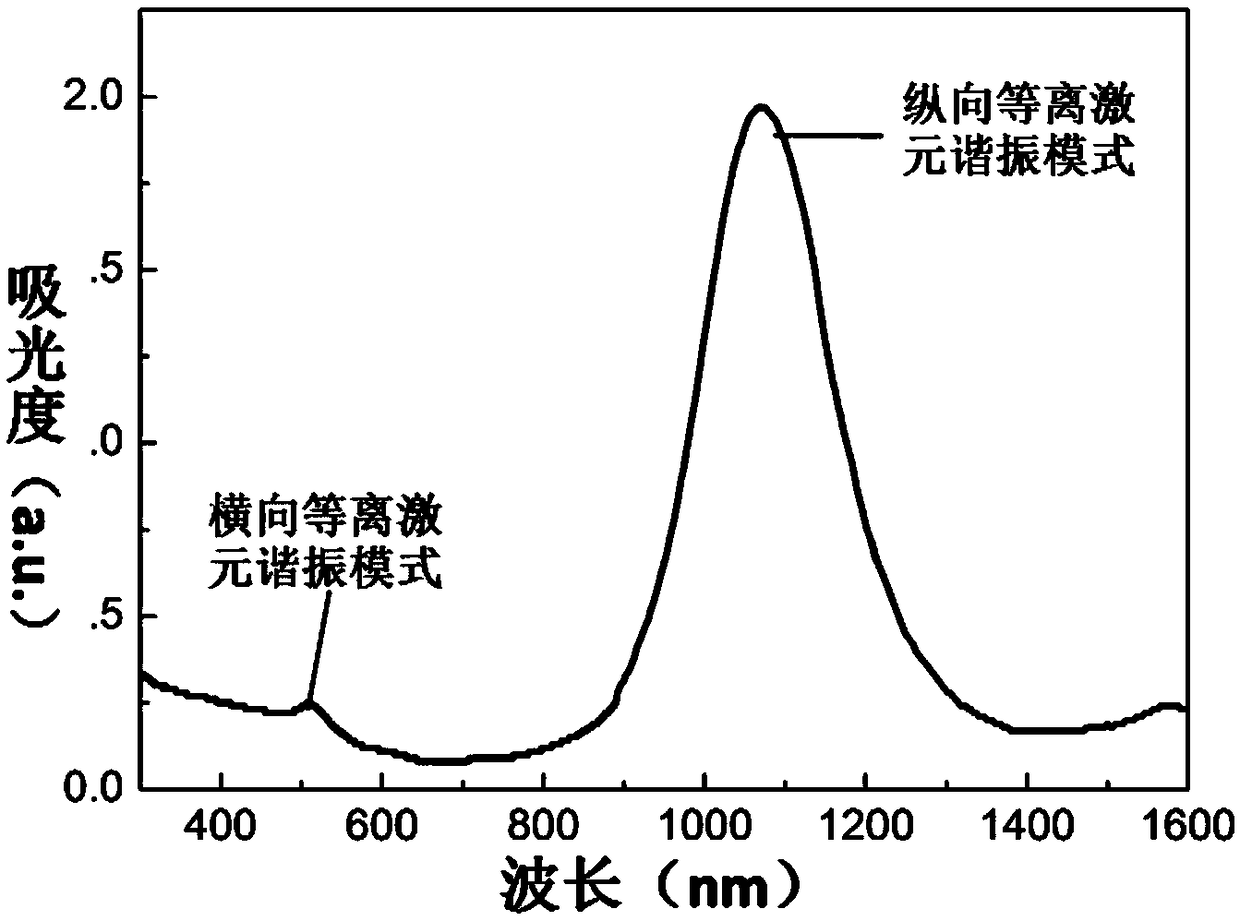
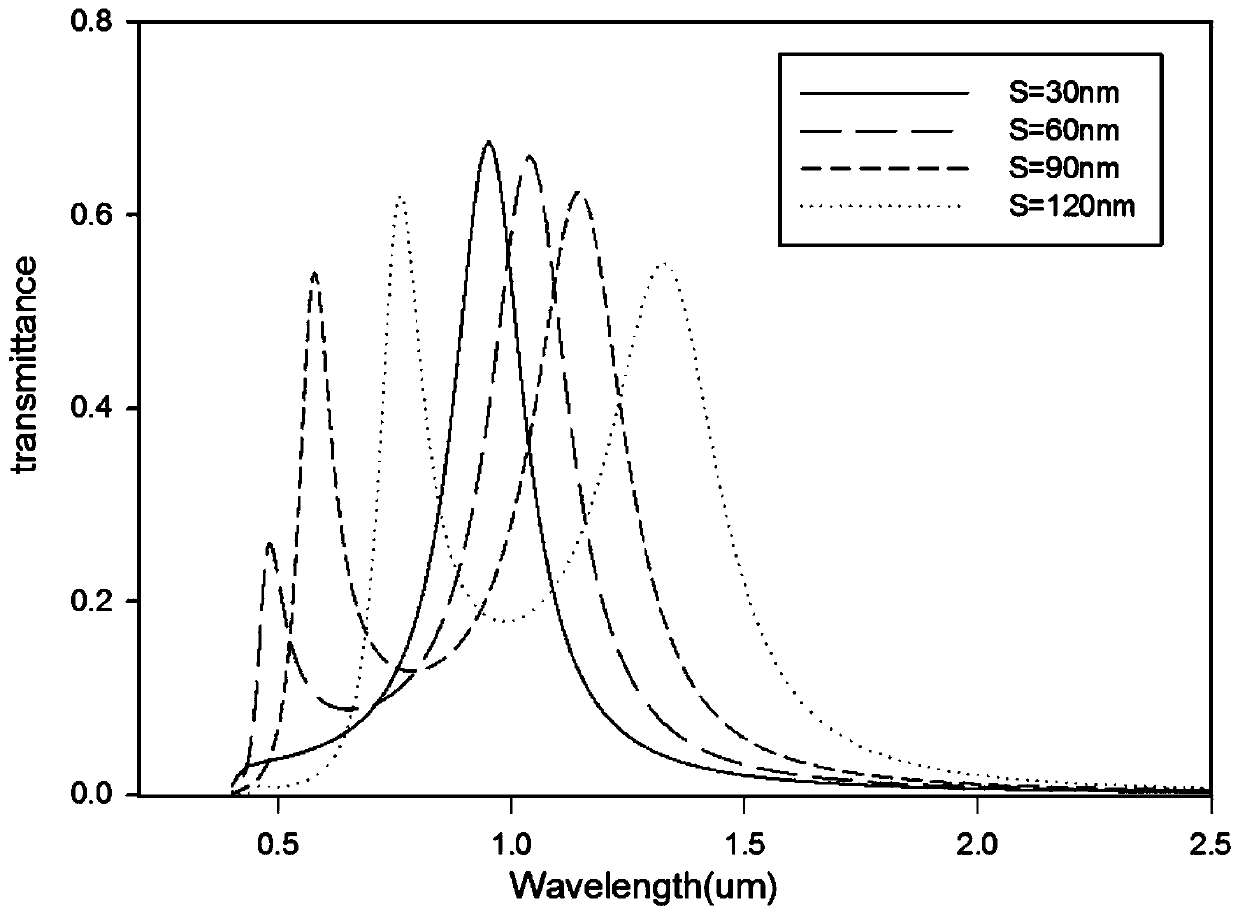
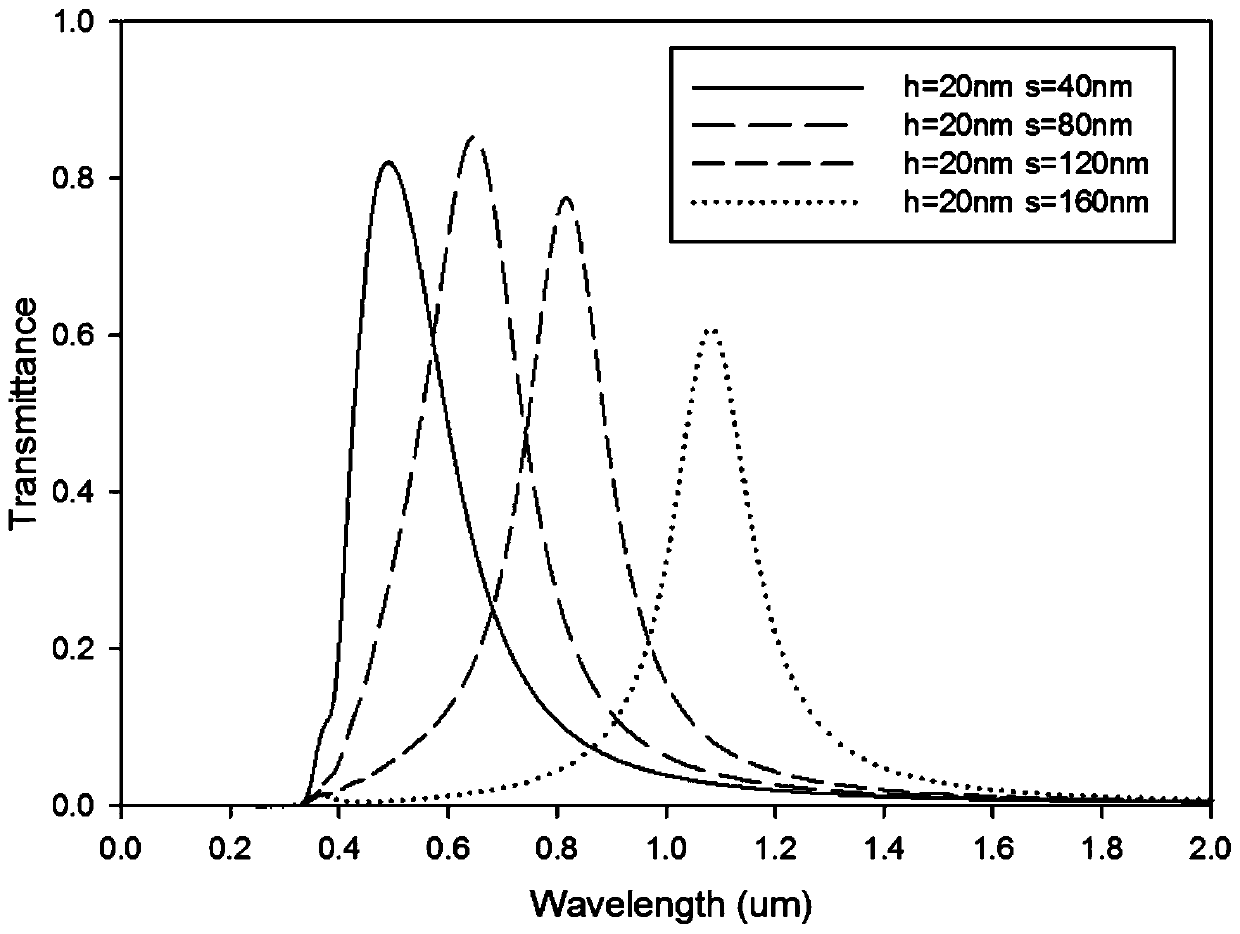
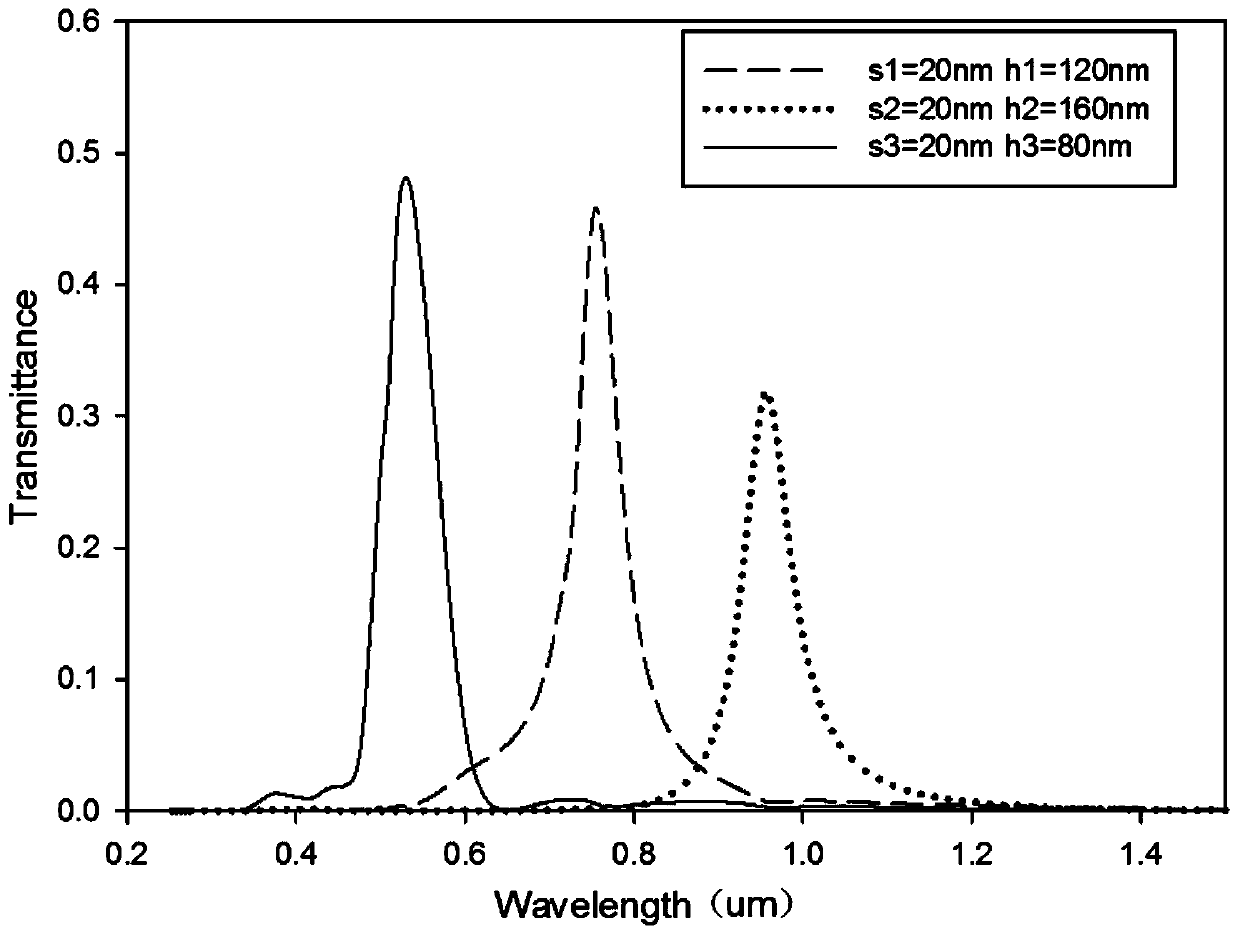
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Plasmon excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
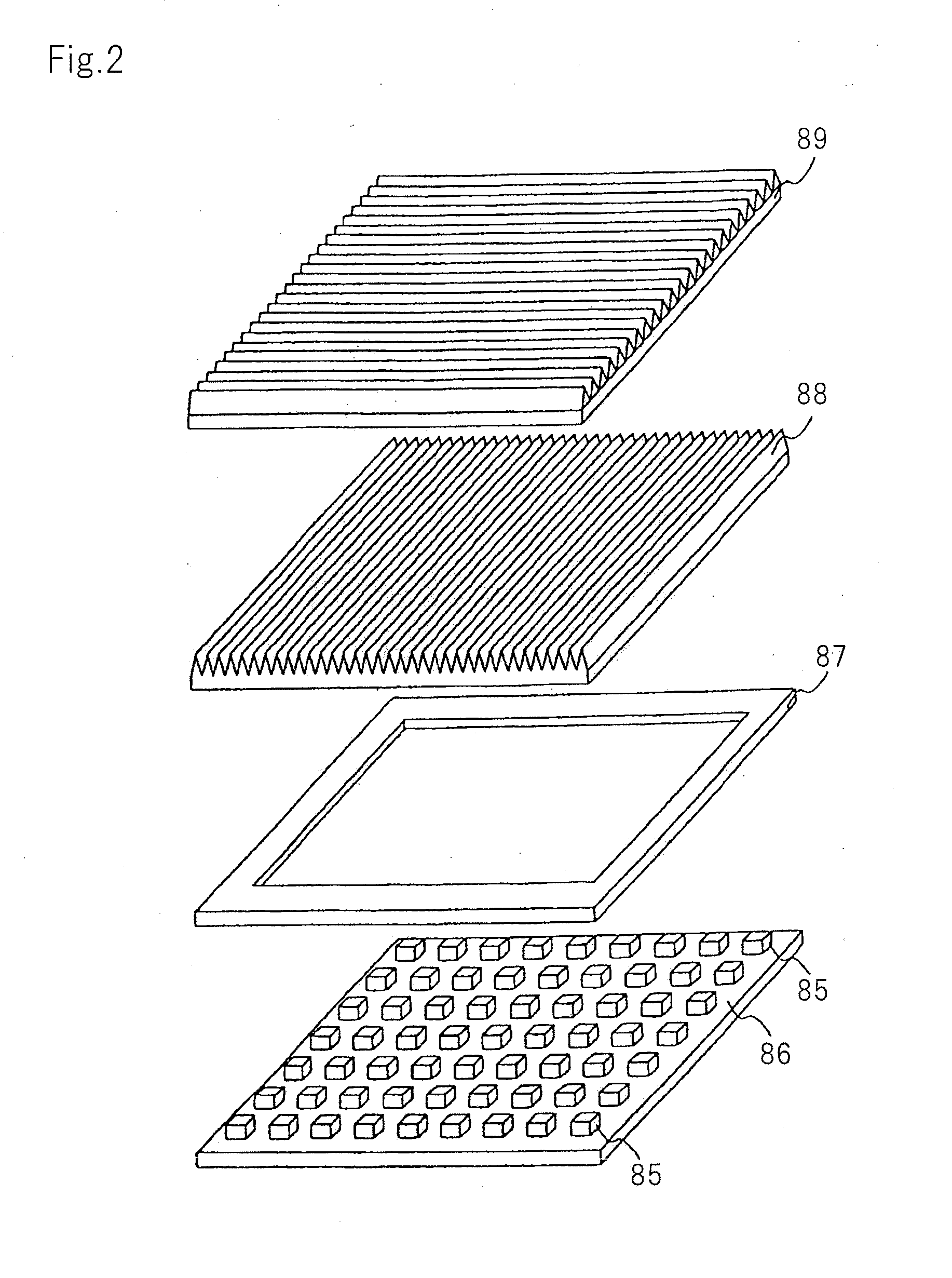
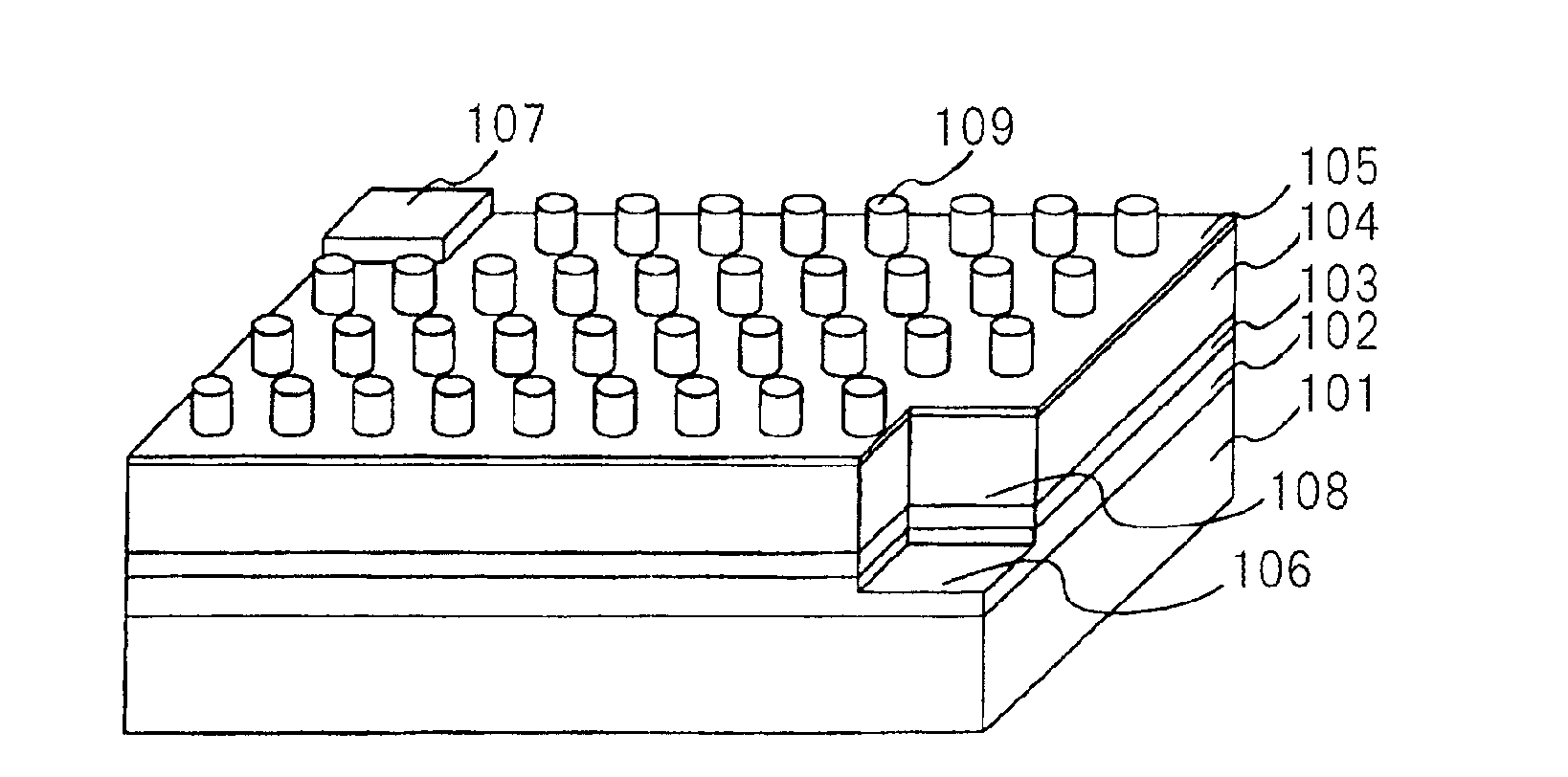
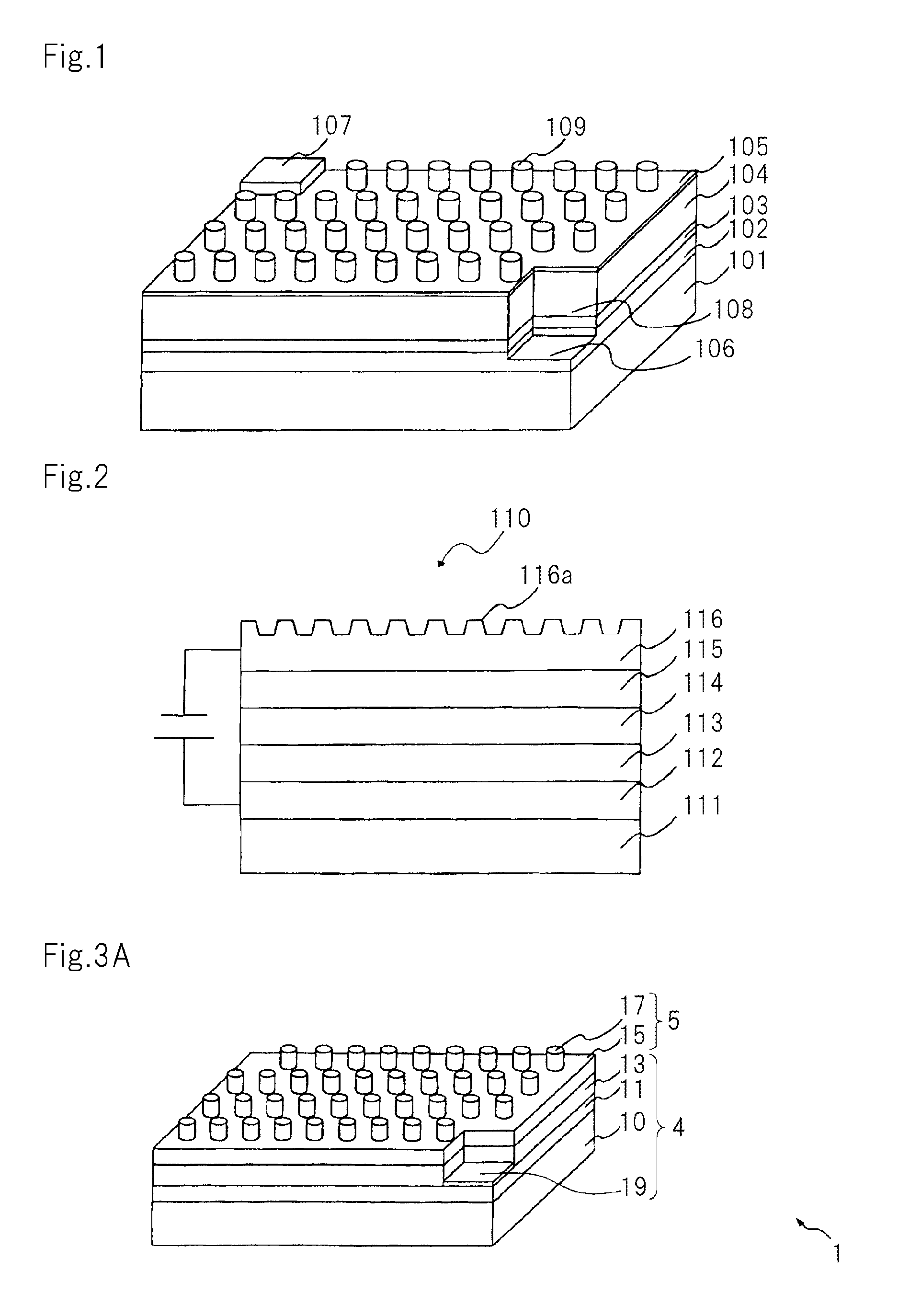
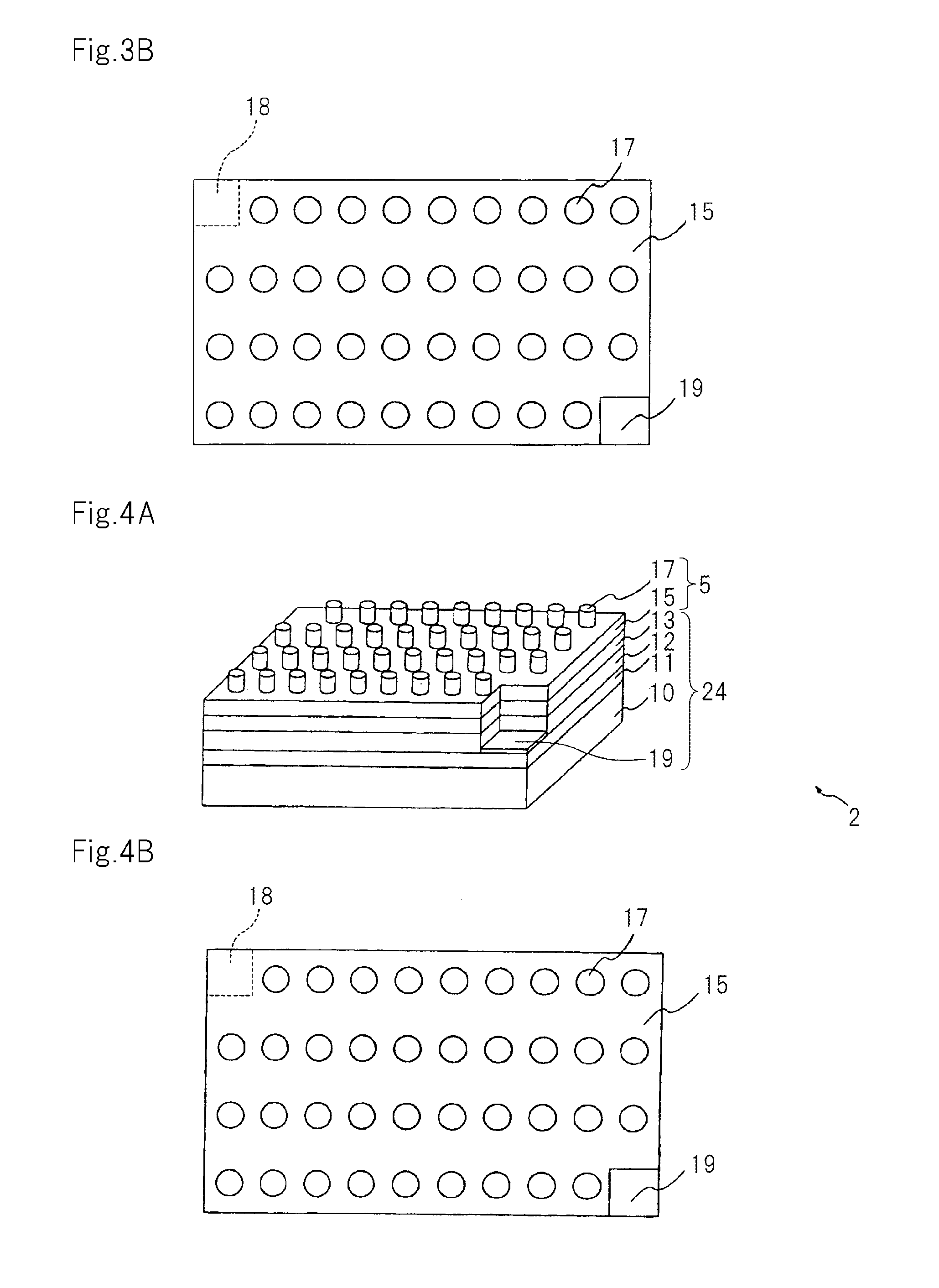
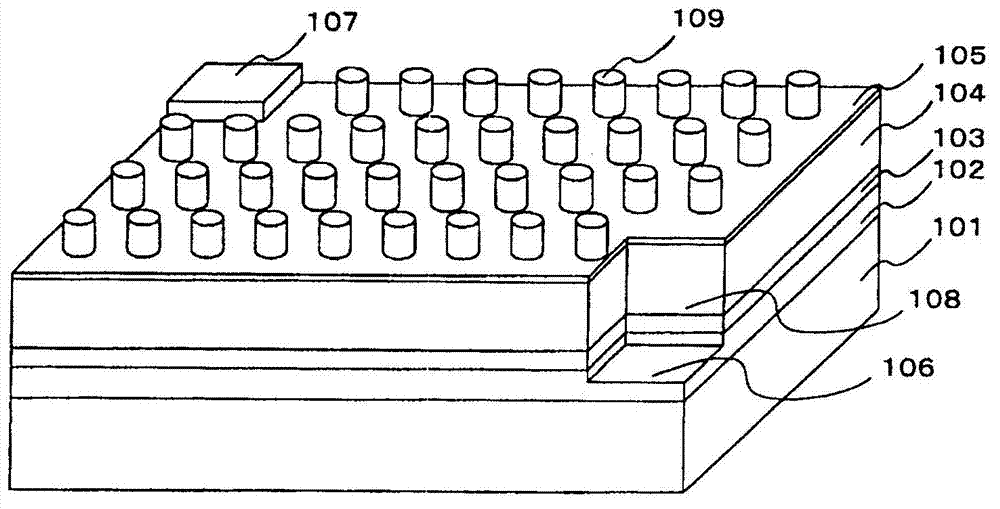
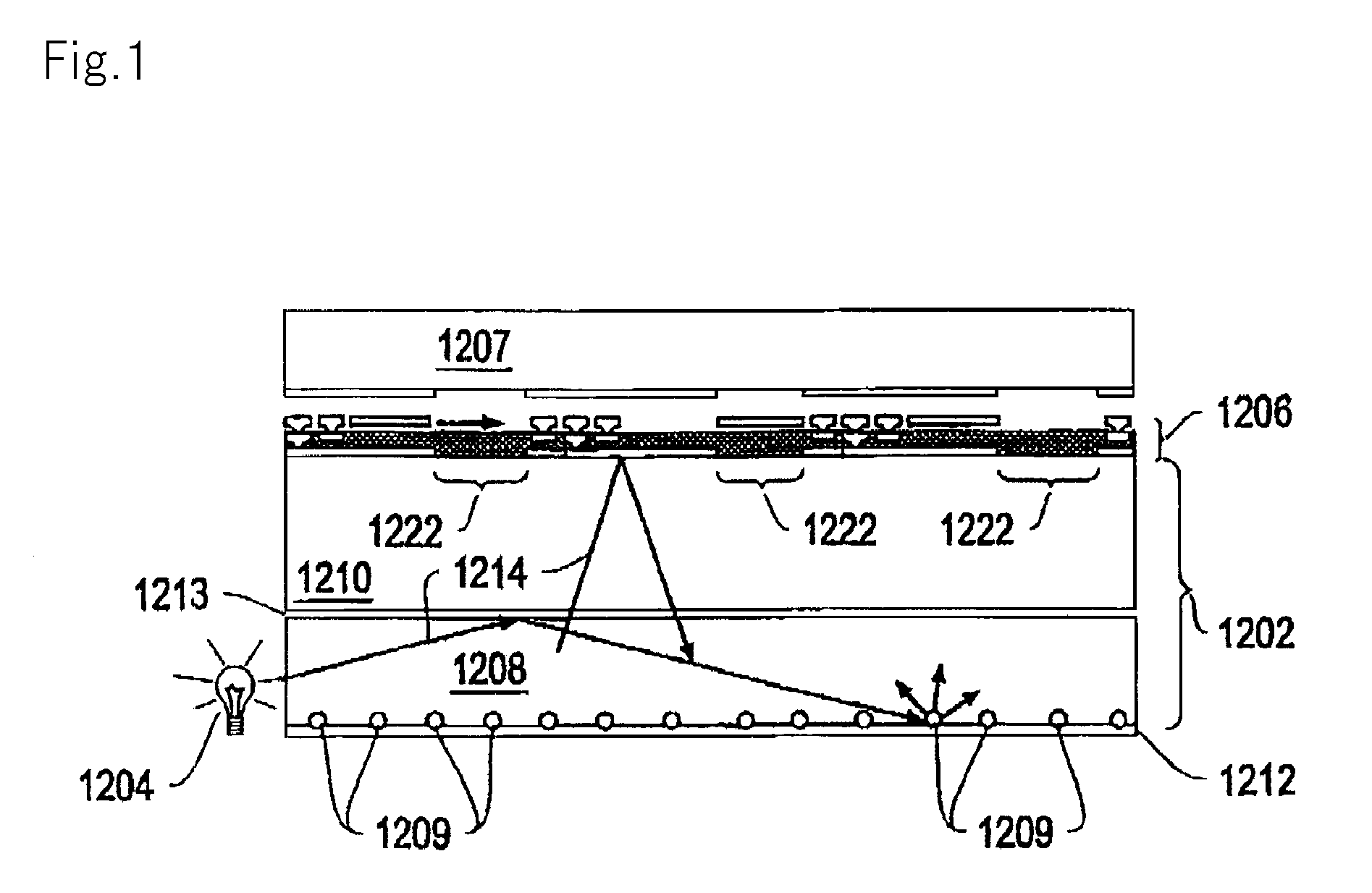
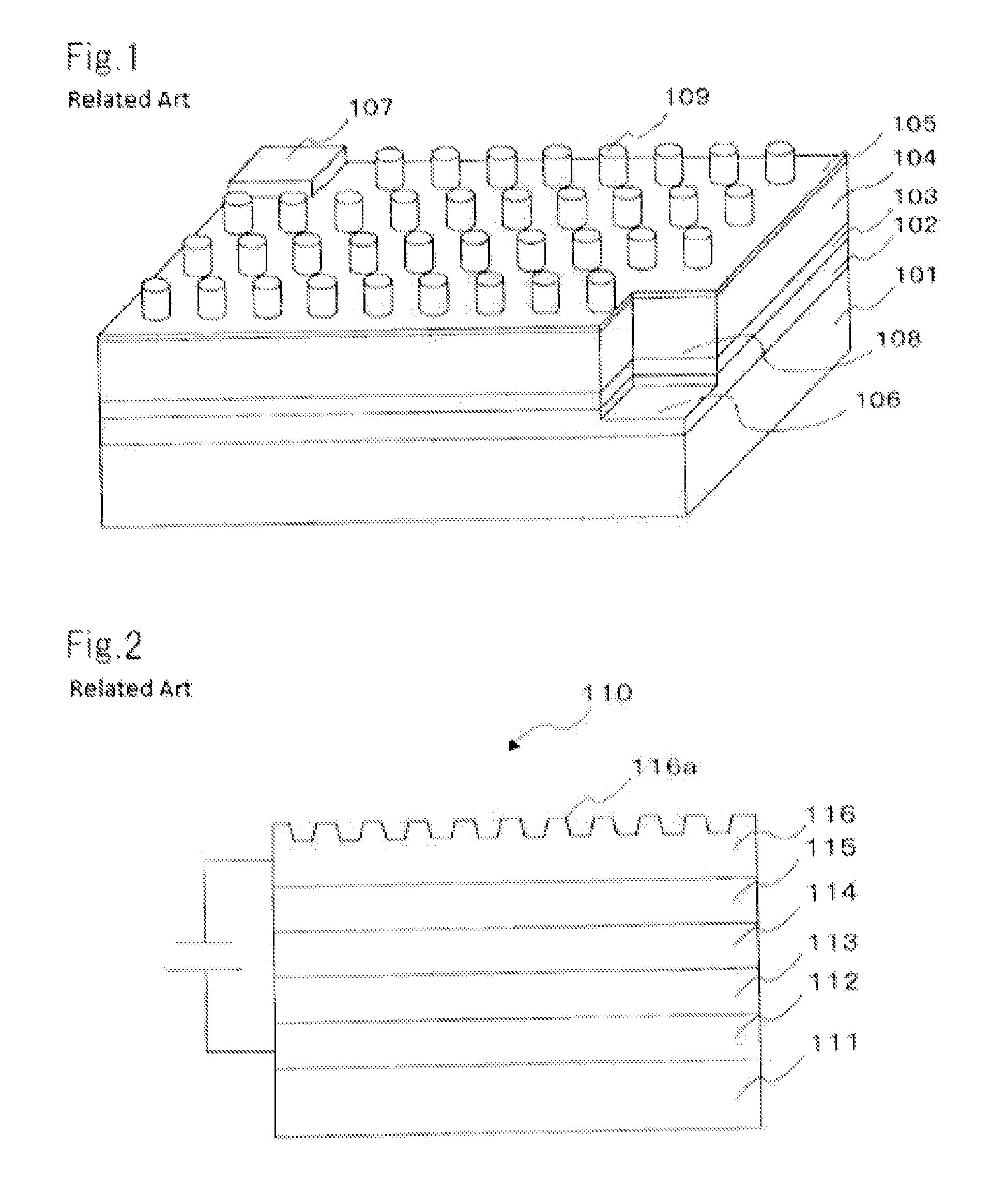
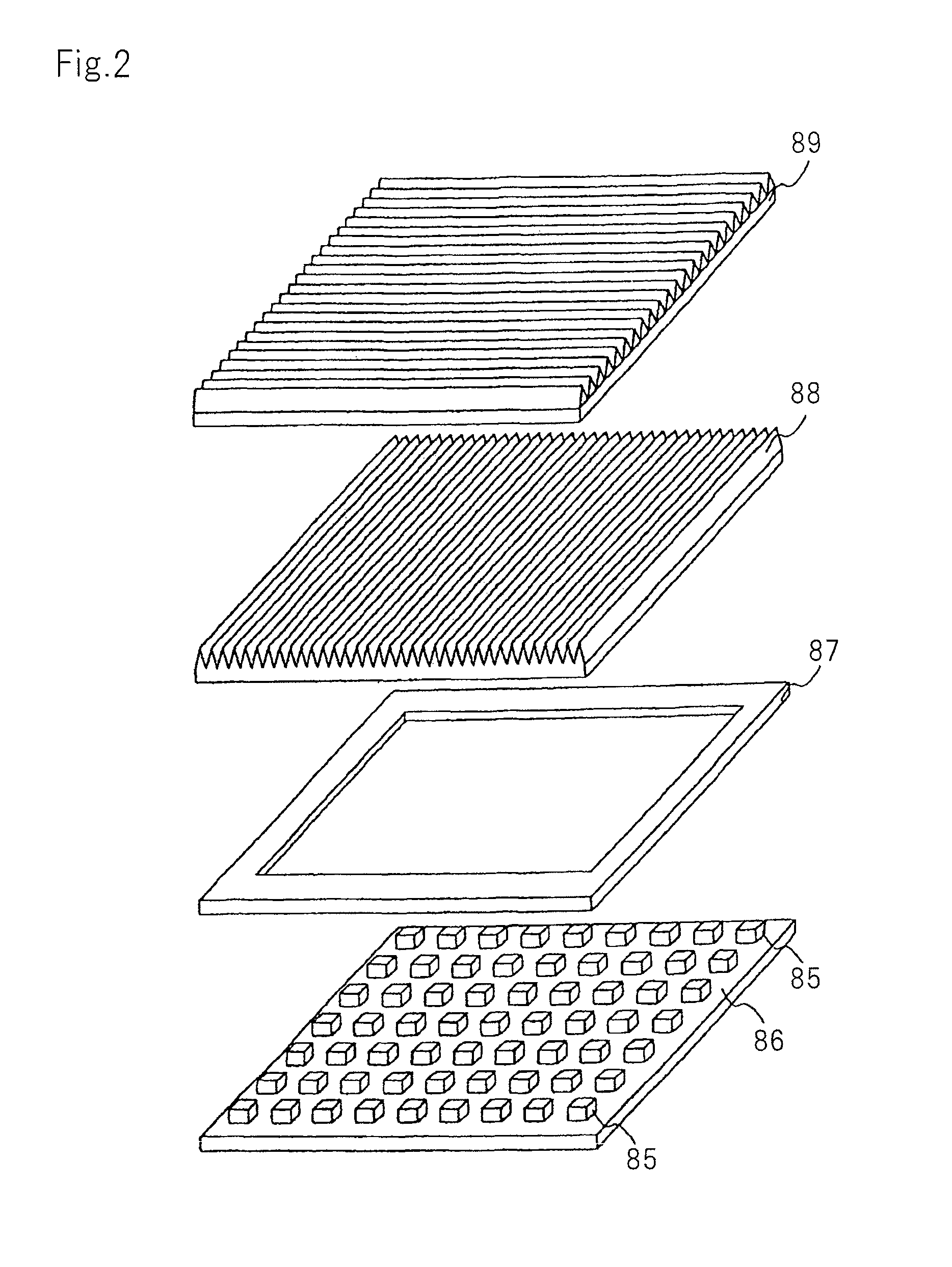
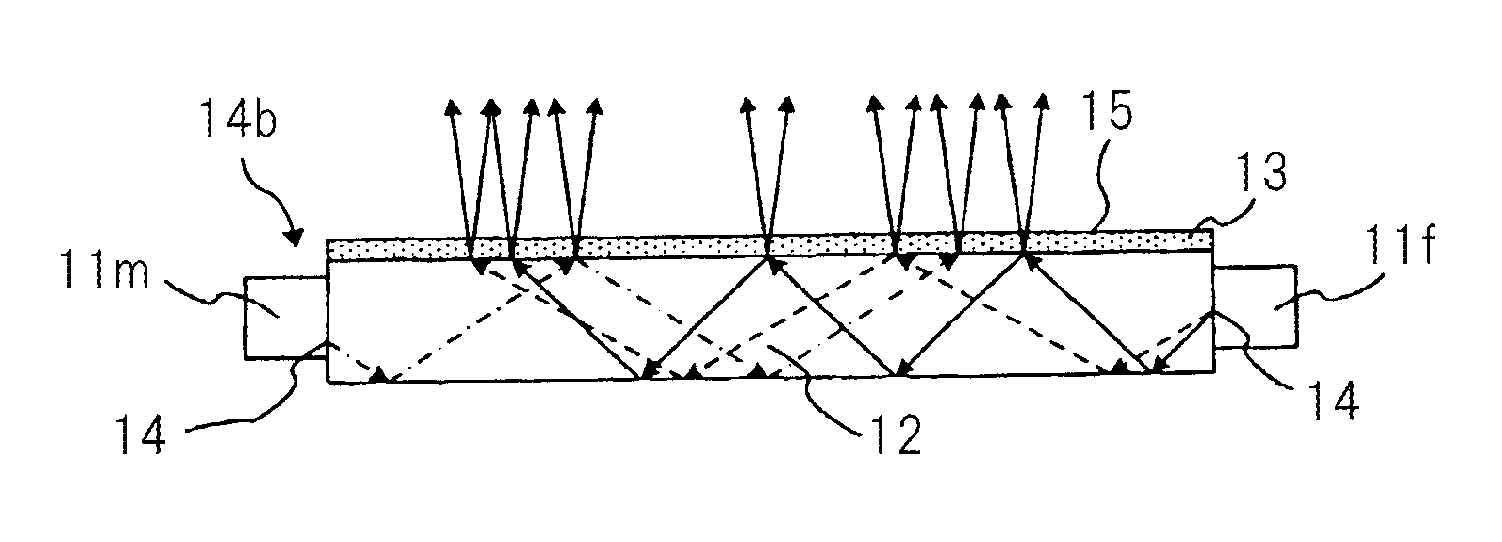
Information recording medium, information recording method, and information reproducing method
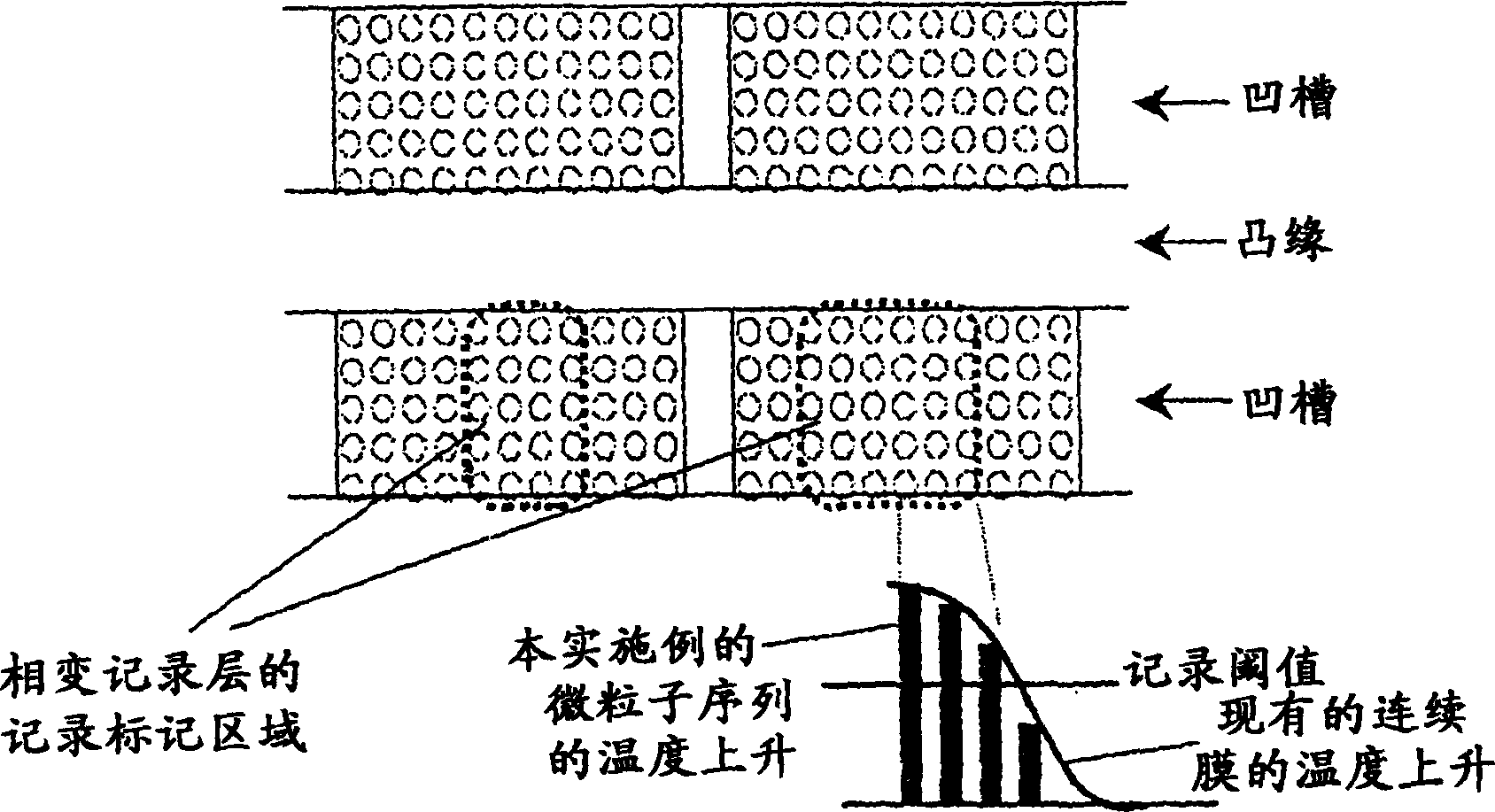
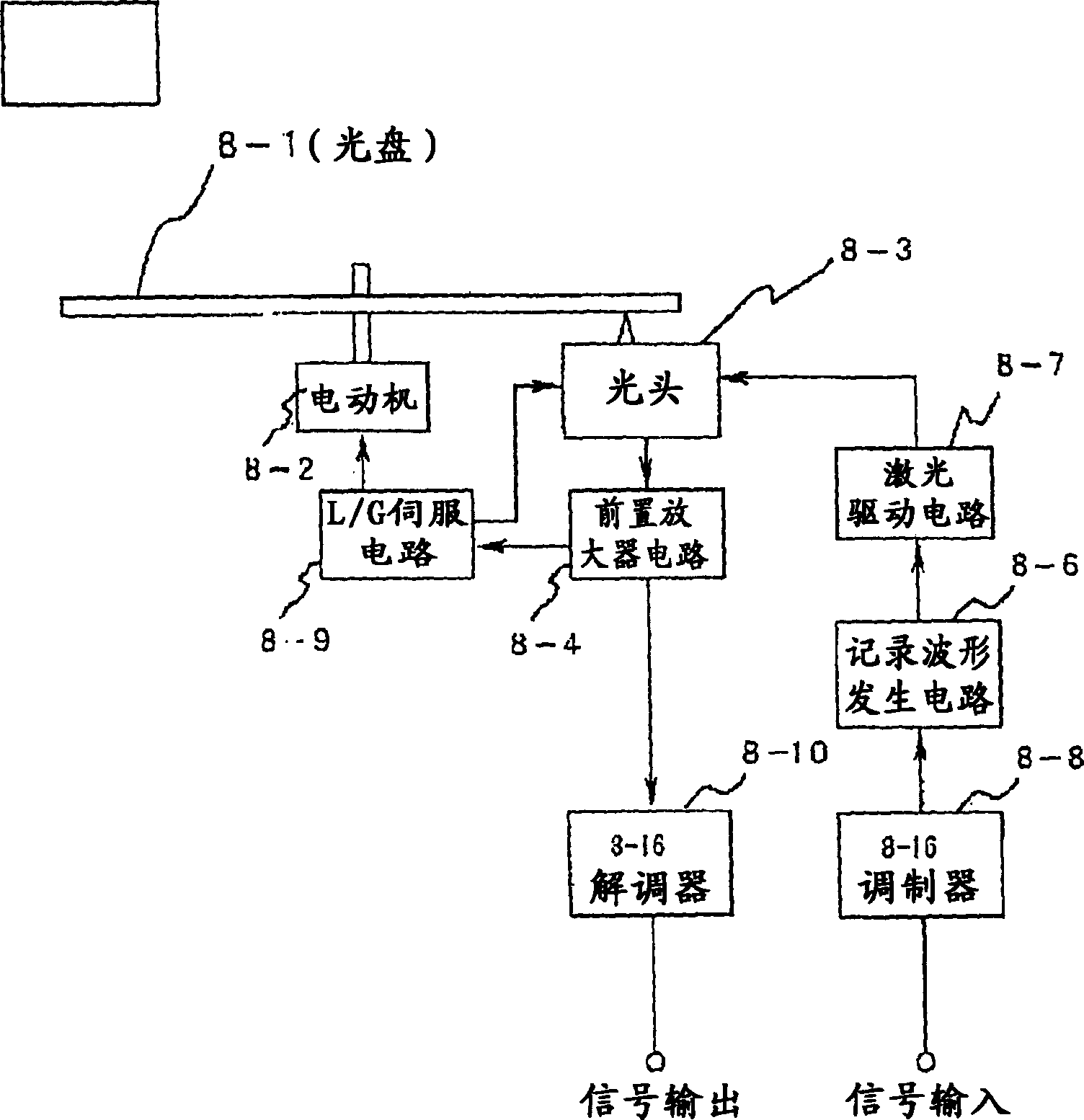
InactiveUS20040028869A1High density recordingImprove recording densityMaterial nanotechnologyOptical flying-type headsElectricityHigh density
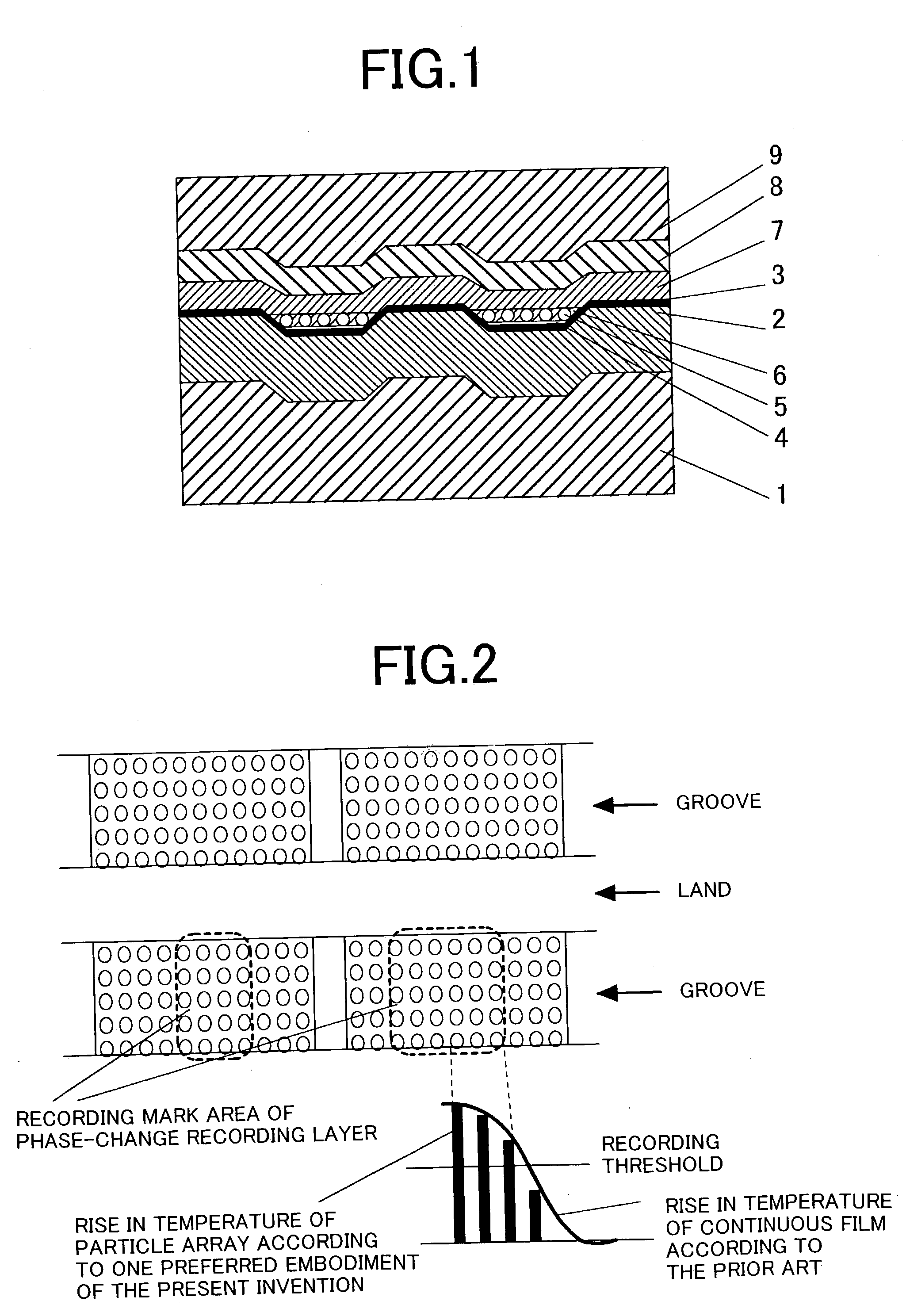
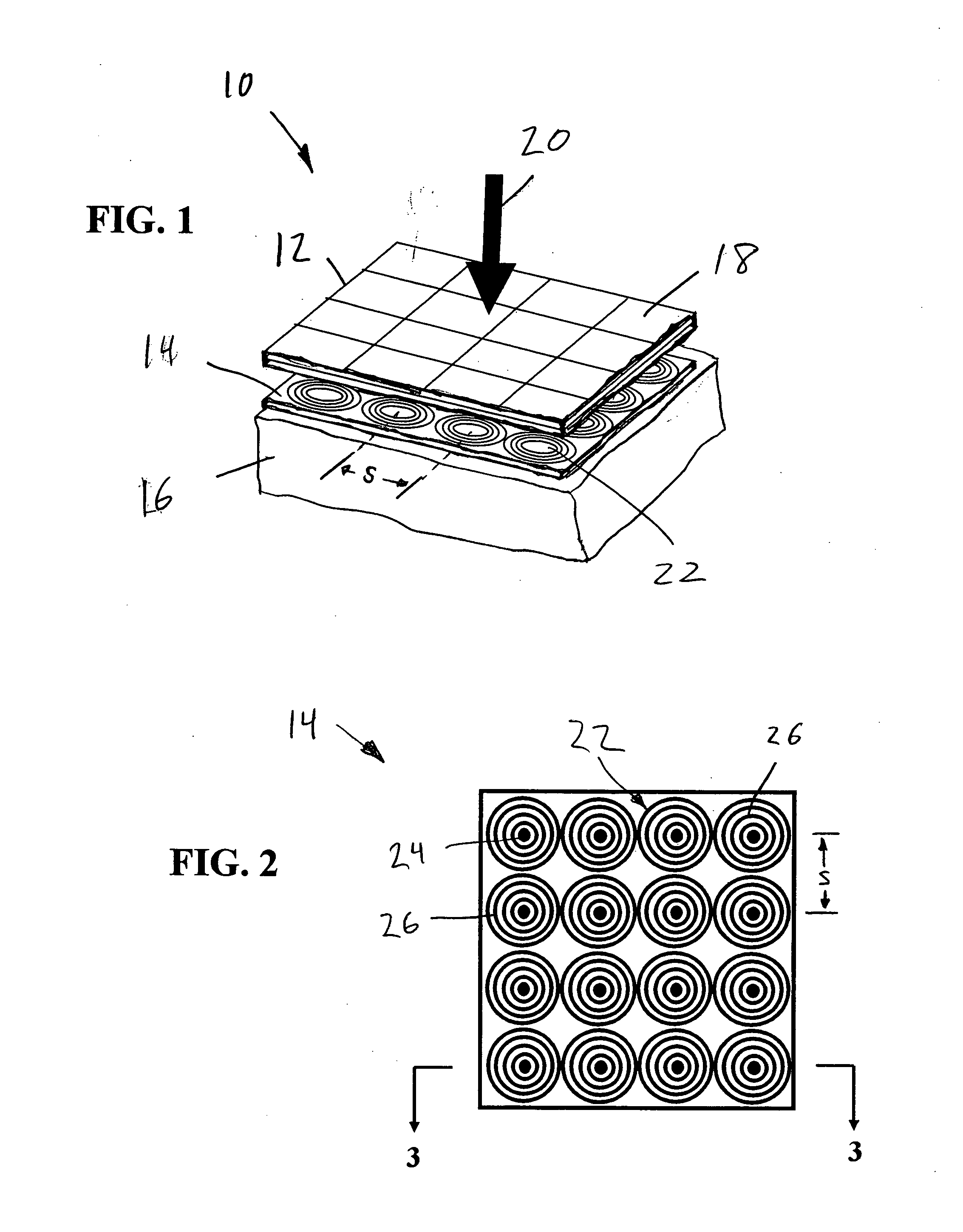
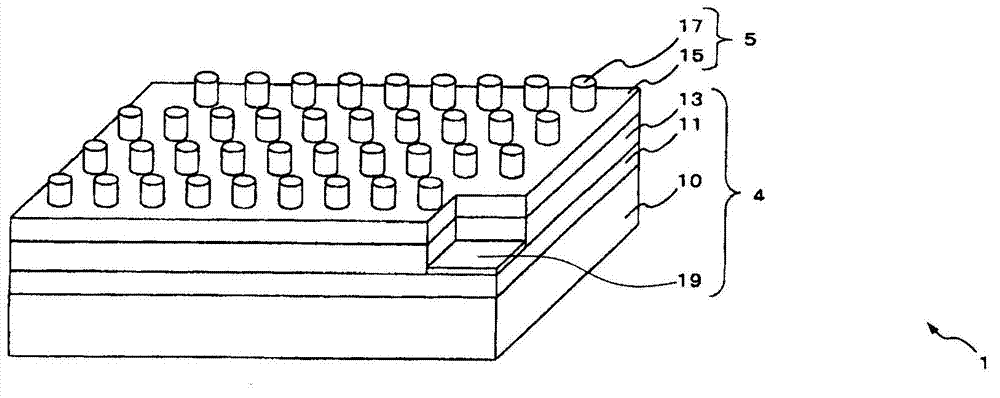
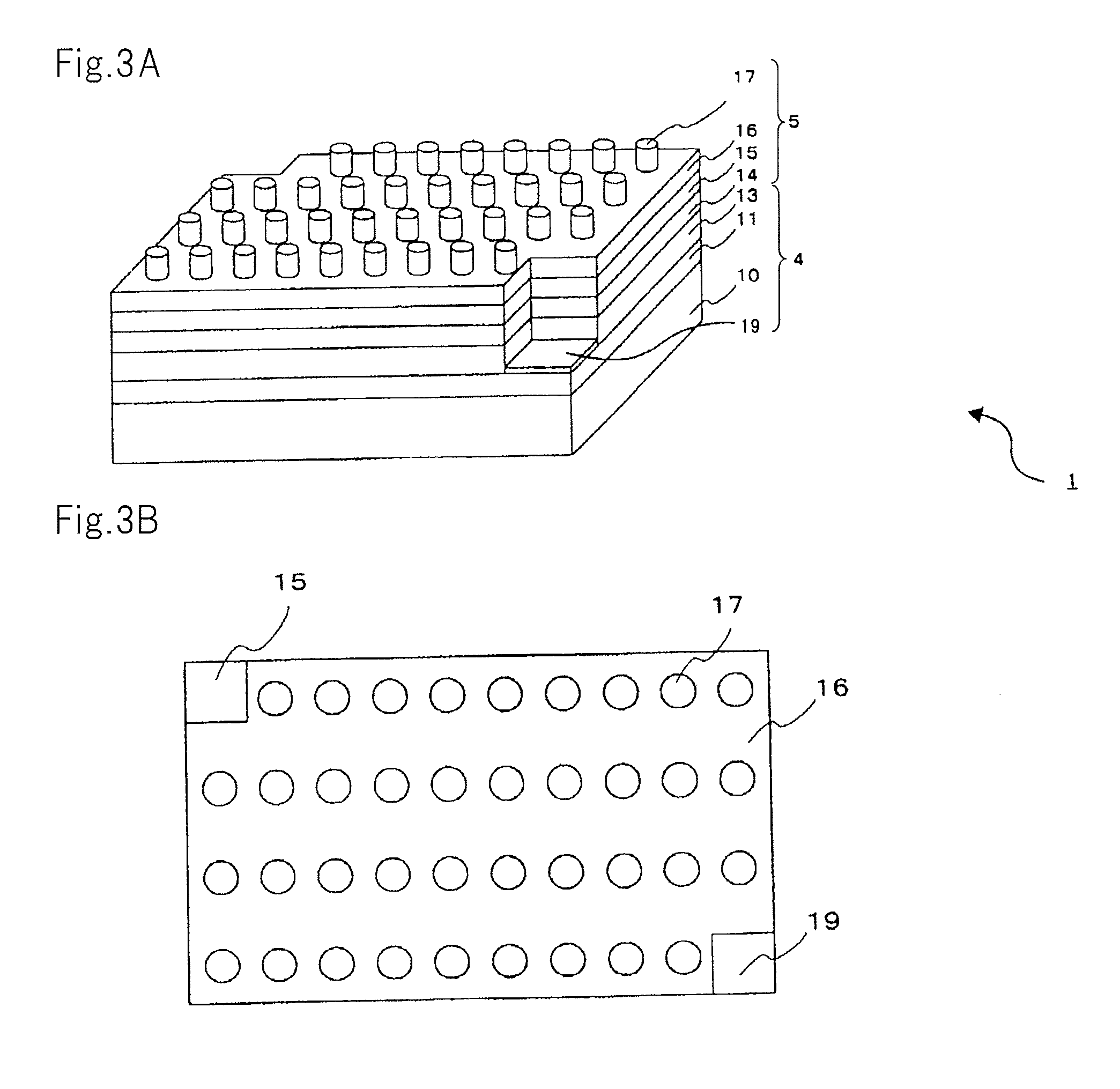
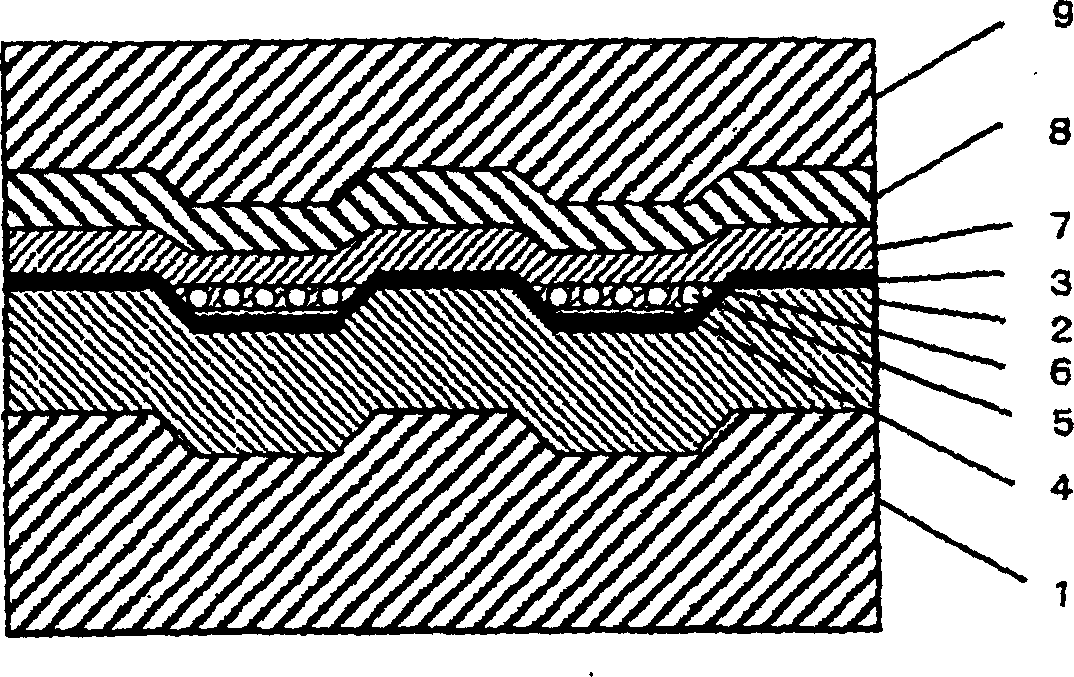
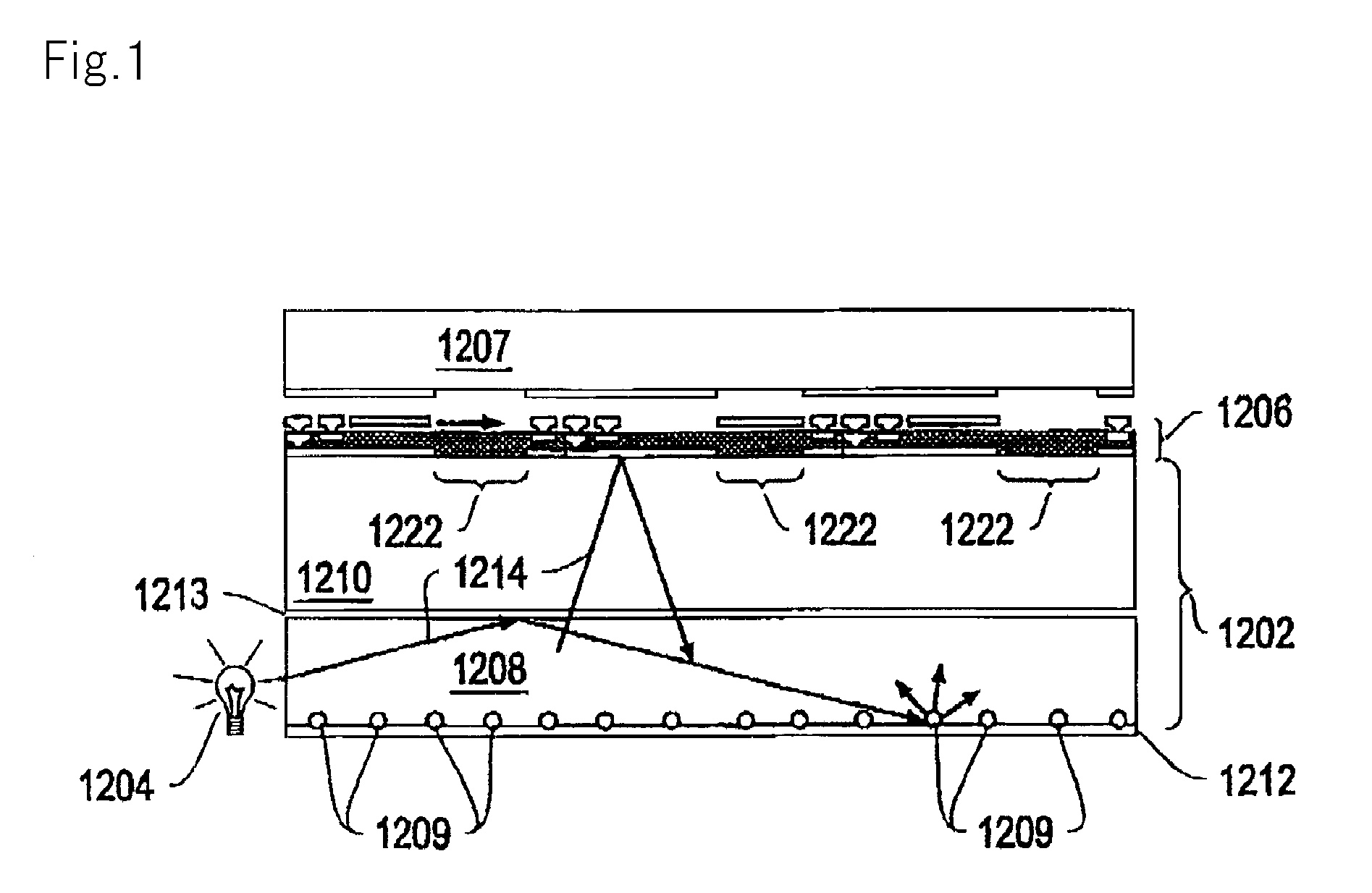
The information recording medium accosting to the preferred embodiment of the present invention achieves high-speed, high-density recording. The layer, in which ultra-particles made from an optical absorption metal, dielectric, or recording material are formed into regular arrays, is deposited. Resonant Plasmon excitation and resonance absorption of ultra-particles enable the edges of the recorded marks to be identified clearly and intense absorption to occur only in the given layer depending on the wavelength in the case of the multi-layer medium, achieving high-density, large-capacity recording.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Methods of controlling nanoparticle growth
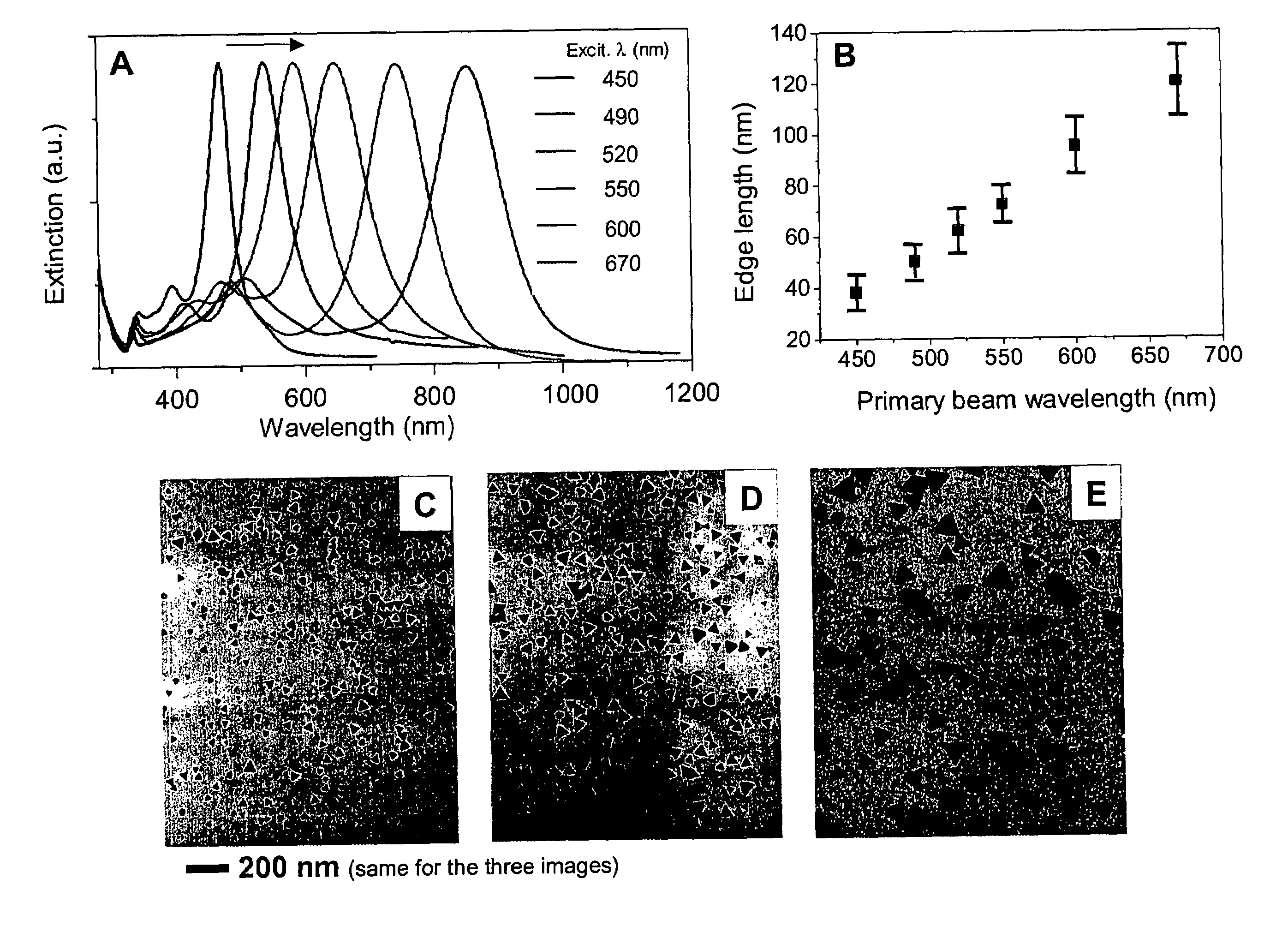
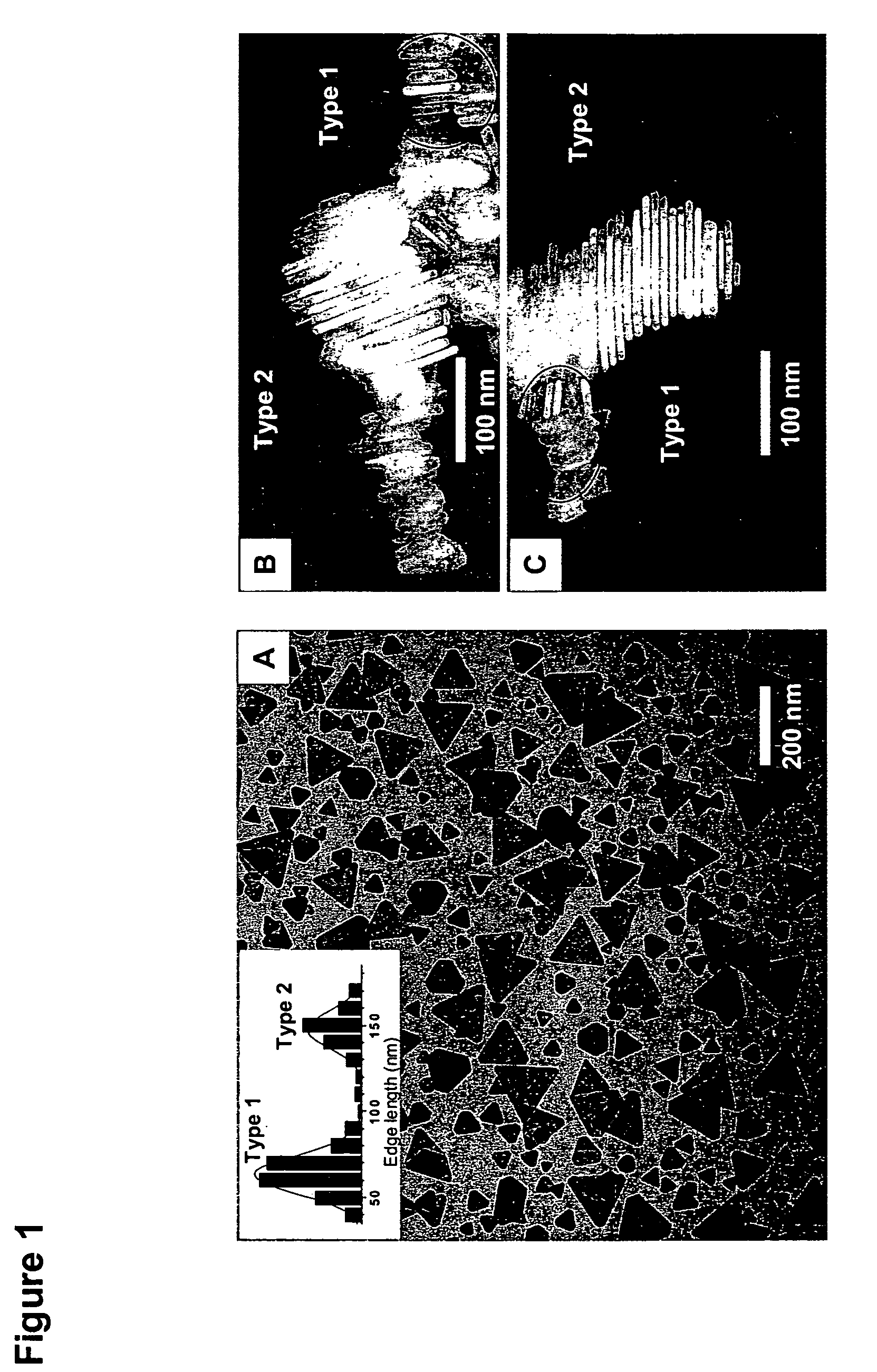
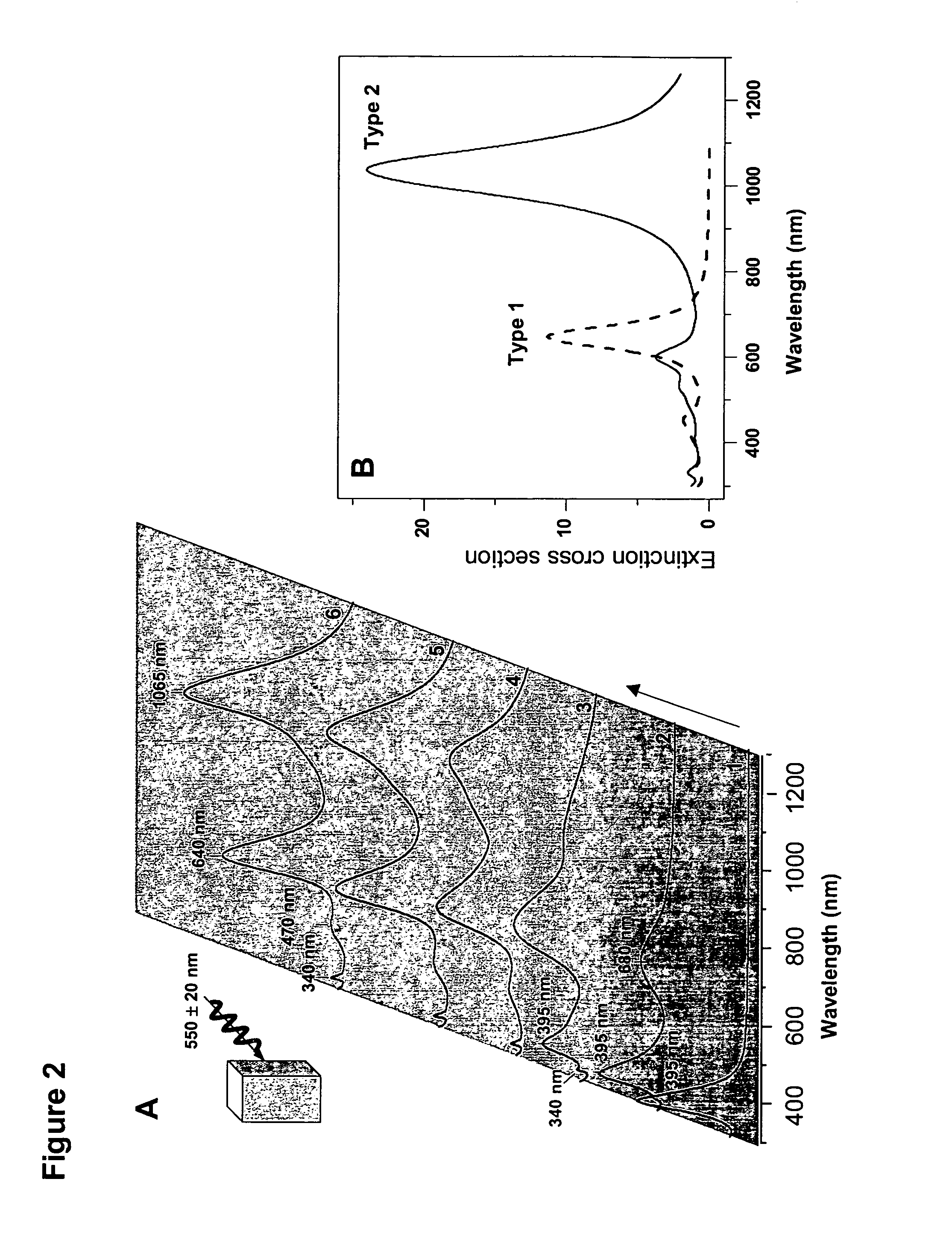
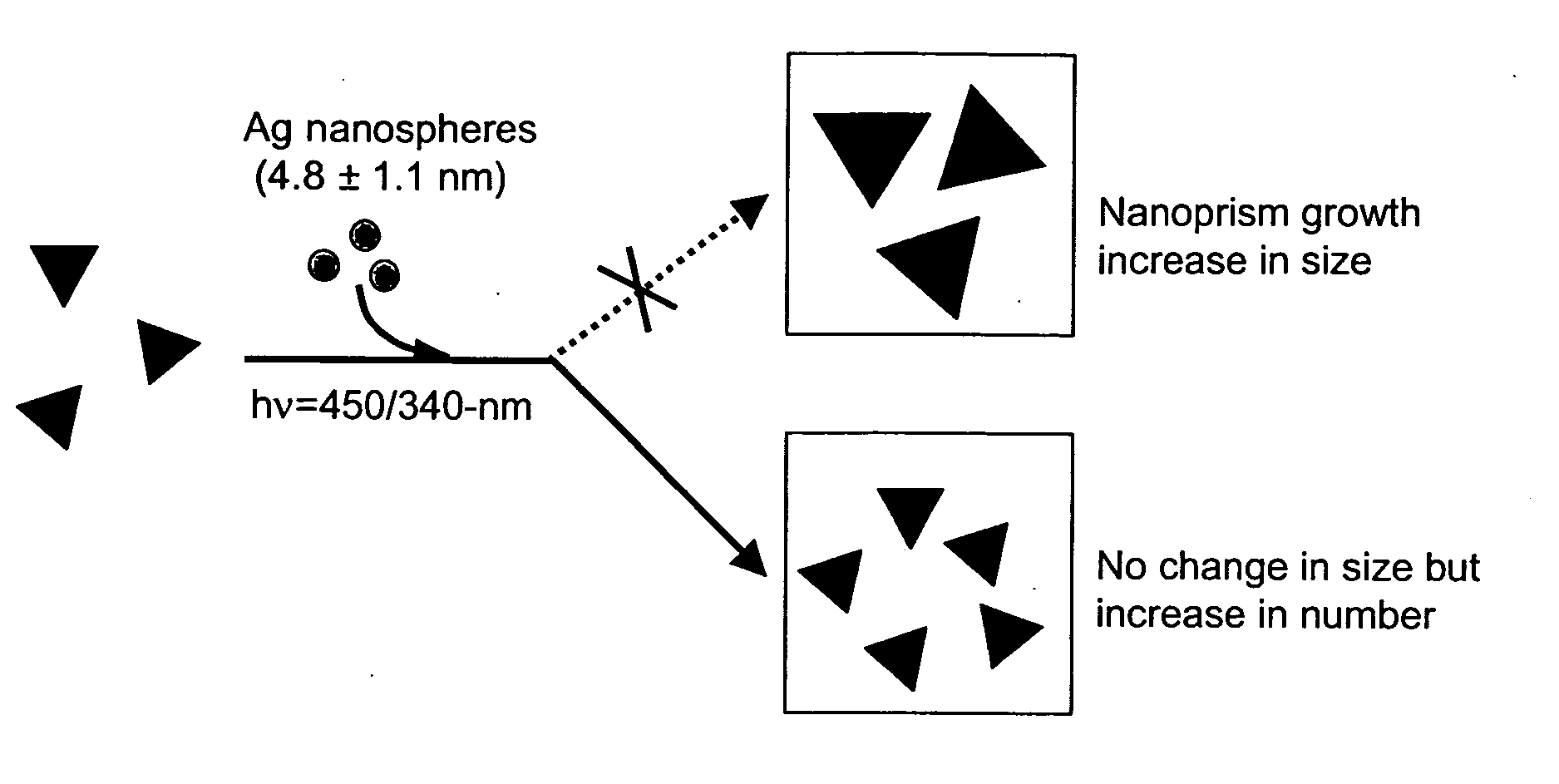
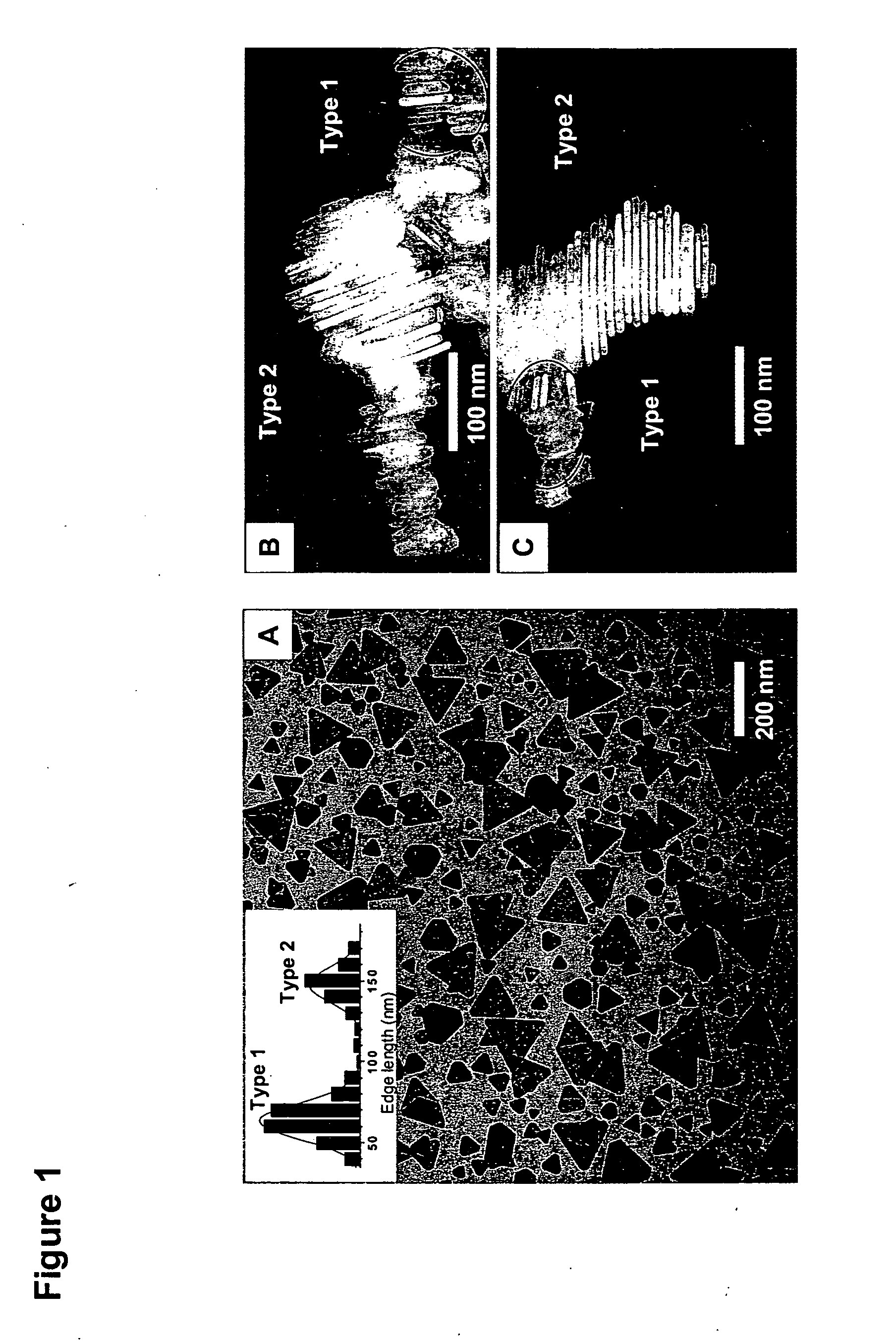
