Patents
Literature
51results about How to "Requires low equipment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
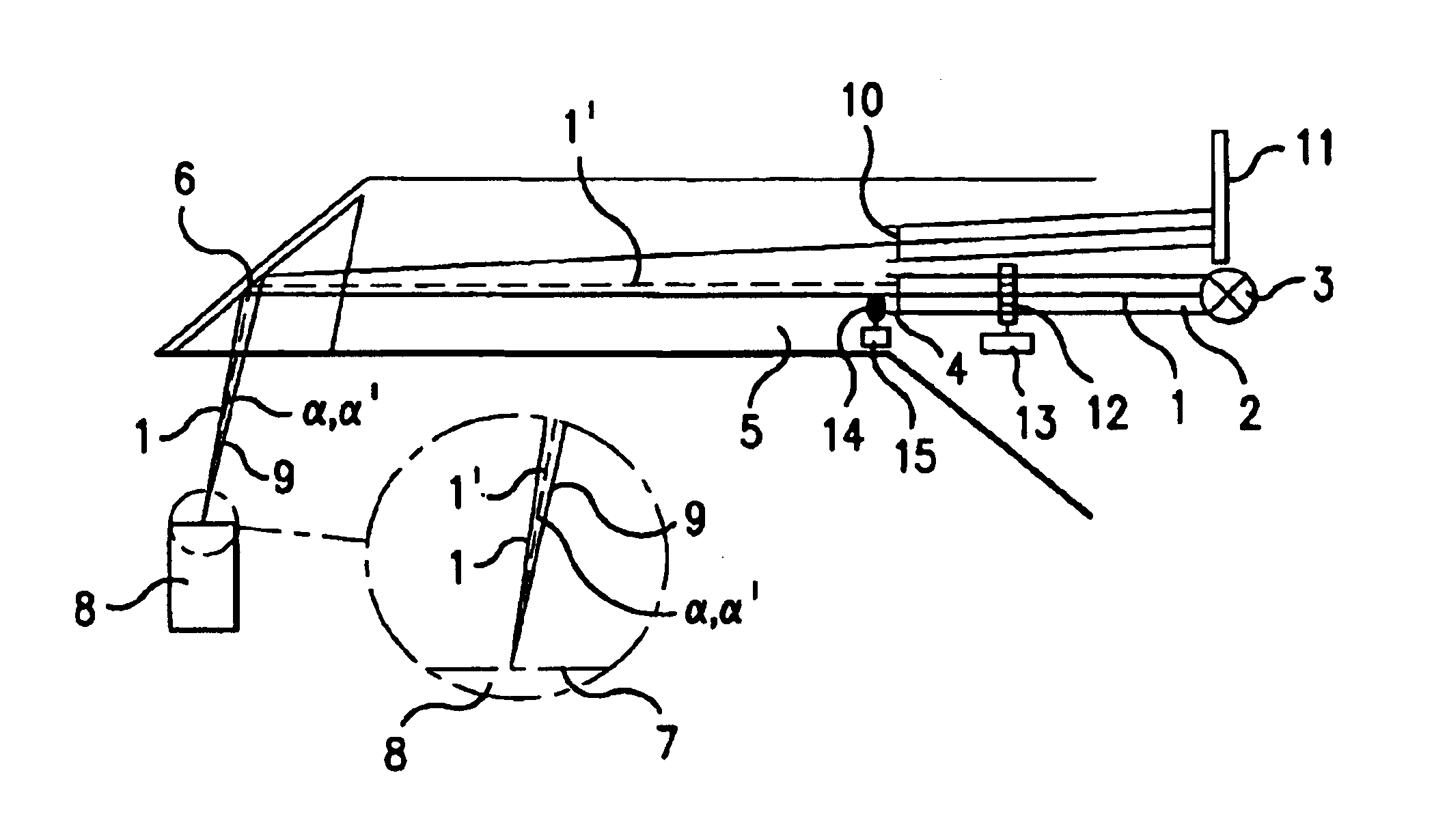
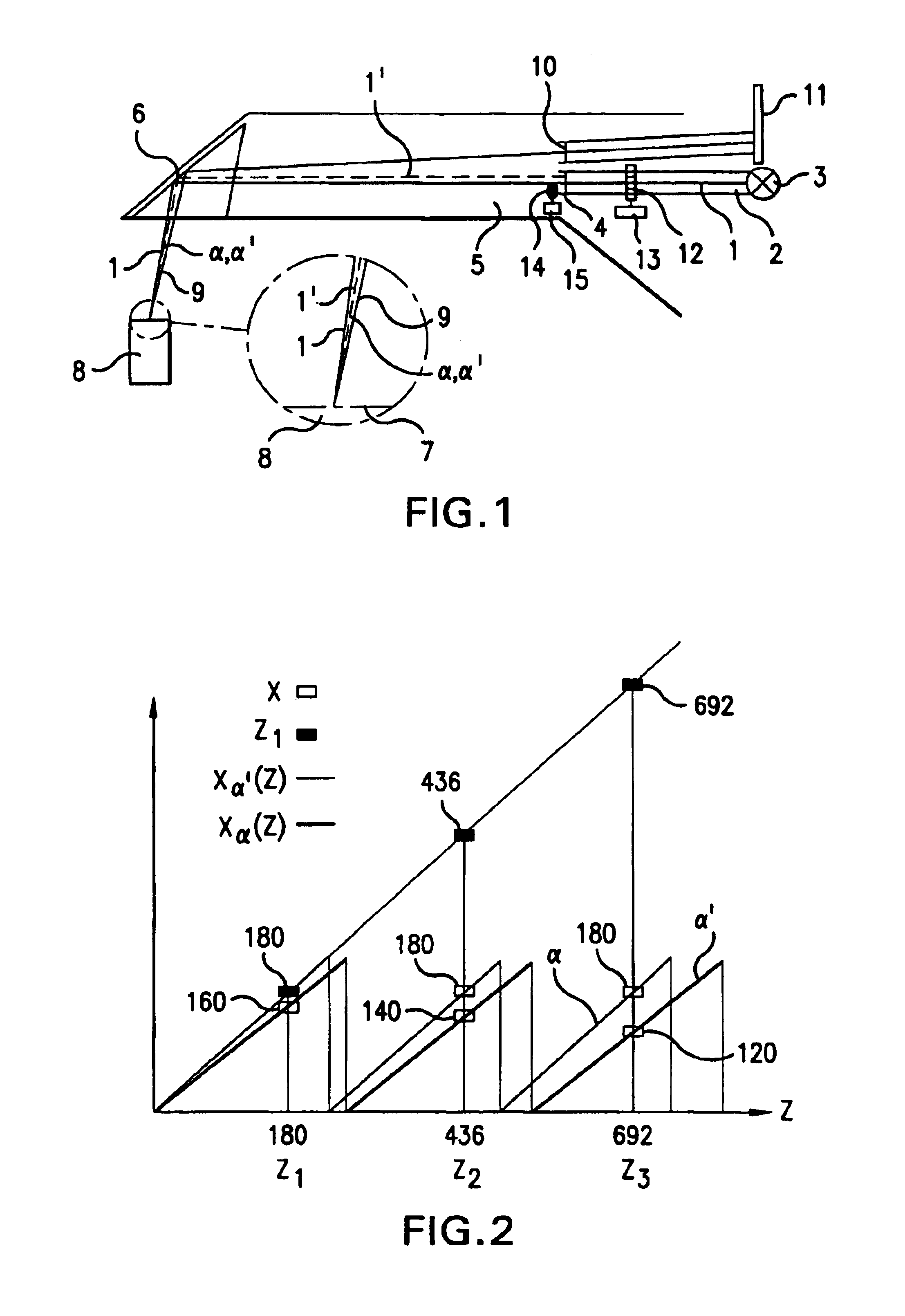
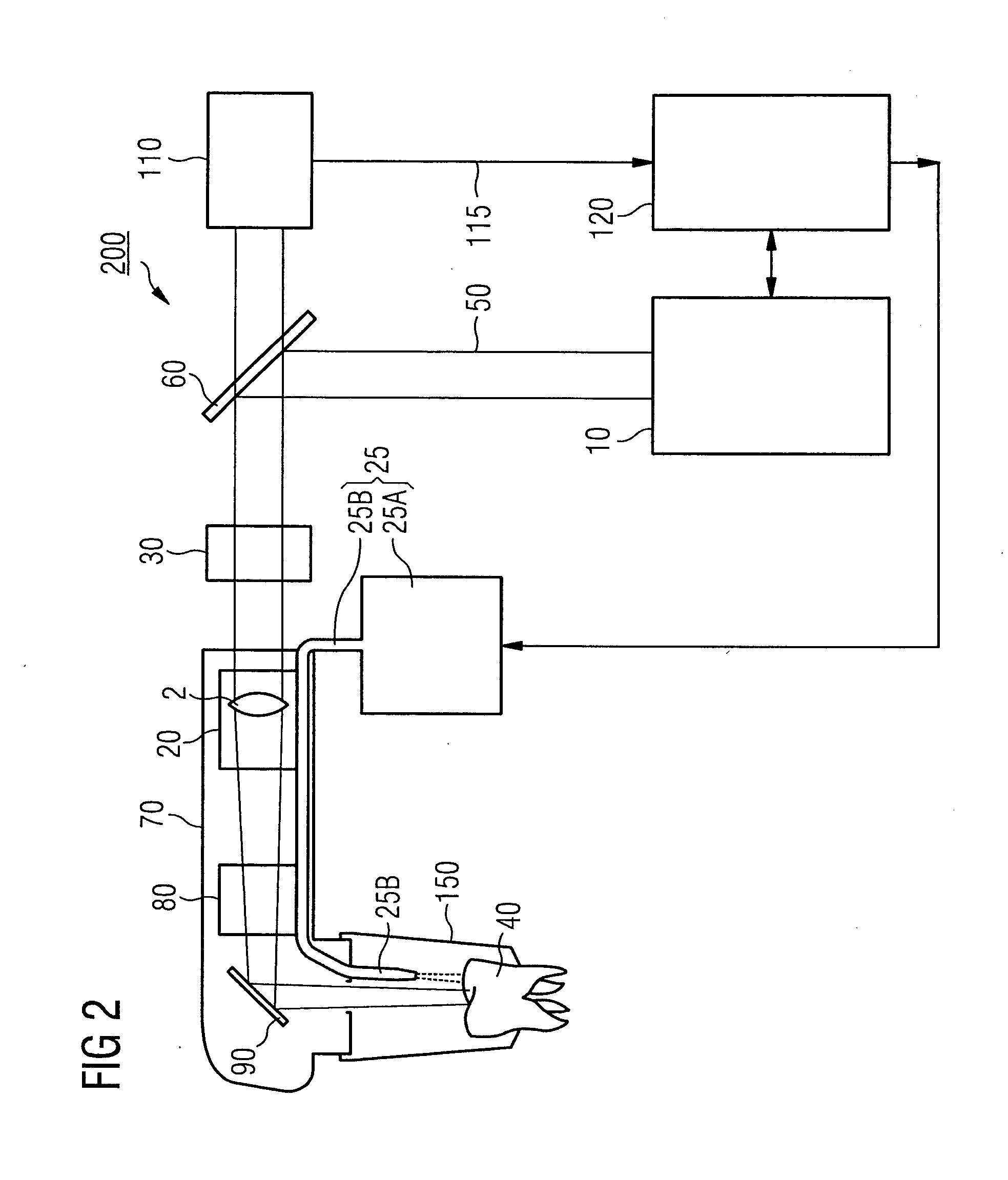
3-D camera for recording surface structures, in particular for dental purposes
InactiveUS6885464B1Reduced measurement accuracyRequires low equipmentImpression capsOptical rangefindersTriangulationLight beam
A 3-D camera and a method for recording surface structures on an object of interest by triangulation, in particular for dental purposes. The camera provides for producing a group of light beams in order to illuminate the object of interest via a projection optical path, an image sensor for receiving light back-scattered by the object of interest via an observation optical path, and provides, in the projection optical path, for producing a pattern projected onto the object of interest. To avoid ambiguities in the event of large height differences, the camera provides for the projection optical path and / or the observation optical path for altering the triangulation angle, which is defined by the angle between the centroid beam of the projection optical path and the centroid beam of the observation optical path. The proposed process involves the taking of at least two 3-D measurements of the same object of interest with different triangulation angles.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
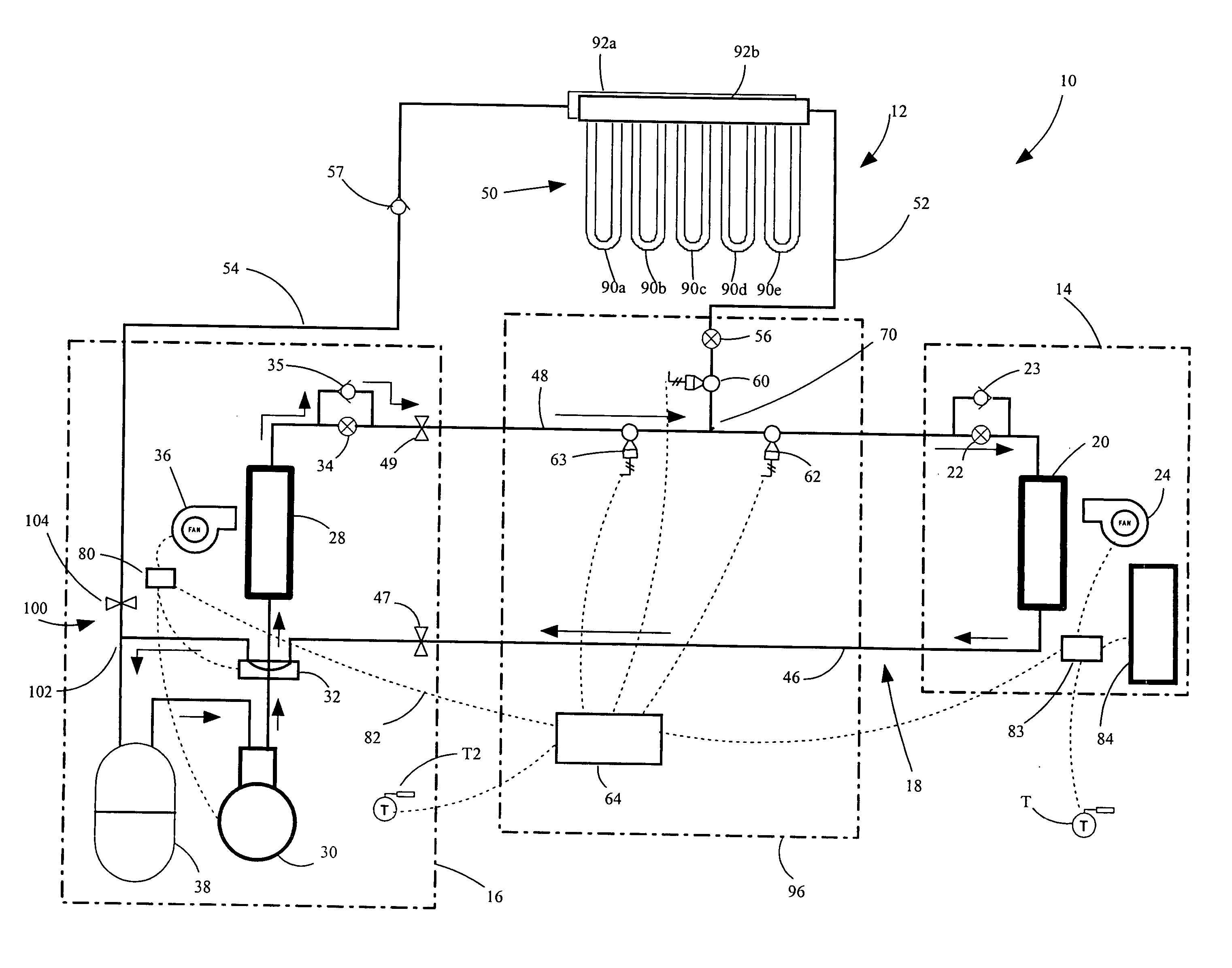
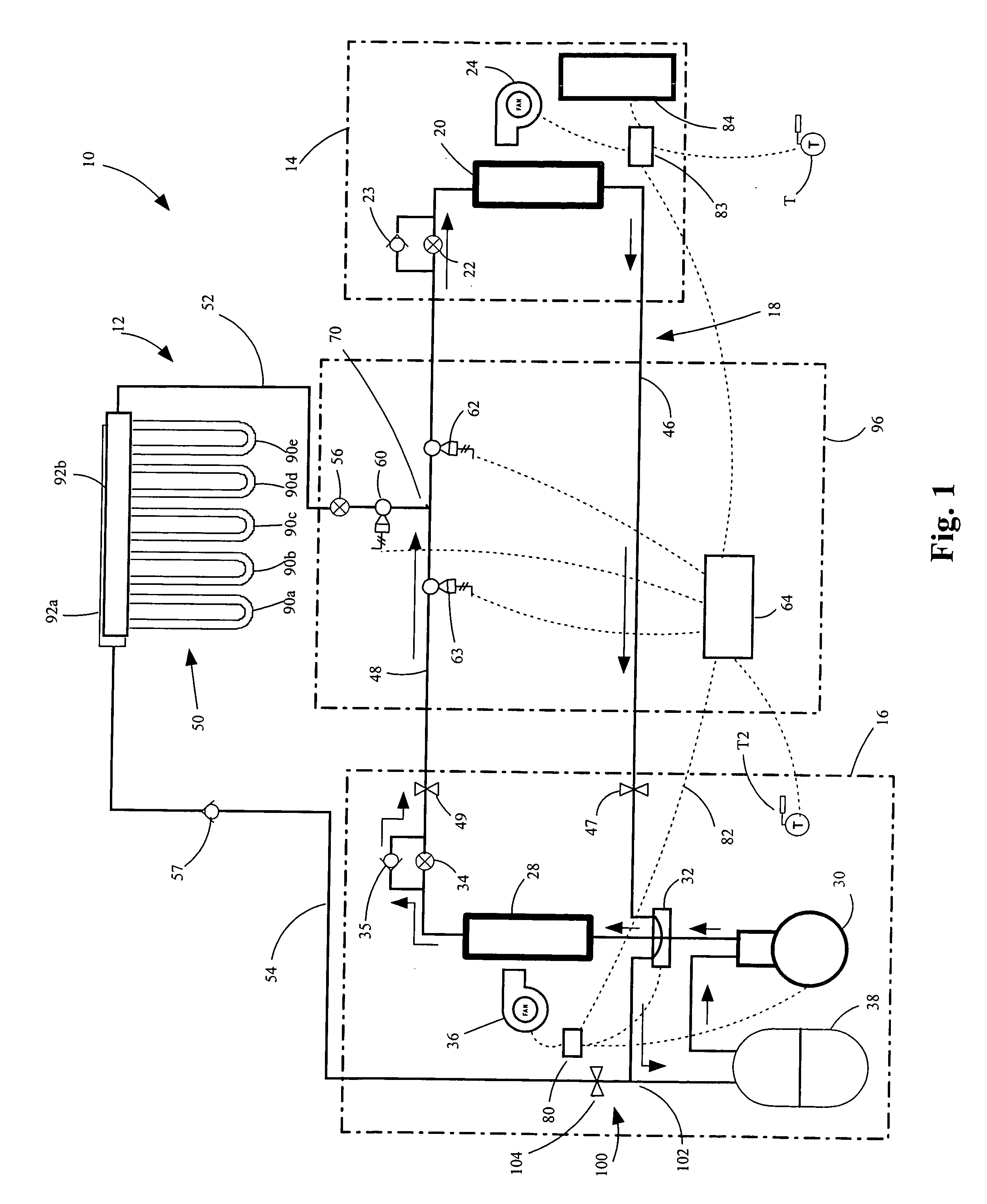
Hybrid heating and cooling system
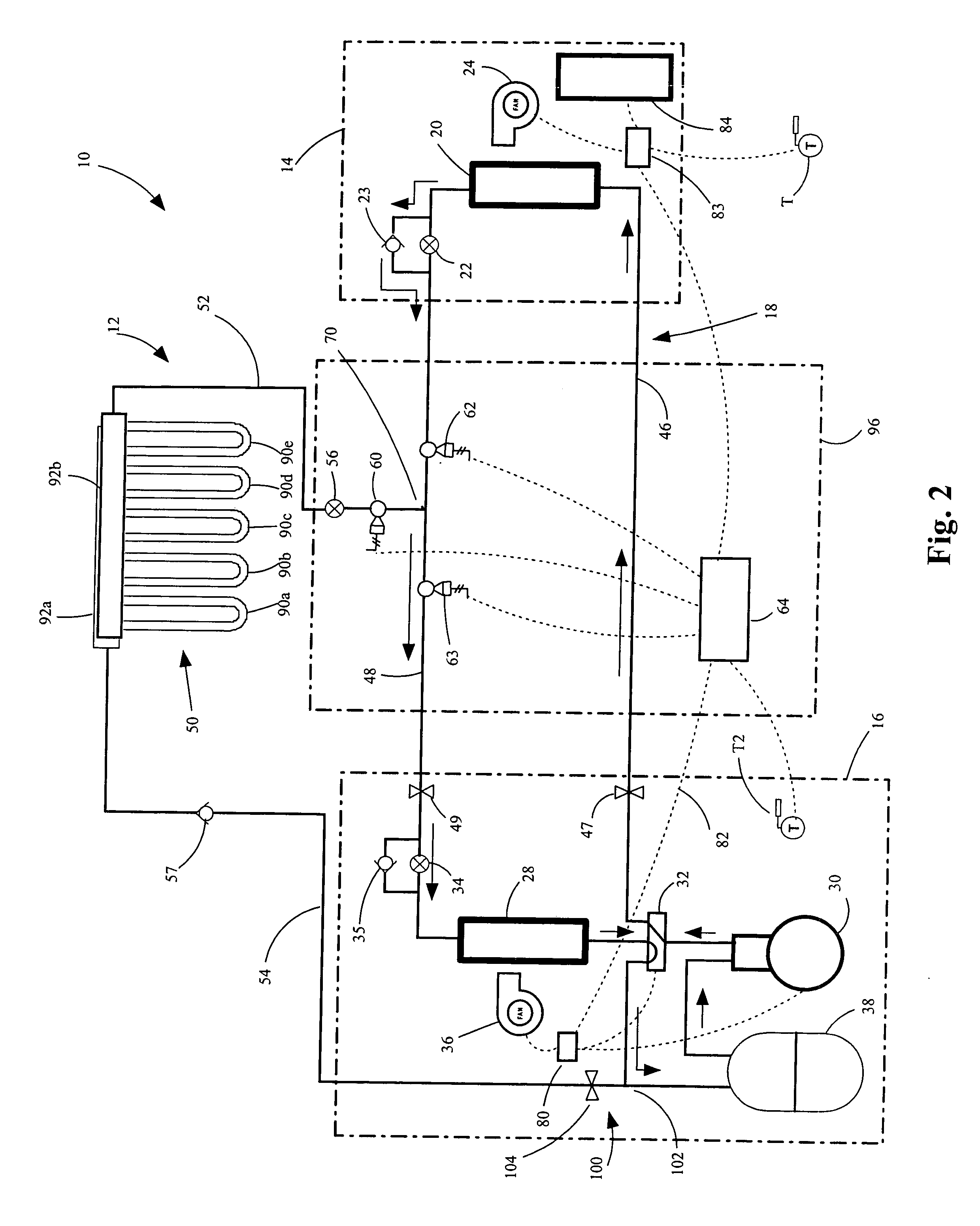
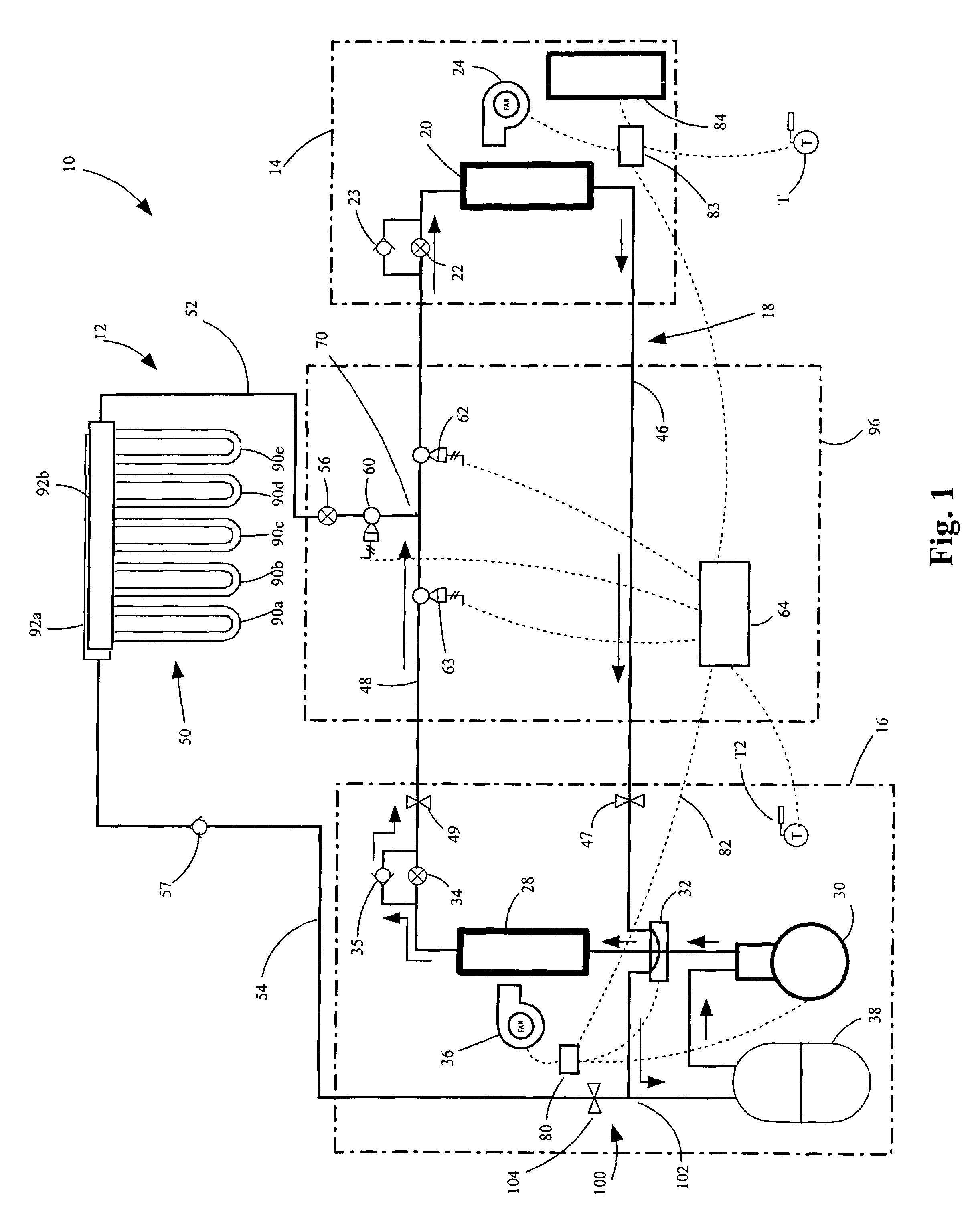
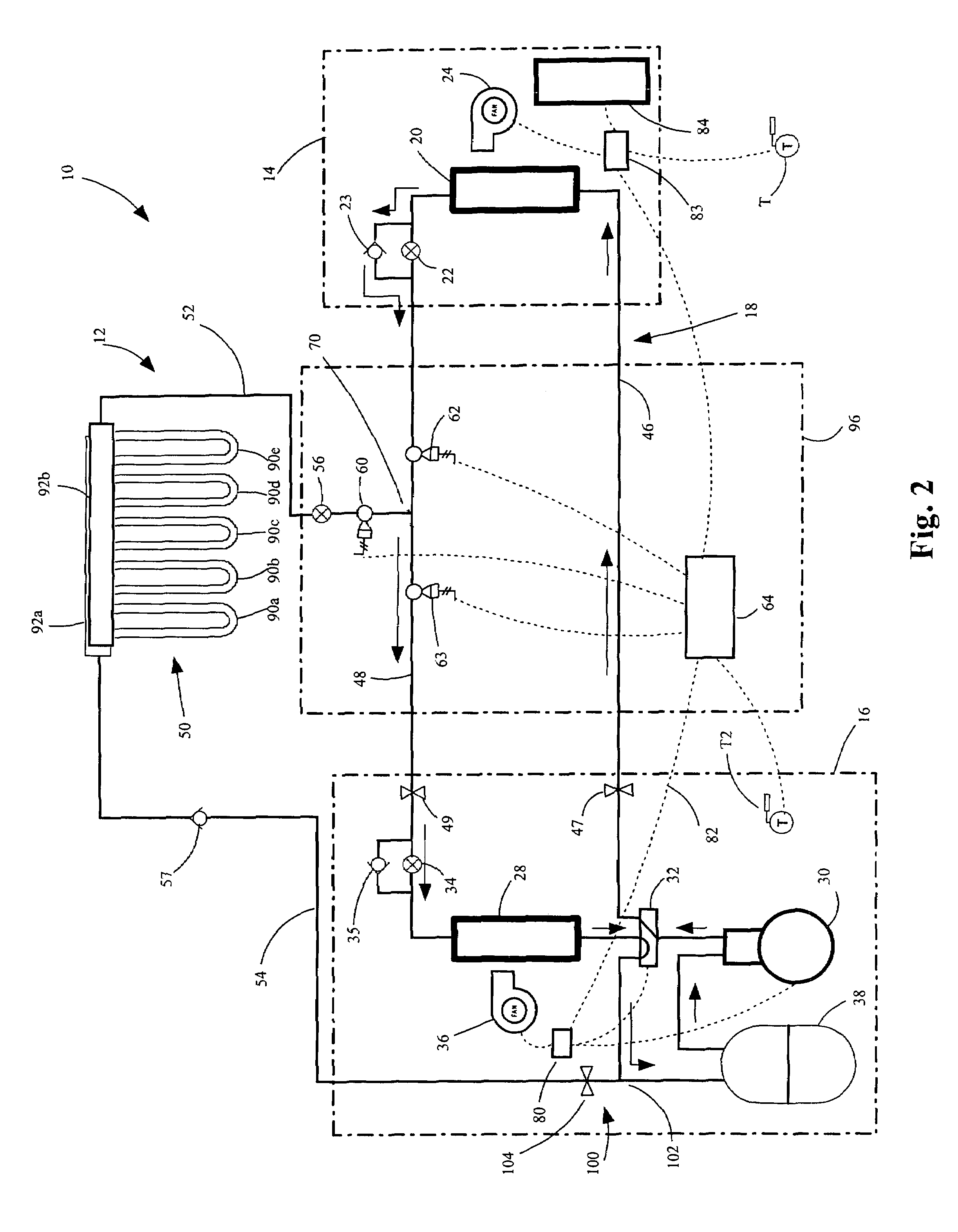
InactiveUS20060288724A1Improve the level ofImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusHeat pumpsGeothermal heatingControl system
A heat and cooling system having an indoor air coil subcircuit, an outdoor air coil subcircuit, a geothermal subcircuit, and a control system for selectively operating the system in air-to-air heating, air-to-air cooling, geothermal heating, air-to-air defrost (optionally) and geothermal defrost modes. The various subcircuits may be connected to one another in parallel. The heating and cooling system may include a control system that permits refrigerant to be selectively routed through any two of the heat exchangers to provide the various modes of operation. In one embodiment, the control system may generally include a circuit having a single reversing valve, a plurality of check valves, a plurality of solenoid valves and a plurality of expansion devices.
