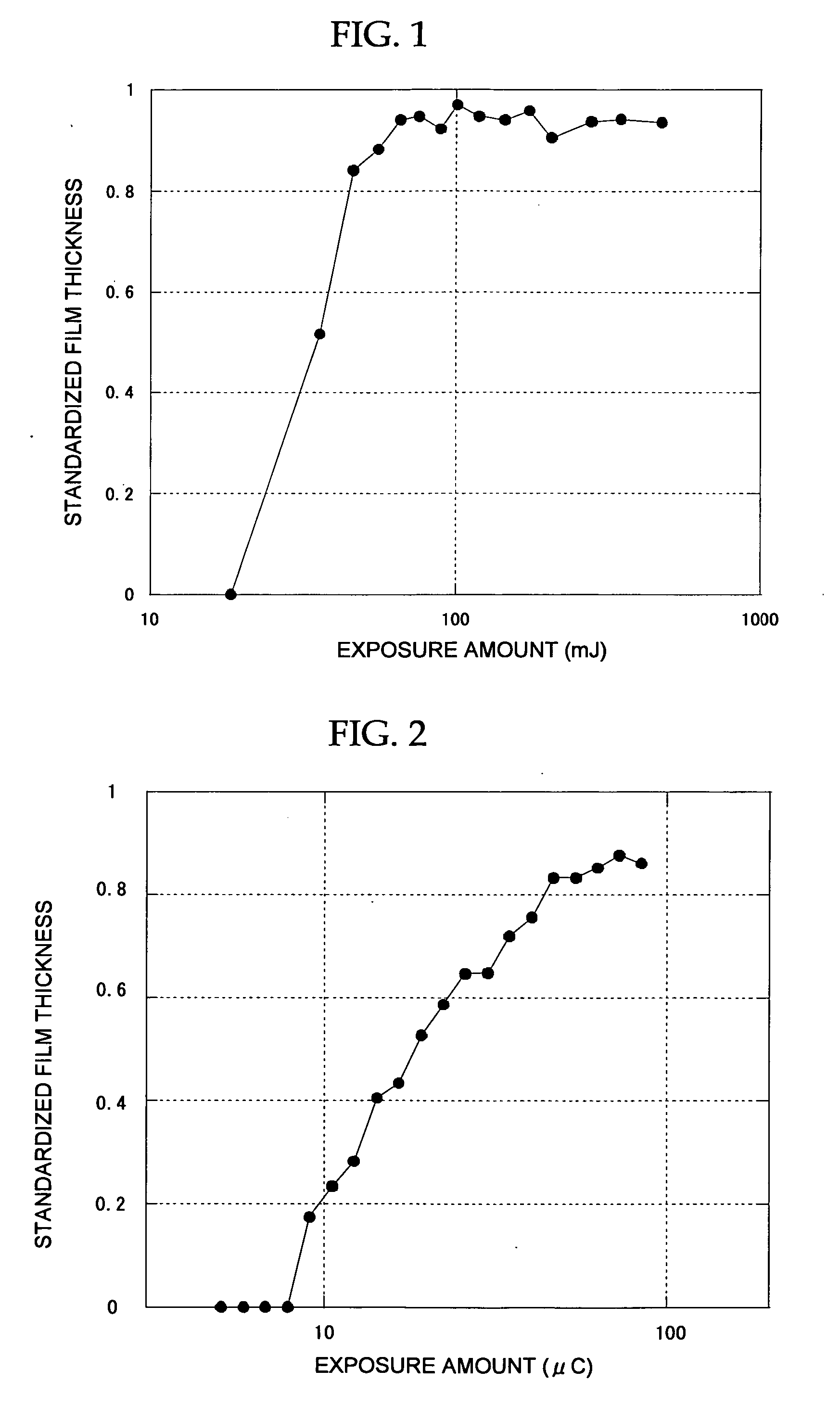
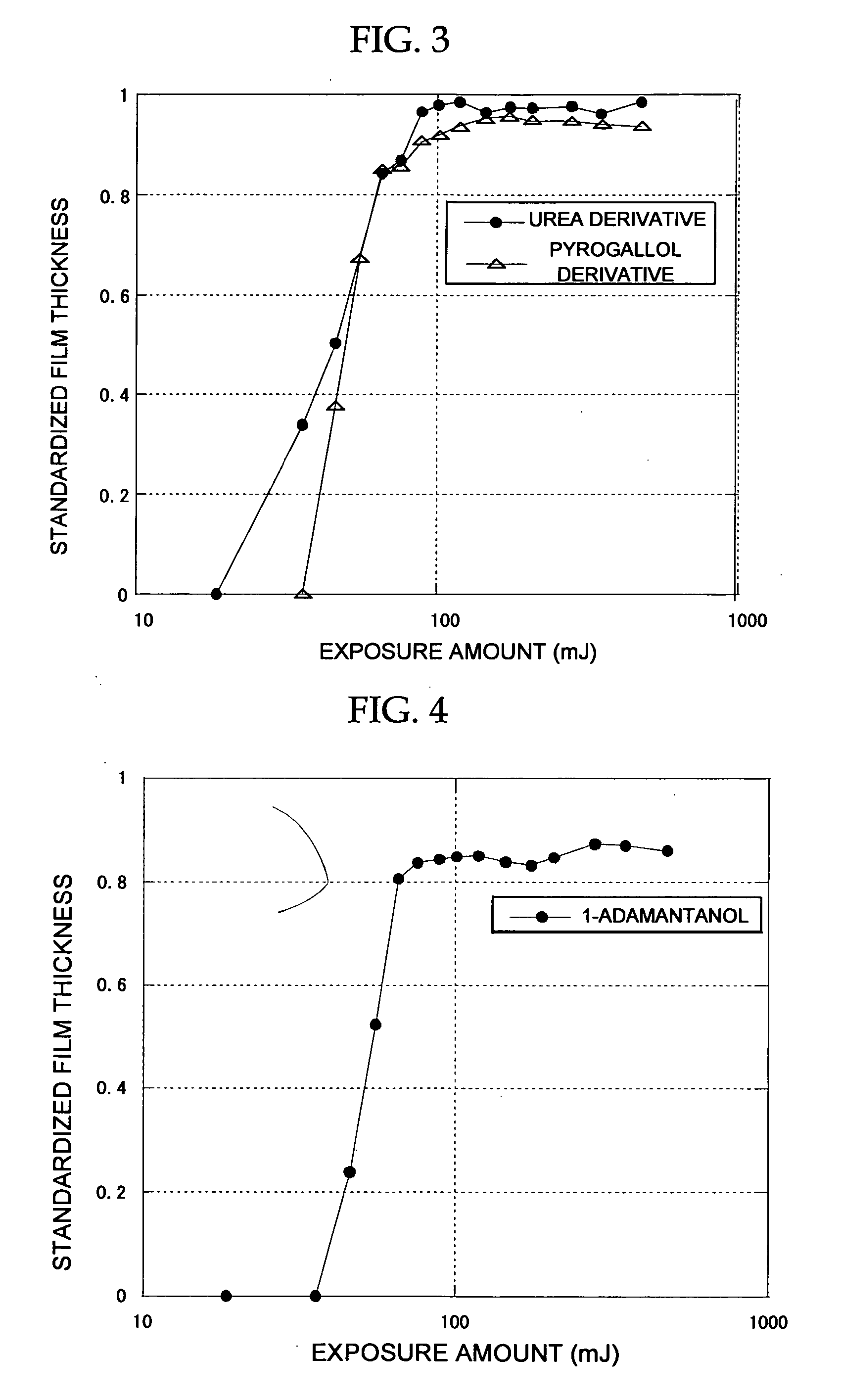
Resist composition, method of forming resist pattern, semiconductor device and method of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS20070003862A1High dimensional accuracyManufacturePhotomechanical apparatusDiazo compound compositionsResistEtching
The resist composition of the present invention contains at least one of a tannin and a derivative thereof. The method of forming a resist pattern of the present invention includes: forming a resist film on a surface of an object to be processed, by using the resist composition; and exposing and developing the resist film. The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device of the present invention includes: forming a resist film on a surface of an object to be processed, by using the resist