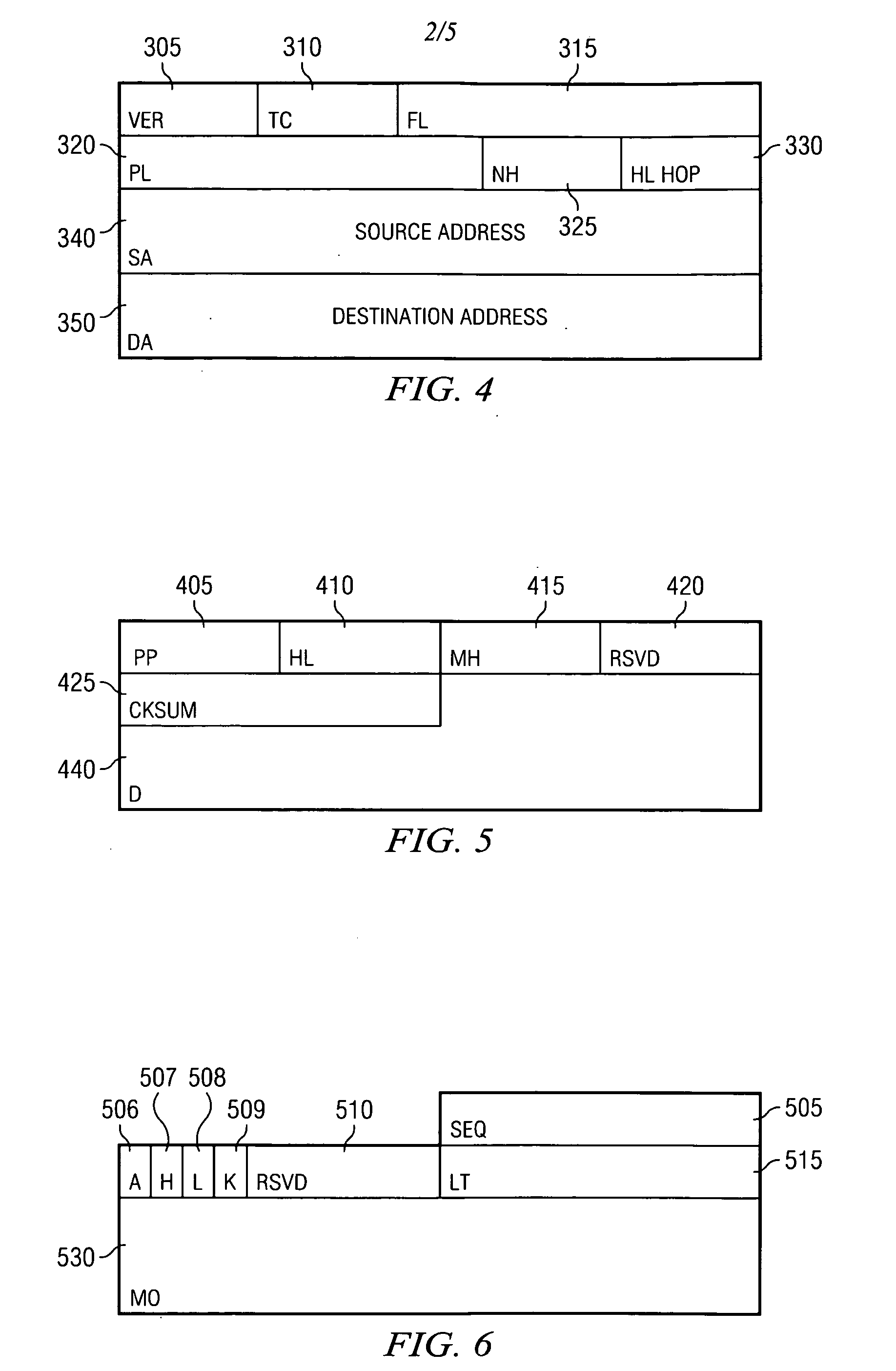
Patents
Literature
355 results about "Network Access Identifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer networking, the Network Access Identifier (NAI) is a standard way of identifying users who request access to a network. The standard syntax is "user@realm". Sample NAIs include (from RFC Network Access Identifiers were originally defined in RFC 2486, which was superseded by RFC 4282, which has been superseded by RFC 7542. The latter RFC is the current standard for the NAI. NAIs are commonly found as user identifiers in the RADIUS and Diameter network access protocols and the EAP authentication protocol.
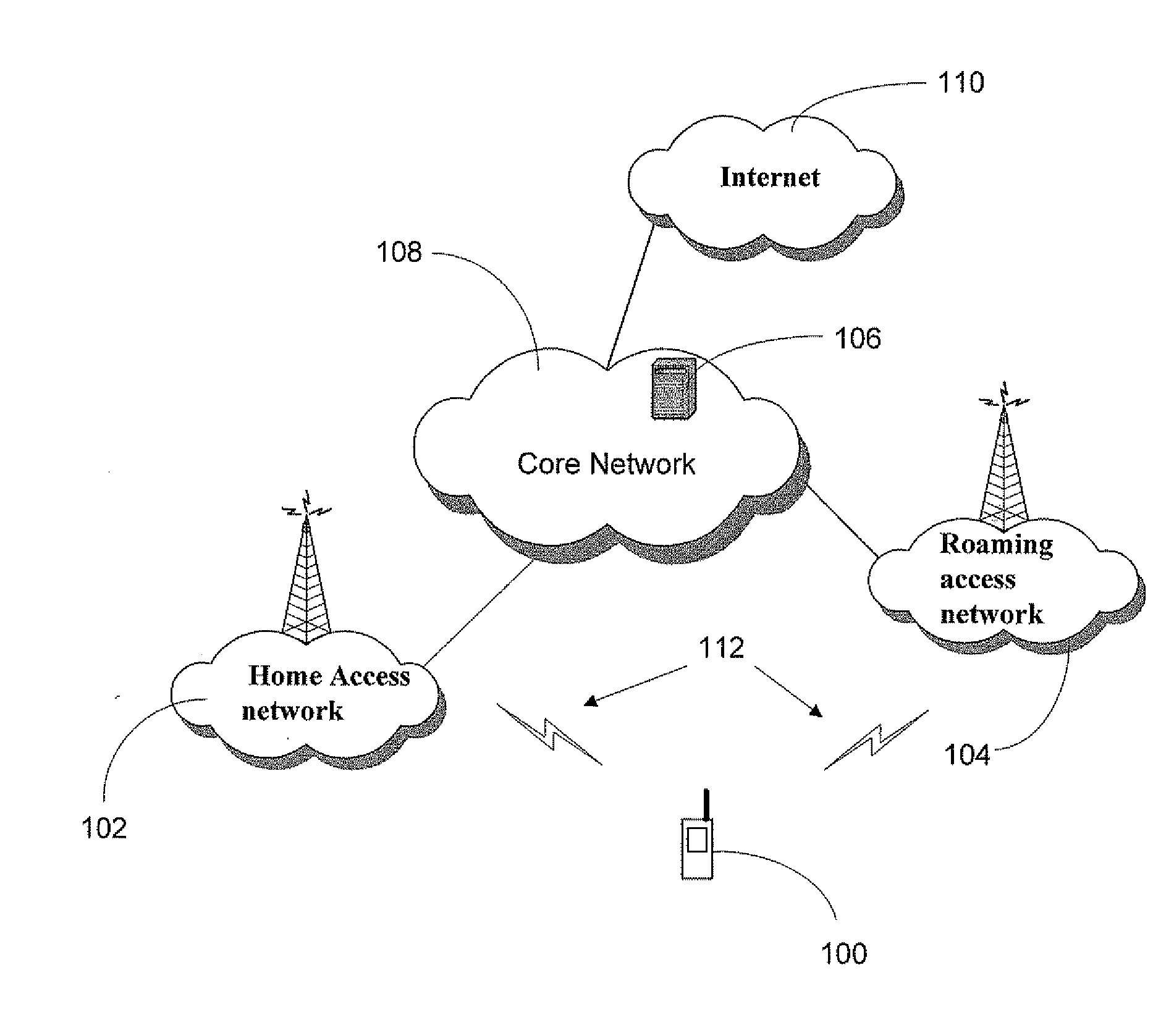
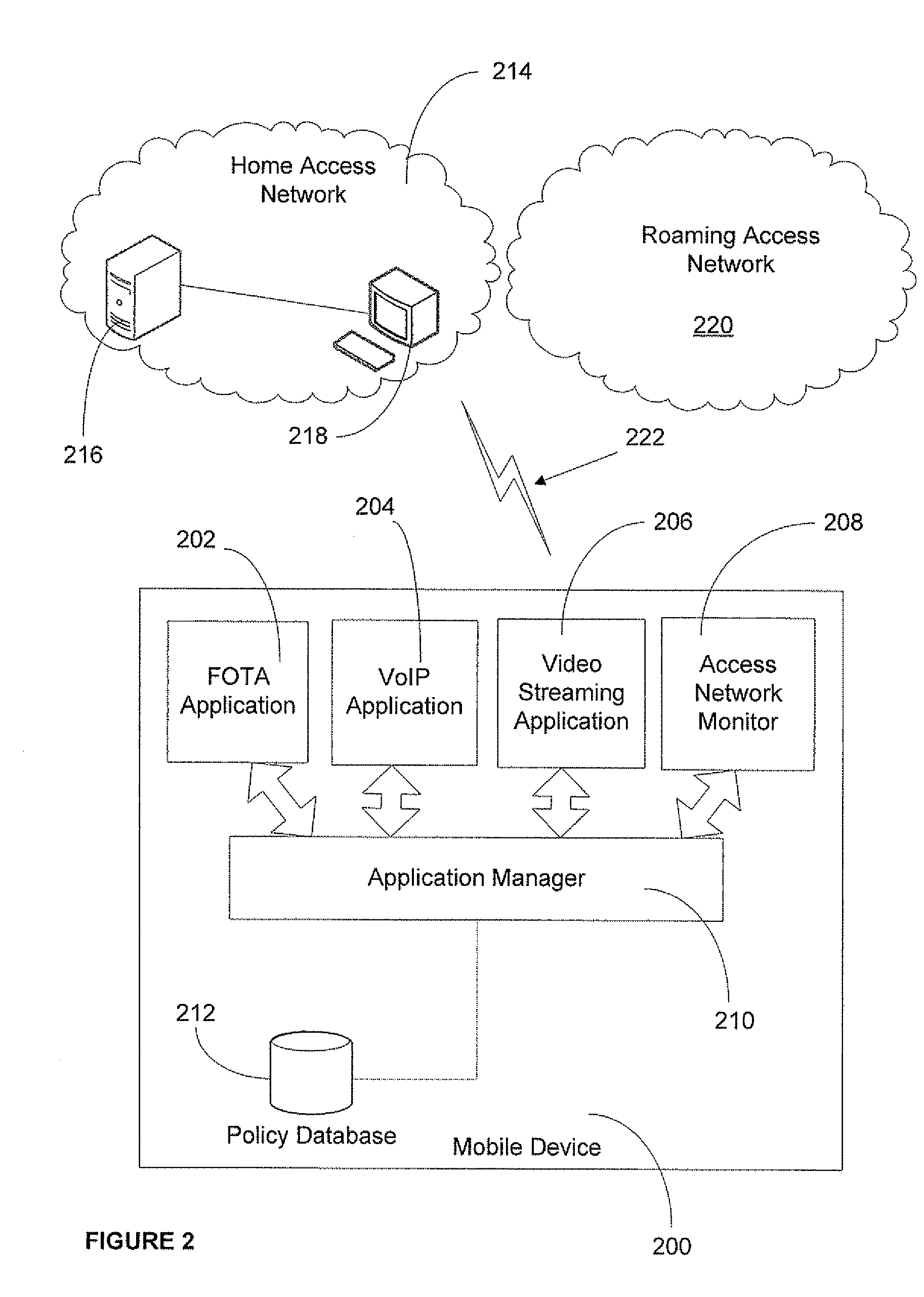
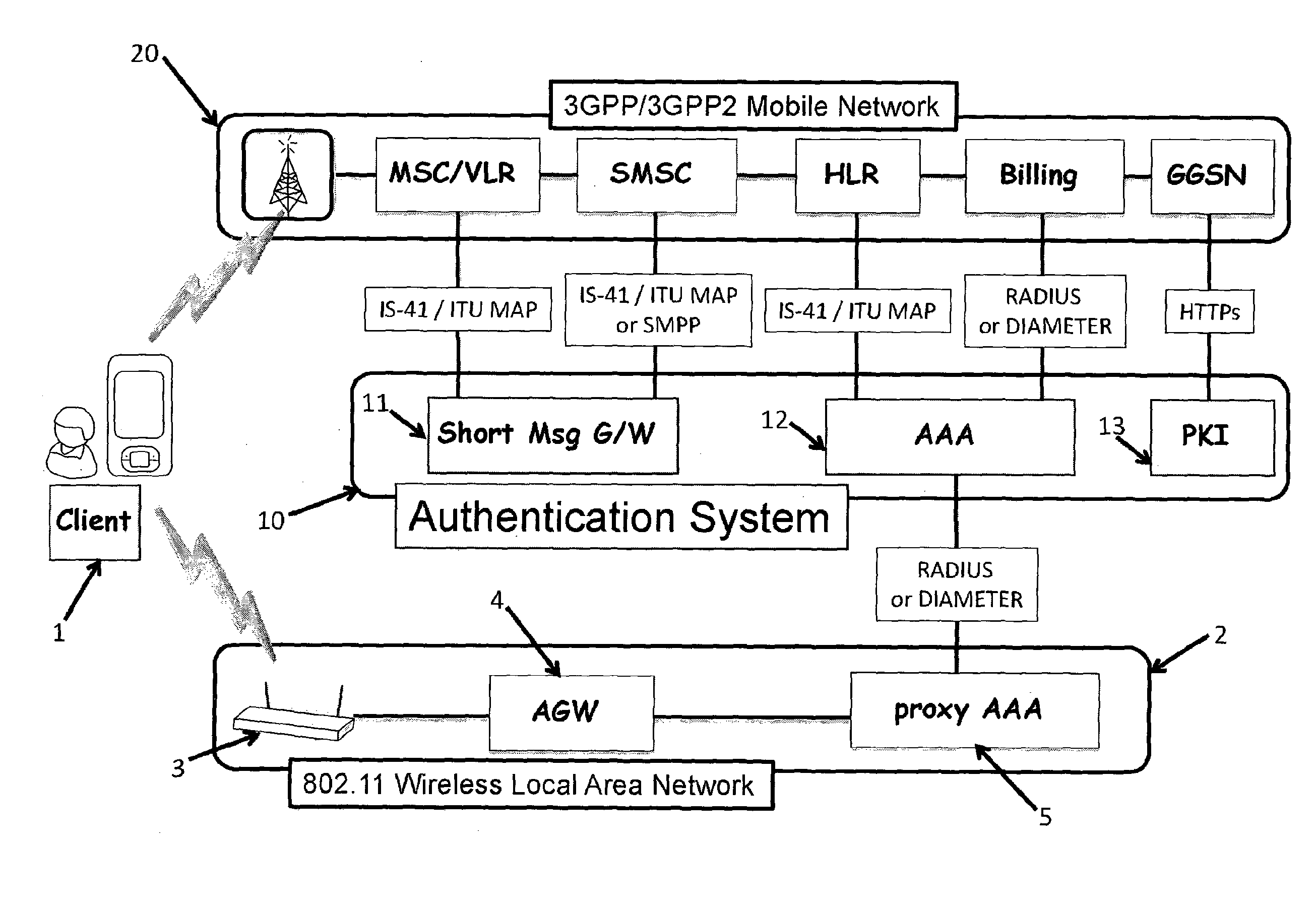
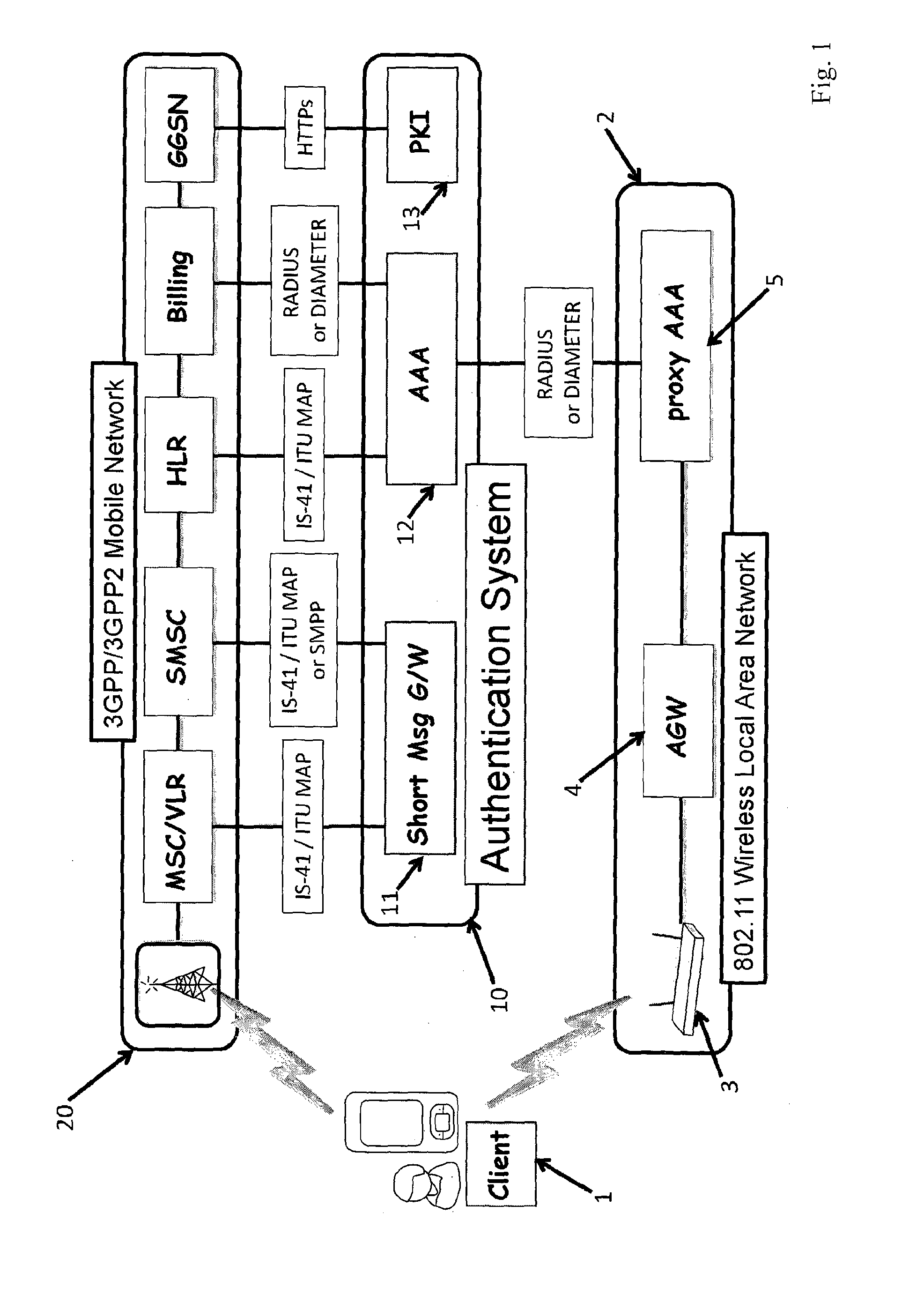
Application access control in a mobile environment
ActiveUS20080160958A1Avoid unwanted roaming chargeAvoid runningUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsData connectionAccess network
A system and method are described whereby a mobile device controls access to mobile applications based on access conditions associated with a current access network. To prevent mobile applications from running when the access conditions are not suitable, the mobile device includes a policy database used to store a list of access conditions that are inappropriate for launching the installed applications. The access conditions are based on the type of the current access network used by the mobile device for launching or maintaining the requested application session. The access conditions indicate whether the mobile device is currently accessing its home network or roaming on another provider's network. Similarly, the access conditions indicate the type of network access interface used by the current network to provide the data connection necessary to run the requested application. The policy database correlates predetermined actions with the access conditions associated with a given application session.
Owner:U S CELLULAR
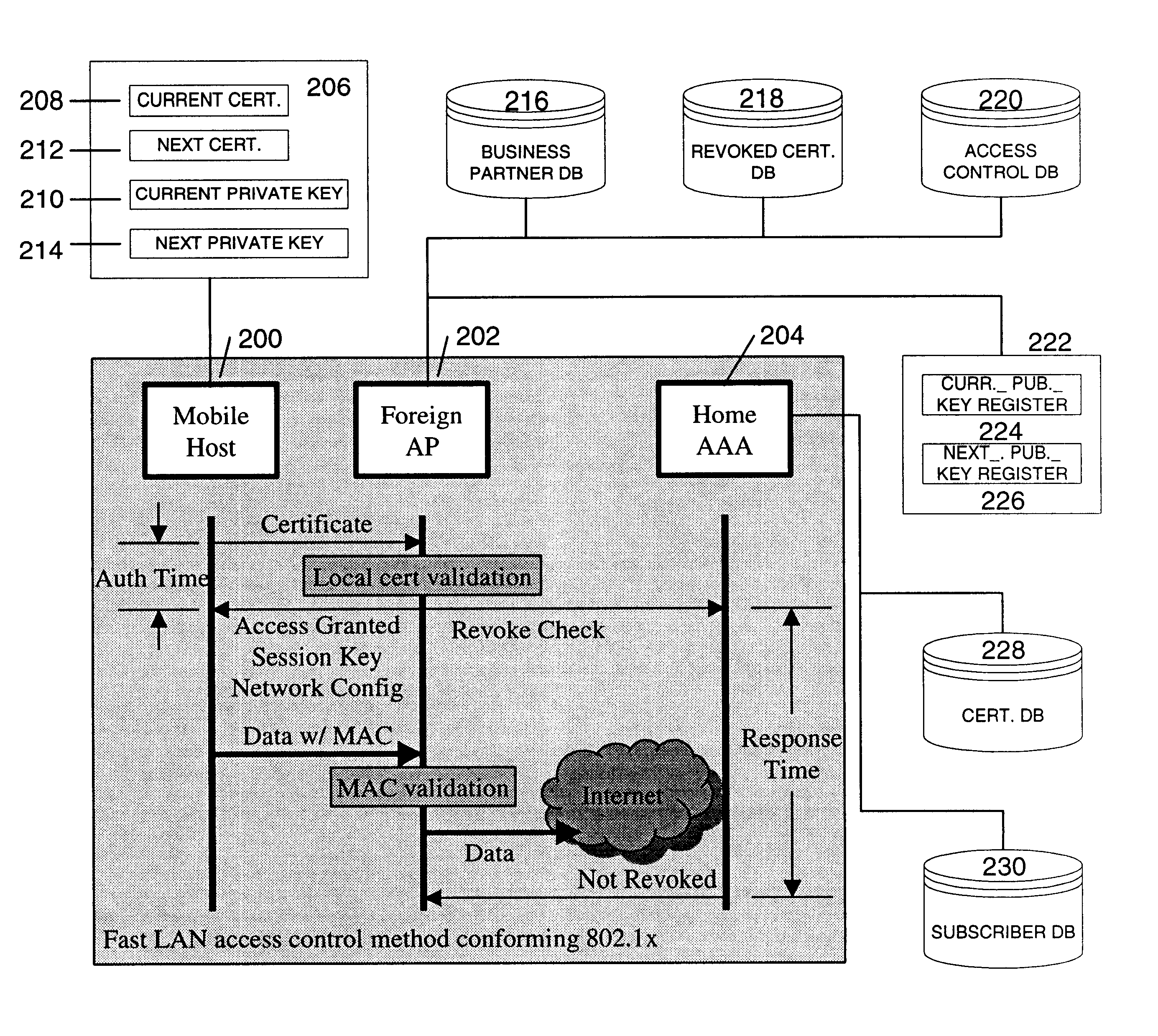
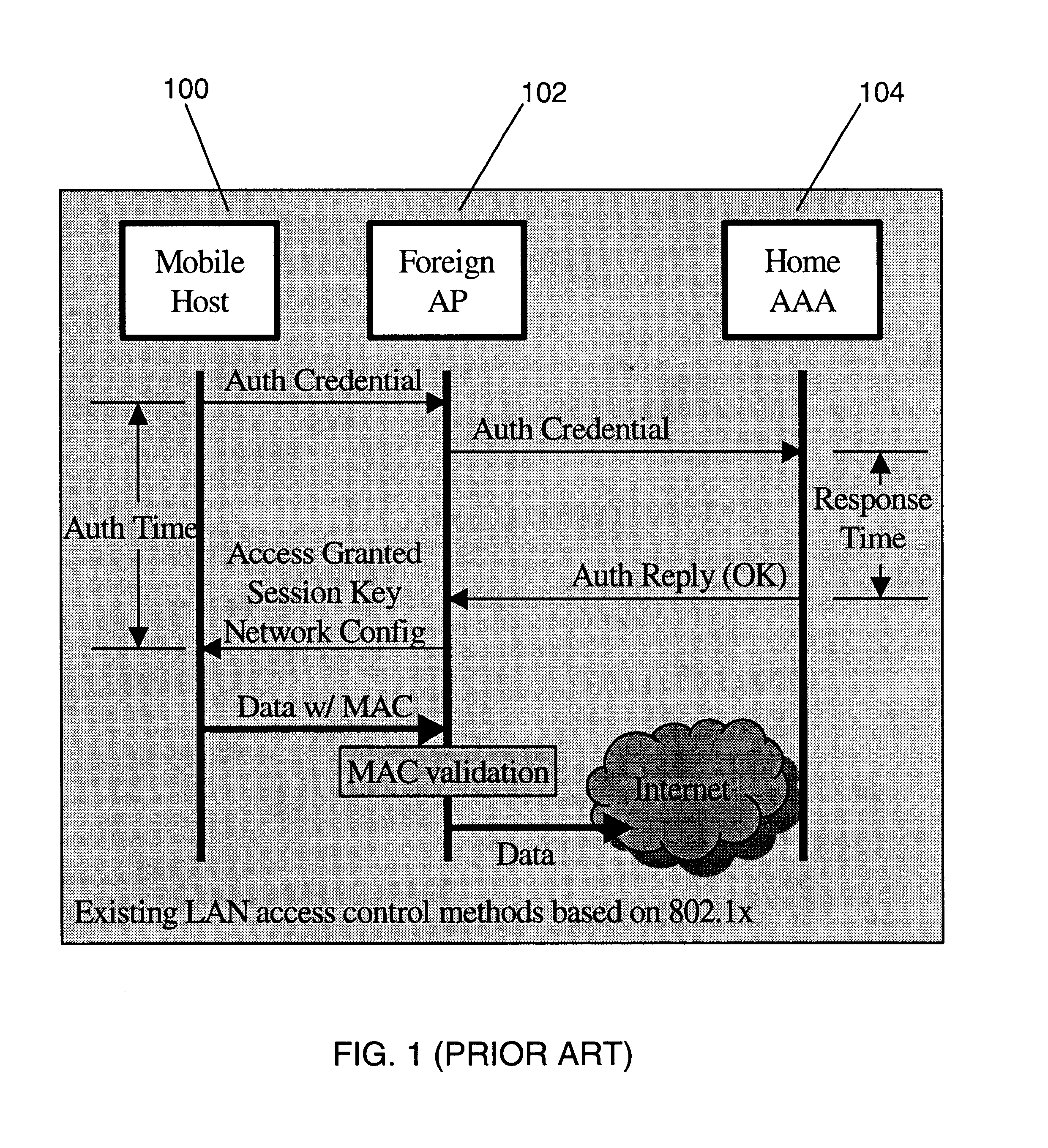
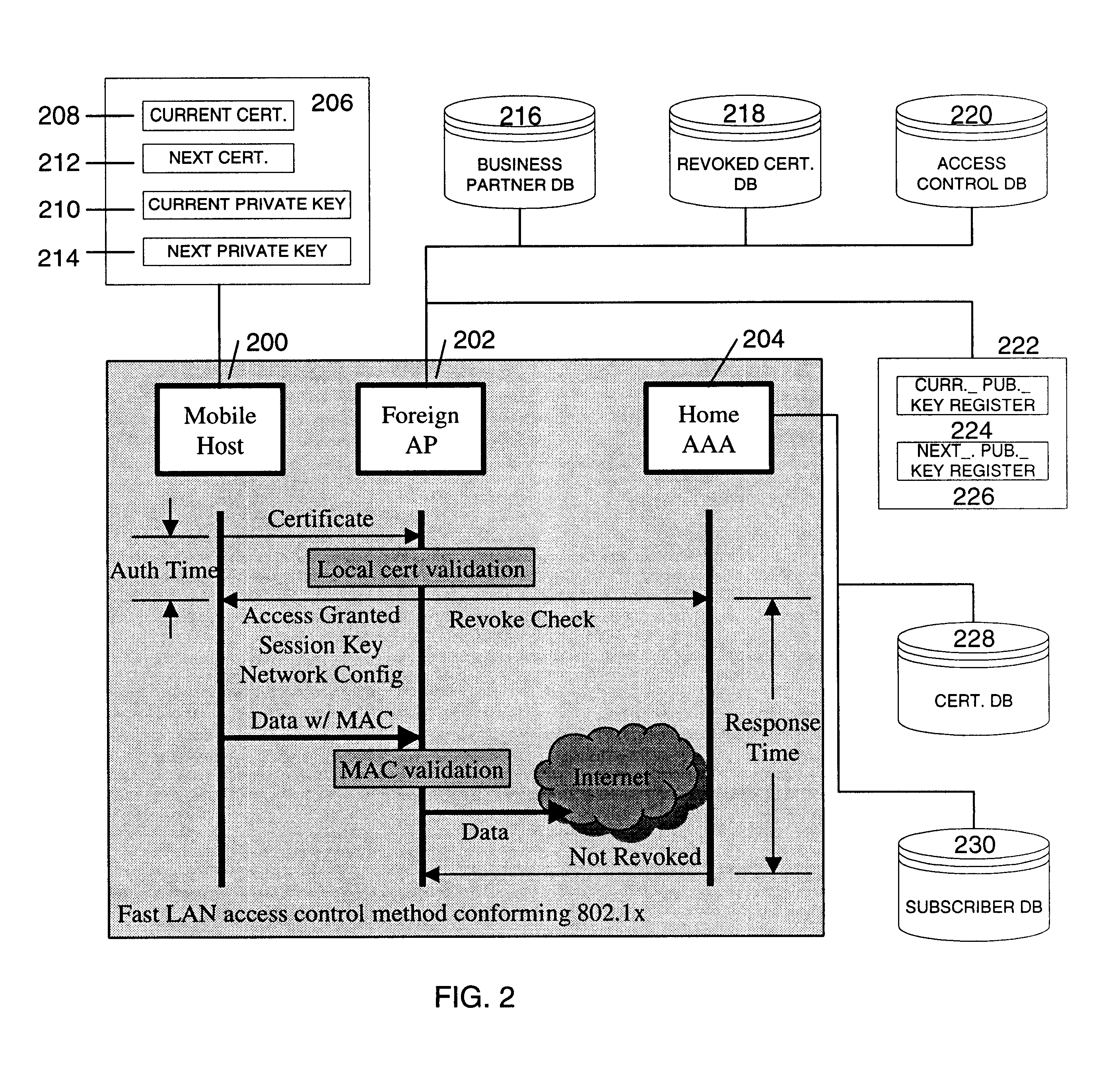
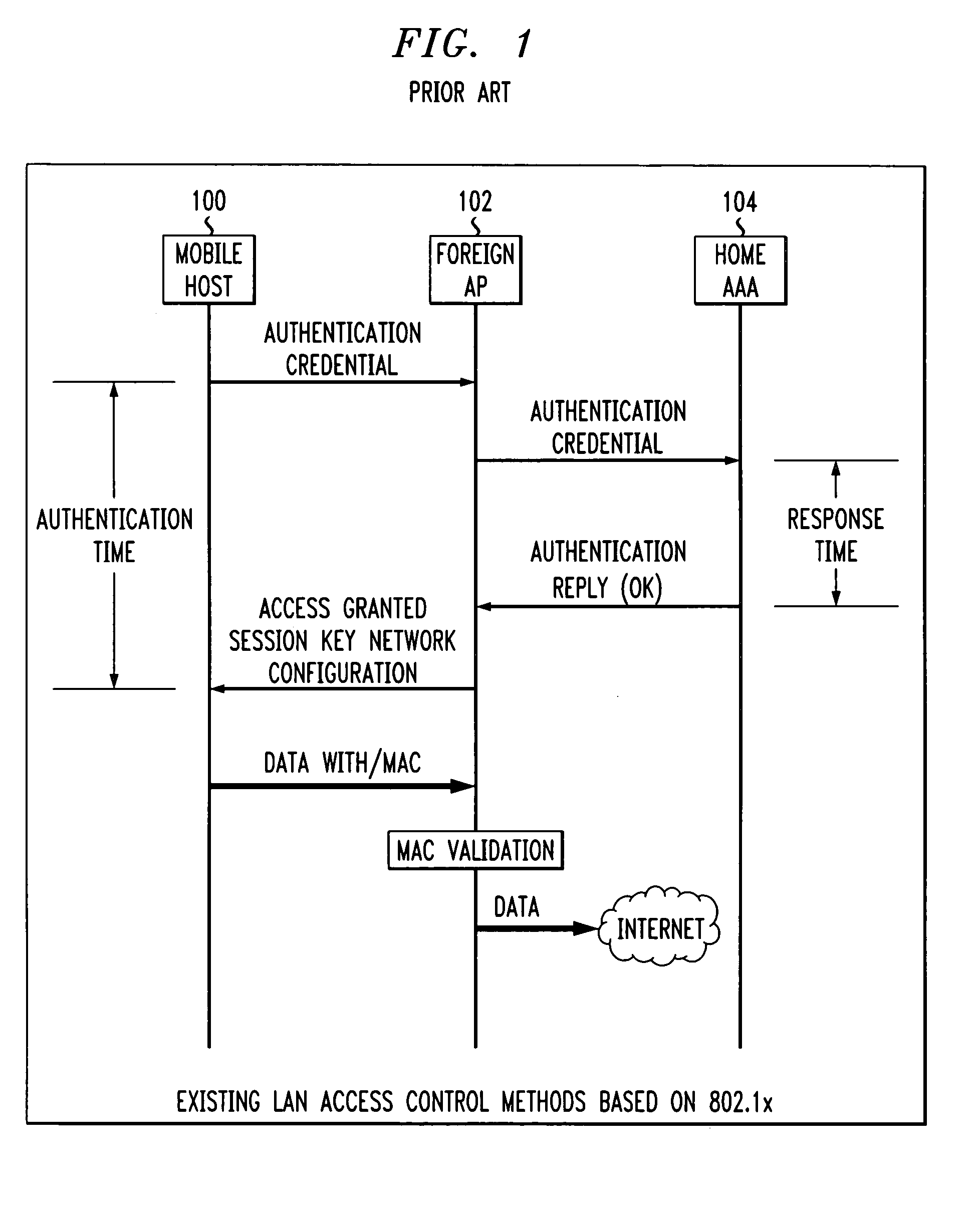
Fast authentication and access control system for mobile networking
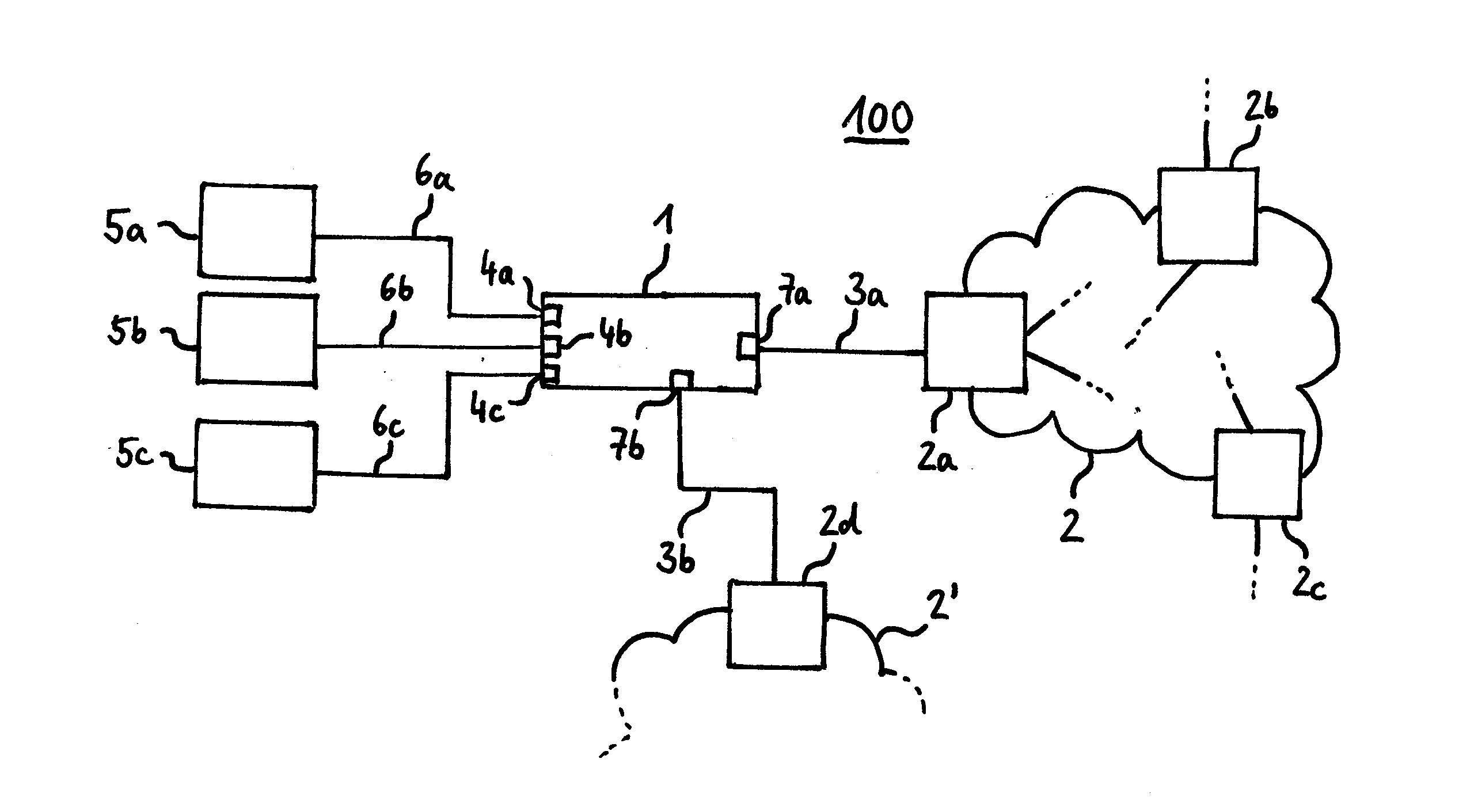
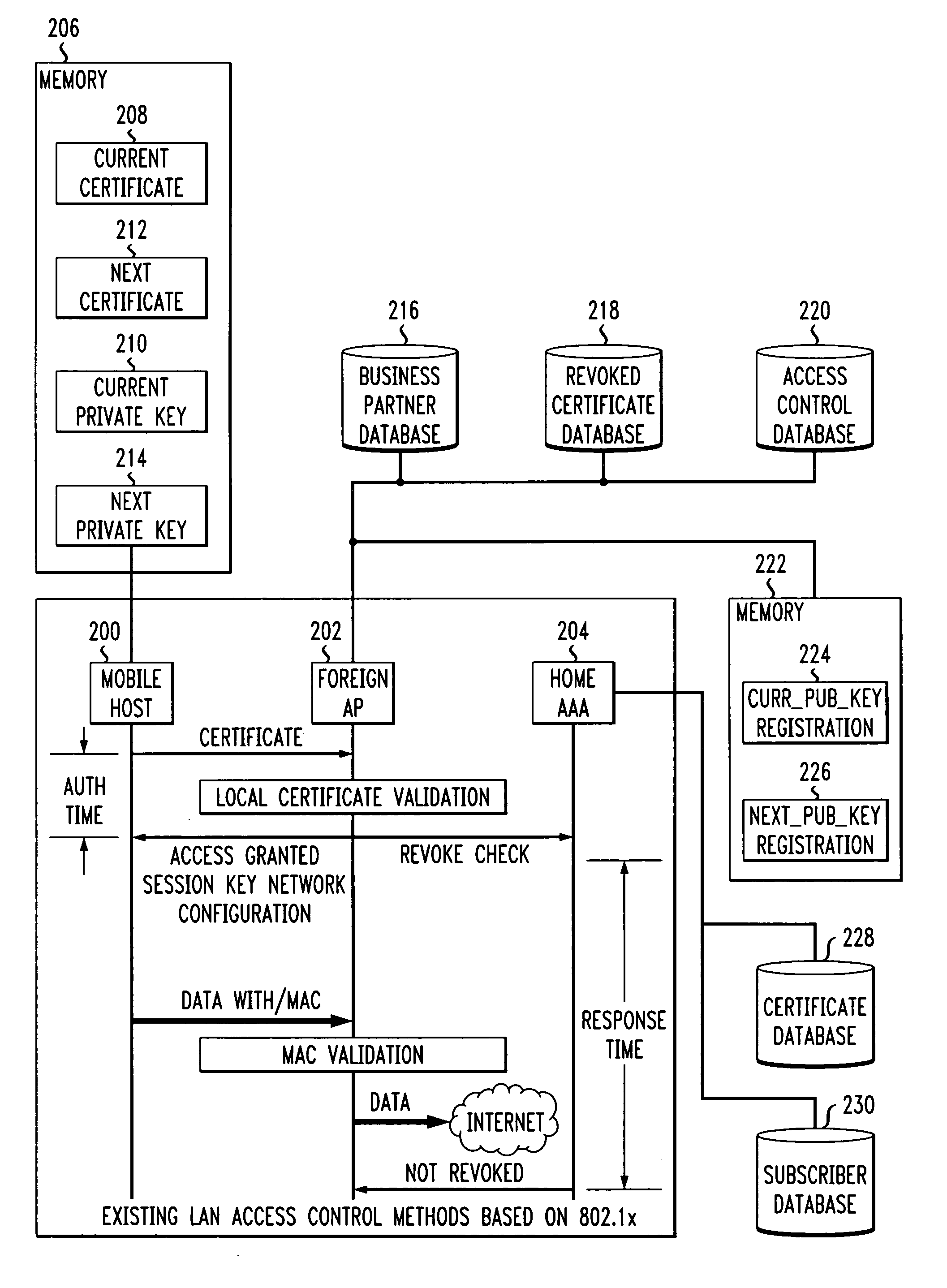
InactiveUS6856800B1Easy to switchReduce certification timeUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsExpiration TimeWeb authentication
A fast authentication and access control method of authenticating a network access device to a communications network having an access point communicating with a remote authentication (home AAA) server for the network access device. The method includes the step of receiving an access request having an authentication credential from the network access device at the access point. The authentication credential includes a security certificate having a public key for the network access device and an expiration time. The security certificate is signed with a private key for the remote authentication server. The access point locally validates the authentication credential by accessing the public key of the remote authentication server from a local database, and checking the signature and expiration time of the security certificate. If the authentication credential is validated at the access point, the access point grants the network access device conditional access