Patents
Literature
380 results about "MSISDN" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MSISDN (pronounced as /'em es ai es di en/ or MISS-den) is a number uniquely identifying a subscription in a Global System for Mobile communications or a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System mobile network. It is the mapping of the telephone number to the subscriber identity module in a mobile or cellular phone. This abbreviation has several interpretations, the most common one being "Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number".
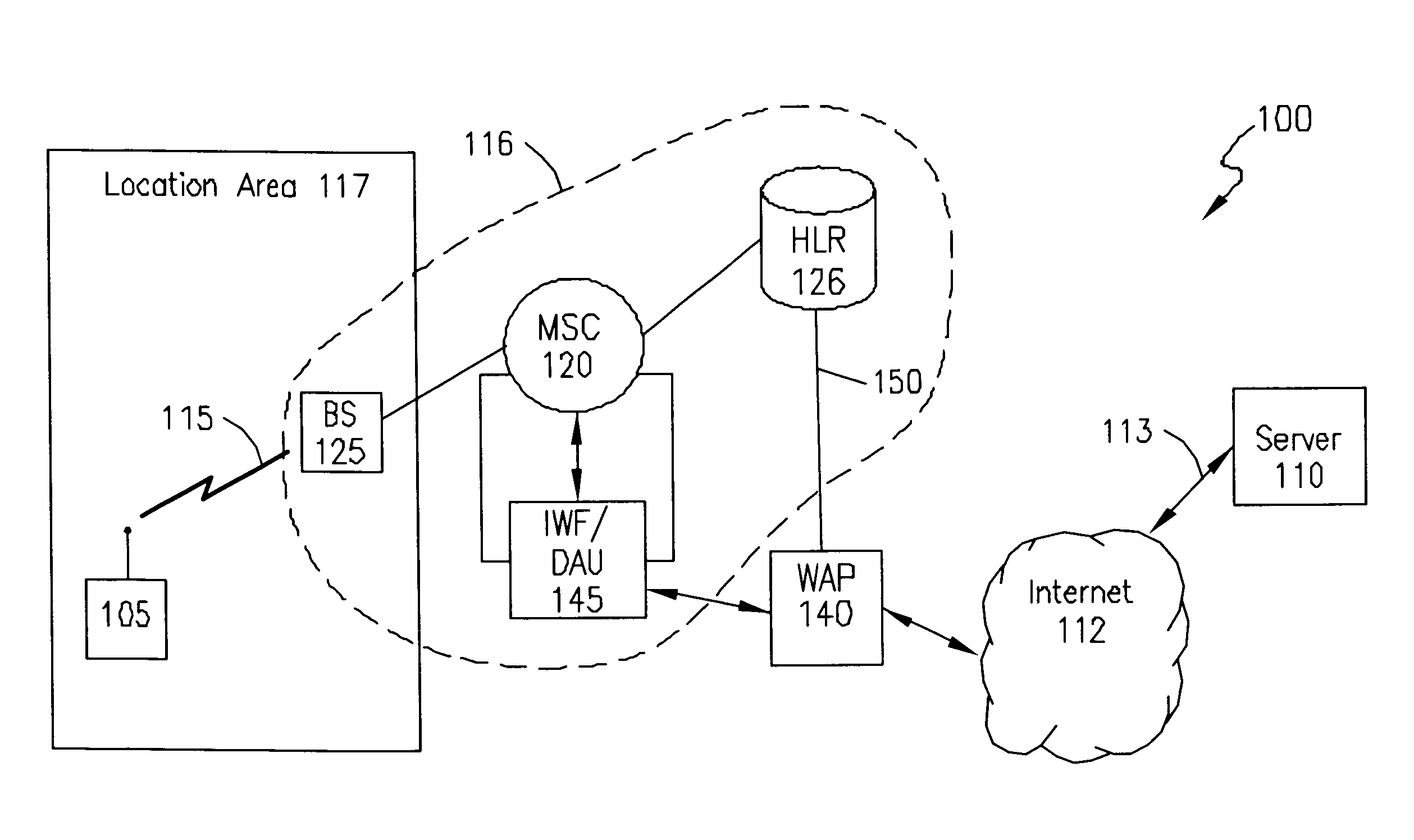
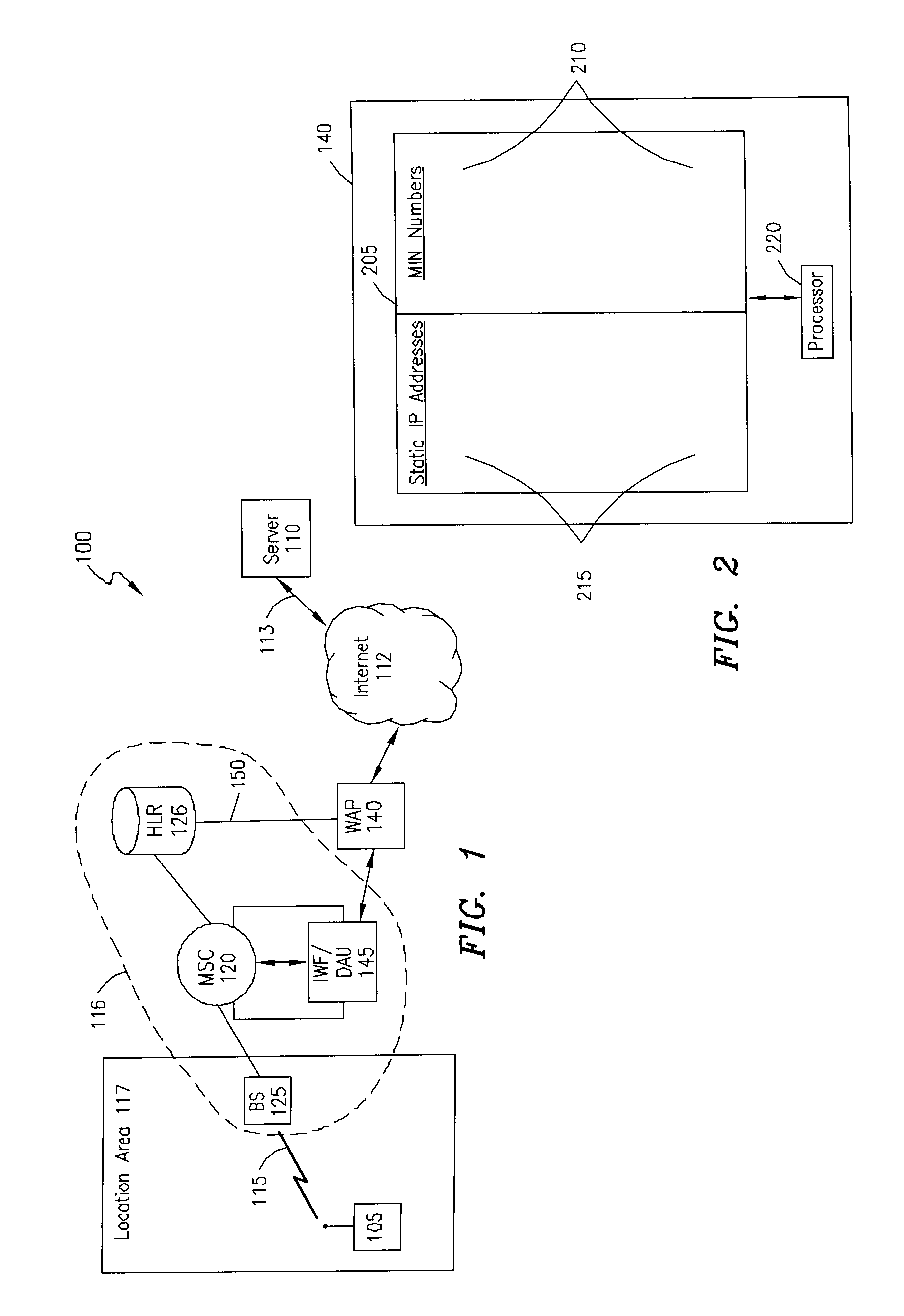
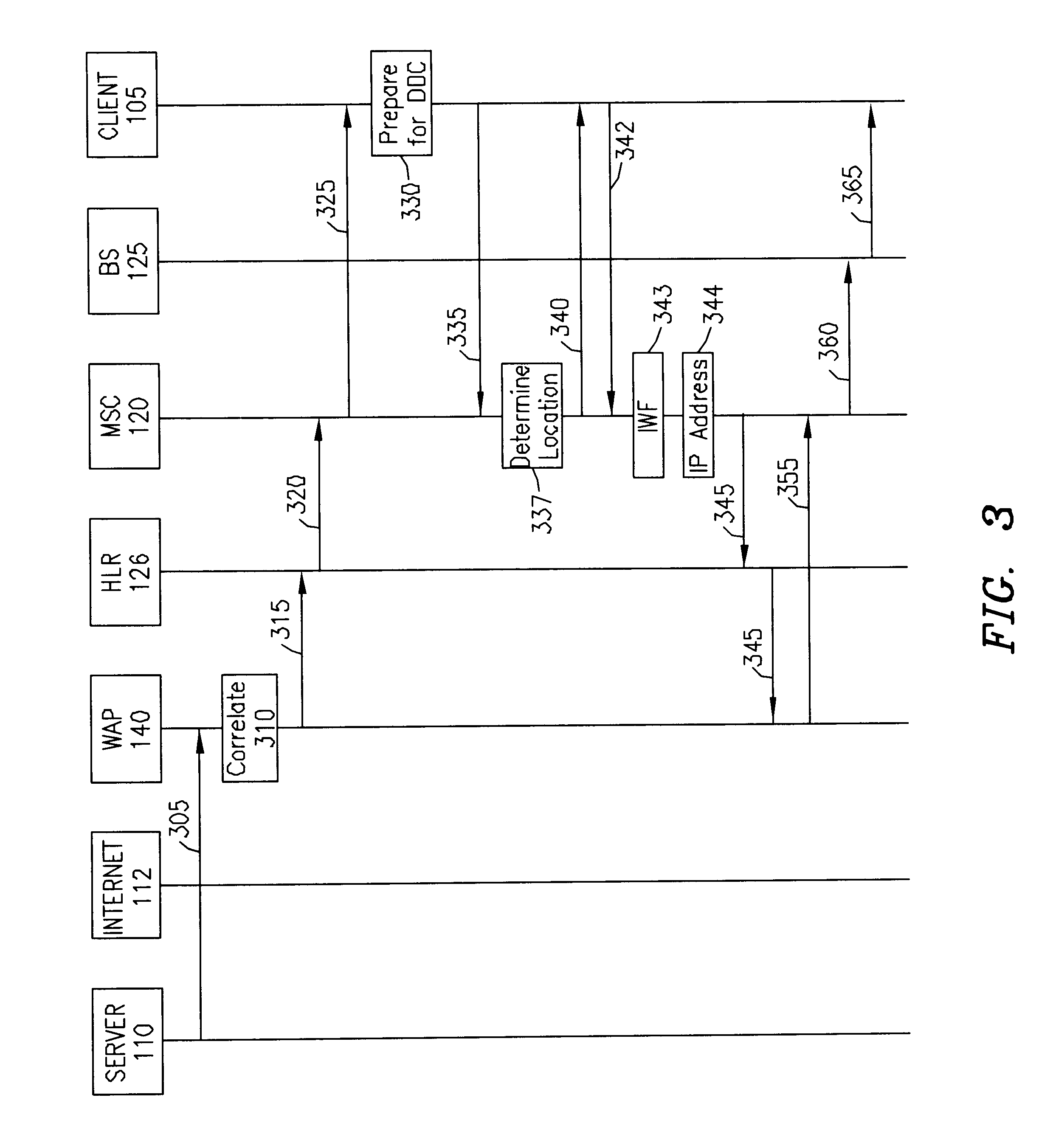
System, method, and apparatus for pushing data in a direct digital call environment
InactiveUS6549776B1Time-division multiplexWireless network protocolsDigital dataMobile identification number
A system, method, and apparatus for transmitting a packet from a server to a wireless client, using direct digital calls, wherein the server initiates the call are presented. The server transmits a packet to addressed to an Internet Protocol (IP) address associated with the wireless client. The packet is received by a wireless application gateway which maintains a table correlating IP addresses with mobile services integrated services digital network (MSISDN) numbers or mobile identification numbers (MIN). The MSISDN / MIN number is then used to request routing information. In response to the request, a dynamic IP address and a traffic channel are allocated to the wireless client. The dynamic IP address is transmitted to the wireless application protocol gateway. Upon receiving the IP address, the wireless application protocol gateway transmits the digital data communication towards the IP address. The digital data communication is received by a serving mobile switching center which causes the digital data communication to be transmitted to the wireless client using the allocated traffic channel.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
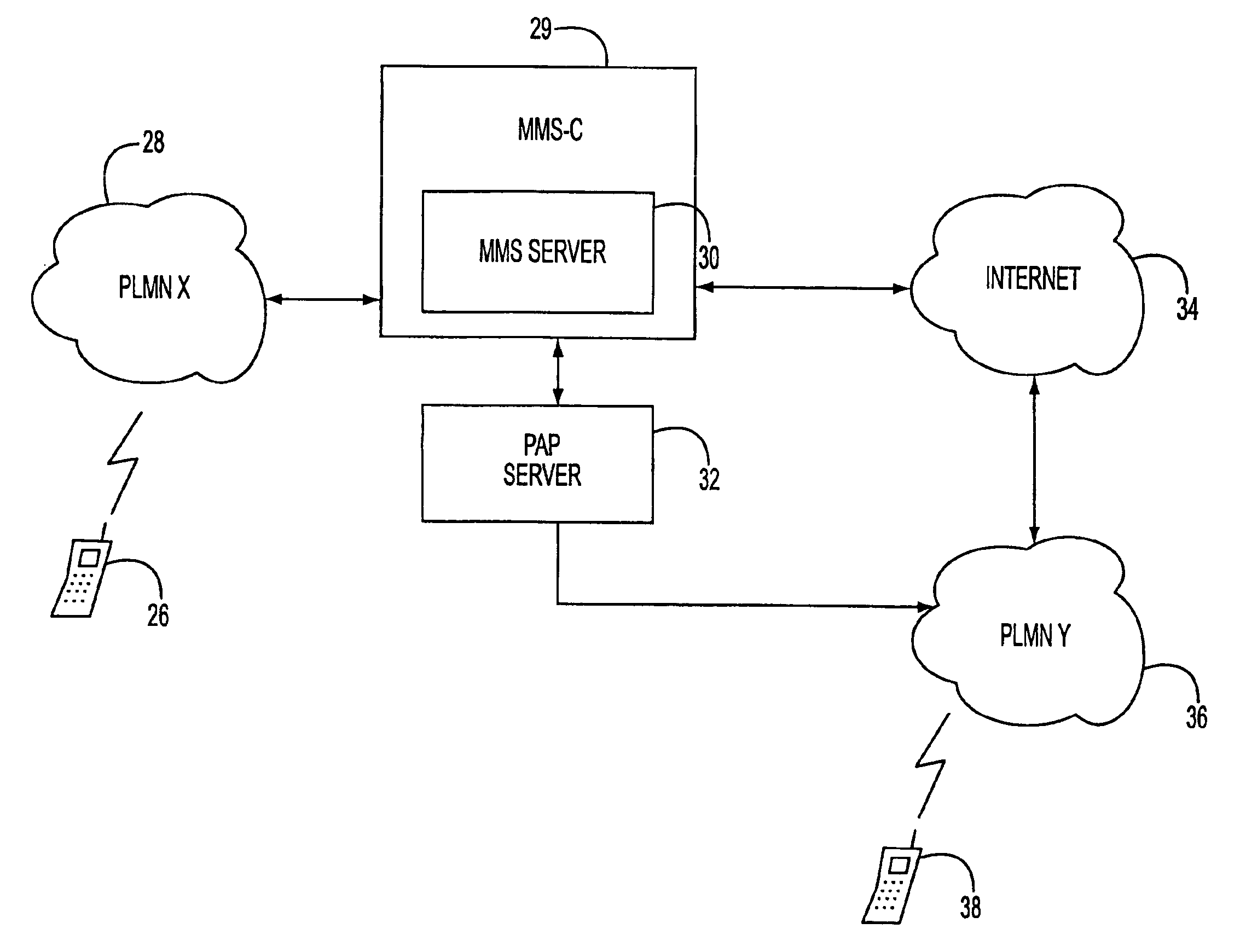
Multimedia messaging service routing system and method
InactiveUS6947738B2Special service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingThe InternetMobile device
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Session continuity for providing content to a remote device
InactiveUS20060069687A1Digital data information retrievalTransmissionMobile identification numberGraphics
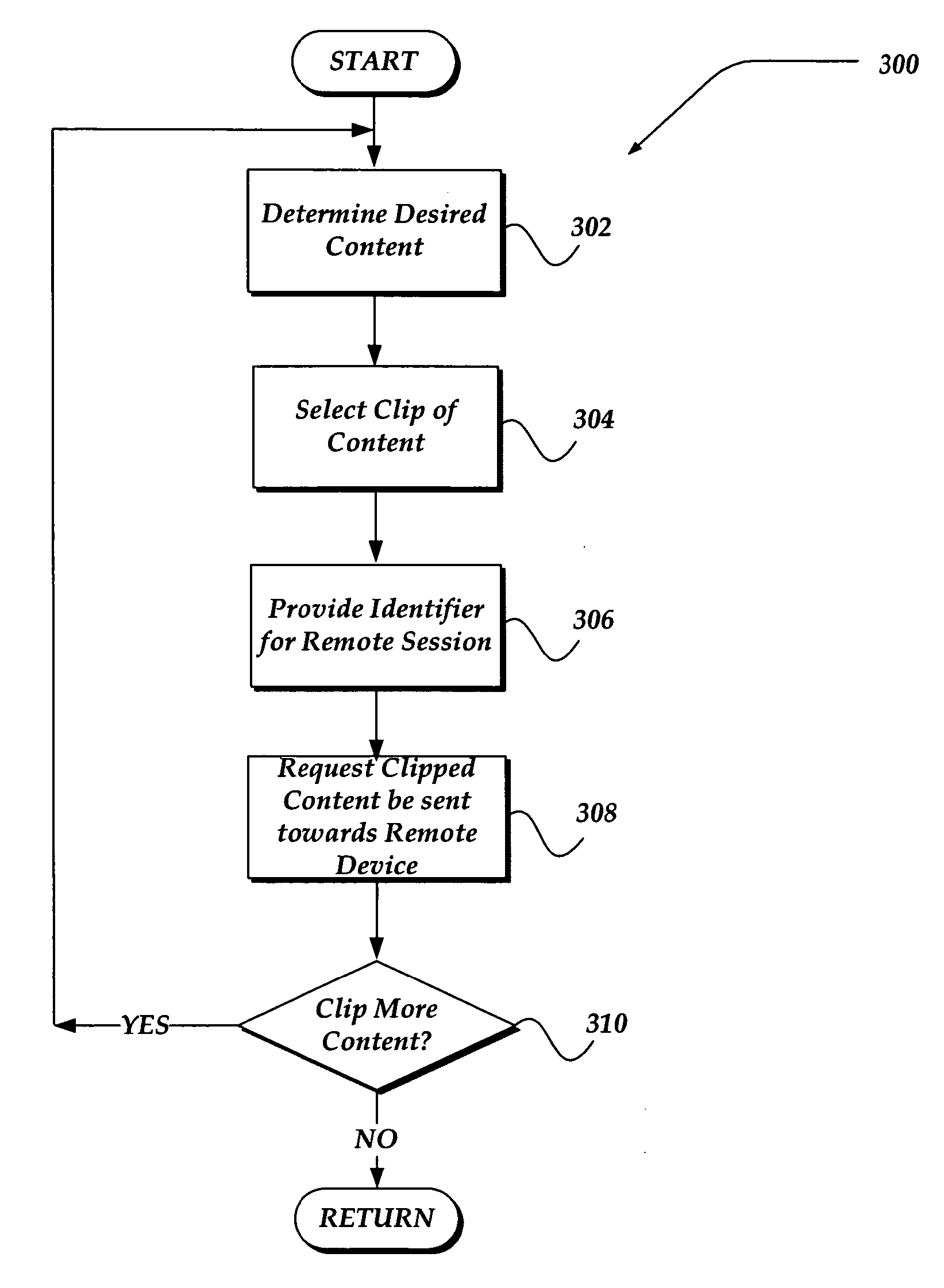
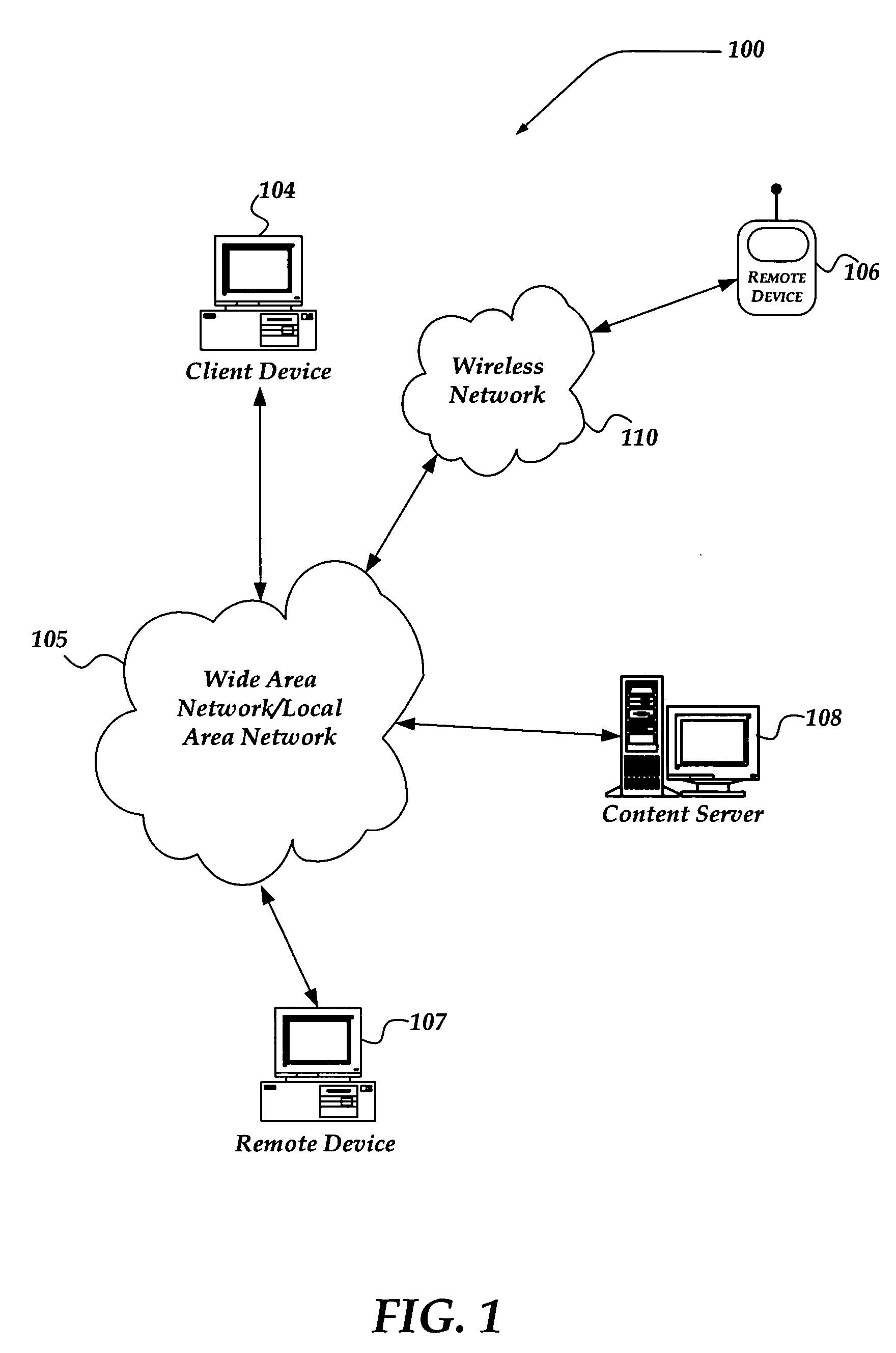
A method and apparatus is directed to provide a clip of content to a remote device, such as a mobile device. The invention enables an end-user to select content from a networked device, such as a personal computer. The selected content may include content from a webpage, graphic images, audio files, and the like. Selecting the content includes entry of an identifier such as a Mobile Identification Number (MIN), and a Mobile Station International ISDN Number (MSISDN). When the end-user employs the remote device to access the content, a server employs the identifier to determine if the remote device is authenticated and authorized to access the content. If it is, then the server provides the content to establish session continuity with the remote device. The content may then be transmitted to the remote device using any of a variety of messaging protocols.
Owner:OATH INC
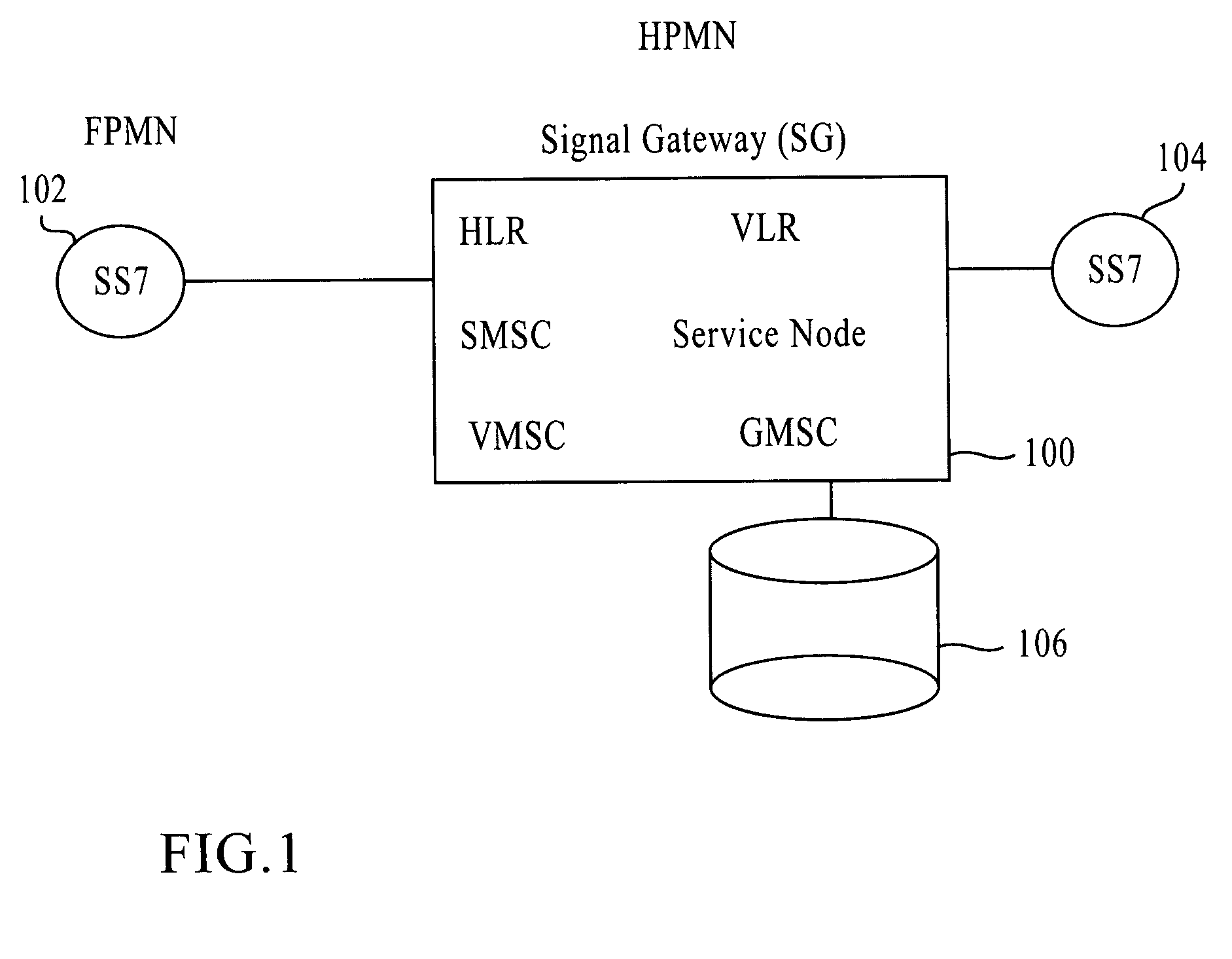
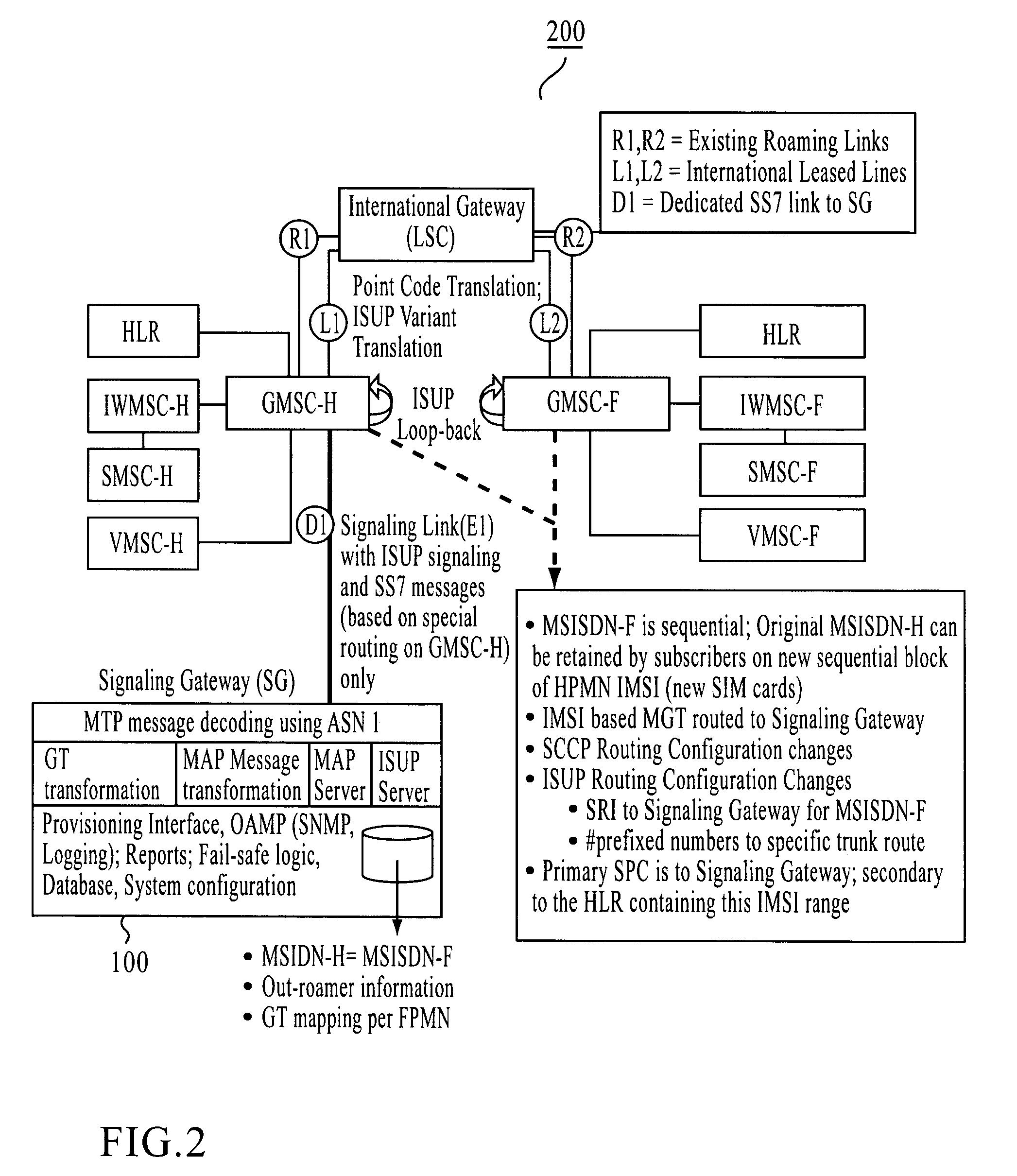
Signaling gateway with multiple IMSI with multiple MSISDN (MIMM) service in a single SIM for multiple roaming partners
InactiveUS20050070278A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentFamily networkCommunication device
A method and apparatus for mobile communication in multiple mobile communications networks. Embodiments include installing a SIM that includes at least one IMSI and at least one MSISDN in a mobile communications device. The SIM is used to receive and place calls while the user is in the user's home network and while the user is roaming in another network. In various embodiments, one of a home MSISDN and a local MSISDN is used.
