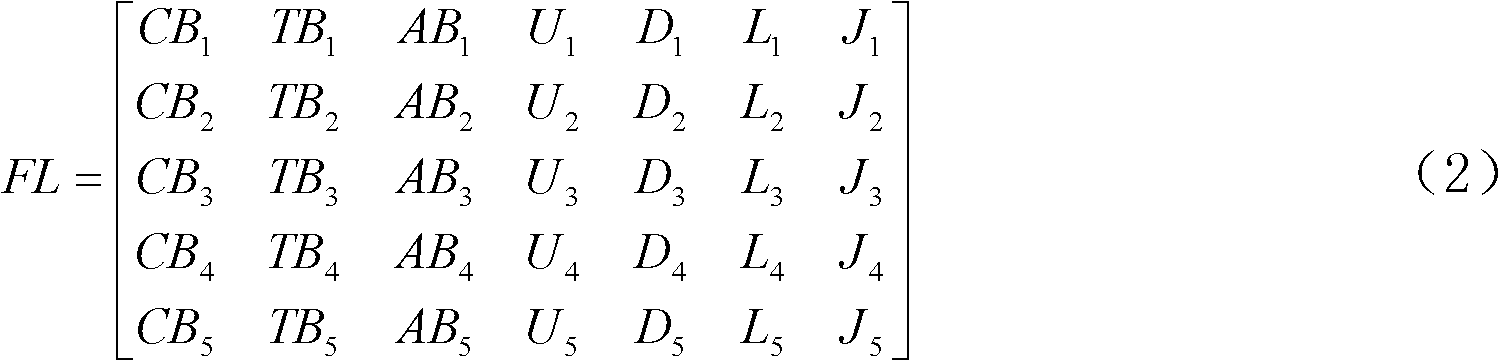Patents
Literature
70 results about "Multihoming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
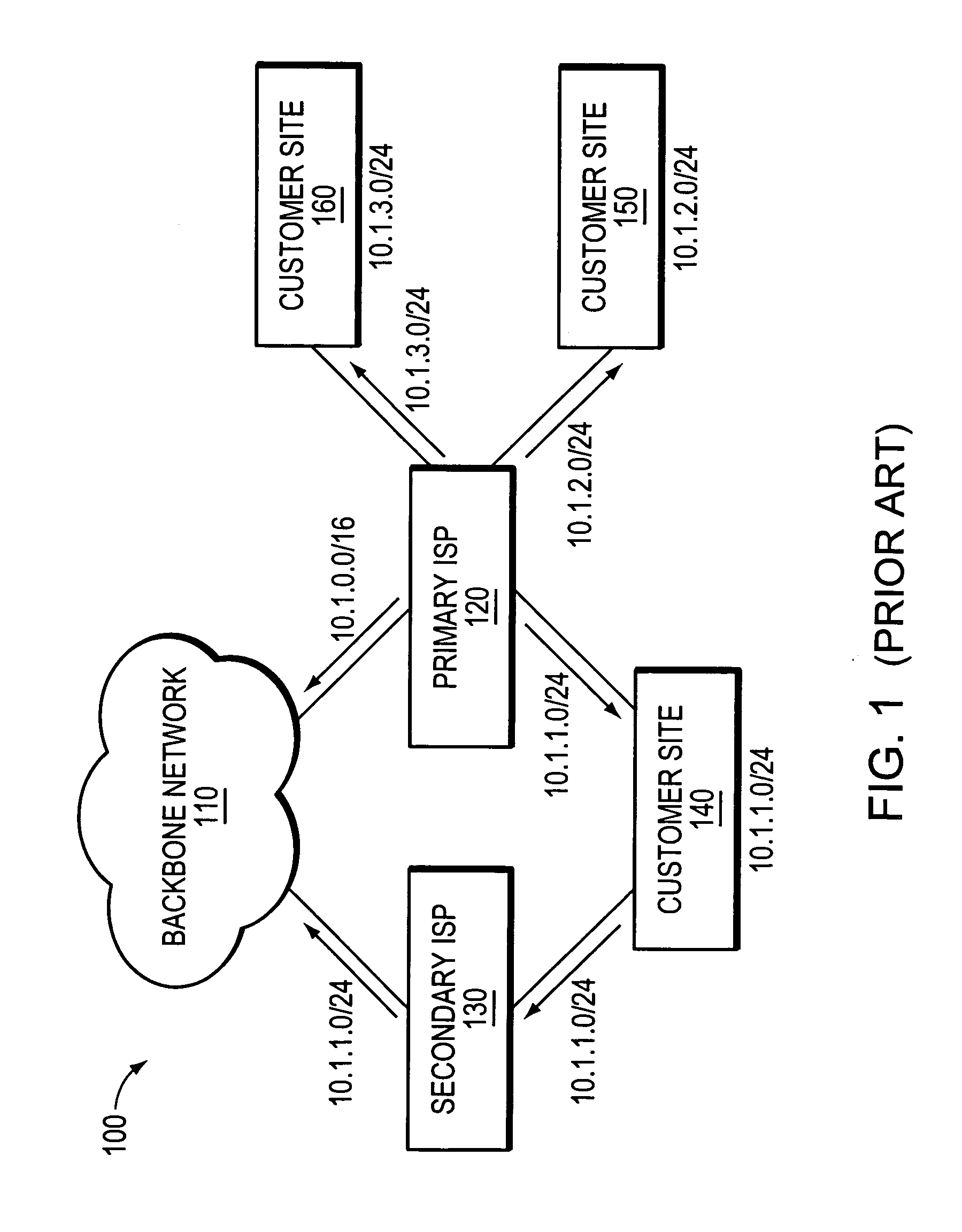
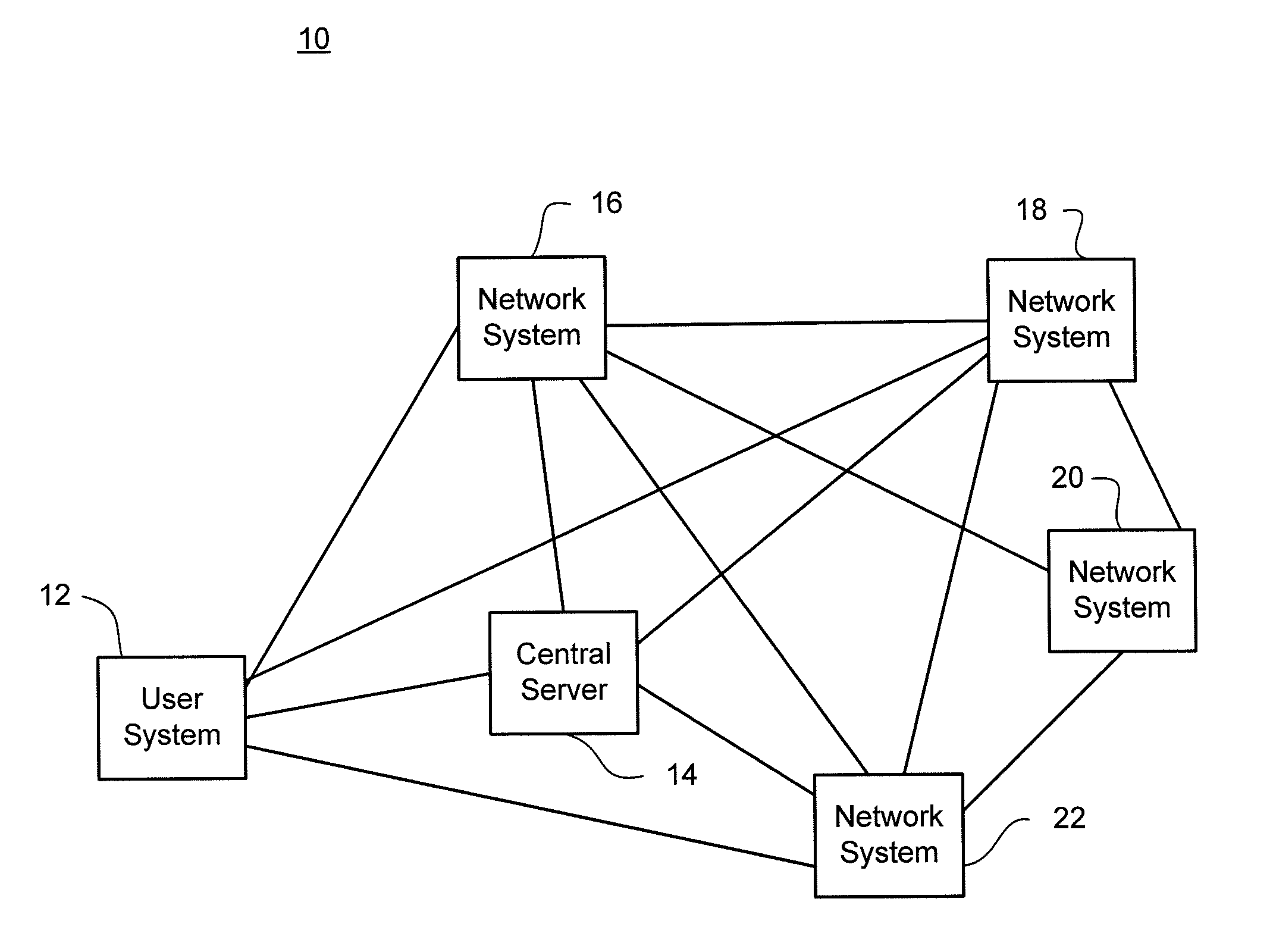
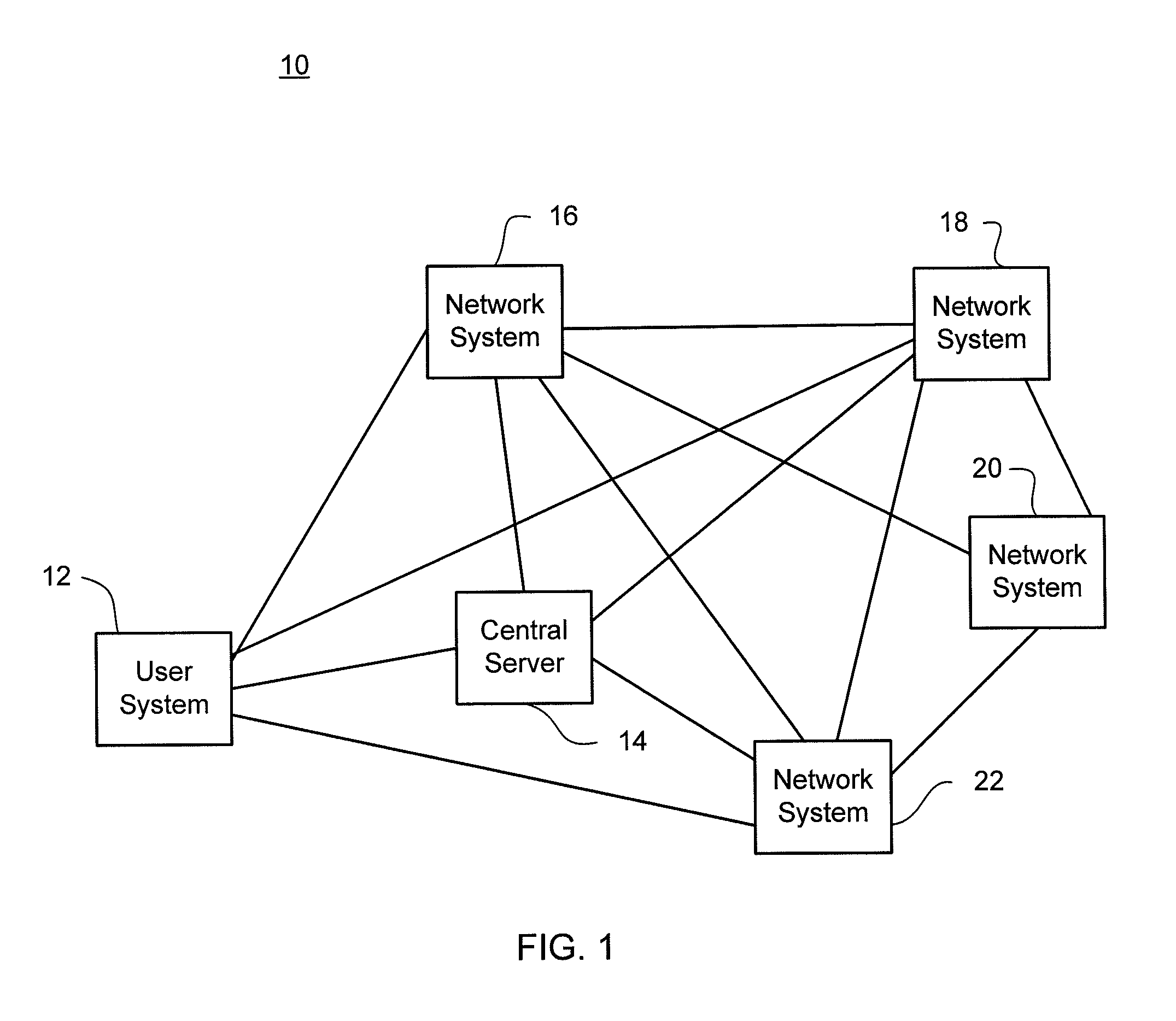
Multihoming is the practice of connecting a host or a computer network to more than one network. This can be done in order to increase reliability or performance. A typical host or end-user network is connected to just one network. In many circumstances, it can be useful to connect a host or network to multiple networks, in order to increase reliability (if a single link fails, packets can still be routed through the remaining networks) and to improve performance (depending on the destination, it may be more efficient to route through one network or the other).
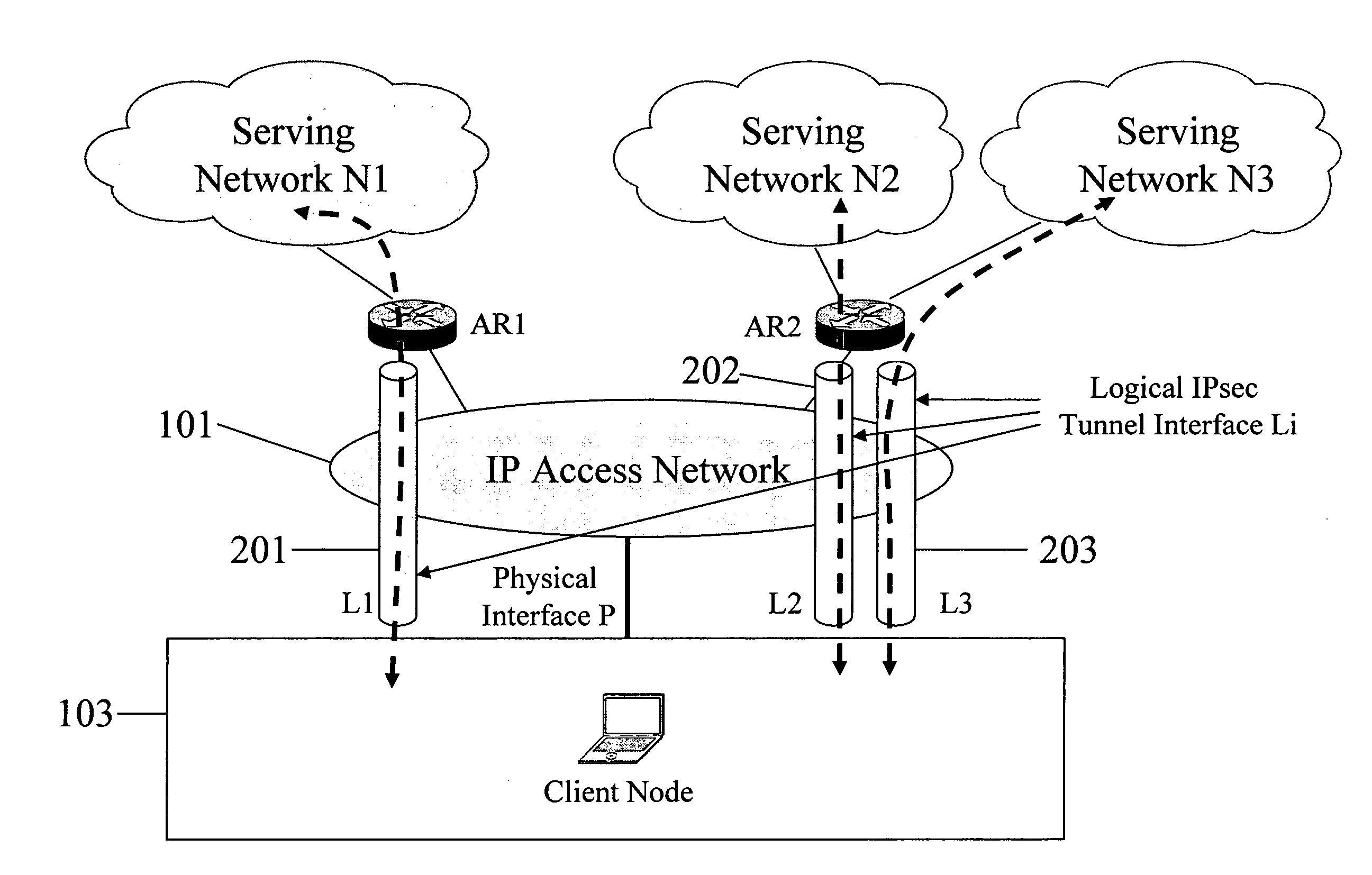
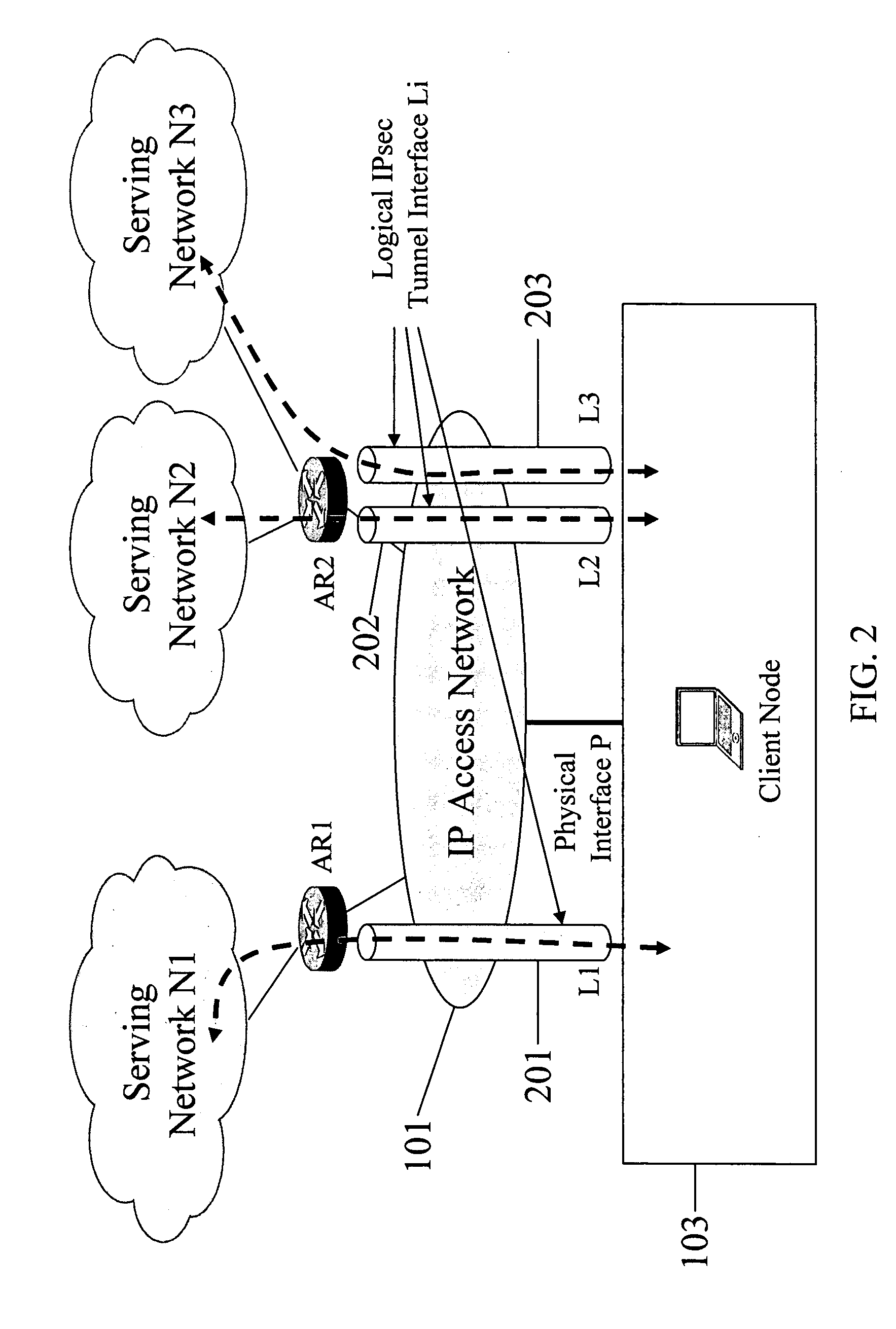
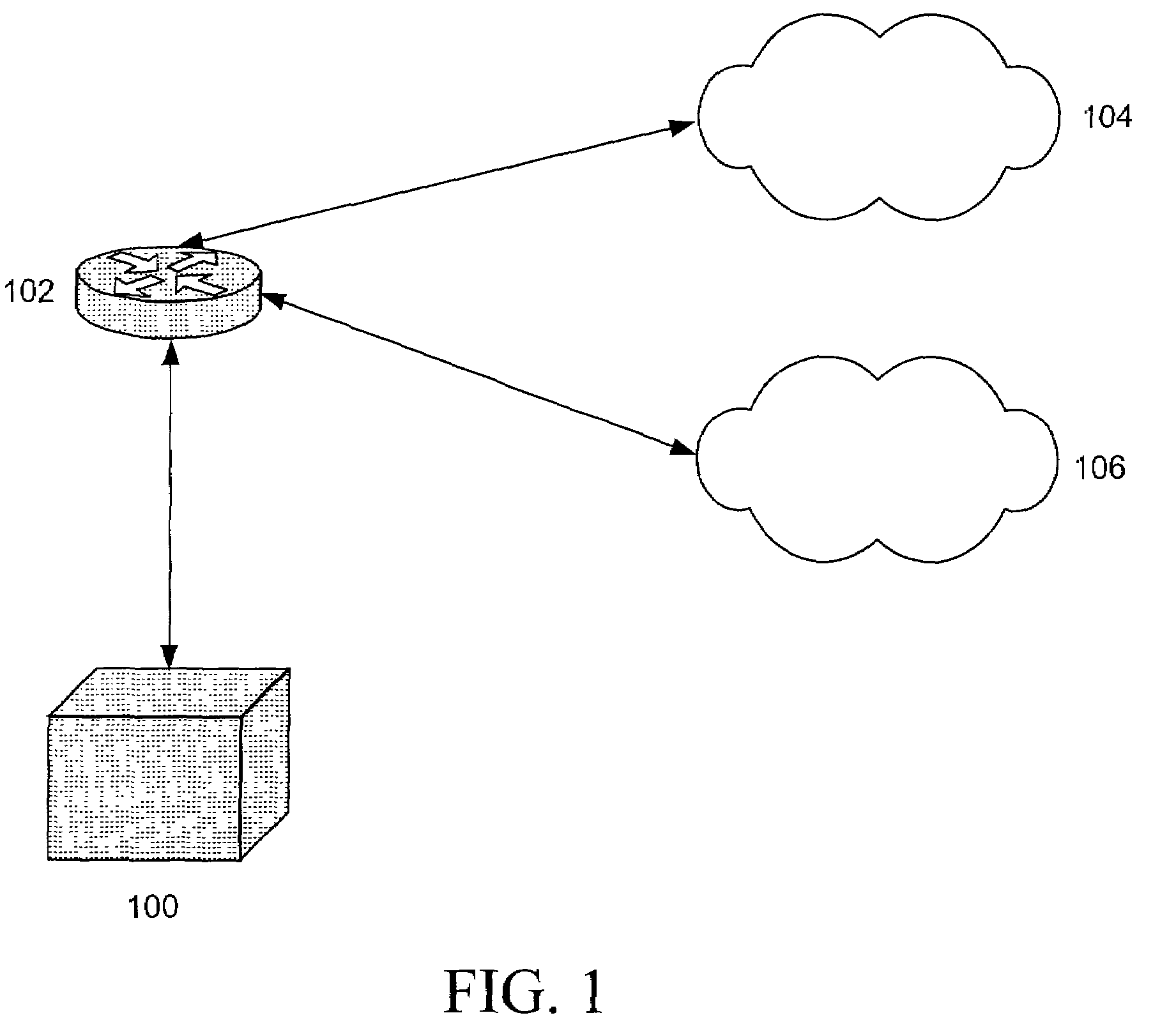
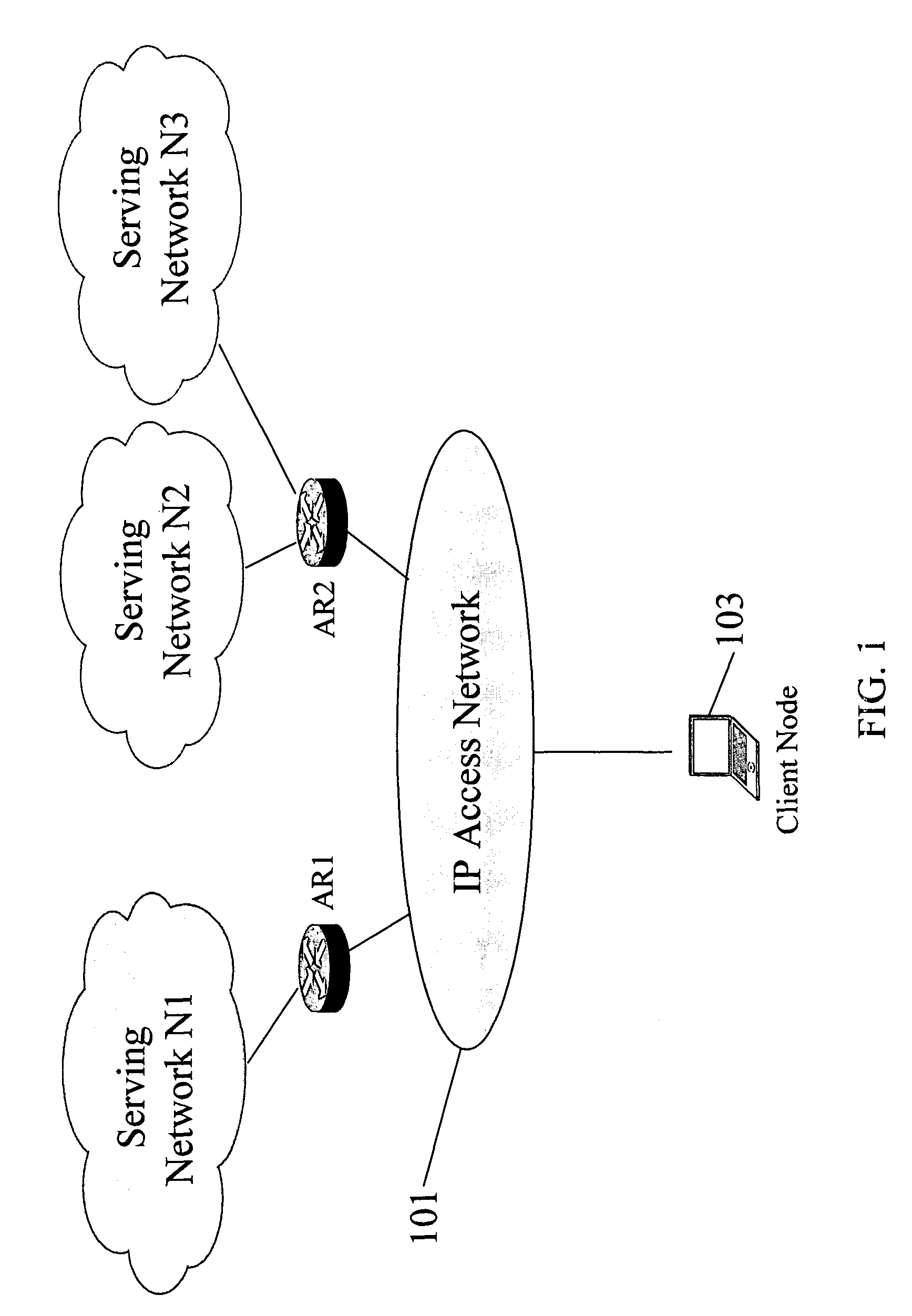
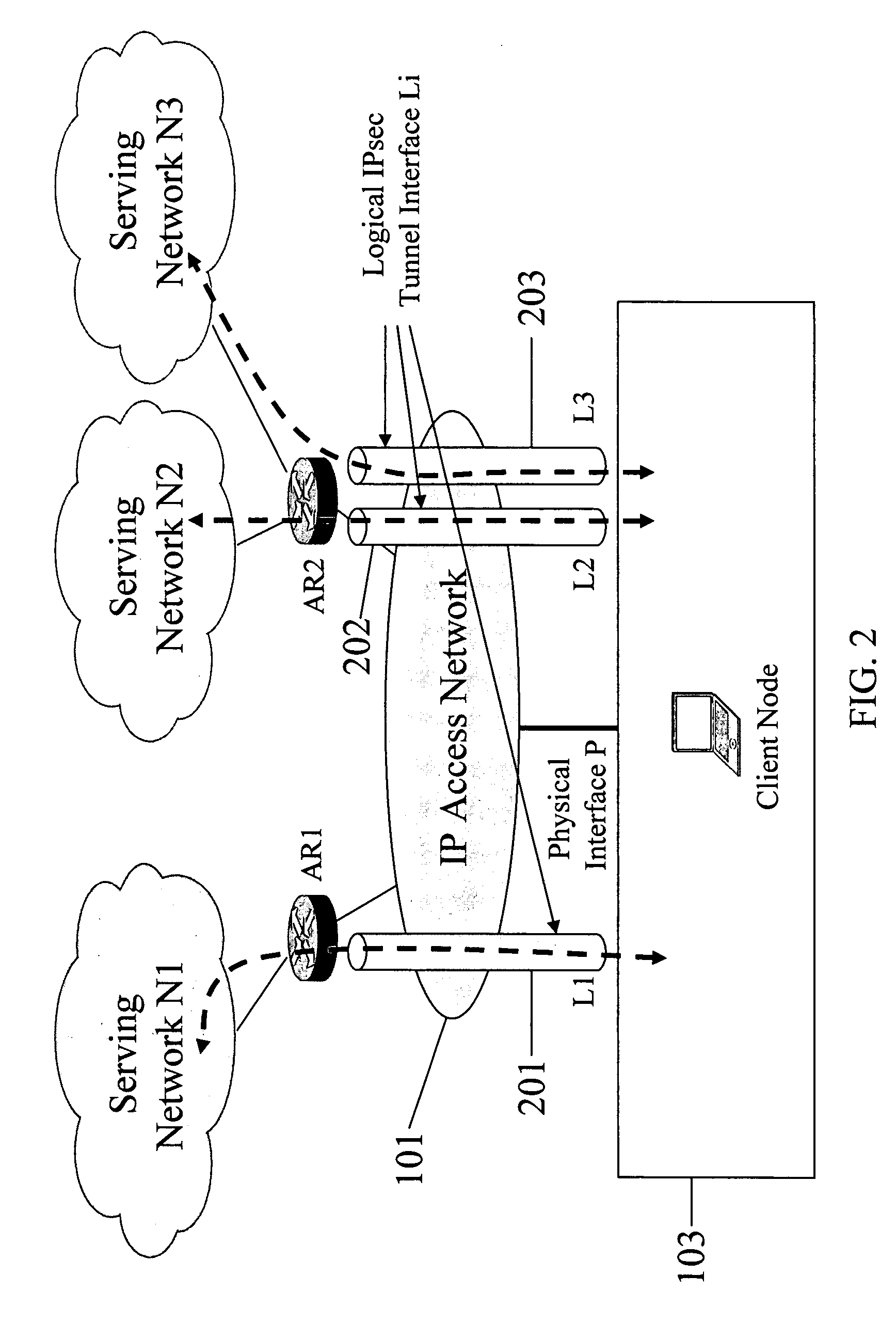
Serving network selection and multihoming using IP access network
InactiveUS20050165953A1Simple methodAssess restrictionMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess networkClient-side
In some illustrative embodiments, an IP-layer based network selection and multihoming method is provided that enables a flexible and secure dynamic selection of one or more serving networks for use by a client node. The method is independent of any link-layer technology. A serving network can be an ISP network, a NAP network exchange facility, a VLAN, or the like. Network information is advertised to a client node, the client node is authenticated and authorized for use of an access router, and a secure tunnel is established between the client node and the access router. The method can be implemented by using standard protocols, and can work over any existing or future link-layer technologies that are able to carry IP datagrams, without any modification.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +2
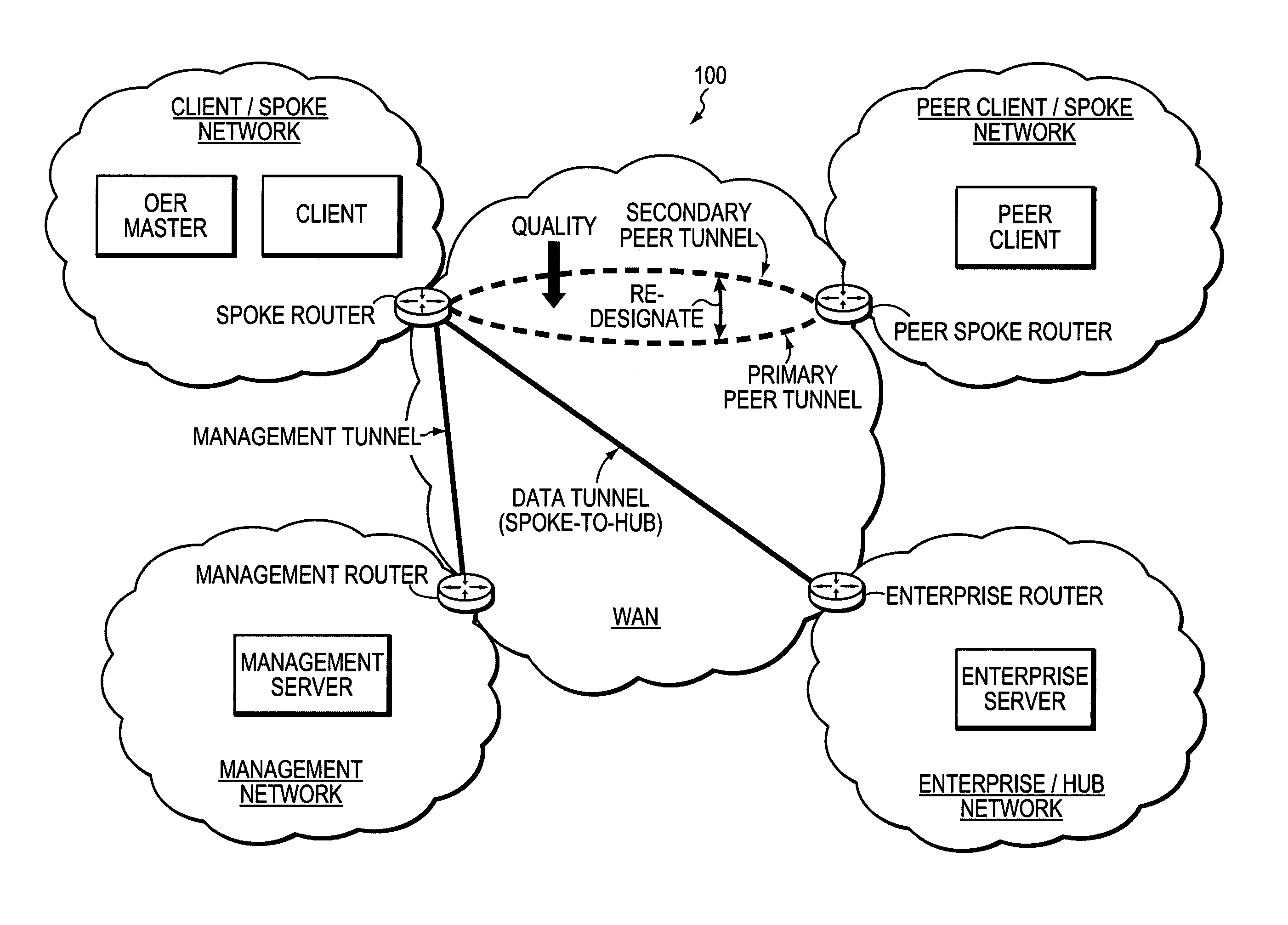
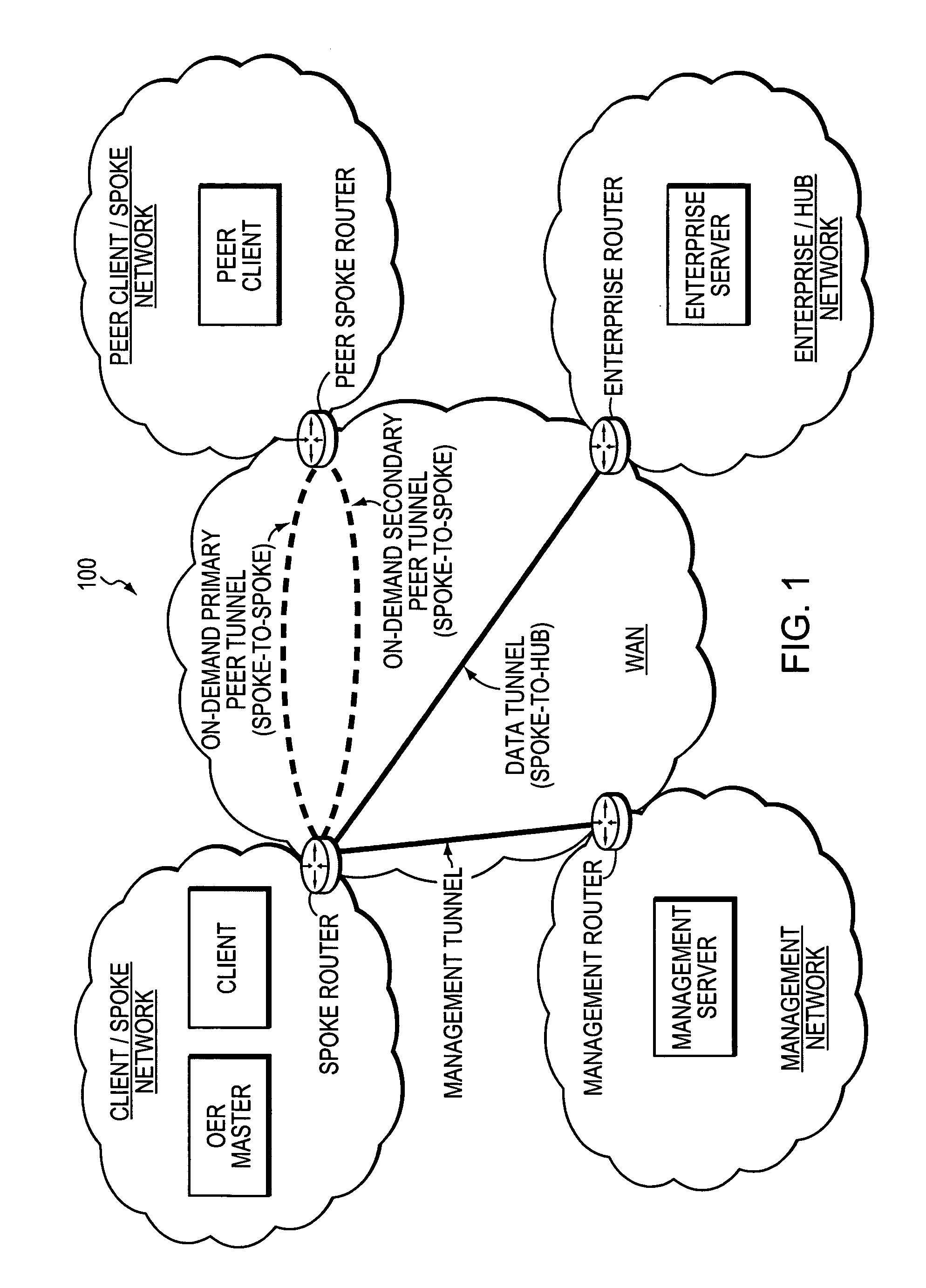
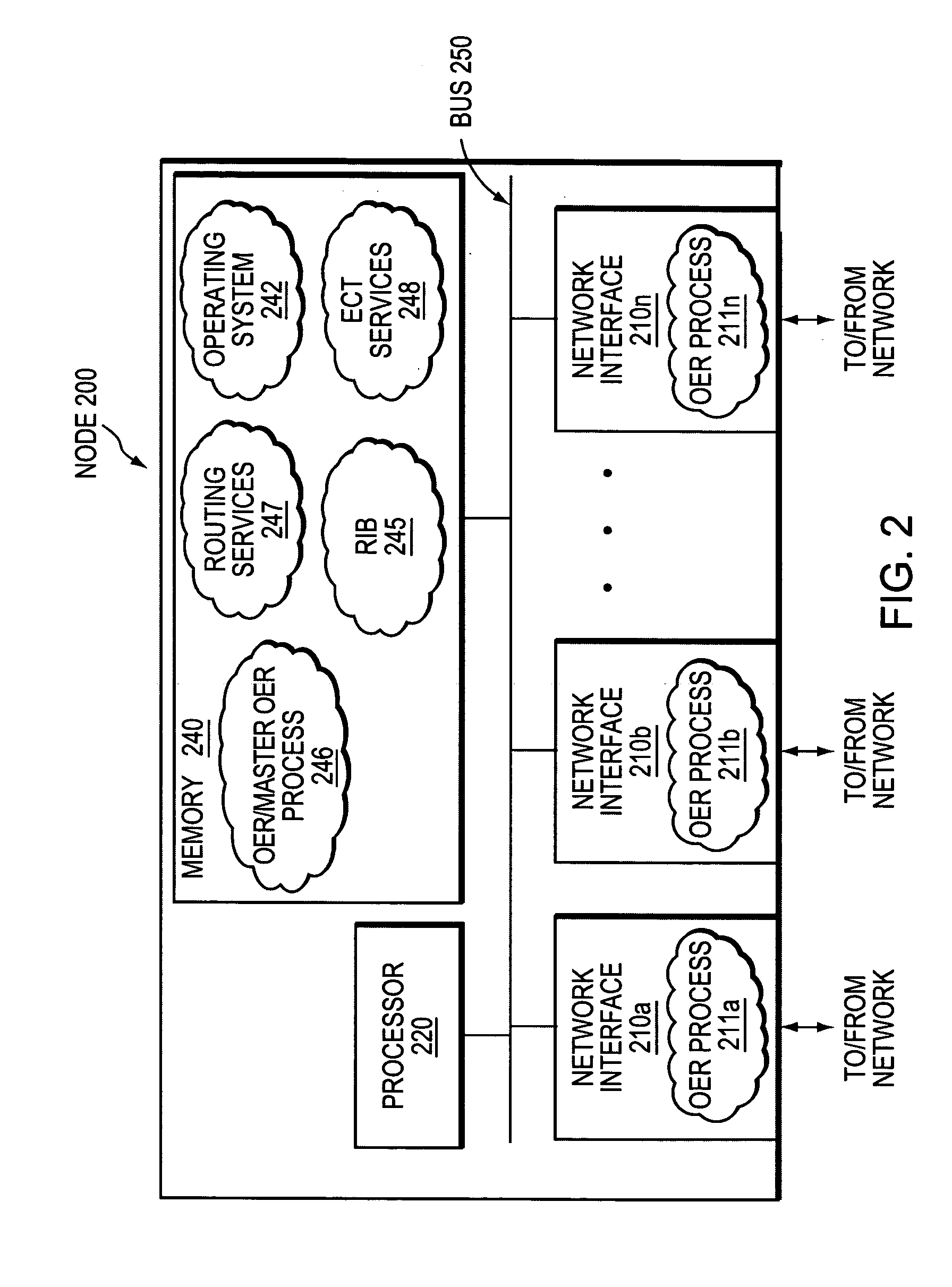
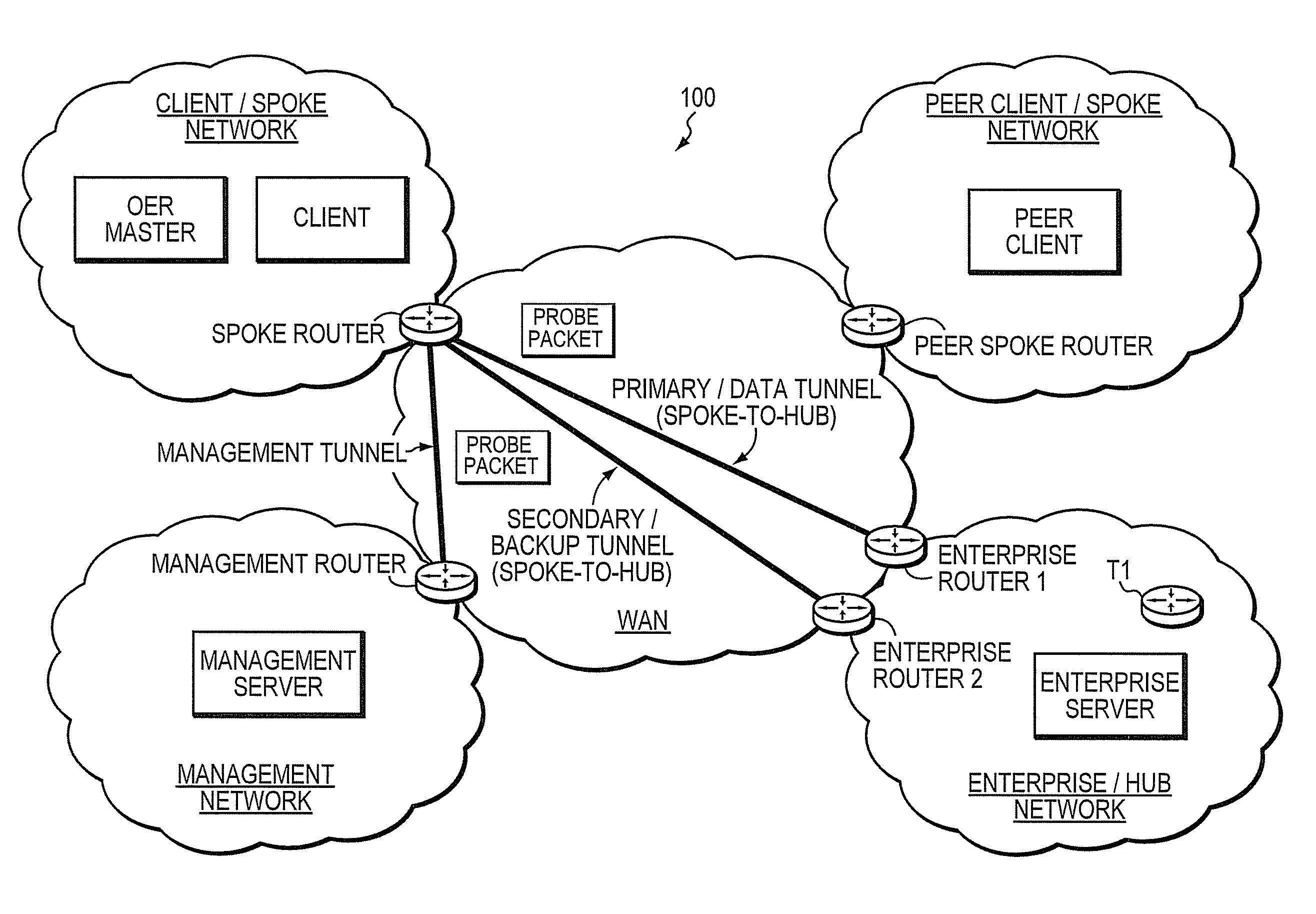
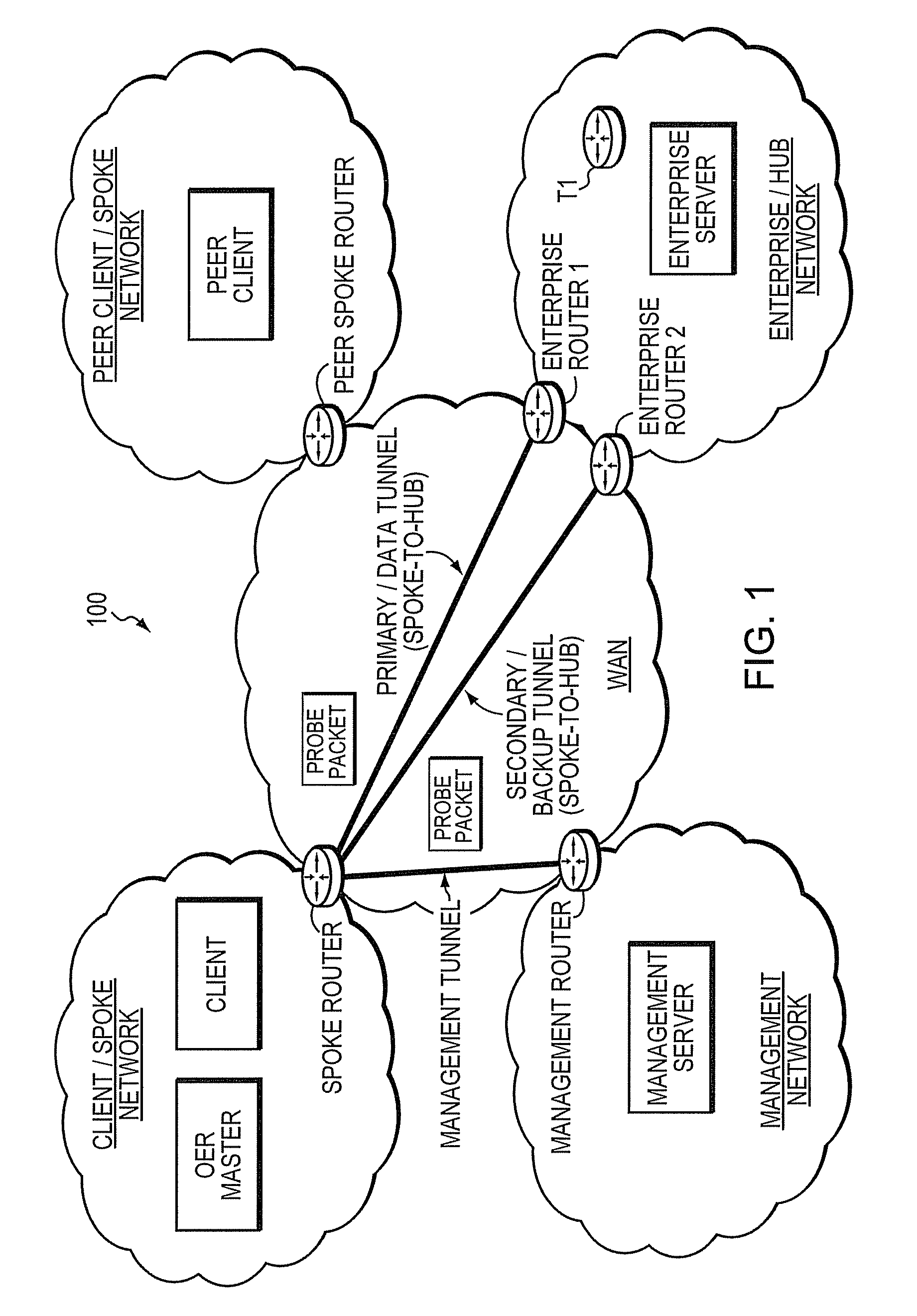
Technique for using OER with an ECT solution for multi-homed spoke-to-spoke sites
InactiveUS7801030B1Extended run timeImprove usabilityError preventionTransmission systemsStationPrivate network
A technique dynamically creates and utilizes a plurality of multi-homed Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnels from a client node of one spoke network to a client node of another spoke network in a computer network. According to the technique, a VPN client node, e.g., a “spoke,” creates at least one VPN tunnel with an enterprise network, e.g., a “hub.” Once the spoke-to-hub tunnel is established, the spoke may dynamically create a plurality of VPN tunnels with a peer spoke network, e.g., a “peer spoke.” The spoke designates (e.g., for a prefix) one of the tunnels as a primary tunnel and the other tunnels as secondary tunnels, and monitors the quality (e.g., loss, delay, reachability, etc.) of all of the dynamic tunnels, such as, e.g., by an Optimized Edge Routing (OER) process. The spoke may then dynamically re-designate any one of the secondary tunnels as the primary tunnel for a prefix based on the quality of the tunnels to the peer spoke. Notably, the spoke may also dynamically load balance traffic to the peer spoke among the primary and secondary tunnels based on the quality of those tunnels.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
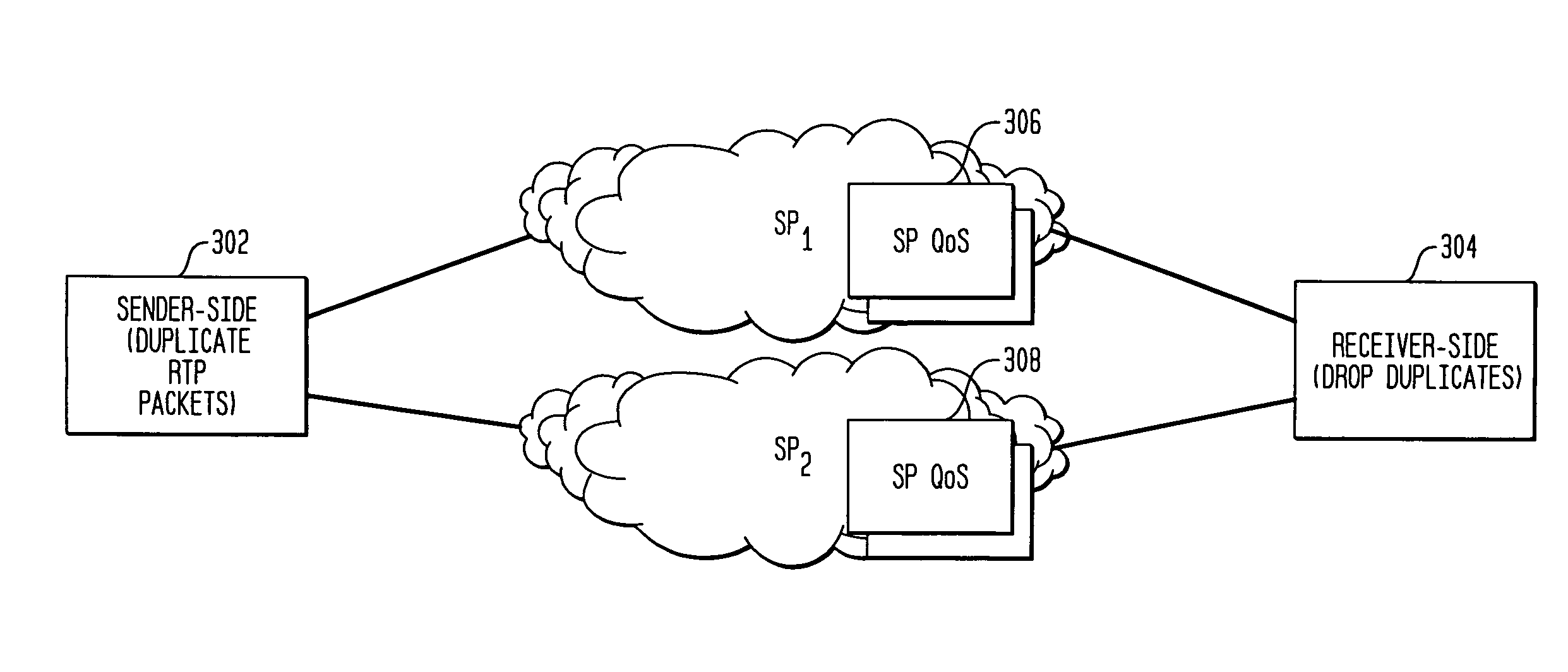
System and method to improve the resiliency and performance of enterprise networks by utilizing in-built network redundancy