Owner:GEOFURNACE DEV
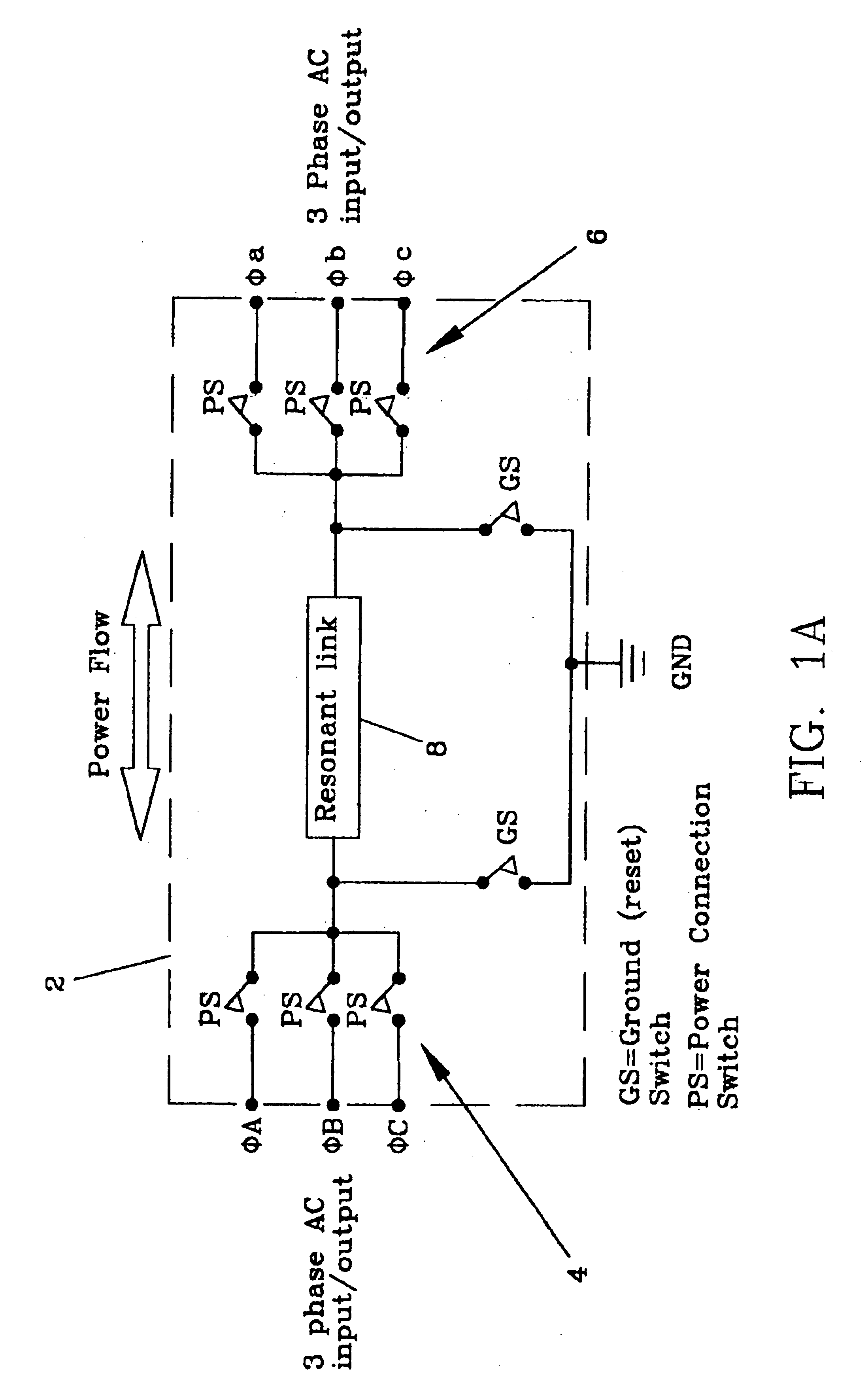
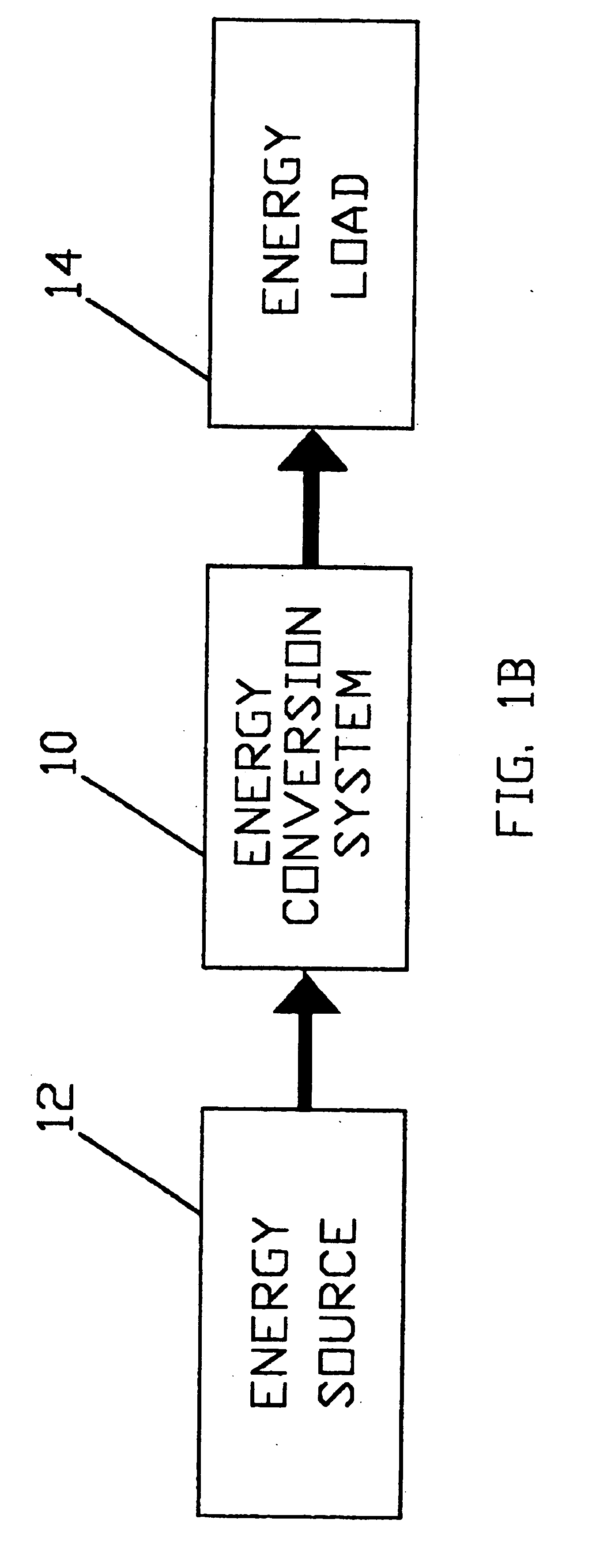
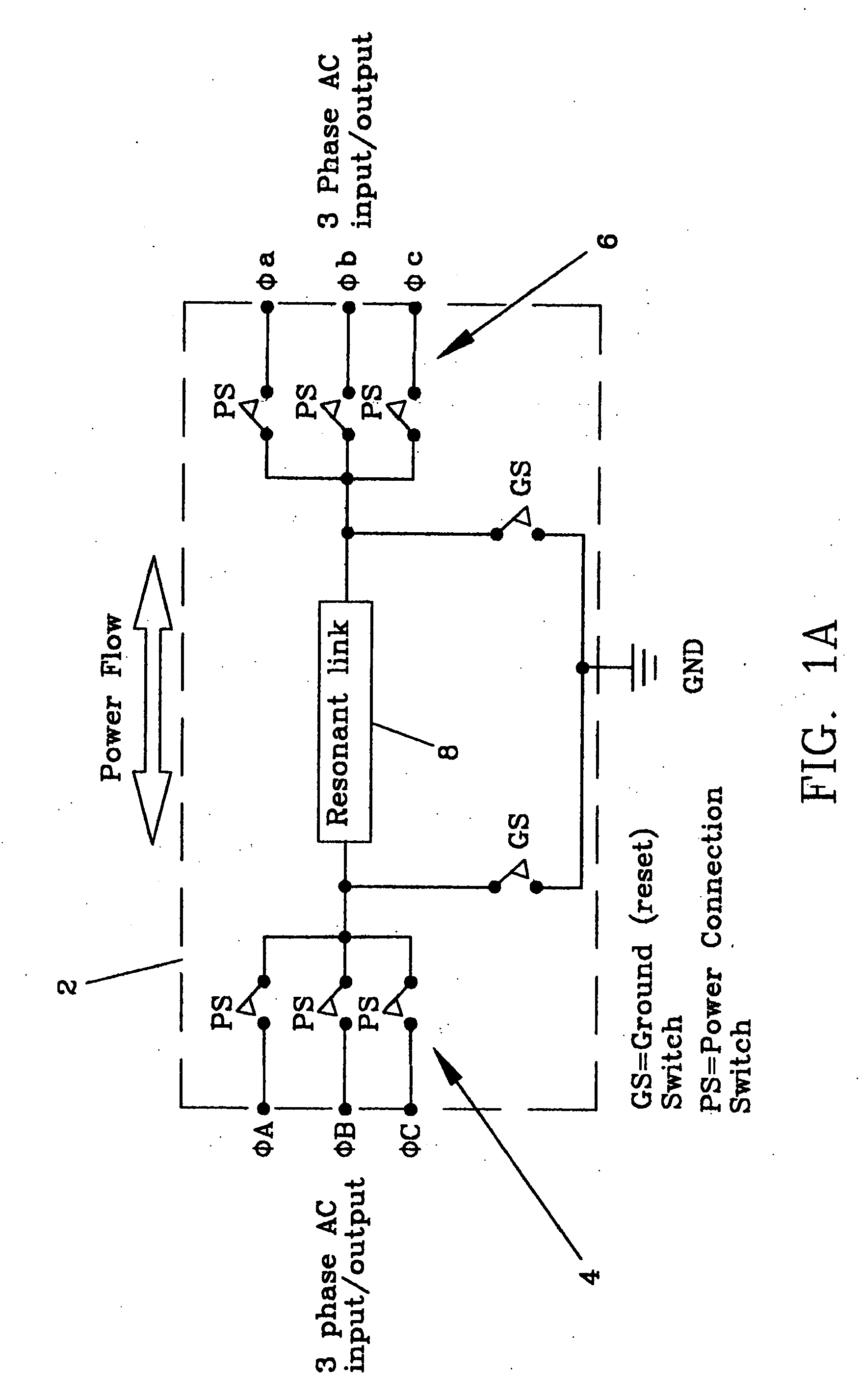
Electro-mechanical energy conversion system having a permanent magnet machine with stator, resonant transfer link and energy converter controls
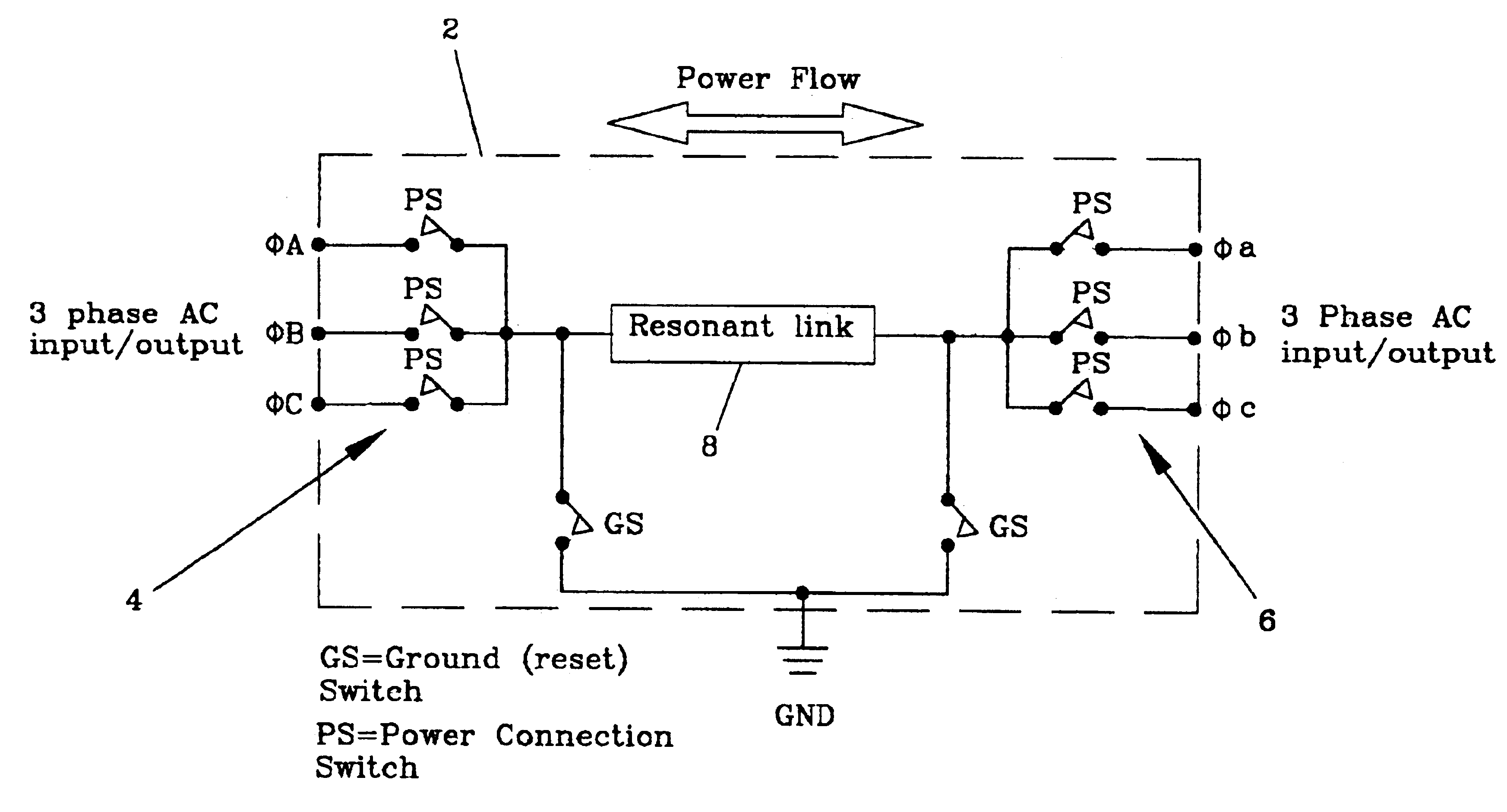
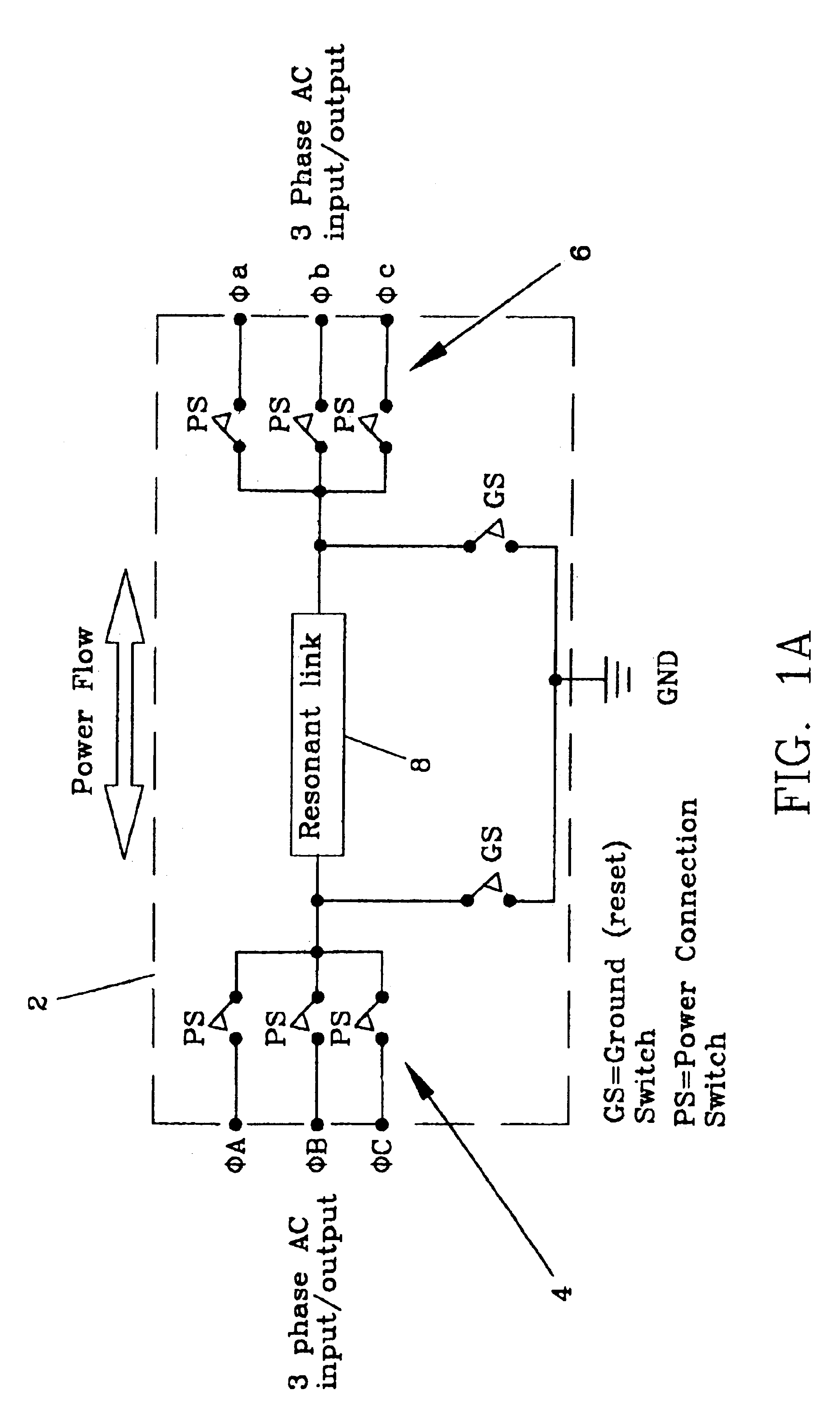
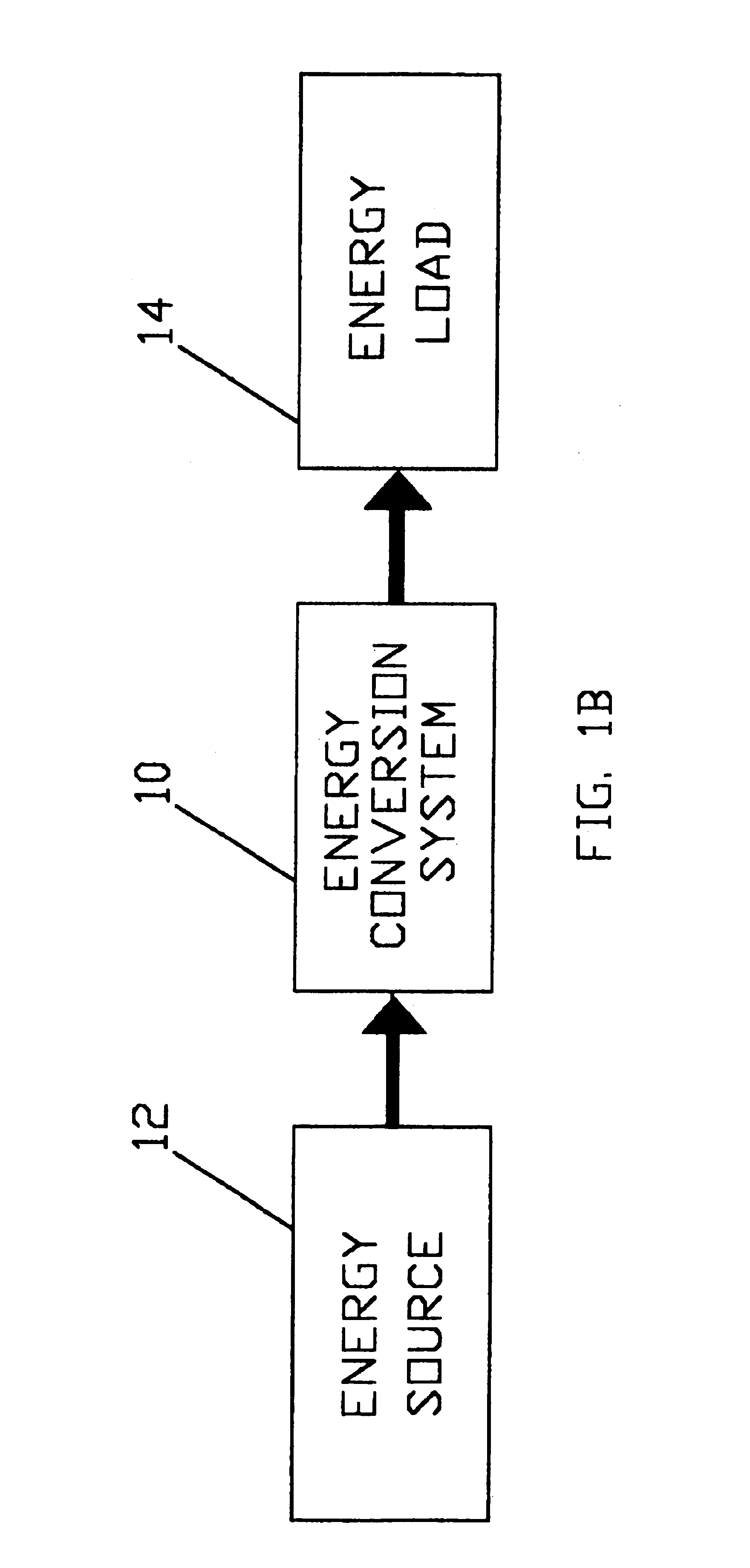
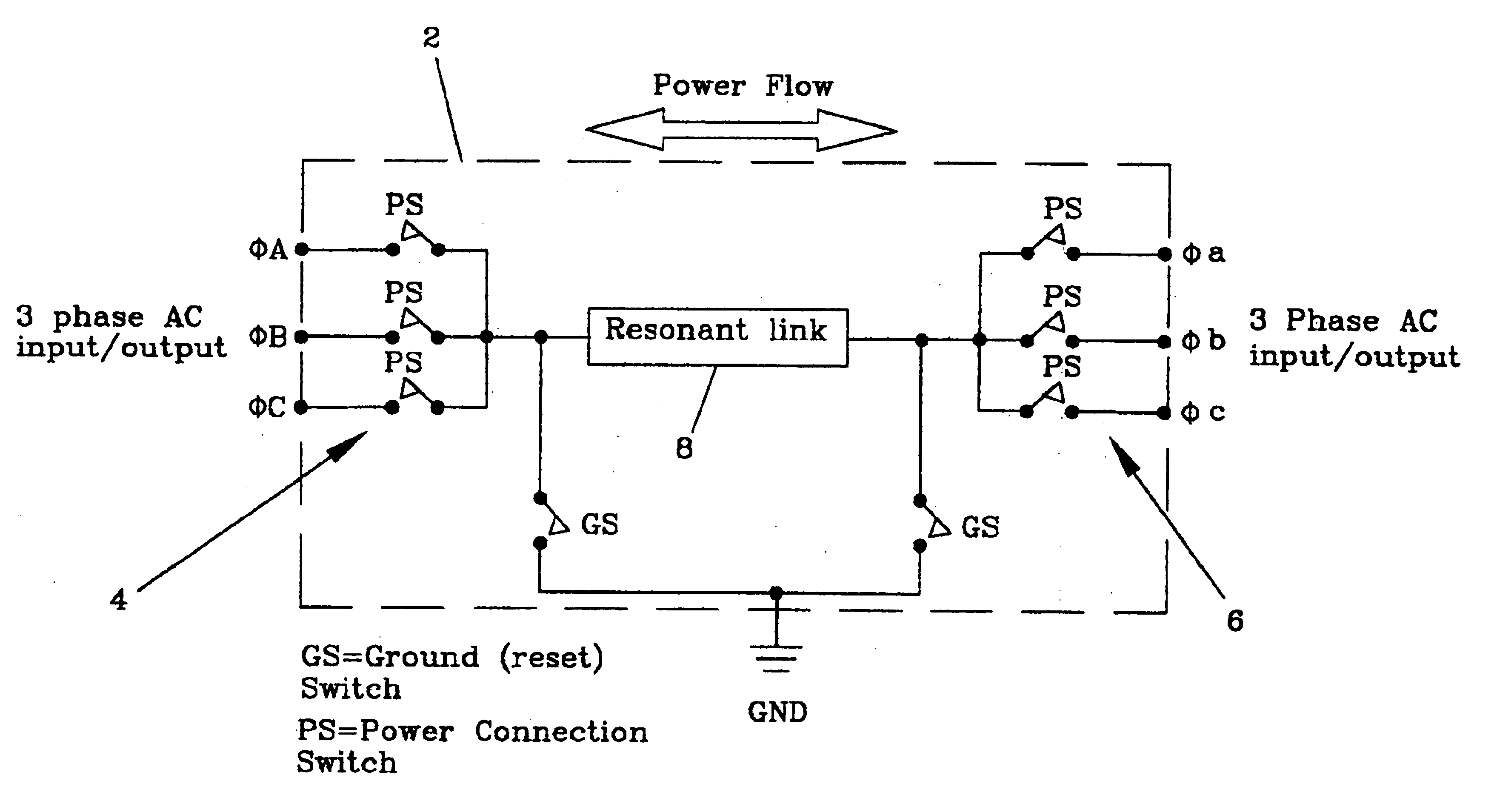
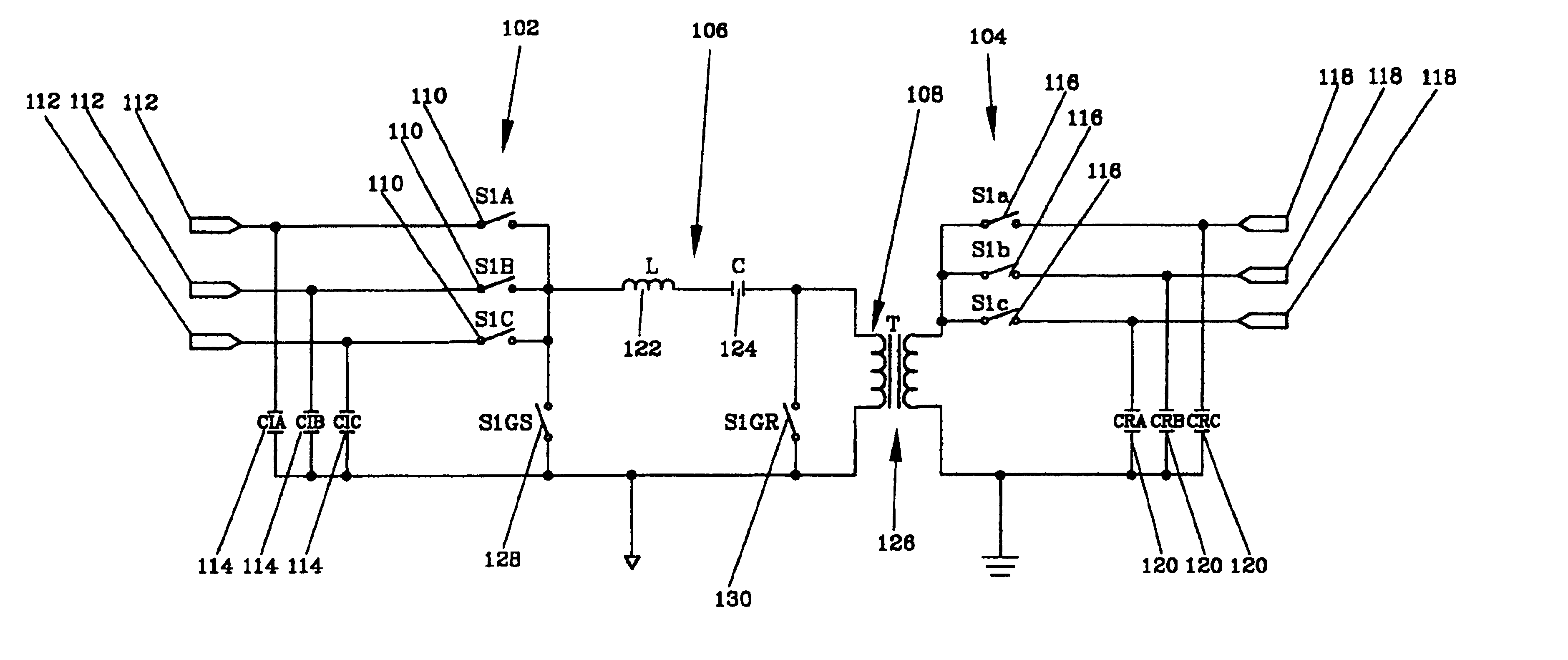
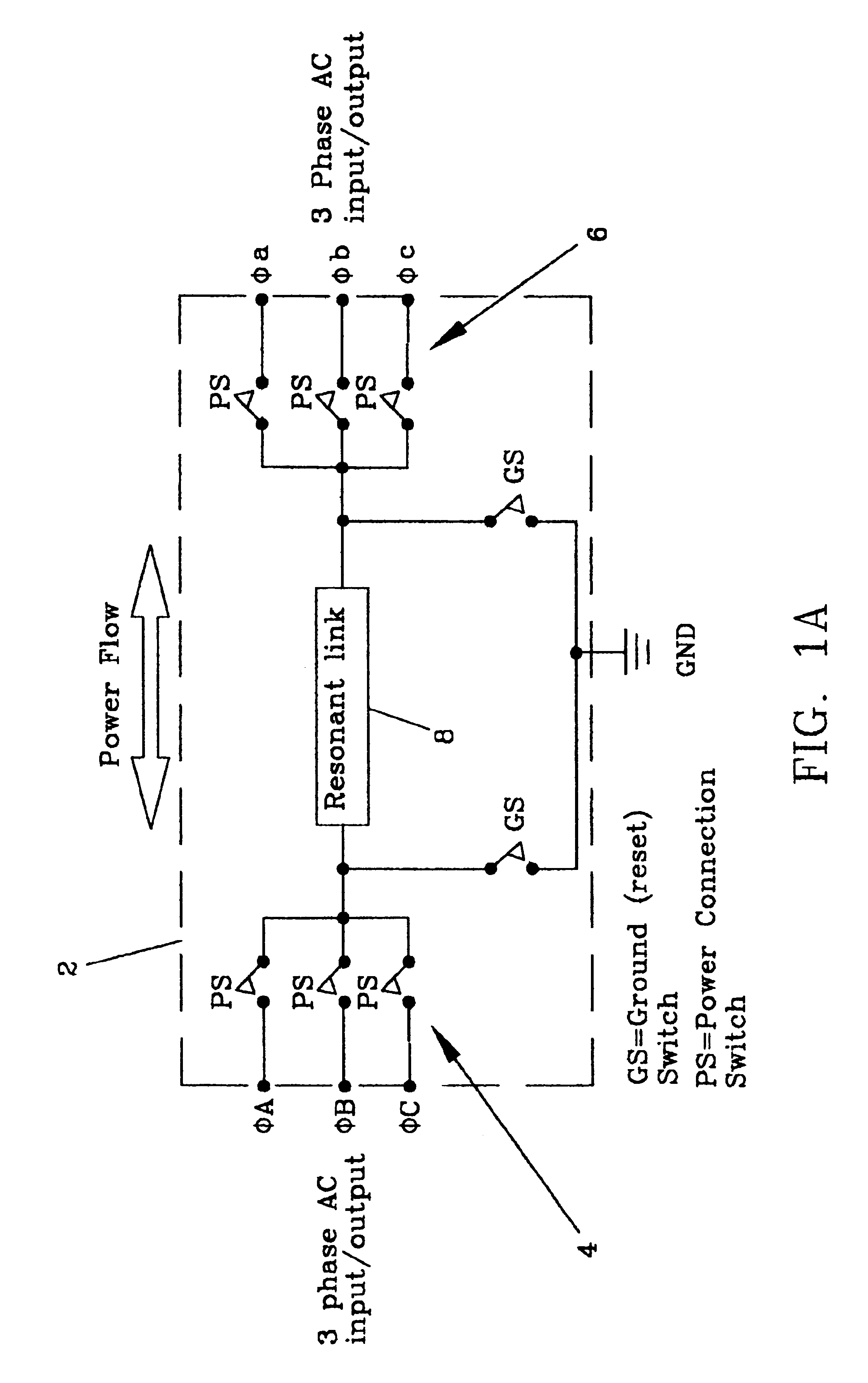
ActiveUS6984897B2Raise the ratioImprove efficiencyAC motor controlWind motor controlEnergy transferMultiplexer
An electro-mechanical energy conversion system coupled between an energy source and an energy load comprising an energy converter device including a permanent magnet induction machine coupled between the energy source and the energy load to convert the energy from the energy source and to transfer the converted energy to the energy load and an energy transfer multiplexer to control the flow of power or energy through the permanent magnetic induction machine.
Owner:SPELLMAN HIGH VOLTAGE ELECTRONICS
Folding tower
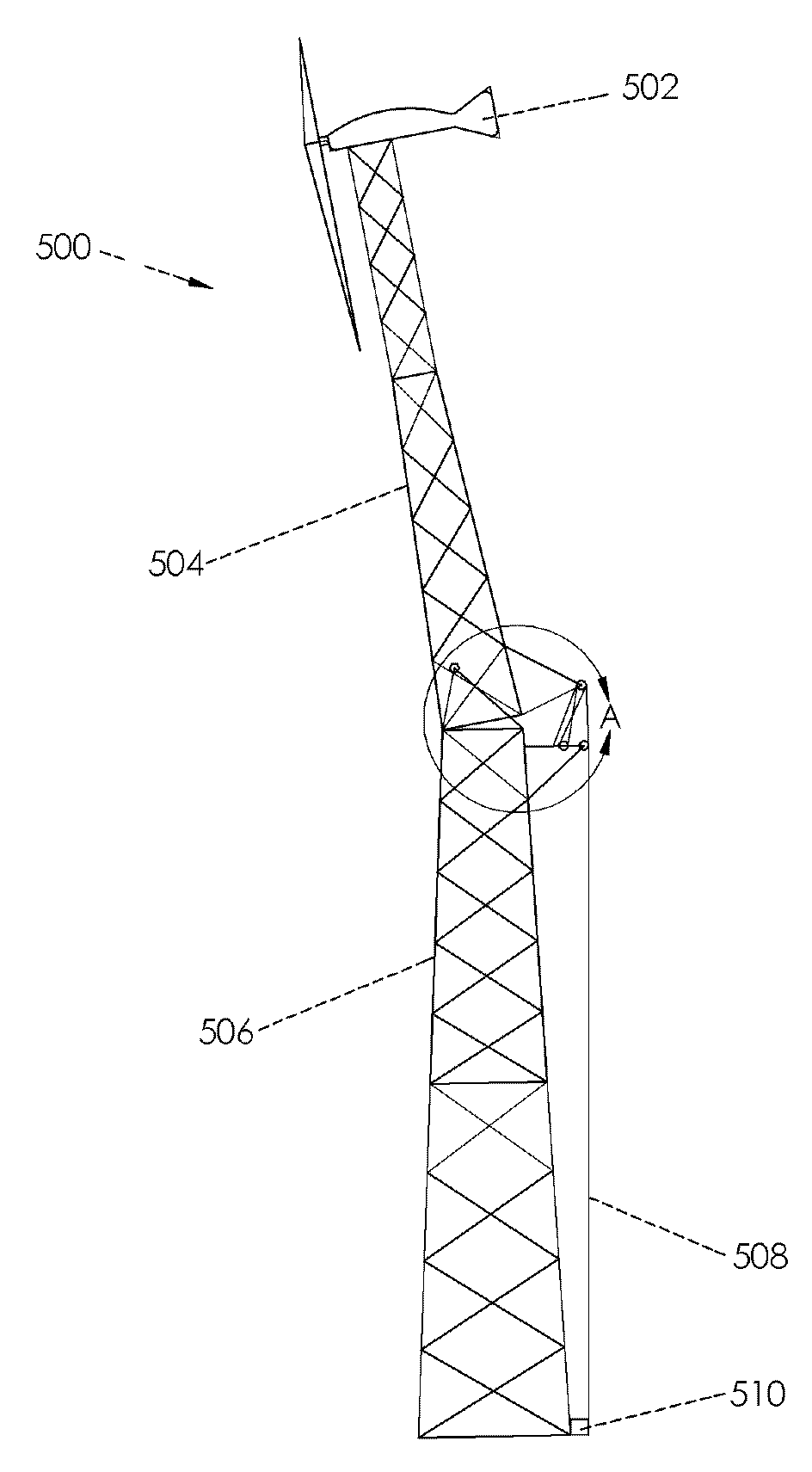
InactiveUS20110283640A1Reduce installation costsLow costWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsTowerTurbine
A multi-section folding tower for supporting wind turbines, windmills, power generation, communication, lighting, and measurement machines comprises an upper tower section and a lower tower section pivotally connected at an upper hinge, a lever, and a lower hinge attaching the lower tower section to an anchor foundation not requiring concrete wherein equipment mounted to the top of the tower is accessible by lowering a portion of the tower. The two tower sections and lever are assembled on the ground by connecting the upper and lower sections with a hinge, and the lower tower section is hinged to the tower foundation. The hinged tower sections are raised by first pulling the lower tower section to a vertical position, and a removable installation wheel attached to the tower top enables the lower section to be raised to a vertical position. The upper section is raised to a vertical position by pulling the lever.
Owner:CATADON SYST
Doubly fed induction machine
InactiveUS6954004B2Raise the ratioImprove efficiencySingle-phase induction motor startersGenerator control circuitsEnergy transferMultiplexer
Owner:SPELLMAN HIGH VOLTAGE ELECTRONICS
Doubly fed induction machine
ActiveUS20050012487A1Raise the ratioImprove efficiencySingle-phase induction motor startersGenerator control circuitsEnergy transferMultiplexer
An electro-mechanical energy conversion system coupled between an energy source and an energy load comprising an energy converter device including a doubly fed induction machine coupled between the energy source and the energy load to convert the energy from the energy source and to transfer the converted energy to the energy load and an energy transfer multiplexer to control the flow of power or energy through the doubly fed induction machine.
Owner:SPELLMAN HIGH VOLTAGE ELECTRONICS
Fabrication method for hollow microneedles for drug delivery
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Hybrid heating and cooling system
InactiveUS7228696B2Improve the level ofImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusHeat pumpsGeothermal heatingControl system
Owner:GEOFURNACE DEV
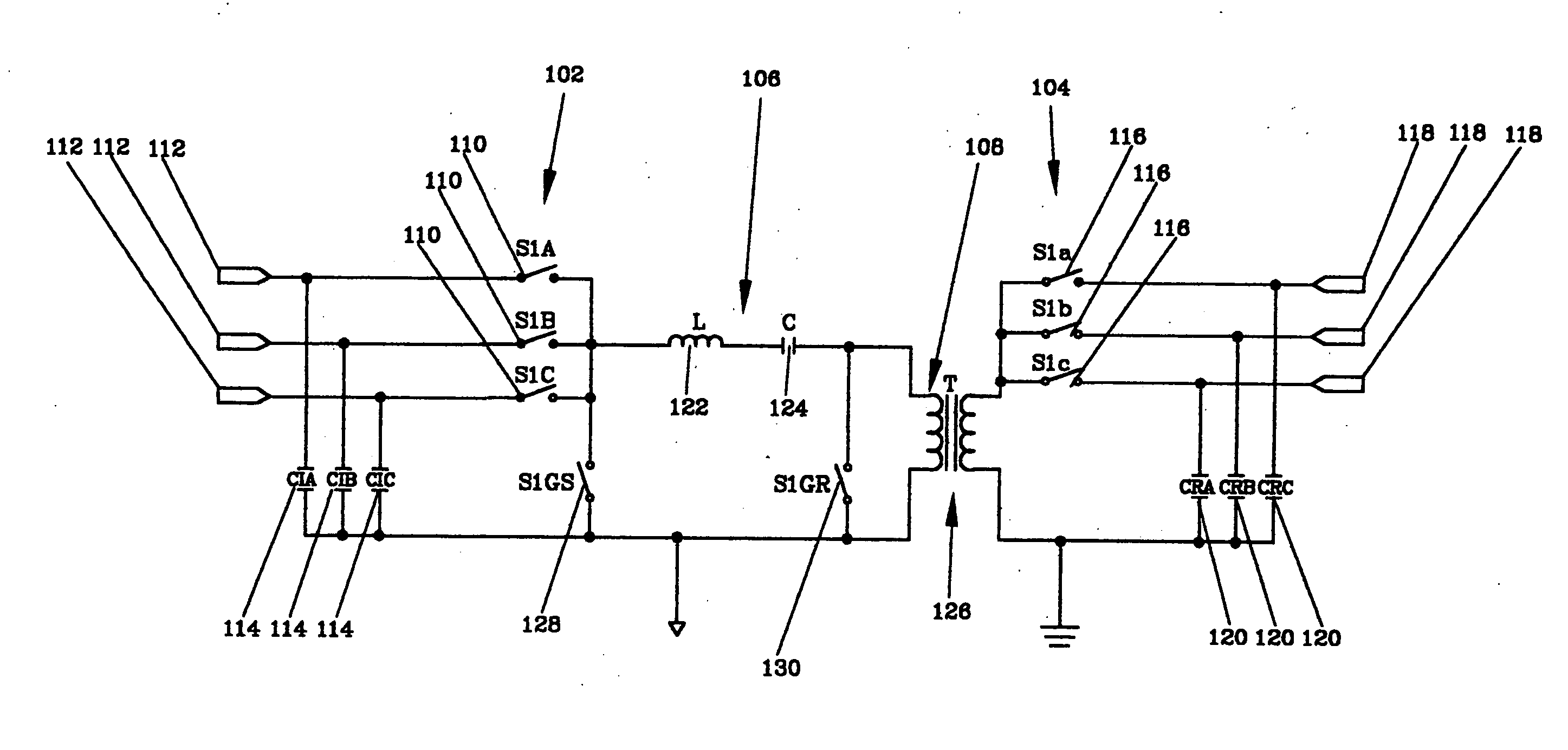
Energy transfer multiplexer
ActiveUS6924991B2Raise the ratioImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEnergy transferMultiplexer