Owner:GLOBETOUCH
Signaling gateway with Multiple IMSI with Multiple MSISDN (MIMM) service in a single SIM for multiple roaming partners
ActiveUS20060276226A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsTelecommunicationsFamily network
A method and apparatus for mobile communication in multiple mobile communications networks. Embodiments include installing a SIM that includes at least one IMSI and at least one MSISDN in a mobile communications device. The SIM is used to receive and place calls while the user is in the user's home network and while the user is roaming in another network. In various embodiments, one of a home MSISDN and a local MSISDN is used.
Owner:GLOBETOUCH
Signaling gateway with multiple IMSI with multiple MSISDN(MIMM) service in a single SIM for multiple roaming partners
ActiveUS7369848B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsTelecommunicationsComputer science
A method and apparatus for mobile communication in multiple mobile communications networks. Embodiments include installing a SIM that includes at least one IMSI and at least one MSISDN in a mobile communications device. The SIM is used to receive and place calls while the user is in the user's home network and while the user is roaming in another network. In various embodiments, one of a home MSISDN and a local MSISDN is used.
Owner:GLOBETOUCH
Network and method for registration of mobile devices and management of the mobile devices
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Multimedia messaging service routing system and method
InactiveUS20020126708A1Special service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingThe InternetMobile device
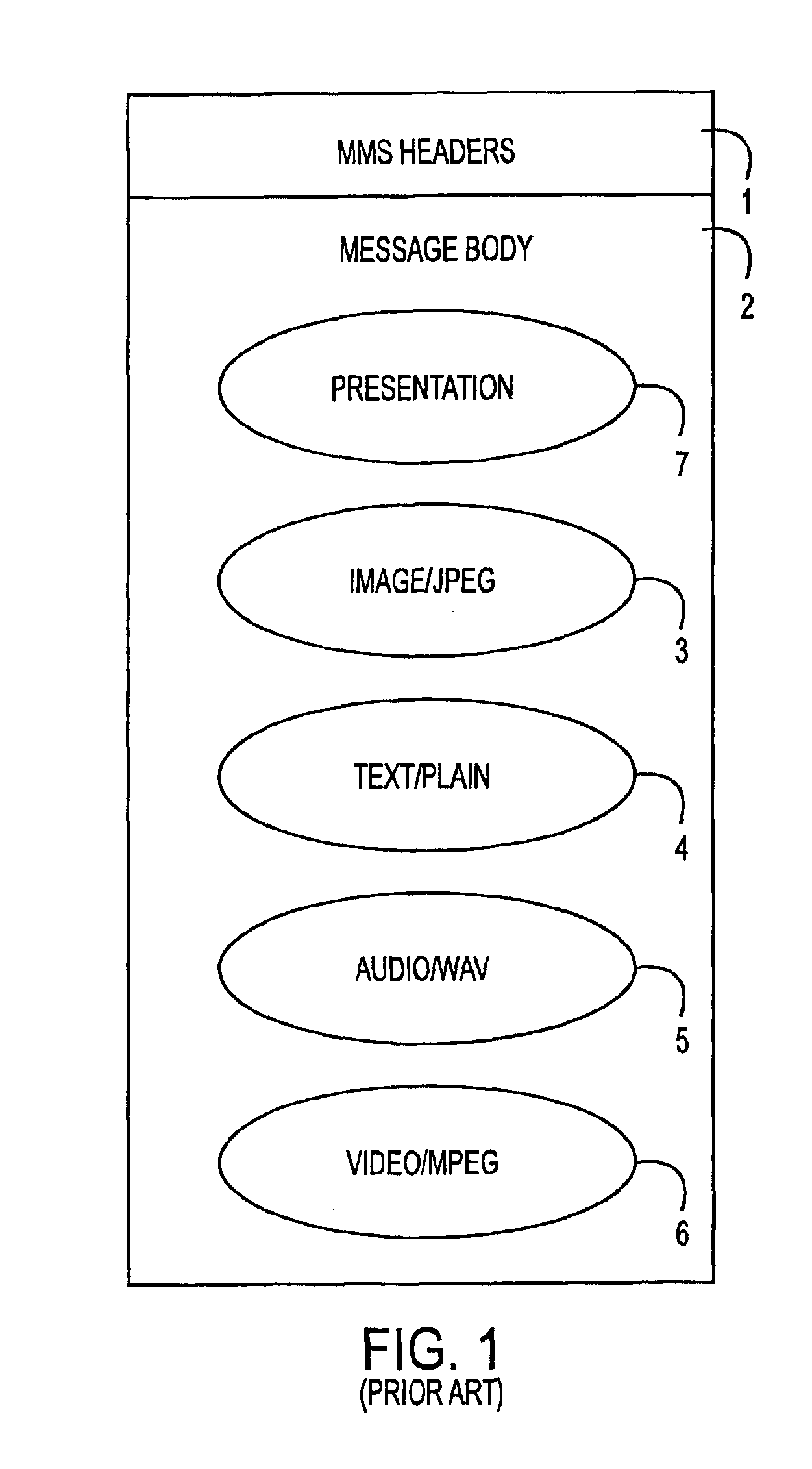
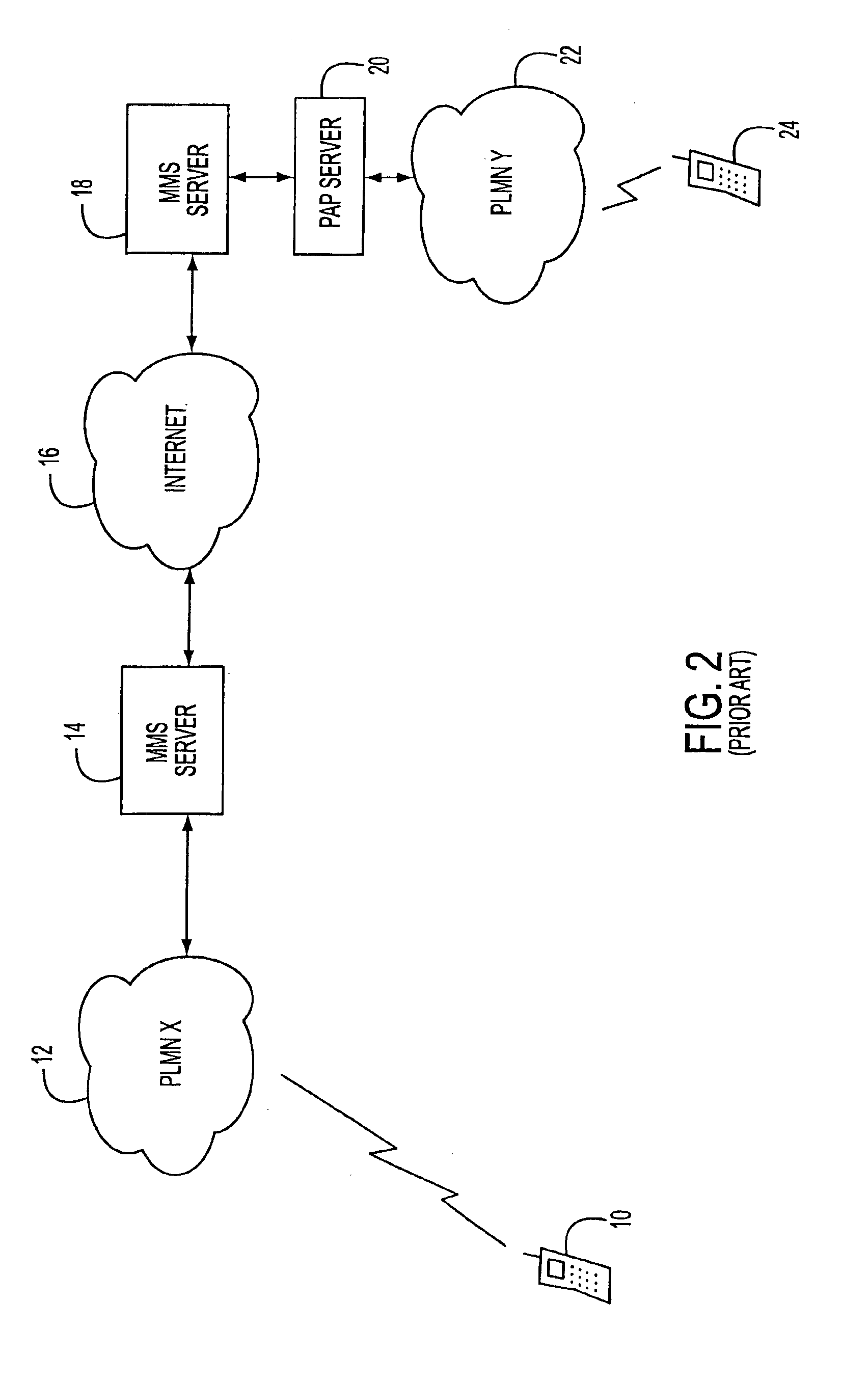
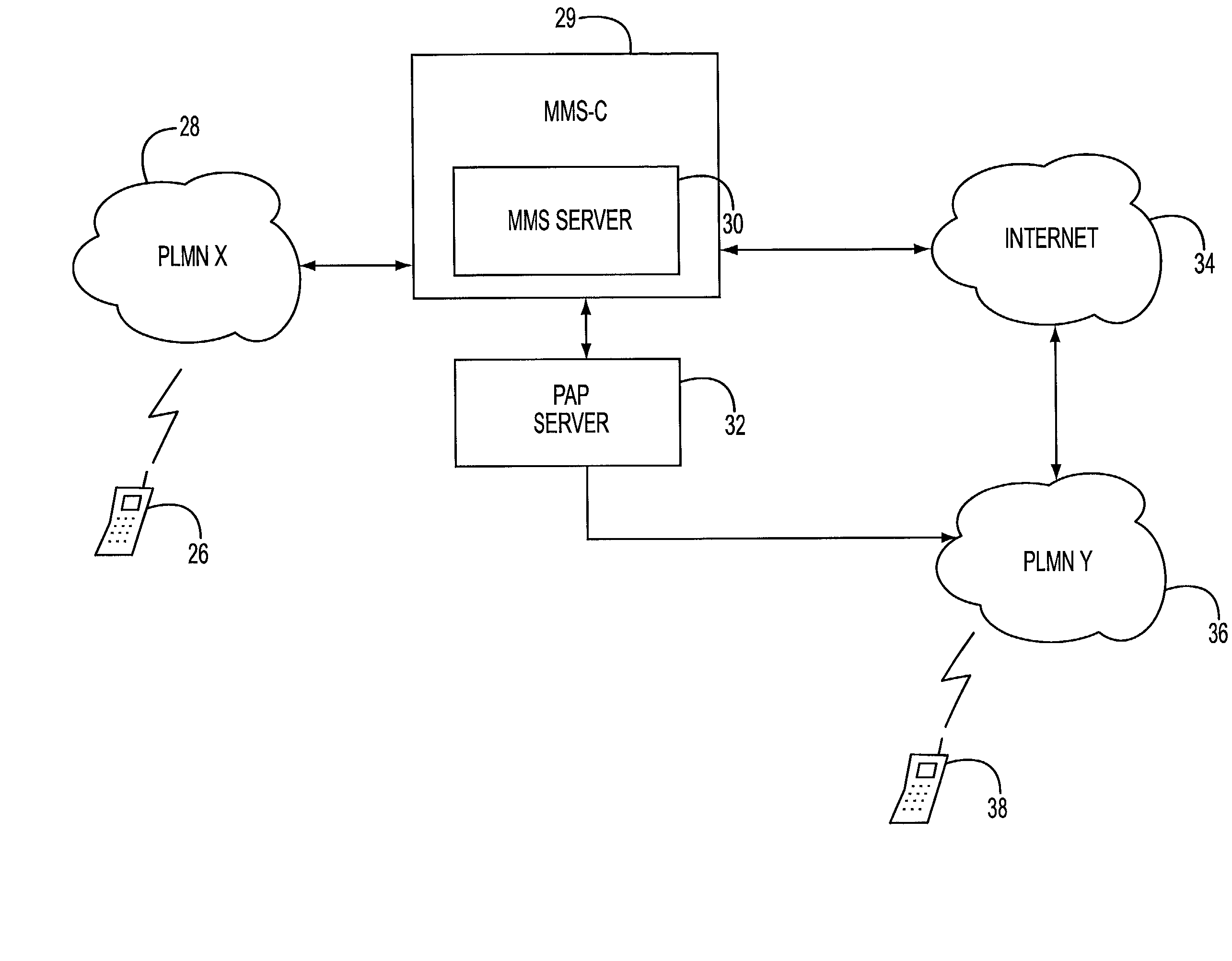
A multimedia messaging system for sending and receiving multimedia MMS messages. The MMS messages are sent to a MMS server and addressed to the recipient's MSISDN number. MMS server sends a notification to a PAP server that sends the notification as a WAP Push to the recipient mobile device telling the mobile device to retrieve the message. If the recipient mobile device is engaged in an on going or dedicated session with the Internet, the notification is sent to the recipient mobile device during the session. The recipient mobile device then initiates a HTTP GET request to retrieve the multimedia message via the voice or data channel of a PLMN. If the recipient mobile device is not engaged in an on going or dedicated session with the Internet, the notification is sent to the recipient mobile device as a WAP Push using SMS as bearer via the signaling channel of the PLMN. The recipient mobile device then initiates a HTTP GET request to retrieve the multimedia message via the voice or data channel of the PLMN.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
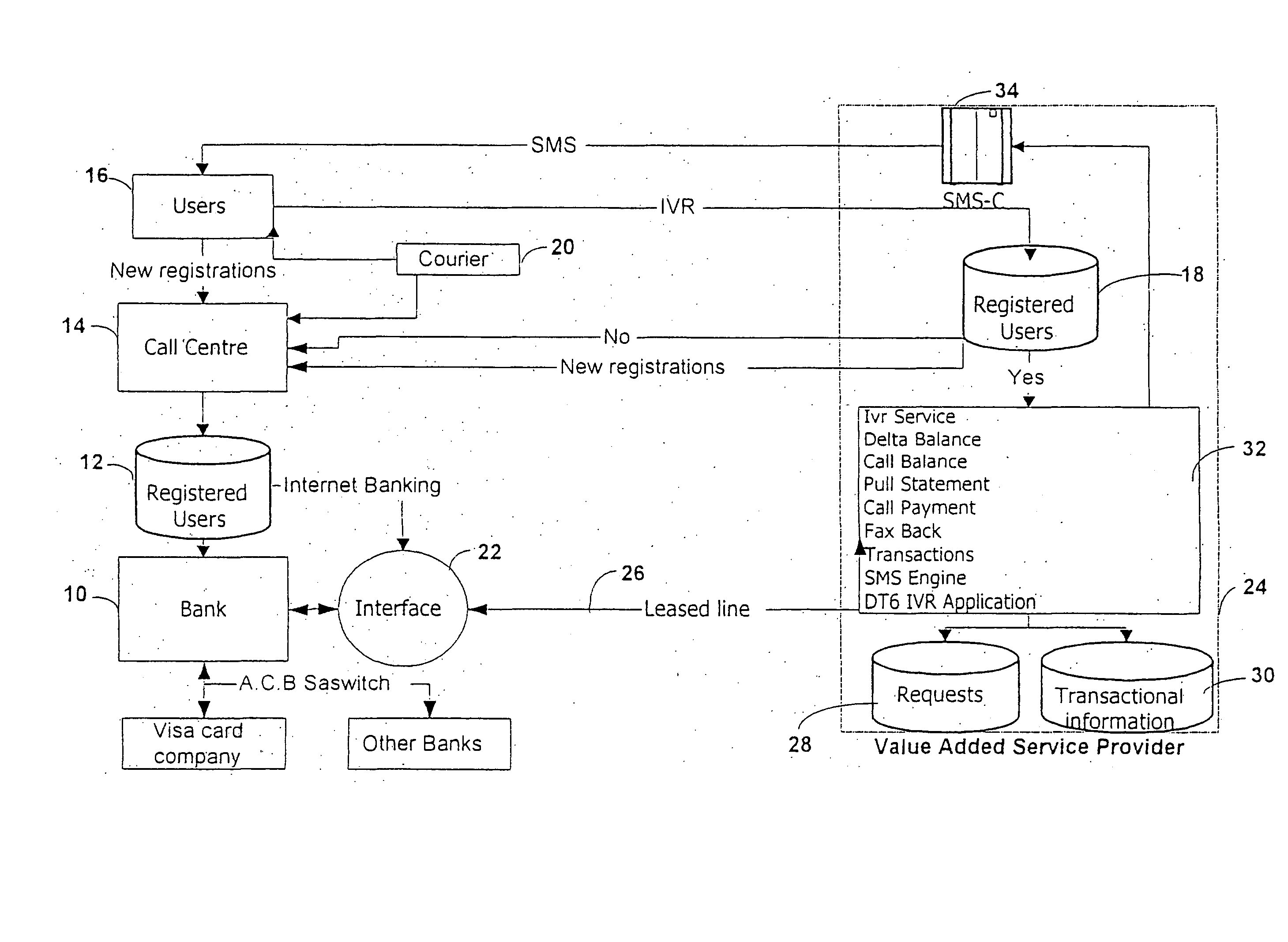
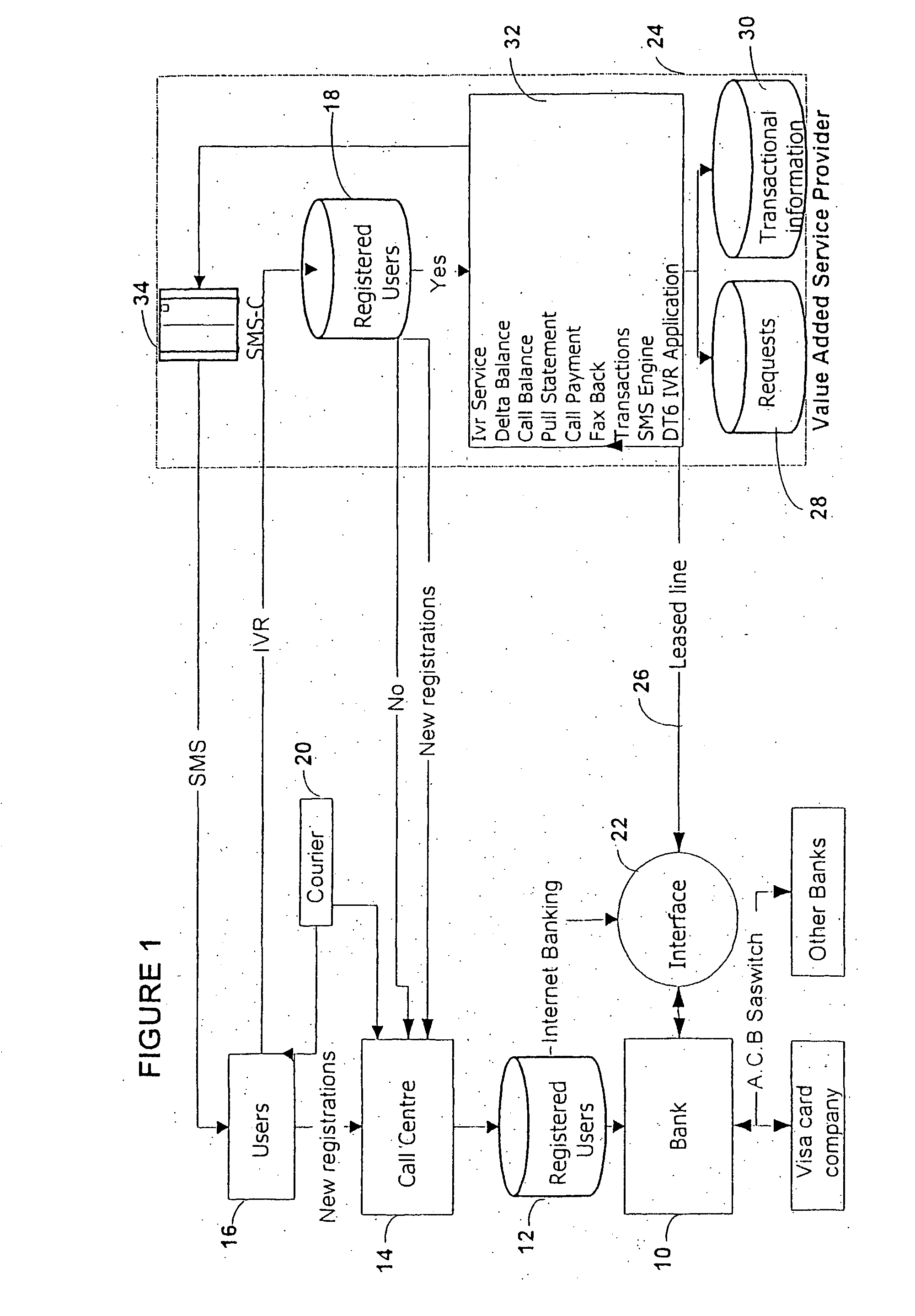
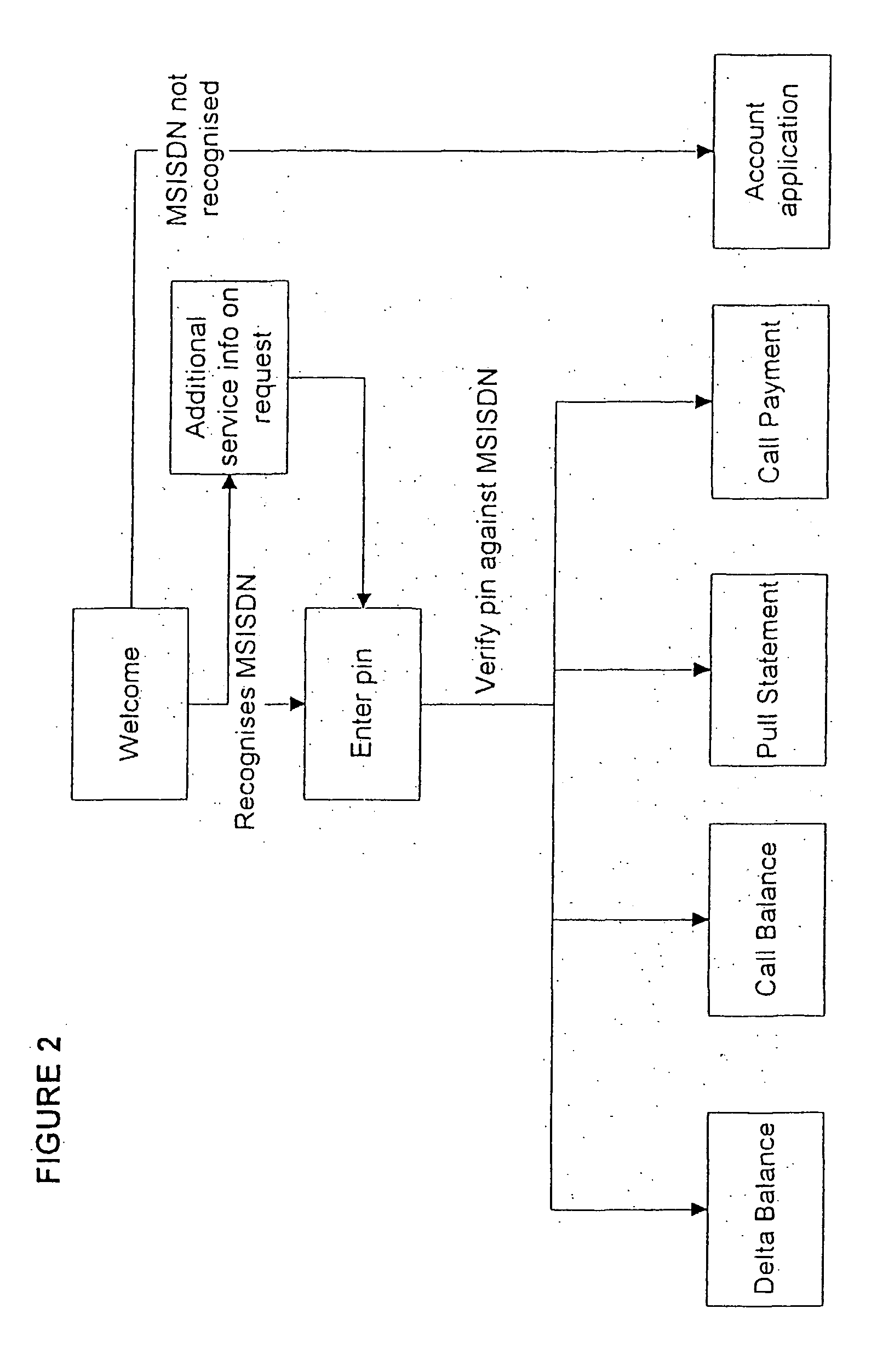
Method and system for operating a banking service
A method and system for operating a banking service are included. The system includes a database (12) for storing client registration data and a unique number, which is preferably the MSISDN or mobile telephone number of the client. This number is used as the client's account number. A call center (14) receives calls from clients and verifies their identity from data transmitted by their mobile telephones. The system allows clients to conduct various banking transactions including balance, statement and payment transactions. A database stores details of balances and / or transactions in each user's account. The system serves for clients to be notified by an SMS transmitted to their mobile telephone of transactions, such as changes to their bank balances or the crediting or debiting of their account. The system can also interface with conventional banking services.