composition; exposing and developing the resist film to form a resist pattern; and patterning the surface of the object by performing an etching through the resist pattern as a mask.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Event reconstruct through image reporting
InactiveUS20180316901A1Optimization of detailsImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsComputer visionData science
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
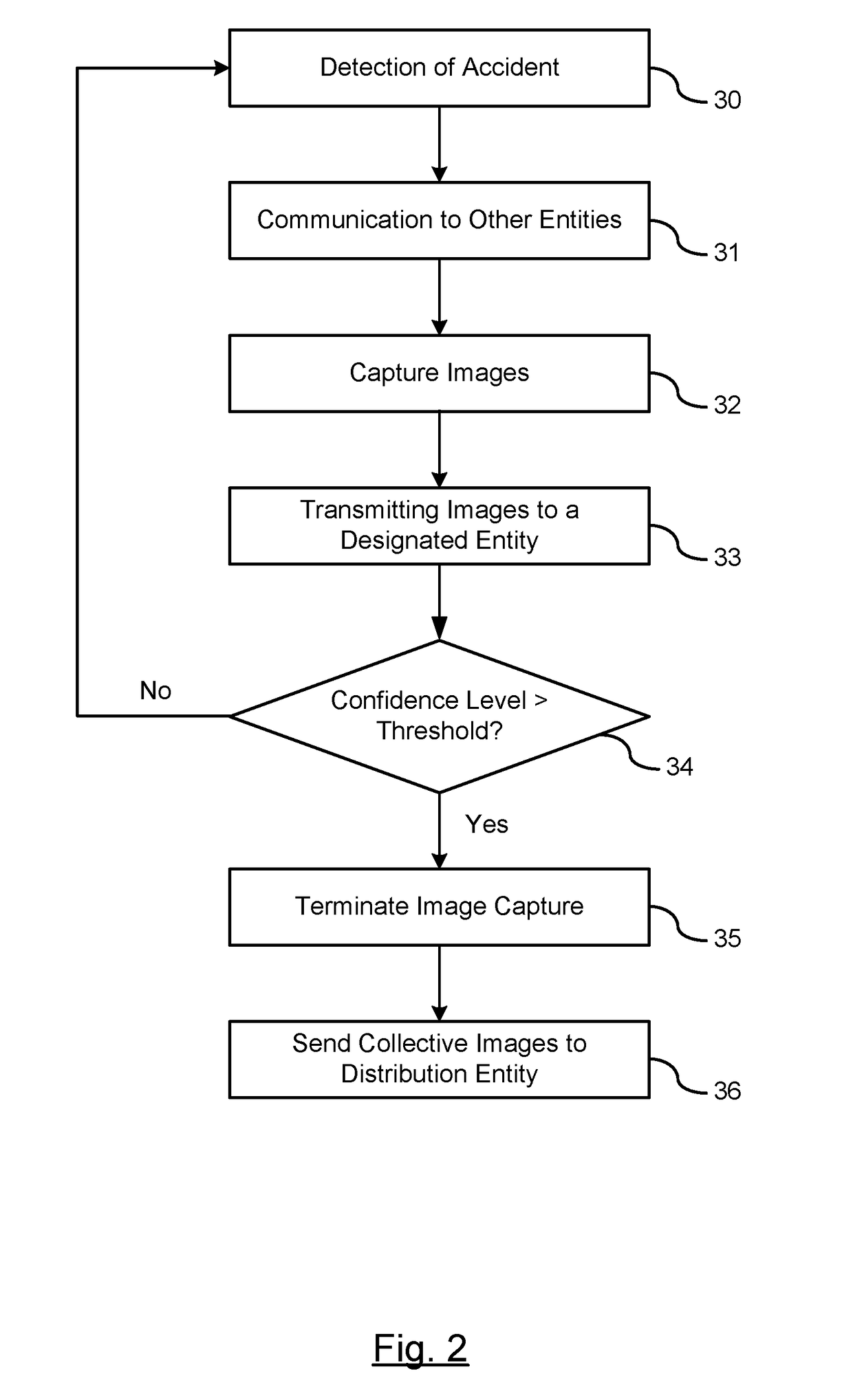
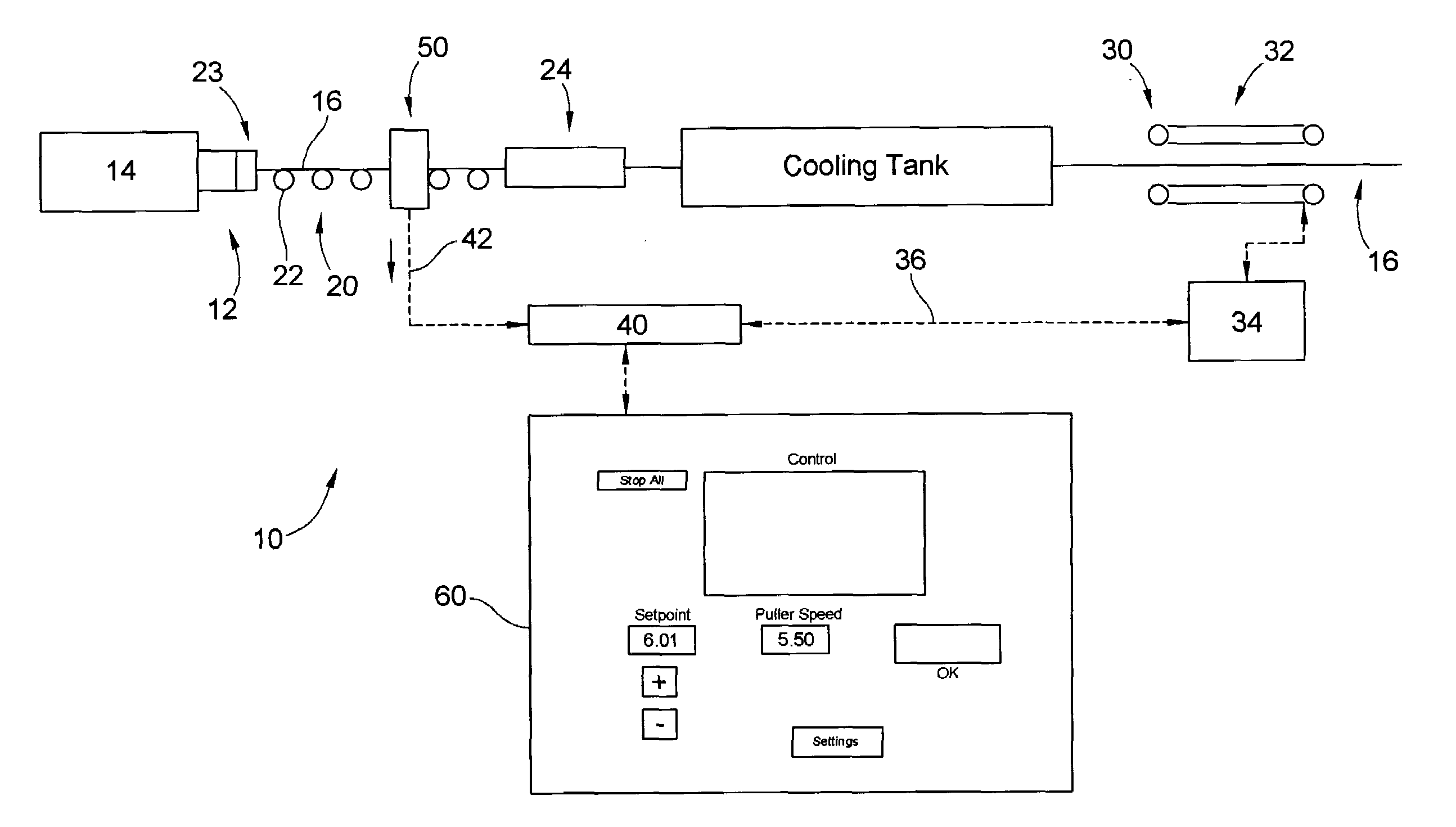
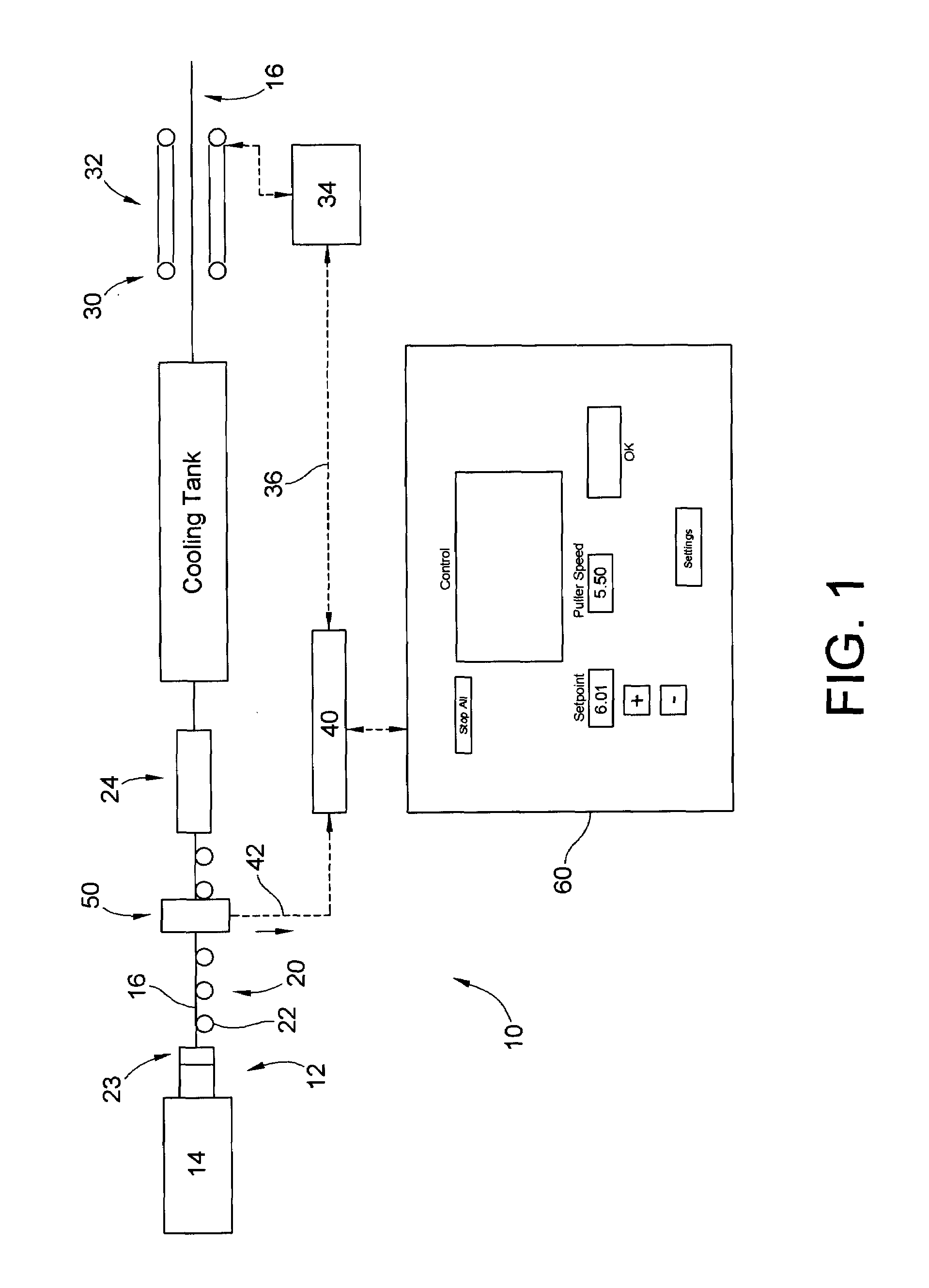
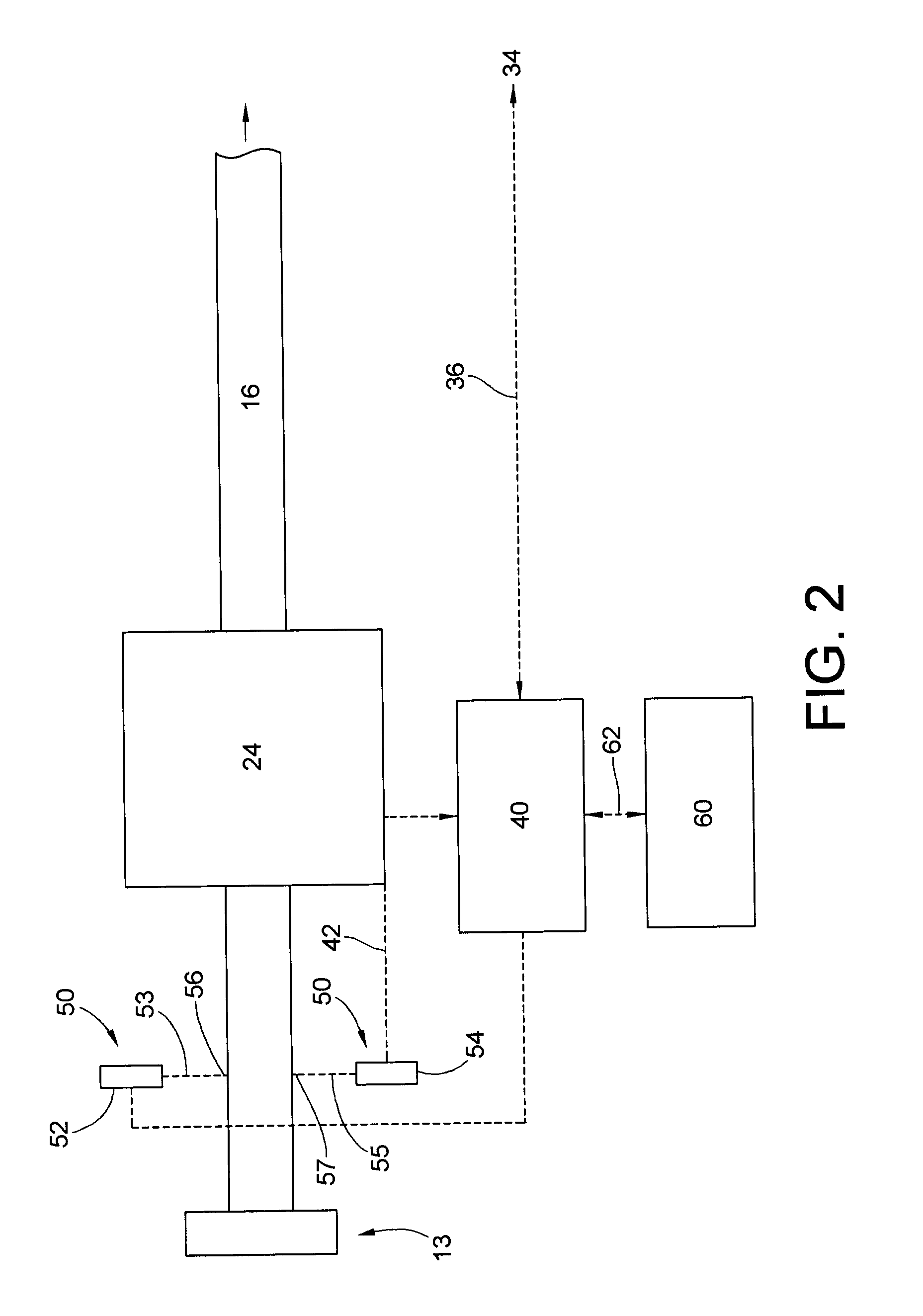
Puller speed control device for monitoring the dimensions of an extruded synthetic wood composition
ActiveUS20080088049A1Easy to controlReduced strengthWood working apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusMeasurement deviceLight beam
A system for controlling the dimensions of an extrudate exiting an extruder and for compensating for the variations in the extrusion rate of the extruder, expansion rate and rate of travel of the extrudate through sizing devices by changing the speed of an extrudate puller device, includes an extruder which extrudes the extrudate; a conveyor system comprising rollers and a series of sizing devices; a puller device for pulling the extrudate through the sizing devices; and a laser proximity measuring device to assist the system in keeping the desired shape of the extrudate. The laser proximity measuring device includes at least one pair of optical non-contact displacement transducers, a real time processor, and an interactive touch screen display. The transducers emit a laser beam which provides a laser point on the side of the extrudate.