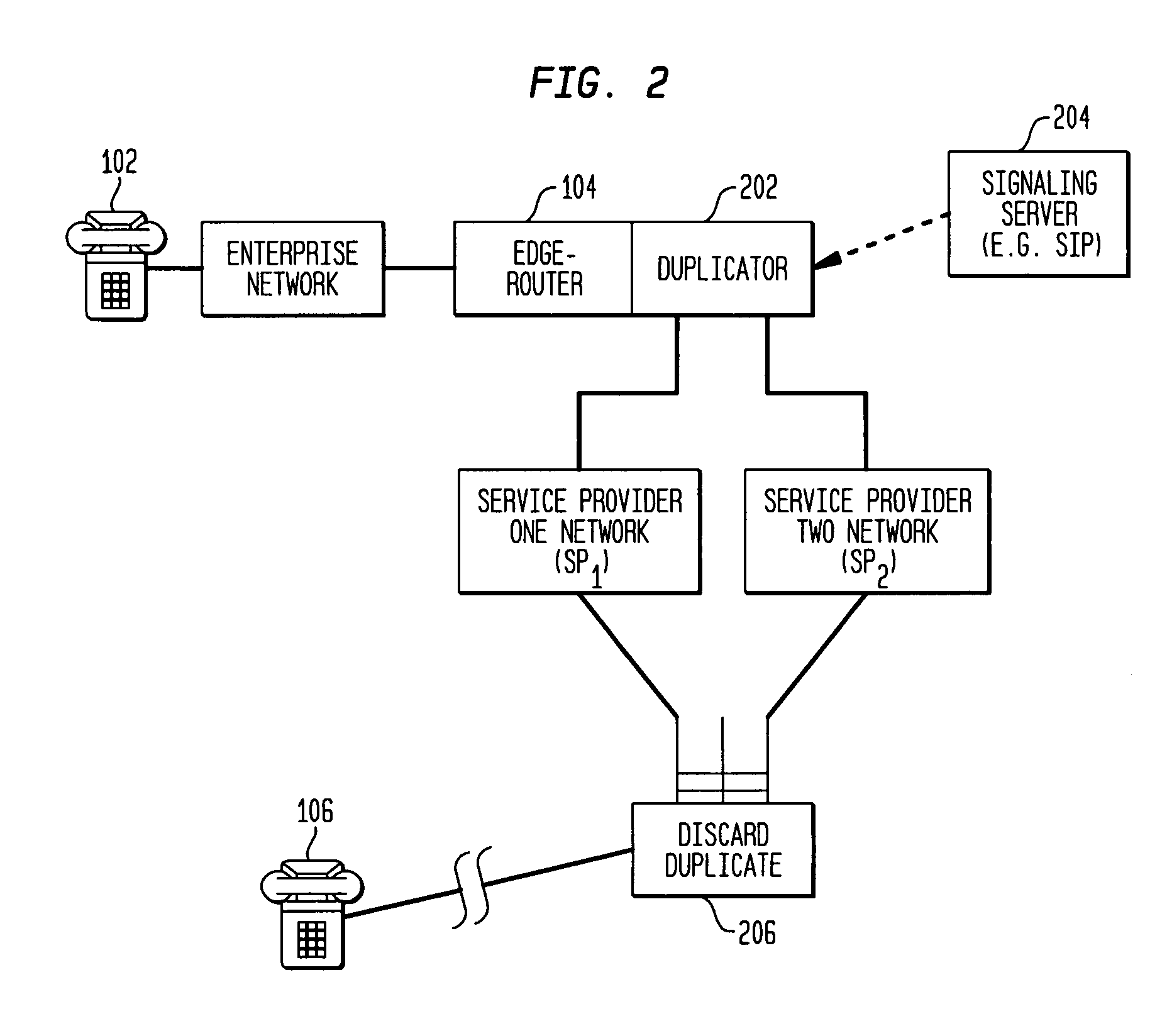
ActiveUS7188189B2Improve reliabilityImprove performanceData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsService provisionNetwork packet
The present invention is a system and method to improve the reliability and performance of existing enterprise IP networks which have dual-homed (or multi-homed) network architectures. In one aspect of the invention packets related to a selected category of transmission (e.g., VoIP) are duplicated at an edge router and sent over both (multiple) service providers. After traversing the service provider networks, only the first-to-arrive packets are kept and the later-arriving copies are discarded. In so doing, the result is better protection against node failures, link failures, and packet errors, and also better QoS performance under normal (fault-free) operation.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Technique for using OER with an ECT solution for multi-homed sites
ActiveUS8260922B1Extended run timeImprove usabilityDigital computer detailsTransmissionTraffic capacityReachability
A technique dynamically utilizes a plurality of multi-homed Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnels from a client node to one or more enterprise networks in a computer network. According to the technique, a VPN client node, e.g., a “spoke,” creates a plurality of multi-homed VPN tunnels with one or more servers / enterprise networks, e.g., “hubs.” The spoke designates (e.g., for a prefix) one of the tunnels as a primary tunnel and the other tunnels as secondary (backup) tunnels, and monitors the quality (e.g., loss, delay, reachability, etc.) of all of the tunnels, such as, e.g., by an Optimized Edge Routing (OER) process. The spoke may then dynamically re-designate any one of the secondary tunnels as the primary tunnel for a prefix based on the quality of the tunnels to the enterprise. Notably, the spoke may also dynamically load balance traffic to the enterprise among the primary and secondary tunnels based on the quality of those tunnels.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
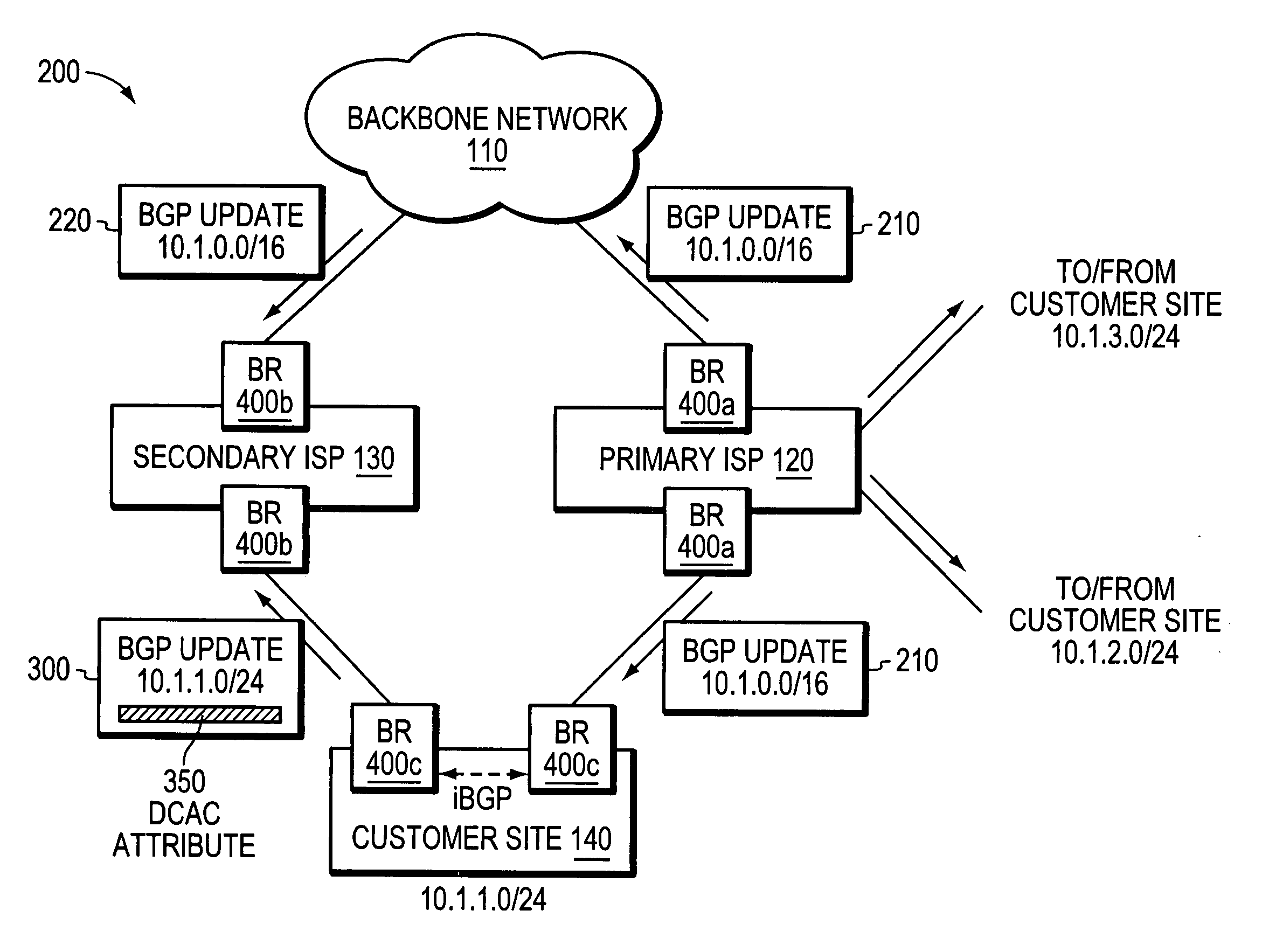
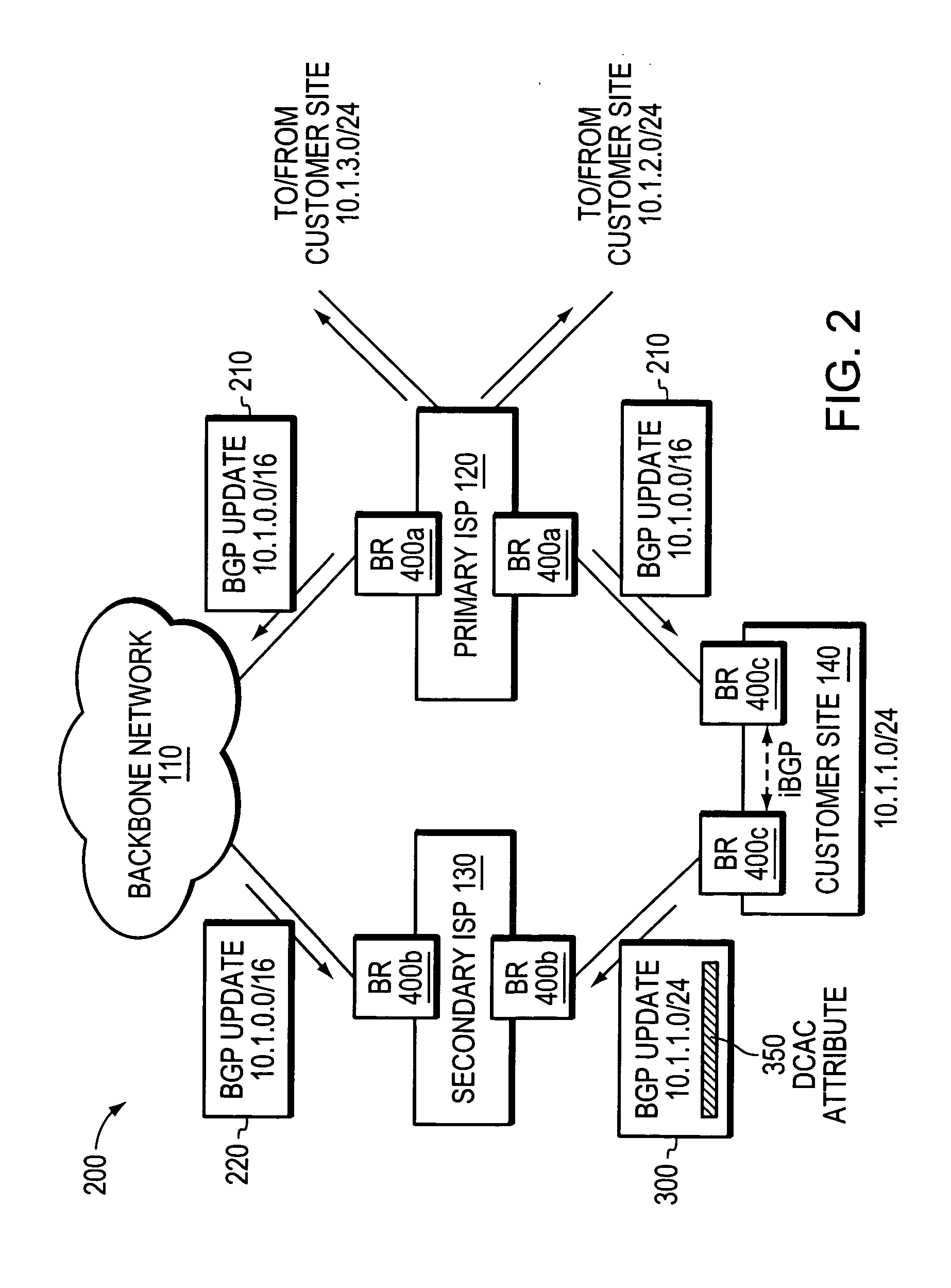
Multi-homing using controlled route leakage at a backup service provider
ActiveUS20060268681A1Faster network convergenceBetter bandwidth utilizationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork addressingNetwork address
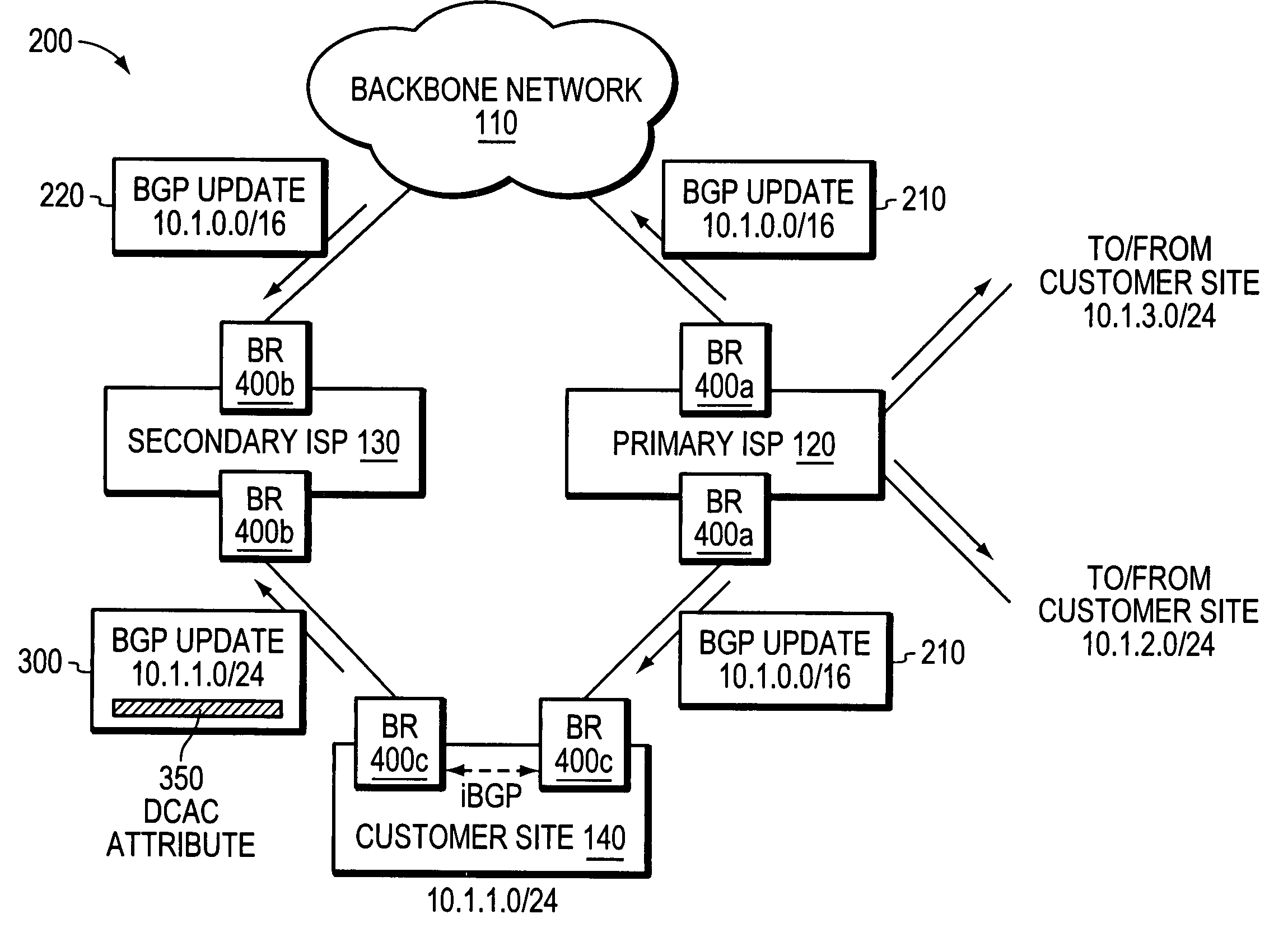
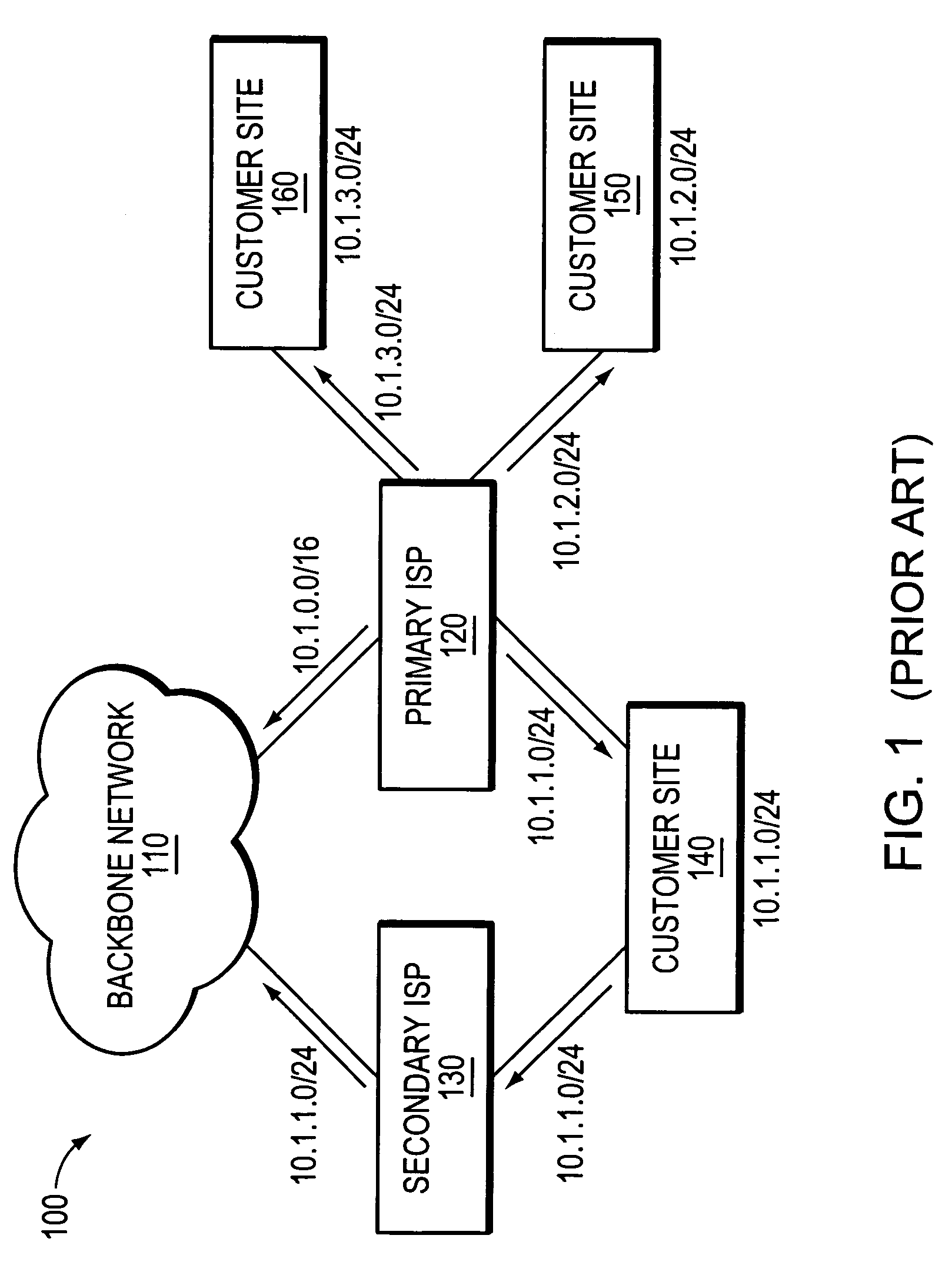
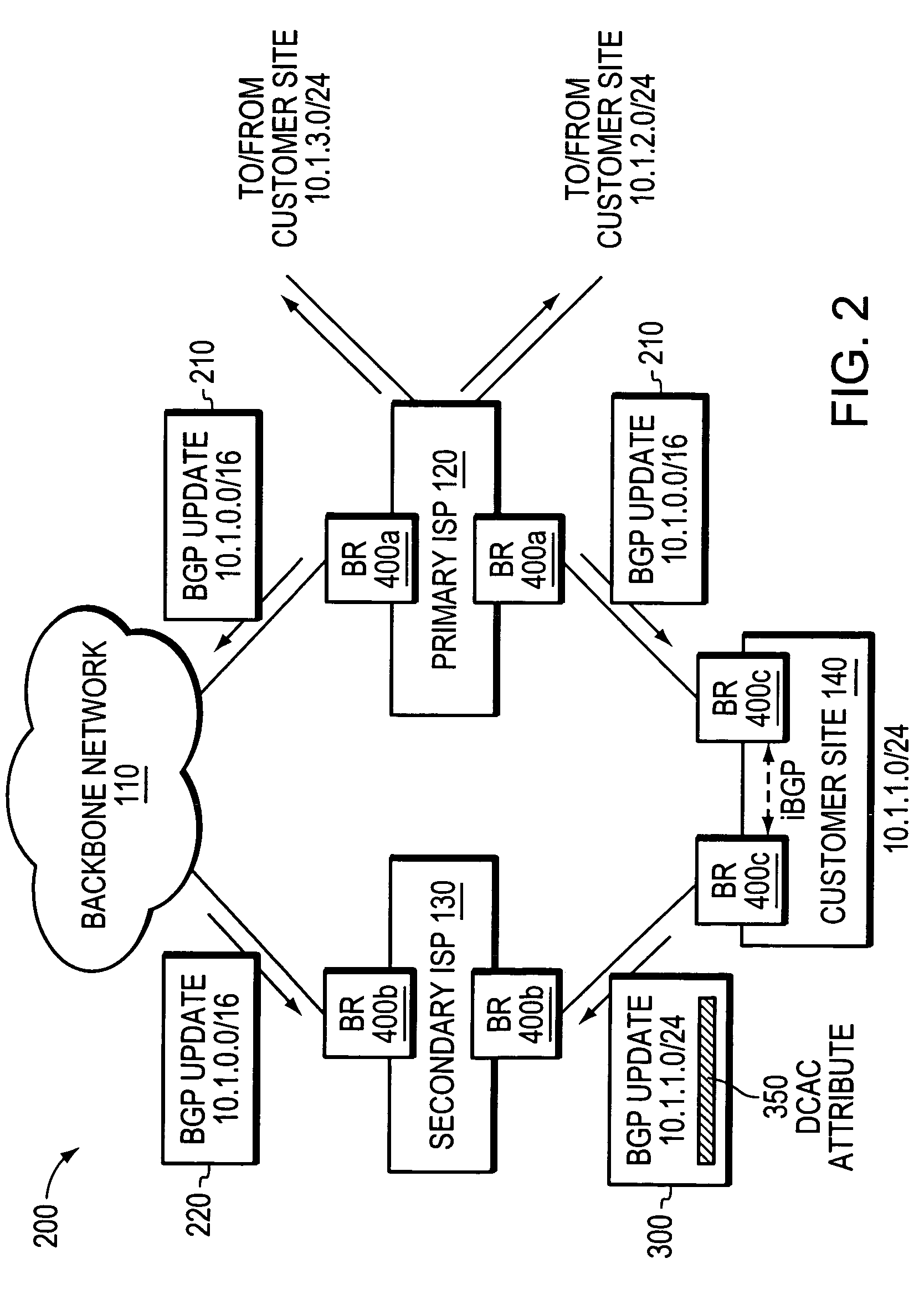
A technique is provided for implementing route aggregation in a computer network containing a multi-homed customer site connected to primary and second networks, which in turn are both connected to a common “backbone” network. According to the technique, the primary network allocates a block of network addresses for the customer site, and the customer site notifies the secondary network of its allocated addresses. The secondary network first determines whether the primary network has already advertised an aggregated route which incorporates the customer site's route. If so, the secondary network “suppresses” (i.e., does not advertise) the customer site's route. The secondary network only “unsuppresses” the customer site's route if it detects that the primary network has lost connectivity to the customer site and / or the backbone network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for performance and cost optimization in an internetwork