Owner:VIIJOEN NIEL EBEN
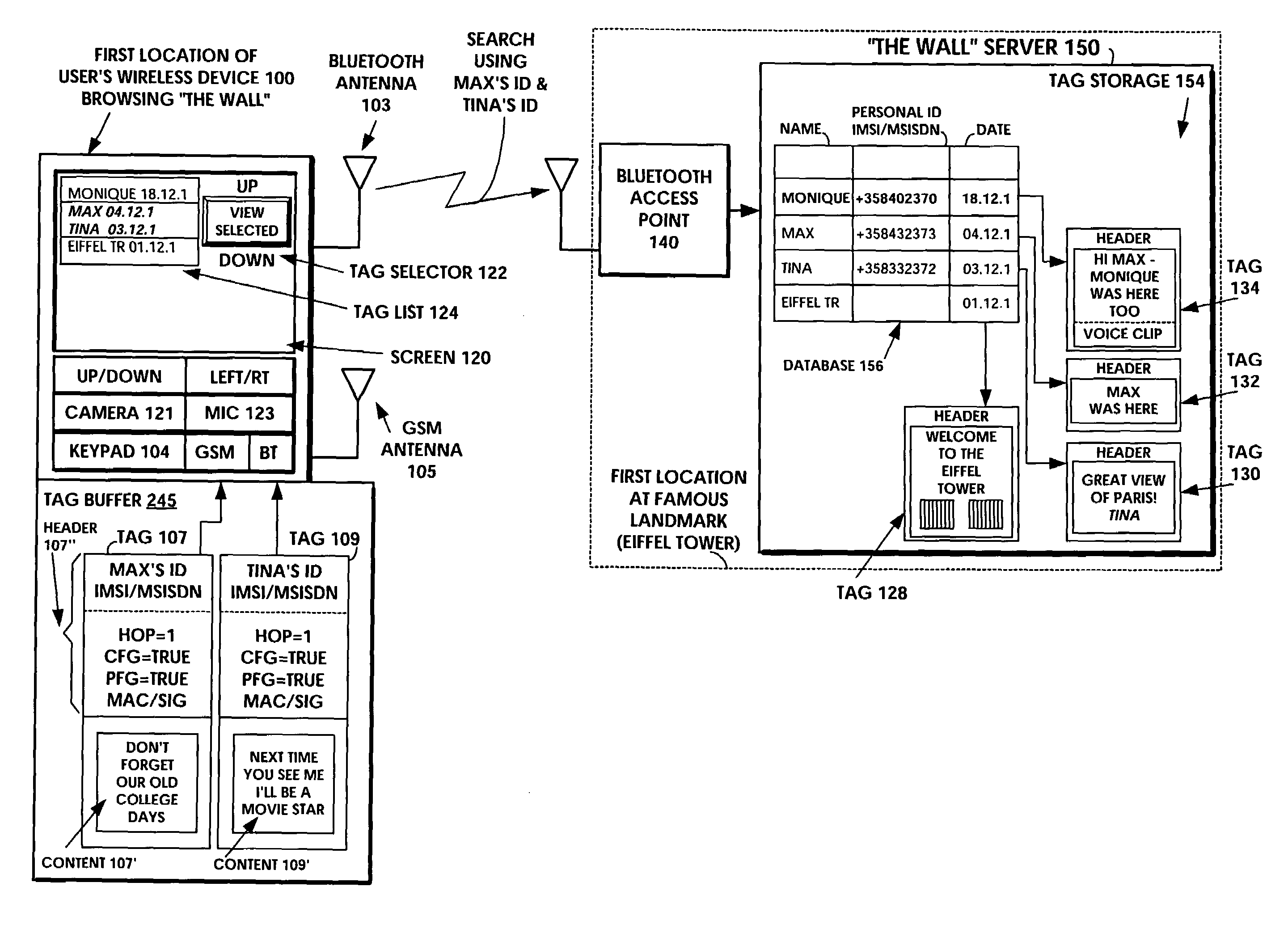
Short-range wireless system and method for multimedia tags
InactiveUS7340214B1Storage requirements is greatly reducedAvoid receivingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareHiperLAN
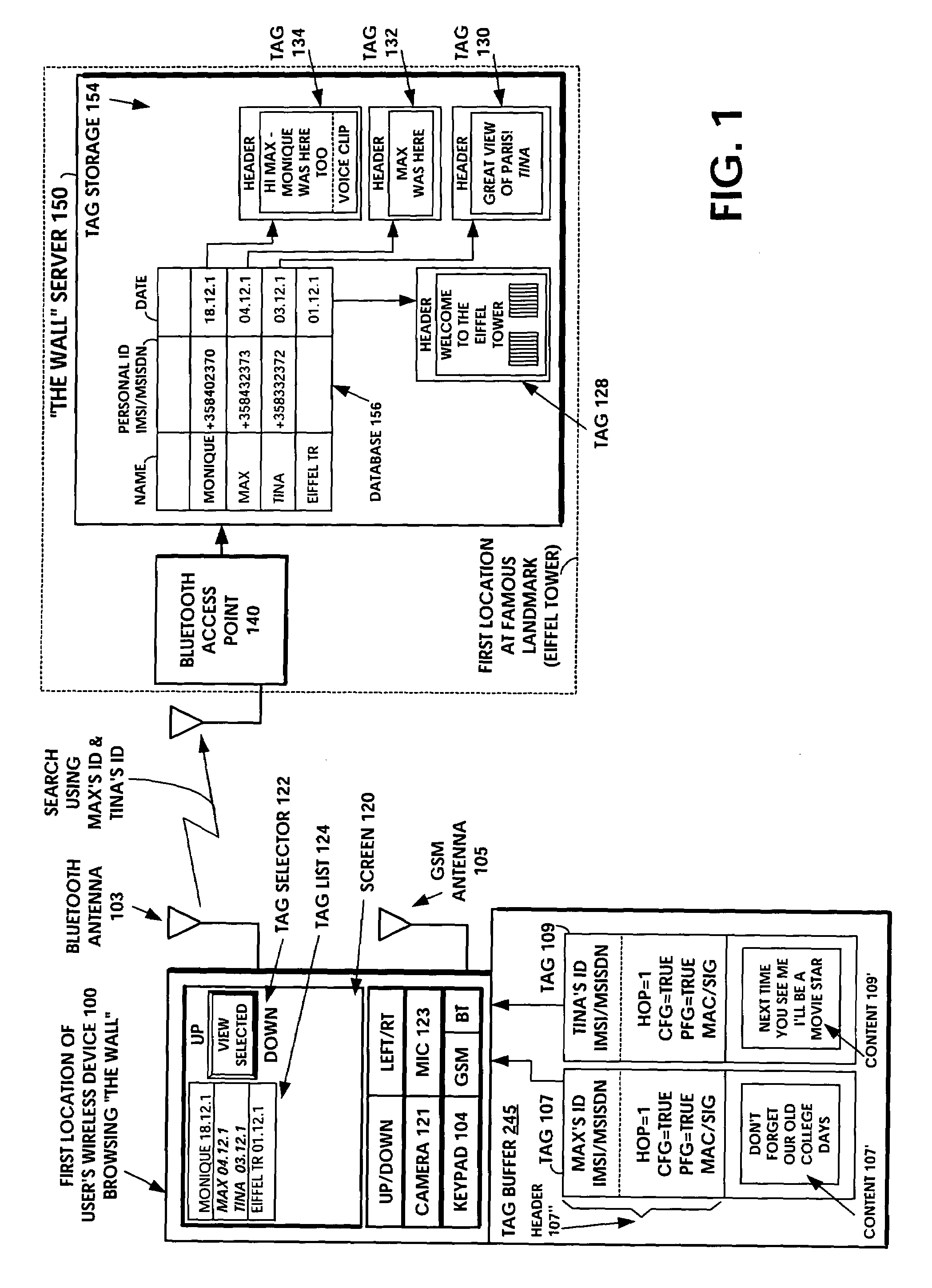
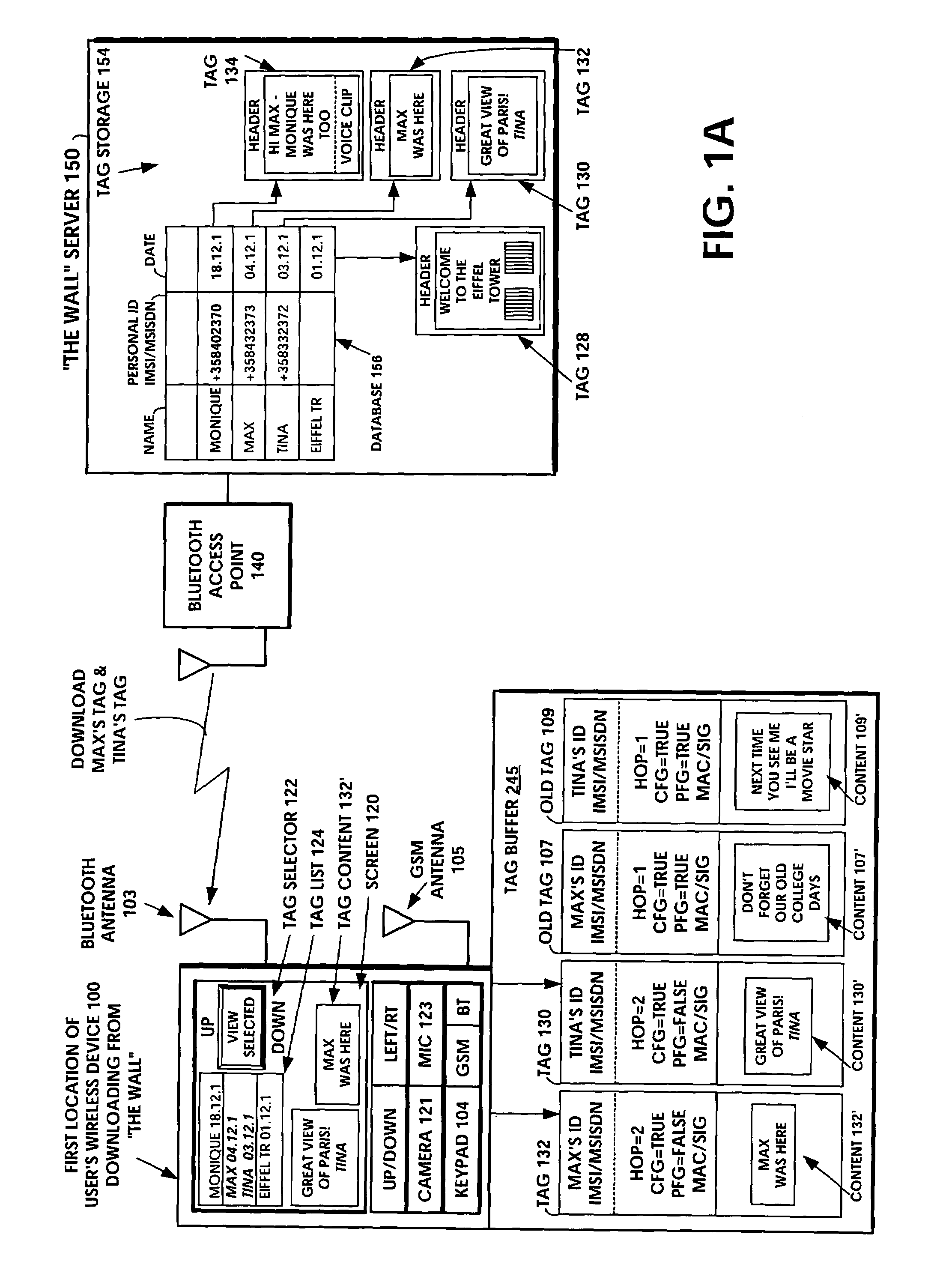
A short-range wireless system and method is disclosed to store and transfer a new type of multimedia data construct called a tag. A user can write text, create a voice clip and append it to the text, take a digital picture and append it to the text, to create a multimedia file as the content of a tag. The creation or modifying of the multimedia file can be done in the user's mobile wireless device or off line and then stored in the mobile device. The multimedia file is then incorporated into the tag or it can be referenced by a pointer in the tag. The multimedia file is artistic expression of the user and the tag uniquely associates the user's identity with the multimedia file by prohibiting alteration of the content after the user completes its creation. A content-originator flag (CFG) value in the tag is set to “false” during the period when the user is creating or modifying the tag's content. When the user completes editing the content of the tag, the content-originator flag (CFG) value is set to true, thereby freezing the content. The tag includes the user's ID, such as his / her international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) or mobile station ISDN number (MSISDN). Subsequent viewers of the content can make a copy of the content and can then modify it, but they cannot authentically attribute the modified copy to the original user. The system can be implemented as a wireless personal area network (PAN) such as provided in the Bluetooth Standard or a wireless local area network (LAN) such as provided in the IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN Standard and the HIPERLAN Standard.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
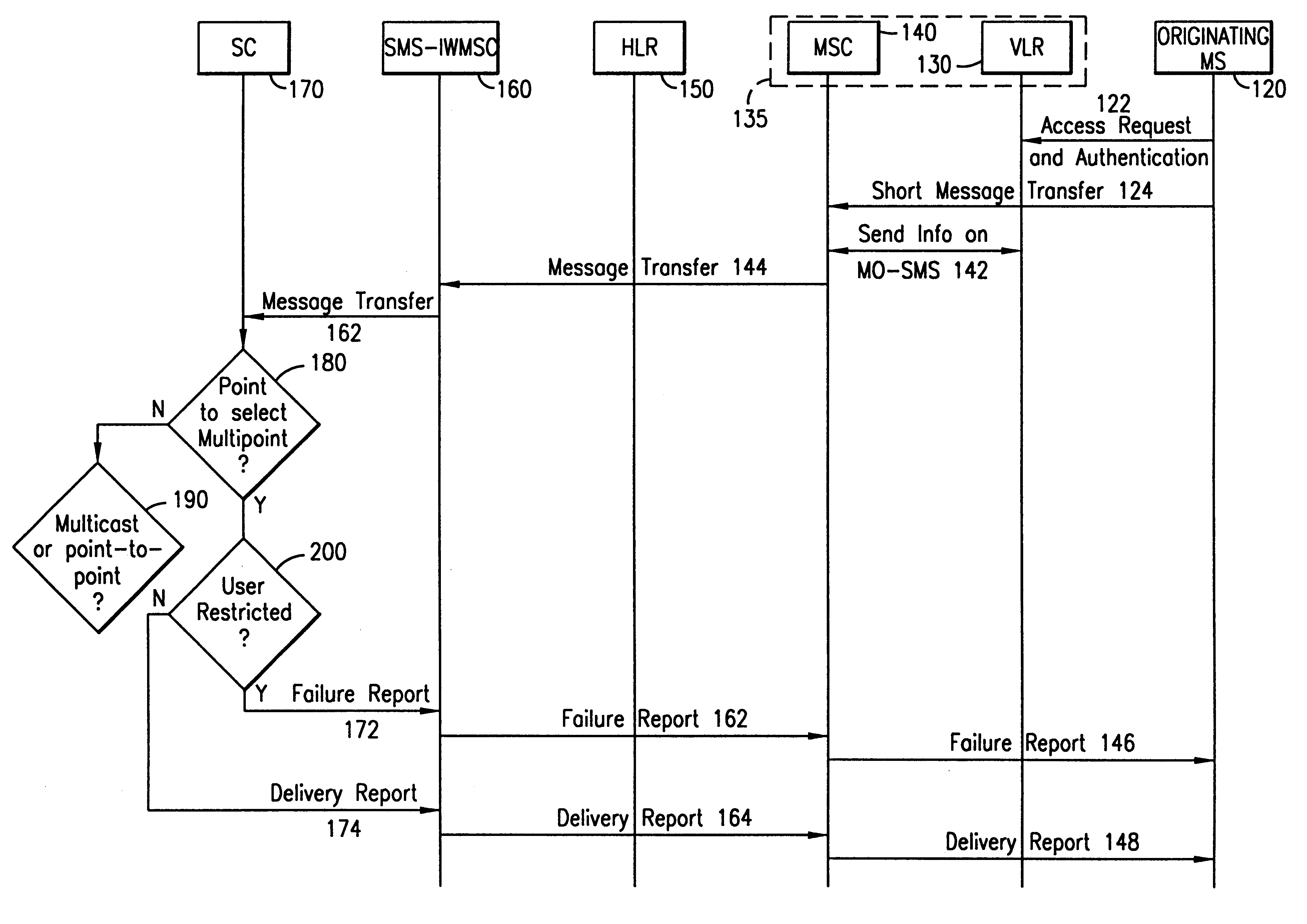
System and method for selective multipoint transmission of short message service messages
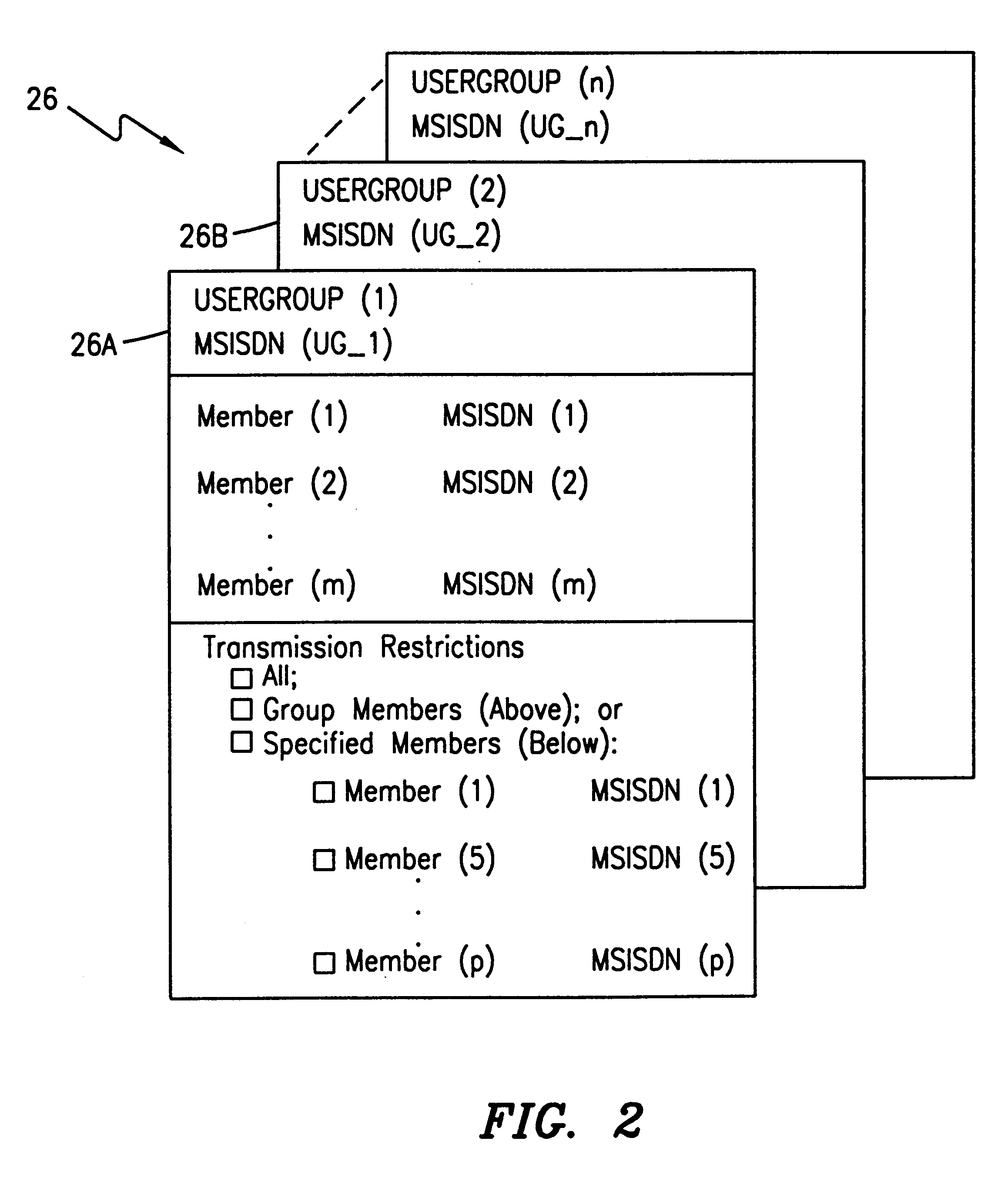
InactiveUS6289223B1Broadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsShort message service centerMSISDN
A system and method in a telecommunications system for enabling an originating mobile unit to deliver SMS messages to a select plurality of destination mobile units. A mobile station ISDN number (MSISDN) is assigned to a usergroup wherein this usergroup contains at least one and preferably a plurality of member MSISDNs. An originating mobile unit may then transmit an SMS message to a plurality of destination units by transmitting an SMS message addressed to a predefined usergroup MSISDN thereby eliminating the necessity of the originating mobile unit addressing and transmitting the SMS message to each member of the defined usergroup. Allowances are made to restrict such transmission to specified originating units.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
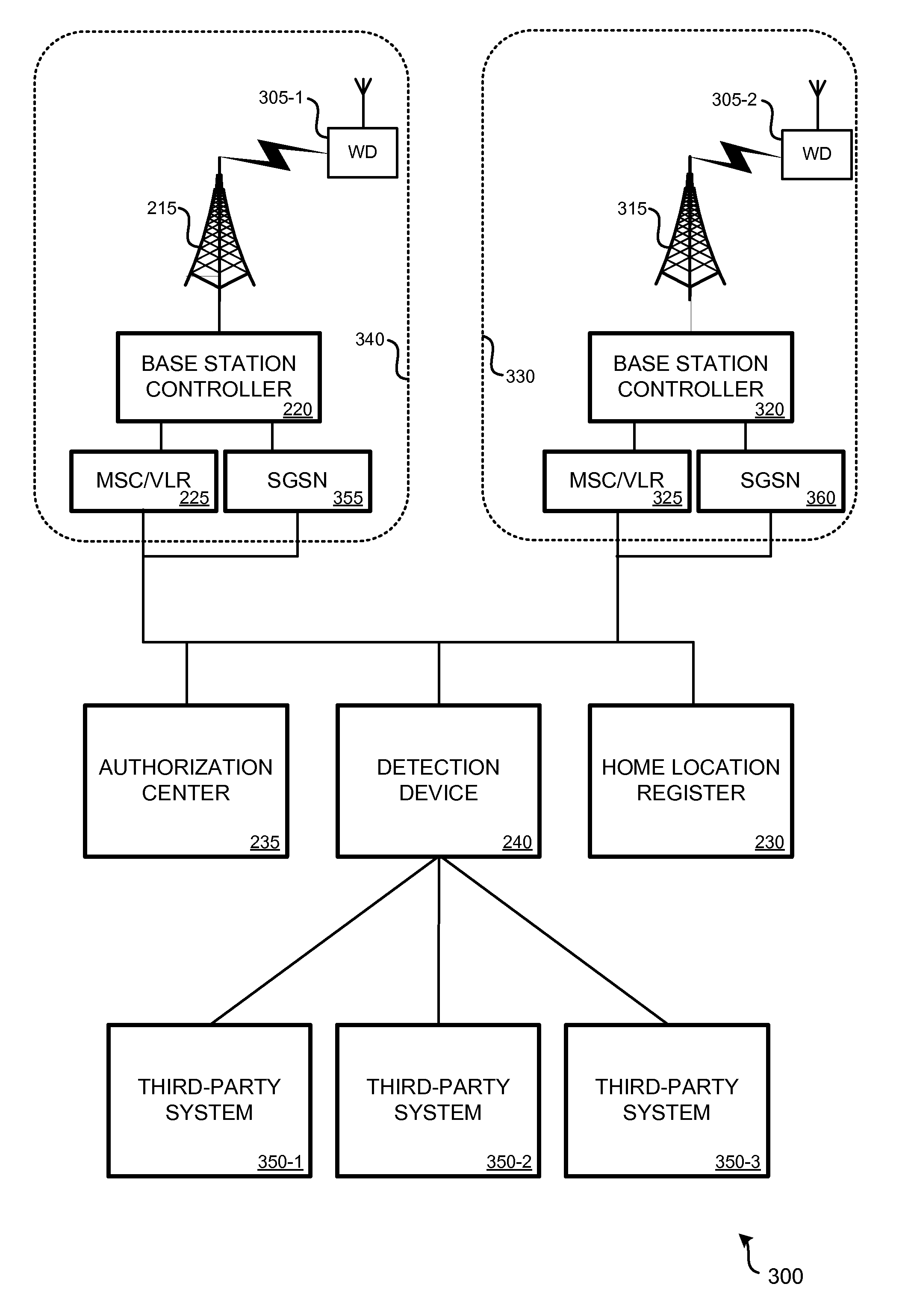
Method and system for keeping all phone numbers active while roaming with diverse operator subscriber identity modules
ActiveUS20070213050A1Facilitating mobile communicationFacilitate communicationSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSystems approachesSubscriber identity module
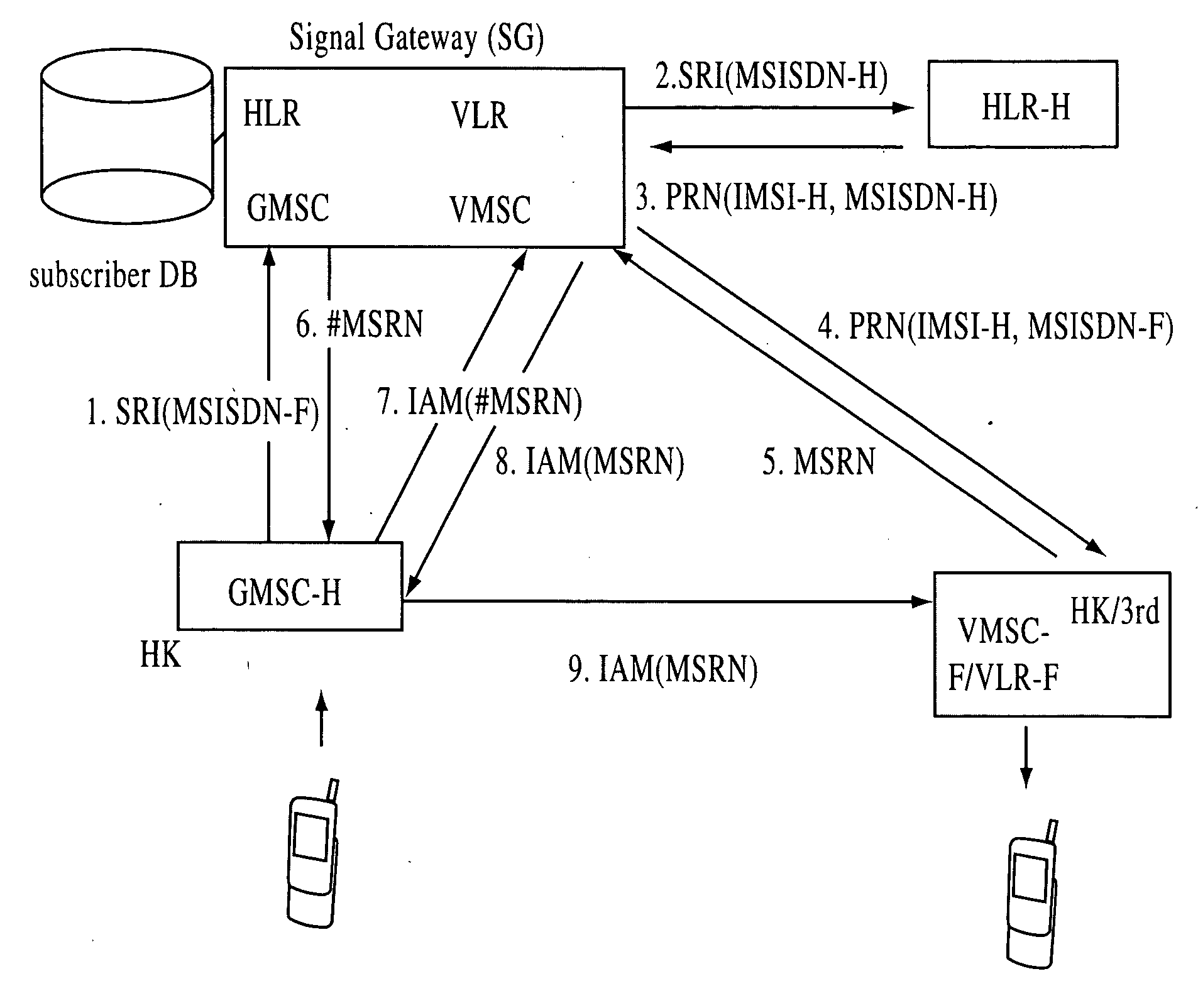
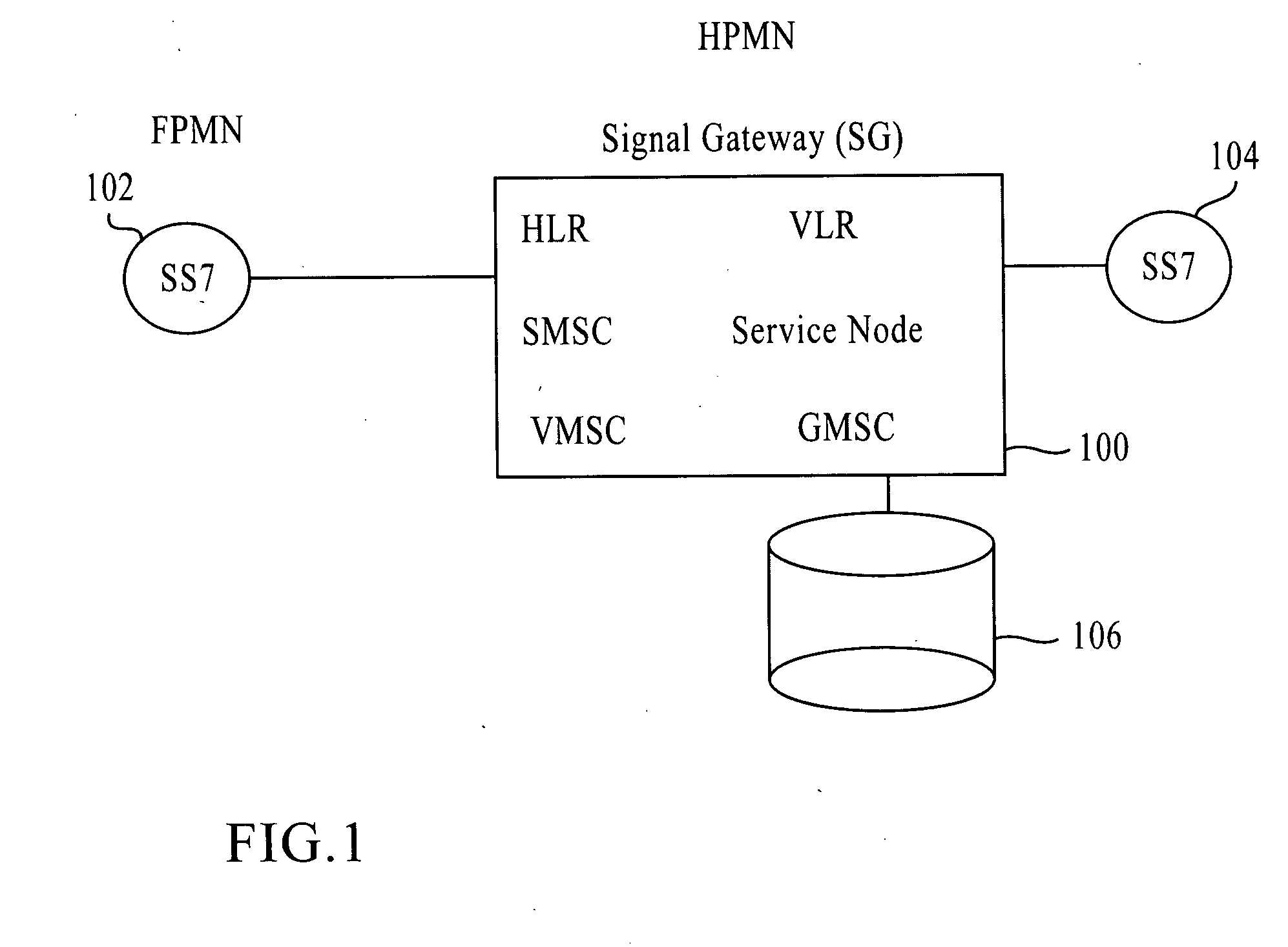