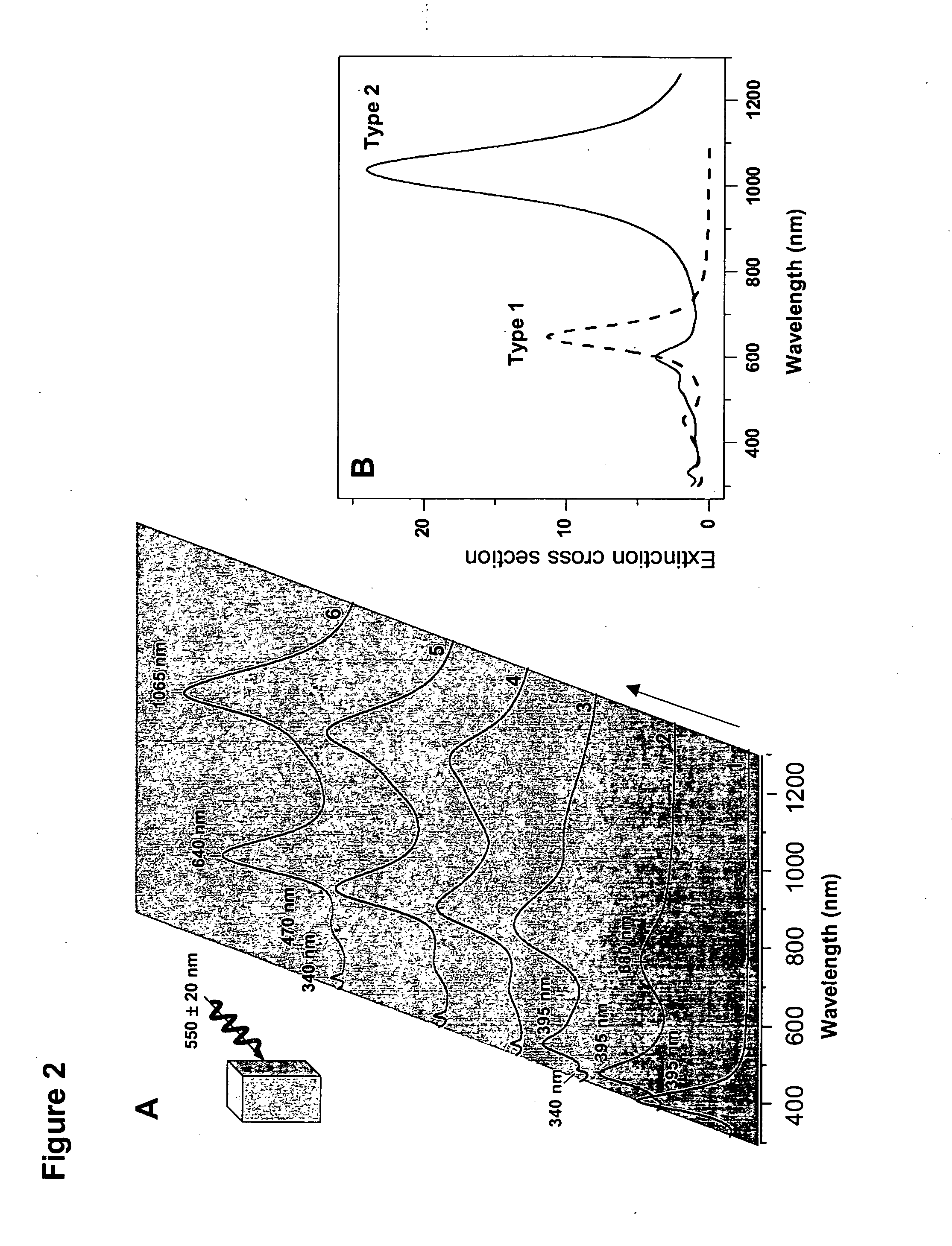
The invention provides new types of plasmon-driven growth mechanism for silver nanostructures involving the fusion of triangular nanoprisms. This mechanism, which is plasmon excitation-driven and highly cooperative, produces bimodal particle size distributions. In these methods, the growth process can be selectively switched between bimodal and unimodal distributions using dual beam illumination of the nanoparticles. This type of cooperative photo-control over nanostructure growth enables synthesis of monodisperse nanoprisms with a preselected edge length in the 30–120 nm range simply by using one beam to turn off bimodal growth and the other (varied over the 450–700 nm range) for controlling particle size.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Optical element, light source device, and projection display device
ActiveUS20120176766A1Reduce lightReduced etendueNanoopticsPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideCharge carrier
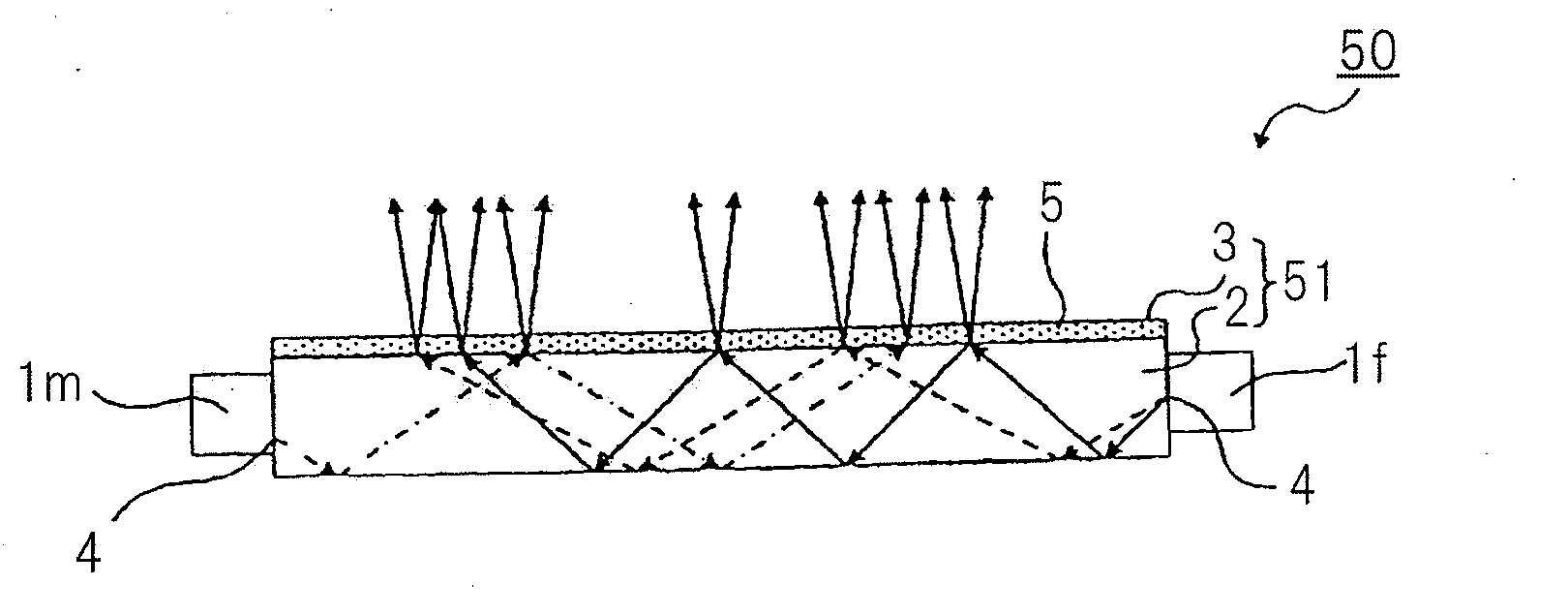
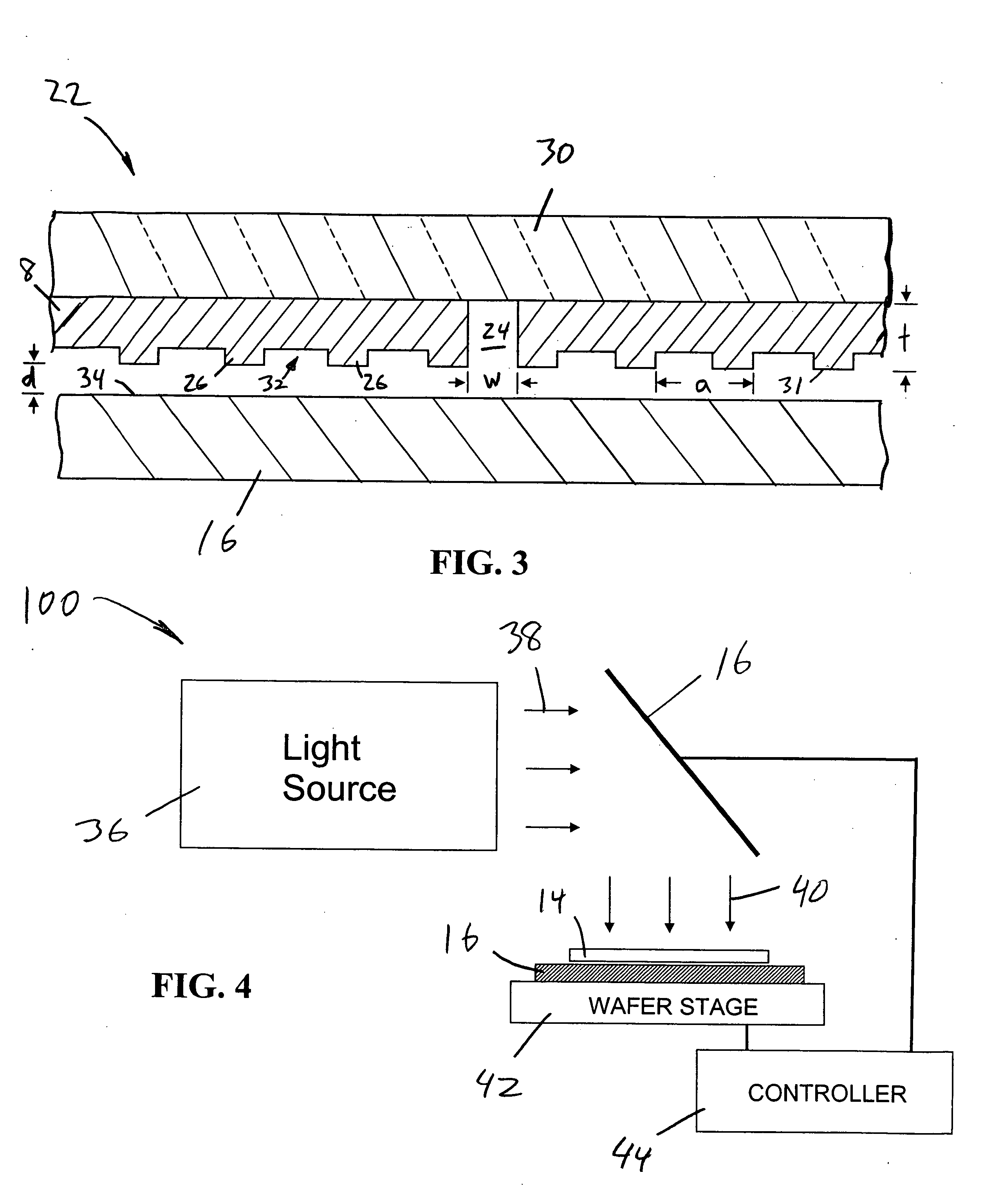
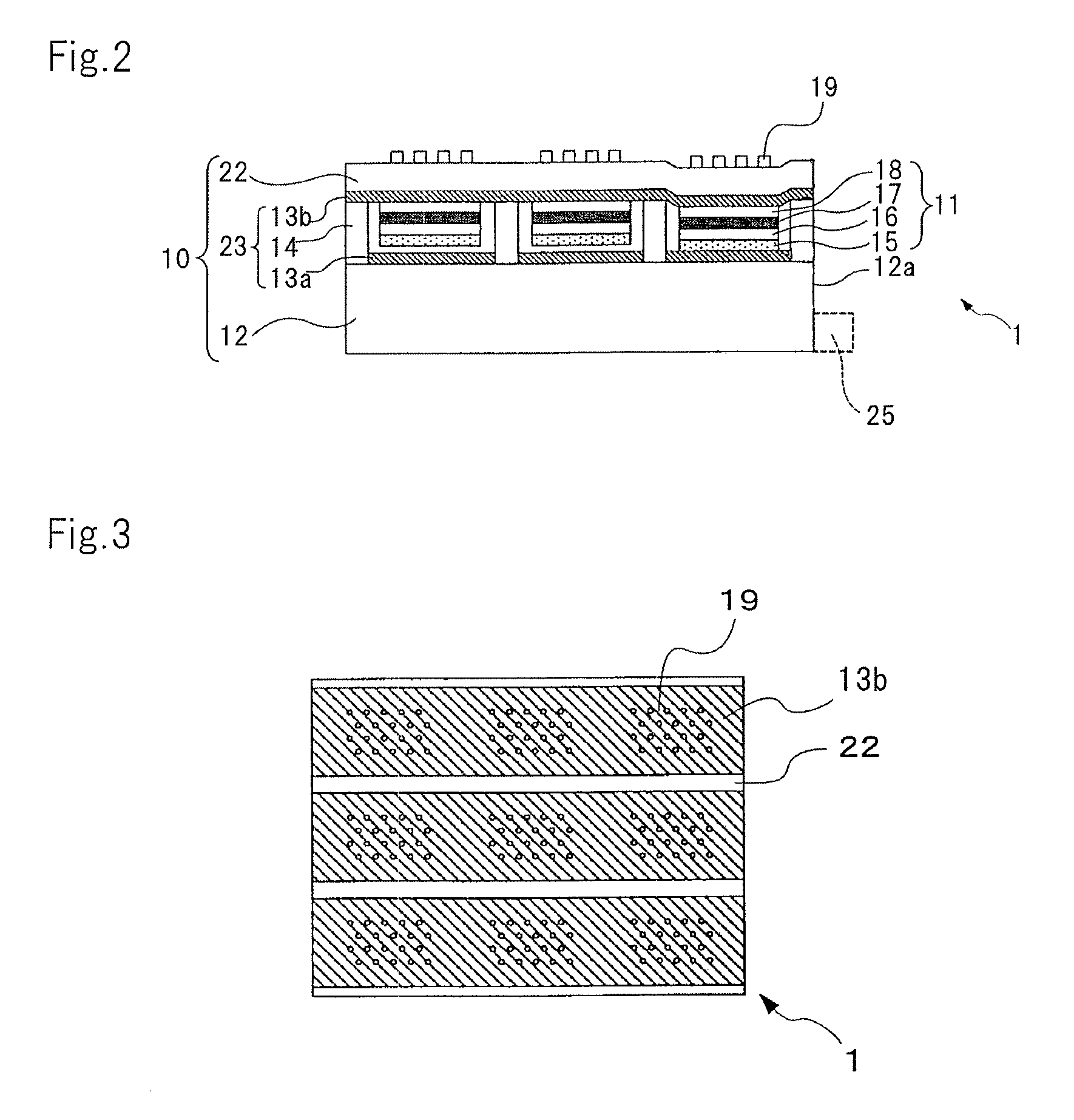
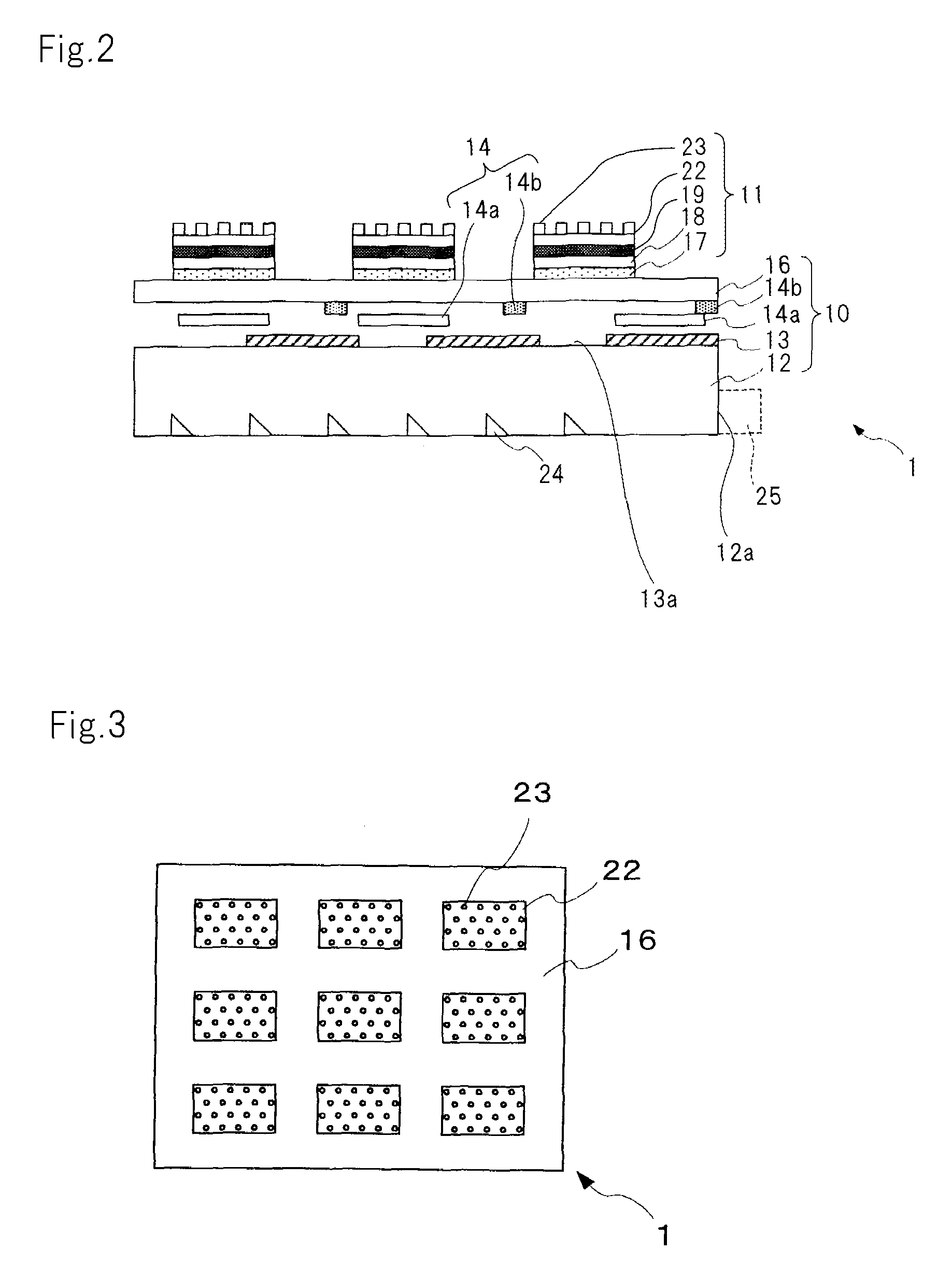
Disclosed is an optical element that includes: a light guide body into which light from a light-emitting element enters; carrier generation layer (6) formed in the light guide body, in which carriers are generated by the light from the light guide body; plasmon excitation layer (8) stacked on carrier generation layer (6), which has a plasma frequency higher than the frequency of light generated when carrier generation layer (6) is excited by the light from the light-emitting element; and wave vector conversion layer (10) stacked on plasmon excitation layer (8), which converts light incident from plasmon excitation layer (8) into light having a predetermined exit angle to output the light. Plasmon excitation layer (8) is sandwiched between low dielectric constant layer (7) and high dielectric constant layer (9).
Owner:NEC CORP
Light emitting element, light source device, and projection display device