Systems and methods are described for supporting routing intelligence for evaluating routing paths based on performance measurements. The routing intelligence may include processes executed in a self-contained device. This device may control one or more edge routers, based on performance data from end users. In other embodiments, the routing intelligence device may be used solely to monitor one or more edge routers, producing reports but not effecting any changes to routing. Routing decisions may be injected to the edge routers via BGP updates. The devices may be stationed at the premises of a multihomed organization, such as an enterprise, ISP, government organization, university, or other organization supporting a sub-network coupled to an internetwork. In other embodiments, the routing intelligence comprises processes executed on a router.
Owner:AVAYA INC
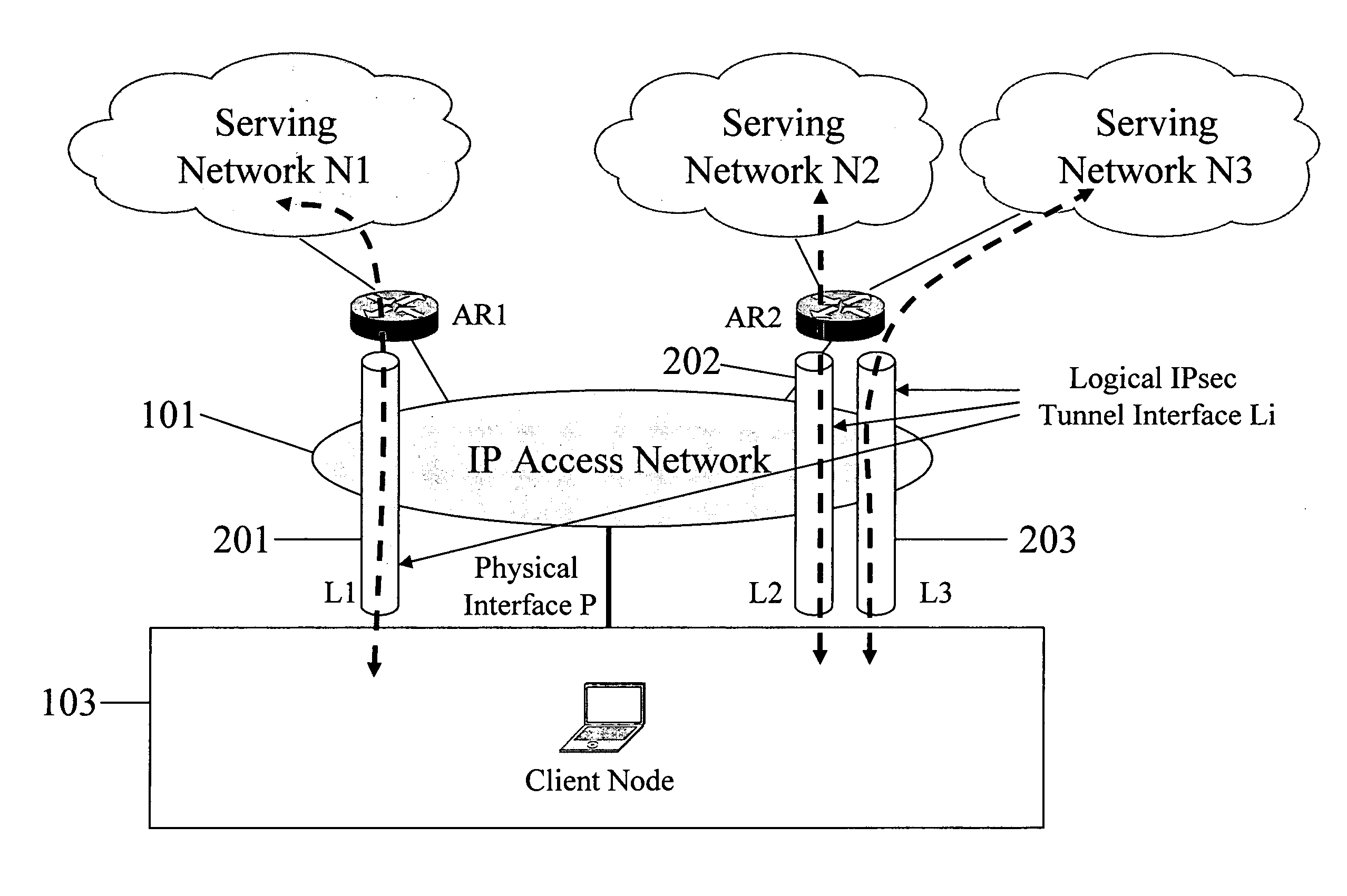
Establishing a secure tunnel to access router
InactiveUS7860978B2Assess restrictionMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
In some illustrative embodiments, an IP-layer based network selection and multihoming method is provided that enables a flexible and secure dynamic selection of one or more serving networks for use by a client node. The method is independent of any link-layer technology. A serving network can be an ISP network, a NAP network exchange facility, a VLAN, or the like. Network information is advertised to a client node, the client node is authenticated and authorized for use of an access router, and a secure tunnel is established between the client node and the access router. The method can be implemented by using standard protocols, and can work over any existing or future link-layer technologies that are able to carry IP datagrams, without any modification.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +2
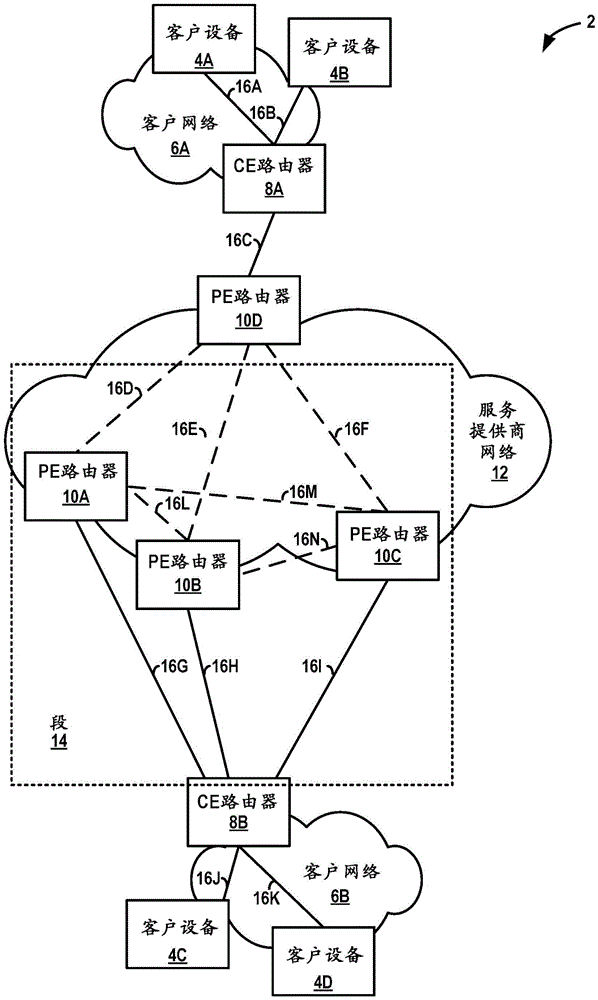
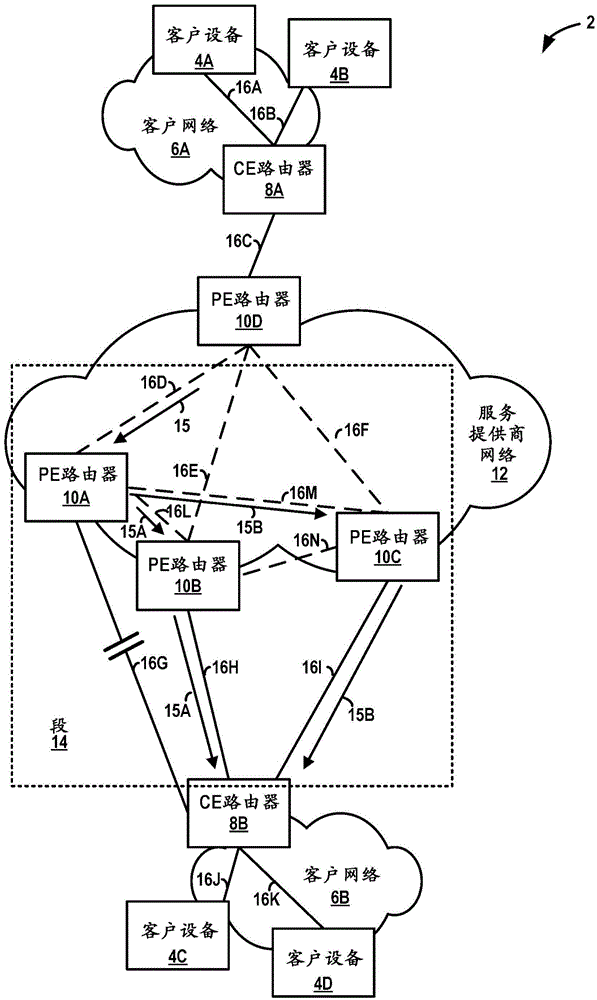
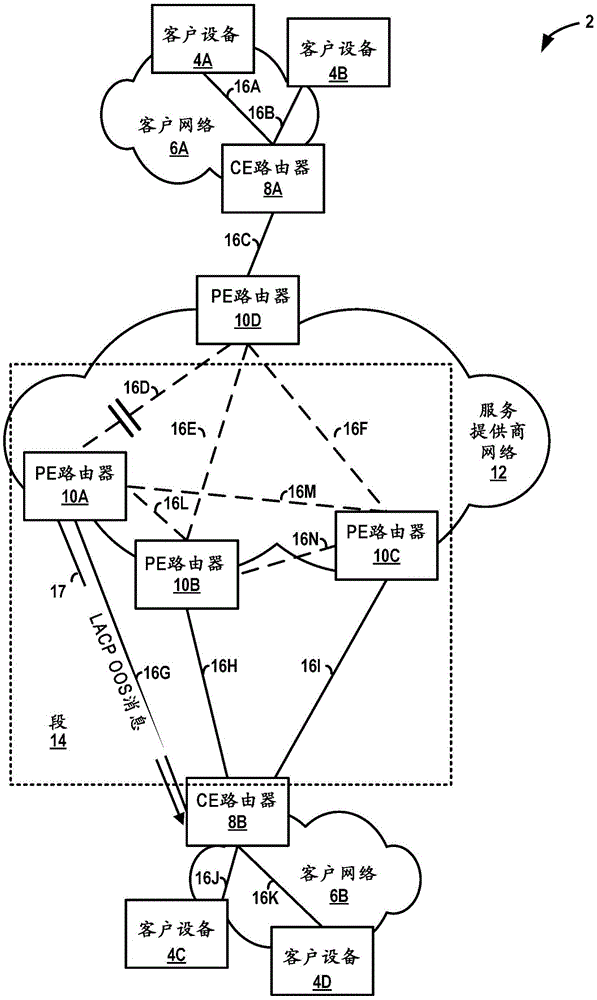
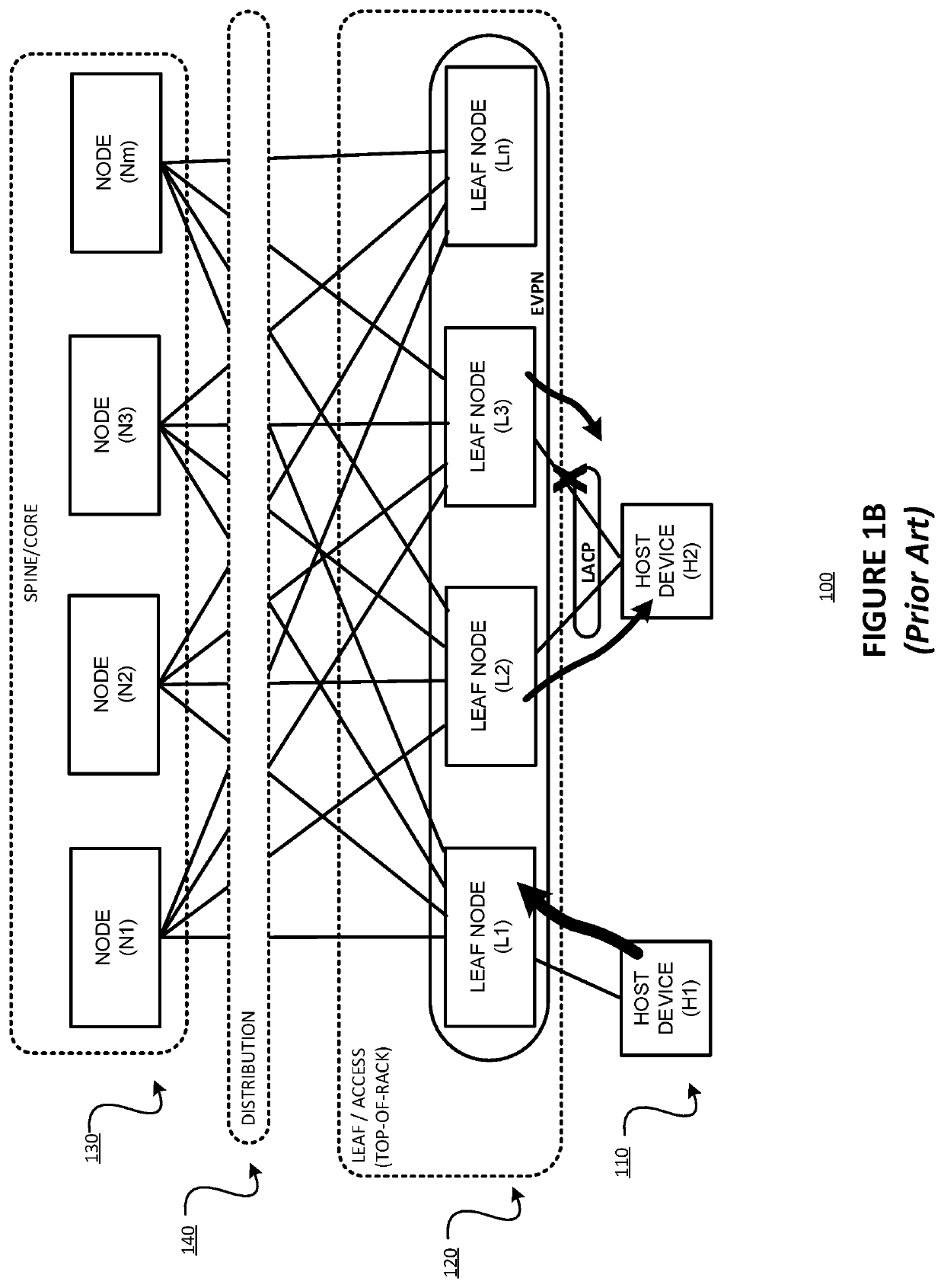
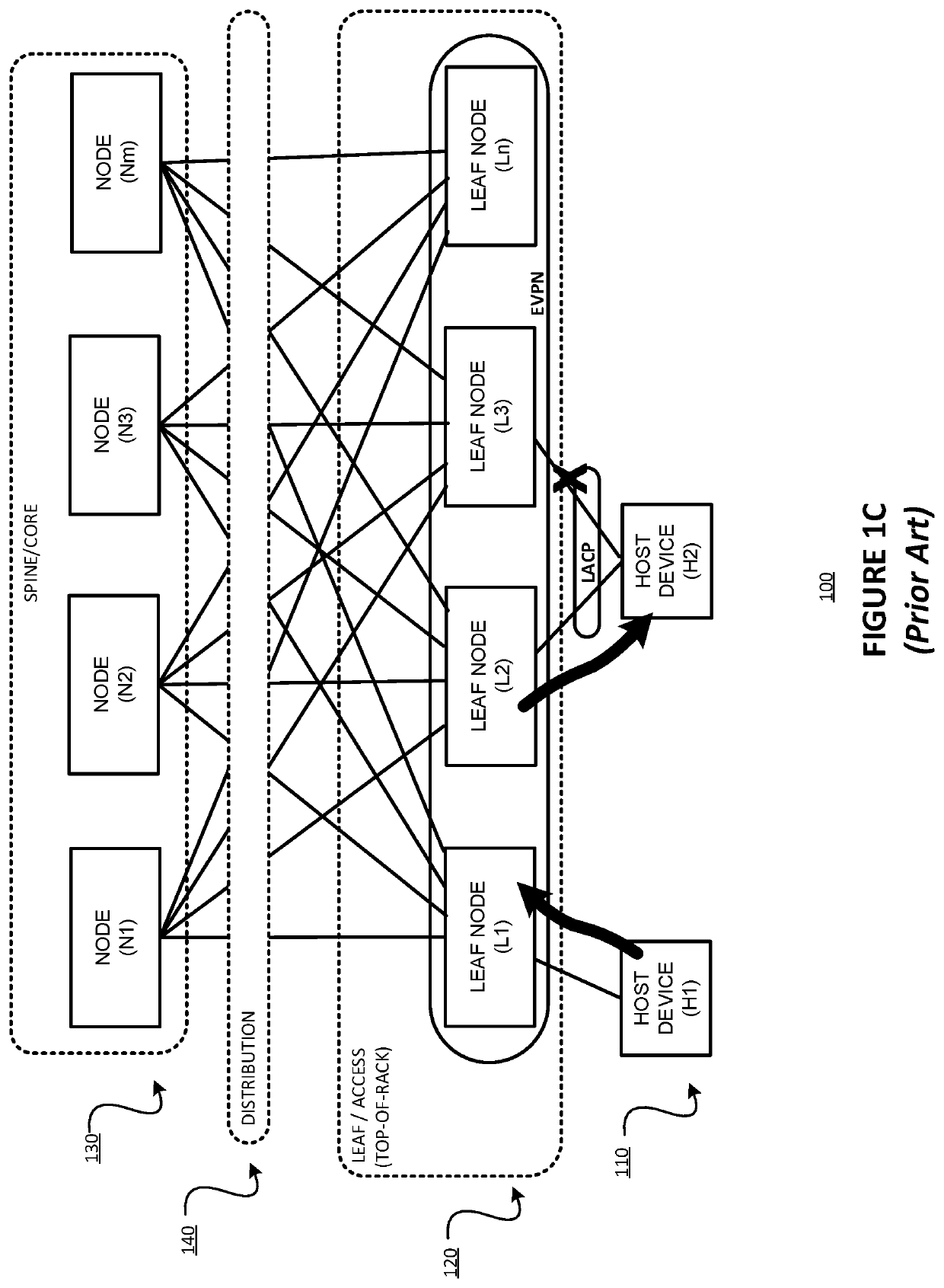
Fast convergence on link failure in multi-homed ethernet virtual private networks
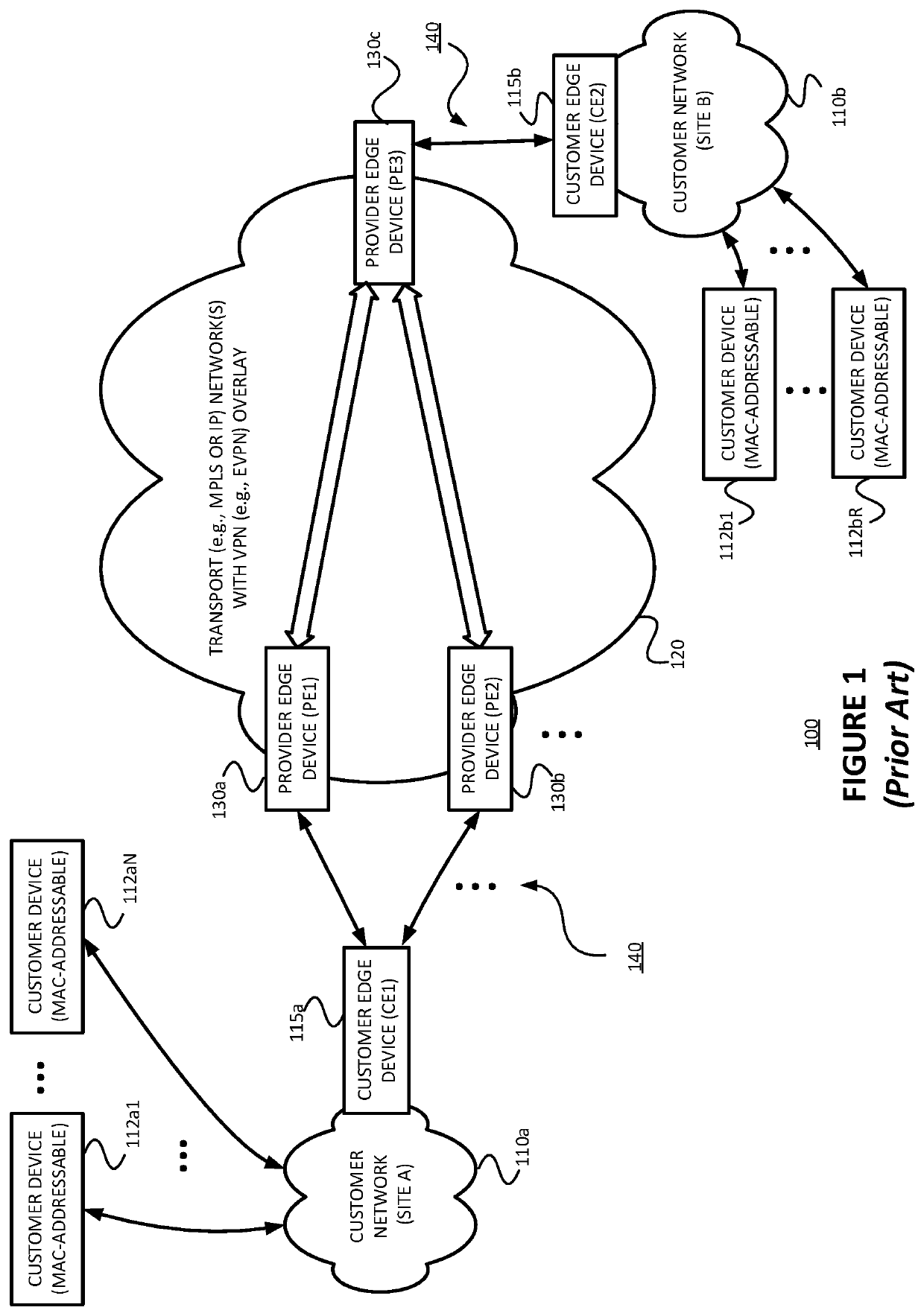
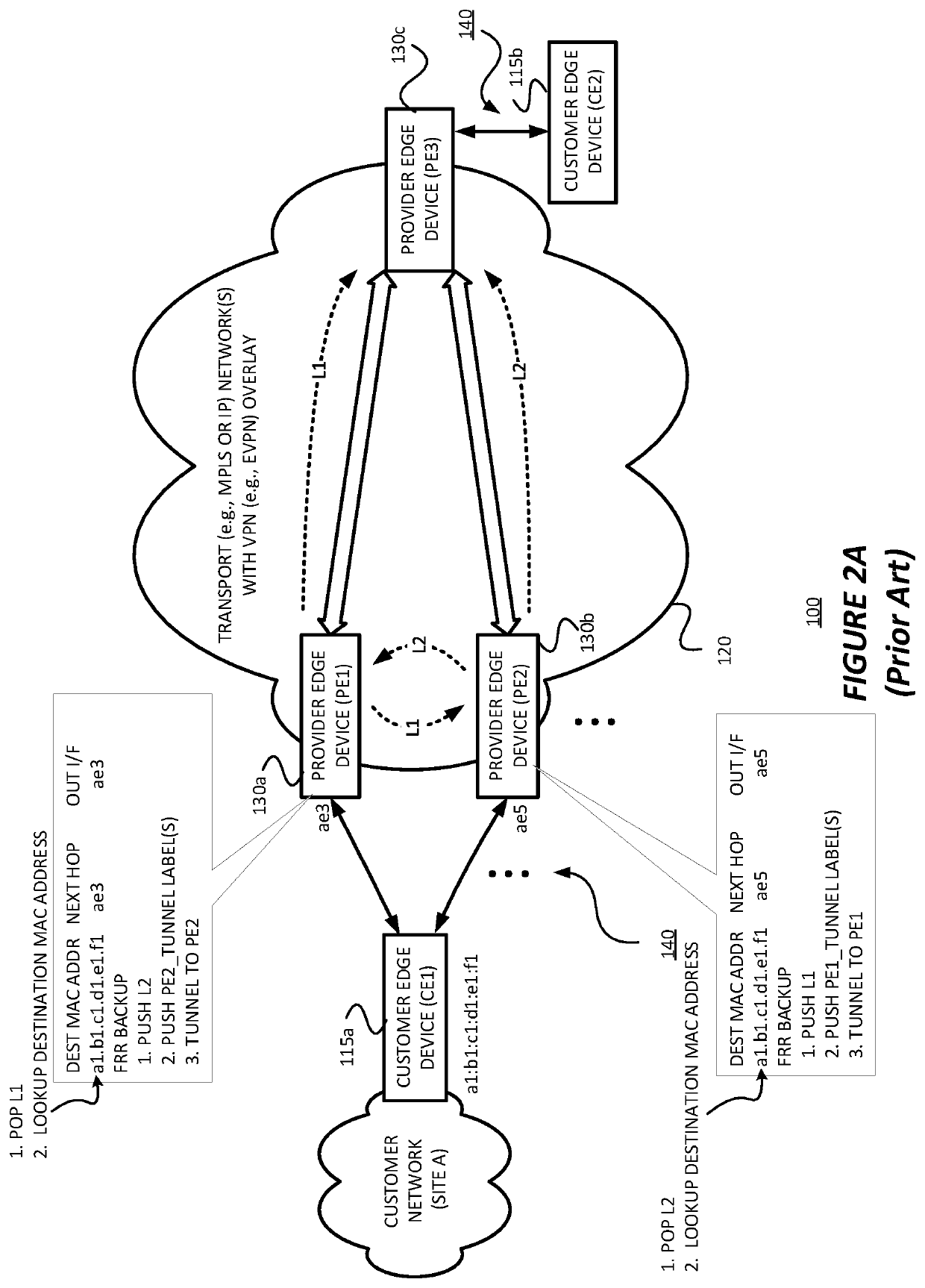
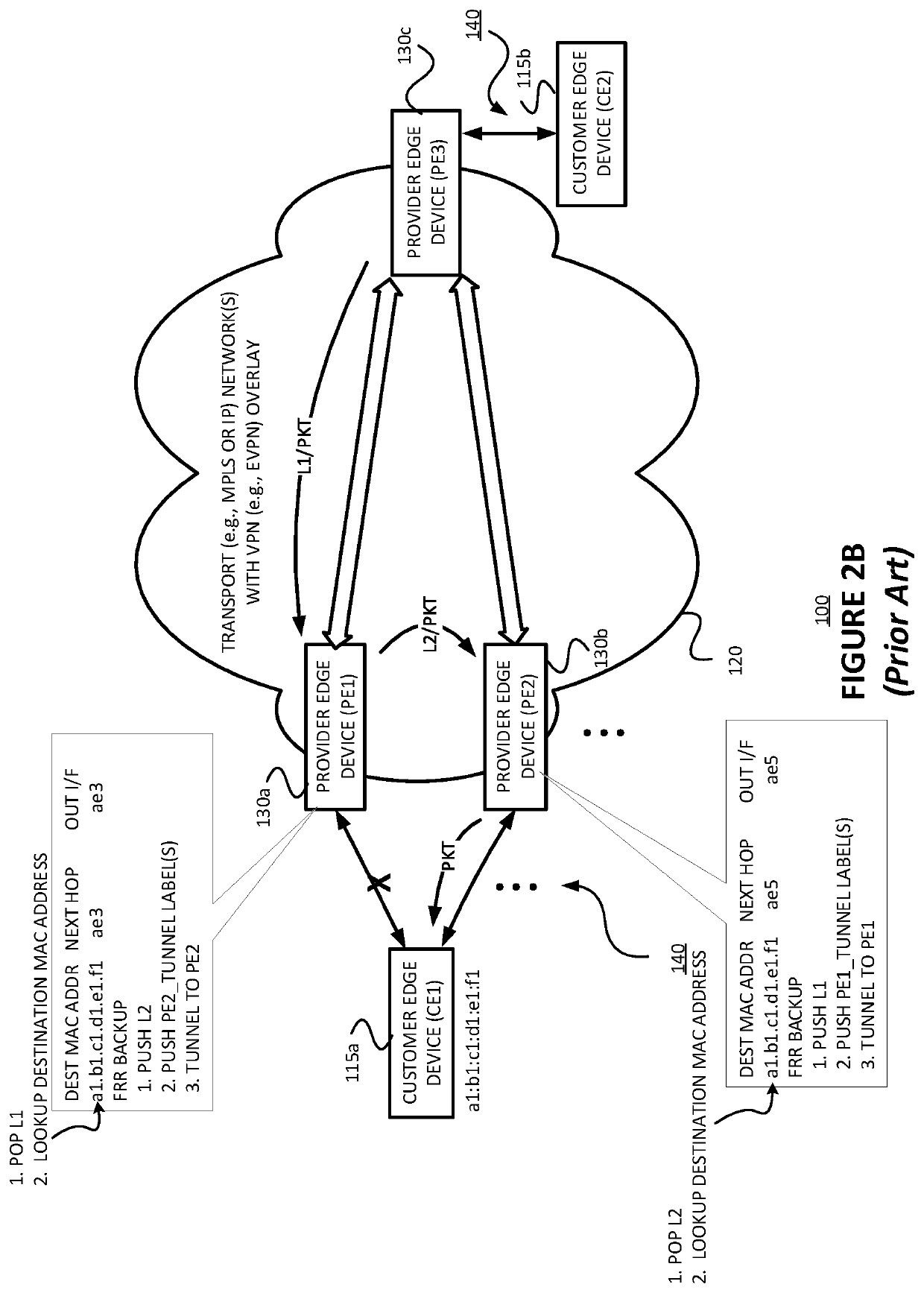
Techniques are described for providing fast convergence in the event of a link failure in an all-active multi-homed Ethernet virtual private network. A provide edge (PE) network device may pre-configure an interface next hop and secondary next hops. The secondary next hops may be logical links to other PE network devices in the same Ethernet segment. In the event of a link failure in the interface next hop between the PE network device and a customer edge (CE) network device, the PE network device may be configured to forward data traffic to the CE network device using the secondary next hops. In the event of a link failure between the PE network device and a core network, the PE network device may be configured to send an out-of-service message to the CE network device that instructs the CE network device to stop sending traffic to the PE network device.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Mobile terminal and network node
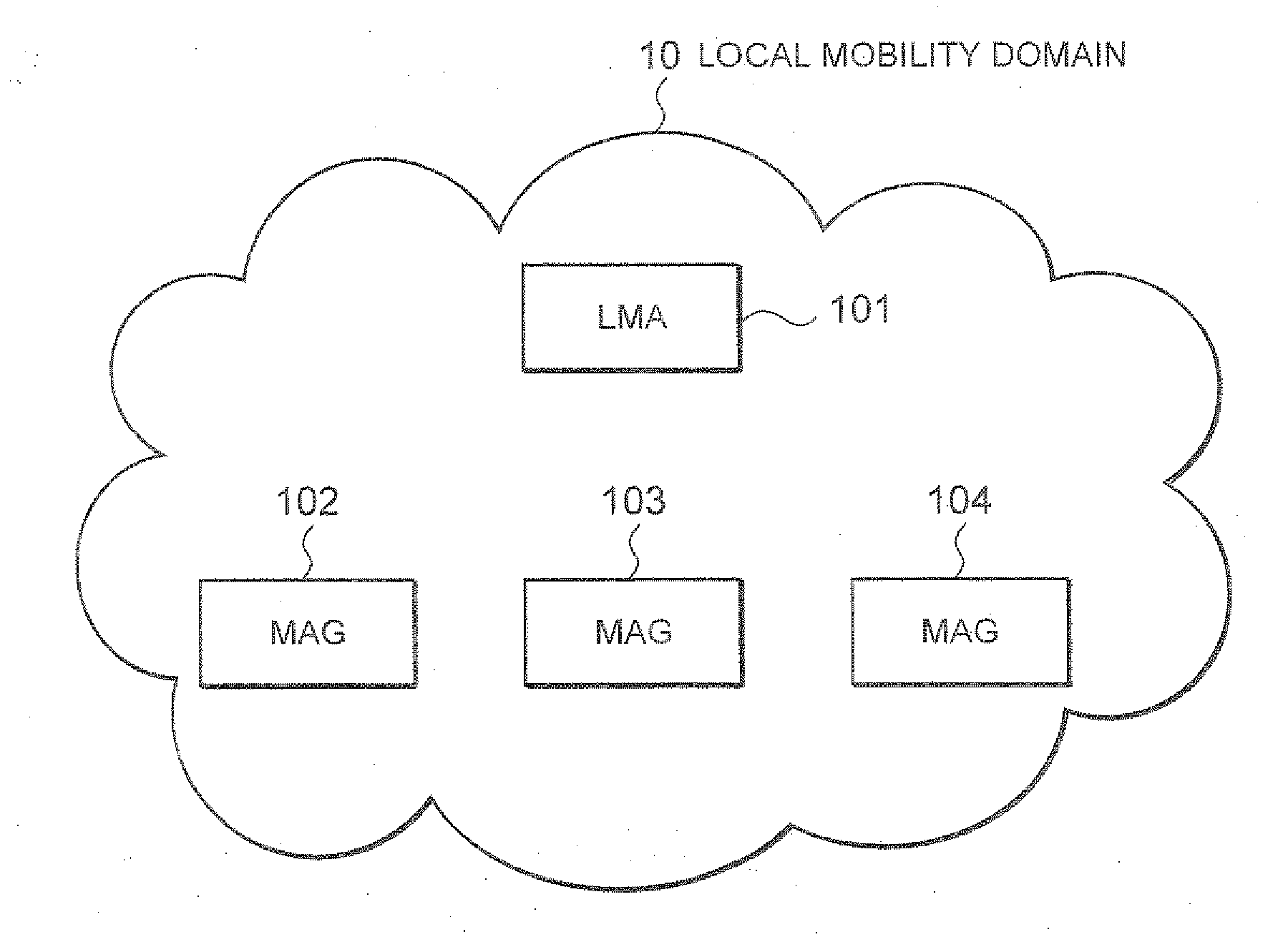
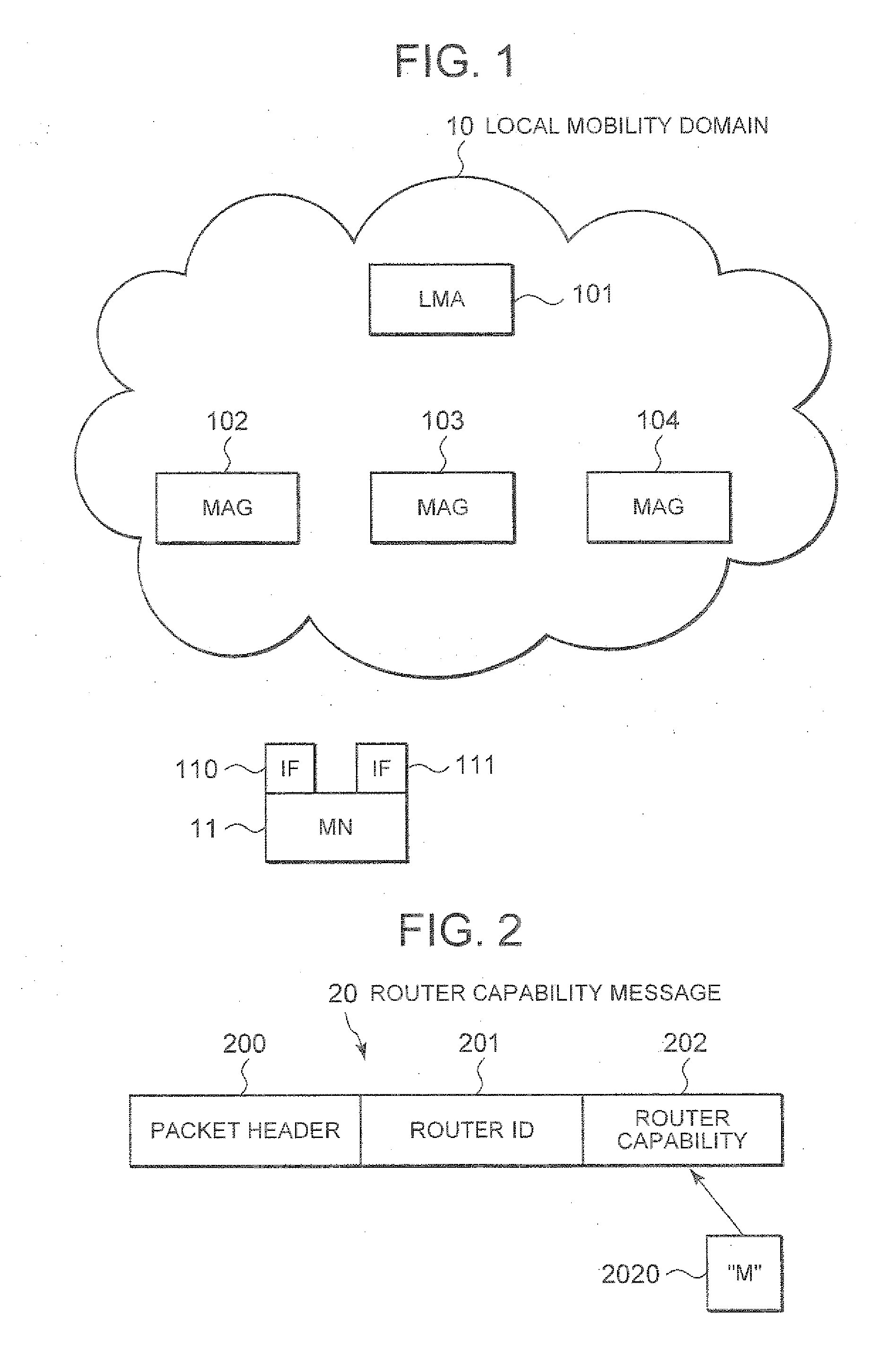
InactiveUS20110116450A1Accurate specificationsMaintain support effectDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationComputer scienceMultihoming
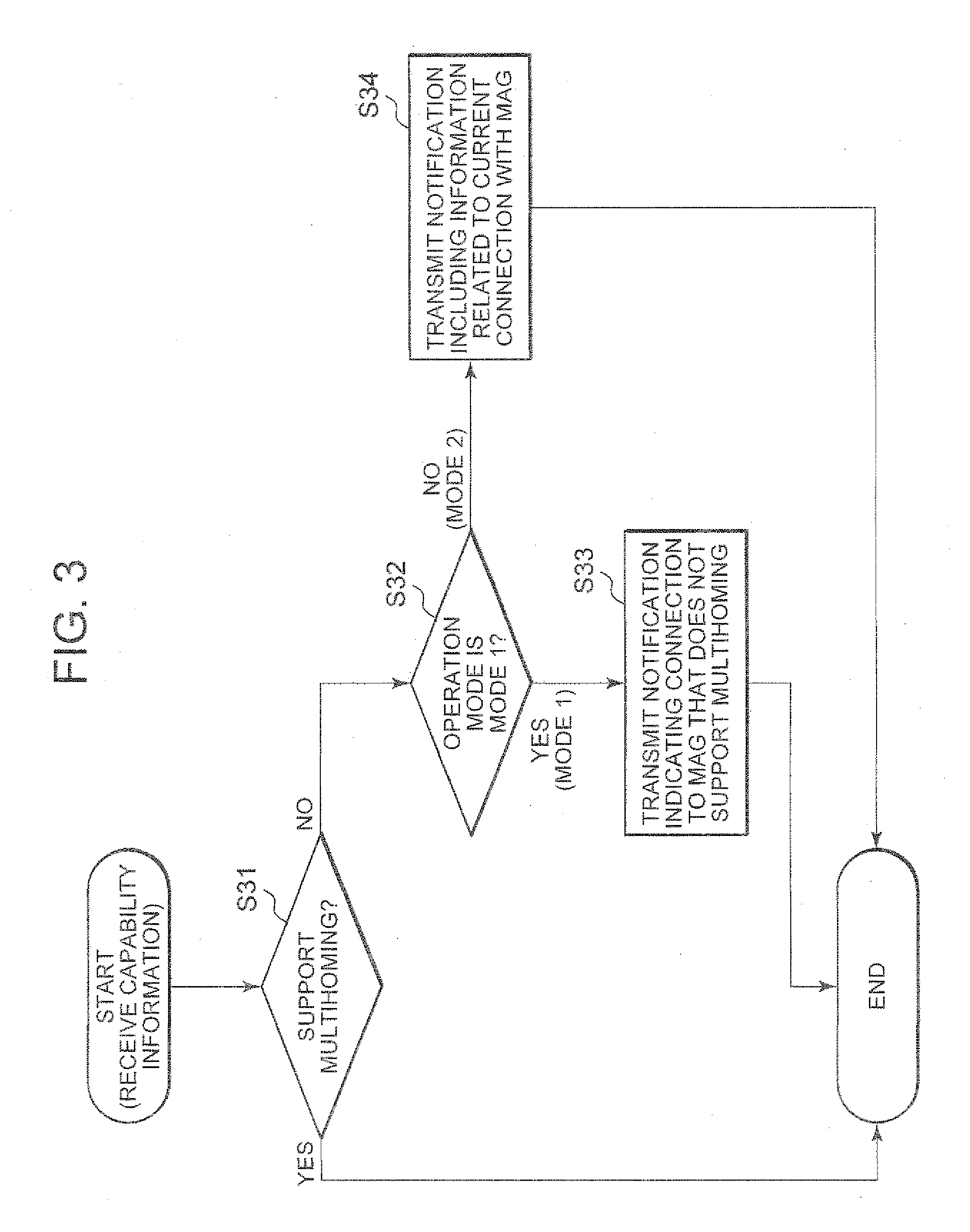
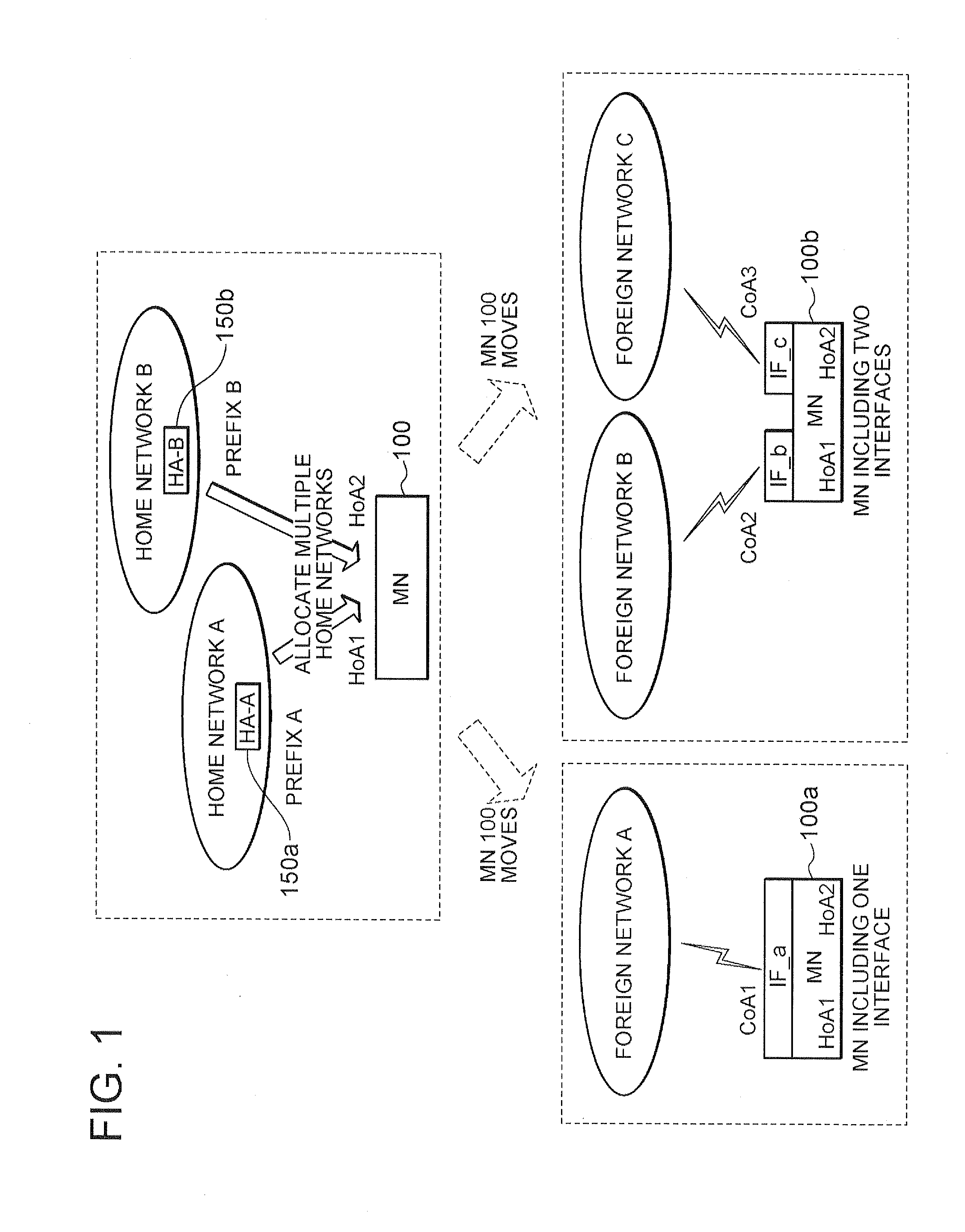
Disclosed is a technique for surely supporting multihoming for a mobile terminal (mobile node) moving in a local mobility domain. A mobile node (MN) 11 connects via an IF 110 to a mobile access gateway (MAG) 102 that supports multihoming, and further attempts to connect via an IF 111 to a MAG 103 that does not support multihoming. Under these conditions, according to this technique, when the MN recognizes that the MAG 103 does not support multihoming, the MN notifies a local mobility domain that the MAG 103 does not support multihoming if connection with the MAG 103 is not yet established, and notifies the local mobility domain of information on a connection to a local mobility domain other than the MAG 103 (connection with the MAG 102) if the connection with the MAG 103 is already established.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Communication Node and Communication Control Method