An energy transfer multiplexer to control the flow of power or energy between an energy source and an energy load comprising a bi-directional inverter including a first bank or plurality of switches or first plurality of energy transfer control points and a second bank or plurality of switches or second plurality of energy transfer control points operatively coupled by a series resonant transfer link to selectively control the direction of power or energy flow between the first and second bank or plurality of switches or the first and second plurality of energy transfer control points.
Owner:SPELLMAN HIGH VOLTAGE ELECTRONICS
Conductive polymer materials and preparing method and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130334467A1Improve Capacitive PerformanceEasy to operateElectrolysis componentsHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitancePolymer science
A conductive polymer material and preparing method and uses thereof are provided. The conductive polymer material comprises conductive polymer and fluorinated graphene doping thereof. The weight ratio of the conductive polymer to the fluorinated graphene is 1:0.05-1. The conductive polymer is one of polythiophene or its derivatives, polypyrrole or its derivatives, and polyaniline or its derivatives. The cycle stability of the conductive polymer material is greatly enhanced for doping of the fluorinated graphene, and the conductive polymer contributes to the good capacitance properties. The preparing method can be operated simply with cheaper cost and lower request for equipments, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD
Consolidation and densification methods for fibrous monolith processing
InactiveUS20020140139A1Low production costImprove effectivenessCeramic shaping apparatusClaywaresEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ADVANCED CERAMICS
Fabrication method for hollow microneedles for drug delivery
ActiveUS20100062142A1Quality improvementProduced in massMicroneedlesGlovesContinuous useBiological tissue
A novel method suitable for commercially mass production of hollow microneedle with high quality for delivery of drugs across or into biological tissue is provided. It typically includes the following processes: (1) coating an elongated template of a first material with a second material to form a cover; (2) removing tips of the template and cover to form an opening in the cover; and (3) removing the template of the first material to obtain hollow microneedles of the second material. This simple, efficient and cost-effective fabrication method can mass produce hollow microneedle arrays involving no complicated and expensive equipments or techniques, which can be used in commercial fabrication of hollow needles for delivering drugs or genes across or into skin or other tissue barriers with advantages of minimal damage, painless, long-term and continuous usages.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
System and method for bandwidth handling
InactiveUS20100050215A1Requires low equipmentLow costPulse modulation television signal transmissionClosed circuit television systemsDisplay devicePersonal computer
A system and method for monitoring and distributing available bandwidth within a home network by- use of a home gateway is provided. The system comprises a home Gateway, one or several Set-Top Boxes and one or several home display units such as e.g. a TV, mobile phone and personal computer When the user selects a movie, a point-to-point unicast connection is set up between the user's set-top-box and the delivering streaming server located outside the local network. Accordingly, the home gateway receives a request signal for a displaying a movie from the set-top box, which signal includes bandwidth information, the home gateway monitor the home gateway if there is available bandwidth. An accept signal will be sent to the STB if there is available bandwidth and the set-top box will send an join-message to the delivering streaming server and the movie is displayed on the home device.