ActiveUS20120224148A1Increase brightnessImprove directionalityProjectorsSolid-state devicesControl layerTransport layer
Light source layer (4) includes substrate (10) and a pair of layers, namely, hole-transport layer (11) and electron-transport layer (13), formed on substrate (10). Directional control layer (5) includes plasmon excitation layer (15) stacked on a side of light source layer (4), which is opposite to the side of substrate (10) of light source layer (4), and which has a plasma frequency higher than a frequency of light output from light source layer (4), and wave vector conversion layer (17) stacked on plasmon excitation layer (15), which converts light incident from plasmon excitation layer (15) into light having a predetermined exit angle to output the light. Plasmon excitation layer (15) is sandwiched between low dielectric constant layer (14) and high dielectric constant layer (16).
Owner:NEC CORP
Light emitting element, light source device, and projection display device
InactiveUS20120314189A1Increase brightnessImprove directivityProjectorsSolid-state devicesDielectricTransport layer
The present invention includes light source layer (4) and directivity controlling layer (5) into which light emitted from light source layer (4) enters. Light source layer (4) has a pair of hole transport layer (11) and electron transport layer (13) formed on substrate (10). Directivity controlling layer (5) has plasmon excitation layer (15) that is laminated on non-substrate (10) side of light source layer (4) and that has a higher plasma frequency than light emitted from light source layer (4) and wave number vector conversion layer (17) that converts surface plasmons that are generated in plasmon excitation layer (15) into light having a predetermined emission angle and emits the light having the predetermined emission angle. Plasmon excitation layer (15) is sandwiched between two layers having dielectricity. The effective dielectric constant of the incident side portion including the entire structure laminated on light source layer (4) side of plasmon excitation layer (15) is greater than that of the emission side portion including the entire structure laminated on wave number vector conversion layer (17) side of plasmon excitation layer (15) and a medium that contacts wave number vector conversion layer (17).