Owner:CPG INT
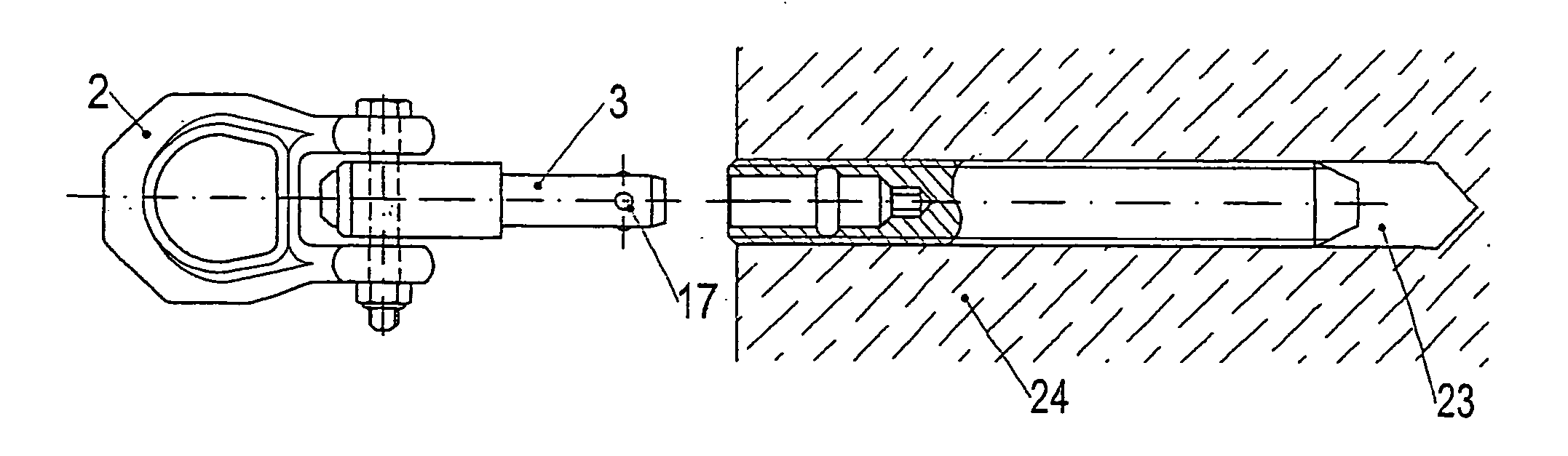
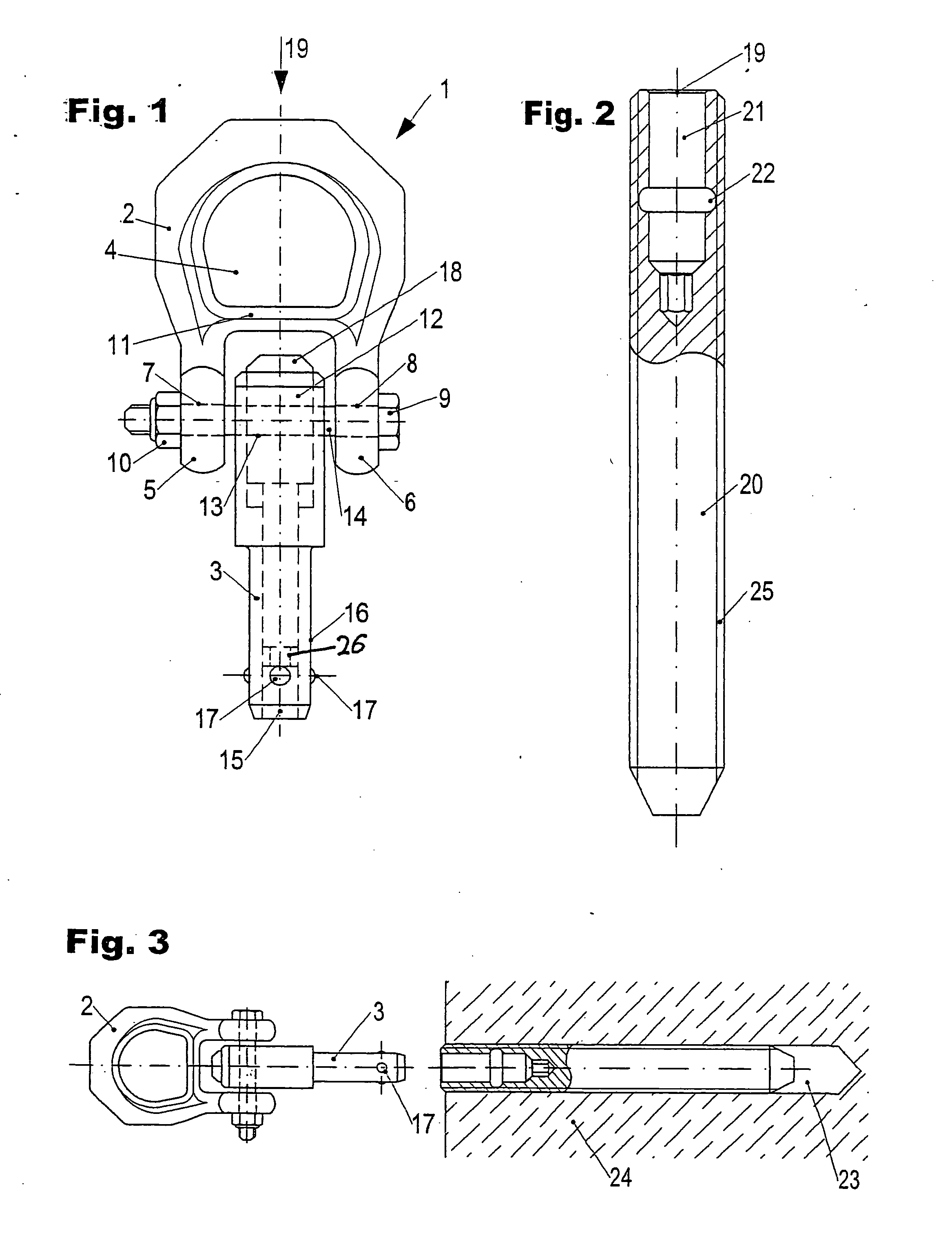
Eye bolt
A fastening element in the form of an eye bolt, which has a ring body encompassing a ring opening. The ring body is connected with an end area of a fastening bolt, which has, at a distance from said end area, in its fastening position, balls with a part of their surface protruding from the surface shell of the fastening bolt. The balls are held in their fastening position by a bolt element guided within the fastening bolt. The bolt element is axially longitudinally moveable against the force of a spring and is intended to provide a solution which improves the characteristics of use and handling of such an actuation element. This is achieved by the fact that the ring body is extended in the manner of a shackle beyond its ring opening and the end area of the fastening bolt is fixed so as to pivot between the shackle ends.