ActiveUS20080259848A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPacket communicationCommunication control
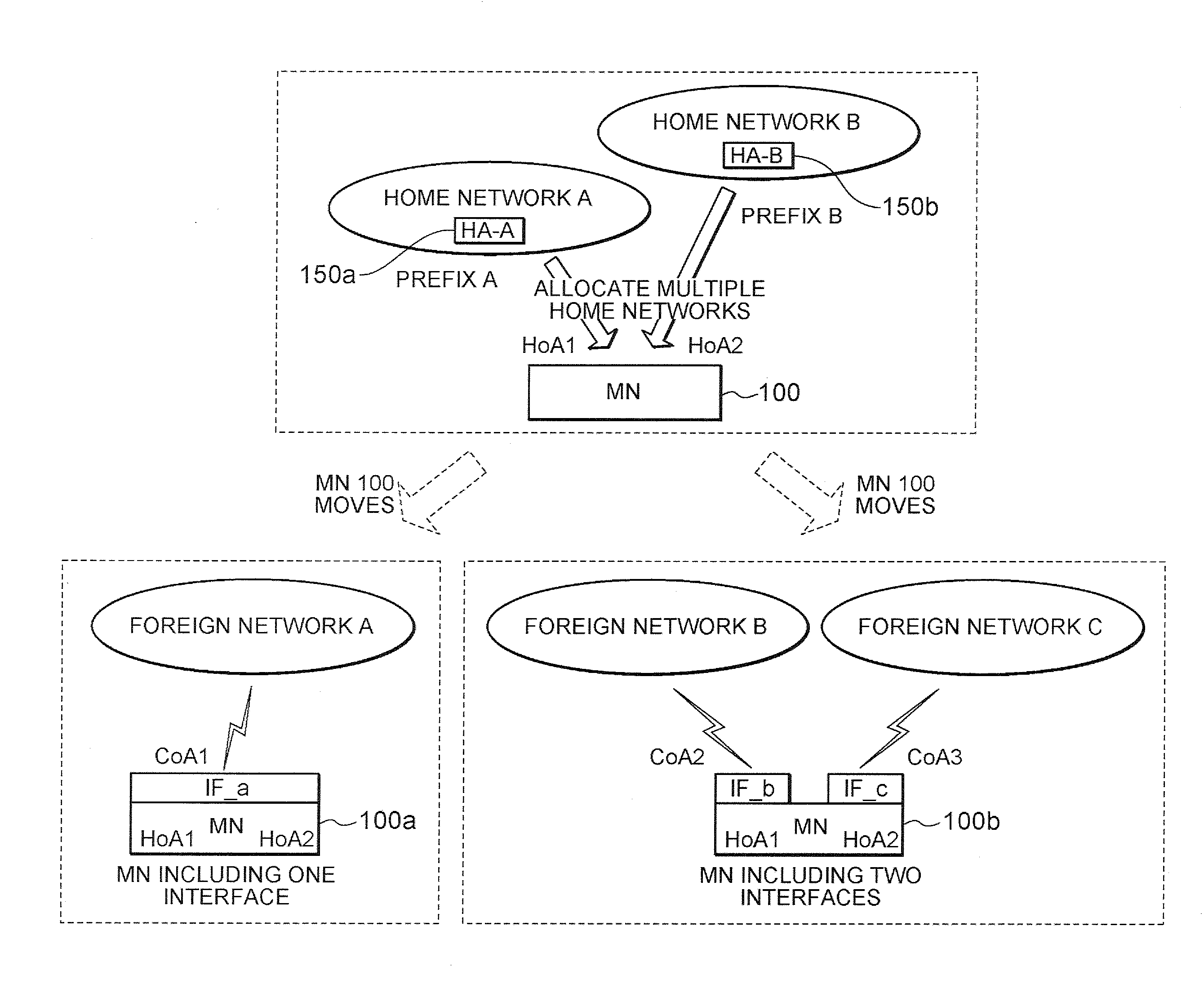
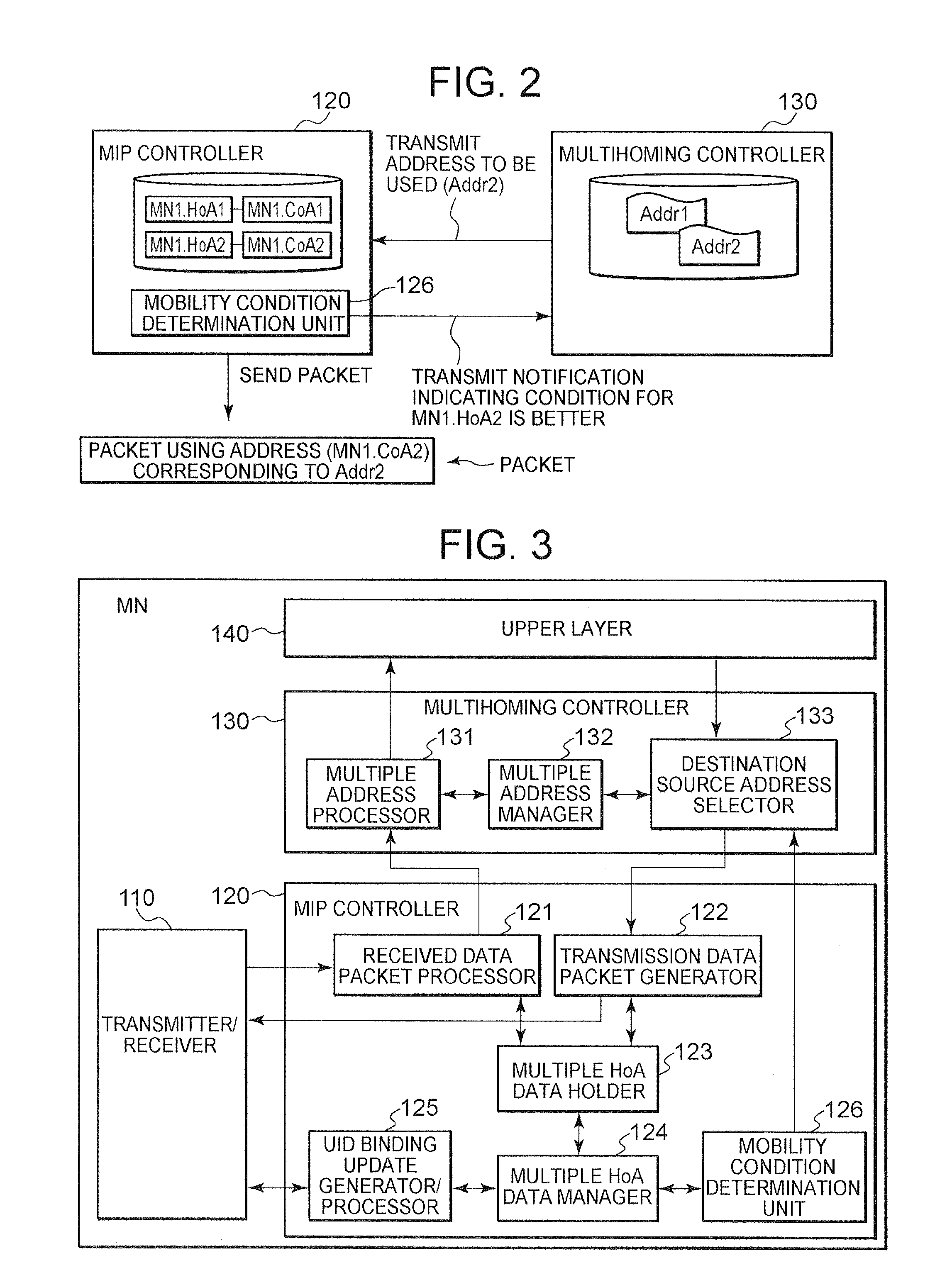
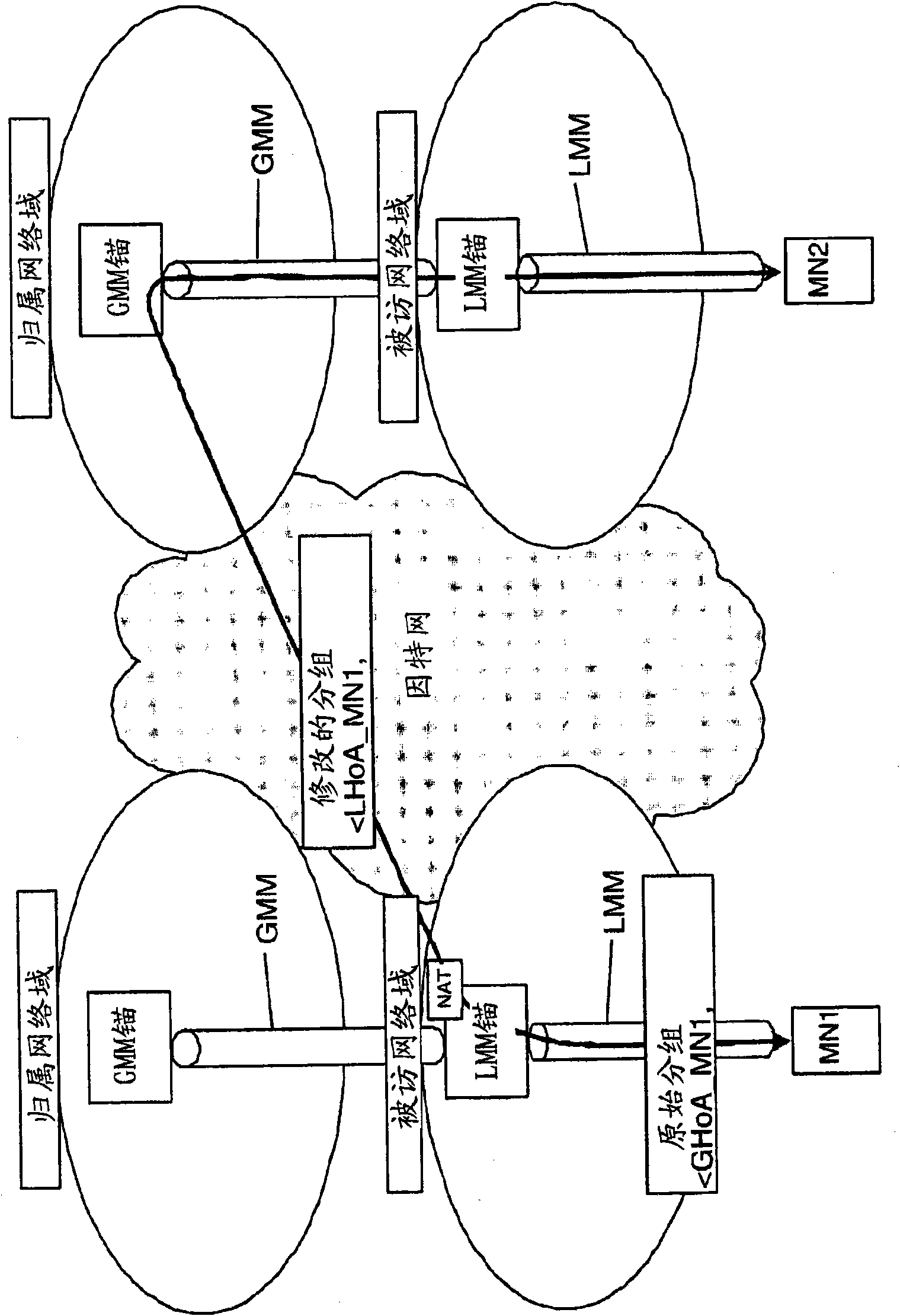
A technique is disclosed whereby, in the case of wherein a communication node includes both a mobility management function and a multihoming function, based on a condition that occurs due to moving, an appropriate address can be selected from multiple addresses in a multihomed state. According to the technique, a mobility condition determination unit 126, provided in an MIP controller 120 that manages moving of a communication node, obtains and examines various conditions that has occurred as a communication node is moving, selects an appropriate HoA (e.g., the home address of an MN1) for the current connection situation, and transmits, to a multihoming controller 130, a notification indicating that a set of the selected HoA and a CoA is appropriate addresses to be used. Upon receiving the notification from the mobility condition determination unit, the multihoming controller transmits, to the MIP controller, an address (Addr2) consonant with the received HoA, and the MIP controller performs packet communication using the HoA or the CoA consonant with the address.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Multi-homing using controlled route leakage at a backup service provider
ActiveUS7630392B2Fast internetImprove utilizationBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexNetwork addressingNetwork address
A technique for implementing route aggregation in a computer network containing a multi-homed customer site connected to primary and second networks, which in turn are both connected to a common “backbone” network. According to the technique, the primary network allocates a block of network addresses for the customer site, and the customer site notifies the secondary network of its allocated addresses. The secondary network first determines whether the primary network has already advertised an aggregated route which incorporates the customer site's route. If so, the secondary network “suppresses” (i.e., does not advertise) the customer site's route. The secondary network only “unsuppresses” the customer site's route if it detects that the primary network has lost connectivity to the customer site and / or the backbone network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Routing system for internet traffic
ActiveUS20150103662A1Fine granularityMaximizes total sumError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternet trafficGlobal optimal
A deterministic approach for route selection in the Internet and other multi-homed networks is presented that is based upon a mathematical model that takes into consideration performance and costs while satisfying commitment constraints. The approach is expressed with a linear programming formulation that can be solved with conventional linear programming solver software. Performance metrics can be defined and combined in order to achieve the best route selection depending on requirements. Some of the potential benefits of the approach include: a global optimal solution for routing traffic (using metrics such as performance, cost, and other constraints), a dynamic weight assignment for performance metrics, and a flexible problem definition to add routing rules (e.g. static and restricted routes) to the model.