Owner:NEC CORP
Plasmonic array for maskless lithography
In various embodiments, a photolithography system comprises a spatial light modulator and a plasmonic lens array. The spatial light modulator comprises a plurality of pixels, and the plasmonic lens array comprises a plurality of plasmonic lenses. The pixels are optically aligned with the plasmonic lenses such that light from the pixels is substantially focused by the lenses. The plasmonic lenses each comprise an optical aperture and a plurality of metal features proximal to the aperture. The metal features have a dimension and arrangement configured to couple optical energy incident on one side of the plasmonic lens into plasmon excitation supported by the metal and to reemit optical energy through the aperture.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Optical element, light source device, and projection display device
Disclosed is an optical element that includes: carrier generation layer (16) in which carriers are generated by light from light guide body (12) into which light from a light-emitting element enters; plasmon excitation layer (17) that has a plasma frequency higher than the frequency of light generated when carrier generation layer (16) is excited by light from the light-emitting element; and wave vector conversion layer (18) that converts surface plasmon generated by plasmon excitation layer (17) light having a predetermined exit angle to output the light. Plasmon excitation layer (17) is sandwiched between two layers having dielectric properties. The effective dielectric constant of the incident side portion of plasmon excitation layer (17) including an entire structure stacked above light guide body (12) side is higher than that of the exit side portion of plasmon excitation layer (17) including the entire structure stacked above wave vector conversion layer (18) side and the medium in contact with wave vector conversion layer (18).
