Surgical device with tack-free gel and method of manufacture
a surgical device and gel technology, applied in the field of surface treatment, can solve the problems of difficult manufacture, aggravating use, and severe limitations of use, and achieve the effects of avoiding significant drag forces, significant tear strength, and high complian
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
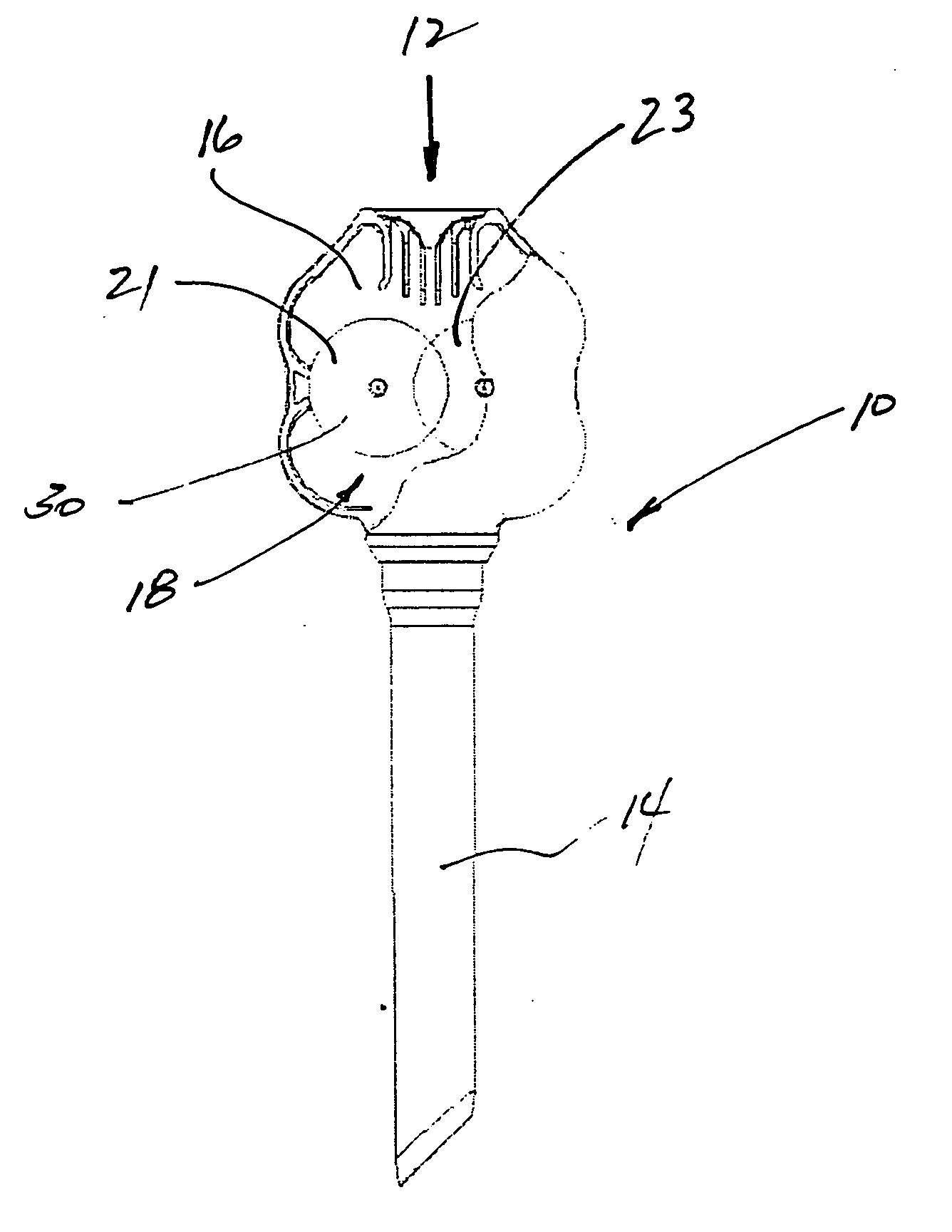
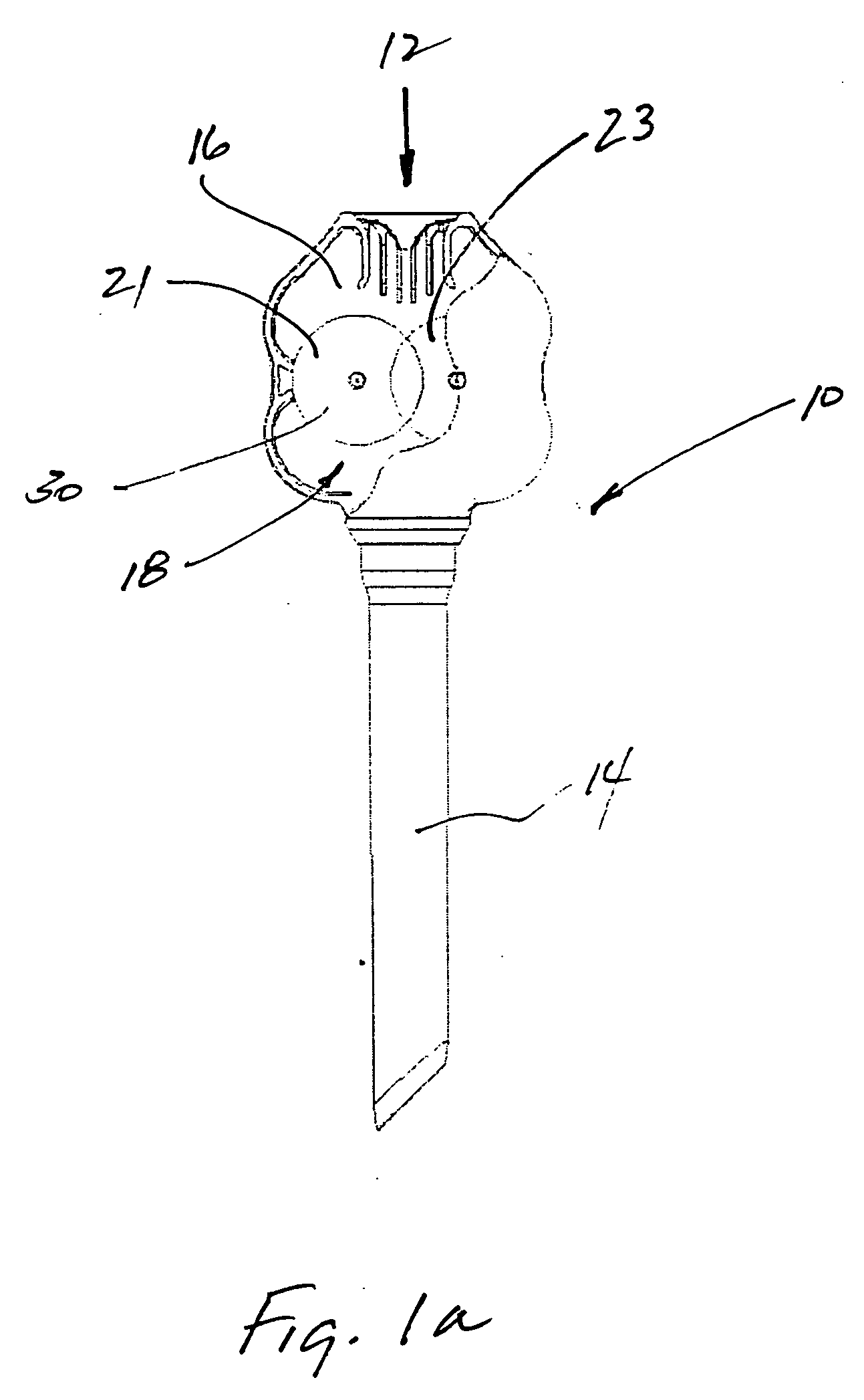
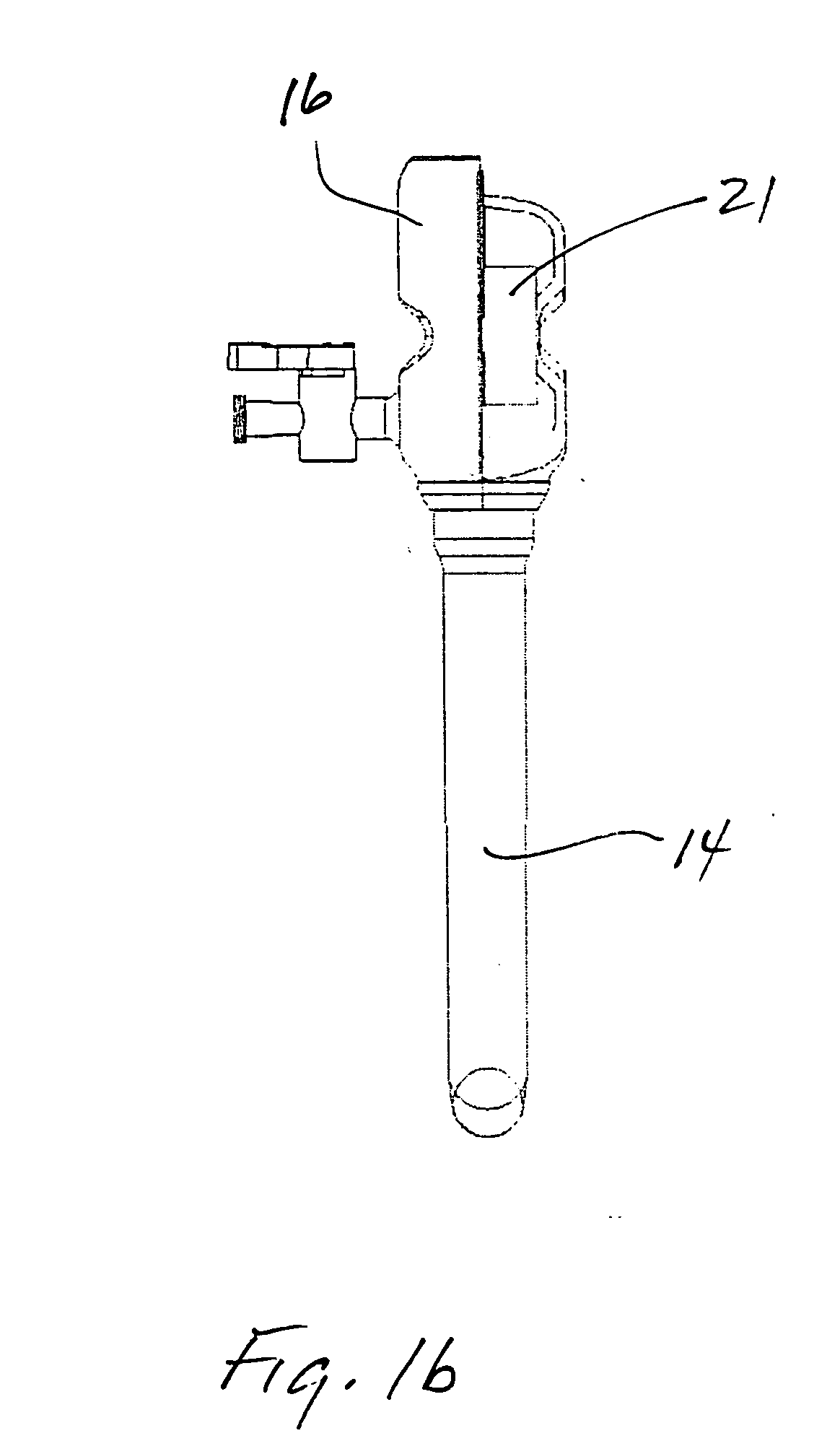
[0038] A trocar is illustrated in FIG. 1 and designated by the reference numeral 10. The trocar 10 is an access device commonly used in surgeries to provide a working channel 12 across a body wall and into a body cavity. The working channel 12 in this case is defined by a cannula 14 and a seal housing 16. Within the seal housing, a seal apparatus 18 is formed by a pair of opposing rollers 21 and 23. These rollers 21 and 23 are typically formed of a gel material 30 that provides the seal apparatus 18 with a high degree of compliance, significant tear strength and exceptional elongation. In this case, the gel rollers 21 and 23 are merely representative of any gel structure adapted for use in a medical device, such as the trocar 10.
[0039] The gel materials contemplated for the rollers 21 and 23 typically have a high melting temperature and exhibit a tacky surface as previously discussed. These two properties, normally considered disadvantages, become advantages in a method of manufact...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com