Owner:BECKERS LUDWIG
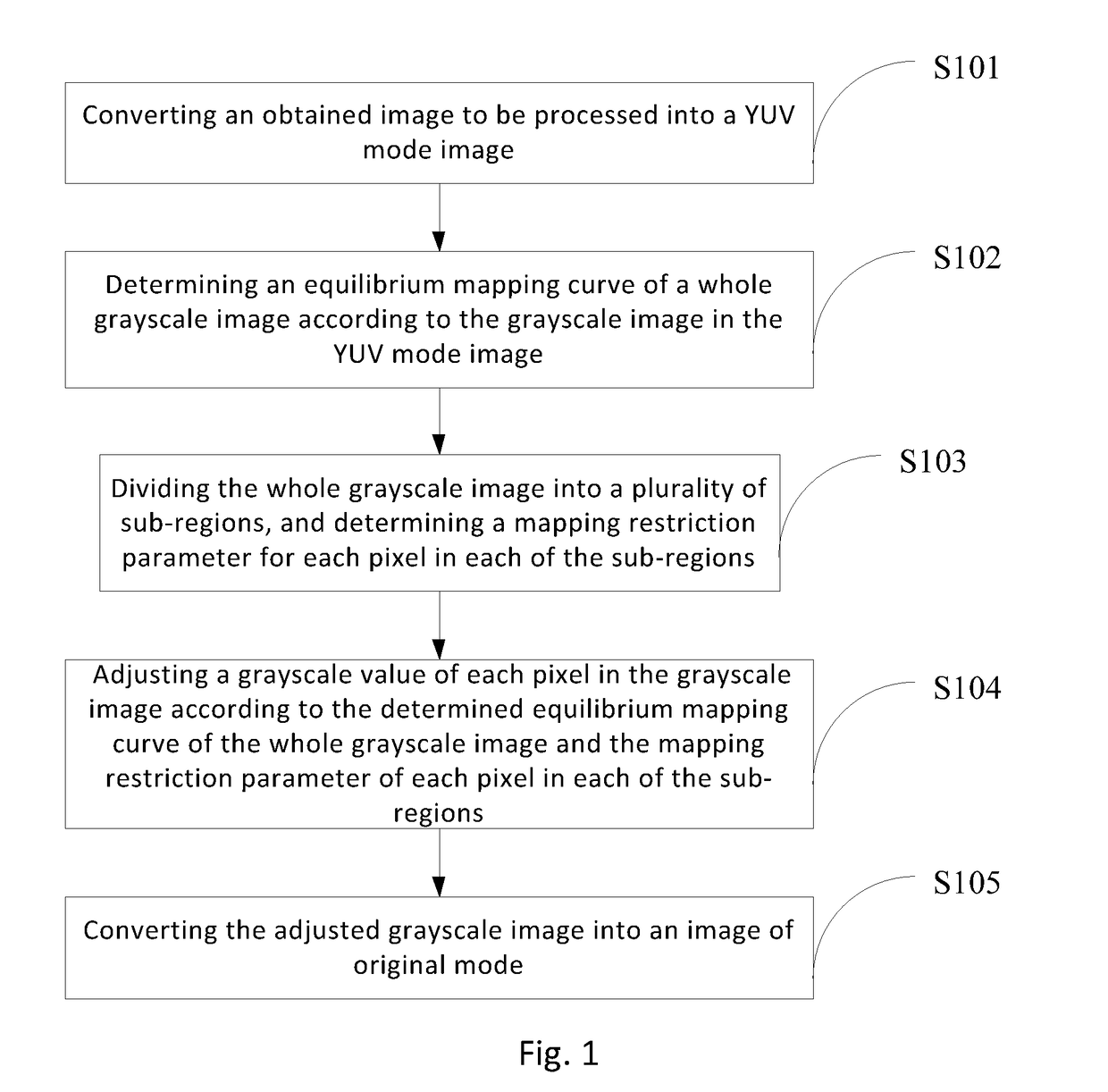
Image processing method and device
ActiveUS20190080441A1Reduce amount of calculationEnhance displayed imageImage enhancementImage analysisImage processingChrominance
An image processing method and device is configured to convert an obtained image to be processed into a grayscale chrominance YUV mode image; determine an equilibrium mapping curve of a whole grayscale image according to the grayscale image in the YUV mode image; divide the whole grayscale image into a plurality of sub-regions, and determine a mapping restriction parameter for each pixel in each of the sub-regions; adjust a grayscale value of each pixel in the grayscale image according to the determined equilibrium mapping curve of the whole grayscale image and the mapping restriction parameter of each pixel in each of the sub-regions; and convert the adjusted grayscale image into an image of original mode. an image is processed using an equilibrium mapping curve and a plurality of mapping restriction parameters present the image details well and greatly reduce the calculation amount.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Method of producing a castable high temperature aluminum alloy by controlled solidification
ActiveUS7584778B2Heating fastOptimization of detailsFoundry mouldsAerodynamics improvementRare-earth elementInvestment casting