to the network by sending an access granted message to the network access device. The access granted message includes a session key encrypted with a public key for the network access device. The session key is stored in a database associated with the access point. The access point contacts the remote authentication server to check a revocation status of the security certificate for the network access device. If the access point receives a message from the remote authentication server that the authentication credential for the network access device has been revoked, it suspends network access for the network access device.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
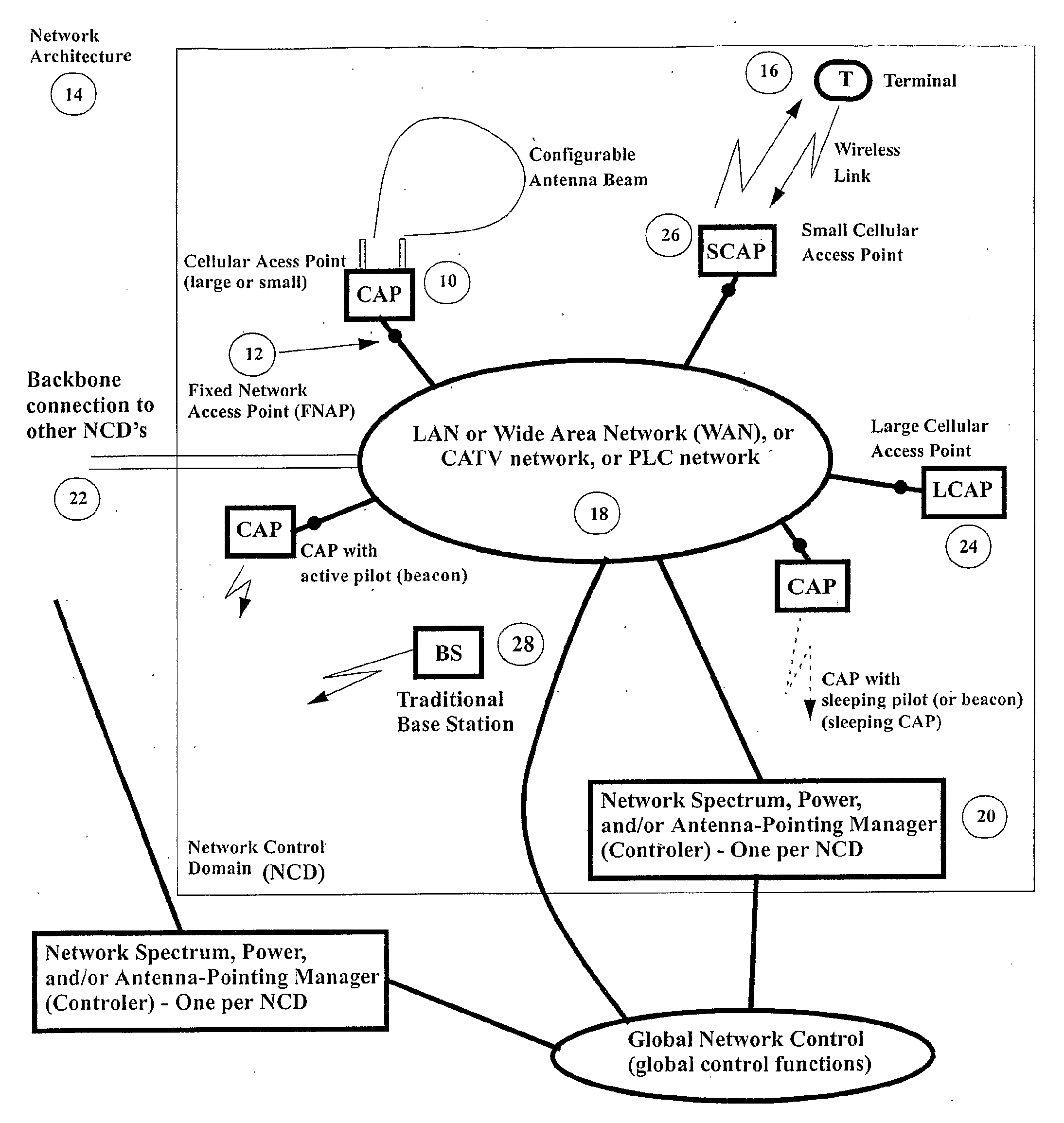
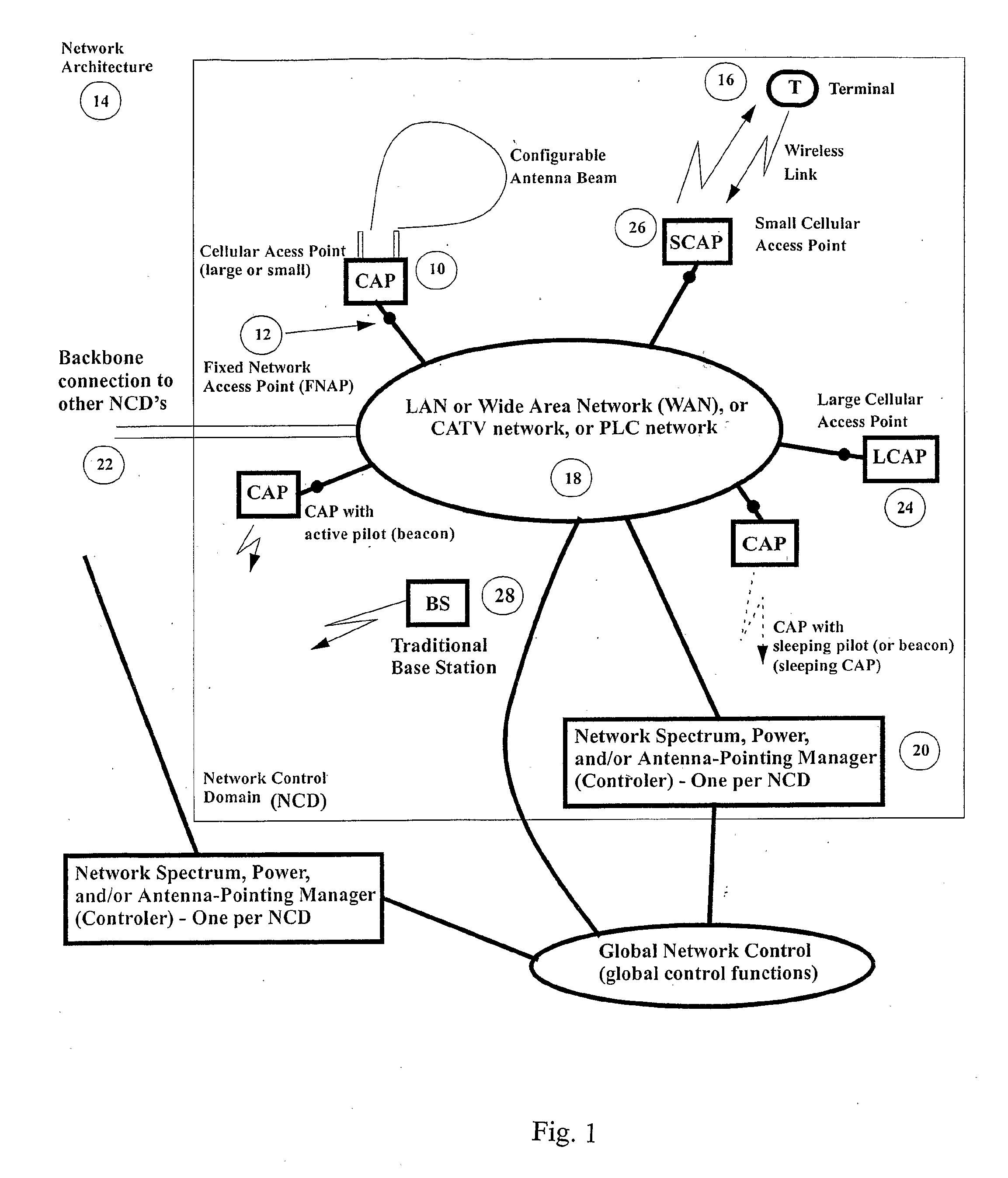
Autonomous Infrastructure Wireless Networks
InactiveUS20080298275A1Large network capacityLow costNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless mesh networkData transmission
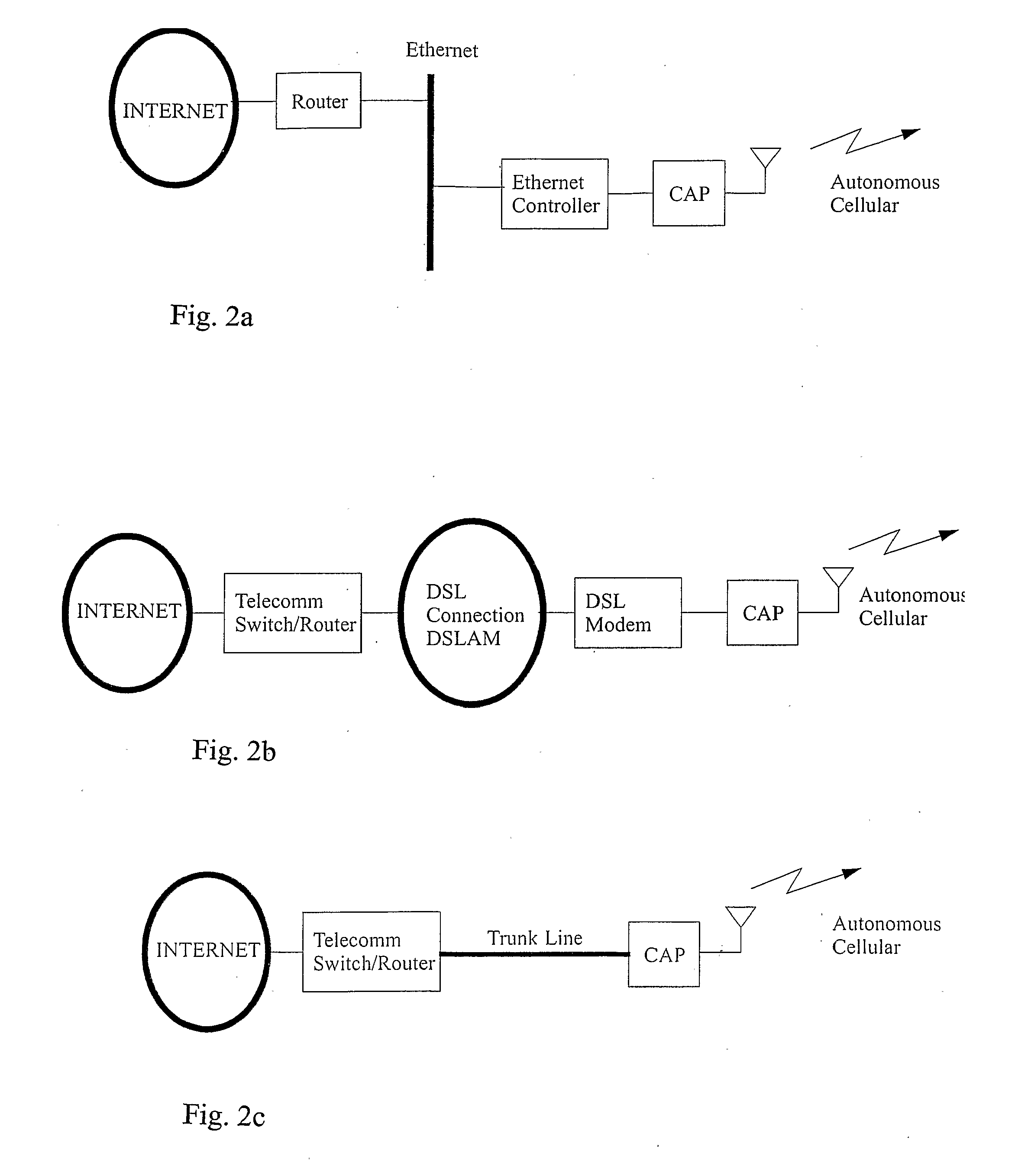
A method for deploying a cellular wireless communication network is provided. The method consists of: providing one or more micro base stations; autonomously deploying the micro base stations using a network access point linked to a cellular wireless communication network; and enabling configuration of the micro base stations to execute network operation commands from a network controller associated with the wireless communication network. Another aspect consists of enabling cooperation and network connectivity between micro base stations and other base stations, including micro base stations and large network base stations. Network connectivity to one or more cellular communication terminals associated with individuals or businesses subscribing to the cellular wireless communication network is enabled. A wireless network is also provided which is configurable to link a cellular wireless network through a high data transmission connection so as to define at least one access point between the micro base station and the wireless network. The network includes a wireless interface and receives operation commands from a network controller for configuration of micro base stations, to support the linking of cellular wireless terminals to the wireless network via the wireless interface by operation of the micro base station, as an intermediary. A corresponding system and computer readable medium is also provided
Owner:DE SOUSA ELVINO SILVEIRA MEDINA
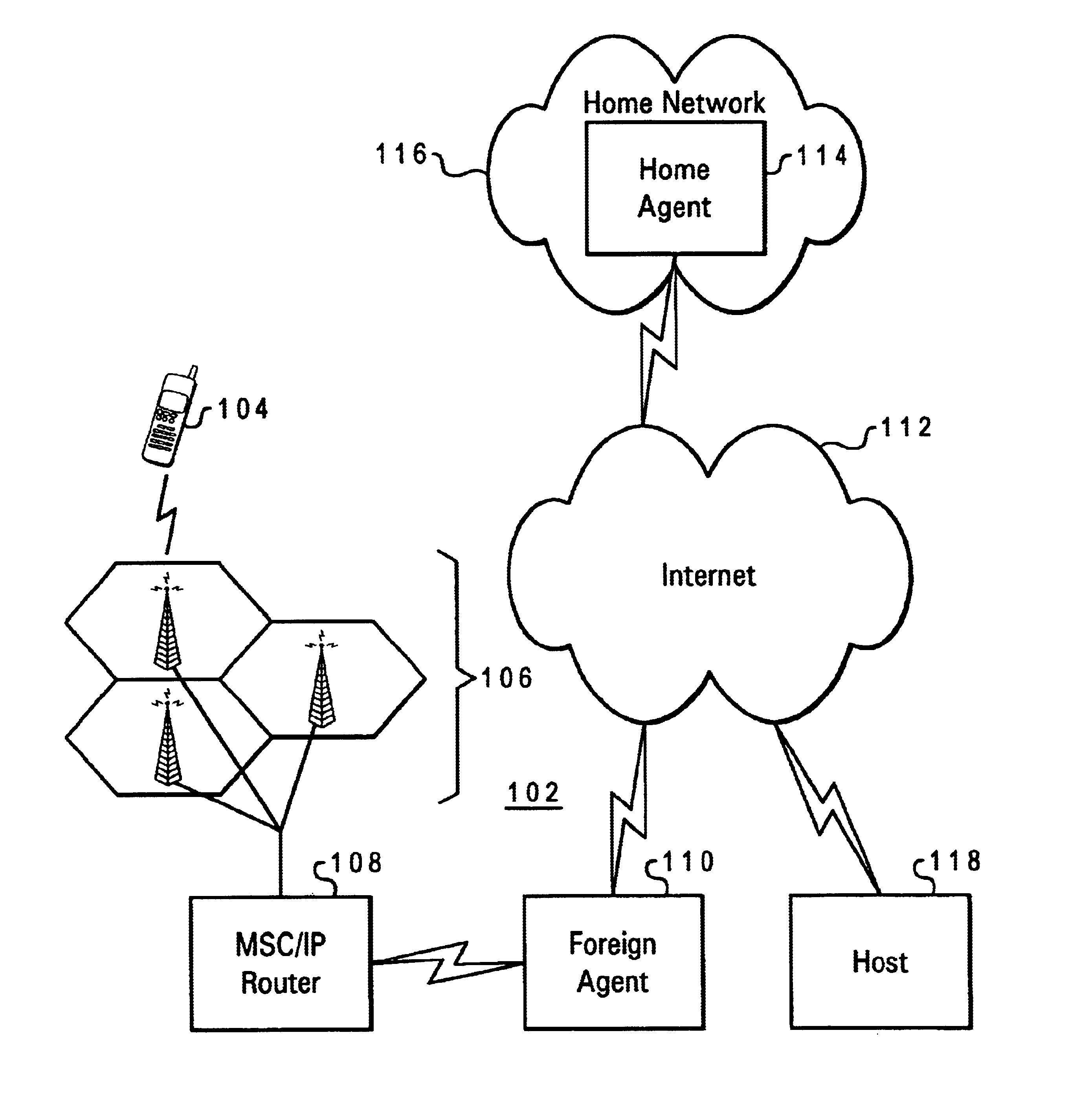
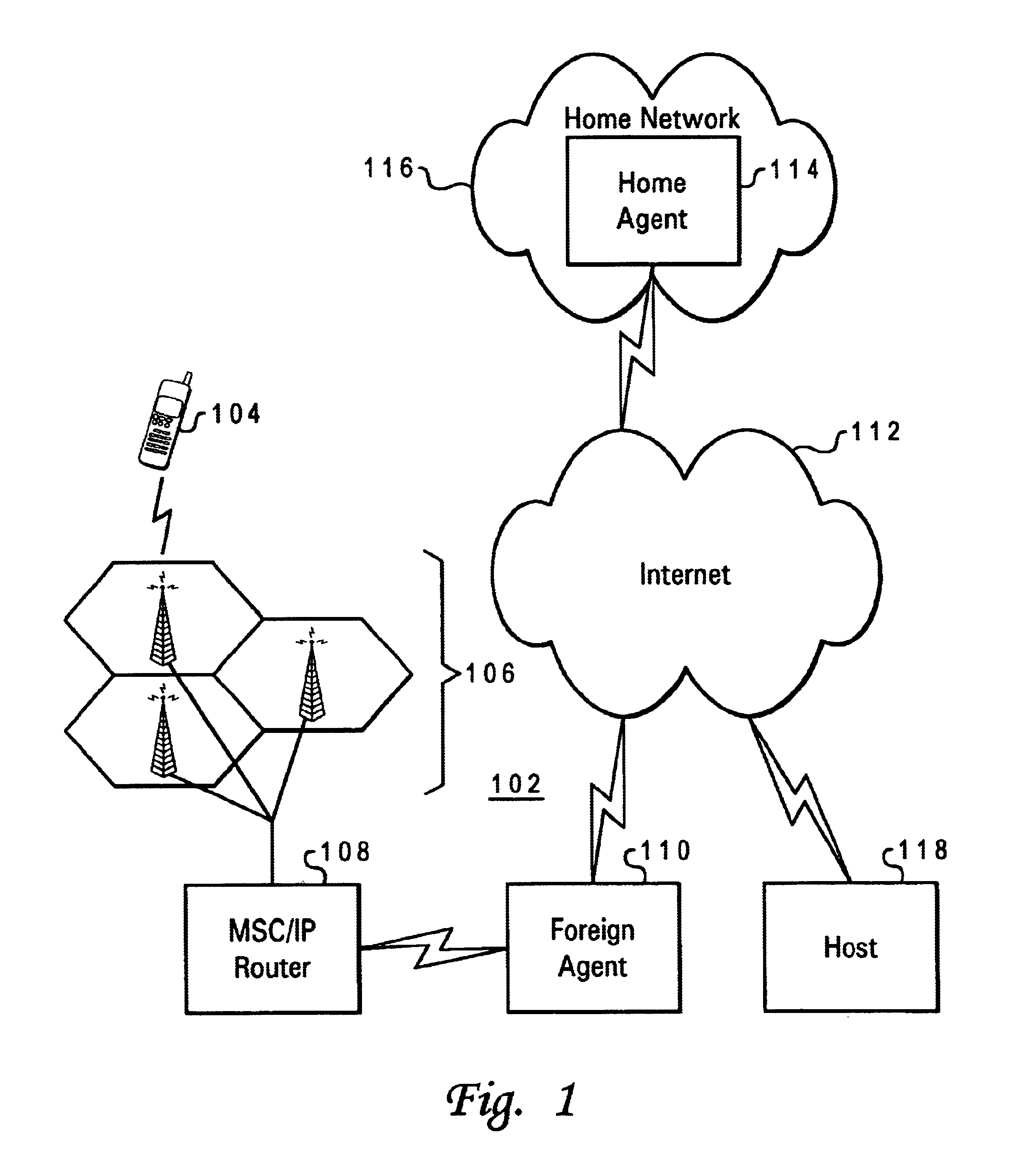
Simple multicast extension for mobile IP SMM
InactiveUS6988146B1Multiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsComputer networkForeign agent
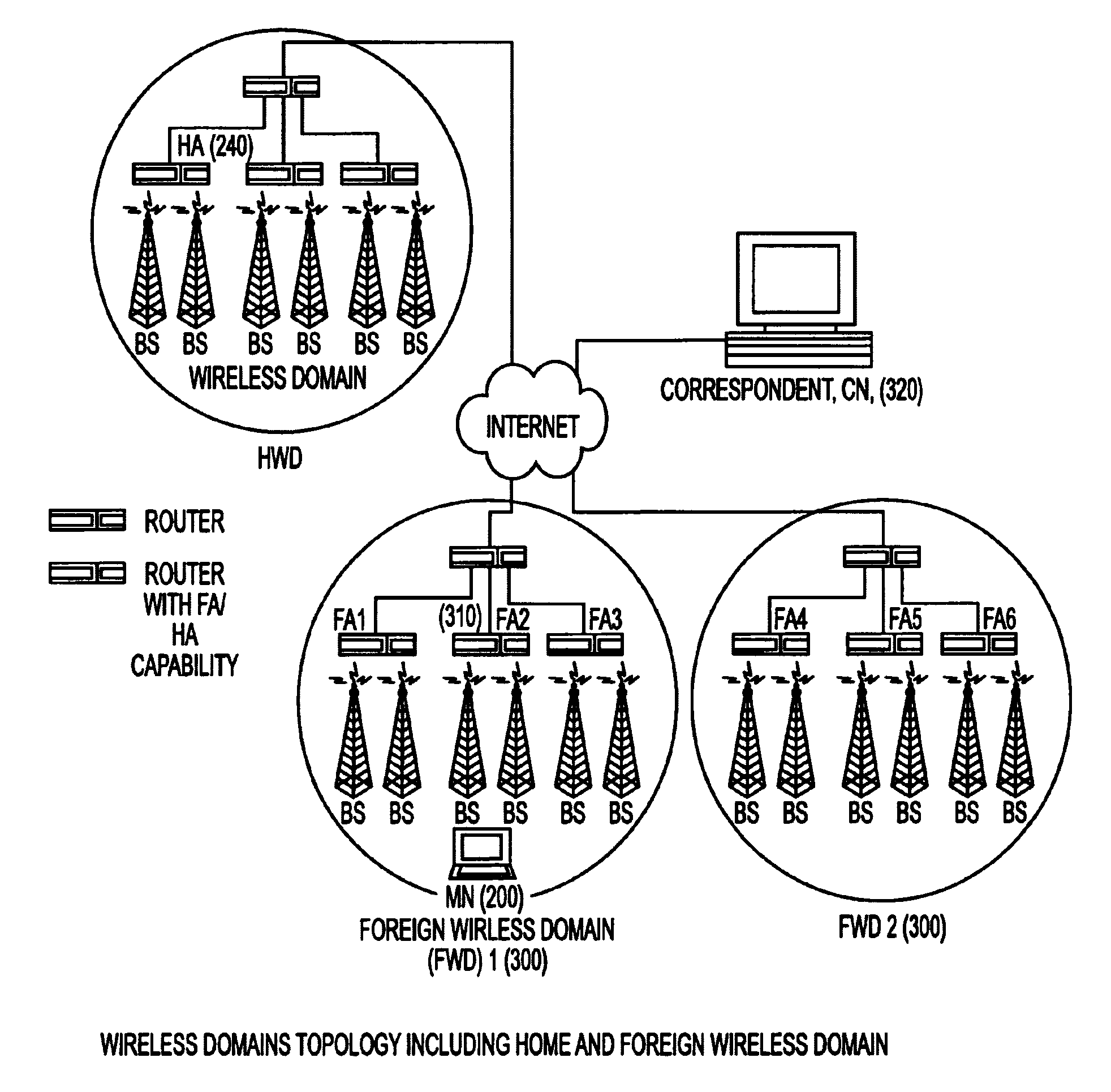
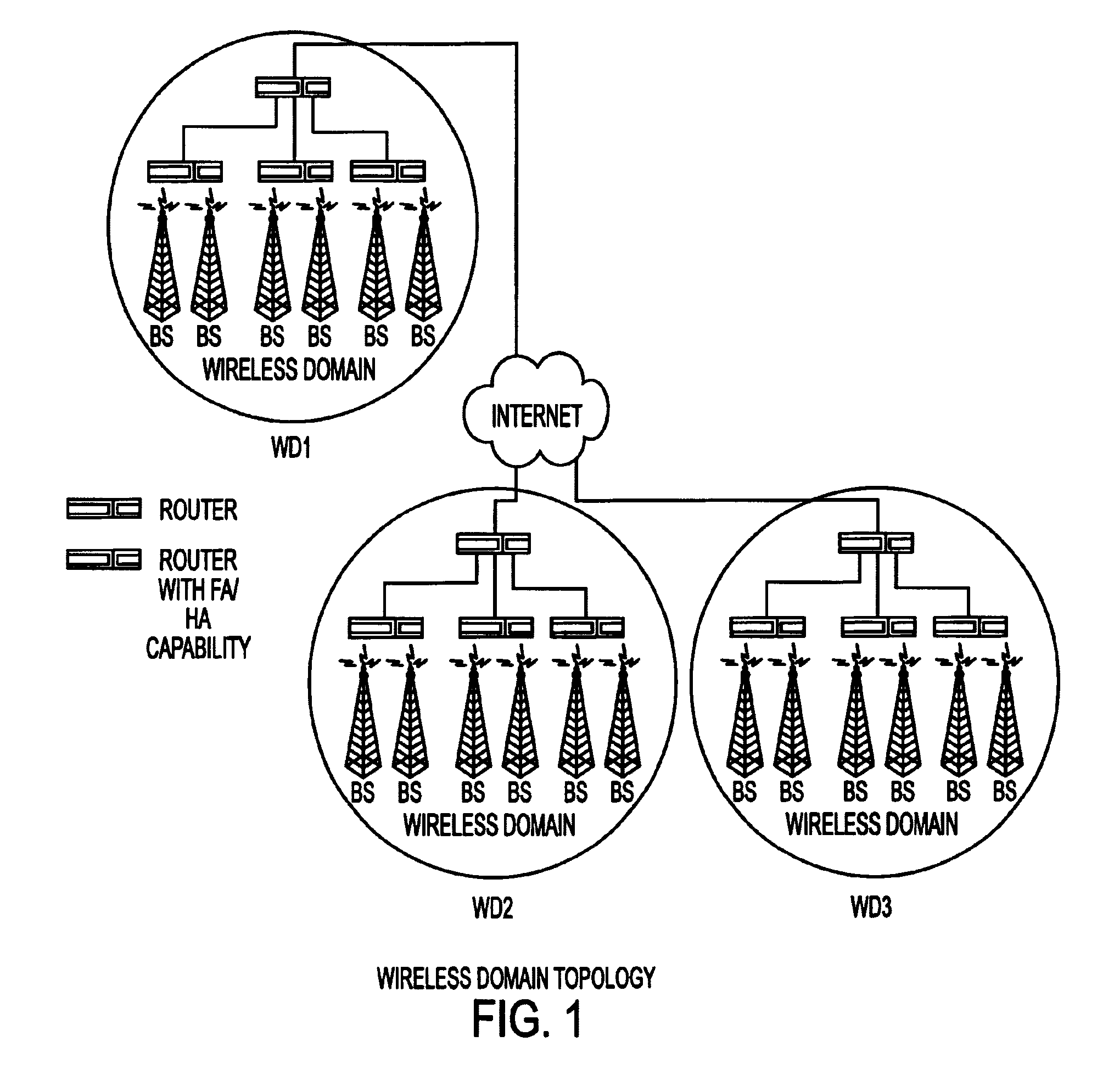
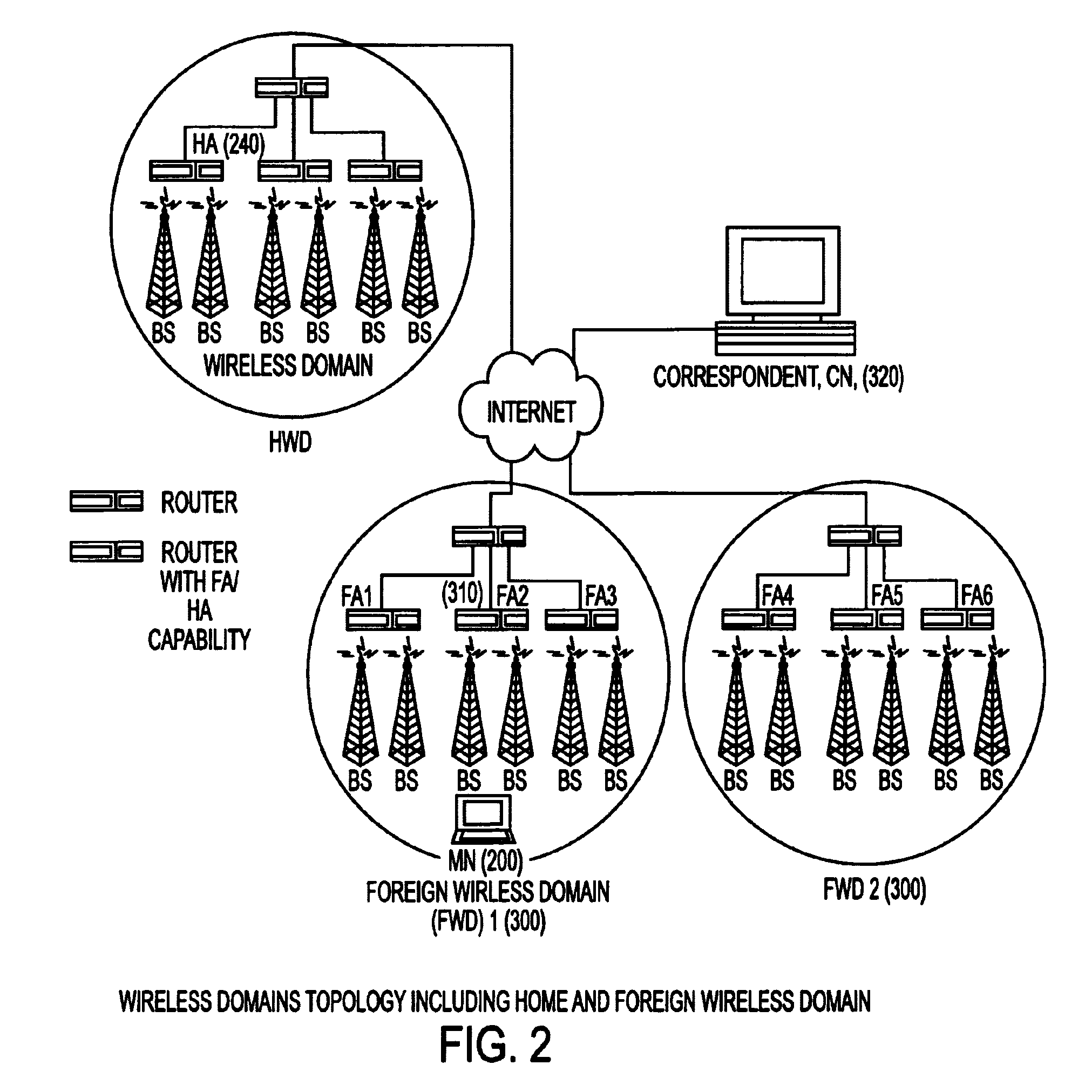
Under Simple Multicast Extension for Mobile IP, when a mobile node arrives at a foreign wireless domain, it listens for an agent advertisement sent by a foreign agent. The foreign agent attaches a network access identifier (NAI) extension to the agent advertisement. The mobile node uses the NAI extension to decide which action to take. If the mobile node determines that it is receiving an agent advertisement message from the same foreign agent it previously was in communication with, no action is required. If the mobile node discovers that it has entered a new foreign domain, it sends a registration request to the foreign agent. If the mobile node identifies that it is still