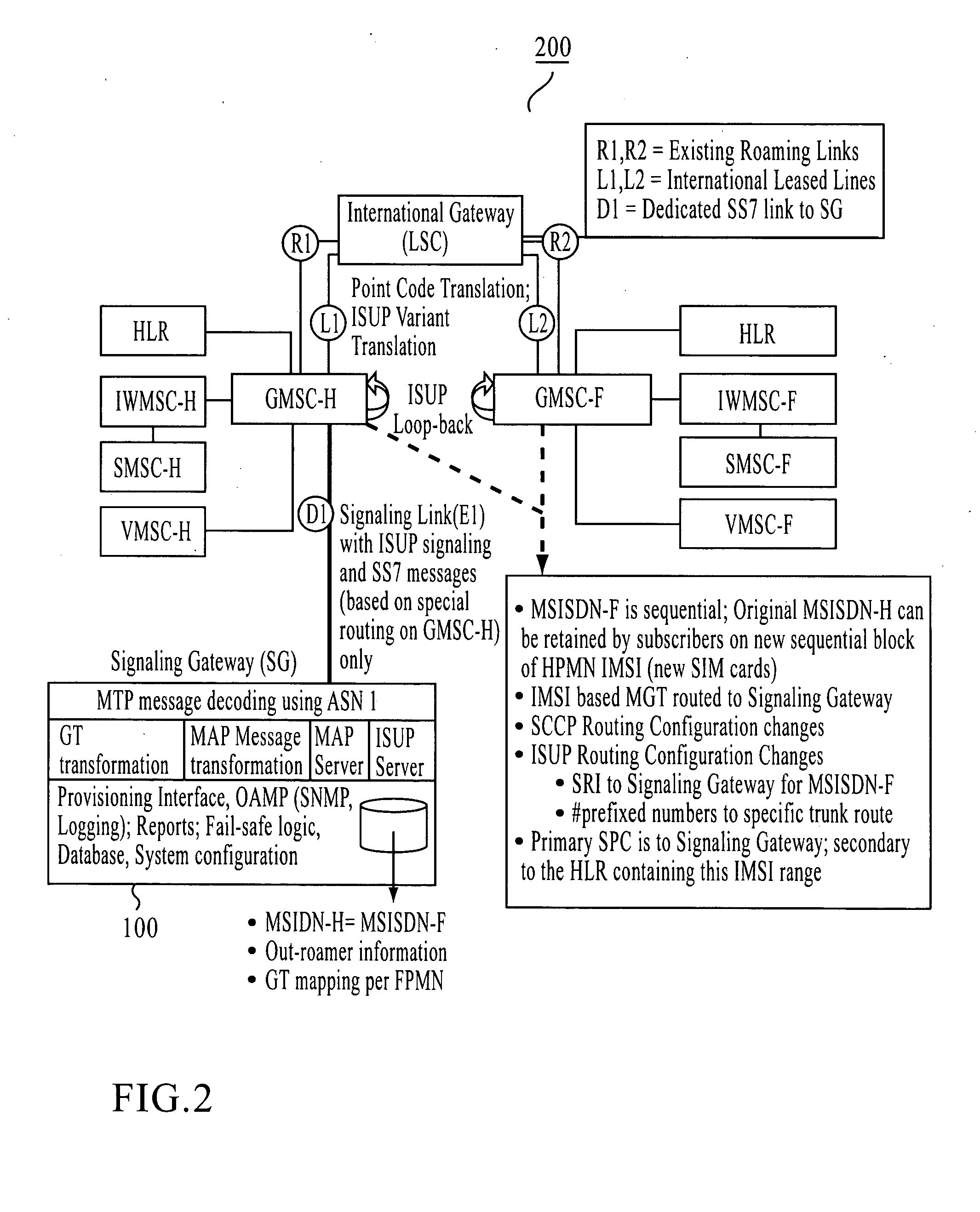
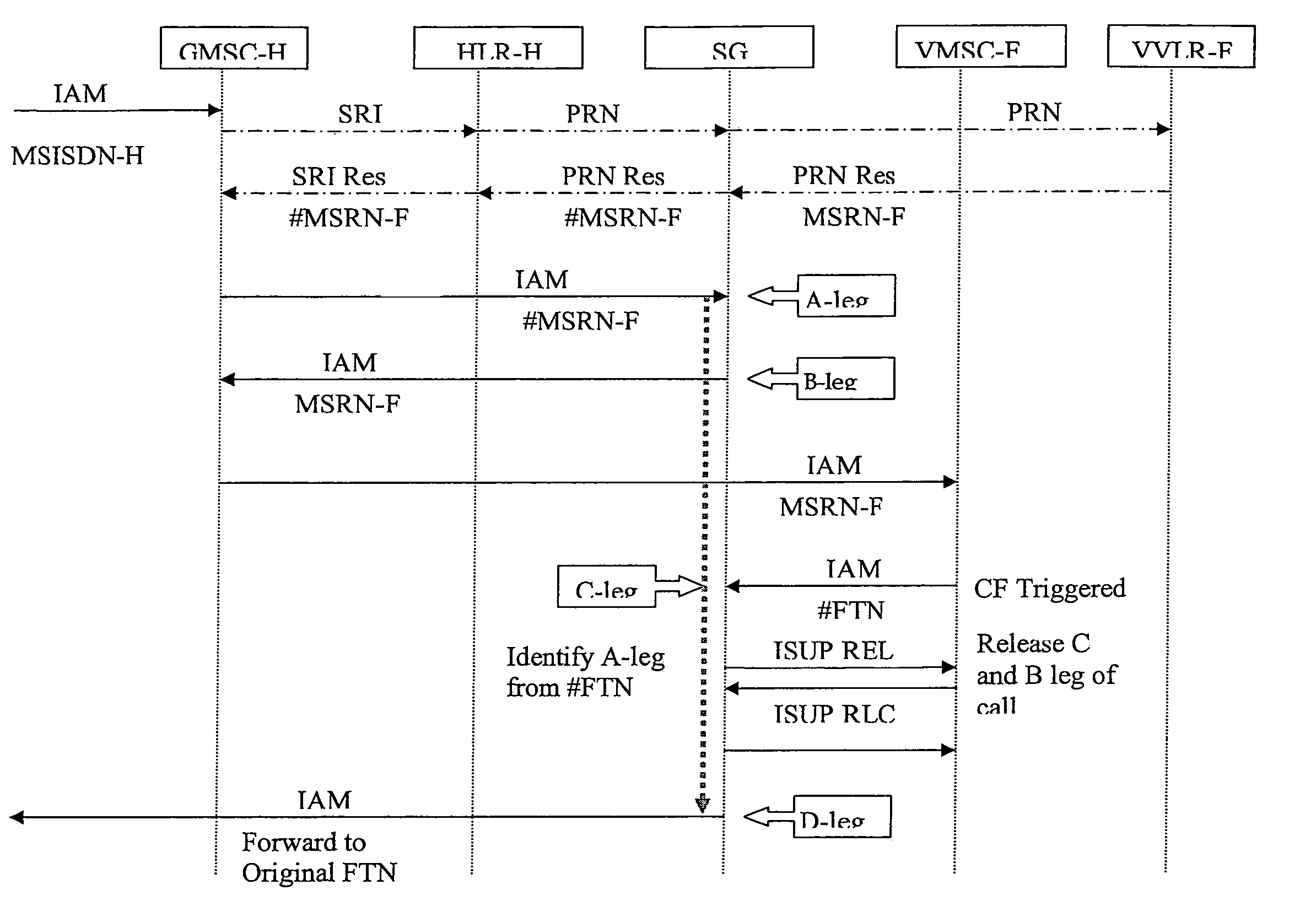
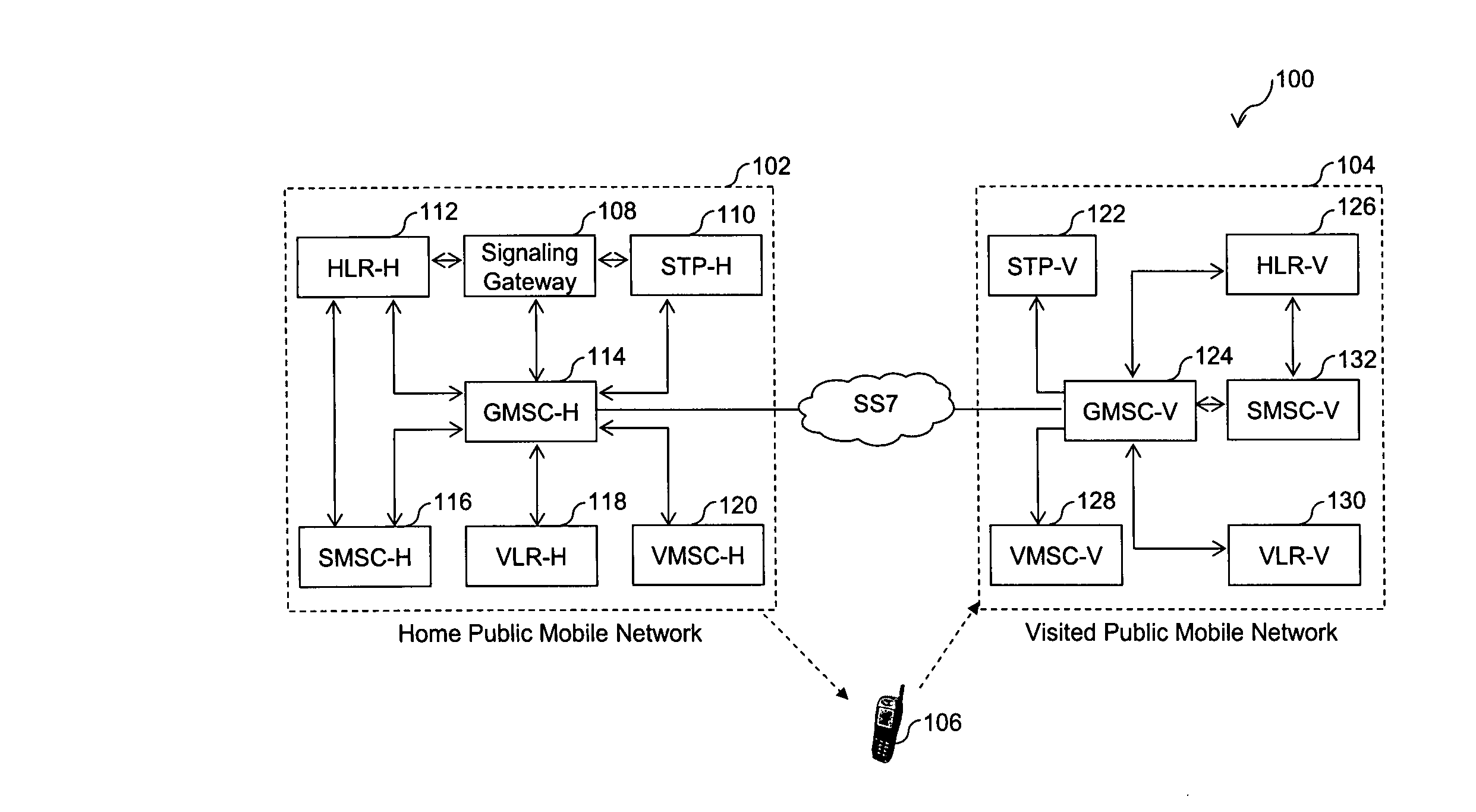
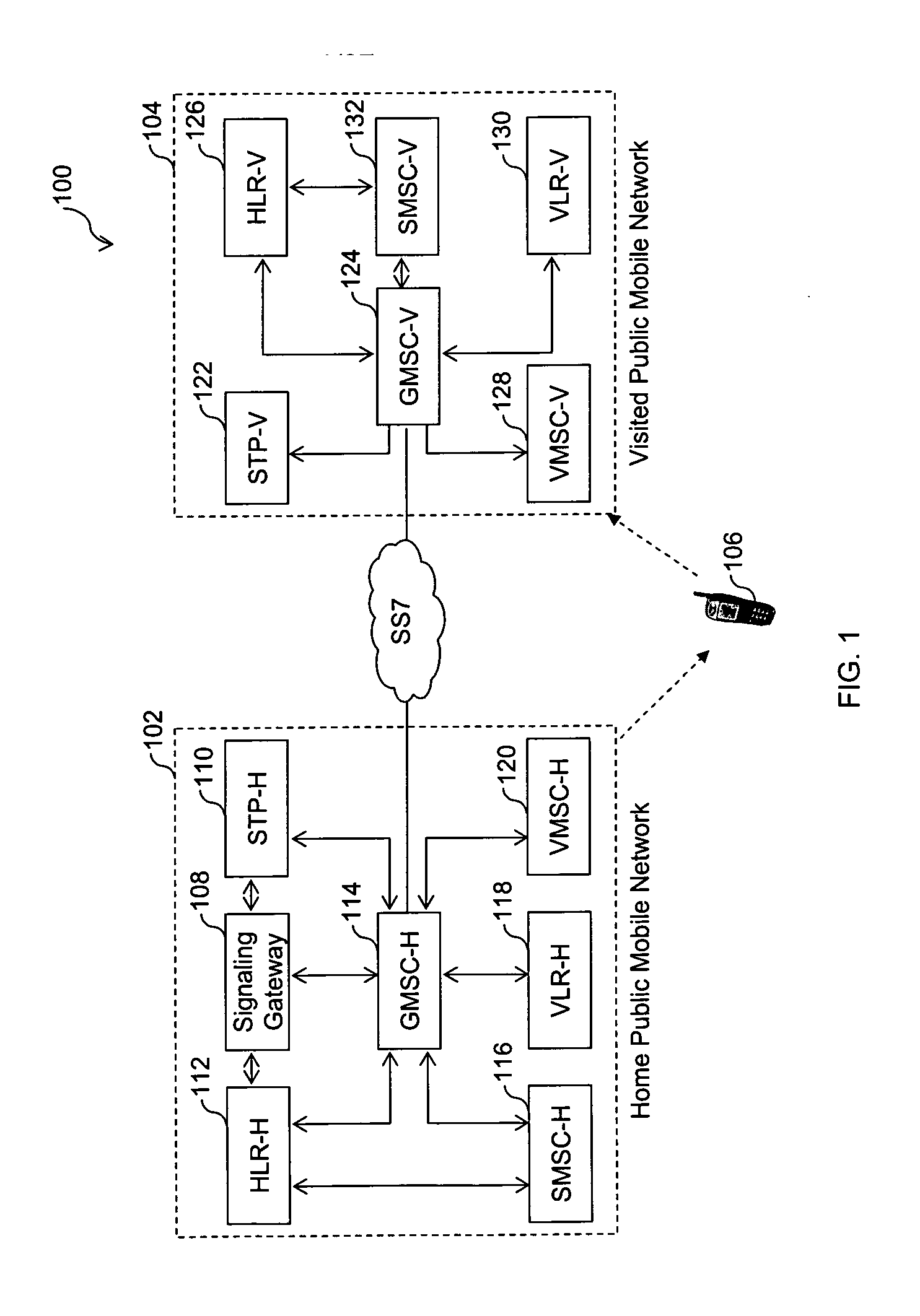
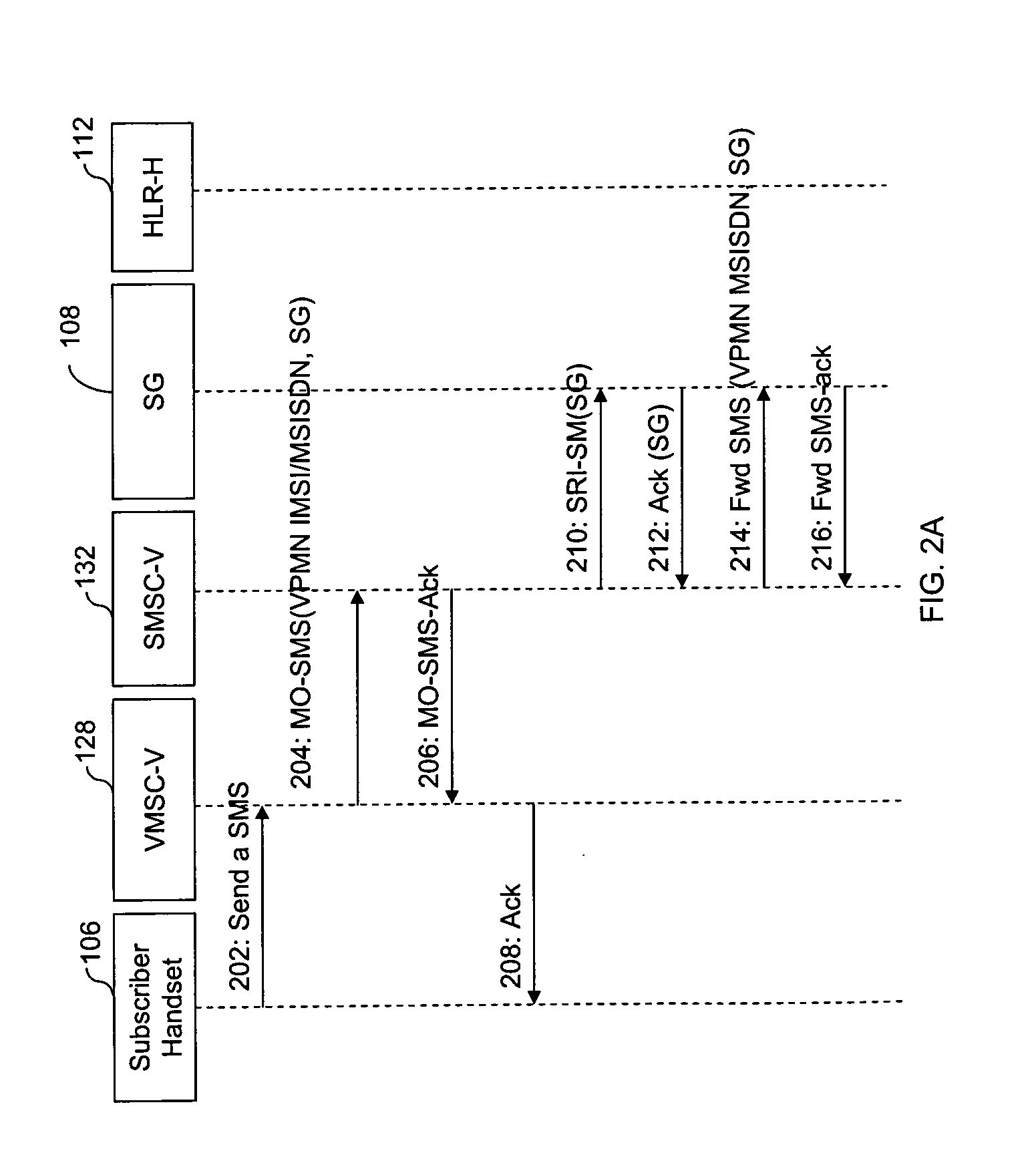
A system, method, and computer product are provided for facilitating mobile communication corresponding to Multiple MSISDNs associated with Multiple IMSIs of a subscriber. The system includes a Signaling Gateway (SG) coupled to a first network. The SG receives one or more association messages from a subscriber for associating a first IMSI, corresponding to the first network, with one or more other IMSIs, corresponding to one or more VPMN networks. The first and other IMSIs are associated with the subscriber using at least one SIM. The SG associates MSISDNs corresponding to the associated IMSIs. Further, the SG facilitates mobile communication corresponding to any associated IMSI and the corresponding associated MSISDN, irrespective of the IMSI being activated in the SIM.
Owner:MOBILEUM INC
System and method for locating a mobile subscriber terminal when roaming
InactiveUS20120253957A1Reduce in quantityPoint-of-sale network systemsTransmissionTelecommunicationsComputer terminal
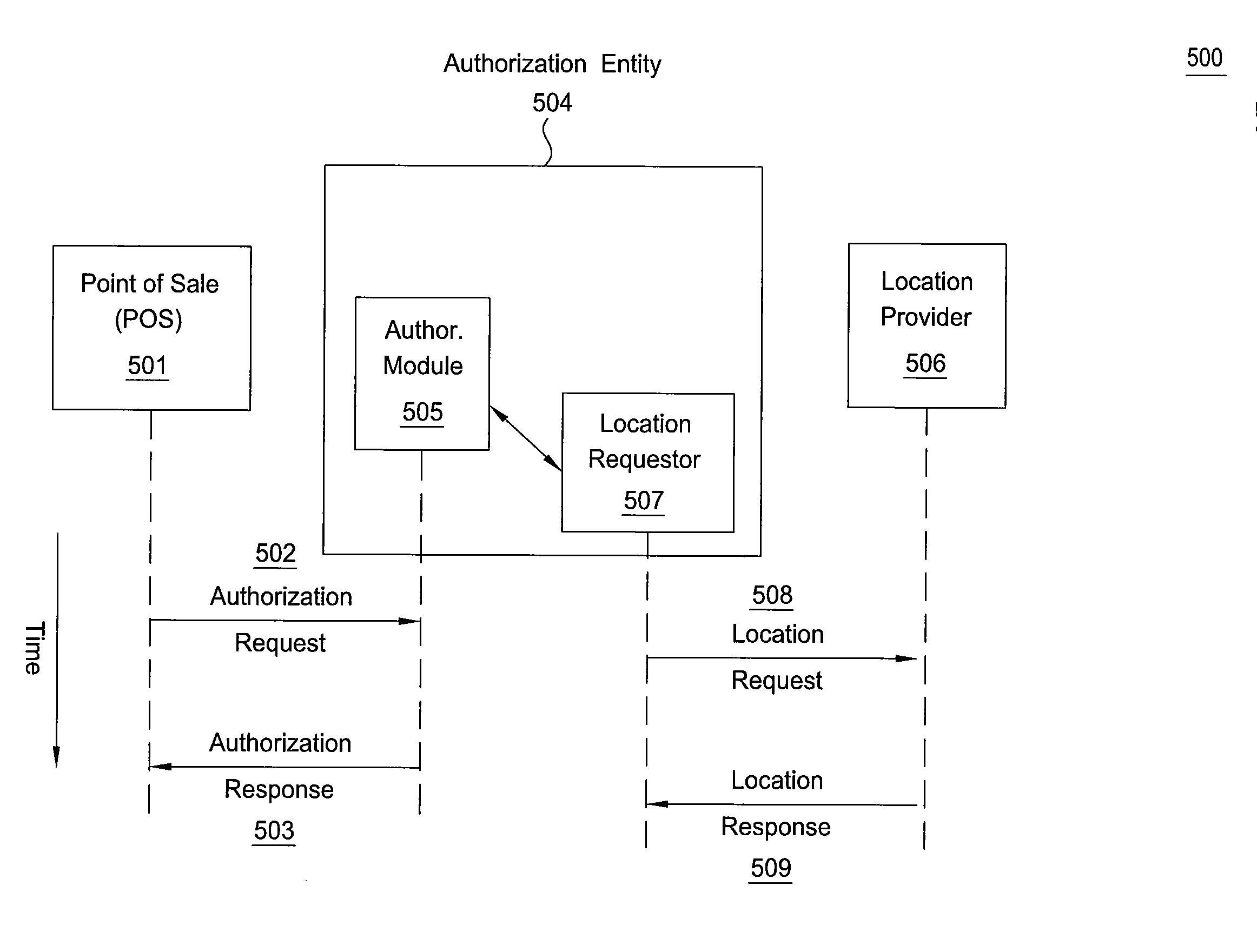
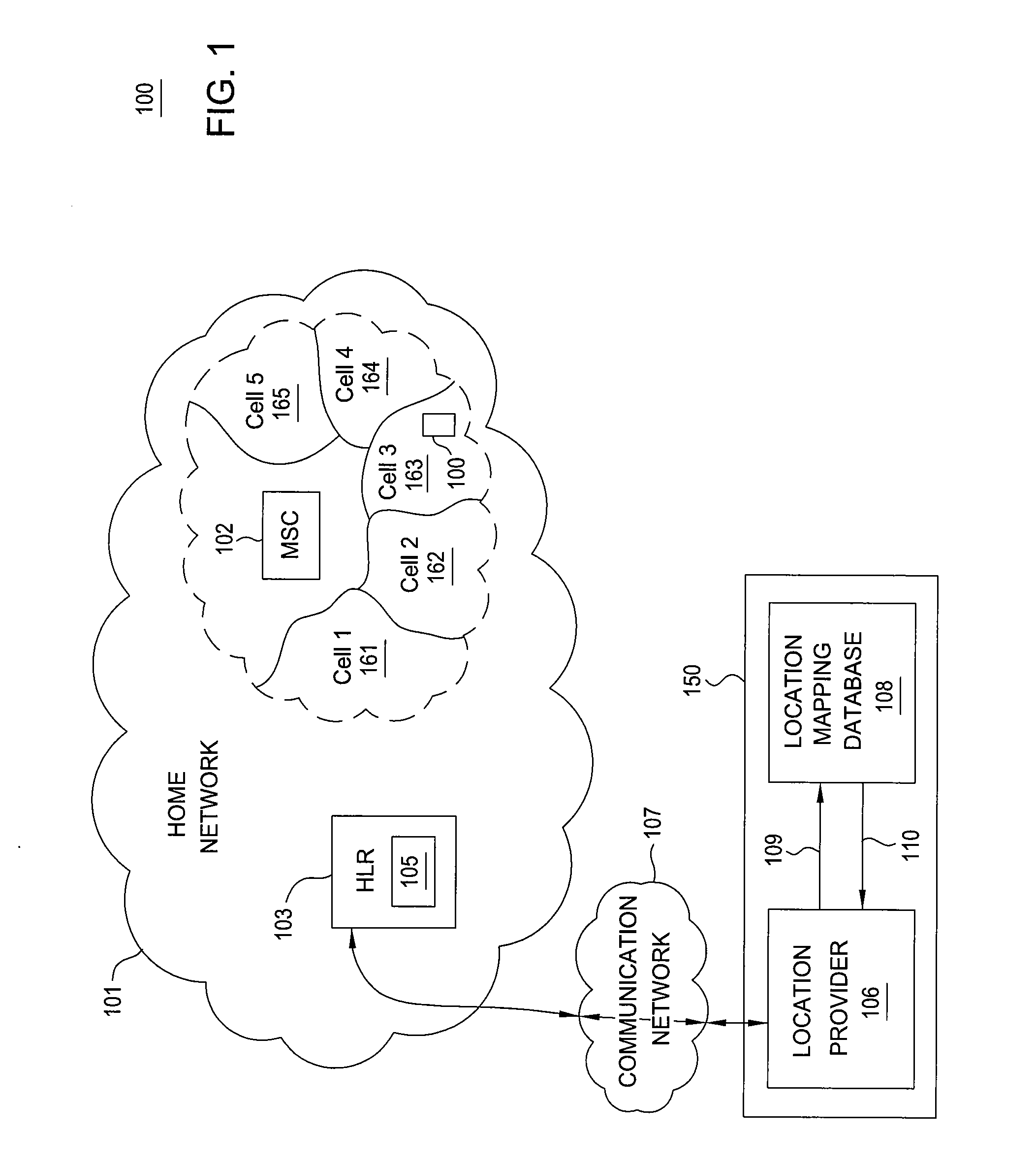
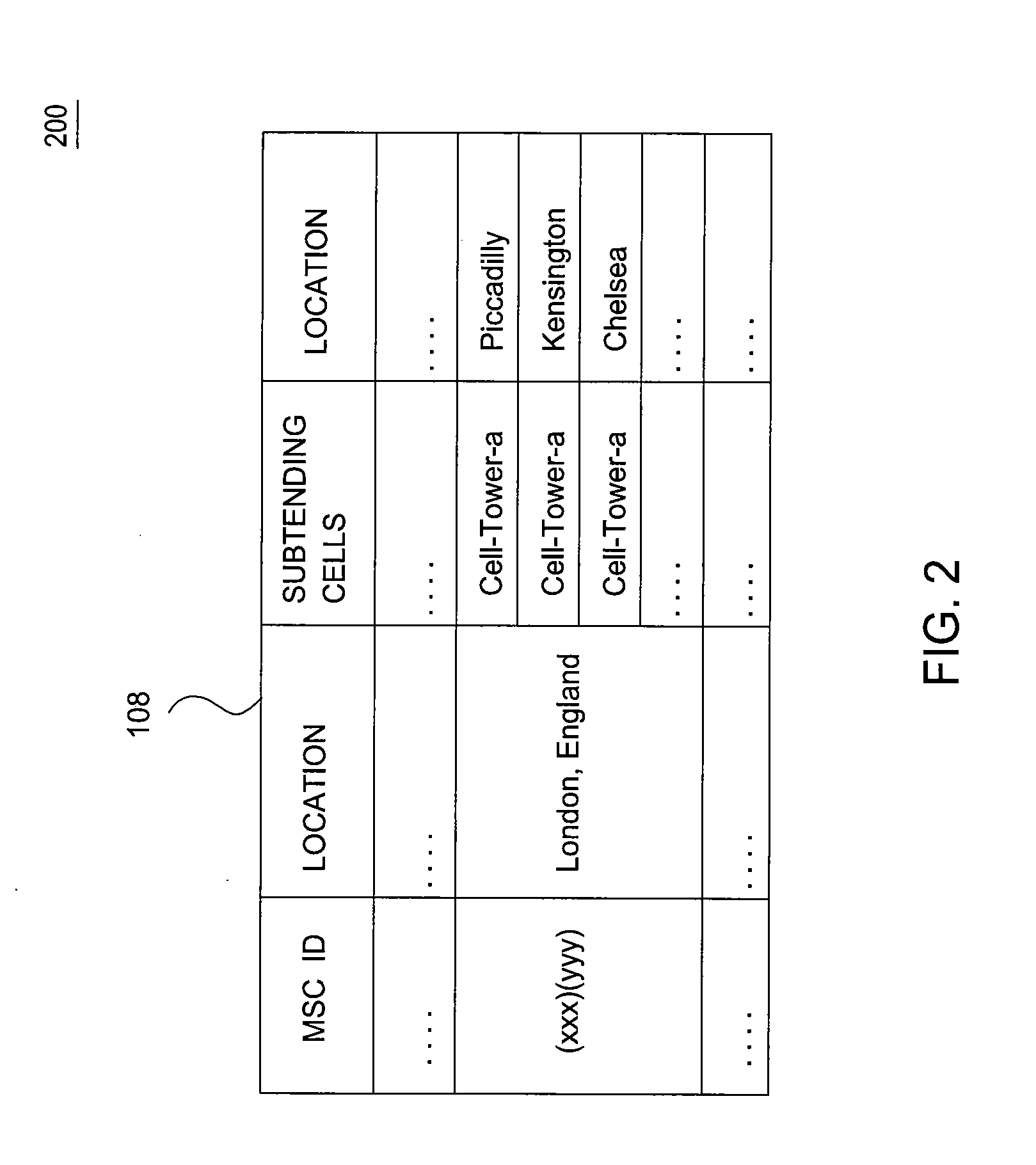
The location of a mobile subscriber roaming outside a home network may be used to authorize a transaction initiated by the mobile subscriber or to authenticate the mobile subscriber when signing into secure accounts. The location of the mobile subscriber is determined by providing a unique mobile subscriber identifier, such as the MSISDN, to an application that communicates with the home network and the roaming network. By communicating with the roaming network, the application can determine the current location of the roaming mobile subscriber terminal with location resolution down to the specific cell in which the mobile subscriber terminal is located. The location of the mobile subscriber terminal may be saved locally in a database associated with an authorization entity, thereby advantageously reducing the number of location look-ups requested by the authorization entity.
Owner:ZUMIGO
Method and System for Dynamic Managing of Subscriber Devices in Mobile Networks
ActiveUS20160183081A1Ensure safety and integrityStorage spaceAccounting/billing servicesSubstation equipmentDynamic dataMobile device
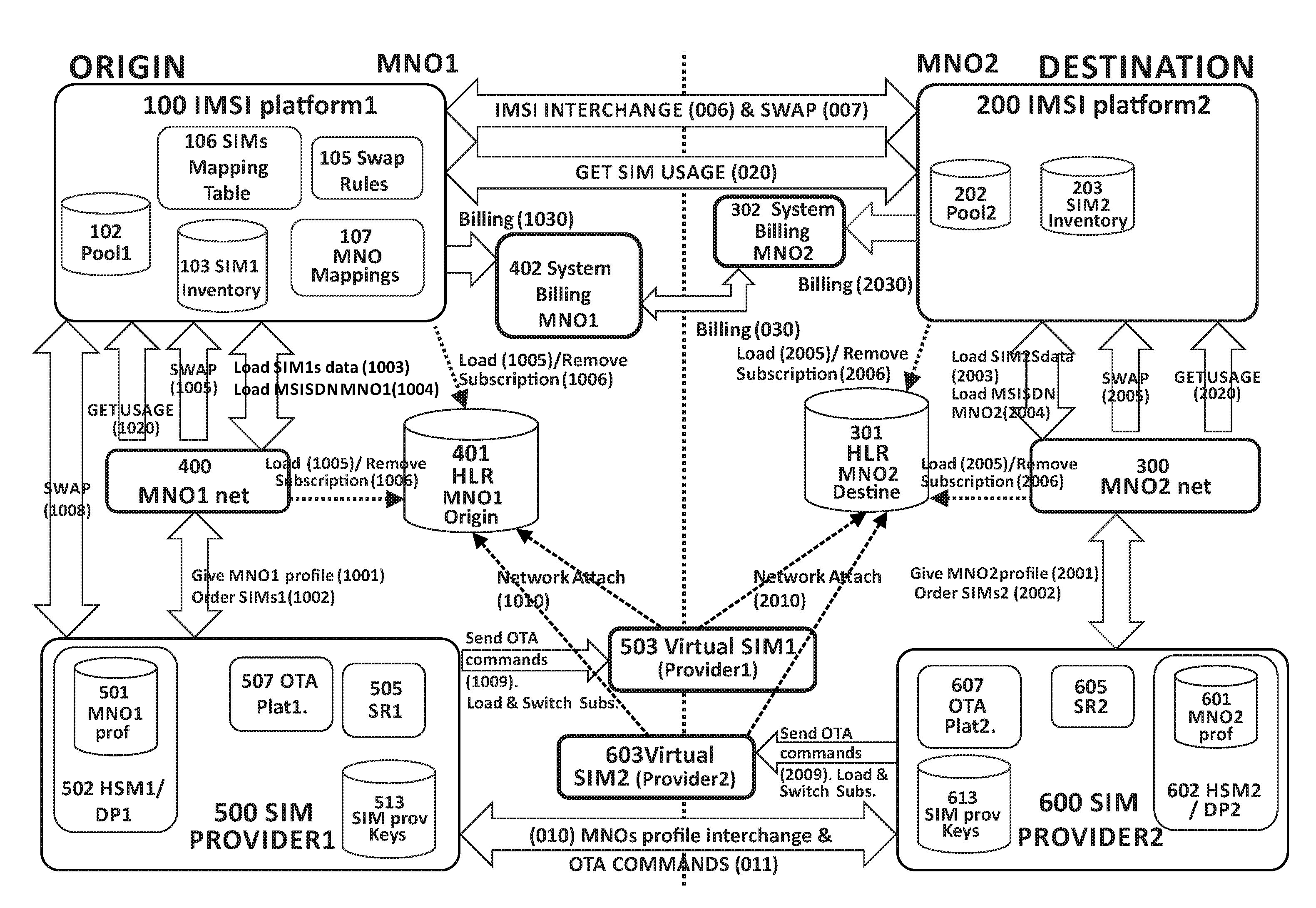
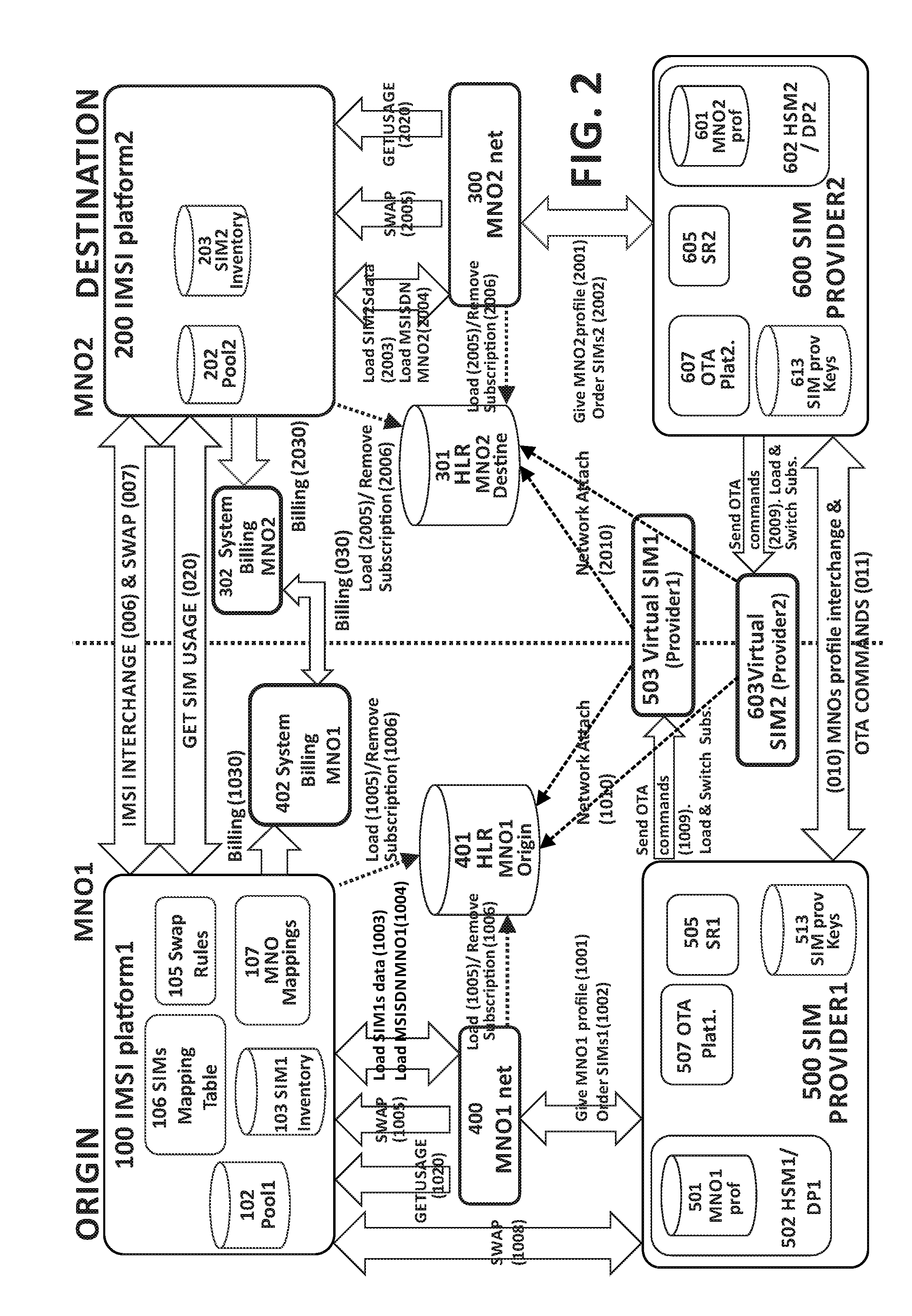
A system and method for managing subscriber mobile devices comprising:a home network (400) of a first mobile network operator (MNO1), in which data associated with at least one physical SIM of a subscriber device with an embedded SIM card (eUICC) is obtained, anda destination network (300) of a second mobile network operator (MNO2) which the device travels to, obtaining static data and dynamic data associated with at least one virtual SIM (503, 603) of the device.The dynamic data comprise a subscriber authentication key (Ki) and is obtained from a SIM provider platform (500, 600) on which the destination network (300) relies. The static data comprise IMSI / MSISDN identities and is stored in a pool (202) of the destination network (300).For a given virtual SIM, it is checked whether there is an association in a mapping table (106) of the first mobile network operator (MNO1) between the static data from the pool (202) and the physical SIM data from the home network (400).