Owner:TELIASONERA
Consolidation and densification methods for fibrous monolith processing
InactiveUS6740286B2Low production costImprove effectivenessCeramic shaping apparatusClaywaresFiberPolymer science
Methods for consolidation and densification of fibrous monolith composite structures are provided. Consolidation and densification of two- and three-dimensional fibrous monolith components having complex geometries can be achieved by pressureless sintering. The fibrous monolith composites are formed from filaments having at least a first material composition generally surrounded by a second material composition. The composites are sintered in an inert gas or nitrogen gas at a pressure of no more than about 30 psi to provide consolidated and densified fibrous monolith composites.
Owner:ADVANCED CERAMICS
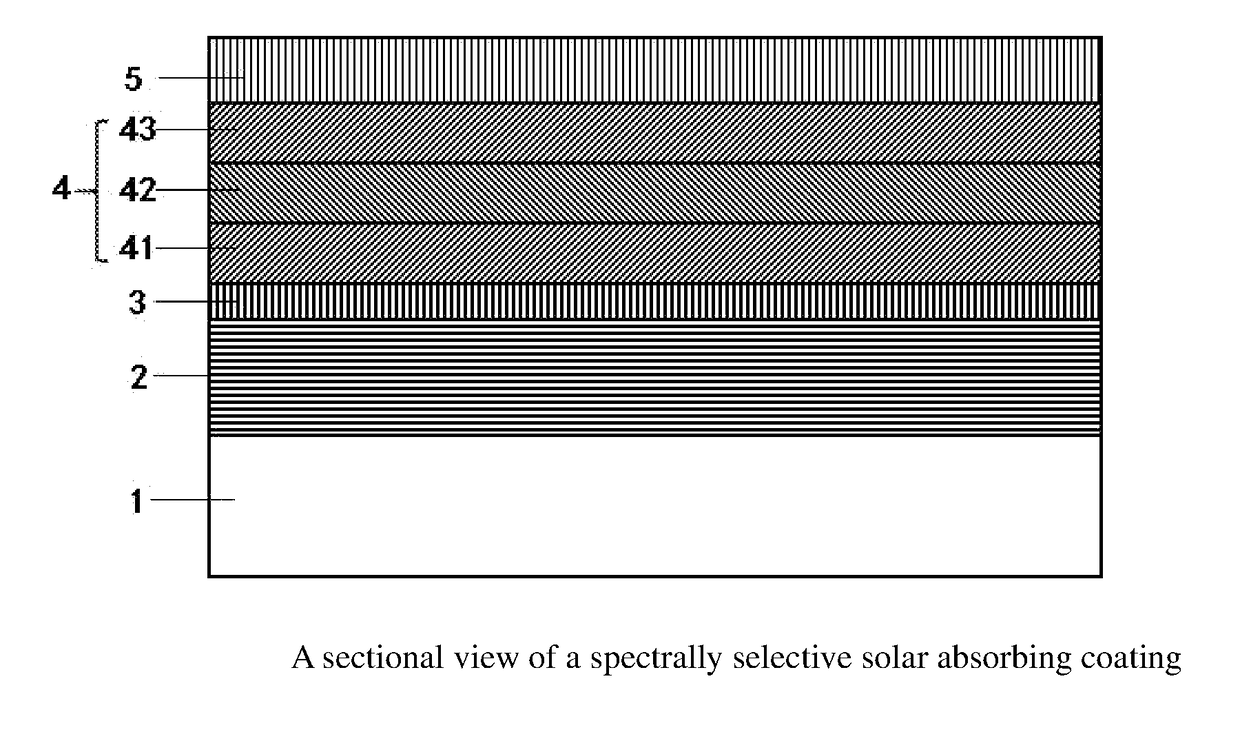
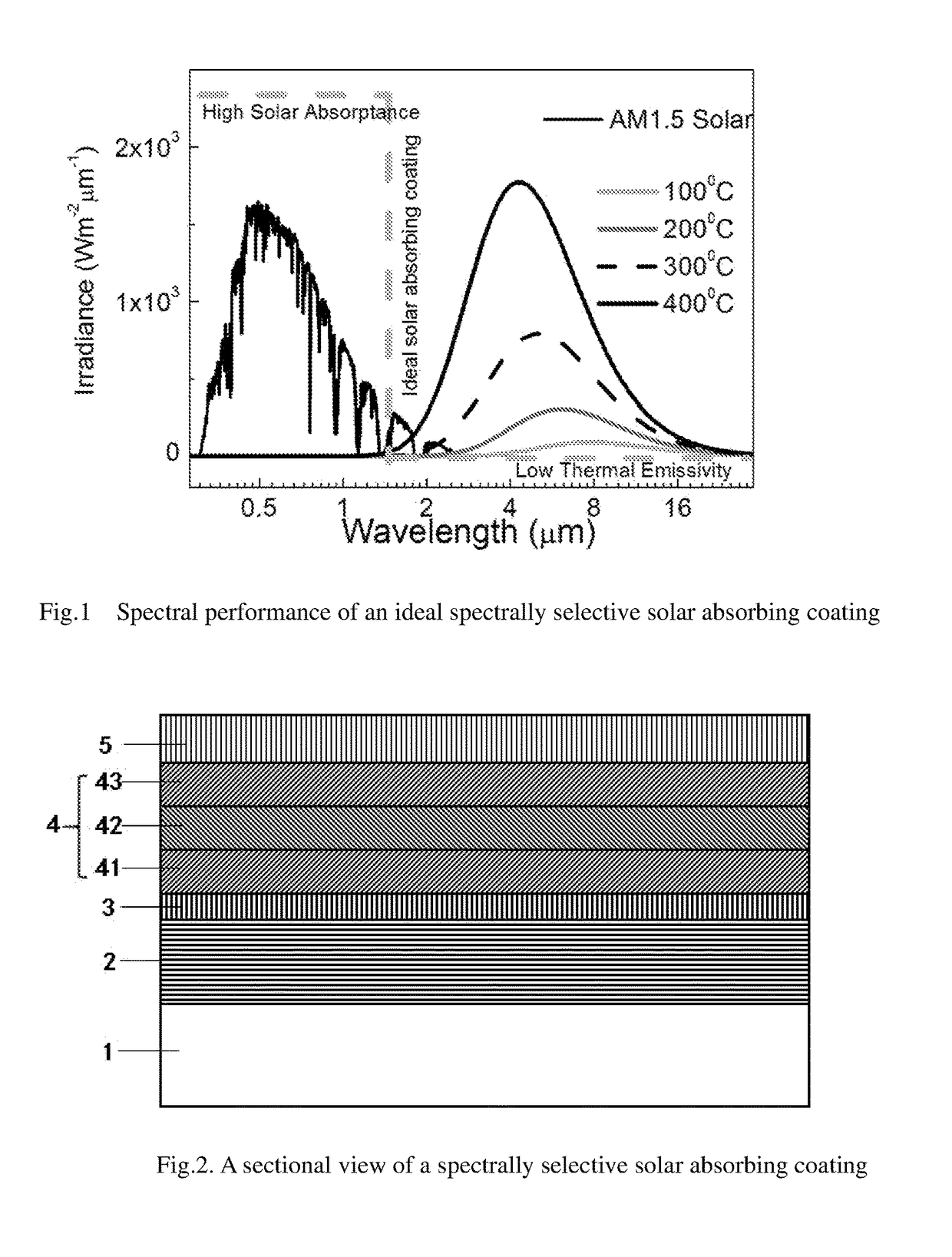
Spectrally selective solar absorbing coating and a method for making it
ActiveUS20180076342A1High refractive indexEnhance solar absorptanceSilicaSolar heat devicesNitrogen gasMetal
Disclosed is a spectrally selective solar absorbing coating and a method for making same. The spectrally selective solar absorbing coating includes a multilayer stack including, from the substrate to the air interface: substrate (1), infrared reflective layer (2), barrier layer (3), composite absorbing layer (4) consisting of metal absorbing sublayer (4.1), metal nitride absorbing sublayer (4.2), and metal oxynitride absorbing sublayer (4.3), and antireflective layer (5). Therefore, the solar absorbing coating has good high and low temperature cycle stability and superior spectrum selectivity, with a steep transition zone between solar absorption and infrared reflection zones. It has a relatively high absorptance α>95%, and a low thermal emissivity ∈≦4%, PC (performance criterion)=−0.3. The solar absorbing multilayer stack can be obtained by reactively magnetron sputtering the metal target in argon or other inert gas with some amounts of gas containing oxygen or nitrogen or their combination.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
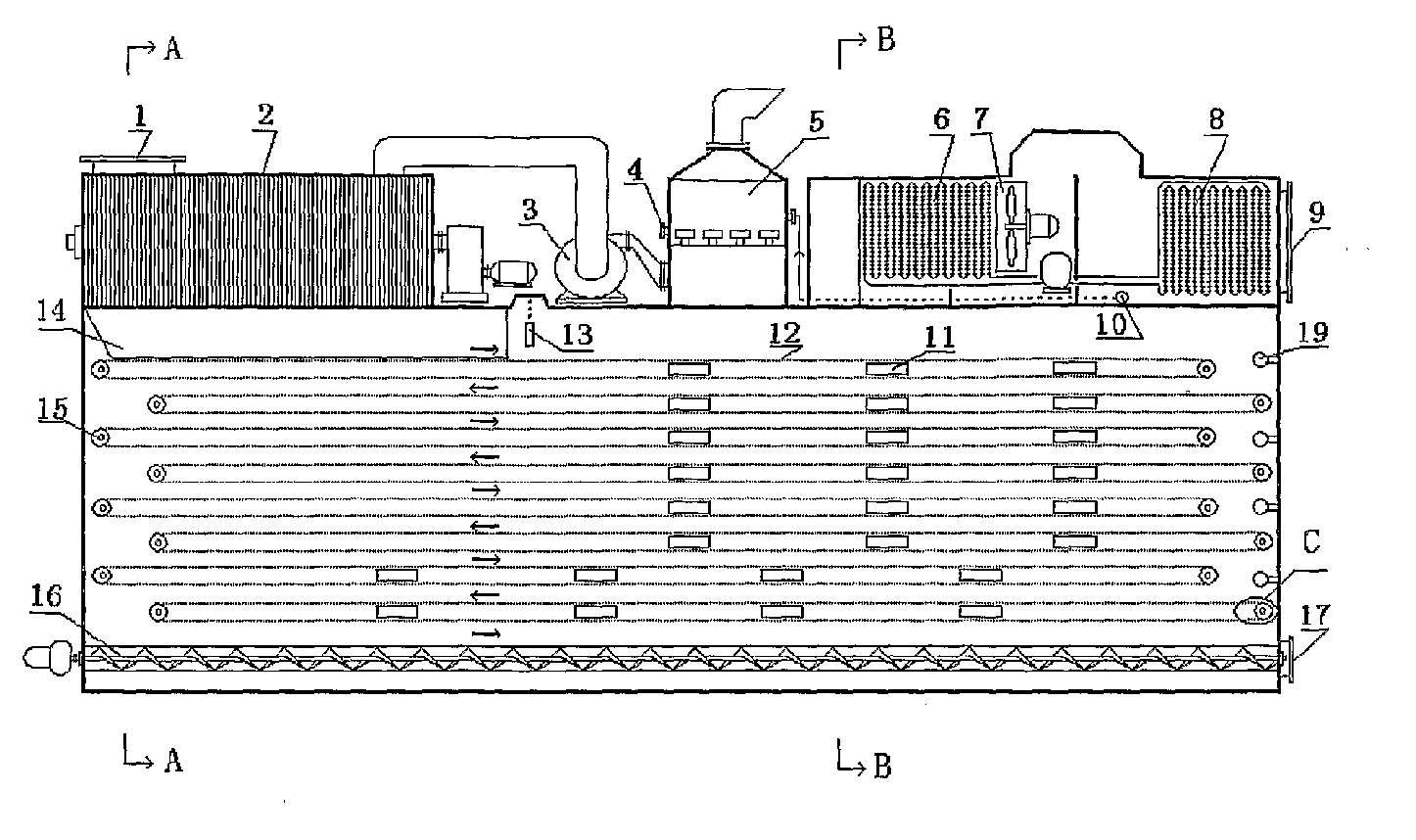
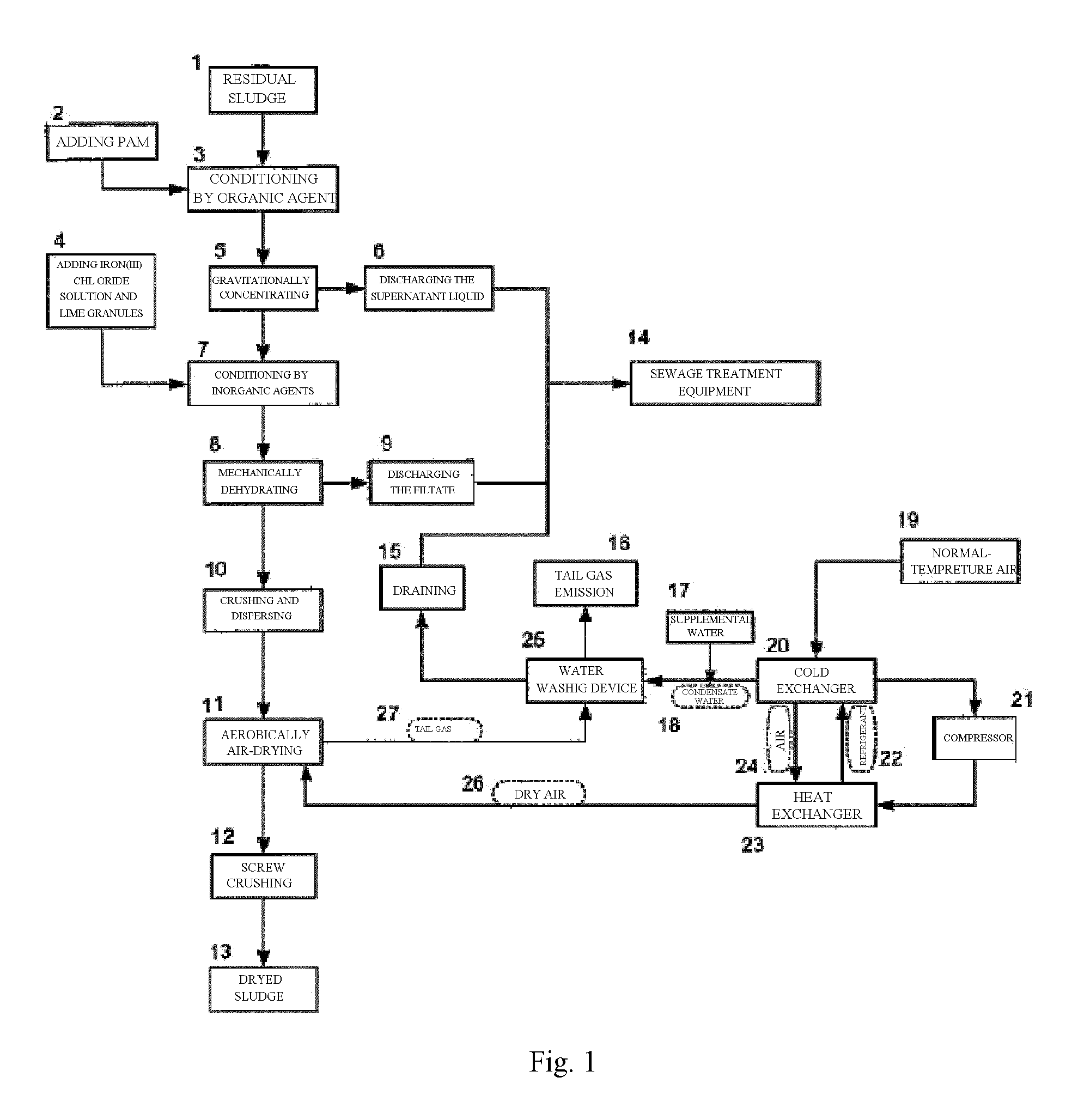
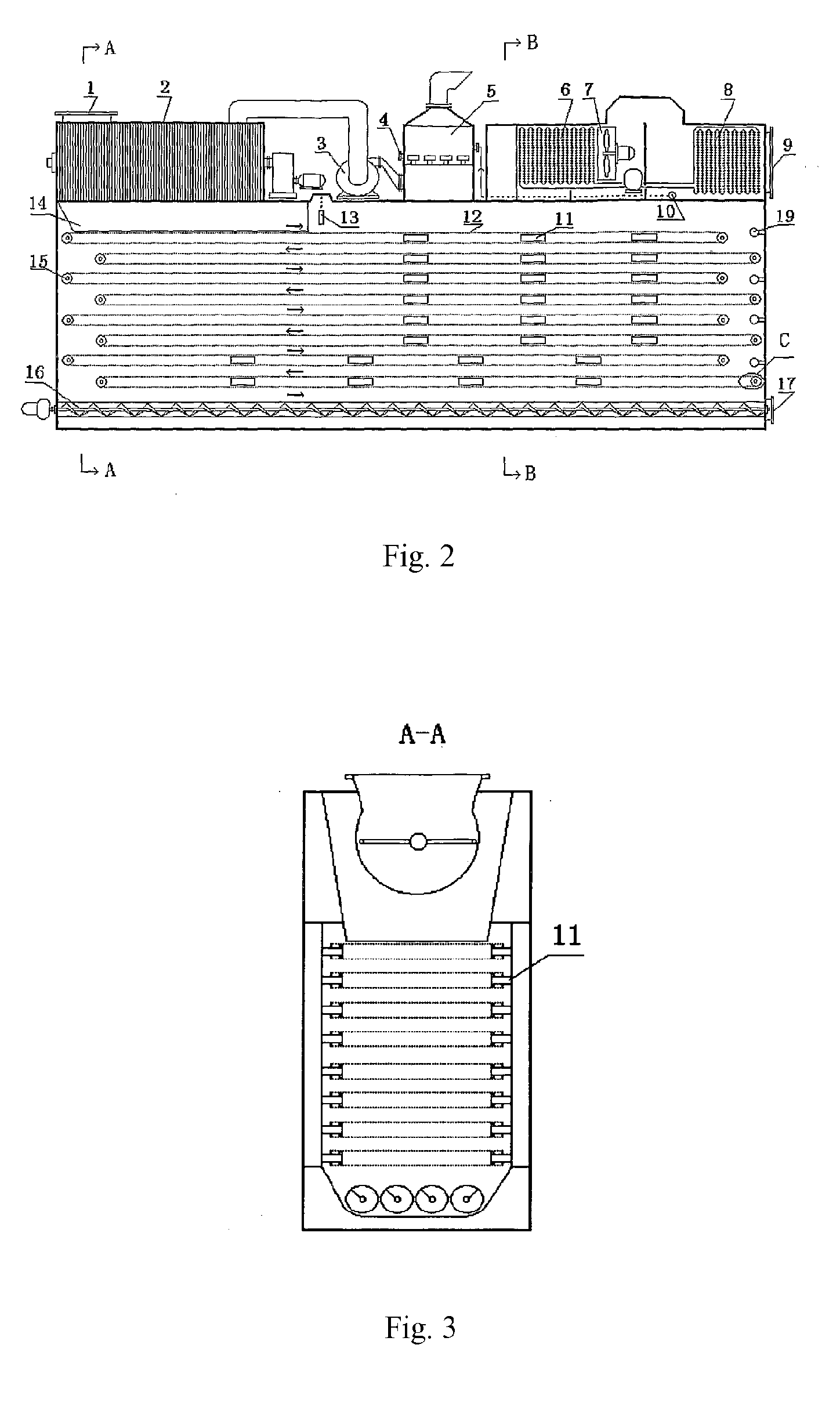
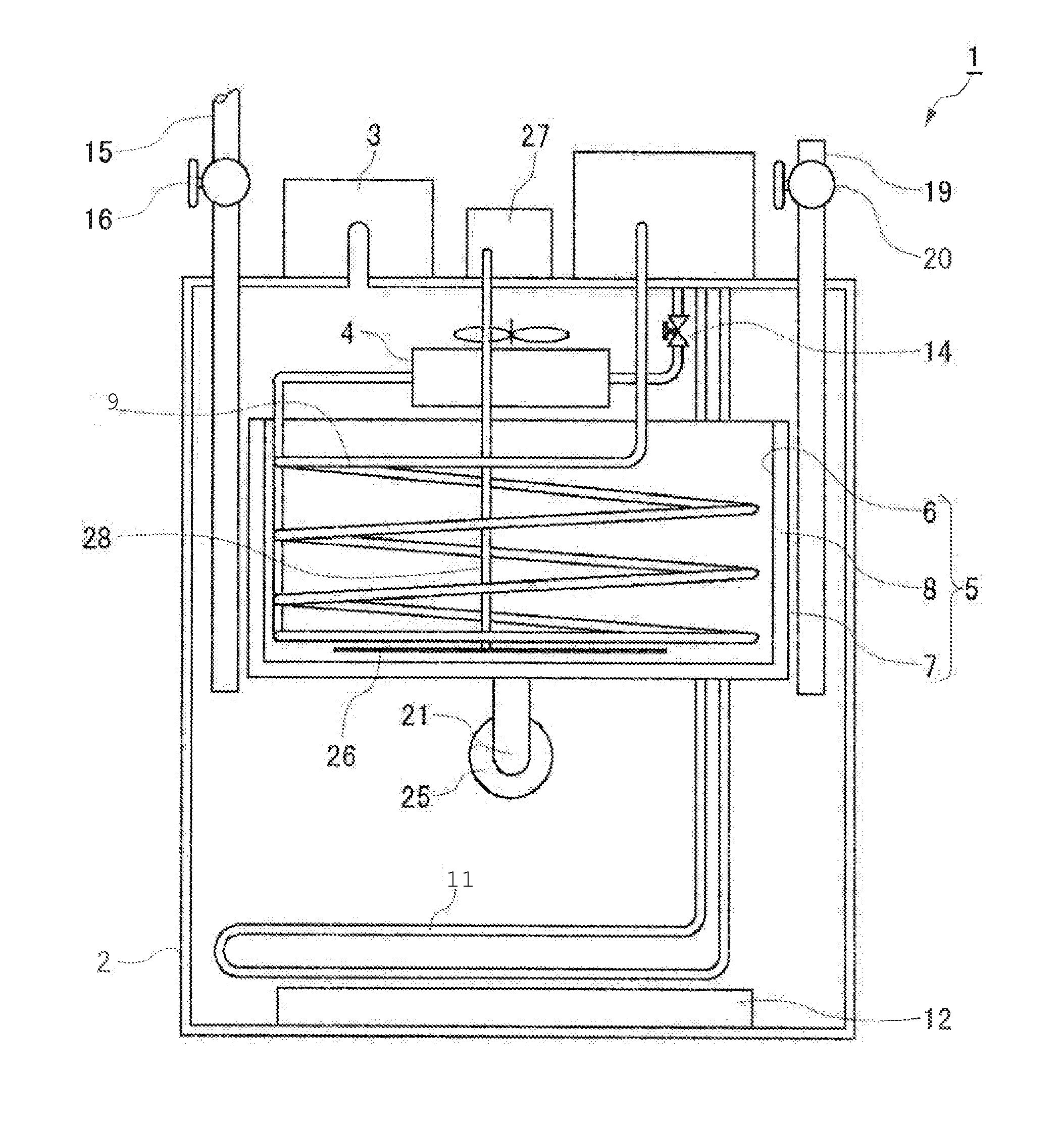
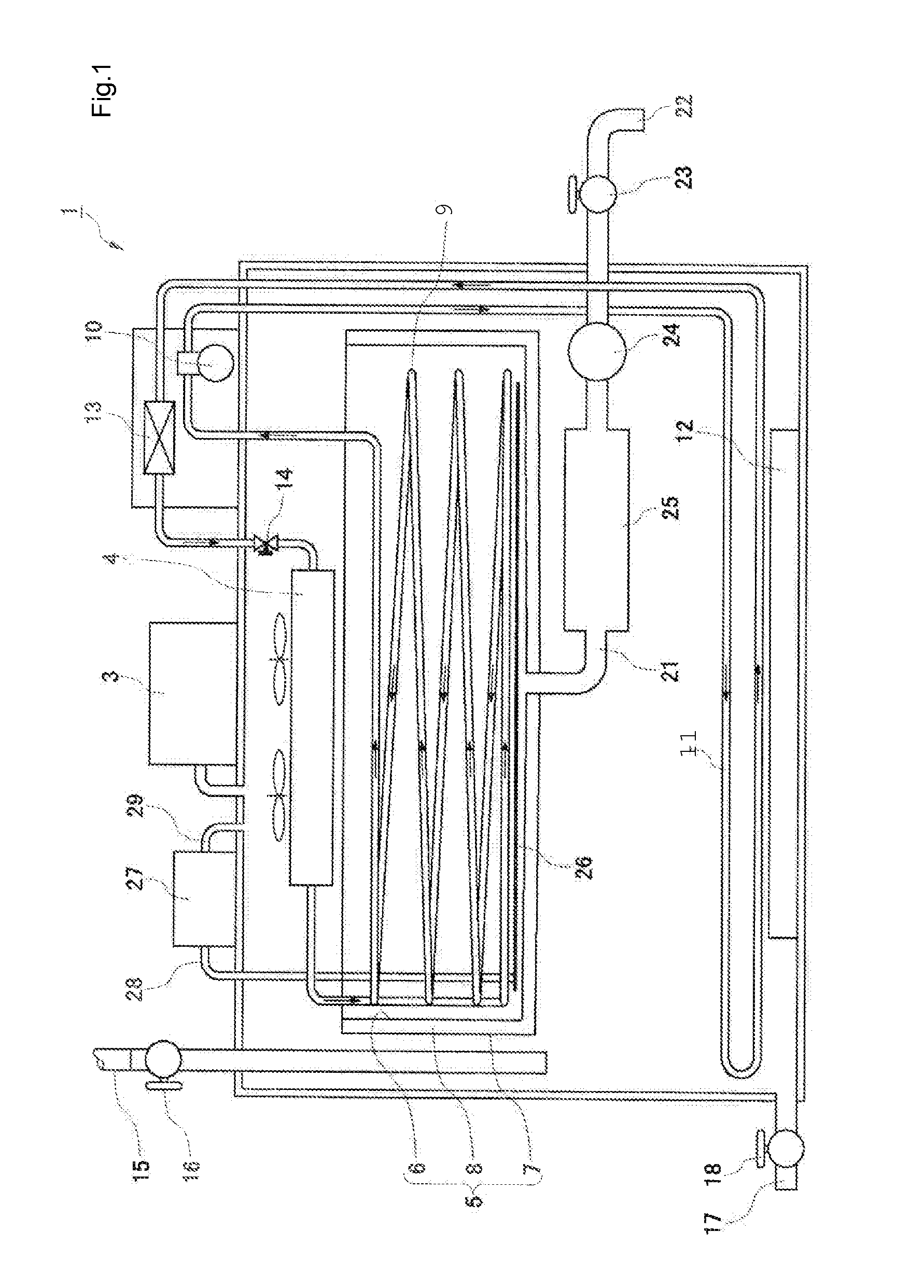
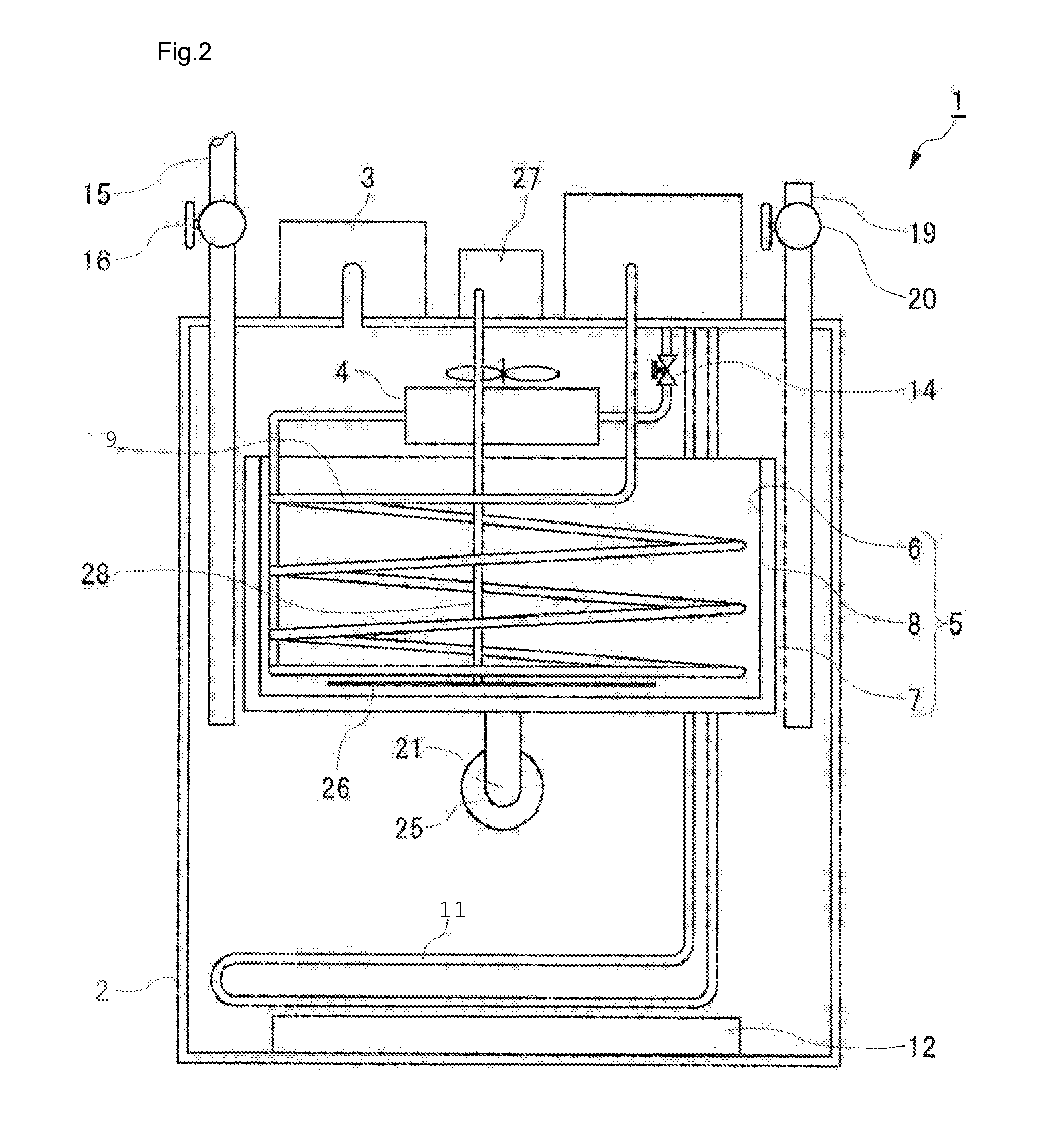
Method of Integration of Concentration-Dehydration and Aerobic Air-drying of Sewage Sludge
ActiveUS20120247165A1Minimize destructionLarge specific surface areaTreatment using aerobic processesExcrement fertilisersLow speedSludge
A method of integration of concentration-dehydration and aerobic air-drying of sewage sludge comprises the following steps: (a) conditioning by an organic agent (3); (b) gravitationally concentrating (5) the residual sludge conditioned by the organic agent; (c) conditioning by inorganic agents (7); (d) mechanically dehydrating (8); (e) crushing and dispersing (10); and (t) aerobically air-drying (11). The method has the following advantages: (i) to improve the sedimentation performance of the residual sludge, thus improving the concentration efficiency of sludge, reducing the concentrating time and reducing the volume of the concentrating pool; (ii) to reduce the volume of the dehydrated sludge correspondingly, thus reducing the subsequent heat treatment load; (iii) to have low energy consumption for drying; (iv) the sludge granules moving at low speed during the drying process, thus being produced stably and securely without powder; (v) the dried exhaust air can reach environmental-friendly standard discharge after being washed by water; (vi) the output sludge granules are not compact, which is good for reclamation.