in the same domain but has moved from a previous foreign agent to a new one, it sends a multicast subscription request to the new foreign agent.If a home agent supports the Simple Multicast Extension for Mobile IP, it allocates a source specific multicast address and inserts the address in a source specific multicast address extension after the registration reply. In addition, tunneling is used to route datagrams from correspondent nodes to the mobile node while the mobile node is in a foreign domain. The destination address of the tunnel is set to the source specific multicast previously allocated. Finally, update messages are used to inform correspondent nodes of a mobile nodes' new location.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
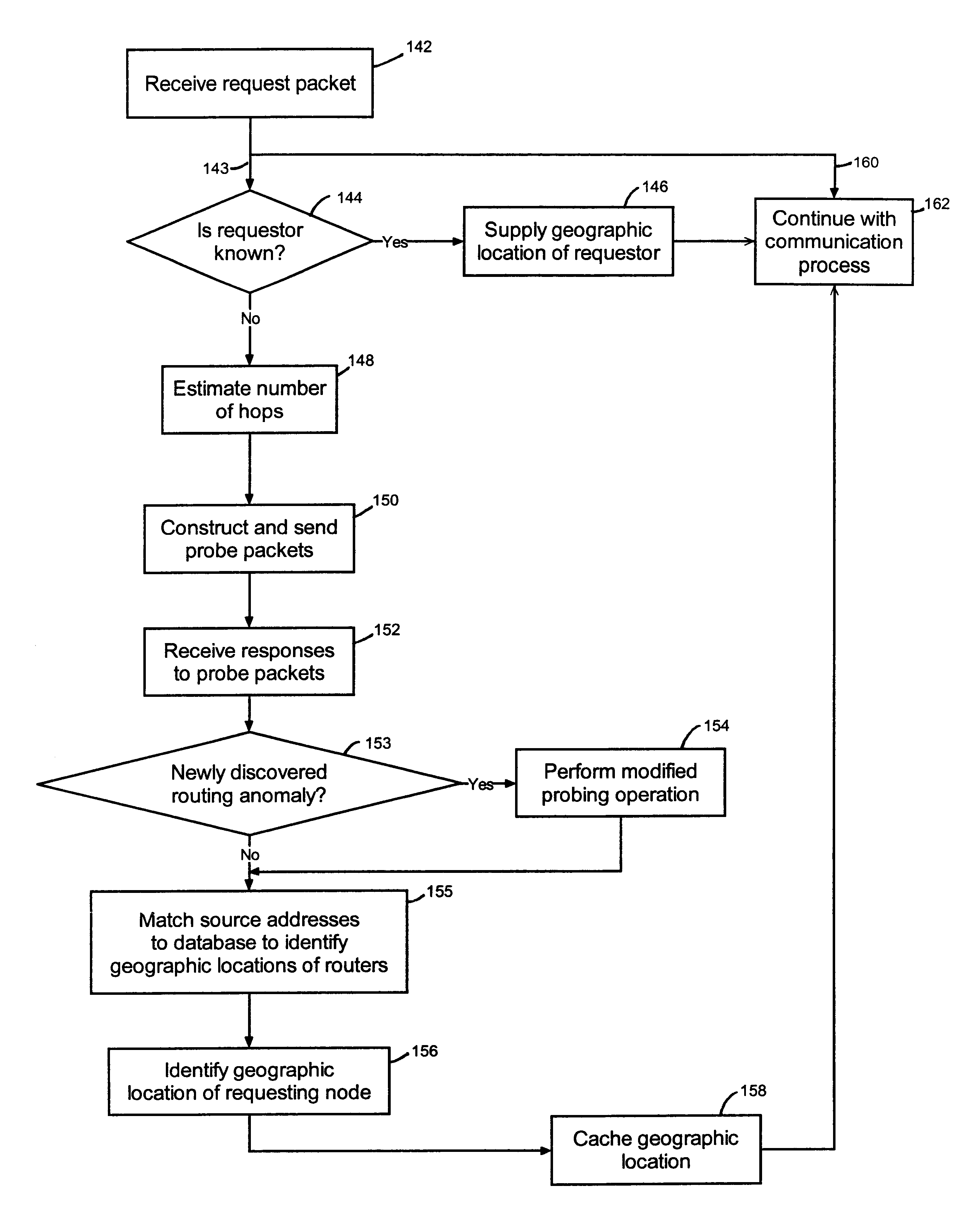
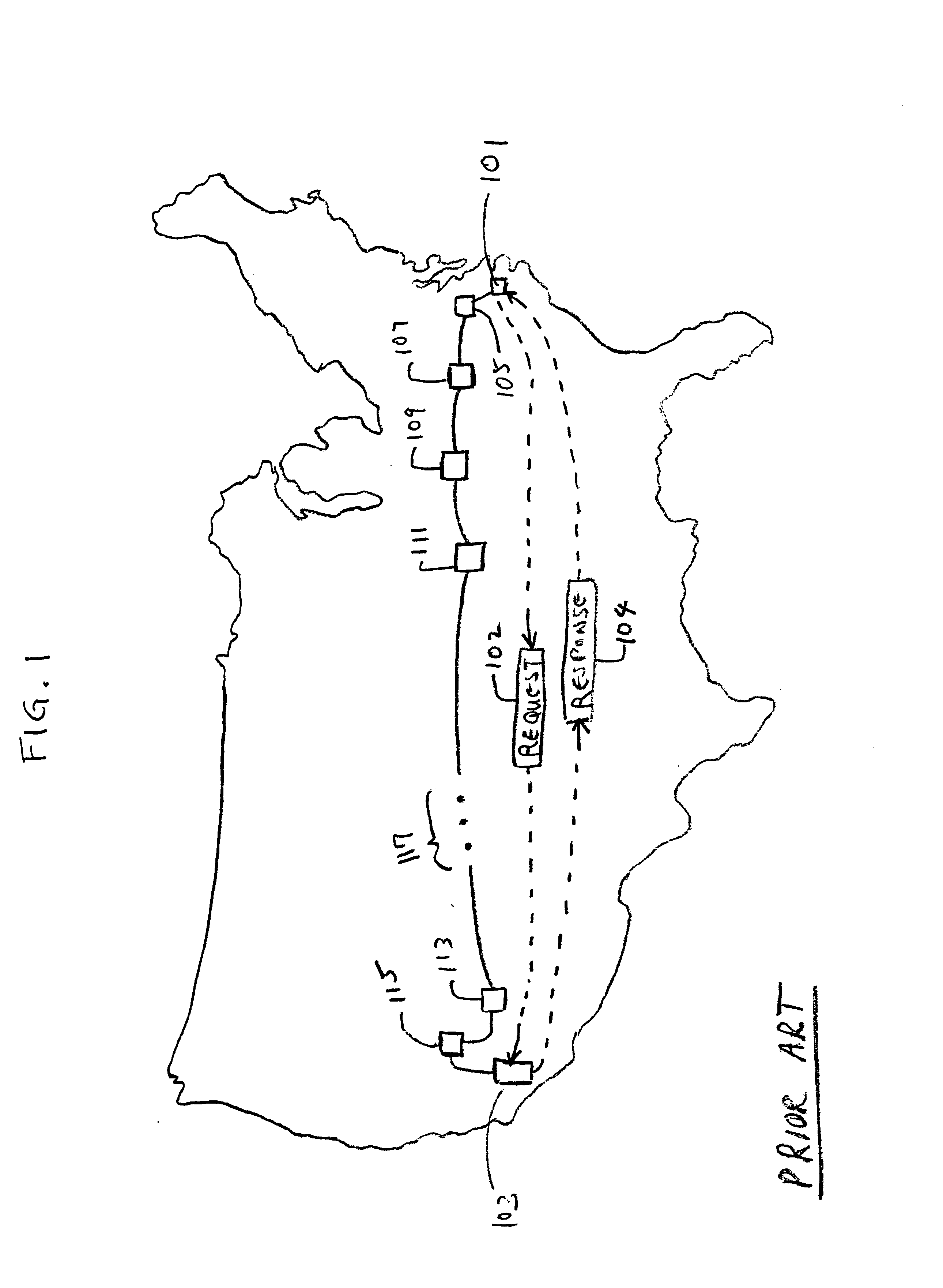
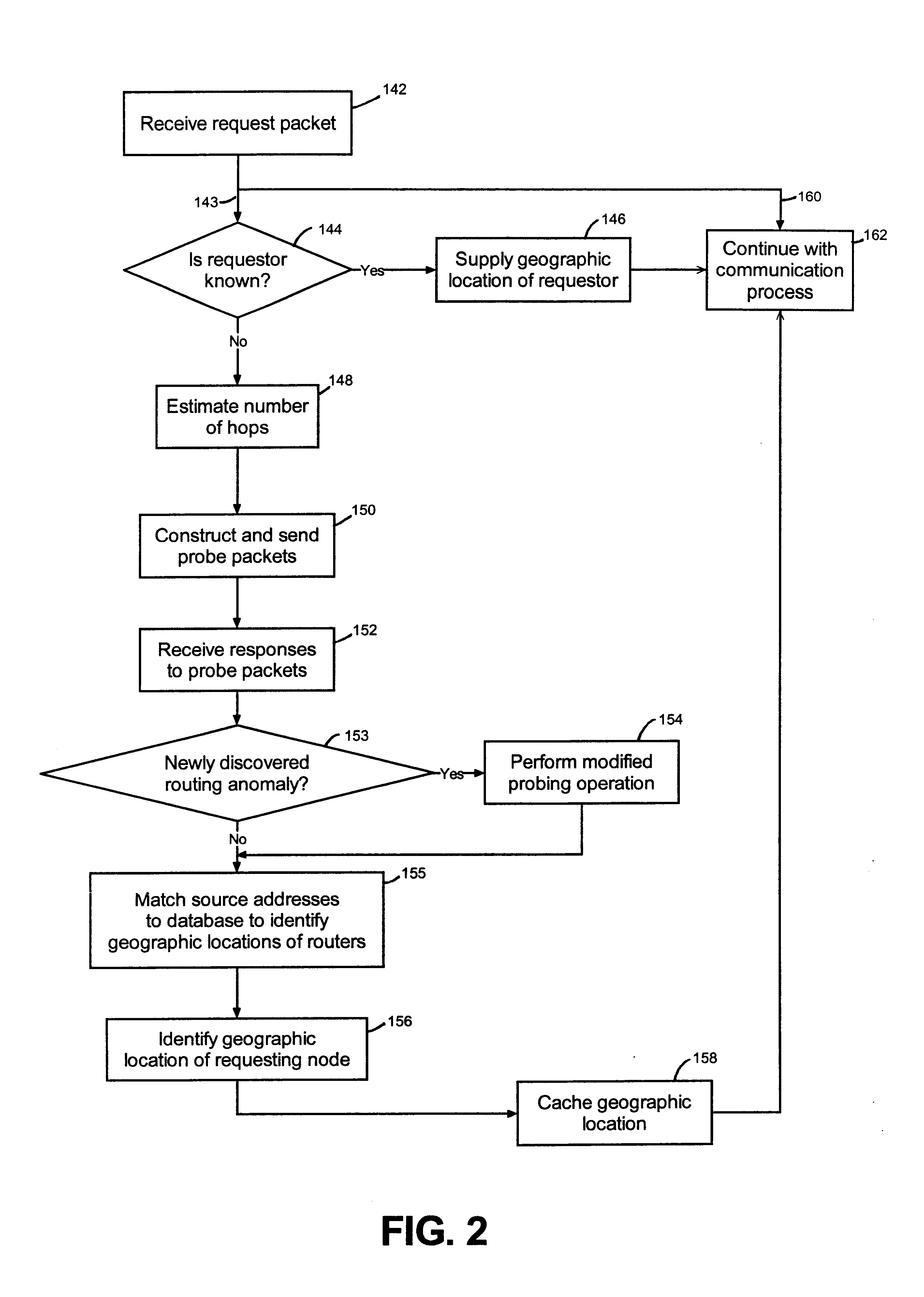
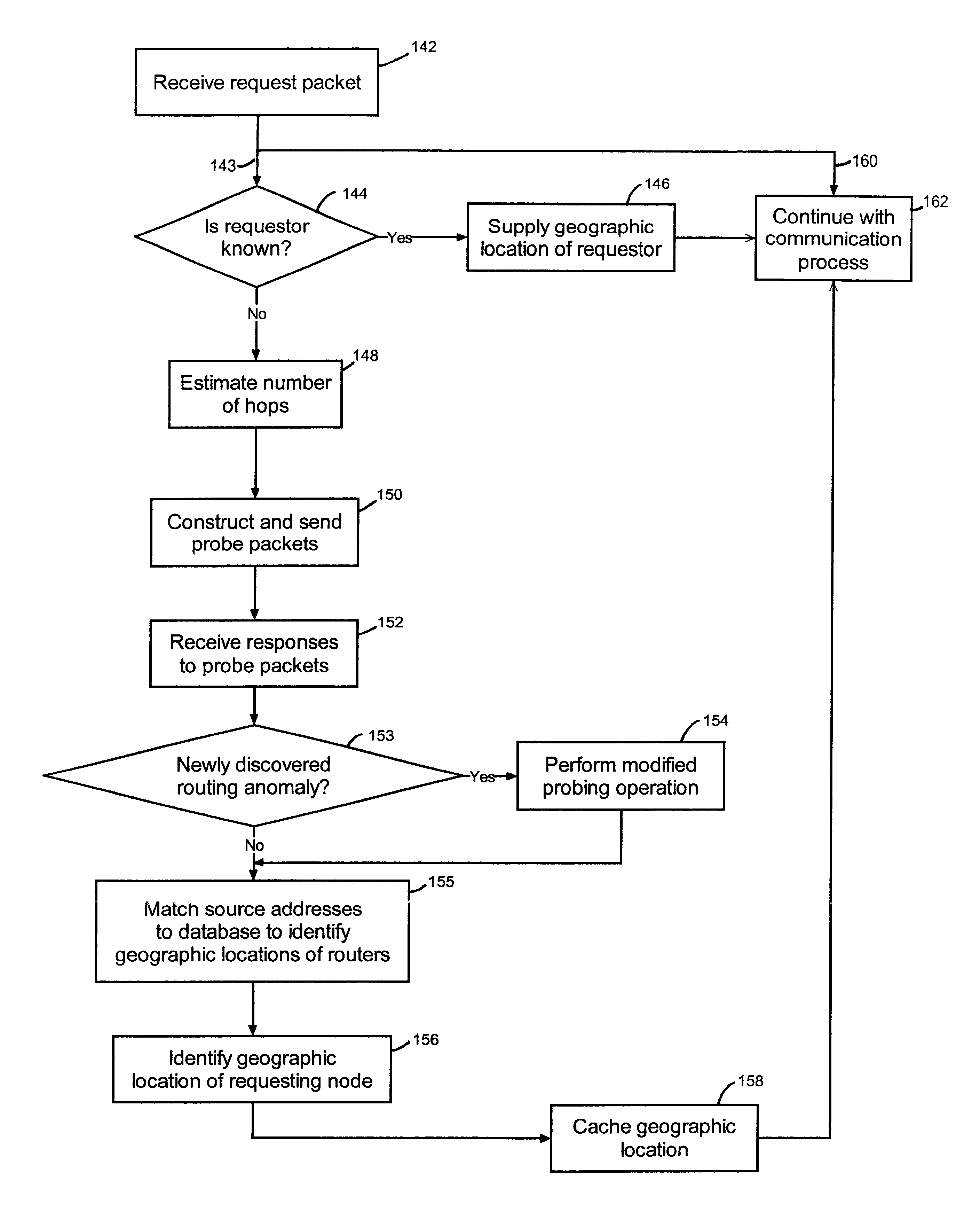
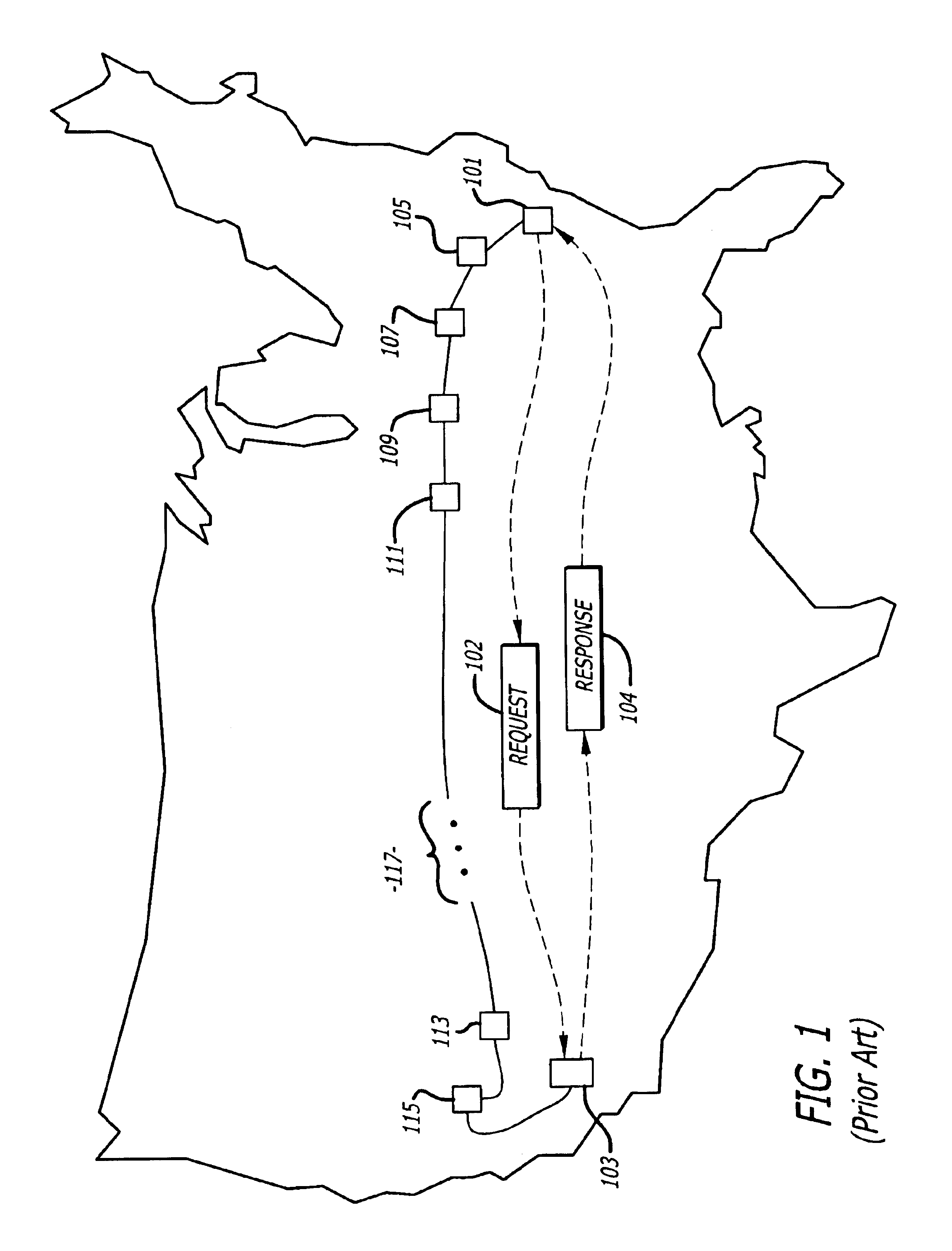
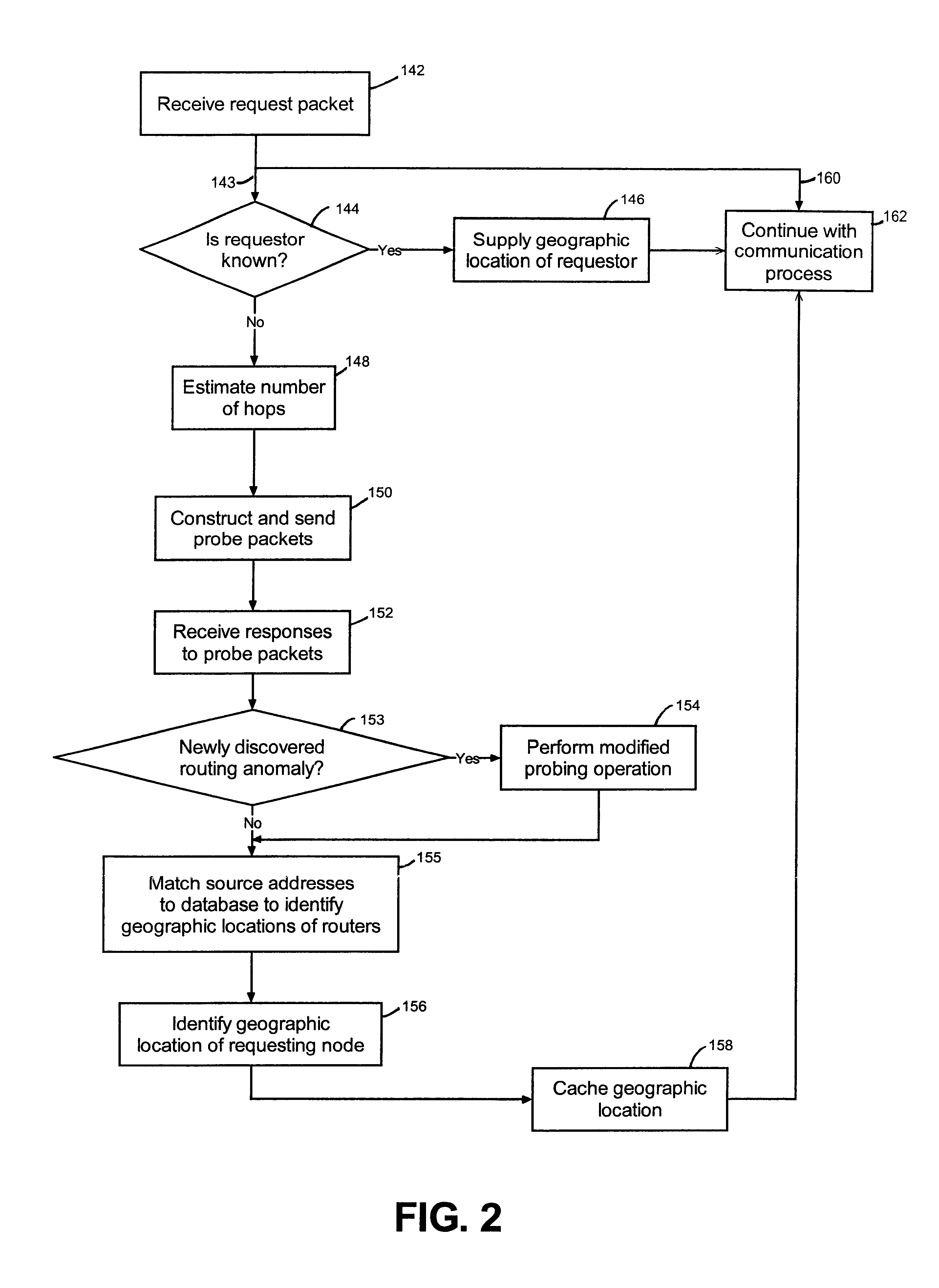
Creating a geographic database for network devices
InactiveUS6778524B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork connectionGeolocation
A database is populated with geographic locations for network devices by providing a node on a network and making a connection into a network service provider (NSP) point of presence (POP) to obtain a connection to the network via the NSP. A message is then transmitted to the node over the network connection obtained from the NSP. The message is received at the node and a source network identifier is extracted from the message. The source network identifier is then associated with a known geographic location for the POP in a database. The foregoing steps are then repeated for multiple different POPs. Also, a database is populated with geographic locations for network devices by providing a node on a network and making a connection into a network service provider (NSP) point of presence (POP) to obtain a connection to the network via the NSP. A message is then transmitted to the node over the network connection obtained from the NSP. The message is received at the node and a source network identifier is extracted from the message. The route over the network between the node and the POP is then probed to obtain network identifiers for routers along the route. The foregoing steps are then repeated for multiple different POPs.
Owner:RESOURCE CONSORTIUM LTD LLC
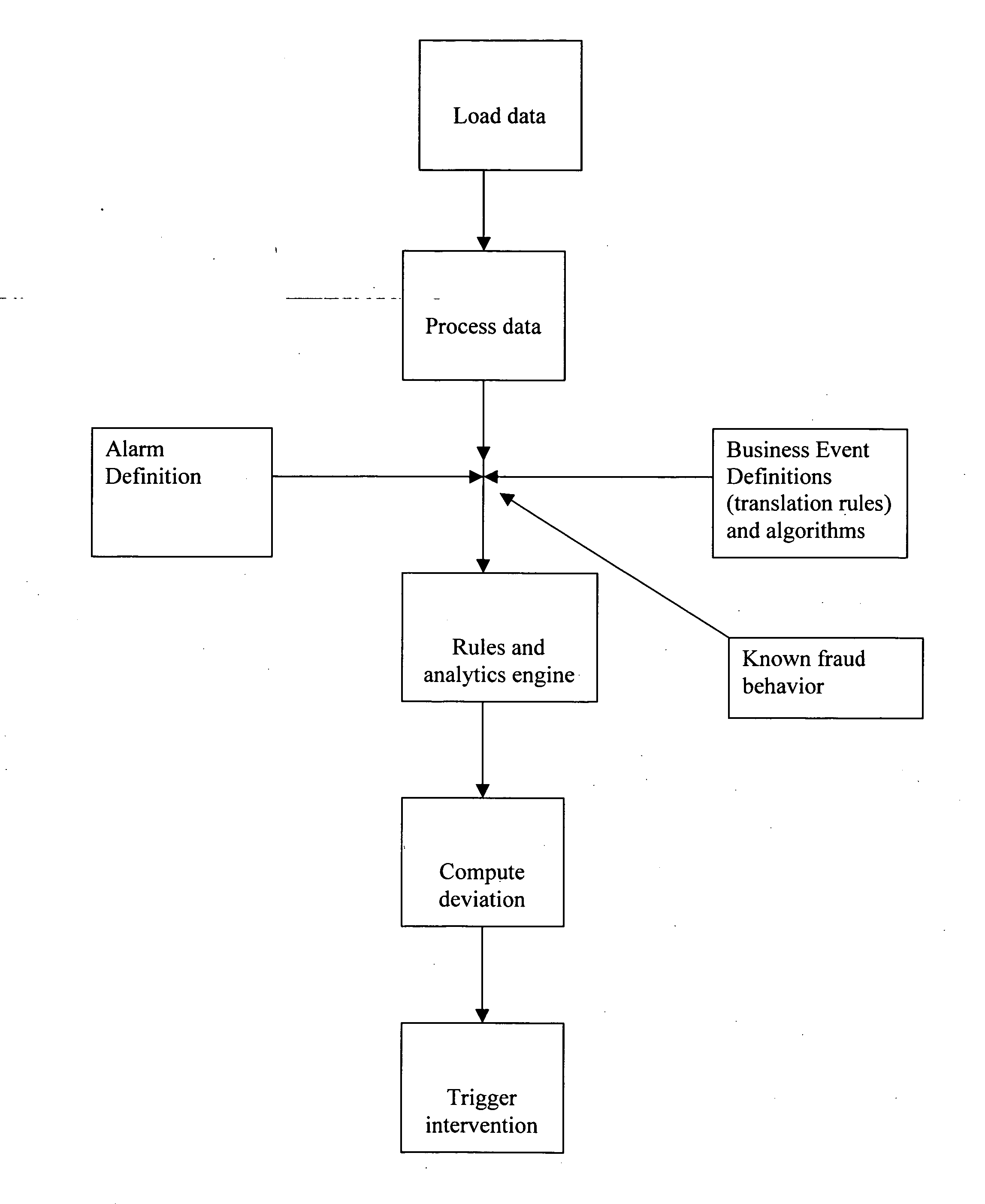
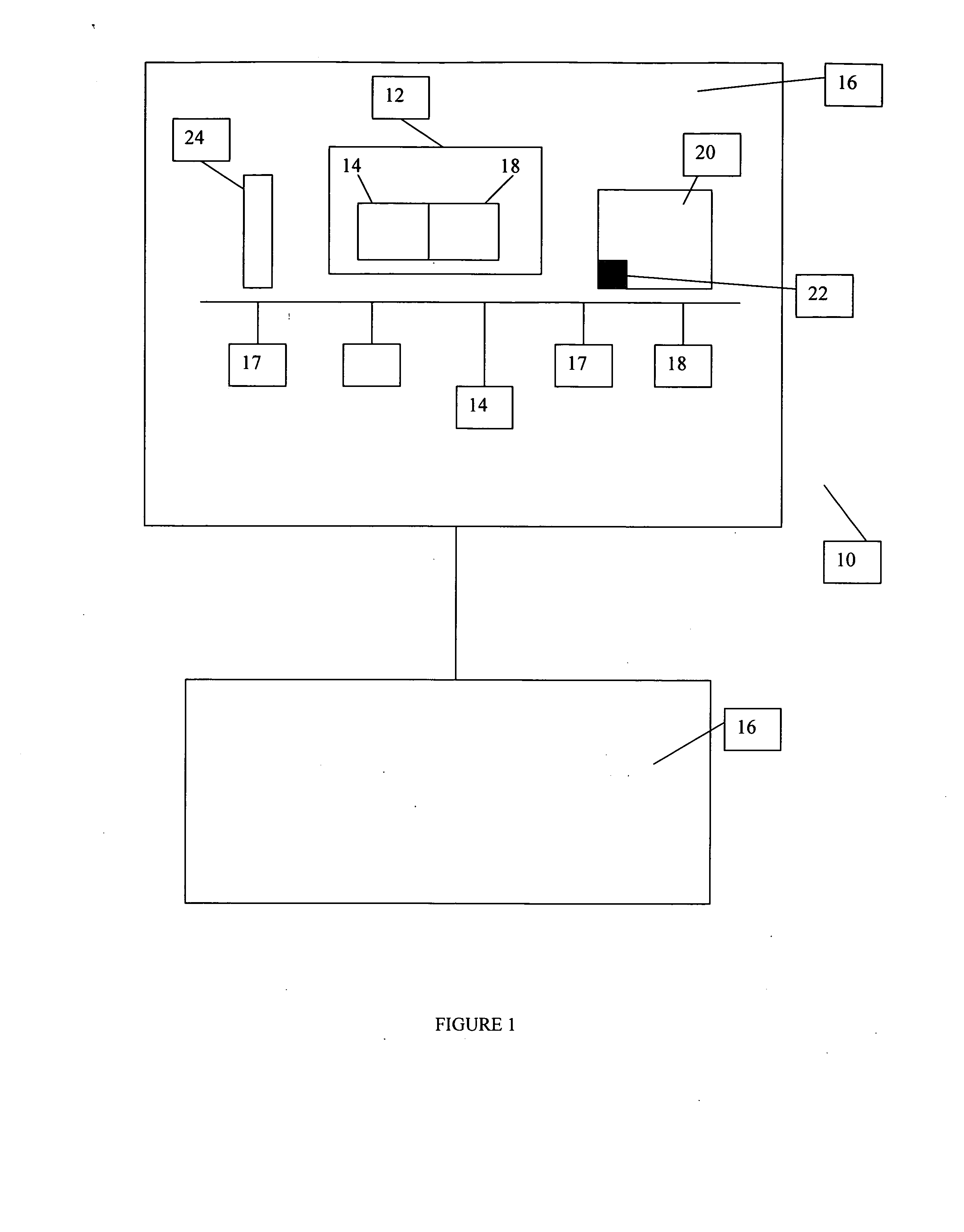
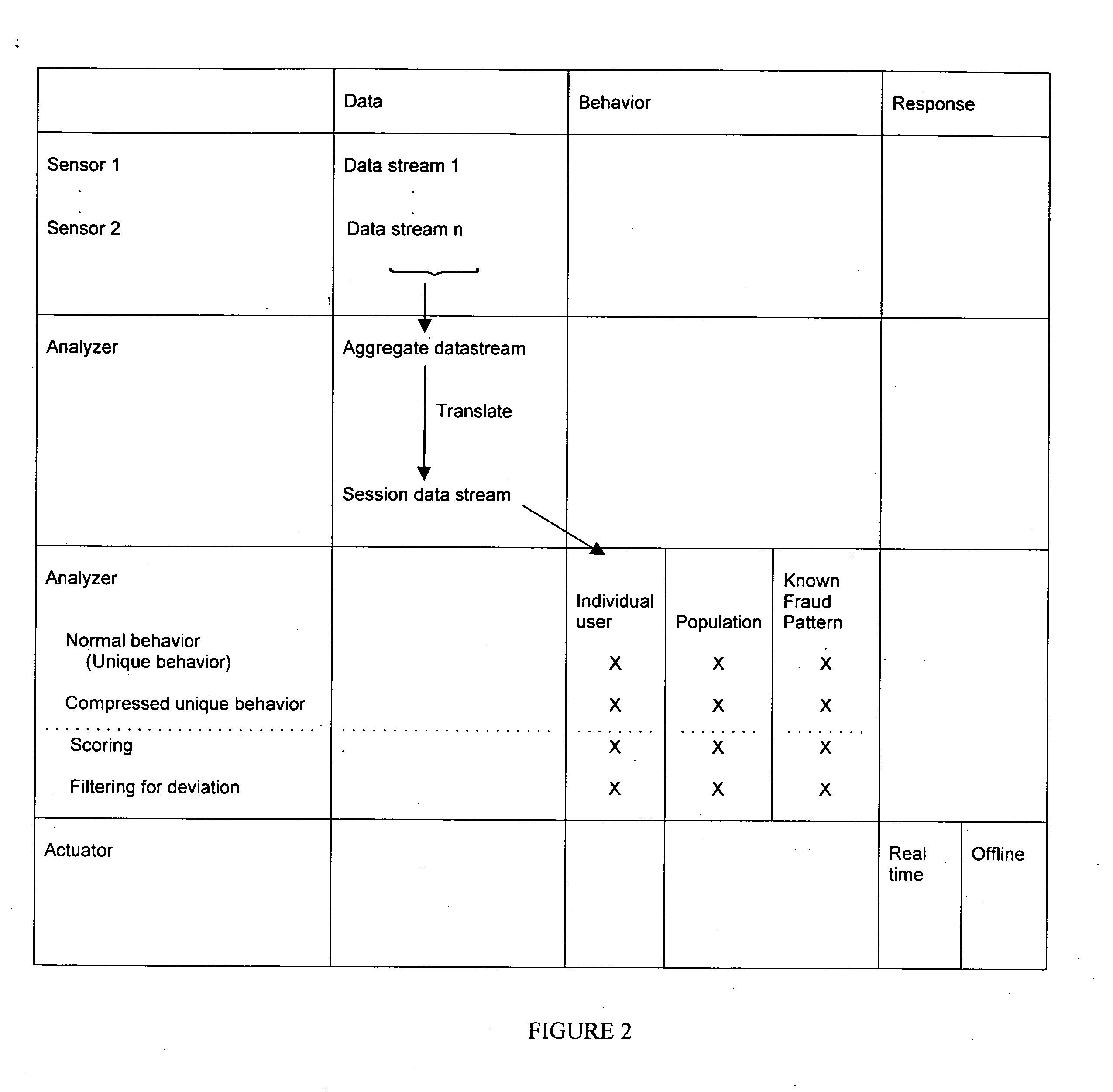
System and method for conducting surveillance on a distributed network
A method is provided for conducting surveillance on a network. Data is captured on a network for a plurality of aggregated channels. The data is from individuals with network access identifiers that permit the individuals to gain access to the network, or applications on the network. The data is used to construct a plurality of session data streams. The session data streams provide a reconstruction of business activity participated in by the application or the individual with the network. A window of data is read in at least one of the plurality of session data streams to determine deviations. The window of data is tested against at least one filter. The at least one filter detects behavioral changes in the applications or the individuals that have the network access identifiers to access to the network. Defined intervention are taken in response to the deviations.