Owner:TELEFONICA SA
Method and system to enable mobile roaming over ip networks and local number portability
InactiveUS20090129371A1Overcomes additional integration costMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTraffic capacityThe Internet
A method and system for creating a virtual roaming solution for a MSISDN using a softphone over an IP network. The system involves (i) implementation of a novel virtual mobile network (VMN) comprising virtual visitor location register (vVLR), virtual home location register (vHLR) and virtual multiple switching centre (vMSC) on an IP server responsible for managing IP call traffic administration, and (ii) implementation of a novel mobile to internet gateway (MIG) comprising an VoIP gateway for diverting call traffic from the mobile network to the IP network, and an IP server with vMSC functionality to translate routing information from the VMN to GSM network so as to appear to the GSM network as a traditional mobile operator. The system dynamically registers the subscriber to the IP network, and provides valid routing information to the MSC (Mobile Switching Centre) or public telephone switch to route the call over to the NGN (next generation network) operator in the IP space.
Owner:BISHAY SAMER
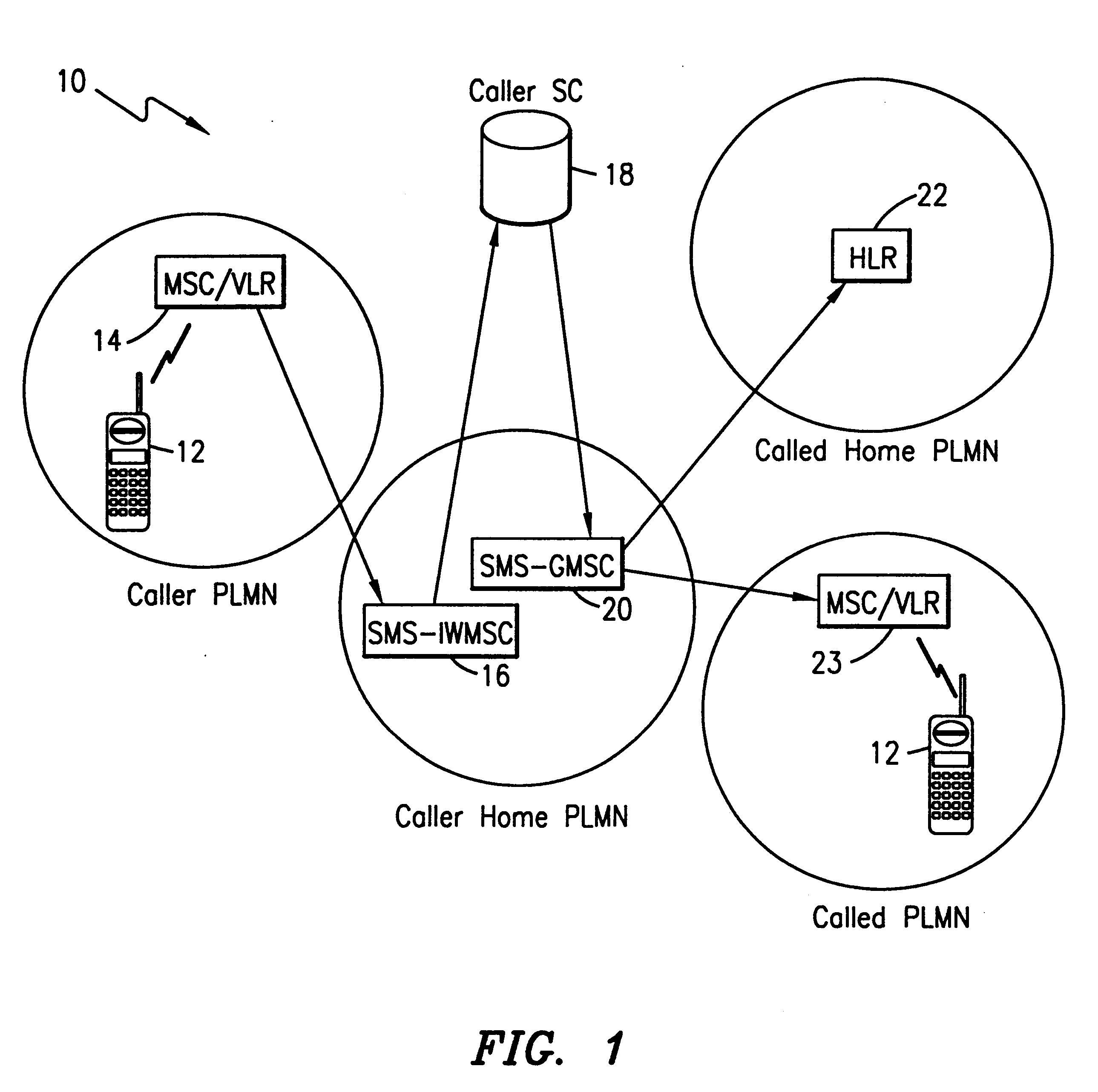
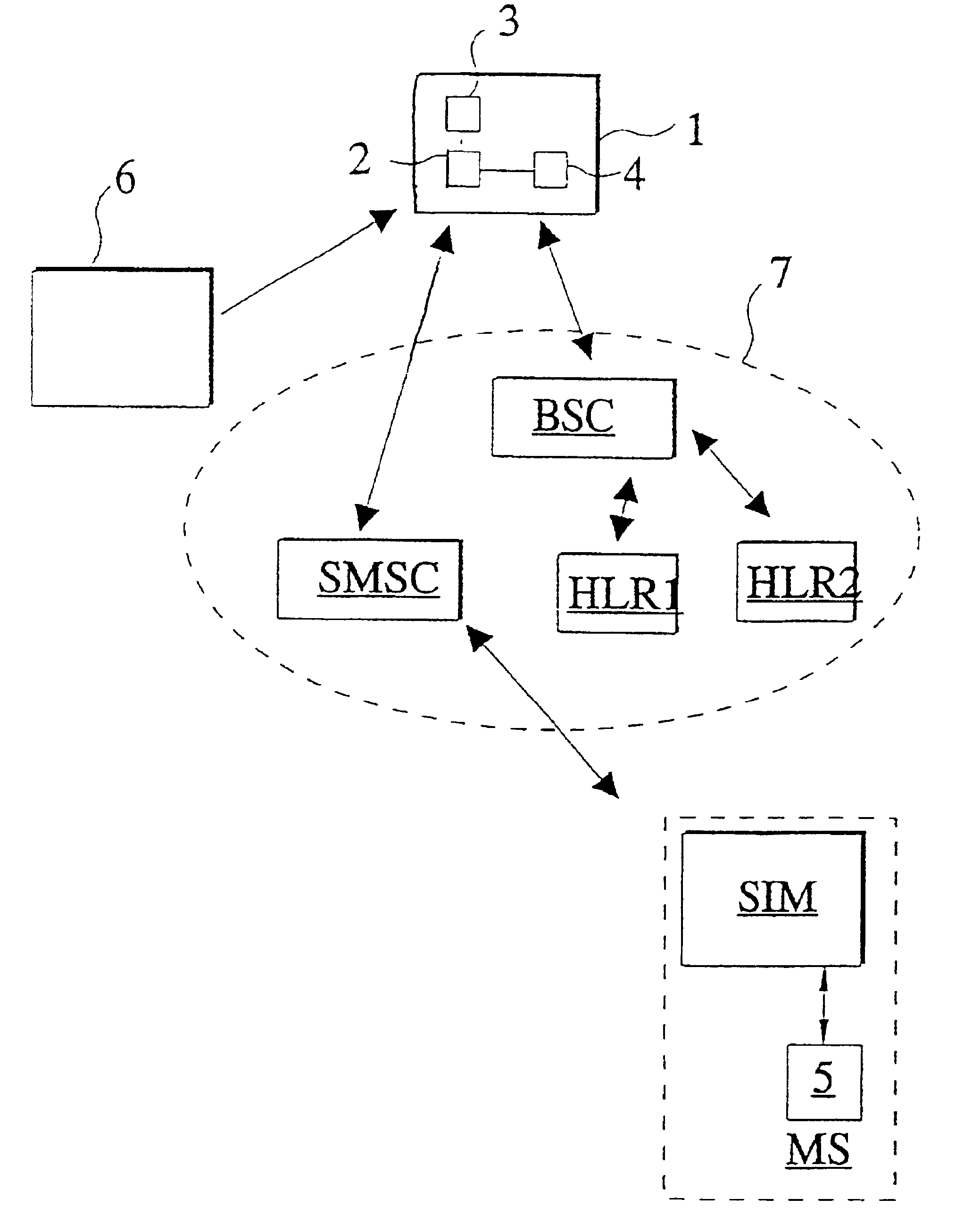
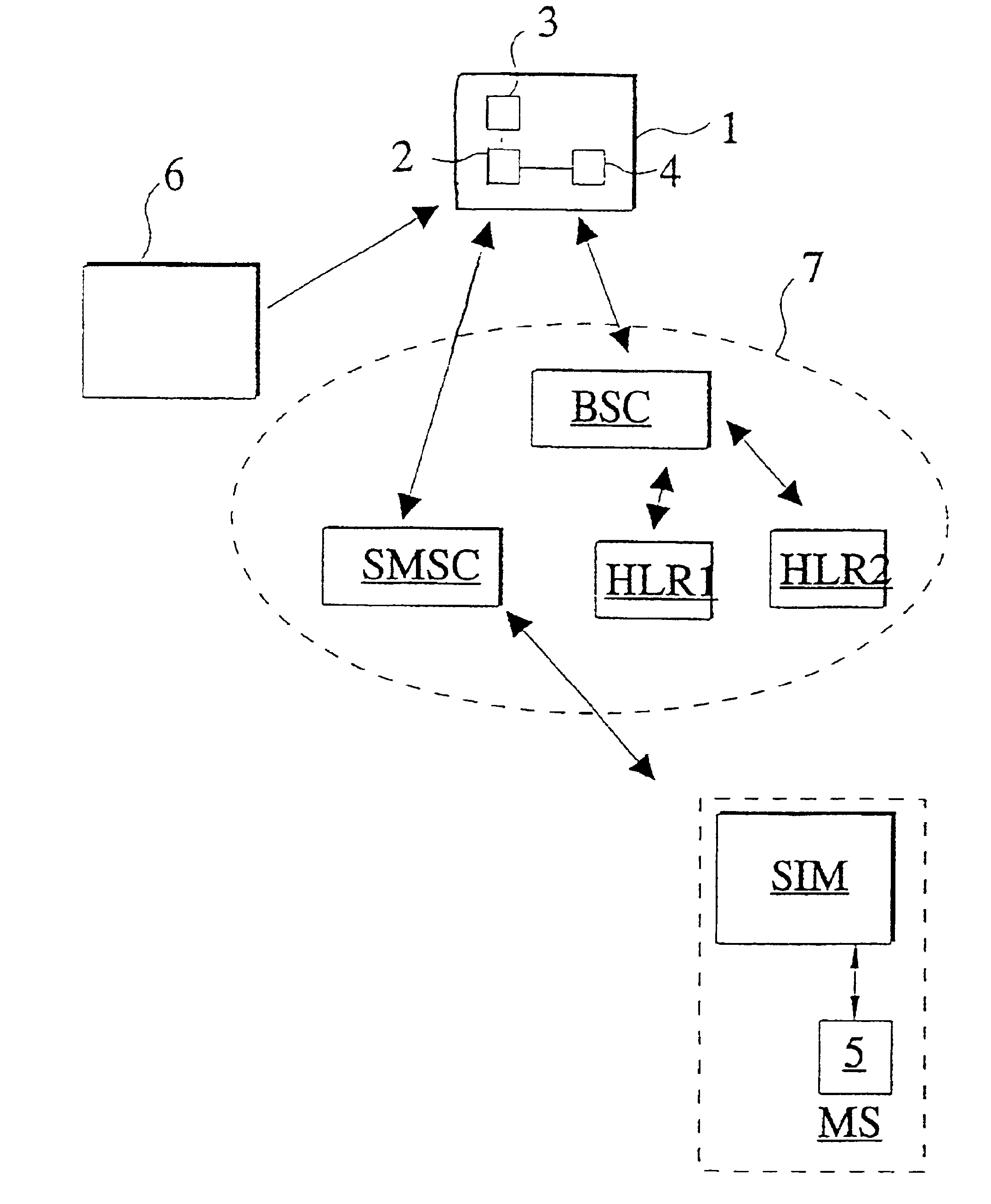
Method and apparatus for control of a subscriber identity module in a data communication system
InactiveUS6934391B1Avoid logistical problemFaster customer serviceUser identity/authority verificationHardware monitoringTransport systemCommunications system
A method and apparatus for the control of a subscriber identity module (SIM) in a data communication system, preferably a mobile communication system. The data communication system includes first and second subscriber registers (HLR1, HLR2) for maintaining subscriber records defining a subscriber identity module registry, a short message transmission system (SMSC) for transmission of messages in the communication system, and a mobile station (MS) connected to the subscriber identity module (SIM) for use by a subscriber in effecting mobile communications through the data communication system. The subscriber identity module (SIM) stores therein data comprising a first subscriber code (IMSI1) and an encrypted code key (Ki) corresponding to a first subscription for the mobile station subscriber and associated with the subscriber identity module A record of data corresponding to the first subscription is created in the first subscriber register (HLR1) when the first subscription is opened, the record comprising a first subscription specific call number (MSISDNx), the encryption code key (Ki) and a subscriber identity code (IMSI1) for the mobile station subscriber. A second subscription for the mobile station subscriber and associated with the subscriber identity module (SIM) is opened; a record corresponding to the opened second subscription and comprising a second subscription-specific call number (MSISDN), a second subscriber identity code (IMSI1) and the encryption key (Ki) is created in the second subscriber register (HLR2); a message (SMS) is sent through the communication system directed to the first subscription and instructing that the data stored in the subscriber identity module be changed from data corresponding to the first subscription to data corresponding to the second subscription.
Owner:SONERA
Controlled access to a wireless network
ActiveUS8509767B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsRemote system
Owner:PARTNER ONE ACQUISITIONS INC
Multimedia message service apparatus
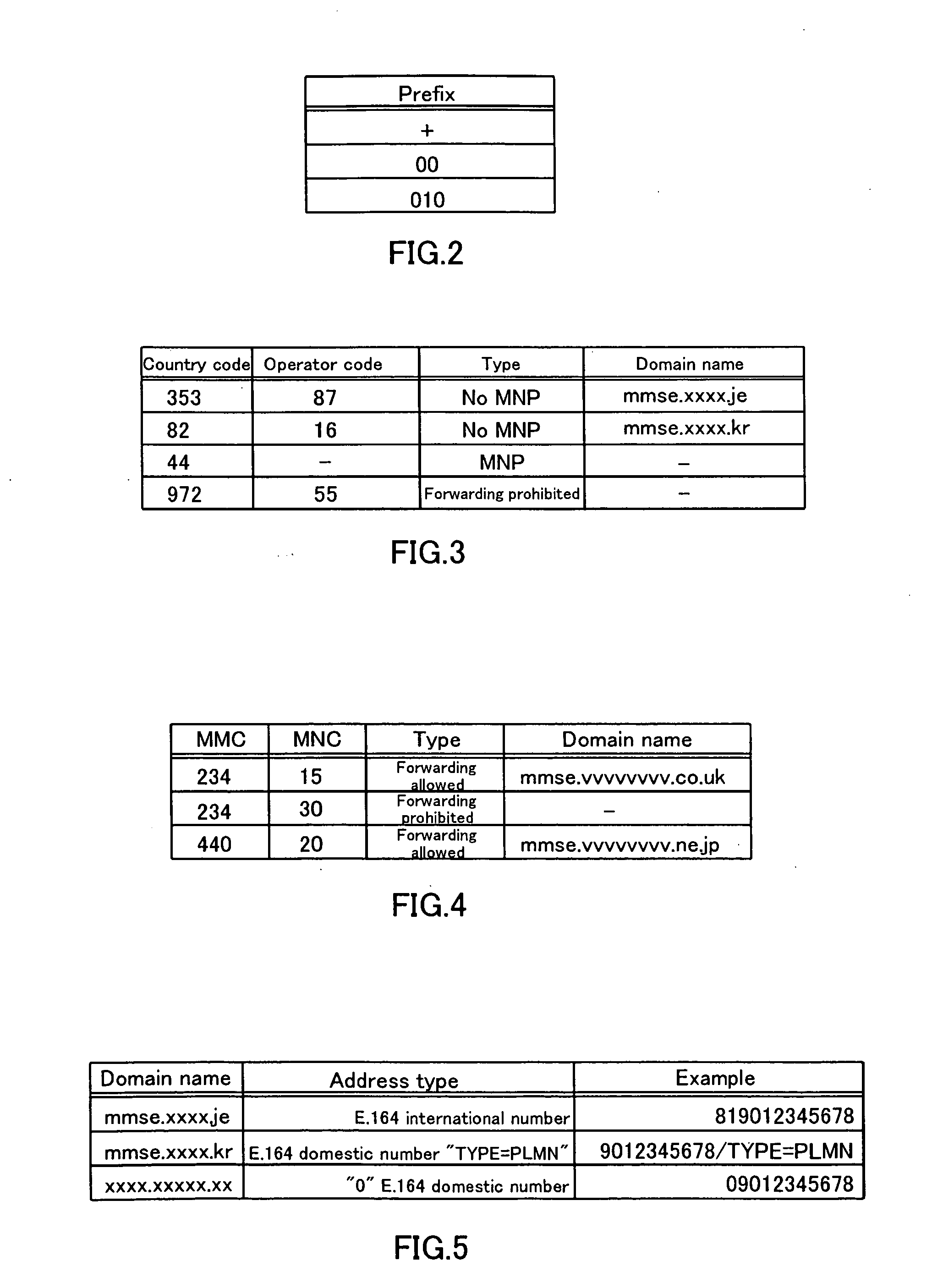
InactiveUS20060053197A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersDomain nameRouting table
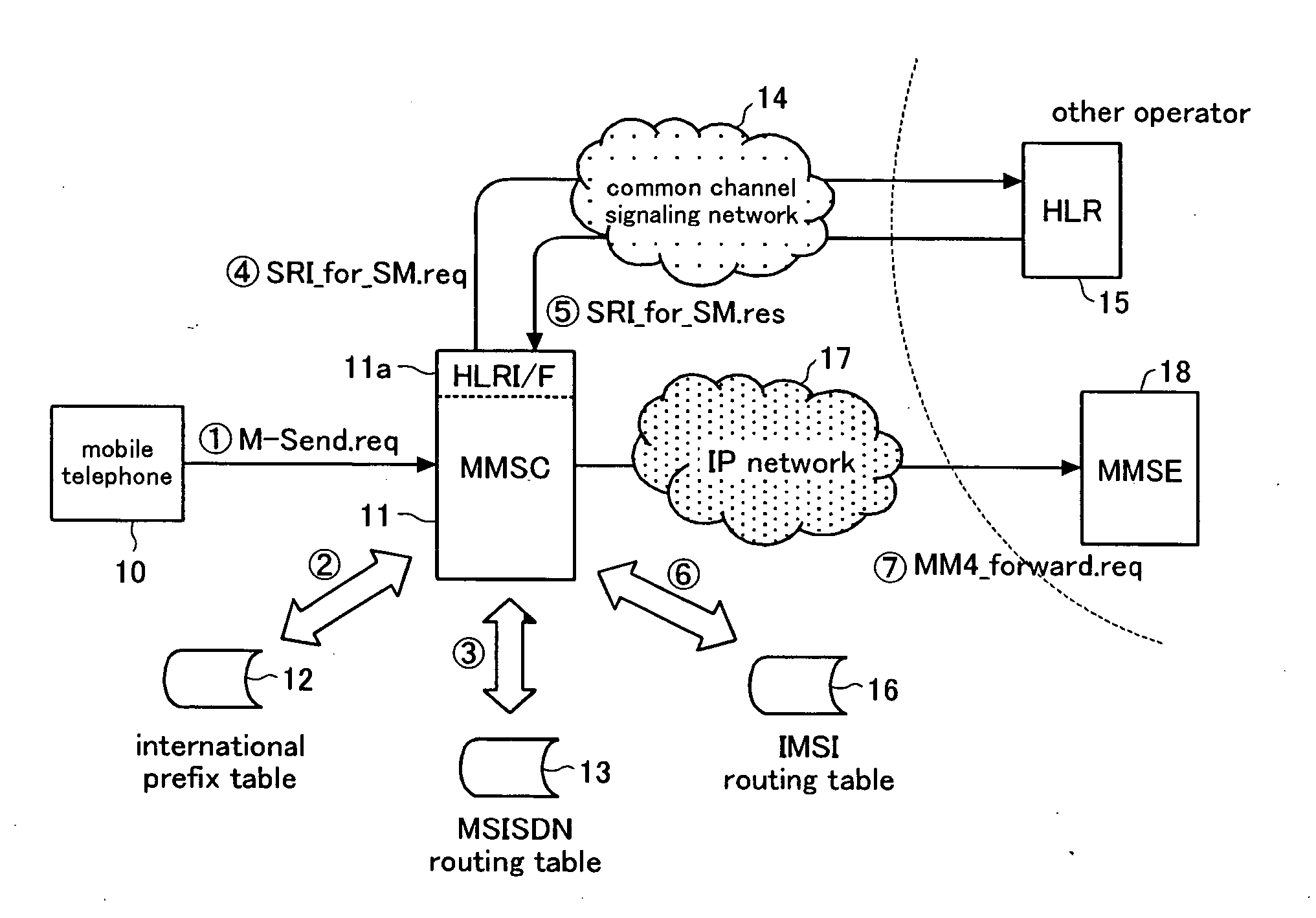
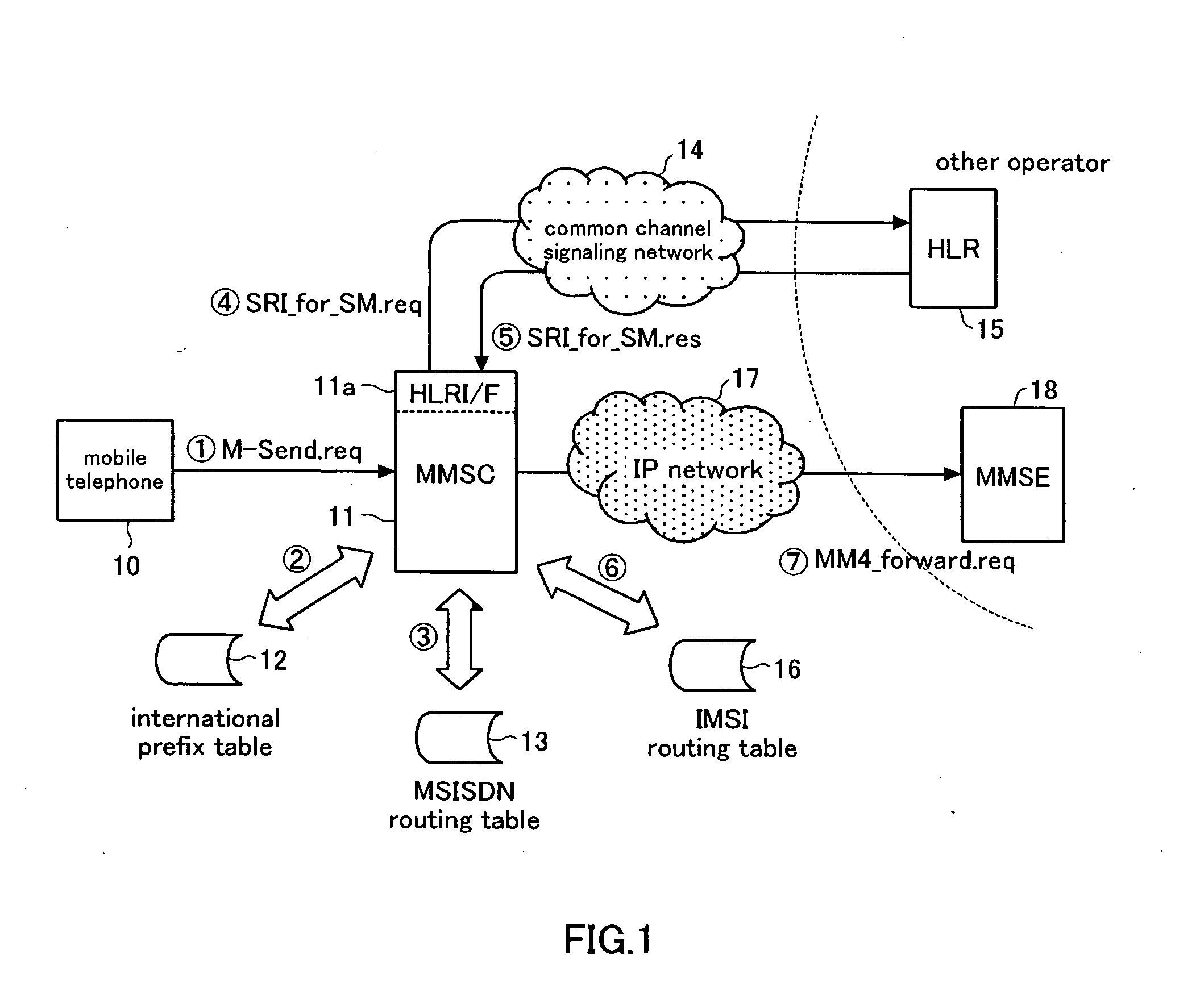
With the object of making it possible to generate international multimedia message calls, an MMSC 11 determines from the destination MSISDN of the header of a multimedia message that the call is an international transmission and, at the same time, determines whether or not the forwarding destination supports number portability, by referencing the MSISDN routing table 13. If number portability is supported, it acquires the IMSI corresponding to the destination MSISDN by inquiring the HLR 15. Next, the MMSC 11 acquires the domain name of the MMSE of the forwarding destination by referencing the IMSI routing table 16 from the IMSI that has thus been acquired and forwards the multimedia message to this MMSE. If number portability is not supported, it forwards the multimedia message to the MMSE of the domain name acquired by referencing the MSISDN routing table 13.
Owner:VODAFONE GRP PLC
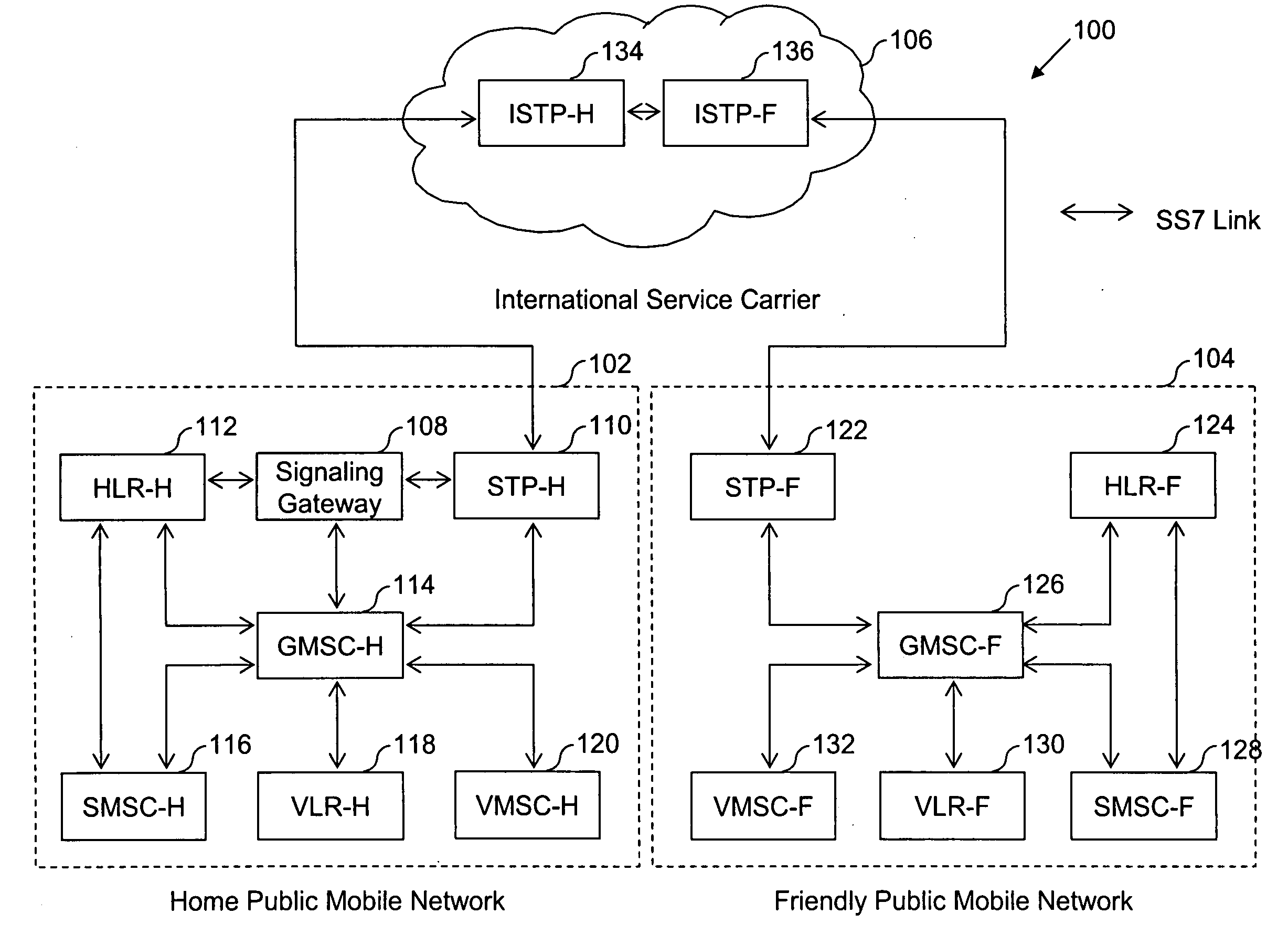
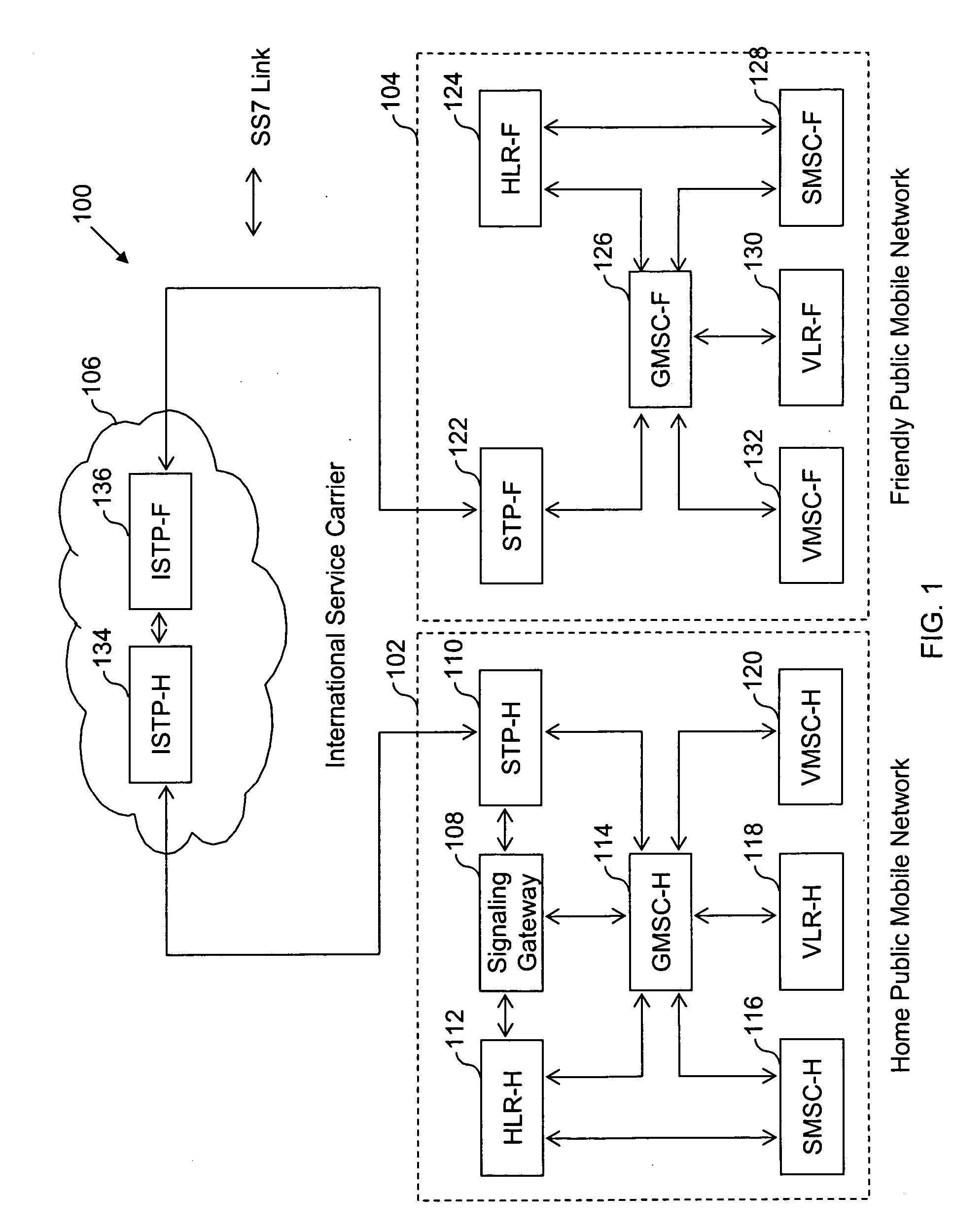
Method and system for providing mobile communication corresponding to multiple MSISDNs associated with a single IMSI
InactiveUS20070213075A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesDirectory numberBiological activation
The present invention proposes a method for mobile communication. The method includes assigning one or more Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Numbers (MSISDNs) to a subscriber of a Home Public Mobile Network (HPMN) upon receiving a subscription activation message from the subscriber at a Signaling Gateway (SG). The subscriber has an HPMN Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) with a corresponding HPMN International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and an HPMN MSISDN. The method further includes creating an association of the MSISDNs with the HPMN MSISDN to facilitate signaling corresponding to the HPMN MSISDN and the MSISDNs associated with the subscriber.