Owner:INTERNAP HLDG LLC
Multi-homed data forwarding storage
Methods and apparatus, including computer program products, for multi-homed data forwarding storage. A method includes, in a computer system having multiple non-loopback network addresses, receiving a request to store data, directing the data to a memory location associated with a first non-loopback network address available to receive the data, continuously forwarding the data from the memory location associated with the first non-loopback network address to a memory location associated with another non-loopback network address in the computer system without storing on any physical storage device in the computer system. The continuously forwarding can include detecting a presence of the data in a memory location associated with a specific non-loopback network address, and forwarding the data to another memory location of another non-loopback network address in the computer without storing on any physical storage device.
Owner:DISTRIBUTED MEDIA SOLUTIONS LLC
Technique for determining multi-path latency in multi-homed transport protocol
InactiveUS7761562B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionMulti pathDistributed computing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for realizing location management of multihomed terminals in universal network
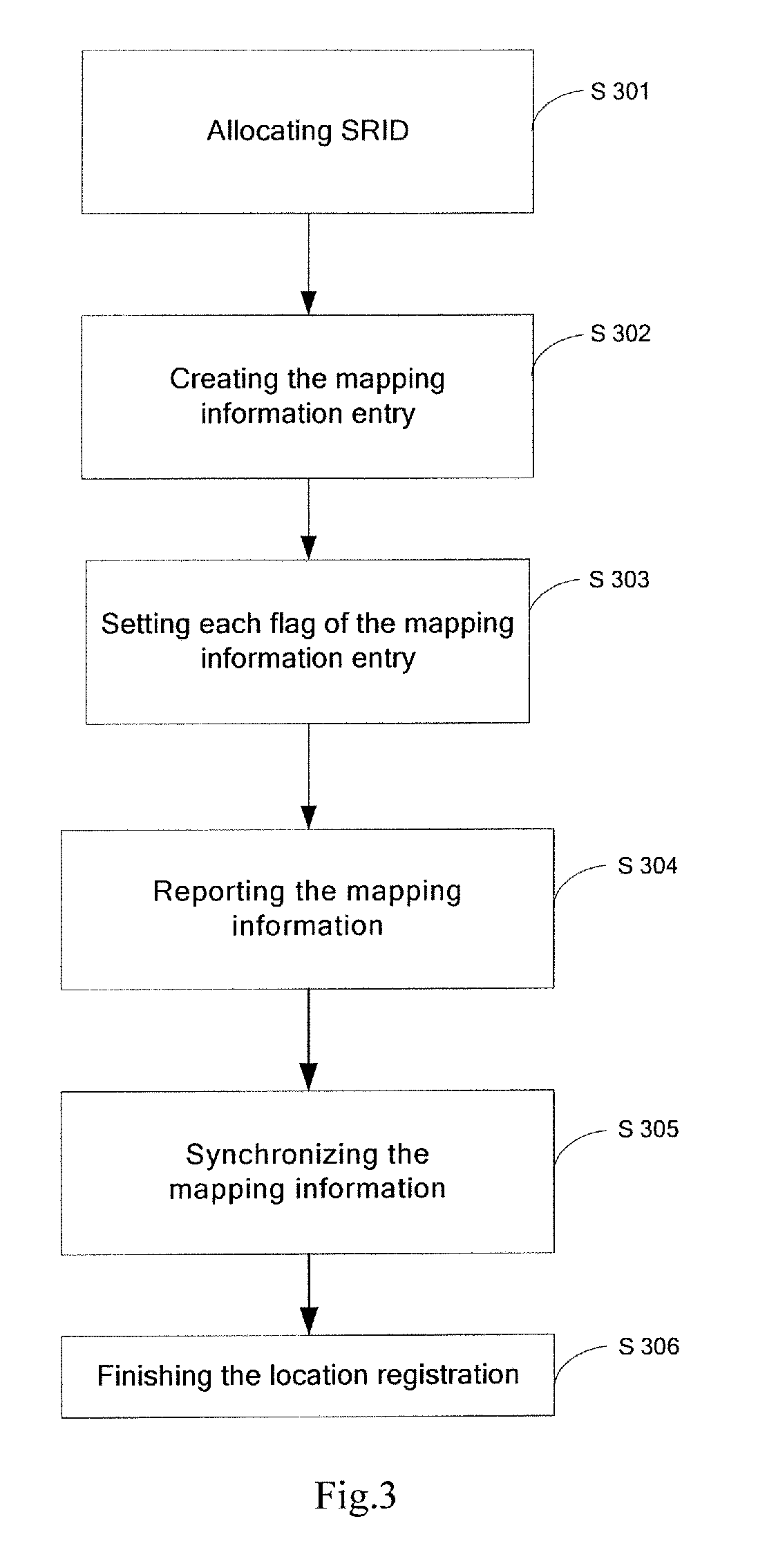
InactiveUS20100208617A1Facilitate location updateMaintain continuityData switching by path configurationNetwork data managementComputer networkService provision
In Universal Network, there is disclosed a method and system for realizing location management of multihomed terminals, the system comprises home domains and foreign domains, in which the home domains of a multihomed terminal refer to the domains managing the multihomed terminal; the other domains are the foreign domains of the multihomed terminal; each domain includes at least one Identifier Mapping Server and one Accessing-Switching Router; the Identifier Mapping Server memorizes and manages the mapping information; and the Accessing-Switching Router allocates the mapping information for multihomed terminals. This invention facilitates the implement of multihoming in the Internet and makes the network resources be used efficiently. Especially, the Internet service providers can manage the multihomed terminals easily and efficiently.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
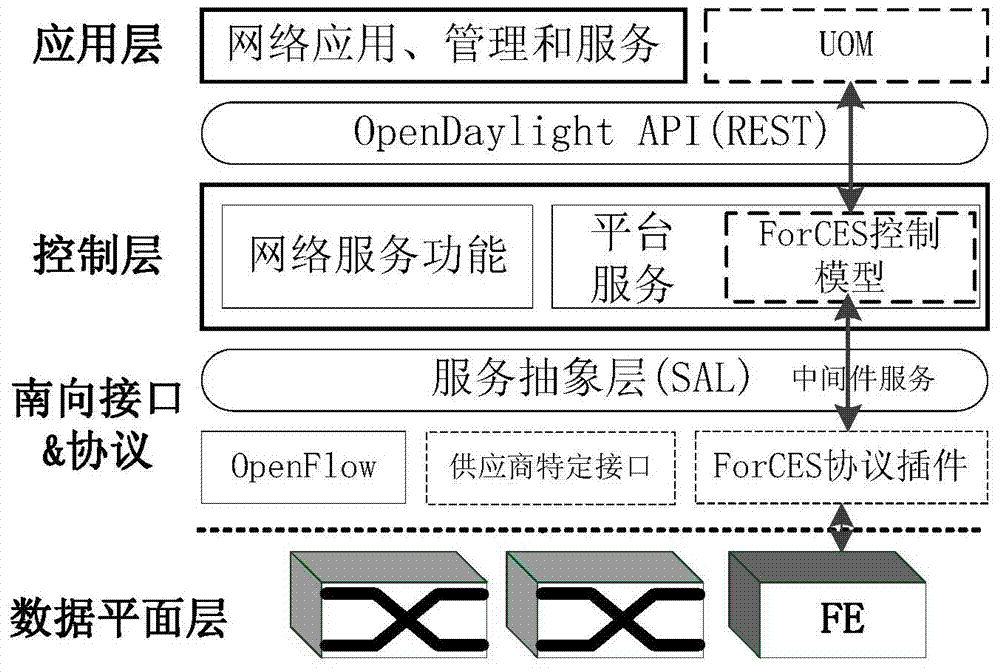
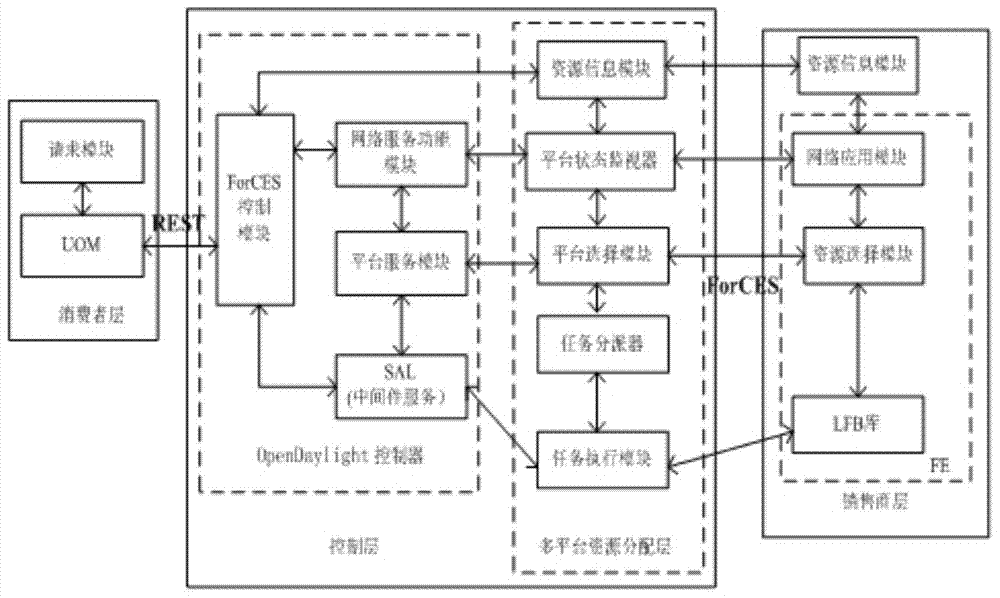
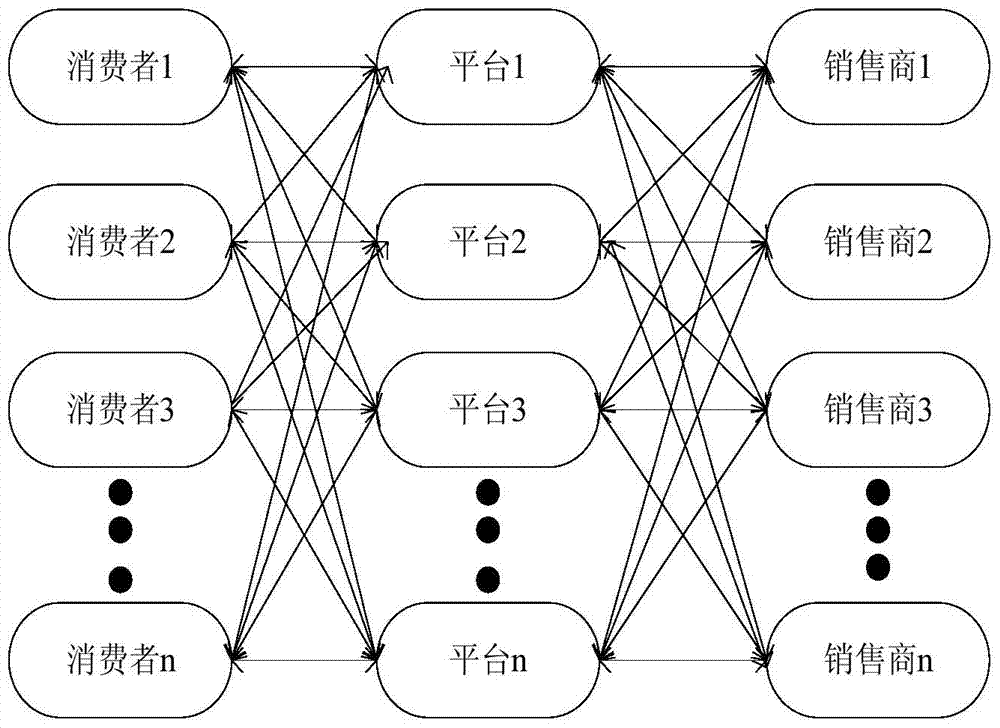
SDN resource distribution method based on two-sided market multihoming structure
ActiveCN103929379AEmbody innovationMeet the needs of the taskData switching networksControl layerStructure of Management Information
The invention discloses an SDN resource distribution method based on a two-sided market multihoming structure. The SDN resource distribution method based on the two-sided market multihoming structure comprises the steps that firstly, an SDN resource distribution frame is divided into a customer layer, a control layer and a retailer layer; secondly, after the customer layer receives application requests of different users, summarizes the application requests into a request information list and transmits the request information list to the control layer through a northbound interface; thirdly, the retailer layer transmits resource information to the control layer in real time through a southbound interface; fourthly, the control layer comprises a plurality of independent control platforms, each control platform receives the resource information from the retailer layer and sends the resource information and expense information of the control platforms to the customer layer, and the users in the customer layer carry out selection from the multiple control platforms according to the self needs; fifthly, each customer requires needed resources from the multiple control platforms, and carries out selection according to a resource cost-performance ratio provided by each control platform by using a resource combination strategy. The SDN resource distribution method based on the two-sided market multihoming structure meets the requirements for tasks of users, makes full use of network resources, and improves the reliability of the network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
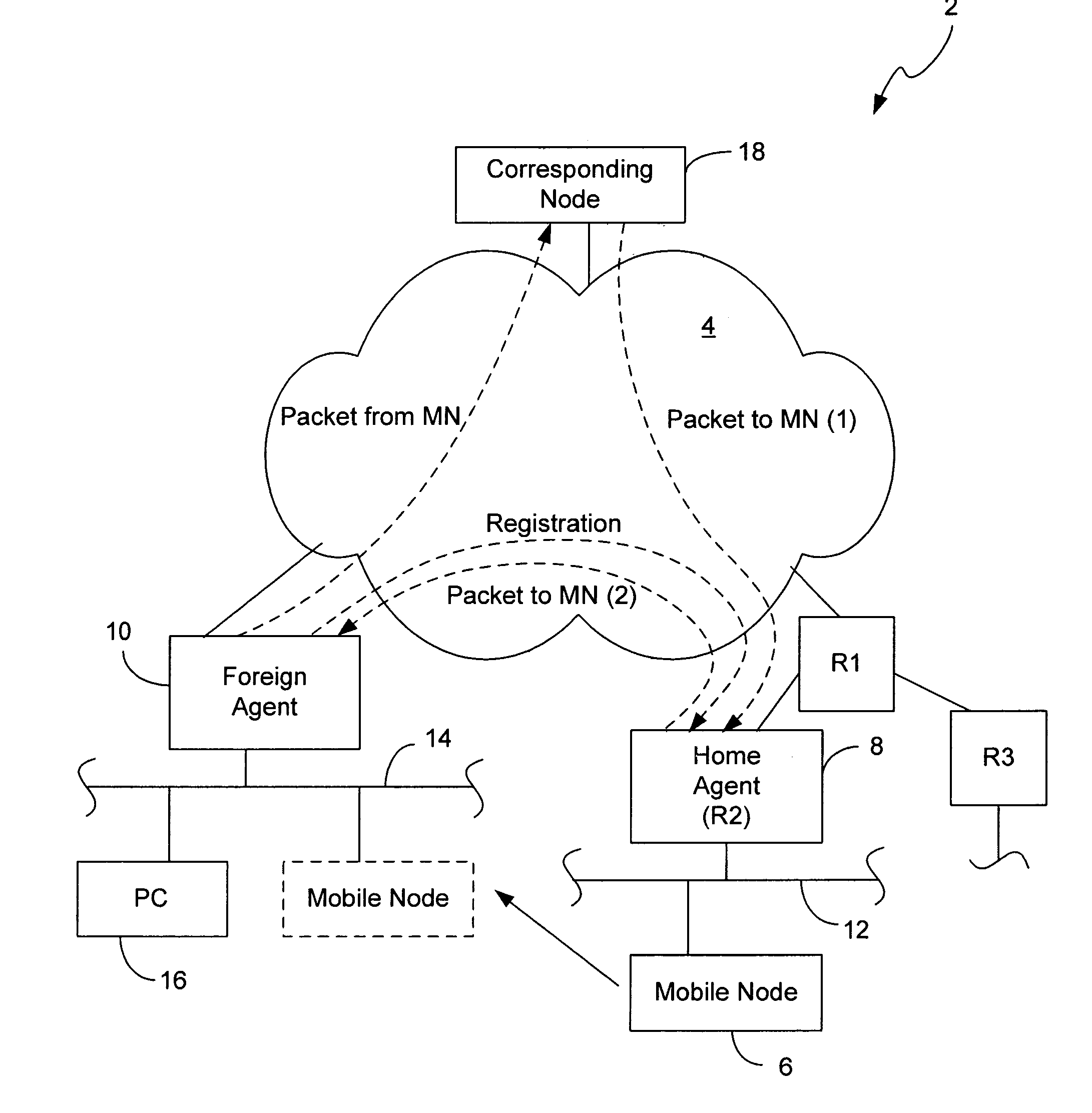
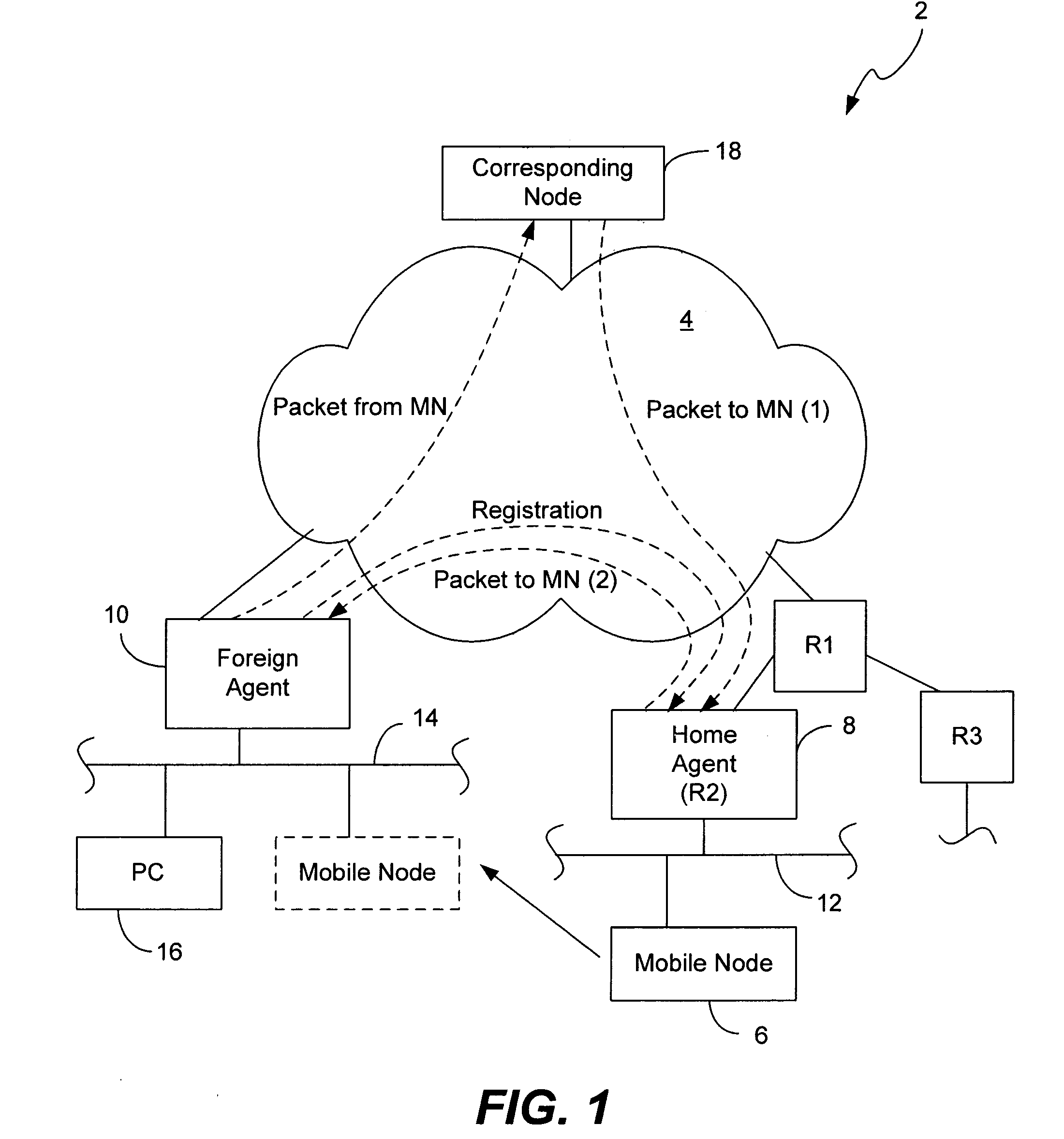
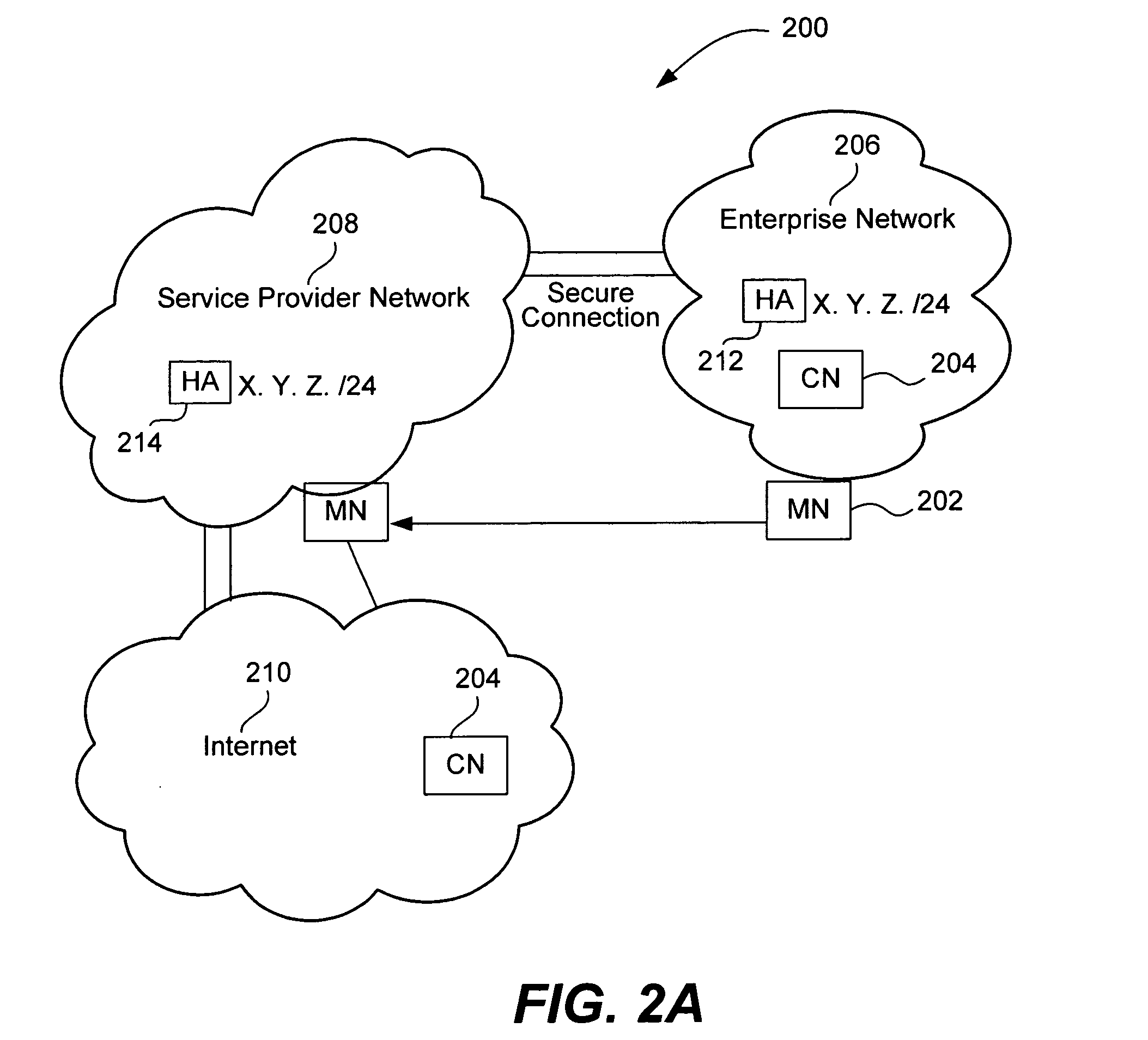
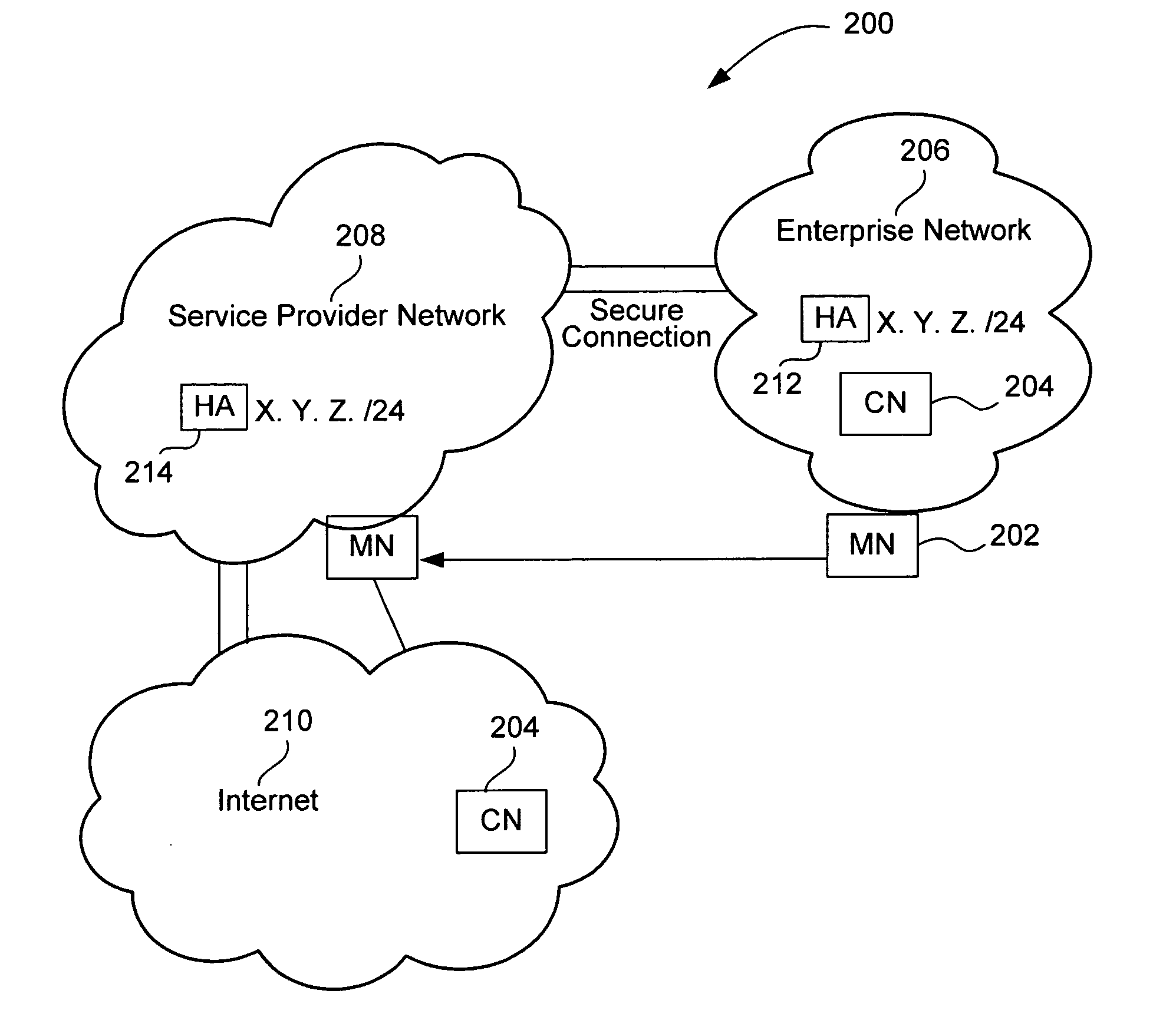
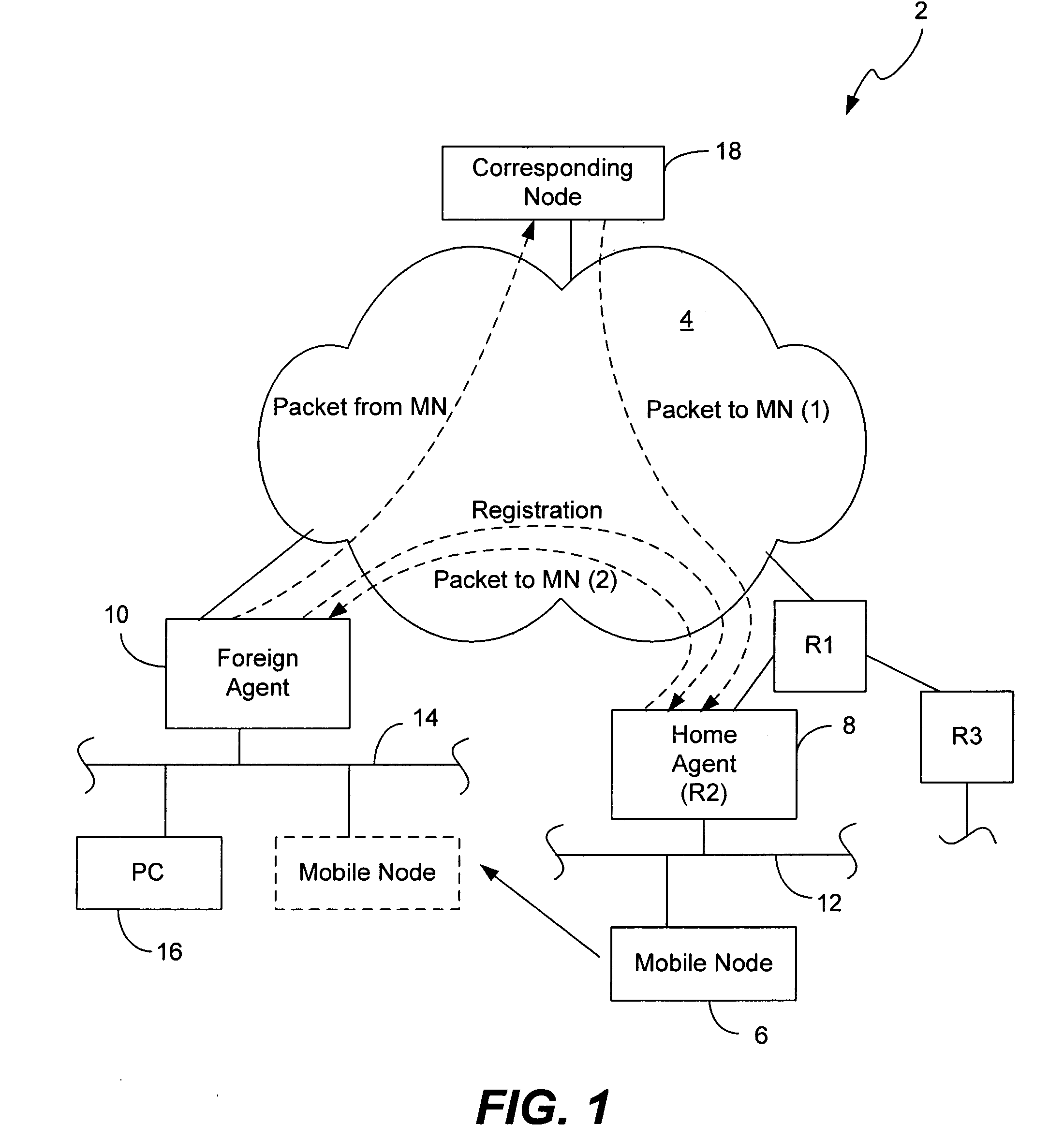
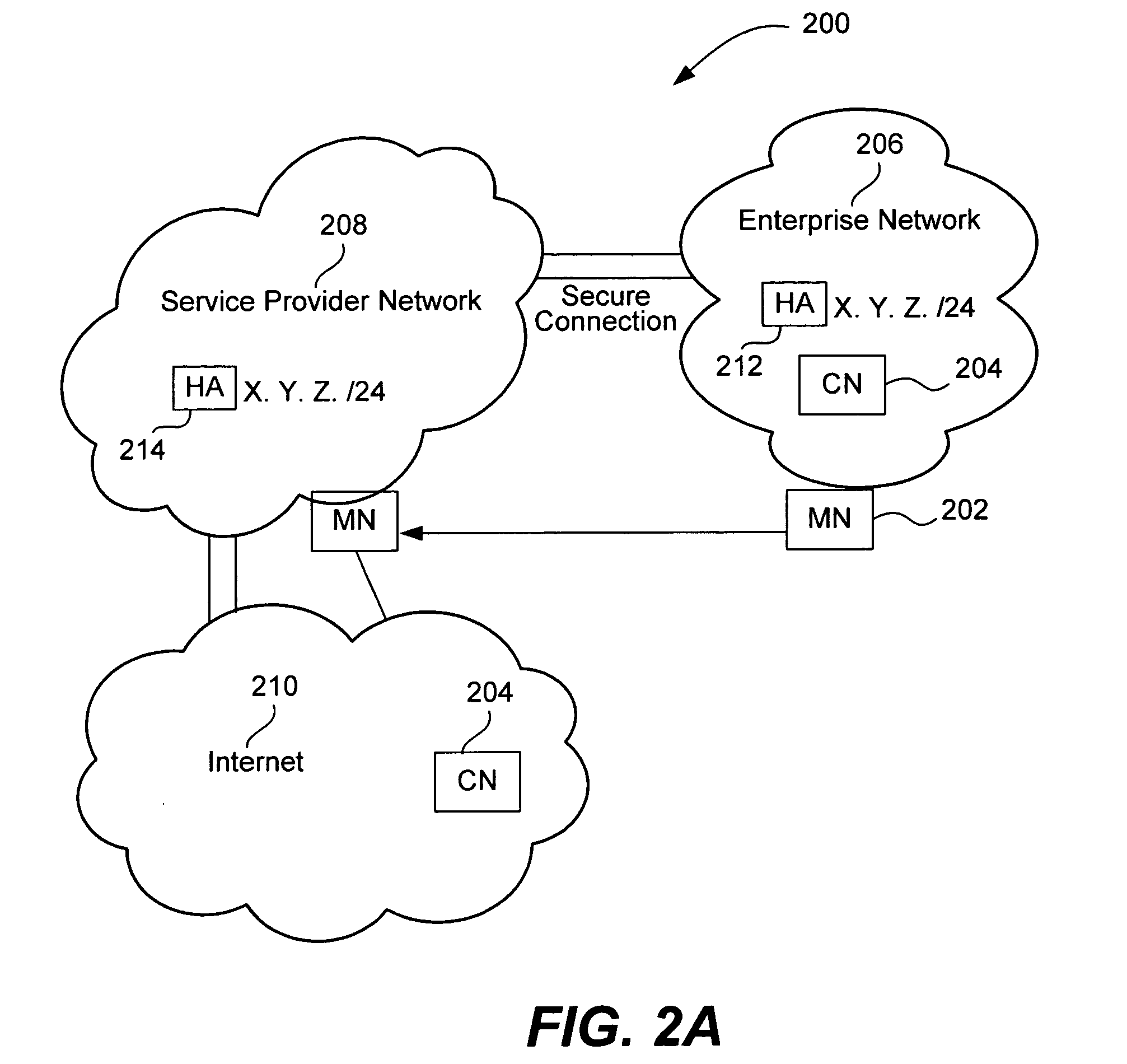
Mobile network operator multihoming and enterprise VPN solution
ActiveUS20070248062A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkMobile network operator
The disclosed embodiments support mobility internal and external to enterprise networks. Service providers provide mobility by providing Home Agent functionality corresponding to each Enterprise network. In this manner, mobility may be provided to Mobile Nodes both internal and external to their enterprise networks. Moreover, data packets may be transmitted by Mobile Nodes to Correspondent Nodes, whether they are within their enterprise network, the Service Provider network, or the Internet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