Owner:SWISON CREATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTIONS CO LTD
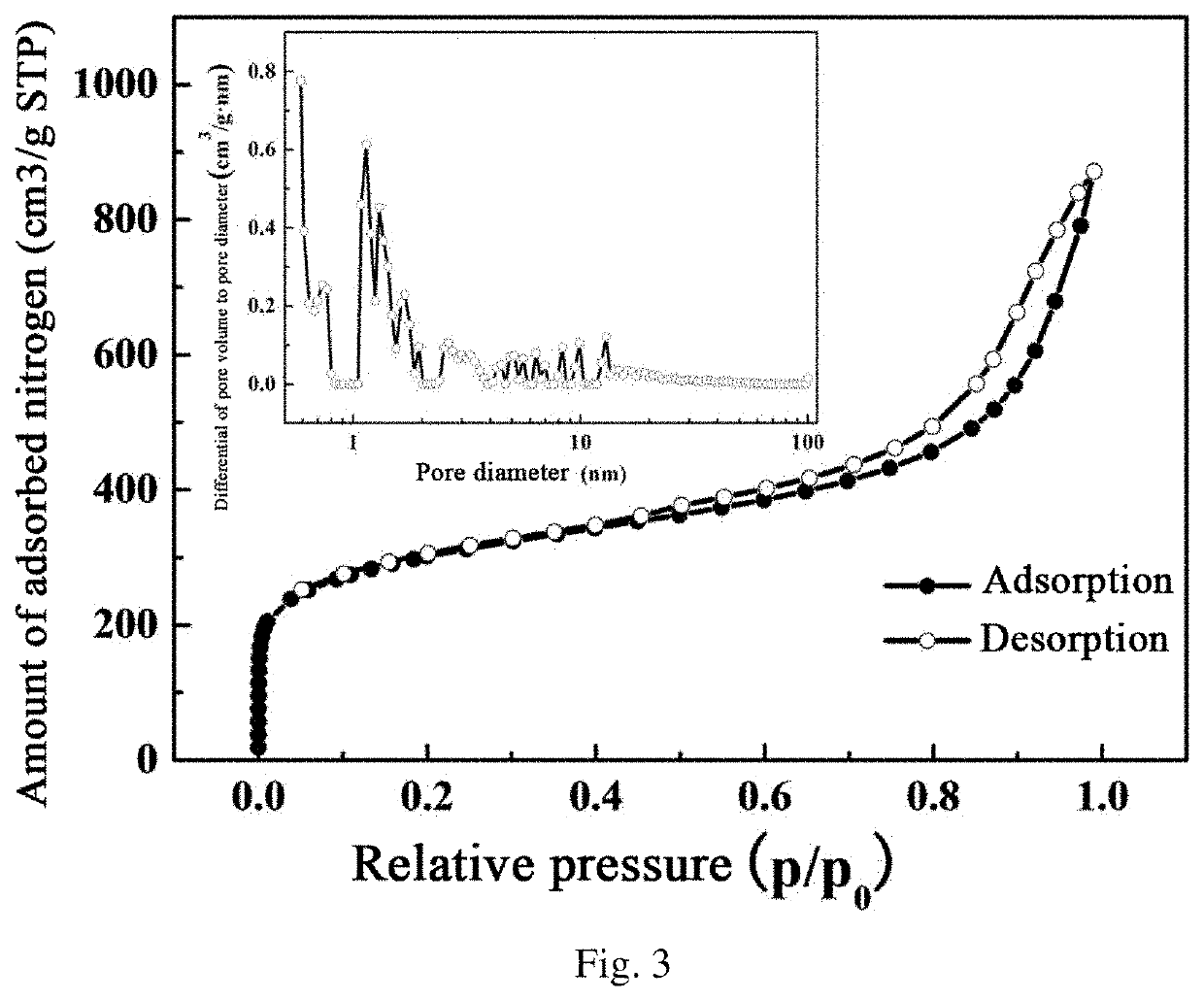
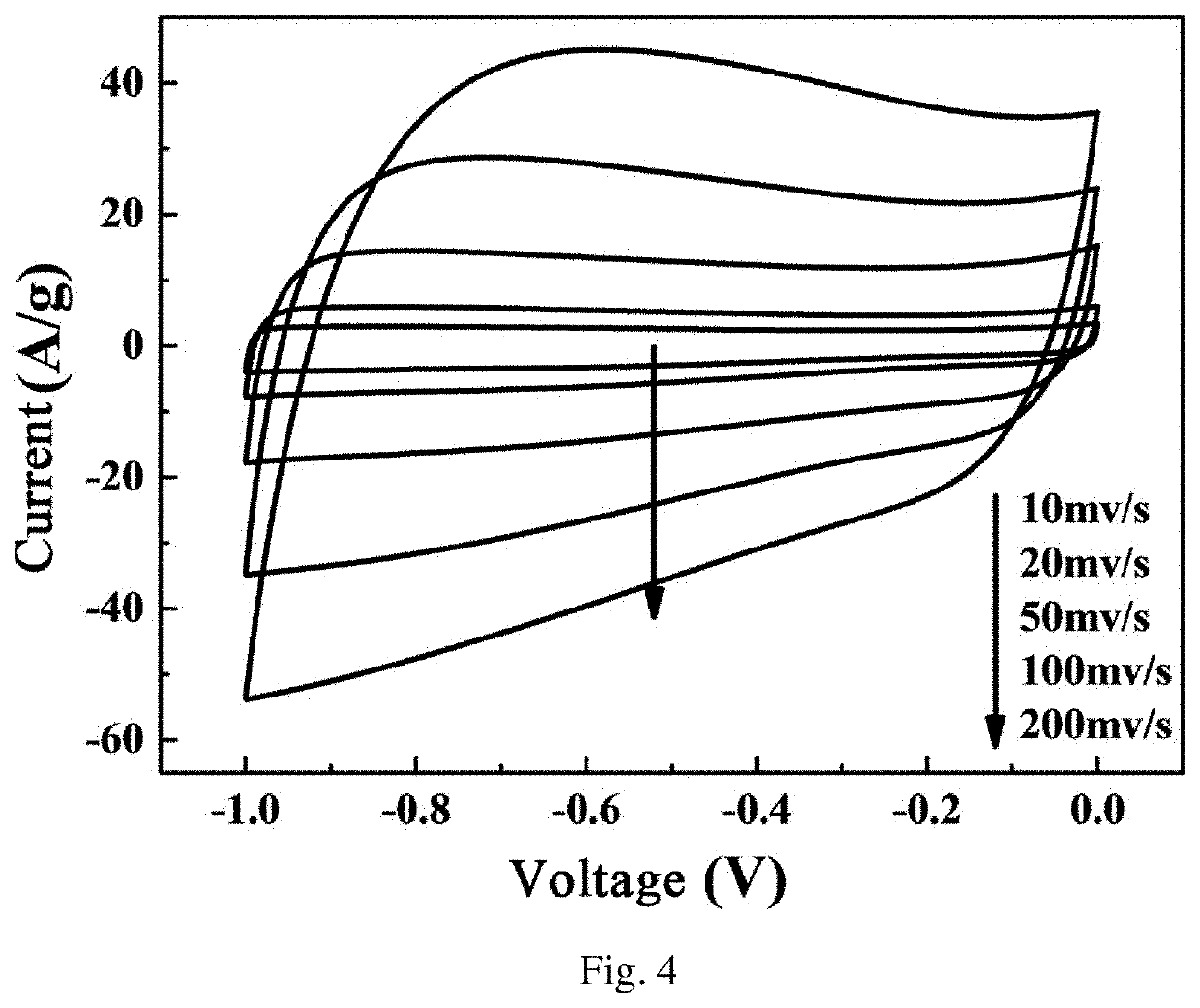
Lignin Porous Carbon Nanosheet, Preparation Method Therefor, and Application Thereof in Supercapacitor Electrode Materials
PendingUS20210323825A1Reasonable pore structureAbundant poreHybrid capacitor electrodesNano-carbonCapacitancePorous carbon
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biomass carbon materials, and relates to a lignin porous carbon nanosheet, a preparation method therefor, and an application thereof in supercapacitor electrode materials. The method of the present invention performs layer-by-layer self-assembly of sulfonated lignin and oxalate in a selective solvent to prepare a layer-by-layer self-assembled lignin / oxalate composite, which is then carbonized and pickled to obtain the lignin porous carbon nanosheets. The lignin porous carbon nanosheets prepared by the above method of the present invention have a specific surface area of 200-1500 m2 / g, a micropore specific surface area of 100-500 m2 / g, a mesoporous specific surface area of 100-1000 m2 / g, a pore diameter of 0.5-30 nm, and a pore volume of 0.5-1.5 cm3 / g; they can be applied to supercapacitor electrode materials, showing higher specific capacitance and excellent rate performance (with a specific capacitance retention rate of 76.6%), having good potential application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon with carbon dioxide hydrogenation
ActiveUS20190071374A1Low selectivityHigh selectivityHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveHydrogen
A method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons with carbon dioxide hydrogenation, comprising: directly converting a mixed gas consisting of carbon dioxide and hydrogen with the catalysis of a composite catalyst under reaction conditions of a temperature of 250-450° C., a pressure of 0.01-10.0 MPa, a feedstock gas hourly space velocity of 500-50000 mL / (h·gcat) and a H2 / CO2 molar ratio of 0.5-8.0, to produce aromatic hydrocarbons. The composite catalyst is a mixture of a first component and a second component. The first component is an iron-based catalyst for making low-carbon olefin via carbon dioxide hydrogenation, and the second component is at least one of metal modified or non-modified molecular sieves which are mainly used for olefin aromatization. In the method, CO2 conversion per pass may be above 33%, the hydrocarbon product selectivity may be controlled to be above 80%, the methane content is lower than 8%, C5+ hydrocarbon content is higher than 65% and the proportion of the aromatic hydrocarbons in C5+ hydrocarbons may be above 63%.
Owner:ZHUHAI FUTIAN ENERGY TECH CO LTD
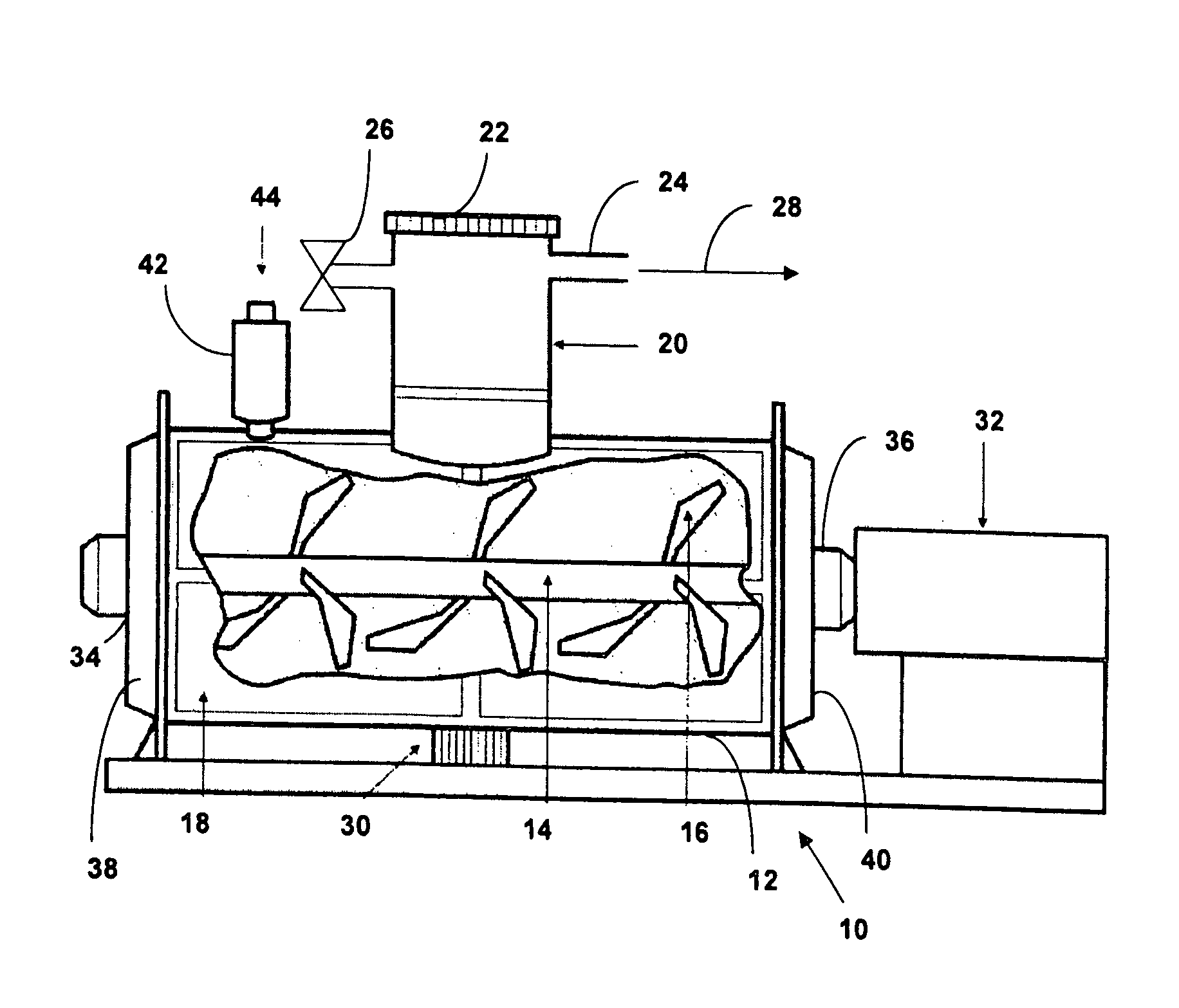
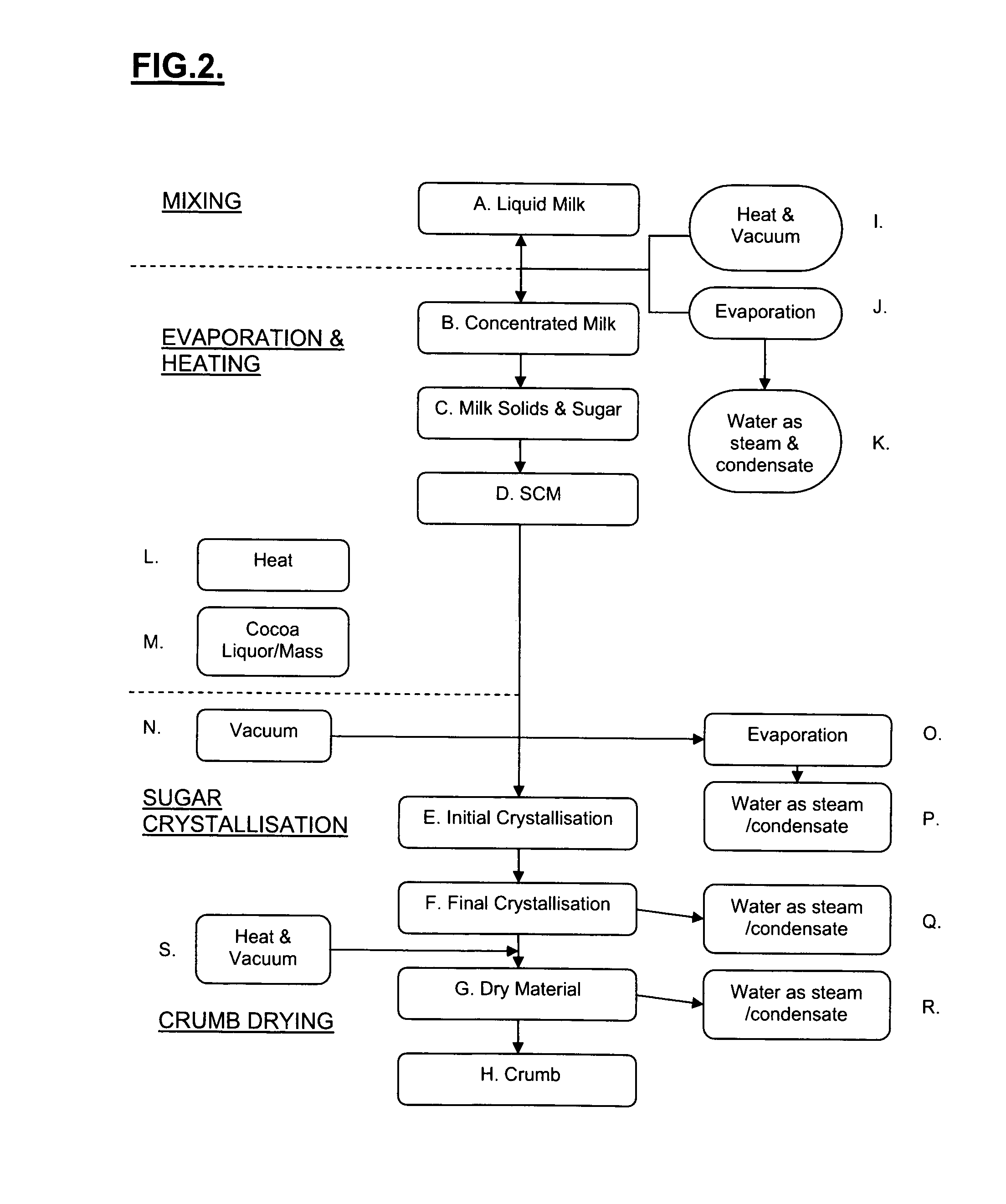
Process for preparing chocolate crumb
The present invention relates to a process for chocolate crumb manufacture and to chocolate crumb and confectionery products made using the process. The process comprises: a) providing a milk and sugar mixture or mixing together milk and sugar so as to form a mixture; b) heating the mixture to a temperature in the range of 55-110° C. under a lowered pressure in the range of 18-25 kPa so as to effect evaporation of liquid from the mixture; c) adding cocoa mass / liquor to the mixture during and / or after step (a) and / or step (b); d) subjecting the mixture to conditions effective to bring about sugar crystallisation in the mixture; and e) drying the mixture so as to form chocolate crumb. Evaporation takes place at a reduced temperature and pressure so as to produce a sweetened condensed milk. In one embodiment the milk and sugar mix is evaporated to between 85-88% solids by heating the mixture to between about 85° C. to 95° C. under a lowered pressure of approximately 24 kPa for 30 minutes.