Owner:ROAMWARE
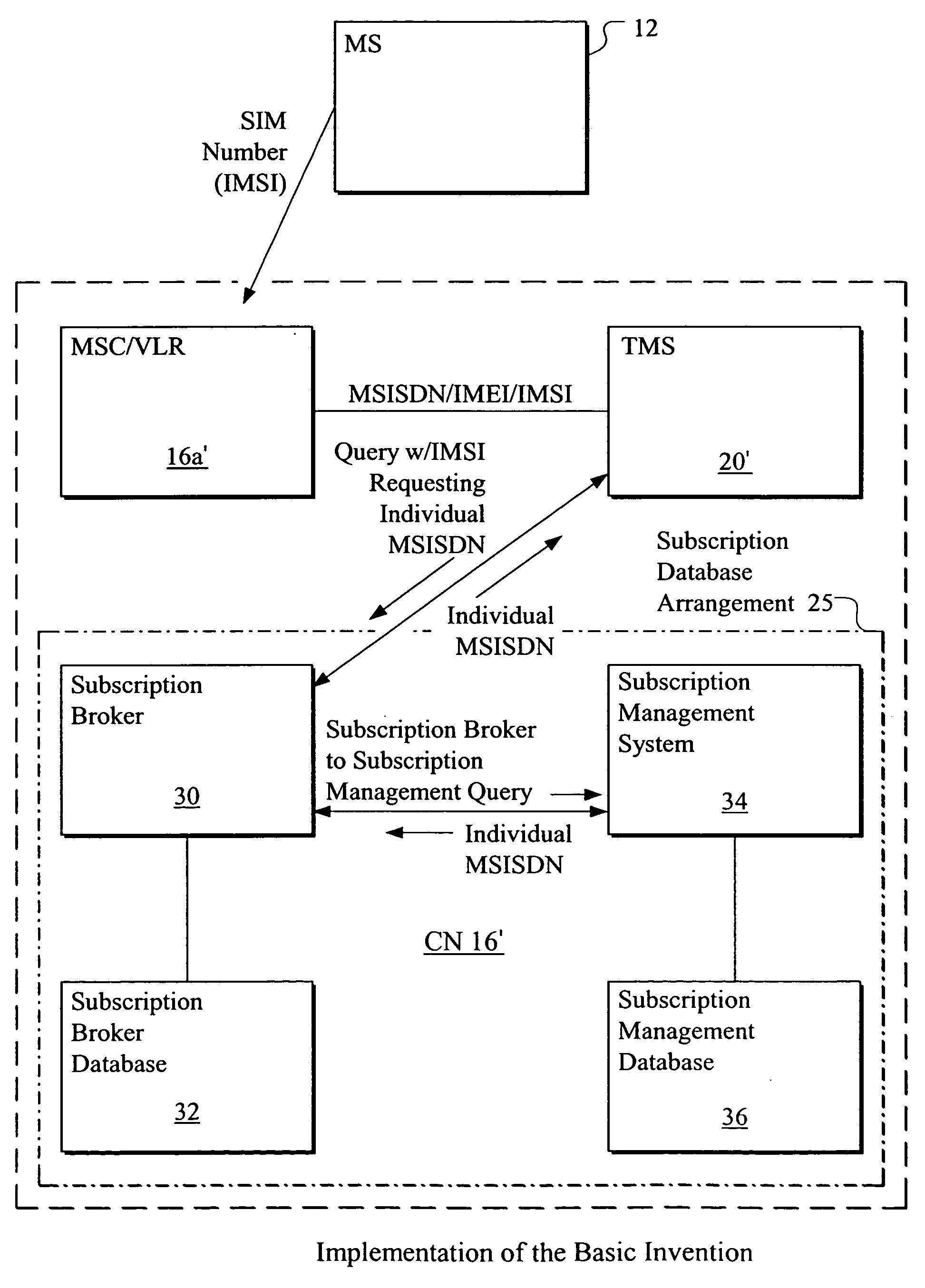
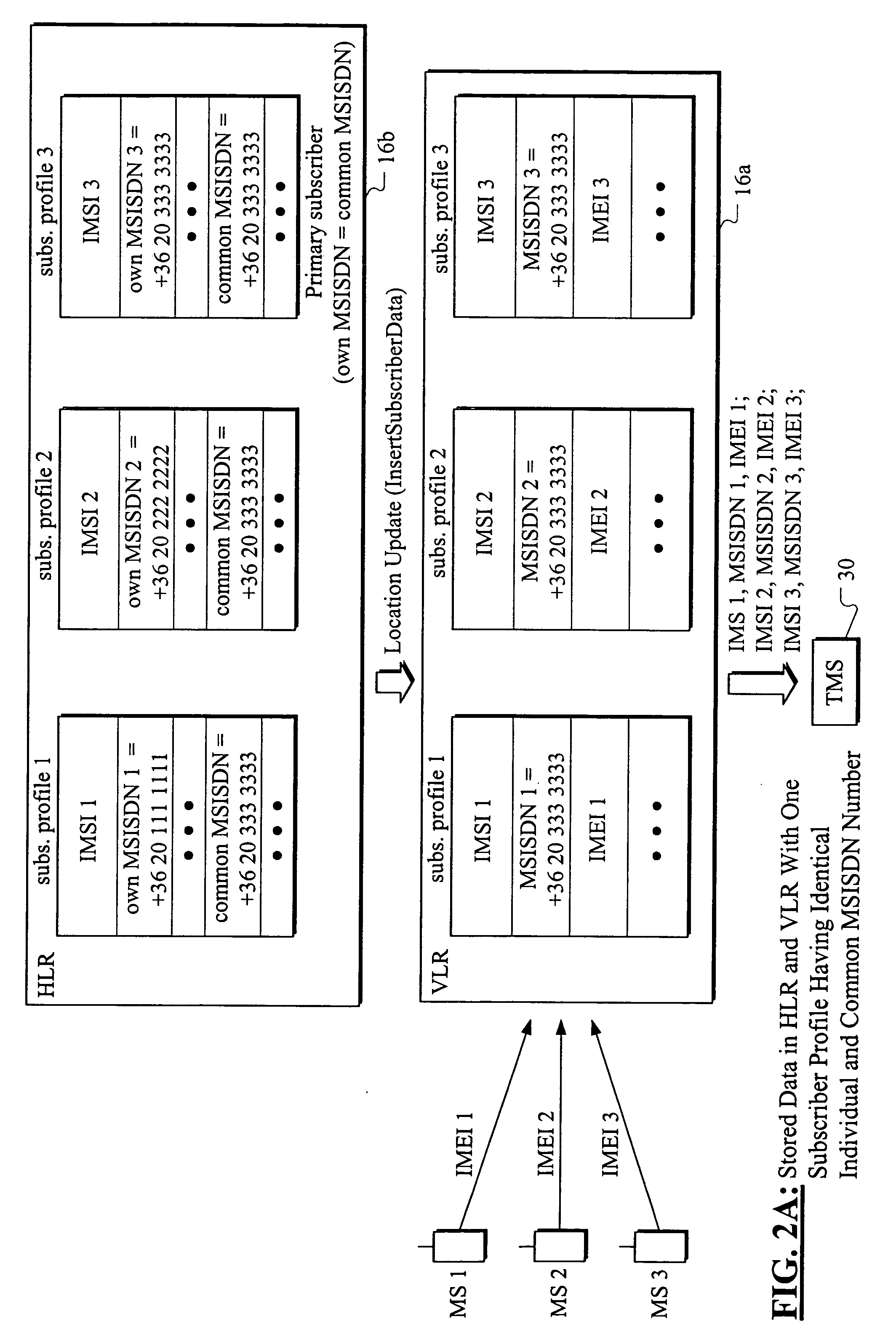
Method and apparatus for determining individual or common mobile subscriber number in mobile network for handling multiple subscribers having the same calling line identity
InactiveUS20040180676A1Special service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsIntegrated Services Digital NetworkMobile Web
The present invention provides a mobile network for handling multiple subscribers having the same calling line identity. Each multiple subscriber has an individual mobile subscriber number and a common mobile subscriber number that can be used to replace the individual mobile subscriber number. One mobile subscriber has an identical individual and common mobile subscriber number, and the mobile network receives a mobile subscriber number from a multiple subscriber. The mobile network has a terminal management server that determines whether the mobile subscriber number is either the individual mobile subscriber number or the common mobile subscriber number. Each individual mobile subscriber number and common mobile subscriber number is a Mobile Subscriber Integrated Services Digital Network (MSISDN) number. The mobile subscriber number is used during a location update procedure.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
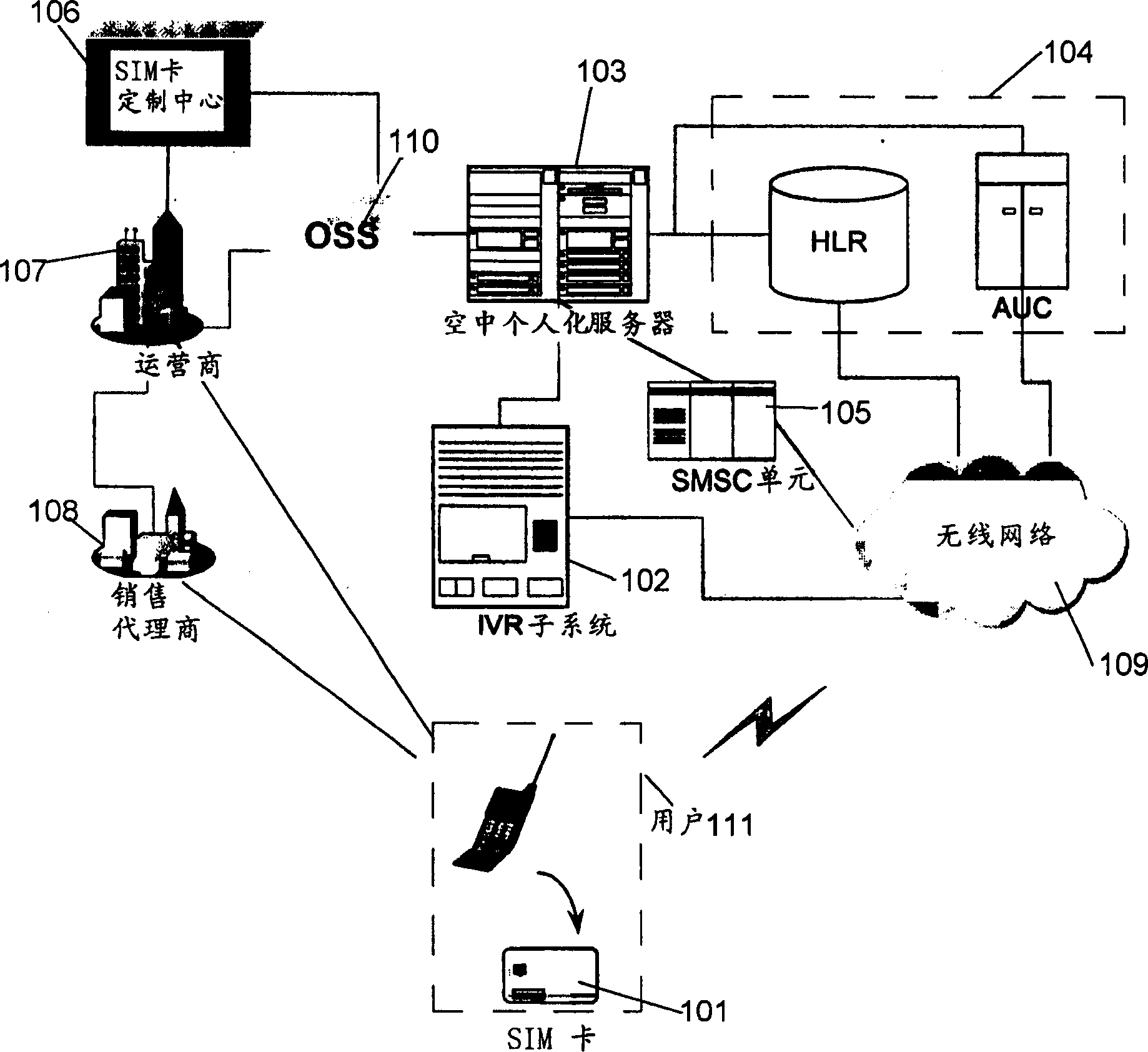
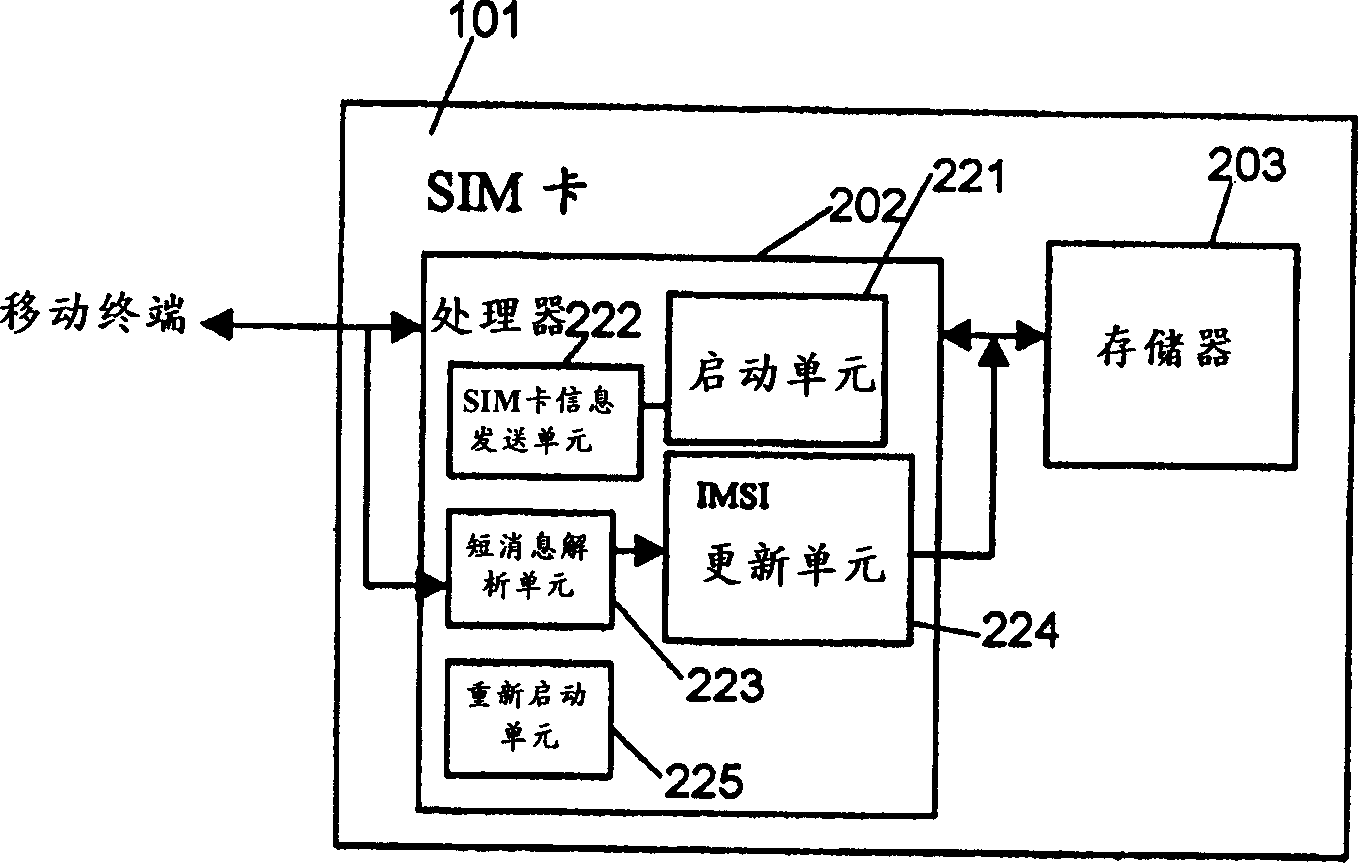
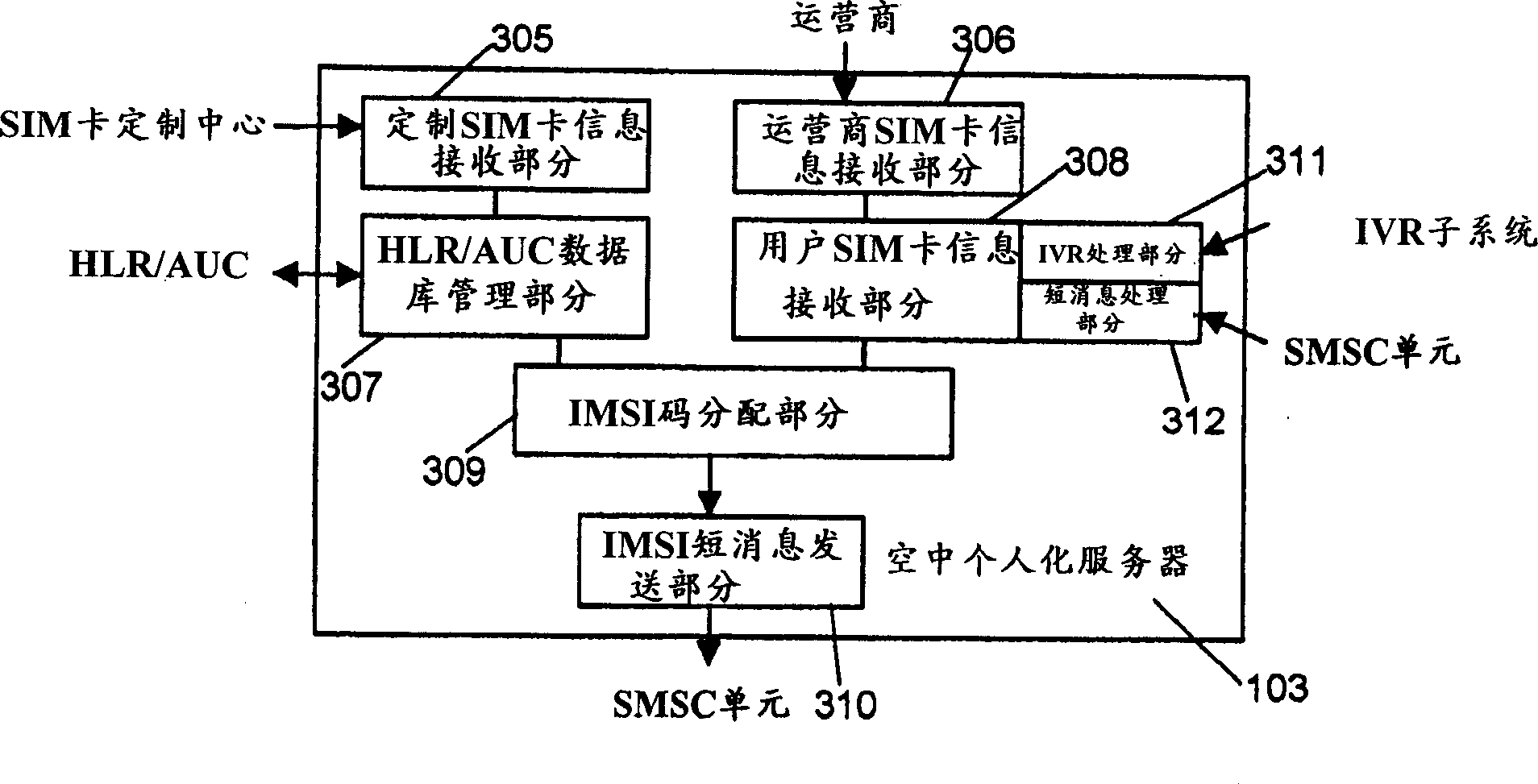
User identification module card, method for activating user identification module card in sky and its system
InactiveCN1444414ARemove restrictionsImprove utilization efficiencyUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSpecial service for subscribersComputer moduleSubscriber identity module
A method for aerial activating SIM card and system and SIM card is to make SIM card distribute a false IMSI code to each SIM card, runners assigns a MSISDN number to every SIM card to transfer SIM information including MSISDN number and the false IMSI code to OTA server recording the SIM card information in GLR / AUC and activate the user when selling a SIM card. When a mobile terminal is on, it transfers the above mentioned tow codes to OTA to assign a new IMSI code to SIM card and renew records of users at HLR / AUC. The OTA sends short message about new IMSI code to user terminal and renew IMSI code and restart the mobile terminal with IMSI code.