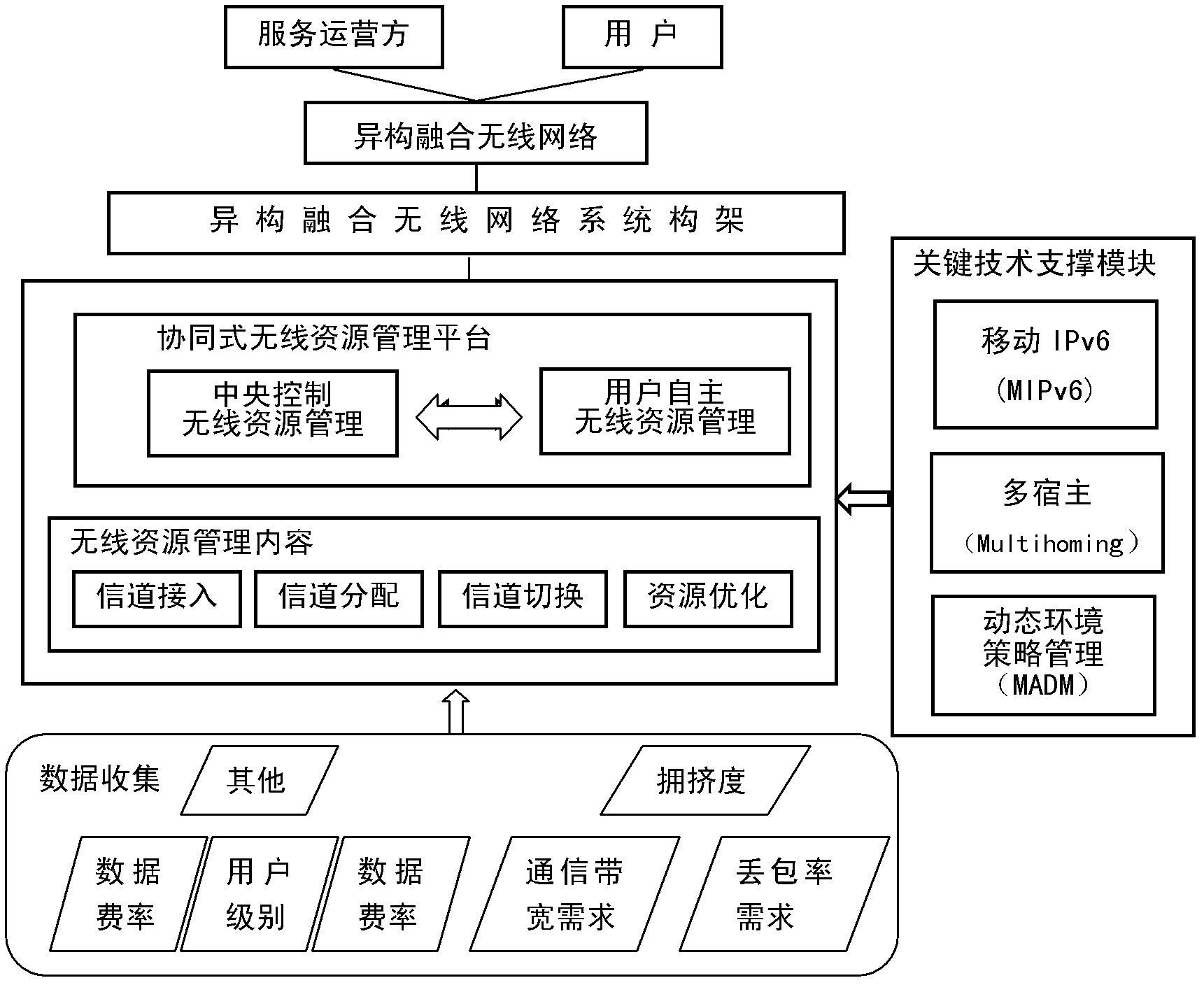
A mobile management system and management method based on IPv6 heterogeneous converged network
InactiveCN102291746AGuarantee unimpededEasy to findWireless communicationNetwork managementNetwork mobility
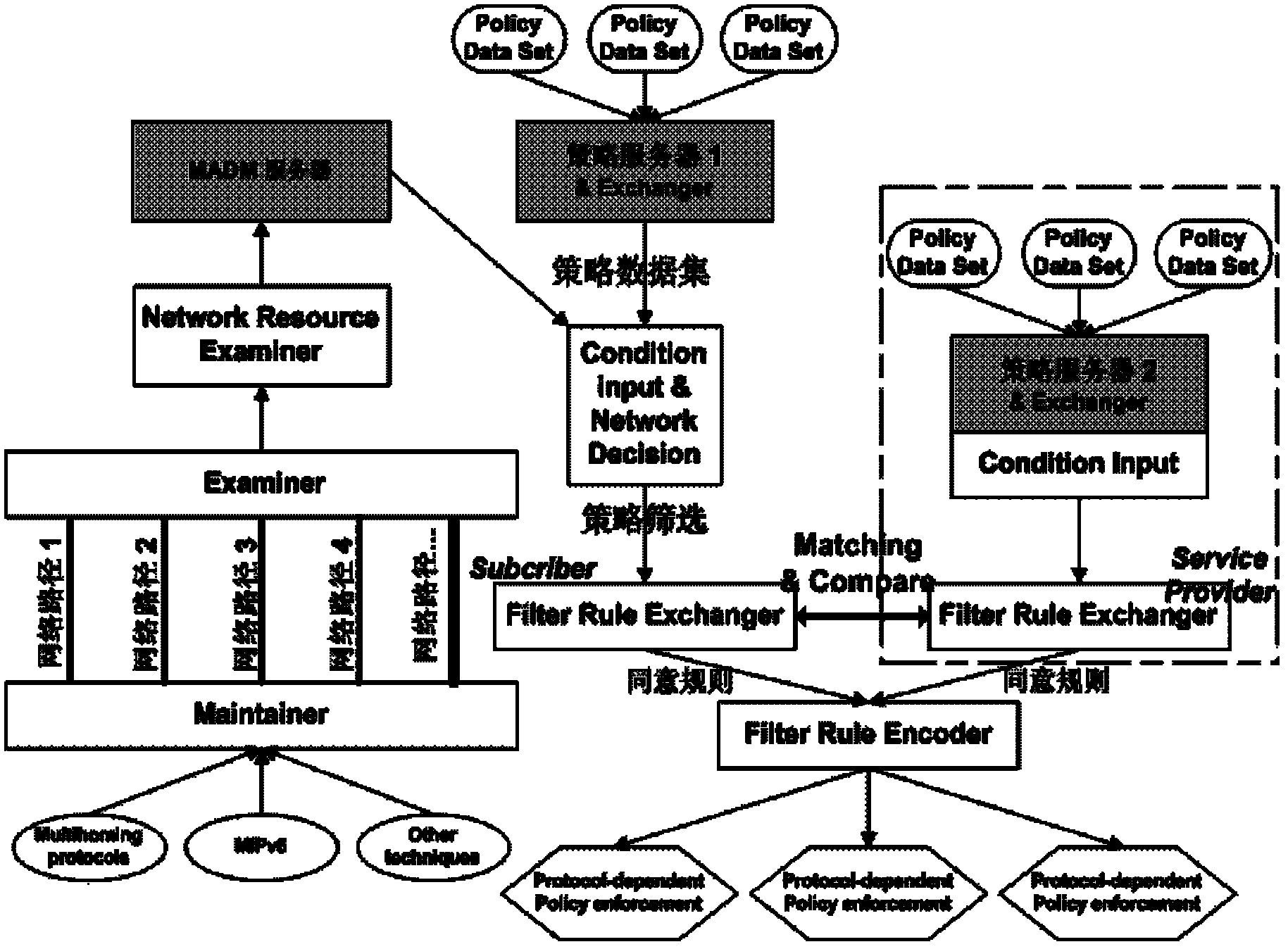
The invention discloses a mobile management system and management method based on IPv6 heterogeneous fusion network. The system introduces key technologies such as mobile IPv6 (MIPv6), multihoming (Multihoming), and dynamic environment In order to meet the needs of coordinated transmission of communication information in the environment, the traffic policy rules between heterogeneous converged networks are designed, so that each traffic is regulated by the policy to identify the network traffic of the bound flow of the heterogeneous interface, and the wireless resources of the heterogeneous converged network are optimized. Manage content. Beneficial effects of the present invention: the application of mobile IPv6, multi-homing, dynamic environment strategy management and multi-attribute decision-making key technologies greatly improves the flexibility of network selection, flow distribution, vertical (horizontal) switching and dynamic matching process, and improves Quality of Service (QoS) and Quality of Experience (QoE) for ubiquitous connectivity.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
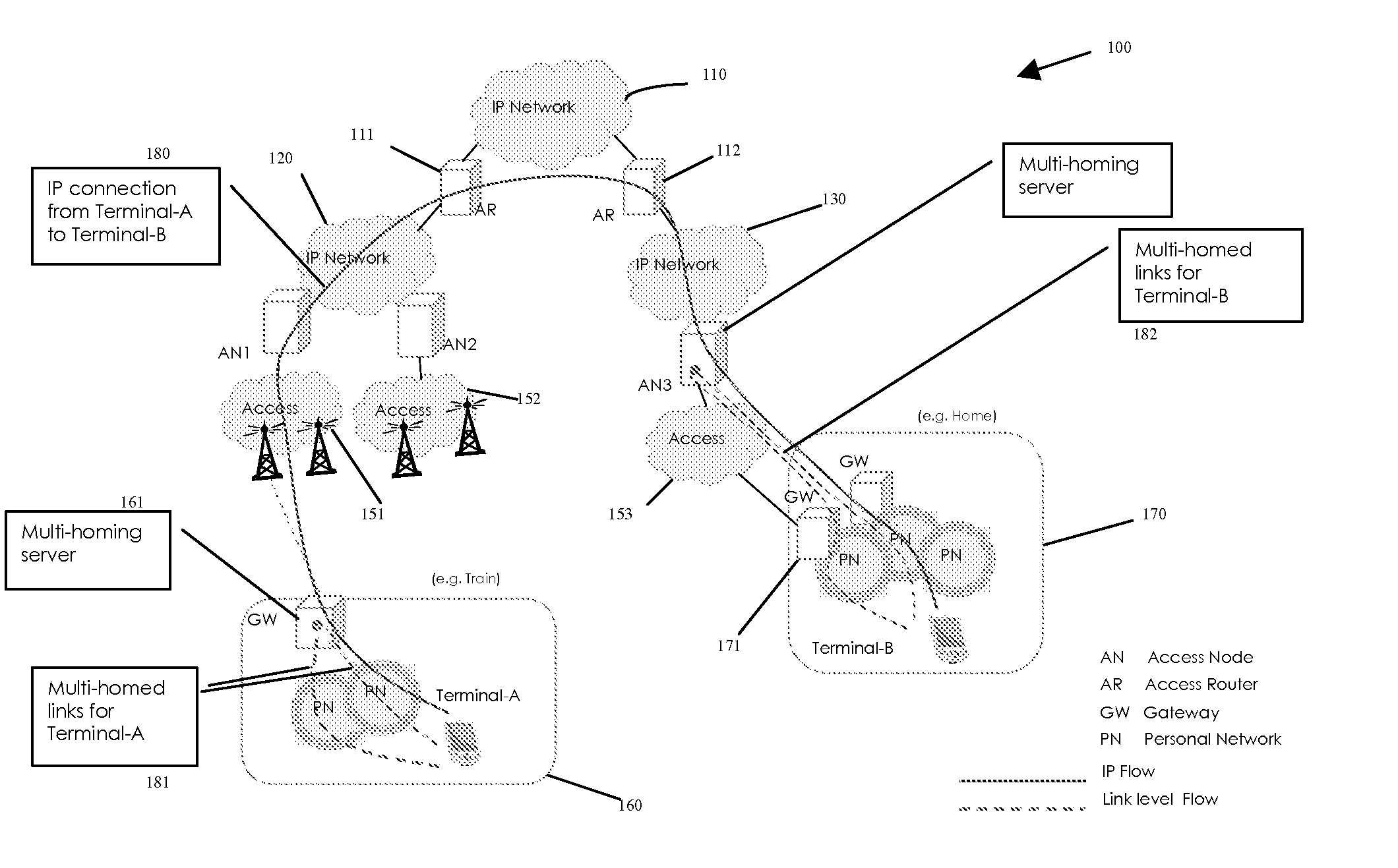
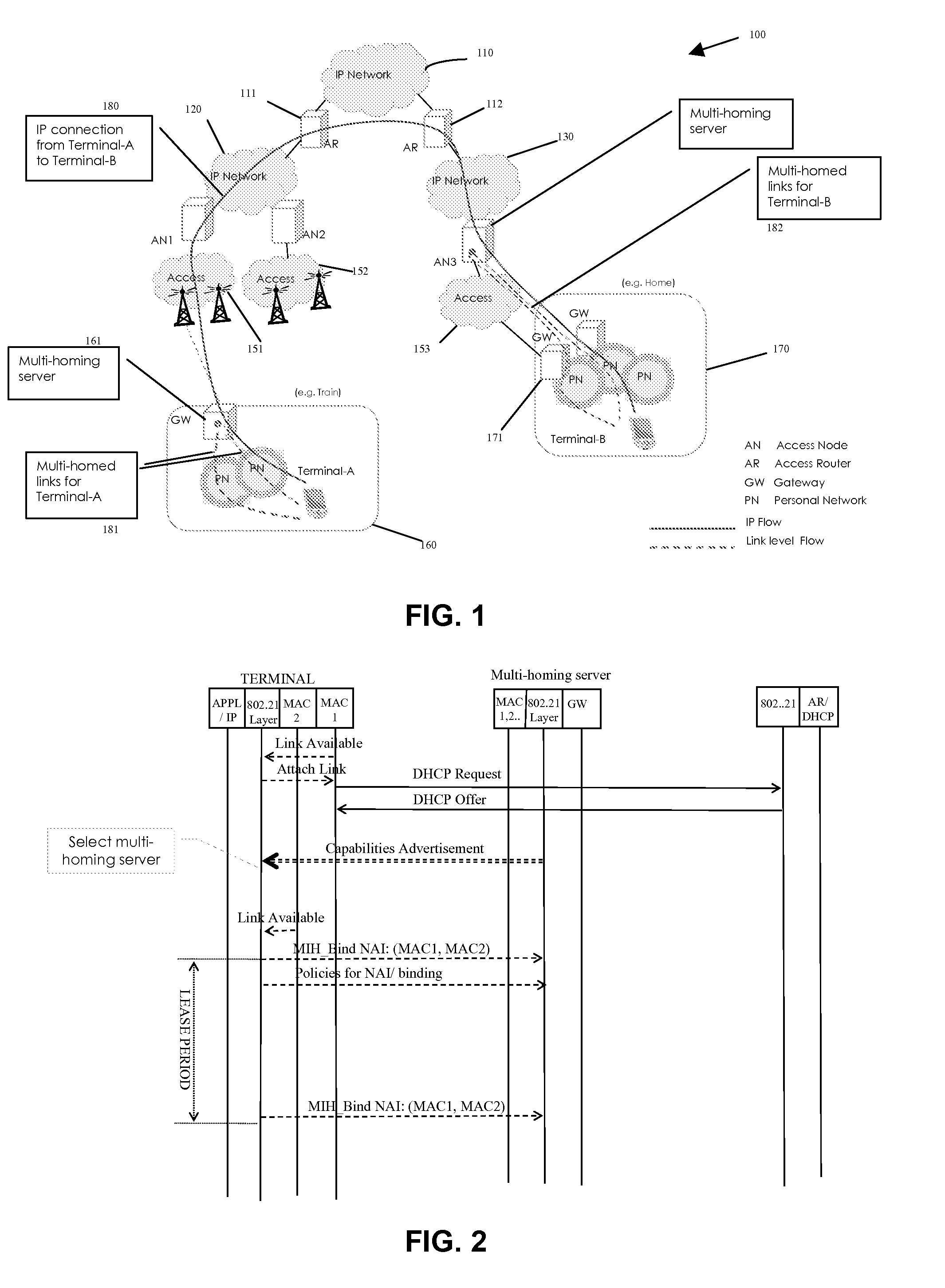
System for link independent multi-homing in heterogeneous access networks
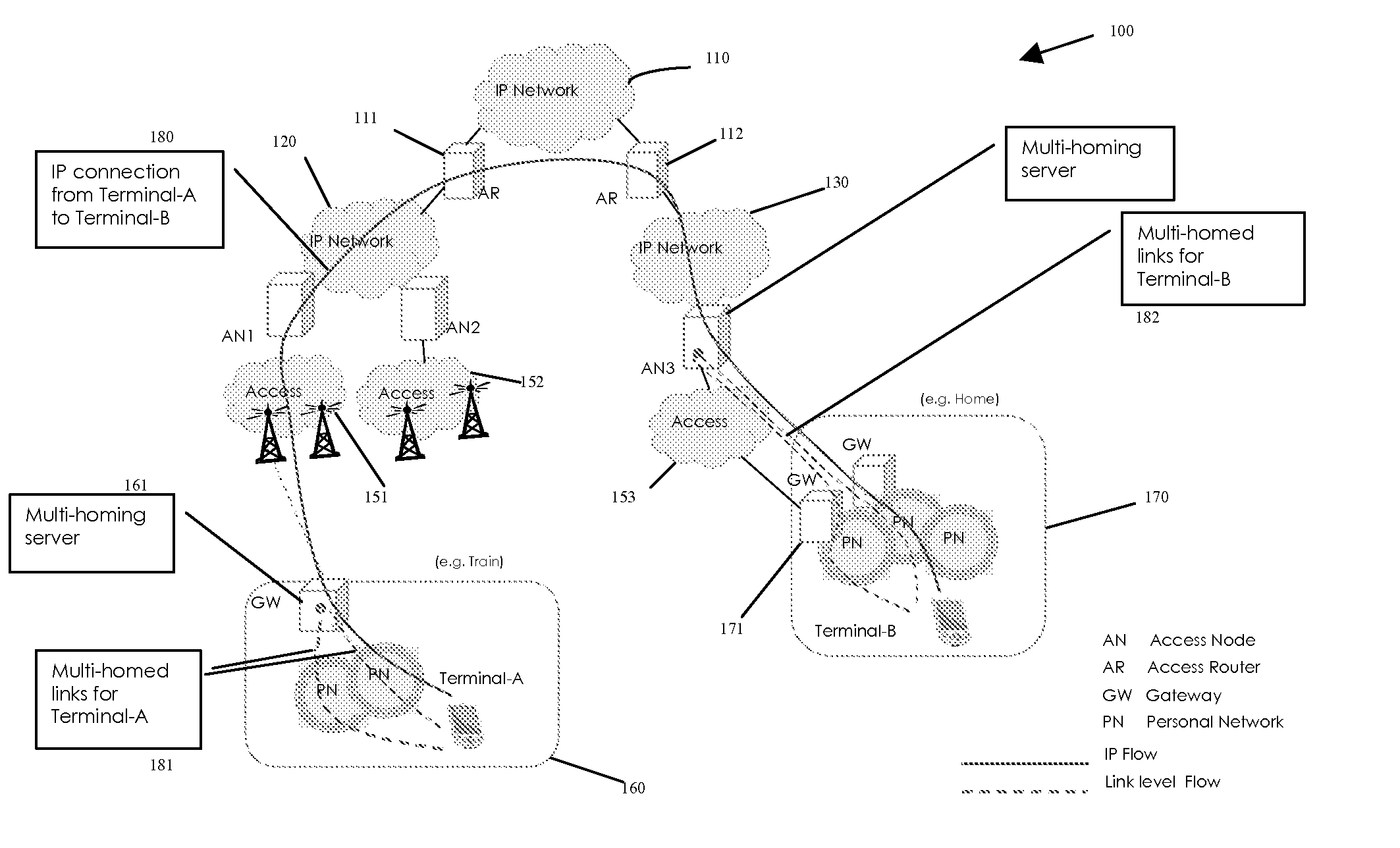
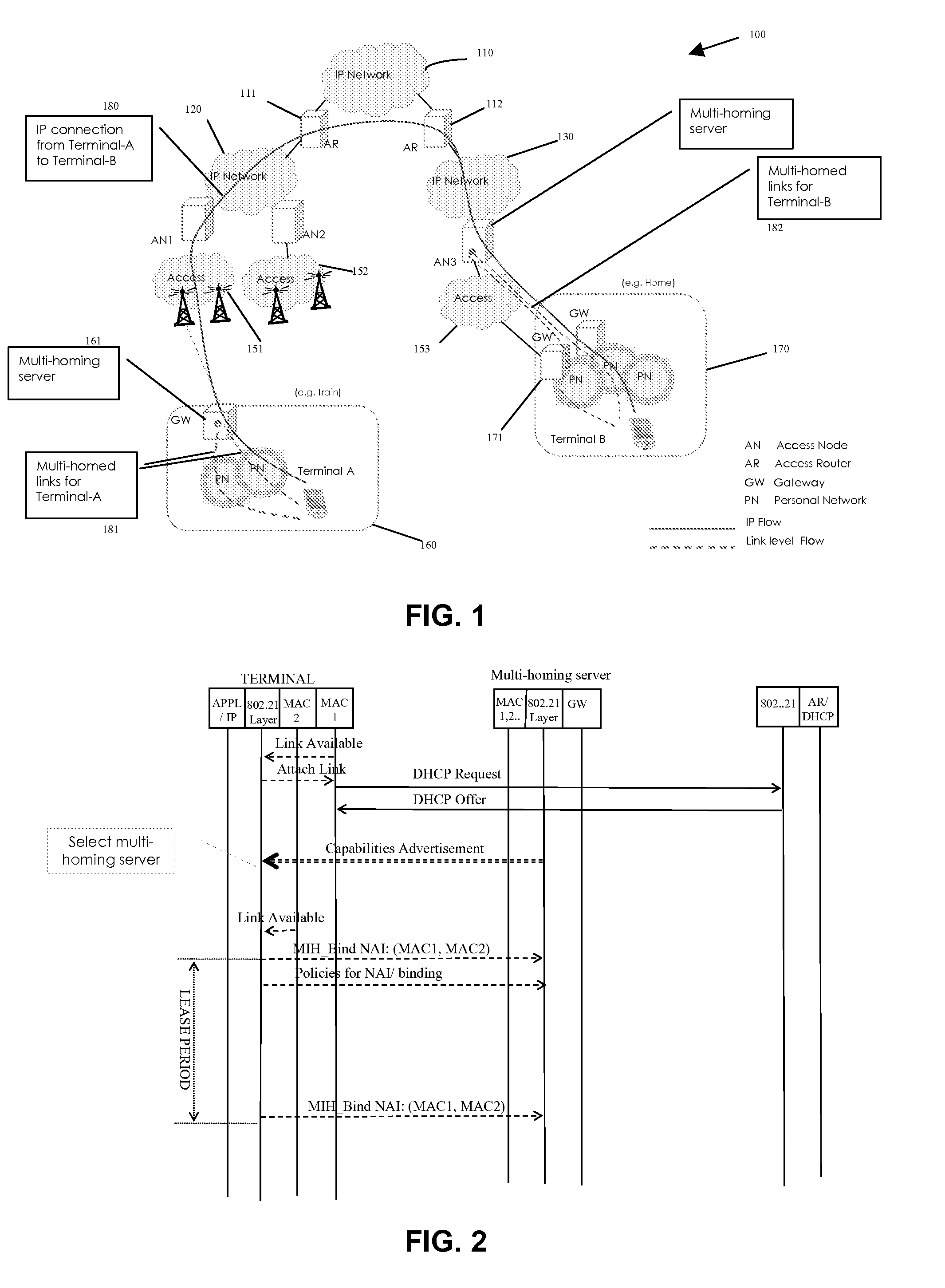
ActiveUS20080013556A1Data switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesAccess networkMedia access control
A system for link-independent multihoming in a network having heterogeneous access network technologies is disclosed, providing such multihoming in a manner transparent to IP connections. The system of the present invention provides constructs and methods for: discovering and selecting a multihoming server; selecting a primary media access control (MAC) address; associating multiple link addresses with a MAC address; and forwarding packets via the multihoming server based on certain defined policies.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Method and apparatus for route selection of host in multihoming site
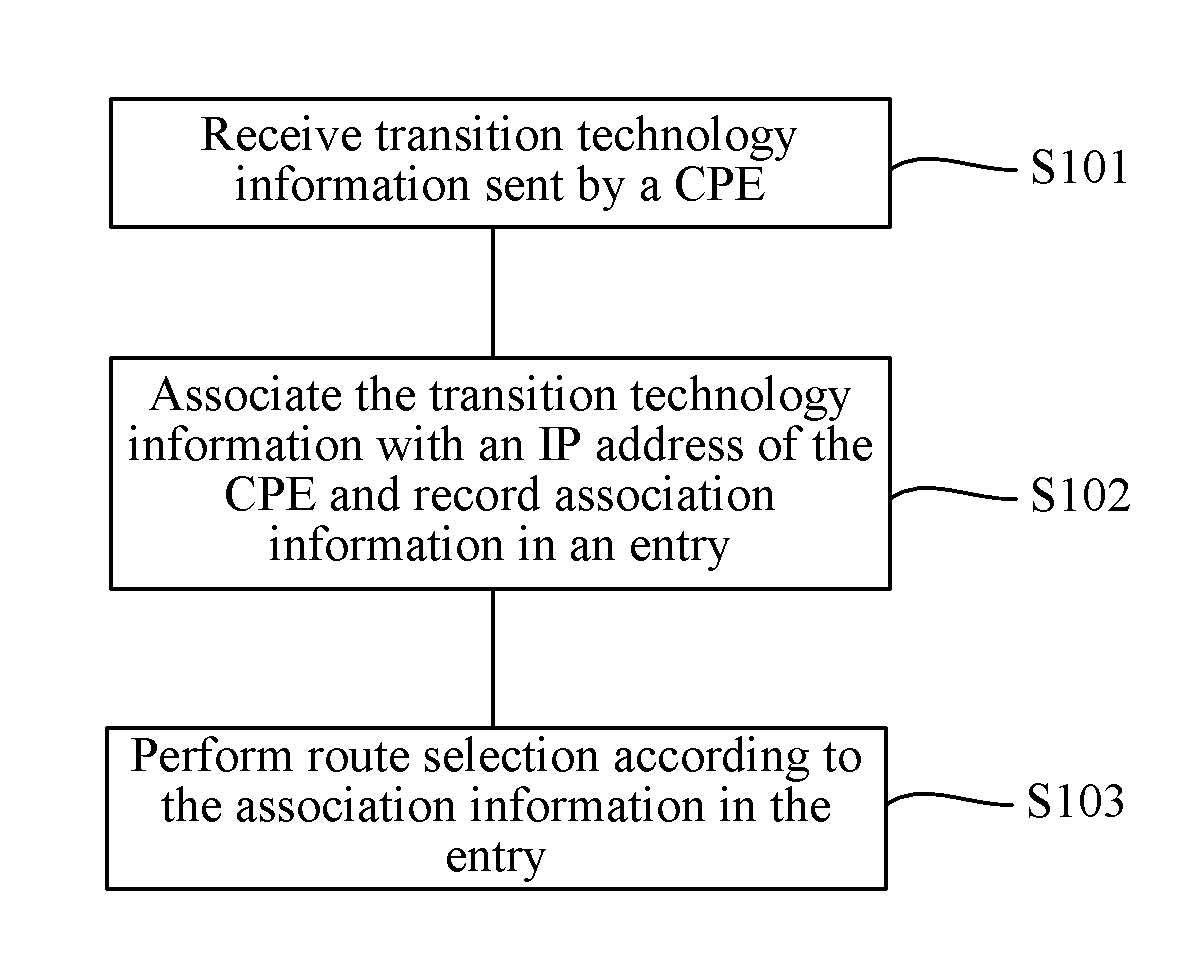
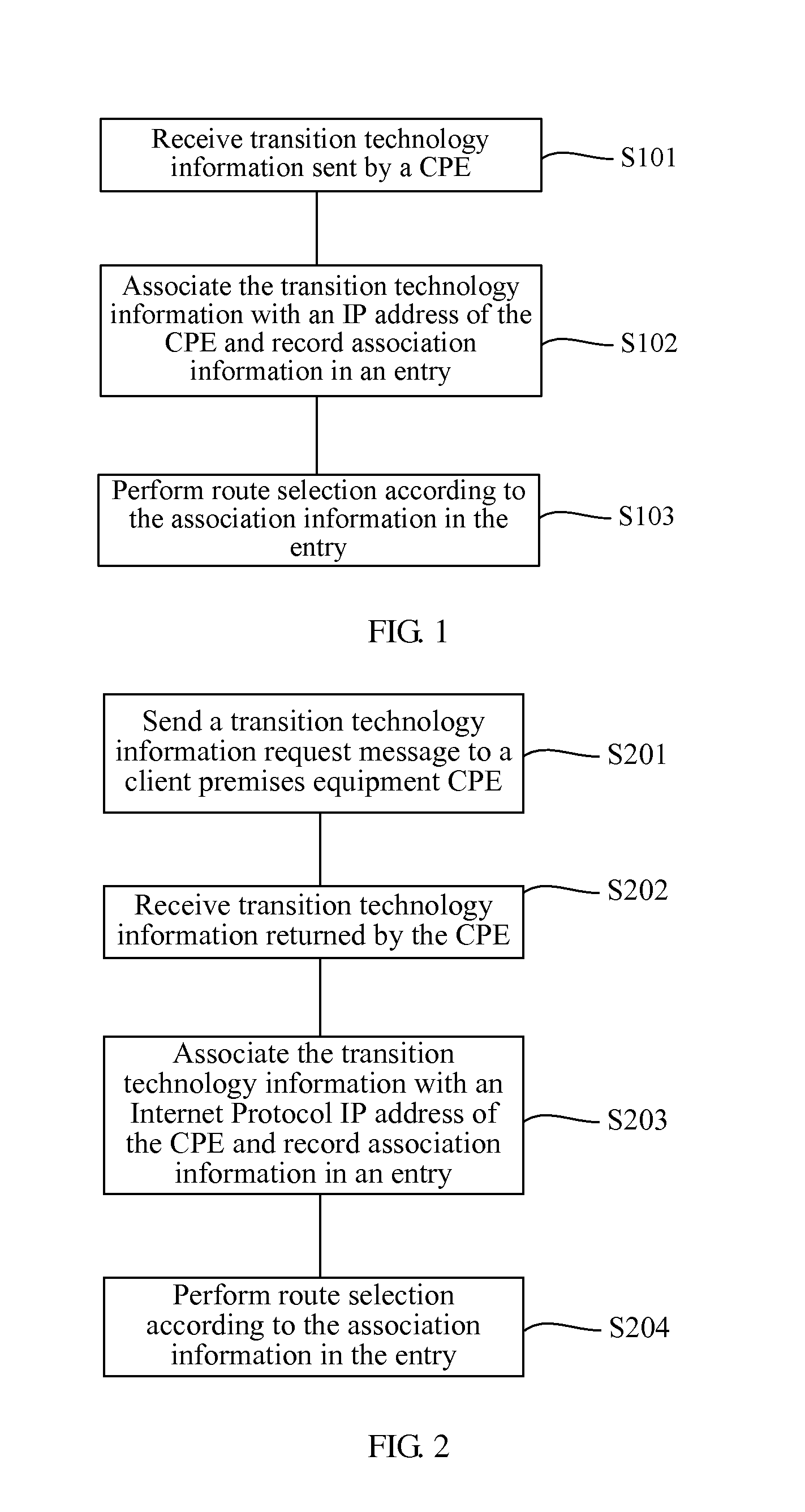
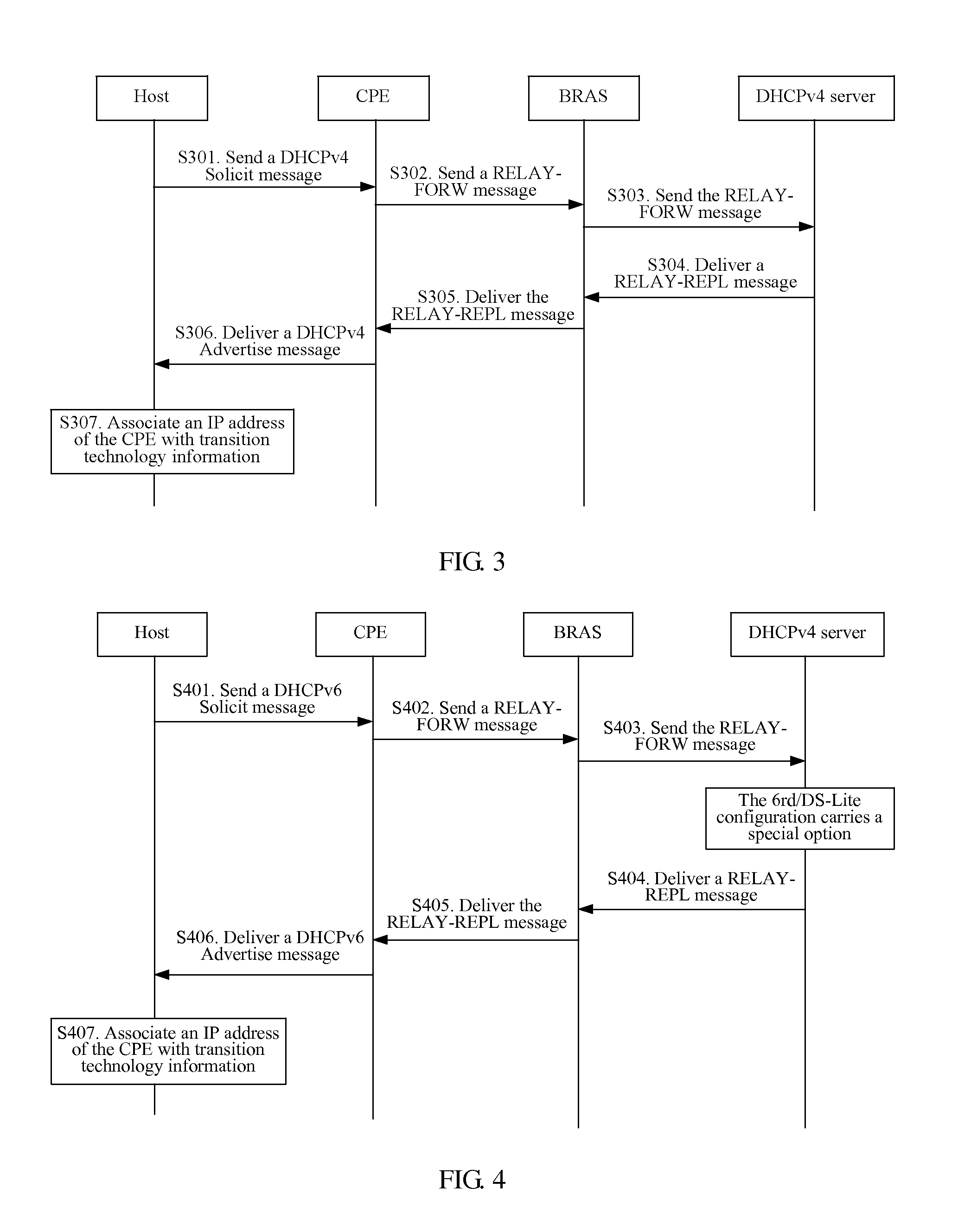
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and an apparatus for route selection of a host in a multihoming site. The method includes: receiving transition technology information sent by a client premises equipment CPE; associating the transition technology information with an Internet Protocol IP address of the CPE and recording association information in an entry; and performing route selection according to the association information in the entry. In the embodiments, the transition technology information is associated with the IP address of the CPE, that is, the CPE corresponds to a corresponding transition technology, so that a host is capable of clearly learning a transition technology used by a home network of the CPE. Therefore, a proper CPE can be selected during routing, and selecting a best route can be ensured.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Mobile network operator multihoming and enterprise VPN solution
ActiveUS8526404B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDistributed computingMobile network operator
The disclosed embodiments support mobility internal and external to enterprise networks. Service providers provide mobility by providing Home Agent functionality corresponding to each Enterprise network. In this manner, mobility may be provided to Mobile Nodes both internal and external to their enterprise networks. Moreover, data packets may be transmitted by Mobile Nodes to Correspondent Nodes, whether they are within their enterprise network, the Service Provider network, or the Internet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
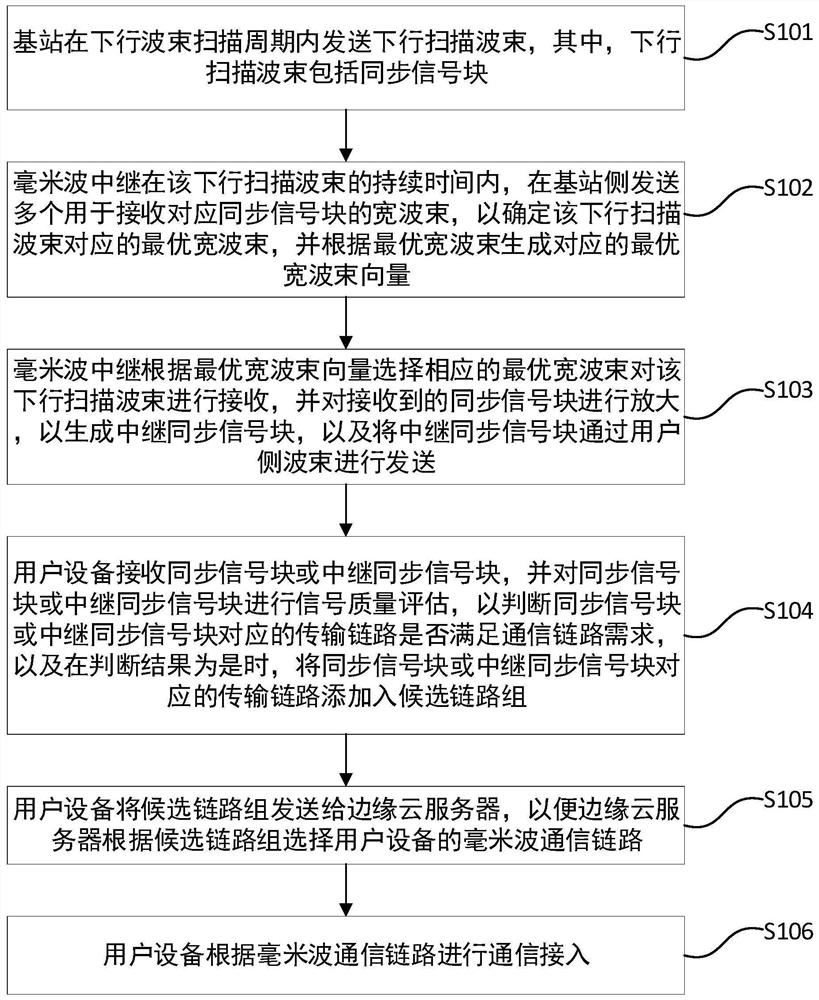
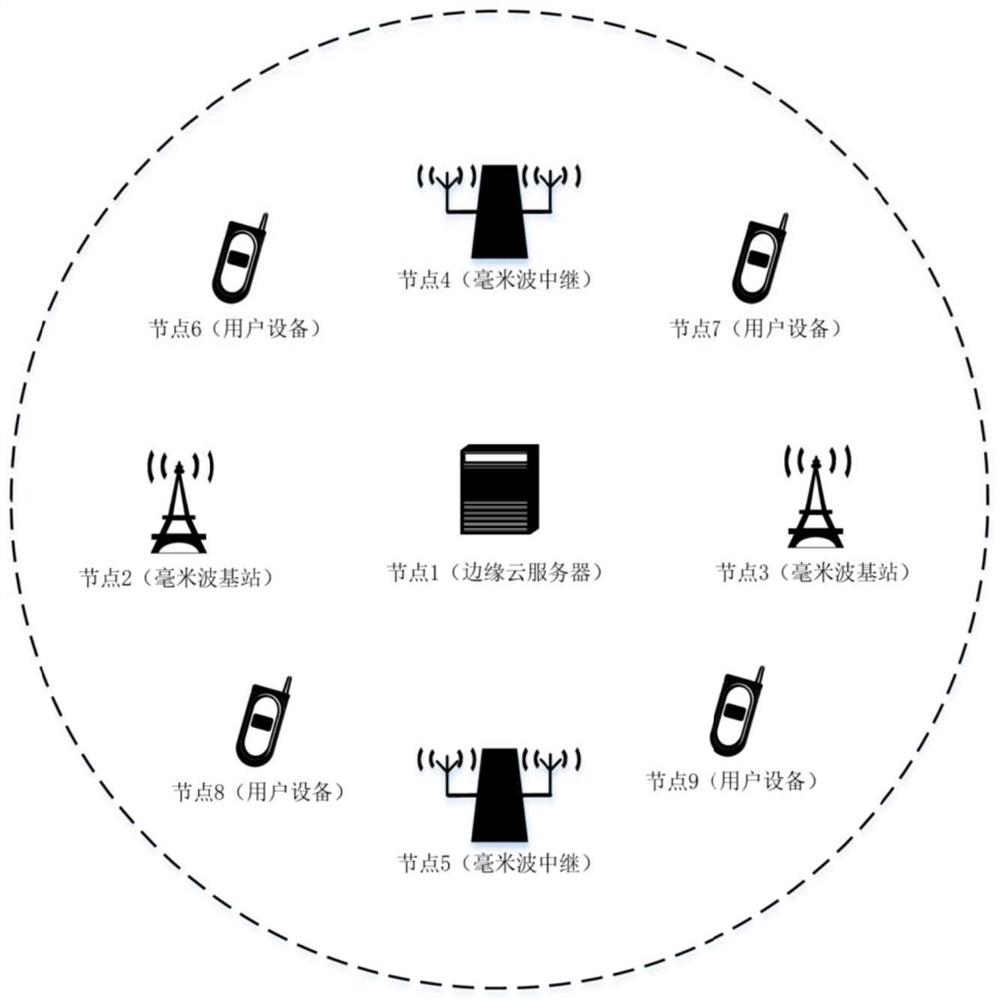
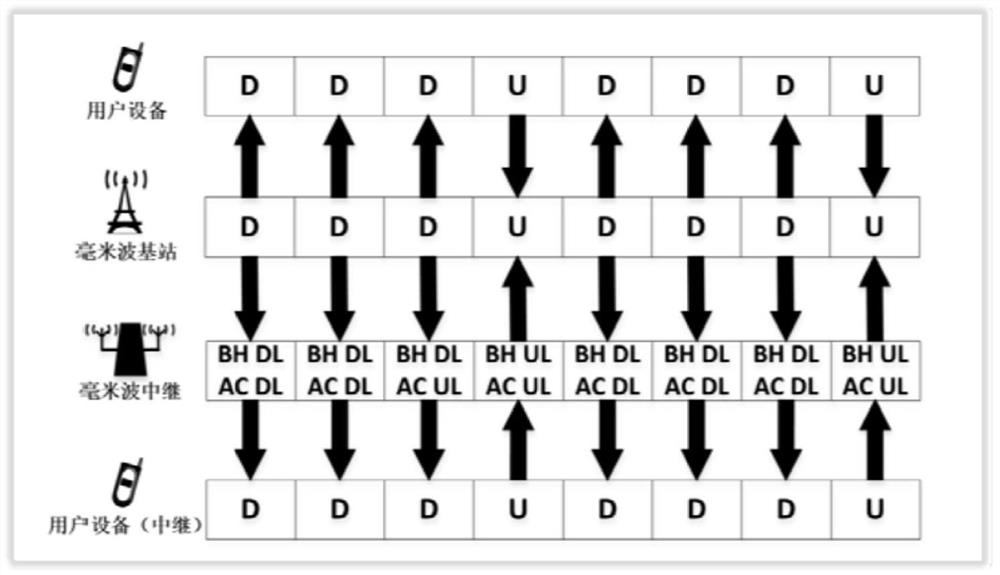
Multi-homed millimeter wave relay system and access method thereof
The invention discloses a multi-homed millimeter wave relay system, a medium and an access method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: a base station sends a downlink scanning beam; a millimeter wave relay sends a plurality of wide beams to the base station side in each downlink scanning beam time interval to determine an optimal wide beam until an optimal wide beam vector is generated; the optimal wide beam corresponding to each downlink scanning beam is selected to receive the downlink scanning beam, a relay synchronization signal block is generated, and the relay synchronization signal block is sent to a user side; user equipment receives the synchronization signal block or the relay synchronization signal block, evaluates the synchronization signal block or the relay synchronization signal block to judge whether the synchronization signal block or the relay synchronization signal block meets requirements or not, and adds the synchronization signal block or the relay synchronization signal block into a candidate link group if yes; a edge cloud server selects a millimeter wave communication link; the user equipment performs communication access through the millimeter wave communication link; the directionality and bandwidth advantages of millimeter wave wireless communication can be brought into full play, the coverage range of millimeter wave signals is expanded, and ultra-high-speed transmission of data is achieved through a millimeter wave wireless communication system.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