Owner:NEC CORP
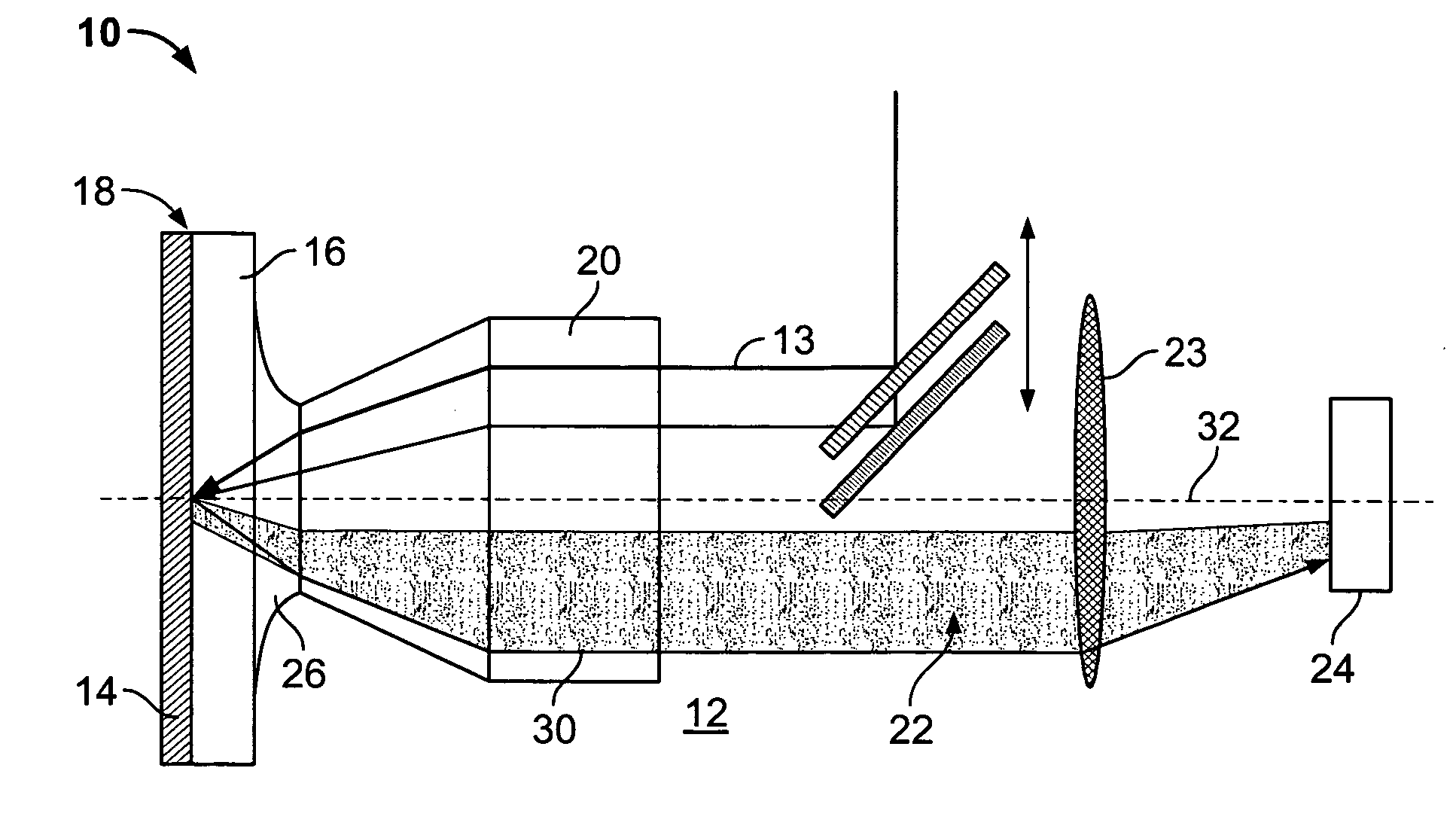
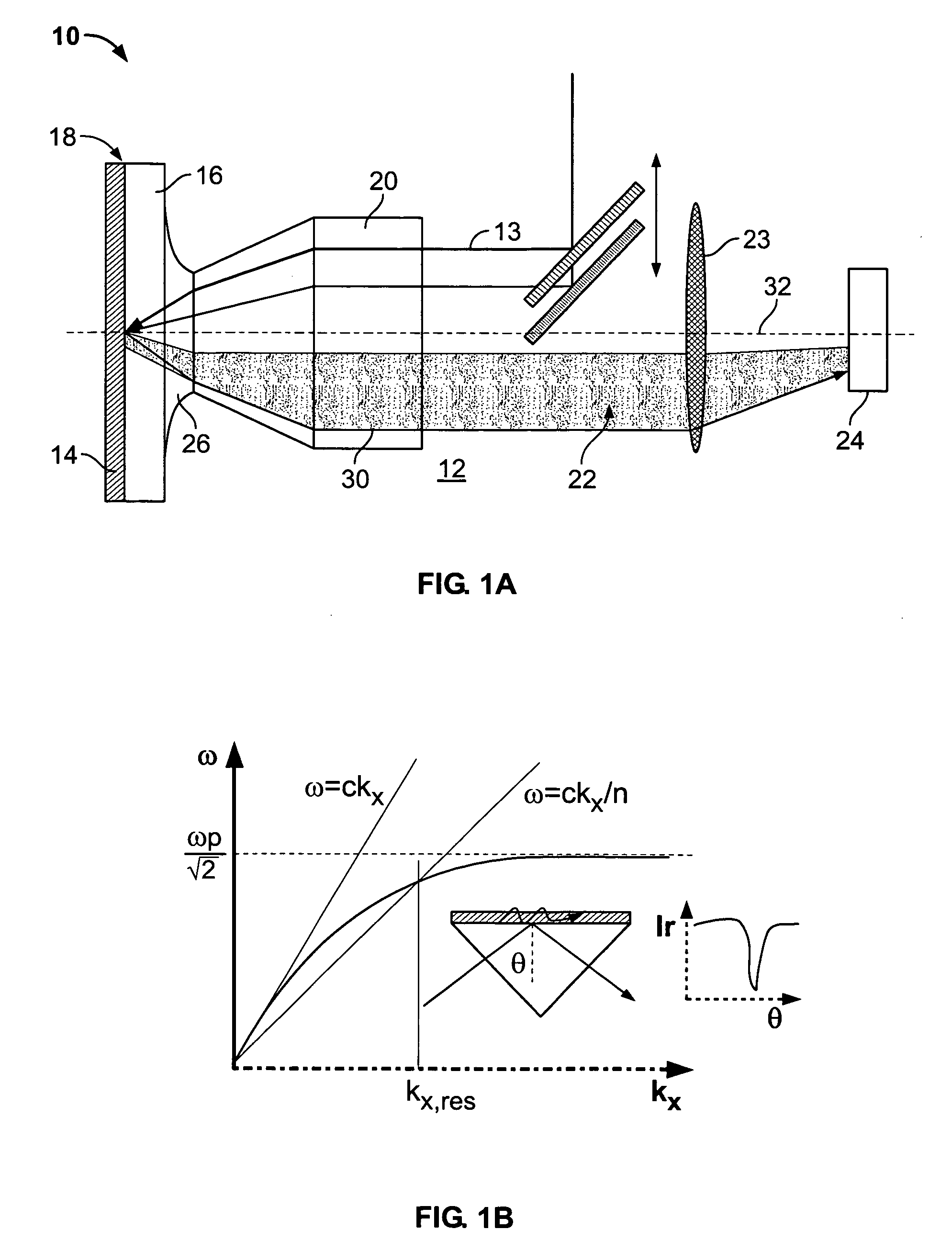
Broadband surface plasmon jets: direct observation of plasmon propagation for application to sensors and optical communications in microscale and nanoscale circuitry
InactiveUS20060221343A1Relatively large bandwidthLarge frequencyScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteHigh bandwidth
A system and method for generating and using broadband surface plasmons in a metal film for characterization of analyte on or near the metal film. The surface plasmons interact with the analyte and generate leakage radiation which has spectral features which can be used to inspect, identify and characterize the analyte. The broadband plasmon excitation enables high-bandwidth photonic applications.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF THE +1
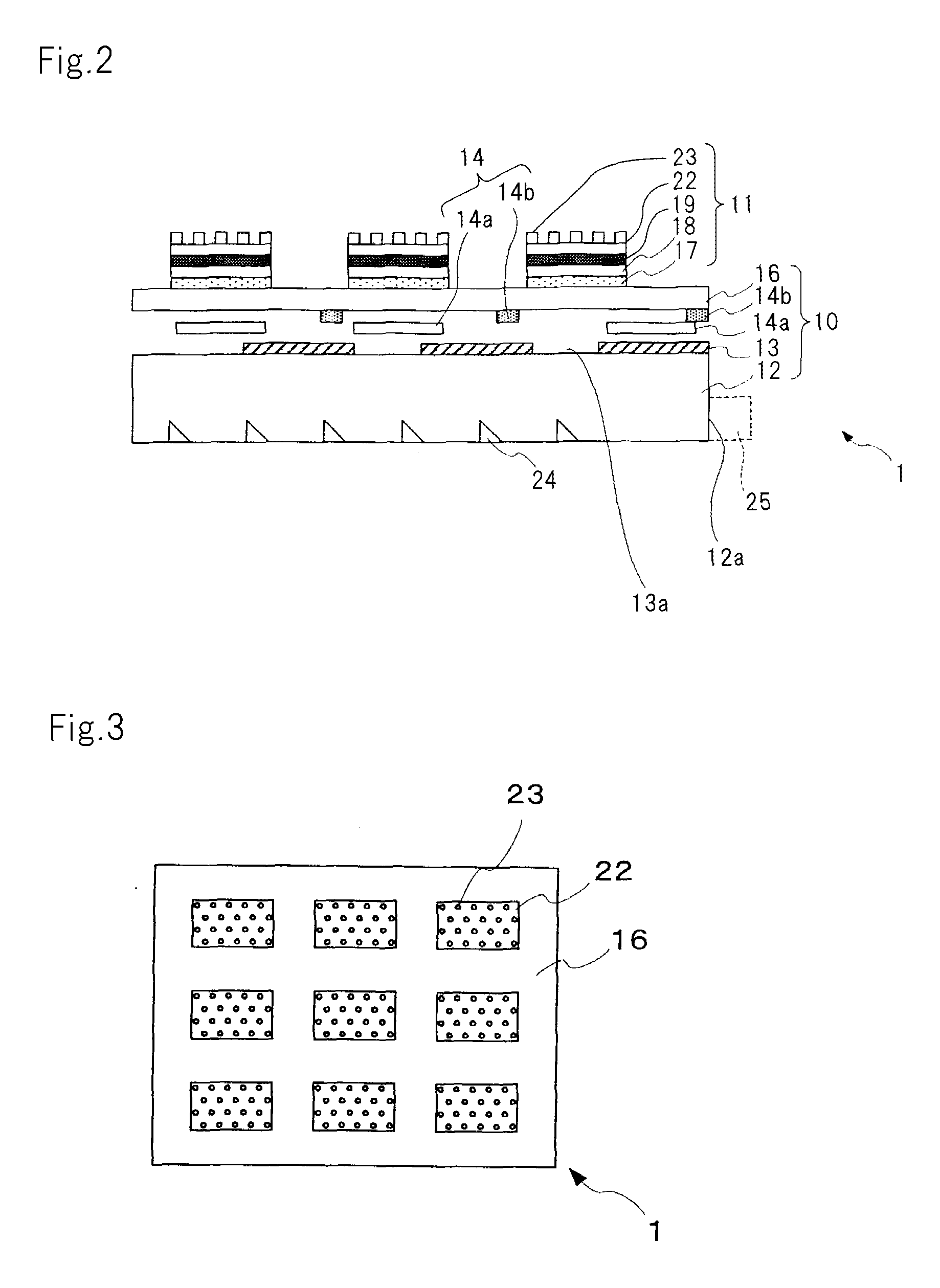
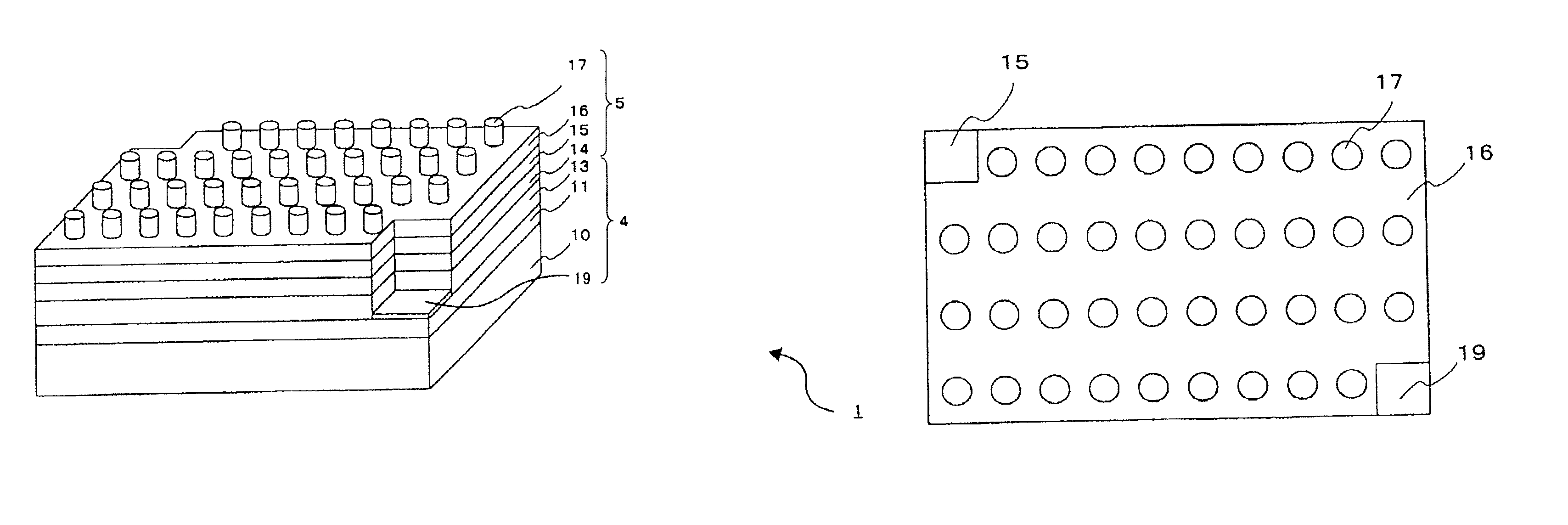
Display element, display device, and projection display device
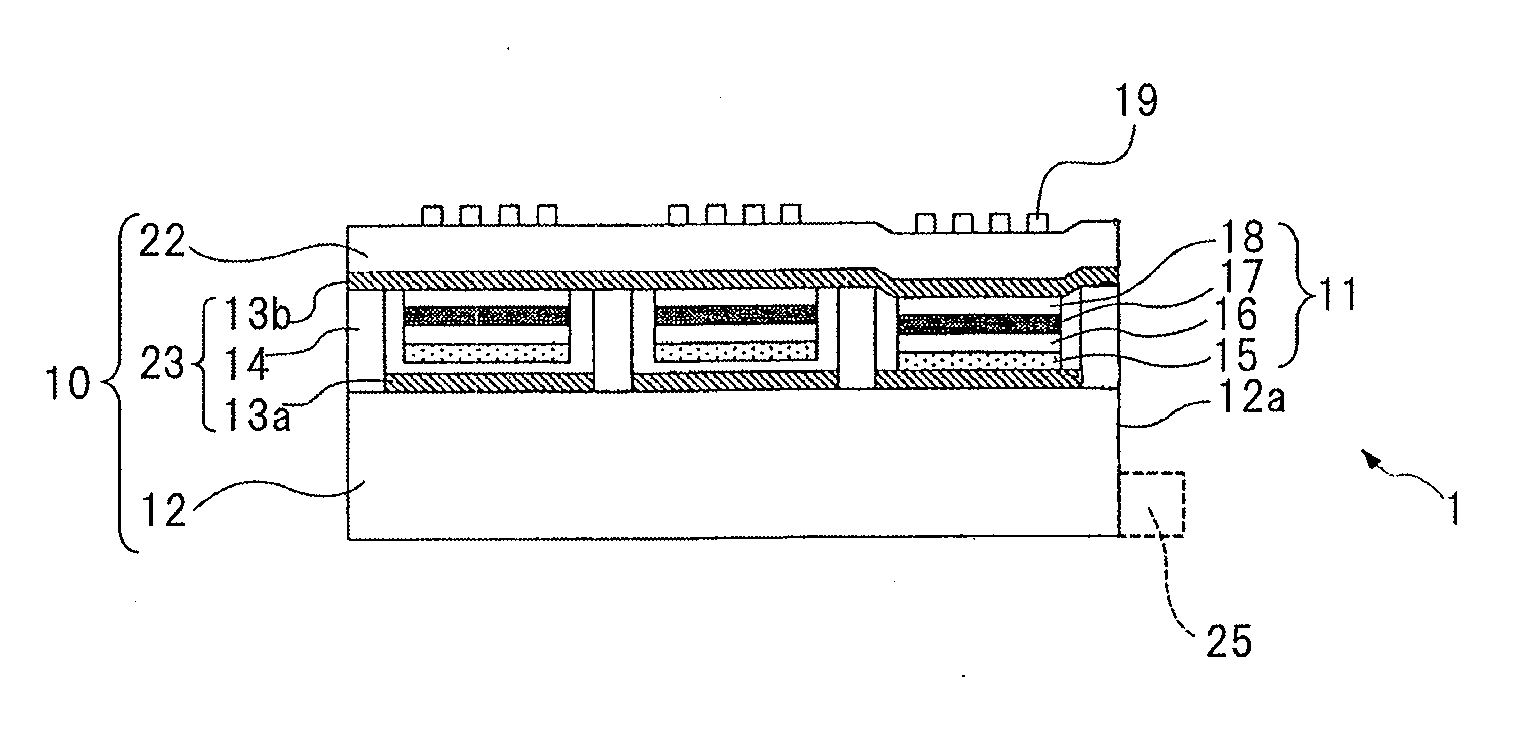
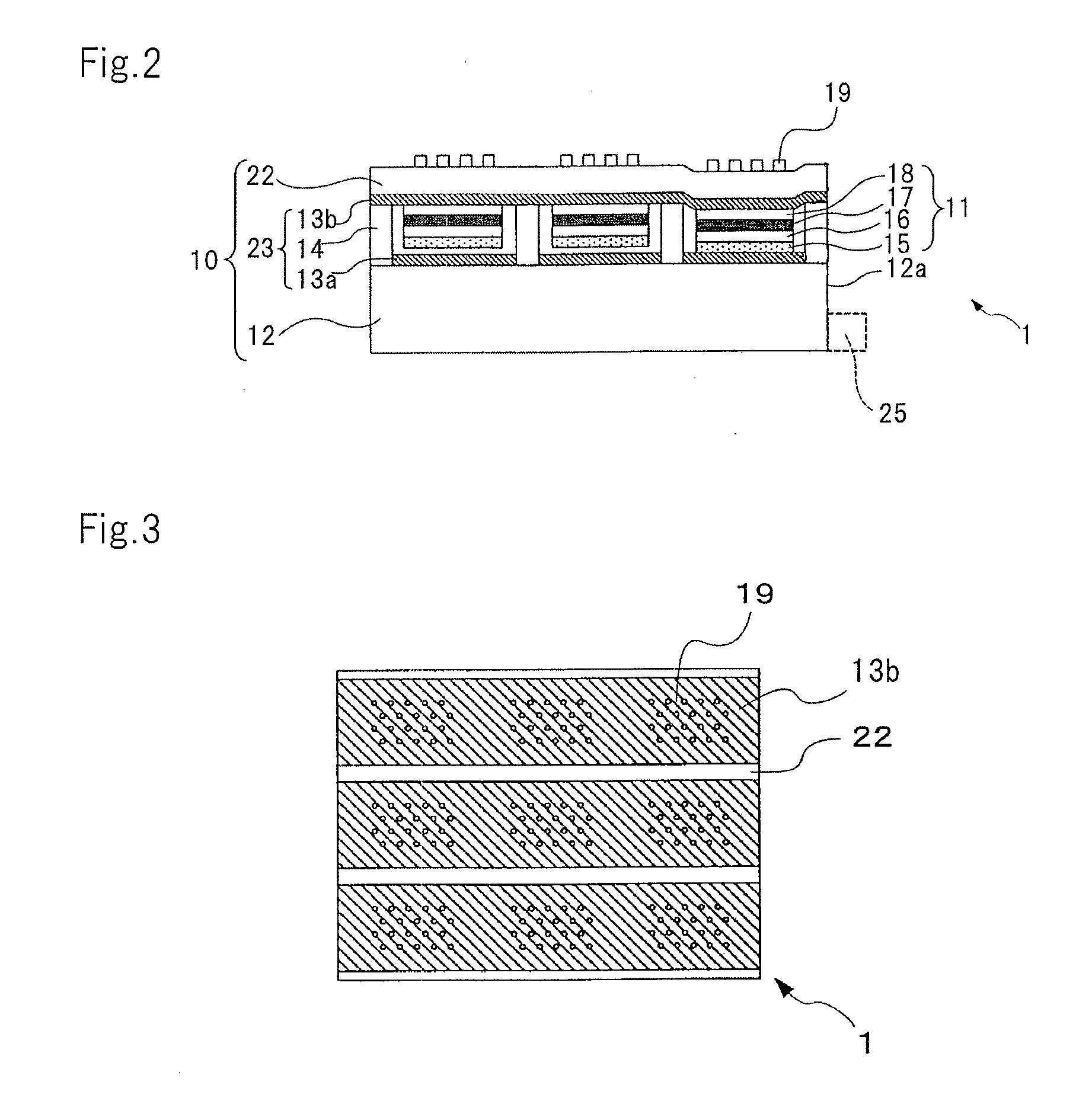
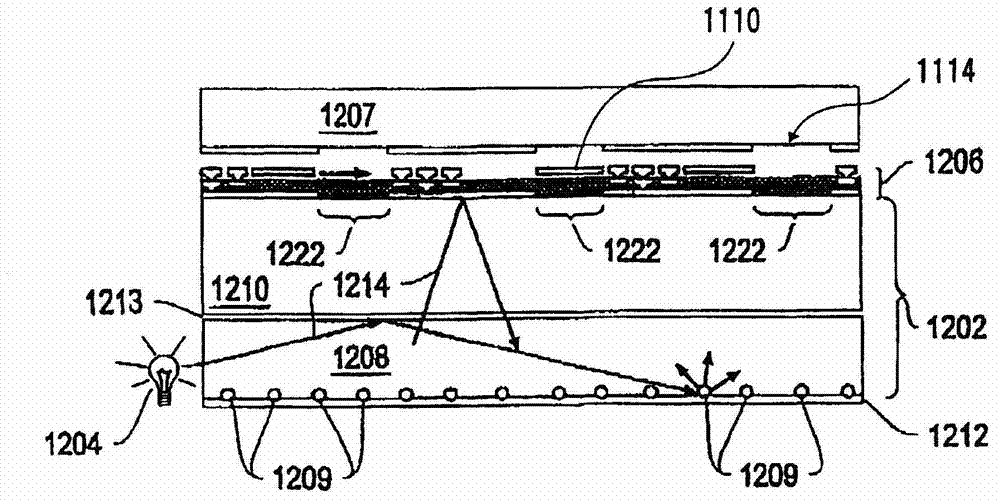
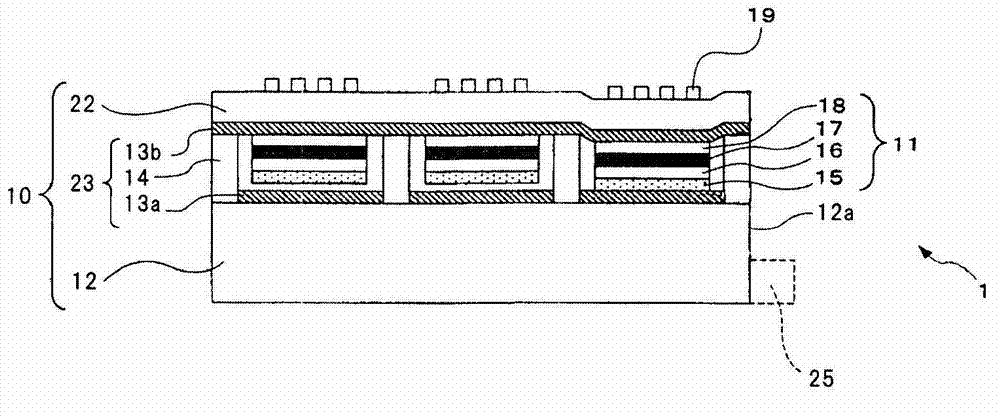
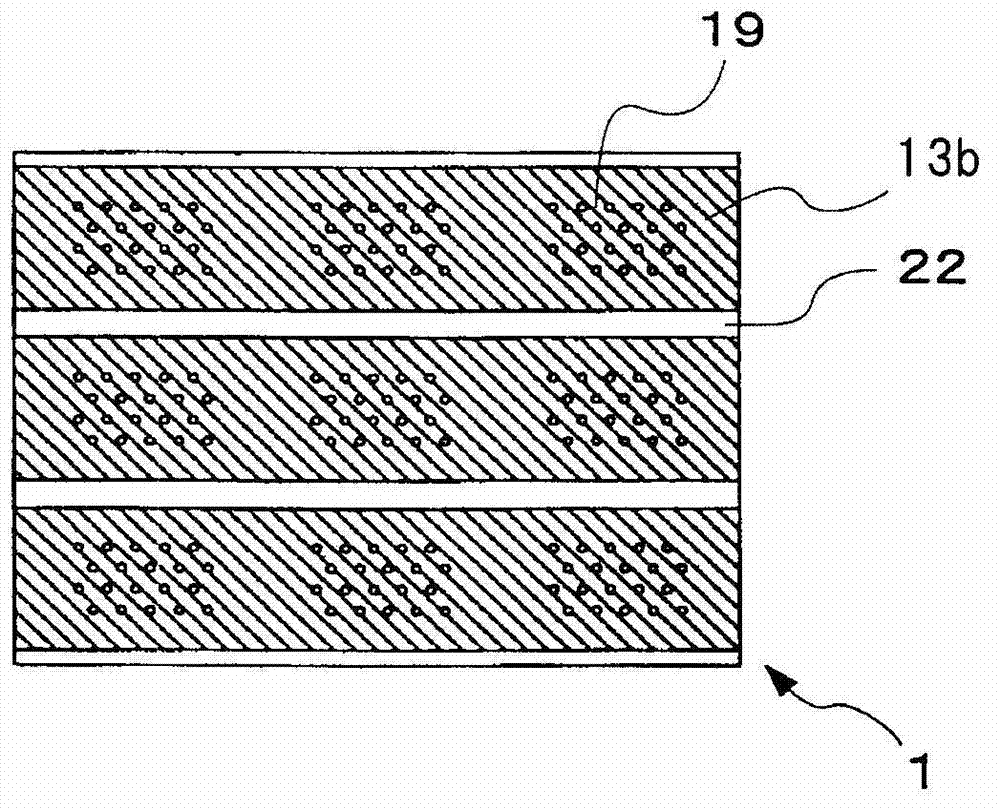
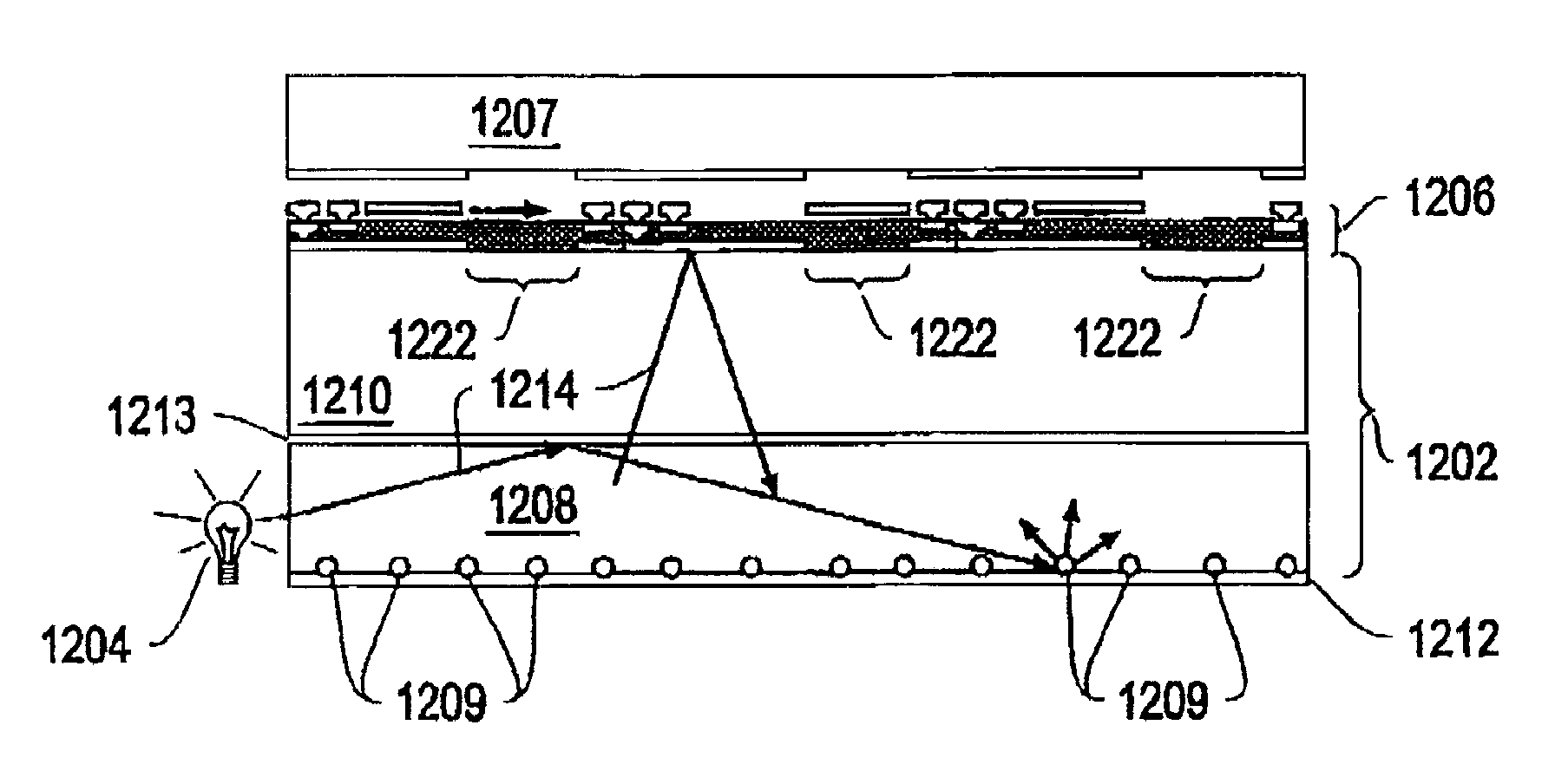
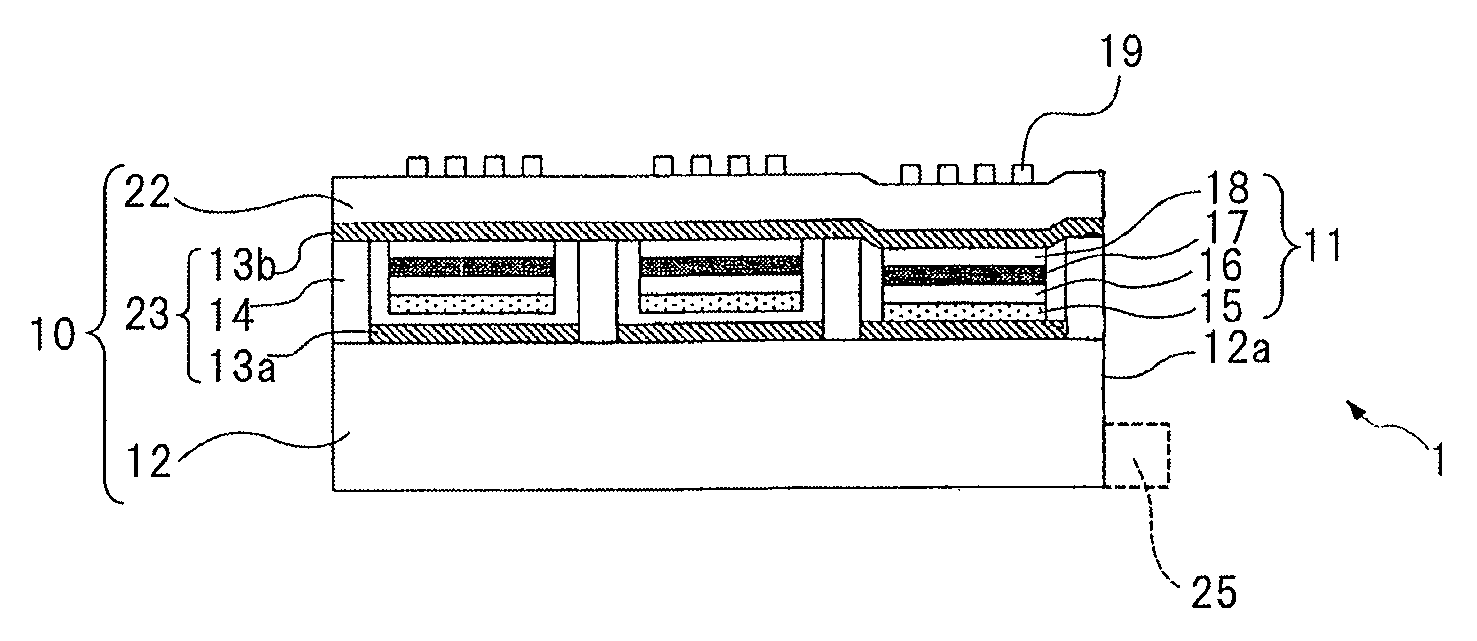
ActiveUS20130057938A1Increase brightnessImprove directivityTelevision system detailsProjectorsExit angleCharge carrier
The present invention includes light valve section (10) having substrate (22) through which light that exits plurality of optical connection mechanisms (23) that switch between the transmitting state and the shading state of light emitted from light emitting element (25) transmits and plasmon coupling section (11) that is arranged in light valve section (10) and that causes plasmon coupling to occur with light that exits light emitting element (25). Plasmon coupling section (11) includes carrier generation layer (15) that generates carriers with light that exits light emitting element (25) and plasmon excitation layer (17) that has a higher plasma frequency than the frequency of light that is generated in carrier generation layer (15) excited with the light emitted from light emitting element (25). Wave number vector conversion layer (19) is arranged on substrate (22). Wave number vector conversion layer (19) converts the light or surface plasmons generated in plasmon excitation layer (17) into light having a predetermined exit angle. Plasmon excitation layer (17) is sandwiched between first dielectric constant layer (16) and second dielectric constant layer (18).