Owner:MONDELEZ UK HLDG & SERVICES
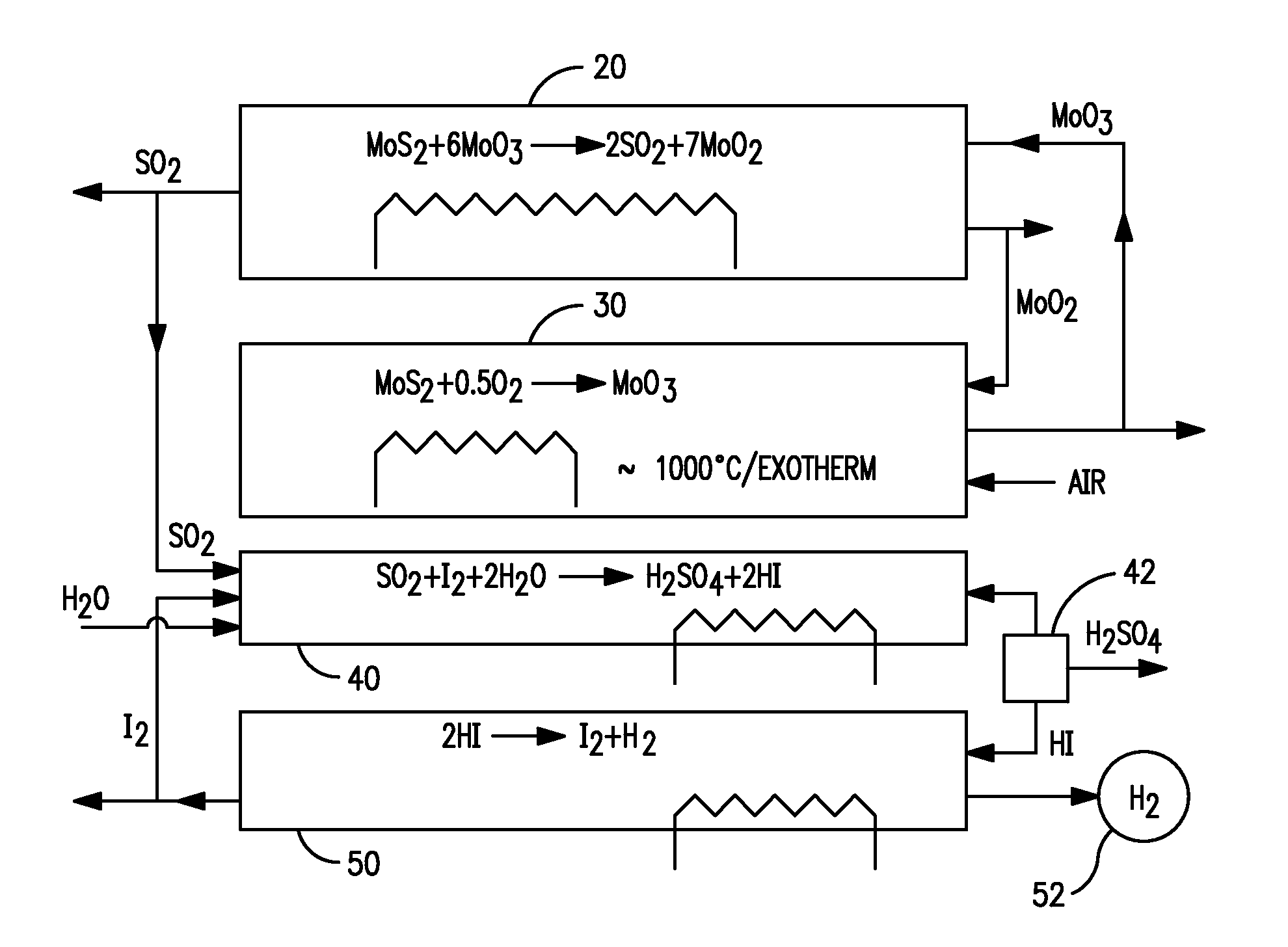
Production of hydrogen through oxidation of metal sulfides
InactiveUS20120034154A1Good benefitEfficiency benefitSulfur-dioxide/sulfurous-acidHydrogen productionMetallic sulfideTwo step
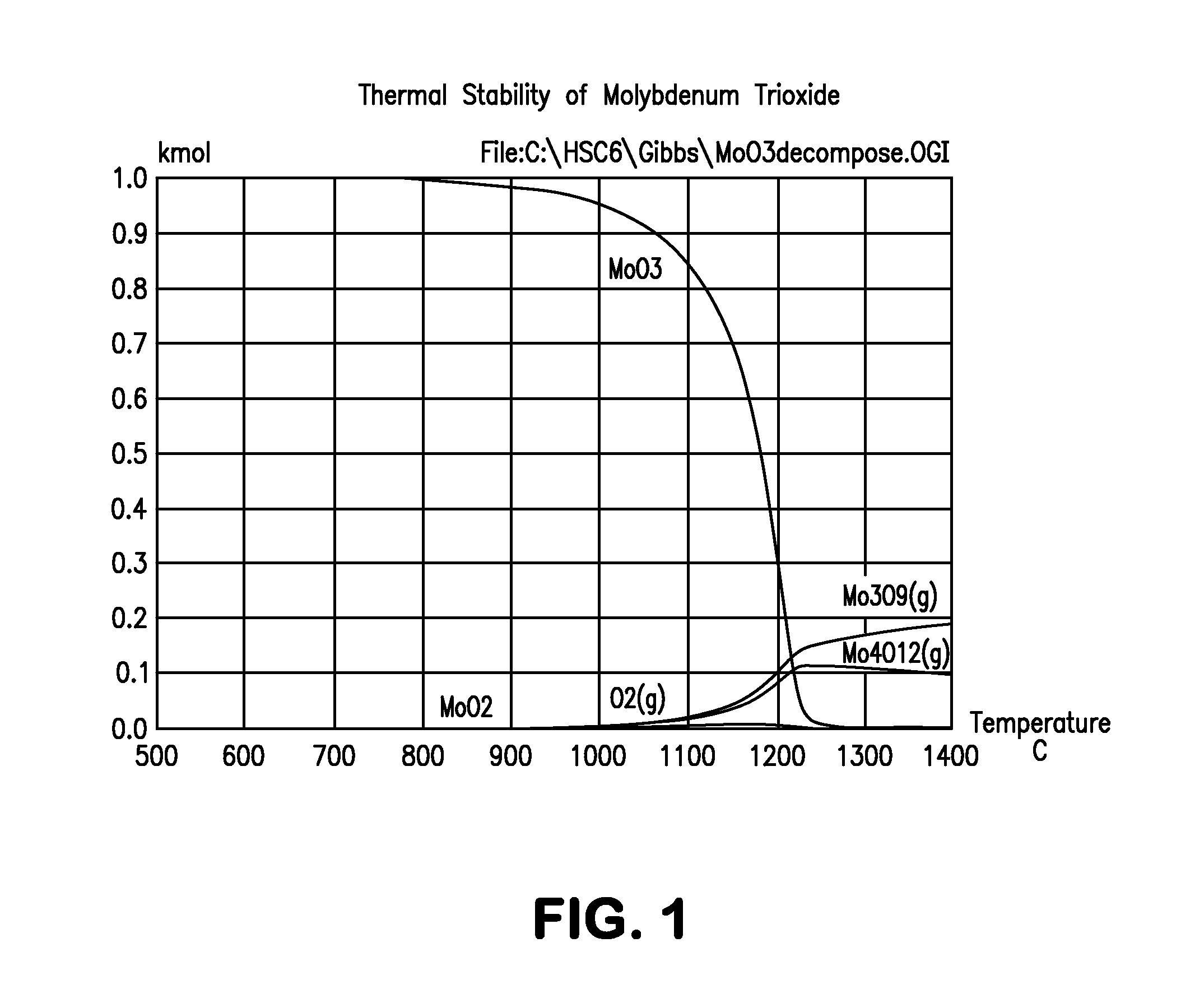
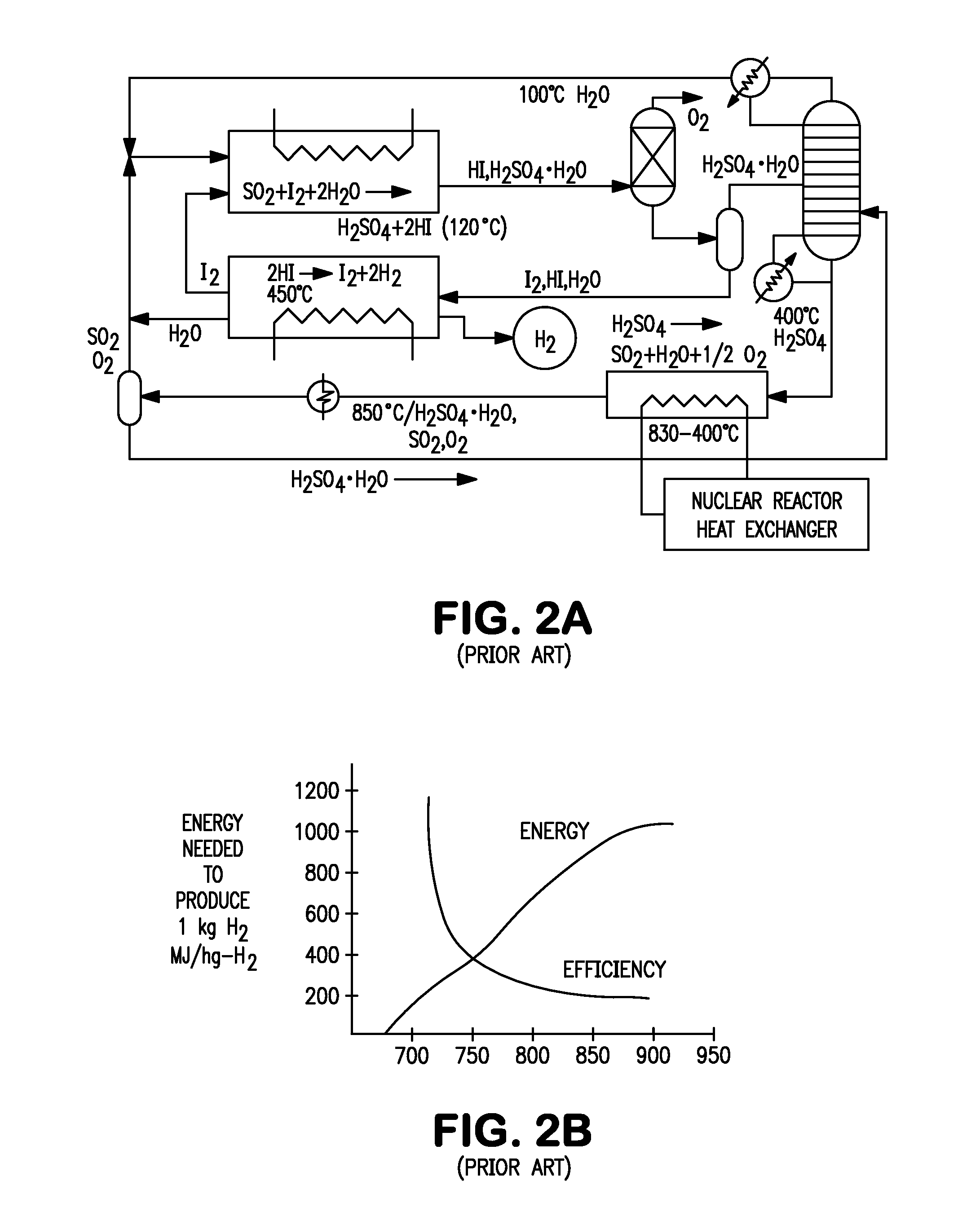
Utilization of process and equipment for oxidation of metal sulfides, preferably two step metal sulfide oxidation reactions, and more preferably with looping back of second step oxide to the first step as an oxidizing agent, to generate sulfur dioxide and a useful metal or metal oxide, and react the sulfur dioxide with halogen (iodine or bromine) and water to produce sulfuric and halogen acid under moderate process conditions and equipment requirements and then dissociating the halogen acids (HI or HBr) to halogen and hydrogen as an overall environmentally and cost efficient and otherwise acceptable safe process for producing hydrogen and other useful products.
Owner:ORCHARD MATERIAL TECH
Method and laser processing device for processing tissue
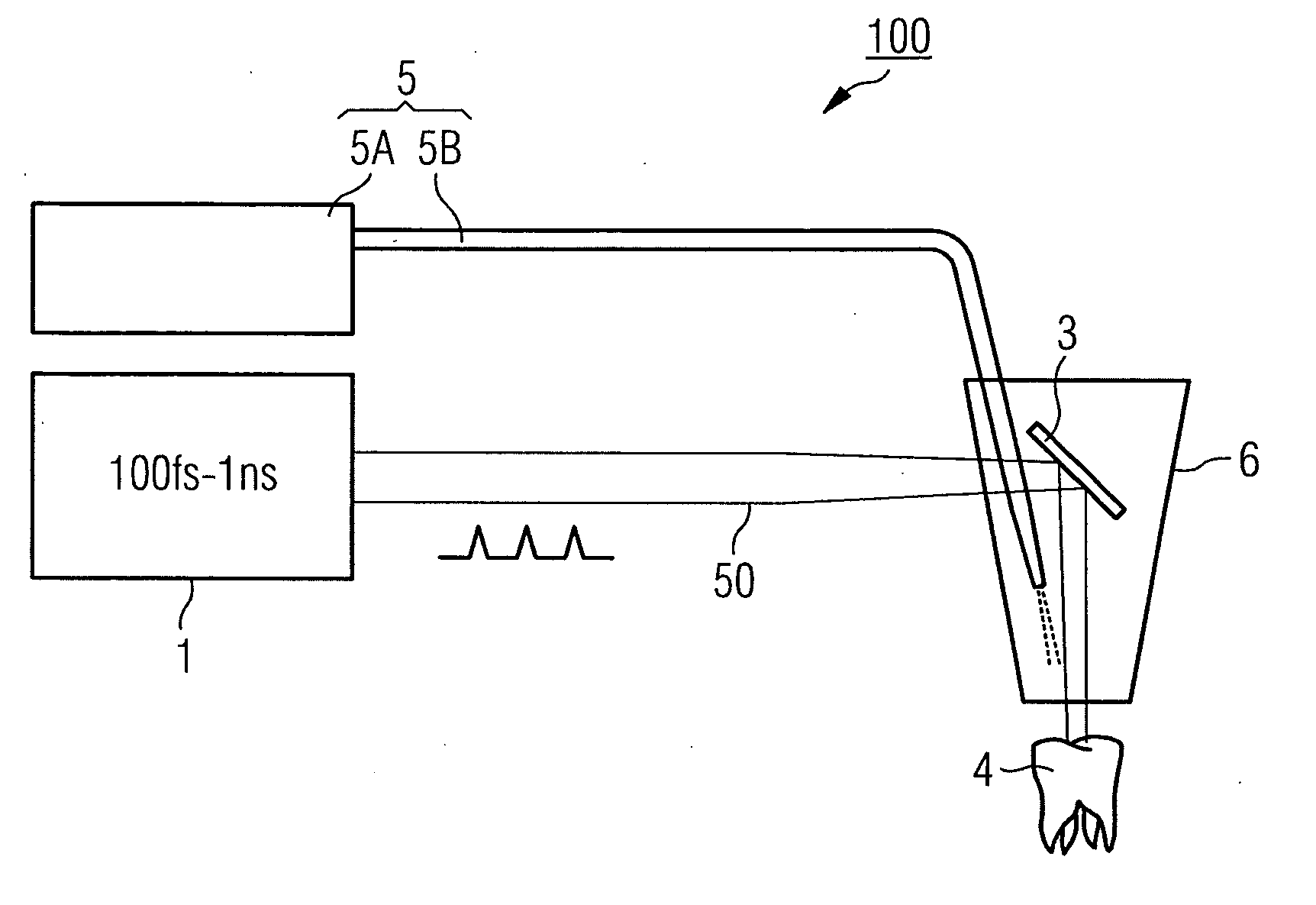
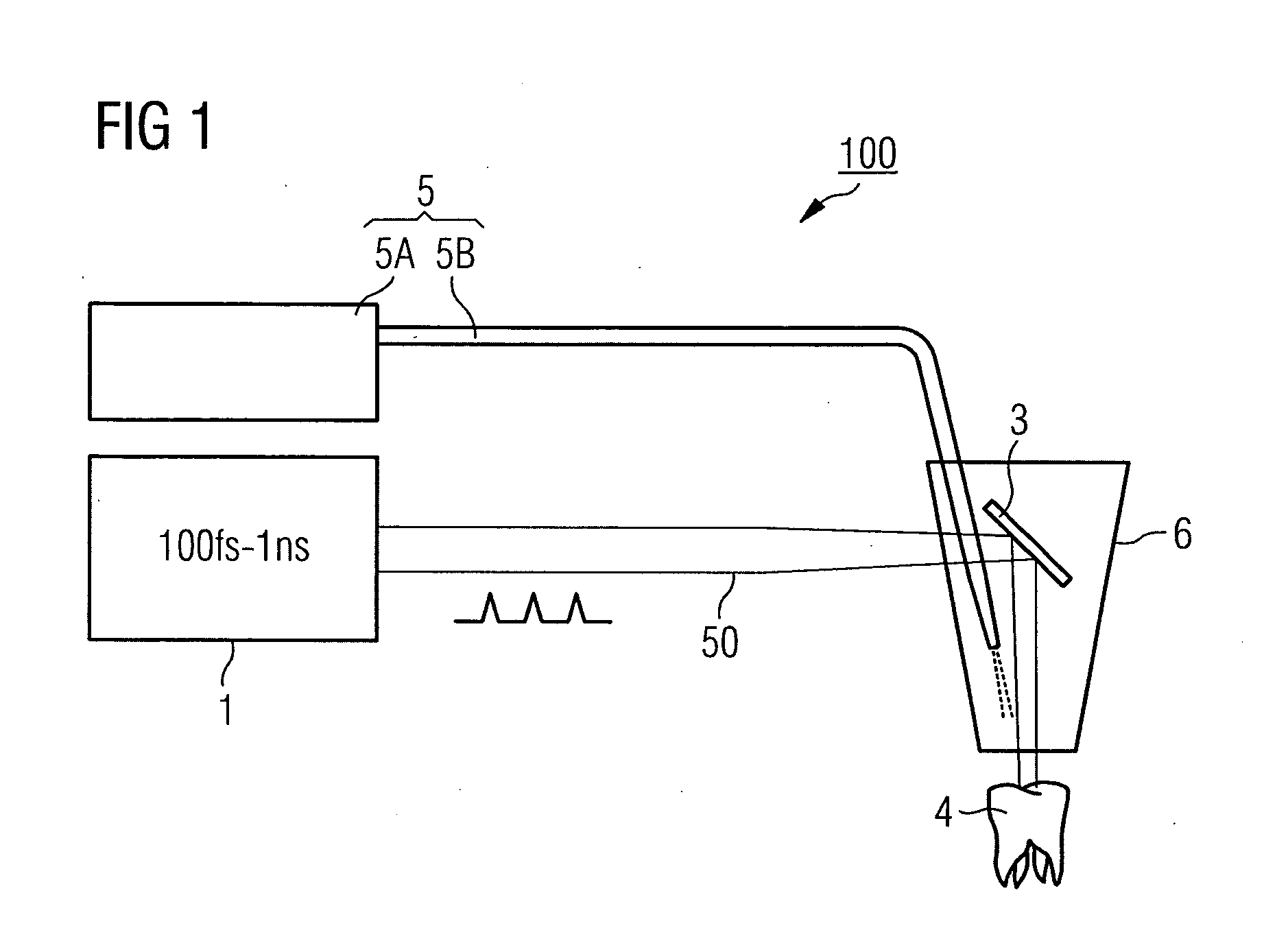
InactiveUS20110300504A1Avoiding and minimizing damaging effect of tissueIncrease flexibilityDental toolsSurgical instrument detailsPhotosensitizerNanosecond
Method and laser processing device to process tissue. In a general aspect, the method to process tissue may include applying a photosensitizer into an area surrounding a region of the tissue to be processed, and irradiating the region of the tissue to be processed with the pulsed processing laser beam, the laser beam emitting laser pulses with a temporal full width at half maximum in a range between about 100 femtosecond and about 1 nanosecond. In another general aspect, the laser processing device to process tissue may include a laser radiation source to provide a pulsed processing laser beam providing emitting laser pulses, a laser beam decoupling unit to decouple the laser beam towards a region of the tissue to be processed, and an output device to output a photosensitizer in a direction of an area surrounding the region of the tissue to be processed, the output device being connected to the decoupling unit.
Owner:LUMERA LASER +1
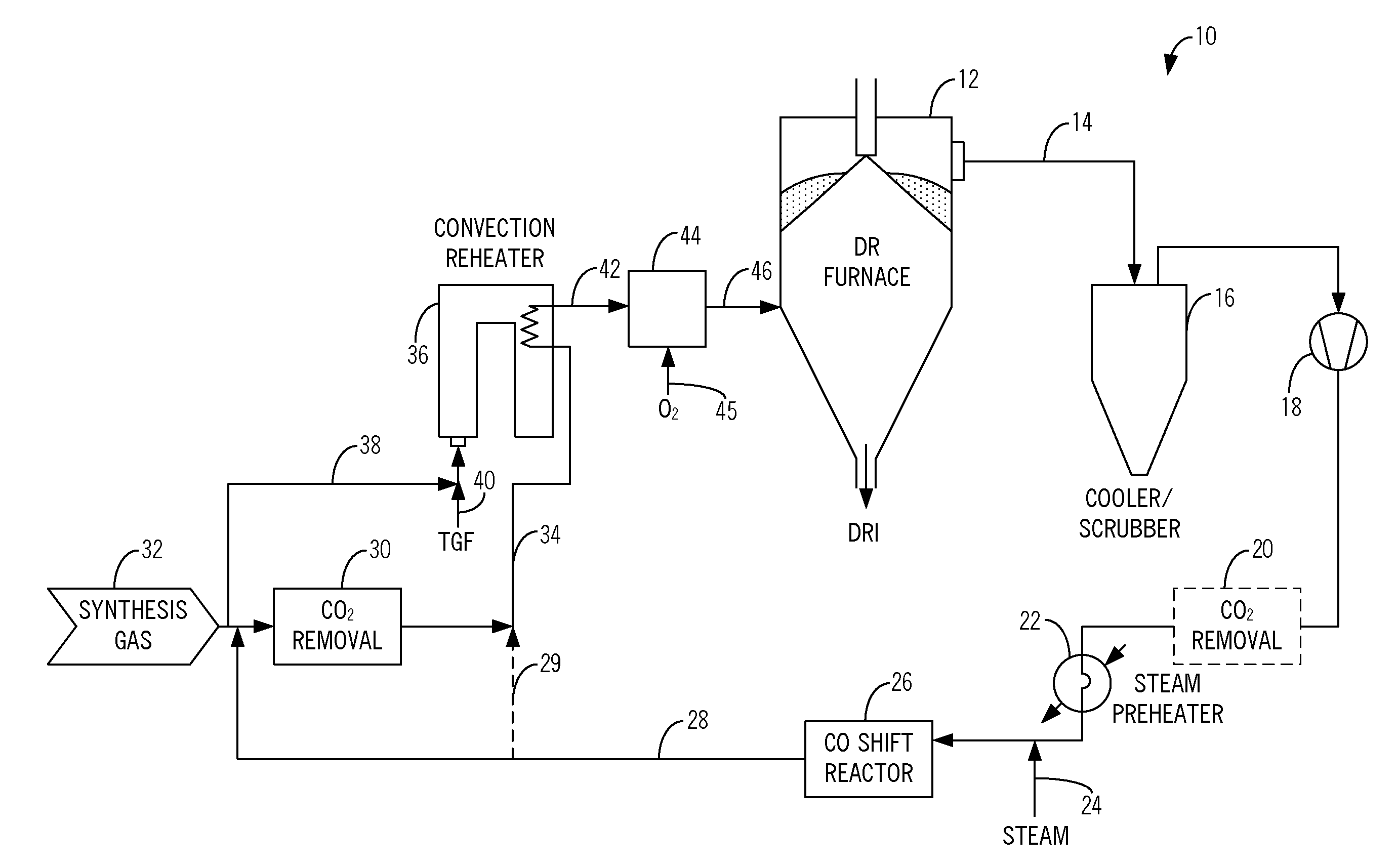
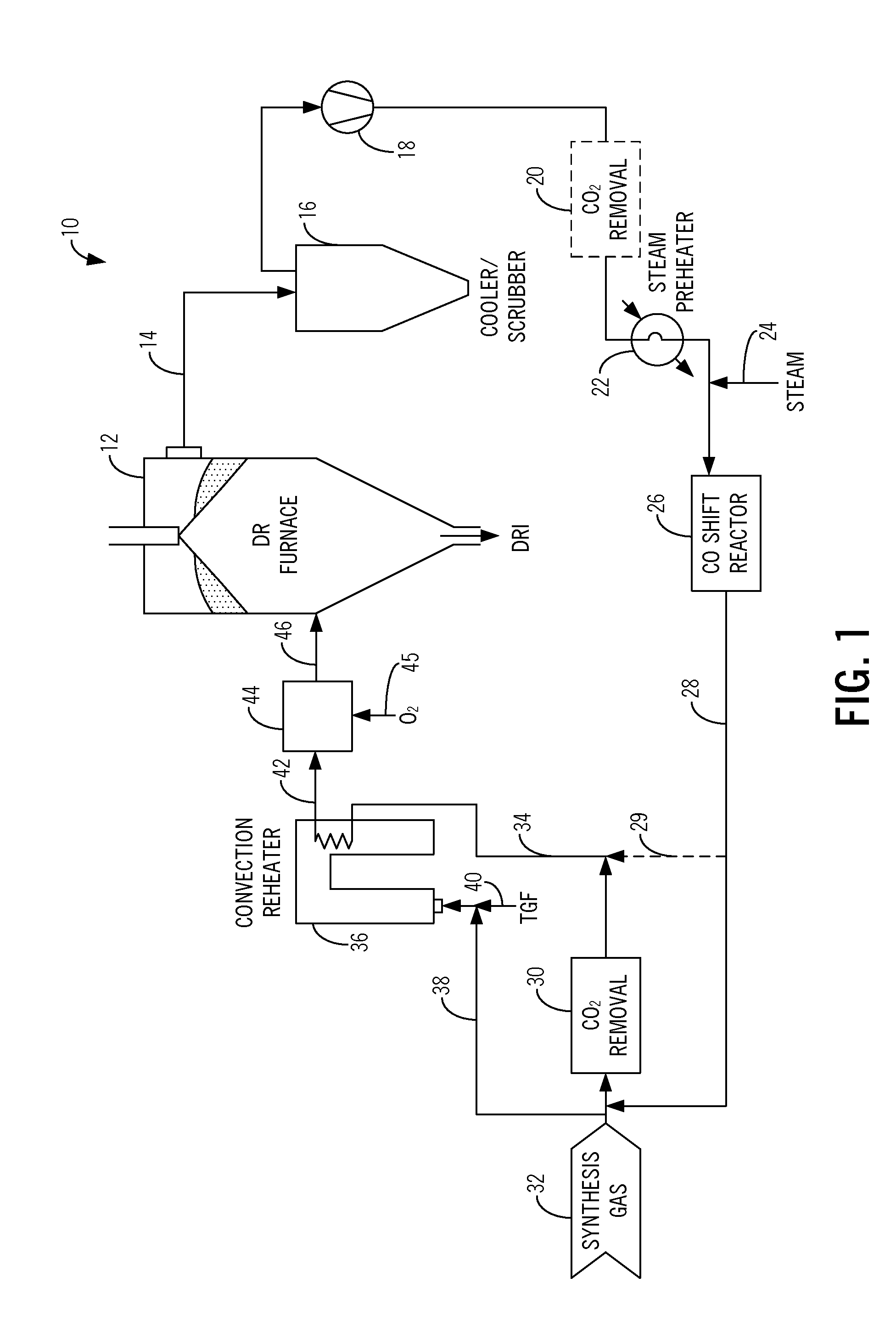
Method and system for the production of direct reduced iron using a synthesis gas with a high carbon monoxide content
ActiveUS20130205951A1Increase contentMinimized in sizeFurnace componentsBlast furnace detailsHigh carbonProduct gas
Methods and systems for the production of direct reduced iron, including: removing a top gas from a direct reduction furnace; carbon monoxide shifting the top gas using a carbon monoxide shift reactor to form a carbon monoxide shifted top gas having a reduced carbon monoxide content; adding one of a coal gas, a synthesis gas, and an export gas to at least a portion of the carbon monoxide shifted top gas to form a combined gas; removing carbon dioxide from the combined gas using a carbon dioxide removal unit to form a carbon dioxide lean combined gas; and providing the carbon dioxide lean combined gas to the direct reduction furnace as a reducing gas for producing direct reduced iron after heating to reduction temperature. Optionally, the method includes removing carbon dioxide from the top gas using a carbon dioxide removal unit prior to carbon monoxide shifting the top gas.