Owner:斯伦贝谢(北京)智能卡科技有限公司
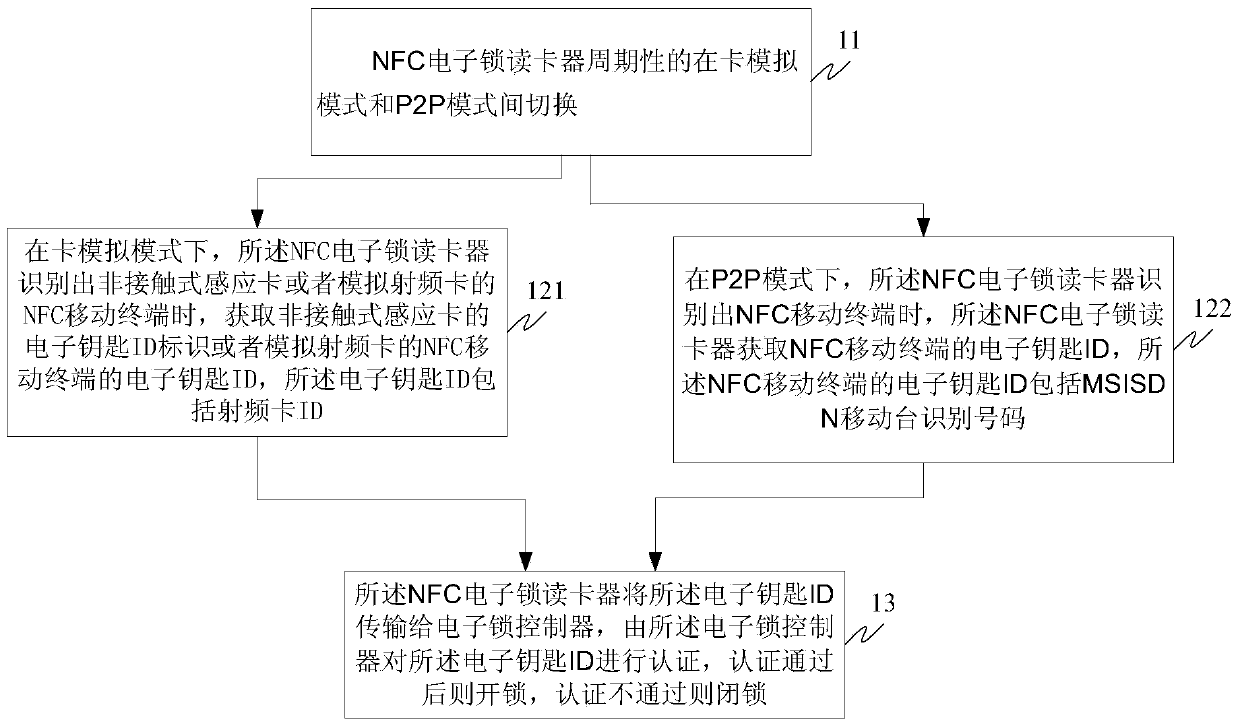
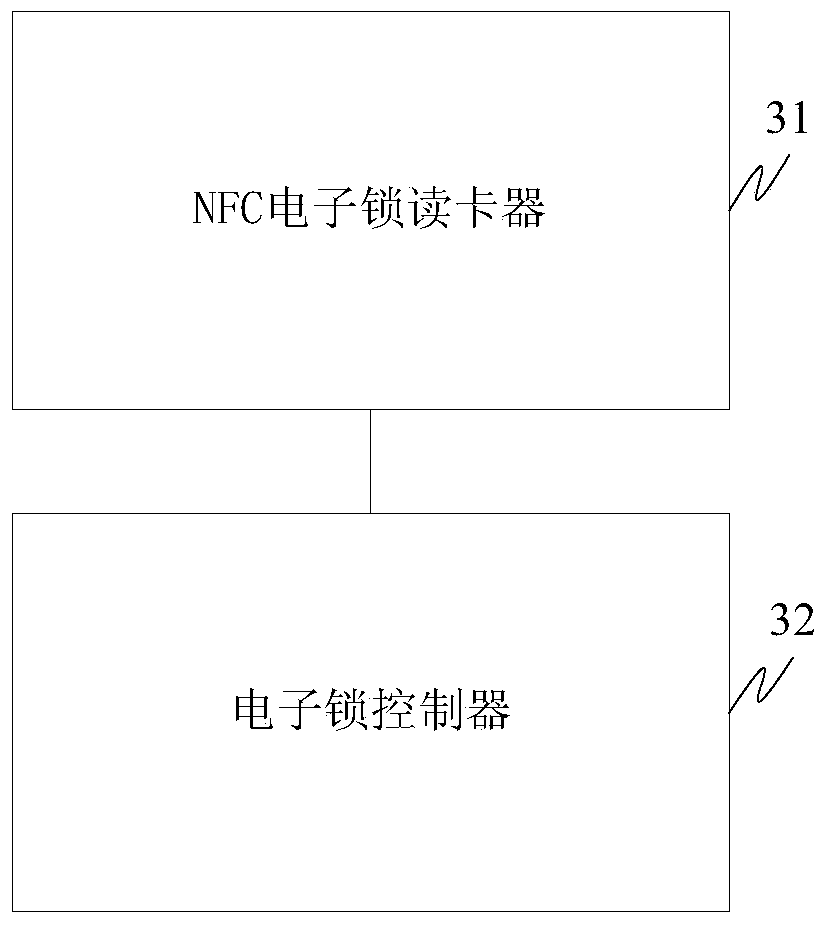
Realization method and system of NFC (near field communication) electronic lock and NFC electronic lock card reader
InactiveCN103778705AReduce Legal RiskReduce use costIndividual entry/exit registersComputer terminalCard reader
The invention discloses a realization method and system of an NFC (near field communication) electronic lock and an NFC electronic lock card reader. The method comprises the following steps: the NFC electronic lock card reader is periodically switched between a card simulation mode and a P2P (peer-to-peer) mode; in the card simulation mode, the NFC electronic lock card reader obtains the electronic key ID of a non-contact induction card or the electronic key ID of an NFC mobile terminal simulating a radio frequency card, wherein the electronic key ID includes the card ID; in the P2P mode, the NFC electronic lock card reader obtains the electronic key ID of the NFC mobile terminal, wherein the electronic key ID of the NFC mobile terminal includes MSISDN; the NFC electronic lock card reader transmits the electronic key ID to an electronic lock controller which authenticates the electronic key ID; and if the electronic key ID passes the authentication, the lock is opened; otherwise, the lock is shut. The electronic lock is opened by the NFC mobile terminal.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGTAI FANGXIN TECH
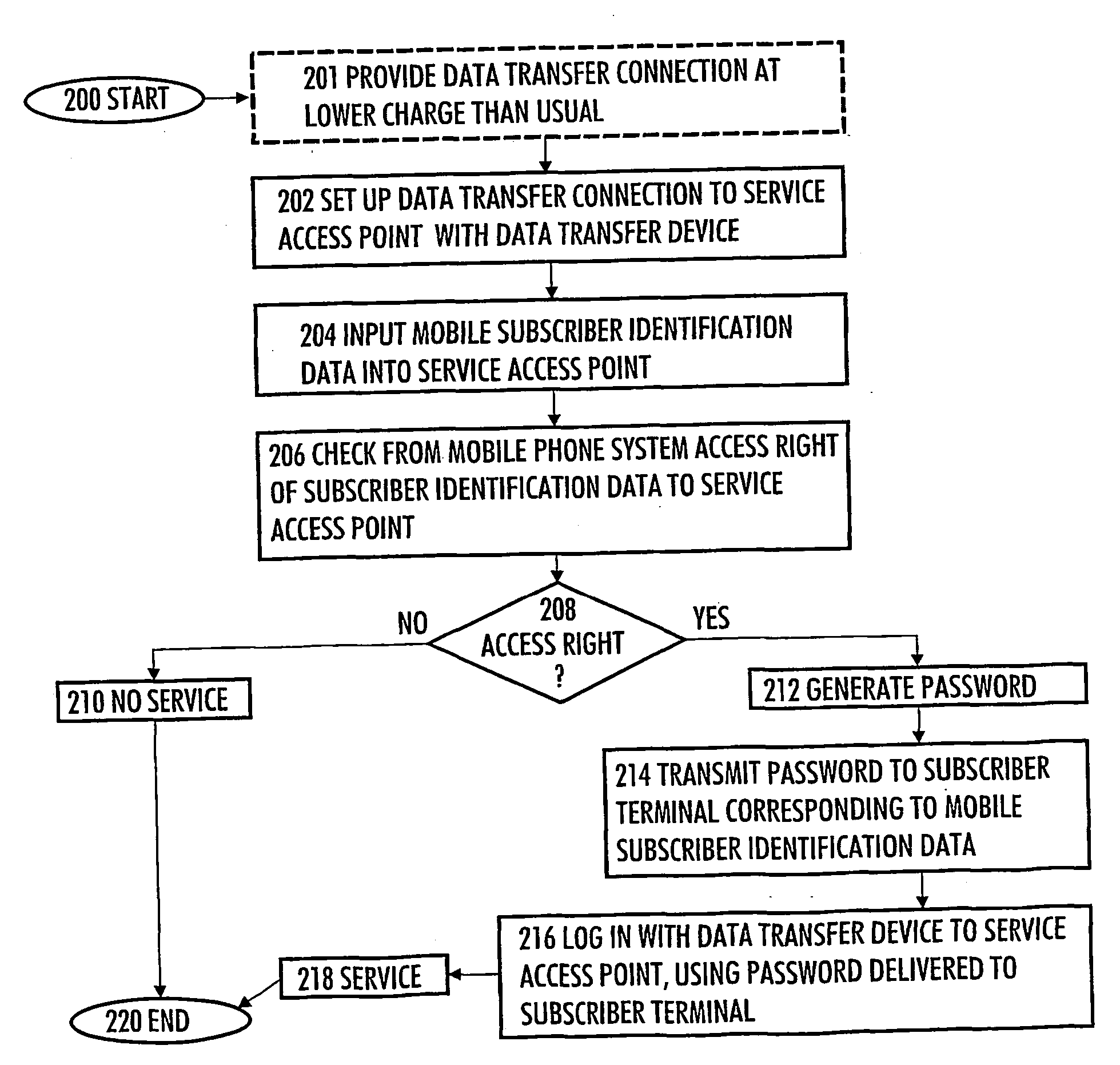
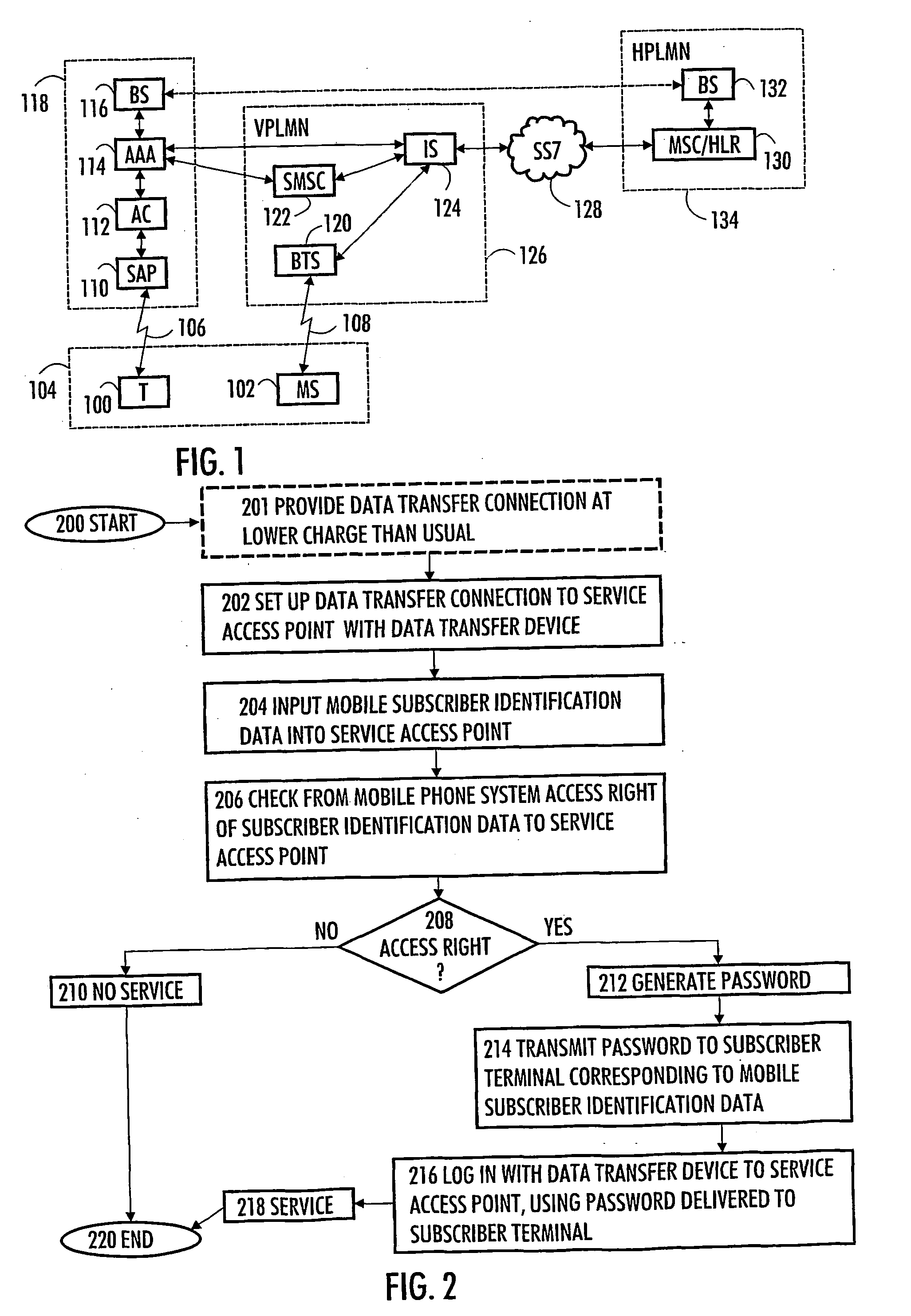
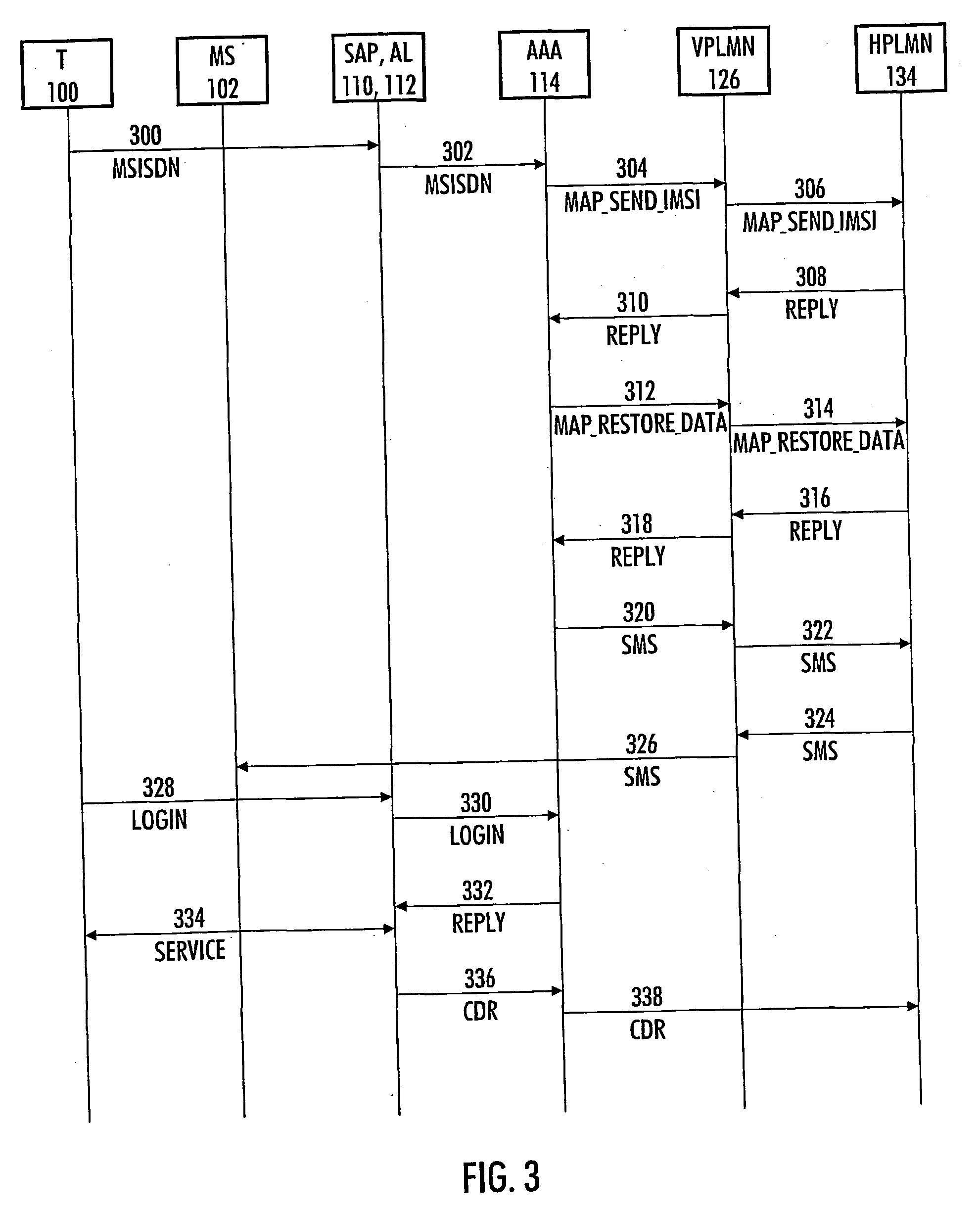
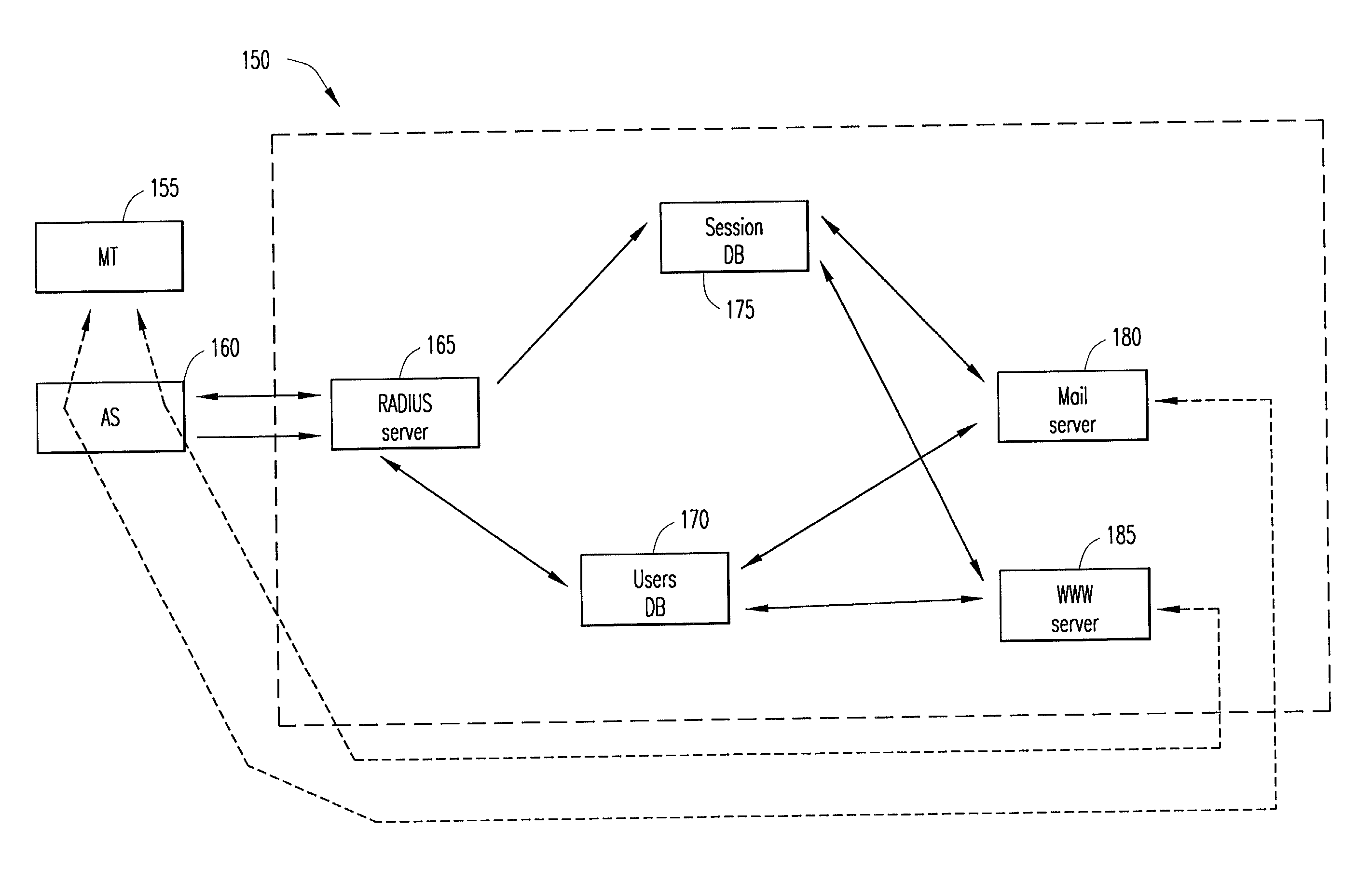
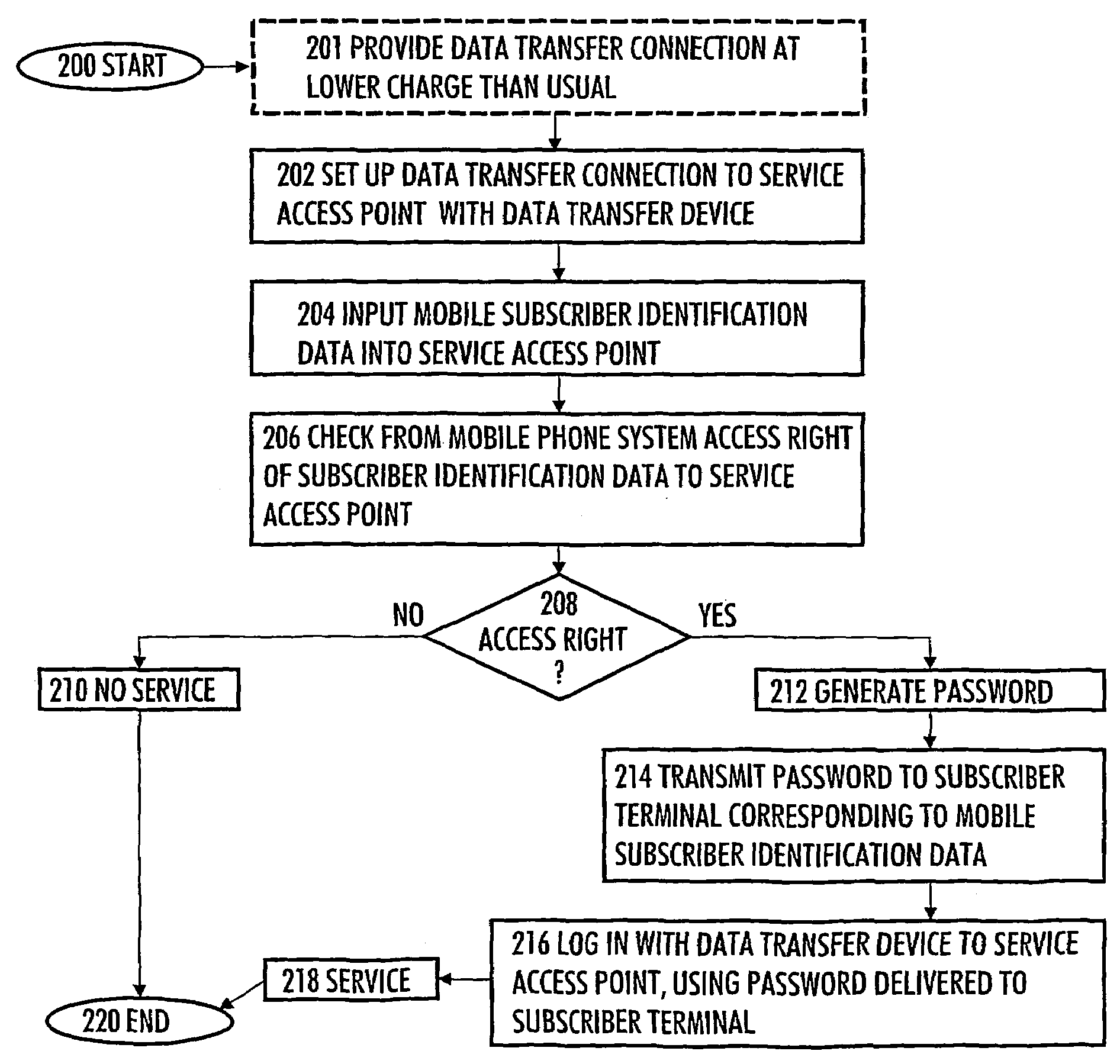
Method and system for authenticating user of data transfer device
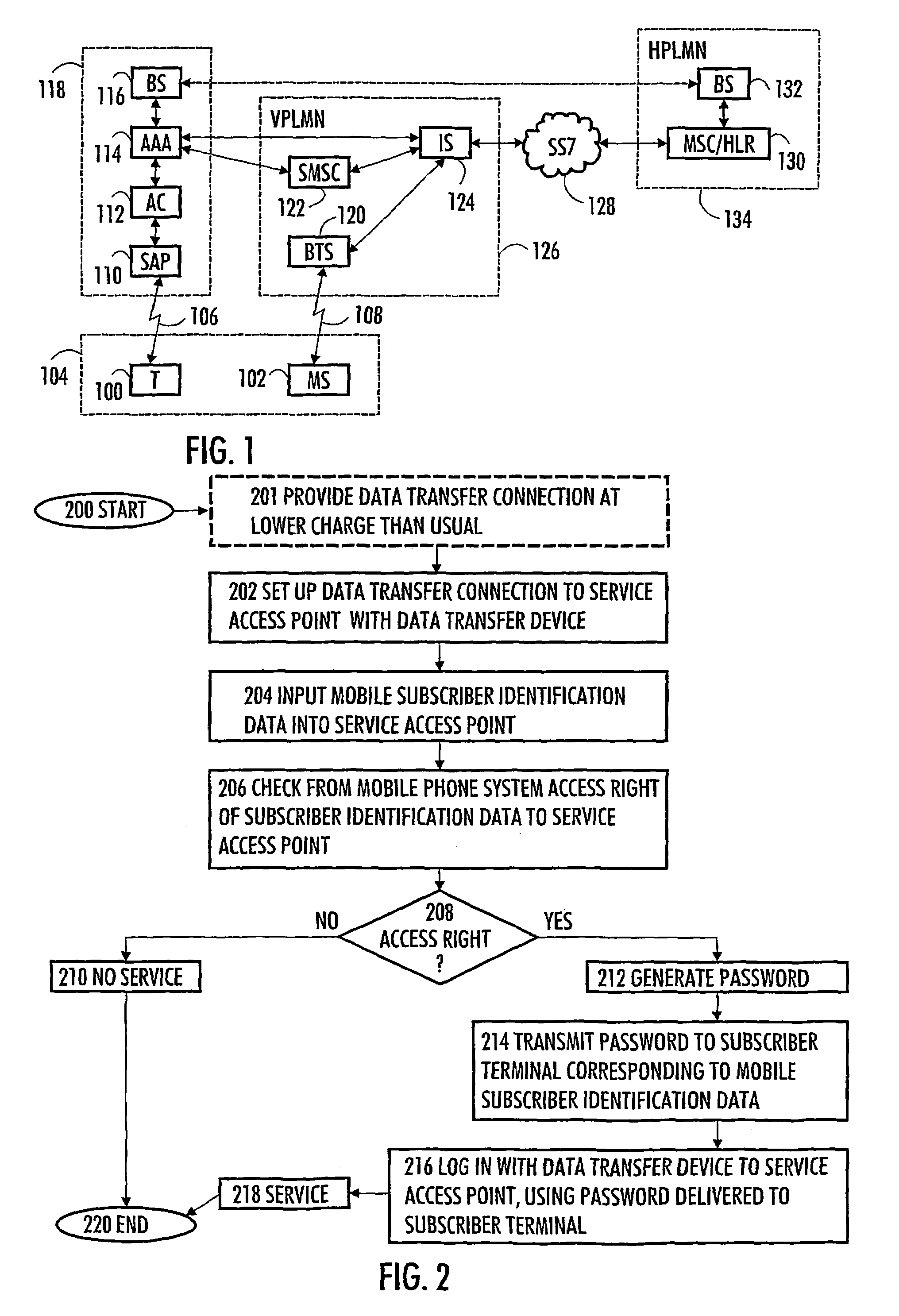
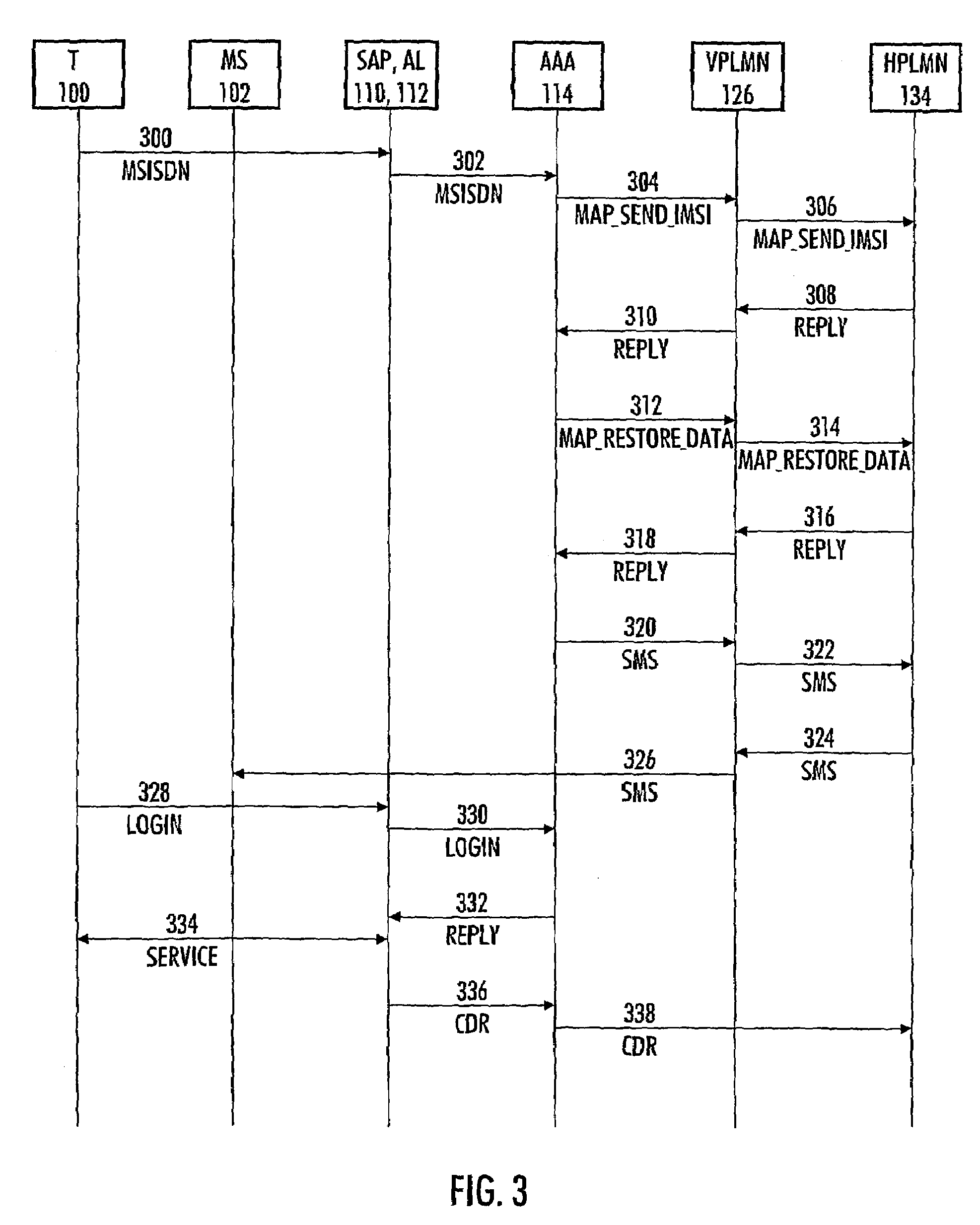
ActiveUS20050176407A1Convenient for operatorsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCommunications systemPassword
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and system for reducing call setup by roaming number caching
InactiveUS6408181B1Reduce processing requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentSystem capacityProcessor register
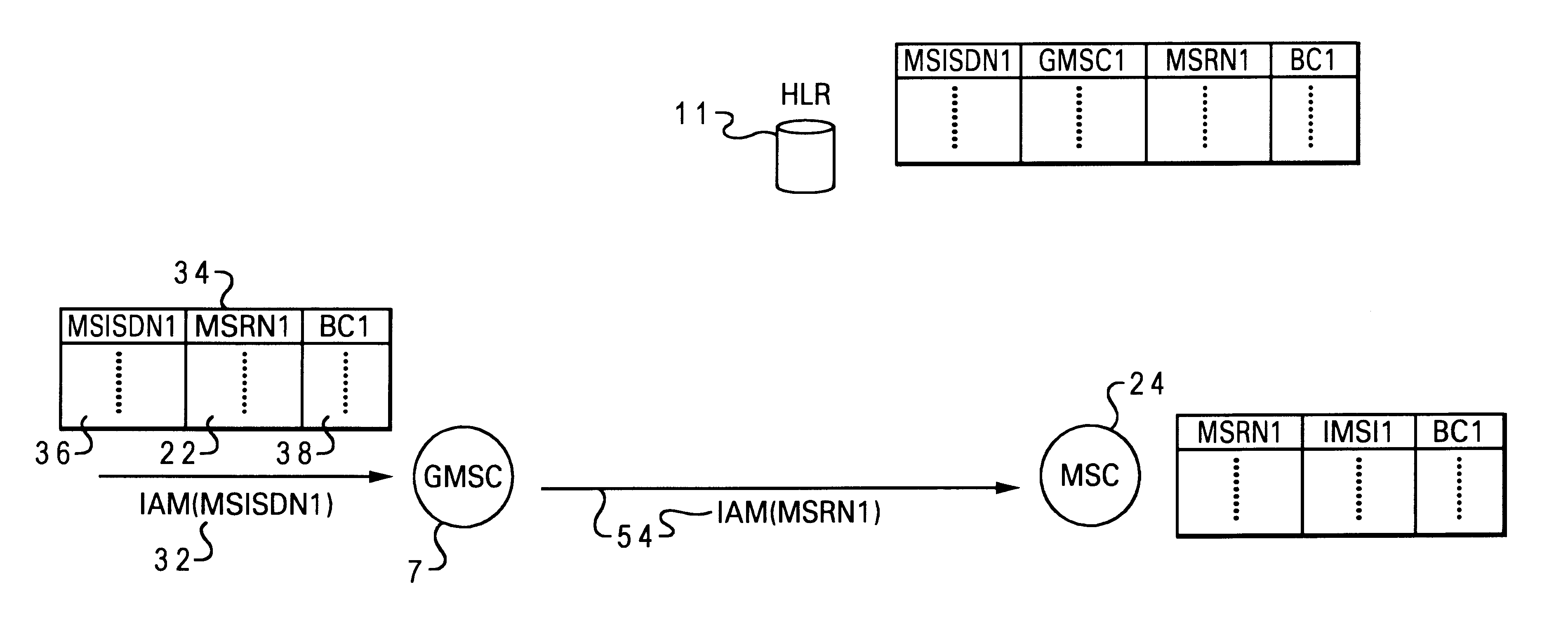
A method and system for improving overall system capacity in GSM networks by reducing the number of home location register and visitor location register queries is disclosed. The method and system allows the reuse of the MSRN by allocating the MSRN to a mobile terminal and using it for future calls. The method of the present invention allows the GMSC to cache the MSRN for a called mobile terminal. During a first call setup, an entry is recorded at a cache register that maps the Mobile Subscriber ISDN Number (MSISDN) of the mobile terminal to a previously allocated MSRN. Additionally, the Bearer Capability (BC) associated with this MSRN is also recorded in the cache register. When the next call arrives, the GMSC first checks if a MSRN for that called mobile terminal already exists in its cache register. If a cached MSRN is available and the BC associated with the cached MSRN matches the BC requested by the current call, then the GMSC uses the cached MSRN to route the call to the VMSC. The method and system of the present invention makes it unnecessary to query the HLR and VLR when a land-to-mobile call arrives thereby increasing network capacity while reducing processing load.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
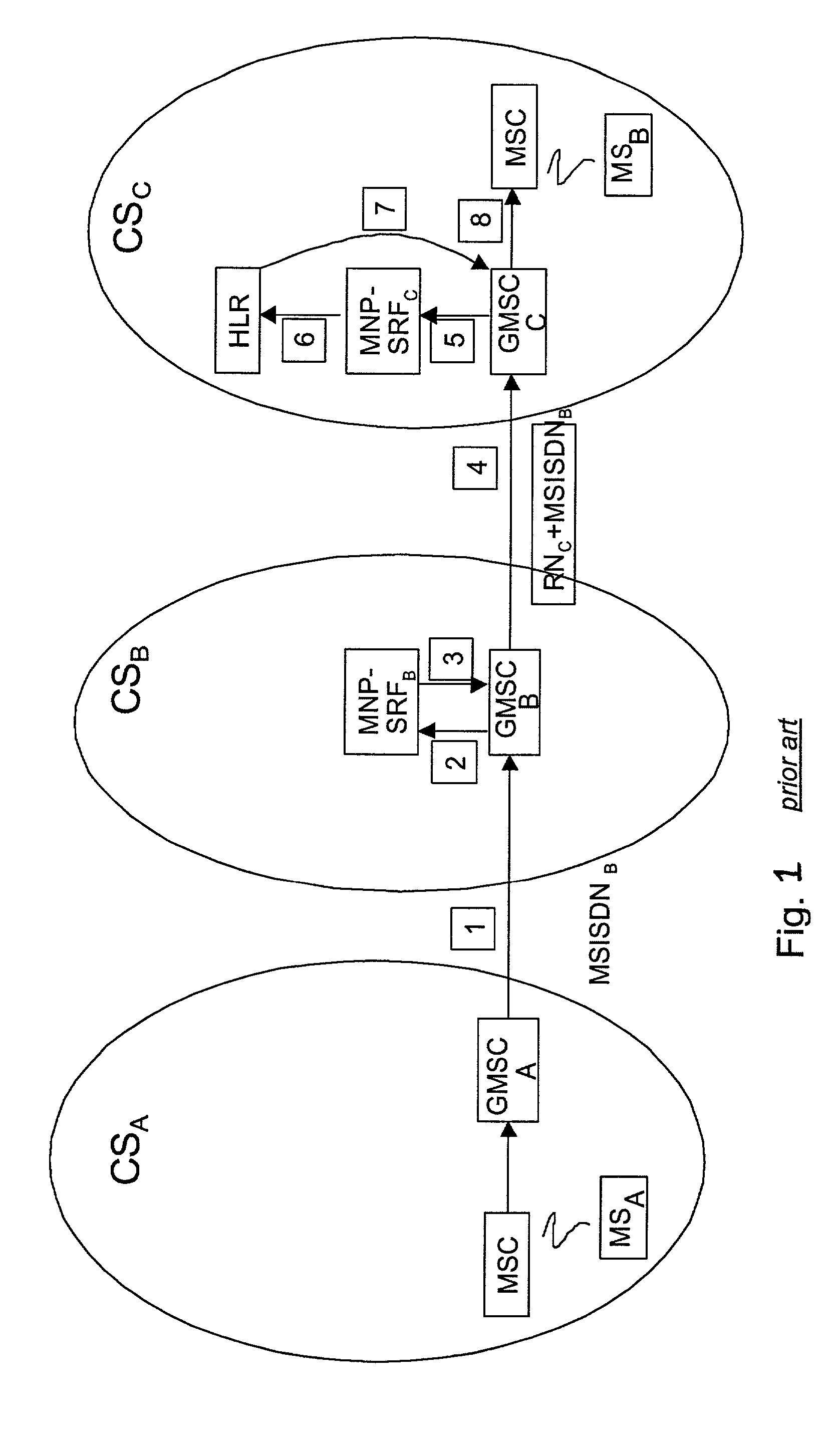
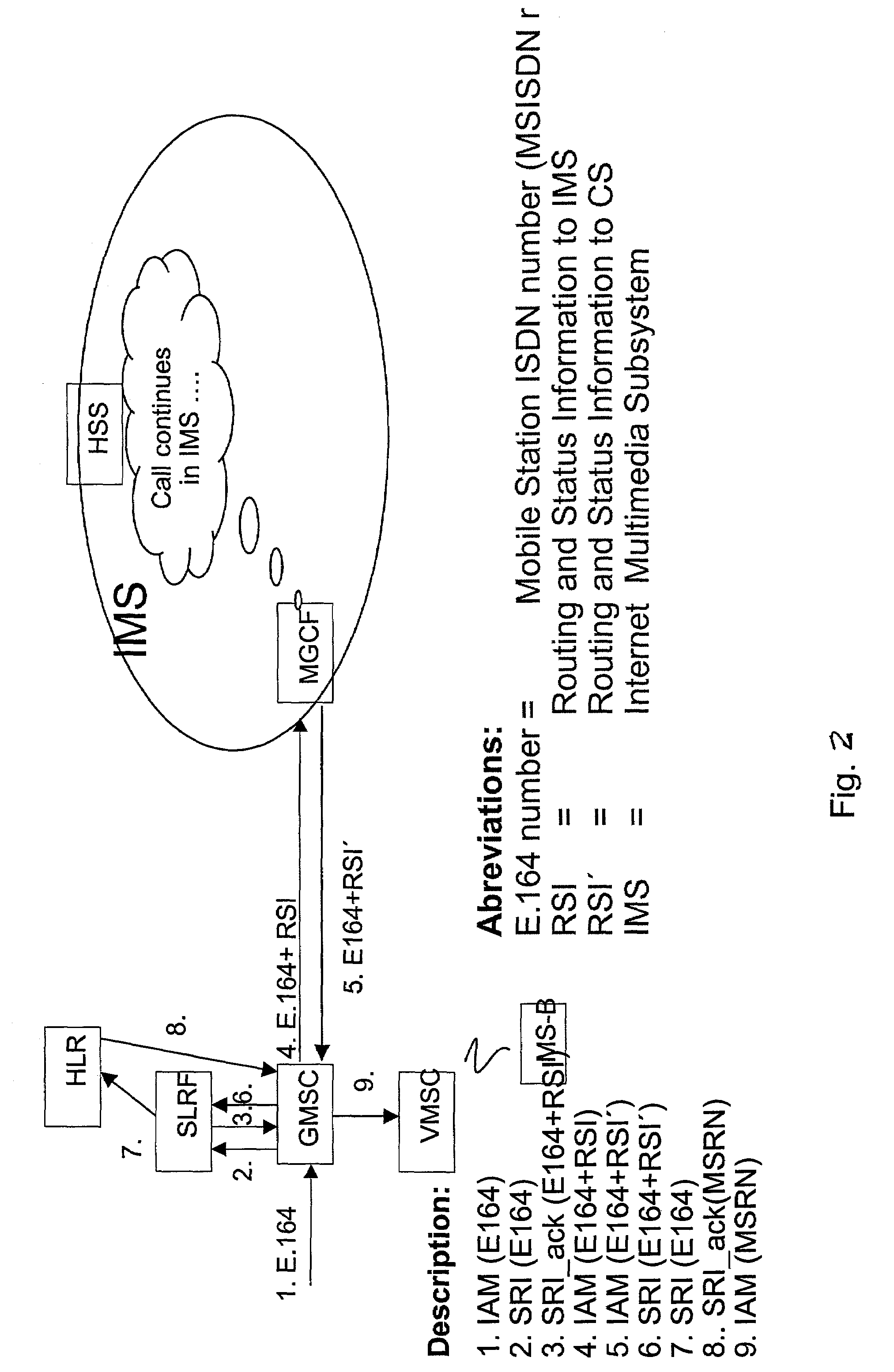
Routing a call between different types of networks
ActiveUS7027433B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCall routingComputer science
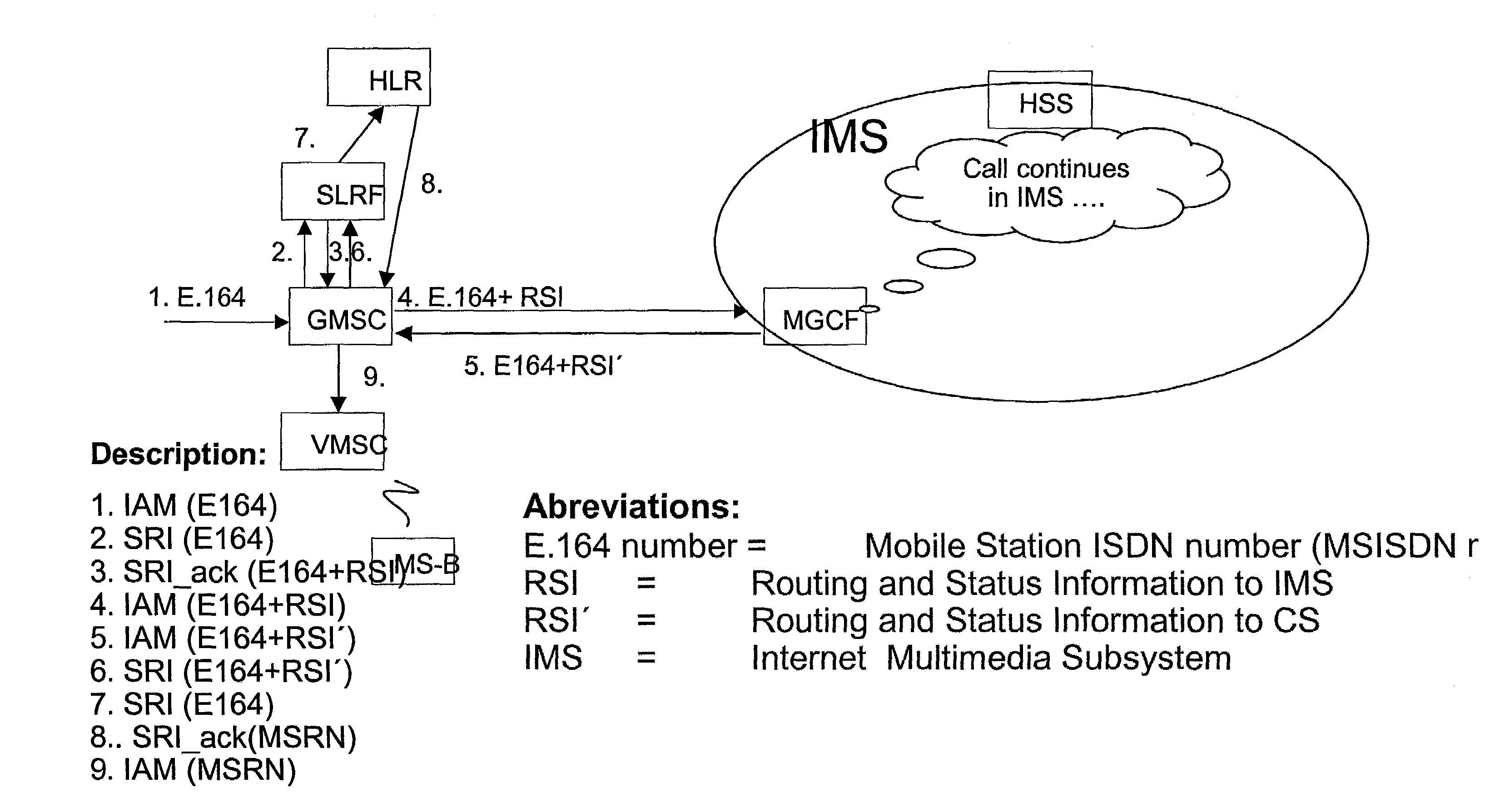
The basic idea is to enhance functionality of the Signaling Relay Function for support of MNP (MNP-SRF) so that the normal HLR query in the circuit switched domain is bypassed and the call is routed to an IMS domain. The SLRF, upon receipt from a GMSC a SRI message containing the real MSISDN number of the called party, translates the MSISDN number to a new MSISDN number and responds to the query by sending a message containing routing information to the IMS domain and the new MSISDN number. Alternatively, the original MSISDN number is used in the response message but a certain identifier is then added into the message. Then the called subscriber is first tried to reach in the IMS domain where the subscriber is likely residing. In case the subscriber yet resides in the circuit switched domain the call is routed from the IMS domain back to the circuit switched domain and not until then the normal HRL query is performed.