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Preferential tone scale for electronic displays
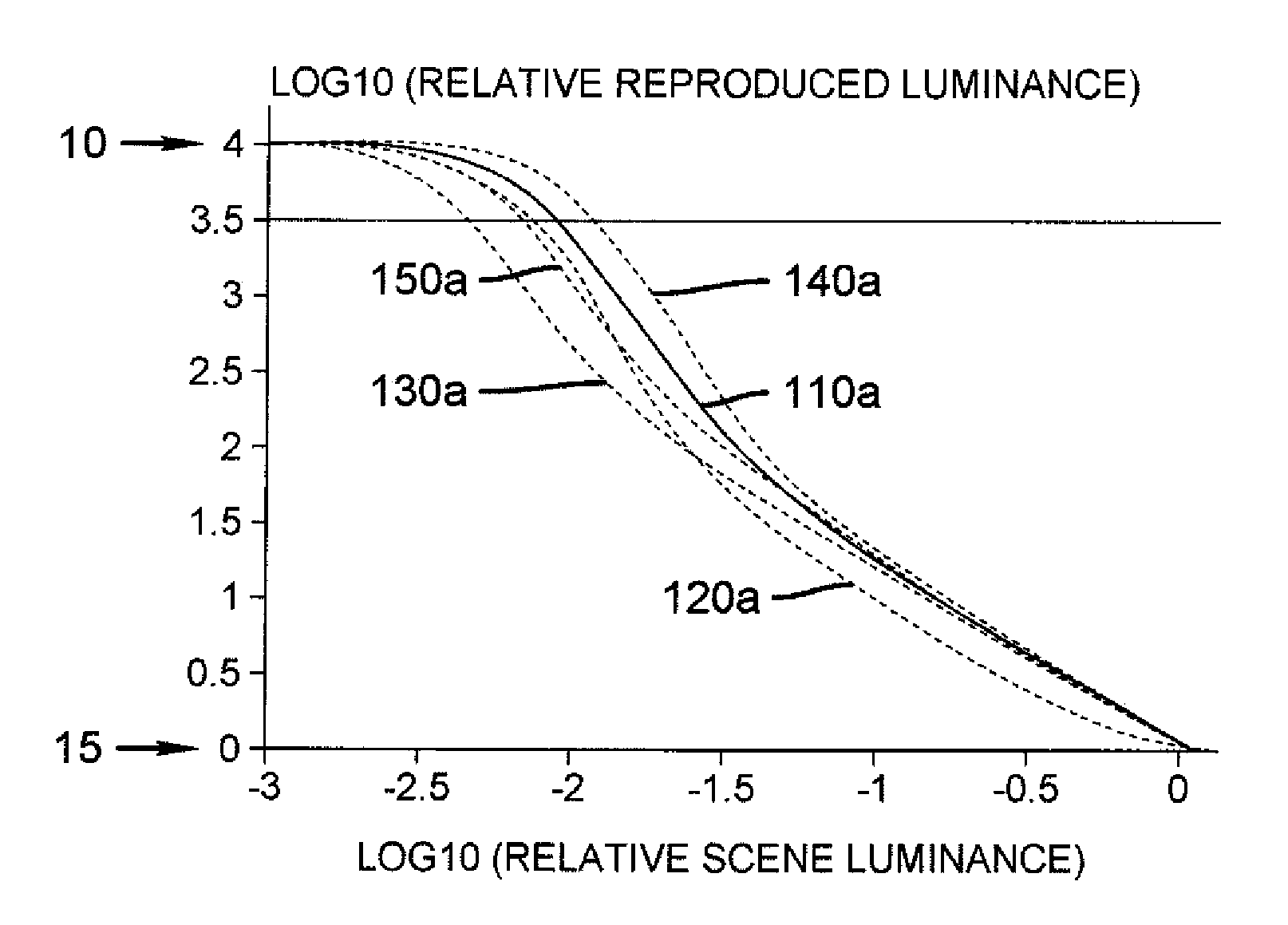
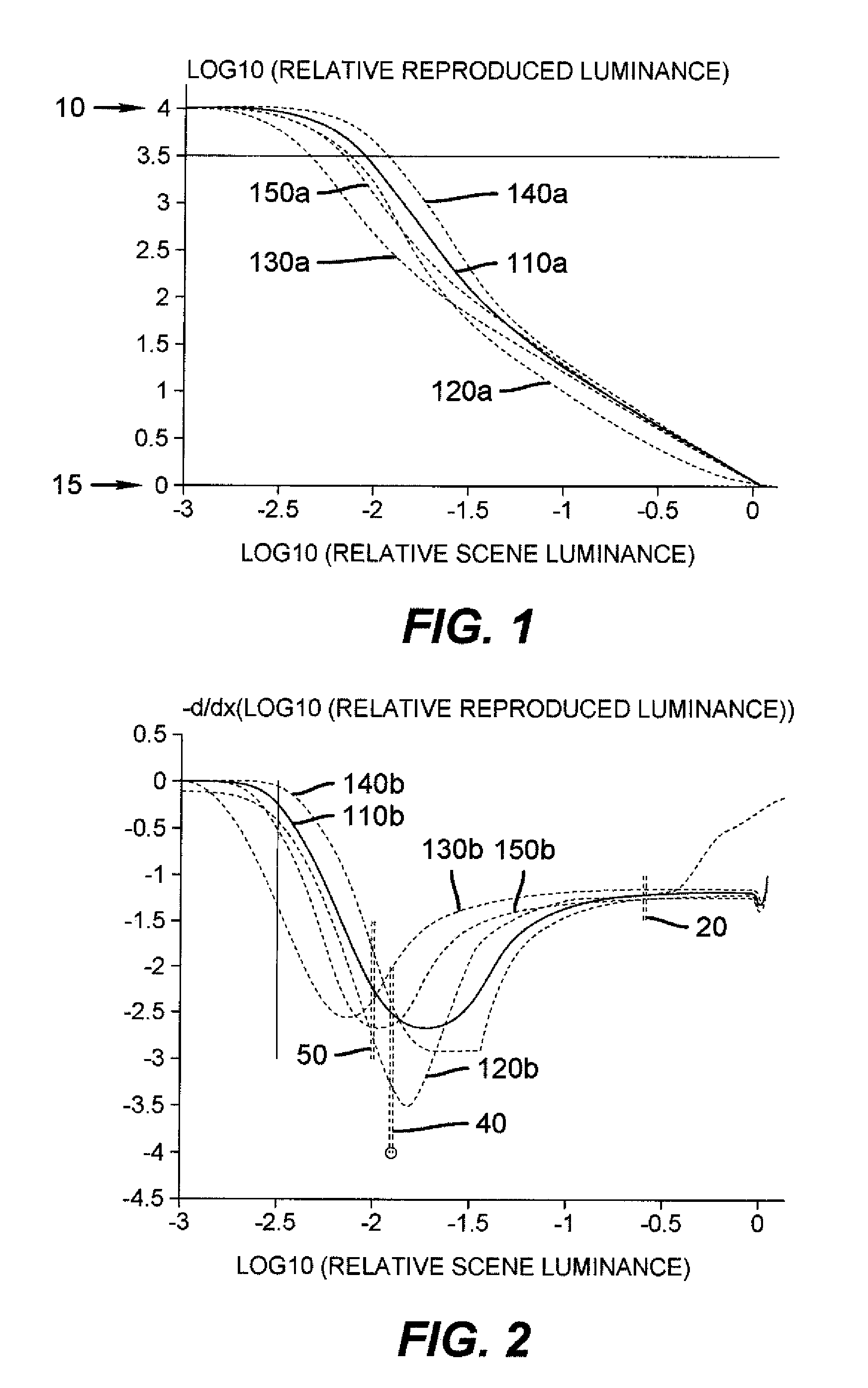
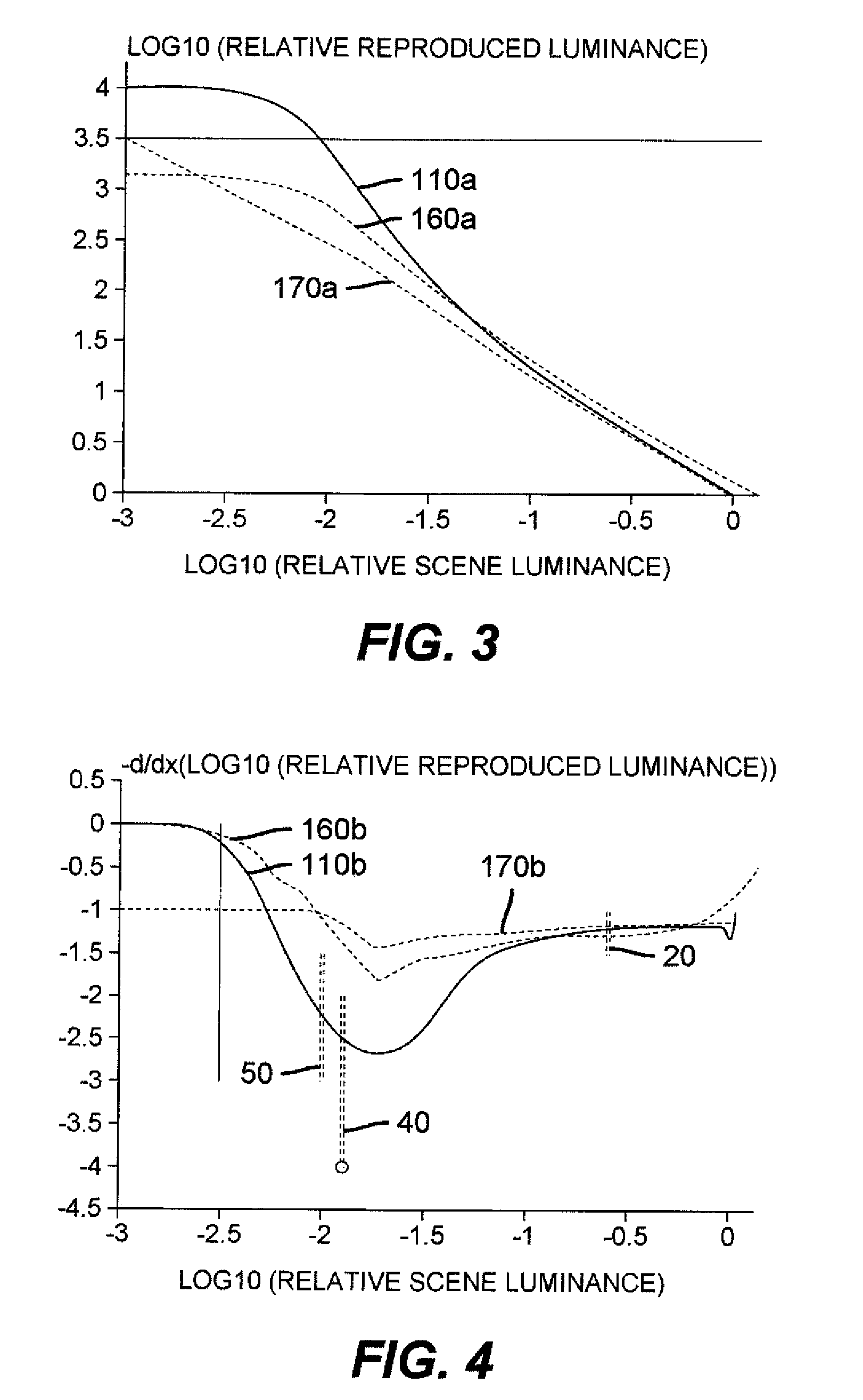
ActiveUS20090079753A1Large dynamic rangeOptimization of detailsImage enhancementImage analysisTone mappingComputer graphics (images)
A method of displaying on a display a visual reproduction of an original scene with a preferential tone mapping; said display having a selected display white point and a selected display black point separated by more than 3.5 decades of luminance; the method comprising the steps of capturing original scene parameters, performing a transformation on said captured scene parameters, and displaying a visual reproduction of the scene on the display from the transformed captured scene parameters; wherein said transformation, taken in conjunction with untransformed characteristics of the capturing and displaying steps, results in a reproduced tone mapping having: a. a dynamic range greater than 3.5 decades; b. a first derivative value of minus log reproduced luminance relative to log original scene luminance between −1.1 and −1.51 inclusive for a log scene luminance of −0.6, measured relative to a 100% diffuse reflector in the original scene; c. a first derivative value less than or equal to −1.9 and greater than −4.0 for a log scene luminance of −1.9; d. a first derivative value between −1.5 and −3.0 inclusive for a log scene luminance of −2.0; and e. a first derivative value at a log scene luminance of −2.5 greater than the first derivative value at a log scene luminance of −2.0.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
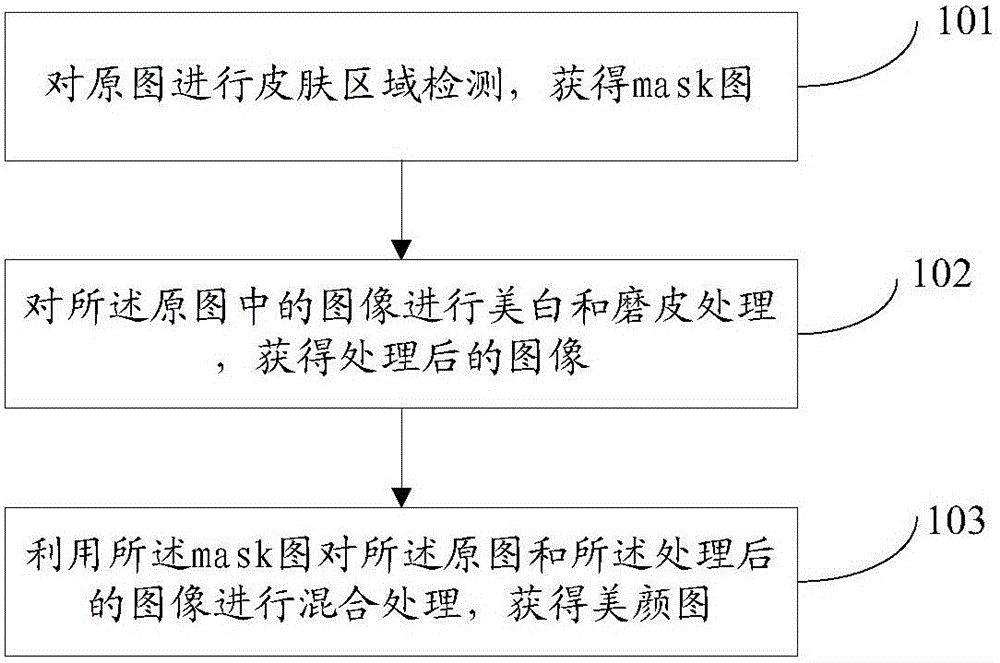
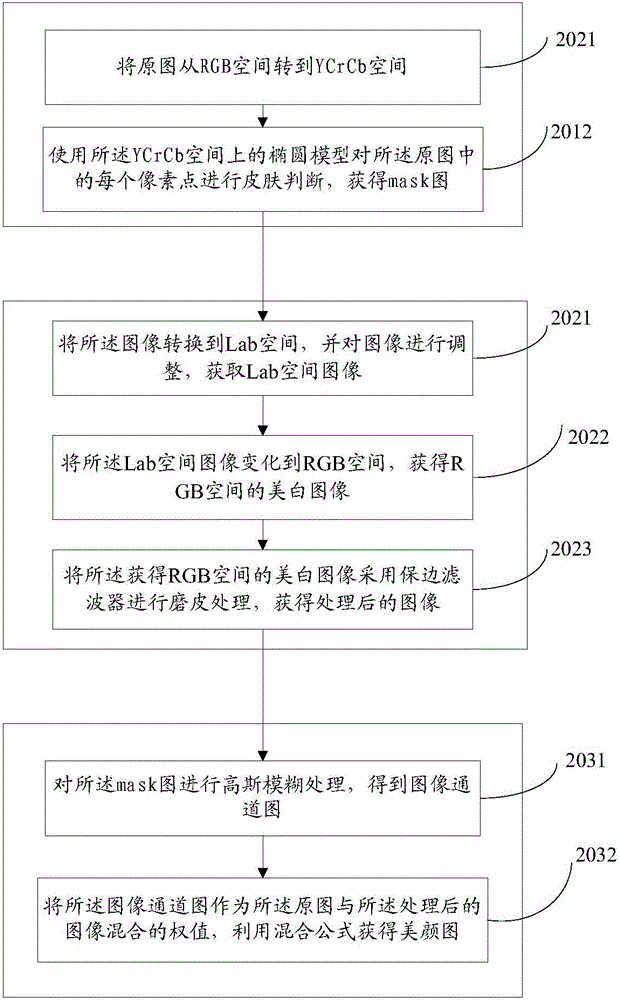
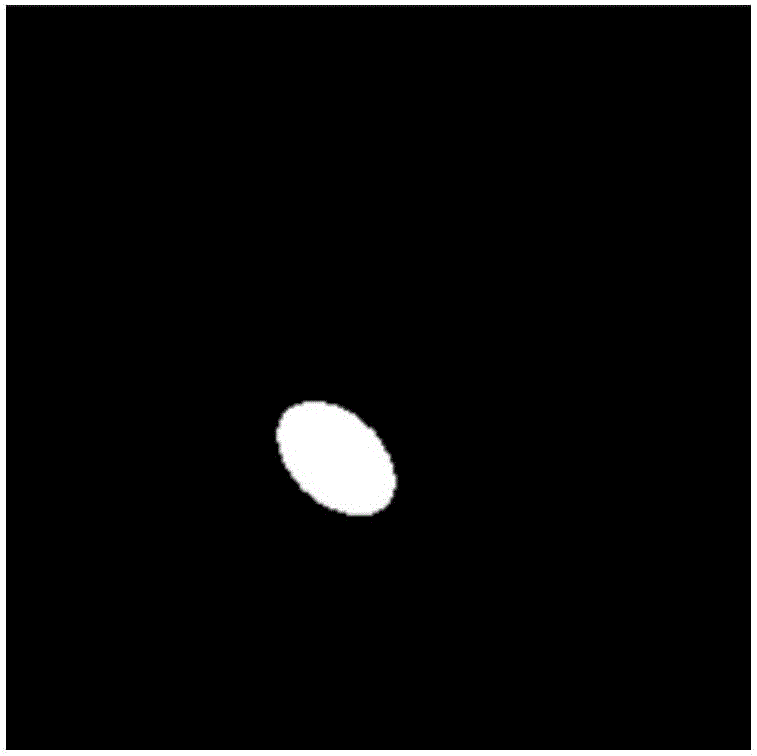
Method and device for quick photo beautifying
InactiveCN105913376AMeet real-time requirementsAchieve whitening treatmentGeometric image transformationComputer vision
The invention provides a method and a device for quick photo beautifying. The method comprises the steps of performing skin area detection on an original photo for obtaining a mask photo; performing whitening and buffering on an image in the original photo, and obtaining a processed photo; and mixing the original photo with the processed photo by means of a mask picture, thereby obtaining a beautified photo, and settling a problem of no enough attractive image caused by incapability of applying the beautified image into the video in real time and incapability of whitening the whole photo.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
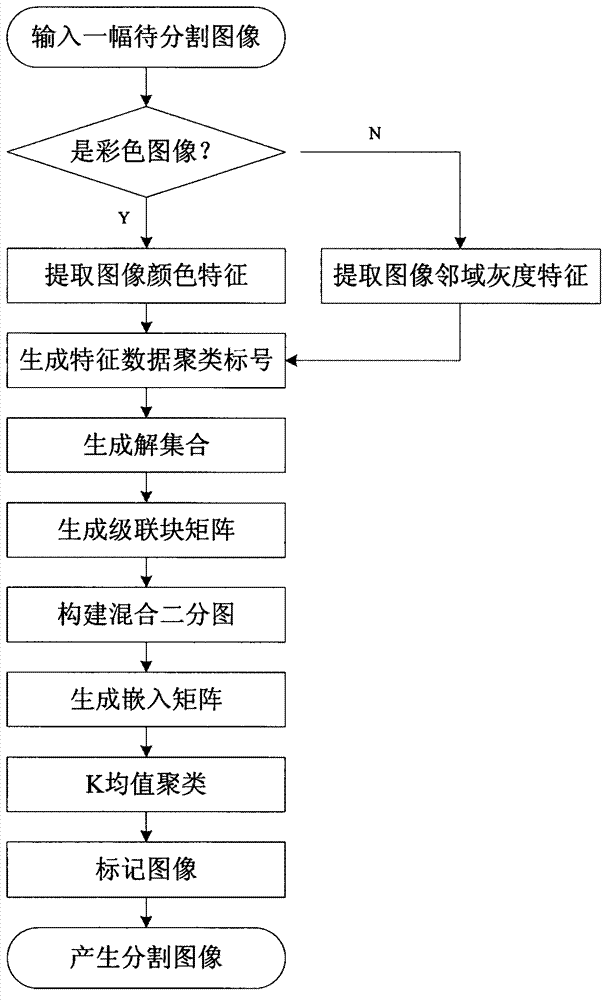
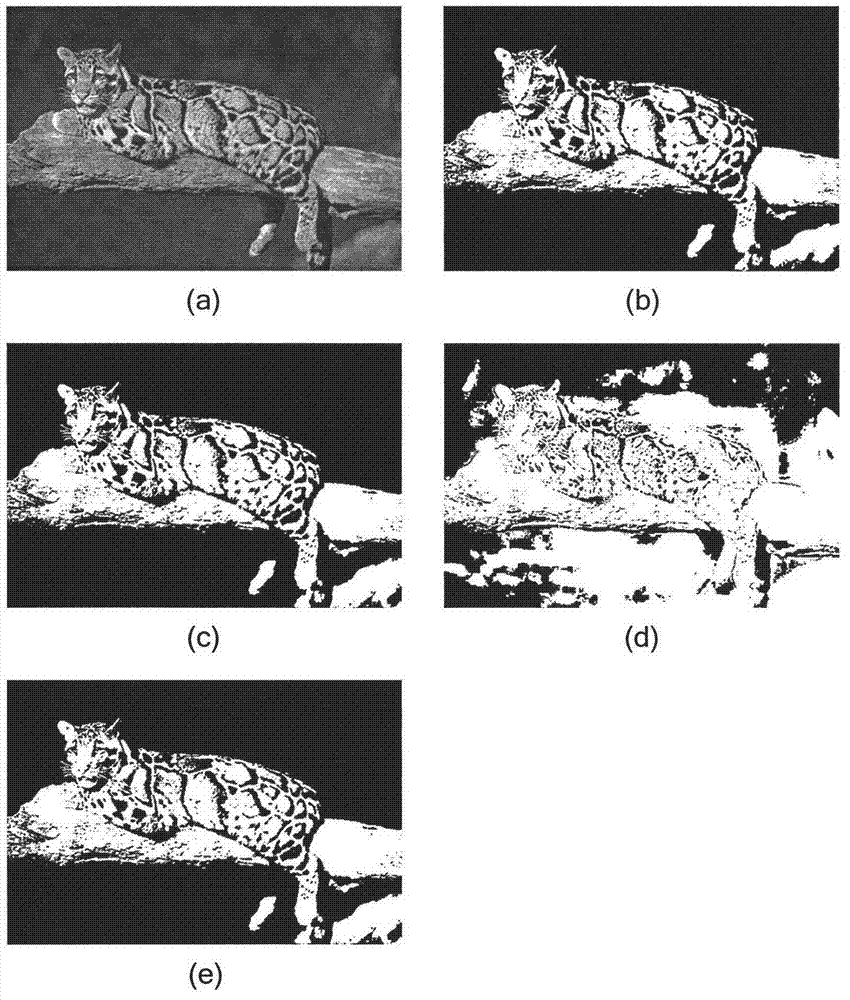
Image partitioning method based on mixed bipartite graph clustering integration
InactiveCN102737381AOvercome the disadvantage of large influence of sub-test sample setOptimal Ensemble Segmentation ResultsImage analysisColor imagePattern recognition
The invention discloses an image partitioning method based on mixed bipartite graph clustering integration, and mainly solves the problems that type marks are required to be registered during integrated, and information utilization is insufficient in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) inputting an image to be partitioned; (2) judging whether the image is a color image; (3) extracting image characteristics; (4) generating a characteristic data clustering grade; (5) generating a solution set; (6) generating a cascade block matrix; (7) constructing a mixed bipartite graph; (8) generating an embedding matrix; (9) clustering K mean values; (10) marking the image; and (11) partitioning the image. By the method, data and type information in a primary partitioning result of the image are effectively used, so that more details can be found; during integration, the type marks are not required to be registered, so that calculation resources are saved; all the image pixel characteristic data are integrated; and the problem that a sub test sample set has high influence on the partitioning result is solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com