Owner:CYDELITY
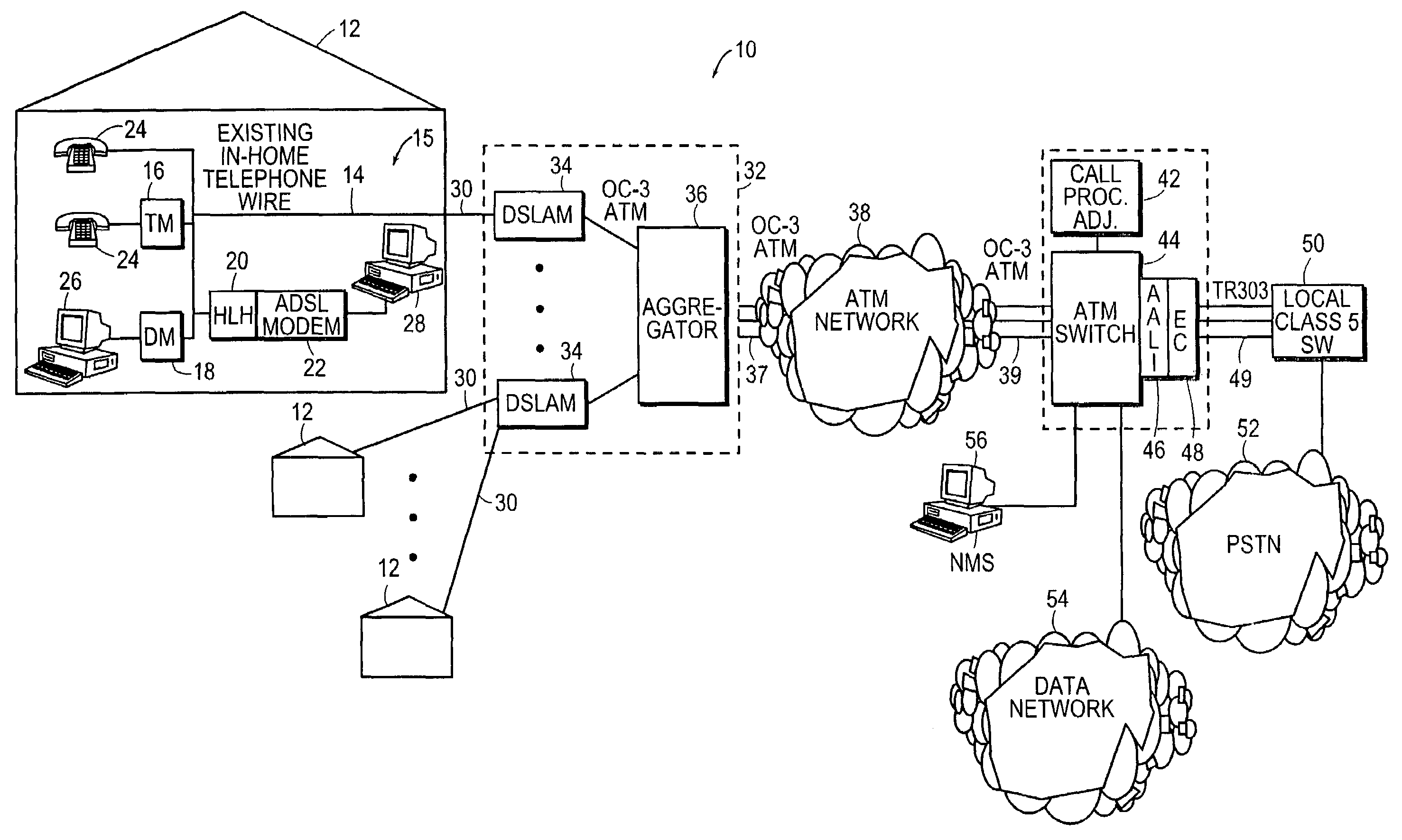
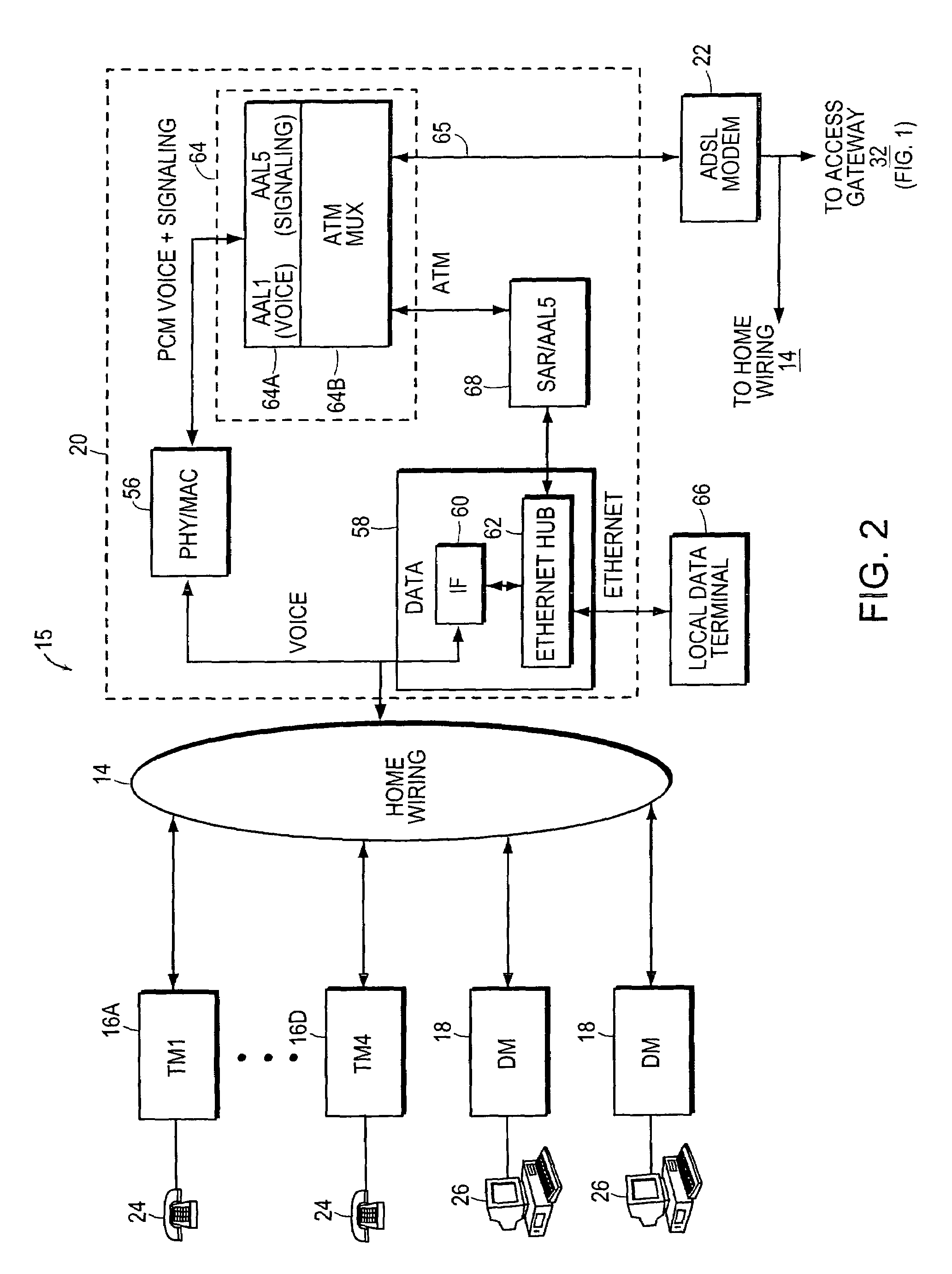
Virtual loop carrier system with gateway protocol mediation
InactiveUS7164694B1Lower unit costReduction in service turn-up timeHybrid switching systemsTime-division multiplexSession Initiation ProtocolCarrier signal
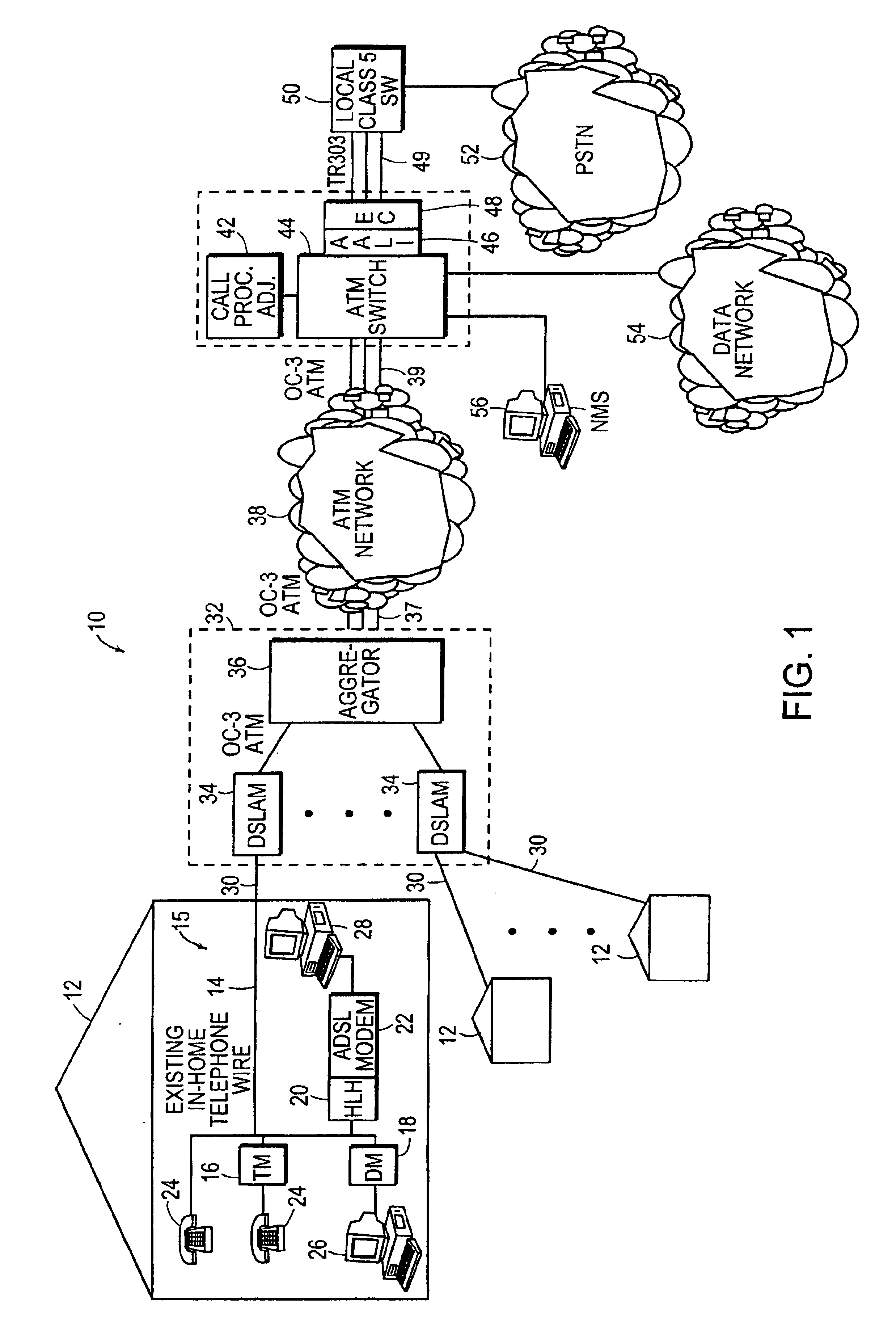
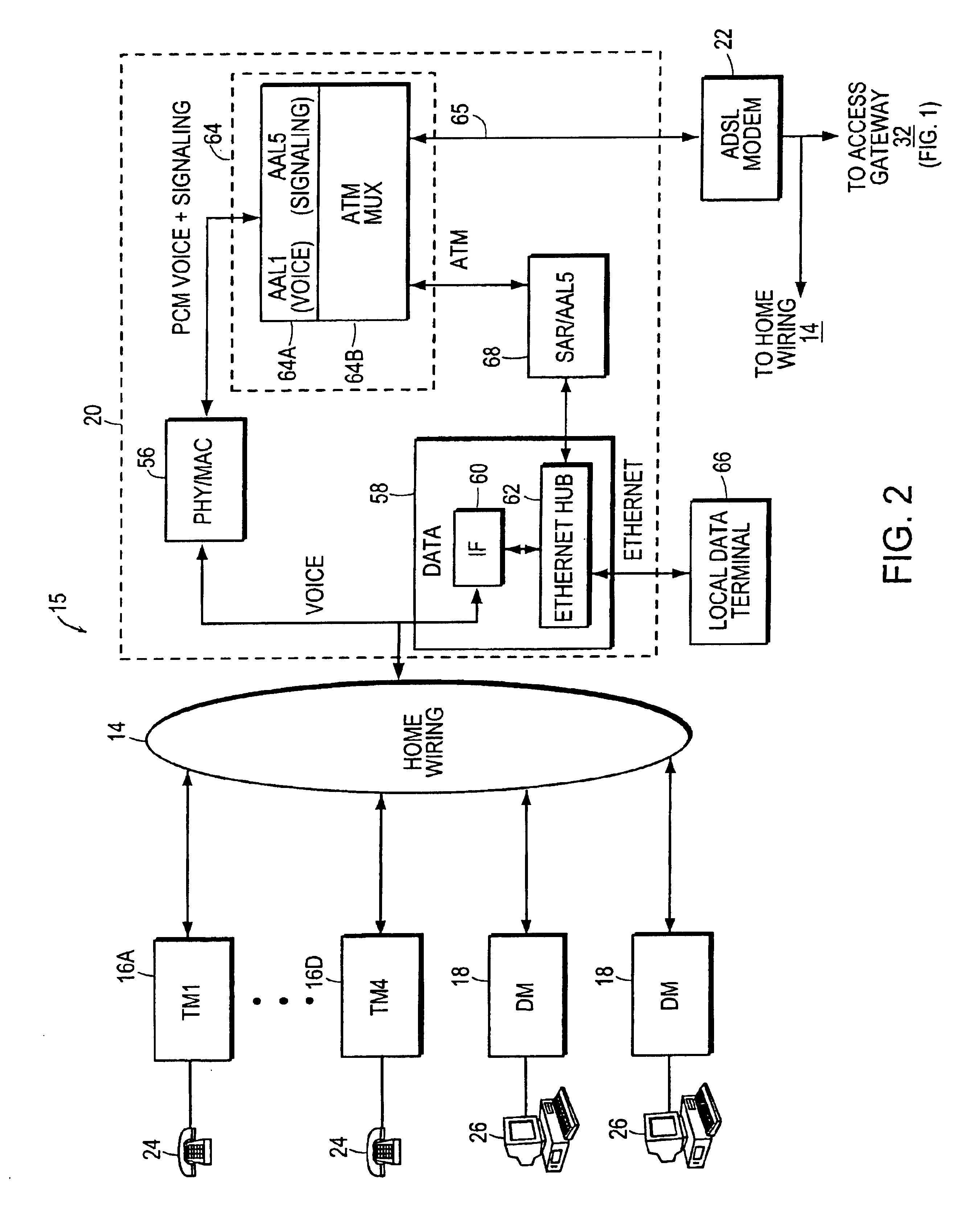
A loop carrier system includes a home local area network having plural telephone modules and a hub coupled to in-home telephone wiring. The telephone modules and the hub communicate voice signals over the in-home wiring in a dedicated frequency band above baseband POTS. The hub converts between voice signals and voice packets and is connected to a network access device for transferring the voice packets from the home local area network to a telecommunications network which routes the voice packets to a gateway. The gateway converts between the voice packets and a circuit format compatible with a local digital voice switch. The gateway includes an ATM switch and a call processing adjunct coupled to the ATM switch. The call processing adjunct controls the conversion between voice packets and the circuit format at the ATM switch. The call processing adjunct communicates with the home local area network using a first signaling protocol such as Media Gateway Control Protocol, Session Initiation Protocol or H.323, and with the local digital switch using a second signaling protocol such as GR-303 for controlling call processing in the communication system.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
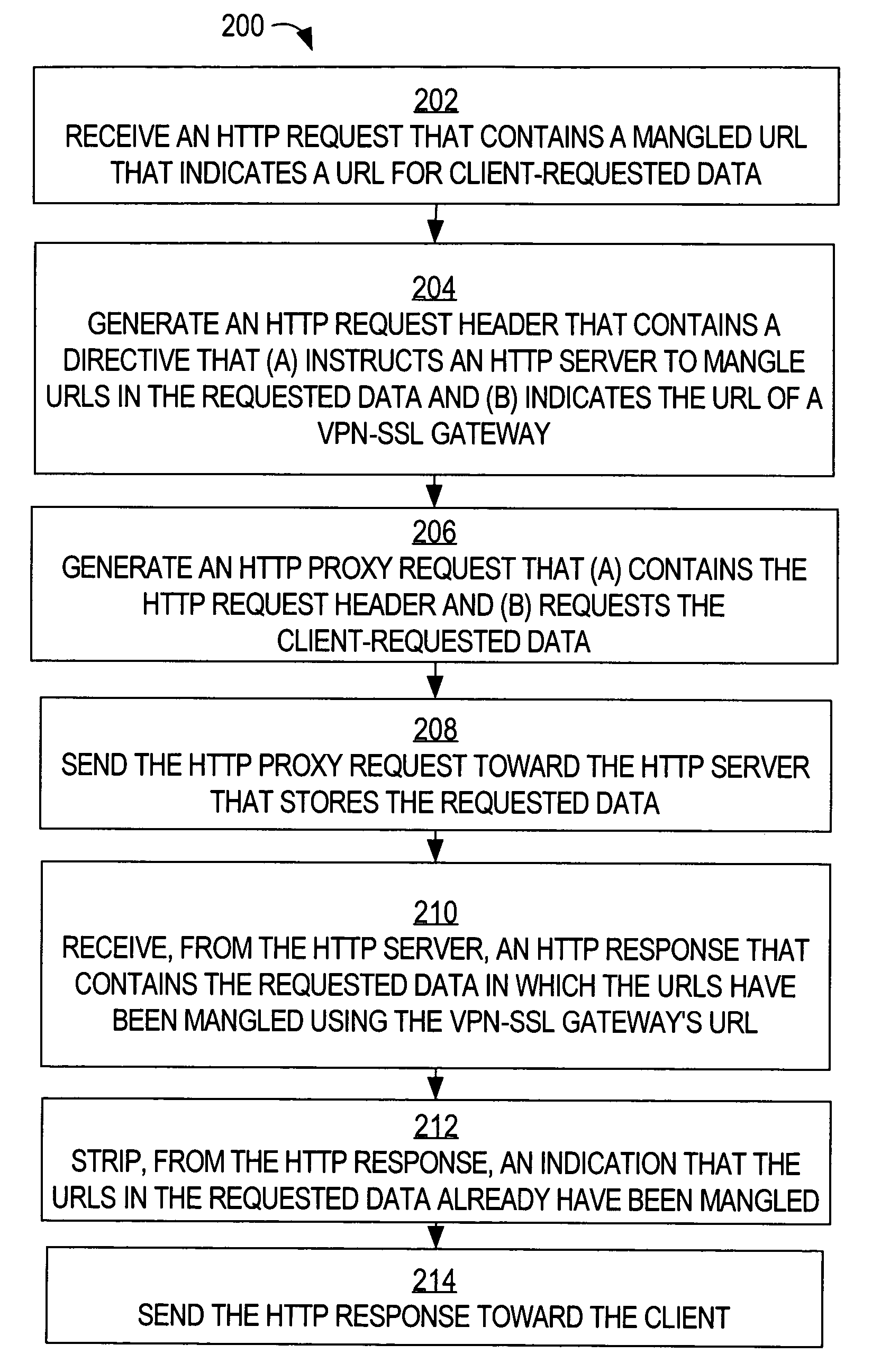
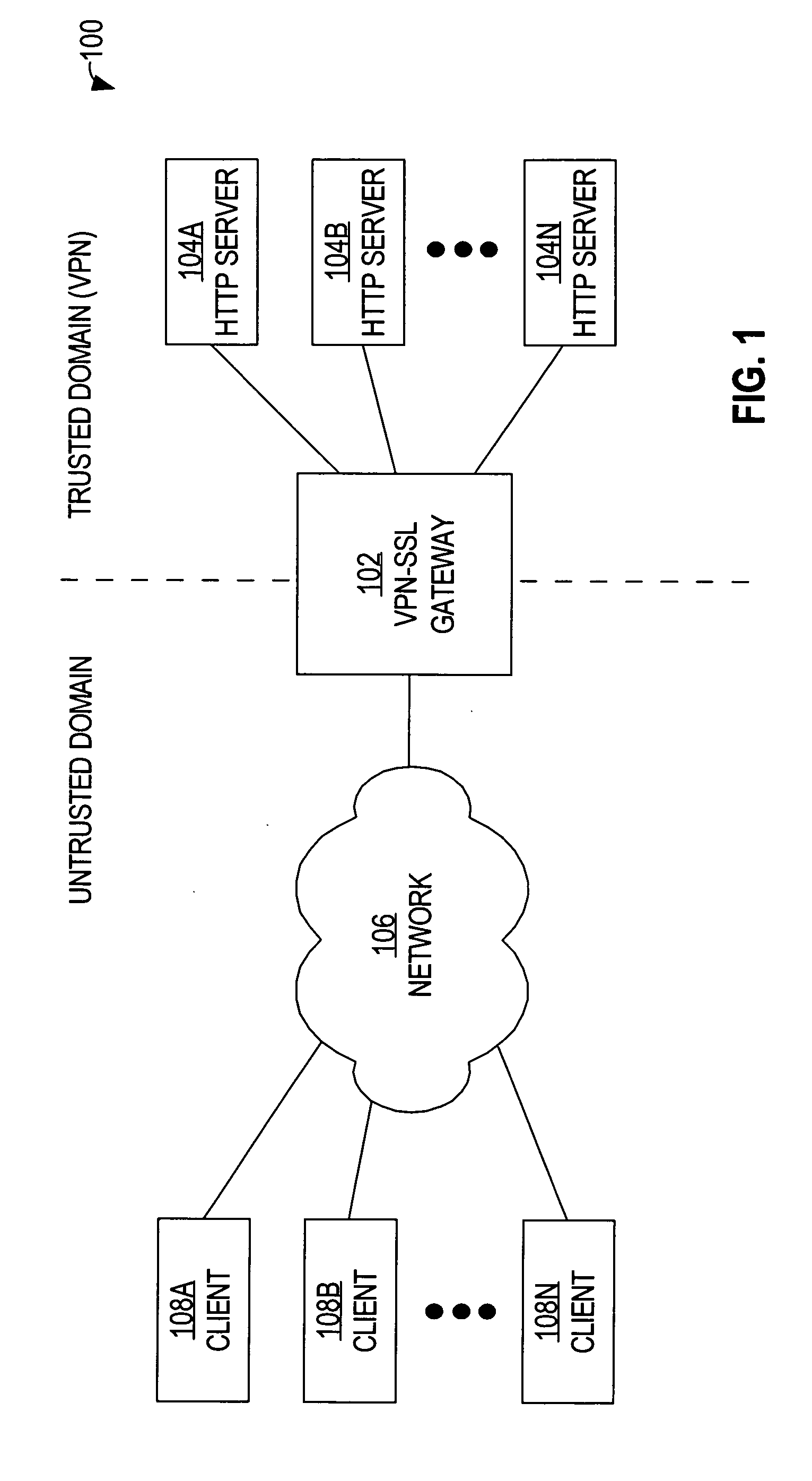
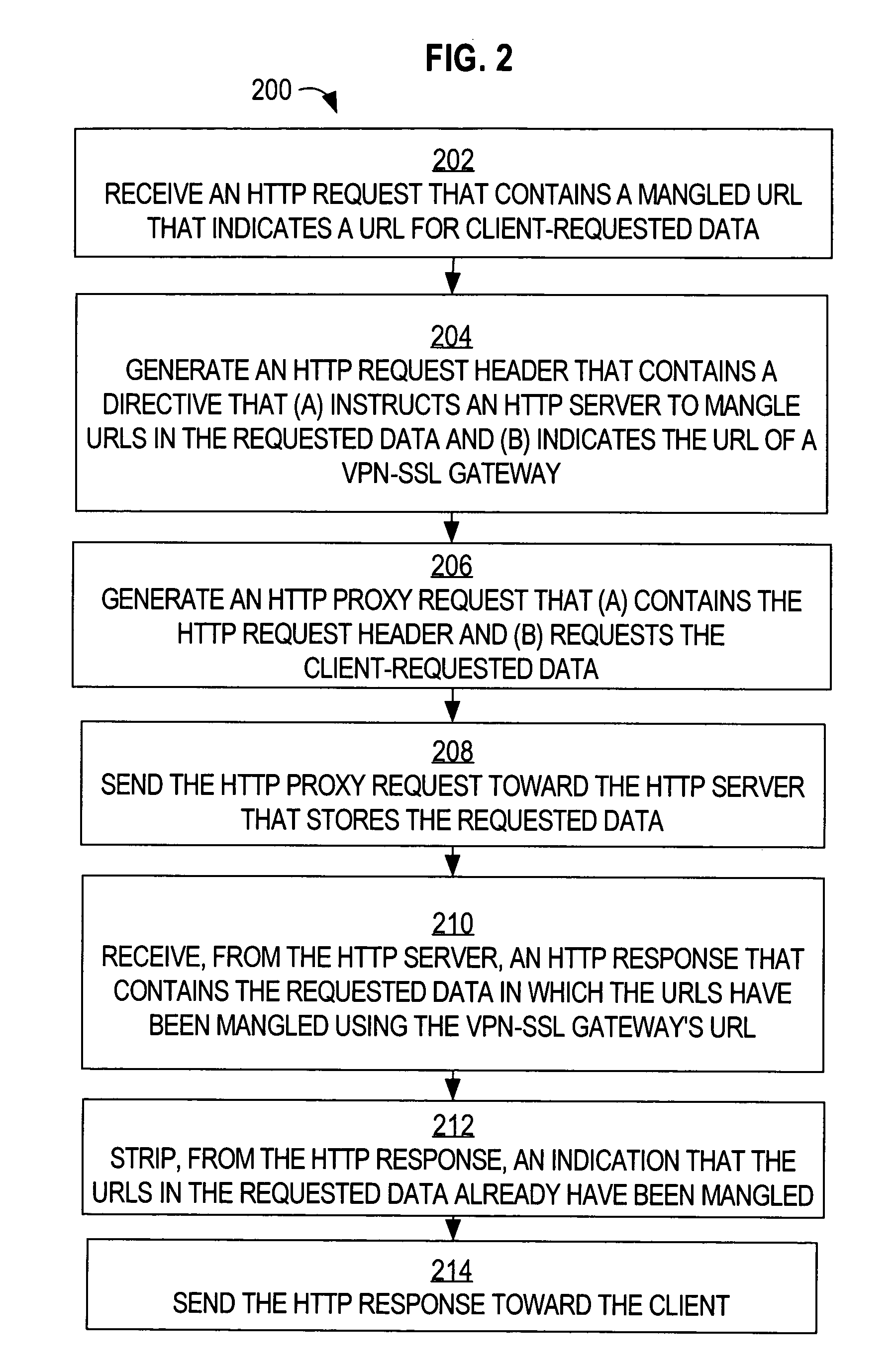
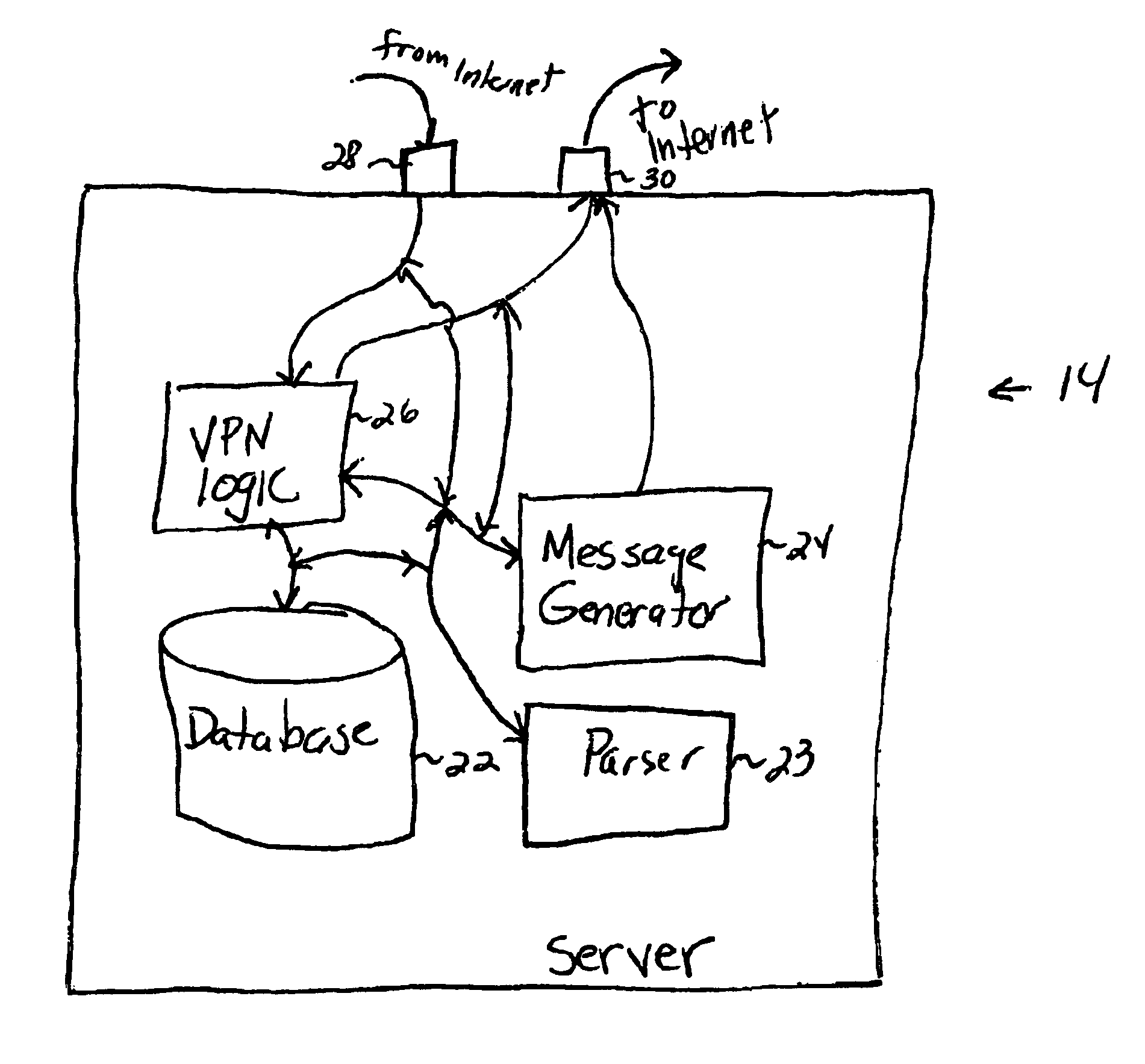
Method and apparatus to modify network identifiers at data servers
A method of modifying network identifiers at data servers is disclosed. A virtual private network (VPN) gateway server generates a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) request. The HTTP request not only requests data from a data server that is within a VPN, but also instructs the data server to modify (“mangle”) URLs that are contained within the requested data so that the URLs refer to the VPN gateway server. The VPN gateway server sends the HTTP request toward the data server. As a result, the data server modifies the URLs so that the VPN gateway server does not need to. When such a modified URLs is selected in a web browser, the web browser generates an HTTP request that is directed to the VPN gateway server's URL, which, unlike the unmodified URLs, can be resolved by domain name servers that are outside of the VPN.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for accessing a network and network access device
ActiveUS20130188634A1Inhibit functioningOptimizationEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationNetwork access serverPrivate network
The invention provides for a method for accessing a virtual private network over a packet switched network, the method comprising sending, by a provider edge router, network labelling information about data packet labels to a network access device using a layer 2 network protocol. The method may be performed for accessing a hierarchical Virtual Private LAN Service network using a link layer distribution protocol as signalling protocol for Multi-Protocol Label Switching labels attached to data packets of the packet switched network.