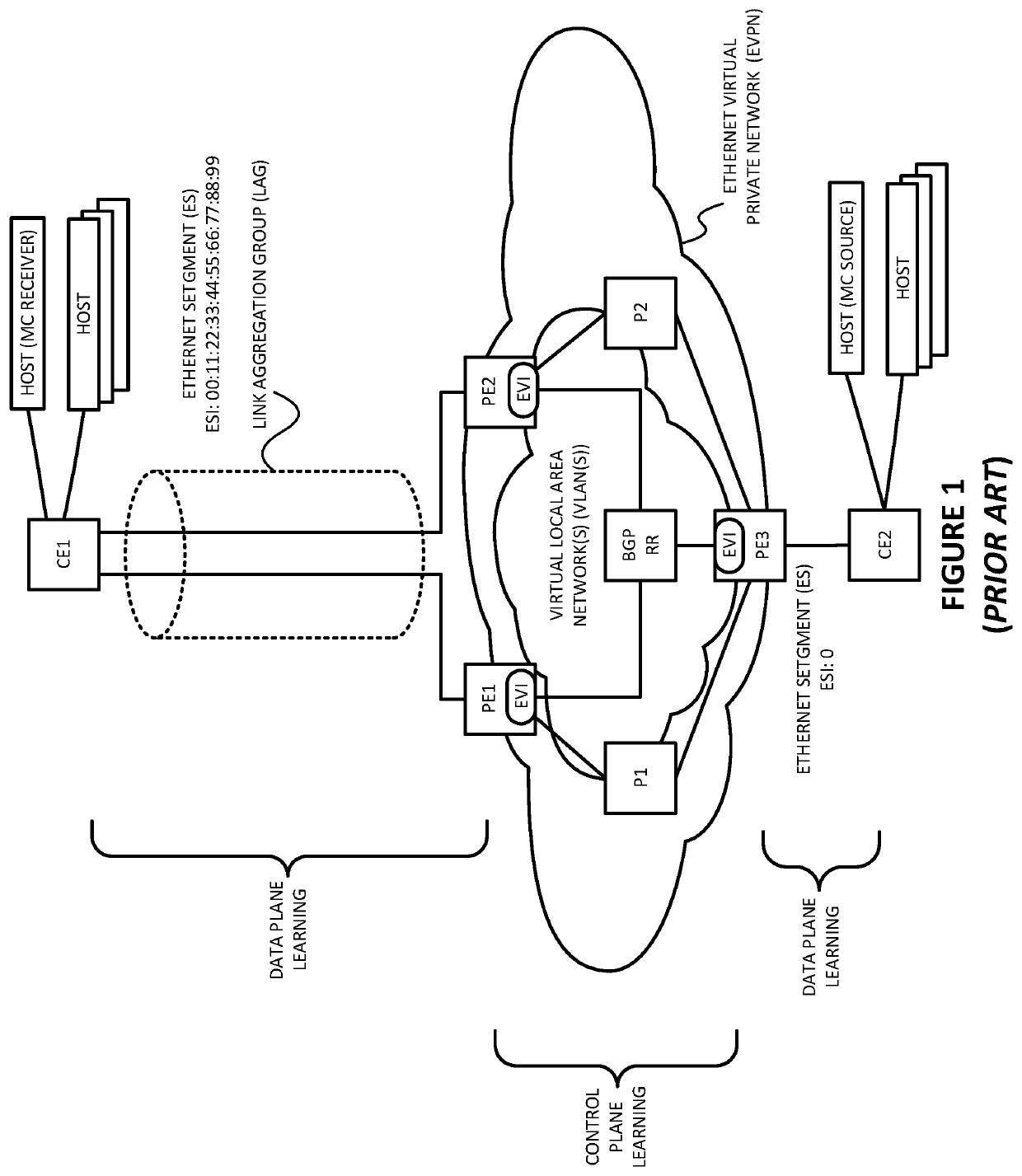
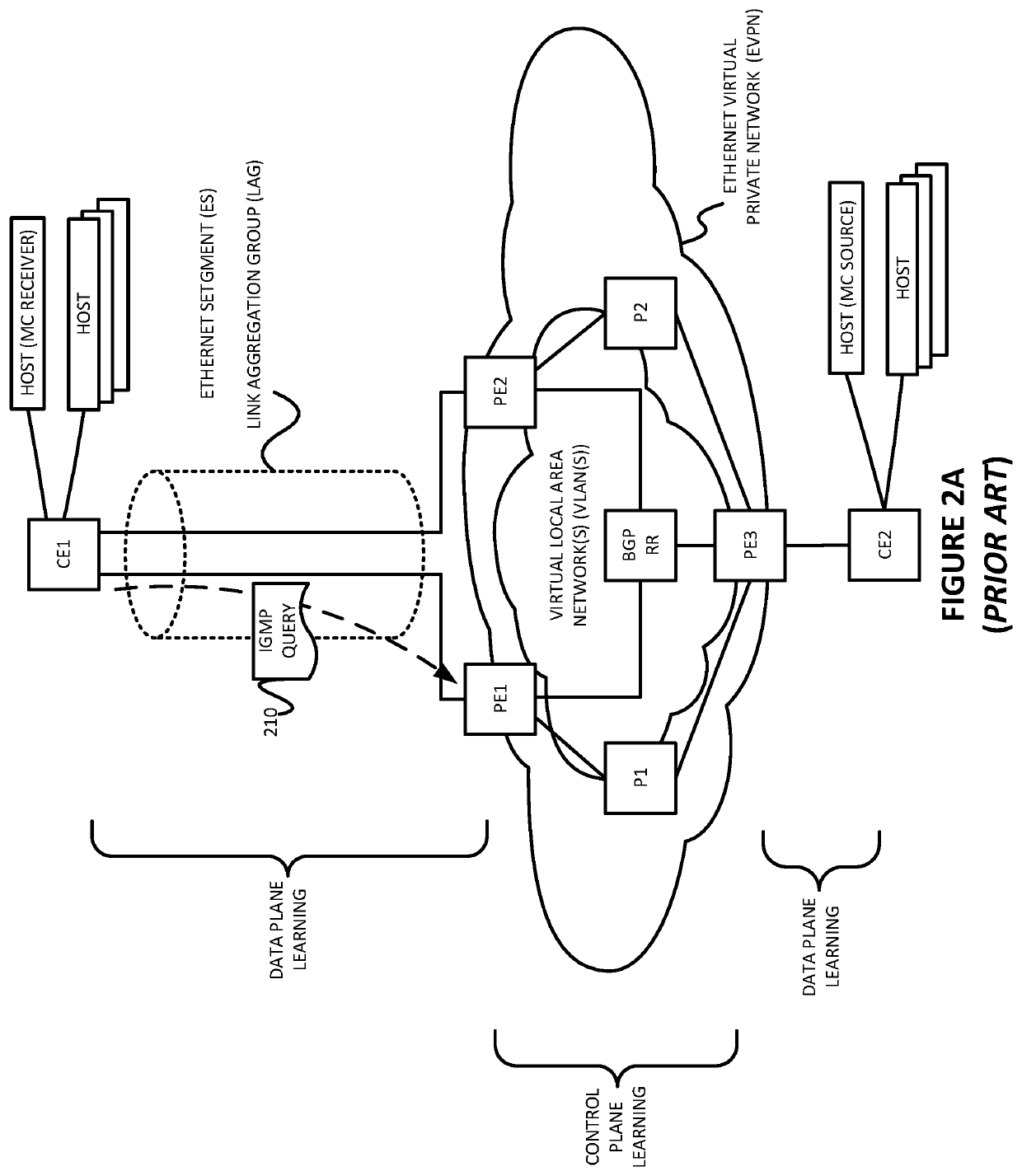
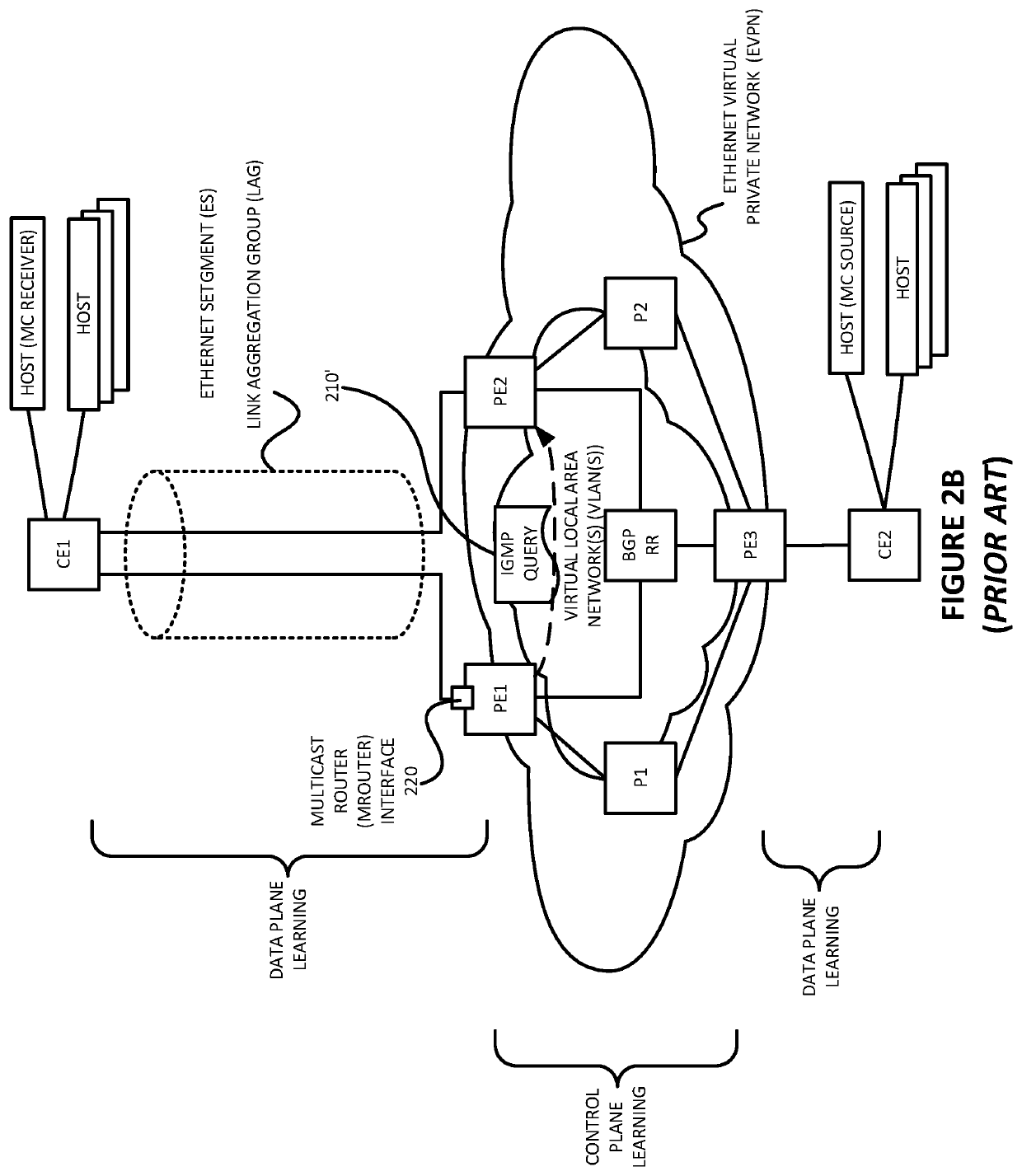
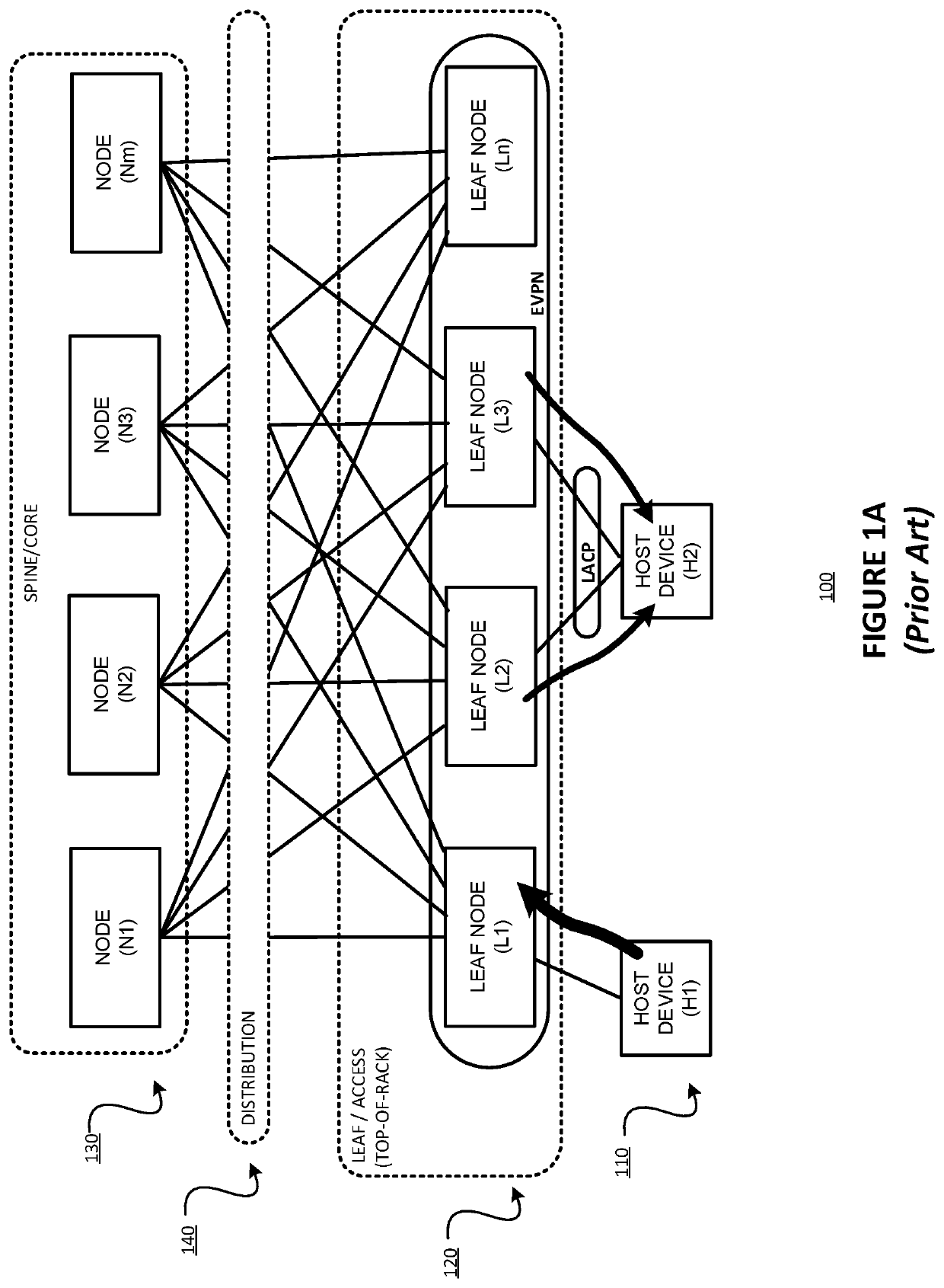
Synchronizing multicast router capability towards ethernet virtual private network (EVPN) multi-homed protocol independent multicast (PIM) device
Port synchronization is provided for multicast on an Ethernet segment (ES) in which a device (CE) is multihomed to at least two devices (PE1 and PE2) of a VLAN. Such example embodiments may do so by providing computer-implemented method for use in a first device belonging to an Ethernet virtual private network (EVPN) and an Ethernet segment (ES), the ES including a second device and a third device, the second device also belonging to the EVPN, the third device being multihomed to the first device and the second device via the ES, and the first and second devices having snooping enabled for multicast group messages, the computer-implemented method comprising: (a) detecting, on a first interface of the first device, from the third device via the ES, a multicast query message, wherein the multicast query message is not detected by the second device via the ES; (b) marking the first interface of the first device as a multicast router port; (c) generating a message identifying the ES and including information encoding that the multicast query message was detected on the ES; and (d) sending, via the EVPN, the message generated to the second device so that the second device will mark an interface, on the ES, with the third device, as a multicast router port.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Loop avoidance and egress link protection with ethernet virtual private network (EVPN) fast reroute (FRR)
The problem of looping at the egress of a transport network with a CE multihomed to a protected egress PE and a backup / protector egress PE can be avoided by (a) enabling the protector egress PE to distinguish between fast reroute (FRR) traffic coming from the protected egress PE and normal known unicast (KU) traffic coming from a PE of the transport network that is not attached to the same multihomed segment; (b) receiving, by the protector egress PE, known unicast data, to be forwarded to the CE; (c) determining, by the protector egress PE, that a link between it and the CE is unavailable; and (d) responsive to determining that the link between the protector egress PE and the CE is unavailable, (1) determining whether the known unicast traffic received was sent from the protected egress PE or from another PE of the transport network that is not attached to the same multihomed segment, and (2) responsive to a determination that the known unicast traffic received was sent from the protected egress PE, discarding the known unicast traffic received, and otherwise, responsive to a determination that the known unicast (KU) traffic received was sent from another PE of the transport network that is not attached to the same multihomed segment, sending the known unicast traffic, via a backup tunnel, to an egress PE which protects the protector egress PE.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Faster fault-detection mechanism, for example using bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD), on network nodes and/or hosts multihomed using a link aggregation group (LAG)
ActiveUS10805193B1Data switching by path configurationHigh level techniquesPathPingBidirectional Forwarding Detection
For use in a system including a first data forwarding device, a second data forwarding device, a third data forwarding device, a first communications link between the first data forwarding device and the second data forwarding device, and a second communications link between the first data forwarding device and the third data forwarding device, the first and second communications links belonging to a link aggregation group (LAG), a method includes (1) generating a message (i) for testing a first path between the first data forwarding device and the second data forwarding device, and a second path between the first data forwarding device and the third data forwarding device, and (ii) including an Internet protocol (IP) datagram including a multicast IP destination address and a payload containing path testing information; and (2) sending, over the LAG, the message from the first data forwarding device to both the second data forwarding device and the third data forwarding device. Responsive to receiving an instance of the message by either of the second or third data forwarding device, such device(s) (1) determine whether or not the received instance of the message is a fault detection on a multihomed link aggregation group message, and (2) processing the received instance of the message based on the determination of whether or not it is a fault detection on a multihomed link aggregation group message.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