Owner:MIDREX TECH INC
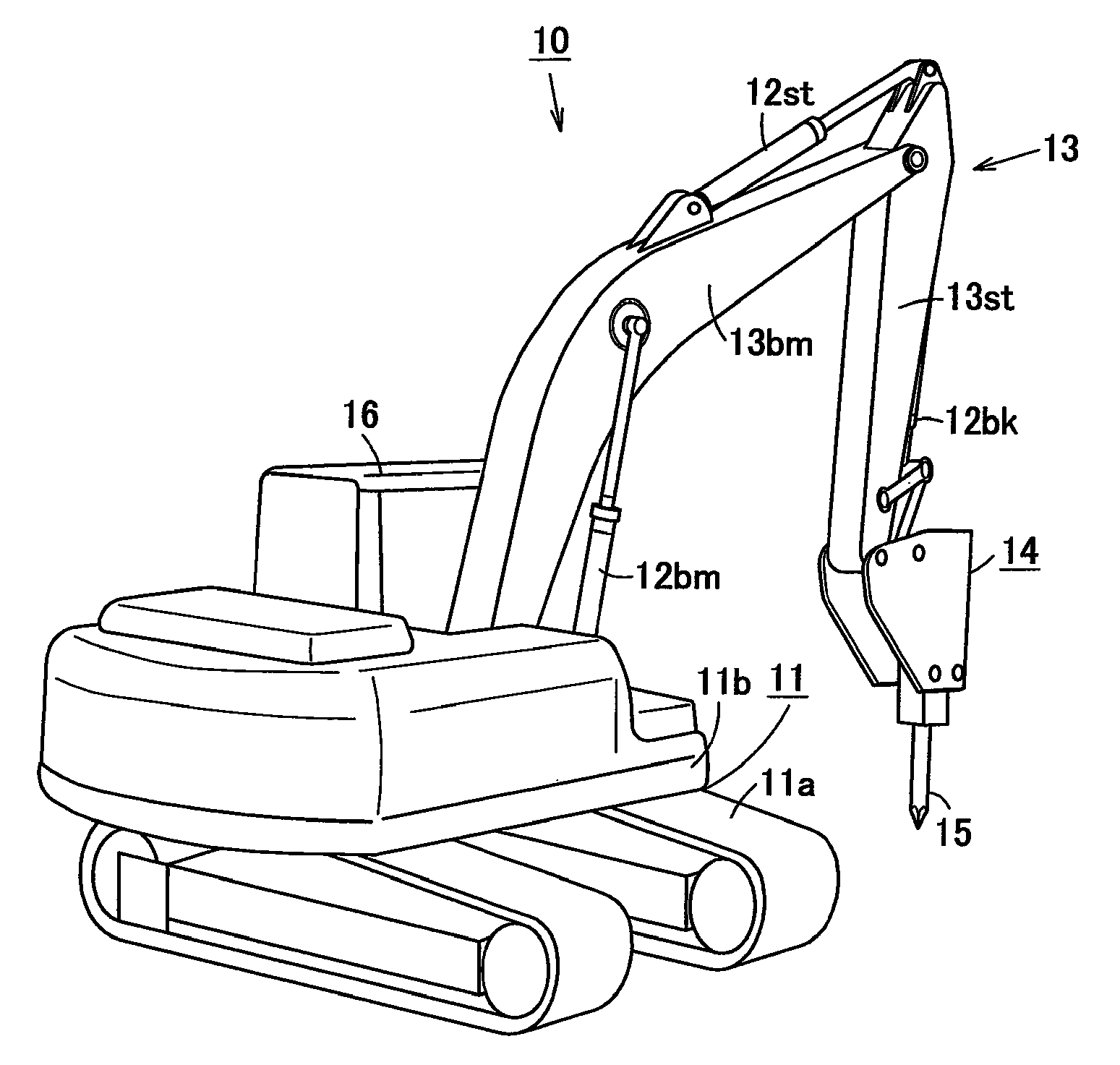
Work machine
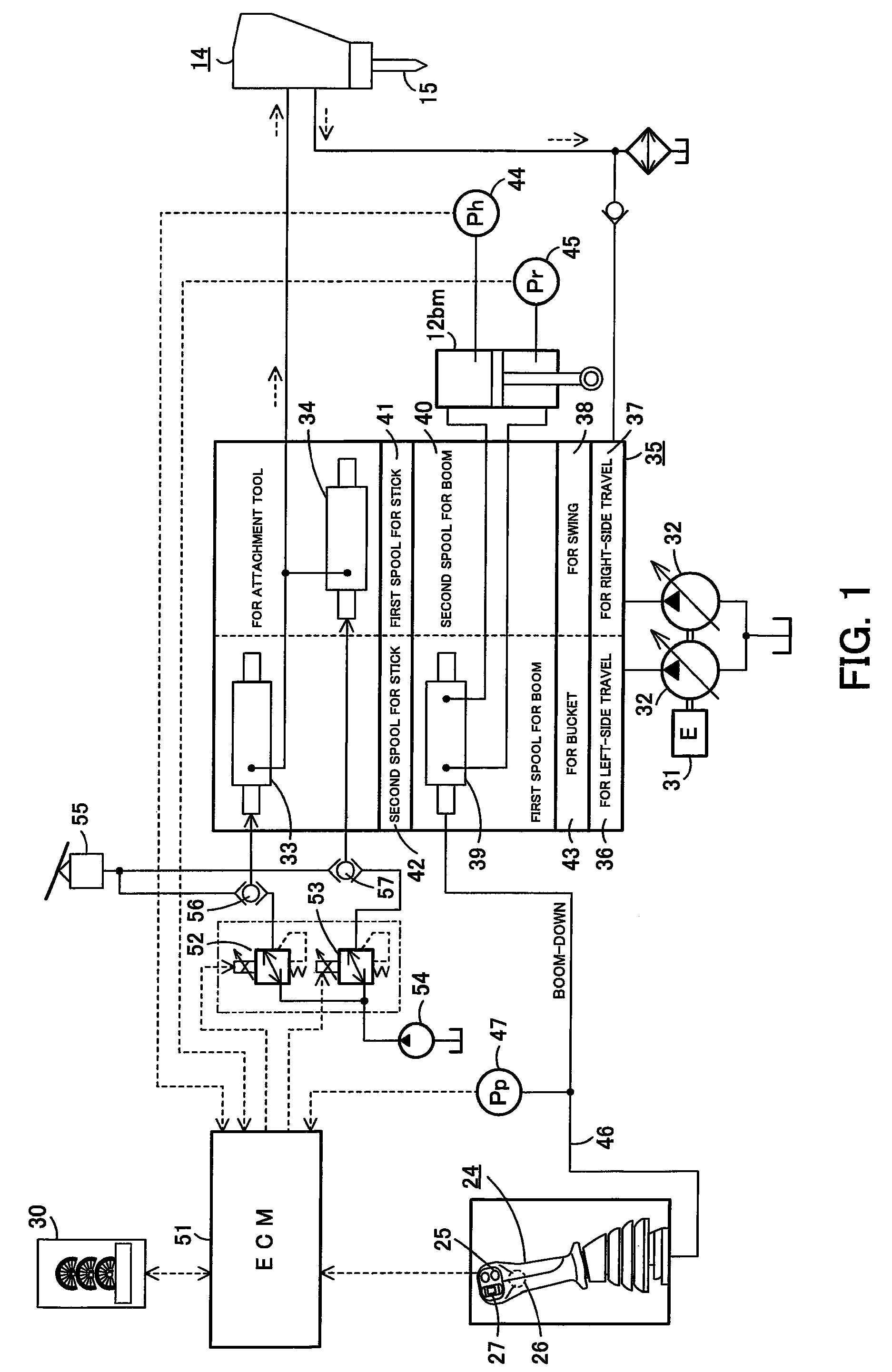
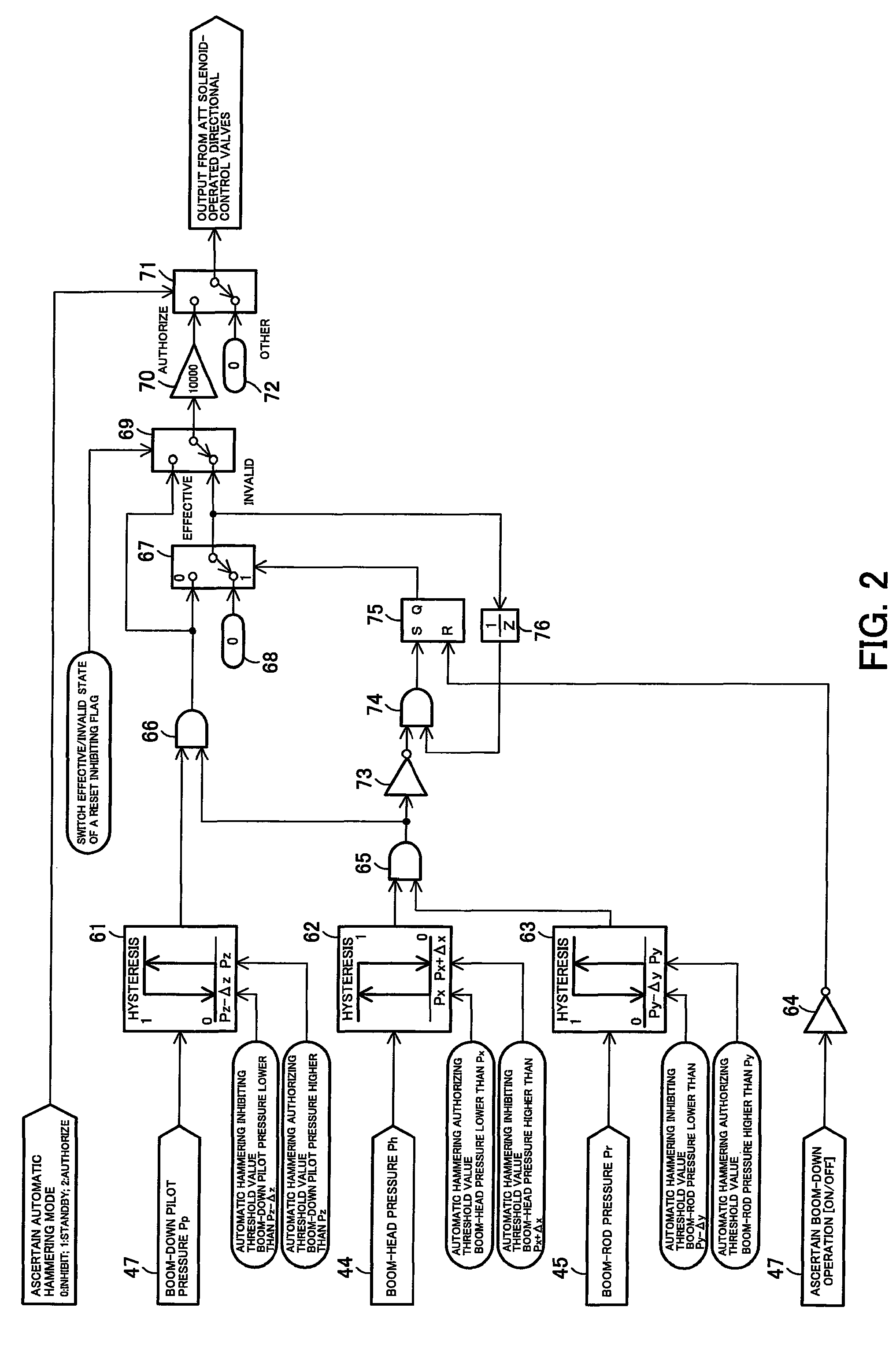
ActiveUS9309649B2Easily switchLow work equipmentReciprocating drilling machinesMechanical machines/dredgersAutomotive engineeringHydraulic brake
A work machine equipped with an automatic hammering function is capable of preventing breakage of the hammer caused by blank firing. Hydraulic oil fed to a hydraulic breaker at the distal end of a work machine is controlled by first and second spools. Operating an operation lever so as to contract single rod type boom cylinders to press the hydraulic breaker against an object to be crushed. Head-side pressure and rod-side pressure of the boom cylinders are respectively detected by pressure sensors. Any one of switches is used to switch the mode of automatic hammering operation between an automatic hammering inhibiting mode and an automatic hammering authorizing mode. In the automatic hammering authorizing mode, a controller controls the first and second spools of the hydraulic breaker so as to open them only when head-side pressure and rod-side pressure of the boom cylinders are in a given range of pressing force.
Owner:KEJTERPILLAR R L
Sorting apparatus
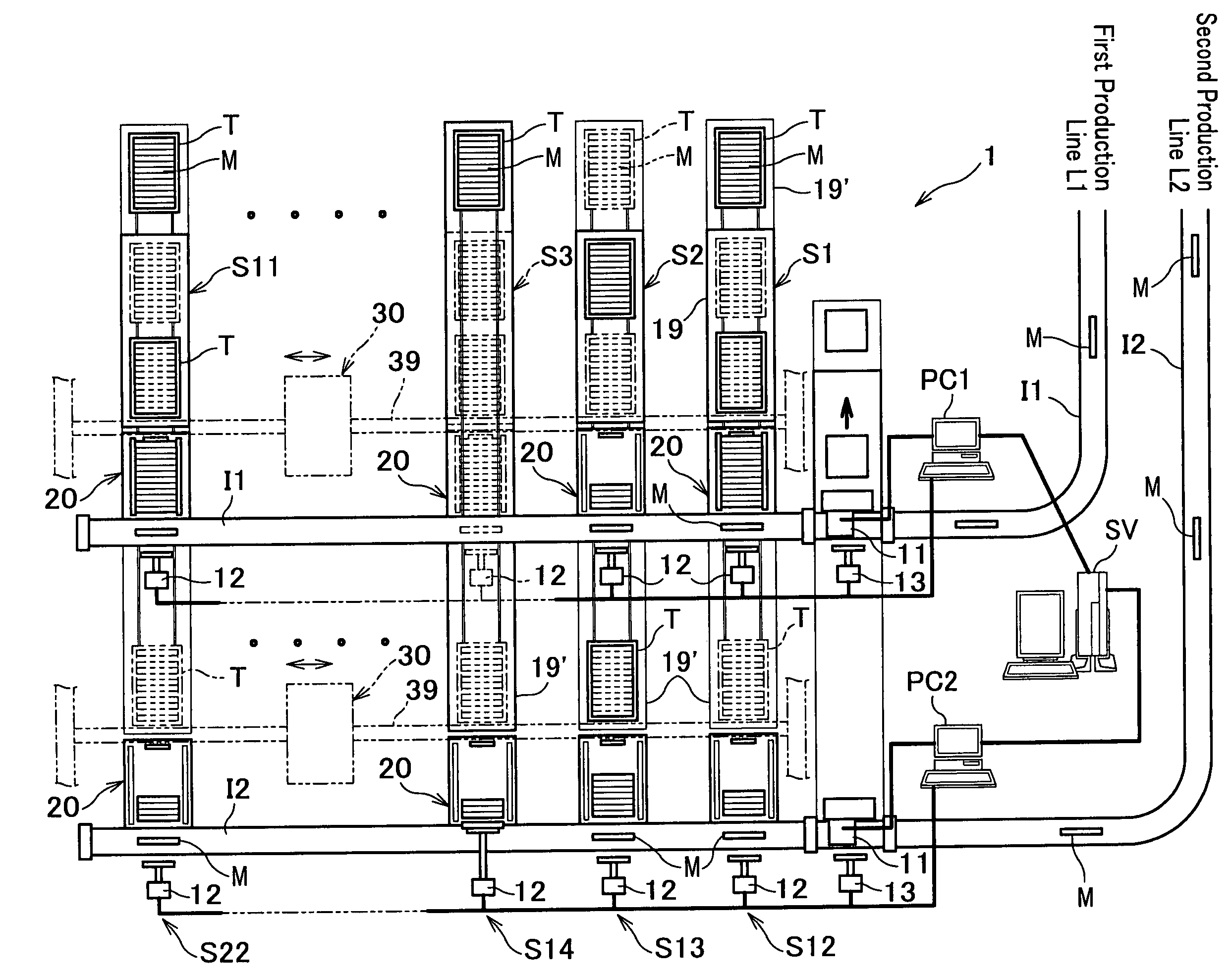
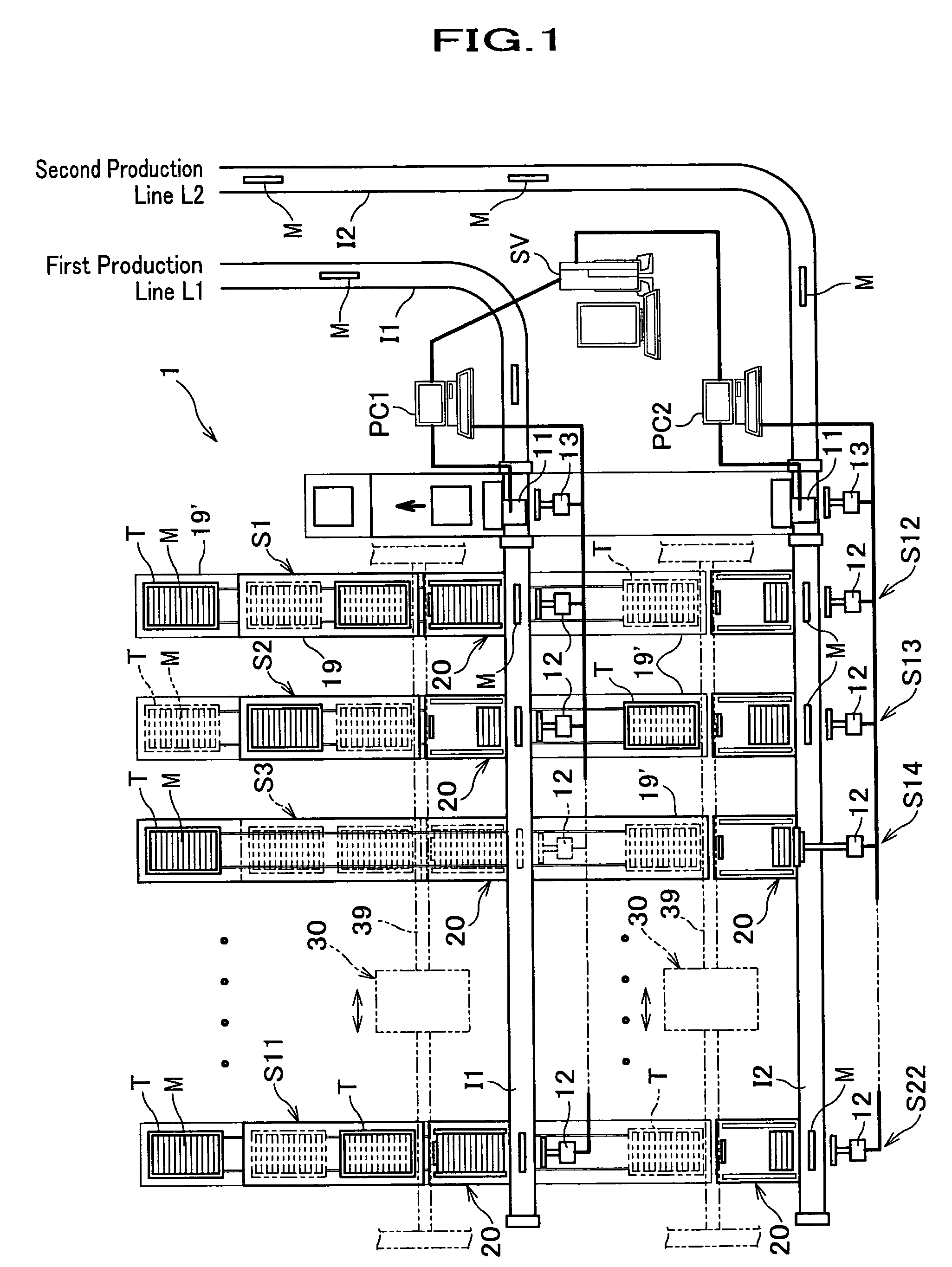
InactiveUS7080740B2Easy to useReduce equipment costsConveyorsStacking articlesProduction lineIndustrial engineering
A sorting apparatus which separates a work according to a predetermined standard flowing on a production line and arrays the work in one column is characterized by being equipped with a carrying-in line carrying in the work, a work identifying machine provided on the way of the carrying-in line, a plurality of columns of temporary accumulating units installed neighboring the carrying-in line at an approximately same height as the carrying-in line, a plurality of trays provided respectively corresponding to the temporary accumulating units of plurality of columns of temporary accumulating units, a pusher pushing out a work which flows in said carrying-in line into one column of the temporary accumulating units based on a result identified by the work identifying machine, and a transfer machine gripping / transferring a predetermined number of works all together to the trays corresponding to the temporary accumulating units when the predetermined number of works is accumulated in a temporary accumulating unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
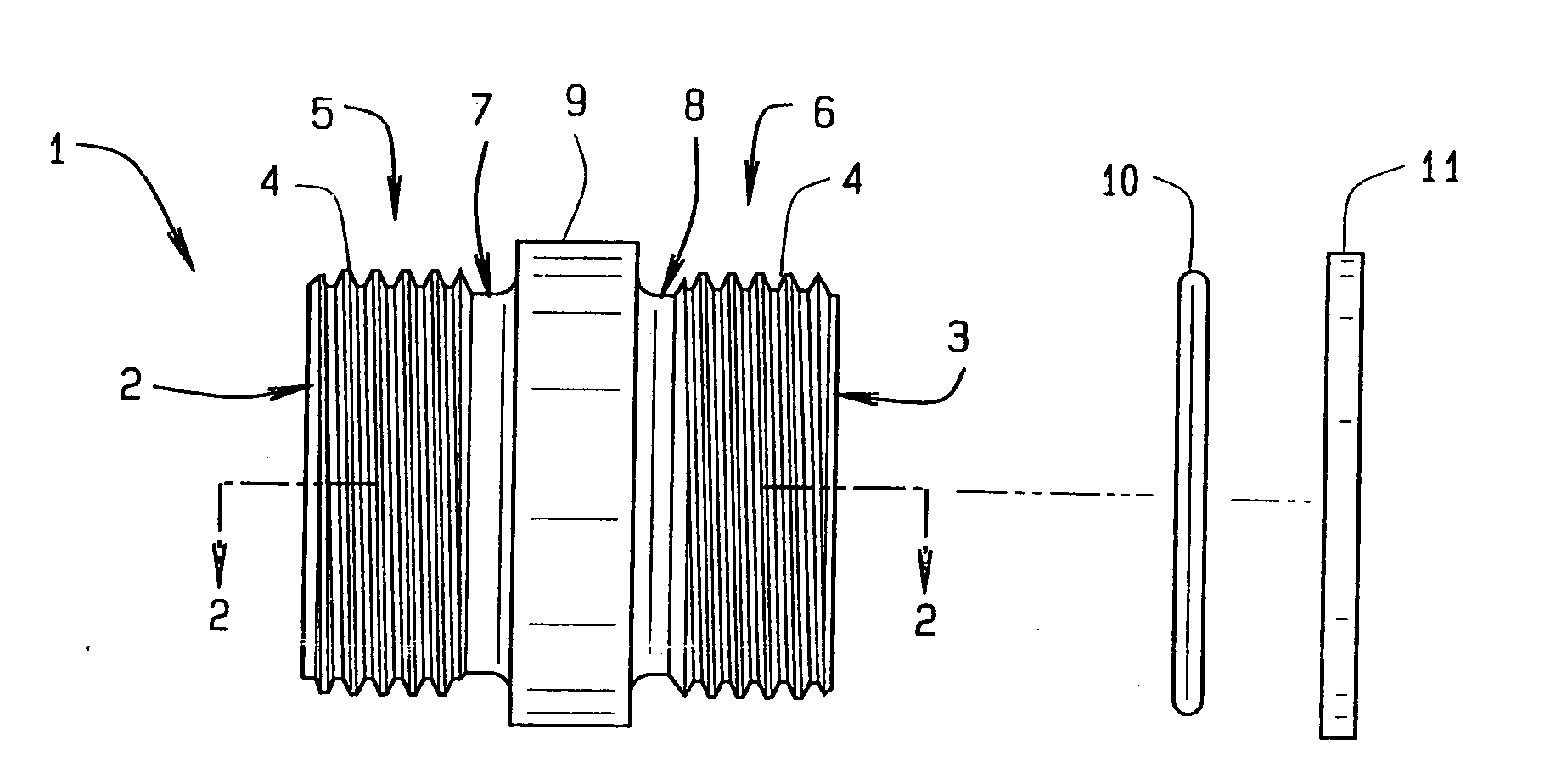
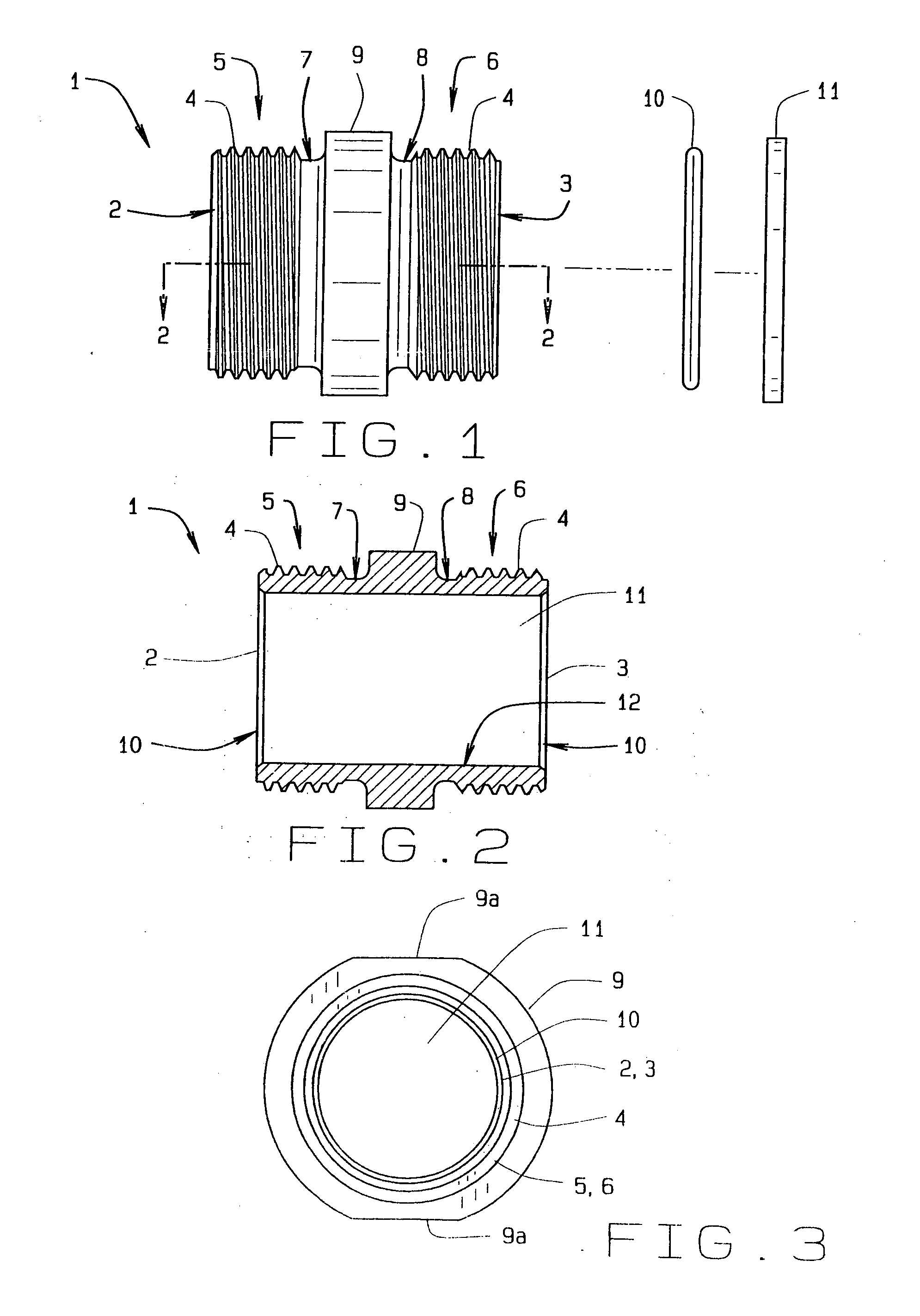
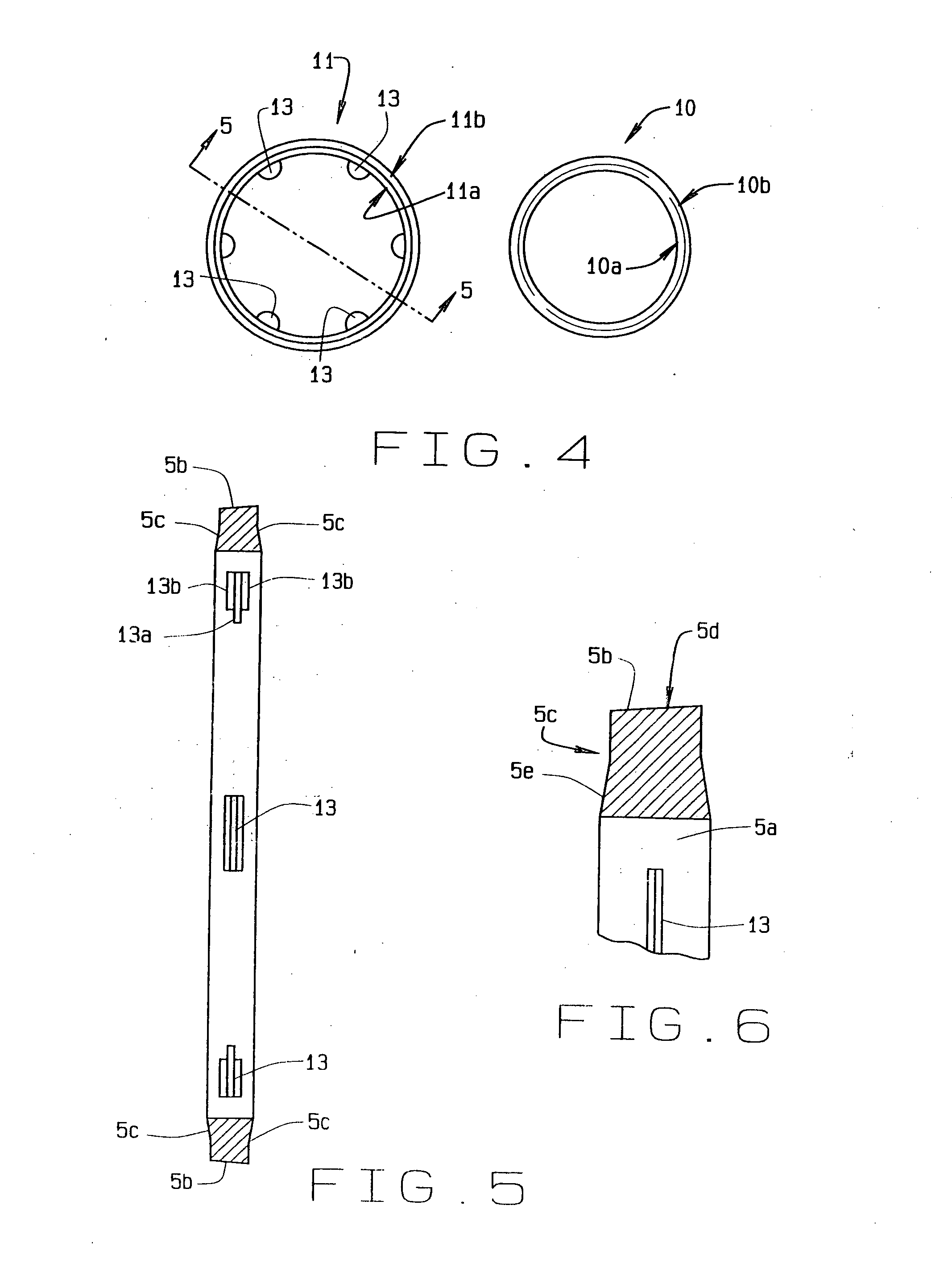
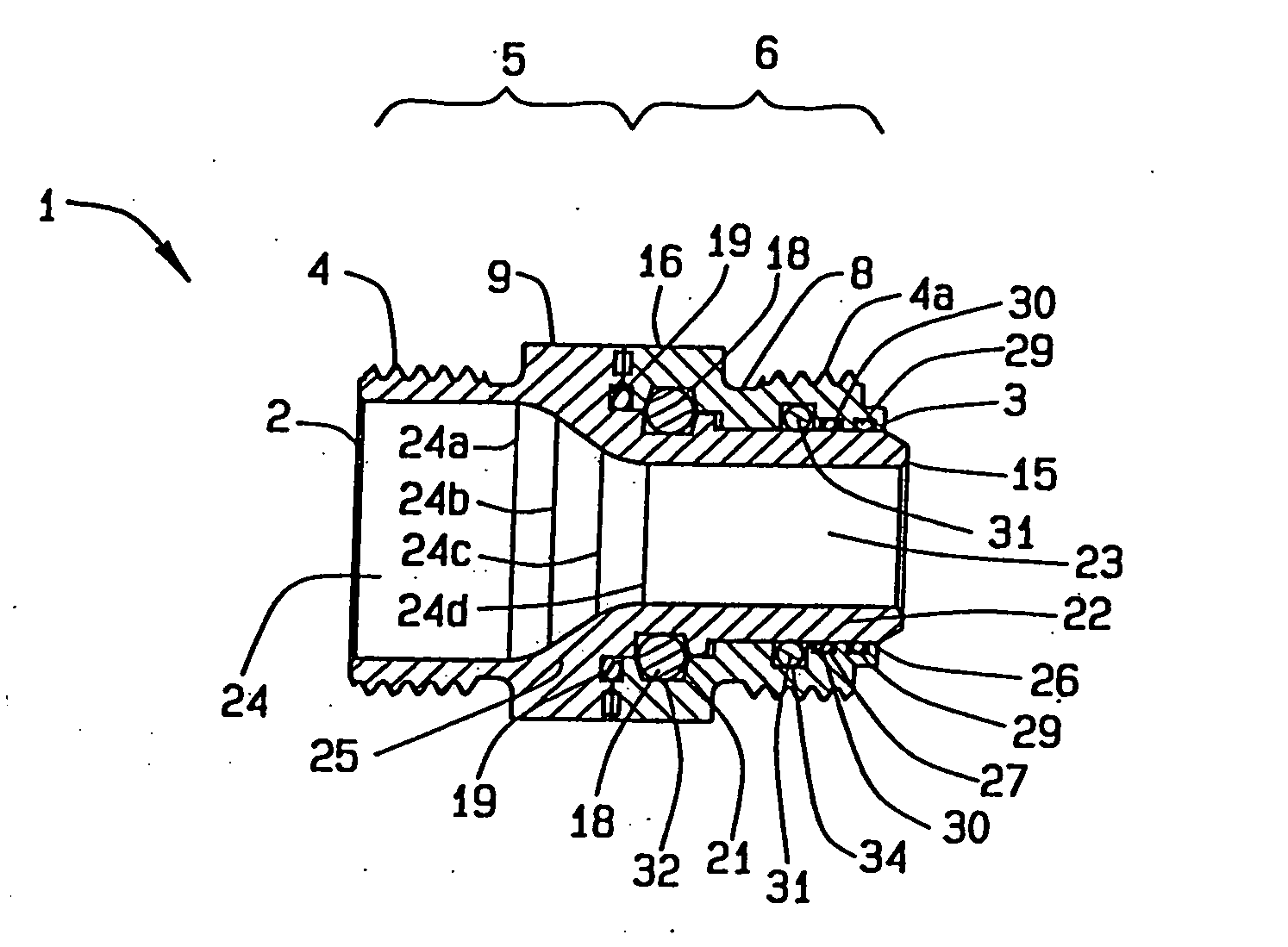
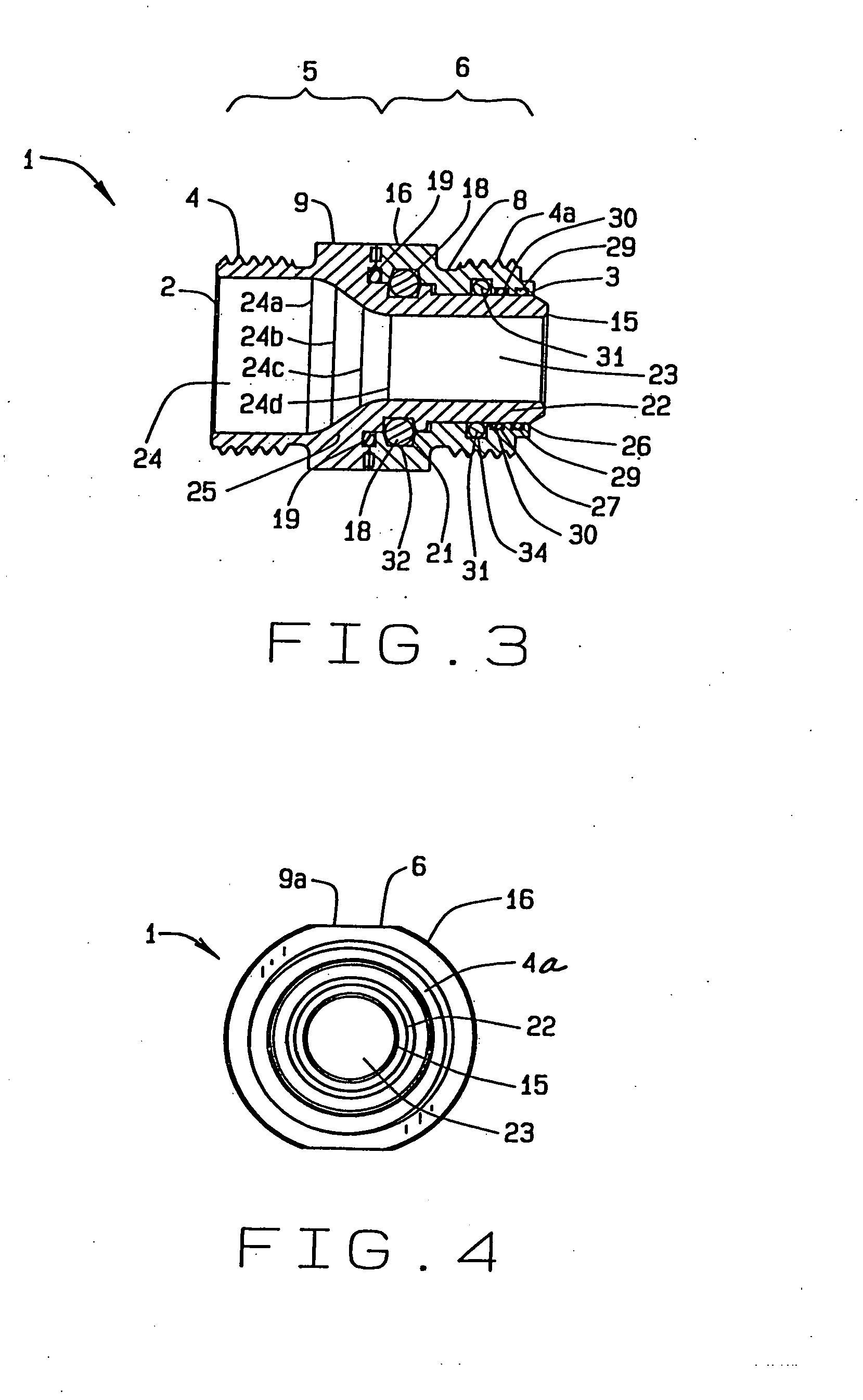
Threaded adaptor
ActiveUS20130049360A1Low costEasy to buyFluid pressure sealed jointsJoints with sealing surfacesEngineeringScrew thread
A threaded adaptor has a first end and an opposite second end of a generally hollow cylinder. At least one end has threading for connection to a hose or fitting and the ends form the male half of the connection. Centered upon the adaptor, a collar provides at least two faces for gripping of the adaptor by a tool. Within the adaptor, the two ends open into a smooth chamber that allows for uninterrupted fluid flow. To further seal the adaptor, at least one O-ring and at least one gasket are provided as alternate embodiments. In another alternate embodiment, the adaptor has one threaded end, an opposite barbed end with a clamp, and a collar with six faces. These two ends open into a chamber with a stepped diameter. The adaptor provides for flow of fluid with little turbulence.
Owner:HUSKY
Recovery of benzene and benzene derivatives from gasoline fractions and refinery streams
InactiveUS20130345486A1Improved propertyAdequate shiftingDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsAlkaneExtractive distillation
A process for the separation of the aromatic compounds benzene, toluene and xylene from an aromatics-containing reformate gasoline and pyrolysis gasoline or a coke-oven light oil or an aromatics-containing refinery stream, in which the aromatics are separated by an extractive distillation uses a novel solvent combination made up of the compounds n,n′-diformyl piperazine or 2,2-bis-(cyanoethyl)ether in a combination with n-formyl morpholine as a second solvent for extractive distillation so that the solvent combination obtained shows a higher selectivity with regard to the aromatics to be extracted so that a lower solvent load is required. The aromatics-containing feed mixture is first submitted to a pre-distillation so that the obtained fraction has a narrow boiling point range. This fraction is then submitted to an extractive distillation in a first column, in which an aromatics-lean head product of predominantly paraffinic hydrocarbons is obtained as well as an aromatics-enriched bottom product. The bottom product is passed to a second column in which an aromatics-rich raffinate is obtained by reducing the pressure or increasing the temperature so that the extracting solvent combination obtained as bottom product can be recycled into the process.