Owner:ADVA OPTICAL NETWORKING SE
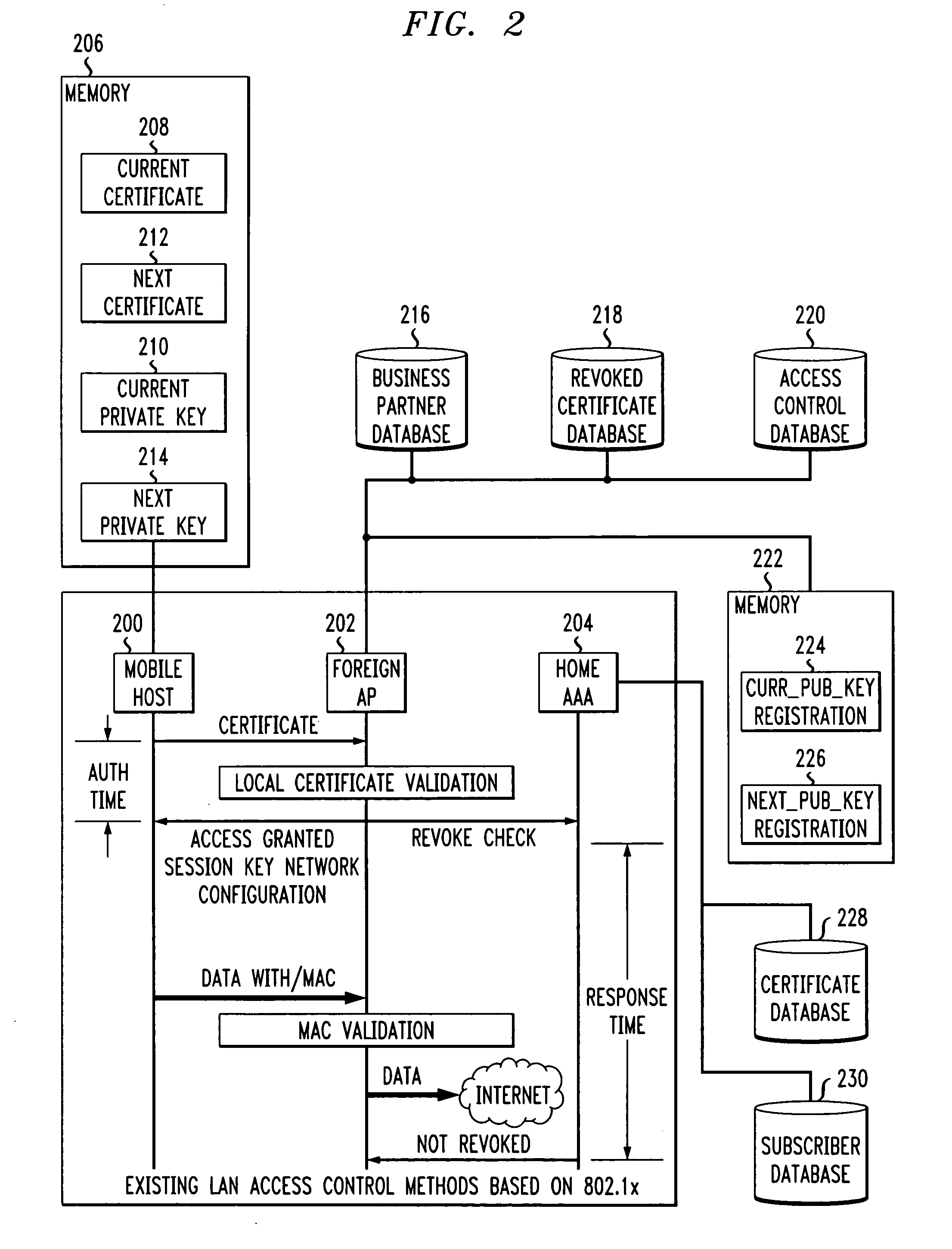
Fast authentication and access control method for mobile networking
InactiveUS7174456B1Easy to switchReduce certification timeDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationExpiration TimeWeb authentication
A fast authentication and access control method of authenticating a network access device to a communications network having an access point communicating with a remote authentication (home AAA) server for the network access device. The method includes the step of receiving an access request having an authentication credential from the network access device at the access point. The authentication credential includes a security certificate having a public key for the network access device and an expiration time. The security certificate is signed with a private key for the remote authentication server. The access point locally validates the authentication credential by accessing the public key of the remote authentication server from a local database, and checking the signature and expiration time of the security certificate. If the authentication credential is validated at the access point, the access point grants the network access device conditional access to the network by sending an access granted message to the network access device. The access granted message includes a session key encrypted with a public key for the network access device. The session key is stored in a database associated with the access point. The access point contacts the remote authentication server to check a revocation status of the security certificate for the network access device. If the access point receives a message from the remote authentication server that the authentication credential for the network access device has been revoked, it suspends network access for the network access device.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
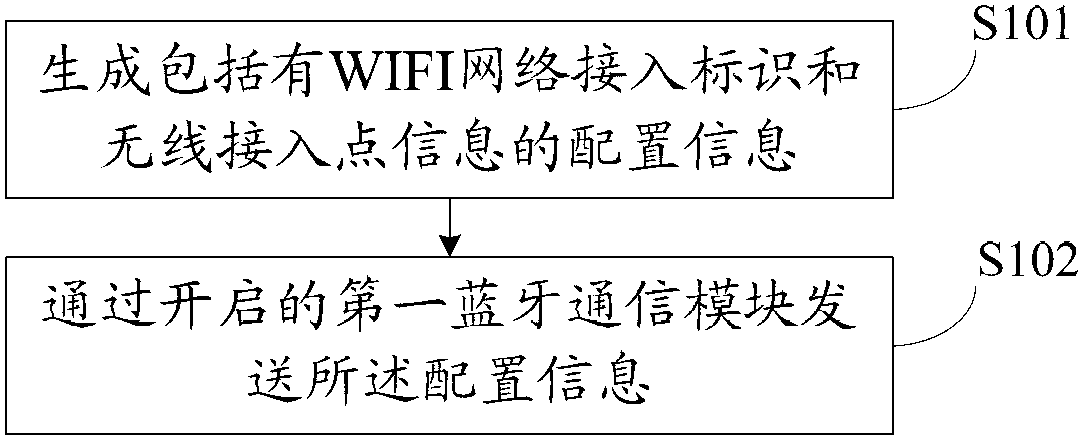
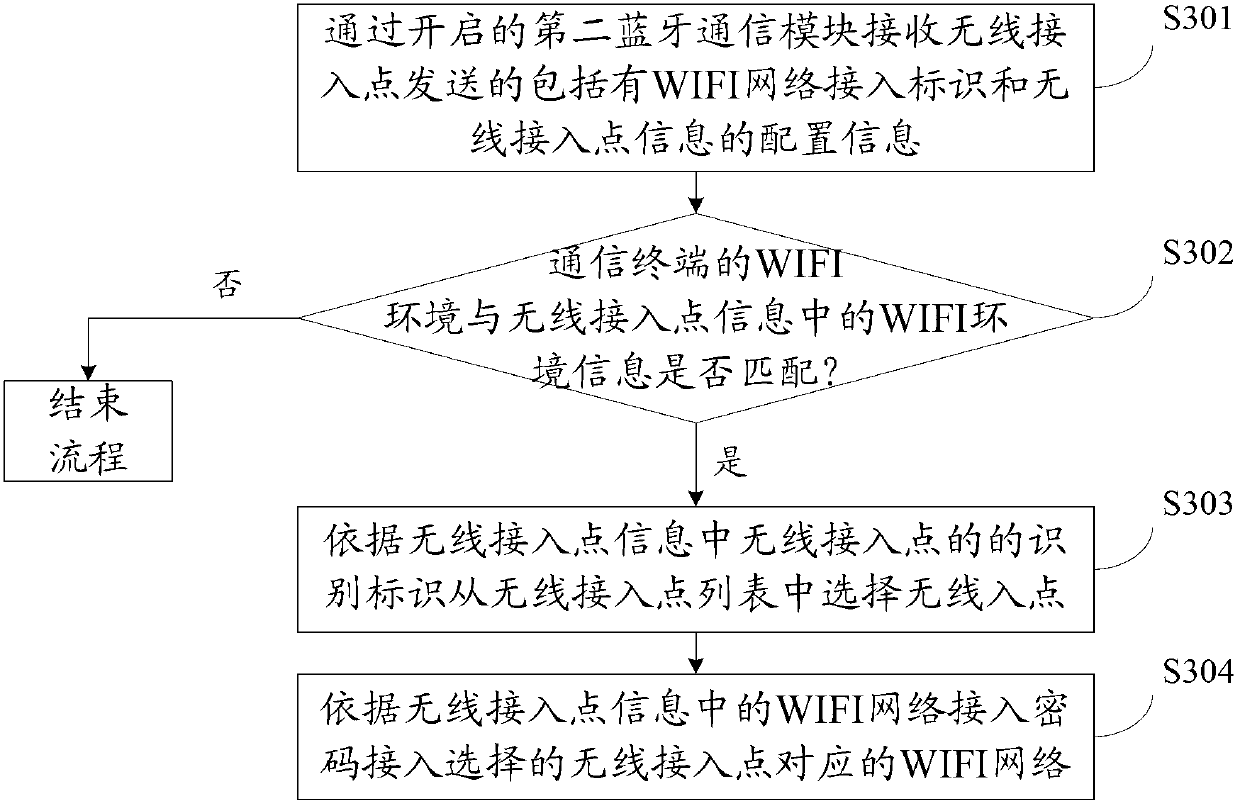
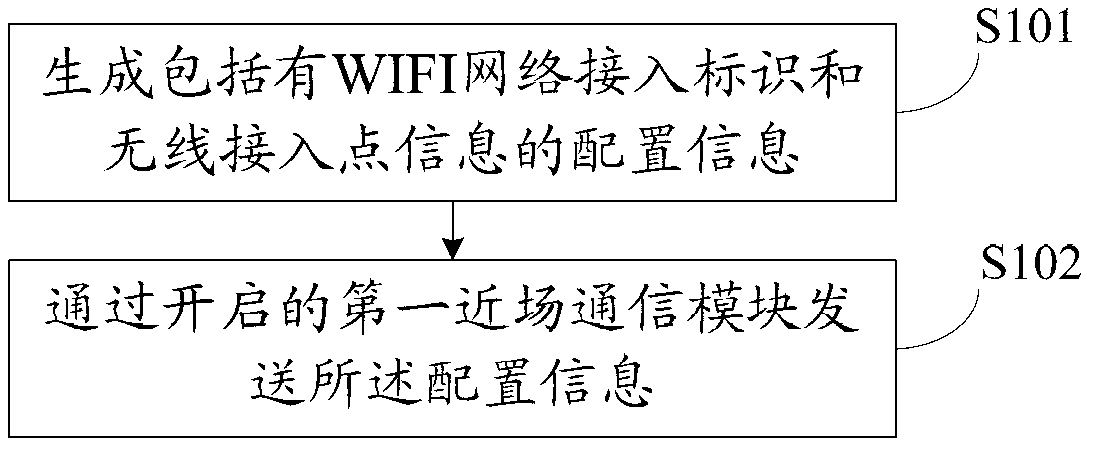
WIFI (wireless fidelity) network access method and device, electronic equipment and communication system
The invention discloses a WIFI (wireless fidelity) network access method, which is applied to a wireless access point, and comprises the steps that the wireless access point sends configuration information including a WIFI network access identifier and wireless access point information to a communication terminal through a bluetooth communication module, wherein the configuration information is used for indicating the communication terminal which receives the configuration information to select a wireless access point according to the identification information of the wireless access point, and accessing a WIFI network according to a WIFI network access password in the wireless access point information. In such a way, the communication terminal can automatically access the WIFI network without receiving input information of a user for multiple times or responding to a human-machine interaction request triggered by the user for multiple times, so that the process of accessing the WIFI network is simplified. The invention also discloses a WIFI network access device, electronic equipment and a communication system.
Owner:BEIJING RISING INT SOFTWARE
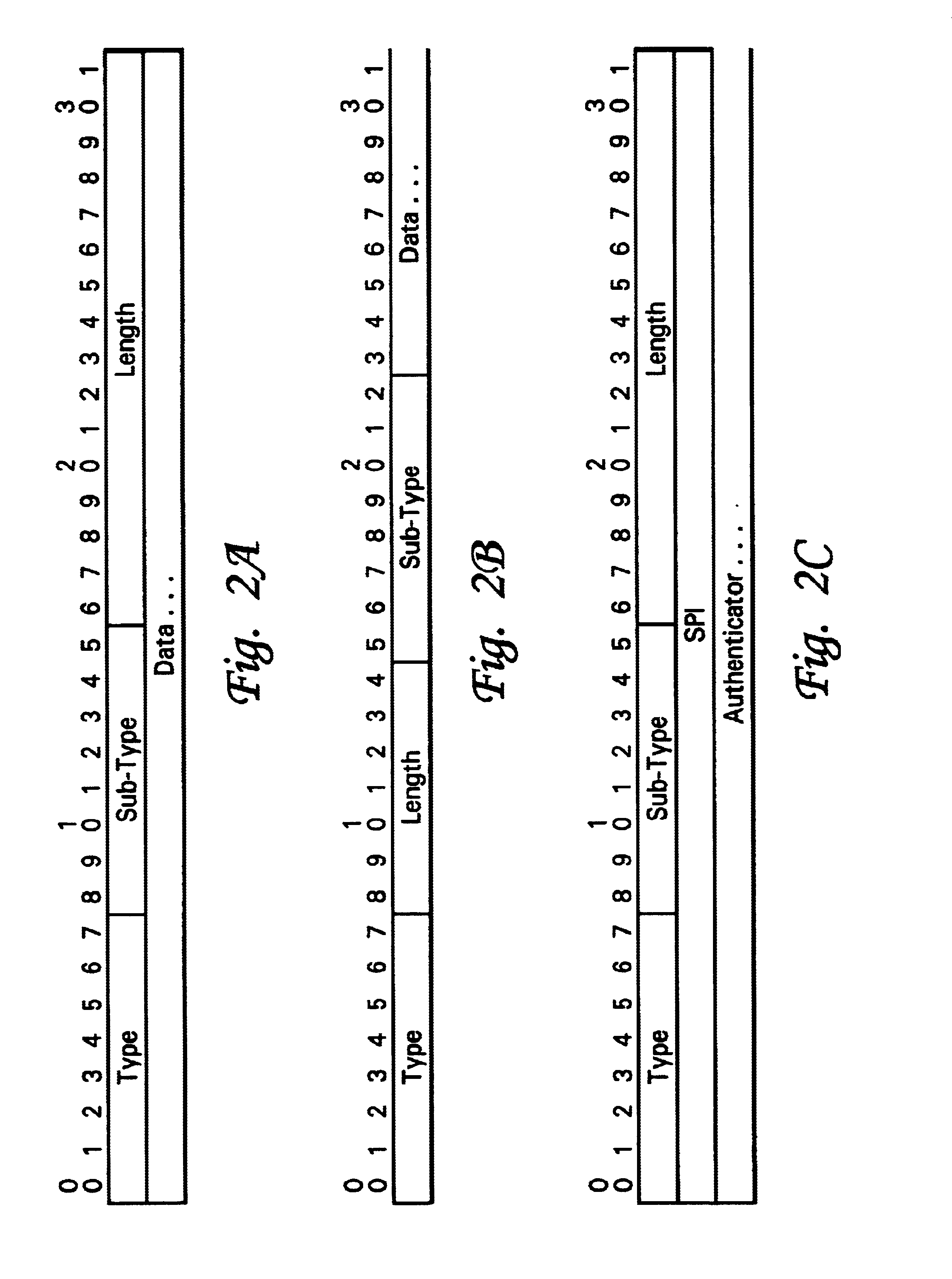
Mobile IP extensions rationalization (MIER)
InactiveUS6922404B1Reduce usageUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer networkForeign agent
A new extensions structure for mobile IP control message extensions is employed to conserve the type field. Certain types of extensions, such as network access identifiers, are initially aggregated and subtypes are employed to identify the precise content of the extension (e.g., mobile node network access identifier, home agent network access identifier, foreign agent network access identifier, etc.). Long and short formats for the new extension structure are defined, with the long format applicable to nonskippable extensions carrying more than 256 bytes and the short format backwards compatible with currently defined skippable extensions with less than 256 bytes of data. This will greatly reduce usage of the type field.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
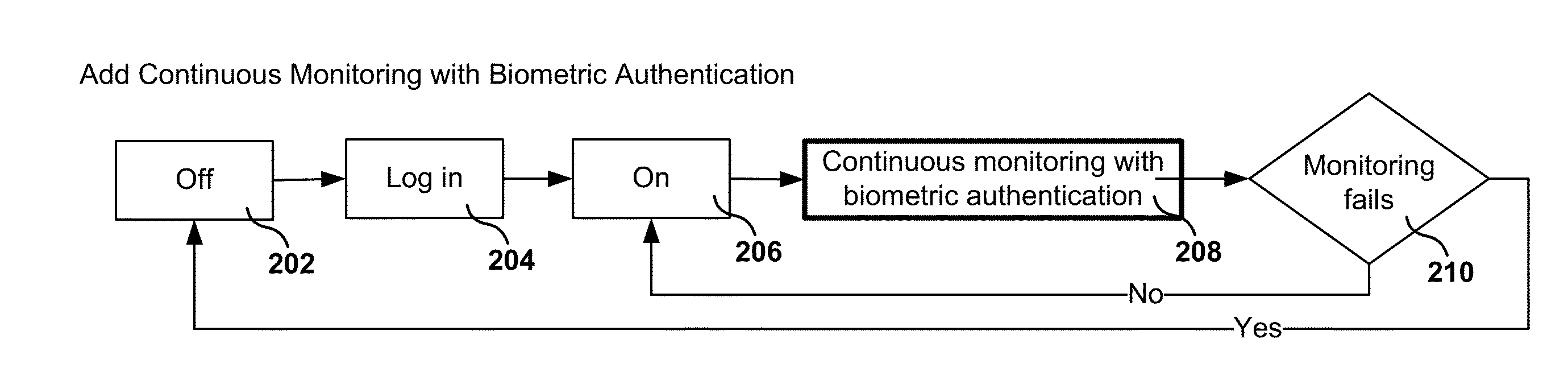
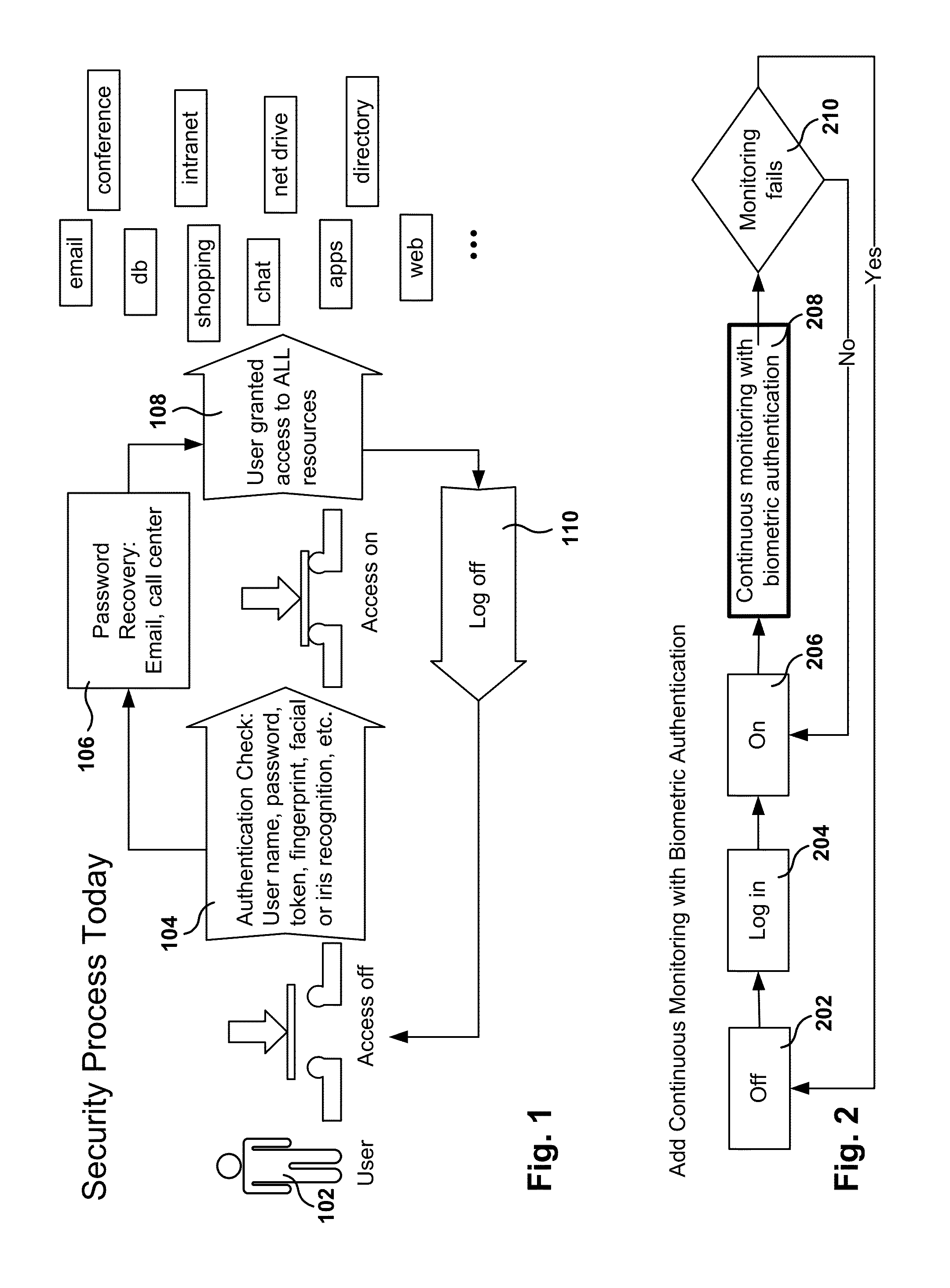
Ongoing Authentication and Access Control with Network Access Device
InactiveUS20140282965A1Disabling useDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsBiometric dataRemote computer
Methods, systems, and computer programs are presented for securing network access. One method includes an operation for granting a user access to remote computer resources after authenticating a login request from the user sent from a secured computer device. In addition, the method includes an operation for receiving a network access request from a network access device to allow the user to access the remote computer resources through the network access device. A network access granted message for the user is sent to the network access device when the user currently has been granted access to the remote computer resources, where the secured computer device performs periodic authentication operations to validate an identification of the user based on biometric data taken of the user. Further, the method includes operations for receiving notification from the secured computer device that one of the authentication operations has failed, and for sending a network access denied for the user to the network access device in response to the notification.
Owner:NSS LAB WORKS
Network probing using overlapping probe packets
Owner:RESOURCE CONSORTIUM LTD LLC
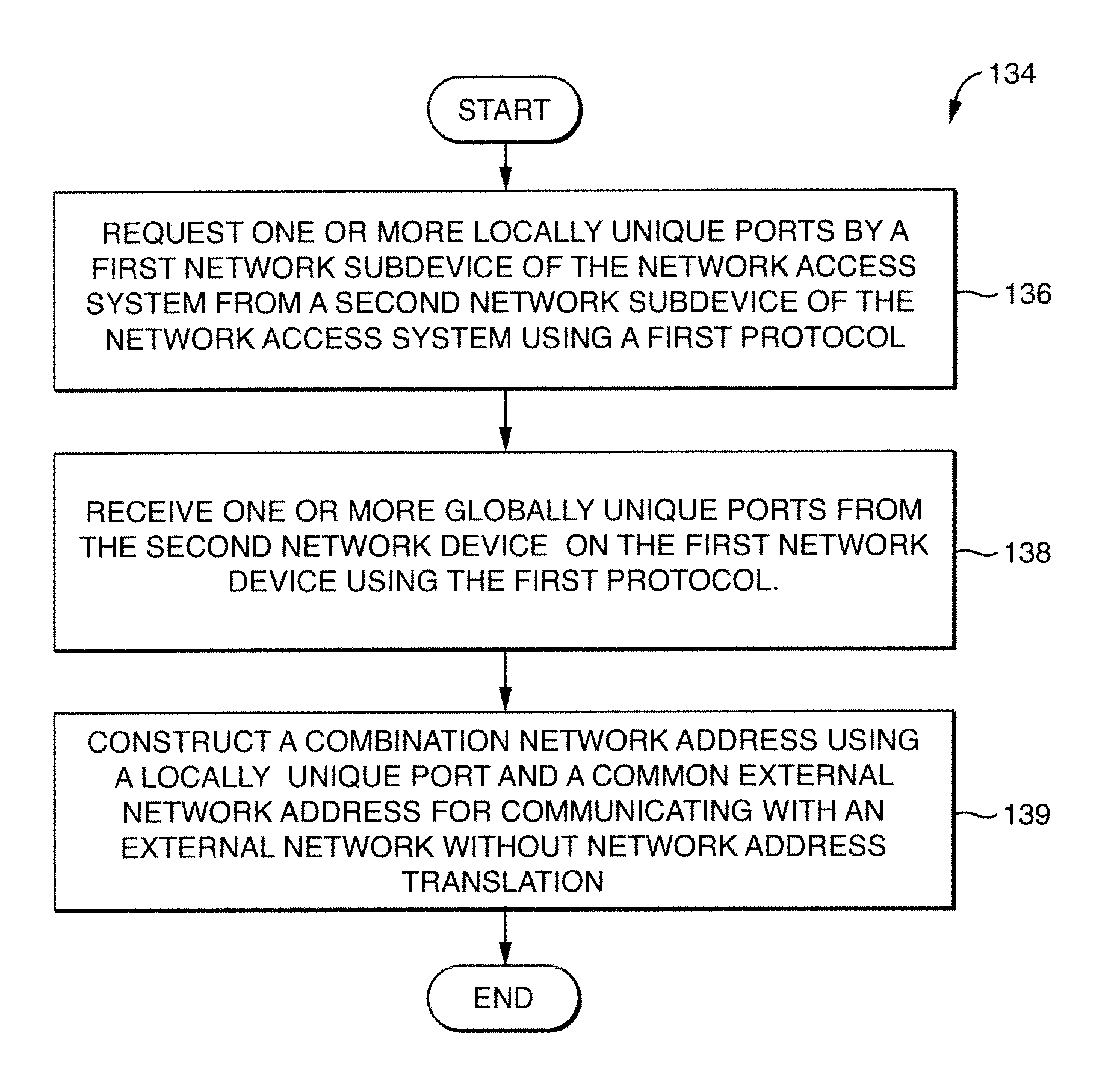
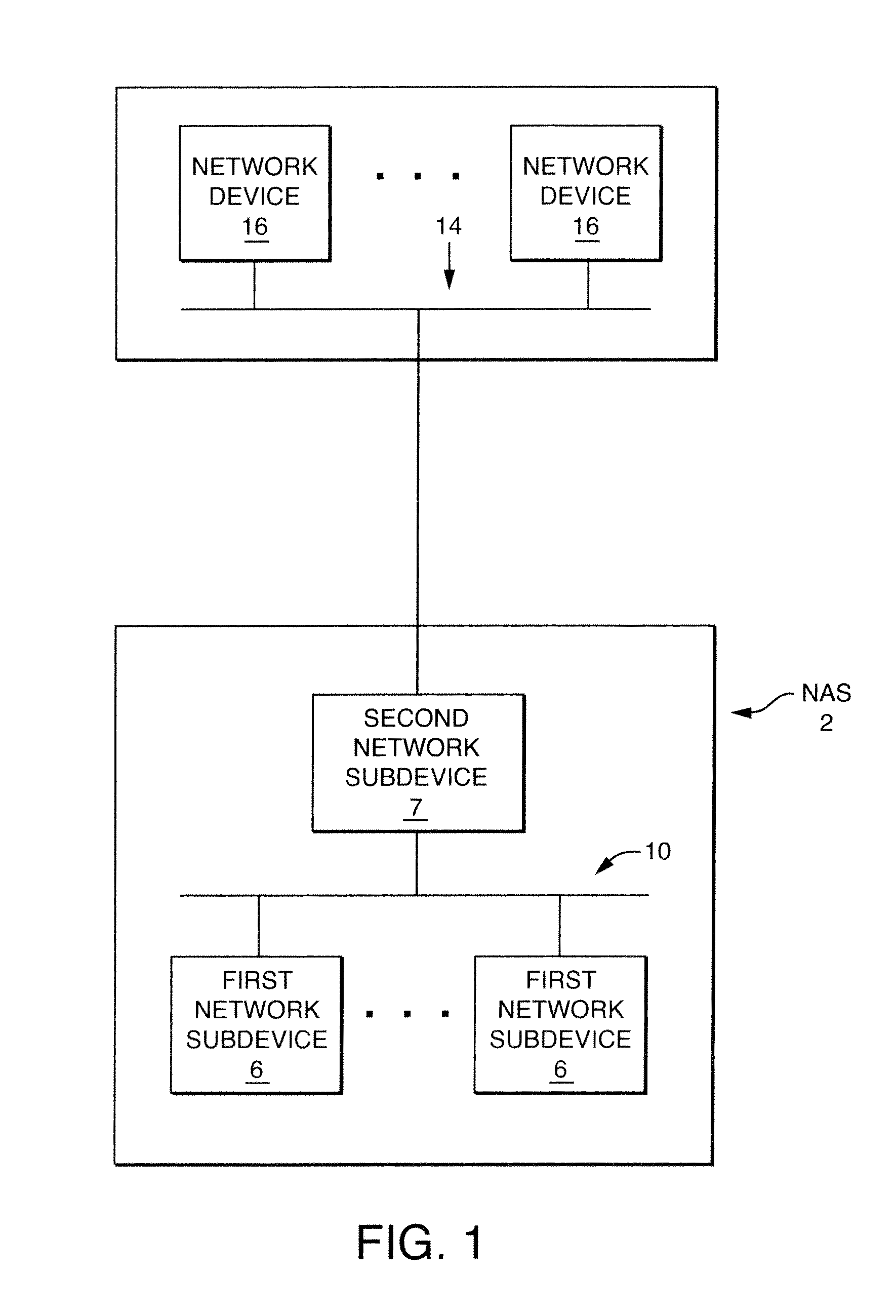
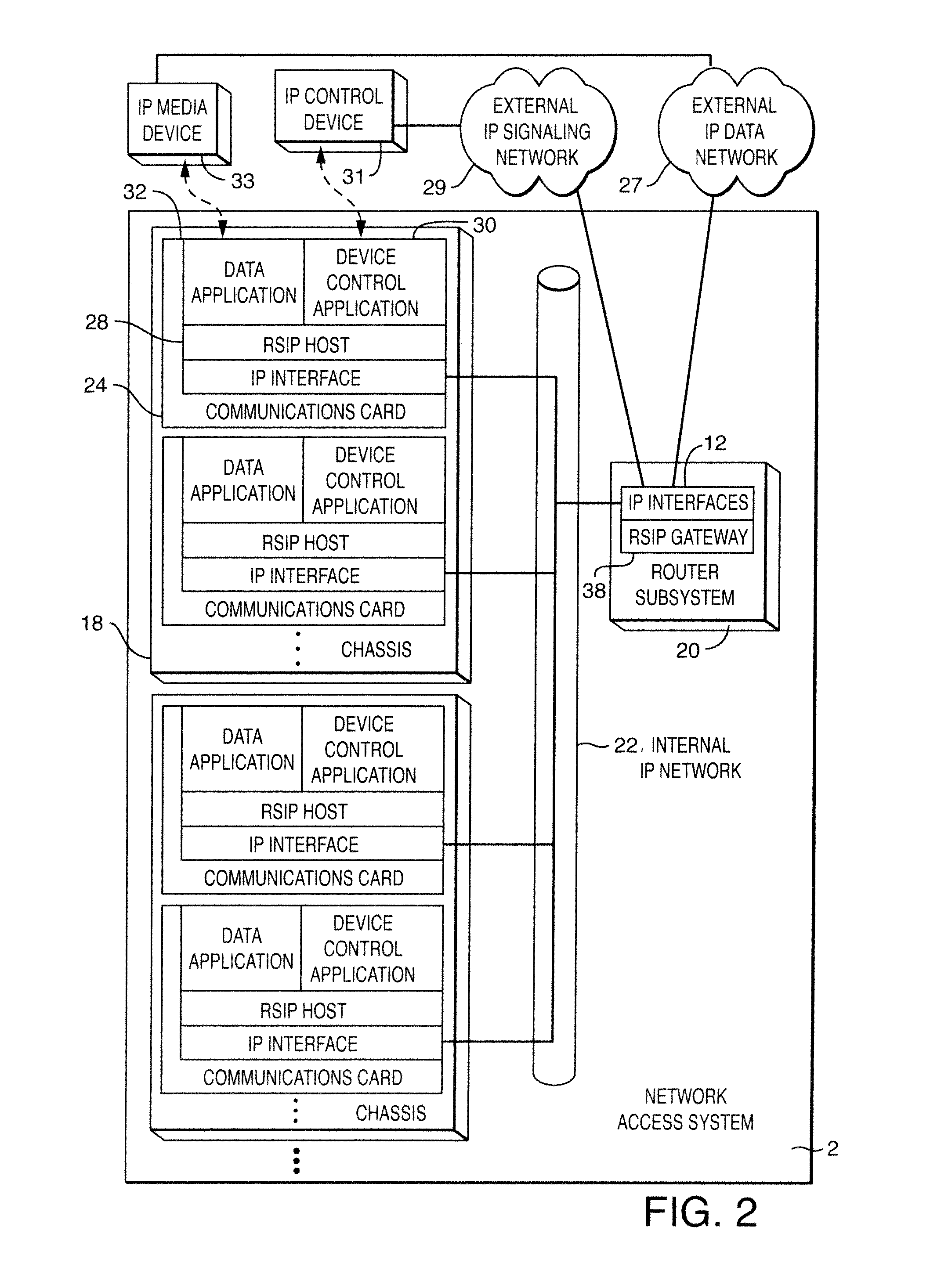
Method for address mapping in a network access system and a network access device for use therewith
InactiveUS7450560B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkPublic network
A method to support the assignment of a globally unique network public address and, optionally, a number of locally unique ports to a first private network subdevice having a private network address on a network access system from a second private network subdevice having a public network address using Realm Specific Internet Protocol, wherein the public network address is used by the first private network device to communicate with network devices on an external network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
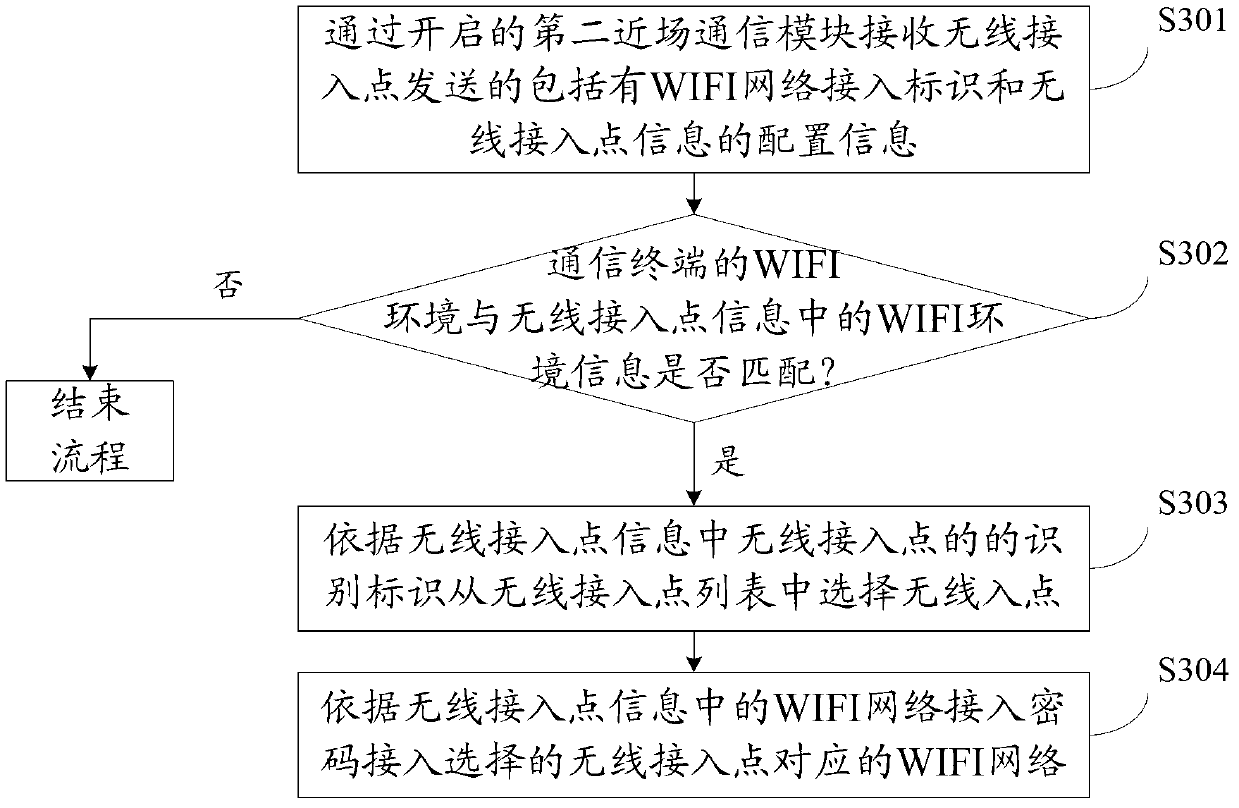
WIFI (wireless fidelity) network access method and device, electronic equipment and communication system
InactiveCN103281759ASimplify the access processAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemAccess method
The invention discloses a WIFI (wireless fidelity) network access method, which is applied to a wireless access point, and comprises the steps that the wireless access point sends configuration information including a WIFI network access identifier and wireless access point information to a communication terminal through a near field communication module, wherein the configuration information is used for indicating the communication terminal which receives the configuration information to select a wireless access point according to the identification information of the wireless access point, and accessing a WIFI network according to a WIFI network access password in the wireless access point information. In such a way, the communication terminal can automatically access the WIFI network without receiving input information of a user for multiple times or responding to a human-machine interaction request triggered by the user for multiple times, so that the process of accessing the WIFI network is simplified. The invention also discloses a WIFI network access device, electronic equipment and a communication system.