Owner:NEC CORP
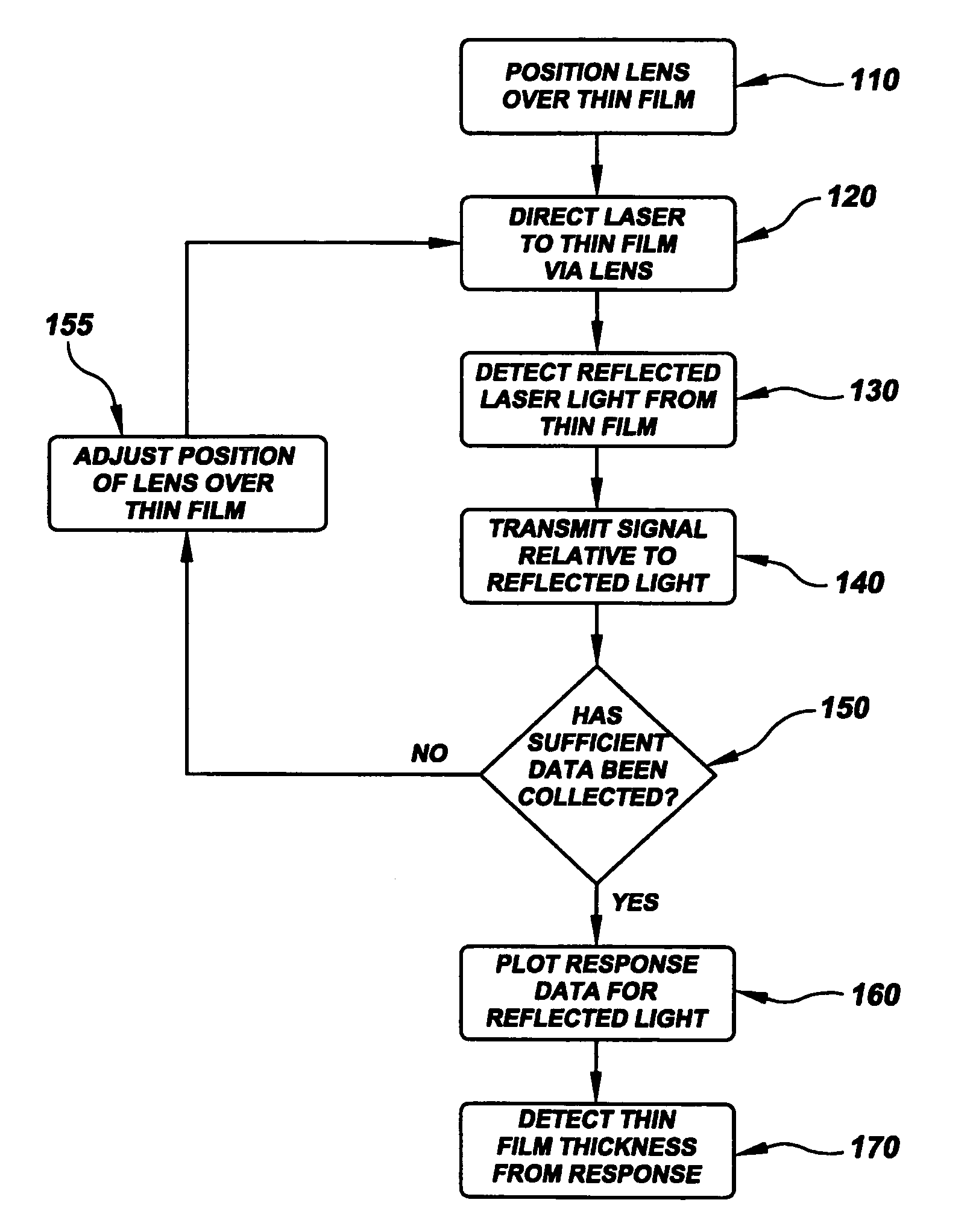
Dimension measurement approach for metal-material
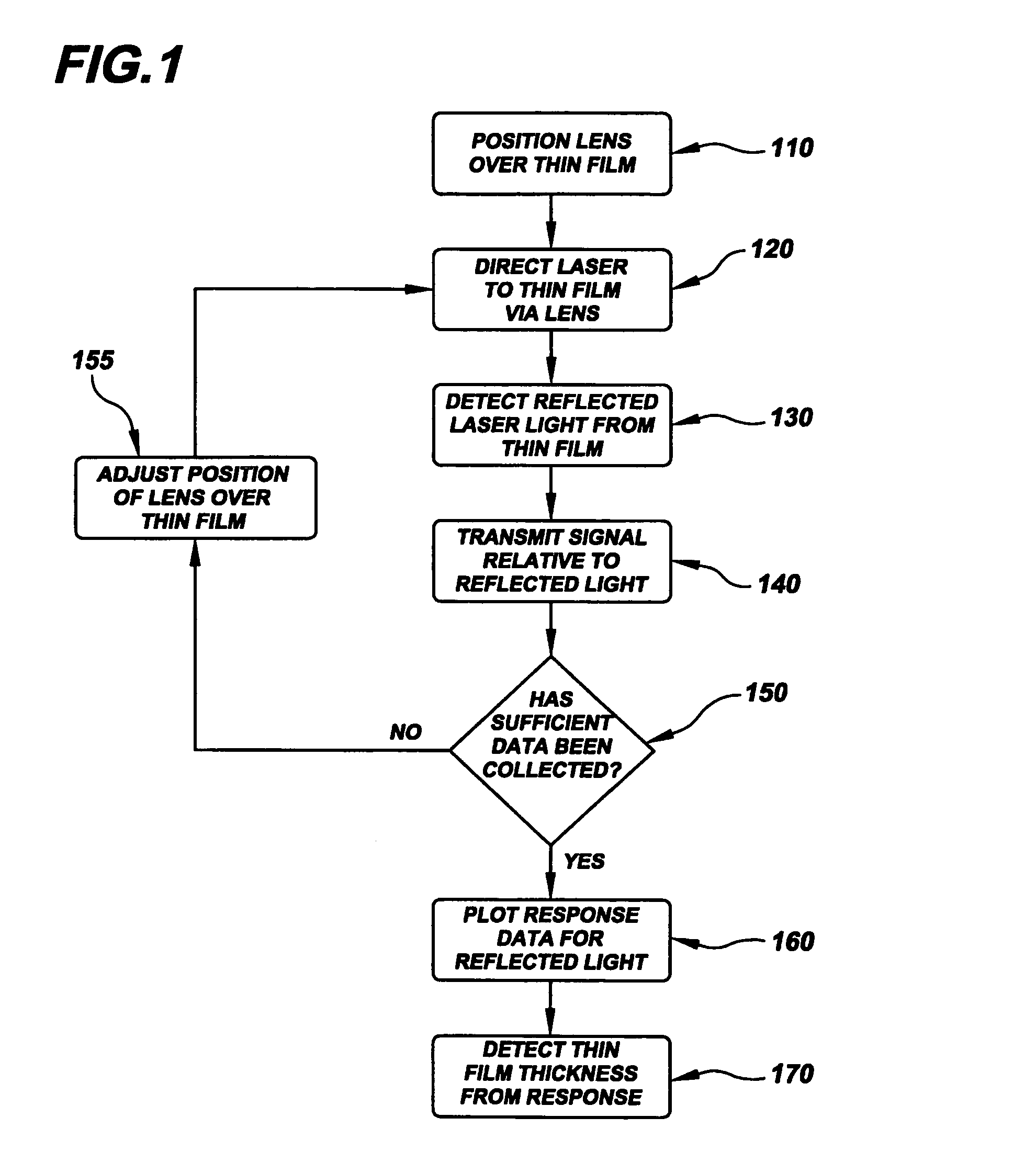
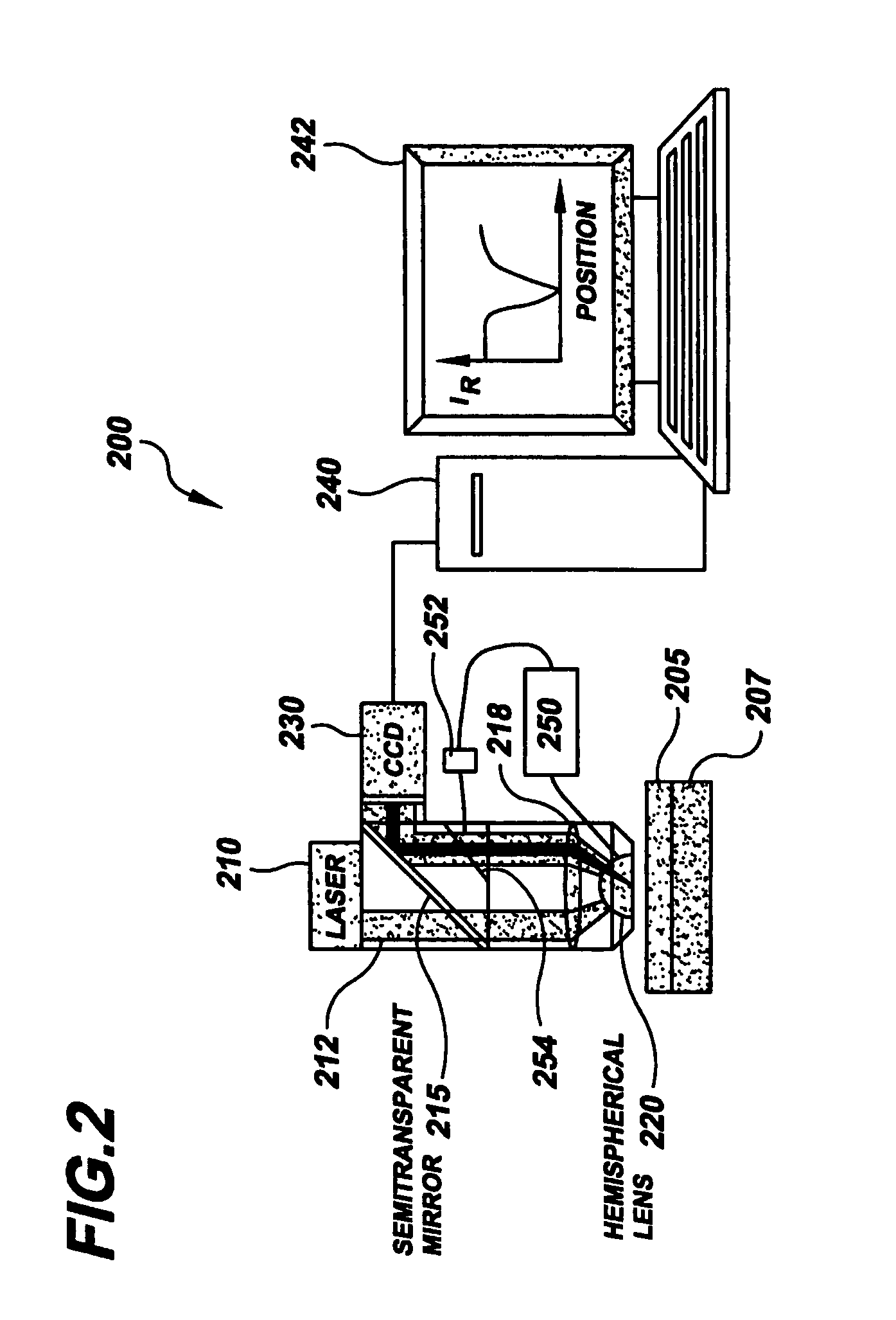
InactiveUS7088449B1Scattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansAngle of incidenceState dependent
Dimensional parameters of metal-containing structures such as films, interconnects, wires and stripes, and nanoparticles are detected using an approach involving plasmon-excitation and one or more metal-constituency characteristics of the metal-containing structures. According to an example embodiment of the present invention, plasmon-exciting light is used to excite plasmons in a structure, the plasmon excitation being responsive to the metal constituency. A characteristic of light reflected from the structure is then used to detect dimensional parameters of the structure. In one implementation, a characteristic of the reflected light that is related to the state of plasmon excitation in the structure is used to detect the dimensional parameters. In another implementation, the angle of incidence of the plasmon-exciting light is used in connection with an intensity-related characteristic of light reflected from structure to detect one or more dimensions of the structure. In still another implementation, the intensity of different wavelengths of the reflected light is used to determine one or more dimensions of the structure. With these approaches, the dimensions of a variety of structures such as metal films, interconnects, wires, and stripes are determined.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
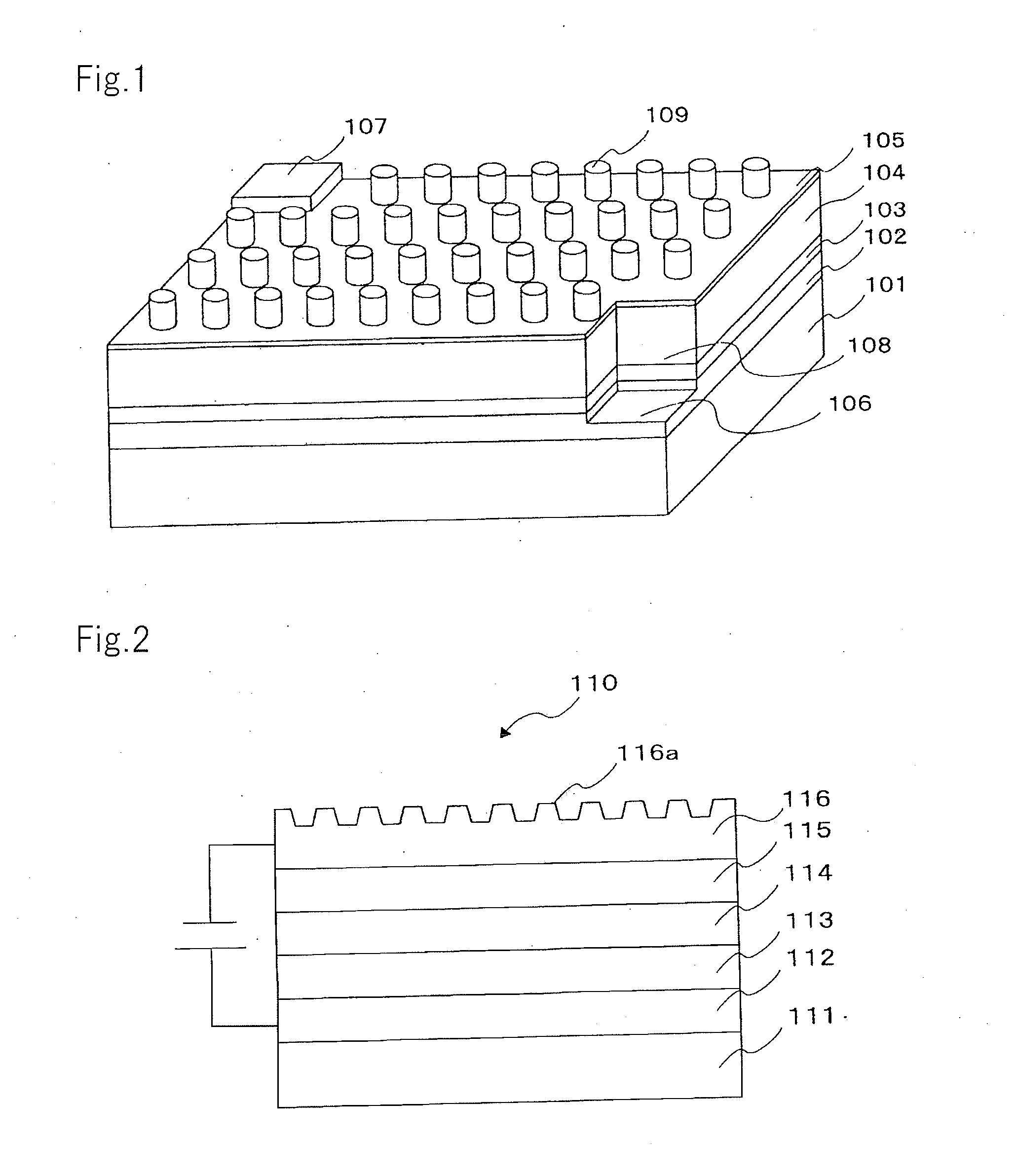
Light-emitting element, light-source apparatus and projection-type display apparatus
InactiveCN102792772AIncrease brightnessGood directionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesControl layerPlasmon excitation
Equipped is a light-source layer (4) and a directional-control layer (5) that incidences light from the light-source layer (4). The light-source layer (4) has a pair of hole-transport layers (11) disposed on a substrate (10), and an electron transport layer (13). The directional-control layer (5) includes plasmon excitation layer (15), laminated at a side opposite the substrate (10) side on the light-source layer (4), having a plasma frequency higher than a light frequency emitted from a light-source layer (4); and a wave number vector conversion layer (17) that converts and emits a surface plasmon generated by the plasmon excitation layer (15), to a predetermined angle of emergence. The plasmon excitation layer (15) is sandwiched between two layers having dielectric properties. An effective dielectric constant of an incidence side portion including an overall structure laminated on the light-source layer (4) side of the plasmon excitation layer (15) is higher than an effective dielectric constant of an emitting side portion that includes an overall structure laminated to a wave number vector conversion layer (17) of the plasmon excitation layer (15), and a medium that touches the wave number vector conversion layer (17).
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical element, light source device, and projection display device
Disclosed is an optical element which comprises: a light guide body into which the light from a light-emitting element enters; a carrier generation layer (6) which is provided to the light guide body and in which carriers are generated by the light from the light guide body; a plasmon excitation layer (8) that is arranged on the carrier generation layer (6) and has a plasma frequency higher than the frequency of the light that is generated when the carrier generation layer (6) is excited by the light from the light-emitting element; and a wave vector conversion layer (10) which is arranged on the plasmon excitation layer (8) and converts the light entering from the plasmon excitation layer (8) into light having a predetermined output angle. The plasmon excitation layer (8) is sandwiched between a low dielectric constant layer (7) and a high dielectric constant layer (9).
Owner:NEC CORP
Display element, display, and projection display device
InactiveCN102893199AIncrease brightnessImprove directionalityTelevision system detailsProjectorsPlasmon excitationPlasmon coupling
The present disclosures are provided with: a lightbulb unit (10) that has a substrate (22) that transmits light from a plurality of optical connection mechanisms (23) that switch the transmission and the blocking of light from a light-emitting element (25); and a plasmon coupling unit (11) that generates plasmon coupling by means of light entering from the light-emitting element (25) and that is disposed within the lightbulb unit (10). The plasmon coupling unit (11) has: a carrier generation layer (15) wherein a carrier is generated by means of light entering from the light-emitting element (25); and a plasmon excitation layer (17) that has a higher plasma frequency than the frequency of light arising when exciting the carrier generation layer (15) with the light of the light-emitting element (25). A wavevector conversion layer (19) that converts surface plasmons or light generated by the plasmon excitation layer (17) into light at a predetermined angle of emergence, and then radiates said light is provided on a substrate (22). The plasmon excitation layer (17) is sandwiched between a first dielectric layer (16) and a second dielectric layer (18).
Owner:NEC CORP
Display element, display device, and projection display device
ActiveUS20130027675A1Increase brightnessImprove directivityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesCharge carrierExit angle
The present invention includes light valve section (10) having a plurality of shutter mechanisms (14) that switch between a transmitting state and a shading state of light emitted from light emitting element (25); and substrate (16) through which light that exits plurality of shutter mechanisms (14) is transmitted. The display element also has plasmon coupling section (11) that causes plasmon coupling to occur with light that exits the light valve section (10). Plasmon coupling section (11) includes carrier generation layer (17) that generates carriers with incident light that exits light valve section (10), plasmon excitation layer (19) that has a higher plasma frequency than the frequency of light that is generated in carrier generation layer (17) excited with the light emitted from light emitting element (25), and wave number vector conversion layer (22) that converts the light or surface plasmons generated in plasmon excitation layer (19) into light having a predetermined exit angle. Plasmon excitation layer (19) is sandwiched between first dielectric constant layer (18) and second dielectric constant layer (22).
Owner:NEC CORP
Light emitting element, light source device, and projection display device
ActiveUS9028071B2Increase brightnessImprove directionalityMechanical apparatusProjectorsControl layerExit angle
Light source layer (4) includes substrate (10) and a pair of layers, namely, hole-transport layer (11) and electron-transport layer (13), formed on substrate (10). Directional control layer (5) includes plasmon excitation layer (15) stacked on a side of light source layer (4), which is opposite to the side of substrate (10) of light source layer (4), and which has a plasma frequency higher than a frequency of light output from light source layer (4), and wave vector conversion layer (17) stacked on plasmon excitation layer (15), which converts light incident from plasmon excitation layer (15) into light having a predetermined exit angle to output the light. Plasmon excitation layer (15) is sandwiched between low dielectric constant layer (14) and high dielectric constant layer (16).