Owner:III HLDG 3
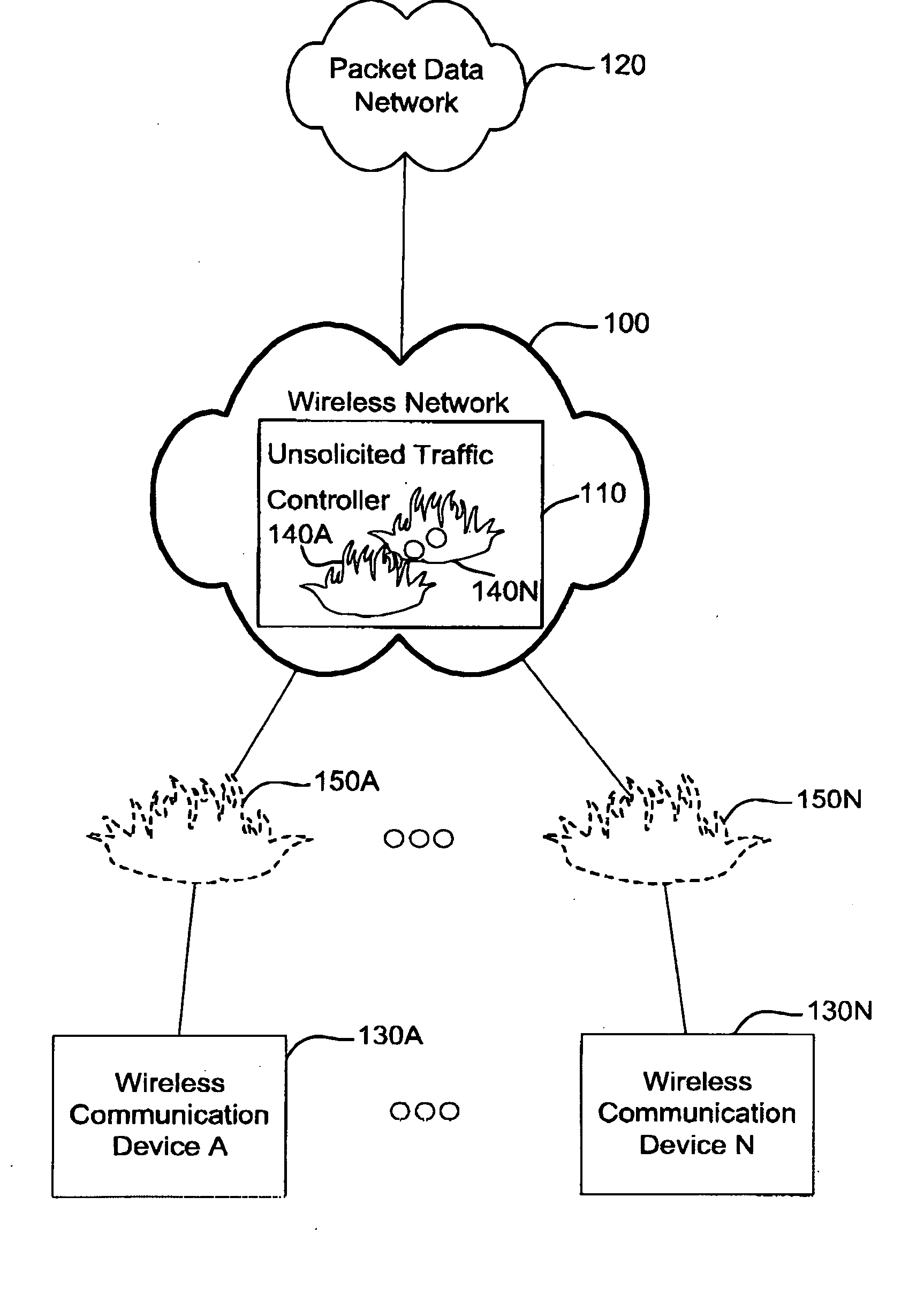
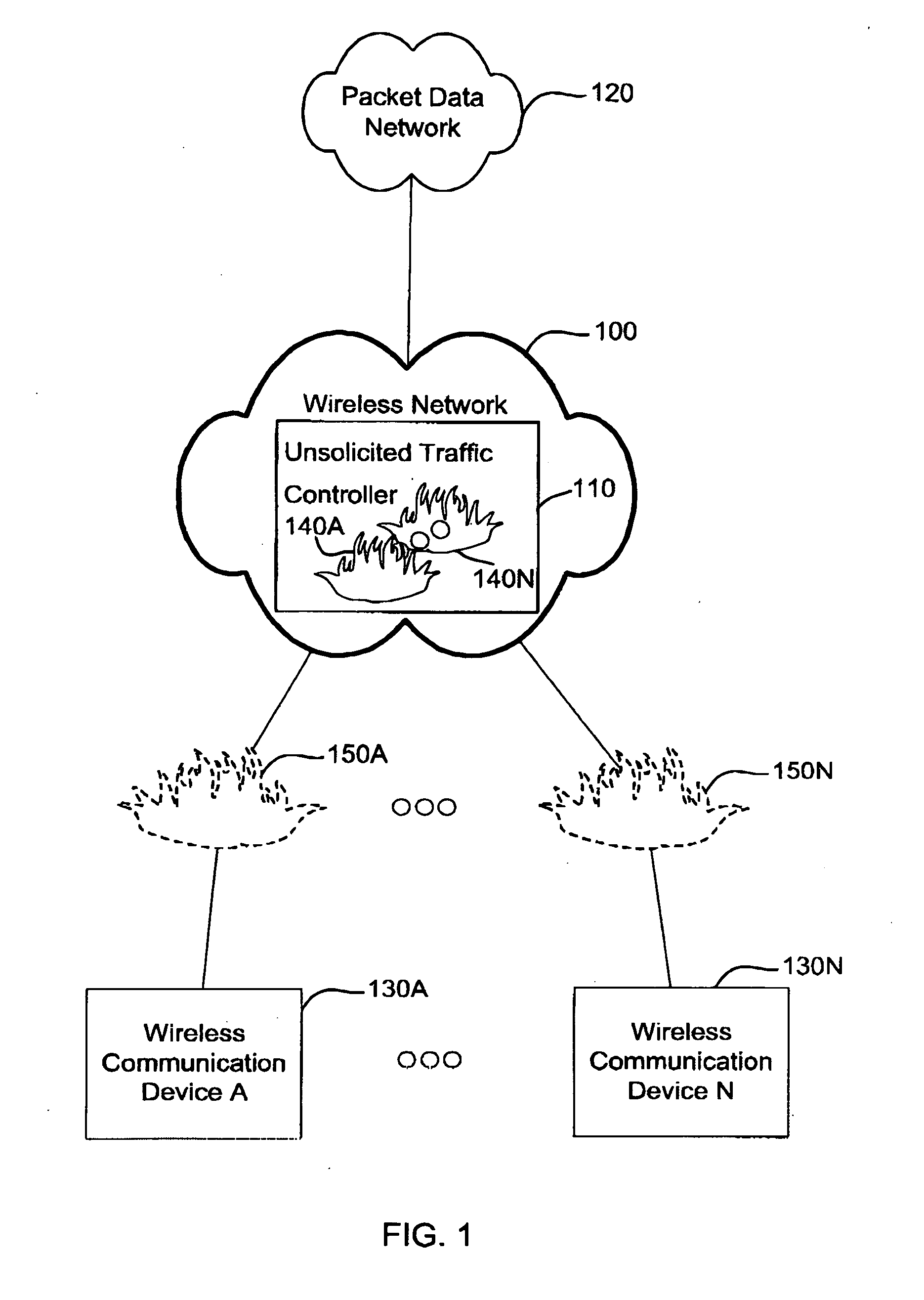
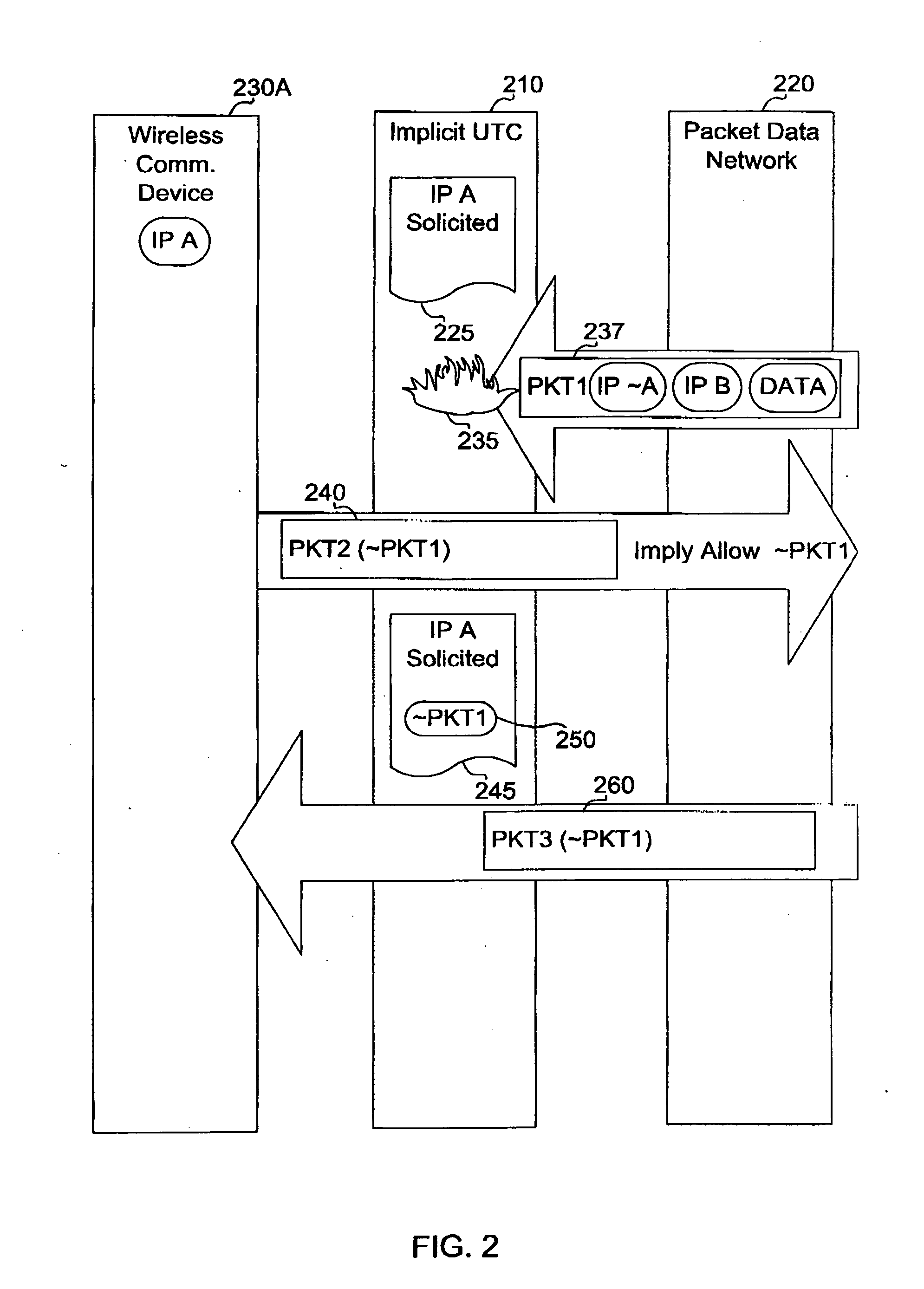
Apparatus and method of controlling unsolicited traffic destined to a wireless communication device
ActiveUS20050122930A1Network traffic/resource managementData taking preventionSession Initiation ProtocolIp address
An apparatus and method of controlling unsolicited traffic are disclosed herein. The apparatus and method can be applied to wireless communication networks such as CDMA2000, UMTS, GPRS and the like so that traffic which is not solicited by wireless communication devices operating on those networks is not sent over the air needlessly. The present application provides techniques to block unsolicited traffic based on the identity of a user (for example based on International Mobile Station Identity (IMSI), Network Access Identifier (NAI), Mobile Station Internet Services Digital Network Number (MSISDN), Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Universal Resource Locator (url)) as opposed to techniques that are based on a session or IP address, such as a traditional firewall. In accordance to this application, user identity based techniques are applied to block unsolicited traffic whenever a user has established a data session. Further in accordance with this application, user identity based techniques are persisted across changes in IP address and / or session.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for managing obfuscated mobile device user identities
InactiveUS20080293411A1Improve securityEnsuring privacyUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsUnique identifierMobile device
A mobile device identifier (such as an MSISDN) that typically accompanies a mobile device request is replaced with an “enriched” identifier that exposes the mobile device user's home operator but obfuscates the mobile device's (and, thus, the device user's) identity. In one embodiment, the identifier comprises a first part, and a second part. The first part comprises a data string that identifies (either directly or through a database lookup) the mobile device user's home operator. The second part, however, is an opaque data string, such as a one-time-use unique identifier (UID) or a value that is otherwise derived as a function of the MSISDN (or the like). The opaque data string encodes the mobile device's identity in a manner that preferably can be recovered only by the user's home operator. The present invention describes a method and apparatus for use in a home network to manage the generation, storage and use of the unique identifiers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for mapping an IP address to an MSISDN number within a service network
InactiveUS6977917B2Overcome problemsTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIp addressData bank
A system and method for associating an MSISDN of a mobile terminal with a temporarily assigned IP address is disclosed. A first server located within a wireless communications network generates and transmits a start packet to a service network responsive to an access request by a mobile terminal. The start packet includes the MSISDN of the mobile terminal and an assigned IP address. A second server within the service network extracts the MSISDN in the IP address from the received start packet and stores this information together within a database. When a service request is made by the mobile terminal to a server in the service network, the MSISDN may be determined from the database and used to access user parameters in a user database.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for authenticating user of data transfer device
InactiveUS7395050B2Convenient for operatorsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCommunications systemPassword
The invention relates to a method and system for authenticating a user of a data transfer device (such as a terminal in a wireless local area network, i.e. WLAN). The method comprises: setting up a data transfer connection from the data transfer device to a service access point. Next, identification data of the mobile subscriber (for example an MSISDN) are inputted to the service access point. This is followed by checking from the mobile communications system whether the mobile subscriber identification data contains an access right to the service access point. If a valid access right exists, a password is generated, then transmitted to a subscriber terminal (for example a GSM mobile phone) corresponding to the mobile subscriber identification data, and login from the data transfer device to the service access point takes place with the password transmitted to the subscriber terminal.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Method and system for implementing flow sharing of multiple mobile terminal cards
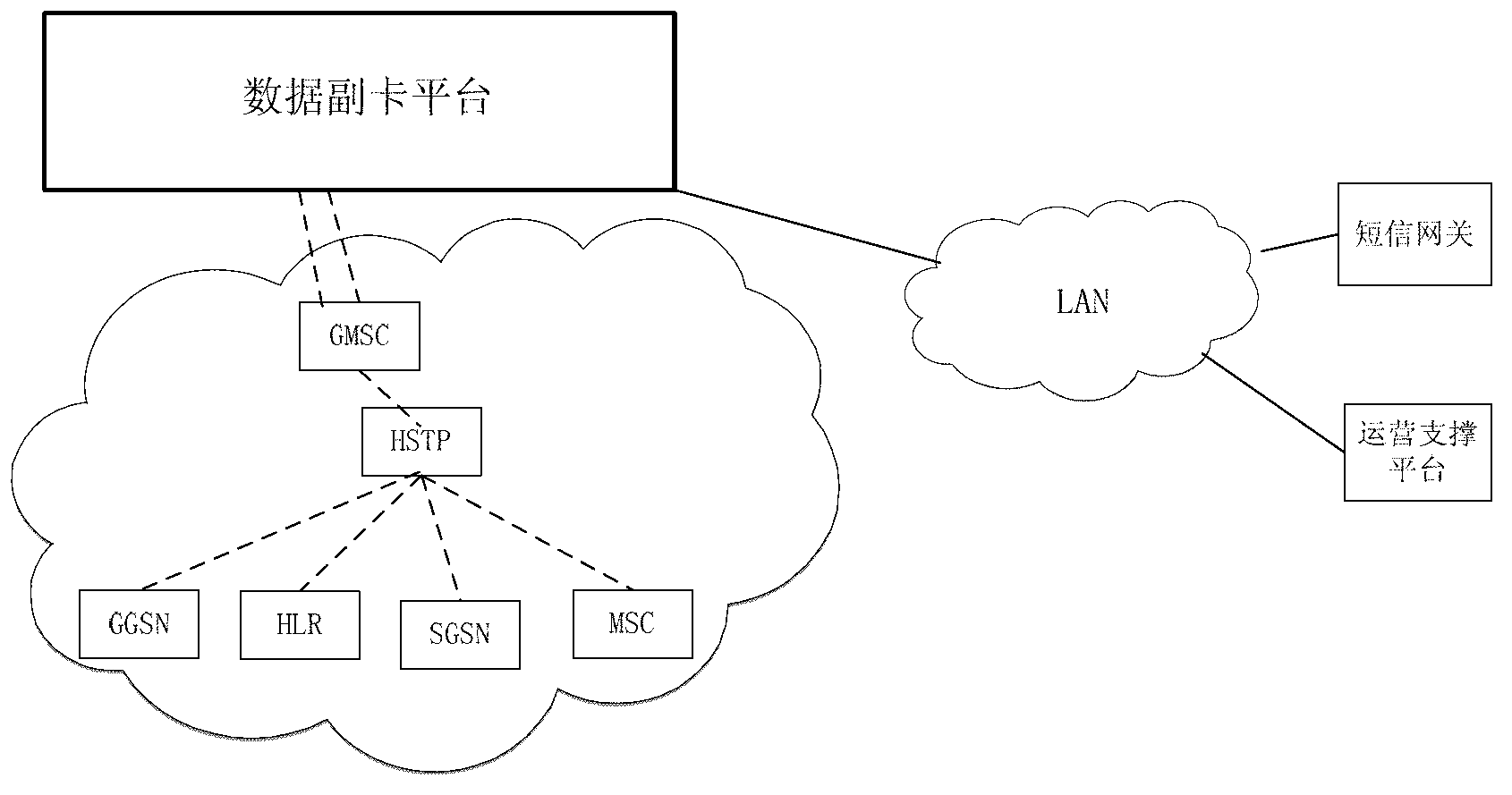
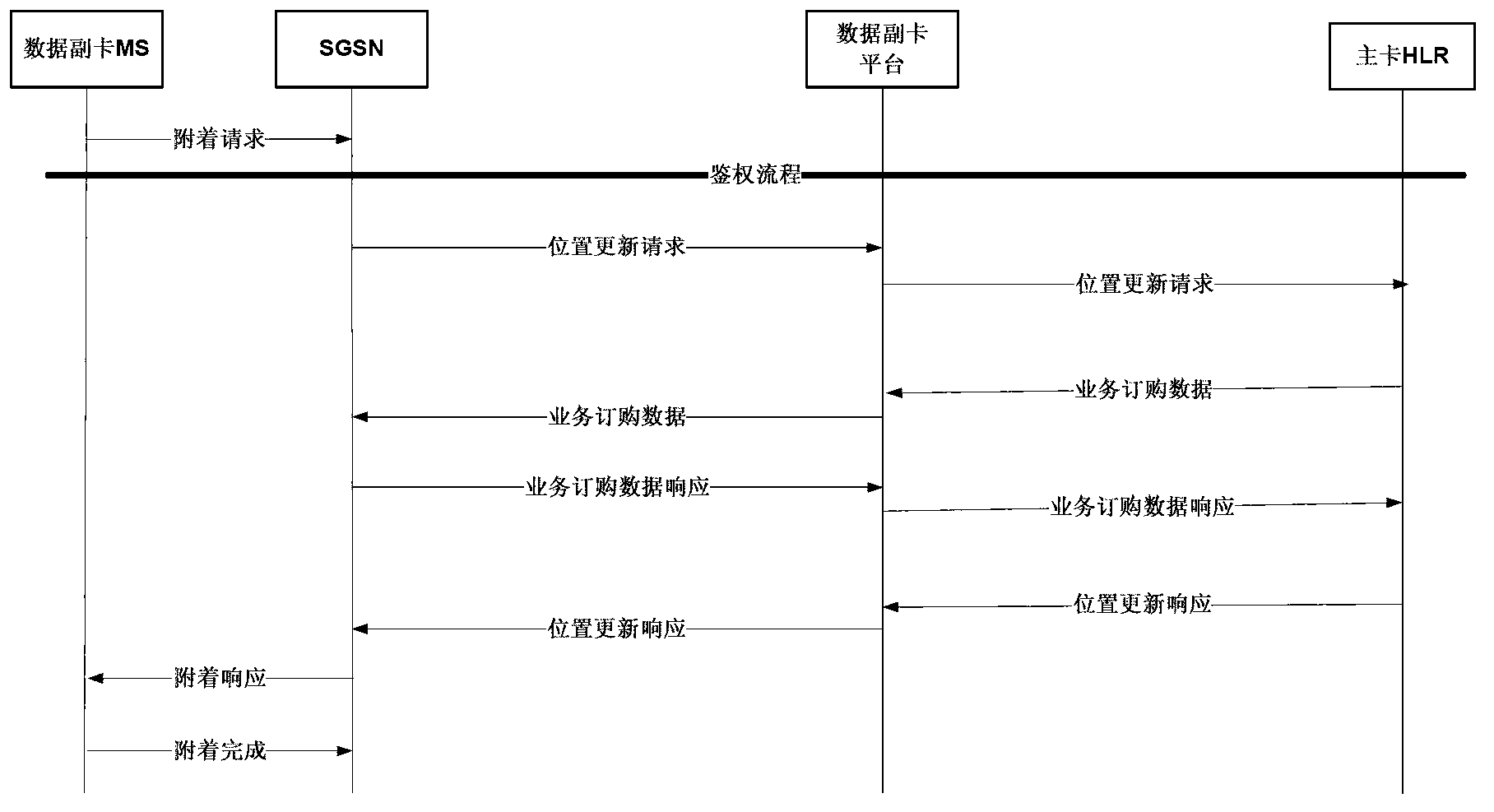
InactiveCN102843668AMeet the conditions for trial commercial useCompliance with specificationsConnection managementNetwork planningGeneral Packet Radio ServiceIntegrated Services Digital Network
The invention provides a method and a system for implementing the flow sharing of multiple mobile terminal cards. The method concretely comprises the following steps: an additional data card platform is established; E. 214 route data are configured for an HSTP (high signaling transfer point), and a special IMSI (international mobile subscriber identity) number segment route for an additional data card is directed to the additional data card platform; the additional data card platform participates in the PS (packet switched) domain attachment process of the additional data card, so that the additional card generates Internet call tickets taking a main card MSISDN (mobile subscriber ISDN (integrated services digital network) number) and an additional card IMSI as identifiers in an SGSN (serving GPRS support node) and a GGSN (gateway GPRS (general packet radio service) support node); and after acquiring a billing center, the call tickets are combined through taking MSISDN as an identifier, so that the Internet call ticket of the additional card is merged into an account of the main card. According to the invention, through providing the additional data card platform, the flow sharing of multiple mobile terminal cards is implemented through the signaling exchange between the additional data card platform and a core network, no improvement on the core network, a BSS (base station subsystem) and a CRM system is required, the service processes of the existing BSS, SGSN (service GPRS supporting node) and CRM and the like are not affected, and no influence is caused on an operator network, thereby realizing the inter-flow sharing of 3G main number packages.
Owner:BEIJING DASCOM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com