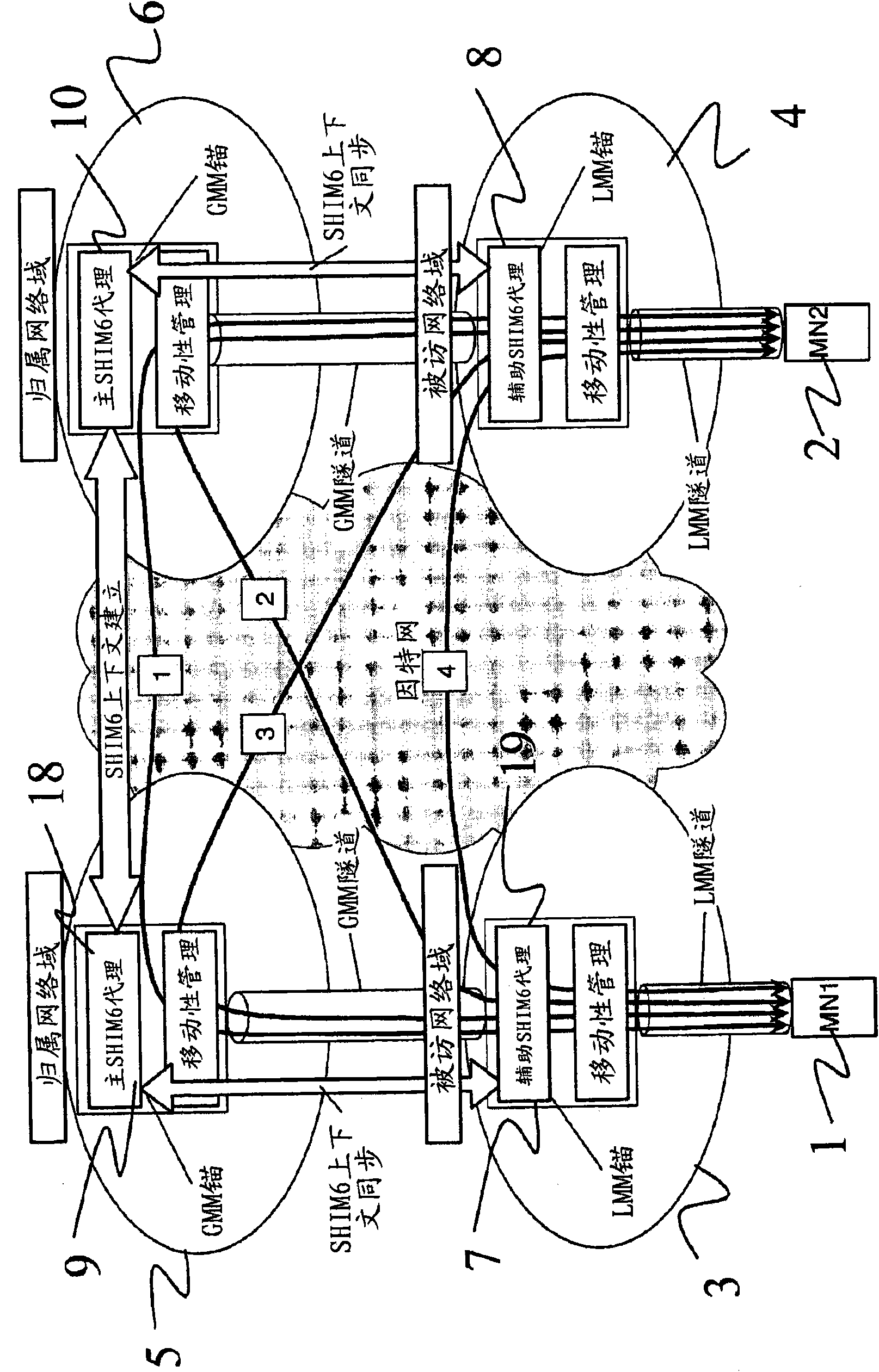
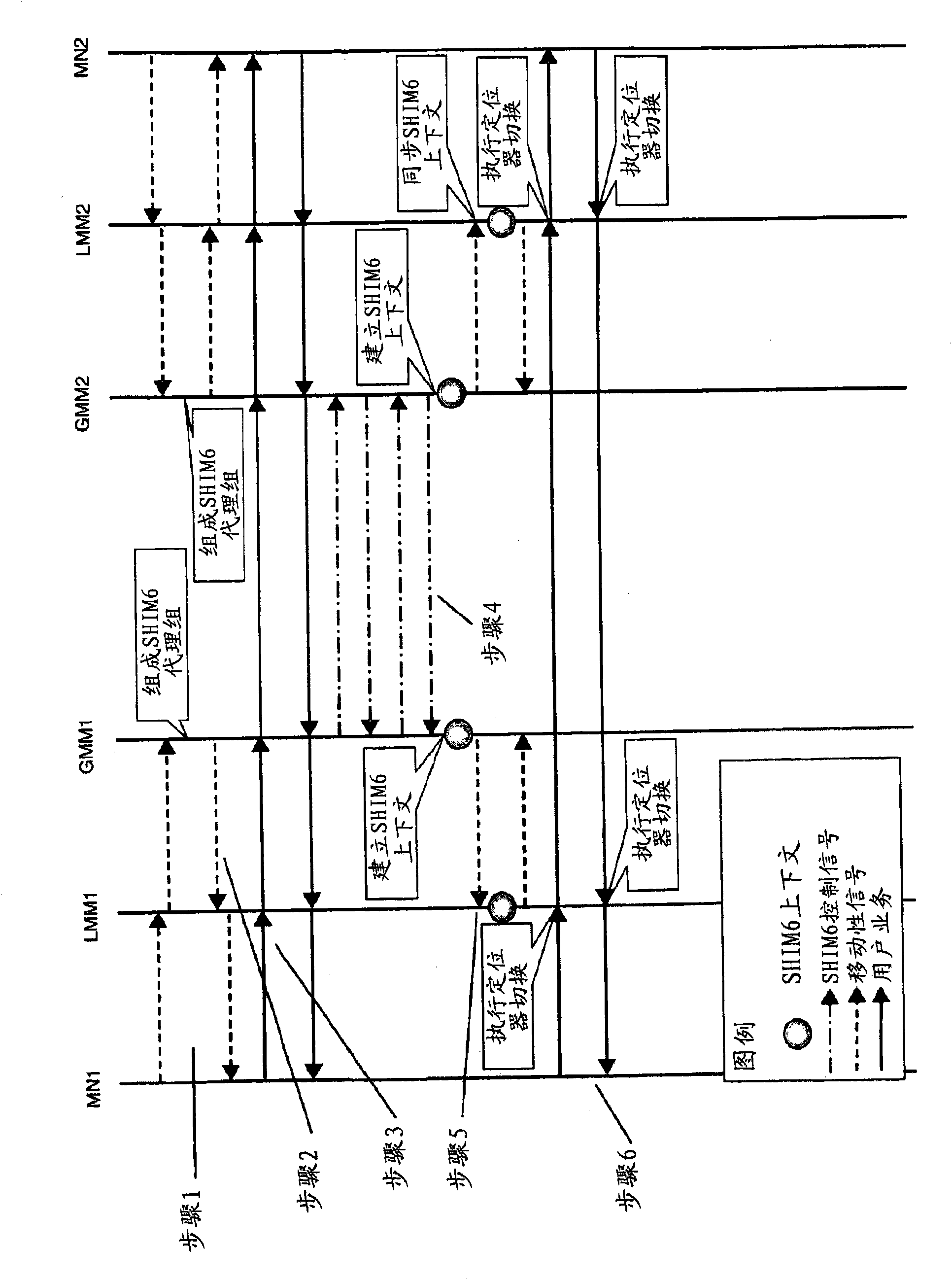
Multihome support method and apparatus
InactiveCN101836416ADoes not solve the problem of implementing multihomingWireless network protocolsTransmissionMobility managementGlobal mobility
A method of facilitating multihoming in the case of a mobile node possessing an Upper Layer Identifier belonging to a home network, where the mobile node is assigned a Global Mobility Management anchor within the home network and a Local Mobility Management anchor within a visited network. The method comprises allocating to the mobile node a primary SHIM6 proxy at said Global Mobility Management anchor, and at least one secondary SHIM6 proxy at said Local Mobility Management anchor. At said primary SHIM6 proxy, a SHIM6 context is established on behalf of the mobile node in respect of a peer node;, and the established context is shared with said secondary SHIM6 proxy. Locator switching is then performed in respect of traffic exchanged between the mobile node and said peer node at one of said primary and secondary SHIM6 proxies.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
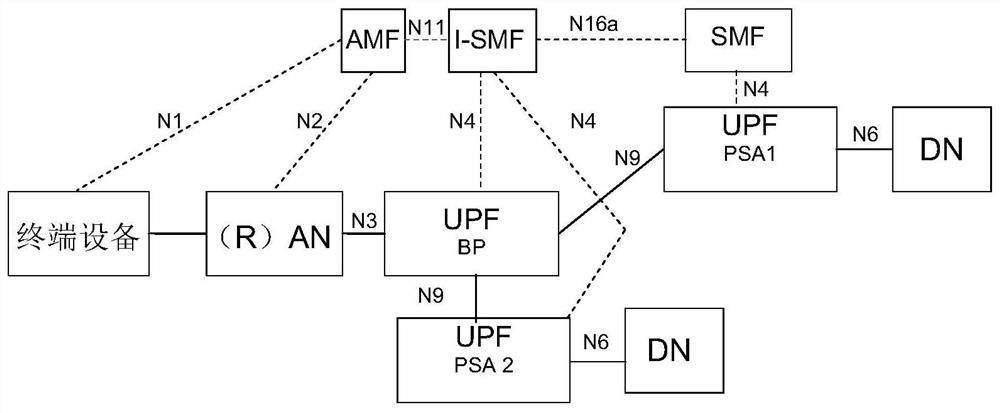
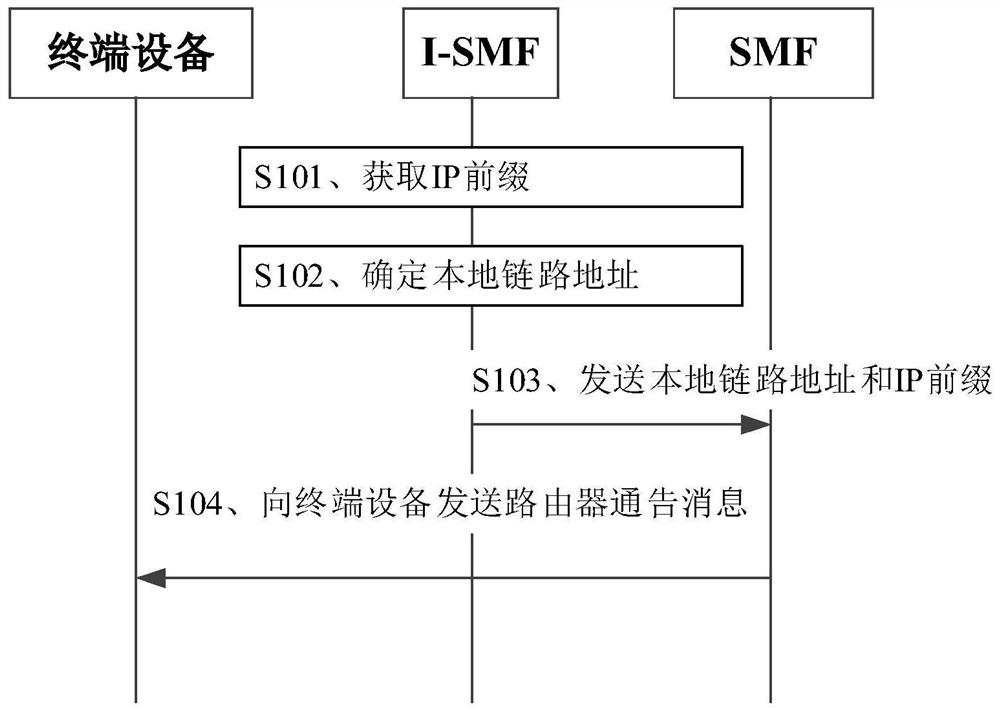
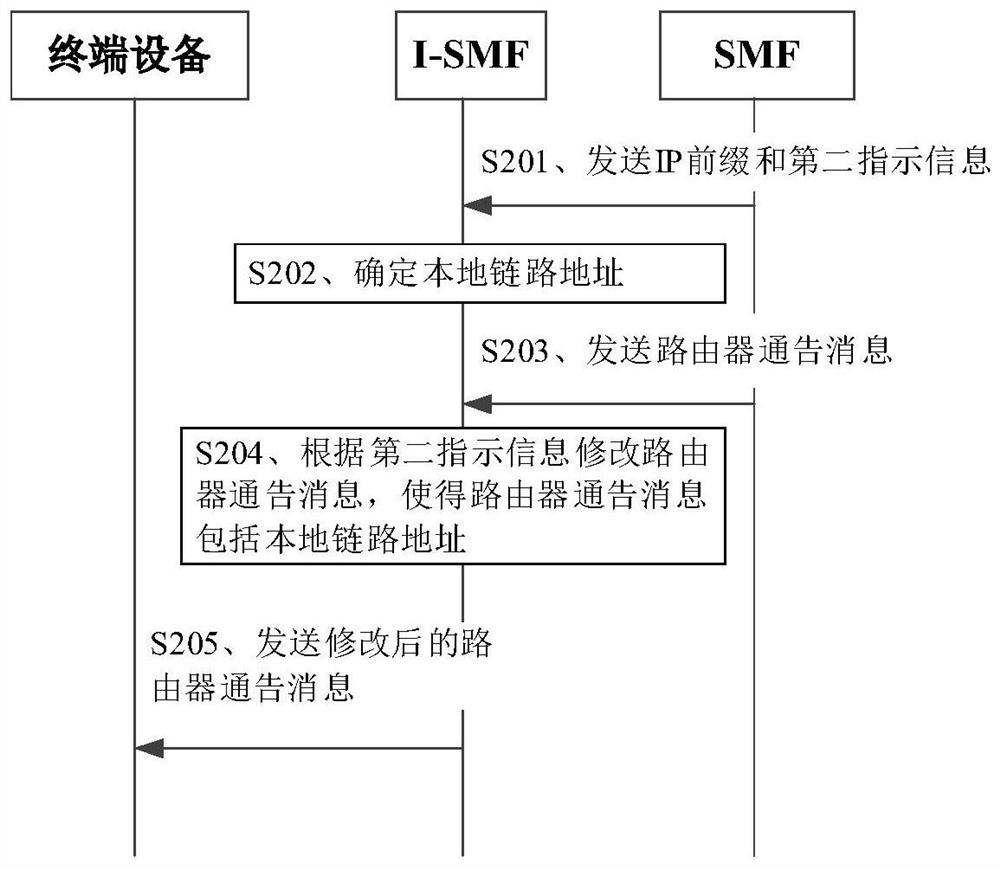
Router notification message sending method and device
The invention provides a router notification message sending method and device. The method comprises the following steps: a session management function network element receives a local link address and an IP prefix from an intermediate session management function network element, wherein the local link address and the IP prefix correspond to a local session anchor function network element managedby the intermediate session management function network element; and the session management function network element sends a router notification message to terminal equipment, wherein the router notification message comprises the local link address and the IP prefix. Therefore, the problem of how to construct or generate the router notification message and send the router notification message to the terminal equipment in a scene of realizing shunting through multiple hosts when the terminal equipment is served by multiple SMFs is solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
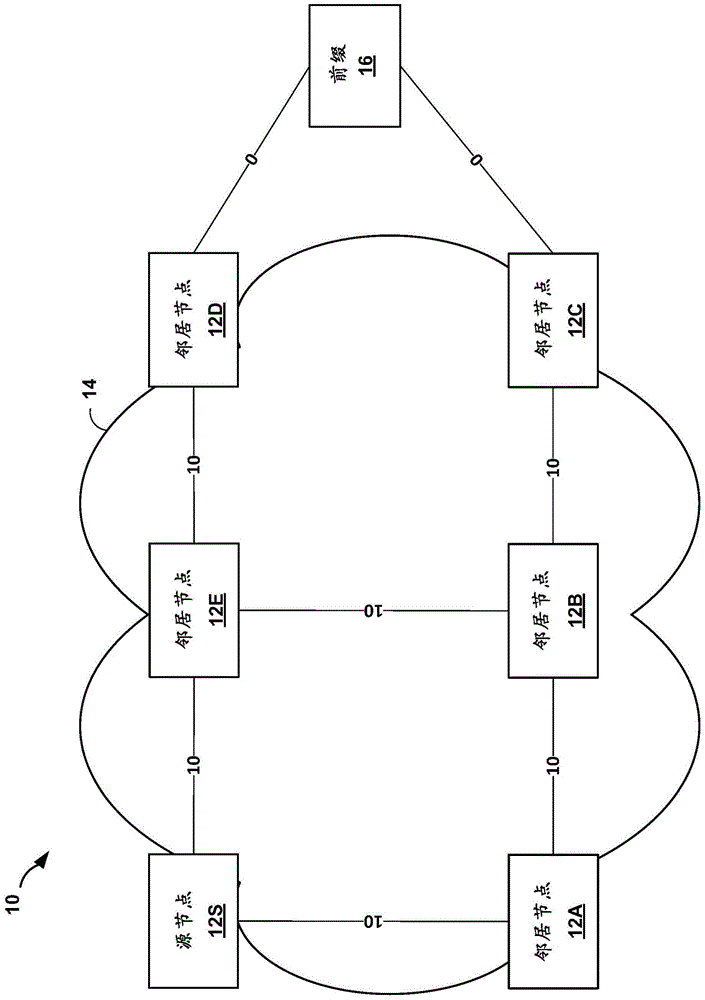
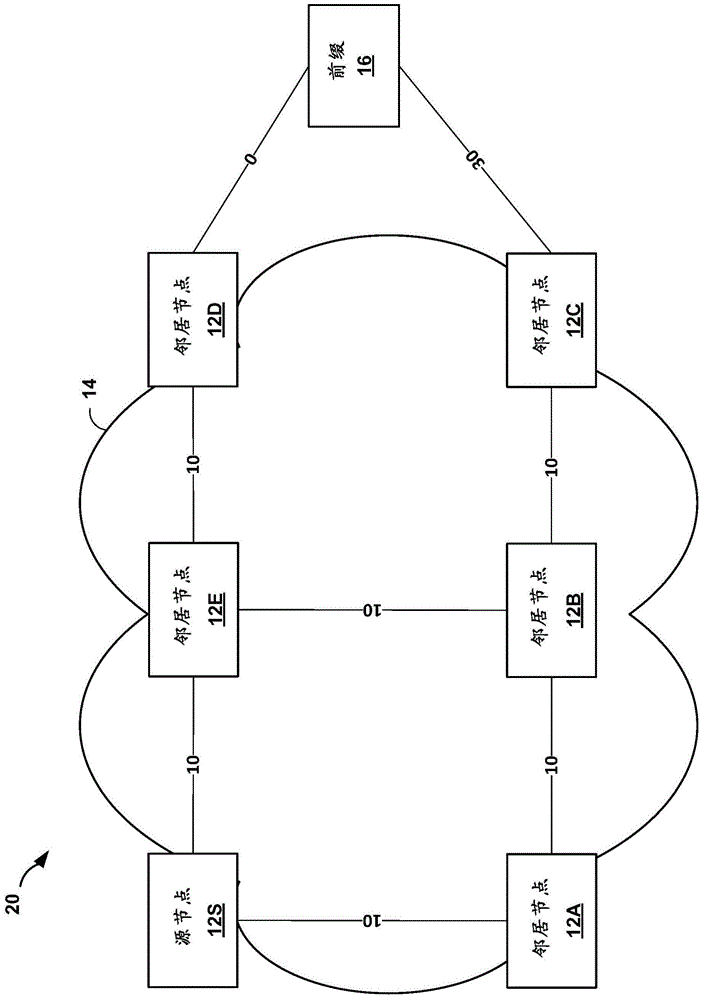
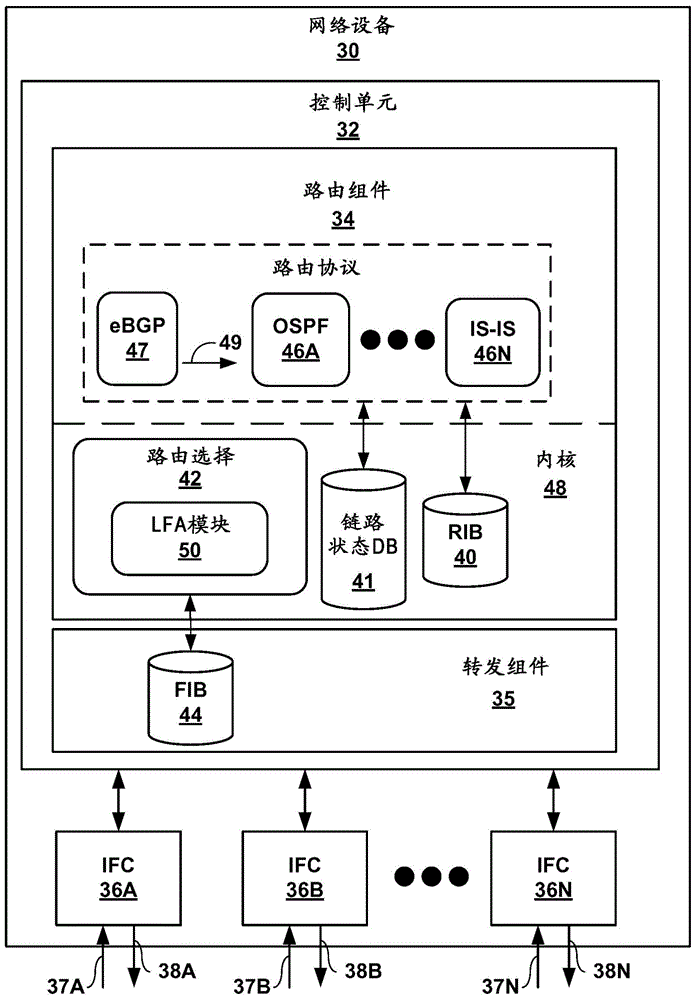
Loop free alternate selection for multi-homed networks
ActiveCN104821912ALess memoryRequire lessData switching networksWireless communicationPathPingRouting domain
In one example, a network device determines a set of candidate loop-free alternate (LFA) next hops for forwarding network traffic from the network device to a multi-homed network by taking into account a first cost associated with a second path from a first border router to the multi-homed network and a second cost associated with a second border router to the multi-homed network, wherein the multi-homed network is external to an interior routing domain in which the network device is located. The network device selects an LFA next hop from the set of candidate LFA next hops, to be stored as an alternate next hop for forwarding network traffic to the multi-homed network, and updates forwarding information stored by the network device to install the selected LFA next hop as the alternate next hop for forwarding network traffic from the network device to the multi-homed network.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
System for link independent multi-homing in heterogeneous access networks
ActiveUS7649888B2Data switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesAccess networkNetwork packet
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
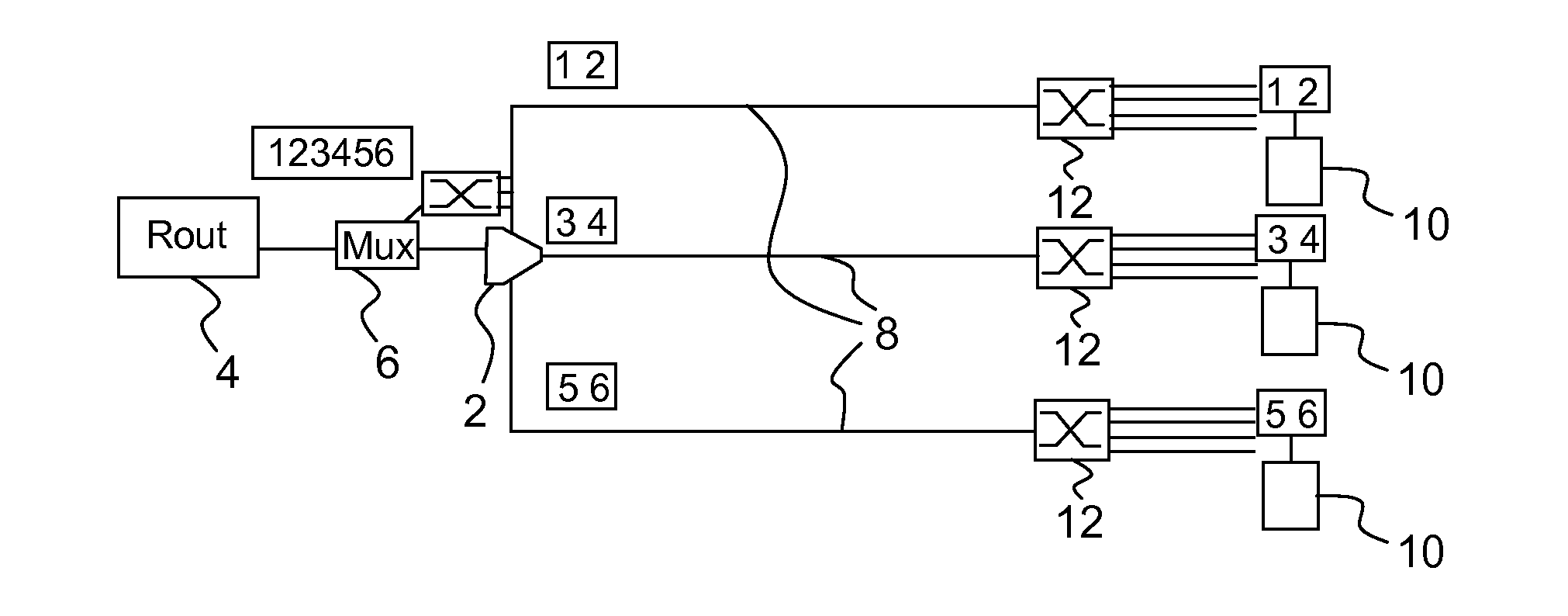
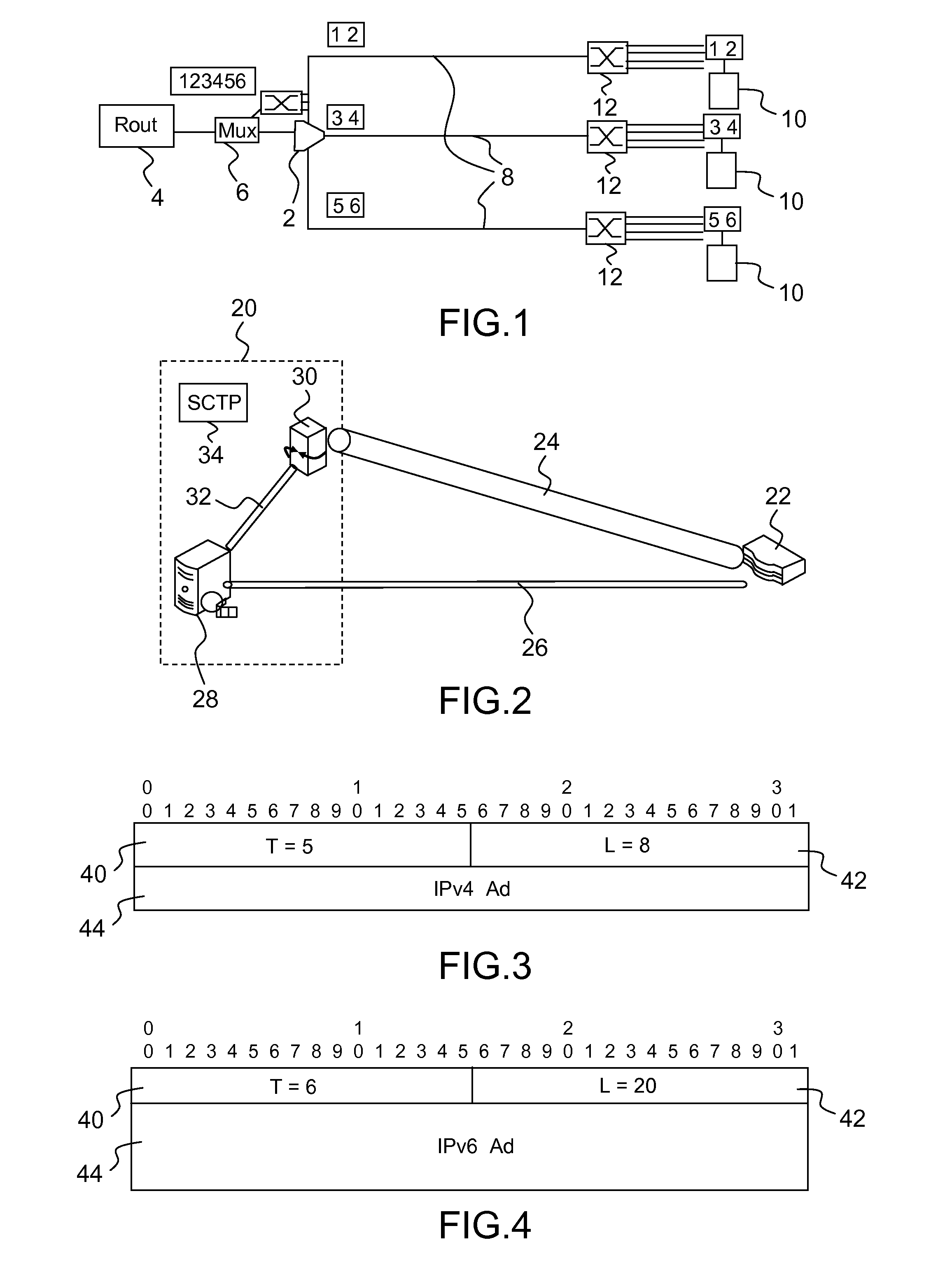
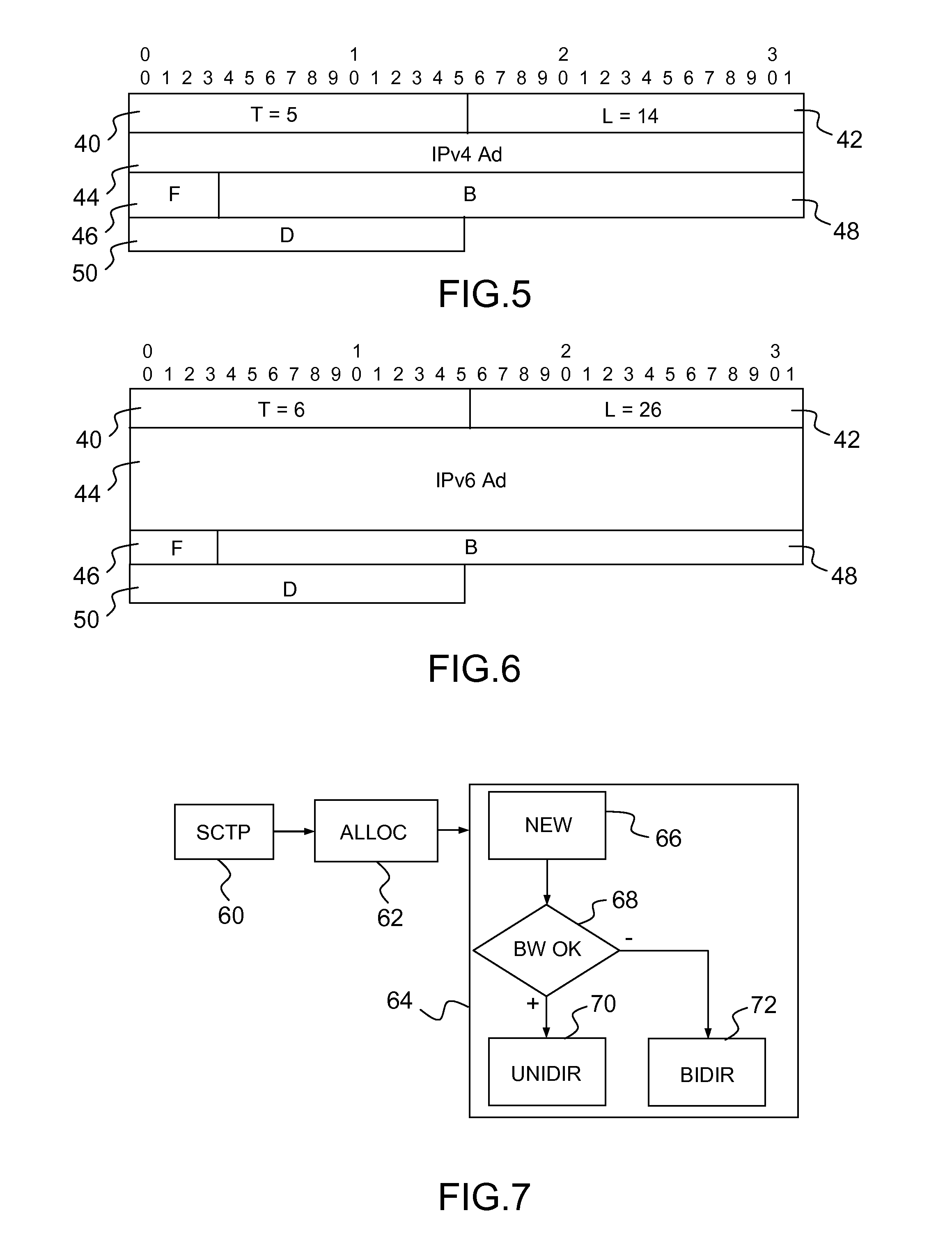
Data transmission using a multihoming protocol as sctp
InactiveUS20130325933A1Improves SCTPEfficient schedulingData switching networksData transmissionProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Method of transmission of data between a server and a client, said transmission using a multihoming protocol, as SCTP, over a network comprising at least one principal link and one secondary link connecting the server and the client, said method comprising the steps of:a) set-up of a connection between the server and the client;b) allocation of a bandwidth over the principal link to the transmission of data from the server to the client;c) transmission of data from the server to the client over the principal link as long as said allocated bandwidth is not fully used; andd) if the allocated bandwidth has been fully used, transmission of data from the server to the client over the secondary link.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com