Owner:NEC CORP
Ultra-wideband absorption heterojunction solar cell
ActiveCN106784334AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltra-widebandHeterojunction
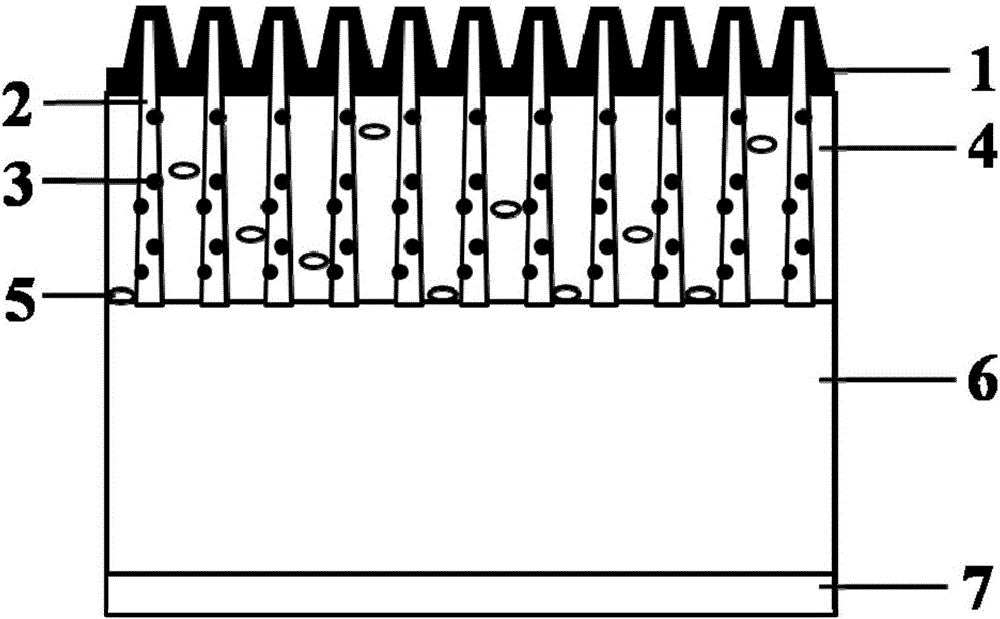
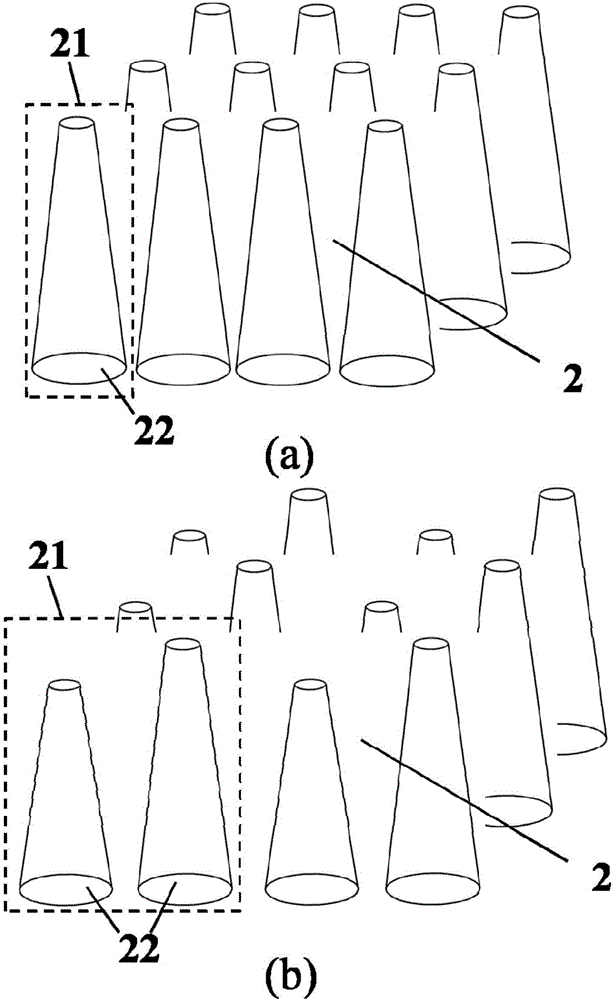
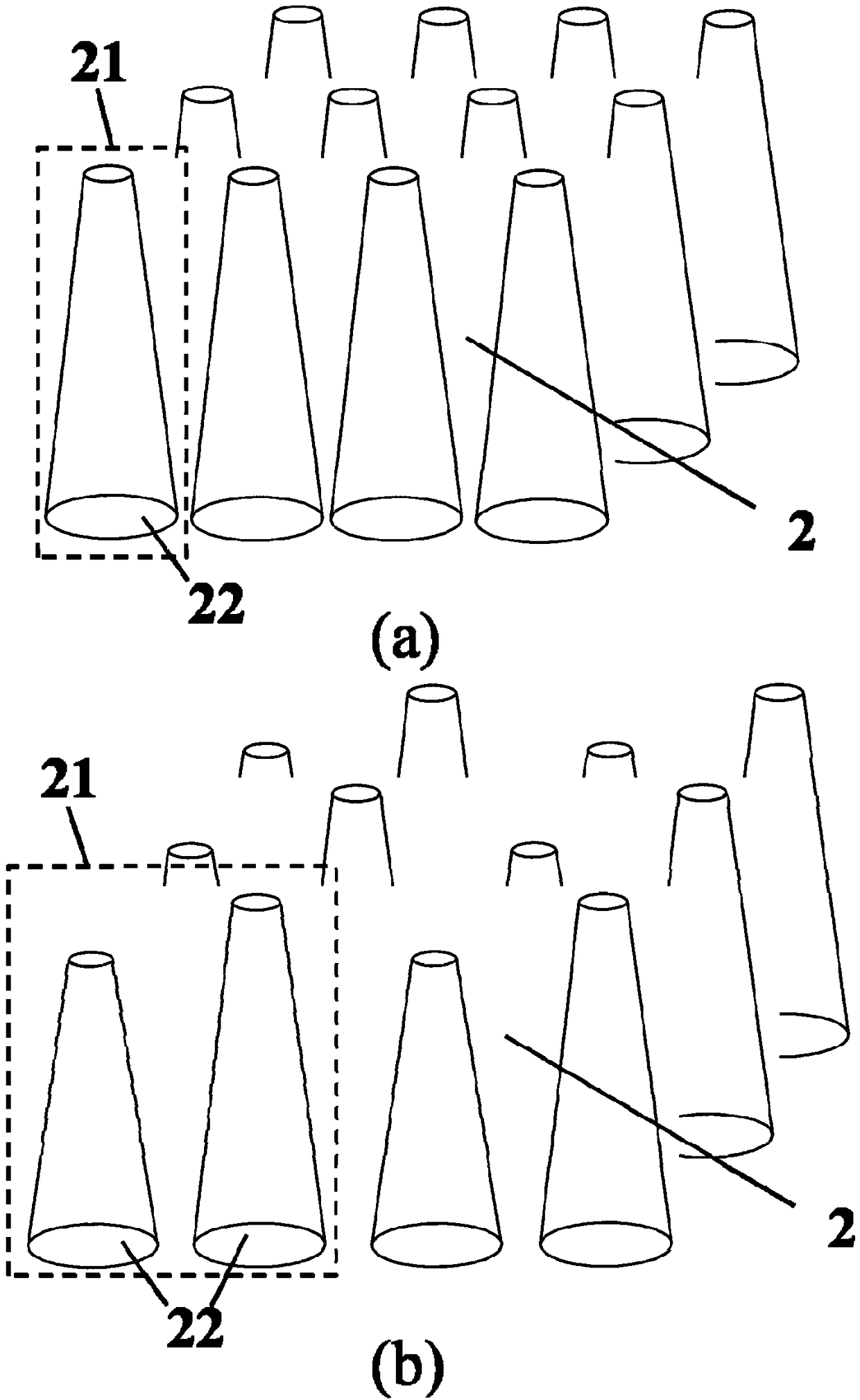
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband absorption heterojunction solar cell, which concretely and structurally comprises a transparent conducting front electrode, a two-dimensional nanocone array superstructure, a lower conversion nanostructure, a plasmon light trapping structure, an organic conducting polymer layer, a semiconductor material layer and a back electrode. For the cell, the lower conversion nanostructure is used for realizing ultraviolet light photon cutting; ultraviolet light is converted into visible light; the two-dimensional nanocone array superstructure with the tip plasmon excitation effect, and the plasmon light trapping structure are used; the light absorption of heterojunction formed by an organic conducting polymer and a semiconductor is enhanced at the visible light wave band; the heterojunction formed by the two-dimensional nanocone array superstructure and the semiconductor is used, so that a device absorbs and converts the infrared light smaller than the semiconductor band gap; the spectral response in the infrared spectrum band of the cell is enhanced. The cell has efficient photovoltaic conversion efficiency in the ultra-wide spectrum range from ultraviolet to infrared, and has the advantages of low cost, simple process, high specific efficiency and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Plasmon excitation by the gaussian-like core mode of a photonic crystal waveguide
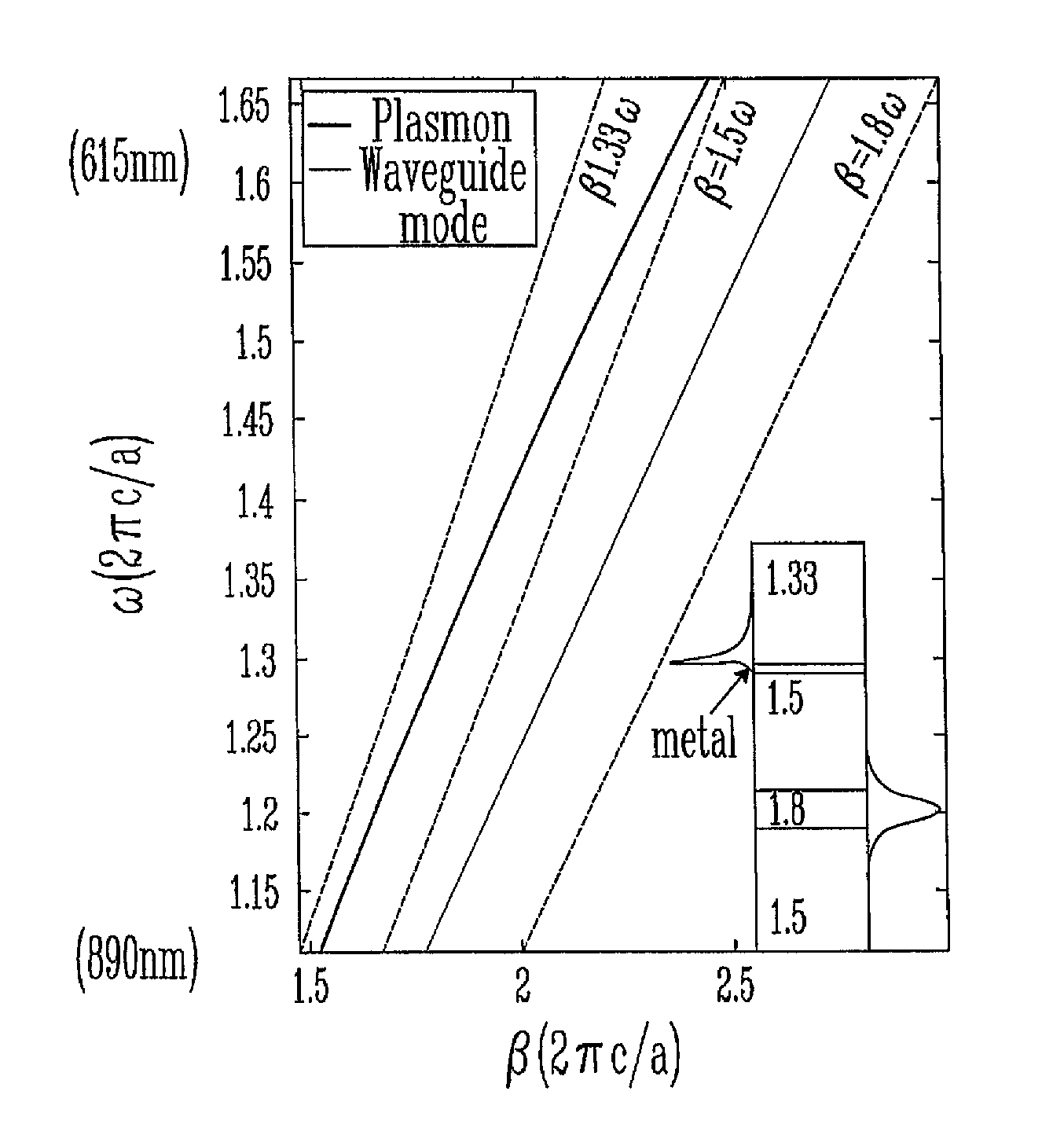
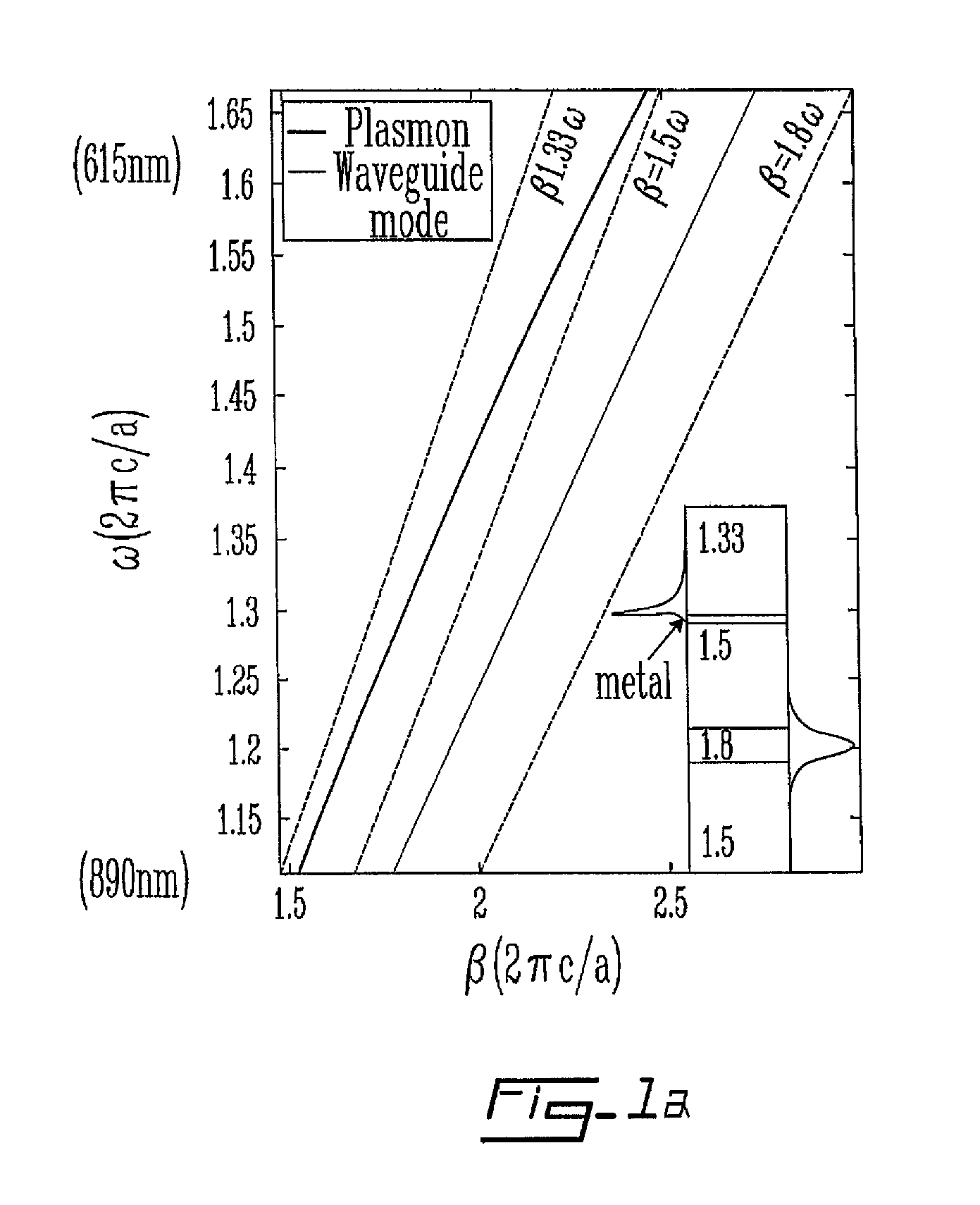
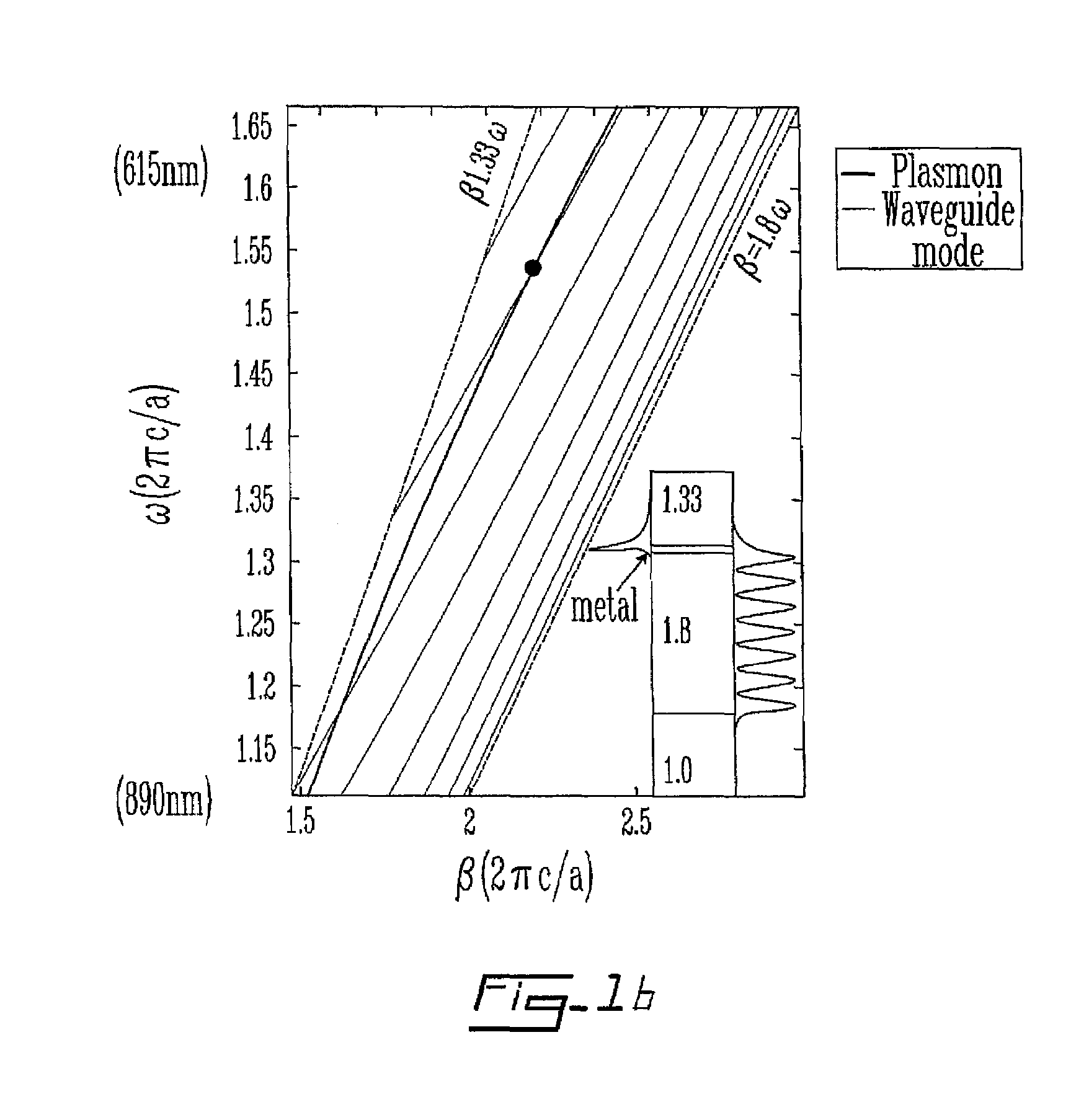
InactiveUS7460238B2Scattering properties measurementsOptical resonator shape and constructionPlasmon excitationElectromagnetic radiation
A sensor and method for surface plasmon resonance sensing, wherein a small variation of the refractive index of an ambient medium results in a large variation of loss of a sensing mode. The surface plasmon resonance sensor comprises an antiguiding waveguide including a core characterized by a refractive index and a reflector surrounding the core. The reflector has an external surface and is characterized by a band gap and a refractive index higher than the refractive index of the core. A coating is deposited on the external surface of the core, the coating defining with the ambient medium a coating / ambient medium interface. In operation, the coating is in contact with the ambient medium, and the antiguiding waveguide is supplied with an electromagnetic radiation to (a) propagate a mode for sensing having an effective refractive index lower than the refractive index of the core and higher than a refractive index of an ambient medium and (b) produce surface plasmons at the coating / ambient medium interface. The mode for sensing is phase-matched with the surface plasmons at a wavelength within the band gap and a variation of the refractive index of the ambient medium results in a variation of loss of the sensing mode to detect a characteristic of the ambient medium.
Owner:CORP DE LECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTREAL
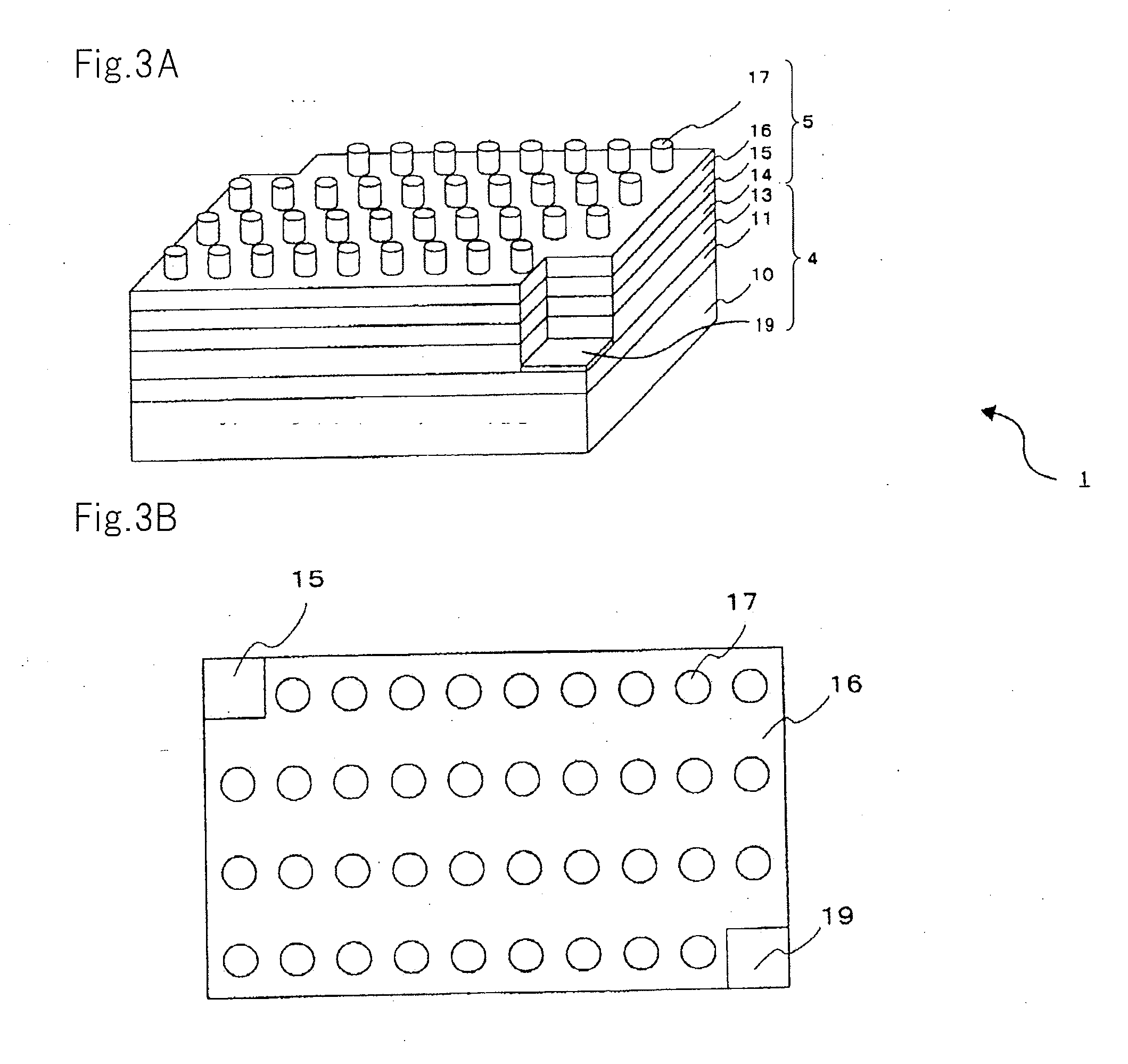
Information record mdeium, information recored method and information replay method
InactiveCN1474392AAchieve ultra-high density recordingMaterial nanotechnologyOptical flying-type headsElectricityHigh density
The information recording medium accosting to the preferred embodiment of the present invention achieves high-speed, high-density recording. The layer, in which ultra-particles made from an optical absorption metal, dielectric, or recording material are formed into regular arrays, is deposited. Resonant Plasmon excitation and resonance absorption of ultra-particles enable the edges of the recorded marks to be identified clearly and intense absorption to occur only in the given layer depending on the wavelength in the case of the multi-layer medium, achieving high-density, large-capacity recording.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Display element, display device, and projection display device
ActiveUS9110357B2Increase brightnessImprove directivityTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusPlasmonic couplingExit angle
The present invention includes light valve section (10) having substrate (22) through which light that exits plurality of optical connection mechanisms (23) that switch between the transmitting state and the shading state of light emitted from light emitting element (25) transmits and plasmon coupling section (11) that is arranged in light valve section (10) and that causes plasmon coupling to occur with light that exits light emitting element (25). Plasmon coupling section (11) includes carrier generation layer (15) that generates carriers with light that exits light emitting element (25) and plasmon excitation layer (17) that has a higher plasma frequency than the frequency of light that is generated in carrier generation layer (15) excited with the light emitted from light emitting element (25). Wave number vector conversion layer (19) is arranged on substrate (22). Wave number vector conversion layer (19) converts the light or surface plasmons generated in plasmon excitation layer (17) into light having a predetermined exit angle. Plasmon excitation layer (17) is sandwiched between first dielectric constant layer (16) and second dielectric constant layer (18).
Owner:NEC CORP
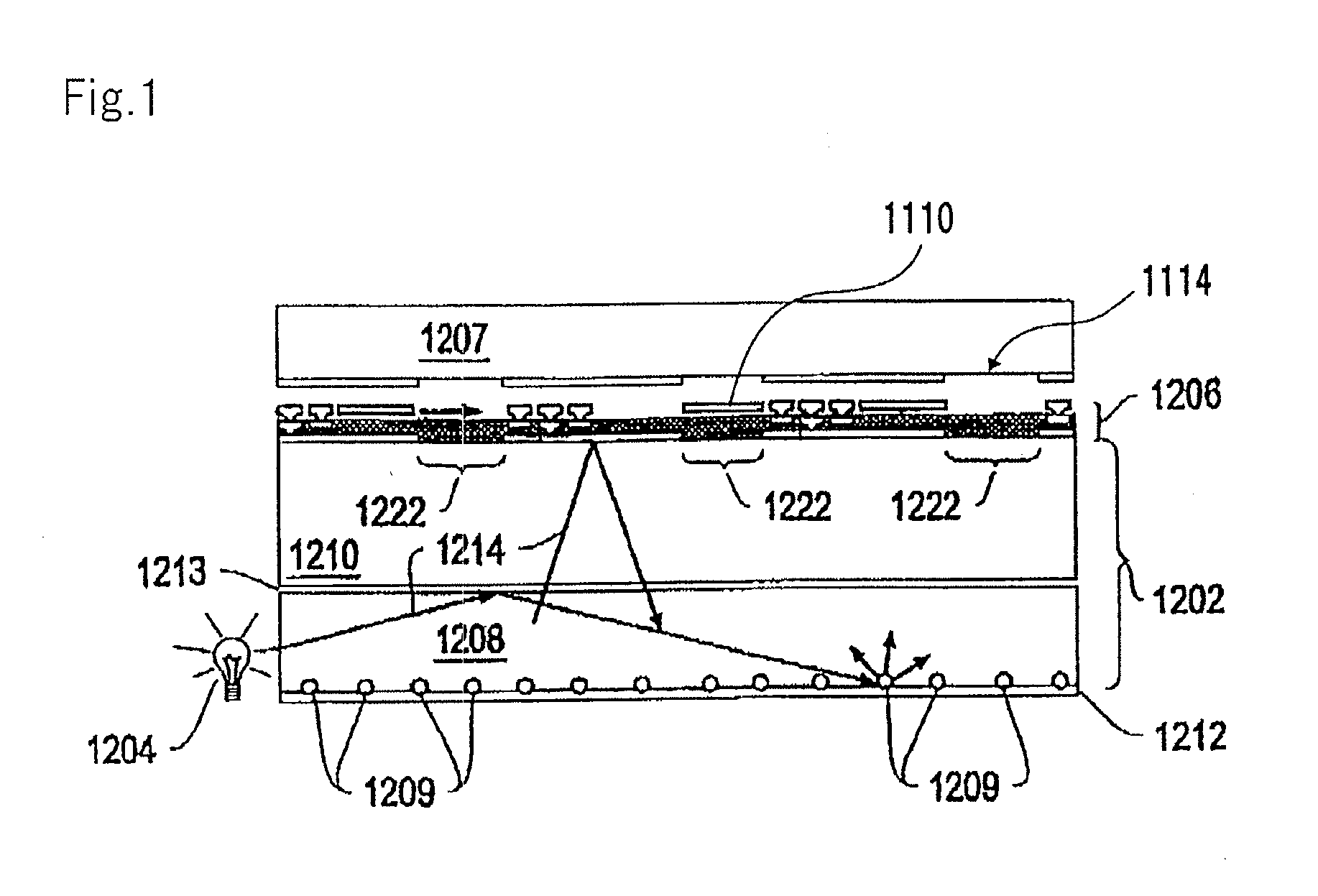
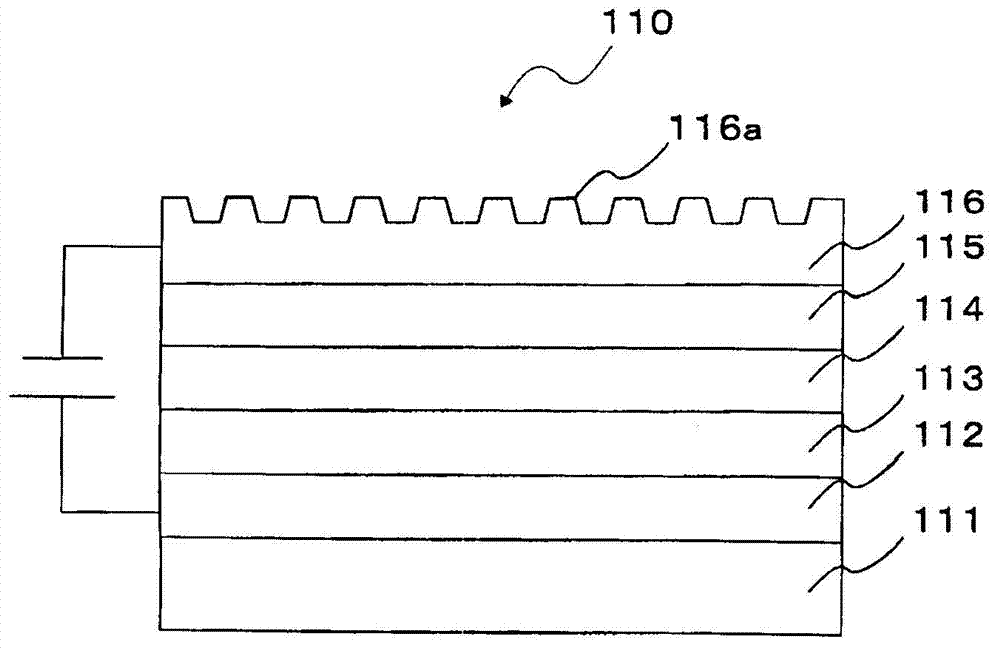
Optical element, illumination device, image display device, method of operating optical element
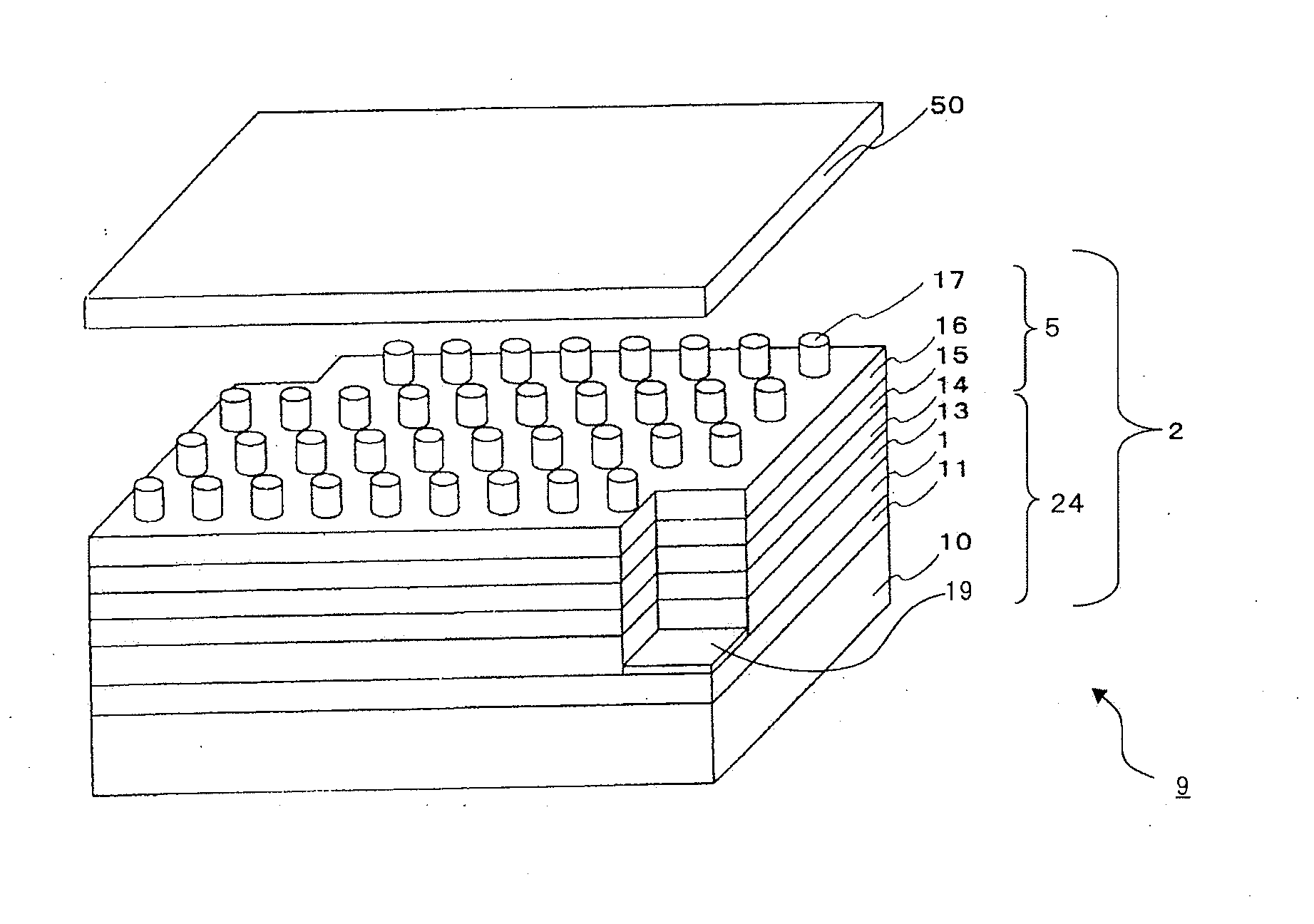
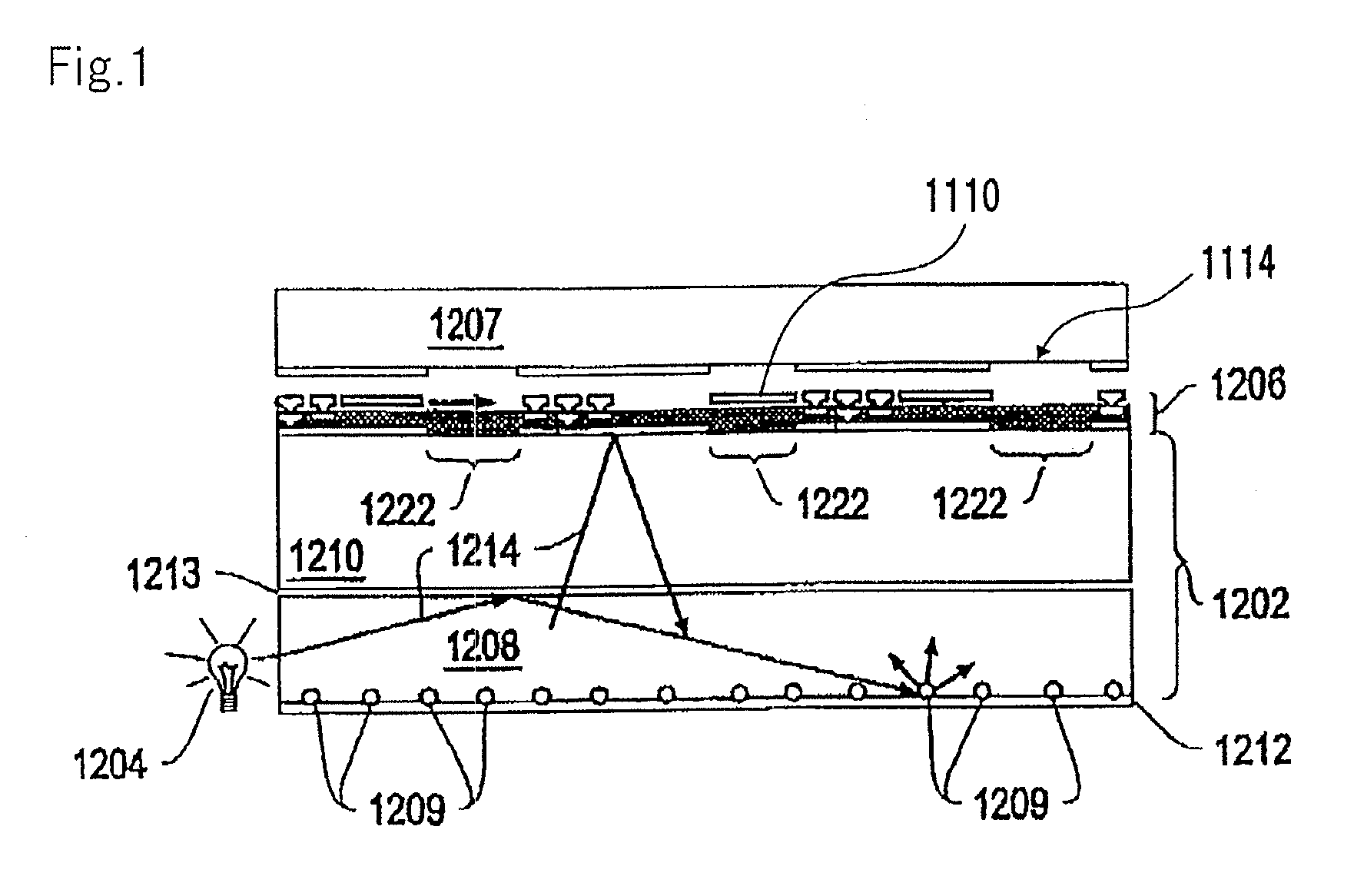
InactiveUS20150301282A1Effective radiationImprove directivityProjectorsSolid-state devicesPlasmon excitationParticle physics
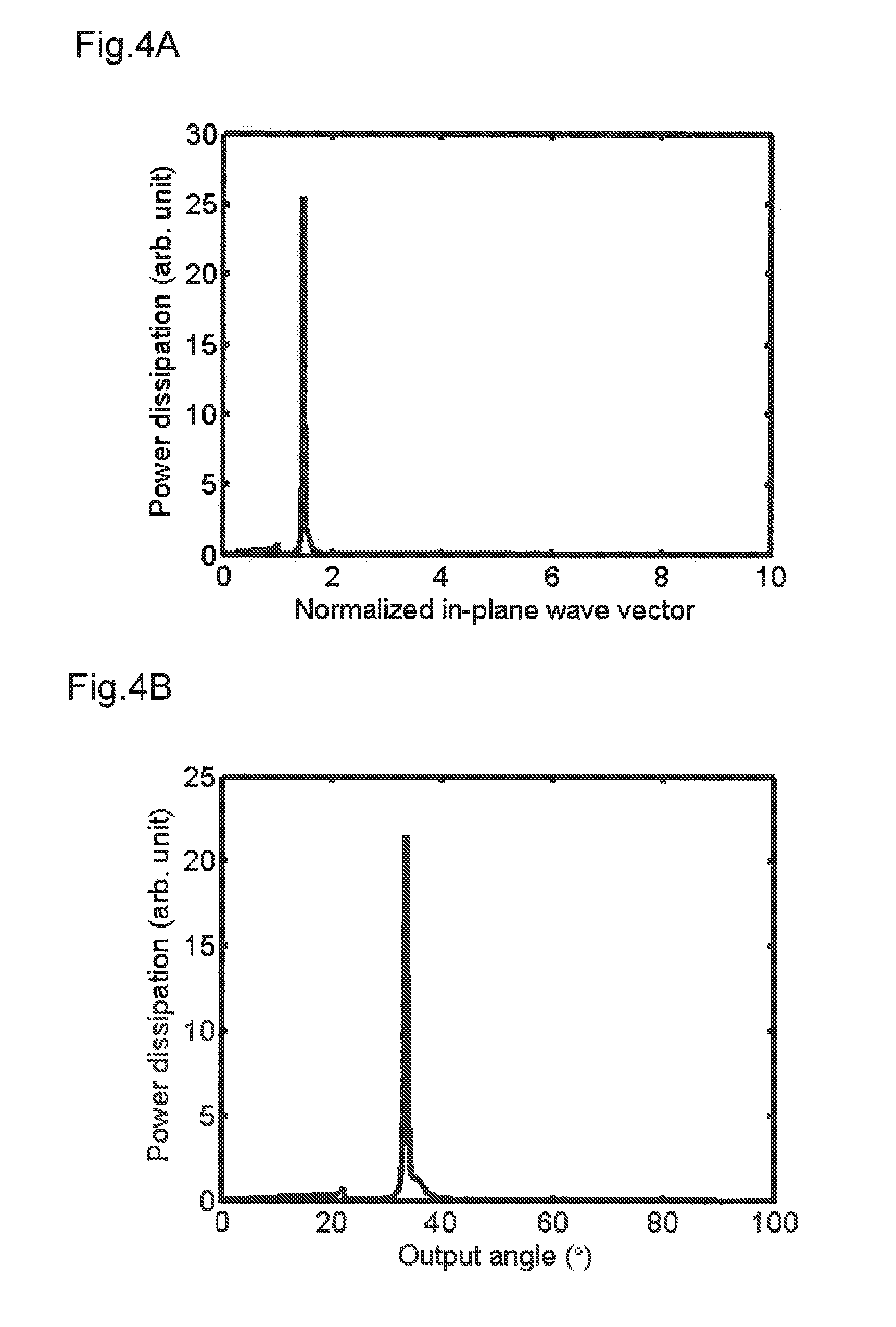
Provided is an optical element that highly efficiently radiates light with high directivity at low etendue. The optical element includes a light emission layer (103) generating an exciton to emit light, a plasmon excitation layer (105) having a higher plasma frequency than a light emission frequency of the light emission layer (103), an output layer (107) converting light or a surface plasmon generated on an upper surface of the plasmon excitation layer (105) into light with a predetermined output angle to output the light, and a dielectric layer (102). In the optical element, a real part of an effective dielectric constant with respect to the surface plasmon is higher in an upper side portion than the plasmon excitation layer (105) than in a lower side portion than the plasmon excitation layer (105); a dielectric constant with respect to the light emission frequency of the light emission layer (103) is higher in a lowest layer than in a layer adjacent to a lower side of the plasmon excitation layer (105); and assuming that a radiation angle of a surface plasmon-derived highly directional radiation from the plasmon excitation layer (105) to the output layer (107) side is θout,spp and a radiation angle of an optical waveguide fundamental mode-derived highly directional radiation is θout,light, an absolute value of a difference between the θout,spp and the θout,light is less than 10 degrees.