Owner:BEIJING RISING INT SOFTWARE
Associating devices and users with a local area network using network identifiers
InactiveUS20160165651A1Easy to identifyEasy to determineAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesDevice PropertiesUnique identifier
Techniques for associating devices and users with a local area network using network identifiers are provided. For example, a method, system, and computer-program product for associating network devices with a local area network using a network identifier are provided. For example, a method may include receiving, at a computing device, a communication including a unique identifier for a network device connected to a network. The method may further include using the unique identifier to determine properties of the network device and generating a network identifier for the network, wherein the network identifier includes an indication of a time at which the network identifier is generated, an indication of the computing device, and an indication of the network device properties. The method can also include transmitting the network identifier, wherein when the network identifier is received, the network identifier facilitates identifying the network and associating the network device with the network.
Owner:BELKIN INT
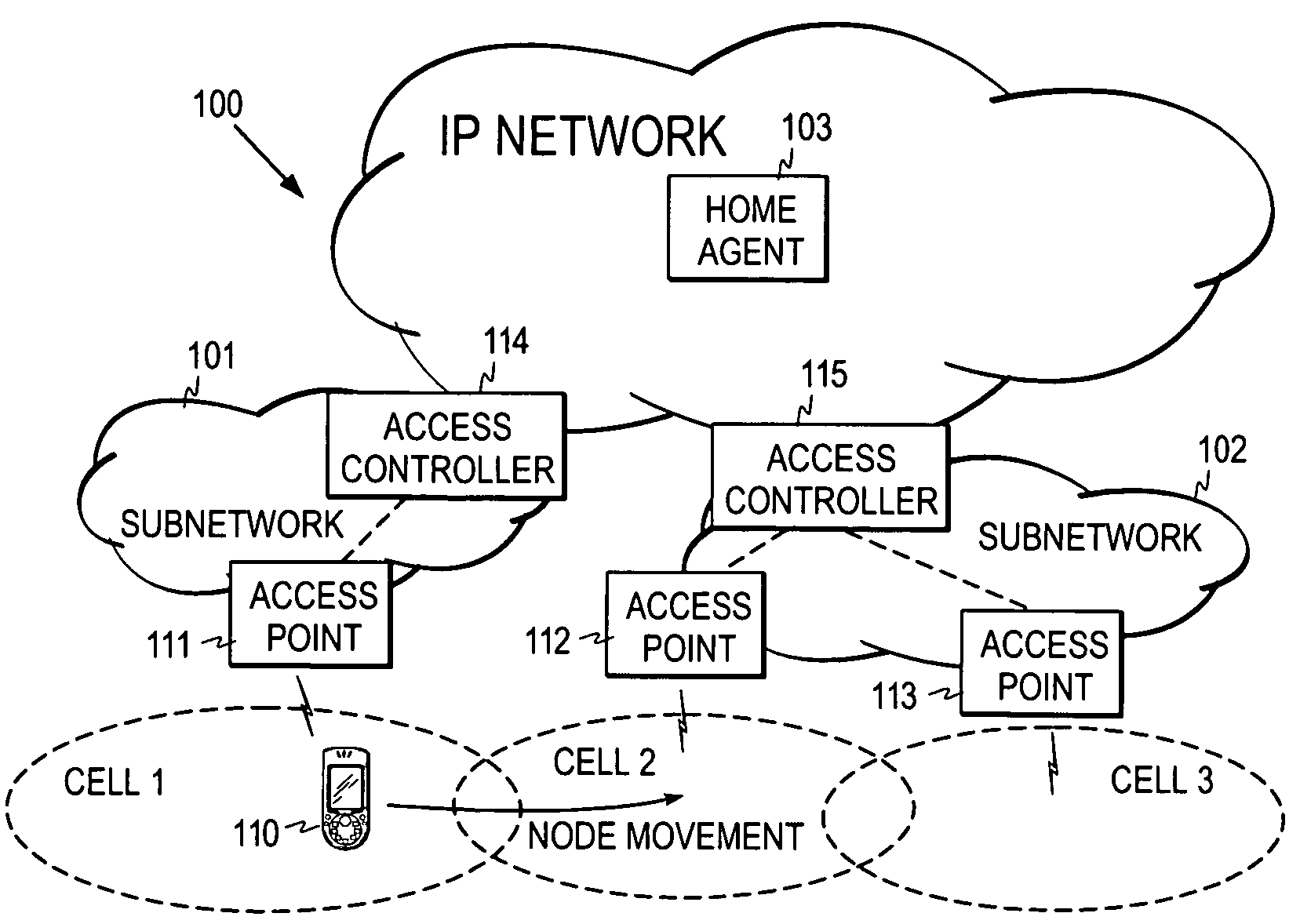
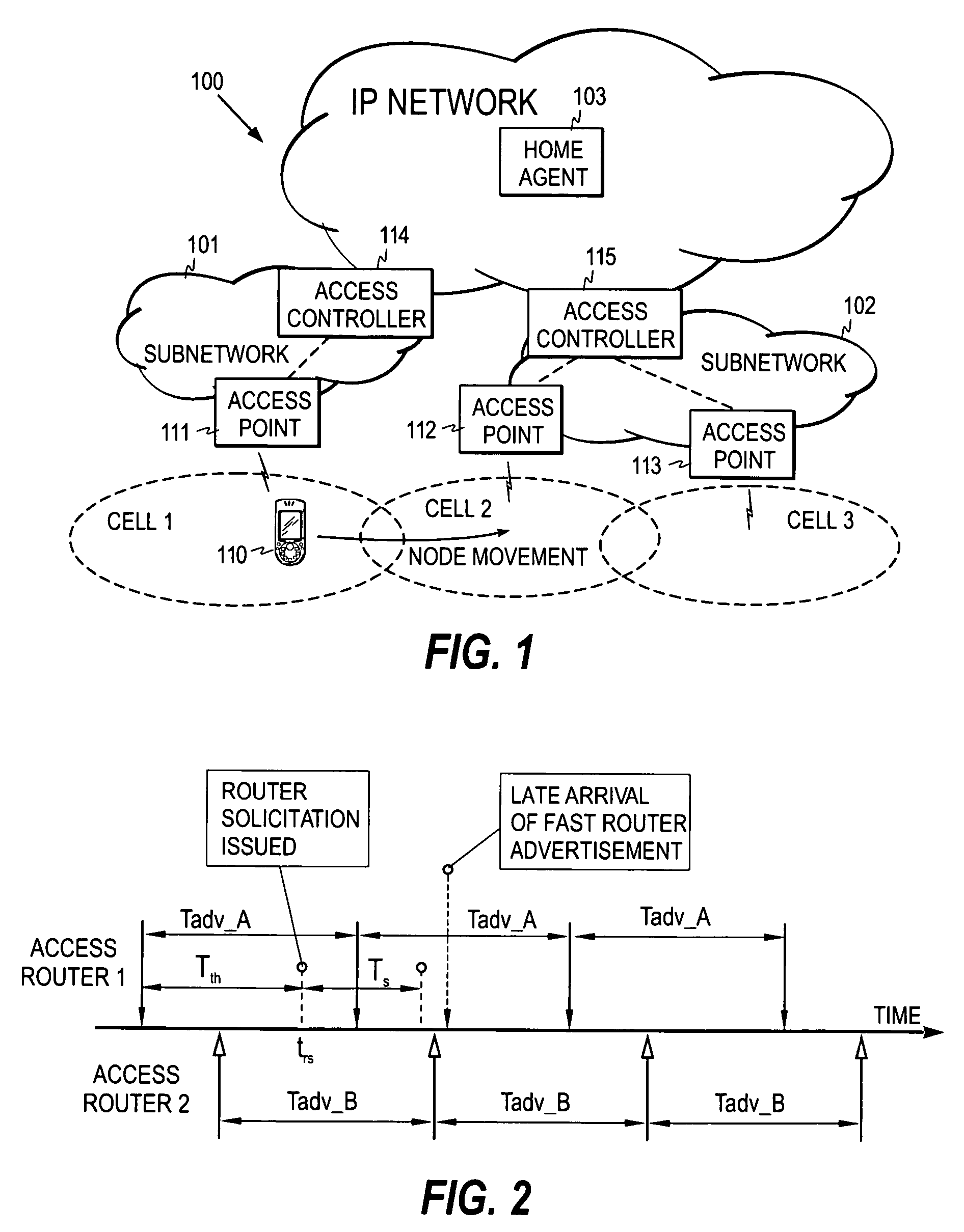
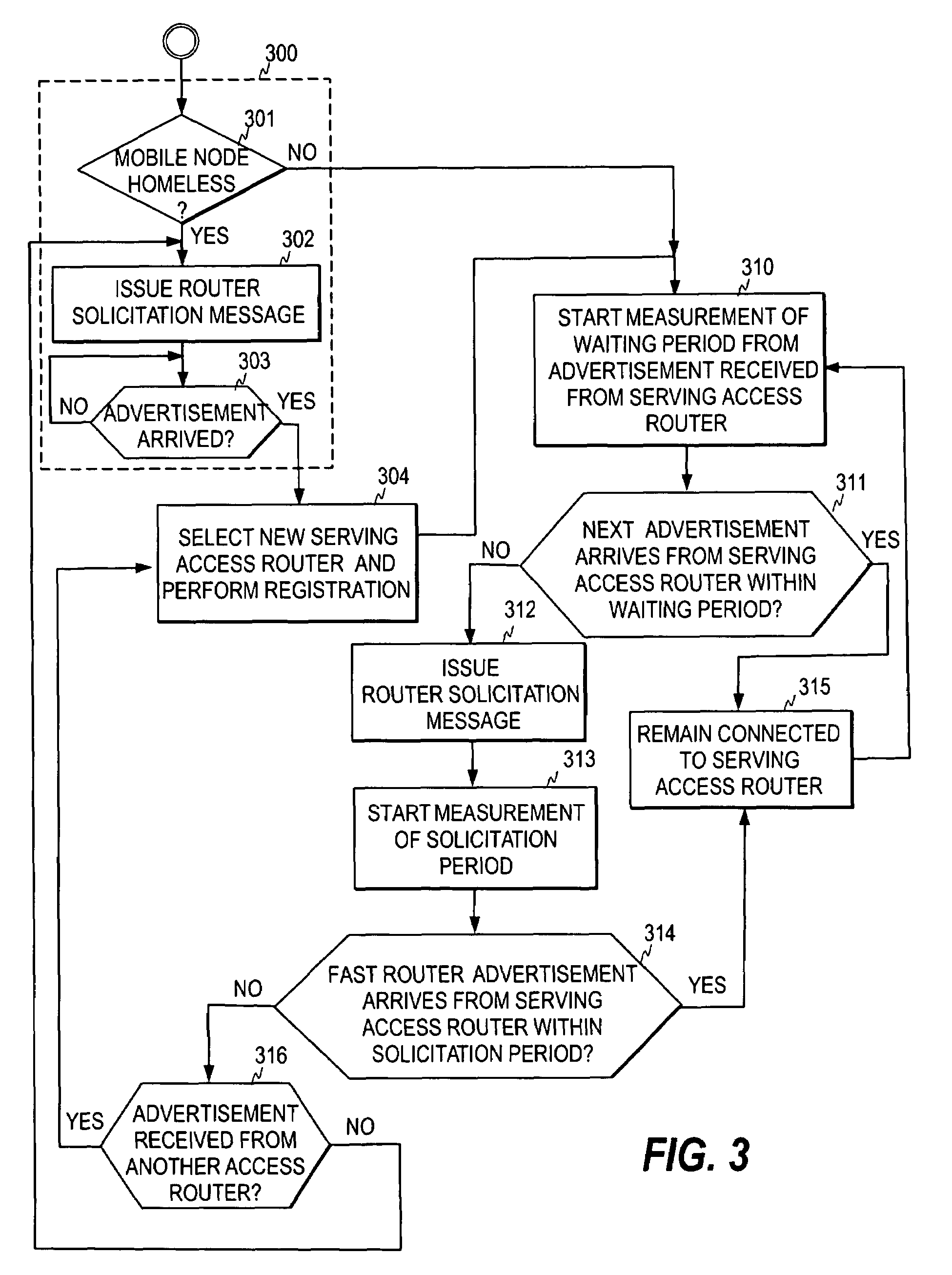
Selection of network access entity in a communication system
ActiveUS7362731B2Tune performanceAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemWaiting period
A mechanism for selecting a serving network access entity for a mobile node in a communication system including network access entities broadcasting periodic advertisement messages. The method utilizes a waiting period measured from a first reference moment. When no advertisement message is received within the waiting period from the network access entity being currently the serving network access entity for the mobile node, the node issues a router solicitation message and initiates a measurement of a solicitation period from a second reference moment. The mobile node further monitors whether a response to the router solicitation message is received from the network access entity within the solicitation period, and based on the monitoring step decides whether it remains connected to the said network access entity.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
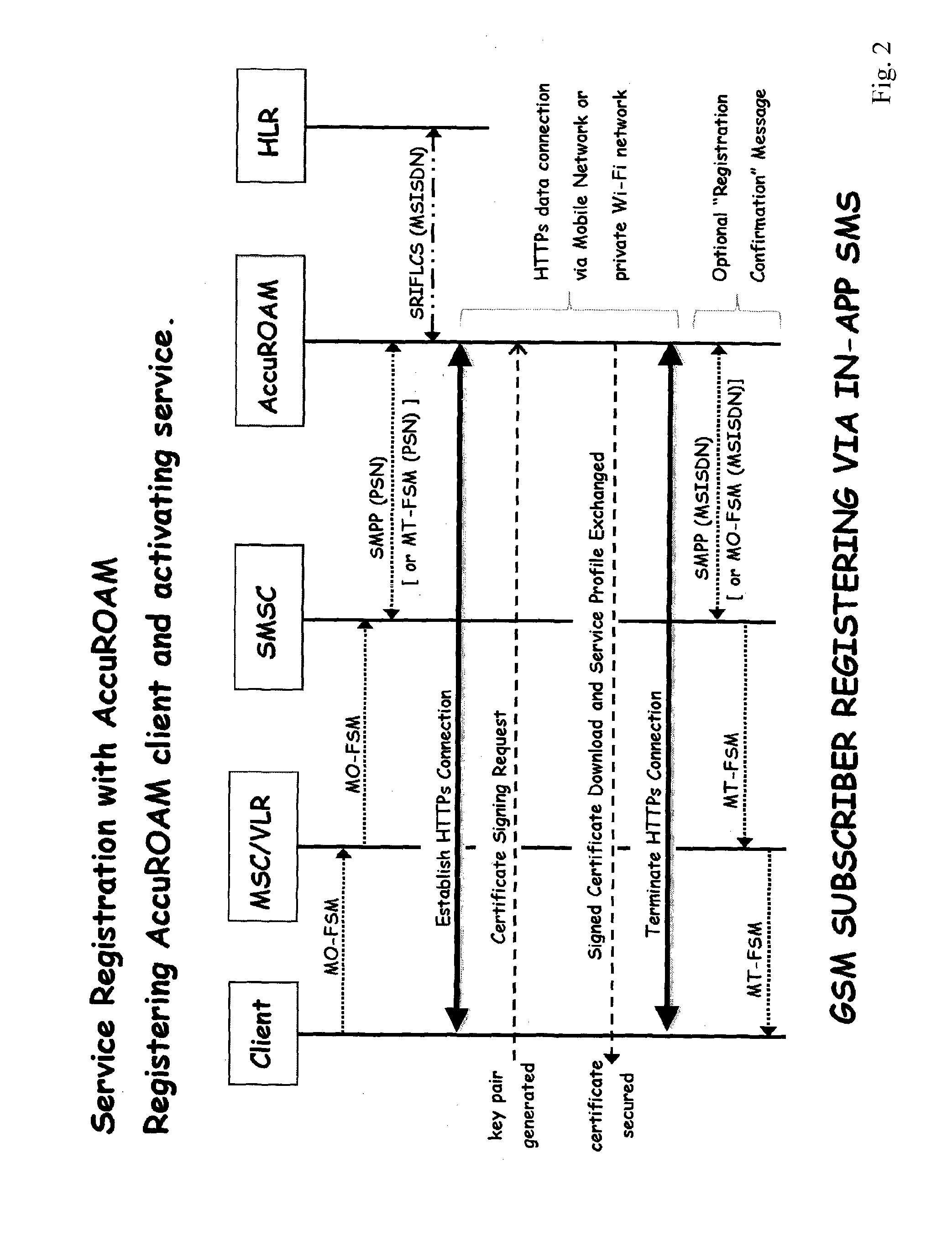
Device authentication method and devices
ActiveUS20140115676A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsAuthentication systemMobile Web
In a method for authenticating a device on a wireless local area network (WLAN) there is a once-off registration phase in which the device sends registration data in a MO SMS via the mobile network to the authentication system, and the authentication system performs a query to this mobile network to validate the subscriber and resolve the subscriber and device identifiers. The device receives network access information from the authentication system, allowing it to generate network access credentials on an on-going basis. This is permanent unless the registration is revoked due, for example, to the device being stolen. The network access information may be provided by the authentication system generating and signing a unique subscriber certificate during registration, and the device downloading it. The device uses the signed certificate to generate and encrypt the network access credentials for the network access.
Owner:ESW TECH FZ LLC
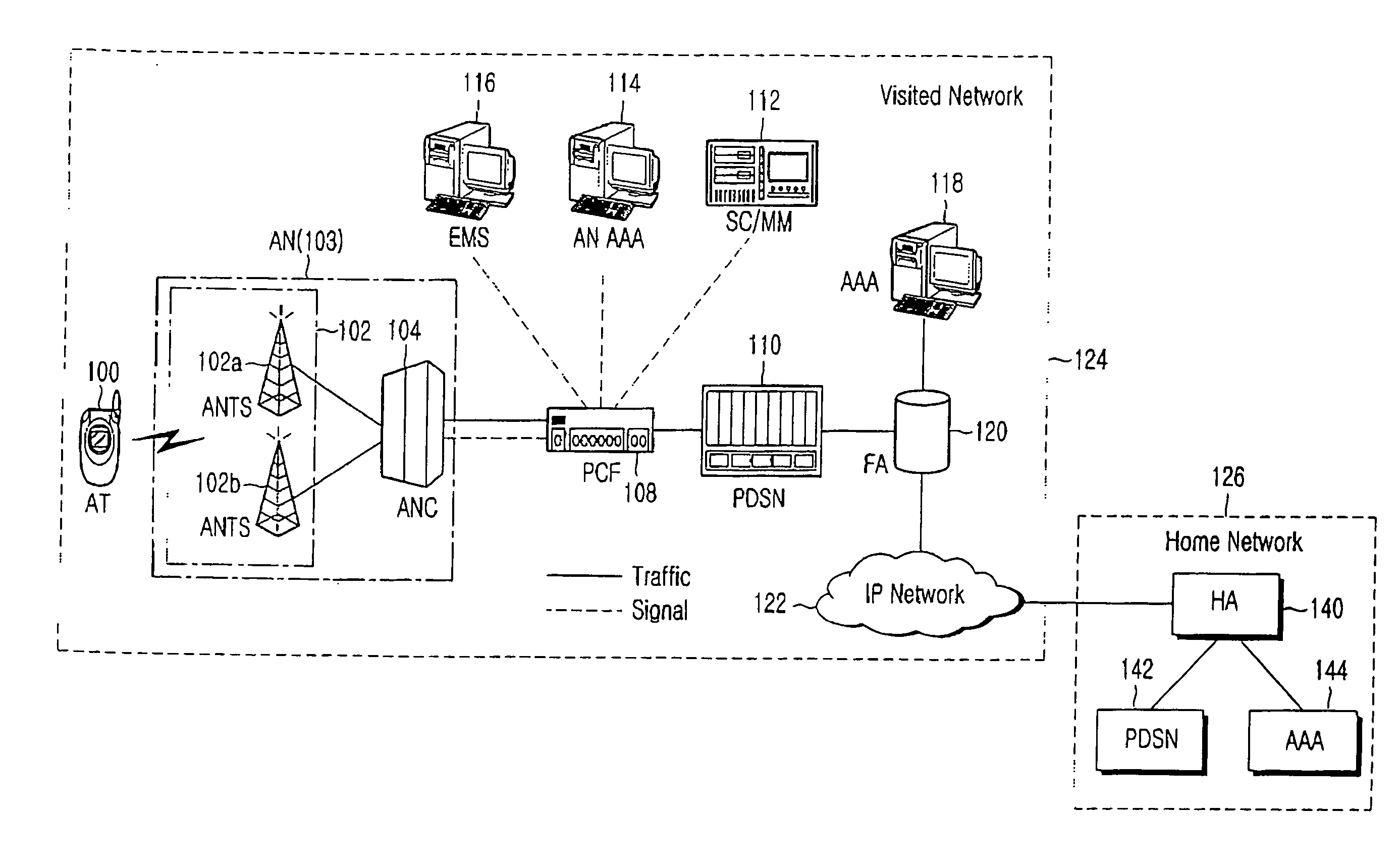
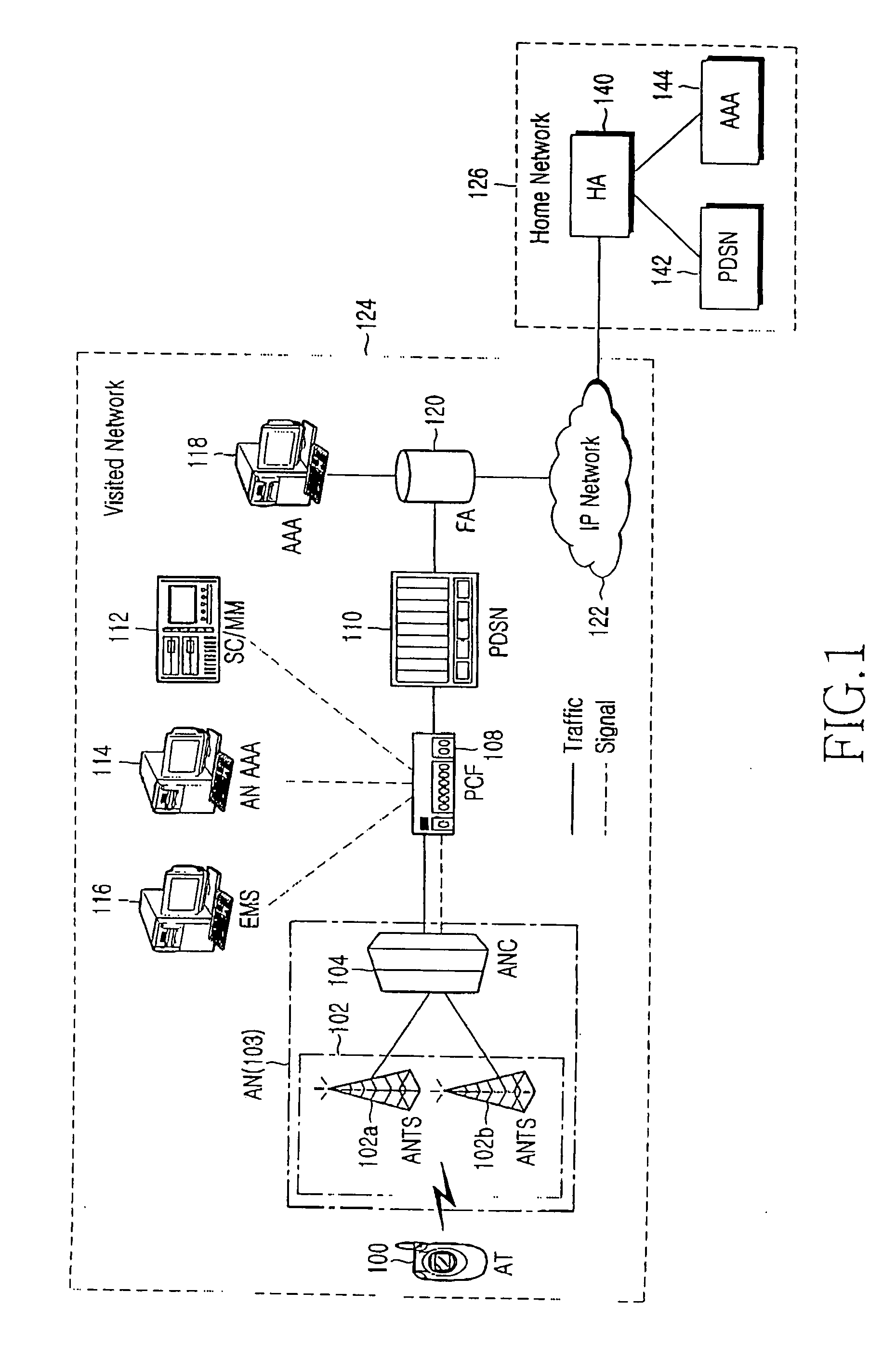
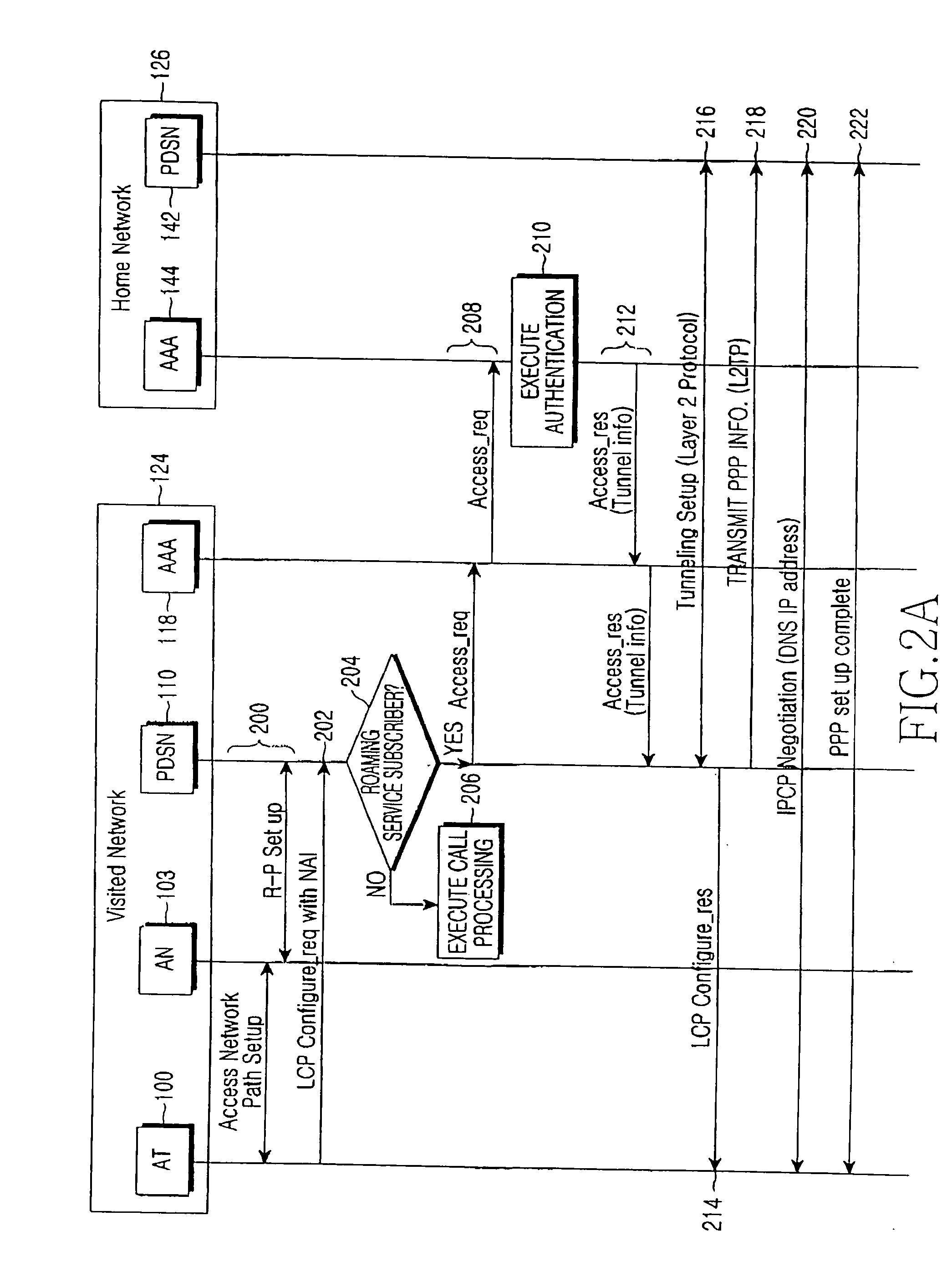
Method and system for providing roaming service in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20070025298A1Accounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket data serving nodeTelecommunications
A method and system for a roaming service in a mobile communication system are provided. The system includes an access terminal for transmitting an NAI (network access identifier) to a packet data serving node of the visited network and an AAA (authentication authorization accounting) of the home network, for transmitting subscriber profile information of the access terminal to the visited network. The packet data serving node of the visited network determines whether or not the access terminal subscribes to the roaming service on the basis of the NAI, and, when it is determined that the access terminal subscribes to the roaming service, sends a request for transmitting the subscriber profile information of the access terminal to the AAA of the home network. The packet data serving node of the visited network also provides at least one data service that the home network has provided to the subscriber, using the subscriber profile information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Virtual private network management system
InactiveUS6931016B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationPrivate networkDistributed computing
An apparatus and method of managing a virtual private network having a set of network devices maintains a network device memory set for storing a set of network device identifiers that identifies each of the set of network device. More particularly, a request to join the virtual private network is received from a given network device having a given network device identifier that identifies the given network device. The set of network device identifiers then is retrieved from the network device memory set to identify all network devices in the set of network devices. A notify message then is forwarded to each of the set of network devices, and a join message is forwarded to the given network device. The notify message includes the given network device identifier, while the join message includes the set of network device identifiers. The given network device identifier then is stored in the network device memory set.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
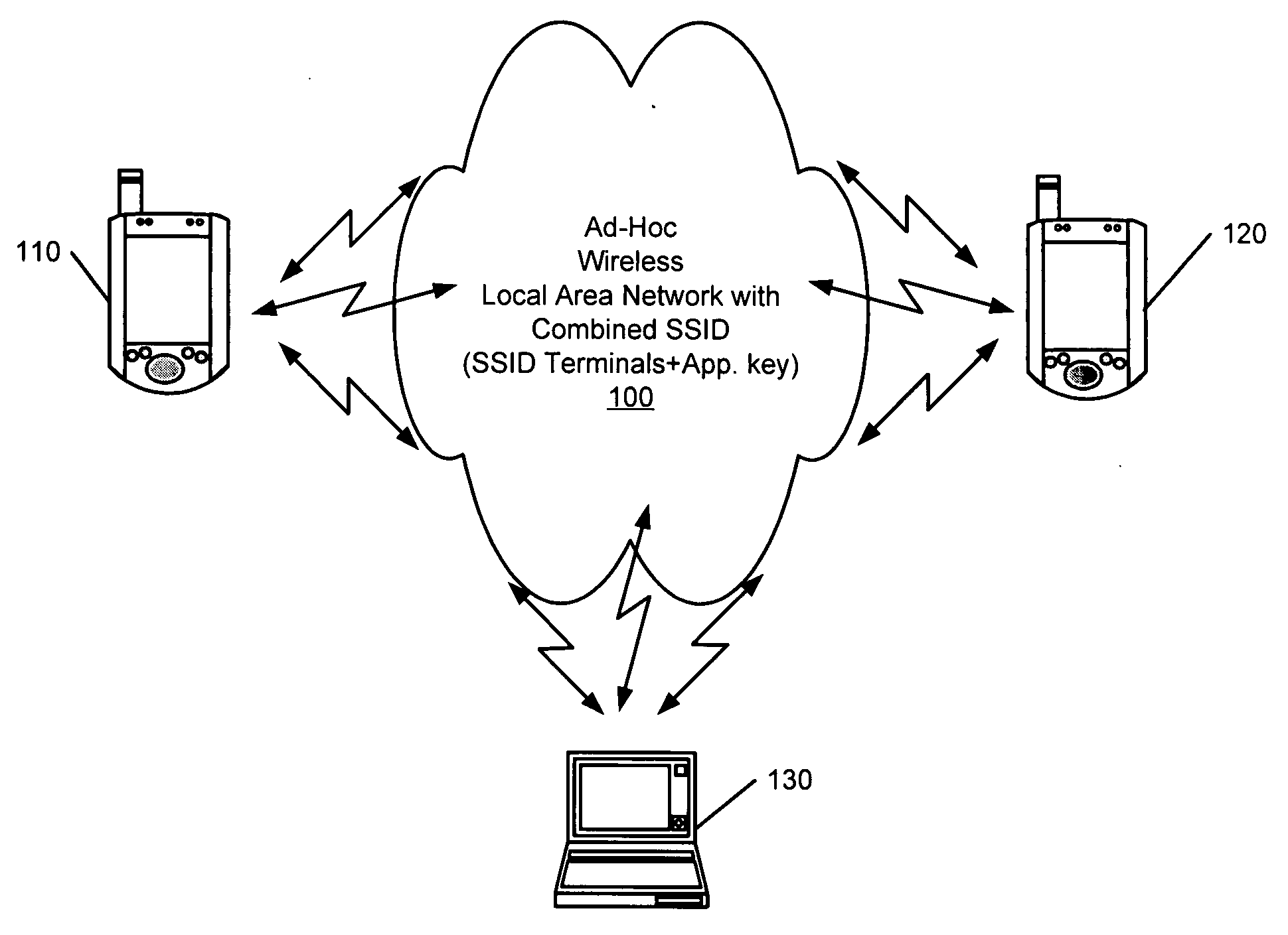