Owner:UHDE GMBH
Reactor with Honeycomb Catalyst for Fuel Reformation
ActiveUS20160228838A1Reduced bed pressureImprove mass transfer efficiencyHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHydrogenCarbon nanotube
A reactor using honeycomb catalyst is provided for fuel reformation with high activity and heat stability. The reactor comprises a heating tube, a methane gas inlet, a three-way steam inlet and a hydrogen-rich gas outlet. The three-way steam inlet is near to the heating tube for providing heat required for reformation and to reduce power consumption. The heating tube is made of an inconel material so that the overall reaction may be carried out at high temperature. The heating tube is set with a honeycomb carrier of cordierite. The honeycomb carrier is pasted with carbon nanotube and heat-treated to increase internal surface area. The honeycomb carrier has a Pt / CeO2 / α-Al2O3 catalyst; is placed in the heating tube; and has honeycomb-pores channels parallel to a main axis of the heating tube.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Distilled water production system
InactiveUS20120261250A1Construction be to be lowReduce equipment costsVacuum condensationGeneral water supply conservationWater vaporWater production
A distilled water production system (1) includes a main tank (2), a pressure reducer (3), a cooler (4) and a pool (5). Sea water or dirty water is contained in the main tank (2) as raw water for producing distilled water. The pressure reducer (3) brings an inside of the main tank (2) into a reduced pressure state. The cooler (4) is disposed in an upper part within the main tank (2) and cools water vapor produced by evaporation of the raw water occurring in the reduced pressure state. The pool (5) is disposed at a position below the cooler (4) within the main tank (2) and contains the distilled water obtained by cooling and condensation of the water vapor by the cooler (4). According to the distilled water production system (1), the running cost and construction and equipment costs can be suppressed to be low.
Owner:NAKAYAMA YOSHINAKA
Method for processing lignocellulose material
ActiveUS20120193049A1Requires low equipmentLow process temperatureFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpBiofuelsAlgluceraseSodium acetate
A method for processing a lignocellulose material, comprises the following steps: (1) crushing and sieving the lignocellulose material, and collecting granules with a particle size of between 0.08 and 0.1 mm; (2) mixing the granules obtained in step (1) with water, and dispersing through a colloid mill to yield a suspension with a particle size of 40-80 μm; (3) homogenizing the suspension obtained in the step (2) under high pressure to have a particle size of between 10 and 40 μm; and (4) buffering the suspension obtained in the step (3) with a buffer solution of sodium acetate and acetic-acid, adding cellulase, β-glucosidase, and xylanase, and performing zymolysis for 36-72 hours.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
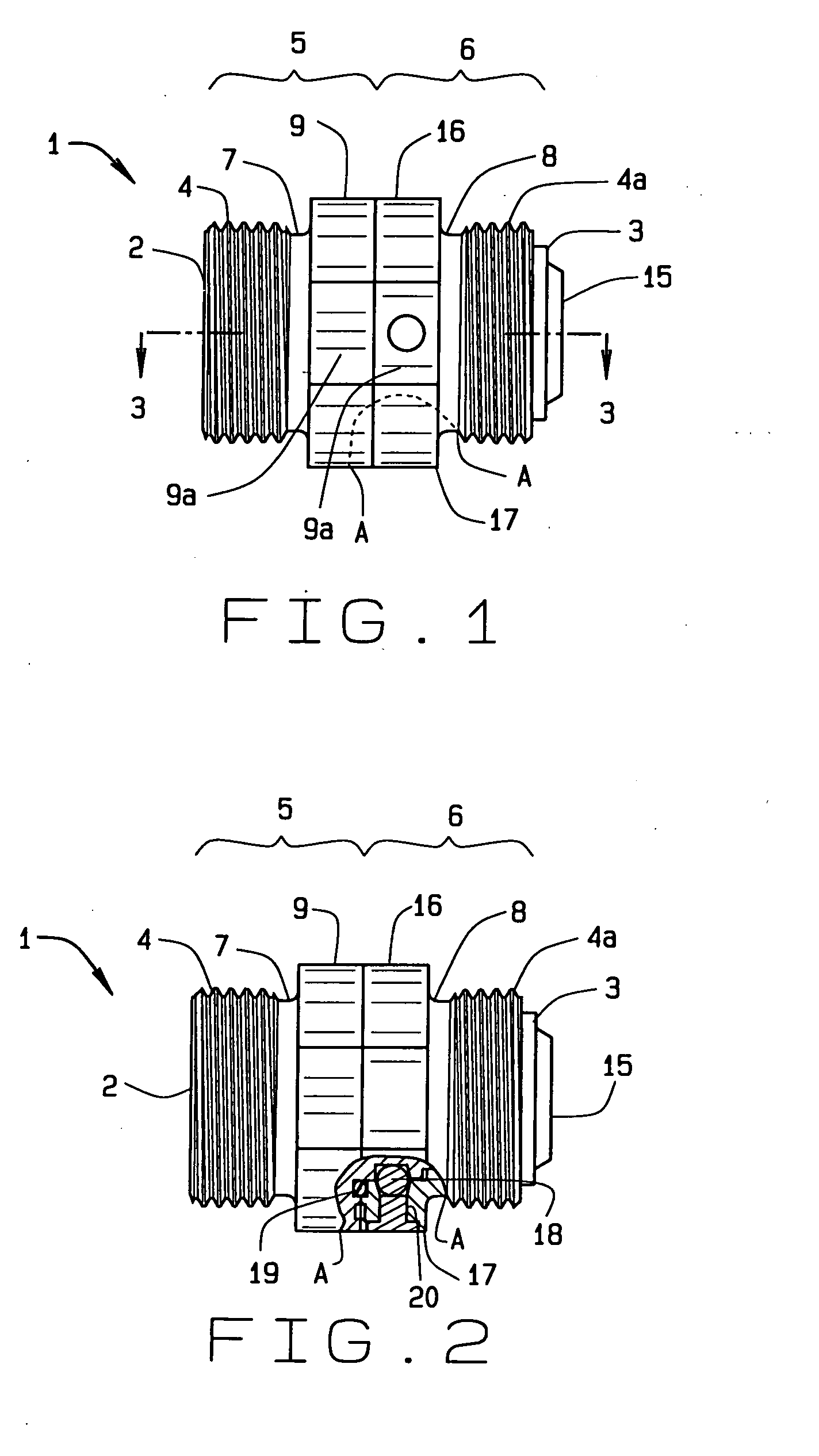
Threaded inline swivel
ActiveUS20140138946A1Requires low equipmentLow laborSleeve/socket jointsAdjustable jointsScrew threadWrench
A threaded inline swivel has a first nut and an opposite second nut each having the form of a generally hollow cylinder with an open end to receive fuel. Each nut has a collar that has a common nominal diameter. A collar provides at least two faces for gripping by a wrench. Each nut has threading for connection to a hose or other fitting. To further seal the swivel to a hose or a fitting, at least one O-ring and at least one gasket are provided as alternative embodiments. In a further alternate embodiment, the swivel has a threaded second nut and an opposite barbed end on the first nut with a clip. The first nut has its chamber that constricts in diameter through a throat as it enters the second nut. The swivel in all embodiments provides for flow of fluid through it with little turbulence.
Owner:HUSKY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com