Owner:NEC CORP
Methods of controlling nanoparticle growth
The invention provides new types of plasmon-driven growth mechanism for silver nanostructures involving the fusion of triangular nanoprisms. This mechanism, which is plasmon excitation-driven and highly cooperative, produces bimodal particle size distributions. In these methods, the growth process can be selectively switched between bimodal and unimodal distributions using dual beam illumination of the nanoparticles. This type of cooperative photo-control over nanostructure growth enables synthesis of monodisperse nanoprisms with a preselected edge length in the 30-120 nm range simply by using one beam to turn off bimodal growth and the other (varied over the 450-700 nm range) for controlling particle size.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Display element, display device, and projection display device
ActiveUS9039201B2Increase brightnessImprove directivityMechanical apparatusStatic indicating devicesPlasmonic couplingExit angle
The present invention includes light valve section (10) having a plurality of shutter mechanisms (14) that switch between a transmitting state and a shading state of light emitted from light emitting element (25); and substrate (16) through which light that exits plurality of shutter mechanisms (14) is transmitted. The display element also has plasmon coupling section (11) that causes plasmon coupling to occur with light that exits the light valve section (10). Plasmon coupling section (11) includes carrier generation layer (17) that generates carriers with incident light that exits light valve section (10), plasmon excitation layer (19) that has a higher plasma frequency than the frequency of light that is generated in carrier generation layer (17) excited with the light emitted from light emitting element (25), and wave number vector conversion layer (22) that converts the light or surface plasmons generated in plasmon excitation layer (19) into light having a predetermined exit angle. Plasmon excitation layer (19) is sandwiched between first dielectric constant layer (18) and second dielectric constant layer (22).
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical element, light source device, and projection display device
Disclosed is an optical element that includes: a light guide body into which light from a light-emitting element enters; carrier generation layer (6) formed in the light guide body, in which carriers are generated by the light from the light guide body; plasmon excitation layer (8) stacked on carrier generation layer (6), which has a plasma frequency higher than the frequency of light generated when carrier generation layer (6) is excited by the light from the light-emitting element; and wave vector conversion layer (10) stacked on plasmon excitation layer (8), which converts light incident from plasmon excitation layer (8) into light having a predetermined exit angle to output the light. Plasmon excitation layer (8) is sandwiched between low dielectric constant layer (7) and high dielectric constant layer (9).
Owner:NEC CORP
WO3-x photocatalyst with visible light region LSPR absorption as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111495355AAchieve absorptionRealize regulationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPtru catalystPlasmon excitation
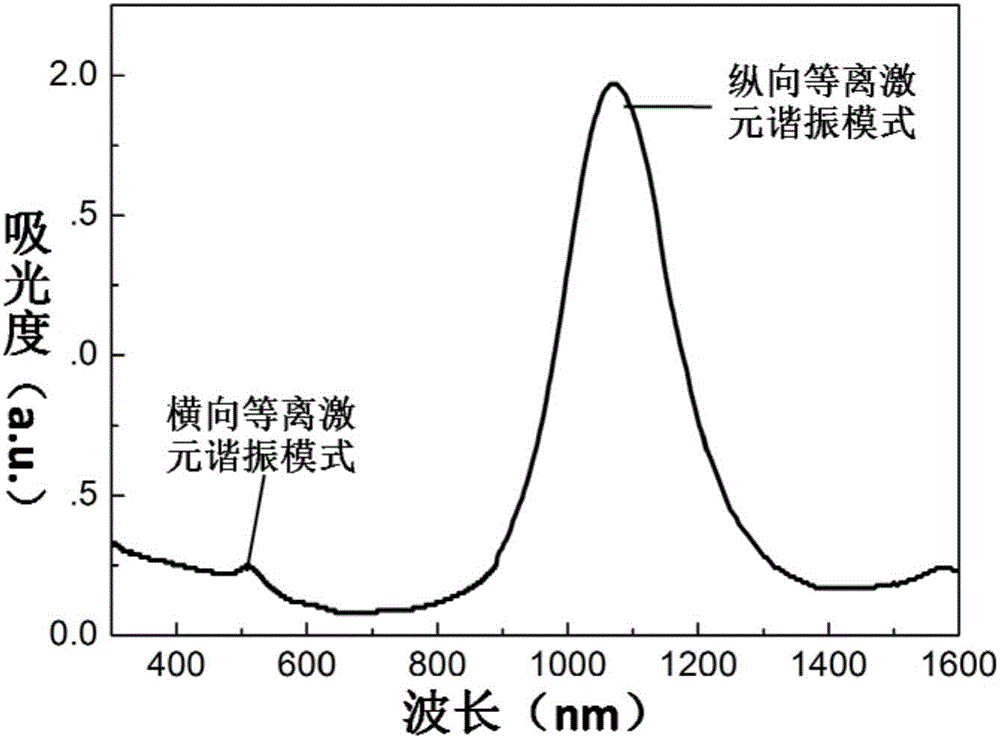
The invention discloses a WO3-x nanosheet photocatalyst with visible light region LSPR absorption as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Tungsten powder, hydrogen peroxide and isopropanol are used as raw materials, a solvothermal method is adopted for preparing a nano tungsten oxide hydrate, then high-temperature reduction is performed to obtain the WO3-x nanosheet photocatalyst,so that LSPR absorption and regulation of WO3-x in a visible light region are achieved, wherein the absorption peak wavelength is smaller than 520 nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, mixing tungsten powder and a hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution, reacting, adding isopropanol, and heating the reactants to 150-170 DEG C in a high-pressure kettle for reaction to obtain a nano tungsten oxide hydrate; and S2, adding the nano tungsten oxide hydrate in a reducing atmosphere, and carrying out heat treatment to obtain the WO3-x nanosheet photocatalyst with visible light region LSPR absorption. The obtained catalyst has strong LSPR absorption in the whole visible light region, thermal charges generated by plasmon excitation can directly catalyze and degrade organic matters, and the catalytic degradation rate of methyl orange can reach 93%.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
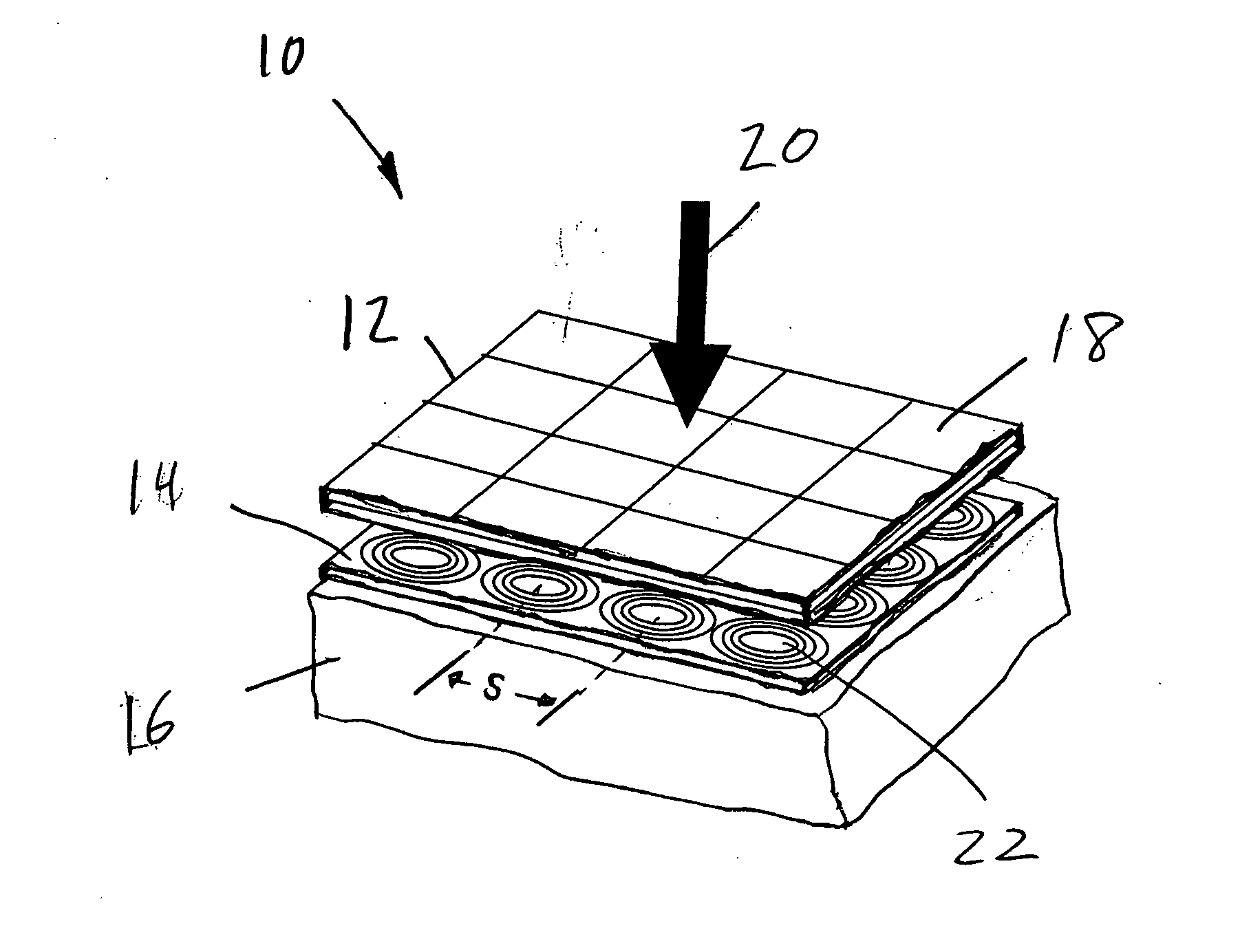
Artificial surface plasmon transmission line excitation apparatus based on micro-strip line interface
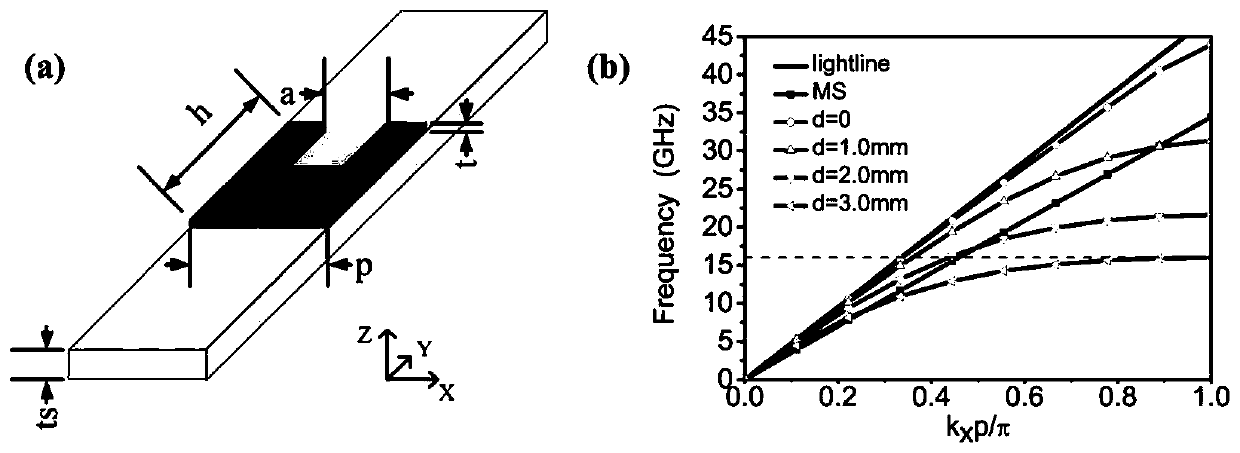
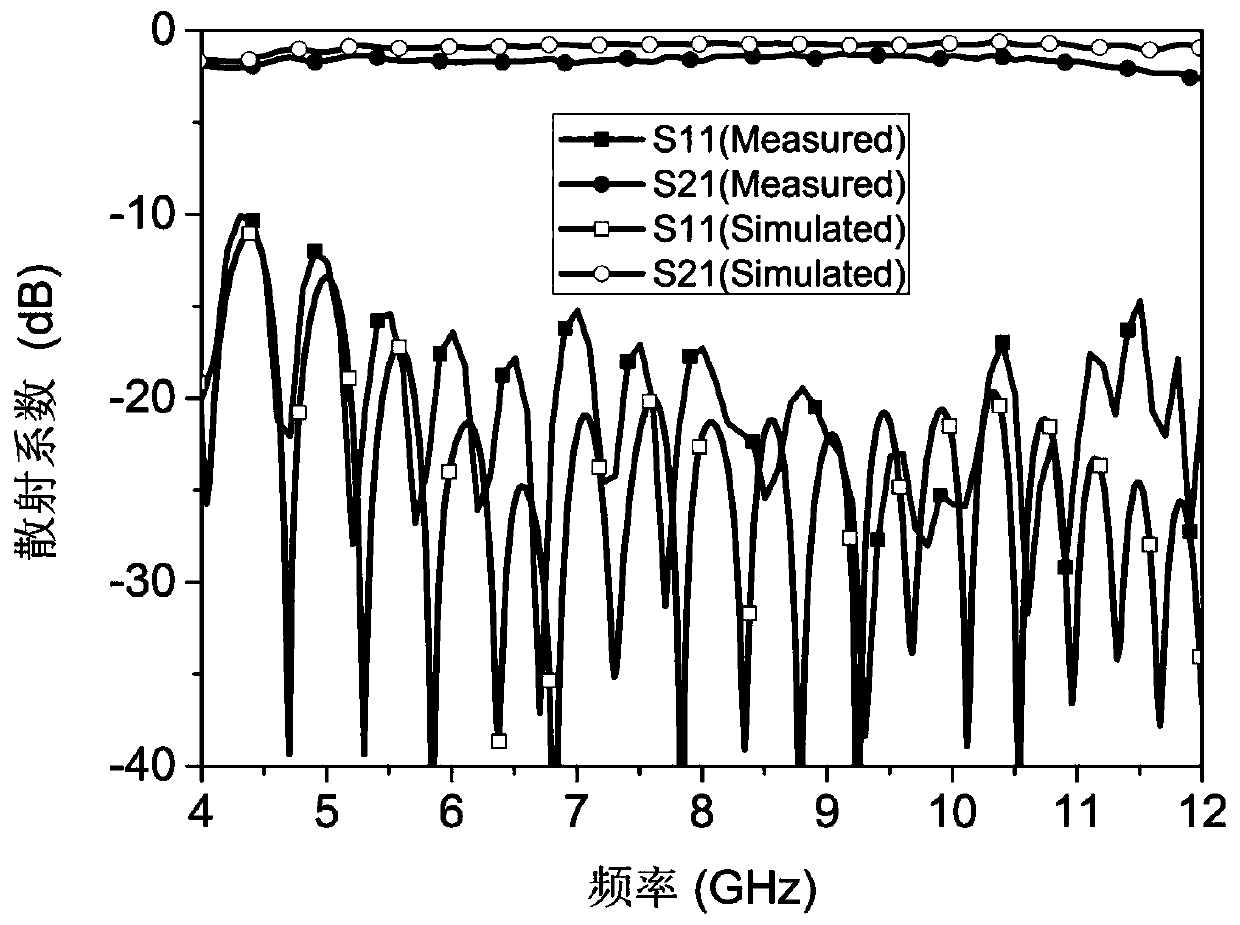
The invention discloses an artificial surface plasmon transmission line excitation apparatus based on a micro-strip line interface. The apparatus is characterized in that the apparatus comprises a metal ground, a dielectric substrate is arranged above the metal ground, a metal strip is arranged on the dielectric substrate, a rectangular groove with a gradually changing depth is formed in one end of the metal strip, and asymmetric exponential metal flaring ground structures with different curvatures are arranged on the metal ground below the two sides of the metal strip correspondingly. The artificial surface plasmon excitation apparatus provided by the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency, simple design, compact structure, easiness in processing and the like. Moreover, theexcitation apparatus provided by the invention is high in universality and easy to transplant, is suitable for other single side slotted or double side slotted single-conductor artificial surface plasmon transmission lines, and has a wide application prospect in the field of novel microwave integrated circuits and devices.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical element, light source device, and projection display device
Disclosed is an optical element that includes: carrier generation layer (16) in which carriers are generated by light from light guide body (12) into which light from a light-emitting element enters; plasmon excitation layer (17) that has a plasma frequency higher than the frequency of light generated when carrier generation layer (16) is excited by light from the light-emitting element; and wave vector conversion layer (18) that converts surface plasmon generated by plasmon excitation layer (17) light having a predetermined exit angle to output the light. Plasmon excitation layer (17) is sandwiched between two layers having dielectric properties. The effective dielectric constant of the incident side portion of plasmon excitation layer (17) including an entire structure stacked above light guide body (12) side is higher than that of the exit side portion of plasmon excitation layer (17) including the entire structure stacked above wave vector conversion layer (18) side and the medium in contact with wave vector conversion layer (18).
Owner:NEC CORP
An ultra-broadband absorption heterojunction solar cell
ActiveCN106784334BImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionUltra-wideband
The invention discloses a heterojunction solar cell with ultra-broadband absorption. The specific structure includes a transparent conductive front electrode, a two-dimensional nanocone array superstructure, a down-conversion nanostructure, a plasmon light-trapping structure, and an organic conductive polymer layer. , a semiconductor material layer and a back electrode. The cell uses down-conversion nanostructures to achieve photon cutting of ultraviolet light, converting ultraviolet light into visible light; using a two-dimensional nanocone array superstructure with tip plasmon excitation effect, and plasmon light trapping structure, in visible light The wavelength band enhances the light absorption of the heterojunction formed by the organic conductive polymer and the semiconductor; and uses the heterojunction formed by the two-dimensional nanocone array superstructure and the semiconductor to make the device absorb and convert infrared light smaller than the semiconductor band gap, and enhance the battery infrared The spectral response within the band. The battery has high photoelectric conversion efficiency in the ultraviolet to infrared ultra-wide spectrum range, and has the advantages of low cost, simple process, high specific efficiency and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A Plasmon Resonant Wavelength Division Multiplexer
ActiveCN107884874BAchieve resonant couplingReflect the coupling effectOptical waveguide light guideResonant cavityMultiplexer
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Optical element, light-source apparatus, and projection-type display apparatus
A light-source apparatus is provided with: a carrier generation layer (16) wherein carriers are generated by light coming from a light-guiding body (12), into which light enters from light-emitting elements; a plasmon excitation layer (17) that has a plasma frequency higher than the frequency of light generated when the carrier generation layer (16) is excited by the light of the light-emitting elements; and a wave vector conversion layer (18) that converts surface plasmon generated by the plasmon excitation layer (17) into light having a prescribed angle of emergence, and radiates the light. The plasmon excitation layer (17) is sandwiched in between two layers having dielectricity. The effective dielectric constant of the incident-side section including the whole structure laminated at the light-guiding body (12) side of the plasmon excitation layer (17) is higher than the effective dielectric constant of the exit-side section, which includes the whole structure laminated at the wave vector conversion layer (18) side of the plasmon excitation layer (17) and the medium that is in contact with the wave vector conversion layer (18).
Owner:NEC CORP
A surface plasmon electric excitation source with a medium-metal near-field coupling structure and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN104269472BImprove excitation efficiencyImprove quantum efficiencySemiconductor devicesSemiconductor quantum wellsDielectric
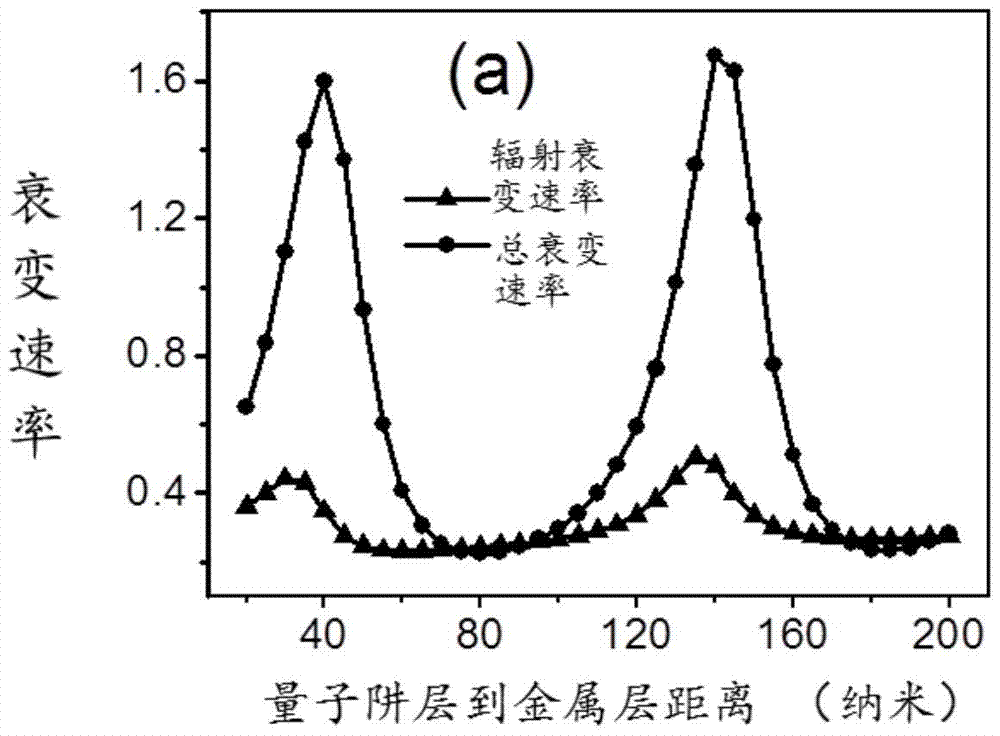
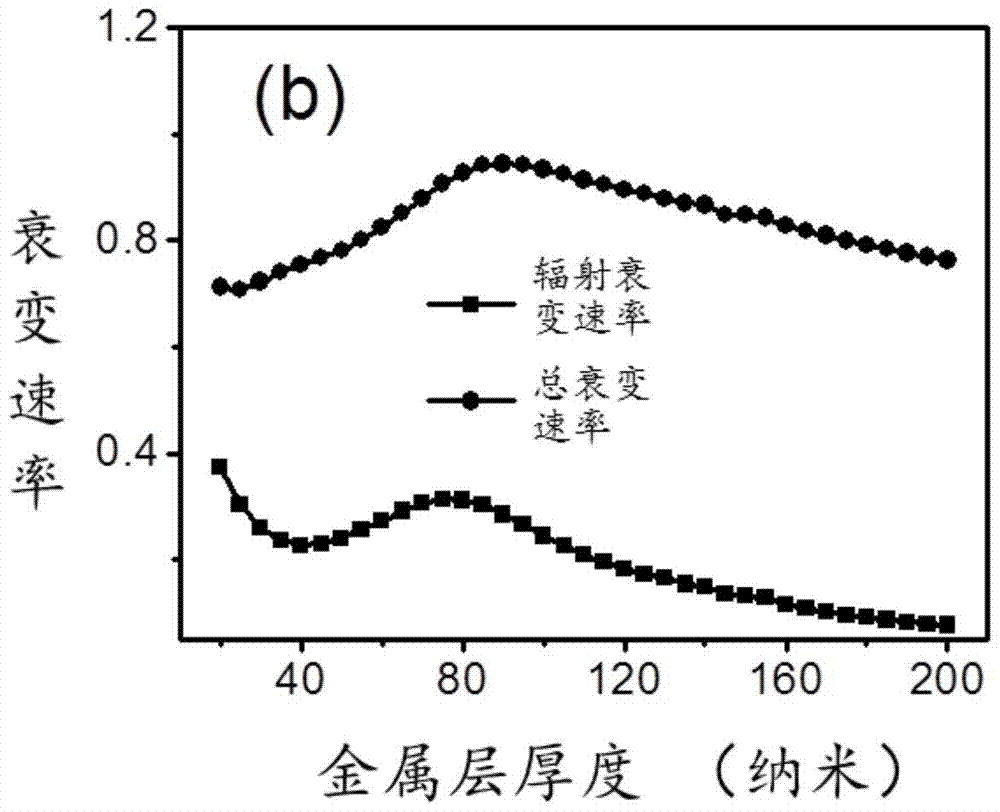
The invention discloses a surface plasmon excimer electrically-induced excitation source with a medium-metal near field coupling structure. The surface plasmon excimer electrically-induced excitation source comprises a substrate, semiconductor quantum well epitaxial layer, a metal layer and a coupling output structure. The semiconductor quantum well epitaxial layer is loaded on the surface of the substrate. The metal layer is loaded on the surface of the semiconductor quantum well epitaxial layer. The coupling output structure is located in the metal layer. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the surface plasmon excimer electrically-induced excitation source. The method includes the steps that the semiconductor quantum well epitaxial layer is grown on the substrate; a device unit is etched on the grown semiconductor quantum well epitaxial layer; the metal layer is deposited on the etched device unit; the coupling output structure is manufactured in the deposited metal layer. According to the surface plasmon excimer electrically-induced excitation source, the semiconductor quantum well material is adopted to serve as an active medium, based on the near field coupling principle, the quantum efficiency is high, the light emitting wavelength range is wide, the excitation efficiency is high, the manufacturing process is simple, integration is conducted conveniently, and the surface plasmon excimer electrically-induced excitation source and the manufacturing method have great research value and application prospects.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com