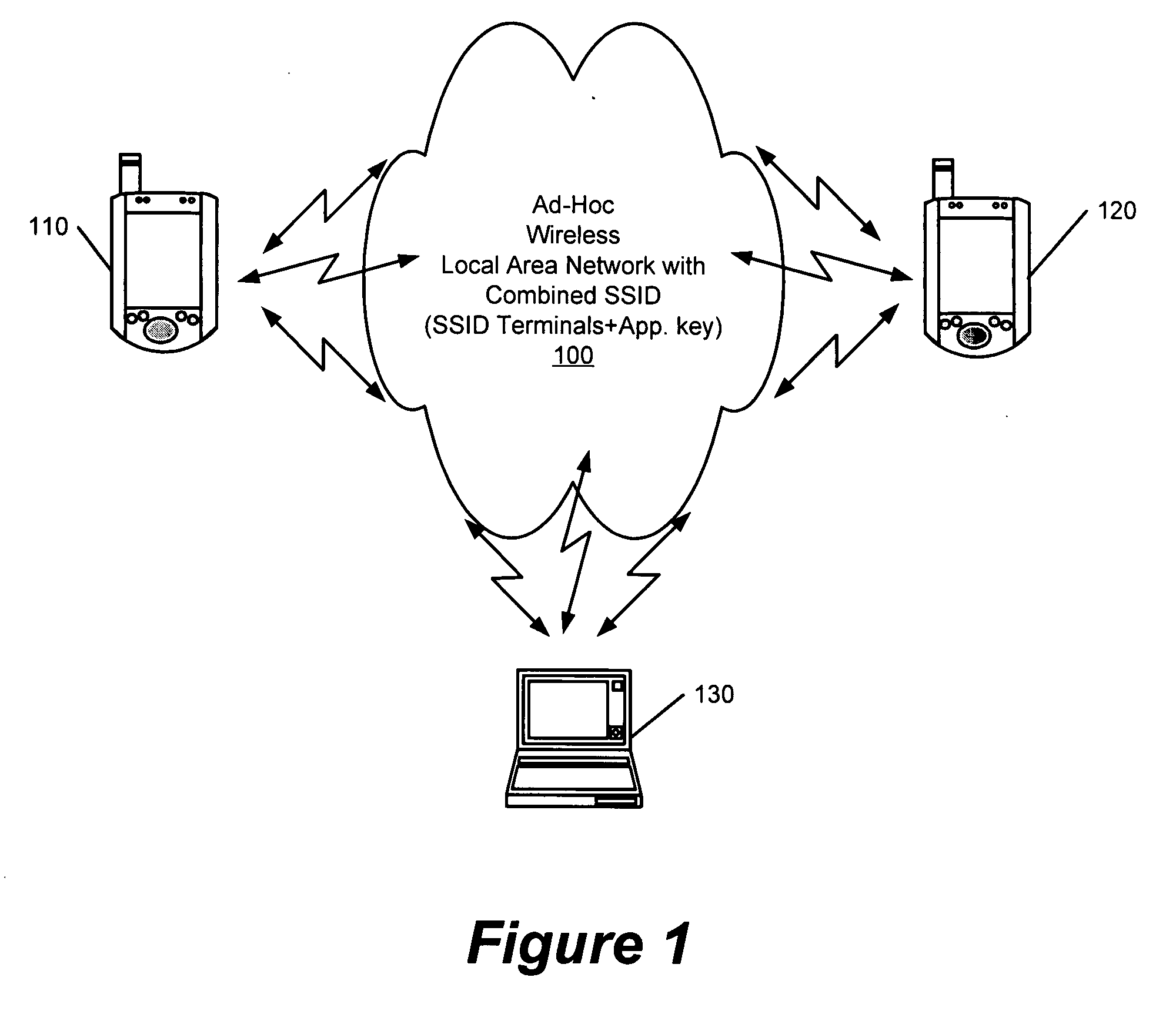
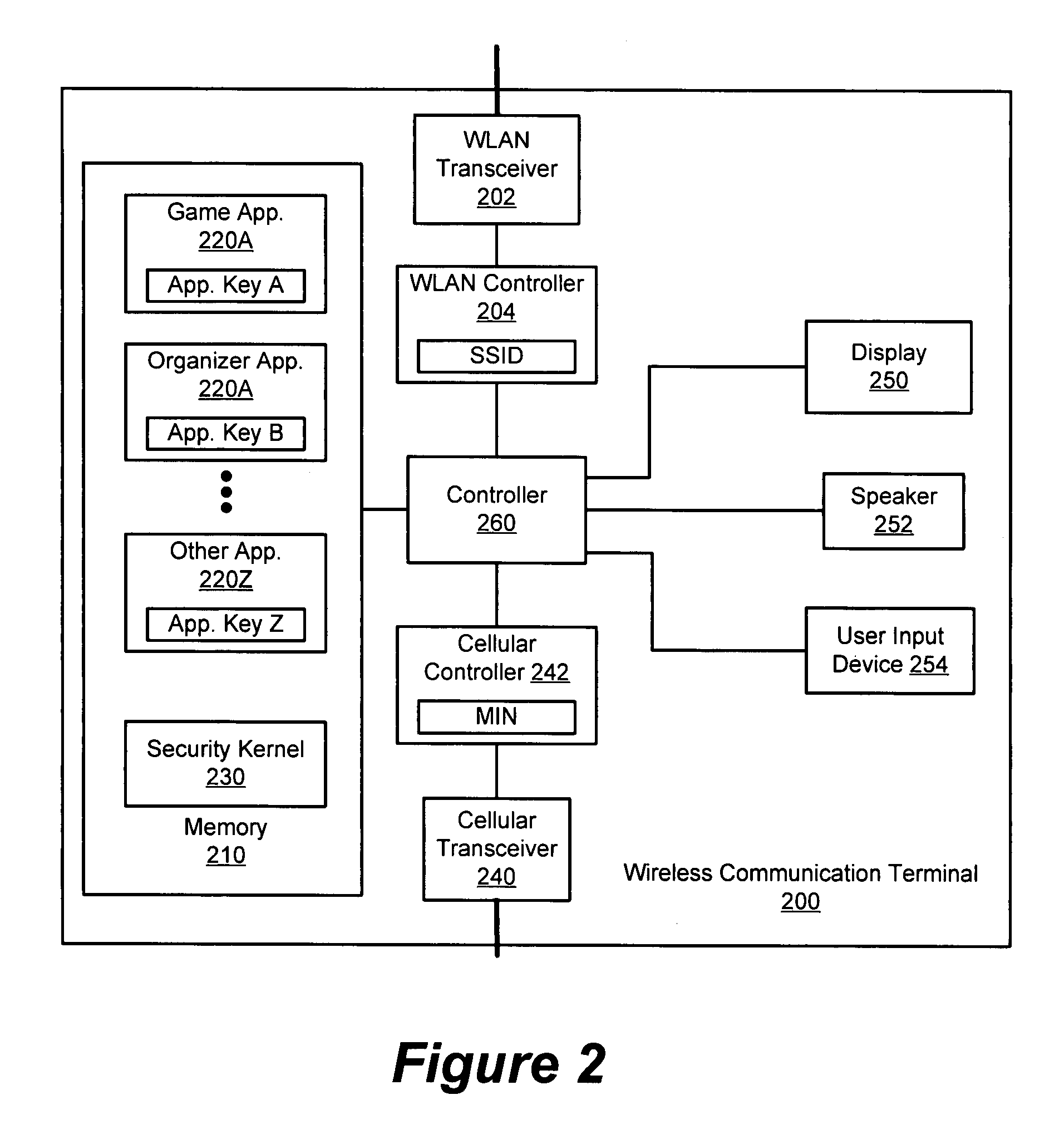
Operating ad-hoc wireless local area networks using network identifiers and application keys
InactiveUS20080298375A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsNetwork Access Identifier
Methods wireless communication terminals are disclosed that operate an ad-hoc wireless local area network. A network identifier and an application key are maintained within a first wireless communication terminal. The application key is defined for at least one application program hosted on the first wireless communication terminal. An ad-hoc wireless local area network is established between the first wireless communication terminal and a second wireless communication terminal using the network identifier and the application key.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Method of controlling network access and its system
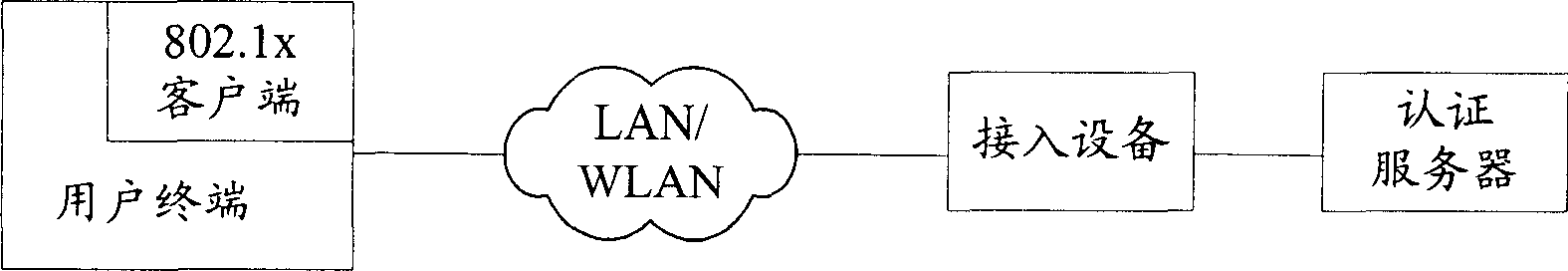
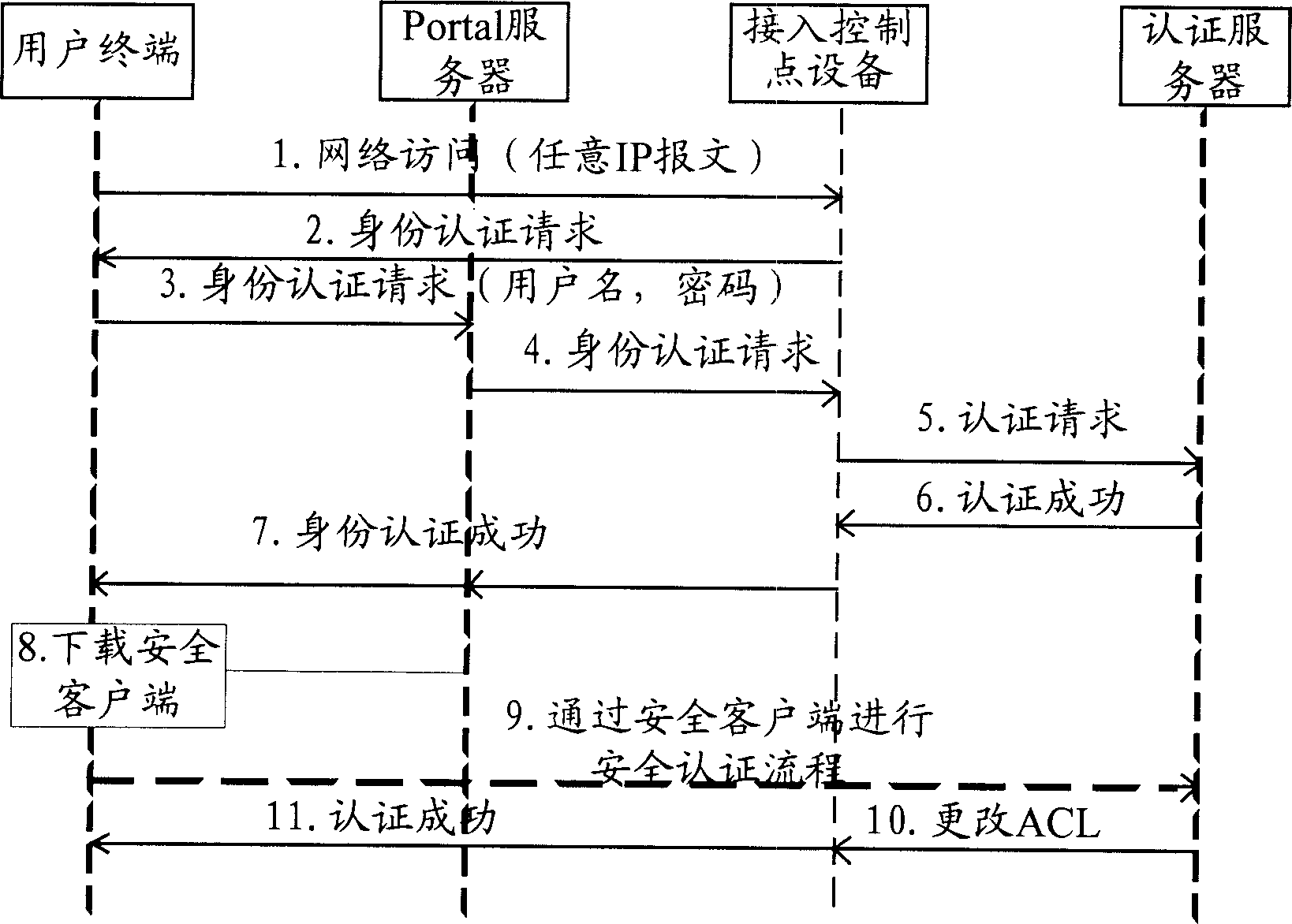
ActiveCN1753364AEasy to useNot threatenedData taking preventionUser identity/authority verificationSystem maintenanceClient-side
This invention discloses a network access control method and a system including: limiting the access extent of authority to users on-line by the web certification of a portal server to limit it to access the limited network resources only, a user downloads the safety UE by the Web, when the user accesses the protected network resources, the safety UE is used to certificate the safety of the UE and users passing through the safety certification access the protected network resources freely. The system includes: network access devices connected by network, a portal server and an AAA server.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
NAI based AAA extensions for mobile IPv6
InactiveUS20050190734A1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsPacket communicationSecurity association
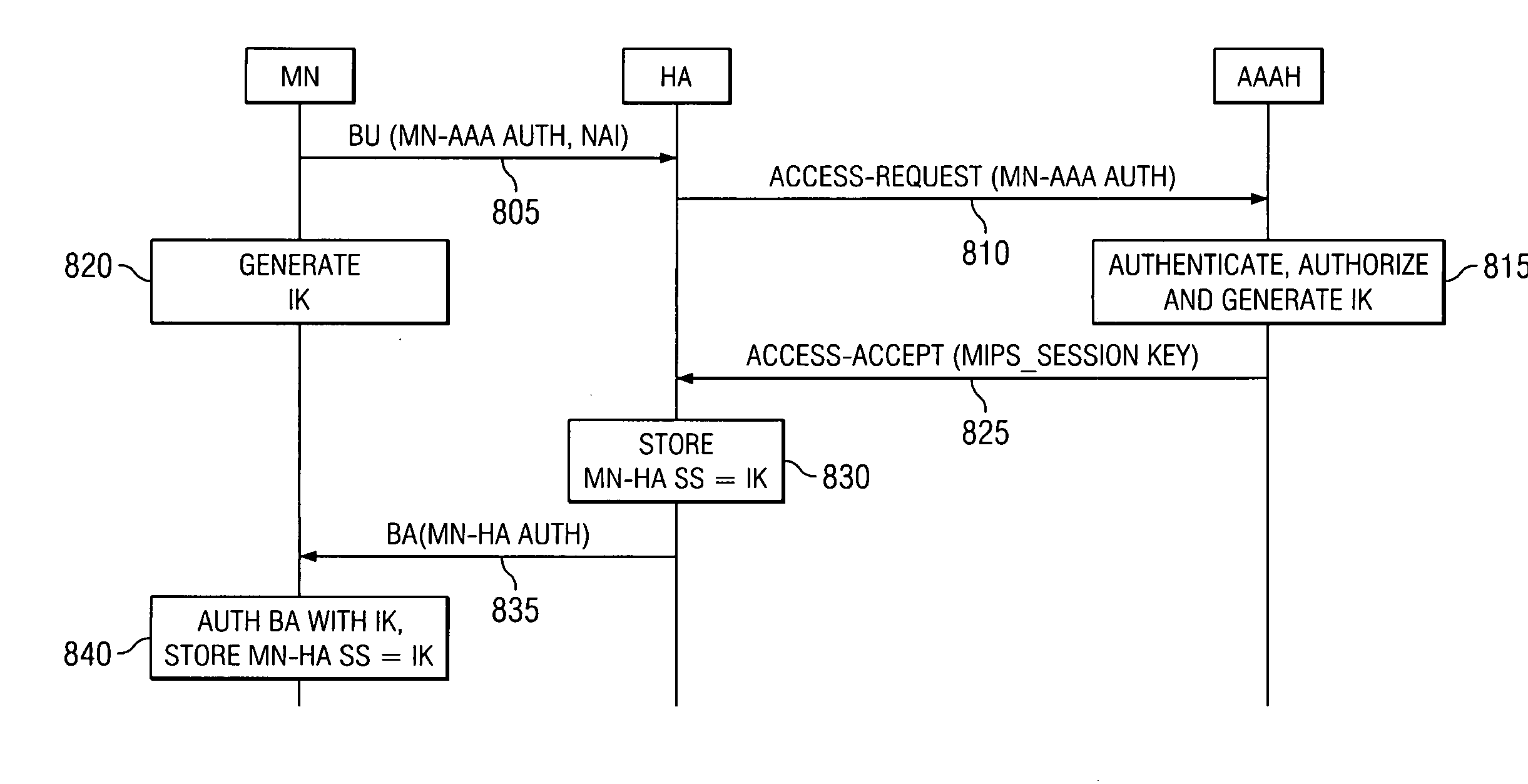
The present invention supports a protocol for a mobile node to specifically designate a home agent and Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) server to use in a communication session. By specifying the AAA server, a specific security association can be selected to support secure information packet transmission between a specified home agent and a mobile node. The specific home agent and AAA server are designated using a network access identifier extension on a binding update message, and the security association data is transmitted back to the mobile node using an extension to the binding acknowledgment message. The mobile node and the home agent then use the security association generated by the AAA server to support information packet communication between the mobile node and the home agent.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
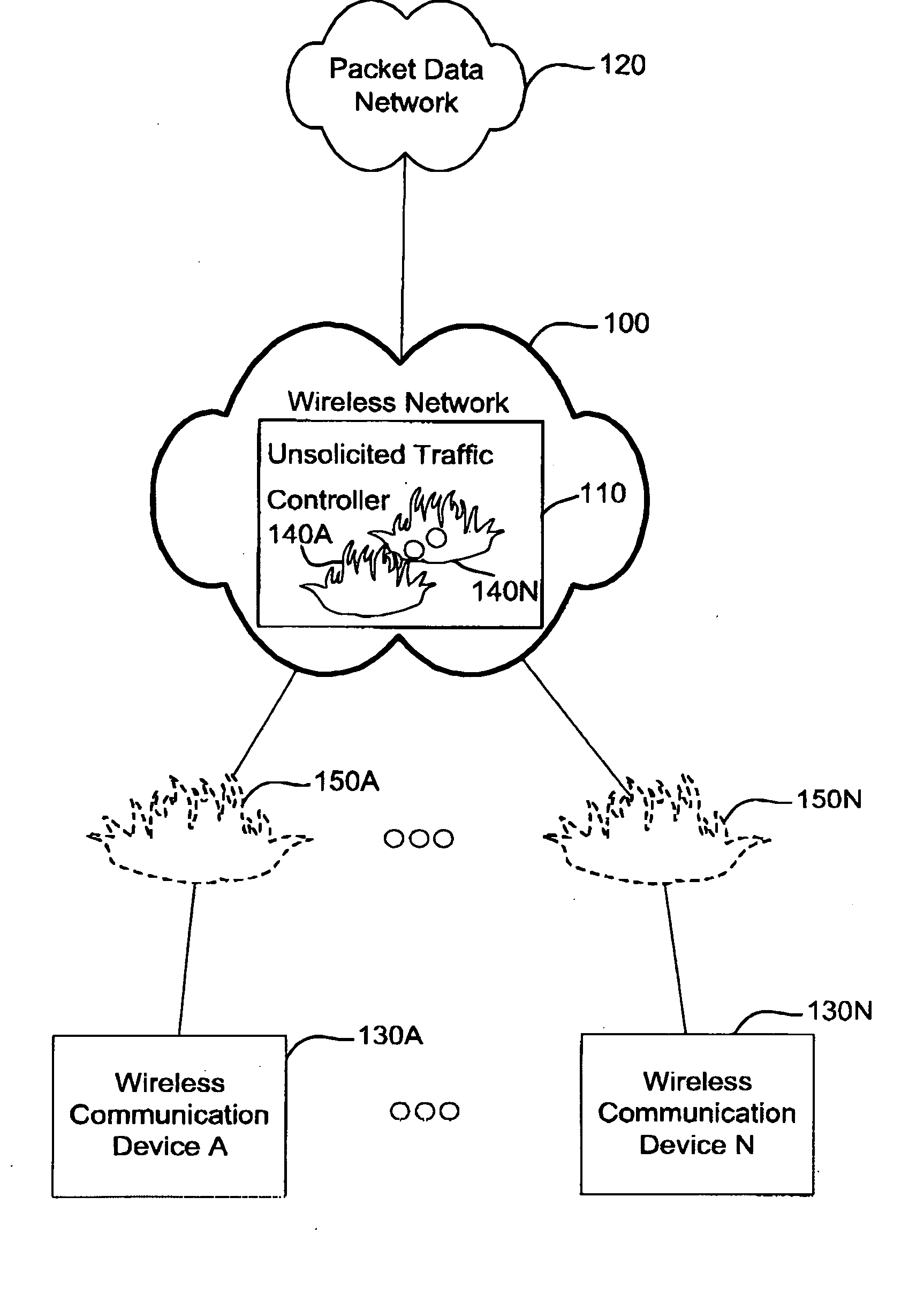
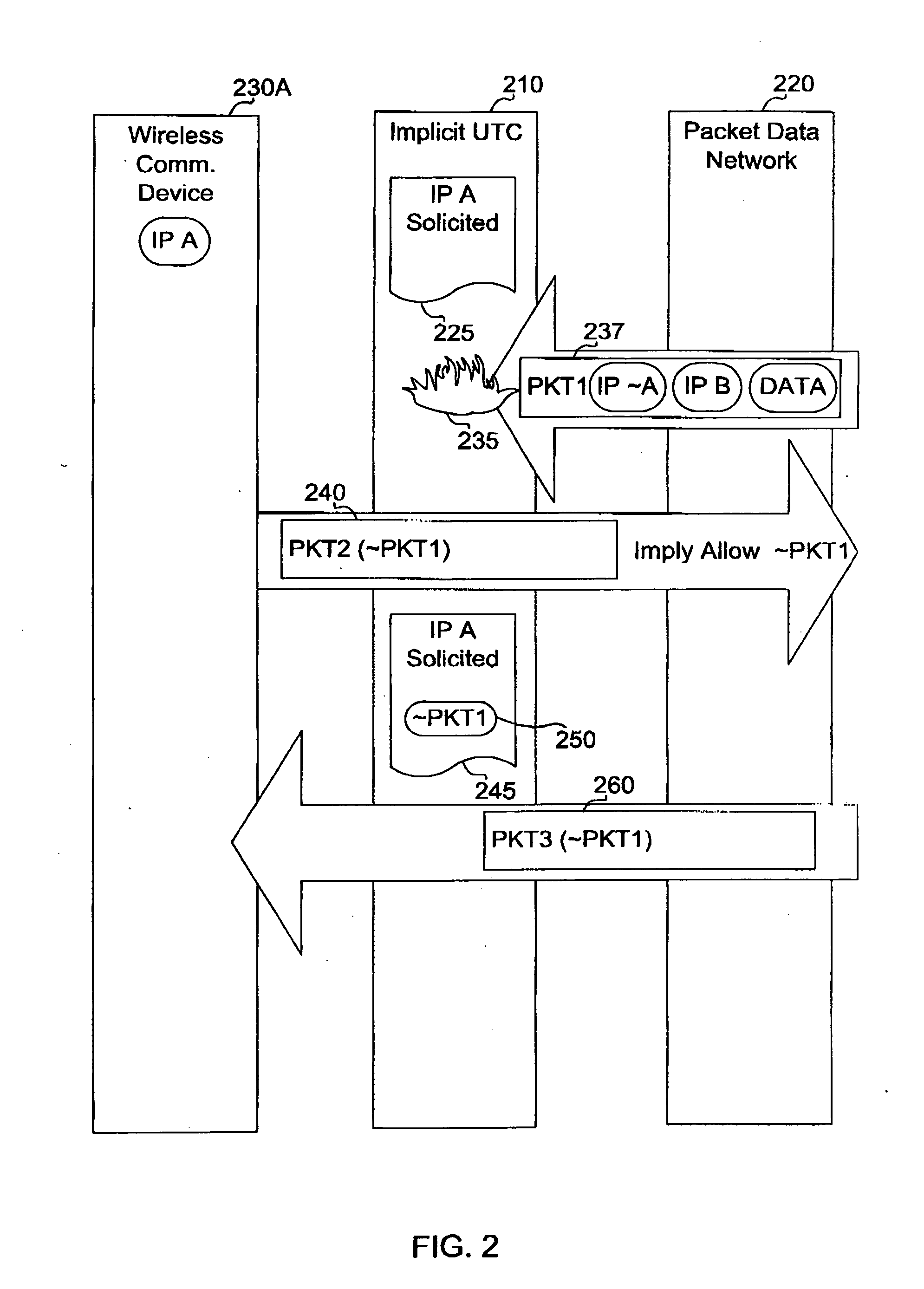
Apparatus and method of controlling unsolicited traffic destined to a wireless communication device
ActiveUS20050122930A1Network traffic/resource managementData taking preventionSession Initiation ProtocolIp address
An apparatus and method of controlling unsolicited traffic are disclosed herein. The apparatus and method can be applied to wireless communication networks such as CDMA2000, UMTS, GPRS and the like so that traffic which is not solicited by wireless communication devices operating on those networks is not sent over the air needlessly. The present application provides techniques to block unsolicited traffic based on the identity of a user (for example based on International Mobile Station Identity (IMSI), Network Access Identifier (NAI), Mobile Station Internet Services Digital Network Number (MSISDN), Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Universal Resource Locator (url)) as opposed to techniques that are based on a session or IP address, such as a traditional firewall. In accordance to this application, user identity based techniques are applied to block unsolicited traffic whenever a user has established a data session. Further in accordance with this application, user identity based techniques are persisted across changes in IP address and / or session.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
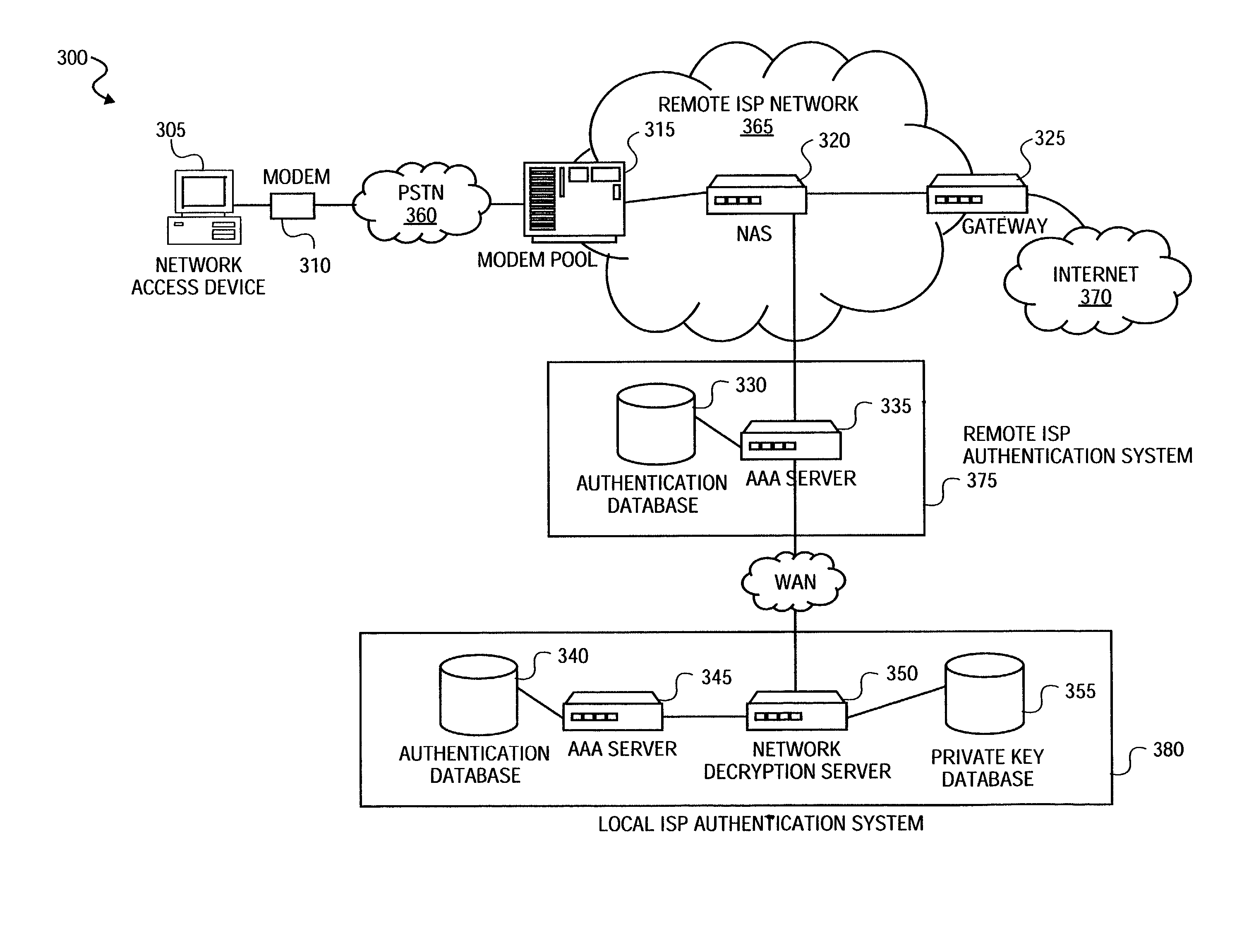
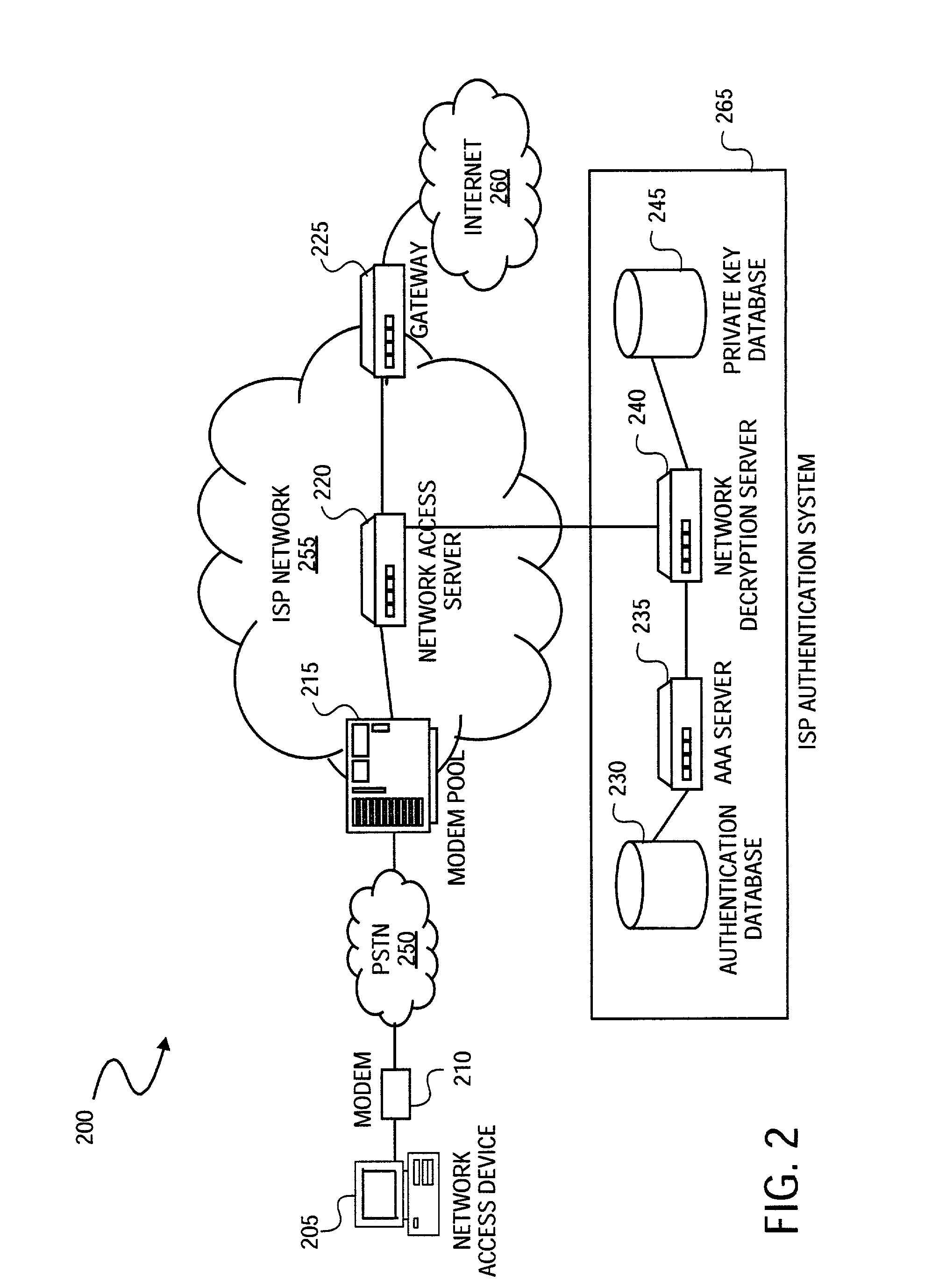
Method and system for securely authenticating network access credentials for users
InactiveUS7921290B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket LayerDirectory Access Protocol
A method is provided to securely authenticate user credentials. The method includes encrypting a user credential with a public key at an access device wherein the public key is part of a public / private key pair suitable for use with an encryption algorithm. The encrypted network user credential is transmitted from the access device to a decryption server where it is decrypted with a private key, the private key being part of the public / private key pair suitable for use with the encryption algorithm. The decrypted user credential is then transmitted from the decryption server to an authentication server for verification. The decryption server typically forms part of a multi-party service access environment including a plurality of access providers, the method including decrypting the user credential of a user proximate an access provider associated with the user credential. The method can be used in legacy protocols such as Point-to-Point protocol (PPP), Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP), Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) protocol, Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) protocol, Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), NT Domain authentication protocol, Unix password authentication protocol, HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP), HyperText Transfer Protocol over Secure sockets layer (HTTPS), Extended Authentication Protocol (EAP), Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, Token Ring protocol and / or Secure Remote Password protocol (SRP).
Owner:CHANNEL IP BV
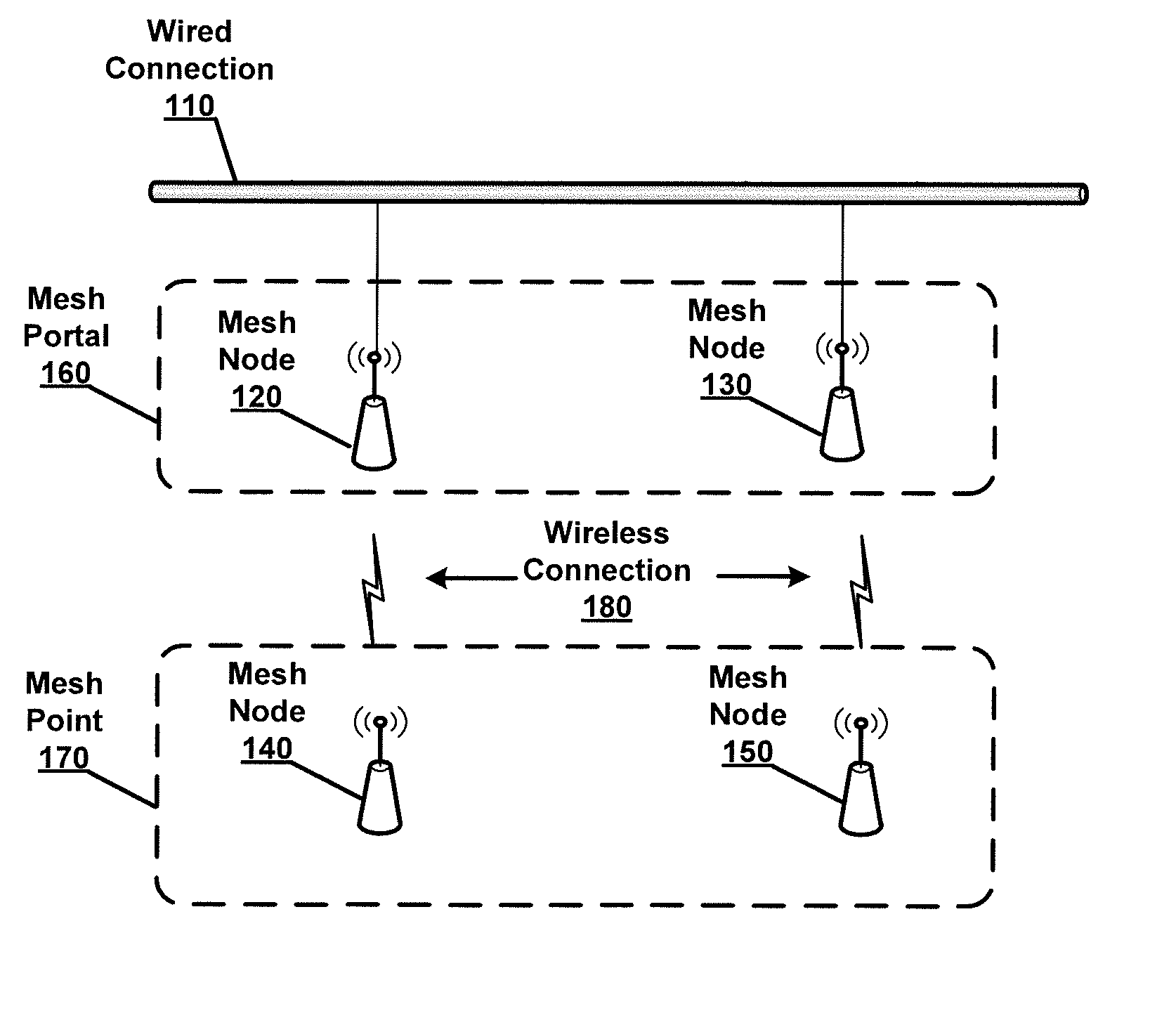
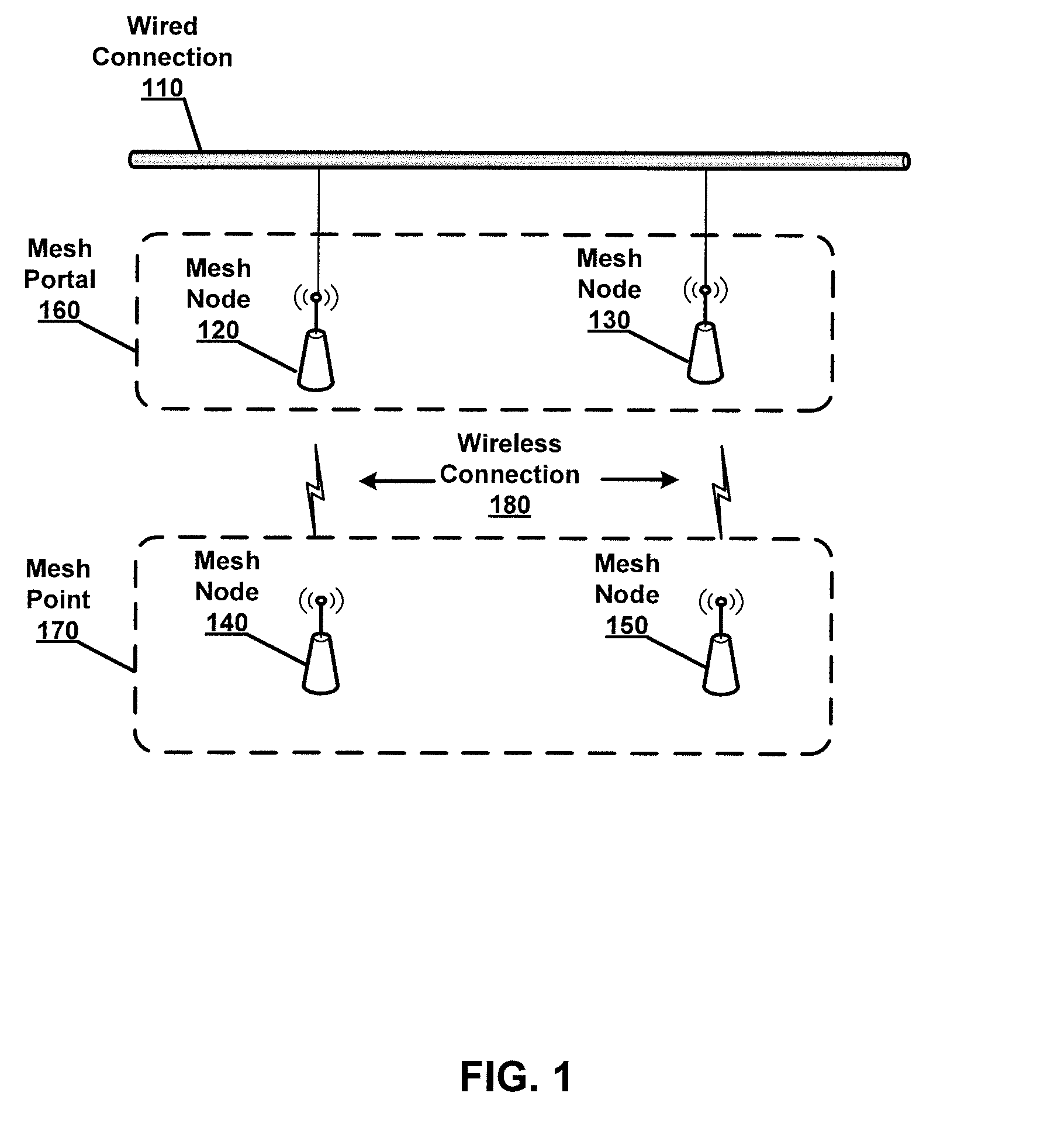
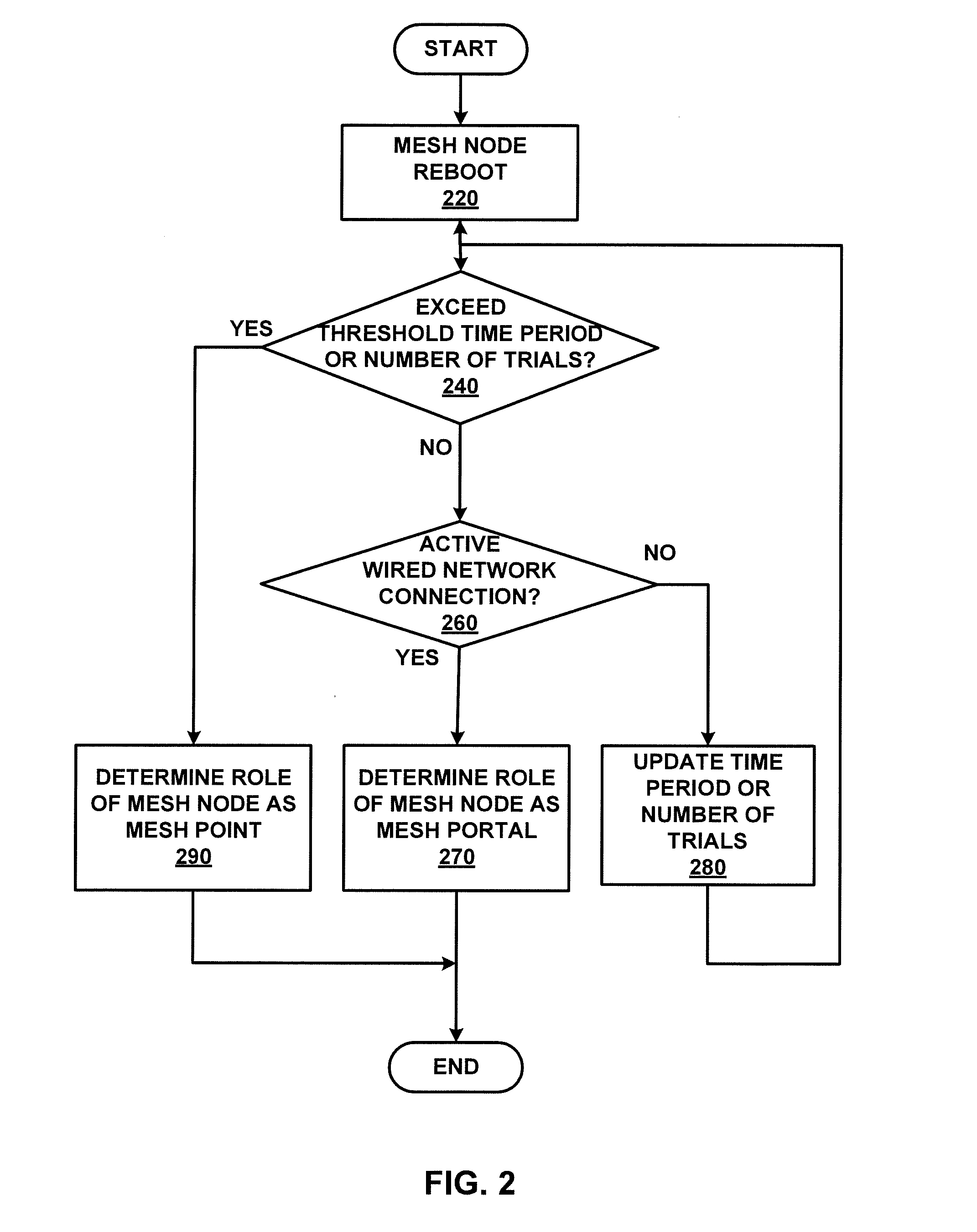
Mesh Node Role Discovery and Automatic Recovery
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for configuring and managing mesh nodes during occasional failure of mesh nodes or addition of new mesh nodes. The disclosed system first determines whether a mesh node is a mesh portal or a mesh point. If it is a mesh portal, the mesh node will advertise its capacity as a mesh portal to other mesh nodes in the network. If it is a mesh point, the mesh node attempts to automatically recover connection to the wireless mesh network if it identifies a unique wireless network based on its associated network identifier. If more than one network identifiers are discovered, the mesh node delays establishing connection to the wireless mesh network until a selection is received.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method for processing network selection information for a user terminal in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20060212700A1Assess restrictionUser identity/authority verificationAccess networkWireless lan
The present invention discloses a method for processing network selection information for a user terminal in wireless local area network (WLAN). When a WLAN user terminal accesses a wireless communications network via a WLAN access network (WLAN AN), the WLAN user terminal sends to the WLAN AN an authentication signal carrying network selection information. This network selection information of the user terminal may be placed in a user identity field defined in the format of a network access identifier (NAI). This invention enables the user terminal to select an appropriate wireless communication network to access when attempting to access a network via a WLAN connecting a plurality of wireless communication networks.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
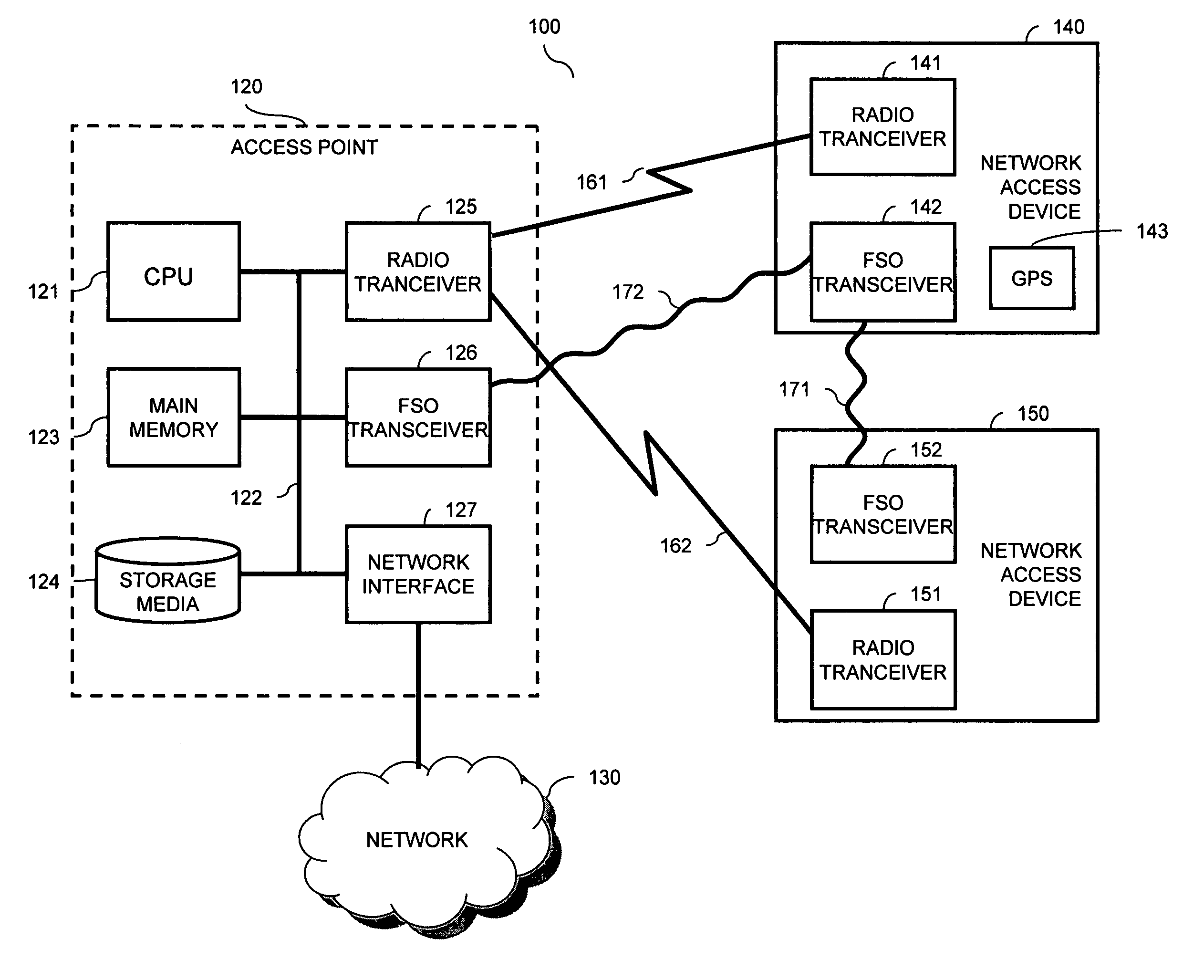
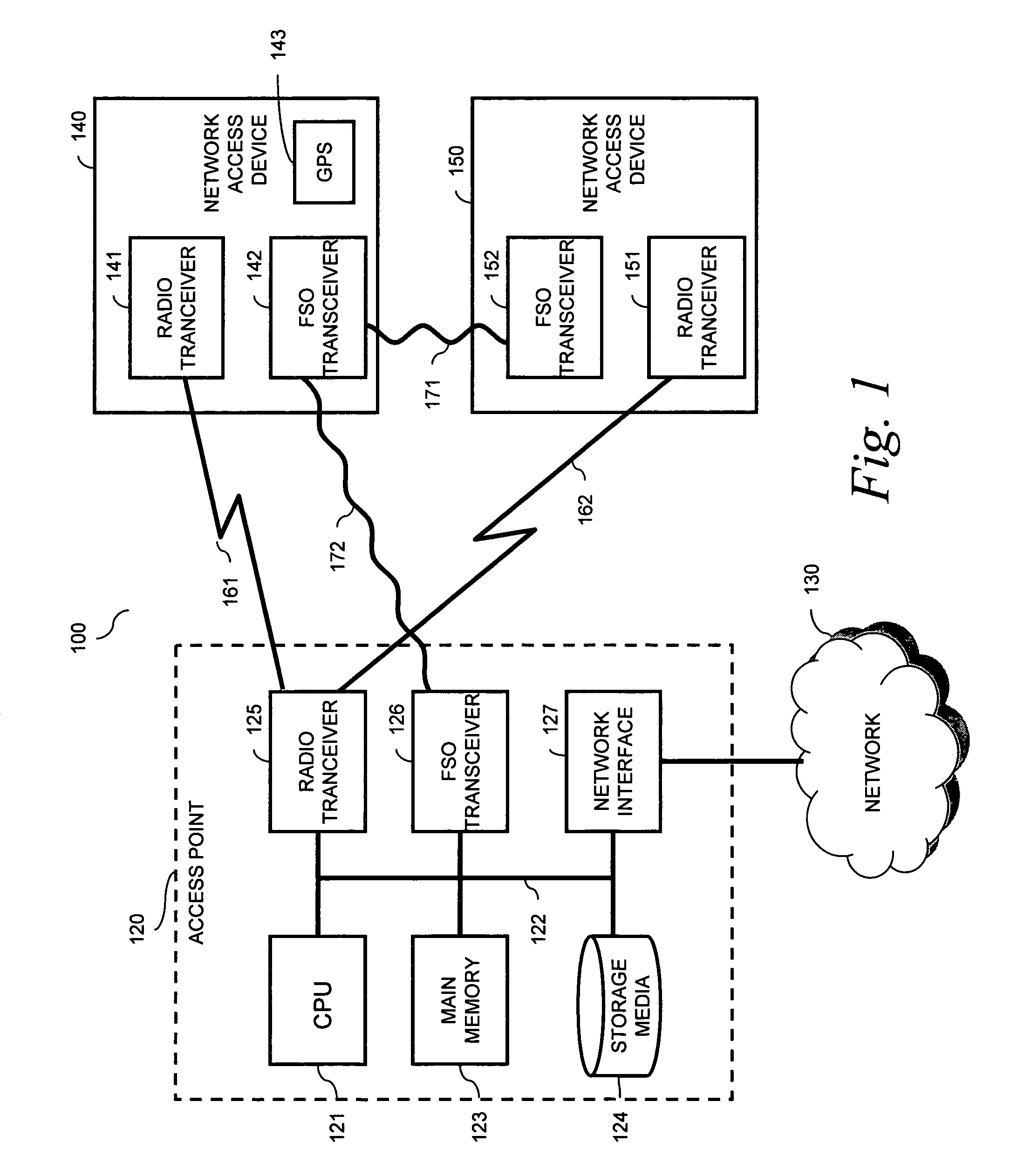
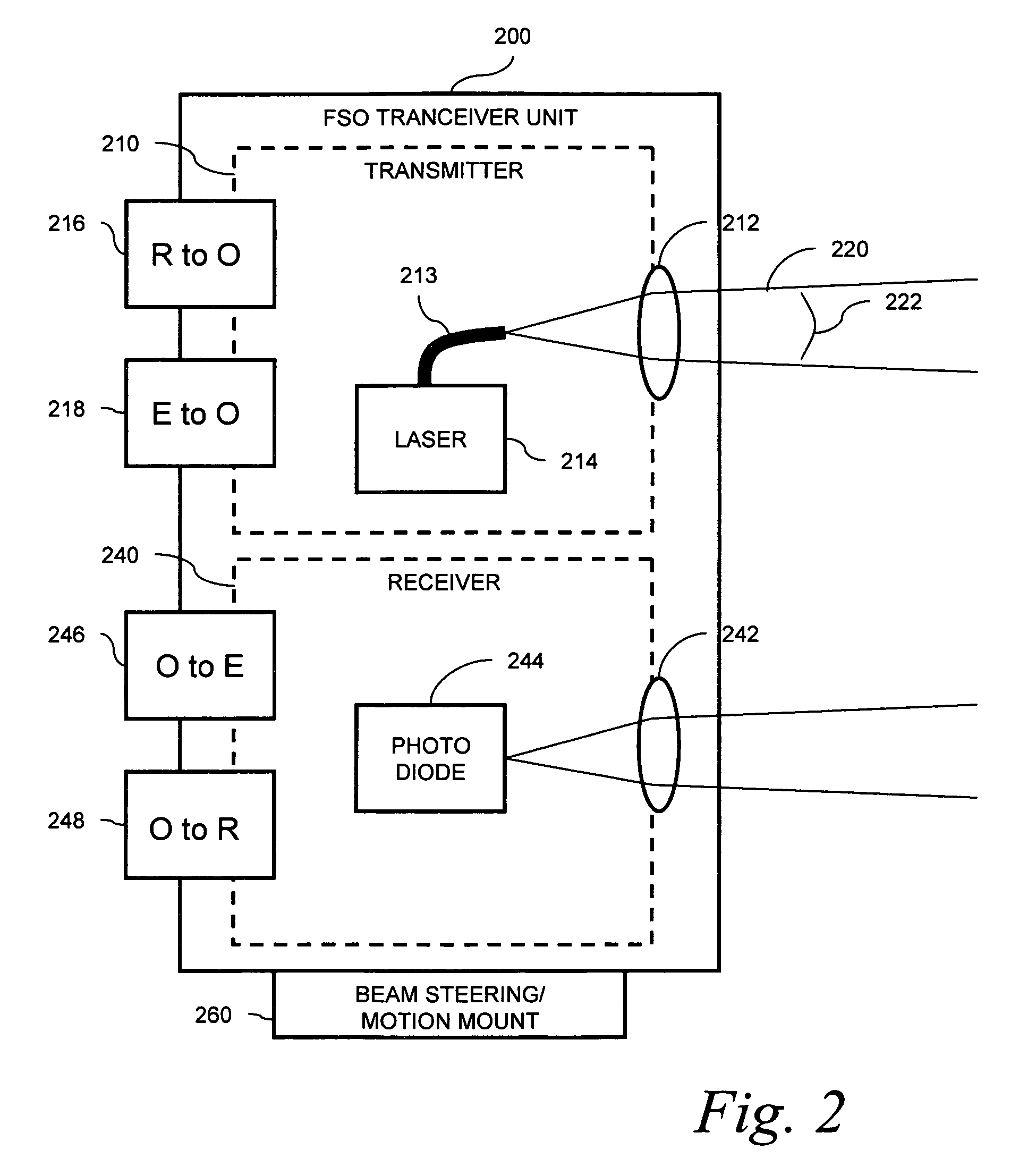
Enterprise cognitive radio integrated with laser communications
A wireless data access system is provided to ameliorate bursty traffic occurring in a radio communications link such as a WiFi, WiMAX, 3G or cellular telephone link to a wireless network access device. A data traffic event is detected relating to traffic in the link. The traffic event may be a traffic burst exceeding a predetermined threshold. Based on detecting the data traffic event, a free-space optical communications link is established to the network access device to handle the traffic burst. The established radio link may be used to set-up and coordinate the free-space optical link.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Virtual loop carrier system with cobra interface for gateway control
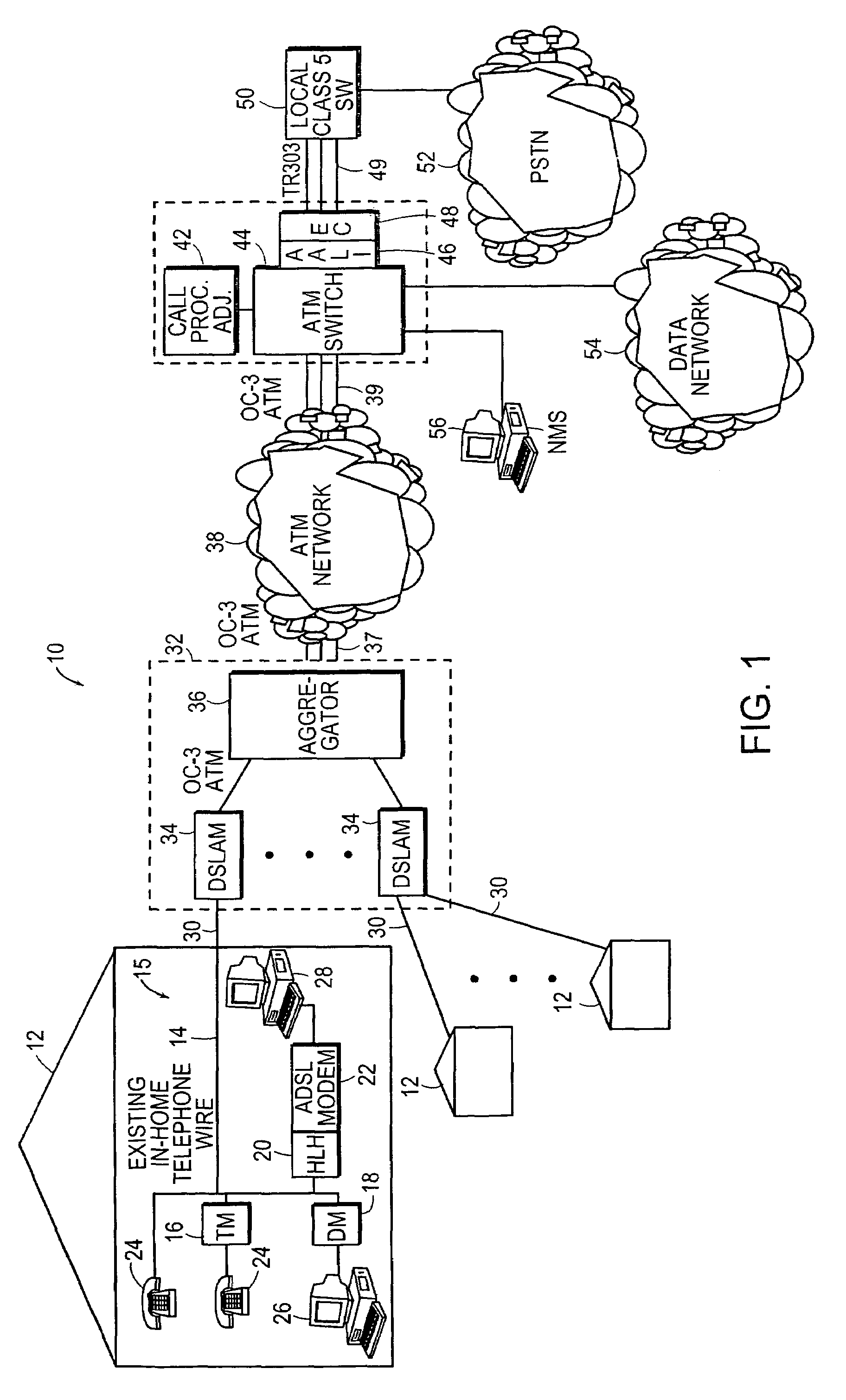
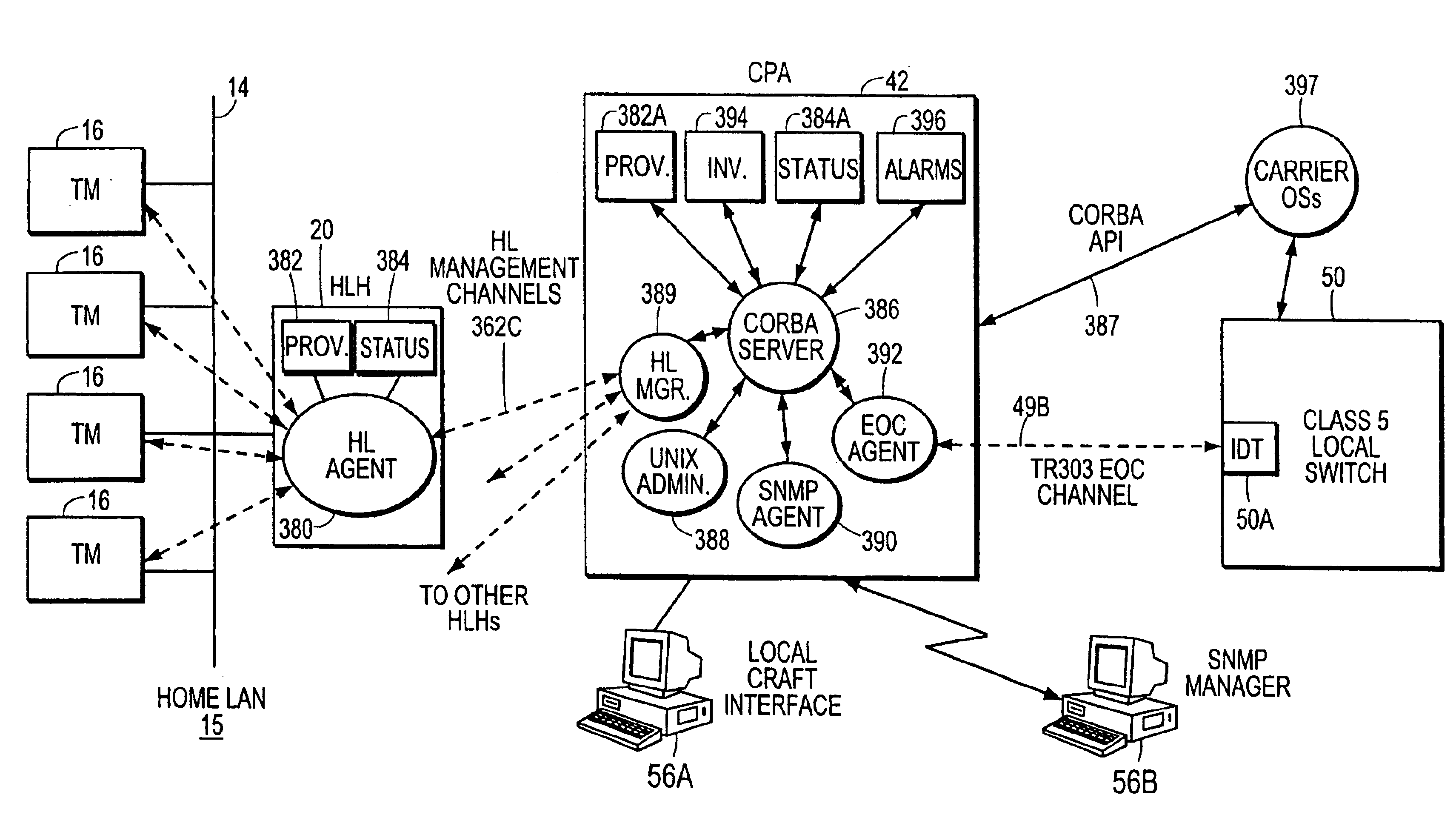
InactiveUS6915521B1Lower unit costReduction in service turn-up timeMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsCarrier signalCarrier system
A loop carrier system includes a home local area network having plural telephone modules and a hub coupled to in-home telephone wiring. The telephone modules and the hub communicate voice signals over the in-home wiring in a dedicated frequency band above baseband POTS. The hub converts between voice signals and voice packets and is connected to a network access device for transferring the voice packets from the home local area network to a telecommunications network which routes the voice packets to a gateway. The gateway converts between the voice packets and a circuit format compatible with a local digital voice switch. A network element includes a Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA)-based server, CORBA-based managed objects accessible by the CORBA-based server and a CORBA-based applications programming interface (API). The CORBA-based API is coupled to an external operations support system which can manage the plural CORBA-based managed objects directly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com